Essay on Human Resource Management (HRM): Top 6 Essays
In this essay we will discuss about ‘Human Resource Management’. Find paragraphs, long and short essays on ‘Human Resource Management’ especially written for school and college students.
- Essay on Human Resource Management
Essay Contents:
- Essay on the Functions of Human Resource Management

Essay # 1. Introduction to Human Resource Management :
Men, materials, machines and money are considered as the main factors of production. Out of all these factors, men are considered as an important factor. It is very difficult to handle the other factors of production without the efficient use of human resources.
Several terms have been used by various management thinkers to represent human resources. These include ‘personnel’, ‘people at work’, ‘manpower’, ‘staff’ and ’employees. Whatever may be the term used, human resource of any organization consists of all individuals engaged in any of the organizational activities at all levels.
The importance of human factor can be judged from the point that some people consider management and personnel/human resource management as one and the same thing. Lawrence A. Appley observed that “Management and personnel administration are one and the same. They should never be separated. Management is personnel administration”. Of all the tasks of management, managing the human component is the central and most important task, because all else depends on how well it is done.
With the increase in number of employees in an organization, greater emphasis is being placed on personnel management and also on the adoption of standardized procedures and compensation plans. The personnel department helps management in using and developing appropriate manpower to achieve organizational goals.
Human resource management is responsible for how people are treated in organizations. It is responsible for bringing people into the organization, helping them perform their work, compensating them for their labors, and solving problems that arise.
Essay # 2. Definition of Human Resource Management :
Human Resource Management (HRM) has come to be recognized as an inherent part of management, which is concerned with the human resources of an organization.
Some of the definitions of human resource management as given by various persons are:
Human Resource Management is the function within an organization that focuses on recruitment, management, and providing direction for the people who work in the organization.
Human Resource Management is the understanding and application of the policy and procedures that directly affect the people working within the project team and working group. These policies include recruitment, retention, reward, personal development, training and career development.
Human Resource Management is the effective use of human resources in order to enhance organizational performance.
Human Resource Management is the organizational function that deals with issues related to people such as compensation, hiring, performance management, organization development, safety, wellness, benefits, employee motivation, communication, administration, and training.
Essay # 3. Scope of Human Resource Management :
The scope of HRM is very wide.
It covers the following aspects:
(i) Personnel Aspect :
This is concerned with manpower planning, recruitment, selection, placement, transfer, promotion, training and development, layoff and retrenchment, remuneration, incentives, productivity etc.
(ii) Welfare Aspect :
It deals with working conditions and amenities such as canteens, creches, rest and lunch rooms, housing, transport, medical assistance, education, health and safety, recreation facilities, etc.
(iii) Industrial Relations Aspect :
This covers union-management relations, joint consultation, collective bargaining, grievance and disciplinary procedures, settlement of disputes, etc.
Essay # 4. Objectives of Human Resource Management :
Objectives are predetermined goals to which individual or group activity in an organization is directed. Objectives of human resource management are influenced by organizational objectives and individual goals.
Some of the objectives of HRM are:
a. To ensure effective utilization of human resources.
b. To ensure respect for human beings.
c. To identify and satisfy the needs of individuals.
d. To achieve and maintain high morale among employees.
e. To provide the organization with well-trained and well-motivated employees.
f. To increase to the fullest the employee’s job satisfaction and self-actualization.
g. To develop and maintain a quality of work life.
h. To provide better conditions of employment.
i. To develop overall personality of each employee in its multidimensional aspect.
j. To enhance employee’s capabilities to perform the present job.
k. To provide fair wages to employees.
l. To inculcate the sense of team spirit, team work and inter-team collaboration.
Essay # 5. Nature of Human Resource Management :
Human Resource Management is a process of bringing people and organizations together so that the goals of each are met.
The various features of HRM include:
a. It is pervasive in nature as it is present in all enterprises.
b. Its focus is on results rather than on rules.
c. It tries to help employees develop their potential fully.
d. It encourages employees to give their best to the organization.
e. It is all about people at work, both as individuals and groups.
f. It tries to put people on assigned jobs in order to produce good results.
g. It helps an organization meet its goals in the future by providing for competent and well- motivated employees.
h. It tries to build and maintain cordial relations between people working at various levels in the organization.
i. It is a multidisciplinary activity, utilizing knowledge and inputs drawn from psychology, economics, etc.
Essay # 6. Functions of Human Resource Management:
Every manager in an organization has to perform the personal functions in one form or the other in order to get the things done through others.
The functions of human resource management can be classified as:
(i) Managerial Functions.
(ii) Operative Functions.
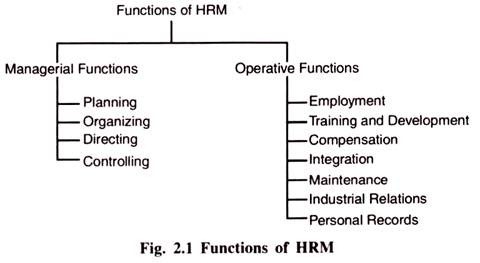
(i) Managerial Functions :
The managerial functions are mainly concerned with planning, organizing, directing and controlling the various activities of personnel management.
These functions are explained below:
(a) Planning:
Planning is deciding in advance what to do; how to do; where to do; and who is to do it. For personnel manager, planning means the determination in advance of personnel programme. Planning is concerned about present manpower positions, what number and kind of people are required for the organization.
(b) Organization:
After the establishment of organizational goals and objectives, human resource manager must design and develop organization structure to carry out the various operations. Organization involves identification and grouping the activities to be performed and dividing them among the individuals and creating authority and responsibility relationships among them.
(c) Directing:
Directing as a managerial function involves building sound industrial and human relations among people working in the organization. The direction function of the personnel manager is meant to motivate and guide the people to achieve organization goals. The employees can be motivated through salary administration, career planning, provision of health and safety requirements etc.
(d) Controlling:
Controlling function is concerned with regulation of activities in accordance with the personnel plans. It includes checking, verifying and comparing actual with the plans, identifying deviations if any and correcting them. Auditing, training programmers, analysing, labor turnover records, conducting separate interviews are some of the means for controlling the personnel management function.
(ii) Operative Functions :
Operative functions are those functions which are usually delegated to the human resource department as these require specialized skills and knowledge in their performance. All these operative functions are interacted by managerial functions. Further these functions are to be performed in conjunction with management functions.
Some of the operative functions of human resource management are:
(a) Employment :
It is the first operative function of HRM. Employment is concerned with securing and employing the people possessing required kind and level of human resources necessary to achieve the organizational objectives. It covers the functions such as job analysis, human resources planning, recruitment, selection, placement and induction.
(i) Job Analysis:
It is the process of study and collection of information relating to the operations and responsibilities of a specific job.
It includes:
i. Collection of data, information, facts and ideas relating to various aspects of jobs including men, machines and materials.
ii. Preparation of job description, job specification, job requirements and employee specification which help in identifying the nature, levels and quantum of human resources.
(ii) Human Resources Planning:
Human resource planning involves forecasting the human resource requirements of an organization and the future supply of human resources. It is a process for determination and assuring that the organization will have an adequate number of qualified persons, available at proper times, performing jobs which would meet the needs of the organization.
(iii) Recruitment:
It is the process of seeking and attracting prospective candidates against a vacancy in an organization.
After having determined the number of persons required for different jobs and requirements of different jobs, the recruitment process will begin.
The term recruitment may be defined as the process of searching the candidates for employment and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization. In other words, the term ‘recruitment’ stands for discovering the sources from where potential employees will be selected.
(iv) Selection:
Selection is the process of identifying and establishing the credentials of a candidate for a job to ensure success.
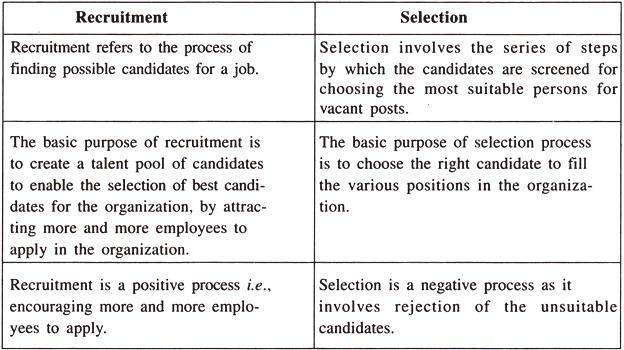
Recruitment vs. Selection :
Both recruitment and selection are the two phases of the employment process. Recruitment comes first and is followed by Selection.
(v) Induction and Orientation:
Induction and orientation are the techniques by which a new employee is rehabilitated in the changed surroundings and introduced to the practices, policies, purposes and people etc., of the organization.
(b) Training and Development :
This process aims to train and develop employees to improve and update their knowledge and skills, so as to help them perform their jobs better. The process also includes developing the attitudes, beliefs and values of the employees to match the organizational needs. This comprises of performance appraisal, training, management/executive development, career planning and development.
(i) Performance Appraisal:
It is the process of evaluating the performance of an employee on the job and developing a plan for improvement.
(ii) Training:
Training is the systematic development of the knowledge, skills and attitudes required to perform a job.
After the employee is selected, the most important part of human resource program is to impart training to the employee. Training plays a significant role in human resource development. Human resources are the life-blood of any organization. Only through trained and efficient employees, the organization can achieve its objectives.
Training is defined as “the art of increasing the knowledge and skill of an employee for doing a particular job”.
Since training involves time, effort and money by an organization, so an organization should carefully design its training program. The objectives and need for training should be clearly identified and the method or type of training should be chosen according to the needs and objectives established.
Need of Training:
Training is necessary both for existing and new employees. It increases the skill of the employees.
The need of training arises because of the following factors:
(a) Rapid Changes in Technology:
As the technology is changing at as fast pace, so employees must learn new techniques to make use of advanced technology.
(b) Frequent Accidents:
Due to increase in number of industrial accidents, an effective training program should be made for the safety of the employees.
(c) Quality Conscious Customers:
As the customers have become quality conscious, so there is need of training to employees for improving the quality of products.
(d) Increase in Productivity:
Effective training helps in increasing productivity and reduction in production costs of an organization.
(e) Supply of Trained Personnel:
Training ensures an efficient supply of trained employees at all levels of organization.
Benefits of Training :
Some of the benefits of training are:
a. Better performance of employees both in terms of quantity and quality of output.
b. Elimination of wastages which leads to reduction in cost of production.
c. Reduction in needs of supervision.
d. It helps in developing and improving the organizational culture.
e. Increase in morale of the employees.
f. Reduction in number of accidents.
g. Improvement in quality of work.
h. Reduction in machine breakdown and maintenance cost.
i. Increase in productivity which results in enhanced earnings for employees.
j. Increase in self-confidence.
k. More opportunity for growth/promotions.
(iii) Development:
It is the concept of developing the employees in an organization to meet future changes and challenges.
(iv) Career Planning and Development:
It refers to identifying one’s career goals and formulating plans of reaching them. It attempts to harmonize an individual’s career aspiration with organizational needs.
(c) Compensation :
Compensation function is concerned with securing adequate and equitable remuneration to persons for their contribution. Fixation of compensation or wage rates for different categories of employees is an important task of management. Function related to job evaluation, wage and salary administration, incentives, bonus and fringe benefits falls under this category.
Compensation is what employees receive in exchange for their contribution to the organization.
Generally, employees offer their service for three types of rewards:
b. Incentives.
c. Benefits.
Pay refers to the base wages and salaries employees normally receive. Incentives in the form of bonuses, commissions and profit sharing plans are incentives designed to encourage employees to produce results beyond normal expectations.
Benefits such as insurance, medical, recreational, retirement etc. represent a more indirect type of compensation.
So, the term compensation is a comprehensive one including pay, incentives, and benefits offered by employers for hiring the services of employees. In addition to these, managers have to observe legal formalities for offering physical as well as financial security to employees. All these play an important role in any HR department efforts to obtain, maintain and retain an effective workforce.
(i) Job Evaluation:
It is the systematic determination of the value of each job in relation to other jobs in the organization.
(ii) Wage and Salary Administration:
The process of formulating and operating a suitable wage and salary program is known as wage and salary administration.
(iii) Incentives:
Incentives are the rewards an employee earns in addition to regular salary based on his performance or of the collective performance.
(iv) Bonus:
Bonus is primarily a share in the surpluses and is often directly related to the organization performance.
(v) Fringe Benefits:
Fringe benefits are monetary and non-monetary benefits including disablement benefits, housing facilities, canteen facilities, conveyance facilities, educational facilities, recreational facilities, medical and welfare facilities, post-retirement benefits, etc.
(d) Integration :
The basic objective of human resource management is to secure maximum performance from the employees in order to accomplish the objectives of an organization. This is possible through better integration between the organization and its employees. The integration between the two can be achieved through three things-motivation, leadership and communication.
(e) Maintenance :
Maintenance function is basically concerned with the working conditions and welfare facilities provided to the employees. Morale and motivation of the employees is greatly influenced by these conditions. Working conditions include measures taken for health, safety and comfort of the employees. Welfare facilities include provisions of rest rooms, cafeteria, safe drinking water, education for children of employees etc.
(f) Industrial Relations :
It is the responsibility of human resource manager to maintain industrial peace in the organization. This can be done through collective bargaining, joint consultation and settlement of disputes, whenever they arise.
(g) Personnel Records :
Another function of human resource manager is to maintain the records of the employees. This is helpful in taking decisions relating to transfers and promotions, performance appraisal etc. These also help in identifying the weaknesses in the employees and the areas in which they need training.
Related Articles:
- Essay on Human Resource Management | HRM
- Essay on Merit Rating: Top 5 Essays | Human Resource Management
- Notes on Human Resource Management (HRM): Meaning and Nature
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
- Dissertation
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Book Report/Review
- Research Proposal
- Math Problems
- Proofreading
- Movie Review
- Cover Letter Writing
- Personal Statement
- Nursing Paper
- Argumentative Essay
- Research Paper
- Discussion Board Post
Top 7 Examples of Essay on Human Resources

Table of Contents
Human capital is a valuable part of any business establishment, so the business must adapt to the growing need to invest in the proper management, development and retention of its people. Accordingly, many companies are now scrutinizing the science of human resource management. If you are a student in management or entrepreneurship, you will have to write at least one essay on human resources.
The main goal of this assignment for the student is to show his competence and ability to express his thoughts and information correctly. At first glance, it might seem like writing an essay on human resources is a daunting task because it involves a lot of effort. But if you stick to the guidelines, you can quickly and easily allocate time and effort to further write an essay on human resources. Find out how to do this below and get inspired by sample essays.
5 Tips on How to Write an Essay on Human Resources
Writing an essay on human resources can take you a lot of effort and time. Therefore, you need to know a few recommendations before starting work. They will help you make the process of writing an essay on human resources easy, fun and short-lived because you will learn how to allocate your energy and time properly.
- Choose a direction that is good and relevant to you about the essay on human resources. To not drown in this ocean of possibilities, first determine what is most interesting to you. What do you think about most often when faced with the study and writing essay on human resources? What gets your attention to the point where you forget about everything else? What would you like to improve in human resource management methodology?
- Once you’ve decided on the direction of writing an essay on human resources, find out what you like best. Depending on this, your essay will be descriptive, analytical, reflective, critical, or otherwise. Once you’ve combined a topic that interests you with the look of an essay on human resources, sketch out a few options for topics. At this stage, it is not the exact formulation of the important topic but understanding the essence of the problem and the potential for its solution when writing an essay on human resources.
- Remember that not every student can write a good essay on human resources without knowledge and information. Therefore, take the time to gather all the information you need to write an essay on human resources.
- When exploring the potential of an essay on human resources topic, pay attention to the availability of literary sources. In some cases, it is more logical to first find the necessary information in the sources, and then begin to form thoughts in the form of essay on human resources. And remember that this knowledge will help you write an essay and when performing other types of academic work.
- After selecting specific topics for an essay on human resources, evaluate each topic for how meaningful you can cover it. Do you have interesting observations and ideas on this topic? Can you surprise the reader with something? Do you feel inspired when discussing this topic? In writing an essay on human resources, you should understand that you will have to formulate a specific thesis and then prove it with arguments. Will you be able to do this for the selected topics?
7 Examples of Human Resource Management Essays
This selection of 7 essays on human resources will help you find the topic you would like to write an essay about in Human Resource Management. After reading, you will be inspired, and it will be easier for you to decide what you would like to write about because this topic touches on many aspects of this type of management. You will also acquire new and valuable write an essay and perform knowledge about human resources to later independently write an essay on human resources.
Human Resource Essay Example 1: “Do I See Myself as a Competent and Good Manager?”
A manager is a person who holds a permanent managerial position and is empowered to make decisions about specific activities of an organization. This person must have higher education and bear a huge responsibility for the success of the company or projects. I believe that a competent human resource manager should know how to correctly use management mechanisms, tools and management methods.
The relevance of these phenomena is due to several factors. Firstly, there is no doubt that the efficiency of the organization as a whole, the effectiveness of the labour activity of employees, etc. directly depends on the level of construction of the management system. Within the framework of the new paradigm of personnel management, the human resource is positioned as the most important resource of the organization, since it is the source of the formation of strategic competitive advantages. Therefore, the functioning of all systems of the organization directly depends to one degree or another on the human factor.
Secondly, do not forget that management in some countries has a rather short history of development in comparison with developed countries. And so every manager needs to constantly learn and experiment. And this necessitates the adaptation of foreign management experience to domestic realities. In our time, many authors have published a significant number of works within the framework of this discipline, and many management models have also been formed. I believe that according to the requirements a manager:
- must be confident in their decisions, be fair;
- must continuously learn and apply new knowledge in practice;
- suggest new good and proven techniques improve the outcome of the project;
- be able to competently and quickly analyze a large flow of information.
In modern conditions, a manager must have many qualities that will help him solve all the issues that arise. After all, a manager must be a purposeful, energetic and persistent innovator who knows how to manage subordinates. It is these qualities that I also possess, which gives me the opportunity to apply for this position.
It is also worth noting that in modern conditions, the correctness of the behaviour of a business entity in the market to a decisive extent depends on the adequacy and timeliness of managerial decision-making by the head. After all, the following points can be identified, which entirely depend on the personality of the leader, his business and human qualities:
- choosing the right direction of the business;
- the ability to anticipate the development of the market situation;
- the correct choice of development strategy;
- selection of team members;
- correct setting of tasks for team members;
- the ability to build viable plans;
- the ability to establish relationships with other entities: suppliers, consumers, governing bodies and others;
- many other points are related to the development of the organization in a constantly changing market environment.
All these aspects of the organization’s activities are understandable and important to me, therefore I am ready to make effective management decisions on them. Therefore, I see myself as a manager and consider myself a worthy candidate.
Human Resource Essay Example 2: “Purpose, Tasks and Functions of Human Resource Management”
Currently, in the age of information technology, when there is an active change in the structure of society and the consciousness of people, it is extremely important to carry out a process to improve the management processes in the organization. But first, every person who has to improve the quality of human resource management needs to understand the basic functions and tasks of such a complex and responsible process.
Human resources are all employees and their responsibilities in any organization. They include production personnel and management personnel. Throughout the development of mankind and civilizations, people had to regulate relationships for the sake of survival and improving the quality of life. Therefore, in our time, human resource management is a complex system that includes interconnected and interdependent subsystems for the creation, use and development of labour resources.
What are the types of definitions of such a phenomenon as human resource management? Human resource management is an approach to a person as the main factor in achieving the goals of an organization. This is an approach to a person as a source of income and an investment. This is an analysis of the organization’s human resource needs. This is an analysis of the situation with human resources in the environment external to the organization. And also this is the formation of the organization’s human resources and the creation of a system of employee interactions.
The main goal of this process is to ensure the use of company employees and their human resources in such a way that the employer can get the maximum possible benefit from their skills and abilities, and the employees can get the maximum possible material and psychological satisfaction from their work. This process is based not only on the ability to organize a team from a quantitative and qualitative point of view, but also on the ability to use psychological techniques.
Each manager should be prepared for the fact that personnel management is a more complex process than managing the technological part of the production. This is due to the high likelihood of conflict situations on both work and personal issues.
Depending on the line of business of a particular company, a human resource manager must perform the functions inherent in this activity. They are different and each of them gives a certain desired result if the process is established by the manager correctly and correctly. What are the most common and working functions of managers or people involved in human resource management?
- Forecasting the need for personnel working;
- planning the number and quality structure of personnel in the divisions of the enterprise;
- searching for qualified personnel;
- holding competitions for vacancies;
- certification of applicants for work;
- organization of the adaptation process for new employees;
- organization of personnel training;
- development of recommendations for professional development;
- organization of personnel retraining;
- organization of management training and a number of others.
Since the functioning of any enterprise is based on the human factor, there is an objective need to regulate this process. It can be argued that the final result of any project depends on the properly organized activities of the staff, be it a small project or a large-scale project to create an innovative product.
Human Resource Essay Example 3: “Staff and Manager Motivation in Human Resource Management”
As you know, human resources are the foundation of any production process, since it is on them that the effectiveness of a particular activity depends. Therefore, project human resource management is a process that results in the efficient use of human resources. The human resource management process of a project involves the organization, management and leadership of the team that directly implements the process. And I think that this should be given special attention.
In any organization, each person involved in the production process is endowed with certain responsibilities. Otherwise, they can be called project personnel. In my opinion, the basis of the project’s human resource management process is the motivation of the participants. The level of staff motivation is desirable for their high-quality and organized work, both with clients and within the enterprise, because their work directly affects the efficiency of the organization. And so we can conclude that employees are one of the key and important resources of the company.
But sometimes crisis situations provoke a difficult situation for the enterprise, due to which panic can arise in the state. Such an environment, naturally, demotivates employees, and the reasons may be different. This can be uncertainty about the future, a decrease or delay in wages, reductions, and increased workload.
The leader plays an important role in motivating employees. The leader is obliged to take part in all areas of the organization. Everyone understands that the market is now in stagnation and that no one has any illusions about this. But the employee must understand what is being done in the company to overcome the unfavourable situation. And to be sure that the management will not abandon them, that they are needed, they are engaged in important business and receive a worthy reward for it.
It is very important to correctly decompose the project and divide it into manageable stages, if necessary, into subprojects and other components. This procedure is performed at the initial stage of the project. Its purpose is to provide a good basis for sound planning. It ensures that plans are made for reasonably chosen time horizons.
When dividing the project, it is necessary to describe the goals of each component and, at least in the first approximation, estimate the resource requirements for their implementation. It is equally important to draw up a milestone achievement plan and milestone level charts prior to each project phase. Moreover, participants must agree on which milestones are particularly critical to the project and ensure that everyone understands the severity of the implications.
In order for the project to achieve its ultimate goal, it is extremely important to organize and provide for all possible nuances. It can be argued that the processes of organizing a project contain three components.
- The first is organizational planning, which involves drawing up a plan and analyzing all stages of work.
- The second link is the appointment of personnel, in accordance with the required tasks and goals.
- And finally, the third stage is team development. An important point here is the motivation of the personnel, the general focus, the team’s ability to work, and the fighting spirit.
Therefore, of course, the success of any project must be backed by a very competent and wise leader who knows the psychological characteristics of each employee, who knows how to properly organize the production process, is able to set incentives and motivation for the staff. Thus, the success of the project is ensured even in crisis situations.
Human Resource Essay Example 4: “Variety Management”
The structural basis of management in the field of various art consists of an organization (theatre, production centre, a philharmonic society, etc.), whose effectiveness will depend on the correctly found model, as well as the personality and professional training of the manager. Each direction on the stage has its own management models, together with the criteria for its effectiveness.
The main goals of management in the field of pop are such as the creation of the most favourable conditions for the promotion of creation and the dissemination of art, for creativity, as well as the professional growth of performers, the development of genres of professional art, copyright protection, and the achievement of optimal financial results. Management in the field of professional art is, in general, a combination of management of the artistic process, economic and organizational activities. The solution of these problems is inextricably linked with the improvement of the culture of serving the population and the formation of services for different categories of the population.
If you were to find yourself behind the scenes of any performance, you would witness total chaos. For example, there might be actors in one corner rehearsing their lines, while tailors and seamstresses hemming their suits at the same time. The background can swirl right and left while the team stands by, ready to carry furniture for the next scene. However, at the centre of all this chaos is a critical person and this is the leader. He coordinates all aspects of the production, from costumes, sets to actors and rehearsals, so that everything goes well.
Stage managers typically provide practical and organizational support to the director, actors, designers, theatre crew and technicians throughout the production process. I believe that such a position presupposes high professionalism and moral training, which will positively influence the work process during crisis situations in an institution or in a team.
Human Resource Essay Example 5: “How to Start the Process of Human Resource Development and How to Avoid Problems?”
Human potential tends to grow constantly. This is due to the fact that over time, an enterprise or organization begins to demand more and more efficiency from its employees. That is why the development of human resources is one of the key issues of the firm’s management.
One of the most difficult periods for any employee is his adaptation to the enterprise. Not only do newcomers have to familiarize themselves with all the organizational issues, but they also have to take a certain place in the team and go through serious psychological pressure. The introduction of a person into a new position is also of great importance, namely, acquaintance with official duties.
The policy of the enterprise management on these issues is of great importance in the course of these processes. A friendly atmosphere is also important, and methodological support is also required. For example, large firms have practices such as conducting lectures and seminars for new personnel, as well as introducing training programs. Thus, the development of the potential of each employee can be quick and beneficial for the company or organization.
But the enterprise can often face difficulties. One of the most important problems faced by the human resource of an enterprise is paying insufficient attention to this issue. Nevertheless, managing people requires specialized knowledge, as well as skills and mechanisms. So, the first thing worth paying attention to is the development of leadership in the team. Moreover, this should relate specifically to the working moments, and not to the personal relationships of employees. Unfortunately, this is often neglected by many businesses.
Another important problem of the organization is paying insufficient attention or completely ignoring the need for human resource management. However, it should be understood that cadres do not have the ability to self-regulate. A clear policy should be developed on this issue.
Also, one of the most serious shortcomings of modern management is considering the organization separately from the staff. So, sometimes employees are not ready for changes in the work of the enterprise. Therefore, the manager must understand the main concept of personnel management. This category includes several aspects:
- economic component;
- strict subordination to a single leader;
- definition of a clear management hierarchy;
- development of discipline norms, as well as a system of rewards and penalties;
- clear definition of the area of responsibility of each of the employees;
- development of organizational culture, thanks to which the personnel feel the unity of the work collective.
In conclusion, I can say that the biggest mistake can be considered an underestimation of the human component in the work of an enterprise, which interferes with the development of human resources. It is often this leadership oversight that causes serious economic problems.
Human Resource Essay Example 6: “What Recommendations Can I Give on the Management of Human Resources?”
In every enterprise or organization, the main motive for development is the competent management of human resources and their improvement. In order for the use of human resources in the enterprise to be effective, managers must be guided by a number of recommendations in their activities. For example, the best motivation for employees will be a clear demonstration of the career growth of senior management. Why is this done? Personnel must set specific goals for themselves and be aware of the reality of their achievement.
Another of the most important aspects is decent wages, even in the most difficult and crisis periods. Employees must receive the agreed amount in order to realize their value to the organization. In any case, the employee will leave the company if he cannot fully support himself and his family.
Also, employees must thoroughly know comprehensive information about their enterprise, as well as the mechanism for making a profit. The knowledge of employees should not be limited to a narrow range of their duties. It is important to note that in communicating with each of the employees, respect should be guided because each of them has the opportunity to leave for another organization.
But the main recommendation is that the manager thoroughly knows and learns new methods of human resource management in the organization. What it is? Methods are a way of influencing a team or an individual employee to achieve a set goal, coordinating his activities in the production process.
Administrative methods are based on power, discipline and punishment. They rely on the administrative subordination of the object to the subject, based on the existing management hierarchy. The main functions of administrative methods are to provide a stable legal environment for the activities of an organization, to protect a specific environment, to guarantee rights and freedoms. And economic methods are based on the use of economic incentives. With their help, material incentives for the team, individual workers are carried out.
By the mechanisms of the economic method, the state has a tax, credit and financial system, a price system, the size of the minimum wage, and plans for economic development.
Socio-psychological methods are based on the use of moral incentives to work and influence personnel with the help of psychological mechanisms in order to translate an administrative task into a conscious responsibility, an inner need of a person. This can be achieved through:
- building a team, creating a normal psychological climate and creative atmosphere;
- personal example;
- meeting the cultural and spiritual needs of workers;
- the establishment of social norms of behaviour and social stimulation of the development of the team;
- the establishment of moral sanctions and encouragement;
- social protection.
In conclusion, it should be noted that the role of human resources should be clearly understood at all levels. This is one of the most important elements of the functioning of not only a single enterprise, but also the state as a whole. It is important to remember that a person is of the highest value, and his abilities and intelligence are of the greatest economic interest. Therefore, managers should not neglect the trust of their employees.
Human Resource Essay Example 7: “What Are the Main Directions of the Psychologist’s Activity in the Human Resource Management System?”
The place of a psychologist at an enterprise is very important because it is this person with a higher education who can objectively assess many human qualities and ways of their development. I believe that the main focus of a psychologist is to create a reserve for the internal growth of a specialist, as well as to participate in career planning. This is done by describing the personal qualities of employees and their development strategies. Determination of opportunities and boundaries for growth and self-development is very important for the categories of specialists and managers.
Also, a specialist in the field of psychology, in my opinion, should be engaged in identifying factors that prevent the emergence and development of conflicts since conflicts cause enormous damage to the organization. It is possible to reduce the likelihood of conflicts by carrying out the correct selection and placement of personnel, taking into account not only professional but also psychological characteristics.
Other cases in which a specialist psychologist can help identify motivation and needs for changing the system of material incentives. In general, with any organizational change, a psychologist’s participation is necessary to reduce the resistance of employees. Latent resistance is especially dangerous. What other types of psychologist activities are there in the human resource management system?
Professional selection is a procedure that, in the case of professions with relative professional suitability, helps assess the effectiveness of an employee and establish a forecast of his professional development. Personnel selection – creating a reserve, completing departments following specific criteria (professional competence, specialization features, etc.) Personnel adaptation is the process of getting new employees acquainted with the organization, with new working conditions and changes in the behaviour and psychological climate of the organization.
Personnel assessment is one of the most critical areas of work with personnel. It is carried out constantly throughout all stages of the personnel life cycle: recruiting, adaptation, consolidation (stabilization), development, leaving (moving personnel to subsidiaries, branches), etc. Assessment is a method of a comprehensive assessment of personnel that every psychologist should know in organizations. It is based on using a system of complementary methods, focused on the real work behaviour of the evaluated employees and taking into account the specifics of the requirements of job positions.
Psychological support of human resource management is a set of technologies, activities, procedures, and application principles, involving the use of psychological mechanisms and patterns of human functioning, who acts as a subject of labour, a collective subject of activity and a social community. I think that the role of psychological support is to optimize the ergonomic, organizational, informational, hygienic prerequisites for the activities of the personnel of the enterprise.
Still, essential tasks for a psychologist are such procedures as psychological, educational activities and psychological examination. Increasing the psychological literacy of staff, creating a favourable image of both the psychologist’s activities in the organization and the tasks of psychological support, popularizing and explaining the latest psychological research, developing the need for psychological knowledge and skills among staff and the desire to use them in professional activities and other life situations.
Expertise is understood as the study of any issue requiring special knowledge, with the presentation of a reasoned opinion. For example, to establish the compliance of professionals with the requirements of the labour post. As well as a study of organizational projects, regulatory documents, workplaces, working conditions, work and rest regimes, incentive and motivation systems for work, systems for the distribution of labour functions, corporate culture, causes of conflicts and causes of injury.
Therefore, do not neglect a specialist in the field of psychology. In my opinion, he can best understand how to properly manage human resources and have the best influence on personnel to achieve better results in an organization or an enterprise.
As you can see, an essay on human resources can be a fun and educational assignment for you, which will open you up to important new knowledge in this area. With the right effort, you can write an essay on human resources well and then it will be easier for you to write more complex academic work while at university. So don’t be afraid to get started!

10 Best Books for a Business Student

I Want to Write My Essay, But I Can’t Figure Out How

Introducing an anxiety research paper
Essay on Human Resource Management
Introduction
Human resource management is a sensitive matter that any organization has to take into consideration for all activities and operations to run flawlessly. Companies that ensure employees are well handled are more likely to do better in business as compared to firms that have no regard for their workers (Mankins & Garton, 2017). Studying human resource management is essential as it helps many understand various notions and concepts on the topic of discussion. The course has been interesting as it enlightens the society on the role of such departments within a working organization. A thorough analysis of the course indicates that three major insights are vital for the achievement of the desired results. The first idea is based on employees being an essential part of the business (Cascio, 2015). The second idea on human resource management that is evident throughout the course is that firms should invest heavily in their employees. The third concept that can be learnt from the course materials is the fact that human resource management should always apply the right strategies and ensure that decisions are made in a consultative manner (Mankins & Garton, 2017). The paper aims to examine the three insights, their practical application, and why they are valuable in establishing proper human resource management.
HRM Application
Human resource management is vital for every organization as it shapes the direction that operations take within the organization. It is important to examine critically how HRM influences employee relationships within the workplace. From the course materials provided, one can presume that employees of any company are as important as customers (Mankins & Garton, 2017). Employees form an essential part of the company as they spearhead various programs that are important for the continuity of company operations. Without a workforce that is committed to achievement of set objectives, a firm will fail in its quest to become a top company in the industry. Established human resource departments are always committed to ensuring that employees are kept comfortable and satisfied for better delivery during company operations. Employers must provide a conducive working environment for their employees, including safety and health conditions (Mankins & Garton, 2017). Learning of human resource concepts helps one gain essential skills of employee management, performance assessment, and proper supervision of operations. When an employer wants to introduce a quality product in the market, he/she should first provide quality employment.
The second idea that is evident from the course is the fact that investing heavily in employees pays significantly. For instance, companies that leave their employees demoralized and unsatisfied end up posting poor performance at the end of the day (Cascio, 2015). Investing in employees includes preparing training workshops and developmental programs that aim at improving the skills of each employer. There is a need for every firm to implement policies that aim to improve employee happiness as it is a prerequisite for proper performance. The course materials highlight the importance of motivation and commitment among employees that work for any organization (Cascio, 2015). Employee assistance initiatives such as therapy programs and other facilities within a workplace motivate employees to deliver their best. Constructing and availing such amenities to employees is capital intensive, and not all firms within the industry can be able to achieve such a status. Investing heavily in employee relations can prove helpful for any firm that intends to do better in business.
The third insight that one can learn from the course material is the idea of being open-minded and inclusive when it comes to decision making within an organization. Human resource departments should be at the forefront of ensuring that decisions are arrived at after a thorough consultative process within the organization (Bolman & Deal, 2017). Firms should consult their employees before implementing various rules that shape operations within the working environment. There should be a specific approach tailored to handle multiple problems that arise during work operations. Every HRM department must provide the best conditions that can lead to the achievement of set objectives. For instance, when an employee messes within the work setting, the HRM must apply the set guidelines to handle the matter. Procedures applied should be void from biasness and rigidity in a bid to ensure justice and inclusivity (Bolman & Deal, 2017). Studying principles of human resource management enlightens one on how to value employees’ opinions, especially within an organization with a huge floor area.
Learning assessment
Learning of HRM concepts helps one understand why treating employees better can help a company do better. For instance, through proper management of resources, one can come up with organizational structures and designs that promote performance among employees. Corporate design is also an essential aspect in the definition of roles that each individual should play within the work setting (Ugoani, 2020). The concepts learnt in class change one’s way of thinking and approaching of various issues within the community. From learning experience, companies lose a significant productive power to time-wasting, which has derailed improvement of operations. Firms must consider proper management of resources an critical factor that influences production activities.
Critical Analysis
Learning concepts on human resource management helps those in leadership positions to weigh what is essential for employees and organizational growth. Companies that have incorporated HRM principles in their workplaces do better as compared to those that are insensitive to employee issues (Nazir & Islam, 2017). Employee motivation and happiness evoke a sense of responsibility in an individual, prompting such employees to deliver even better. Ethical standards that are acceptable internationally must apply for the HRM department to serve effectively with purpose. In essence, it is through the learning of HR concepts that one can develop knowhow on the handling of various managerial predicaments that arise at a workplace. Inclusivity and open-mindedness are essential virtues that can help a leader implement a culture that aims to promote performance (Mankins & Garton, 2017). Practitioners in this field can learn a lot from the course as it directs individuals on basics that must be incorporated for proper human resource management.
To sum it up, HR management principles require high levels of ethical standards that regard employee happiness. Company goals should be aligned with resources that are present for disposal. Employees should be considered in every decision making process as they form an essential part of the business. Employee welfare should be prioritized to ensure they are comfortable to deliver professionally. Apprising employees and allowing them to go for vacation contributes significantly to employee happiness and eventual retention. Equally, investing heavily in employees can prove helpful in achieving the set goals for the firm. By borrowing theoretically from concepts learnt in class, HR departments have an obligation of ensuring that productivity is improved, given the available scarce resources. Decision making within an organization should be done through consultations, which include employees. The course is relevant to principles that encompass the concept of human resource management within any organization.
Bolman, L. G., & Deal, T. E. (2017). Reframing organizations: Artistry, choice, and leadership . John Wiley & Sons.
Cascio, W. F. (2015). Managing human resources . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mankins, M. C., & Garton, E. (2017). Time, Talent, Energy: Overcome Organizational Drag and Unleash Your Team s Productive Power . Harvard Business Review Press.
Nazir, O., & Islam, J. U. (2017). Enhancing organizational commitment and employee performance through employee engagement. South Asian Journal of Business Studies .
Ugoani, J. N. N. (2020). Managing Employee Relations and its Effect on Organizational Success. International Journal of Social Sciences Perspectives , 6 (1), 1-10.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Did Hitler Destroy the Weimar Republic or Was It Doomed by th...
- Essay on Employers and Background Checks
- Essay on Corona Pandemic: To What Extent May the Fundamental Rights of...
- What influences have precipitated the change in anthropological method...
- Essay on Uncertainty and Climate Change Adaption
- Essay on Industry Analysis of Yahoo Inc
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice, Essay Example
Pages: 14
Words: 3957
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Introduction
Human resources management (HRM) emerged together with the need to operate large numbers of workforce and fit the demands of the most valuable corporate assets, the employees, with the company objectives, and to ensure adequate conditions for workers of various kinds, types and categories. The HRM field reflects the major part of people management, i.e. coordination of all policies, processes and practices connected with managing people currently employed in a certain organization. The HRM has faced much criticism currently, and is even considered to be the barrier in building the flexible and supportive environment in an organization, acting as a restrictive tool for reducing payroll and contributing to the employee turnover (Mathis and Jackson 4).
Indeed, at times the activities of HRM executives seem to be more directed at activities than results; nonetheless, the importance of human resources and effective management thereof has long ago been recognized as a vital element of successful competition in the market. More than that, HRM is fairly considered to be one of the companies’ core competencies, under the condition of good coordination and organization (Mathis and Jackson 4). HRM also helps the company find the proper balance in the realm of legal requirements restraining the work of organizations and protecting employees; it ensures compensation reconsiderations according to the employee performance, and serves as a driving force for employee motivation in performance increases.
The significance of HRM has been recognized as soon as the inner processes governing the activity of any organization have been detected. It is obvious that any organization has a set of assets it manages in the process of its activity: they include physical, financial, intangible, and human resources. Nonetheless, even being equal in row with other resources, the human resources really make the activity of any company work; they represent the ‘glue’ that combines and coordinates the resources, making them bring profit for the company. Logically, one should realize that there is no way to keep the company functioning without human resources, and even under the condition of poor functioning thereof (Mathis and Jackson 4). Proper HRM can help the company save considerable costs for recruiting and retraining, talent detection may help it educate its own leaders and managers etc. – there are numerous examples of the way HRM may benefit a company. They explain the current close attention to HRM and outline the main areas of research in the field of its improvement and successful implementation.
The modern focus on HRM and its implementation in business structures is explained by the wish to establish fast and responsive organizations that can quickly handle the changes in the external and internal environment. The HRM provides the company with the ability to recruit, train and retain employees, and to align their activities with corporate objectives. The traditional, isolated approach to HRM is no longer used, with the organization giving additional responsibilities and powers to HR managers in the overall struggle for better performance of the whole business unit.
Before defining the concept of ‘human resources management’, one has to track its evolution from the term ‘personnel management’ that emerged in the 20 th century to denote the response of employees to public policies and union activities and changed gradually under the pressure of the global change, socio-economic changes and tendencies etc. (Bratton and Gold 6). The full definition of the HRM concept looks as follows:
“That part of the management process that specializes in the management of people in work organizations. HRM emphasizes that employees are critical to achieving sustainable competitive advantage, that human resources practices need to be integrated with the corporate strategy, and that human resource specialists help organizational controllers to meet both efficiency and equity objectives” (Bratton and Gold 11).
However, even upon seeing the definition, one still may not have a clear idea of what management really stands for in the described situation, and what human resources mean in the given context. The human resources actually mean the human capital that represents one of the company’s assets (alongside with the physical, financial and intangible ones) (Mathis and Jackson 5). The human capital is viewed in the collection of all capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experience, motivation etc. that employees of a certain organization possess. Hence, management thereof refers to the proper distribution of positions, adequate rewards corresponding to the employee performance, training and staffing etc. Consequently, one may understand the definition as a way to manage the human capital in the most productive and efficient way so that the company could enhance its core competencies and ensure a firmer position in the marketplace.
Features and Characteristics of HRM
There is a set of features defining the nature of HRM and its place within the organizational framework. The first feature refers to knowledge management; it pertains to any aspect of creating, obtaining, sharing and utilizing knowledge of any kind (Armstrong 9). The key role of HRM concerning knowledge is to conduct activities to develop, generate, and preserve any knowledge specific for the needs of the company. It is also essential to note that knowledge in the focus of HRM derives from organizational learning processes (Armstrong 9).
The next feature is reward management; it results directly from the incentive of HRM professionals to increase motivation, job management, and commitment of employees towards their company. These practices can be achieved by introducing policies of showing that employees are valued and rewarded according to their performance (Armstrong 9). It is essential to implement various reward instruments and schemes so that they would suit the whole range of competencies and skills of the company’s staff. In addition, the successful HRM strategy should not focus on restrictive sanctions for employees who fall behind in their performance; instead, it should emphasize strengths and promote potentially creative and committed individuals.
Fostering constructive and supportive employee relations is another feature of HRM. Promoting the working climate with productive and harmonious relationships is made possible through positive partnership between management and workplace (Armstrong 9). Trade unions are also involved in the employee relations to ensure the comprehensive effect of HRM in building the coherent and mutually satisfied employee structure. The main challenge of this process is in the next feature of HRM: meeting diverse needs of all company stakeholders (Armstrong 10). Individual and group needs have to be taken into account to design equal opportunities for all employees disregarding the peculiarities of their working style, aspirations, and capabilities.
Finally, the HRM feature is bridging the gap between rhetoric and reality. The company’s mission and vision, HR strategy and corporate responsibility are laid down in all written codes and regulations of the company, annual reports and presentations for shareholders. However, as soon as the planned HR practices are implemented, a number of barriers (including limited support, inadequate infrastructure, lack of resources etc.) preclude those strategies from being successfully introduced. Hence, the ability of HRM nowadays is in identifying such gaps and allocating proper resources for making HR strategies a commonplace organizational reality (Armstrong 10).
Drawing certain conclusions from the discussed HRM features, one can come to understanding the key HRM characteristics shaping its modern image and structure. They are as follows:
diverse (it is essential to encourage diversity in HRM practices because of the integrated, comprehensive and over-grasping focus of HRM aimed at creating a harmonious, homogeneous, and at the same time individually tailored structure of employee relationships with management) (Armstrong 9):
- strategically focused, with emphasis on integration (there is no place for an isolated approach anymore; HRM is embedded in all aspects of corporate functioning, striving to the creation of a coherent, interlinked employee system) (Armstrong 9);
- oriented on commitment (only under the condition of employee trust and loyalty towards the company, HRM can achieve the stipulated corporate goals and make the human resources act as a unifying and enacting force for other company assets) (Armstrong 9);
- HRM is based on the belief that working individuals should be treated as assets, i.e. the human capital (in other way common HRM strategies and assessment tools would not work) (Armstrong 9);
- unitarist and individualistic approach towards employee relations (the workforce should act as a unified, congruent force, but at the same time individual needs, wants, aspirations and ambitions should be taken into account and encouraged to ensure corporate growth and accumulation of intelligence and knowledge) (Armstrong 9);
- management-driven (HRM is seen as a line management responsibility, changing the nature of HRM delivery) (Armstrong 10);
- focused on business values (human resources are nurtured, developed and managed, but always with the proper respect to the company objectives; the HRM should always be consistent with business objectives) (Armstrong 10).
There are a large number of specific and general goals pursued by modern HRM, but considerable research and review have allowed to focus on the twelve dominant policy goals proposed by Caldwell (2004) and cited in Armstrong:
- People constituting an organizational workforce should be treated as the asset crucial for the creation of the competitive advantage for the company in the marketplace. The essence of the goal is to gain the competitive level of performance for the company to become a strong contender with a firm position in the market; it is vital to realize that even under the condition of having plentiful resources of other kind, the company will never achieve success because of the inability to utilize the resources. Without the workforce, there will be no tools for operating and manipulating the company’s resources for the sake of economic profit. Hence, the human capital is the most essential asset possessed by the company, and it has to be treated accordingly (Armstrong 10).
- The HRM policies have to be aligned with the business policies and corporate strategy of every given company. This goal explains the very purpose of HRM existence – through the effective and thoughtful management of the company’s human capital, the HRM department assists the company in gaining the competitive advantage in the market and increasing the employee performance through commitment and encouragement of creativity (Armstrong 10).
- The HRM system is aimed at developing a close fit of HR policies, procedures and systems with one another. Only under the condition of the close connection and alignment of all HR elements within the organizational structure, the successful implementation of HRM principles becomes possible and potentially profitable for the company (Armstrong 10).
- The HRM is responsible for creating a flatter and more flexible organization. The ultimate goal of that effort is to make the company more responsive to the changes of the internal and external business environment. The modern business world is characterized by a high level of turbulence and uncertainty, crises in all spheres of human activity, hence only the affluent and flexible business entities can survive in the harsh atmosphere of making business. The HRM effort can make the company stronger from the inside and reinforce its outer strengths (Armstrong 10).
- The HRM should encourage teamwork and cooperation inside the organization. The specific advantage of such efforts can be seen in the strengthening of the employee interconnection, mutual support and emotional intelligence (Armstrong 10).
- The creation of a strong customer-first philosophy throughout the organization is another policy goal of HRM; the main focus of HRM is driven on the individually correct but still corporately shaped system of employee management, training and rewarding. The employees have to realize their value for the company to be able to provide their respect and commitment to the customer in turn (Armstrong 10).
- Employees have to be empowered for self-management, learning and development. HRM creates the basis for corporate leadership programs to educate the company’s leaders, professionals and inspirers instead of hiring them from outside (Armstrong 10).
- HRM should develop rewarding strategies directly tied to employee performance. Despite the commonly known criticism of the approach, financial incentives still remain a powerful driving force in the increase of performance and commitment (Armstrong 11).
- Internal communication improvement is the goal for HRM effort because of its importance for employee involvement in the company issues. The better the employees are informed about the internal matters of their company, the more trusting their relationships with the employer are, and the higher the commitment is (Armstrong 11).
- A more general HRM is in building the greater employee commitment; it can be achieved by additional means other than financial ones, including strengthening the corporate culture, involving employees in extra-work events and promoting various activities exploring the employees’ talents, ambitions and abilities (Armstrong 11).
- Increasing line management responsibility for the HR policies is another major goal of HRM; as it has been already mentioned, HRM is growing in its importance and grasps others areas of company functioning. Therefore, HRM is equal in responsibilities with line management, providing more ties and interconnections between the internal aspects of management (Armstrong 11).
- Finally, HRM should empower managers in the role of enablers. This refers both to the allocation of financial resources for solving some urgent business matters, and to the empowerment of capable employees offering their potential and creativity to the company (Armstrong 11).
Strategic HRM
Strategic HRM is substantially different from the RHM process itself because it focuses mainly on the activities affecting the behavior of individuals in an effort to formulate and introduce strategic needs of the business (Armstrong and Baron 41). Hence, one can understand that the strategic HRM reflects not the real-time, but the future intentions of the organization regarding the HRM organization, procedures and policies. It includes the long-term people issues, defining the HR strategies that have to be identified for the future effort of the HRM department. In addition, the strategic HRM peculiarity is that it concerns the macro-concerns at the organizational level, including the structure, values, culture, performance, rewards, motivation etc. The aim of strategic HRM deriving from its features consists in the creation of the strategic capability for the company to possess the highly committed, skilled and motivated employees to enhance the company’s competitive advantage in terms of human assets. In order to achieve that aim, the strategic HRM needs to fulfill the individual and collective needs of the employees to further on implement coherent and practical HR policies and programs (Armstrong and Baron 41-42).
Before proceeding to the practical discussion of existing HRM strategies, one has to identify the modern approaches to HRM strategy; they include the classical, processual and systemic ones, having many proponents and followers in the global theoretical HRM thought. The classical approach defends the ‘cold’ analysis of organizational environment and the company’s internal resources, with the further identification of strategic options and final implementation of the chosen strategy (Wilczek 2). It is vital to remember that there is a clear distinction between the authorities responsible for strategy generation and implementation thereof. According to the classical approach, strategies are created by top management and implemented by operational managers (Wilczek 2).
The processual approach promotes the strategic flexibility of the company; it argues that strategies are formulated and implemented in an integrated, non-disruptive manner at all levels of an organization. The approach is more viable for the company in a turbulent environment, with the clear need for expertise and creativity at all levels of the organizational structure (Wilczek 3). The third approach, however, includes the socio-cultural and economic context of the countries in which the strategy is formulated into the strategic HRM process. The proponents of the systemic approach argue that cultural and geographical differences seriously affect the process of strategy formation as well as its outcomes (Wilczek 3).
Consequently, proceeding to the models of strategic HRM, one has to identify its nature as a search of the ‘best fit’ within the organizational structure. The strategic fit is the central concept of strategic HRM, also called the matching model. The essence of the model is in making the HR strategy aligned with business strategies of the company (representing the vertical fit) (Armstrong and Baron 44). The vertical fit is the integral part contributing to the business planning process in an organization; it has to match the life cycle stages of the company and be individually tailored to the dynamics of its development (Armstrong and Baron 46).
The horizontal fit is nevertheless as important as the vertical one, as the HR strategies have to be aligned from the inside, i.e. there should be a high level of coherence between the different elements of people strategies (Armstrong and Baron 44). The logical interconnection among the mutually supportive practices of the HR strategy can ensure the success of the horizontal fit, making the HR strategy the ‘best fit’, the chief objective of the overall corporate strategy. The resource-based approach to HRM strategy also provides a sound foundation for the development and implementation of strategic HRM within the organization; it dictates the resource-based approach to all tangible and intangible assets possessed by the company, and utilization thereof with the purpose of being competitive in the market (Armstrong and Baron 53).
Functions Reflected in Business Practices
The success of any organization depends on the allocation of proper human resources in proper positions to ensure their full engagement, job satisfaction and adequate rewards for the performance; however, the current review of staffing practices has shown much incongruence with the ideal objectives stipulated in each HRM department. The wrongdoings include hoarding professionals at the expense of the organization, fostering promotions on biased principles without consideration of organization-wide options, limiting individual opportunities and depriving them from feedback, promoting decrease of confidence etc. (Fombrun, Tichy, and Devanna 58). All of them lead to employee turnover and loss of intelligence, knowledge and expertise.
Introducing the strategic HRM practices in staffing now plays the crucial role in the success of the organization in the accomplishment of its business objectives. The key processes are the specification of qualification, identification of people possessing those skills, and relocating the employees to the positions that fit them the most (Fombrun et al. 58). The staffing policies are affected by the dominant corporate culture and the stage of business development (the start-up business will conduct recruiting activities to form the staff, while the business at a stage of decline can relocate the existing staff or even involve professionals from external resources to revitalize the organization). Some constructive modern HRM practices regarding staffing within an organization include job posting, management development, and succession planning for the sake of HRM integration in all fields of organizational functioning (Fombrun et al. 65).
Performance Appraisal
Performance appraisal is another central element of successful HRM because it provides the assessment and identification of critical job behaviors of the management, specifying the objectives of each manage, and agreeing on the steps and resources necessary for the achievement of those objectives (Fombrun et al. 87). There is a high risk of selective focusing in the performance appraisal, especially concerning the top management, because of lack of subjectivity and absence of anonymity. Hence, the innovative HRM practices in appraisal have to be introduced to ensure the successful accomplishment of business goals and strategies.
There are several categories of measures that can be used for performance appraisal; outcome measures are a strong indicator, but they fail to support the appraisal system in full because of the focus on results depriving managers of the opportunity to assess the process of achieving results. This approach may cause the deterioration of the system instead of its improvement, so the behavioral measures should complement the outcome ones (Fombrun et al. 91). Behavioral measures help identify the critical behavior that may aid employees in completing the objectives stipulated for their position, and the critical incident technique may be implemented for the assessment of the employee correspondence to their positions. Behavior measures are also highly helpful in selecting employees and establishing monetary rewards (Fombrun et al. 94).
The job behavioral analysis is utilized to identify the activities top managers have to conduct to implement the strategic plan. Here two types of training programs have proven to assist in objective achievement: accurate recording of what is seen, and giving feedback as well as setting the performance goals. These programs ensure objectivity and enhance the development of self-management capabilities to promote business strategies on the organization-wide level (Fombrun et al. 100).
Compensation and Benefit
The reward system in any organization may play both functional and dysfunctional roles because of the motivation or discouragement that it may bring to the employees. However, it is essential to note that the compensation system, in case it is properly designed, may become the key contributor to the effectiveness of the HR strategy and employee commitment increase. The strategic role of the reward system lies within the behavioral effect it may produce on employees, hence it has to be thoroughly considered in order to estimate the drives and incentives to be used in the effective HRM system design (Fombrun et al. 127).
The first outcome a successful reward system may offer to the company is the attraction and retention of employees. It is widely known that the companies offering the highest monetary rewards still attract the largest numbers of employees and retain them stronger and longer than other companies do. Hence, the monetary motivation turns out to be fairly strong nowadays (Fombrun et al. 128). In addition, the motivation outcome is also the direct consequence of the properly designed reward system – employees who earn more are more committed to their company, they possess a higher level of loyalty and resourcefulness towards their employer.
The organizational culture is also affected by the reward system; the way rewards are developed, administered and managed affect the culture and shape its type, e.g. participant, entrepreneurial or other ones (Fombrun et al. 128). Reinforcement and definition of the company structure are also affected by the reward system – as usual, the hierarchical structure of corresponding rewarding systems for different levels of management (Fombrun et al. 128). Finally, the compensation to employees affects the cost structure of the company. The salaries to employees traditionally constitute a large share of the company’s operating costs; hence, the thoughtful design of rewards and appraisals may save the company a considerable sum of money and help it allocate resources more productively.
HRM now plays an increasingly important role in building the business strategy and achieving the competitive advantage in the marketplace. With the emergence of the innovative approach to human resources as the strongest company asset, a variety of HRM approaches has been developed to assist the company in aligning people management with the business objectives and strategies. Therefore, it is totally possible to state that the modern organizational structure welcomes an integrated HRM system having equal opportunities and responsibilities with line management and operating in a wide range of areas to sustain the company’s consistence with its strategies.
The basis of the HRM processes is successful staffing, planning, management, identification of reward systems, identification of the company’s internal resources etc. All these activities are called to enhance the company’s competitive position and to reinforce its human capital potential. Strategic HRM is focused on the future perspectives pursued by the company, so it is directed at the macro-environment of the organization. The key processes and functions of strategic HRM constitute effective staffing (that is, proper allocation of employees according to their potential and skills), performance appraisal (both according to the behavioral patterns and outcome measures), and design of effective reward systems that would assist the company in accomplishing its business strategy.
Works Cited
Armstrong, Michael. A handbook of human resource management practice . 10 th ed. London: Kogan Page Publishers, 2006. Print.
Armstrong, Michael, and Angela Baron. Strategic HRM: the key to improved business performance . London: CIPD Publishing, 2002. Print.
Bratton, John, and Jeffrey Gold. Human Resource Management: Theory and Practice . 2 nd ed. New Jersey: Routledge, 2001. Print.
Fombrun, J. Charles, Tichy, M. Noel, and Mary Anne Devanna. Strategic human resource management. San Francisco: John Wiley and Sons, 1984. Print.
Mathis, L. Robert, and John H. Jackson. Human resource management . 12 th ed. Mason, OH: Cengage Learning, 2008. Print.
Wilczek, Tim. The “Classical Model” for Practising Human Resource Management: …or is There a Need for an Integrated Approach Including Specialised Human Resource Strategies? Norderstedt, Germany: GRIN Verlag, 2008. Print.
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Take All My Crap, Essay Example
Parental Involvement Scheme, Dissertation Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Relatives, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 364
Voting as a Civic Responsibility, Essay Example
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
Human Resources essay samples, topics and guides
16 February, 2022
30 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
If you study at a Management department, you will receive a Human Resources essay as a home assignment sooner or later. What is this type of task? How can you write it to impress your supervisor? Here we uncover all the fundamentals of HR writing to help you jumpstart the writing process and get a […]

If you study at a Management department, you will receive a Human Resources essay as a home assignment sooner or later. What is this type of task? How can you write it to impress your supervisor? Here we uncover all the fundamentals of HR writing to help you jumpstart the writing process and get a high grade for the academic paper.
Let’s start with a definition. A Human Resources essay is a type of academic work that approaches some subject related to managing a company’s staff, either public or private, and resolving issues arising in the process.
Thus, when you are tasked with writing an essay about HR, you can choose among various topics, such as hiring and retaining staff, resolving interpersonal conflict, organizing teamwork, and deciding on the proper staff rewards to keep them motivated and engaged. You can also choose among different approaches to analysis; it may be either a purely theoretical piece that examines various theories and methods or an applied case study considering an example of a specific company.
When you proceed to Human Resources essay writing, it’s vital to understand the principles and peculiarities distinguishing this piece of homework from other assignments you might face at the HR department. Here are the basics of competent and professional composition on HR-related topics:
- To sound competent and knowledgeable about the topic, you need to include practical examples and statistics to argue your point.
- Choose a theme to your liking and focus on something of personal interest; it will be much easier to write a paper on the topic you like.
- Study a couple of Human Resources school essay examples available online to see how others have approached this subject.
If you’re still unsure how to complete your home assignment, and the time of its submission is already coming, you can always hire a professional Human Resources essay writer from our team. We’ve here 24/7, always on standby to help you out with any academic task. Thus, you will always stay on top of the class in terms of grades and timeliness without overstretching yourself or draining your resources.
Human Resources Essay Format
Now let’s proceed to discuss the Human Resources essay format. It has some specifics to consider for the sake of meeting your professor’s expectations and getting a high grade for the assignment. First, we want to note that a Human Resources school essay has the same components as other essays possess, so you don’t need to invent the wheel when approaching this task.
All you need to do is compose an introduction of your paper, a body, and a conclusion.
H3: Introduction
In this part of your Human Resources plan essay, you need to indicate the overall topic of your study and the problem you’re going to examine. You should end this part with a detailed and concise thesis statement showing how you will approach the problem and from which angles you will explore it.
This is the central part of your Human Resources essay in which you present your arguments on a chapter-by-chapter basis. Keep in mind that every paragraph should deal with only one subject, which is typically reflected in the topic sentence. In this way, your essay will have a proper structure and will be readable.
This part of your essay should focus on summarizing the main points you’ve discussed in the paper’s body, restating the thesis statement, and drawing the readers’ attention to broader implications of the subject.
Write Human Resources essay in 5 Steps
Stumbling upon how to write a Human Resources management essay? Here is a simple algorithm that will help you cope with any assignment at hand, including HR writing:
- Study your course materials in detail to see what a professor wants from this assignment.
- Pick a topic from the list of available options based on your interest in the subject and the materials’ availability.
- Conduct in-depth research on Google and across several academic databases to identify credible, fresh literary evidence supporting your arguments and standpoint.
- Find a couple of real-life examples to illustrate your points and prove the applicability of your ideas in HR practice.
- Complete the writing piece according to all academic conventions (e.g., paragraph structure, essay format, grammar and style, originality, etc.).
Human Resources Essay Topics (250)
Choosing a topic is always the most challenging part of the essay composition process. You can’t move further until you’re clear with what to look for and in which direction to move. Thus, we’ve created a list of Human Resources essay topics to help you out and speed up your homework process:
- Does organizational success depend solely on the efficiency of HRM?
- Differences between HR management in public and private organizations.
- Personnel management and transition methods in HRM.
- Strategic HR planning: the essentials.
- HRM principles in healthcare organizations.
- Statistical methods of analysis in HRM.
- The Michigan model of HRM.
- The most significant barriers to effective HRM.
- Job evaluation techniques for HR managers.
- The HRIS technique in HRM.
- Four competencies necessary for career management.
- The variety of career planning techniques.
- The most important managerial competencies in the global HR marketplace.
- Staff competency development models of large corporations.
- Megatrends in the executive development via HRM.
- HRM and online training.
- Primary tenets of performance management practices.
- Approaches to employee recognition.
- What mentoring practices work in the period of COVID-19 distance work?
- Principles of Quality of Work Life (QWL) and HR managers’ role in staff’s work-life balance.
- How can HR managers recognize and promote charismatic leaders in the workplace?
How to Start a Human Resources Essay
Starting a Human Resources essay is not always simple, as you might have a clear plan and roadmap in mind. Otherwise, the process of working on this home task may transform into an unexpected challenge taking too much time and energy from you.
Here are some tips and recommendations from our pros on how to start an HR essay quicker:
- Find a topic that you like and know much about. This will be an excellent start for your essay writing process, as you will have enough background information at hand and will know what to look for online.
- Find a suitable Human Resources essay example in Google or your college library to see how other people have studied the subject of your interest. It may be a good idea to compare several essay samples and develop your own, authentic argumentation on that topic.
- Develop a detailed outline to guide your writing. If you have that roadmap for the whole process of composition, you won’t need to waste time consulting the prompt and double-checking whether you’re on-topic.
- Always opt for the argumentative Human Resources essay topics as they are debatable and offer a freedom of choice. You can study the available sources discussing that topic and choose your standpoint. Argumentative subjects also offer rich evidence on both sides of the debate.
As you can see, starting an HR task is not that hard. But anyway, if you don’t feel like spending another evening over books, maybe it’s time to contact our managers and get professional assistance with the assignment? You can take a rest and relax, dedicating some vital time to yourself and your needs, knowing that your HR home task is in good hands.
We provide all kinds of assistance with essay writing, Human Resources included, so you will never feel shortchanged when working with our experts.
The paper ‘The Recruitment, Selection and Induction Process ” is a great example of a human resources research proposal. This is a working document to focus on the purpose and structure of student essays, which reflects the intent and outlook of their research. It is quite likely and permissible that as students progress with their essays, several aspects of content, direction or emphasis of their essay will change. It is vitally important that students keep their academic supervisor informed of any such changes – as such changes may require students to reconsider any or all of the content of this proposal form.
Section 1: Briefly describe your research topic for Essay 1
The research topic is to identify the recruitment, selection and induction process which organizations need to adopt so that they are able to determine the mechanism through which correct hiring of people takes place. The research concentrates on indentifying the basic things which need to be included in all the process and also stresses on the need of having different process based on the different needs of the organization. The research brings forward the different methods of recruitment, selection and induction process which forms part of every organization. This has helped to identify the different core factors which are part of the recruitment, selection and induction process and the manner in which business effectiveness and changes are witnessed in the hiring process. The research will help organizations to improve their recruitment, selection and induction process as it will garner a path through which different aspect will be included and will help to improve the overall mechanism of hiring people.
Section 2: Briefly outline any frameworks, theories or models you anticipate using:
The research has looked to identify the different patterns which are globally accepted and the research is based on secondary sources. The findings from different research are bring used to find out the manner in which the recruitment, selection and induction process can be improved and changes can be made and moulded based on the different needs and requirements of the organization. The framework which has been followed is one where linkage has been developed between recruitment, selection and induction process so that one process leads to the other and provides a basis through which the different dimensions which impact the hiring process can be understood. The overall impetus of the research is thereby towards finding out the different areas and dimensions which will help to facilitate and improve the process of achieving better results and multiplying the overall effectiveness of hiring people.
Section 3: Briefly provide the main authors and themes relevant to your topic.
Some of the different sources which have been used and are relevant to the area of research are
Arnold, J. (2005). Work Psychology: Understanding human behaviour in the workplace 4th ed. Harlow: FT Prentice Hall.
Cable, D. & Judge, T. (2006). Person-organization fit, job choice decisions, and organizational entry. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 67 (3), 294–311
Dipboye, R. (2002). Selection interviews: Process perspectives . Human Resource Selection (3rd ed.). Orlando, FL: Dryden Press
Hogan, R. (2001). Personality and personality measurement. In M.D. Dunnette & L.M. Hough (Eds.), Handbook of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, Vol. 2 (2nd ed.) 873–919
Ryan, A. & Schmit, M. (2003). Assessing organizational fit in employee selection. Paper presented at the 8th Annual Conference of the Society for Industrial & Organizational Psychology, San Francisco, CA
Thompson, P. and McHugh, D. (2009). Work Organizations: A critical approach , 4 th ed. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan
The different themes which the different authors and work provided are related to the manner in which overall changes and dimensions are being witnessed in the hiring process. This will help to understand the core areas which the different research has identified and will help to come to a conclusive conclusion regarding the manner in which different factors and aspect has an impact on the hiring process and different things which need to be included so that the mechanism which has been adopted improves and provides a better understanding of the different business environment.
Section 4: Identify opportunities for further study in Essay 2 and/or gaps in research understanding that will refine your research questions.
The research has been carried outlooks to provides a general perspective of the different factors and areas which needs to be included while designing the recruitment, selection and induction process. The research provides a general idea of the different things which have to be included. This provides an opportunity where future research can be carried out by looking towards an organization or an industry where a specific process of recruitment, selection and induction process is being used. This is an area that can be further researched as it will provide useful information pertaining to a particular industry or organization and will show the different dimensions and aspects which needs to be included in the recruitment, selection and induction process. This will help to understand the application of the different methods in a real organization and will provide useful impetus regarding the manner in which the organization is able to gain due to it. This will thereby help to improve the understanding and having applicability in the real organization will magnify the overall value of the research.
The paper “Performance and Reward Management” is a comprehensive example of human resources case study. Performance management in human resources refers to a holistic process whereby many elements are brought together to successfully manage people, enabling them to meet their goals and targets. It can focus on the performance of a Company, a section, or even an employee (Armstrong 2000).
TPL has a very traditional command and control approach to management across its manufacturing function, employees are not given an opportunity to demonstrate their ability and explore their talent and potential fully. The Management has an old type of leadership known as autocratic. According to Cameron and Green (2012), he described authoritarian is a style of leadership used by leaders who want to make decisions alone, having total authority. Negotiation and consultation are highly discouraged by these leaders. Whatever they say is final. This leadership style is good for employees that need close supervision to perform certain tasks. This simply indicates the organization applying theory X whereby the management feels and assumes that there are lazy and must be supervised closely. This theory has been proven to be counter-effective in modern practice. The management of TPL needs to change its style of leadership and management and come up with a more democratic approach. This will help the Company in giving the employees confidence and therefore increase productivity (Cameron & Green 2012).
Poor performance appraisal and review process can also be witnessed in TPL, where it is done so casually biannually as a chat between a supervisor and a subordinate. TPL should improve on the way it conducts the performance appraisal and review process, all the parties should be involved by aligning performance with the strategic goals of the organization (Armstrong 2000). For example, TPL supervisors should provide more specific feedback that will help them describe the gap that exists between actual performance and what is expected of the employees.
Reward Management
Reward management in human resources also referred to as a reward system means any financial reward that an organization gives to employees in return for their labor. The reward must not only be a material reward but also non-material rewards. The financial reward consists of basic pay and any other benefit to employees. Non- financial rewards include promotions, recognition, and personal growth (Price 2011).
TPL has a very poor reward system; the pay system is very simple that technical, senior management, and employees earn flat salaries on a single payment. There is also a yearly salary increment regardless of their performance. This pay system is very unprofessional as it forgets the core reason for working. People work to be paid and if your system does not reward employees according to the effort they make.
TPL should adopt a reward system that is linked to performance; the payment should vary depending on the quality and quantity of work done by an employee. Attention should be given to employees’ achievement or success-oriented individual bonuses (Price 2011). For example, in a sales department, the salespeople should be paid on the basis of turnover. The salesperson who moves a large stock should be rewarded more than the one who moves little stock. TPL should also seize from using a profit-related bonuses element paid shortly before Christmas. This method can easily demotivate the members of staff if no payment is to be made at the end of the year as in the case when the organization does not make any profit.
Employee turnover in TPL is really high; this is due to a poor reward system and low morale. The organization is wasting a lot of money on recruiting new employees as well as training them to be conversant with the work to be done. David McClelland’s theory of motivation involving three basic needs: achievement, power, and affiliation. When employees achieve their target they are motivated, organizations should give power to employees to make independent decisions. TPL should employ theory Z that focuses on increasing employee loyalty to the Organization when treated well (Cameron & Green 2012).
Human Resource Development
Human resource development in the area of human resources can be termed as a curriculum used to help employees develop their careers by improving personal and organizational skills, abilities, and knowledge. It includes training employees, employee career development, and mentoring when planning for succession (Joy-Matthews, Megginson & Surtees 2004).
TPL staff training in terms of how to carry out the functions of their role is generally very thorough but surprisingly many employees are injured in accidents. What could be the reason for accidents occurring despite employees’ training? The main reason is that on-the-job training is not done appropriately; the reason being that it is provided by consultants off-site which is very expensive.
TPL should make training compulsory to the entire employee workforce in all the departments and it should be done on a quarterly basis. Re-training is very important as it refreshes the employee’s minds and improves their skills in their field (Joy-Matthews, Megginson & Surtees 2004).
Equality and Diversity
Equality in human resources refers to a situation whereby employees have an equal right to employment, payment, and equal access to training and development. The organization should put in place measures that will allow equality. Diversity is a situation whereby an organization encourages a diverse workgroup helping the Company to be more effective (Cornelius 2002).
TPL claims to be an equal opportunities employer but it is ironic that people from ethnic minorities are very few in the organization. This tarnishes the organization’s name as it is an indicator of discrimination leading to inequality. Gender imbalance can also be observed in TPL, fewer women are employed in the organization and therefore a form of discrimination. TPL should come up with a policy that will encourage people of all gender, tribe, and color to be employed.
TPL does not employ people with disabilities or those who are physically challenged. This is a very serious form of discrimination. The organization should come up with policies that will allow a certain percentage of employees to be disabled. It is so unfortunate that the organization does not cater to the dietary need of its employees, there is only one locker room and the TPL canteen does not appear to cater to any variety of dietary needs.
#3 Top Paints Limited- Human Resource Development and Reward Management
The paper “Top Paints Limited- Human Resource Development and Reward Management” is a persuasive example of human resources case study. Top Paints Limited is continuously facing problems related to human resources and the matter has complicated to such an extent that the business has witnessed loss, increase in the number of casualties, increase in staff turnover, and problems that need to be addressed at the earliest. This report identifies the problems faced by Top Paints Limited and looks towards providing alternatives to deal with those.
Top Paints Limited is facing serious issues which have complicated the manner in which business was conducted and needs to be addressed so that a solution to those can be found out as it will help the organization to perform effectively. The issues are
- Top Paints Limited looks to compensate their employees through a model which is outdated. The employees have compensated a fixed salary and the perks are defined beforehand which the employees receive at the end of the year irrespective of the performance which has reduced the efforts made by the employees
- The hierarchical model of the passing of responsibility from the top management to the bottom has restricted the employees from taking initiative in completing the task as they have to follow the ways that have been prescribed to them is another problem that is making it difficult for Top Paints Limited to sustain
- An increase in the accidents rates which are consistent and similar accidents occur shows that lack of training and awareness has made it difficult to deal with the complex issue
- The organization has a dominance of male employees and fewer females and people from the backward class highlighting the fact that despite preaching that there has to be equality and diversity in the workforce the organization has resorted to differentiation making it difficult to conduct business smoothly
Performance Management
Top Paints Limited need to look towards moving away from the traditional system where employees have compensated a fixed salary to a flexible one where the performance of the employees acts as a major force in deciding the salary. Productivity should be measured and based on it employees should be compensated.
The performance-based approach should look towards identifying the performance measures, quality measures, and objectives and look towards control monitoring so that the actual performance is gauged which will facilitate in determining a performance-based pay for its employees.
This will also help Top Paints Limited to ensure that measuring the performance based on the manner the employees have achieved their task will help to understand the manner in which the business will be able to identify the future talent and will guide the management to deal with the future requirements better and have a pool to talent which are able to carry out their responsibilities in the most efficient manner
This is an aspect that Top Paints Limited needs to consider and needs to design the compensation package in such a manner that performance acts as a major point in securing a sound compensation. This would mean moving away from the traditional system where employees have compensated a fixed salary to a flexible one where the performance of the employees acts as a major force in deciding the salary. This would mean using the performance pay approach in compensating the employees. Using Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory will help to design a compensation package where the organization understand the needs and requirements of the employees and based on its look towards package
While designing the reward package special care should be given to ensure that the compensation package has both fixed and flexible pay. Further, through Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory Top Paints Limited needs to look towards ensuring that intrinsic reward is provided to the employees through recognition, promotion, and other ways so that the employees are able to associate themselves with the organization. Using the Herzberg theory of motivation and hygiene will also act as a mechanism through which accidents reduce and the organization is able to gain efficiency in gaining the maximum from the employees and will help to reduce the high turnover that the business is facing and will make the employees work for longer period
Top Paints Limited needs to identify the training tools and methods which will help to reduce the number of casualties that the business is witnessing. Top Paints Limited needs to identify the training requirements both on and off the job so that the employees understand the manner in which they should deal with different situations. They should look towards a processual approach that relies less on top-down strategy as it will help to reduce accidents and ensure better working conditions
Top Paints Limited through their process of training will also be able to motivate the workforce and ensure that all employees are able to come together and work towards a common purpose. They should look towards rating scales and surveillance to ensure that the workforce is able to learn during the training and don’t repeat the mistakes again. This will help the business to ensure that the inter-personal relationship between the employees improves and they are able to work as a team.
Equality & Diversity
Top Paints Limited needs to look towards having a mix of people from different cultures and backgrounds so that they are able to demonstrate diversity in the workforce. While recruiting and selecting employees they should look towards using informal contacts, formal contacts, notice boards, advertising, and external sources so that people from all backgrounds are picked in the organization. This will make the employees feel that the organization is looking towards all and will help Top Paints Limited to find new recruits easily.
Having equality and diversity in the workforce will ensure that the employees are able to associate with the company and will help to reduce the turnover rate. Special care should be taken through monitoring which will help to reduce discrimination through stereotyping, marginalization, and invisibilization. This will thereby help Top Paints Limited to prepare properly in the manner they will deal in the future and ensure that a strategy is developed through which the business can be developed.
Recommendations
Top Paints Limited needs to look towards bringing a change in which the compensation is provided by ensuring that performance is a key in determining the manner in which the employees will be compensated. Further, steps should be taken to ensure that turnover rates and accidents are reduced by taking steps where the business is able to ensure better results. Further, Top Paints Limited needs to look towards ensuring a restructuring in the manner the business is done by ensuring equality and diversity so that the business is able to ensure a strategy where they are able to work in all direction and ensure growth for the business
Top Paints Limited needs to work on different aspects of the business so that they are able to improve the manner in which business is conducted. This will help Top Paints Limited to ensure major changes in the manner work is done and will help to reduce the number of casualties and ensure better turnover rates which will help Top Paints Limited to ensure that the business is able to earn profits over a longer period of time.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

- Essay Writing Guides
Human Resources Essay for A+ Student Guide
Students of management departments frequently face the need to compose a Human Resources essay because they need to learn to manage both people and processes. Thus, if you’re a student of this specialty, you will face the need to compose a Human Resources school essay sooner or later. Here we explain what an HR essay is, what format you should keep to, how you can complete such a paper quickly and efficiently, and what topics are trending now in the sphere of HRM.
If you’re wondering how to write a Human Resources essay, read on to find all the details here. Experts of our essay writing service team have prepared a guide for newbies to instruct you on all the writing steps. Still, if you feel unable to compose this work independently, it’s probably a good idea to hire a skilled Human Resources essay writer from our team.
Don’t hesitate to contact us and get a well-written, properly structured, and polished paper deserving an A; we’ve got you covered and can help you with any academic emergency you might experience at an HR course. You can easily place an “ do my assignment ” order on our website and get an expert with years of industry-specific expertise assigned to your project in minutes.
Human Resources Essay Format
When discussing the Human Resources essay format, you need to keep in mind that it’s still an essay, differing from other works of this type only by the topic. However, all essays follow the same format and structuring, knowing which can help you complete such a paper hassle-free. You can see this universal structure in many Human Resources school essay examples available online.
Let’s recap the basic essay structure in relation to the HR specialization.
Introduction
The introductory part of your Human Resources plan essay should include a discussion of your area of focus. HRM is a broad sphere of professional practice and research interest, so you need to find a subtopic within that area and explain it to the readers. After describing the context, you need to specify the problem you’re going to explore and end the introductory section with a concise thesis statement.
The body of your essay should focus on the arguments you’ve elicited when researching the chosen topic. As you might see in any Human Resources essay example, the body is typically divided into paragraphs, each of which is dedicated to one specific argument. Follow this structure as well to enhance your essay’s readability and make it coherent.
A conclusion is the final part of any Human Resources essay writing process. You can’t do without a brief and precise summary of your content. You also need to revisit your thesis statement and explain how your knowledge progressed throughout this paper’s writing. A strong finale of any essay is a reference to the broader context and explanation of how your research informs the broader HRM field.
Write Human Resources Essay in 5 Steps
When it comes to essay writing, Human Resources is not that challenging. The only thing you need to remember is that following an explicit, understandable research and writing algorithm makes the task much more manageable.
Here’s the algorithm our pros recommend to students regardless of their level of expertise:
- Select a topic that speaks to you. It should be exciting and relatively new so that you can advance your knowledge and derive pleasure from examining a subject of your personal interest.
- Be clear about the outcome of your essay; you need to know what goals you’re trying to achieve, developing your content according to the predetermined scenario.
- Research the subject to collect reliable, valuable evidence on the subject.
- Produce an outline to have a roadmap and stay on topic during the whole writing process.
- Record all sources you have used in content creation and reference them correctly to avoid plagiarism accusations.
Follow 55K+ satisfied students. Get your papers done by pros.
Human resources essay topics.
Topic selection is one of the most widespread challenges students face when approaching an HR essay task. To help you cover this step quickly, writers of our essay service have formulated a handy list of Human Resources essay topics.
- How well are equal employment opportunities provided in the 21st century?
- HR planning and retention: implications for the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Essentials of strategic HR management.
- Has the traditional HR management survived the coronavirus pandemic?
- Key steps of job analysis.
- Training human resources in the conditions of remote work.
- Risk management techniques in the HR field.
- Different approaches to calculating paid leave.
- Workplace techniques for interpersonal conflict resolution.
- The role of HR in the company’s preservation of competitive advantage in the global market.
- Determining the right mix of monetary and non-monetary rewards for staff.
- The role of personality traits in team composition.
- Agile approaches to HRM.
- Modern techniques and approaches to international staff management.
- A goal-oriented approach to staff productivity and morale improvement.
- A variety of workplace violence manifestations.
- Implications of psychological counseling provision to employees in the workplace.
- Presence of gender disparities in work terms and pay.
- Various faces of workplace discrimination: examining the causes and responses to those incidents.
- What are the best methods of complying with the equal employment opportunity legislation?
- Managing diversity in the workplace: 21st-century implications.
- Leadership training and promotion among staff.
- The strategic benefits of in-house leadership training for business performance.
- New talent acquisition: innovative techniques and approaches.
- An ideal employee profile for SMEs.
- Experience vs. talent in new employee recruitment.
- The role of HR in fostering compliance with COVID-19 rules.
- Contribution of HR to compliance with health and safety recommendations.
- What steps can HR managers take to identify, manage, and prevent employee burnout?
- HR strategies directed at long-term staff retention.
- The contribution of AI to HR activities and functions.
- Is virtual onboarding as effective as offline one?
- Should businesses pay for their staff’s education?
- Soft vs. hard skills’ consideration in the recruitment process.
- Different approaches to compensation package design.
How to Start a Human Resources Essay
The final point we’d like to discuss here is the art of starting a Human Resources essay. It’s essential to give your essay a good start; otherwise, you may spend much more time on its composition than you initially planned, thus wasting the vital free time or the hours you previously allocated for other assignments. Here are the principles of a quick, easy essay start:
- Choose the right topic to simplify the writing process.
It should be relevant to your class material, engaging, and new to a certain degree. Expand your existing knowledge instead of trying to explore something entirely new for you.
- Research the subject extensively.
Don’t start writing before you’re sure that you have enough material for the whole paper. Students often get stuck in the middle of their essays because they haven’t conducted thorough research from the very beginning.
- Use practical examples.
HR is an applied sphere of human activity, so you can never produce a high-quality paper without referring to real-life evidence.
It’s also vital to choose argumentative Human Resources essay topics, as they are sure to give you more ideas and avenues for proving your standpoint and examining various evidence from multiple angles.
The paper “Top Paint Limited – Theoretical Vis-a-Vis Practical Aspects of HR Factors” is an intriguing example of human resources case study. This paper is an evaluation of Human Resource (HR) faced by Top Paints Limited (TPL). This evaluation involves the evaluation of theoretical vis-a-vis practical aspects of HR factors.
Performance Management
The purpose of managing employee performance is not only to improve productivity. It is also to ensure that the employees find their work environment (e.g. in terms of culture, policies, style, systems of communication, etc) tolerable (Shore & Strauss, 600). The premise here is that if an employee finds the working environment to be in conflict with his/her career and other related expectations, then his/her performance is affected from the start, and no performance management strategies can help him/her. Besides specific strategies to boost the performance of the existing workforce, the first and most important performance management tool is strategic recruitment and selection.
The contemporary organization/company places emphasis on the organizational culture. This has led to the need for besides a written contract- psychological contract, i.e. an unwritten (psychological) understanding of the expectations that both the employee and employer have of each other, and that both parties will reciprocate each other’s efforts (Bratton & Gold 278). This is part of managing employee behavior. The premise here is that it is only those employees whose expectations are within the scope of the organizational culture and expectations who will have the right motivation for good performance.
What this implies is that the role and level of performance are not only in the hands of the employees. In fact, how employees perform primarily depends on whether the organizational structure and culture, as reflected in its leadership, helps it (Bratton & Gold 279). TPL’s structure, i.e. the traditional approach to command and control is a major impediment to employee freedom, creativity, motivation, and ultimately, performance. And while the organization uses performance appraisal for measuring employee performance, measurability being a major aspect of performance, it is not taken seriously. Instead, it is a mere routine.
Reward Management
The reward can be both monetary and non-monetary (e.g. psychological reward, the satisfaction of challenge, etc) (Bratton & Gold, 278). Indeed, reward management is a key tool for facilitating sound competition between employees, boosting employee motivation, and ultimately improving performance. Therefore, reward, as a tool for performance management, encourages and enhances positive employee attitudes and behaviors and financial gains.
TPL has established a reward system for its employees. This is especially through career development, e.g. promotion, and annual pay increment. Both of these are monetary forms of reward. For instance, promotion comes with a pay increase. Unfortunately, there are two key implications here. One, TPL does not seem to recognize the fact that, as Bratton and Gold (279) put it, financial rewards have bearing on cost-effectiveness and financial profitability. In other words, rewards mean expenditure. TPL’s profits have been on the decline for ten years so that the recent failure to make profits has or should have been anticipated. Yet the company still sticks by its monetary reward system, thereby adding more pressure to its already declining finances. This first implication leads to another, i.e. TPL has overlooked other reward methods and systems. In another word, it has failed to recognize that financial rewards are merely ‘superficial’ and must be accompanied by other rewards systems.
But all this equally raises one big question: if the company has been on the decline, then what has it been rewarding its employees for? Even further, why has the organization not realized that its rewards are not resulting in the reasons for which rewards are given? This is not to say that the company should not reward its employees. Instead, it should also consider non-monetary rewards, .e. g. psychological contract through encouraging employee freedom and creativity. Equally, the company should recognize that rewards are not the only tools for improving employee performance. This must work in conjunction with other organizational and management elements. However, all this depends on the HRM.
Human Resource Development
This refers to strategic efforts by a company’s Human Resource Management (HRM) (Bratton & Gold 279; Torrington et al 599) to develop its workforce in line with its key business strategies. In other words, it involves strategic recruitment and selection of employees who will enhance a company’s chances of reaching its goals and objectives. The first step towards strategic human resources development, therefore, is to identify the strategies to be undertaken. Identifying strategies depends on proper study and understanding of both the internal and external organizational environment.
TPL, to begin with, seems to lack any key strategy. The company controls the whole value chain of its products all the way from inception to manufacturing and delivery. Considering the company’s financial troubles, it should be clear that this control is overwhelming for its capacity. In other words, it is about time that the company gave up some of its control(s) to other parties, e.g. distribution to other wholesalers and retailers. This would help it focus its workforce on specific strategies. This would facilitate the company’s strategic recruitment and selection, and retention of employees.
Part of strategic HRD is training. It is clear that the problem here is the approach used. While the company encourages training, it focuses mainly on a theoretical approach, i.e. the training does not subject employees to one-on-one interaction with job practicalities. In other words, employees lack on-the-job experience.
Equality and Diversity
Equality and diversity are part of strategic HRD. The external environment, unlike TPL’s internal environment, is made of a diverse population: men and women, young and old, able-bodied and disabled, people from various ethnicities, including minority groups, etc. Winning a competitive advantage in a diverse marketplace requires an equally diverse workplace (Kirton & Greene, 7). Unfortunately, TPL has failed in this. The company has fewer employees from minority groups and women. While some of these are in the technical and managerial levels, the company has provided and encouraged their career progress. Further, the whole Board of Directors is composed of white males, as are other senior managers.
Diversity does not merely mean recruiting people from diverse ethnic and cultural backgrounds, of different ages and generations, gender, etc. It has to be incorporated and reflected in the organizational culture, with the organizational leadership being a notable symbol of that culture (Kirton & Greene, 53).
The paper “Human Resource Development at Top Paint Limited” is an apposite example of human resources case study. The problems facing Top Paints Limited can be addressed by focusing on the root cause of the problems facing the individual employees. Statistics indicate that the company’s workforce is paralyzed and is characterized by such symptoms as low productivity, poor working relationships, and low morale. The decline in the company’s performance stems from the problems facing the workforce which would call for a change in the company’s HR policies for the company to regain its strength. This paper will refer to human resource theories and practices to help address the problems facing the company. Four areas of HR policy and practices will be evaluated: performance management, human resource development, and reward management.
Performance management
Performance management is an ongoing process in which an organization identifies, measures,s and develops the output or performance of individuals or teams and later compares this with the goals set by the organization. Performance management arises from the complexities arising from the world of business (Mabey, Salaman & Storey, 1999). Several models of performance management have been adopted but there is no one universally accepted model. Mabey, Salaman, and Storey (1999) argue that any model of performance management should include these elements:
- Feedback of performance results
- Setting objectives
- Amendments to activities and objectives
- Reward system based on performance outcomes
- Measuring of performance
The goal-setting theory was proposed by Edwin Locke (1968). According to this theory, individual goals that are established by an employee perform crucial roles in motivating the employee to have increased performance (Salaman, Storey & Billsberry, 2005). This assumption arises from the fact that the employees keep monitoring their goals; failure to achieve these goals call for the employee to increase their performance or adjust their goals so that they become real. The end result of setting the goal is thus to improve the employees’ performance.
According to expectancy theory, employees in an organization will adjust their behaviors based on the anticipated satisfaction of the goals they have set. As such, individuals will adjust their behaviors in a manner that will lead them to attain their goals. Employees of the TPL seem not to have these theories in mind since the company has employed a command and control management approach. As such, the employees cannot show their capabilities since they work under the instructions of their superior.
To address the problem, TPL should implement a performance management system instead of the command and control approach.
The system can work well if the employees are provided an opportunity to set their goals as per the company requirement. The employees should be allowed to work freely as long as they are able to achieve these goals; this can be determined by measuring the performance (Mabey, Salaman & Storey, 1999). Further, the performance management system should clearly set the rewards that an employee can get based on the expected outcome as mentioned in the expectancy theory; this helps to motivate the employee.
Reward management
This entails developing, maintaining, and establishing a system whose main aim is to reward employees within a firm or a business. This system provides a fair and equitable way of appreciating the values of the employees whose output to the organization is considered valuable. Various theories have been formulated in the field of human resources to address the issue of reward management. An example of such theories is motivation theory which calls for the motivation of employees for them to be beneficial or more productive to an organization. Salaman, Storey, and Billsberry (2005) consider the reward to be either monetary or non-monetary.
Victor Vroom’s theory referred to as “Vroom’s Valence x Expectancy Theory” better helps to understand the relationship between reward and motivation. According to Gellman (2009), this theory entails the mental process involved in the choices made by an employee. According to this theory, there is a direct relationship between the predisposition to act in a certain manner and the strength of the expectations or rewards that may come as a result of the act (Gellman, 2009). When the employees are assured that there is a better performance appraisal, they are motivated to improve their performance (Salaman, Storey & Billsberry, 2005). For employees to be motivated, this theory sets three conditions that must be met: additional effort would result in better performance, the well-done job should be associated with rewards like pay-rise or bonuses, rewards provided should be satisfactory to the employee.
TPL has not been able to retain its employees since it does not motivate the able employees to stay. To address this problem, the company should have a reward system through bonuses whenever performance is improved. The current company’s pay system is very inflexible since the salary is increased on yearly basis regardless of personal or company performance. With the current pay system, the employees do not need to work extra harder as they are not guaranteed any rewards. TPL should thus introduce a flexible reward system so that it can motivate the employee and retain them instead of losing and recruiting new ones.
Equity and diversity
Workforce diversity entails the inclusion of all types of persons in corporate performance. Today, many organizations view diversity as a competitive advantage which gives rise to economic advantage to the organization when incorporated into the strategic business goals (Bratton & Gold, 2003). In many countries, workforce diversity is streamlined in the policy and the legal framework that provides provisions for anti-discrimination cases (Thompson, 2003). According to Dickens (1999), diversity is the variety of cultural and social identities among people in a common employment setting. Various cultural and social attributes determine diversity: gender, race, education, beliefs, religion, age, disability among others. Various approaches can be employed in managing diversity. One such approach is the mainstream approach that refers to self-categorization and the self-identity theories. The self-identity theory entails group membership and behaviors. On the other hand, the self-categorization theory entails how individuals stereotype their attitudes and behaviors so that they can associate themselves with particular groups. These theories help to avoid any group conflict that may have a negative impact on workplace performance (Bratton & Gold, 2003).
TPL has failed to address the issue of equality and diversity since there are few women and people from ethnic minorities. Further, this group of employees does not progress in terms of promotion even when they are the very-able. For TPL to progress, there is a need for the company to create equal opportunities for all the employees. Failure to create such an opportunity for the minority people, disabled, and women would make them feel discriminated and thus their output is affected.
Human resource development
The concept of human resource development is considered as a theory that aims at developing human capital by developing the individual and the organization to improve their performances (Wang, 2004). Human resource capacities can be developed through further education. This can be done through career development and training. The outcome of HRD has increased competencies which ensure that current and future jobs are performed effectively (Wang, 2004).
TPL has been training its staff on how to carry out their functions whenever new roles and new technologies are introduced. It is thus expected that the accident rate below and performance should be improved. However, this is not the case since most training is done off-site. To avoid the problem, TPL’s consultant should train the employees at the site in order to improve efficiency. A paradigm shift from off-site to on-site would thus yield positive results towards improved performance since the employee would acquire real practical knowledge.
The paper “The Human Resource Management Difficulties Experienced by Top Paint Limited” is a dramatic example of human resources case study. Top Paints Limited (TPL) has been facing many challenges. It has experienced a steady decline from a relevant strong position ten years ago where it made no profit this year for the first time ever. The entire workforce in TPL has been creating a lot of dissatisfaction, which has led to low morale, low productivity, and poor relationships at work. This has also resulted in an increase in absenteeism, product complaints, and service complaints. Thus, this shows a flawed human resource activity in TPL and there is a need to give priority in the following areas to find a lasting solution to these problems in TPL; performance management, reward management, human resource development, and equality and diversity.
The employees in TPL lack the opportunity to be initiative since the top-level management is always acting on instructions. This shows a lack of cooperation between the employees and the top management that in turn reduced their morale in working and in turn reducing their productivity. This calls for the employment of management processes in order to manage individuals in an effective manner with an aim of achieving high levels in the performance of the organization. There is a need to close the gap between management and employees by establishing a shared understanding to develop a strong workforce for the achievement of TPL’s goals. As the employees have developed negative attitudes between them and management, individuals need to be guided in order to feel that work satisfying, fulfilling, and capable of development in any way. This can be supported by the application of the goal-setting theory in order to link the performance of the tasks with goal setting. Because the entire company seems to have lost its main objective, there is a need to set specific goals that are challenging in addition to appropriate feedback in order to come up with better performance. This will give the employees a path or a direction to follow on the needs to be done and the efforts required to achieve the goal. This will be achieved if the employees are also given the opportunities to be initiative. The main source of motivation for the job will be the willingness of the employees to freely work towards the achievement of goals. If the employees will be provided with clear and specific goals in addition to being open to their comments on work. With the provision of challenging and realistic goals, the employees will have the reason to work and feel proud and as triumphant as they achieve the goals. Another important thing that failed to work in TPL is the provision of appropriate feedback on employee’s performance. Feedback will be essential as a way of making clarifications, regulating difficulties in goals, gaining a reputation in a way that the involvement of the employees will lead to job satisfaction and being more productive. On the other hand, the managers should ensure that they should interact and behave in a way that promotes and allows better relationships in work. They should also be able to gauge themselves according to output such that, if the job is interesting, the performance should also be better (Armstrong, 1998)
From the case study, it is clear that the salaries earned by the employees are flat. The pay spine is very inflexible such that the talented people end up looking for greener pastures in better-paying companies while the less competitive are left due to lack of any other option. This leads to low productivity and low performance. In addition, there is no reward in case of any improvement in performance. Due to this, there is a need for a reward management process that will involve the development and implementation of the company’s strategies and policies. This will enable the firm to achieve its objectives as well as retaining its competitive employees in accordance with the needs of the employees through increasing their commitment and motivation. If the employees will be rewarded according to their value and their potential contributions to the company, they will feel comfortable working in a firm that recognizes their efforts. The management must also recognize each employee’s capability and set goals that match with their intuitiveness (Armstrong, 495). This can be supported by a broad banding structure or system that shows that the progress of employees is more dependent on improvement than promotion, the flexibility of the system, putting decisions on managers’ hands so that they have more responsibility towards the staff and finally employees increase their incentives in achieving their goals. This means that the success of the organization is dependent on the recognition of the efforts of each employee through rewards that later lead to more efforts and profitability (Stredwick, 13).
Although TPL carries through training of its staff, there are still complaints and accidents due to repetition of mistakes. In addition, there is hostility and disbelief in case one tries to bring change or being initiative. In this case, human resources development is very essential, as the success of TPL will depend on the management of the workforce. Thus, there is a need to develop strategies that will ensure an increase in manufacturing and gaining a competitive advantage through proper management and development of employees to be more productive. This is enhanced through the development of strategies based on informed decisions and the involvement of the employees. TPL needs also to develop a policy on recruitment and selection to ensure the selection of a competitive and diverse workforce (Beardwell, 197).
This is supported by classical approach theory, which ensures that the strategy process will involve a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external environment, selecting on strategic choices and implementation of the plans, and ensuring management decisions flow from top to down ensuring the involvement of all levels. This makes the employees initiative thus increasing the productivity and performance (Miller, 148).
Equality and diversity
This is also a major problem in TPL as there are very few ethnic minorities and women and the few that are recruited later resign. This shows a lack of comfort for the minorities in working in the TPL environment. Thus, management needs to ensure that everyone is treated the same as well as recognizing that various groups and individuals are different. To do this, the company must be flexible and observe uniformity in addressing the needs of its employees in order to change its culture. This is enhanced by making sure that the working environment will support women and ethnic minorities by totally involving them in decision-making. It is also important to consider the development of a new policy in recruitment that promotes diversity and equality. This is supported by a short approach that is similar to a liberal approach wherein advocates for the elimination of bias on sex in the practice of human resource management, increasing opportunities for women and minorities in management and technical fields, and being flexible in terms and conditions (Noon, 226).
The difficulties experienced by TPL can be associated with poor work relationships, lack of recognition of efforts made by staff, criticism, between management and employees and poor culture of the firm, and the entire management of the activities in the firm that has led to low productivity and lack of profits. These issues are addressed through performance management, equity and diversity, reward management, and human resource development. This will result in better utilization of human resources, a wide customer base, wider and competitive recruitment of labor, and a positive image of the company.


Essay on Human Resources
Students are often asked to write an essay on Human Resources in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Human Resources
Understanding human resources.
Human Resources (HR) is a department in organizations that manages people. They handle hiring, training, and employee benefits. HR plays a crucial role in building a positive workplace culture.
Roles of HR
The HR team recruits new employees and trains them. They also develop policies for a comfortable work environment. HR ensures employees are treated fairly and respectfully.
Importance of HR
HR is important because they help to maintain harmony in a company. They resolve conflicts and promote employee well-being. Therefore, HR is vital for a successful organization.
250 Words Essay on Human Resources
Introduction.
Human Resources (HR) is a multifaceted discipline that lies at the heart of any organization. It encompasses the management of people within an organization, focusing on policies, systems, and practices that influence employee behavior, attitudes, and performance.
The Evolution of HR
Key functions of hr.
HR is responsible for a wide range of functions. These include recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, employee relations, and compensation and benefits. Each function plays a crucial role in managing the organization’s human capital.
HR and Organizational Performance
Effective HR management can significantly impact an organization’s performance. By ensuring that the right people are in the right jobs, providing opportunities for growth and development, and fostering a positive work environment, HR contributes to increased productivity and profitability.
In conclusion, HR is an indispensable part of any organization. Its role has evolved from a purely administrative function to a strategic one, influencing every aspect of an organization’s operations. As businesses continue to evolve in a rapidly changing world, the role of HR is likely to become even more critical.
500 Words Essay on Human Resources
The evolution and importance of human resources.
The concept of Human Resources (HR) has significantly evolved over the years. Initially, businesses viewed employees merely as tools for production, but today, they are recognized as the most valuable asset of an organization. The HR department plays a pivotal role in managing these assets, ensuring that both their welfare and the company’s strategic goals are harmoniously aligned.
The Role of Human Resources
The primary role of the HR department is to manage people, which includes tasks like hiring, training, evaluating, and retaining employees. They are also responsible for ensuring a safe and healthy work environment, addressing employee grievances, and fostering a positive work culture. Moreover, HR professionals work towards aligning the workforce with the company’s strategic goals, thereby driving organizational success.
HR and Organizational Strategy
The changing landscape of human resources.
The HR landscape is continuously evolving, driven by factors such as technological advancements, changing demographics, and globalization. For instance, the advent of HR technology has revolutionized HR practices. Tools like HRIS (Human Resource Information Systems) and ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems) have automated routine tasks, thereby allowing HR professionals to focus more on strategic activities. Moreover, the rise of remote work and diversity in the workforce has necessitated the development of new HR policies and practices.
Challenges Faced by HR Professionals
Despite the significant strides made in the HR field, HR professionals face numerous challenges. These include managing a diverse workforce, dealing with the changing nature of work, ensuring employee engagement and well-being, and navigating the legal and ethical issues related to HRM. Additionally, in an era of rapid technological change, HR professionals must continually update their skills and knowledge.
Future of Human Resources
In conclusion, the HR department plays a crucial role in managing the most valuable asset of an organization – its people. By aligning the workforce with the company’s strategic goals, fostering a positive work culture, and adapting to the changing business environment, HR professionals can drive organizational success.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium

105 HRM Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a vital aspect of any organization, as it focuses on managing the most important resource of all – people. HRM encompasses a wide range of topics, from recruitment and selection to training and development, performance management, and employee relations. If you are studying HRM or looking for essay topics to explore in this field, here are 105 HRM essay topic ideas and examples to inspire you:
- The impact of technology on HRM practices
- Diversity and inclusion in the workplace
- The role of HRM in organizational culture
- Employee motivation and engagement
- Workplace health and safety
- Talent management strategies
- Performance appraisal methods
- The importance of training and development
- Employee benefits and compensation
- Recruitment and selection best practices
- HRM in the gig economy
- Work-life balance initiatives
- Employee retention strategies
- HRM in the age of remote work
- Conflict resolution in the workplace
- Leadership development programs
- HRM in multinational corporations
- The impact of globalization on HRM
- Ethics in HRM
- Employee wellness programs
- HRM in the public sector
- Managing a multigenerational workforce
- The role of HRM in change management
- Employee performance management systems
- HRM in the healthcare industry
- The use of data analytics in HRM
- HRM in the non-profit sector
- Employee empowerment and autonomy
- HRM in the hospitality industry
- The future of HRM
- Strategic human resource management
- HRM in the retail industry
- Employee feedback and performance improvement
- HRM in the education sector
- Employer branding and recruitment
- HRM in the technology industry
- The role of HRM in organizational success
- HRM in the manufacturing sector
- Employee recognition and rewards
- HRM in the financial services industry
- The impact of artificial intelligence on HRM
- HRM in the energy sector
- Employee relations and conflict resolution
- HRM in the automotive industry
- The role of HRM in employee engagement
- HRM in the telecommunications sector
- Employee training and development in the digital age
- HRM in the pharmaceutical industry
- The importance of diversity and inclusion in HRM
- HRM in the entertainment industry
- Employee performance appraisal and feedback
- HRM in the construction sector
- The role of HRM in talent acquisition
- HRM in the fashion industry
- Employee health and wellness programs
- HRM in the transportation sector
- The impact of social media on HRM
- HRM in the hospitality sector
- Employee communication and engagement
- HRM in the real estate industry
- The role of HRM in organizational change
- HRM in the food and beverage industry
- Employee training and development programs
- HRM in the tourism sector
- The importance of employee feedback in HRM
- HRM in the agriculture industry
- HRM in the logistics sector
- The role of HRM in talent management
- HRM in the sports industry
- Employee recognition and rewards programs
- HRM in the media and entertainment sector
- HRM in the healthcare sector
- Employee engagement and motivation strategies
- Employee wellness and mental health programs
- Employee training and development initiatives
- HRM in the technology sector
- HRM in the construction industry
- HRM in the pharmaceutical sector
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade

ESSAY SAUCE
FOR STUDENTS : ALL THE INGREDIENTS OF A GOOD ESSAY
Essay: Human resources (HR)
Essay details and download:.
- Subject area(s): Business essays
- Reading time: 3 minutes
- Price: Free download
- Published: 9 August 2018*
- Last Modified: 23 July 2024
- File format: Text
- Words: 609 (approx)
- Number of pages: 3 (approx)
- Tags: Human resource management essays
Text preview of this essay:
This page of the essay has 609 words.
According to Leon C. Megginson human resource is “The total of knowledge, creative abilities, talent, altitudes skills and belief of a firm’s workforces as well as attitude, beliefs and values of the persons involved”.
HR Practices
Human Resource Management is the process of hiring and developing employees so that they become more valuable to the organization. Human Resource Management includes conducting job analyses, planning personnel needs, recruiting the right people for the job, orienting and training, managing wages and salaries, providing benefits and incentives, evaluating performance, resolving disputes, and communicating with all employees at all levels. Examples of core qualities of HR management are extensive knowledge of the industry, leadership, and effective negotiation skills.
Human Resource Management (HRM) refers to the policies and practices involved in carrying out the ‘Human Resource(HR)’ aspects of a management position including human resource planning, job analysis, recruitment, selection, orientation, compensation, performance appraisal, training and development, and labour relations (Dessler, 2007). HRM is composed of the policies, practices, and systems that influence employees’ behaviour, attitude, and performance (Noe, Hollenbeck, Gerhart, and Wright, 2007).
Human Resource Management (HRM) is the function in an organization which focuses on recruitment, management, and provides direction for the employees who work in the company or organization. It is the function of organization that deals with issues related to people such as compensation, hiring, performance management, organization development, safety, wellness, benefits, employee motivation , communication, administration, and training. HRM is also a premeditated and whole or complete approach to manage people and the workplace environment and culture. Effective human resource management enables employees to contribute productively and effectively to the overall company direction and achieving the organization’s goals and objectives.
Human resource management is moving away from traditional personnel, administration, and transactional approach, which are increasingly outsourced. HRM is now expected to add value to the tactical utilization of employees and that employee programs impact the business in computable ways. The new role of HRM involves strategic direction and HRM metrics and measurements to demonstrate value.
HR is a product of the human relations movement of the early 20th century, when researchers began documenting ways of creating business value through the strategic management of the workforce. The function was initially dominated by transactional work, such as payroll and benefits administration, but due to globalization , company consolidation, technological advancement, and further research, HR now focuses on strategic initiatives like mergers and acquisitions, talent management , succession planning, industrial and labor relations, and diversity and inclusion.
In startup companies, HR’s duties may be performed by trained professionals. In larger companies, an entire functional group is typically dedicated to the discipline, with staff specializing in various HR tasks and functional leadership engaging in strategic decision making across the business. To train practitioners for the profession, institutions of higher education, professional associations, and companies themselves have created programs of study dedicated explicitly to the duties of the function.
In the current global work environment, all global companies are focused on retaining the talent and knowledge held by the workforce. All companies are focused on lowering the employee turnover and preserving knowledge. New hiring not only entails a high cost but also increases the risk of the newcomer not being able to replace the person who was working in that position before. HR departments also strive to offer benefits that will appeal to workers, thus reducing the risk of losing knowledge.
Discover more:
- Human resource management essays
Recommended for you
- Human resource management (focus on police department)
- Function and responsibilities of Human Resource Management
- Social networking and recruitment
About this essay:
If you use part of this page in your own work, you need to provide a citation, as follows:
Essay Sauce, Human resources (HR) . Available from:<https://www.essaysauce.com/business-essays/human-resources-hr/> [Accessed 28-09-24].
These Business essays have been submitted to us by students in order to help you with your studies.
* This essay may have been previously published on EssaySauce.com and/or Essay.uk.com at an earlier date than indicated.
Essay Categories:
- Accounting essays
- Architecture essays
- Business essays
- Computer science essays
- Criminology essays
- Economics essays
- Education essays
- Engineering essays
- English language essays
- Environmental studies essays
- Essay examples
- Finance essays
- Geography essays
- Health essays
- History essays
- Hospitality and tourism essays
- Human rights essays
- Information technology essays
- International relations
- Leadership essays
- Linguistics essays
- Literature essays
- Management essays
- Marketing essays
- Mathematics essays
- Media essays
- Medicine essays
- Military essays
- Miscellaneous essays
- Music Essays
- Nursing essays
- Philosophy essays
- Photography and arts essays
- Politics essays
- Project management essays
- Psychology essays
- Religious studies and theology essays
- Sample essays
- Science essays
- Social work essays
- Sociology essays
- Sports essays
- Types of essay
- Uncategorised
- Zoology essays

How to Write a Human Resources Essay
The human resources management plays an essential role in today’s modern business situation. Inviting, choosing and evaluating the human resources obtainable for a specific area of interest is sometimes the primary aspects of firms spending money and effort. A human resource paper is written similarly as other kinds of essay, but just with some differences that we will tackle as you read on. To be able to know how to write a human resources essay, you must pick a similar or appropriate subject and then work on it in an objective point of view. Start with the stages of the research.
The research stage
If you wish to learn how to write a human resources essay , there are 2 things you must keep in mind and should consider at the same time, these are the HR subject itself and the particular field that you will work on. For instance, the essay might tackle about the management, human resources in a specific field, in this case, you will need a particular level of comprehension about the particular part of the field, if you are to use the human resources theory to it. More so, the research stage suggests not just a strong documentation on HR, but some guidelines are also about the part wherein you will think of the management.
When you learn how to write a human resources essay is more or not as close to working with some other essay types, collect all the materials from some of the most respected sources of information, regardless if they are from the web, Books or from a local library. Then again, you shouldn’t be deceived in trusting that the general information sites can actually give good and quality materials. Wikipedia and various sites can offer some of the fundamental guidelines about the topic, but for a high grade, you must not cite the websites.
There is another practice bit of advice and this is about time management. As soon as you get the assignment, you need to come up with a schedule for the development stages. Learning how to write a human resources essay necessitates you to to have the skills in organizing the paper, for instance, you need to allot at least 2-3 days in collecting all the materials from the library or bookstore, another 2-3 days if the essay needs to be very long, you also need to fix your schedule, so that you will be able to submit and make the paper ready for the deadline. As soon as you are satisfied with the materials you have collected, you may now go on with the rest of the paper.
The writing stage
Your paper must be well written and it must be in a precise manner & impartial in style, so be sure you avert from using generalized sentences and unessential figures of speech. Figures, numerals & surveys must be seen in your paper to be able to sustain the facts written there. As soon as you start the thesis, you have to start by composing the abstract wherein you will describe the approach you used in a short manner and that must be linked with the topic of the HR. How will you argue? Are you going to be for it or against it and the conclusion that you want to achieve afterwards. The title page must have the title of the essay, your whole name and the name of the lecturer and the date the assignment is due.
The introduction
It must be short enough. It should contain the truth that you will discuss in the paper without being too detailed. There is a big possibility that you will provide a general information about the writer’s approach to be tackled in the topic, along with some of the important details. The key is to provide a well discussed topic in the introductory page and make sure it is catching for the readers, so it must be clear enough, brief, obvious and try to refrain from losing yourself in some unnecessary details.
The main body
The main body of the essay is where you will make your arguments and increase on the primary ideas written in the abstract. Those who are familiar with the ways of how to write a human resources essay will reach in a professional way of writing the paper, use a standardized formatting style like MLA, APA, Harvard and other styles that may be required by the lecturer. There must be 4 primary points in the main body of your paper.
- It must have a well interpreted primary literature sources used with quotes, related data and formulas too.
- The methodological problems happen while working on the theoretical thoughts or other troublesome instances.
- Analyzing the present state of the research in the field of HR along with probable solutions.
- It is optional, since I usually consists of your own viewpoint about the subject that depends on how well you learn the application of the theory of HR and the ideas in it, that you might pick to perform or skip the step.
The conclusion
This part of the paper should not be a problem if you know how to come up with an essay that mandate you to be intense in making a summary good with sustainable interpretations and observations in the main body of the essay. Moreover, the answer to the questions have been left unreciprocated.
The reference page and appendices
The reference page and appendices are associated at the end of the paper. If you are familiar with the ways of how to come up with a human resources essay, then you can realize the essence of referencing. The reference page must have a well detailed information about the sources you have cited, this is in relation to the referencing style you have picked. The appendix part of the list with survey, graph, statistics and charts that doesn’t show in the body of the essay.
The revision stage
When you know how to compose a human resource paper suggests that having an appropriate attention to the details is very essential. The revision stage is very essential, since it will order the final form of the essay. A special check is the very first step of the revision. Studying the language by yourself might not be as effective as having someone else read the paper for you and letting you know which part of the paper you can still improve.
INSTANT PRICE
Get an instant price. no signup required.

We respect your privacy and confidentiality!
Share the excitement and get a 15% discount
Introduce your friends to The Uni Tutor and get rewarded when they order!
Refer Now >

FREE Resources
- APA Citation Generator
- Harvard Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- MLA Referencing Generator
- Oscola Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- Turabian Citation Generator
New to this Site? Download these Sample Essays
- Corporate Law Thesis
- Political Philosophy
- Legal Writing Rules
- Sample Philosophy Thesis
Send me free samples >
How The Order Process Works
- Order Your Work Online
- Tell us your specific requirements
- Pay for your order
- An expert will write your work
- You log in and download your work
- Order Complete
Amazing Offers from The Uni Tutor Sign up to our daily deals and don't miss out!

Contact Us At
- e-mail: info@theunitutor.com
- tel: +44 20 3286 9122

Brought to you by SiteJabber

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2002-2024 - The Uni Tutor - Custom Essays. 10347001, info@theunitutor.com, +44 20 3286 9122 , All Rights Reserved. - Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy
The Uni Tutor : We are a company registered in the United Kingdom. Registered Address London, UK , London , England , EC2N 1HQ

Home — Essay Samples — Business — Human Resources — The Intricacies of on Human Resource Management
The Intricacies of on Human Resource Management
- Categories: Employee Engagement Human Resources
About this sample

Words: 529 |
Updated: 29 March, 2024
Words: 529 | Page: 1 | 3 min read

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof Ernest (PhD)
Verified writer
- Expert in: Business

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2157 words
4 pages / 2024 words
4 pages / 1749 words
5 pages / 2303 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Human Resources
Human resources are a crucial component of the tourism industry. Without well-trained and motivated employees, businesses in the travel and hospitality sectors would fail to attract and retain customers, resulting in lost [...]
Employee self-ealuation is a process where employees assess their own performance and prode feedback to their supersors. The purpose of self-ealuation is to promote self-reflection, self-awareness, and professional growth. It is [...]
Human Resource (HR) is a critical aspect of organizational management, playing a pivotal role in shaping the culture, performance, and success of businesses. This essay aims to explore the definition, functions, and importance [...]
Compensation is a critical component of an organization's overall strategy for attracting, retaining, and motivating employees. Two primary forms of compensation are intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic compensation refers to the [...]
The major problem at Pak Sweets is running a factory with different ethnicities that have continually resulted to conflicts. The ethnic conflicts at the Pak Sweets factory have escalated into riots, which have led to damage of [...]
The Importance of Talent Management and Why You Should Invest in It Talent management is not just a simple Human Resources key terms that you come across. Talent management is the organization’s commitment to hire, manage, [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.2 Writing the HRM Plan
Learning objective.
- Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan.
As addressed in Section 2.1 “Strategic Planning” , the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the strategic plan in that it is more detailed and more focused on the short term. The six parts described here are addressed in more detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” , Chapter 5 “Selection” , Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , Chapter 7 “Retention and Motivation” , Chapter 8 “Training and Development” , Chapter 9 “Successful Employee Communication” , Chapter 10 “Managing Employee Performance” , and Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” .
How Would You Handle This?
Compensation Is a Touchy Subject
As the HR manager, you have access to sensitive data, such as pay information. As you are looking at pay for each employee in the marketing department, you notice that two employees with the same job title and performing the same job are earning different amounts of money. As you dig deeper, you notice the employee who has been with the company for the least amount of time is actually getting paid more than the person with longer tenure. A brief look at the performance evaluations shows they are both star performers. You determine that two different managers hired the employees, and one manager is no longer with the organization. How would you handle this?
As you can see from this figure, the company strategic plan ties into the HRM strategic plan, and from the HRM strategic plan, the HR plan can be developed.
The six parts of the HRM plan include the following:
- Determine human resource needs. This part is heavily involved with the strategic plan. What growth or decline is expected in the organization? How will this impact your workforce? What is the economic situation? What are your forecasted sales for next year?
- Determine recruiting strategy. Once you have a plan in place, it’s necessary to write down a strategy addressing how you will recruit the right people at the right time.
- Select employees. The selection process consists of the interviewing and hiring process.
- Develop training. Based on the strategic plan, what training needs are arising? Is there new software that everyone must learn? Are there problems in handling conflict? Whatever the training topics are, the HR manager should address plans to offer training in the HRM plan.
- Determine compensation. In this aspect of the HRM plan, the manager must determine pay scales and other compensation such as health care, bonuses, and other perks.
- Appraise performance. Sets of standards need to be developed so you know how to rate the performance of your employees and continue with their development.
Each chapter of this text addresses one area of the HR plan, but the next sections provide some basic knowledge of planning for each area.
Determine Human Resource Needs
The first part of an HR plan will consist of determining how many people are needed. This step involves looking at company operations over the last year and asking a lot of questions:
- Were enough people hired?
- Did you have to scramble to hire people at the last minute?
- What are the skills your current employees possess?
- What skills do your employees need to gain to keep up with technology?
- Who is retiring soon? Do you have someone to replace them?
- What are the sales forecasts? How might this affect your hiring?
These are the questions to answer in this first step of the HR plan process. As you can imagine, this cannot be done alone. Involvement of other departments, managers, and executives should take place to obtain an accurate estimate of staffing needs for now and in the future. We discuss staffing in greater detail in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Many HR managers will prepare an inventory of all current employees, which includes their educational level and abilities. This gives the HR manager the big picture on what current employees can do. It can serve as a tool to develop employees’ skills and abilities, if you know where they are currently in their development. For example, by taking an inventory, you may find out that Richard is going to retire next year, but no one in his department has been identified or trained to take over his role. Keeping the inventory helps you know where gaps might exist and allows you to plan for these gaps. This topic is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
HR managers will also look closely at all job components and will analyze each job. By doing this analysis, they can get a better picture of what kinds of skills are needed to perform a job successfully. Once the HR manager has performed the needs assessment and knows exactly how many people, and in what positions and time frame they need to be hired, he or she can get to work on recruiting, which is also called a staffing plan . This is addressed further in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” .
Recruitment is an important job of the HR manager. More detail is provided in Chapter 4 “Recruitment” . Knowing how many people to hire, what skills they should possess, and hiring them when the time is right are major challenges in the area of recruiting. Hiring individuals who have not only the skills to do the job but also the attitude, personality, and fit can be the biggest challenge in recruiting. Depending on the type of job you are hiring for, you might place traditional advertisements on the web or use social networking sites as an avenue. Some companies offer bonuses to employees who refer friends. No matter where you decide to recruit, it is important to keep in mind that the recruiting process should be fair and equitable and diversity should be considered. We discuss diversity in greater detail in Chapter 3 “Diversity and Multiculturalism” .
Depending on availability and time, some companies may choose to outsource their recruiting processes. For some types of high-level positions, a head hunter will be used to recruit people nationally and internationally. A head hunter is a person who specializes in matching jobs with people, and they usually work only with high-level positions. Another option is to use an agency that specializes in hiring people for a variety of positions, including temporary and permanent positions. Some companies decide to hire temporary employees because they anticipate only a short-term need, and it can be less expensive to hire someone for only a specified period of time.
No matter how it is done, recruitment is the process of obtaining résumés of people interested in the job. In our next step, we review those résumés, interview, and select the best person for the job.
After you have reviewed résumés for a position, now is the time to work toward selecting the right person for the job. Although we discuss selection in great detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , it is worth a discussion here as well. Numerous studies have been done, and while they have various results, the majority of studies say it costs an average of $45,000 to hire a new manager (Herman, 1993). While this may seem exaggerated, consider the following items that contribute to the cost:
- Time to review résumés
- Time to interview candidates
- Interview expenses for candidates
- Possible travel expenses for new hire or recruiter
- Possible relocation expenses for new hire
- Additional bookkeeping, payroll, 401(k), and so forth
- Additional record keeping for government agencies
- Increased unemployment insurance costs
- Costs related to lack of productivity while new employee gets up to speed
Because it is so expensive to hire, it is important to do it right. First, résumés are reviewed and people who closely match the right skills are selected for interviews. Many organizations perform phone interviews first so they can further narrow the field. The HR manager is generally responsible for setting up the interviews and determining the interview schedule for a particular candidate. Usually, the more senior the position is, the longer the interview process takes, even up to eight weeks (Crant, 2009). After the interviews are conducted, there may be reference checks, background checks, or testing that will need to be performed before an offer is made to the new employee. HR managers are generally responsible for this aspect. Once the applicant has met all criteria, the HR manager will offer the selected person the position. At this point, salary, benefits, and vacation time may be negotiated. Compensation is the next step in HR management.
Determine Compensation
What you decide to pay people is much more difficult than it seems. This issue is covered in greater detail in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” . Pay systems must be developed that motivate employees and embody fairness to everyone working at the organization. However, organizations cannot offer every benefit and perk because budgets always have constraints. Even governmental agencies need to be concerned with compensation as part of their HR plan. For example, in 2011, Illinois State University gave salary increases of 3 percent to all faculty, despite state budget cuts in other areas. They reasoned that the pay increase was needed because of the competitive nature of hiring and retaining faculty and staff. The university president said, “Our employees have had a very good year and hopefully this is a good shot in the arm that will keep our morale high” (Pawlowski, 2011).
Determination of compensation systems is a balancing act. Compensation should be high enough to motivate current employees and attract new ones but not so high that it breaks the budget.
Nathan Rupert – Venice Beach Tightrope Walker – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
The process in determining the right pay for the right job can have many variables, in addition to keeping morale high. First, as we have already discussed, the organization life cycle can determine the pay strategy for the organization. The supply and demand of those skills in the market, economy, region, or area in which the business is located is a determining factor in compensation strategy. For example, a company operating in Seattle may pay higher for the same job than their division in Missoula, Montana, because the cost of living is higher in Seattle. The HR manager is always researching to ensure the pay is fair and at market value. In Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits” , we get into greater detail about the variety of pay systems, perks, and bonuses that can be offered. For many organizations, training is a perk. Employees can develop their skills while getting paid for it. Training is the next step in the HR planning process.
Develop Training
Once we have planned our staffing, recruited people, selected employees, and then compensated them, we want to make sure our new employees are successful. Training is covered in more detail in Chapter 8. One way we can ensure success is by training our employees in three main areas:
- Company culture. A company culture is the organization’s way of doing things. Every company does things a bit differently, and by understanding the corporate culture, the employee will be set up for success. Usually this type of training is performed at an orientation, when an employee is first hired. Topics might include how to request time off, dress codes, and processes.
- Skills needed for the job. If you work for a retail store, your employees need to know how to use the register. If you have sales staff, they need to have product knowledge to do the job. If your company uses particular software, training is needed in this area.
- Human relations skills. These are non-job-specific skills your employees need not only to do their jobs but also to make them all-around successful employees. Skills needed include communication skills and interviewing potential employees.
Perform a Performance Appraisal
The last thing an HR manager should plan is the performance appraisal. While we discuss performance appraisals in greater detail in Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” , it is definitely worth a mention here, since it is part of the strategic plan. A performance appraisal is a method by which job performance is measured. The performance appraisal can be called many different things, such as the following:
- Employee appraisal
- Performance review
- Career development review
No matter what the name, these appraisals can be very beneficial in motivating and rewarding employees. The performance evaluation includes metrics on which the employee is measured. These metrics should be based on the job description, both of which the HR manager develops. Various types of rating systems can be used, and it’s usually up to the HR manager to develop these as well as employee evaluation forms. The HR manager also usually ensures that every manager in the organization is trained on how to fill out the evaluation forms, but more importantly, how to discuss job performance with the employee. Then the HR manager tracks the due dates of performance appraisals and sends out e-mails to those managers letting them know it is almost time to write an evaluation.
Human Resource Recall
Have you ever been given a performance evaluation? What was the process and the outcome?
Communication Is Key in Performance Evaluations
(click to see video)
Communication is imperative in any workplace, but especially when giving and receiving a performance evaluation.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning is a process that is part of the strategic plan. It involves addressing specific needs within the organization, based on the company’s strategic direction.
- The first step in HR planning is determining current and future human resource needs. In this step, current employees, available employees in the market, and future needs are all analyzed and developed.
- In the second step of the process, once we know how many people we will need to hire, we can begin to determine the best methods for recruiting the people we need. Sometimes an organization will use head hunters to find the best person for the job.
- After the recruiting process is finished, the HR manager will begin the selection process. This involves setting up interviews and selecting the right person for the job. This can be an expensive process, so we always want to hire the right person from the beginning.
- HR managers also need to work through compensation plans, including salary, bonus, and other benefits, such as health care. This aspect is important, since most organizations want to use compensation to attract and retain the best employees.
- The HR manager also develops training programs to ensure the people hired have the tools to be able to do their jobs successfully.
- Of the parts of HR planning, which do you think is most difficult, and why? Which would you enjoy the most, and why?
- Why is it important to plan your staffing before you start to hire people?
- What is the significance of training? Why do we need it in organizations?
Crant, J., “How Long Does an Interview Process Take?” Jobsinminneapolis.com, December 2, 2009, accessed October 28, 2010, http://www.jobsinminneapolis.com/articles/title/How-Long-Does-an-Interview-Process-Take/3500/422 .
Herman, S., Hiring Right: A Practical Guide (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1993), xv.
Pawlowski, S., “Illinois State University to Get Salary Bump,” WJBC Radio, July 11, 2011, accessed July 11, 2011, http://wjbc.com/illinois-state-university-faculty-to-get-salary-bump .
Human Resource Management Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Essay on Human Resources
In this essay we will discuss about Human Resources. After reading this essay you will learn about: 1. Meaning and Importance of Human Resources 2. Importance of Human Resources 3. Role in Economic Development.
- Essay on the Role of Human Resources in Economic Development
Essay # 1. Meaning of Human Resources :
By the term human resources we mean the size of population of a country along-with its efficiency, educational qualities, productivity, organisational abilities and farsightedness. By human resource we mean human capital. Human capital implies the abilities, skills and technical knowhow among the population of the country. A country should introduce manpower planning for the development of its human resources.
Human resources must be considered both from the angle of assets as well as the liabilities connected with the attainment of economic development. For the attainment of economic development, proper utilisation of both natural as well as human resources is very much essential.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Proper utilisation of natural endowments and the level of production of national wealth depend very much on the extent and efficiency of human resources.
But too much population will again eat up all the fruits of development. Thus from the point of view of economic welfare, it is quite essential to study human resources in detail. It should be equally stressed that human beings are the vital instrument of production and at the same time, fruits of all economic activities are rested on the betterment of conditions of living of human beings.
Thus in view of its importance, it is quite essential to know both in quantitative and qualitative terms, the size, rate of growth, the composition, distribution and all other demographic features of population of India.
Essay # 2. Importance of Human Resources:
(i) proper utilisation of resources:.
Human resources are considered important type of resources for attaining economic development of a country. Among various types of resources, human resources are the most active type of resources. Qualitative and quantitative development of human resources is very much required for the proper utilisation of natural resources of the country.
Thus the human capital formation according to Prof. Meier is “the process of acquiring and increasing the number of persons who have skills, education and experience which are critical for the economic and political development of the country.”
(ii) Increased Productivity:
Human capital has been playing an important role in the economic development of a country. Schultz, Kenderick and Harbison have made some important studies recently so as to point out that a major part of the growth of national output in USA can be attributed to increased productivity which has been mostly realised out of capital formation.
In this connection Prof. Galbraith was of the view that “we now get the larger part of industrial growth not from more capital investment but from investment in men and improvements brought about by improved men.”
(iii) Development of Skills:
Slow growth in underdeveloped countries is mostly resulted from lack of investment in human capital. These countries are suffering from lack of critical skills required for its industrial sector and also face the problem of surplus labour force in its farm sector. Thus human capital formation is very much required for the economic development of the underdeveloped countries.
In this connection, Prof. Myint observes that, “It is now increasingly recognised that many UDCs may be held back, not so much by a shortage of savings as by a shortage of skills and knowledge resulted in a limited capacity of their organisational framework to absorb capital in productive investment.”
Thus the underdeveloped countries are suffering from shortage of technically trained and highly skilled and educated persons and the developed countries are maintaining high level of investment on the development of manpower resources.
Accordingly Prof. Meier observed that, “While investment in human beings has been a major source of growth in advanced countries, the negligible amount of human investment in UDCs has done little to extend the capacity of the people to meet the challenge of accelerated development.”
Thus in order to attain an all round development of the country, the human capital formation through adequate volume of investment on human development is very much important under the present context of development.
(iv) Increased Volume of Output:
As a result of human resource development, the production increases as the knowledgeable and skilled workers can make a rational use of all resources at their disposal. With the imparted knowledge, workers try to increase his output and income. Attainment of vocational skills helps the workers and all categories of manpower to earn higher level of income in various professions.
The higher education and training at higher educational set up like college and universities usually enables workers to contribute liberally towards faster expansion of output in technical, engineering, machine building, accounting, management etc. Moreover, improved health facility can enhance physical capacity of workers. Thus all these factors positively contribute towards increased output.
(v) Addition to Productive Capacity:
Human resource development in the form of human capital formation can make necessary addition to the productive capacity of a country in humorous ways. By upgrading the technological scenario along with improved knowledge and skill can modernise the production technologies and thereby can add to the productive capacity of the country in general.
Transfer of technology from foreign countries can pave the way for adoption of modern technology into production and thereby can improve the productive capacities. Moreover, human capital formation can promote higher growth of the economy by adding physical stock of capital of the country.
(vi) Raises Per capita Income:
Human resources development can raise per capita income of the country through increased formation of human capital. Imparting knowledge can improve the productivity of workers and therefore, can raise the per capita income.
(vii) Tool for Economic Change:
Human resource development can make the people knowledgeable, skilled and physically fit. This can also change the attitudes of the people and improve the personal qualities of people.
Such changes are conducive to the development of innovative capacity and entrepreneurship which usually motivates people to work hard, take risks, do research and apply them to produce new products and also to develop new processes of production. All these can work as a tool for economic change.
(viii) Improving Quality of Life:
Human resources development can pave the way for improving quality of life for the people in general. This can be made possible through improvements in the three components of Human Development Index (HDI), i.e., rise in per capita income, higher educational attainments and increase in life expectancy.
Essay # 3. Role of Human Resource in Economic Development:
Human resources are playing an important role in attaining economic development of a country. Economic development of country involves proper utilisation of its physical resources by its labour force and other forms of manpower for the proper utilisation of production potential of the country.
Thus economic development normally involves achievement of three conditions:
(a) An increase in the per capita income to raise the level of living of the people;
(b) A fall in the magnitude and rate of unemployment and
(c) A consequent reduction in the number of people living below poverty line.
Although the labour force of the country is making positive contribution towards development but the rapidly growing population retards the process of development and thus considered harmful for economic development of the country.
Related Articles:
- Human Capital Formation: Meaning, Importance and Composition
- Essay on Energy Resources in India
- Essay on Human Capital | Economic Growth | Economics
- Human Capital Formation in India: Subject Matter and Stocks
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 27 September 2024
Mapping the main research themes in digital human resources
- Laura García-Fernández 1 ,
- Marta Ortiz-de-Urbina-Criado ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7527-6798 1 &
- María-José García-López 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1267 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Business and management
- Information systems and information technology
The COVID-19 pandemic sped up the digitalization process and revolutionized the world of the digital employee. And today, advances in artificial intelligence are having a major impact on the field of Digital HR. In that context, further literature review work is needed on the term Digital HR to complement previous studies and lay the foundation for more pioneering literature on this topic. Then, the aim of this paper is to provide a framework for organizing the main themes discussed in the pioneering literature on digital HR by answering the following research question: What is the knowledge structure of the research in the field of digital human resources? An adaptation of the PRISMA model is used to structure the research design. Applying a mixed methodology, this paper uses a bibliometric technique to identify the main topics studied in Digital HR. Subsequently, in-depth analysis and logical reasoning are applied and a model is proposed based on four questions (how, what, where, who) in order to understand and develop research on digital HR. The RQ4 Digital-HR model constitutes a useful tool in academic, practical, professional, and social contexts. It is worth highlighting the importance of the inclusion of artificial intelligence in the daily processes of a company, and therefore in the progress of the proposed research topic.
Similar content being viewed by others
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on HR practices in the UAE

Barriers and facilitators to utilizing digital health technologies by healthcare professionals
A bibliometric analysis of knowledge mapping in Chinese education digitalization research from 2012 to 2022
Introduction.
The world is witnessing constant change due to digitalization and its effects on companies and their staff. The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies, which had an immense impact on all business sectors and brought about permanent changes in the workplace (Gkinko and Elbanna, 2023 ). Many organizations started working in hybrid mode, combining digital ways of working with the traditional ways of working prior to the pandemic. Moreover, the use of digital technologies and the acceptance of more agile and flexible procedures and rules have changed the way in which work is being done (Mićić and Mastilo, 2022 ).
In general, our daily lives have been altered by technological advances, one of the most innovative being the advances in artificial intelligence, which is transforming the way people carry out their daily activities of work, communication, and decision making (Duke, 2022 ). The concept of artificial intelligence seems to be relatively recent, and in many cases, its true meaning or significance is unclear. However, it was not until the 2010s that the AI paradigm was reconfigured to be based on the classification and storage of massive data (Cetindamar et al. 2024 ).
Human resource management has evolved over time. Twenty-five years ago, its main focus was on implementing practices that promoted the development of organizations. However, the need for organizations to adapt to more competitive environments has forced businesses to adjust the traditional business management model, moving from strategic management to a more sustainable management approach (Villajos et al. 2019 ). One of the main factors influencing the adaptation of human resources management to the new sustainable management model has been digitalization (Le et al. 2024 ). Through digitalization, all employees, professionals, managers and business leaders, who are key to making the necessary changes to increase workplace productivity, can see their tasks facilitated through this phenomenon. In this context, human resources management develops practices that promote the welfare of the employee and the company (Le et al. 2024 ). Thus, in recent years, and especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, Digital Human Resources (Digital HR) has received a great deal of attention, particularly regarding Digital Employees and Digital Leaders. Advances in artificial intelligence are having a major impact on the field of Digital HR (Gkinko and Elbanna, 2023 ). Although there are still few publications on the acceptance of the effects of AI on workers and how the current increase in the use of digital technologies affects the skills and expectations of the digital workforce (Alan, 2023 ; Cetindamar et al. 2024 ).
In the academic context, there has been a surge in the literature on Digital HR. However, literature review studies on this topic are lacking, with most of them focusing on analyzing the digital workplace phenomenon (De Moraes et al. 2024 ; Marsh et al. 2022 ; Mićić and Mastilo, 2022 ), digital employee experience (Moganadas and Goh, 2022 ), and workforce training in digital workplaces (Patino and Naffi, 2023 ). Only two reviews address the issue of Digital HR more generally. Theres and Strohmeier ( 2023 ) conducted a meta-analysis to analyze theories applied in research on Digital HRM adoption and proposed a unified theory. Alan ( 2023 ) performed a co-word analysis, considering Electronic Human Resources Management (e-HRM) as the main term, and analyzed previous literature found in the Web of Science (WoS) for the period of 2012–2022.
Thus, further literature review work is needed on the term Digital HR that analyzes the literature published before and during the pandemic to complement previous studies and lay the foundation for more pioneering literature on this topic. The interest in analyzing changes during the pandemic is motivated by the fact that adapting to the new context requires new human resources actions that are closely related to the phenomenon of digitalization. Digital HR is a constantly evolving topic, and pioneering studies are fundamental to understanding this new phenomenon. Today, there is also the challenge of appropriately and ethically adopting artificial intelligence in the context of human resources (Cetindamar et al. 2024 ; Gkinko and Elbanna, 2023 ). In the face of a novel topic, it is important to gain an overview of the aspects studied, to understand the changes that have occurred around the pandemic, and to provide a logical framework of analysis by which to explore such phenomena.
This paper aims to provide an overview of the pioneering research landscape in the field of digital HR, filling in some of the existing research gaps. As a complement to Alan’s ( 2023 ) work, this research will focus on the topic of ‘digital HR’ and conduct a co-word analysis to identify the main themes studied. Moreover, a second step, which is not usually included in previous literature reviews on this topic, will be carried out to detect the applications of digital human resources. To this end, a model based on questions (how, what, where, who) is proposed to facilitate the understanding and development of digital HR research.
Thus, the aim of this study is to provide a framework for the organization of the main themes that are discussed in the pioneering literature on Digital HR. The research question addressed is What is the knowledge structure of the research in the field of digital human resources? To answer this question, the Background section is developed and a mixed methodology is applied, adapting the PRISMA process. A bibliometric technique is used to identify the main topics studied in Digital HR. Subsequently, in-depth analysis and logical reasoning are applied to propose a model and some lines of future research. Finally, the Conclusion section contains theoretical and practical implications, the study limitations, and future lines of research.
This paper is an original contribution. Literature reviews, and more on rapidly developing novel topics, play an important role in advancing research as they help to synthesize and organize existing knowledge and identify areas or topics for future research. This article proposes an integrative review (Patriotta, 2020 ) that offers another voice to guide and write new articles on digital human resources. Authors such as Post et al. ( 2020 ) have also highlighted the importance of literature reviews as they can serve several purposes such as helping researchers understand the research topic, discerning important and under-examined areas and connecting research findings from disparate sources to create new perspectives and phenomena. Moreover, the topic “Digital HR” calls for looking for models that help connect academic research with the business world. As Markman ( 2022 ) proclaims, academia is challenged to develop research that addresses current problems affecting people, business and society to make the world a better place. In that line, the RQ4 Digital-HR model constitutes a useful tool for academic, practical, professional, and social contexts.
The global pandemic has accelerated digital transformation in every sense, and the rise of digital technology in the workplace is unstoppable (Kalischko and Riedl, 2021 ). Technology plays a vital role in our day-to-day lives. Digitization has arrived, yet what that means or entails at a work and/personal level remains unclear. According to Kraus et al. ( 2022 ), it is necessary to have a fundamental understanding of literature reviews as independent studies. Therefore, the key texts must be identified that lay the foundations of Digital Human Resources Management (Digital HRM) before undertaking a bibliometric study.
Main concepts
Few papers over the last decades have provided a clear, agreed-upon definition of the term “Digital Human Resources Management” that is shared by the scientific community. Most papers have only superficially addressed the whole social and economic context that affects the new confection of digital employee models. Moreover, papers have tended to narrow their focus to a specific aspect of human resources management (Alan, 2023 ; Costa et al. 2022 ), digital employee experience (Moganadas and Goh, 2022 ), and job performance (Kalischko and Riedl, 2021 ; Marsh et al. 2022 ), analyzing the situation individually and rather than as a whole. Therefore, the starting point for this study is to introduce some of the terms or concepts commonly used in previous literature on digital HR. Two widely used terms are “digital worker” and “digital employee”. A key resource in any company is the employee, the one who can contribute to superior and solid performance over time (Moganadas and Goh, 2022 ). For example, Fuchs ( 2014 ) defines digital employees as the workforce required for the existence, use, and application of digital media. Other studies define digital employees as those employees whose work is performed primarily using digital resources (Nelson, 2018 ). IBM ( 2024 ) states that “in the past, the term ‘digital worker’ described a human employee with digital skills, but more recently, the market has defined it as a category of software robots, which are trained to perform specific tasks or processes in partnership with their human colleagues.”
Another concept used is “digital workplace.” As management has adapted to new technologies, the workplace has also had to adapt. This new leadership style brings with it concepts such as flexibility, which in this context refers to the non-limitation of the workspace to a specific physical location. This new digital workplace refers to the set of technologies that employees use to perform their functions (Marsh, 2018 ) and includes, among others, the intranet, communication tools, e-mail, CRM, etc. It also refers to a set of procedures and rules that maximize productivity and improve collaboration, communication, and knowledge management (Mićić et al. 2022 ). Some researchers use the term “digital labor”, which initially referred to the unpaid work performed by consumers online during leisure time. However, this term is now used to describe all work in which digital technology plays a role (Jarrett, 2022 ). The term has also been used to describe employees who work independently, receiving low wages and no social security, in business models supported by digital platforms, such as Uber (Fumagalli et al. 2018 ), or to describe the workforce that uses other business models that are also based on digital platforms, such as Facebook or Google, and that capture information to transform it into big data (Fuchs and Sevignani, 2013 ).
In that context, another important concept is digital platform. Digital platforms are transforming almost every industry today (Reuver et al. 2018 ). They are continuously evolving and becoming increasingly complex. These digital platforms are the ones that facilitate online communities of consumers (Reuver et al. 2018 ). While there are several definitions of digital platforms that refer to the codes, software, and hardware of which they are composed, for this study the most suitable definition of digital platform would be the environment in which companies combine all the information available from their stakeholders to generate or co-create value (Karhu et al. 2018 ). According to Murati ( 2021 ), a digital platform is an open infrastructure that exercises a facilitator role or a high level of control and influence over providers and users.
The meeting point of each one of these concepts is the term Human Resource Management, which is understood as the processes that involve activities from recruitment to salary management and that are carried out simultaneously (Alan, 2023 ). All of these processes have been equipped with more technology and innovative methods over time. Thus, the concept has evolved to Digital Human Resource Management (HRM), understood as the set of software, hardware, and digital resources designed to automate the HR function (Jani et al. 2021 ; Marler and Parry, 2016 ), or in other words, to develop consistent, efficient and high-quality HR practices through the use of digital transformation and new technologies (Bondarouk and Brewster, 2016 ).
Previous literature reviews
Previous literature reviews established a set of definitions that, despite using common concepts, have left nuances that have yet to be fully addressed in subsequent works. Most of the work that reviews previous literature has focused on studying digital workplaces. Mićić and Mastilo ( 2022 ) conducted a systematic literature review on the digital transformation of the workplace and employees’ workplace preferences. The search terms used were “digital workplace”, “COVID-19”, and “innovation”, and the search was limited to English language papers published after 2010. The benefits of digital workplace transformation are analyzed and the critical success factors and significant challenges are identified.
Marsh et al. ( 2022 ) studied the application of digital technologies in the workplace with a particular focus on their dark side. They conducted an integrative literature review and limited the search to papers published between January 2007 and June 2020 that were written in English and carried out in Western countries only (in the United States, Europe, Canada, Australia, Latin America, and New Zealand). De Moraes et al. ( 2024 ) conducted a systematic review of the literature on the design of digital workplaces. Their main results include a definition of digital workplace and a four-phase model with guidelines for designing digital workplaces. Patino and Naffi ( 2023 ) conducted a systematic review of training approaches and resources for workforce development in digital workplaces. Using the PRISMA model, they analyzed articles published between 2020 and 2022. Their paper offers research-based perspectives and recommendations for employee training in highly digitalized workplaces.
Another aspect that has been studied is the experience of the digital worker. Moganadas and Goh ( 2022 ) discuss the concept of digital employee experience (DEX). They conducted a comprehensive literature review on DEX by analyzing the content of academic publications and professional reports. They used the Scopus and Google Scholar databases to identify “DEX” or “digital employee experience” in their title, abstract, and keywords and found 17 articles between 2016 and 2022. To complement these papers, they included grey literature to identify studies that addressed a similar topic, such as digital transformation, digital workplace, and employee experience.
Finally, a few papers have reviewed the literature on human resource management in a digital environment. Theres and Strohmeier ( 2023 ) analyzed the phenomenon of digital HRM. In their paper, they present an overview of the theories applied in digital HRM adoption research and propose a unified theory. To test their theory, they performed a combination of meta-analysis and structural equation modelling. Alan ( 2023 ) presented a systematic bibliometric analysis of electronic human resource management (e-HRM) by conducting a literature search in the Web of Science (WoS) for the period of 2012–2022.
Methodology
Figure 1 presents the methodological process used in this study. The methodological design used includes two parts. In the first, a multi-step process has been followed to perform the bibliometric analysis: sample selection, filtering of documents and keywords, and co-word analysis. In the second, a reflexive analysis was carried out. To facilitate the understanding of the process followed, the PRISMA 2020 statement has been adapted, which has been designed primarily for systematic reviews of studies (Moher et al. 2010 ; Page et al. 2021 ). The adaptation of the PRISMA process provides a more transparent view of the methodology used and the analyses carried out.
Own elaboration based on the PRISMA model.
The Scopus database was used. There is an open debate regarding whether Scopus or WoS is superior. Both have advantages and disadvantages (Stahlschmidt and Stephen, 2020 ). The Scopus database was chosen for this paper because it offered a larger sample of documents than did WoS. Although the research on Digital HR began over 35 years ago, most of the articles have been published in the last three years, demonstrating the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on this topic. Until the year 2016, contributions were sporadic, and it is not until a year later, in 2017, that the research begins to approach 25 articles per year. Of the total of articles (347), 56% (196) were published between 2020 and 2022, with 2021 being the most important year, when a total of 82 articles (25%) were published.
A co-word analysis in conjunction with the SciMat program was used to identify the various themes covered in the literature on Digital HR (Cobo et al. 2012 ). Of the many tools that enable co-word analysis, SciMat was chosen for its ability to carry out the analysis with simplicity and rigor. Moral-Muñoz et al. ( 2019 ; 2020 ) describe the various tools that are available for bibliometric analysis and comment on SciMat as being a valid tool for co-word analysis. SciMat was suitable for achieving the objective of this paper because it analyzes the keywords of selected articles and calculates the strategic diagrams and networks for each thematic group. Moreover, SciMat incorporates all the necessary elements (methods, algorithms, and measurements) for performing a co-word analysis and obtaining its visualizations (Cobo et al. 2012 ).
Regarding the strategic diagram, centrality and density are calculated for each thematic group (Cobo et al. 2018 ). Centrality is a measure of the importance of a theme in the development of a field of knowledge. Density reflects the strength of a network’s internal relationships, thus identifying the level of development of that theme. The strategic diagram classifies the themes into four groups (Cobo et al. 2018 ). In the upper-right quadrant are the motor themes, which comprise themes that have strong centrality and high density. In the upper-left quadrant are the well-developed and/or isolated themes. The themes in the lower-left quadrant are presented as emerging or disappearing themes, while in the lower-right quadrant are themes that are considered basic and transversal themes.
This section presents the results of the co-word analysis. The bibliometric technique is suitable for identifying the knowledge structure of a research topic. Given the volume of articles published between 2020 and 2022, two periods of analysis were carried out to compare the networks that emerged prior to and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Figure 2 shows the evolution of all the topics mentioned, their typology, and how, depending on the period, they transform into a new topic.
Results from SciMat, diagram composed of themes by number of documents for all the periods.
Table 1 presents the evolution that Digital HR research has experienced during these years.
Main themes studied in Digital HR
Regarding the total period (1984–2022), previous research focused on “digital workplace” and “digital platform” and “digital employee” as the motor themes. “Digital labor” appears as an emerging topic and as something remarkable. Despite not being connected to the human resources area, this entire digitization process is linked to the topic “enterprise bots”, a concept that had previously been highly developed in scientific fields. During the pre-COVID period (1984–2019), the motor theme was the “digital workplace”. During the COVID period (2020–2022), the motor themes were “digital employee” and “digital workplace”. Lastly, the emerging theme for all the periods is “digital labor”.
During the first period (1984–2019), only one theme, “digital workplace”, is positioned as a motor theme. It makes sense that after the 4 th industrial revolution, developed between 1950 and 1970, a study period would begin regarding how this digitization has affected the workspaces as well as how to continue innovating and improving them. Companies have needed workplaces to be transformed from a traditional perspective to a digital one (Colbert et al. 2016 ; Kaarst-Brown et al. 2018 ), since this change is key to organizational success (Colbert et al. 2016 , Köffer, 2015 ).
In the 2020–2022 period, two additional topics to those appearing in the previous period emerge. These are “digital employee” and “digital labor”, positioned as a motor and an emerging theme, respectively. These topics correlate with what occurred during the pandemic, which forced the digitalization of all types of situations. As a result, the research on this area has focused on the employee and, above all, the digitization of work that, as mentioned, appears as an emerging topic.
Based on these results and for the completion of the analyses, a manually and logical regrouping of themes was conducted in the SciMat program, and another strategic diagram was identified. Figure 3 , which presents the strategic diagram obtained from this new analysis, shows that the motor themes are “digital platform” and “workplace”. “Manufacturing”, “digital employee”, and “social media” are well-developed themes. “Digital”, “learning”, and “labor” are positioned as basic themes. Finally, the emerging theme is “artificial intelligence”. A logical knowledge structure of the study topics can be observed. On the one hand, what emerges are the themes related to the more digital aspect of work, namely “digital”, “digital platform”, and “digital employee”. On the other hand, there are items that refer to the more physical aspect, “labor” and “workplace”. Tangential to the most digital aspect linked to work is the communication channel or media used at work, “social media”. In turn, in the main sector where the research is applied or where the literature has further explored these issues, the theme of “manufacturing” is also well defined.
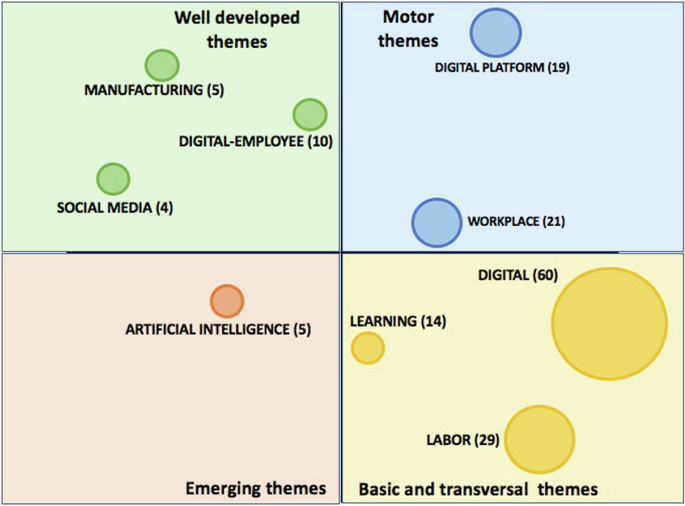
Results from SciMat, diagram composed of themes by a number of documents for all the periods.
Also evident in the diagram is the channel through which employees can progress in the work environment, through “learning”, a Human Resources practice that has been developed for some time but has become more crucial in recent years. Learning is the key to employees acquiring digital competencies and feeling comfortable in digital work environments. Finally, as an emerging topic, is everything related to “artificial intelligence”. This topic, of relatively recent creation, has all the works published in the year 2022 or later, and is creating a highly critical space in the business environment, and in this particular case, in everything related to Human Resources and how to implement it in departmental processes.
Thematic networks in Digital HR
It is interesting to know the thematic networks in which the most significant keyword (the one with the highest centrality) is placed at the center. The size of each node represents the number of documents containing that word, and the thickness of the line indicates the strength of the association between those topics.
Digital platform
Analysis of the “Digital Platform” subnetwork (Fig. 4 ) for the period 1984–2022, reveals four documents and a wide network of terms that correlate with each other. The most notable relationships are those related to health care. However, within our scope, there are several studies that focus on the use of digital platforms as a means of offering work in the “gig economy.” Taylor et al. ( 2017 ) define the concept of Gig Economy as the use of applications or platforms for work.
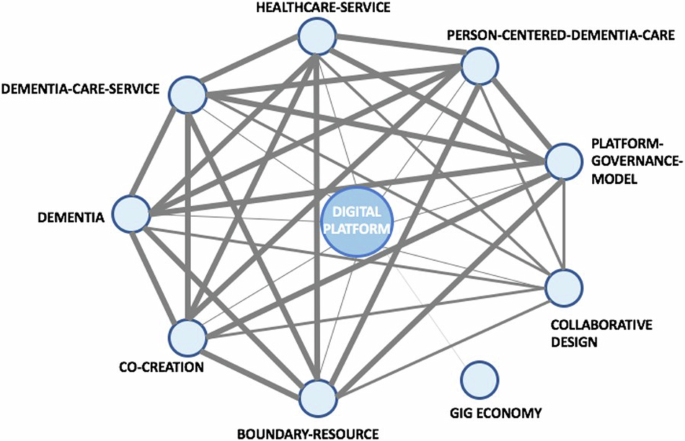
Results from SciMat cluster network for the digital platform.
The analysis also revealed the importance of collaborative work for the improvement of digital platforms, as shown through the connections between the terms “collaborative designs” and “co-creation”. The research also showed two important advances in what has been studied in recent years: the flexibility that this type of work facilitates (Soriano and Cabanes, 2020 ) and how these new jobs can change the lifestyle of digital employees (Graham et al. 2017 ).
Digital workplace
The “Digital workplace” network (Fig. 5 ) for the period 1984–2022 includes six documents and shows that the most important keywords in the cluster are “digital transformation” and “artificial intelligence”. Again, it is crucial for this network to talk about “collaboration”, as well as “cross-functional teams” and their “dynamic capabilities” that play a special role in developing the digital workplace. As Selimović et al. ( 2021 ) posit, the inclusion of the employee in the decisions on digital transformation is a key to its success. Moreover, the use of artificial intelligence, through the “chatbots” makes improvement in the workplace possible (Cetindamar et al. 2024 ). In both cases, the focus is placed on the inclusion of the employee as a key part of these processes. This demonstrates a strong relationship between digital and emotions in the cluster, since understanding how the use of technology affects employees’ emotions (Gkinko and Elbanna, 2022 ) is one of the most relevant topics in the current research.
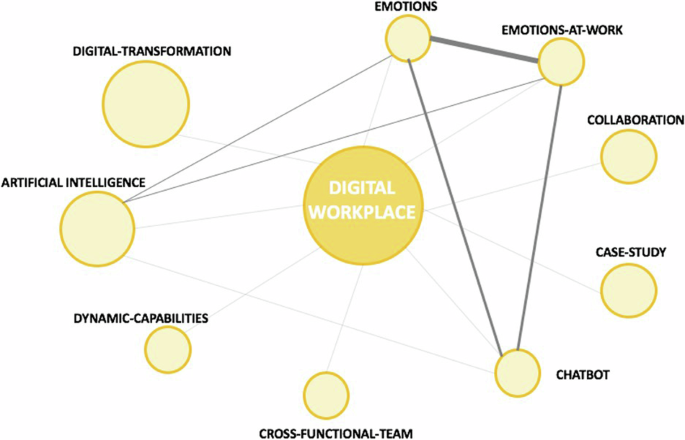
Results from SciMat cluster network for the digital workplace.
The analysis of the “Digital workplace” network (Fig. 6 ) for the period 1984–2019, which contains 15 documents, reveals the strong presence of terms related to a collaborative work environment, such as “collaboration”, “cloud”, “cloud computing”; or even advancing further in the collaboration itself, it becomes necessary to talk about “digital platforms” or “crowdsourcing”, as means for it, being the key tools for developing the digital workplace (White, 2012 ; Attaran et al. 2019 ). Indeed, the most remarkable aspect of the network is the strong connection between “cloud computing” and “mobile working”. It must be considered that during these years, prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, the now-standardized option of mobile working was merely a practice applied by a few companies. Thus, it makes sense that during these years of strong digitization, research focuses on it. There is also one term, “artificial intelligence” (here also mentioned as “social software”), that researchers start to investigate during these years, since its use in the digital workplace is continuing to increase (Martensen et al. 2016 ) and, as could be seen throughout the paper, it will also become of vast importance for other networks.
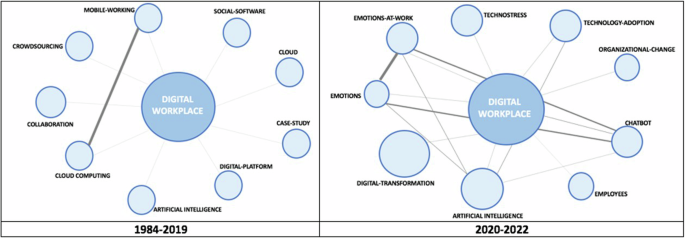
For the last years (2020–2022), “Digital workplace” network (Fig. 6 ) contains the highest number of documents (16) and shows two remarkable themes “digital transformation” and “artificial intelligence”. In the figure can be seen a triangle formed by “emotions”, “emotions at work”, and “chatbot”, as employee users experience a connection emotion when using artificial intelligence (Gkinko and Elbanna, 2022 ), and there is an effort to understand how employees will accept these new systems in the enterprise context (Brachten et al. 2021 ). Moreover, in these recent years, the changes that companies must make to achieve the digitalization of the workplaces takes on a special relevance. Thus, it is not surprising that the investigation is linked to “organizational change” and “technology-adoption”. It should not be overlooked that none of these changes would be possible without including the “employees” in said decisions (Cetindamar et al. 2024 ).
There is a topic that remains throughout the analysis: “artificial intelligence” (Fig. 6 ). However, there is a positive evolution between the topics analyzed prior to the pandemic and those analyzed after it. In the first period (1984–2022), the topics were focused on how the workplace should be or what it should contain and how it should be digitized, as well as on platforms and software and everything related to the cloud. However, during the pandemic period, some changes were perceived, with the introduction of themes arising from having been forced to implement the digital work modality. These topics include technostress, emotions, and employees, as well as everything related to organizational change.
Digital employee
The “Digital employee” network (Fig. 7 ) for the period 1984–2022 contains 10 documents and shows, as previously mentioned, the relevance of the pandemic in this research. In this sense, it is crucial to understand how this situation affected the employee, the work itself, and the life experience of employees (Muszyński et al. 2021 ). Above all, it shows a strong connection between the concepts related to “Robotic Process Automation” (RPA), “digital automation process”, and “software robot”, as a means to increasing productivity in a company, leaving the routine tasks to RPA and assigning employees to perform more difficult tasks (Choi et al. 2021 ). Clearly, it is crucial to talk about the “digital competencies” that employees have or need to acquire to be included in the “new work” that globalization is forcing us to implement.
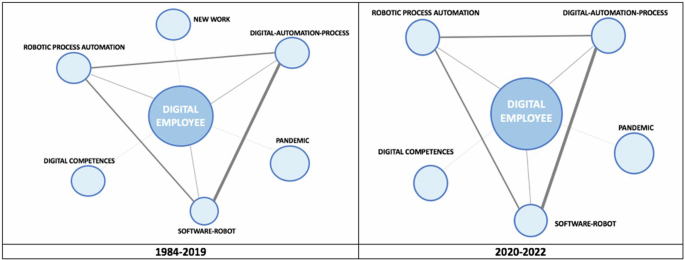
Results from SciMat cluster network for digital employees.
The “Digital employee” network, for the last years (2020–2022) (Fig. 7 ), with eight documents, shows that there have been no changes in recent years compared to what was already being studied. The only difference is that the research in these years does not focus on the new types of work, implemented post-pandemic, but studies how to improve the implementation of RPA (Costa et al. 2022 ) to achieve better economic results and an improved digital employee experience.
Digital labor
The “Digital labor” network (Fig. 8 ) for the years 1984–2022, contains nine documents and shows a star-shaped network characterized by the presence of keywords that only correlate with the cluster topic. The main theme of the cluster is the work itself with its main versions, with research on the best type of work being very common (Babapour Chafi et al. 2022 ): office work or digital work (commonly called digital nomadism). There is also an important connection with the information society.
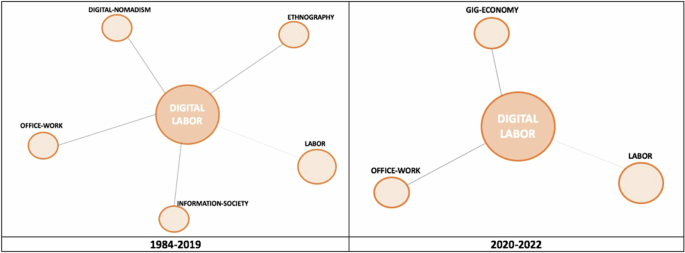
Results from SciMat cluster network for digital labor.
“Digital Labor”, for the last years (2020–2022), provides six documents (Fig. 8 ). Studies related to the “gig economy” and the types of jobs related to digital platforms proliferate during this period. In addition, once the pandemic period was over, it was expected that employees would return to office work. Thus, there arises a need to understand which work model (remote, face-to-face, or hybrid) is more productive and which is more valued by the employee (Babapour Chafi et al. 2022 ).
A comparison of studies prior to the pandemic with those of recent years reveals that initially there were several issues related to digital work, whereas in recent years these have been reduced to two issues: office work or work through digital platforms.
Enterprise bots
The “Enterprise bots” network for the period 1984–2022 (Fig. 9 ) contains two documents that co-relate two concepts, virtual assistants and virtual agents, as being crucial to understanding the differences between them, and above all, to understanding the differences in use between the individual and the business context (Stieglitz et al. 2018 ). The focus was therefore on teaching an employer how to effectively introduce these systems in the company (Brachten et al. 2021 ).
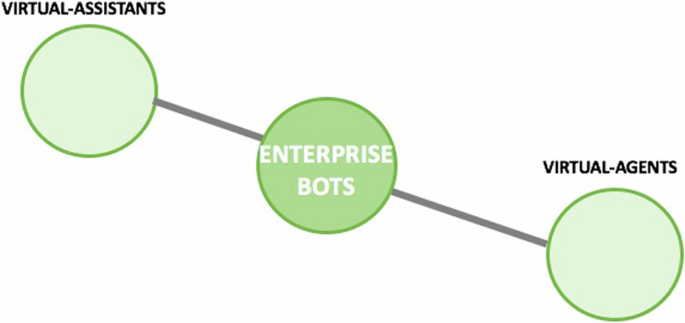
Results from SciMat cluster network for enterprise bots.
The results of this study complement those of previous literature review studies. Alan ( 2023 ) focused on the term Electronic Human Resources Management (e-HRM) and conducted a review of the literature included in WoS from 2012 to 2022. Our study focused on the term “digital human resources” and used the Scopus database. Our study also included pioneering literature up to 2022 and an analysis of the differences between the pre-pandemic period (1984 to 2019) and the peak years of the pandemic (2020–2022).
Alan ( 2023 ) categorizes the research on this topic into three groups: the theoretical studies and theories used in the studies reviewed, empirical qualitative studies, and empirical quantitative studies. Alan ( 2023 ) presents summary tables for each category that include following information: related theoretical framework, related terms, studies, typology of study, aim of the study, and the main findings and propositions. In a complementary way, this current paper presents the studied themes and classifies them into four groups according to the strategic diagram and analyses the networks for each thematic group. Additionally, based on the results obtained in the previous section, a process of analysis and reflection was carried out to establish the roadmap of topics studied and to define the emerging and future topics. Four main research questions (how, what, where, who) are considered to propose a model (Fig. 10 ).
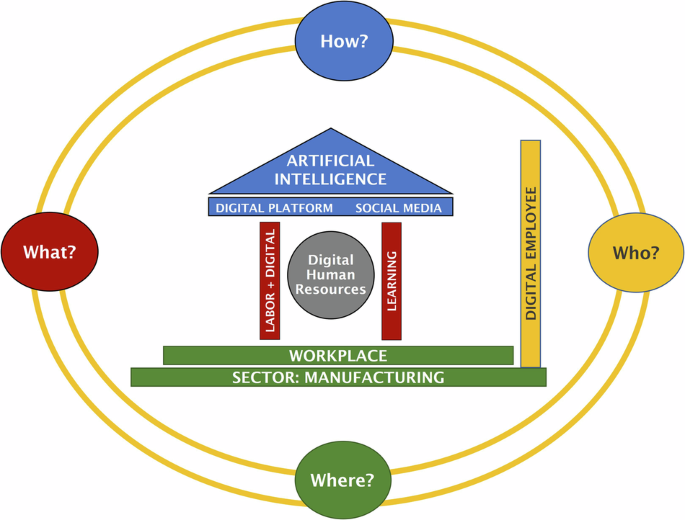
Own elaboration.
The RQ4 Digital-HR model presents four fundamental questions for understanding and developing research on digital HR -Research Questions for Digital HR.
The basis of the proposed model (Fig. 10 ) refers to “where” to apply it. The results of the analysis show that there is a sector where deep research on the subject has already been carried out, the manufacturing sector. However, the research should not stop there. Future research should take this model to other sectors of much greater complexity and scope, such as the service sector.
The pillars that support the model, “the what,” are on two levels: the advances in the digitalization of work on the one hand and, on the other hand, all the learning that a company can guarantee to its employees and that employees are able to assimilate. Clearly, the cross-cutting issue, “the who,” is the digital employee, the workforce member that drives the change, the one who is able to implement any Human Resources practice, and therefore the one who is able to assimilate business-driven change.
The roof of the model is “the how.” The implementation of all the changes we are forced to make is only possible through the implementation and improvement of three items in our daily processes: firstly, the digital platforms that we use every day at work, secondly, the management of information through the channels provided by the company, and thirdly—and most importantly—the inclusion of artificial intelligence in all our processes, as a means of improving productivity. This technology is transforming, and revolutionizing, the future of workspaces to make them more productive (Gkinko and Elbanna 2022 ), but again studies on the subject do not address how to accomplish this. Most of the texts reviewed on the subject focus on investigating some aspect of the implementation of artificial intelligence systems and their errors (Costa et al. 2022 ) or on employees’ acceptance of or trust in such technology (Gkinko and Elbanna, 2023 ). However, the work of Gkinko and Elbanna ( 2022 ) offers a starting point for how to incorporate this technology into a company, since the emotions of employees need to be taken into account when such tools are being created in order to facilitate their inclusion in day-to-day activities.
This makes it vital to focus the research on Digital HR, which requires researchers to collaborate to determine the what, where, how, and who. Based on the questions in the model, a further step has been taken to identify the aspects that would be interesting to analyze in future work to answer each of these fundamental questions.
WHAT: In reference to this, it is important to discover what digital processes should be introduced in our daily lives, what learning tools will help us to channel digitization, and what new labor trends can be found in the post-COVID stage.
WHERE: Future research should focus on analyzing what kind of workspaces exist in the labor market. This first line of research will undoubtedly lead towards the different sectors of activity, so it is also important to see what we know about the different sectors and their relationship with Digital HR, especially in the service sector, since globally it is the most present sector of activity.
HOW: Research should continue to determine how to do this and, as broken down in the table, it is important to address how to adopt digital platforms in the work environment, how to adapt existing social networks to the business context, and how to apply new artificial intelligence models.
WHO: As mentioned in this paper, digital HR is a transversal entity in all these lines of research. However, it is not left out of the future lines of research since it is essential to understand who this digital HR includes.
Finally, based on the results of this study (thematic groups) and the proposed model (questions), Table 2 presents a proposal for future research lines and questions.
The proposed model revolves around four fundamental research questions (Fig. 10 ). The importance of researchers developing the ability to formulate questions has an epistemological background expressed by Bachelard ( 1982 , p. 16) as ‘for a scientific spirit all knowledge is an answer to a question. If there was no question, there can be no scientific knowledge’. It should be noted that the quality of the questions asked is closely related to the prior knowledge they have about a given topic (Neber and Anton, 2008 ). Systematic questioning about different phenomena fosters meaningful learning by drawing on prior knowledge in a non-arbitrary and non-literal way (Moreira, 2000 ). Furthermore, knowing the background of a subject facilitates scientific modelling, an activity inherent to science, which can be understood as a process of constructing models for the purpose of apprehending reality (Giere, 1988 ) and providing answers to questions formulated about real facts or assumptions (Halloun, 1996 ). The model presented in Fig. 10 and developed in Table 2 , helps to logically order the themes studied in the previous literature and to propose emerging and current themes of great interest for the development of the literature on digital HR.
In addition, the model helps to sort out what company should focus on meeting the needs of its employees without leaving its own needs behind, first the basis, then the pillars and finally the roof. In this regard, it is important to start managing the workers’ workplaces to adapt them to the environment. Subsequently, the training needs of employees must be addressed, along with the necessary adaptations to enable them to function digitally. Thirdly, companies must develop internal and external communication systems that allow them to be in contact with all their stakeholders. Only having developed these points will be able to focus on meeting current social demands and introducing artificial intelligence in their daily work.
Therefore, if companies’ human resources departments understand this model and its order, will be able to act effectively and thus be more ethical and sustainable. On the other hand, acting in an inverted order will leave some of the pillars of the Triple Bottom Line uncovered, with the risks that this entails. The Triple Bottom Line (triple P´s) model is a model that calls for corporate commitment to measure its social (Person), environmental (Planet), and financial (Profit) impact. This is why it becomes necessary to have a human resources management model adapted to the current and changing context of the organization (Kramar, 2014 ).
In turn, for the employee, the implementation of a model will help them to prioritize their needs to be covered by the company so that, once managed, they can lead to a higher and better performance and thus achieve a high level of well-being at work. Ruiz-Palomino et al. ( 2019 ) explain that a good way to improve a company productivity is to promote corporate wellness and entrepreneurship.
Conclusions
This paper has answered the question What is the knowledge structure of pioneering research in the field of digital human resources? A mixed methodology was used to identify the main topics studied in Digital HR and to propose a model and some future research lines and questions.
This article presents an integrative review to generate ordered knowledge spaces, which as Patriotta ( 2020 ) explains serves to ‘put boundaries around an existing area of research in order to provide an organized sample of what is available and build a platform for future research’ (p. 1274).
Implications
Theoretical implications.
In terms of theoretical implications, this paper highlights the interest of extending current research to concretely define what the digitalization of work means as well as its implications and requirements. This will enable the discovery or even the proposal of new digital work models, incorporating those positions redefined as a result of the incorporation of artificial intelligence and thus make it possible to delimit digital HR. On the other hand, it is noted that the incorporation of new trends in the market must be reflected in the teaching/learning methods to achieve greater professionalization. In turn, a company will become the protagonist in designing these new training processes that are linked to its specific professional activity and the profile of its employees. On the other hand, emphasis can be placed on studying how to increase productivity through the application of artificial intelligence in routine tasks.
In addition, based on the proposed model, an expansion of research on Digital HR human resources is proposed, incorporating new lines and research questions, which will lead to a new categorization of workplaces according to their capacity to adopt digital models. This will lay the foundation for a new labor framework and the development of innovative capabilities in this regard. This broadening of research can be related to the development of thematic lines and professional sectors, especially in the service sector, thus accommodating the most important sector for the European economy. Future research can consider the development of new TAM (Technology Acceptance Model) models to measure the adoption of digital technologies in digital work environments. Social networks used in the work environment can also be investigated to detect those that best help to channel the processes of labor digitalization.
Practical implications
In terms of practical implications, the results obtained and the proposed model can be used to encourage the application of new technologies in the work environment; guarantee employees digital learning processes to increase productivity, facilitating this new learning process; and create policies and standards that include artificial intelligence and social networks in the business environment, thus standardizing their proper use to generate greater productivity and economic results. New and innovative workspaces can also be developed in order to integrate the improvements derived from digitalization and artificial intelligence. Information channels can also be developed to connect the new processes with stakeholders and adapt the work activity to the new demand of employees and the market, thus including, from its conception, digital natives in the entire process.
Social Implications
The results also have social implications. In this sense, the study of the digitization of human resources helps to adapt the usual performance of employees to the inclusion of new technologies in the business environment and to involve employees in training processes to promote professional and labor development. In turn, it can be used to involve employees in the development of new workspaces to maximize productivity, for the implementation of new work models designed by the company and the use of social networks as a means of labor communication. As a corollary, artificial intelligence can be considered as a tool to improve productivity, reducing the volume of monotonous or routine tasks and reinforcing those in which only the employee can provide real value.
Limitations and future research lines
The authors acknowledge the limitations of the methodology used in this study and call for further research to expand our understanding of the topic. Future studies could complement the co-word analysis with other bibliometric techniques such as co-citation analysis and develop theoretical and empirical models on the applications of digital human resources.
Data availability
Documents that support the findings of this study can be consulted in the Scopus database by following the search procedure indicated in the methodology section.
Alan H (2023) A systematic bibliometric analysis on the current digital human resources management studies and directions for future research. J Chin Hum Resour Manag 14:38–59. https://doi.org/10.47297/wspchrmWSP2040-800502.20231401
Article Google Scholar
Attaran M, Attaran S, Kirkland D (2019) The need for digital workplace: increasing workforce productivity in the information age. Int J Enterp Inf Syst 15:1–23. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJEIS.2019010101
Babapour Chafi M, Hultberg A, Bozic Yams N (2022) Post-Pandemic office work: perceived challenges and opportunities for a sustainable work environment. Sustainability 14(1):294. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14010294
Bachelard G (1982) La formación del espíritu científico. Siglo XXI Editores, México
Google Scholar
Bondarouk T, Brewster C (2016) Conceptualising the future of HRM and technology research. Int J Hum Resour Man 27(21):2652–2671. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2016.1232296
Brachten F, Kissmer T, Stieglitz S (2021) The acceptance of chatbots in an enterprise context–A survey study. Int J Inf Manage 60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2021.102375
Cetindamar D, Kitto K, Wu M, Zhang Y, Abedin B, Knight S (2024) Explaining AI literacy of employees at digital workplaces. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 71:810–823. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEM.2021.3138503
Choi D, R’bigui H, Cho C (2021) Robotic process automation implementation challenges. In: Pattnaik PK, Sain M, Al-Absi AA, Kumar P (eds) Proceedings of International Conference on Smart Computing and Cyber Security. SMARTCYBER 2020. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems vol 149. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7990-5_29
Cobo MJ, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Herrera F (2012) SciMAT: a new science mapping analysis software tool. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec 63(8):1609–1630. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22688
Cobo MJ, Jürgens B, Herrero-Solana V, Martínez MA, Herrera-Viedma E (2018) Industry 4.0: a perspective based on bibliometric analysis. Procedia Comput Sci 139:364–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.278
Colbert A, Yee N, George G (2016) The digital workforce and the workplace of the future. Acad Manag J 59(3):731–739. https://doi.org/10.5465/amj.2016.4003
Costa D, Mamede H, Mira da Silva M (2022) Robotic process automation (RPA) adoption: a systematic literature review. Eng Manag Prod Serv 14:1–12. https://doi.org/10.2478/emj-2022-0012
De Moraes CR, da Cunha PR, Ramos I (2024) Designing digital workplaces: a four-phase iterative approach with guidelines concerning virtuality and enterprise integration obituaries. Pac Asia J Assoc Inf 16(1):74–98. https://aisel.aisnet.org/pajais/vol16/iss1/4 . Available at Accessed 03 June 20
Duke B (2022) 24/7 Digital work-based spy: the effects of technological panopticism on workers in the digital age. J Labor Soc 25(4):520–558. https://doi.org/10.1163/24714607-bja10068
Fuchs C, Sevignani S (2013) What is digital labour? what is digital work? what’s their difference? and why do these questions matter for understanding social media? TripleC-Commun Capit 11 (2). https://doi.org/10.31269/triplec.v11i2.461
Fuchs C (2014) Digital labour and Karl Marx. Routledge, New York
Book Google Scholar
Fumagalli A, Lucarelli S, Musolino E, Rocchi G (2018) Digital labour in the platform economy: the case of Facebook. Sustainability 10(6):1757. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10061757
Giere R (1988) Explaining science: a cognitive approach. Chicago: University of Chicago
Gkinko L, Elbanna A (2022) Hope, tolerance and empathy: employees’ emotions when using an AI-enabled chatbot in a digitized workplace. Inf Technol Peopl 35(6):1714–1743. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-04-2021-0328
Gkinko L, Elbanna A (2023) Designing trust: the formation of employees’ trust in conversational AI in the digital workplace. J Bus Res 158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2023.113707
Graham M, Hjorth I, Lehdonvirta V (2017) Digital labour and development: impacts of global digital labour platforms and the gig economy on worker livelihoods. Transf -Lond 23(2):135–162. https://doi.org/10.1177/1024258916687250
Halloun I (1996) Schematic modeling for meaningful learning of physics. J Res Sci Teach 33(9):1019–1041
IBM (2024). The IBM register: https://www.ibm.com/topics/digital-worker Accesed on January 2024
Jani A, Muduli A, Kishore K (2021) Human resource transformation in India: examining the role digital human resource technology and human resource role. Int J Organ Anal 31(4):959–972. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-08-2021-2886
Jarrett K (2022) Digital Labor. Cambridge, UK
Kaarst-Brown M, Quesenberry J, Niederman F, Weitzel T (2018) Special issue editorial: new approaches to optimizing the digital workplace. Mis Q Exec 18(1):9–14. https://aisel.aisnet.org/misqe/vol18/iss1/3
Kalischko T, Riedl R (2021) Electronic performance monitoring in the digital workplace: conceptualization, review of effects and moderators, and future research opportunities. Front Psychol 12:633031. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.633031
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Karhu K, Gustafsson R, Lyytinen K (2018) Exploiting and defending open digital platforms with boundary resources: android’s five platform forks. Inf Syst Res 29(2):479–497. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.2018.0786
Köffer S (2015) Designing the digital workplace of the future–what scholars recommend to practitioners. ICIS 2015 Proceedings. 4. https://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2015/proceedings/PracticeResearch/4
Kramar R (2014) Beyond strategic human resource management: is sustainable human resource management the next approach? Int J Hum Resour Man 25(8):1069–1089. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2013.816863
Kraus S, Breier M, Lim WM (2022) Literature reviews as independent studies: guidelines for academic practice. Rev Manag Sci 16:2577–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11846-022-00588-8
Le KBQ, Sajtos L, Kunz WH, Fernandez KV (2024) The Future of Work: Understanding the Effectiveness of Collaboration Between Human and Digital Employees in Service. J Serv Res 0(0). https://doi.org/10.1177/10946705241229419
Markman GD (2022) Will your study make the world a better place? J Manag Stud 59(6):1597–1603. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12843
Marler J, Parry E (2016) Human resource management, strategic involvement and e-HRM technology. Int J Hum Resour Man 27(19):2233–2253. https://doi.org/10.1080/09585192.2015.1091980
Marsh E (2018) Understanding the effect of digital literacy on employees’ digital workplace continuance intentions and individual performance. Int J Digital Lit Digital Competence 9(2):15–33. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJDLDC.2018040102
Marsh E, Pérez-Vallejos E, Spence E (2022) The digital workplace and its dark side: An integrative review. Comput Hum Behav 128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.107118
Martensen M, Ryschka S, Blesik T, Bick M (2016) Collaboration in the consulting industry: Analyzing differences in the professional use of social software. Bus Process Manag J 22(4):693–711. https://doi.org/10.1108/BPMJ-06-2015-0093
Mićić L, Khamooshi H, Rakovic L, Matkovic P (2022) Defining the digital workplace: a systematic literature review. Strateg Manag 27(2):29–43. https://doi.org/10.5937/straman2200010m
Mićić L, Mastilo Z (2022) Digital workplace transformation: innovative approach after Covid-19 pandemic. Economics 10(2):63–76. https://doi.org/10.2478/eoik-2022-0014
Moganadas SR, Goh GGG (2022) Digital employee experience constructs and measurement framework: a review and synthesis. Int J Technol 13(5):999–1012. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v13i5.5830
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma Group (2010) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int J Surg 8(5):336–341. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.b2535
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Moral-Muñoz JA, López-Herrera AG, Herrera-Viedma E, Cobo MJ (2019) Science mapping analysis software tools: a review. In: Glänzel W, Moed HF, Schmoch U, Thelwall M (eds) Springer Handbook of Science and Technology Indicators. Springer Handbooks. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-02511-3_7
Moral-Muñoz JA, Herrera-Viedma E, Santisteban-Espejo A, Cobo MJ (2020) Software tools for conducting bibliometric analysis in science: An up-to-date review. Prof Info 29(1). https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2020.ene.03
Moreira MA (2000) Aprendizaje significativo: teoría y práctica. Visor, Madrid
Muszyński K, Pulignano V, Domecka M, Mrozowicki A (2021) Coping with precarity during COVID-19: A study of platform work in Poland. Int Labour Rev 161(3):463–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/ilr.12224
Murati E (2021) What are digital platforms? An overview of definitions, typologies, economics, and legal challenges arising from the platform economy in EU. Eur J Priv Law Technol 2021(1):19–55. https://universitypress.unisob.na.it/ojs/index.php/ejplt/article/view/1264/662
Neber H, Anton M (2008) Promoting pre-experimental activities in high-school chemistry: focusing on the role of students’ epistemic questions. Int J Sci Educ 30(13):1801–1821
Nelson T (2018) Unions in digital labour studies: a review of information society and Marxist autonomist approaches. TripleC-Commun Capit 16(2). https://doi.org/10.31269/triplec.v16i2.1065
Page MJ, McKenzie J, Bossuyt PM et al. (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst Rev 10(89):2–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-021-01626-4
Patino A, Naffi N (2023) Lifelong training approaches for the post-pandemic workforces: a systematic review. Int J Lifelong Educ 42(3):249–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/02601370.2023.2214333
Patriotta G (2020) Writing impactful review articles. J Manag Stud 57(6):1272–1276. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12608
Post C, Sarala R, Gatrell C, Prescott E (2020) Advancing theory with review articles. J Manag Stud 57(2):351–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12549
Reuver M, Sørensen C, Basole (2018) The digital platform: a research agenda. J Inf Technol -UK 33(2):124–135. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41265-016-0033-3
Ruiz-Palomino P, Linuesa-Langreo J, Kelly L (2019) Hacia nuevos modelos empresariales más sociales y humanos: El papel de las mujeres en procesos de emprendimiento social y economía de comunión. Empresa y Humanismo 22(2):87–122. https://doi.org/10.15581/015.XXII.2.87-122
Selimović J, Pilav-Velić A, Krndžija L (2021) Digital workplace transformation in the financial service sector: investigating the relationship between employees’ expectations and intentions. Technol Soc 66:101640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101640
Soriano C, Cabanes JV (2020) Entrepreneurial solidarities: social media collectives and Filipino digital platform workers. Soc Media Soc 6(2):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305120926484
Stahlschmidt S, Stephen D (2020) Comparison of Web of Science, Scopus and dimensions databases. KB Forschungspoolprojekt 2020. Available at: https://bibliometrie.info/downloads/DZHW-Comparison-DIM-SCP-WOS.PDF
Stieglitz S, Brachten F, Kissmer T (2018) Defining bots in an enterprise context. International Conference on Interaction Sciences. CIS 2018 Proceedings. 5. https://aisel.aisnet.org/icis2018/impact/Presentations/5
Taylor M, Marsh G, Nicole D, Broadbent P (2017) Good work: the Taylor review of modern working practices. Available via https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/good-work-the-taylor-review-of-modern-working-practices Accessed 03 June 2024
Theres C, Strohmeier S (2023) Consolidating the theoretical foundations of digital human resource management acceptance and use research: a meta-analytic validation of UTAUT. Manag Rev Q https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00367-z
Villajos E, Tordera N, Peiró JM, van Veldhoven M (2019) Refinement and validation of a comprehensive scale for measuring HR practices aimed at performance-enhancement and employee-support. Eur Manag J 37(3):387–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2018.10.003
White M (2012) Digital workplaces: vision and reality. Bus Inf Rev 29(4):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1177/0266382112470412
Download references
Acknowledgements
This paper has been supported by Project PID2021-124641NB-I00 of the Ministry of Science and Innovation (Spain) and by research group in Open Innovation, Universidad Rey Juan Carlos (Spain). Open Access funding enabled and organized by Project V1313 “Sustainability Support”, signed under Article 60 of the LOSU between the Universidad Rey Juan Carlos (Spain) and the company Triple Sustainability SLU to carry out scientific-technical work and training activities.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Universidad Rey Juan Carlos, Madrid, Spain
Laura García-Fernández, Marta Ortiz-de-Urbina-Criado & María-José García-López
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Authors contributed equally to this work, and they jointly supervised this work. Contributors to the concept or design of the article: LGF, MOUC, MJGL. Contributed to analysis and interpretation of data: LGF, MOUC, MJGL. Drafting work or critically revising it for important intellectual content: LGF, MOUC, MJGL. Final approval of the version: LGF, MOUC, MJGL. Agreement to be responsible for all aspects of work: LGF, MOUC, MJGL.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Laura García-Fernández .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
García-Fernández, L., Ortiz-de-Urbina-Criado, M. & García-López, MJ. Mapping the main research themes in digital human resources. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1267 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03795-8
Download citation
Received : 29 May 2023
Accepted : 16 September 2024
Published : 27 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03795-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Human Resource Management Challenges Analytical Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Recommendations, reference list.
Today’s businesses are facing many problems and challenges that relate to human resource management. While the human resource section is the most important arm of any organisation, it is also one of the most challenging areas to manage to ensure maximum productivity.
In recognition of the challenges that face human resource managers and organisations in managing this vital resource, many studies and approaches have been suggested to offer important insights into how organisations can effectively manage the human resource for good productivity and outcomes for the organisations (Caliskan, 2010). Despite the availability of the suggested approaches, implementing them is also a major issue.
Organisations find themselves in major problems and challenges with their human resources. The situation can lead to poor performance, non-attendance, low morale, low job satisfaction, and high rates of turnover that make it difficult for an organisation to achieve its goals (Krishnan & Singh, 2006).
A good example of an organisation that is facing human resource challenges is evident in the new owners of a mining company where there have been higher levels of conflicts that have led to strikes, low productivity, and absenteeism among other problems.
This paper aims at identifying the challenges the organisation is facing and making important strategic human resource management strategies that the organisation should adopt to turn around the current relations between the management and employees.
Major Problems that the Organisation’s Human Resource is Facing
It is evident that the new owners have inherited a myriad of challenges in the human resource from the previous management. This case has greatly affected the company’s ability to achieve its potential in terms of productivity. These challenges must be addressed appropriately to ensure that the organisation can meet its production capacity and financial obligations in the highly competitive sector.
The company is facing major problems in the area of employee motivation and commitment to work. In this case, the high levels of absenteeism and underperformance, which have been witnessed in the company, have greatly hindered its overall performance. Secondly, the company has a limited control and authority over the employees.
Besides causing major rifts between the management and the employees, the situation has led to the establishment of a big divide of employees versus the management. Lastly, the company also lacks elaborate strategies regarding recruitment and selection, training and development, and employees’ welfare.
This gap has led to the formation of informal unionism, which has worked to the disadvantage of the organisation, thus leading to many strikes and industrial actions that are too costly to the organisation. In this case, it is evident that the management must find new strategic human resource management approaches to turn around its current situation into a more robust management and employee performance, which will benefit the organisation and employees.
Key Factors of Consideration in Formulating HRM and ER Strategy for the Company
In the process of formulating a strategic HRM and ER strategy, many factors must be considered to ensure that the adopted strategies give the organisation the best opportunity towards effectiveness, efficiency, and productivity. The first factor of consideration is the organisation or stakeholders’ aims and goals.
According to Nankervis, Baird, Shields, and Coffey (2014), each organisation has its main agenda or a central goal. The company’s main goal is geared towards the production of coal for profit making purposes. Therefore, any issues that are preventing it from achieving this goal must be addressed.
The company’s human resource is the biggest challenge, owing to the low productivity, low morale, and frequent strikes among other challenges that emanate from the employees (Ross & Bamber, 2009). The organisation must review its recruitment and selection strategies to ensure that workers who have the right skills and motivation receive the opportunity to work for the company.
Situational factors also affect the organisation from outside and from within. The Harvard HRM model provides situational factors as a key area of consideration when coming up with a strategic HRM (Zheng, Rolfe & Di Milia, 2007).
Workforce characteristics, labour market, unions, laws and societal values, and task technology among other considerations are very critical in coming up with an elaborate and effective strategic human resource management approaches (Hutchings, De Cieri & Shea, 2011). It is evident that the coal-mining sector is still deeply unionised. Hence, many organisations follow the tenets of the pluralist theory.
The company needs to change the current structures of the informal workers union to ensure that they are registered in a lawful and recognised union as guided by the labour regulations. The third important factor is the human resource policy in place. The role of human resource relations is to ensure the recruitment and retention of highly qualified individuals to guarantee the achievement of the organisation’s goals.
In this case, the role of HR at the organisation has not been well defined. The situation has allowed the thriving of a low performance culture and poorly qualified and trained human resources (Edwards, 2013). The human resource department needs to take its rightful place in ensuring competency, employee motivation, job satisfaction, and high employee discipline (Ross & Bamber, 2009).
For instance, when attracting and retaining highly qualified employees, the organisation must apply specially designed selection strategies that focus on good remuneration and employee safety, which will warrant the recruitment of the best personnel (Zheng et al., 2007). The role of the management is another major factor that the organisation must consider.
In this case, while the management of employees and the approach towards a unionised workforce indicates a move towards pluralist approaches to management, the implementation of better human resource approaches that focus on better employee training and development, safety considerations, and better pay will give the top management more authority and legitimacy over the employees (Bowen & Barry, 2015).
Such authority and mandate will be in line with a unitarist theory and its approaches where power is concentrated on the management (Caliskan, 2010). In this case, it is important for the human resource management to implement the key tenets of its policies to guarantee high discipline requirements and effective recruitment and selection strategies so that employees can remain loyal to the management.
It is evident that the organisation is facing major problems in its human resource management function and hence the need for changes in how the organisation is managed. The main strategic approaches that the organisation will consider will relate to increasing employee motivation and commitment to work.
Further, the organisation will focus on ensuring that it has elaborate HR policies, which will guide the way the organisation will implement the strategies. As guided by the requirements of pluralist approach, ensuring that the organisation advocates a formal, rather than an informal union, will be a move to the right direction.
However, in ensuring more legitimacy and authority of the management, putting in place measures that address employees’ welfare in terms of training, development, and safety will be an important step towards a unitarist approach. The challenges that the organisation will face such as opposition to change, financial implications, and conformity to laws and regulations in the industry will be well addressed using the above approaches.
While a change is inevitable in any organisation, it attracts many challenges, which if not well handled, may derail any progress towards the required changes. At the coal-mining company, the implementation of new HRM strategies will attract various problems and challenges that must be well addressed for success to be achieved.
The first challenge is financial implications of the changes. In this case, while the main goal of the new strategies is to ensure better financial performance in the organisation, the strategies may pose big challenges in the short-term (Ross & Bamber, 2009).
In fact, implementing new training strategies, recruiting new personnel, and terminating unnecessary contracts have immediate financial implications. The organisation needs to understand that while the new strategies have immediate financial implications on the organisation, the organisation will greatly benefit in terms of organisational effectiveness and efficiency, which will lead to better financial gains.
The organisation can also implement the strategies in phases, which will ensure that the financial burden on the organisation is spread over a long duration. According to Mitchell, Obeidat, and Bray (2013), the use of expert strategists and consultants is also an important way of implementing important cost reduction approaches to minimise the overall operations cost.
The second challenge is opposition from the employees who are informally but strongly unionised as evident from the successful strikes and industrial actions that the company has faced. The current suggestion towards ensuring that workers are formally unionised may not go well with the leaders of the informal union at the company.
Such opposition may lead to ‘go-slows’ or other actions that may derail the company’s desire to move towards more effective management approaches. To counter the above challenge, the organisation should form consultative forums with employees and their informal leaders to ensure that they are part of the process and changes that the organisation will undertake.
Bowen, B., & Barry, M. (2015). Recasting industrial relations: Productivity, place and the Queensland coal industry, 2001–2013. Journal of Industrial Relations, 57 (1), 48-71.
Caliskan, N. (2010). The impact of strategic human resource management on organisational performance. Journal of Naval science and engineering, 6 (2), 100-116.
Edwards, M. (2013). Industrial Relations in Mining – A Growing Cost to the Industry in Australia?. Web.
Hutchings, K., De Cieri, H., & Shea, T. (2011). Employee attraction and retention in the Australian resources sector. Journal of Industrial Relations, 53 (1), 83-101.
Krishnan, S., & Singh, M. (2006). Strategic Human Resource Management: Three-Stage Process and Influencing Organisational Factors. Human Resource Management, 1 (1), 1-37.
Mitchell, R., Obeidat, S., & Bray, M. (2013). The Effect of Strategic Human Resource Management on Organisational Performance: The Mediating Role of High-Performance Human Resource Practices. Human Resource Management, 52 (6), 899-921.
Nankervis, A., Baird, M., Shields, J., & Coffey, J. (2014). Human Resource Management: Strategy and Practice . South Melbourne: Cengage Learning.
Ross, P., & Bamber, J. (2009). Strategic choices in pluralist and unitarist employment relations regimes: a study of Australian telecommunications. Industrial & Labour Relations Review, 63 (1), 24-41.
Zheng, C., Rolfe, J., & Di Milia, L. (2007). Strategic human resource management and business performance of the regional coal mining industry in central Queensland. Web.
- Delivering Strategic Human Resource Management
- Using the Three Risks Strategy to Analyze Legal Risks in Human Resource Management
- Concept of Recruitment Model in HRM
- Human Resource Management (HRM) in a Multinational Enterprise
- HRM Practices at Atkins: Training, Development, and Recruitment
- Leadership, Power, and Management
- The Role of Technology in Organization Development
- Information System Management in Organizations
- Journal of Organizational Change Management
- Change Management and Innovation Promotion
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, June 23). Human Resource Management Challenges. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-management-challenges/
"Human Resource Management Challenges." IvyPanda , 23 June 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-management-challenges/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Human Resource Management Challenges'. 23 June.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Human Resource Management Challenges." June 23, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-management-challenges/.
1. IvyPanda . "Human Resource Management Challenges." June 23, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-management-challenges/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Human Resource Management Challenges." June 23, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/human-resource-management-challenges/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .

COMMENTS
Essay # 5. Nature of Human Resource Management: Human Resource Management is a process of bringing people and organizations together so that the goals of each are met. The various features of HRM include: a. It is pervasive in nature as it is present in all enterprises. b. Its focus is on results rather than on rules.
Remember that not every student can write a good essay on human resources without knowledge and information. Therefore, take the time to gather all the information you need to write an essay on human resources. When exploring the potential of an essay on human resources topic, pay attention to the availability of literary sources.
Published: 2021/11/12. Number of words: 1288. Introduction. Human resource management is a sensitive matter that any organization has to take into consideration for all activities and operations to run flawlessly. Companies that ensure employees are well handled are more likely to do better in business as compared to firms that have no regard ...
Introduction. Human Resource Management commonly known as HRM entails the use of human beings in a productive manner to achieve the organizational goals and objectives. Human resources management could be defined as a field of management that is concerned with planning, organizing and controlling the workforce in an organization.
Human resource planning (HRP) enables an organization to better realize its goals by ensuring that it makes efficient and effective use of its human capital. Today's workforce is characteristically ambitious and hence, volatile. Rosenberg (n.d.) reiterates that employees switch careers an approximated three times in their working life.
The human resources actually mean the human capital that represents one of the company's assets (alongside with the physical, financial and intangible ones) (Mathis and Jackson 5). The human capital is viewed in the collection of all capabilities, knowledge, skills, life experience, motivation etc. that employees of a certain organization ...
This essay aims at exploring a portfolio of subjects related to human resource management and reflecting them with the seminar activities. Developing the practitioner In order to maintain a competitive advantage and retention of high quality staff, companies must ensure that training and development of the human resources is given high priority.
Write Human Resources essay in 5 Steps. Human Resources Essay Topics (250) How to Start a Human Resources Essay. #1. #2. Reward Management. Human Resource Development. Equality and Diversity. #3 Top Paints Limited- Human Resource Development and Reward Management.
Here are the principles of a quick, easy essay start: Choose the right topic to simplify the writing process. It should be relevant to your class material, engaging, and new to a certain degree. Expand your existing knowledge instead of trying to explore something entirely new for you. Research the subject extensively.
Students are often asked to write an essay on Human Resources in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on Human Resources The Evolution and Importance of Human Resources.
HRM encompasses a wide range of topics, from recruitment and selection to training and development, performance management, and employee relations. If you are studying HRM or looking for essay topics to explore in this field, here are 105 HRM essay topic ideas and examples to inspire you: The impact of technology on HRM practices.
This page of the essay has 609 words. INTRODUCTION. "Human resources are the energies, knowledge and skills of people which are applicable to the production of goods or rendering useful services. It is the method of measuring and identifying and about human resources and communicating the information to interested persons or parties.".
A human resource paper is written similarly as other kinds of essay, but just with some differences that we will tackle as you read on. To be able to know how to write a human resources essay, you must pick a similar or appropriate subject and then work on it in an objective point of view. Start with the stages of the research. The research stage.
The first factor of good Human Resources essay writing is the proper establishment of the central research question. This is the one that an essay writer should answer during the writing process. In fact, a human resources essay should have a primary argument that you as a writer will try to convey, prove, and evolve for the possible further ...
SHRM builds on the need to create human resource strategies that exhibit capacity to satisfy multiple stakeholders of the organization. In this way, there is always need to create SHRM practices and strategies that address the concerns of key stakeholders in the organization (Schuler and Jackson, 2007). We will write.
The genesis of on human resource management was marked by the need to organize, manage, and oversee the workforce within organizations effectively. This field draws upon various disciplines, including psychology, sociology, and economics, to optimize the employment lifecycle, from recruitment to retirement.
Pages: 10 Words: 3490. Human esources Technology. The Human esource Management within organizations has gained escalation strategic prominence accompanied by the significant of its existing configuration of HM and respective business strategies is well acknowledged (Colomo-Palacio et al., 2012).
Describe the steps in the development of an HRM plan. As addressed in Section 2.1 "Strategic Planning", the writing of an HRM strategic plan should be based on the strategic plans of the organization and of the department. Once the strategic plan is written, the HR professional can begin work on the HR plan. This is different from the ...
Storey (1995) defines that human resource management is an individual approach to employment management which seeks to achieve competitive advantage through the strategic deployment of a highly committed and capable workforce, using an integrated array of cultural, structural and personnel techniques. II. THE ROLE OF HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT.
Disclaimer: This essay is provided as an example of work produced by students studying towards a human resources degree, it is not illustrative of the work produced by our in-house experts.Click here for sample essays written by our professional writers.. Any opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect ...
In your essay on HR, you can write about modern trends in human resource management. For example, you can research the process of conducting interviews. In addition, you can write about how technologies, like AI, are used in employment. Another option is to explain the future of HR according to your vision.
Contents: Essay # 1. Meaning of Human Resources: By the term human resources we mean the size of population of a country along-with its efficiency, educational qualities, productivity, organisational abilities and farsightedness. By human resource we mean human capital. Human capital implies the abilities, skills and technical knowhow among the ...
Then, the aim of this paper is to provide a framework for organizing the main themes discussed in the pioneering literature on digital HR by answering the following research question: What is the ...
Organisations find themselves in major problems and challenges with their human resources. The situation can lead to poor performance, non-attendance, low morale, low job satisfaction, and high rates of turnover that make it difficult for an organisation to achieve its goals (Krishnan & Singh, 2006). A good example of an organisation that is ...