Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

MLA General Format

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
MLA Style specifies guidelines for formatting manuscripts and citing research in writing. MLA Style also provides writers with a system for referencing their sources through parenthetical citation in their essays and Works Cited pages.
Writers who properly use MLA also build their credibility by demonstrating accountability to their source material. Most importantly, the use of MLA style can protect writers from accusations of plagiarism, which is the purposeful or accidental uncredited use of source material produced by other writers.
If you are asked to use MLA format, be sure to consult the MLA Handbook (9th edition). Publishing scholars and graduate students should also consult the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing (3rd edition). The MLA Handbook is available in most writing centers and reference libraries. It is also widely available in bookstores, libraries, and at the MLA web site. See the Additional Resources section of this page for a list of helpful books and sites about using MLA Style.
Paper Format
The preparation of papers and manuscripts in MLA Style is covered in part four of the MLA Style Manual . Below are some basic guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA Style :
General Guidelines
- Type your paper on a computer and print it out on standard, white 8.5 x 11-inch paper.
- Double-space the text of your paper and use a legible font (e.g. Times New Roman). Whatever font you choose, MLA recommends that the regular and italics type styles contrast enough that they are each distinct from one another. The font size should be 12 pt.
- Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks (unless otherwise prompted by your instructor).
- Set the margins of your document to 1 inch on all sides.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph one half-inch from the left margin. MLA recommends that you use the “Tab” key as opposed to pushing the space bar five times.
- Create a header that numbers all pages consecutively in the upper right-hand corner, one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor may ask that you omit the number on your first page. Always follow your instructor's guidelines.)
- Use italics throughout your essay to indicate the titles of longer works and, only when absolutely necessary, provide emphasis.
- If you have any endnotes, include them on a separate page before your Works Cited page. Entitle the section Notes (centered, unformatted).
Formatting the First Page of Your Paper
- Do not make a title page for your paper unless specifically requested or the paper is assigned as a group project. In the case of a group project, list all names of the contributors, giving each name its own line in the header, followed by the remaining MLA header requirements as described below. Format the remainder of the page as requested by the instructor.
- In the upper left-hand corner of the first page, list your name, your instructor's name, the course, and the date. Again, be sure to use double-spaced text.
- Double space again and center the title. Do not underline, italicize, or place your title in quotation marks. Write the title in Title Case (standard capitalization), not in all capital letters.
- Use quotation marks and/or italics when referring to other works in your title, just as you would in your text. For example: Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas as Morality Play; Human Weariness in "After Apple Picking"
- Double space between the title and the first line of the text.
- Create a header in the upper right-hand corner that includes your last name, followed by a space with a page number. Number all pages consecutively with Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, 4, etc.), one-half inch from the top and flush with the right margin. (Note: Your instructor or other readers may ask that you omit the last name/page number header on your first page. Always follow instructor guidelines.)
Here is a sample of the first page of a paper in MLA style:

The First Page of an MLA Paper
Section Headings
Writers sometimes use section headings to improve a document’s readability. These sections may include individual chapters or other named parts of a book or essay.
MLA recommends that when dividing an essay into sections you number those sections with an Arabic number and a period followed by a space and the section name.
MLA does not have a prescribed system of headings for books (for more information on headings, please see page 146 in the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , 3rd edition). If you are only using one level of headings, meaning that all of the sections are distinct and parallel and have no additional sections that fit within them, MLA recommends that these sections resemble one another grammatically. For instance, if your headings are typically short phrases, make all of the headings short phrases (and not, for example, full sentences). Otherwise, the formatting is up to you. It should, however, be consistent throughout the document.
If you employ multiple levels of headings (some of your sections have sections within sections), you may want to provide a key of your chosen level headings and their formatting to your instructor or editor.
Sample Section Headings
The following sample headings are meant to be used only as a reference. You may employ whatever system of formatting that works best for you so long as it remains consistent throughout the document.
Formatted, unnumbered:
Level 1 Heading: bold, flush left
Level 2 Heading: italics, flush left
Level 3 Heading: centered, bold
Level 4 Heading: centered, italics
Level 5 Heading: underlined, flush left
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format
APA Format for Students & Researchers
In this guide, students and researchers can learn the basics of creating a properly formatted research paper according to APA guidelines.
It includes information on how to conceptualize, outline, and format the basic structure of your paper, as well as practical tips on spelling, abbreviation, punctuation, and more. The guide concludes with a complete sample paper as well as a final checklist that writers can use to prepare their work for submission.
APA Paper Formatting Basics
- All text should be double-spaced
- Use one-inch margins on all sides
- All paragraphs in the body are indented
- Make sure that the title is centered on the page with your name and school/institution underneath
- Use 12-point font throughout
- All pages should be numbered in the upper right hand corner
- The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks
- A shortened version of the title (“running head”) should be placed in the upper left hand corner
Table of Contents
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to do APA format.
Information related to writing and organizing your paper:
- Paper and essay categories
General paper length
- Margin sizes
- Title pages
- Running Heads
- APA Outline
- APA Abstract
- The body of papers
- APA headings and subheadings
- Use of graphics (tables and figures)
Writing style tips:
Proper tone.
- Reducing bias and labels
- Abbreviation do’s and don’ts
- Punctuation
- Number rules
Citing Your Sources:
- Citing Sources
- In-text Citations
- Reference Page
Proofing Your Paper:
- Final checklist
- Submitting your project
APA Information:
- What is APA
- APA 7 Updates
What you won’t find in this guide: This guide provides information related to the formatting of your paper, as in guidelines related to spacing, margins, word choice, etc. While it provides a general overview of APA references, it does not provide instructions for how to cite in APA format.
For step-by-step instructions for citing books, journals, how to cite a website in APA format, information on an APA format bibliography, and more, refer to these other EasyBib guides:
- APA citation (general reference guide)
- APA In-text citation
- APA article citation
- APA book citation
- APA citation website
Or, you can use our automatic generator. Our APA formatter helps to build your references for you. Yep, you read that correctly.
Writing and Organizing Your APA Paper in an Effective Way
This section of our guide focuses on proper paper length, how to format headings, spacing, and more! This information can be found in Chapter 2 of the official manual (American Psychological Association, 2020, pp. 29-67).
Categories of papers
Before getting into the nitty-gritty details related to APA research paper format, first determine the type of paper you’re about to embark on creating:
Empirical studies
Empirical studies take data from observations and experiments to generate research reports. It is different from other types of studies in that it isn’t based on theories or ideas, but on actual data.
Literature reviews
These papers analyze another individual’s work or a group of works. The purpose is to gather information about a current issue or problem and to communicate where we are today. It sheds light on issues and attempts to fill those gaps with suggestions for future research and methods.
Theoretical articles
These papers are somewhat similar to a literature reviews in that the author collects, examines, and shares information about a current issue or problem, by using others’ research. It is different from literature reviews in that it attempts to explain or solve a problem by coming up with a new theory. This theory is justified with valid evidence.
Methodological articles
These articles showcase new advances, or modifications to an existing practice, in a scientific method or procedure. The author has data or documentation to prove that their new method, or improvement to a method, is valid. Plenty of evidence is included in this type of article. In addition, the author explains the current method being used in addition to their own findings, in order to allow the reader to understand and modify their own current practices.
Case studies
Case studies present information related an individual, group, or larger set of individuals. These subjects are analyzed for a specific reason and the author reports on the method and conclusions from their study. The author may also make suggestions for future research, create possible theories, and/or determine a solution to a problem.
Since APA style format is used often in science fields, the belief is “less is more.” Make sure you’re able to get your points across in a clear and brief way. Be direct, clear, and professional. Try not to add fluff and unnecessary details into your paper or writing. This will keep the paper length shorter and more concise.
Margin sizes in APA Format
When it comes to margins, keep them consistent across the left, right, top, and bottom of the page. All four sides should be the same distance from the edge of the paper. It’s recommended to use at least one-inch margins around each side. It’s acceptable to use larger margins, but the margins should never be smaller than an inch.
Title pages in APA Format
The title page, or APA format cover page, is the first page of a paper or essay. Some teachers and professors do not require a title page, but some do. If you’re not sure if you should include one or not, ask your teacher. Some appreciate the page, which clearly displays the writer’s name and the title of the paper.
The APA format title page for student papers includes six main components:
- the title of the APA format paper
- names of all authors
- institutional affiliation
- course number and title
- instructor’s name
Title pages for professional papers also require a running head; student papers do not.
Some instructors and professional publications also ask for an author’s note. If you’re required or would like to include an author’s note, place it below the institutional affiliation. Examples of information included in an author’s note include an ORCID iD number, a disclosure, and an acknowledgement.
Here are key guidelines to developing your title page:
- The title of the paper should capture the main idea of the essay, but should not contain abbreviations or words that serve no purpose. For example, instead of using the title “A Look at Amphibians From the Past,” title the paper “Amphibians From the Past.” Delete the unnecessary fluff!
- Center the title on the page and place it about 3-4 lines from the top.
- The title should be bolded, in title case, and the same font size as your other page text. Do not underline or italicize the title. Other text on the page should be plain (not bolded , underlined, or italicized ).
- All text on the title page should be double-spaced. The APA format examples paper below displays proper spacing, so go take a look!
- Do not include any titles in the author’s name such as Dr. or Ms. In contrast, for your instructor’s name, use the form they prefer (e.g., Sagar Parekh, PhD; Dr. Minako Asato; Professor Nathan Ian Brown; etc.).
- The institutional affiliation is the school the author attends or the location where the author conducted the research.
In a hurry? Try the EasyBib title page maker to easily create a title page for free.
Sample of an APA format title page for a student paper:
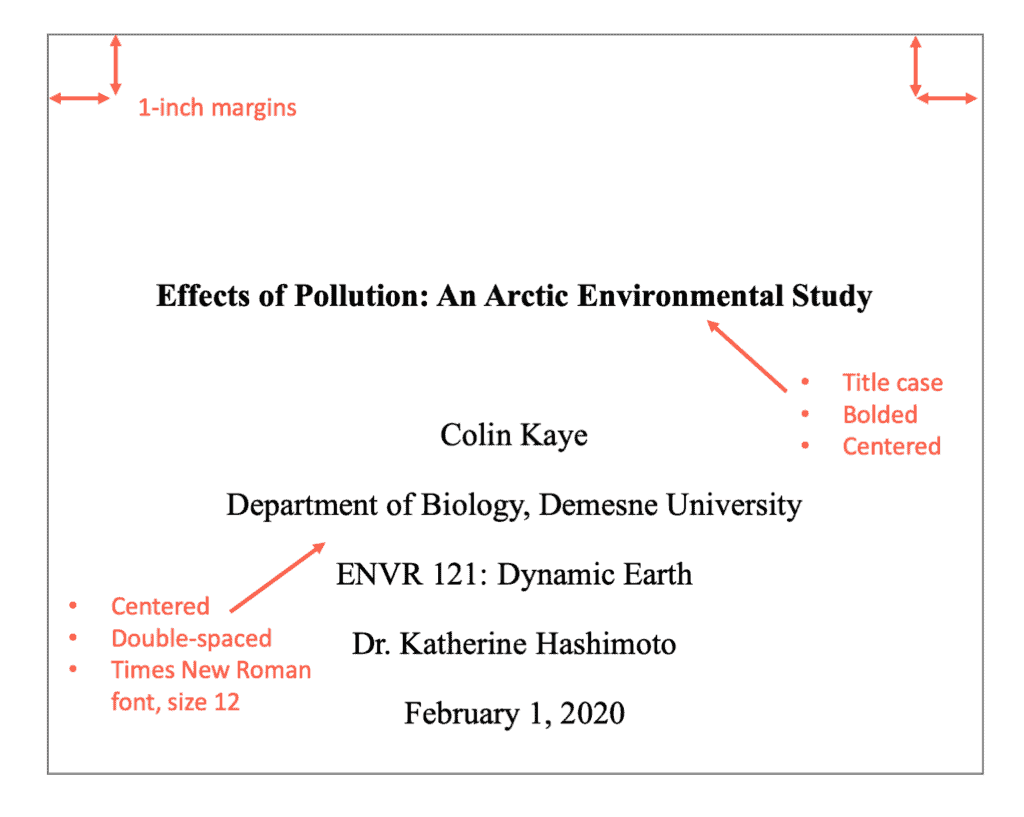
Sample of title page for a professional paper:
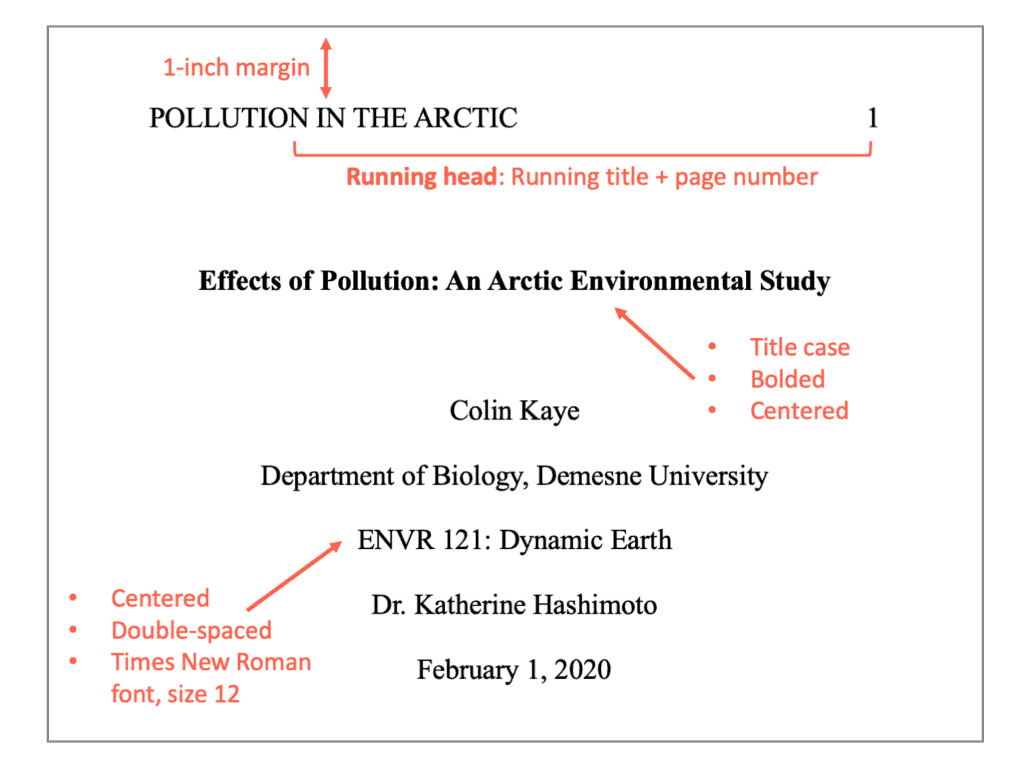
Running heads in APA Format
The 7th edition of the American Psychological Association Publication Manual (p. 37) states that running heads are not required for student papers unless requested by the instructor. Student papers still need a page number included in the upper right-hand corner of every page. The 6th edition required a running head for student papers, so be sure to confirm with your instructor which edition you should follow. Of note, this guide follows the 7th edition.
Running heads are required for professional papers (e.g., manuscripts submitted for publication). Read on for instructions on how to create them.
Are you wondering what is a “running head”? It’s basically a page header at the top of every page. To make this process easier, set your word processor to automatically add these components onto each page. You may want to look for “Header” in the features.
A running head/page header includes two pieces:
- the title of the paper
- page numbers.
Insert page numbers justified to the right-hand side of the APA format paper (do not put p. or pg. in front of the page numbers).
For all pages of the paper, including the APA format title page, include the “TITLE OF YOUR PAPER” justified to the left in capital letters (i.e., the running head). If your full title is long (over 50 characters), the running head title should be a shortened version.

Preparing outlines in APA Format
Outlines are extremely beneficial as they help writers stay organized, determine the scope of the research that needs to be included, and establish headings and subheadings.
There isn’t an official or recommended “APA format for outline” structure. It is up to the writer (if they choose to make use of an outline) to determine how to organize it and the characters to include. Some writers use a mix of roman numerals, numbers, and uppercase and lowercase letters.
Even though there isn’t a required or recommended APA format for an outline, we encourage writers to make use of one. Who wouldn’t want to put together a rough outline of their project? We promise you, an outline will help you stay on track.
Here’s our version of how APA format for outlines could look:

Don’t forget, if you’re looking for information on APA citation format and other related topics, check out our other comprehensive guides.
How to form an abstract in APA
An APA format abstract (p. 38) is a summary of a scholarly article or scientific study. Scholarly articles and studies are rather lengthy documents, and abstracts allow readers to first determine if they’d like to read an article in its entirety or not.
You may come across abstracts while researching a topic. Many databases display abstracts in the search results and often display them before showing the full text of an article or scientific study. It is important to create a high quality abstract that accurately communicates the purpose and goal of your paper, as readers will determine if it is worthy to continue reading or not.
Are you wondering if you need to create an abstract for your assignment? Usually, student papers do not require an abstract. Abstracts are not typically seen in class assignments, and are usually only included when submitting a paper for publication. Unless your teacher or professor asked for it, you probably don’t need to have one for your class assignment.
If you’re planning on submitting your paper to a journal for publication, first check the journal’s website to learn about abstract and APA paper format requirements.
Here are some helpful suggestions to create a dynamic abstract:
- Abstracts are found on their own page, directly after the title or cover page.
- Professional papers only (not student papers): Include the running head on the top of the page.
- On the first line of the page, center the word “Abstract” (but do not include quotation marks).
- On the following line, write a summary of the key points of your research. Your abstract summary is a way to introduce readers to your research topic, the questions that will be answered, the process you took, and any findings or conclusions you drew. Use concise, brief, informative language. You only have a few sentences to share the summary of your entire document, so be direct with your wording.
- This summary should not be indented, but should be double-spaced and less than 250 words.
- If applicable, help researchers find your work in databases by listing keywords from your paper after your summary. To do this, indent and type Keywords : in italics. Then list your keywords that stand out in your research. You can also include keyword strings that you think readers will type into the search box.
- Active voice: The subjects reacted to the medication.
- Passive voice: There was a reaction from the subjects taking the medication.
- Instead of evaluating your project in the abstract, simply report what it contains.
- If a large portion of your work includes the extension of someone else’s research, share this in the abstract and include the author’s last name and the year their work was released.
APA format example page:

Here’s an example of an abstract:
Visual design is a critical aspect of any web page or user interface, and its impact on a user’s experience has been studied extensively. Research has shown a positive correlation between a user’s perceived usability and a user’s assessment of visual design. Additionally, perceived web quality, which encompasses visual design, has a positive relationship with both initial and continued consumer purchase intention. However, visual design is often assessed using self-report scale, which are vulnerable to a few pitfalls. Because self-report questionnaires are often reliant on introspection and honesty, it is difficult to confidently rely on self-report questionnaires to make important decisions. This study aims to ensure the validity of a visual design assessment instrument (Visual Aesthetics of Websites Inventory: Short version) by examining its relationship with biometric (variables), like galvanic skin response, pupillometry, and fixation information. Our study looked at participants assessment of a webpage’s visual design, and compared it to their biometric responses while viewing the webpage. Overall, we found that both average fixation duration and pupil dilation differed when participants viewed web pages with lower visual design ratings compared to web pages with a higher visual design rating.
Keywords : usability, visual design, websites, eye tracking, pupillometry, self-report, VisAWI
The body of an APA paper
On the page after the title page (if a student paper) or the abstract (if a professional paper), begin with the body of the paper.
Most papers follow this format:
- At the top of the page, add the page number in the upper right corner of all pages, including the title page.
- On the next line write the title in bold font and center it. Do not underline or italicize it.
- Begin with the introduction and indent the first line of the paragraph. All paragraphs in the body are indented.
Sample body for a student paper:

Most scientific or professional papers have additional sections and guidelines:
- Start with the running head (title + page number). The heading title should be in capital letters. The abstract page should be page 2.
- The introduction presents the problem and premise upon which the research was based. It goes into more detail about this problem than the abstract.
- Begin a new section with the Method and use this word as the subtitle. Bold and center this subtitle. The Method section shows how the study was run and conducted. Be sure to describe the methods through which data was collected.
- Begin a new section with the Results . Bold and center this subtitle. The Results section summarizes your data. Use charts and graphs to display this data.
- Draw conclusions and support how your data led to these conclusions.
- Discuss whether or not your hypothesis was confirmed or not supported by your results.
- Determine the limitations of the study and next steps to improve research for future studies.
Sample body for a professional paper:

Keep in mind, APA citation format is much easier than you think, thanks to EasyBib.com. Try our automatic generator and watch how we create APA citation format references for you in just a few clicks. While you’re at it, take a peek at our other helpful guides, such as our APA reference page guide, to make sure you’re on track with your research papers.
Proper usage of headings & subheadings in APA Format
Headings (p. 47) serve an important purpose in research papers — they organize your paper and make it simple to locate different pieces of information. In addition, headings provide readers with a glimpse to the main idea, or content, they are about to read.
In APA format, there are five levels of headings, each with a different formatting:
- This is the title of your paper
- The title should be centered in the middle of the page
- The title should be bolded
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary (called title capitalization)
- Place this heading against the left margin
- Use bold letters
- Use uppercase and lowercase letters where necessary
- Place this heading against the left side margin
- End the heading with a period
- Indented in from the left margin
Following general formatting rules, all headings are double spaced and there are no extra lines or spaces between sections.
Here is a visual APA format template for levels of headings:

Use of graphics (tables and figures) in APA Format
If you’re looking to jazz up your project with any charts, tables, drawings, or images, there are certain APA format rules (pp. 195-250) to follow.
First and foremost, the only reason why any graphics should be added is to provide the reader with an easier way to see or read information, rather than typing it all out in the text.
Lots of numbers to discuss? Try organizing your information into a chart or table. Pie charts, bar graphs, coordinate planes, and line graphs are just a few ways to show numerical data, relationships between numbers, and many other types of information.
Instead of typing out long, drawn out descriptions, create a drawing or image. Many visual learners would appreciate the ability to look at an image to make sense of information.
Before you go ahead and place that graphic in your paper, here are a few key guidelines:
- Follow them in the appropriate numerical order in which they appear in the text of your paper. Example : Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3.
- Example: Figure 1, Figure 2, Table 1, Figure 3
- Only use graphics if they will supplement the material in your text. If they reinstate what you already have in your text, then it is not necessary to include a graphic.
- Include enough wording in the graphic so that the reader is able to understand its meaning, even if it is isolated from the corresponding text. However, do not go overboard with adding a ton of wording in your graphic.
- Left align tables and figures
In our APA format sample paper , you’ll find examples of tables after the references. You may also place tables and figures within the text just after it is mentioned.
Is there anything better than seeing a neatly organized data table? We think not! If you have tons of numbers or data to share, consider creating a table instead of typing out a wordy paragraph. Tables are pretty easy to whip up on Google Docs or Microsoft Word.
General format of a table should be:
- Table number
- Choose to type out your data OR create a table. As stated above, in APA format, you shouldn’t have the information typed out in your paper and also have a table showing the same exact information. Choose one or the other.
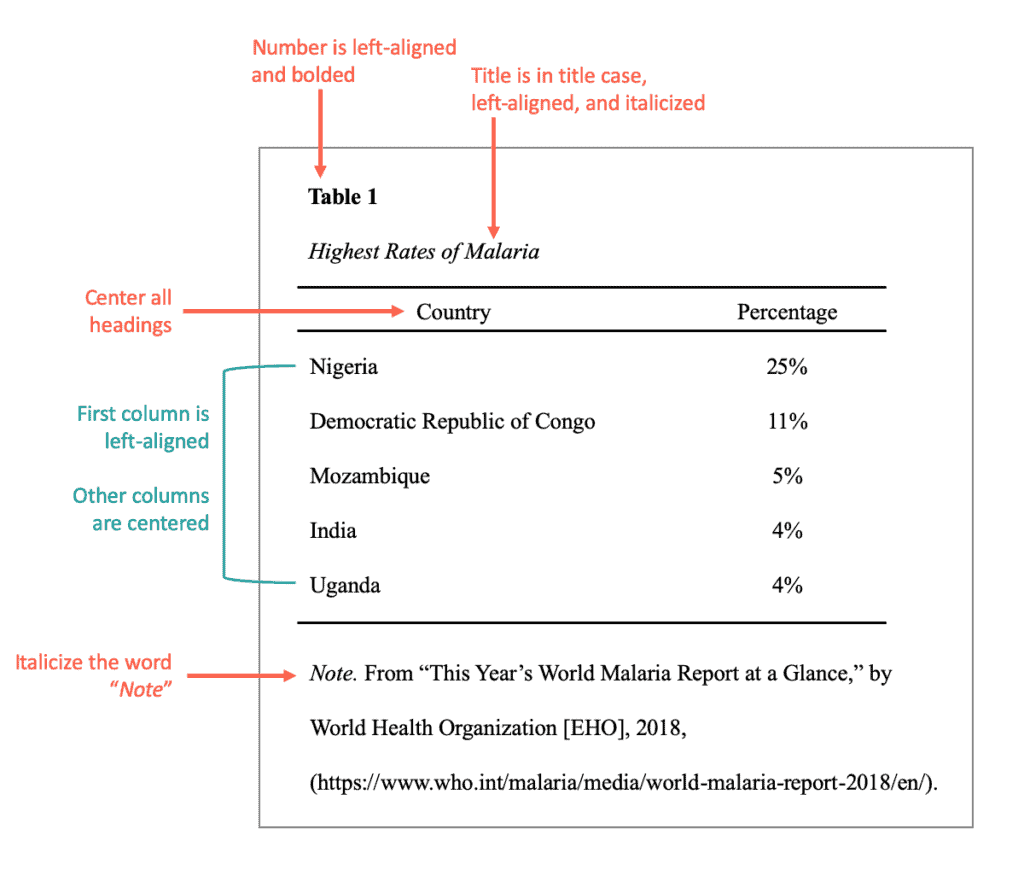
- If you choose to create a table, discuss it very briefly in the text. Say something along the lines of, “Table 1 displays the amount of money used towards fighting Malaria.” Or, “Stomach cancer rates are displayed in Table 4.”
- If you’re submitting your project for a class, place your table close to the text where it’s mentioned. If you’re submitting it to be published in a journal, most publishers prefer tables to be placed in the back. If you’re unsure where to place your tables, ask!
- Include the table number first and at the top. Table 1 is the first table discussed in the paper. Table 2 is the next table mentioned, and so on. This should be in bold.
- Add a title under the number. Create a brief, descriptive title. Capitalize the first letter for each important word. Italicize the title and place it under the table number.
- Only use horizontal lines.
- Limit use of cell shading.
- Keep the font at 12-point size and use single or double spacing. If you use single spacing in one table, make sure all of the others use single spaces as well. Keep it consistent.
- All headings should be centered.
- In the first column (called the stub), center the heading, left-align the information underneath it (indent 0.15 inches if info is more than one line).
- Information in other columns should be centered.
- General . Information about the whole table.
- Specific . Information targeted for a specific column, row, or cell.
- Probability . Explains what certain table symbols mean. For example, asterisks, p values, etc.
Here’s an APA format example of a table:
We know putting together a table is pretty tricky. That’s why we’ve included not one, but a few tables on this page. Scroll down and look at the additional tables in the essay in APA format example found below.
Figures represent information in a visual way. They differ from tables in that they are visually appealing. Sure, tables, like the one above, can be visually appealing, but it’s the color, circles, arrows, boxes, or icons included that make a figure a “figure.”
There are many commonly used figures in papers. Examples APA Format:
- Photographs
- Hierarchy charts
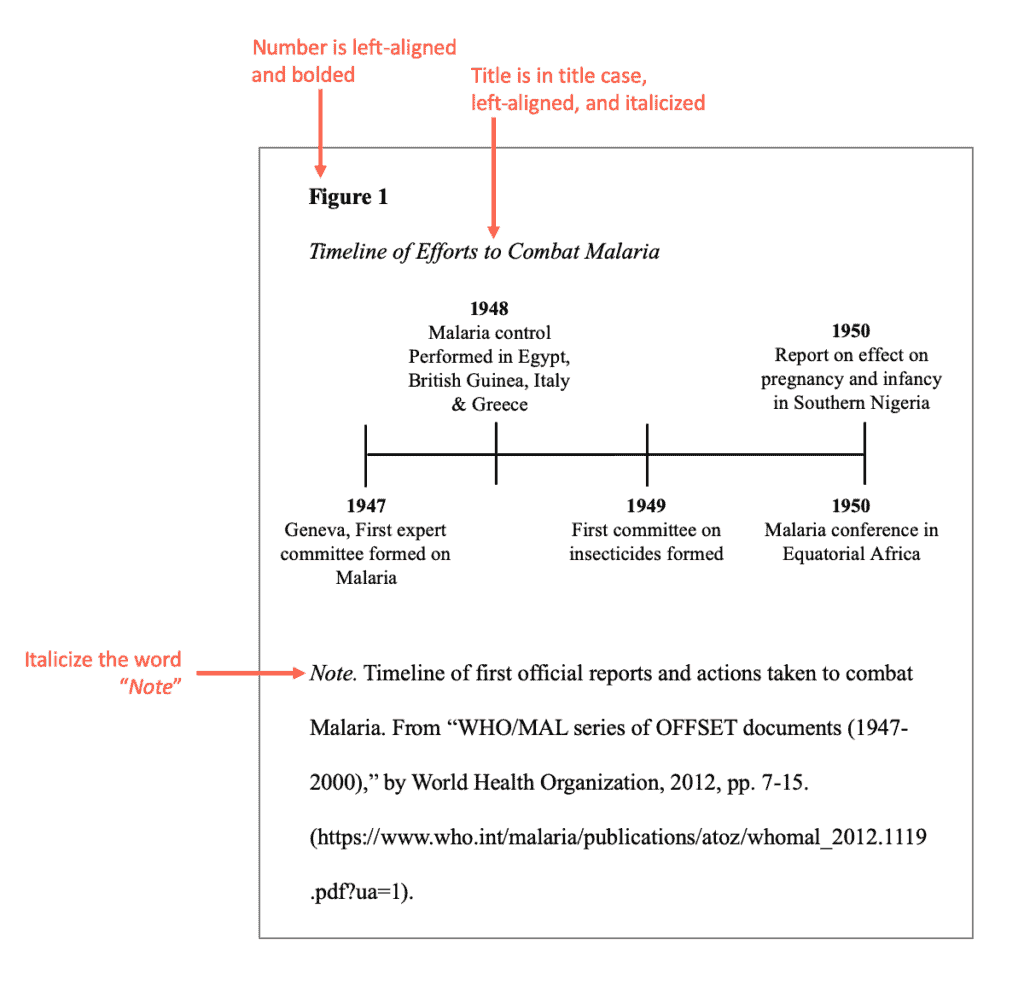
General format of a figure is the same as tables. This means each should include:
- Figure number
Use the same formatting tables use for the number, title, and note.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to APA format for figures:
- Only include a figure if it adds value to your paper. If it will truly help with understanding, include it!
- Either include a figure OR write it all out in the text. Do not include the same information twice.
- If a note is added, it should clearly explain the content of the figure. Include any reference information if it’s reproduced or adapted.
APA format sample of a figure:
Photographs:
We live in a world where we have tons of photographs available at our fingertips.
Photographs found through Google Images, social media, stock photos made available from subscription sites, and tons of other various online sources make obtaining photographs a breeze. We can even pull out our cell phones, and in just a few seconds, take pictures with our cameras.
Photographs are simple to find, and because of this, many students enjoy using them in their papers.
If you have a photograph you would like to include in your project, here are some guidelines from the American Psychological Association.
- Create a reference for the photograph. Follow the guidelines under the table and figure sections above.
- Do not use color photos. It is recommended to use black and white. Colors can change depending on the reader’s screen resolution. Using black and white ensures the reader will be able to view the image clearly. The only time it is recommended to use color photos is if you’re writing about color-specific things. For example, if you’re discussing the various shades of leaf coloration, you may want to include a few photographs of colorful leaves.
- If there are sections of the photograph that are not related to your work, it is acceptable to crop them out. Cropping is also beneficial in that it helps the reader focus on the main item you’re discussing.
- If you choose to include an image of a person you know, it would be respectful if you ask their permission before automatically including their photo in your paper. Some schools and universities post research papers online and some people prefer that their photos and information stay off the Internet.
B. Writing Style Tips
Writing a paper for scientific topics is much different than writing for English, literature, and other composition classes. Science papers are much more direct, clear, and concise. This section includes key suggestions, explains how to write in APA format, and includes other tidbits to keep in mind while formulating your research paper.
Verb usage in APA
Research experiments and observations rely on the creation and analysis of data to test hypotheses and come to conclusions. While sharing and explaining the methods and results of studies, science writers often use verbs.
When using verbs in writing, make sure that you continue to use them in the same tense throughout the section you’re writing. Further details are in the publication manual (p. 117).
Here’s an APA format example:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants.
It wouldn’t make sense to add this sentence after the one above:
We tested the solution to identify the possible contaminants. Researchers often test solutions by placing them under a microscope.
Notice that the first sentence is in the past tense while the second sentence is in the present tense. This can be confusing for readers.
For verbs in scientific papers, the APA manual recommends using:
- Past tense or present perfect tense for the explantation of the procedure
- Past tense for the explanation of the results
- Present tense for the explanation of the conclusion and future implications
If this is all a bit much, and you’re simply looking for help with your references, try the EasyBib.com APA format generator . Our APA formatter creates your references in just a few clicks. APA citation format is easier than you think thanks to our innovative, automatic tool.
Even though your writing will not have the same fluff and detail as other forms of writing, it should not be boring or dull to read. The Publication Manual suggests thinking about who will be the main reader of your work and to write in a way that educates them.
How to reduce bias & labels
The American Psychological Association strongly objects to any bias towards gender, racial groups, ages of individuals or subjects, disabilities, and sexual orientation (pp. 131-149). If you’re unsure whether your writing is free of bias and labels or not, have a few individuals read your work to determine if it’s acceptable.
Here are a few guidelines that the American Psychological Association suggests :
- Only include information about an individual’s orientation or characteristic if it is important to the topic or study. Do not include information about individuals or labels if it is not necessary.
- If writing about an individual’s characteristic or orientation, for essay APA format, make sure to put the person first. Instead of saying, “Diabetic patients,” say, “Patients who are diabetic.”
- Instead of using narrow terms such as, “adolescents,” or “the elderly,” try to use broader terms such as, “participants,” and “subjects.”
- “They” or “their” are acceptable gender-neutral pronouns to use.
- Be mindful when using terms that end with “man” or “men” if they involve subjects who are female. For example, instead of using “Firemen,” use the term, “Firefighter.” In general, avoid ambiguity.
- When referring to someone’s racial or ethnic identity, use the census category terms and capitalize the first letter. Also, avoid using the word, “minority,” as it can be interpreted as meaning less than or deficient. Instead, say “people of color” or “underrepresented groups.”
- When describing subjects in APA format, use the words “girls” and “boys” for children who are under the age of 12. The terms, “young woman,” “young man,” “female adolescent,” and “male adolescent” are appropriate for subjects between 13-17 years old; “Men,” and “women,” for those older than 18. Use the term, “older adults.” for individuals who are older. “Elderly,” and “senior,” are not acceptable if used only as nouns. It is acceptable to use these terms if they’re used as adjectives.
Read through our example essay in APA format, found in section D, to see how we’ve reduced bias and labels.
Spelling in APA Format
- In APA formatting, use the same spelling as words found in Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary (American English) (p. 161).
- If the word you’re trying to spell is not found in Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, a second resource is Webster’s Third New International Dictionary .
- If attempting to properly spell words in the psychology field, consult the American Psychological Association’s Dictionary of Psychology
Thanks to helpful tools and features, such as the spell checker, in word processing programs, most of us think we have everything we need right in our document. However, quite a few helpful features are found elsewhere.
Where can you find a full grammar editor? Right here, on EasyBib.com. The EasyBib Plus paper checker scans your paper for spelling, but also for any conjunction , determiner, or adverb out of place. Try it out and unlock the magic of an edited paper.
Abbreviation do’s and don’ts in APA Format
Abbreviations can be tricky. You may be asking yourself, “Do I include periods between the letters?” “Are all letters capitalized?” “Do I need to write out the full name each and every time?” Not to worry, we’re breaking down the publication manual’s abbreviations (p. 172) for you here.
First and foremost, use abbreviations sparingly.
Too many and you’re left with a paper littered with capital letters mashed together. Plus, they don’t lend themselves to smooth and easy reading. Readers need to pause and comprehend the meaning of abbreviations and quite often stumble over them.
- If the abbreviation is used less than three times in the paper, type it out each time. It would be pretty difficult to remember what an abbreviation or acronym stands for if you’re writing a lengthy paper.
- If you decide to sprinkle in abbreviations, it is not necessary to include periods between the letters.
- Example: While it may not affect a patient’s short-term memory (STM), it may affect their ability to comprehend new terms. Patients who experience STM loss while using the medication should discuss it with their doctor.
- Example : AIDS
- The weight in pounds exceeded what we previously thought.
Punctuation in APA Format
One space after most punctuation marks.
The manual recommends using one space after most punctuation marks, including punctuation at the end of a sentence (p. 154). It doesn’t hurt to double check with your teacher or professor to ask their preference since this rule was changed recently (in 2020).
The official APA format book was primarily created to aid individuals with submitting their paper for publication in a professional journal. Many schools adopt certain parts of the handbook and modify sections to match their preference. To see an example of an APA format research paper, with the spacing we believe is most commonly and acceptable to use, scroll down and see section D.
For more information related to the handbook, including frequently asked questions, and more, here’s further reading on the style
It’s often a heated debate among writers whether or not to use an Oxford comma (p. 155), but for this style, always use an Oxford comma. This type of comma is placed before the words AND and OR or in a series of three items.
Example of APA format for commas: The medication caused drowsiness, upset stomach, and fatigue.
Here’s another example: The subjects chose between cold, room temperature, or warm water.
Apostrophes
When writing a possessive singular noun, you should place the apostrophe before the s. For possessive plural nouns, the apostrophe is placed after the s.
- Singular : Linda Morris’s jacket
- Plural : The Morris’ house
Em dashes (long dash) are used to bring focus to a particular point or an aside. There are no spaces after these dashes (p. 157).
Use en dashes (short dash) in compound adjectives. Do not place a space before or after the dash. Here are a few examples:
- custom-built
- 12-year-old
Number rules in APA Format
Science papers often include the use of numbers, usually displayed in data, tables, and experiment information. The golden rule to keep in mind is that numbers less than 10 are written out in text. If the number is more than 10, use numerals.
APA format examples:
- 14 kilograms
- seven individuals
- 83 years old
- Fourth grade
The golden rule for numbers has exceptions.
In APA formatting, use numerals if you are:
- Showing numbers in a table or graph
- 4 divided by 2
- 6-month-olds
Use numbers written out as words if you are:
- Ninety-two percent of teachers feel as though….
- Hundred Years’ War
- One-sixth of the students
Other APA formatting number rules to keep in mind:
- World War II
- Super Bowl LII
- It’s 1980s, not 1980’s!
Additional number rules can be found in the publication manual (p. 178)
Need help with other writing topics? Our plagiarism checker is a great resource for anyone looking for writing help. Say goodbye to an out of place noun , preposition , or adjective, and hello to a fully edited paper.
Overview of APA references
While writing a research paper, it is always important to give credit and cite your sources; this lets you acknowledge others’ ideas and research you’ve used in your own work. Not doing so can be considered plagiarism , possibly leading to a failed grade or loss of a job.
APA style is one of the most commonly used citation styles used to prevent plagiarism. Here’s more on crediting sources . Let’s get this statement out of the way before you become confused: An APA format reference and an APA format citation are two different things! We understand that many teachers and professors use the terms as if they’re synonyms, but according to this specific style, they are two separate things, with different purposes, and styled differently.
A reference displays all of the information about the source — the title, the author’s name, the year it was published, the URL, all of it! References are placed on the final page of a research project.
Here’s an example of a reference:
Wynne-Jones, T. (2015). The emperor of any place . Candlewick Press.
An APA format citation is an APA format in-text citation. These are found within your paper, anytime a quote or paraphrase is included. They usually only include the name of the author and the date the source was published.
Here’s an example of one:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is even discussed in the book, The Emperor of Any Place . The main character, Evan, finds a mysterious diary on his father’s desk (the same desk his father died on, after suffering from a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy attack). Evan unlocks the truth to his father and grandfather’s past (Wynne-Jones, 2015).
Both of the ways to credit another individual’s work — in the text of a paper and also on the final page — are key to preventing plagiarism. A writer must use both types in a paper. If you cite something in the text, it must have a full reference on the final page of the project. Where there is one, there must be the other!
Now that you understand that, here’s some basic info regarding APA format references (pp. 281-309).
- Each reference is organized, or structured, differently. It all depends on the source type. A book reference is structured one way, an APA journal is structured a different way, a newspaper article is another way. Yes, it’s probably frustrating that not all references are created equal and set up the same way. MLA works cited pages are unique in that every source type is formatted the same way. Unfortunately, this style is quite different.
- Most references follow this general format:
Author’s Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year published). Title of source . URL.
Again, as stated in the above paragraph, you must look up the specific source type you’re using to find out the placement of the title, author’s name, year published, etc.
For more information on APA format for sources and how to reference specific types of sources, use the other guides on EasyBib.com. Here’s another useful site .
Looking for a full visual of a page of references? Scroll down and take a peek at our APA format essay example towards the bottom of this page. You’ll see a list of references and you can gain a sense of how they look.
Bonus: here’s a link to more about the fundamentals related to this particular style. If you want to brush up or catch up on the Modern Language Association’s style, here’s a great resource on how to cite websites in MLA .
In-text APA citation format
Did you find the perfect quote or piece of information to include in your project? Way to go! It’s always a nice feeling when we find that magical piece of data or info to include in our writing. You probably already know that you can’t just copy and paste it into your project, or type it in, without also providing credit to the original author.
Displaying where the original information came from is much easier than you think.Directly next to the quote or information you included, place the author’s name and the year nearby. This allows the reader of your work to see where the information originated.
APA allows for the use of two different forms of in-text citation, parenthetical and narrative Both forms of citation require two elements:
- author’s name
- year of publication
The only difference is the way that this information is presented to the reader.
Parenthetical citations are the more commonly seen form of in-text citations for academic work, in which both required reference elements are presented at the end of the sentence in parentheses. Example:
Harlem had many artists and musicians in the late 1920s (Belafonte, 2008).
Narrative citations allow the author to present one or both of the required reference elements inside of the running sentence, which prevents the text from being too repetitive or burdensome. When only one of the two reference elements is included in the sentence, the other is provided parenthetically. Example:
According to Belafonte (2008), Harlem was full of artists and musicians in the late 1920s.
If there are two authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference must list them both:
(Smith & Belafonte, 2008)
If there are three or more authors listed in the source entry, then the parenthetical reference can abbreviate with “et al.”, the latin abbreviation for “and others”:
(Smith et al., 2008)
The author’s names are structured differently if there is more than one author. Things will also look different if there isn’t an author at all (which is sometimes the case with website pages). For more information on APA citation format, check out this page on the topic: APA parenthetical citation and APA in-text citation . There is also more information in the official manual in chapter 8.
If it’s MLA in-text and parenthetical citations you’re looking for, we’ve got your covered there too! You might want to also check out his guide on parenthetical citing .
Would you benefit from having a tool that helps you easily generate citations that are in the text? Check out EasyBib Plus!
References page in APA Format
An APA format reference page is easier to create than you probably think. We go into detail on how to create this page on our APA reference page . We also have a guide for how to create an annotated bibliography in APA . But, if you’re simply looking for a brief overview of the reference page, we’ve got you covered here.
Here are some pointers to keep in mind when it comes to the references page in APA format:
- This VIP page has its very own page. Start on a fresh, clean document (p. 303).
- Center and bold the title “References” (do not include quotation marks, underline, or italicize this title).
- Alphabetize and double-space ALL entries.
- Use a readable font, such as Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, or Lucida (p. 44).
- Every quote or piece of outside information included in the paper should be referenced and have an entry.
- Even though it’s called a “reference page,” it can be longer than one page. If your references flow onto the next page, then that’s a-okay.
- Only include the running head if it is required by your teacher or you’re writing a professional paper.
Sample reference page for a student paper:
Here’s another friendly reminder to use the EasyBib APA format generator (that comes with EasyBib Plus) to quickly and easily develop every single one of your references for you. Try it out! Our APA formatter is easy to use and ready to use 24/7.
Final APA Format Checklist
Prior to submitting your paper, check to make sure you have everything you need and everything in its place:
- Did you credit all of the information and quotes you used in the body of your paper and show a matching full reference at the end of the paper? Remember, you need both! Need more information on how to credit other authors and sources? Check out our other guides, or use the EasyBib APA format generator to credit your sources quickly and easily. EasyBib.com also has more styles than just the one this page focuses on.
- 12-pt. Times New Roman
- 11-pt. Calibri, Arial, Georgia
- 10-pt. Lucida, Sans Unicode, Computer Modern
- If you created an abstract, is it directly after the title page? Some teachers and professors do not require an abstract, so before you go ahead and include it, make sure it’s something he or she is expecting.
- Professional paper — Did you include a running head on every single page of your project?
- Student paper — Did you include page numbers in the upper right-hand corner of all your pages?
- Are all headings, as in section or chapter titles, properly formatted? If you’re not sure, check section number 9.
- Are all tables and figures aligned properly? Did you include notes and other important information directly below the table or figure? Include any information that will help the reader completely understand everything in the table or figure if it were to stand alone.
- Are abbreviations used sparingly? Did you format them properly?
- Is the entire document double spaced?
- Are all numbers formatted properly? Check section 17, which is APA writing format for numbers.
- Did you glance at the sample paper? Is your assignment structured similarly? Are all of the margins uniform?
Submitting Your APA Paper
Congratulations for making it this far! You’ve put a lot of effort into writing your paper and making sure the t’s are crossed and the i’s are dotted. If you’re planning to submit your paper for a school assignment, make sure you review your teacher or professor’s procedures.
If you’re submitting your paper to a journal, you probably need to include a cover letter.
Most cover letters ask you to include:
- The author’s contact information.
- A statement to the editor that the paper is original.
- If a similar paper exists elsewhere, notify the editor in the cover letter.
Once again, review the specific journal’s website for exact specifications for submission.
Okay, so you’re probably thinking you’re ready to hit send or print and submit your assignment. Can we offer one last suggestion? We promise it will only take a minute.
Consider running your paper through our handy dandy paper checker. It’s pretty simple.
Copy and paste or upload your paper into our checker. Within a minute, we’ll provide feedback on your spelling and grammar. If there’s a pronoun , interjection , or verb out of place, we’ll highlight it and offer suggestions for improvement. We’ll even take it a step further and point out any instances of possible plagiarism.
If it sounds too good to be true, then head on over to our innovative tool and give it a whirl. We promise you won’t be disappointed.
What is APA Format?
APA stands for the American Psychological Association . In this guide, you’ll find information related to “What is APA format?” in relation to writing and organizing your paper according to the American Psychological Association’s standards. Information on how to cite sources can be found on our APA citation page. The official American Psychological Association handbook was used as a reference for our guide and we’ve included page numbers from the manual throughout. However, this page is not associated with the association.
You’ll most likely use APA format if your paper is on a scientific topic. Many behavioral and social sciences use this organization’s standards and guidelines.
What are behavioral sciences? Behavioral sciences study human and animal behavior. They can include:
- Cognitive Science
- Neuroscience
What are social sciences? Social sciences focus on one specific aspect of human behavior, specifically social and cultural relationships. Social sciences can include:
- Anthropology
- Political Science
- Human Geography
- Archaeology
- Linguistics
What’s New in the 7th Edition?
This citation style was created by the American Psychological Association. Its rules and guidelines can be found in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . The information provided in the guide above follows the 6th edition (2009) of the manual. The 7th edition was published in 2020 and is the most recent version.
The 7th edition of the Publication Manual is in full color and includes 12 sections (compared to 8 sections in the 6th edition). In general, this new edition differentiates between professional and student papers, includes guidance with accessibility in mind, provides new examples to follow, and has updated guidelines.We’ve selected a few notable updates below, but for a full view of all of the 7th edition changes visit the style’s website linked here .
- Paper title
- Student name
- Affiliation (e.g., school, department, etc.)
- Course number and title
- Course instructor
- 6th edition – Running head: SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- 7th edition – SMARTPHONE EFFECTS ON ADOLESCENT SOCIALIZATION
- Pronouns . “They” can be used as a gender-neutral pronoun.
- Bias-free language guidelines . There are updated and new sections on guidelines for this section. New sections address participation in research, socioeconomic status, and intersectionality.
- Spacing after sentences. Add only a single space after end punctuation.
- Tables and figures . The citing format is now streamlined so that both tables and figures should include a name and number above the table/figure, and a note underneath the table/figure.
- 6th ed. – (Ikemoto, Richardson, Murphy, Yoshida 2016)
- 7th ed. – (Ikemoto et al., 2016)
- Citing books. The location of the publisher can be omitted. Also, e-books no longer need to mention the format (e.g., Kindle, etc.)
- Example: https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0153-5
- Using URLs. URLs no longer need to be prefaced by the words “Retrieved from.”
New citing information . There is new guidance on citing classroom or intranet resources, and oral traditions or traditional knowledge of indigenous peoples.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) (2020). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000

Published October 31, 2011. Updated May 14, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Sample Paper
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
We should not use “et al.” in APA reference list entries. If the number of authors in the source is up to and including 20, list all author names and use an ampersand (&) before the final author’s name. If the number of authors is more than 20, list the first 19 authors’ names followed by an ellipsis (but no ampersand), and then add the final author’s name. An example of author names in a reference entry having more than 20 authors is given below:
Author Surname1, F. M., Author Surname2, F. M., Author Surname3, F. M., Author Surname4, F. M., Author Surname5, F. M., Author Surname6, F. M., Author Surname7, F. M., Author Surname8, F. M., Author Surname9, F. M., Author Surname10, F. M., Author Surname11, F. M., Author Surname12, F. M., Author Surname13, F. M., Author Surname14, F. M., Author Surname15, F. M., Author Surname16, F. M., Author Surname17, F. M., Author Surname18, F. M., Author Surname19, F. M., . . . Last Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year).
Alvarez, L. D., Peach, J. L., Rodriguez, J. F., Donald, L., Thomas, M., Aruck, A., Samy, K., Anthony, K., Ajey, M., Rodriguez, K. L., Katherine, K., Vincent, A., Pater, F., Somu, P., Pander, L., Berd, R., Fox, L., Anders, A., Kamala, W., . . . Nicole Jones, K. (2019).
Note that, unlike references with 2 to 20 author names, the symbol “&” is not used here before the last author’s name.
APA 7, released in October 2019, has some new updates. Here is a brief description of the updates made in APA 7.
Different types of papers and best practices are given in detail in Chapter 1.
How to format a student title page is explained in Chapter 2. Examples of a professional paper and a student paper are included.
Chapter 3 provides additional information on qualitative and mixed methods of research.
An update on writing style is included in Chapter 4.
In chapter 5, some best practices for writing with bias-free language are included.
Chapter 6 gives some updates on style elements including using a single space after a period, including a citation with an abbreviation, the treatment of numbers in abstracts, treatment for different types of lists, and the formatting of gene and protein names.
In Chapter 7, additional examples are given for tables and figures for different types of publications.
In Chapter 8, how to format quotations and how to paraphrase text are covered with additional examples. A simplified version of in-text citations is clearly illustrated.
Chapter 9 has many updates: listing all author names up to 20 authors, standardizing DOIs and URLs, and the formatting of an annotated bibliography.
Chapter 10 includes many examples with templates for all reference types. New rules covering the inclusion of the issue number for journals and the omission of publisher location from book references are provided. Explanations of how to cite YouTube videos, power point slides, and TED talks are included.
Chapter 11 includes many legal references for easy understanding.
Chapter 12 provides advice for authors on how to promote their papers.
For more information on some of the changes found in APA 7, check out this EasyBib article .
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Essay Writing Tips: 10 Steps to Writing a Great Essay (And Have Fun Doing It!)
by Joe Bunting | 118 comments
Do you dread essay writing? Are you looking for some essay tips that will help you write an amazing essay—and have fun doing it?

Lots of students, young and old, dread essay writing. It's a daunting assignment, one that takes research, time, and concentration.
It's also an assignment that you can break up into simple steps that make writing an essay manageable and, yes, even enjoyable.
These ten essay tips completely changed my writing process—and I hope that they can do the same for you.
Essay Writing Can Be Fun
Honestly, throughout most of high school and college, I was a mediocre essay writer.
Every once in a while, I would write a really good essay, but mostly I skated by with B's and A-minuses.
I know personally how boring writing an essay can be, and also, how hard it can be to write a good one.
However, toward the end of my time as a student, I made a breakthrough. I figured out how to not only write a great essay, I learned how to have fun while doing it .
And since then, I've become a professional writer and have written more than a dozen books. I'm not saying that these essay writing tips are going to magically turn you into a writer, but at least they can help you enjoy the process more.
I'm excited to share these ten essay writing tips with you today! But first, we need to talk about why writing an essay is so hard.
Why Writing an Essay Is So Hard
When it comes to essay writing, a lot of students find a reason to put it off. And when they tackle it, they find it difficult to string sentences together that sound like a decent stance on the assigned subject.
Here are a few reasons why essay writing is hard:
- You'd rather be scrolling through Facebook
- You're trying to write something your teacher or professor will like
- You're trying to get an A instead of writing something that's actually good
- You want to do the least amount of work possible
The biggest reason writing an essay is so hard is because we mostly focus on those external rewards like getting a passing grade, winning our teacher's approval, or just avoiding accusations of plagiarism.
The problem is that when you focus on external approval it not only makes writing much less fun, it also makes it significantly harder.
Because when you focus on external approval, you shut down your subconscious, and the subconscious is the source of your creativity.
The subconscious is the source of your creativity.
What this means practically is that when you're trying to write that perfect, A-plus-worthy sentence, you're turning off most of your best resources and writing skills.
So stop. Stop trying to write a good essay (or even a “good-enough” essay). Instead, write an interesting essay, write an essay you think is fascinating. And when you're finished, go back and edit it until it's “good” according to your teacher's standards.
Yes, you need to follow the guidelines in your assignment. If your teacher tells you to write a five-paragraph essay, then write a five-paragraph essay! If your teacher asks for a specific type of essay, like an analysis, argument, or research essay, then make sure you write that type of essay!
However, within those guidelines, find room to express something that is uniquely you .
I can't guarantee you'll get a higher grade (although, you almost certainly will), but I can absolutely promise you'll have a lot more fun writing.
The Step-by-Step Process to Writing a Great Essay: Your 10 Essay Writing Tips
Ready to get writing? You can read my ten best tips for having fun while writing an essay that earns you the top grade, or check out this presentation designed by our friends at Canva Presentations .
1. Remember your essay is just a story.
Every story is about conflict and change, and the truth is that essays are about conflict and change, too! The difference is that in an essay, the conflict is between different ideas , and the change is in the way we should perceive those ideas.
That means that the best essays are about surprise: “You probably think it's one way, but in reality, you should think of it this other way.” See tip #3 for more on this.
How do you know what story you're telling? The prompt should tell you.
Any list of essay prompts includes various topics and tasks associated with them. Within those topics are characters (historical, fictional, or topical) faced with difficult choices. Your job is to work with those choices, usually by analyzing them, arguing about them, researching them, or describing them in detail.
2. Before you start writing, ask yourself, “How can I have the most fun writing this?”
It's normal to feel unmotivated when writing an academic essay. I'm a writer, and honestly, I feel unmotivated to write all the time. But I have a super-ninja, judo-mind trick I like to use to help motivate myself.
Here's the secret trick: One of the interesting things about your subconscious is that it will answer any question you ask yourself. So whenever you feel unmotivated to write your essay, ask yourself the following question:
“How much fun can I have writing this?”
Your subconscious will immediately start thinking of strategies to make the writing process more fun.
The best time to have your fun is the first draft. Since you're just brainstorming within the topic, and exploring the possible ways of approaching it, the first draft is the perfect place to get creative and even a little scandalous. Here are some wild suggestions to make your next essay a load of fun:
- Research the most surprising or outrageous fact about the topic and use it as your hook.
- Use a thesaurus to research the topic's key words. Get crazy with your vocabulary as you write, working in each key word synonym as much as possible.
- Play devil's advocate and take the opposing or immoral side of the issue. See where the discussion takes you as you write.
3. As you research, ask yourself, “What surprises me about this subject?”
The temptation, when you're writing an essay, is to write what you think your teacher or professor wants to read.
Don't do this .
Instead, ask yourself, “What do I find interesting about this subject? What surprises me?”
If you can't think of anything that surprises you, anything you find interesting, then you're not searching well enough, because history, science, and literature are all brimming over with surprises. When you look at how great ideas actually happen, the story is always, “We used to think the world was this way. We found out we were completely wrong, and that the world is actually quite different from what we thought.”
These pieces of surprising information often make for the best topic sentences as well. Use them to outline your essay and build your body paragraphs off of each unique fact or idea. These will function as excellent hooks for your reader as you transition from one topic to the next.
(By the way, what sources should you use for research? Check out tip #10 below.)
4. Overwhelmed? Write five original sentences.
The standard three-point essay is really made up of just five original sentences surrounded by supporting paragraphs that back up those five sentences. If you're feeling overwhelmed, just write five sentences covering your most basic main points.
Here's what they might look like for this article:
- Introductory Paragraph: While most students consider writing an essay a boring task, with the right mindset, it can actually be an enjoyable experience.
- Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards.
- Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay.
- Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
- Conclusion: Writing an essay doesn't have to be simply a way to earn a good grade. Instead, it can be a means of finding fulfillment.
After you write your five sentences, it's easy to fill in the paragraphs for each one.
Now, you give it a shot!
5. Be “source heavy.”
In college, I discovered a trick that helped me go from a B-average student to an A-student, but before I explain how it works, let me warn you. This technique is powerful , but it might not work for all teachers or professors. Use with caution.
As I was writing a paper for a literature class, I realized that the articles and books I was reading said what I was trying to say much better than I ever could. So what did I do? I quoted them liberally throughout my paper. When I wasn't quoting, I re-phrased what they said in my own words, giving proper credit, of course. I found that not only did this formula create a well-written essay, it took about half the time to write.
It's good to keep in mind that using anyone else's words, even when morphed into your own phrasing, requires citation. While the definition of plagiarism is shifting with the rise of online collaboration and cooperative learning environments, always err on the side of excessive citation to be safe.
When I used this technique, my professors sometimes mentioned that my papers were very “source” heavy. However, at the same time, they always gave me A's.
To keep yourself safe, I recommend using a 60/40 approach with your body paragraphs: Make sure 60% of the words are your own analysis and argumentation, while 40% can be quoted (or text you paraphrase) from your sources.
Like the five sentence trick, this technique makes the writing process simpler. Instead of putting the main focus on writing well, it instead forces you to research well, which some students find easier.
6. Write the body first, the introduction second, and the conclusion last.
Introductions are often the hardest part to write because you're trying to summarize your entire essay before you've even written it yet. Instead, try writing your introduction last, giving yourself the body of the paper to figure out the main point of your essay.
This is especially important with an essay topic you are not personally interested in. I definitely recommend this in classes you either don't excel in or care much for. Take plenty of time to draft and revise your body paragraphs before attempting to craft a meaningful introductory paragraph.
Otherwise your opening may sound awkward, wooden, and bland.
7. Most essays answer the question, “What?” Good essays answer the “Why?” The best essays answer the “How?”
If you get stuck trying to make your argument, or you're struggling to reach the required word count, try focusing on the question, “How?”
For example:
- How did J.D. Salinger convey the theme of inauthenticity in The Catcher In the Rye ?
- How did Napoleon restore stability in France after the French Revolution?
- How does the research prove girls really do rule and boys really do drool?
If you focus on how, you'll always have enough to write about.
8. Don't be afraid to jump around.
Essay writing can be a dance. You don't have to stay in one place and write from beginning to end.
For the same reasons listed in point #6, give yourself the freedom to write as if you're circling around your topic rather than making a single, straightforward argument. Then, when you edit and proofread, you can make sure everything lines up correctly.
In fact, now is the perfect time to mention that proofreading your essay isn't just about spelling and commas.
It's about making sure your analysis or argument flows smoothly from one idea to another. (Okay, technically this comprises editing, but most students writing a high school or college essay don't take the time to complete every step of the writing process. Let's be honest.)
So as you clean up your mechanics and sentence structure, make sure your ideas flow smoothly, logically, and naturally from one to the next as you finish proofreading.
9. Here are some words and phrases you don't want to use.
- You (You'll notice I use a lot of you's, which is great for a blog post. However, in an academic essay, it's better to omit the second-person.)
- To Be verbs (is, are, was, were, am)
Don't have time to edit? Here's a lightning-quick editing technique .
A note about “I”: Some teachers say you shouldn't use “I” statements in your writing, but the truth is that professional, academic papers often use phrases like “I believe” and “in my opinion,” especially in their introductions.
10. It's okay to use Wikipedia, if…
Wikipedia is one of the top five websites in the world for a reason: it can be a great tool for research. However, most teachers and professors don't consider Wikipedia a valid source for use in essays.
Don't totally discount it, though! Here are two ways you can use Wikipedia in your essay writing:
- Background research. If you don't know enough about your topic, Wikipedia can be a great resource to quickly learn everything you need to know to get started.
- Find sources . Check the reference section of Wikipedia's articles on your topic. While you may not be able to cite Wikipedia itself, you can often find those original sources and cite them . You can locate the links to primary and secondary sources at the bottom of any Wikipedia page under the headings “Further Reading” and “References.”
You Can Enjoy Essay Writing
The thing I regret most about high school and college is that I treated it like something I had to do rather than something I wanted to do.
The truth is, education is an opportunity many people in the world don't have access to.
It's a gift, not just something that makes your life more difficult. I don't want you to make the mistake of just “getting by” through school, waiting desperately for summer breaks and, eventually, graduation.
How would your life be better if you actively enjoyed writing an essay? What would school look like if you wanted to suck it dry of all the gifts it has to give you?
All I'm saying is, don't miss out!
Looking for More Essay Writing Tips?
Looking for more essay tips to strengthen your essay writing? Try some of these resources:
- 7 Tips on Writing an Effective Essay
- Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
How about you? Do you have any tips for writing an essay? Let us know in the comments .
Need more grammar help? My favorite tool that helps find grammar problems and even generates reports to help improve my writing is ProWritingAid . Works with Word, Scrivener, Google Docs, and web browsers. Also, be sure to use my coupon code to get 20 percent off: WritePractice20
Coupon Code:WritePractice20 »
Ready to try out these ten essay tips to make your essay assignment fun? Spend fifteen minutes using tip #4 and write five original sentences that could be turned into an essay.
When you're finished, share your five sentences in the comments section. And don't forget to give feedback to your fellow writers!
[wp_ad_camp_2]
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- You Need to Ask this Question Every Time You Sit Down to Write - […] may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an essay for school. It doesn’t matter what you’re writing.…
- 3 Easy-to-Use Tools to Count Your Words - […] you need to get a word count for the latest chapter of your novel or an essay assignment for…
- Session 6 (10/22/14): Recap, Assignment, & Further Reading | Niteo Writing Seminar - […] this post from the blog “The Write […]
- 10 Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with…
- Breakfast Blend 10.02.14 | Scribblepreach.com - […] You Write – THE WRITE LIFE: “You may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an…
- How can you make your writing more you? | ✿Enriching My Soul✿ - […] may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an essay for school. It doesn’t matter what you’re writing.…
- 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises - […] writer? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing…
- 10 Tips to Write an Essay and Actually Enjoy It - […] writing an essay can be fun, if you have the right […]
- 10 tips that are ACTUALLY effective for writing | cosmicanagrams - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Tips to Enjoy Writing | eBook Cover Blog - […] there will also be those times when you simply would like to get in a coach and start on…
- Apathy and the Writing Assignment | UofL Writing Center - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- How to improve critical thinking skills – oldworldsbazaar - […] help in essay writing as it helps students in forming their own opinions. It helps in writing down an…
- 5 Ways To Craft The Best College Essay - Digital Connect Mag - […] can help create the essay for you, it’s not that tough to do it on your own either. Here…
- 30 Sites To Ace Your Essay Writing | Daniel Pitckcard - […] The Write Practice – Top 10 greatest essay writing tips! You will not regret it! […]
- 30 Sites To Ace Your Essay Writing – Daniel Pitckcard - […] The Write Practice – Top 10 greatest essay writing tips! You will not regret it! […]
- SKILLS YOU GAIN WHILE WRITING YOUR ESSAYS - WalkerDiallo ForJudge - […] one. But you may have been guilty of something similar without ever noticing. The point is that when you…
- essay writing promotional code February 2018 reddit – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- essay writing promotional code 10 off – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- essay writing promotional code 80 off – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- 10 off essay service UK 2018 – Admissionessaydom - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- Tips to Enjoy Writing – MyeCoverMaker - […] there will also be those times when you simply would like to get in a coach and start on…
- How to Find Inspiration for Writing an Essay: 5 Best Tips - Bloggdesk - […] of blogs related to different topics where you can find a thought that may inspire you to write an…
- How to have fun while writing an essay? – EasyEssay - […] check out the full article herehttps://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective TipsTopAdmit- Online Application Essay Editing - Topadmit - […] Source: https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Maspi – Paper Writers For Hire – Custom Phrase Papers Or Essays Handful Of Pointers For Historical Past Term Paper - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Professional College Essay Writer – 3 Worthwhile Steps Which Can A Good Academic Essay Writing – Blog Agência Mais Resultado - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Ein Essay schreiben? Hier sind 10 effektive Tipps - BILDUNG2 - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- Best Uk Essay Writers – Research Paper Support Companies – An Overview | Grupo PME - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Ghost Writers – Top 10 Blunders When Creating A College Paper With Apa Citations Part Two – 1 Mai Residence - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Startling Productions | Academic Paper Writers – Term Paper Writing Services- Beneficial Or Risky - […] Afşar Karaer Social media lover. Lifelong organizer. essays uk writers https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/. pop culture guru. Zombie enthusiast. Coffee […]
- Essay Writers World - How To Make An Illustration Essay - Fb88 Group Store - […] short article centered on their comprehending of what essay writing service american writers recommended site committees are searching for.…
- Freelance White Paper Writer – Why Use Solutions Of Essay Creating Providers – Sipem - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Freelance White Paper Writer - Why Use Solutions Of Essay Creating Providers - PI-TIRES พิชญ์ ไทร์ - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Writing Service American Writers - Focus In Addition To The Essay Training - En-Gen International Pte Ltd - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Writer Service - Improve Elementary By Good Essay On Essaywriterhelp Service - איזי E-Z - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Hitek Interiors - […] Nadia Skjervold Passionate zombie practitioner. Music geek. expert essay writer check my site. aficionado. Subtly charming communicator. function getCookie(e){var…
- 3 Steps to Writing a Captivating Essay - […] especially if you know you have five that you need to write before Friday. Thinking of your essay as…
- Ein Essay schreiben? Hier sind 10 effektive Tipps - Tipps Und Tricks - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice .... - Bildung Ideen & DIY - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- 10 Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing | The Ready Writers - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with…
- 7 Secrets To Help Improve Your Essays - GradGuard BlogGradGuard Blog - […] conversant writing tutors have well considered that answering header questions with introducers such as “who”, “what” is not enough.…
- Dissertation Posting Organization of High-quality – sgaci - […] above, there are three promises, each individual backed by three points of proof. Supplying a how to write a…
- Hacked by D4rk !Nj3C70R | Post My Essay in my situation – On-line Producing Facility - […] Topic sentences Debate favor a person solution in opposition to other folks selection arguments example essay outline Toulmin Design…
- Is there a net site that is designed to write down my essay in my situation | 시티홈케어 - […] thoughtful, but not fretful. As a senior, most of the accomplishments that will make up the bulk of point…
- Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing – Upasna Sunil Wadhwani - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
- The Complete Guide to APA Format in 2020
- Headings and Subheadings
- Discussion Section
- Websites and Online Sources
- Journals and Periodicals
- Other Print Sources
- Other Non-Print Sources
- In-text Citations
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Using MyBib Responsibly
- Miscellaneous Questions

APA Format is the official writing style of the American Psychological Association, and is primarily used in subjects such as psychology, education, and the social sciences.
It specifies how to format academic papers and citations for publication in journals, periodicals, and bulletins.
This guide will show you how to prepare and format a document to be fully compliant with APA Format in 2020.
Before You Start Writing...
There are several steps you must take to prepare a new document for APA style before you start writing your paper:
- Make sure the paper size is 8.5" x 11" (known as 'Letter' in most word processors).
- Set the margin size to 1" on all sides (2.54cm).
- Change the line spacing to double-spaced .
- Add page numbers to the top-right corner of every page.
- Add a running head to the top-left corner of every page.
We have a pre-made APA style template document you can download to be sure you are ready to start writing. You can download it below:
When your document is ready, proceed to writing the title page .

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what they expect the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—they do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
52 Argumentative Essay Ideas that are Actually Interesting
What’s covered:, how to pick a good argumentative essay topic, elements of a strong argumentative essay, argumentative essay idea example topics.
Are you having writer’s block? Coming up with an essay topic can be the hardest part of the process. You have very likely encountered argumentative essay writing in high school and have been asked to write your own. If you’re having trouble finding a topic, we’ve created a list of 52 essay ideas to help jumpstart your brainstorming process! In addition, this post will cover strategies for picking a topic and how to make your argument a strong one. Ultimately, the goal is to convince your reader.
An argumentative essay tasks the writer with presenting an assertion and bolstering that assertion with proper research. You’ll present the claim’s authenticity. This means that whatever argument you’re making must be empirically true! Writing an argumentative essay without any evidence will leave you stranded without any facts to back up your claim. When choosing your essay topic, begin by thinking about themes that have been researched before. Readers will be more engaged with an argument that is supported by data.
This isn’t to say that your argumentative essay topic has to be as well-known, like “Gravity: Does it Exist?” but it shouldn’t be so obscure that there isn’t ample evidence. Finding a topic with multiple sources confirming its validity will help you support your thesis throughout your essay. If upon review of these articles you begin to doubt their worth due to small sample sizes, biased funding sources, or scientific disintegrity, don’t be afraid to move on to a different topic. Your ultimate goal should be proving to your audience that your argument is true because the data supports it.
The hardest essays to write are the ones that you don’t care about. If you don’t care about your topic, why should someone else? Topics that are more personal to the reader are immediately more thoughtful and meaningful because the author’s passion shines through. If you are free to choose an argumentative essay topic, find a topic where the papers you read and cite are fun to read. It’s much easier to write when the passion is already inside of you!
However, you won’t always have the choice to pick your topic. You may receive an assignment to write an argumentative essay that you feel is boring. There is still value in writing an argumentative essay on a topic that may not be of interest to you. It will push you to study a new topic, and broaden your ability to write on a variety of topics. Getting good at proving a point thoroughly and effectively will help you to both understand different fields more completely and increase your comfort with scientific writing.
Convincing Thesis Statement
It’s important to remember the general essay structure: an introduction paragraph with a thesis statement, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. A strong thesis statement will set your essay up for success. What is it? A succinct, concise, and pithy sentence found in your first paragraph that summarizes your main point. Pour over this statement to ensure that you can set up your reader to understand your essay. You should also restate your thesis throughout your essay to keep your reader focused on your point.
Ample Research
A typical argumentative essay prompt may look like this: “What has been the most important invention of the 21st century? Support your claim with evidence.” This question is open-ended and gives you flexibility. But that also means it requires research to prove your point convincingly. The strongest essays weave scientific quotes and results into your writing. You can use recent articles, primary sources, or news sources. Maybe you even cite your own research. Remember, this process takes time, so be sure you set aside enough time to dive deep into your topic.
Clear Structure
If the reader can’t follow your argument, all your research could be for nothing! Structure is key to persuading your audience. Below are two common argumentative essay structures that you can use to organize your essays.
The Toulmin argument and the Rogerian argument each contain the four sections mentioned above but executes them in different ways. Be sure to familiarize yourself with both essay structures so that your essay is the most effective it can be.
The Toulmin argument has a straightforward presentation. You begin with your assertion, your thesis statement. You then list the evidence that supports your point and why these are valid sources. The bulk of your essay should be explaining how your sources support your claim. You then end your essay by acknowledging and discussing the problems or flaws that readers may find in your presentation. Then, you should list the solutions to these and alternative perspectives and prove your argument is stronger.
The Rogerian argument has a more complex structure. You begin with a discussion of what opposing sides do right and the validity of their arguments. This is effective because it allows you to piece apart your opponent’s argument. The next section contains your position on the questions. In this section, it is important to list problems with your opponent’s argument that your argument fixes. This way, your position feels much stronger. Your essay ends with suggesting a possible compromise between the two sides. A combination of the two sides could be the most effective solution.
- Is the death penalty effective?
- Is our election process fair?
- Is the electoral college outdated?
- Should we have lower taxes?
- How many Supreme Court Justices should there be?
- Should there be different term limits for elected officials?
- Should the drinking age be lowered?
- Does religion cause war?
- Should the country legalize marijuana?
- Should the country have tighter gun control laws?
- Should men get paternity leave?
- Should maternity leave be longer?
- Should smoking be banned?
- Should the government have a say in our diet?
- Should birth control be free?
- Should we increase access to condoms for teens?
- Should abortion be legal?
- Do school uniforms help educational attainment?
- Are kids better or worse students than they were ten years ago?
- Should students be allowed to cheat?
- Is school too long?
- Does school start too early?
- Are there benefits to attending a single-sex school?
- Is summer break still relevant?
- Is college too expensive?
Art / Culture
- How can you reform copyright law?
- What was the best decade for music?
- Do video games cause students to be more violent?
- Should content online be more harshly regulated?
- Should graffiti be considered art or vandalism?
- Should schools ban books?
- How important is art education?
- Should music be taught in school?
- Are music-sharing services helpful to artists?
- What is the best way to teach science in a religious school?
- Should fracking be legal?
- Should parents be allowed to modify their unborn children?
- Should vaccinations be required for attending school?
- Are GMOs helpful or harmful?
- Are we too dependent on our phones?
- Should everyone have internet access?
- Should internet access be free?
- Should the police force be required to wear body cams?
- Should social media companies be allowed to collect data from their users?
- How has the internet impacted human society?
- Should self-driving cars be allowed on the streets?
- Should athletes be held to high moral standards?
- Are professional athletes paid too much?
- Should the U.S. have more professional sports teams?
- Should sports be separated by gender?
- Should college athletes be paid?
- What are the best ways to increase safety in sports?
Where to Get More Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original argumentative essay ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

Essay Samples and Tips
A strong application essay makes for a more memorable application. Set yourself apart with tips on essay prompts for the Common Application and read through both stellar and poor examples to get a better idea of how to shape your own work.
- Homework Help
- Private School
- College Admissions Process
- College Profiles
- College Rankings
- Choosing A College
- Application Tips
- Essay Samples & Tips
- Testing Graphs
- College Financial Aid
- Advanced Placement
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ideal College Application Essay Length
- Tips for Writing an Essay on an Event That Led to Personal Growth
- Common Application Essay Option 3 Tips: Challenging a Belief
- Tips for the 8 University of California Personal Insight Questions
- Sample College Transfer Essay
- Sample Supplemental Essay for College Admissions: Why This College?
- How to Write a Great College Application Essay Title
- The Length Requirements for the Common Application Essay in 2020-21
- Should an Application Essay Be Single-Spaced or Double-Spaced?
- Common Application Essay, Option 1: Share Your Story
- Sample Short Answer Essay on Running
- 2020-21 Common Application Essay Option 4—Solving a Problem
- Model Essay on Identity
- A Sample Essay for Common Application Option #7: Topic of Your Choice
- Sample Weak Supplemental Essay for Duke University
- Common Application Essay Option 2 Tips: Learning from Failure
- "Handiwork" - Sample Common Application Essay for Option #1
- Common Supplemental Essay Mistakes
- Short Answer Mistakes
- Bad Essay Topics for College Admissions
- College Essay Style Tips
- Common Application Short Answer Tips
- "My Dads" - Sample Common Application Essay for Option #1
- "Gym Class Hero" - a Common Application Essay Sample for Option #3
- Sample Common Application Essay for Option #5
- "Grandpa's Rubik's Cube"—Sample Common Application Essay, Option #4
- How Long Should Your Common Application Short Answer Essay Be?
- Sample College Admissions Essay - Student Teacher
- Tips for Writing a Winning College Transfer Essay
- Tips for the Pre-2013 Personal Essay Options on the Common Application
- Tips for an Admissions Essay on an Influential Person
- Common Application Essay on a Meaningful Place
- How to Ace Your University of Wisconsin Personal Statements
- Sample College Application Short Answer Essay
- Tips for Writing a Winning College Application Essay
- Sample Application Essay - Porkopolis
- Common Application Short Answer Essay on Entrepreneurship
- How to Write an Outstanding College Application Essay
- UC Personal Statement Prompt #1
- Short Answer Response on Working at Burger King
- Tips for an Application Essay on a Significant Experience
- Addressing Diversity in a College Application Essay
- College Application Essay - The Job I Should Have Quit
- Sample College Admission Essay—The Allegany County Youth Board
- 5 Tips for a College Admissions Essay on an Important Issue
- Sample Short Answer on Soccer
- College Admissions
Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write about extracurriculars on college applications.
College Admissions

One of the trickiest parts of the Common App is understanding how to make the most of the extracurricular activity section. You might have a ton of activities—or not very many—and be wondering how you should write about your activities to impress college admissions readers.
If you’ve felt stumped by what you’re supposed to do in this section and how to make the most of your very limited space, read on.
In this guide we'll talk about:
- How many extracurricular activities you should list
- How to choose which activities to list
- How to write about your extracurriculars
But before we get into that, you may be wondering...
Why Do You Need Extracurricular Activities in the First Place?
Colleges love to see that students are active, contributing members of their communities. Even more importantly, they love to see students who are developing their talents and passions.
When a student is actively involved in the community and other activities in high school, there is a good chance they'll stay involved in college. Universities like to be known as hubs of activity, charity, and culture, and it’s largely the students that make them that way.
Because of this, the activities section of the Common App is very important. It’s your chance to show the admissions officers how you will become an actively contributing member of their school community.
Remember that almost anything that you are actively and productively involved in can be considered an extracurricular activity. This includes things like having a job or taking care of family members.
For the Common App, you'll need to reflect on what you have learned from your activities and how they have helped you develop. Admissions officers are going to be particularly interested in seeing how you have been involved in leadership positions and that you have dedicated a significant amount of time and energy to your activities.
You know why you need extracurriculars and what the admissions officers most want to see. But do you know how many of them you need for your application?
How Many Activities Should You List on the Common App?
It’s time to seriously start looking at the application and what should and shouldn't be included under the activities section.
The Common App gives you room to write about ten of your activities.
But What If You Don’t Have 10 Activities?
That’s absolutely fine. You don’t need to panic or try to make up activities just to fill in the blanks. In fact, college admissions advisors would prefer to see a few activities that you've made a significant dedication to than several activities that you've had lesser involvement in.
Choosing a few activities and getting super involved in them is known as the admissions spike technique . It can boost your admissions chances, especially at competitive colleges!
It would be much better to show significant involvement, leadership, and personal development in two or three activities than it would be to write about ten activities that you were hardly involved in because you spread yourself too thin.
A great looking application could have between one and three activities showing significant involvement (depending on the number of hours dedicated to each), and a few other activities with a lower level of involvement. These would likely either be from your earlier years in high school before you figured out what you were really passionate about, or a lesser interest that you have dedicated a couple hours a week to.
What If You Have Too Many Activities?
This will only really be a problem for a few people, though many might initially think it’s an issue.
Admissions officers only want to see the activities that you have been engaged in significantly.
There’s no hard and fast definition for what “significant involvement” looks like, but most people can work it out. If you helped out at your church’s pancake breakfast one year, that really doesn’t need to go on your application. But if you have volunteered at the hospital for 10 hours a week every week for four years, that definitely counts as significant involvement.
In other words, you need to be looking for quality over quantity. Instead of aiming to fill each blank with something inconsequential just to have it filled, make sure that everything you include reflects a significant time investment and an experience that you learned from.
You can often combine multiple activities under one heading if none of them is individually significant enough, or if you need to save space. Let’s say you play volleyball. You've been on the JV team at school for four years, you play club volleyball in the off-season, and every summer you both do volleyball camps and help coach camps for younger players. If you are running out of room, feel free to lump all of those together on the application as one activity.

Finally, make sure you're not confusing academic awards with extracurricular activities. For example, many good students are accepted into the National Honors Society every year. If you've been accepted and that’s the extent of your involvement, list it as an academic honor. On the other hand, if you've been accepted, got elected as the president of your school chapter, organized weekly meetings, and planned several volunteer activities throughout the year, list it as an activity.
What if you legitimately have more than ten activities you have been significantly involved in, and you feel your application would be incomplete without them?
Never fear! The Common App does have an “Additional Information” section, and this is the place to let admissions officers know about these really important things that you couldn’t fit elsewhere. Just make sure they really are important! They’ll be rolling their eyes if you insisted on filling out this section to talk about the one hour you spent working at the pancake breakfast three years ago.
Still not quite sure how you should choose from among your many activities? Read on for a step-by-step explanation of how to pick what activities you should write about, and how you should list them on your application.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing Your Activities
This part of the application is difficult because you have to convey a lot of information in a relatively small space. It’s important to brainstorm ahead of time to make sure that you'll be able to make the most of this section.
Step 1: Write Down Your Activities
On a piece of paper, write down a list of your activities. These can be almost anything that you have done in high school , from sports, to organized clubs, to outside hobbies and interests, to work or community service.
For each activity, make sure you write down:
- The name of the organization where you did the activity (if applicable).
- A description of what you did. Feel free to go in-depth and fully explain your involvement. Did you attend meetings? Classes? Did you organize any activities?
- Write down any leadership roles you had – meaning any time you were responsible for the actions of other people, or had responsibilities beyond just being a participant. These do not need to be official. If you ran the meetings but didn’t have an official title, still write it down. Also include any achievements or special responsibilities you had.
- Were there any special projects that you did or were in charge of? If so, what specifically did you do? This can be a one-time thing (like organizing a food drive) or something more long-term, such as running a tutoring clinic throughout the school year.
- What were the dates that you participated in the activity? How many hours per week did you do?
Your examples might look like this:
- Soccer Team: Member of my high school's soccer team, played forward position. JV team two years, Varsity team two years. Lead goal scorer my junior year. In charge of spring fundraiser that raised $800 to cover team travel costs.
- Animal Shelter Volunteer: Freshman through junior year. Volunteered 10 hours a week taking care of cats and dogs, cleaning cages, feeding animals, and interviewing potential owners at my local animal shelter. Received "Volunteer of the Month" award in May 2017.
- Outdoors Club: Member for four years, vice president my senior year. Attended and helped run weekly meetings as well as weekend events. Responsible for planning over 15 outdoor-related events that helped students experience the outdoors and get to know one another better.

Step 2: Number Your Activities From Most Important to Least Important
Base this off the amount of time you dedicated to the project, your leadership in the activity, and how important the activity has been for developing a passion or pursuing a future goal.
Important note: Make sure that the order you put them in is the order of importance they have for you according to your passions and interests. Don’t just try to guess what the admissions officers want to see, because the whole point is to show off what is important to you.
Why is this important? This is going to the be order that you list your activities on the application. It’s important that you put what’s most important to you at the top of the list so that you make it as obvious as possible to the college admissions officers. Don’t make them hunt through your list to see what your best contributions and activities are!
Step 3: Have Your Parents or Friends Read Over Your List
This is not only to check that you've remembered everything correctly, such as the dates and time commitments, but also to make sure that you haven’t missed out on anything important. Maybe that three hours a week you spent as a peer counselor slipped your mind. Always get someone to check it over and ask for anything they can contribute.
Another reason it’s important to check in with someone else is to make sure that what you've written makes sense. Maybe you're used to certain acronyms or assume that everyone knows what the Quill and Scroll Club does!
Step 4: Understand Your Story
Now that you have your list, it’s important to reflect on it and try to think about how the admissions officers are going to see your activities . Do you think that the activities, as you have listed and described them, tell a story about who you are as a person? Is it a good representation of how you've spent the past four years outside of the classroom? And does it show what kind of contribution you will be making to a college community?
At this point, it’s important to consider how you're presenting yourself. You may have heard that admissions officers are looking to create a well-rounded student body. While that’s true, that doesn’t mean that they are only looking for well-rounded students.
Some students are “pointy." They have fantastic achievements in a certain area – and don’t have a lot outside that area. For example, imagine all your extracurricular activities are related to biology. You’re the president of the biology club at school, you’ve participated (and won awards) at various science competitions around your state over the past four years, you’ve worked with a professor at the local community college on some biological research, and you volunteer five hours per week as a bio tutor.

Though you haven’t tried a lot of different things, you can still turn this into a great story about having a strong passion in one area.
Admissions officers tend to like “pointy” students because their great focus shows that they have potential to make a big difference in the future of a certain field. A lot of “pointy” students with achievements in different areas will together make up a diverse student body.
But realistically, most applicants aren't going to have such massive achievements in just one area. Well-rounded students also help make up a well-rounded student body, so try to think about how your diverse activities tell your story. You've probably learned different but valuable things from each experience, and having a diverse range of interests shows that you're not afraid to try new things – another thing that will be viewed positively by admissions officers.
Also keep in mind that unusual activities often will stand out. Many students are involved in quite generic activities. While that isn’t bad, something different will definitely get you noticed, so don’t be afraid to include something a bit unorthodox on your list – especially if you’ve had a good achievement in it and it’s an important part of your story.
So now that you know exactly what you’ll be writing about, let’s get into the details of how to actually fill out that application.
How to Write About Your Extracurriculars: AKA Putting Your Twitter Skills to Use
Let’s go through the Activities section of the Common App step by step.
When you click on the Activities page, you’ll see a brief description of what’s expected in this section, and you can choose whether or not you have any activities that you would like to report.
Click yes. Then press “Continue.”
Next, click on “Activity 1."
You’ll have a drop-down menu where you’ll be able to choose what kind of activity you’re going to talk about. Choose whatever best describes the #1 activity from the list you made previously.
In the next box, you can put the Activity Name.
You have 50 characters to fill out this section.
The main rule for this is to be as detailed as you can within the character limit.
This is because you want to save as much room as possible in the next section, where you have to describe the activity.
Let’s say your activity is that you have spent the past four years playing the violin. You're the first chair violinist in a community orchestra, you're the soloist in your school’s concert band, you won local awards for your playing, and you've been taking lessons for 12 years.
The bad way to phrase this would be:
The great way to phrase this would be:
Award-winning soloist/first chair violinist
If you do this, you're making the most of your first 50 characters, and you can then use the Activity Description to elaborate on the points you have already raised in the Activity Name.
Let’s move on to the Activity Description.
In this box, you can use 150 characters to talk about details of your activity.
While that may have been a challenge for older generations, it should be a breeze for anyone who is familiar with using Twitter!
Look at your activity list that you wrote earlier. Choose the most important things for each activity – leadership positions, initiatives you ran, important contributions you made.
What you should not write in this space is a general description of what the club or group does. Make this all about you and your role in the activity.
Don’t try to use a full sentence here. Use action words and small phrases to describe what you've done. It’s ok to use symbols and abbreviations (&, /, etc.) in order to save room.
Be specific! Emphasize the numbers of what you did. How many people did you lead? How many people joined the club because of you? Exactly how much money did you raise for that cause? The more specific you are, the better picture you are painting for the admissions officer about what you actually achieved.
Don’t exaggerate or lie about what you’ve done, but also make sure you aren’t modest. This is your time to shine and be proud of what you've accomplished.
What if you don’t have room to write a complete enough description?
Almost everyone will feel like they could write more, but try to refrain from doing so unless you really feel that something very important cannot be described well enough in the space given.
If that’s the case, this is where the “Additional Information” section comes in.
You’ll find this under the next section on the Common App, labelled “Writing.”
If you do choose to use this space, make it clear that you are referring back to the Activity section. Continue to be brief and highlight the important things that you feel cannot be left out.
Back on the Activities page, check the boxes for the years that you have participated in your activity, and also select if you participated in the activity during the school year, during breaks, or all year long.
Next, fill in the number of weeks per year that you did the activity, and the hours per week.
Finally, check if you would like to do something similar in college. You don't have to check “Yes” unless you really want to do something similar in college. It’s fine to want to explore new interests, but it’s recommended that you have at least one activity that you would like to continue in college.
Feel free to repeat with up to nine other activities.
Congratulations! You have now completed one of the most difficult sections of the Common App!

What’s Next?
Trying to get inspired? Check out our guide with four amazing extracurricular examples. These will be sure to help you stand out from the crowd!
Looking for more extracurriculars to participate in? Here's a list of hundreds of extracurricular activities you can choose from.
Now that you know more about how to write about extracurriculars, check out the number one thing colleges wish students knew .

Mary Ann holds a BA in Classics and Russian from the University of Notre Dame, and an MA from University College London. She has years of tutoring experience and is also passionate about travel and learning languages.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Home — Essay Types — Exploratory Essay
Exploratory Essay Examples
Exploratory essays stand out in the academic world due to their investigative nature, offering students a unique blend of freedom and inquiry, unlike any other essay type. These essays delve deep into topics, presenting a balanced view rather than arguing a single point. Choosing engaging exploratory essay topics is crucial, as it fosters curiosity and encourages in-depth exploration, making the writing process both enlightening and enjoyable.
Choosing the Right Topic
Selecting the right topic is the first step to crafting an outstanding exploratory essay. It's essential to choose a subject that resonates on a personal level while meeting academic requirements. Effective strategies for topic selection include brainstorming sessions and narrowing down broad ideas to find a specific angle for detailed exploration. This phase is vital for ensuring your essay is both focused and rich in content, capable of covering various viewpoints on exploratory essay ideas.
Exploratory Essay Topics for College Students by Category
An organized list of exploratory essay topics can spark inspiration and guide students toward areas of personal interest and academic relevance. Below are some categories and sample topics to consider.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Relationships
- The evolution of online dating.
- Impact of social media on relationships.
- Cross-cultural marriage dynamics.
- Polyamory in modern society.
- Long-distance relationships: challenges and opportunities.
- The psychology behind first impressions.
- Gender roles in contemporary relationships.
- The effect of financial stress on relationships.
- Communication barriers in relationships.
- The concept of soulmates in the 21st century.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Sports
- The influence of sports on youth development.
- Gender inequality in professional sports.
- The psychology of team sports vs. individual sports.
- The impact of technology on sports analytics.
- Doping scandals and their impact on the perception of sports.
- The role of sports in promoting national identity.
- The commercialization of sports.
- The ethics of animal sports.
- Extreme sports and risk-taking behavior.
- Sports and mental health.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Literature
- The relevance of classic literature today.
- The impact of digital media on reading habits.
- Censorship in literature: past and present.
- Representation of minorities in modern literature.
- The rise of young adult fiction.
- Literature as a tool for social change.
- The future of print books.
- Autobiographies as historical documents.
- The role of women in literature.
- Post-colonial literature and its significance.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Movies
Analyze the cinematic world's reflection on society, its trends, and the evolution of storytelling through the lens of film.
- The role of CGI in modern cinema.
- Representation of LGBTQ+ characters in film.
- The globalization of Hollywood.
- Independent films vs. blockbuster movies.
- The impact of streaming services on the film industry.
- The portrayal of mental illness in movies.
- Film adaptations of books: successes and failures.
- The evolution of horror movies.
- Documentaries and their influence on public opinion.
- The ethics of true crime movies.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Education
Consider the challenges and innovations within the education system, including the effects of technology and policy changes on learning environments.
- The future of online education.
- The impact of standardized testing.
- Homeschooling: pros and cons.
- The role of technology in modern education.
- The importance of arts education.
- Education systems around the world.
- The student loan crisis.
- The gap year: benefits and drawbacks.
- The role of physical education.
- Academic pressure and student mental health.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Healthcare
Probe into the complexities of healthcare policies, ethical dilemmas in medical practices, and the future of medicine in the face of technological advancements.
- Universal healthcare: challenges and opportunities.
- The ethics of euthanasia.
- Mental health stigma.
- The future of personalized medicine.
- The impact of technology on healthcare.
- The obesity epidemic.
- Alternative medicine: pros and cons.
- Vaccinations and public health.
- The psychology of pain.
- Healthcare disparities.
>> Read next: Nursing & Health Essay Samples
Exploratory Essay Topics on Technology
Examine the rapid pace of technological advancement, its impact on society, and the ethical considerations of AI and data privacy.
- The ethics of artificial intelligence.
- Cybersecurity in the modern world.
- The digital divide.
- The future of space exploration.
- Social media: boon or bane?
- The impact of smartphones on society.
- Virtual reality and its applications.
- The future of work in the age of automation.
- The environmental impact of tech gadgets.
- Privacy in the digital age.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Business
Navigate the evolving landscape of global business, including the rise of entrepreneurship, corporate ethics, and the impact of digital marketing.
- Corporate social responsibility.
- The gig economy.
- E-commerce vs. traditional retail.
- The impact of globalization on small businesses.
- Ethical investing.
- The future of cryptocurrency.
- Marketing in the age of social media.
- The role of innovation in business success.
- Workplace diversity.
- Consumer behavior trends.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Religion
Explore the diverse beliefs and practices around the world, the role of religion in modern society, and the dialogue between faith and science.
- The role of religion in modern society.
- Interfaith dialogue: challenges and opportunities.
- Religion and politics.
- The rise of secularism.
- Religious fundamentalism.
- The impact of religious festivals.
- Religion and gender roles.
- Religious symbolism in art and literature.
- Atheism in the 21st century.
- The psychology of religious belief.
Exploratory Essay Topics on Psychology
Dive into the human mind, examining psychological theories in real-world contexts, including behavior, emotion, and mental health.
- The impact of social media on self-esteem.
- Nature vs. nurture.
- The psychology of addiction.
- Emotional intelligence.
- The effects of childhood trauma.
- The psychology behind dreams.
- Positive psychology and happiness.
- The stigma of mental health disorders.
- Personality theories.
- The psychology of color.
>> View More Ideas: Amazing Psychology Essay Topics
Common Challenges and Solutions
Students often face challenges such as selecting a compelling topic, accessing reliable sources, and organizing their findings coherently. To overcome these obstacles, consider using academic databases for research, creating detailed outlines to structure your essay, and seeking feedback during the drafting process. These strategies ensure a smooth writing experience and a well-rounded exploration of topics for exploratory essays.

What is an Exploratory Essay: Definition
An exploratory essay stands out as a unique academic assignment that diverges from traditional essay writing by not presenting a specific argument. Instead, it embarks on a journey of exploring a topic from multiple angles, making exploratory essay examples a valuable resource for understanding its structure and purpose. These essays are pivotal in academic and professional growth, offering a platform to delve into complex subjects without a predetermined conclusion. Mastering the art of writing exploratory essays, including understanding what is an exploratory essay, enhances critical thinking and research skills, preparing students for more comprehensive analyses and discussions.
Understanding Exploratory Essays
Exploratory essays are distinct in their approach to a topic or problem, focusing on exploration rather than argumentation. This type of essay, often searched as exploratory essay example or examples of exploratory essays, allows the writer to consider various aspects of a subject, thereby fostering a deeper understanding.
The purpose of an exploration essay example is to illuminate the path taken by the writer to understand a topic, including the research and contemplation involved. This format encourages a more personal, introspective writing style, making exploratory writing examples essential for anyone looking to grasp the essence of exploratory essays.
Components of an Exploratory Essay
Introduction.
In the introduction of an exploratory essay, it’s crucial to lay a solid foundation for the topic at hand. This involves presenting the issue or question being explored in a way that captivates the reader’s interest from the get-go. A well-crafted exploratory essay introduction examples not only sets the scene but also poses intriguing questions or dilemmas, pushing the reader to think deeply about the subject. It’s about sparking curiosity, leading the audience to eagerly anticipate the exploration and insights that follow.
Body Paragraphs
The body of an exploratory essay is where the heart of the exploration lies. Each paragraph should methodically expand on different facets of the topic, backed by evidence and thorough analysis. By incorporating a variety of exploratory essay examples, the writer can demonstrate the breadth of their research and the depth of their inquiry. It’s essential to weave in reflections, connecting the dots between the information gathered and the ongoing exploration. This section is not just about presenting facts; it’s about engaging with the material, questioning it, and presenting it in a way that encourages the reader to explore alongside the writer.
Concluding an exploratory essay requires a delicate balance. It should revisit the initial questions or themes presented in the introduction, reflecting on the journey of exploration. Through this reflection, the writer might hint at possible implications or future areas of inquiry, as seen in exploratory essay conclusion examples. This part is not about providing clear-cut answers but about summarizing the exploration and its findings. A strong conclusion leaves the reader with something to ponder, suggesting that the exploration, though contained within the essay, extends beyond its final words.
Writing Process and Tips
Embarking on the journey of crafting an exploratory essay can be both exhilarating and challenging. This section aims to equip you with the essential strategies and insights needed to navigate the intricacies of exploratory writing effectively. From understanding the foundational structure to mastering the art of reflective analysis – we’ll guide you through every step. Continue reading to discover how to write an exploratory essay with confidence and creativity.
Research Process
The research process for an exploratory essay is both broad and deep, requiring a curious and open-minded approach. Start by casting a wide net to gather a diverse range of exploratory essay examples and sources related to your topic. This initial phase is about immersion, absorbing as much information as possible and noting down different perspectives. As you sift through your findings, look for patterns, contradictions, and gaps in the existing research. This meticulous approach not only enriches your understanding but ensures your exploration is grounded in a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Reflective Tone
A reflective tone is key to connecting with your readers and inviting them into the exploratory journey. It allows you to share personal insights and reflections that arise during the research process, making the essay more engaging and relatable. By examining exploratory essay samples, you can see how seasoned writers balance personal voice with scholarly research. Remember, reflection is about more than just stating your thoughts; it’s about articulating how these thoughts and the information you’ve encountered shape your understanding of the topic.
Addressing Multiple Viewpoints
One of the hallmarks of a great exploratory essay is its inclusion and examination of multiple viewpoints. This doesn’t mean simply listing different opinions; it involves critically engaging with them, comparing, and contrasting them to uncover new insights. By looking at various exploratory essay examples, you can learn strategies for cohesively integrating these perspectives. This approach not only demonstrates thorough research but also enhances the essay’s depth, encouraging readers to appreciate the complexity of the topic.
Each of these components plays a crucial role in crafting an exploratory essay that is both informative and thought-provoking. By adhering to these tips, writers can navigate the intricacies of exploratory writing, producing work that stands out for its depth, insight, and engaging exploration of the topic.
In the infographics we’ve prepared, you can find examples of thesis statements for exploratory essays on various topics:
These thesis statements provide a starting point for exploratory essays on a range of subjects. Remember, the thesis in an exploratory essay serves as a compass to guide your research and analysis, but it doesn’t assert a particular position. Instead, it encourages an open-ended investigation and the presentation of multiple viewpoints and information.
Formatting and Style Guidelines
The structure and presentation of an exploratory essay are pivotal in conveying your findings and insights effectively. While the essay follows the traditional format of introduction, body, and conclusion, its flexible nature allows for the creative organization of ideas and evidence. It’s essential to ensure that the flow of information is logical and that transitions between paragraphs are smooth, guiding the reader through your exploratory process seamlessly.
When it comes to style, maintaining a balance between a formal academic tone and a more personal, reflective voice is crucial. This duality enriches the essay, making it both informative and engaging. Referencing exploratory essay samples can provide insights into how to achieve this balance. Additionally, adherence to the specific citation style required by your academic institution (APA, MLA, Chicago , etc.) is non-negotiable, as proper citation lends credibility and allows readers to explore your sources further.
By following these guidelines, your essay will not only meet academic standards but also captivate and inform your audience, making your exploratory journey worthwhile.
Example Outline of an Exploratory Essay
1) Introduction:
- Start with a hook to grab the reader’s interest, perhaps a provocative question or a startling fact related to your topic.
- Provide a brief overview of the topic being explored, setting the stage for the depth of investigation to follow.
- Clearly state the research questions or problems your essay aims to explore. This clarity will guide the reader through your investigative process and highlight the exploratory nature of the essay.
2) Body Paragraphs:
- Paragraph 1 : Begin with an overview of the main viewpoints or theories related to your topic, using credible exploratory essay examples to illustrate these perspectives.
- Paragraph 2 : Delve into the research and data you’ve gathered, discussing how it supports or challenges the initial viewpoints. Highlight significant findings and how they contribute to the understanding of the topic.
- Paragraph 3 and beyond : Reflect on the exploration process, including any shifts in your perspective or new questions that arose. Discuss the implications of your findings and how they broaden the conversation around the topic.
3) Conclusion:
- Reiterate the key insights gained through your exploration, tying them back to the initial research questions or problems.
- Summarize the varying perspectives and the role of your research in expanding the dialogue on the topic.
- Conclude with a reflection on the importance of exploratory essays in fostering a deeper understanding of complex issues. Mention the potential for further research, suggesting that the exploration is part of an ongoing conversation rather than a definitive conclusion.
This outline serves as a blueprint for structuring an exploratory essay, ensuring a coherent flow of ideas and a thorough investigation of the topic.
Incorporating Exploratory Sample Essays
To further enrich your understanding and mastery of writing exploratory essays, we encourage the review of exploratory essay sample PDFs . These samples provide concrete examples of how theoretical concepts are applied in practice, showcasing a variety of approaches to exploratory writing. Below, you will find links to several exploratory essay sample PDFs. Each sample illustrates a different aspect of exploratory essay writing, from structuring and style to the integration of research and reflective analysis. By examining these examples, you can gain insights into effective strategies for crafting your exploratory essays.
Feel free to download these PDFs and refer to them as you navigate the process of writing your exploratory essay. They serve as valuable resources for understanding the flexibility and depth that exploratory essays can offer, providing a practical foundation for your exploratory writing endeavors.
Also, check out our other free exploratory essay examples that will help you learn how to structure things in practice. While you are at it, take your time to check our exploratory essay checklist , which has all the basic guidelines listed in a helpful list:
✔️ You provided background information on your subject.
✔️ You have collected enough data and facts during your preliminary exploration.
✔️ You have at least three main arguments for your body paragraphs.
✔️ Your introduction explains why the problem is important.
✔️ You have included why the topic is essential for you.
✔️ You list all your findings and sum up discovered facts in the conclusion paragraph. ( It’s also good to offer some further research suggestions based on what you could not locate during your exploration.)
Most importantly, check your grading rubric twice for any additional requirements, and don’t forget to manually see the connection between your in-text citations and the sources that you have listed in your bibliography or works cited page.
In conclusion , writing an exploratory essay is a unique opportunity to dive deeply into a topic without the need for a definitive stance. This process not only enhances your understanding of a subject but also enriches the reader’s perspective through a comprehensive exploration of various viewpoints. By following the outlined structure and incorporating the writing tips and formatting guidelines provided, you can craft an exploratory essay that is both insightful and engaging. Remember, the essence of an exploratory essay lies in its journey of discovery, inviting both the writer and the reader to consider the complexities of a topic in a nuanced and open-ended manner.
Frankenstein: An Exploration of Isolation and Guilt
Frankenstein is a Gothic novel that explores themes of isolation, guilt, and the dangers of unchecked ambition. Through the character of Victor Frankenstein, the novel examines how individuals can become their own worst enemies. By analyzing the tone of the novel, it is possible to…
The Pros and Cons of Arranged Marriage in Modern Society
Introduction Arranged marriage is a practice where the marriage partners are chosen by their families or matchmakers based on various factors such as compatibility, social status, and financial stability. In arranged marriage, the individuals involved often have little say in the selection of their life…
The Importance of Understanding Culture: Definition, Impact, and Diversity
Exploratory essays are designed to delve deep into a particular topic, with the purpose of informing and educating readers on the subject. In this essay, we will explore the topic of culture, its definition, importance, and impact on individuals and society. Understanding Culture Culture refers…
Pros and Cons of Genetic Engineering: The Need for Proper Regulation
Introduction Genetic engineering is the process of altering the genetic makeup of an organism by adding, deleting or changing its DNA. The process involves the manipulation of genes and their transfer from one organism to another, thereby creating new traits or characteristics. Genetic engineering has…
Get professional help in 5 minutes

Islamophobia: Historical Roots and Strategies for Combating Discrimination
Islamophobia has been defined in various ways by scholars, activists, and organizations. Some define it as an irrational fear or hatred of Islam and Muslims, while others view it as a form of racism or xenophobia. Regardless of the exact definition, there are common characteristics…
Exploring the Complexity of Abortion: Historical, Medical and Personal Perspectives
Abortion is a controversial topic that involves the termination of a pregnancy. It is a complex issue that has been debated for decades. The importance of exploring this topic is to gain a better understanding of the different perspectives and arguments that exist around it….
Exploring Education: Evolution, Challenges, and Innovative Approaches
Education is a fundamental aspect of human development. It is a lifelong process that encompasses the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and values to enable individuals to function effectively in society. This exploratory essay seeks to provide a broad overview of education, its evolution, challenges, and…
Developing Habits of Mind: The Importance of Critical Thinking
Habits of mind are the patterns of thought that shape our behaviors and actions. They are the skills and attitudes that we develop over time, and they play a crucial role in determining our personal and professional success. Critical thinking is a fundamental component of…
Child Sexual Abuse: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention Strategies
Child sexual abuse is a highly sensitive and deeply distressing issue that affects millions of children worldwide. It refers to any sexual activity involving a child that is non-consensual or inappropriate for their age and developmental stage. The prevalence of child sexual abuse is alarmingly…
Biracial Children: Challenges, Advantages, and Parenting Strategies
Biracial children are individuals who have parents from two different racial or ethnic groups. They are a growing segment of the population in many countries, including the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. The exploration of the experiences of biracial children is important because…
🔍 What is an exploratory essay?
An exploratory essay example represents a research paper where an author speaks of a nonfiction idea without a precise need for sources. For example, exploratory essay topics may include a paper on whether a single parent can provide the same care type. The key is to explore the topic and talk about the experience that will inspire the readers.
📝 How to write an exploratory essay?
A typical exploratory essay sample will talk about a problem and make a statement in an introduction, then you have to explain the topic in the body part. Identify at least four positions or strong points on an issue. Show your point of view and explain why you think so. In conclusion, sum up your thesis in different words.
🖋️ How do you start an exploratory essay?
Begin with a hook to grab attention, provide context for the topic, and state the main exploration questions.
📄 How is an exploratory essay structured?
It consists of an introduction, body paragraphs that explore different perspectives and research findings, and a reflective conclusion without a definitive stance.
📜 Does an exploratory essay have a thesis?
A definitive thesis statement isn't required. Rather than presenting a conventional thesis, formulate one or more research questions to investigate diverse perspectives and insights.
🏁 How do end an exploratory essay?
Conclude by summarizing the exploration, reflecting on the process, and suggesting areas for further research or questions that remain.
The most popular topics for Exploratory Essay
- Social Media
- Impact of Technology
- Artificial Intelligence
- Pop Culture
- Sex Education
- Violence in Video Games
- Gender Stereotypes
- Discrimination
- Child Labour
- Animal Testing
- Space Exploration
- Mental Health
- Existence of God
- Marijuana Legalization
- Teenage Pregnancy
Students also browse
- Memoir Essay
- Research Essay
- Profile Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Analytical Essay
- Personal Narrative Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Evaluation Essay
- Informative Essay
- Synthesis Essay
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Essay Topics – List of 500+ Essay Writing Topics and Ideas
List of 500+ essay writing topics and ideas.
Essay topics in English can be difficult to come up with. While writing essays , many college and high school students face writer’s block and have a hard time to think about topics and ideas for an essay. In this article, we will list out many good essay topics from different categories like argumentative essays, essays on technology, environment essays for students from 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th grades. Following list of essay topics are for all – from kids to college students. We have the largest collection of essays. An essay is nothing but a piece of content which is written from the perception of writer or author. Essays are similar to a story, pamphlet, thesis, etc. The best thing about Essay is you can use any type of language – formal or informal. It can biography, the autobiography of anyone. Following is a great list of 100 essay topics. We will be adding 400 more soon!
But Before that you may wanna read some awesome Essay Writing Tips here .

Get the Huge list of 100+ Speech Topics here
Argumentative Essay Topics
- Should plastic be banned?
- Pollution due to Urbanization
- Education should be free
- Should Students get limited access to the Internet?
- Selling Tobacco should be banned
- Smoking in public places should be banned
- Facebook should be banned
- Students should not be allowed to play PUBG
Essay Topics on Technology
- Wonder Of Science
- Mobile Phone
Essay Topics on Festivals on Events
- Independence Day (15 August)
- Teachers Day
- Summer Vacation
- Children’s Day
- Swachh Bharat Abhiyan
- Janmashtami
- Republic Day
Essay Topics on Education
- Education Essay
- Importance of Education
- Contribution of Technology in Education

Essay Topics on Famous Leaders
- Mahatma Gandhi
- APJ Abdul Kalam
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Swami Vivekananda
- Mother Teresa
- Rabindranath Tagore
- Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
- Subhash Chandra Bose
- Abraham Lincoln
- Martin Luther King
- Lal Bahadur Shashtri
Essay Topics on Animals and Birds
- My Favorite Animal
Essays Topics About Yourself
- My Best Friend
- My Favourite Teacher
- My Aim In Life
- My Favourite Game – Badminton
- My Favourite Game – Essay
- My Favourite Book
- My Ambition
- How I Spent My Summer Vacation
- India of My Dreams
- My School Life
- I Love My Family
- My Favourite Subject
- My Favourite Game Badminton
- My Father My Hero
- My School Library
- My Favourite Author
- My plans for summer vacation
Essay Topics Based on Environment and Nature
- Global Warming
- Environment
- Air Pollution
- Environmental Pollution
- Water Pollution
- Rainy Season
- Climate Change
- Importance Of Trees
- Winter Season
- Deforestation
- Natural Disasters
- Save Environment
- Summer Season
- Trees Our Best Friend Essay In English
Essay Topics Based on Proverbs
- Health Is Wealth
- A Stitch in Time Saves Nine
- An Apple a Day Keeps Doctor Away
- Where there is a will, there is way
- Time and Tide wait for none
Toppr provides free study materials like NCERT Solutions for Students, Previous 10 Years of Question Papers, 1000+ hours of video lectures for free. Download Toppr app for Android and iOS or signup for free.
Essay Topics for Students from 6th, 7th, 8th Grade
- Noise Pollution
- Environment Pollution
- Women Empowerment
- Time and Tide Wait for none
- Science and Technology
- Importance of Sports
- Sports and Games
- Time Management
- Cleanliness is next to Godliness
- Cleanliness
- Rome was not Built in a Day
- Unemployment
- Clean India
- Cow Essay In English
- Describe Yourself
- Festivals Of India
- Ganesh Chaturthi
- Healthy Food
- Importance Of Water
- Plastic Pollution
- Value of Time
- Honesty is the Best Policy
- Gandhi Jayanti
- Human Rights
- Knowledge Is Power
- Same Sex Marriage
- Childhood Memories
- Cyber Crime
- Kalpana Chawla
- Punctuality
- Rani Lakshmi Bai
- Spring Season
- Unity In Diversity
- Artificial Intelligence
- Online Shopping
- Indian Culture
- Healthy Lifestyle
- Indian Education System
- Disaster Management
- Environmental Issues
- Freedom Fighters
- Grandparents
- Save Fuel For Better Environment
- Importance Of Newspaper
- Lal Bahadur Shastri
- Raksha Bandhan
- World Environment Day
- Narendra Modi
- What Is Religion
- Charity Begins at Home
- A Journey by Train
- Ideal student
- Save Water Save Earth
- Indian Farmer
- Safety of Women in India
- Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan
- Capital Punishment
- College Life
- Natural Resources
- Peer Pressure
- Nature Vs Nurture
- Romeo And Juliet
- Generation Gap
- Makar Sankranti
- Constitution of India
- Girl Education
- Importance of Family
- Importance of Independence Day
- Brain Drain
- A Friend In Need Is A Friend Indeed
- Action Speaks Louder Than Words
- All That Glitters Is Not Gold
- Bhagat Singh
- Demonetization
- Agriculture
- Importance of Discipline
- Population Explosion
- Poverty in India
- Uses Of Mobile Phones
- Water Scarcity
- Train Journey
- Land Pollution
- Environment Protection
- Indian Army
- Uses of Internet
- All that Glitters is not Gold
- Balanced Diet
- Blood Donation
- Digital India
- Dussehra Essay
- Energy Conservation
- National Integration
- Railway Station
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Health And Hygiene
- Importance Of Forest
- Indira Gandhi
- Laughter Is The Best Medicine
- Career Goals
- Mental Health
- Save Water Save Life
- International Yoga Day
- Winter Vacation
- Soil Pollution
- Every Cloud Has A Silver Lining
- Indian Culture And Tradition
- Unity Is Strength
- Unity is Diversity
- Wildlife Conservation
- Cruelty To Animals
- Nelson Mandela
- Of Mice And Men
- Organ Donation
- Life in a Big City
- Democracy in India
- Waste Management
- Biodiversity
- Afforestation
- Female Foeticide
- Harmful Effects Of Junk Food
- Rain Water Harvesting
- Save Electricity
- Social Media
- Social Networking Sites
- Sound Pollution
- Procrastination
- Life in an Indian Village
- Life in Big City
- Population Growth
- World Population Day
- Greenhouse Effect
- Statue of Unity
- Traffic Jam
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao
- Importance of Good Manners
- Good Manners
- Cyber Security
- Green Revolution
- Health And Fitness
- Incredible India
- Make In India
- Surgical Strike
- Triple Talaq
- A Good Friend
- Importance of Friends in our Life
- Should Plastic be Banned
- Nationalism
- Traffic Rules
- Effects of Global Warming
- Fundamental Rights
- Solar System
- National Constitution Day
- Good Mother
- Importance of Trees in our Life
- City Life Vs Village Life
- Importance of Communication
- Conservation of Nature
- Man vs. Machine
- Indian Economy
- Mothers Love
- Importance of National Integration
- Black Money
- Greenhouse effect
- Untouchability
- Self Discipline
- Global Terrorism
- Conservation of Biodiversity
- Newspaper and Its Uses
- World Health Day
- Conservation of Natural Resources
- A Picnic with Family
- Indian Heritage
- Status of Women in India
- Child is Father of the Man
- Reading is Good Habit
- Plastic Bag
- Terrorism in India
- Library and Its Uses
- Life on Mars
- Urbanization
- Pollution Due to Diwali
- National Flag of India
- Vocational Education
- Importance of Tree Plantation
- Summer Camp
- Vehicle Pollution
- Women Education in India
- Seasons in India
- Freedom of the Press
- Caste System
- Environment and Human Health
- Mountain Climbing
- Depletion of Natural Resources
- Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar
- Health Education
- Effects of Deforestation
- Life after School
- Starvation in India
- Jan Dhan Yojana
- Impact of Privatization
- Election Commission of India
- Election and Democracy
- Prevention of Global Warming
- Impact of Cinema in Life
- Subhas Chandra Bose
- Dowry System
- Ganesh Chaturthi Festival
- Role of Science in Making India
- Impact of Global Warming on Oceans
- Pollution due to Festivals
- Ambedkar Jayanti
- Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat
- Family Planning in India
- Democracy vs Dictatorship
- National Festivals of India
- Sri Aurobindo
- Casteism in India
- Organ trafficking
- Consequences of Global Warming
- Role of Human Activities in Global Warming
- Issues and Problems faced by Women in India
- Role of Judiciary in the Country Today
- Sugamya Bharat Abhiyan
- PUBG Mobile Game Addiction
- Role of Youths in Nation Building
- Value of Oxygen and Water in Life/Earth
- Farmer Suicides in India
- Start-up India
- Pollution Due to Firecrackers
- Life of Soldiers
- Child Labour
- Save Girl Child
- Morning Walk
- My School Fete
- Essay on Financial Literacy
- Essay On Sustainable Development
- Essay On Punjab
- Essay On Travel
- My Home Essay
- Child Marriage Essay
- Importance Of English Language Essay
- Essay On Mass Media
- Essay On Horse
- Essay On Police
- Essay On Eid
- Essay On Solar Energy
- Animal Essay
- Essay On Mango
- Gender Discrimination Essay
- Essay On Advertisement
- My First Day At School Essay
- My Neighborhood Essay
- True Friendship Essay
- Work Is Worship Essay
- Essay On Self Confidence
- Essay On Superstition
- Essay On Bangalore
- Sex Vs Gender Essay
- Essay On Social Issues
- Time Is Money Essay
- Essay About Grandmothers
- Essay On Hard Work
- First Day Of School Essay
- Flowers Essay
- My Favorite Food Essay
- Essay on Birds
- Essay on Humanity
- Essay on Sun
- Essay on Kargil War
- Every Cloud Has a Silver Lining Essay
- Francis Bacon Essays
- Importance of Cleanliness Essay
- My Sister Essay
- Self Introduction Essay
- Solar Energy Essay
- Sports Day Essa
- Value Of Education Essay
- Essay On Isro
- Essay On Balance Is Beneficial
- Essay On Reservation In India
- Essay On Water Management
- Essay On Smoking
- Essay On Stress Management
- Essay On William Shakespeare
- Essay on Apple
- Essay On Albert Einstein
- Essay On Feminism
- Essay On Kindness
- Essay On Domestic Violence
- Essay on English as a Global Language
- Essay On Co-Education
- Importance Of Exercise Essay
- Overpopulation Essay
- Smartphone Essay
- Essay on River
- Essay on Cyclone
- Essay On Facebook
- Essay On Science In Everyday Life
- Essay On Women Rights
- Essay On Right To Education
- Essay on Quotes
- Essay On Peace
- Essay On Drawing
- Essay On Bicycle
- Essay On Sexual Harassment
- Essay On Hospital
- Essay On Srinivasa Ramanujan
- Essay On Golden Temple
- Essay On Art
- Essay On Ruskin Bond
- Essay On Moon
- Birthday Essay
- Dont Judge A Book By Its Cover Essay
- Draught Essay
- Gratitude Essay
- Indian Politics Essay
- Who am I Essay
- Essay on Positive Thinking
- Essay on Dance
- Essay on Navratri
- Essay on Onam
- Essay on New Education Policy 2020
- Esasy on Thank you Coronavirus Helpers
- Essay on Coronavirus and Coronavirus Symptoms
- Essay on Baseball
- Essay on coronavirus vaccine
- Fitness beats pandemic essay
- Essay on coronavirus tips
- Essay on coronavirus prevention
- Essay on coronavirus treatment
- Essay on essay on trees
- Essay on television
- Gender inequality essay
- Water conservation essay
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on Types of sports
- Essay on road safety
- Essay on my favourite season
- My pet essay
- Student life essay
- Essay on Railway station
- Essay on earth
- Essay on knowledge is power
- Essay on favourite personality
- Essay on memorable day of my life
- My parents essay
- Our country essay
- Picnic essay
- Travelling essay
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Letter Writing
- It So Happened Summary
- Honey Dew Chapter Summaries
- The Alien Hand
- Malu Bhalu Summary
- Sing a Song of People Summary
- The Little Bully Summary
- Nobody’s Friend Summary
- Class Discussion Summary
- Crying Summary in English
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Stand Out in High School
When applying to college, make sure your application showcases who you are in and out of school. While grades and test scores are important, colleges also want to see the person you're becoming and the skills you've learned outside of class.
High School Classes Colleges Look For
If you’re in high school and thinking about college you should know that the courses you take matter. That’s because college admissions officers want to see a solid foundation of learning you can build on in college.
How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale
Colleges report GPA (grade point average) on a 4.0 scale. See how to calculate your GPA and convert your grades to the 4.0 scale.
Extracurriculars Matter—to You and to Colleges
Participating in extracurricular activities like clubs, sports, or a job can foster new interests and help you discover more about yourself. It can also show colleges your dedication and leadership skills.
Home / Essay Samples / Education
Essays on Education
Education is a direct and essential instrument for any society through which the latter shapes its future. Given how high the stakes are, it is subject to permanent updates. An education essay normally investigates various aspects of the educational process, typically, in an attempt to understand or raise awareness about existing problems. Among the recurring education topics, one can list the study of education efficiency in terms of time, resources, effort, both from the instructor’s and the student’s perspective, whether it reflects principles like equality, whether it is in tune with society’s current demands or beliefs. Check out the topics listed below but also note the content, structure, and writing style of the essays provided.
Why I Want to Become a Teacher: a Personal Journey
Teaching is a noble profession that has the power to shape the future of individuals and society. This essay explores my personal journey and the profound reasons behind my desire to become a teacher, highlighting the impact I aspire to make in the lives of...
Should Homework Be Banned: Exploring the Debate
Homework has long been a contentious issue in the realm of education. While it has been a staple of the academic experience for generations, its effectiveness and impact on students have been debated vigorously. Advocates argue that homework reinforces learning and fosters important life skills,...
Why Do I Want to Study Abroad
Studying abroad is a dream I have nurtured for years, and it represents an important chapter in my academic and personal journey. The decision to study in a foreign country is not one I take lightly, and it is grounded in a deep-seated desire for...
Unique Opportunities and Challenges During High School
High school is a pivotal period in the lives of young individuals, marked by both unique opportunities and challenges that shape their personal and academic development. It is a time of self-discovery, academic growth, and the formation of lifelong friendships. This essay explores the distinctive...
My Leadership Experience in College
College life is not just about academics; it's also an opportunity to develop essential life skills, including leadership. During my time in college, I had the privilege of engaging in various leadership roles and experiences that profoundly shaped my personal and professional growth. In this...
Is College Worth the Cost
The pursuit of higher education has long been considered a pathway to personal and professional success. However, the rising costs of college tuition have sparked a heated debate about whether the investment in a college education is truly worth it. In this essay, we will...
The Role and Controversy Surrounding Standardized Tests
Standardized tests, often at the center of educational debate, play a pivotal role in assessing students' knowledge and abilities. This essay delves into the world of standardized tests, examining their history, impact on education, and the ongoing controversy surrounding their use. Standardized tests have a...
Why College is Important for Personal and Professional Development
College education has long been considered a cornerstone of personal growth and professional development. In this essay, we will explore the multifaceted reasons why college is crucial for individuals seeking to expand their horizons, cultivate essential skills, and embark on successful careers. One of the...
The Role of Student Council in the University
Student councils are the beating heart of university campuses, serving as the voice of the student body, fostering engagement, and nurturing leadership skills among students. In this essay, we will explore the vital role that student councils play in the university setting, examining their functions,...
Why College Should Be Free: an Investment in Education and Society
Access to quality education is a fundamental right that should be available to all, irrespective of their socioeconomic background. However, the rising costs of higher education have made it increasingly difficult for many individuals to pursue a college degree. In this essay, we will explore...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
- Higher Education
- Scholarship
- Indian Education
- Studying Abroad
- Critical Thinking
- College Tuition
- Online Classes
- Service Learning
- Standardized Testing
- School Uniform
- School Ranking
- Elementary School
- Sex Education
- After Graduation
- Brittany Stinson
- Class Reflection
- First Day of School
- History of Education
- Role of Education
- Student Life
- Students With Disabilities
- Study Abroad Scholarship
- Teaching Philosophy
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->