- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 7th Standard CBSE Mathematics question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 7th Standard CBSE Mathematics books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.

7th Standard CBSE Subjects
7th standard cbse study materials.

Study Materials for Other CBSE Board Standards

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 7th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
CBSE Important Questions Class 7 Maths Chapter 1
Home » CBSE » CBSE Important Questions Class 7 Maths Chapter 1

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 – Integers
Mathematics is an important subject that we need in our daily life too. Students must solve questions to clear their concepts and boost their confidence. The first chapter of Class 7 Mathematics under CBSE curriculum is integers.
Quick Links
Students have learned integers in their previous class. In this chapter, they will learn how to put the integers on the number line, their properties, and the addition and multiplication of integers. It is a very important chapter. Students must practice the textbook exercise and questions from other sources to build their concepts.
Extramarks is a leading company that provides a wide range of study materials related to CBSE and NCERT. Our experts have made the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 to help students in regular practice. They collected the questions from different sources such as the textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers and important reference books. They have solved the questions too. Hence, the question series will help students increase their exam marks.
Extramarks is a leading company that helps students by providing all the important study materials related to CBSE and NCERT. You may register on our official website and download these study materials. You will find the CBSE syllabus, NCERT textbooks, CBSE past years’ question papers, CBSE sample papers, CBSE revision notes, CBSE extra questions, NCERT solutions, NCERT important questions, vital formulas and many more.
Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 – With Solutions
The experts of Extramarks have made this question series so that students can solve the questions daily. They collected the questions from the textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers and important reference books. They have included a few questions from the past years’ question papers so that students may have an idea regarding questions in exams. Experienced professionals have further checked the answers to ensure the best quality of the content. Thus, the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 will help students to score better in exams. The questions are-
Question 1. Following number line given below shows the temperature present in degree celsius at different places on a particular day.
Image Source: Internet / NCERT Textbook
(i) Observe the number line and write down the temperature of the places marked on it.
By observing the above number line, we can find out the temperature of the cities as follows,
The temperature in the city of Lahulspiti is -8°C.
The temperature in the city of Srinagar is -2°C
The temperature in the city of Shimla is 5°C.
The temperature in the city of Ooty is 14°C.
The temperature in the city of Bengaluru is 22°C.
(ii) What is the temperature difference between the hottest and the coldest places among the cities stated above?
From the above number line, we can observe that,
The temperature at the given hottest place, that is, Bengaluru, is 22°C.
The temperature at the given coldest place, that is, Lahulspiti, is -8°C
The temperature difference between the hottest and the coldest place is given as = 22°C – (-8°C)
= 22°C + 8°C
= 30° Celsius
Hence, the total temperature difference between the hottest and the coldest place is 30oC.
(iii) What is the temperature difference between the cities of Lahulspiti and Srinagar?
From the above-given number line,
∴The temperature difference between the cities Lahulspiti and Srinagar is = -2oC – (8oC)
= – 2°C + 8°C
(iv) Can we say that the temperature of Srinagar and Shimla taken together is less than the temperature present at Shimla? Is it also less than the temperature present at Srinagar?
The temperature in the city of Srinagar =-2°C
The temperature in the city of Shimla = 5°C
The temperature of the cities Srinagar and Shimla taken together becomes = – 2°C + 5°C
= 3° degree C
5°C > 3°C
Hence, the temperature of the cities Srinagar and Shimla taken together is indeed less than the temperature present at Shimla.
3° > -2°
And No, the temperature of the cities Srinagar and Shimla taken together is not less than the temperature of the city Srinagar.
Question 2. Mohan deposits ₹ 2,000 in his bank account and then withdraws ₹ 1,642 from it the following day. Now, if the withdrawal of the amount from the account is represented by a negative integer, then how will you represent the total amount deposited? Also, Find the balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal.
Withdrawal of these amounts from the account is represented by a negative integer.
Then, the deposit of the amount to the account is represented by a positive integer.
From the above question,
The total amount that is deposited in the bank account by the Mohan = ₹ 2000
The total amount that is withdrawn from the bank account by the Mohan is = – ₹ 1642
Final Balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal = amount deposited + amount is withdrawn
= ₹ 2000 + (-₹ 1642)
= ₹ 2000 – ₹ 1642
Hence, the total balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal is ₹ 358
Question 3. In the following quiz, positive marks are given for every correct answer and negative marks are given for each incorrect answer. If Jack’s scores in the quiz for five successive rounds were 25, – 5, – 10, 10, and 15 so, what was his total at the end?
Jack’s scores in the five successive rounds are 25, -5, -10, 15 and 10
Hence, Their total score of Jack at the end will be = 25 + (-5) + (-10) + 15 + 10
= 25 – 5 – 10 + 15 + 10
∴ Now, Jack’s total score at the end is 35.
Question 4. In the city of Srinagar, temperature was – 5°C on Monday, and then it dropped by two °C on Tuesday. What was the temperature of the city of Srinagar on Tuesday? On Wednesday, the temperature rose by 4°C. What was the temperature on this day?
The temperature on Monday at Srinagar is = -5C
The temperature on Tuesday at the city of Srinagar is dropped by 2C = Temperature on Monday – 2C
= -7 celsius
The temperature on Wednesday at the city Srinagar rose by 4C = Temperature on Tuesday + 4C.
= -3 celsius
Thus, the temperature on days Tuesday and Wednesday was found to be -7C and -3C, respectively.
Question 5. In a magic square, every row, column and diagonal has the same sum. Check which of these following is a magic square.
Firstly we consider the square (i)
Now By adding these numbers in each of the rows, we get,
= 5 + (- 1) + (- 4) equals to 5 – 1 – 4 = 5 – 5 = 0
= -5 + (-2) + 7 equals to – 5 – 2 + 7 = -7 + 7 = 0
= 0 + 3 + (-3) = 3 – 3 = 0
By adding these numbers in every column we receive,
= 5 + (- 5) + 0 is equal to 5 – 5 = 0
= (-1) + (-2) + 3 equals to -1 – 2 + 3 = -3 + 3 = 0
= -4 + 7 + (-3) equals to -4 + 7 – 3 = -7 + 7 = 0
By adding these numbers in diagonals, we receive,
= 5 + (-2) + (-3) is equal to 5 – 2 – 3 = 5 – 5 = 0
= -4 + (-2) + 0 is equal to – 4 – 2 = -6
Because the sum of one diagonal is not always equal to zero,
Hence, (i) is not a magic square.
Now, we should consider the square (ii)
By adding these numbers to each rows we receive,
= 1 + (-10) + 0 is equal to 1 – 10 + 0 = -9
= (-4) + (-3) + (-2) equal to -4 – 3 – 2 = -9
= (-6) + 4 + (-7) becomes equal to -6 + 4 – 7 = -13 + 4 = -9
By adding these numbers in each column we receive,
= 1 + (-4) + (-6) equals to 1 – 4 – 6 = 1 – 10 = -9
= (-10) + (-3) + 4 equals to -10 – 3 + 4 = -13 + 4
= 0 + (-2) + (-7) equals to 0 – 2 – 7 = -9
= 1 + (-3) + (-7) equals to 1 – 3 – 7 = 1 – 10 = -9
= 0 + (-3) + (-6) equal to 0 – 3 – 6 = -9
Hence This (ii) square is a magic square because the sum of each row, each column and the diagonal becomes equal to -9 (negative).
Question 6. Verify a – (– b) is equal to a + b for the following values of alphabets a and b.
(i) a = 21, b = 18
a = 21 and b = 18
So To verify a – (- b) is equal to a + b
Let us take the Left Hand Side (LHS) = a – (- b)
= 21 – (- 18)
Now, lets take Right Hand Side (RHS) = a + b
By comparing both the LHS and the RHS.
Hence, the value of a and b are verified.
(ii) a = 118, b = 125
a = 118 and b = 125
To verify this a – (- b) = a + b
= 118 – (- 125)
= 118 + 125
Now, take the Right Hand Side (RHS) = a + b
By comparing both the LHS and the RHS
Hence, the values of a and b are verified.
(iii) a = 75, b = 84
a = 75 and b = 84
To verify that the a – (- b) = a + b
= 75 – (- 84)
Now, the Right Hand Side (RHS) = a + b
By comparing both LHS and RHS, we find that,
Hence, the value of a and b is verified as.
(iv) a = 28, b = 11
a = 28 and b = 11
To verify that a – (- b) = a + b
Let us now take Left Hand Side (LHS) = a – (- b)
= 28 – (- 11)
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = a + b
Question 7 . A water tank has stepped inside it. A monkey is sitting on the utter topmost step (which is the first step). The water level is present at the ninth step.
(i) He jumps three steps down the stairs and then successively jumps back two steps upwards. In how many jumps will the Monkey reach the following water level?
Let us consider the steps moved down are represented by a positive integer, and then the steps moved up are represented by a negative integer.
Initially, the Monkey is sitting on the topmost step, which is the first step.
In the 1st jump monkey will be at the step = 1 + 3 = 4 steps
In the 2nd jump monkey will be at the step = 4 + (-2) = 4 – 2 = 2 steps
In the 3rd jump monkey will be at the step = 2 + 3 = 5 steps
In the 4th jump monkey will be at the step = 5 + (-2) = 5 – 2 = 3 steps
In the 5th jump monkey will be at the step = 3 + 3 = 6 steps
In the 6th jump monkey will be at the step = 6 + (-2) = 6 – 2 = 4 steps
In the 7th jump monkey will be at the step = 4 + 3 = 7 steps
In the 8th jump monkey will be at the step = 7 + (-2) = 7 – 2 = 5 steps
In the 9th jump monkey will be at the step = 5 + 3 = 8 steps
In the 10th jump monkey will be at the step = 8 + (-2) = 8 – 2 = 6 steps
In the 11th jump monkey will be at the step = 6 + 3 = 9 steps
∴Monkey took a total of 11 jumps (i.e., 9th step) to reach the water level.
(ii) After drinking water, the Monkey wants to go back. For this, the Monkey jumps four steps up and then successively jumps back two steps down in his every move. In how many total jumps will he reach back to the top step?
Let us consider the steps moved down are represented by the positive integers, and then the steps moved up are represented by the negative integers.
Initially, the Monkey is sitting on the ninth step, i.e., at the water level.
In the 1st jump monkey will be at the step = 9 + (-4) = 9 – 4 = 5 steps
In the 2nd jump monkey will be at the step = 5 + 2 = 7 steps
In the 3rd jump monkey will be at the step = 7 + (-4) = 7 – 4 = 3 steps
In the 4th jump monkey will be at the step = 3 + 2 = 5 steps
In the 5th jump monkey will be at the step = 5 + (-4) = 5 – 4 = 1 step
∴ Hence the Monkey took five jumps to reach back to the top step, i.e., the first step.
Question 8. Fill in the blanks to make the following statements true:
(i) (–5) + (– 8) = (– 8) + (…………)
Let us assume that the missing integer is x,
= (–5) + (– 8) which equals to (– 8) + (x)
= – 5 – 8 = – 8 + x
= – 13 = – 8 + x
By sending – 8 from the RHS to the LHS, it becomes 8,
= – 13 + 8 = x
Now substitute the x value in the place of the blank place present,
(–5) + (– 8) = (– 8) + (- 5) … [This following equation is present in the form of the Commutative law of Addition]
(ii) –53 + ………… = –53
= –53 + x = –53
By sending – 53 from the LHS to the RHS, it becomes 53,
= x = -53 + 53
Now substitute the following x value in the blank place,
= –53 + 0 = –53 … [This equation is present in the form of Closure property of Addition]
(iii) 17 + ………… = 0
= 17 + x = 0
By sending 17 from the LHS to the RHS, it becomes -17,
= x = 0 – 17
Now substitute this x value in the blank place,
= 17 + (-17) = 0 … [This equation is present in the form of Closure property of Addition]
= 17 – 17 = 0
(iv) [13 + (– 12)] + (…………) = 13 + [(–12) + (–7)]
= [13 + (– 12)] + (x) = 13 + [(–12) + (–7)]
= [13 – 12] + (x) = 13 + [–12 –7]
= [1] + (x) = 13 + [-19]
= 1 + (x) = 13 – 19
= 1 + (x) = -6
By sending one from the LHS to the RHS, it becomes -1,
= x = -6 – 1
Now substitute the following x value in the blank place value,
= [13 + (– 12)] + (-7) equals to 13 + [(–12) + (–7)] … [This equation is present in the form of the Associative Property of Addition]
(v) (– 4) + [15 + (–3)] equals to [– 4 + 15] +…………
= (– 4) + [15 + (–3)] is equal to [– 4 + 15] + x
= (– 4) + [15 – 3)] equals to [– 4 + 15] + x
= (-4) + [12] = [11] + x
= 8 = 11 + x
Now, By sending 11 from the RHS to the LHS, it becomes -11,
= 8 – 11 = x
Now substitute the x value in the place of the blank place,
= (– 4) + [15 + (–3)] equals to [– 4 + 15] + -3 … [The following equation is in the form of the Associative property of the Addition]
Question 9. Find the product using the suitable properties:
(i) 26 × (– 48) + (– 48) × (–36)
This given equation is in the form of the Distributive law of the Multiplication property over Addition.
= a × (b + c) becomes equal to (a × b) + (a × c)
Let, a = -48, b = 26, c = -36
= 26 × (– 48) + (– 48) × (–36)
= -48 × (26 + (-36)
= -48 × (26 – 36)
= -48 × (-10)
= 480 … [∵ (- × – = +)
(ii) 8 × 53 × (–125)
The given equation is present in the form of the Commutative law of Multiplication.
= a × b = b × a
= 8 × [53 × (-125)]
= 8 × [(-125) × 53]
= [8 × (-125)] × 53
= [-1000] × 53
(iii) 15 × (–25) × (– 4) × (–10)
This given equation is in the form of the Commutative law of the Multiplication property.
= 15 × [(–25) × (– 4)] × (–10)
= 15 × [100] × (–10)
= 15 × [-1000]
(iv) (– 41) × 102
This given equation is in the form of a Distributive law of the Multiplication property over Addition.
= a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
= (-41) × (100 + 2)
= (-41) × 100 + (-41) × 2
= – 4100 – 82
(v) 625 × (–35) + (– 625) × 65
This given equation is in the form of the Distributive law of Multiplication over Addition.
= 625 × [(-35) + (-65)]
= 625 × [-100]
Question 10. A certain freezing process requires that the room temperature be lowered from 40°C at the rate of 5°C every hour. What will be the final room temperature 10 hours after the actual process begins?
Answer 10:-
From the above question, it is given that
Let us take the lowered temperature as a negative integer,
Initial temperature will be= 40oC
Change in temperature per hour is = -5oC
Change in temperature after 10 hours will be = (-5) × 10 = -50oC
∴The final room temperature after the 10 hours of freezing process = 40oC + (-50oC)
Question 11. In a class test containing about ten questions, five marks are awarded for each correct answer and (–2) marks are awarded for every incorrect answer and 0 for questions which are not attempted.
(i) Mohan gets four correct answers and six incorrect answers on his test. What is his total score?
Marks awarded for one correct answer is = 5
The total marks awarded for his four correct answers are = four × 5 = 20 marks.
Marks awarded for 1 wrong answer = -2 (negative)
Total marks awarded for 6 wrong answers is = 6 × -2 = -12
∴Total score obtained by Mohan = 20 + (-12)
(ii) Reshma gets five correct answers and similarly five incorrect answers; what is her total score?
Total marks awarded for 5 correct answer becomes = 5 × 5 = 25
Marks awarded for one wrong answer is = -2
Total marks awarded for 5 wrong answer becomes = 5 × -2 = -10
∴Total score obtained by Reshma is = 25 + (-10)
(iii) Heena gets two correct answers and five incorrect answers out of the seven questions she attempts. What is her final score?
Total marks awarded for 2 correct answer is = 2 × 5 = 10
Marks awarded for the questions which are not attempted is = 0
∴Total score obtained by Heena is = 10 + (-10)
Question 12. A cement company earns a profit of around ₹ 8 per bag of white cement that is sold and simultaneously a loss of ₹ 5 per bag of grey cement that is sold.
(i) The company sells 3,000 bags of white cement and 5,000 bags of grey cement in a month. What is its profit or loss?
We denote profit by a positive integer and loss by a negative integer,
So From the above question,
The Cement company earns a profit on selling one bag of white cement = ₹ 8 per bag.
The cement company earns a total profit on selling 3000 bags of white cement = 3000 × ₹ 8
And also the,
Loss on selling one bag of grey cement is = – ₹ 5 per bag.
Loss on selling the 5000 bags of the grey cement = 5000 × – ₹ 5
= – ₹ 25000
Total loss or profit earned by these cement companies is = profit + loss.
= 24000 + (-25000)
Hence, a loss of ₹ 1000 will be incurred by the company.
(ii) What is the number of white cement bags that must sell to have neither a profit nor loss if the total number of grey bags sold is 6,400 bags?
We denote the profit as a positive integer and the loss as a negative integer,
The cement company earns the profit on selling one bag of white cement as = ₹ 8 per bag.
Now Let the number of white cement bags present be x.
The cement company earns a profit on selling these x bags of white cement as = (x) × ₹ 8
Loss on selling one bag of grey cement becomes = – ₹ 5 per bag.
Loss on selling 6400 bags of grey cement becomes = 6400 × – ₹ 5
= – ₹ 32000
According to the above question,
Company to have neither profit nor loss, must sell,
= Profit + loss = 0
= 8x + (-32000) =0
By sending -32000 from the LHS to the RHS, it becomes 32000
= 8x = 32000
= x = 32000/8
Hence, the 4000 bags of white cement should sell to have neither profit nor loss.
Question 13. Evaluate each of the following:
(i) (–30) ÷ 10
= (–30) ÷ 10
When we divide the negative integer by a positive integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(ii) 50 ÷ (–5)
= (50) ÷ (-5)
When we divide the positive integer by a negative integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then apply the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(iii) (–36) ÷ (–9)
= (-36) ÷ (-9)
When we divide the negative integer by a similar negative integer, we first divide these as whole numbers and then put the positive sign (+) before the quotient.
(iv) (– 49) ÷ (49)
= (–49) ÷ 49
When we divide the negative integer by a positive integer, we first divide these as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(e) 13 ÷ [(–2) + 1]
= 13 ÷ [(–2) + 1]
= 13 ÷ (-1)
When we divide the positive integer by a negative integer, we first divide these as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(f) 0 ÷ (–12)
= 0 ÷ (-12)
When we divide zero by a negative integer, it gives zero.
(g) (–31) ÷ [(–30) + (–1)]
= (–31) ÷ [(–30) + (–1)]
= (-31) ÷ [-30 – 1]
= (-31) ÷ (-31)
When we divide the negative integer by a negative integer, we first divide these as whole numbers and then put the positive sign (+) before the quotient.
(h) [(–36) ÷ 12] ÷ 3
First, we have to solve these integers within the bracket,
= [(–36) ÷ 12]
= (–36) ÷ 12
When we divide a negative integer by a positive integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(i) [(– 6) + 5)] ÷ [(–2) + 1]
The given question can be written as,
= [-1] ÷ [-1]
Question 14. Verify that a ÷ (b + c) is not equal to (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c) for each of the following symbols of a, b and c.
(i) a = 12, b = – 4, c = 2
From the above question, a ÷ (b + c) ≠ (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c)
Given, a = 12, b = – 4 (negative), c = 2
Now, consider that the LHS = a ÷ (b + c)
= 12 ÷ (-4 + 2)
= 12 ÷ (-2)
When we divide a following positive integer by any of the negative integers, we first divide them as a whole number and then put the minus sign (-) before their quotient.
Then, consider that the RHS is equal to = (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c)
= (12 ÷ (-4)) + (12 ÷ 2)
= (-3) + (6)
By comparing the LHS and RHS, we get,
= LHS ≠ RHS
Hence, the given values have been verified.
(ii) a = (–10), b = 1, c = 1
Given, a = (-10), b = 1, c = 1
= (-10) ÷ (1 + 1)
= (-10) ÷ (2)
When we divide a negative integer by any other positive integer, we first divide them as a whole number and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
Then, consider RHS = (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c)
= ((-10) ÷ (1)) + ((-10) ÷ 1)
= (-10) + (-10)
By comparing LHS and RHS
Hence, the given values are verified.
Question. Fill in the following blanks:
(a) 369 ÷ _____ = 369
= 369 ÷ x = 369
= x = (369/369)
Hence, put the valve of x in the blank place.
= 369 ÷ 1 = 369
(b) (–75) ÷ _____ = –1
= (-75) ÷ x = -1
= x = (-75/-1)
Now, put the above valve of x in the blank place.
= (-75) ÷ 75 = -1
(c) (–206) ÷ _____ = 1
= (-206) ÷ x = 1
= x = (-206/1)
= (-206) ÷ (-206) = 1
(d) – 87 ÷ _____ = 87
= (-87) ÷ x = 87
= x = (-87)/87
= (-87) ÷ (-1) = 87
(e) _____ ÷ 1 = – 87
= (x) ÷ 1 = -87
= x = (-87) × 1
So, put the valve of x in the blank.
= (-87) ÷ 1 = -87
(f) _____ ÷ 48 = –1
= (x) ÷ 48 = -1
= x = (-1) × 48
Now, put the above valve of x in the following blank.
= (-48) ÷ 48 = -1
Question 15. The temperature at 12 noon was 10 degrees C above zero. If it decreases at the rate of 2C per hour until midnight, at what time would the temperature be eight °C below zero? Also, What would be the temperature at midnight?
From the above question, it is given that,
The temperature at the beginning, which is, at 12 noon, is = 10C
The rate of change of temperature becomes = – 2C per hour.
Temperature present at 1 PM = 10 + (-2) = 10 – 2 = 8° C
Temperature present at 2 PM = 8 + (-2) = 8 – 2 = 6° C
Temperature present at 3 PM = 6 + (-2) = 6 – 2 = 4°C
Temperature present at 4 PM = 4 + (-2) = 4 – 2 = 2°C
Temperature present at 5 PM = 2 + (-2) = 2 – 2 = 0°C
Temperature present at 6 PM = 0 + (-2) = 0 – 2 = -2°C
Temperature present at 7 PM = -2 + (-2) = -2 -2 = -4°C
Temperature present at 8 PM = -4 + (-2) = -4 – 2 = -6°C
Temperature present at 9 PM = -6 + (-2) = -6 – 2 = -8°C
∴At 9 PM, the temperature will be 8° C below zero.
The temperature at mid-night which is at 12 AM
Change in the temperature in every 12 hours = -2°C × 12 = – 24°C
So, at midnight the temperature will be = 10 + (-24)
At midnight the temperature will be 14°C below 0.
Question 16. In the following class test, (+ 3) marks are given for every correct answer, (–2) marks are given for every the incorrect answer and no marks are given for not attempting any question.
(i) Radhika scored 20 marks. If she has got around 12 correct answers, then how many questions has she attempted that are incorrect?
(ii) Mohini scores –5 (negative) marks on this test, and though she has got seven correct answers. How many questions has she attempted incorrectly?
Marks awarded for 1 correct answer is = + 3
(i) Radhika, in the test, scored 20 marks
Total marks awarded for every 12 correct answers is = 12 × 3 = 36
Marks awarded for every incorrect answer = Total score – Total marks awarded for 12 correct questions.
So, the number of incorrect answers done by Radhika = (-16) ÷ (-2)
(ii) Mohini scored a total of -5 marks
Total marks awarded for her 7 correct answers is = 7 × 3 = 21
Marks awarded for her incorrect answers = Total score – Total marks awarded for the 12 correct answers.
Hence, the number of incorrect answers made by Mohini = (-26) ÷ (-2)
Question 17. An elevator descends down into a mine shaft at the rate of 6 m per min. If the descent starts from 10 meters above the ground level, how much time will it take to reach – 350 m?
The initial height of the elevator becomes = 10 m
Final depth of elevator is = – 350 m … [the distance descended is denoted by a negative integer]
The total distance to descend by the elevator becomes = (-350) – (10)
Time taken by the elevator to descend (negative) -6 m is = 1 min
So, the total time taken by the elevator to descend – 360 m becomes = (-360) ÷ (-60)
= 60 minutes
= 1 hour Benefits of Solving Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1
Practice is the key to success. The practice habit is very important for students because it will help them in many ways. It will help them to score better in exams. Apart from this, practice will clear doubts, generate interest in the subject matter, and strengthen the concepts. Thus, students must practice sums regularly to improve their exam preparation. The Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 will help students in many ways. These are-
- The experts have collated the questions from various sources. They have accumulated the questions from the textbook exercises, CBSE sample papers, CBSE past years’ question papers and important reference books. Thus, students will find all the vital questions In this article, and they can solve the questions regularly. Thus, students don’t have to search for questions in different books, but they will find them here. Thus, Chapter 1, Class 7 Mathematics Important Questions includes all the important concepts.
- The experts have not only collated the questions but also provided the solutions. They have given a step-by-step solution for each chapter to help students. Experienced professionals have further checked the answers. Thus, we have ensured the best quality of content for the students. They can follow the solutions and check their answers with the experts’ answers. So, the Mathematics Class 7 Chapter 1 Important Questions will help students to clarify their doubts, boost their confidence and build their concepts.
- The subject matter experts of Extramarks understand the student’s needs. They have built the question series to help students with their exam preparation. They have collected all the vital questions so students can find them in a single article. Sometimes, students need more than the textbook. Hence, they can follow the Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 Important Questions because they will find chapter-wise questions for each subject. Regular practice will strengthen their ideas, and they can solve any question that comes in exams. Thus, the question series will help them to score better in exams.
Extramarks is a leading company that provides all the important study materials related to CBSE and NCERT. You can download these after registering on our official website. We provide CBSE syllabus, CBSE past years, question papers, CBSE sample papers, NCERT books, NCERT exemplar, NCERT solutions, important questions, CBSE revision notes, CBSE extra questions, vital formulas and many more. Like the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1, you will also find important questions for other chapters. The links to study materials are given below-
- NCERT books
- Important questions
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE past years’ question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 Which one of the following statements is false?
1. For any two positive integers a and b, a ÷ (–b) = – a ÷ b, where b ≠ 0.
2. The commutativity, associativity and distributivity of integers help to make calculations simpler.
3. The product of three integers does not depend upon the grouping of integers.
4. Division is closed for integers.
Option 4. Explanation
Division is not closed for integers. For example: 2 ÷ 6 =
is not an integer.
Q.2 Which one of the following is false?
Marks: 1 1. Sum of integers a and b is an integer.
2. a + b = b + a, for all integers a and b
3. a – b = b – a, for all integers a and b
4. a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c, for all integers a, b and c
Ans Option3 Explanation
a – b = b – a, for all integers a and b is false. For example, 2 – 4 = – 2 and 4 – 2 = 2 Thus, 2 – 4 ≠ 4 – 2
Q.3 What is the difference between a temperature of 7º C above zero and a temperature of 3º C below zero?
Ans Option 1. Explanation
Difference between a temperature of 7º C above zero and a temperature of 3º C below zero = 7º C – (– 3º C) = 7º C + 3º C = 10º C
Q.4 A plane is flying at the height of 8750 m above sea level. At a particular point, it is exactly above a submarine floating 1340 m below sea level. What is the vertical distance between them?
Marks: 2 Ans
Height of the plane above sea level = 8750 m Distance of submarine below sea level = – 1340 m Vertical distance = 8750 m – (– 1340 m) = 8750 m + 1340 m = 10,090 m
Q.5 A man walks 22 m towards east and then 17 m towards west. The position of the man with respect to his starting point is ______________.
1.5 m towards west
2.5 m towards east
3.39 m towards east
4.39 m towards west
Ans Option 2. Explanation

Let 22 m towards east be represented by +22, then –17 m represents 17 m towards west. On adding, +22 – 17 = +5 (positive) The position of the man with respect to his starting point = 5 m towards east
Please register to view this section
Faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. is class 7 mathematics chapter 1 easy.
Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 under CBSE curriculum is about integers. Students will study the properties of integers, how to add and multiply integers and how to put them on the number line. The concepts may be new to them, but they have studied integers in Class 6. They can easily understand the concepts if they follow the textbook seriously. The chapter is relatively easy. Students can take help from the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 to solve questions from the chapter.
2. How can the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 help students?
The experts of Extramarks have made the question series after taking help from several sources. They have collated the questions from the textbook exercise, CBSE sample papers, important reference books and NCERT exemplar. They have included questions from CBSE past years’ question papers too. Apart from this, they have solved the questions for students, and experienced professionals have further checked the answers. Thus, the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 will help the students to practice the sums regularly. It will boost their confidence and increase their marks in exams.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Class 7
- NCERT 7 Maths
- Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers are available here. When students feel stressed about searching for the most comprehensive and detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths , we at BYJU’S have prepared step-by-step solutions with detailed explanations. We advise students who want to score good marks in Maths, to go through these solutions and strengthen their knowledge.
Download Exclusively Curated Chapter Notes for Class 7 Maths Chapter – 1 Integers
Download most important questions for class 7 maths chapter – 1 integers.
Chapter 1 – Integers contains 4 exercises, and the NCERT Solutions available on this page provide solutions to the questions present in the exercises. Now, let us have a look at some of the concepts discussed in this chapter.
- Introduction of Integers
- Properties of Addition and Subtraction of Integers
- Multiplication of Integers
- Multiplication of a Positive and Negative Integer
- Multiplication of Two Negative Integer
- Properties of Multiplication of Integers
- Division of Integers
- Properties of Division of Integers
carouselExampleControls111

Previous Next
Access Exercises of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
Exercise 1.1 Solutions
Exercise 1.2 Solutions
Exercise 1.3 Solutions
Exercise 1.4 Solutions
Access answers to Maths NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Chapter 1 – Integers
Exercise 1.1 Page: 4
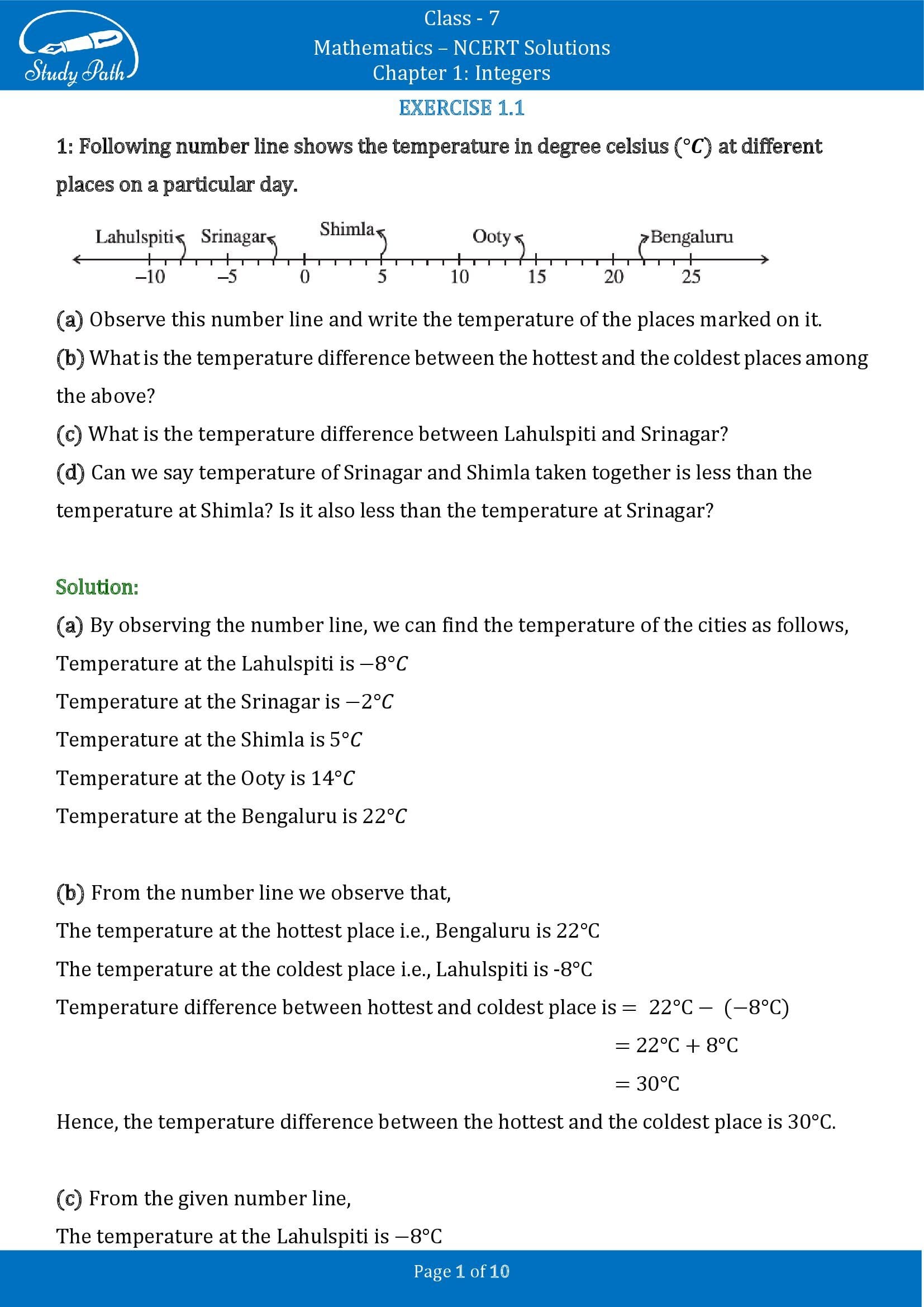
1. Following number line shows the temperature in degree celsius (c o ) at different places on a particular day.

(a) Observe this number line and write the temperature of the places marked on it.
By observing the number line, we can find the temperature of the cities as follows:
The temperature in Lahulspiti is -8 o C
The temperature in Srinagar is -2 o C
The temperature in Shimla is 5 o C
The temperature in Ooty is 14 o C
The temperature in Bengaluru is 22 o C
(b) What is the temperature difference between the hottest and the coldest places among the above?
From the number line, we observe that
The temperature at the hottest place, i.e., Bengaluru, is 22 o C
The temperature at the coldest place, i.e., Lahulspiti, is -8 o C
Temperature difference between hottest and coldest place is = 22 o C – (-8 o C)
= 22 o C + 8 o C
Hence, the temperature difference between the hottest and the coldest place is 30 o C.
(c) What is the temperature difference between Lahulspiti and Srinagar?
From the given number line,
∴ The temperature difference between Lahulspiti and Srinagar is = -2 o C – (8 o C)
= – 2 O C + 8 o C
(d) Can we say the temperature of Srinagar and Shimla, taken together, is less than the
temperature in Shimla? Is it also less than the temperature in Srinagar?
The temperature in Srinagar =-2 o C
The temperature in Shimla = 5 o C
The temperature of Srinagar and Shimla, taken together, is = – 2 o C + 5 o C
∴ 5 o C > 3 o C
So, the temperature of Srinagar and Shimla, taken together, is less than the temperature at Shimla.
3 o > -2 o
No, the temperature of Srinagar and Shimla, taken together, is not less than the temperature of Srinagar.
2. In a quiz, positive marks are given for correct answers and negative marks are given
for incorrect answers. If Jack’s scores in five successive rounds were 25, – 5, – 10,
15 and 10, what was his total at the end?
From the question,
Jack’s score in five successive rounds are 25, -5, -10, 15 and 10
The total score of Jack at the end will be = 25 + (-5) + (-10) + 15 + 10
= 25 – 5 – 10 + 15 + 10
∴ Jack’s total score at the end is 35.
3. At Srinagar temperature was – 5°C on Monday, and then it dropped by 2°C on Tuesday. What was the temperature of Srinagar on Tuesday? On Wednesday, it rose by 4°C. What was the temperature on this day?
The temperature on Monday in Srinagar = -5 o C
The temperature on Tuesday in Srinagar dropped by 2 o C = Temperature on Monday – 2 o C
= -5 o C – 2 o C
The temperature on Wednesday in Srinagar rose by 4 o C = Temperature on Tuesday + 4 o C
= -7 o C + 4 o C
Thus, the temperature on Tuesday and Wednesday was -7 o C and -3 o C, respectively.
4. A plane is flying at the height of 5000 m above sea level. At a particular point, it is exactly above a submarine floating 1200 m below sea level. What is the vertical distance between them?

The plane is flying at a height = 5000 m
Depth of submarine = -1200 m
The vertical distance between plane and submarine = 5000 m – (- 1200) m
= 5000 m + 1200 m
5. Mohan deposits ₹ 2,000 in his bank account and withdraws ₹ 1,642 from it the next day. If the withdrawal of the amount from the account is represented by a negative integer, then how will you represent the amount deposited? Find the balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal.
Withdrawal of the amount from the account is represented by a negative integer.
Then, the deposit of the amount to the account is represented by a positive integer.
Total amount deposited in bank account by the Mohan = ₹ 2000
The total amount withdrawn from the bank account by the Mohan = – ₹ 1642
Balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal = amount deposited + amount withdrawn
= ₹ 2000 + (-₹ 1642)
= ₹ 2000 – ₹ 1642
Hence, the balance in Mohan’s account after the withdrawal is ₹ 358.
6. Rita goes 20 km towards the east from point A to point B. From B, she moves 30 km towards the west along the same road. If the distance towards the east is represented by a positive integer, then how will you represent the distance travelled towards the west? By which integer will you represent her final position from A?

From the question, it is given that
A positive integer represents the distance towards the east.
Then, the distance travelled towards the west will be represented by a negative integer.
Rita travels a distance in the east direction = 20 km
Rita travels a distance in the west direction = – 30 km
∴ Distance travelled from A = 20 + (- 30)
Hence, we will represent the distance travelled by Rita from point A by a negative integer, i.e., – 10 km
7. In a magic square, each row, column and diagonal have the same sum. Check which of the following is a magic square .

First, we consider the square (i)
By adding the numbers in each row, we get
= 5 + (- 1) + (- 4) = 5 – 1 – 4 = 5 – 5 = 0
= -5 + (-2) + 7 = – 5 – 2 + 7 = -7 + 7 = 0
= 0 + 3 + (-3) = 3 – 3 = 0
By adding the numbers in each column, we get
= 5 + (- 5) + 0 = 5 – 5 = 0
= (-1) + (-2) + 3 = -1 – 2 + 3 = -3 + 3 = 0
= -4 + 7 + (-3) = -4 + 7 – 3 = -7 + 7 = 0
By adding the numbers in diagonals, we get
= 5 + (-2) + (-3) = 5 – 2 – 3 = 5 – 5 = 0
= -4 + (-2) + 0 = – 4 – 2 = -6
Because the sum of one diagonal is not equal to zero.
So, (i) is not a magic square
Now, we consider the square (ii)
= 1 + (-10) + 0 = 1 – 10 + 0 = -9
= (-4) + (-3) + (-2) = -4 – 3 – 2 = -9
= (-6) + 4 + (-7) = -6 + 4 – 7 = -13 + 4 = -9
= 1 + (-4) + (-6) = 1 – 4 – 6 = 1 – 10 = -9
= (-10) + (-3) + 4 = -10 – 3 + 4 = -13 + 4
= 0 + (-2) + (-7) = 0 – 2 – 7 = -9
= 1 + (-3) + (-7) = 1 – 3 – 7 = 1 – 10 = -9
= 0 + (-3) + (-6) = 0 – 3 – 6 = -9
(ii) square is a magic square because the sum of each row, each column and the diagonal is equal to -9.
8. Verify a – (– b) = a + b for the following values of a and b.
(i) a = 21, b = 18
a = 21 and b = 18
To verify a – (- b) = a + b
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = a – (- b)
= 21 – (- 18)
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = a + b
By comparing LHS and RHS
Hence, the value of a and b is verified.
(ii) a = 118, b = 125
a = 118 and b = 125
= 118 – (- 125)
= 118 + 125
By comparing LHS and RHS,
(iii) a = 75, b = 84
a = 75 and b = 84
= 75 – (- 84)
(iv) a = 28, b = 11
a = 28 and b = 11
= 28 – (- 11)
9. Use the sign of >, < or = in the box to make the statements true.
(a) (-8) + (-4) [ ] (-8) – (-4)
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = (-8) + (-4)
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = (-8) – (-4)
LHS < RHS
-12 < -4
∴ (-8) + (-4) [<] (-8) – (-4)
(b) (-3) + 7 – (19) [ ] 15 – 8 + (-9)
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = (-3) + 7 – 19
= -3 + 7 – 19
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = 15 – 8 + (-9)
= 15 – 8 – 9
-15 < -2
∴ (-3) + 7 – (19) [<] 15 – 8 + (-9)
(c) 23 – 41 + 11 [ ] 23 – 41 – 11
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = 23 – 41 + 11
= 34 – 41
= – 7
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = 23 – 41 – 11
= 23 – 52
= – 29
LHS > RHS
– 7 > -29
∴ 23 – 41 + 11 [>] 23 – 41 – 11
(d) 39 + (-24) – (15) [ ] 36 + (-52) – (- 36)
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = 39 + (-24) – 15
= 39 – 24 – 15
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = 36 + (-52) – (- 36)
= 36 – 52 + 36
∴ 39 + (-24) – (15) [<] 36 + (-52) – (- 36)
(e) – 231 + 79 + 51 [ ] -399 + 159 + 81
Let us take Left Hand Side (LHS) = – 231 + 79 + 51
= – 231 + 130
Now, Right Hand Side (RHS) = – 399 + 159 + 81
= – 399 + 240
= – 159
-101 > -159
∴ – 231 + 79 + 51 [>] -399 + 159 + 81
10. A water tank has steps inside it. A monkey is sitting on the topmost step (i.e., the first step). The water level is at the ninth step.

(i) He jumps 3 steps down and then jumps back 2 steps up. In how many jumps will he reach the water level?
Let us consider steps moved down are represented by positive integers, and then steps moved up are represented by negative integers.
Initially, the monkey is sitting on the topmost step, i.e., the first step
In 1 st jump, the monkey will be at step = 1 + 3 = 4 steps
In 2 nd jump, the monkey will be at step = 4 + (-2) = 4 – 2 = 2 steps
In 3 rd jump, the monkey will be at step = 2 + 3 = 5 steps
In 4 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 5 + (-2) = 5 – 2 = 3 steps
In 5 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 3 + 3 = 6 steps
In 6 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 6 + (-2) = 6 – 2 = 4 steps
In 7 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 4 + 3 = 7 steps
In 8 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 7 + (-2) = 7 – 2 = 5 steps
In 9 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 5 + 3 = 8 steps
In 10 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 8 + (-2) = 8 – 2 = 6 steps
In 11 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 6 + 3 = 9 steps
∴ The monkey took 11 jumps (i.e., the 9 th step) to reach the water level.
(ii) After drinking water, he wants to go back. For this, he jumps 4 steps up and then jumps back 2 steps down with every move. In how many jumps will he reach back to the top step?
Initially, the monkey is sitting on the ninth step, i.e., at the water level,
In 1 st jump, the monkey will be at step = 9 + (-4) = 9 – 4 = 5 steps
In 2 nd jump, the monkey will be at step = 5 + 2 = 7 steps
In 3 rd jump, the monkey will be at step = 7 + (-4) = 7 – 4 = 3 steps
In 4 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 3 + 2 = 5 steps
In 5 th jump, the monkey will be at step = 5 + (-4) = 5 – 4 = 1 step
∴ The monkey took 5 jumps to reach back to the top step, i.e., the first step.
(iii) If the number of steps moved down is represented by negative integers, and the number of steps moved up by positive integers, represent his moves in parts (i) and (ii) by completing the following: (a) – 3 + 2 – … = – 8 (b) 4 – 2 + … = 8. In (a), the sum (– 8) represents going down by eight steps. So, what will the sum 8 in (b) represent?
The number of steps moved down is represented by negative integers, and the number of steps moved up by positive integers.
Monkey moves in part (i)
= – 3 + 2 – ……….. = – 8
Then, LHS = – 3 + 2 – 3 + 2 – 3 + 2 – 3 + 2 – 3 + 2 – 3
= – 18 + 10
= – 8
∴ Moves in part (i) represent the monkey going down 8 steps because it’s a negative integer.
Monkey moves in part (ii)
= 4 – 2 + ……….. = 8
Then, LHS = 4 – 2 + 4 – 2 + 4
= 12 – 4
∴ Moves in part (ii) represent the monkey going up 8 steps because it’s a positive integer.
Exercise 1.2 Page: 9
1. Write down a pair of integers whose:
(a) sum is -7
= – 4 + (-3)
(b) the difference is – 10
= -25 – (-15)
(c) sum is 0
2. (a) Write a pair of negative integers whose difference gives 8
= (-5) – (- 13)
(b) Write a negative integer and a positive integer whose sum is – 5.
(c) Write a negative integer and a positive integer whose difference is – 3.
Solution :-
= – 2 – (1)
= – 2 – 1
= – 3
3. In a quiz, team A scored – 40, 10, 0 and team B scored 10, 0, – 40 in three successive rounds. Which team scored more? Can we say that we can add integers in any order?
The score of team A = -40, 10, 0
Total score obtained by team A = – 40 + 10 + 0
= – 30
The score of team B = 10, 0, -40
Total score obtained by team B = 10 + 0 + (-40)
= 10 + 0 – 40
Thus, the score of both the A team and B team is the same.
Yes, we can say that we can add integers in any order.
4. Fill in the blanks to make the following statements true.
(i) (–5) + (– 8) = (– 8) + (…………)
Let us assume the missing integer be x,
= (–5) + (– 8) = (– 8) + (x)
= – 5 – 8 = – 8 + x
= – 13 = – 8 + x
By sending – 8 from RHS to LHS, it becomes 8
= – 13 + 8 = x
= x = – 5
Now, substitute the x value in the blank place.
(ii) –53 + ………… = –53
= –53 + x = –53
By sending – 53 from LHS to RHS, it becomes 53
= x = -53 + 53
(iii) 17 + ………… = 0
= 17 + x = 0
By sending 17 from LHS to RHS, it becomes -17
= x = 0 – 17
= x = – 17
= 17 – 17 = 0
(iv) [13 + (– 12)] + (…………) = 13 + [(–12) + (–7)]
= 1 + (x) = 13 – 19
= 1 + (x) = -6
By sending 1 from LHS to RHS, it becomes -1.
= x = -6 – 1
(v) (– 4) + [15 + (–3)] = [– 4 + 15] +…………
Let us assume the missing integer be x.
= (– 4) + [15 + (–3)] = [– 4 + 15] + x
= (– 4) + [15 – 3)] = [– 4 + 15] + x
= (-4) + [12] = [11] + x
= 8 = 11 + x
By sending 11 from RHS to LHS, it becomes -11,
= 8 – 11 = x
Exercise 1.3 Page: 21
1. Find each of the following products:
(a) 3 × (–1)
By the rule of Multiplication of integers,
(b) (–1) × 225
= (-1) × 225
(c) (–21) × (–30)
= (-21) × (-30)
(d) (–316) × (–1)
= (-316) × (-1)
(e) (–15) × 0 × (–18)
= (–15) × 0 × (–18)
∵ If any integer is multiplied by zero, the answer is zero itself.
(f) (–12) × (–11) × (10)
= (–12) × (-11) × (10)
First, multiply the two numbers having the same sign.
(g) 9 × (–3) × (– 6)
= 9 × (-3) × (-6)
(h) (–18) × (–5) × (– 4)
= (-18) × (-5) × (-4)
(i) (–1) × (–2) × (–3) × 4
= – 24
(j) (–3) × (–6) × (–2) × (–1)
= 18 × 2 … [∵ (- × – = +)
2. Verify the following:
(a) 18 × [7 + (–3)] = [18 × 7] + [18 × (–3)]
From the given equation,
Hence, the given equation is verified.
(b) (–21) × [(– 4) + (– 6)] = [(–21) × (– 4)] + [(–21) × (– 6)]
3. (i) For any integer a, what is (–1) × a equal to?
= (-1) × a = -a
When we multiply any integer a with -1, then we get the additive inverse of that integer.
(ii). Determine the integer whose product with (–1) is
Now, multiply -22 with (-1), and we get
= -22 × (-1)
When we multiply integer -22 with -1, then we get the additive inverse of that integer.
Now, multiply 37 with (-1), and we get
= 37 × (-1)
When we multiply integer 37 with -1, then we get the additive inverse of that integer.
Now, multiply 0 by (-1), and we get
Because the product of negative integers and zero gives zero only.
4. Starting from (–1) × 5, write various products showing some pattern to show
(–1) × (–1) = 1.
The various products are,
= -1 × 5 = -5
= -1 × 4 = -4
= -1 × 3 = -3
= -1 × 2 = -2
= -1 × 1 = -1
= -1 × 0 = 0
= -1 × -1 = 1
We concluded that the product of one negative integer and one positive integer is a negative integer. Then, the product of two negative integers is a positive integer.
5. Find the product using suitable properties:
(a) 26 × (– 48) + (– 48) × (–36)
The given equation is in the form of the Distributive Law of Multiplication over Addition.
= a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)
Let, a = -48, b = 26, c = -36
= 26 × (– 48) + (– 48) × (–36)
= -48 × (26 + (-36)
= -48 × (26 – 36)
= -48 × (-10)
= 480 … [∵ (- × – = +)
(b) 8 × 53 × (–125)
The given equation is in the form of the Commutative Law of Multiplication.
= a × b = b × a
= [8 × (-125)] × 53
= [-1000] × 53
= – 53000
(c) 15 × (–25) × (– 4) × (–10)
= 15 × [(–25) × (– 4)] × (–10)
= 15 × [100] × (–10)
= – 15000
(d) (– 41) × 102
= (-41) × (100 + 2)
= (-41) × 100 + (-41) × 2
= – 4100 – 82
= – 4182
(e) 625 × (–35) + (– 625) × 65
= – 62500
(f) 7 × (50 – 2)
The given equation is in the form of the Distributive Law of Multiplication over Subtraction.
= a × (b – c) = (a × b) – (a × c)
= (7 × 50) – (7 × 2)
(g) (–17) × (–29)
(h) (–57) × (–19) + 57
= (57 × 19) + (57 × 1)
6. A certain freezing process requires that room temperature be lowered from 40°C at the rate of 5°C every hour. What will be the room temperature 10 hours after the process begins?
Let us take the lowered temperature as negative.
Initial temperature = 40 o C
Change in temperature per hour = -5 o C
Change in temperature after 10 hours = (-5) × 10 = -50 o C
∴ The final room temperature after 10 hours of freezing process = 40 o C + (-50 o C)
7. In a class test containing 10 questions, 5 marks are awarded for every correct answer and (–2) marks are awarded for every incorrect answer and 0 for questions not attempted.
(i) Mohan gets four correct and six incorrect answers. What is his score?
Marks awarded for 1 correct answer = 5
Total marks awarded for 4 correct answer = 4 × 5 = 20
Marks awarded for 1 wrong answer = -2
Total marks awarded for 6 wrong answer = 6 × -2 = -12
∴ Total score obtained by Mohan = 20 + (-12)
(ii) Reshma gets five correct answers and five incorrect answers; what is her score?
Total marks awarded for 5 correct answer = 5 × 5 = 25
Total marks awarded for 5 wrong answer = 5 × -2 = -10
∴ Total score obtained by Reshma = 25 + (-10)
(iii) Heena gets two correct and five incorrect answers out of seven questions she attempts. What is her score?
Total marks awarded for 2 correct answer = 2 × 5 = 10
Marks awarded for questions not attempted is = 0
∴ Total score obtained by Heena = 10 + (-10)
8. A cement company earns a profit of ₹ 8 per bag of white cement sold and a loss of
₹ 5 per bag of grey cement sold.
(a) The company sells 3,000 bags of white cement and 5,000 bags of grey cement in a month. What is its profit or loss?
We denote profit in a positive integer and loss in a negative integer,
The cement company earns a profit on selling 1 bag of white cement = ₹ 8 per bag
The cement company earns a profit on selling 3000 bags of white cement = 3000 × ₹ 8
Loss on selling 1 bag of grey cement = – ₹ 5 per bag
Loss on selling 5000 bags of grey cement = 5000 × – ₹ 5
= – ₹ 25000
Total loss or profit earned by the cement company = profit + loss
= 24000 + (-25000)
= – ₹1000
Thus, a loss of ₹ 1000 will be incurred by the company.
(b) What is the number of white cement bags it must sell to have neither profit nor loss, if the number of grey bags sold is 6,400 bags?
Let the number of white cement bags be x.
Cement company earns a profit on selling x bags of white cement = (x) × ₹ 8
Loss on selling 6400 bags of grey cement = 6400 × – ₹ 5
= – ₹ 32000
According to the question,
The company must sell to have neither profit nor loss.
= profit + loss = 0
= 8x + (-32000) =0
By sending -32000 from LHS to RHS, it becomes 32000
= 8x = 32000
= x = 32000/8
Hence, the 4000 bags of white cement have neither profit nor loss.
9. Replace the blank with an integer to make it a true statement.
(a) (–3) × _____ = 27
= (–3) × (x) = 27
= x = – (27/3)
Let us substitute the value of x in the place of blank,
(b) 5 × _____ = –35
= (5) × (x) = -35
= x = – (-35/5)
Let us substitute the value of x in the place of the blank.
(c) _____ × (– 8) = –56
= (x) × (-8) = -56
= x = (-56/-8)
(d) _____ × (–12) = 132
= (x) × (-12) = 132
= x = – (132/12)
= x = – 11
Exercise 1.4 Page: 26
1. Evaluate each of the following.
(a) (–30) ÷ 10
= (–30) ÷ 10
When we divide a negative integer by a positive integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(b) 50 ÷ (–5)
= (50) ÷ (-5)
= – 10
When we divide a positive integer by a negative integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put the minus sign (-) before the quotient.
(c) (–36) ÷ (–9)
= (-36) ÷ (-9)
When we divide a negative integer by a negative integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put the positive sign (+) before the quotient.
(d) (– 49) ÷ (49)
= (–49) ÷ 49
= – 1
(e) 13 ÷ [(–2) + 1]
= 13 ÷ (-1)
= – 13
(f) 0 ÷ (–12)
= 0 ÷ (-12)
When we divide zero by a negative integer, it gives zero.
(g) (–31) ÷ [(–30) + (–1)]
= (-31) ÷ (-31)
(h) [(–36) ÷ 12] ÷ 3
First, we have to solve the integers within the bracket.
= (–36) ÷ 12
(i) [(– 6) + 5)] ÷ [(–2) + 1]
The given question can be written as,
2. Verify that a ÷ (b + c) ≠ (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c) for each of the following values of a, b and c.
(a) a = 12, b = – 4, c = 2
From the question, a ÷ (b + c) ≠ (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c)
Given, a = 12, b = – 4, c = 2
Now, consider LHS = a ÷ (b + c)
= 12 ÷ (-4 + 2)
= 12 ÷ (-2)
Then, consider RHS = (a ÷ b) + (a ÷ c)
= (12 ÷ (-4)) + (12 ÷ 2)
= (-3) + (6)
= LHS ≠ RHS
Hence, the given values are verified.
(b) a = (–10), b = 1, c = 1
Given, a = (-10), b = 1, c = 1
= (-10) ÷ (1 + 1)
= (-10) ÷ (2)
= ((-10) ÷ (1)) + ((-10) ÷ 1)
= (-10) + (-10)
3. Fill in the blanks:
(a) 369 ÷ _____ = 369
= 369 ÷ x = 369
= x = (369/369)
Now, put the valve of x in the blank.
= 369 ÷ 1 = 369
(b) (–75) ÷ _____ = –1
= (-75) ÷ x = -1
= x = (-75/-1)
= (-75) ÷ 75 = -1
(c) (–206) ÷ _____ = 1
= (-206) ÷ x = 1
= x = (-206/1)
= (-206) ÷ (-206) = 1
(d) – 87 ÷ _____ = 87
= (-87) ÷ x = 87
= x = (-87)/87
= (-87) ÷ (-1) = 87
(e) _____ ÷ 1 = – 87
= (x) ÷ 1 = -87
= x = (-87) × 1
= (-87) ÷ 1 = -87
(f) _____ ÷ 48 = –1
= (x) ÷ 48 = -1
= x = (-1) × 48
= (-48) ÷ 48 = -1
(g) 20 ÷ _____ = –2
= 20 ÷ x = -2
= x = (20)/ (-2)
= (20) ÷ (-10) = -2
(h) _____ ÷ (4) = –3
= (x) ÷ 4 = -3
= x = (-3) × 4
= (-12) ÷ 4 = -3
4. Write five pairs of integers (a, b) such that a ÷ b = –3. One such pair is (6, –2) because 6 ÷ (–2) = (–3).
(i) (15, -5)
Because, 15 ÷ (–5) = (–3)
(ii) (-15, 5)
Because, (-15) ÷ (5) = (–3)
(iii) (18, -6)
Because, 18 ÷ (–6) = (–3)
(iv) (-18, 6)
Because, (-18) ÷ 6 = (–3)
(v) (21, -7)
Because, 21 ÷ (–7) = (–3)
5. The temperature at 12 noon was 10 o C above zero. If it decreases at the rate of 2 o C per hour until midnight, at what time would the temperature be 8°C below zero? What would be the temperature at midnight?
From the question, it is given,
The temperature at the beginning, i.e., at 12 noon = 10 o C
Rate of change of temperature = – 2 o C per hour
Temperature at 1 PM = 10 + (-2) = 10 – 2 = 8 o C
Temperature at 2 PM = 8 + (-2) = 8 – 2 = 6 o C
Temperature at 3 PM = 6 + (-2) = 6 – 2 = 4 o C
Temperature at 4 PM = 4 + (-2) = 4 – 2 = 2 o C
Temperature at 5 PM = 2 + (-2) = 2 – 2 = 0 o C
Temperature at 6 PM = 0 + (-2) = 0 – 2 = -2 o C
Temperature at 7 PM = -2 + (-2) = -2 -2 = -4 o C
Temperature at 8 PM = -4 + (-2) = -4 – 2 = -6 o C
Temperature at 9 PM = -6 + (-2) = -6 – 2 = -8 o C
∴ At 9 PM, the temperature will be 8 o C below zero.
The temperature at midnight, i.e., at 12 AM
Change in temperature in 12 hours = -2 o C × 12 = – 24 o C
So, at midnight temperature will be = 10 + (-24)
= – 14 o C
So, at midnight, the temperature will be 14 o C below 0.
6. In a class test, (+ 3) marks are given for every correct answer and (–2) marks are given for every incorrect answer and no marks for not attempting any question. (i) Radhika scored 20 marks. If she has got 12 correct answers, how many questions has she attempted incorrectly? (ii) Mohini scored –5 marks on this test, though she got 7 correct answers. How many questions has she attempted incorrectly?
Marks awarded for 1 correct answer = + 3
(i) Radhika scored 20 marks.
Total marks awarded for 12 correct answers = 12 × 3 = 36
Marks awarded for incorrect answers = Total score – Total marks awarded for 12 correct
= – 16
So, the number of incorrect answers made by Radhika = (-16) ÷ (-2)
(ii) Mohini scored -5 marks.
Total marks awarded for 7 correct answers = 7 × 3 = 21
= – 5 – 21
= – 26
So, the number of incorrect answers made by Mohini = (-26) ÷ (-2)
7. An elevator descends into a mine shaft at the rate of 6 m/min. If the descent starts from 10 m above the ground level, how long will it take to reach – 350 m?
The initial height of the elevator = 10 m
The final depth of the elevator = – 350 m … [∵distance descended is denoted by a negative
The total distance to descended by the elevator = (-350) – (10)
= – 360 m
Time taken by the elevator to descend -6 m = 1 min
So, the time taken by the elevator to descend – 360 m = (-360) ÷ (-6)
= 60 minutes
Disclaimer:
Dropped Topics – Introduction, Recall, 1.4.3 Product of three or more negative numbers and 1.5.7 Making multiplication easier.
Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1
Where can i get the accurate solution for ncert solution for class 7 maths chapter 1, is it necessary to solve each problem provided in the ncert solution for class 7 maths chapter 1, list out the concepts covered in ncert solution for class 7 maths chapter 1., leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Thank you🙏🌹🌹❤
Thanks a lot
It is very helpful for us thank you
Thanks it helped me out ☺️☺️
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 6 – 10, 12 for Maths, Science, SST
Cbse case study questions for maths, science, social science.
CBSE Case Study Questions: Case Study Questions for all Class 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11 and 12 by Experienced Teachers. We Net Ex. Arranged here Important Case Based Questions for CBSE Board – Maths, Science, Social Science, English.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, maharashtra board class 4 english chapter 21 flint solution, dav class 5 math solution chapter 4 fractional numbers, sikkim scert class 4 english chapter 6b weather is full of the nicest sounds solution, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 6 – celebrating independence day.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers are provided below. Our solutions covered each questions of the chapter and explains every concept with a clarified explanation. It helps the students to understand slowly and to get practice well to become perfect and again a good score in their examination. Below we have listed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Exercise 1.1, Ex 1.2, Ex 1.3 and Ex 1.4.
These materials are prepared based on Class 7 NCERT syllabus, taking the types of questions asked in the NCERT textbook into consideration. Further, all the CBSE Class 7 Solutions Maths Chapter 1 Integers are in accordance with the latest CBSE guidelines and marking schemes
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.2

NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.3

NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Ex 1.4

Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Textbook Solutions
Chapter 1 Integers has 4 exercises, and the NCERT Solutions available on this page provide solutions to the questions present in the exercises. Now, let us have a look at some of the concepts discussed in this chapter.
- Introduction of Integers
- Properties of Addition and Subtraction of Integers
- Multiplication of Integers
- Multiplication of a Positive and Negative Integer
- Multiplication of two Negative Integer
- Properties of Multiplication of Integers
- Division of Integers
- Properties of Division of Integers
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers and Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Try These Solutions in Hindi and English Medium modified and updated for academic year 2024-25. According to new syllabus and latest textbooks for new session 2024-25, there are only three exercises in chapter 1 of class 7th mathematics.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Solutions in English Medium
- Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Try These
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.1 in English
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.2 in English
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.3 in English
Practicing math concepts like integers from Class 7 can be very beneficial for understanding and mastering the topic. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to effectively practice Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Try These Integers. Preparing Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 (Integers) NCERT solutions involves a structured approach to understanding the concepts, solving problems, and creating clear explanations for students. Pay attention to definitions, examples, and the types of problems presented.
| Class: 7 | Mathematics |
| Chapter 1: | Integers |
| Number of Exercises: | 3 (Three) |
| Content: | NCERT Exercise Solutions |
| Mode: | Text, Images and Videos Format |
| Academic Session: | 2024-25 |
| Medium: | English and Hindi Medium |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Solutions in Hindi Medium
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.1 in Hindi
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.2 in Hindi
- Class 7 Maths Exercise 1.3 in Hindi
- Class 7 Maths Chaper 1 in Videos
- Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 7 Maths Solutions Page
- Class 7 all Subjects Solutions
Make sure you have a clear understanding of the basic concepts of integers, including positive and negative numbers, number line, absolute value, and addition/subtraction of integers. Integers are the central focus of this chapter. Make sure you have a clear understanding of what integers are, how they are represented on a number line, and their properties. Break down the chapter into key concepts and topics. These may include positive and negative integers, addition and subtraction of integers, and properties of integers. Read through the chapter in your textbook. Pay close attention to explanations, examples, and any solved problems.
Work through the practice exercises provided in the NCERT textbook. Solve the problems step by step to ensure you understand the process. Write down the step-by-step solutions for each type of problem. Make sure to explain each step clearly, addressing any potential difficulties students might face. Integers can be represented on a number line. Include diagrams and number lines to visually explain concepts, especially when discussing positive and negative integers.
Integers have real-life applications, like representing temperature, bank balances, and distances. Include relatable examples to help students connect the concept to their daily experiences. Anticipate common mistakes students might make and provide explanations to help them avoid these errors. Include a variety of problems, from basic to more complex, to challenge students’ understanding and problem-solving skills. Integers have certain rules for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Note down these rules for quick reference.

7th Maths Exercise 1.1, Exercise 1.2 and Exercise 1.3 in English Medium and Prashnavali 1.1, Prashnavali 1.2 and Prashnavali 1.3 in Hindi Medium free to download in PDF format for new academic session. CBSE NCERT (https://ncert.nic.in/) Solution are given in simplified format. Videos related to each exercises are also given for better understanding. You can use NCERT solutions 2024-25 online or download in PDF file format without any login or password. Class 7 Maths solutions apps for online as well as offline use are also given free to download. Regular practice is key to mastering any math topic. Dedicate a specific amount of time each day for practicing integer-related problems. In videos, all the questions are described using proper properties of integers. The language of description is kept easy so that everyone can understand easily. For any inconvenience, contact us for help.
NCERT Solutions App for Class 7

Review your solutions for accuracy, clarity, and coherence. Ensure your explanations are in line with the language and understanding of Class 7 students. Begin with easy problems and gradually move on to more complex ones. This will help you build confidence and progressively develop your skills. Format your solutions in a clear and organized manner. Use appropriate fonts, spacing, and headings to make the solutions easy to read. Proofread your solutions for any grammatical or typographical errors. Well-presented solutions enhance the learning experience.
If relevant, provide additional notes or tips for teachers and parents to assist them in explaining concepts effectively to students. Test your solutions with a few students or educators to get feedback. This helps ensure that your solutions are clear and understandable. Remember that the goal is to make Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers NCERT solutions accessible, comprehensive, and engaging for students. Work through the example problems given in your textbook. These problems are designed to illustrate the concepts discussed in the chapter. The solutions should help students grasp the concepts, develop problem-solving skills, and build a strong foundation in mathematics.
NCERT Books for class 7 and CBSE Solutions 2024-25 for other subjects are also available for free download. We have prepared the Solutions in the simplified format so that students can understand easily. Look for additional practice worksheets, online resources, or apps that offer integer-related problems. Many educational websites and apps provide interactive quizzes and exercises. Invent your own integer problems based on real-life scenarios or mathematical concepts. Solving self-created problems can deepen your understanding of the subject. Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 solutions are given below in Hindi and English Medium.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Important Questions
At srinagar temperature was c on monday and then it dropped by c on tuesday. what was the temperature of srinagar on tuesday on wednesday, it rose by c. what was the temperature on this day.
On Monday, temperature at Srinagar = –5 oC On Tuesday, temperature dropped = 2 oC Temperature on Tuesday = –5 oC – 2 oC = –7 oC On Wednesday, temperature rose up = 4oC Temperature on Wednesday = –7 oC + 4 oC = –3 oC Thus, temperature on Tuesday and Wednesday was –7 oC and –3 oC respectively.
A plane is flying at the height of 5000 m above the sea level. At a particular point, it is exactly above a submarine floating 1200 m below the sea level. What is the vertical distance between them?
Height of a place above the sea level = 5000 m Floating a submarine below the sea level = 1200 m The vertical distance between the plane and the submarine = 5000 + 1200 = 6200 m Thus, the vertical distance between the plane and the submarine is 6200 m.
Mohan deposits ₹2,000 in his bank account and withdraws ₹1,642 from it, the next day. If withdrawal of amount from the account is represented by a negative integer, then how will you represent the amount deposited? Find the balance in Mohan’s accounts after the withdrawal?
Deposit amount = ₹2,000 and Withdrawal amount = ₹1,642 Balance = 2,000 – 1,642 = ₹358 Thus, the balance in Mohan’s account after withdrawal is ₹ 358.
A certain freezing process requires that room temperature be lowered from 40 oC at the rate of 5 oC every hour. What will be the room temperature 10 hours after the process begins?
Given: Present room temperature = 40 oC Decreasing the temperature every hour = 5 oC Room temperature after 10 hours = 40 oC + 10 x (–5 oC ) = 40 oC – 50 oC = – 10 oC Thus, the room temperature after 10 hours is – 10 oC after the process begins.
A cement company earns a profit of ₹8 per bag of white cement sold and a loss of ₹ 5 per bag of grey cement sold. The company sells 3,000 bags of white cement and 5,000 bags of grey cement in a month. What is its profit or loss?
Given: Profit of 1 bag of white cement = ₹ 8 And Loss of 1 bag of grey cement = ₹ 5 Profit on selling 3000 bags of white cement = 3000 x ₹ 8 = ₹ 24,000 Loss of selling 5000 bags of grey cement = 5000 x ₹ 5 = ₹ 25,000 Since Profit < Loss Therefore, his total loss on selling the grey cement bags = Loss – Profit = ₹ 25,000 – ₹ 24,000 = ₹ 1,000 Thus, he has lost of `₹1,000 on selling the grey cement bags.
Practice problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of integers. Try these word problems and puzzles that require application of integer concepts. Challenge yourself with more complex problems that require critical thinking and a deep understanding of the concepts. This will help you refine your problem-solving skills.
After solving problems, review your answers. Correcting mistakes is an important part of the learning process. If you’re facing difficulties, don’t hesitate to discuss the problems with your classmates, teacher, or parents. Sometimes, a different perspective can clarify things. Don’t overexert yourself. Take short breaks during your practice sessions to keep your mind fresh and focused.
In 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 Integers, we will explore all the operations based on integer properties. Properties of integers on the operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Take mock tests or create a set of problems to test your understanding. Timed tests can help you practice solving problems under pressure. Schedule regular revision sessions to reinforce your understanding. Revise the concepts, rules, and formulas to keep them fresh in your mind. Remember, consistent practice and a positive attitude towards learning are key factors in succeeding in math. Don’t get discouraged by challenges; instead, view them as opportunities to improve. We have to learn about all the properties like closure, commutative, associative, etc. Integers are Closure under Addition but not under subtraction.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Important Questions for Practice
1. When we divide a positive integer by a negative integer, we first divide them as whole numbers and then put a minus sign (–) before the quotient. That is, we get a negative integer. 2. The product of three integers does not depend upon the grouping of integers and this is called the associative property for multiplication of integers. 3. When we divide a negative integer by a positive integer, we divide them as whole numbers and then put a minus sign (–) before the quotient. We, thus, get a negative integer. 4. Addition is associative for integers, i.e., (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) for all integers a, b and c. 5. Integer 0 is the identity under addition. That is, a + 0 = 0 + a = a for every integer a.
We have prepared Hindi Medium NCERT Solutions for class 7 Maths on the demand of students. Now it is online on website to view online as well as for download. Time to time we modify our website on the basis of student’s suggestions. That is why Class 7 Maths App in English or Kaksha 7 Ganit App in Hindi Medium are developed for offline use.
How many exercises, questions, and examples are there in chapter 1 of class 7th Maths?
According to new syllabus and latest textbooks for session 2024-25, there are three exercises in chapter 1 (Integers) of class 7th Maths. In the first exercise (Ex 1.1), there are 4 questions. Question 1 has three parts, question 2 has three parts, and question 4 has five parts. In the second exercise (Ex 1.2), there are 9 questions. Question 2 has two parts, question 3 has two parts, and question 5 has eight parts. In the third exercise (Ex 1.3), there are seven questions. Question 1 has nine parts, and question 2 has two parts. So, there are in all 20 questions in chapter 1 (Integers) of class 7th Maths. There is a total of 5 examples in chapter 1 (Integers) of class 7th Maths.
What will students study in chapter 1 of class 7th Maths?
In chapter 1 of class 7th Maths, students will study: 1. Properties of integers. 2. Addition and Subtraction of integers. 3. Statement Questions- Addition. 4. Multiplication of integers. 5. Distributive law in integers. 6. Statement Questions- Multiplication. 7. Division of Integers. 8. Statement Questions- Division.
Is chapter 1 of class 7th Maths difficult?
Chapter 1 of class 7th Maths is not easy and not difficult. It lies in the mid of easy and difficult because some parts of this chapter are easy, and some parts are difficult. But, the difficulty level of any chapter varies from child to child. So, Chapter 1 of class 7th Maths is easy or not depends on children also. Some children find it tough, some find it simple, and some find it in the middle of simple and tough.
How much time, students need to do chapter 1 of class 7th Maths?
Students need a maximum of 7-9 days to do chapter 1 of class 7th Maths if they give at least 1-2 hours per day to this chapter. This time is an approximate time. This time can vary because no students have the same working speed, same efficiency, same capability, etc.

Chapter 2: Fractions and Decimals »
Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
Revision Notes on Integers
A whole number, from zero to positive or negative infinity is called Integers . I.e. it is a set of numbers which include zero, positive natural numbers and negative natural numbers. It is denoted by letter Z.
Z = {…,-2,-1, 0, 1, 2…}
Integers on Number Line
On the number line, for positive integers we move to the right from zero and for negative integers move to the left of zero.

Facts about how to Add and Subtract Integers on the Number Line
1. If we add a positive integer, we go to the right.

2. If we add a negative integer, we go to the left.

3. If we subtract a positive integer, we go to the left.

4. If we subtract a negative integer, we go to the right.

The Additive Inverse of an Integer
The negative of any number is the additive inverse of that number.
The additive inverse of 5 is (- 5) and additive inverse of (- 5) is 5.

This shows that the number which we add to a number to get zero is the additive inverse of that number.
| 5 | - 5 |
| 14 | - 14 |
| - 10 | 10 |
| - 6 | 6 |
Properties of Addition and Subtraction of Integers
1. closure under addition.
For the closure property the sum of two integers must be an integer then it will be closed under addition.
2+ (-3) = -1
(-2) + 3 = 1
(-2) + (-3) = -5
As you can see that the addition of two integers will always be an integer, hence integers are closed under addition.
If we have two integers p and q, p + q is an integer.
2. Closure under Subtraction
If the difference between two integers is also an integer then it is said to be closed under subtraction.
7 – 2 = 5
7 – (- 2) = 9
- 7 – 2 = – 9
- 7 – (- 2) = – 5
As you can see that the subtraction of two integers will always be an integer, hence integers are closed under subtraction .
For any two integers p and q, p - q is an integer .
3. Commutative Property
a. If we change the order of the integers while adding then also the result is the same then it is said that addition is commutative for integers .
For any two integers p and q
p + q = q + p
23 + (-30) = – 7
(-30) + 23 = – 7
There is no difference in answer after changing the order of the numbers.
b. If we change the order of the integers while subtracting then the result is not the same so subtraction is not commutative for integers .
p – q ≠ q – p will not always equal.
23 - (-30) = 53
(-30) - 23 = -53
The answer is different after changing the order of the numbers.
4. Associative Property
If we change the grouping of the integers while adding in case of more than two integers and the result is same then we will call it that addition is associative for integers.
For any three integers, p, q and r
p + (q + r) = (p + q) + r
If there are three integers 3, 4 and 1 and we change the grouping of numbers, then

The result remains the same. Hence, addition is associative for integers.
5. Additive Identity
If we add zero to an integer, we get the same integer as the answer. So zero is an additive identity for integers .
For any integer p,
p + 0 = 0 + p =p
(-7) + 0 = (-7)
Multiplication of Integers
Multiplication of two integers is the repeated addition.
3 × (-2) = three times (-2) = (-2) + (-2) + (-2) = – 6
3 × 2 = three times 2 = 2 + 2 + 2 = 6

Now let’s see how to do the multiplication of integers without the number line.
1. Multiplication of a Positive Integer and a Negative Integer
To multiply a positive integer with a negative integer, we can multiply them as a whole number and then put the negative sign before their product.
So the product of a negative and a positive integer will always be a negative integer.
For two integers p and q,
P × (-q) = (-p) × q = - (p × q) = - pq.
4 × (-10) = (- 4) × 10 = - (4 × 10) = - 40

2. Multiplication of Two Negative Integers
To multiply two negative integers, we can multiply them as a whole number and then put the positive sign before their product.
Hence, if we multiply two negative integers then the result will always be a positive integer.
For two integers p and q,
(-p) × (-q) = (-p) × (-q) = p × q
(-10) × (-3) = 30
3. The Product of Three or More Negative Integers
It depends upon the number of negative integers.
a. If we multiply two negative integers then their product will be positive integer
(-3) × (-7) = 21
b. If we multiply three negative integers then their product will be negative integer
(-3) × (-7) × (-10) = -210
If we multiply four negative integers then their product will be positive integer
(-3) × (-7) × (-10) × (-2) = 420
Hence, if the number of negative integers is even then the result will be a positive integer and if the number of negative integers is odd then the result will be a negative integer .
Properties of Multiplication of Integers
1. closure under multiplication.
In case of multiplication, the product of two integers is always integer so integers are closed under multiplication.
For all the integers p and q
p×q = r, where r is an integer
(12) × (-4) = -48
2. Commutativity of Multiplication
If we change the order of the integers while multiplying then also the result will remain the same then it is said that multiplication is commutative for integers.
p × q = q × p
20 × (-30) = – 600
(-30) × 20 = – 600
3. Multiplication by Zero
If we multiply an integer with zero then the result will always be zero.
p × 0 = 0 × p = 0
9 × 0 = 0 × 9 = 0
0 × (-15) = 0
4. Multiplicative Identity
If we multiply an integer with 1 then the result will always the same as the integer.
For any integer q
q × 1 = 1 × q = q
21 × 1 = 1 × 21 = 21
1 × (-15) = (-15)
5. Associative Property
If we change the grouping of the integers while multiplying in case of more than two integers and the result remains the same then it is said the associative property for multiplication of integers.
p × (q × r) = (p × q) × r
If there are three integers 2, 3 and 4 and we change the grouping of numbers, then

The result remains the same. Hence, multiplication is associative for integers .
6. Distributive Property
a. Distributivity of Multiplication over Addition .
For any integers a, b and c
a × (b + c) = (a × b) + (a × c)

Solve the following by distributive property.
I. 35 × (10 + 2) = 35 × 10 + 35 × 2
II. (– 4) × [(–2) + 7] = (– 4) × 5 = – 20 And
= [(– 4) × (–2)] + [(– 4) × 7]
= 8 + (–28)
= –20
So, (– 4) × [(–2) + 7] = [(– 4) × (–2)] + [(– 4) × 7]
b. Distributivity of multiplication over subtraction
a × (b – c) = (a × b) – (a × c)
5 × (3 – 8) = 5 × (- 5) = – 25
5 × 3 – 5 × 8 = 15 – 40 = – 25
So, 4 × (3 – 8) = 4 × 3 – 4 × 8.
Division of integers
1. division of a negative integer by a positive integer.
The division is the inverse of multiplication. So, like multiplication, we can divide them as a whole number and then place a negative sign prior to the result. Hence the answer will be in the form of a negative integer.
For any integers p and q,
( – p) ÷ q = p ÷ (- q) = - (p ÷ q) where, q ≠ 0.
64 ÷ (- 8) = – 8
2. Division of Two Negative Integers
To divide two negative integers, we can divide them as a whole number and then put the positive sign before the result.
The division of two negative integers will always be a positive integer.
(- p) ÷ (- q) = (-p) ÷ (- q) = p ÷ q where q ≠ 0
(-10) ÷ (- 2) = 5
Properties of Division of Integers
For any integers p, q and r
| Closure Property | p ÷ q is not always an integer | 10 ÷ 5 = 2 | The division is not closed under division. |
| Commutative Property | p ÷ q ≠ q ÷ p | 10 ÷ 5 = 2 | The division is not commutative for integer. |
| Division by Zero | p ÷ 0 = not defined | 0 ÷ 10 = 0 | No |
| Division Identity | p ÷ 1 = p | 10 ÷ 1 = 10 | Yes |
| Associative Property | (p ÷ q) ÷ r ≠ p ÷ (q ÷ r) | [(–16) ÷ 4] ÷ (–2) ≠ | Division is not Associative for integers. |
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution
Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free


Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Revision Notes on Simple Equations Algebraic...
Revision Notes on Fractions and Decimals Fractions...
Revision Notes on Practical Geometry Line segment...
Revision Notes on Comparing Quantities Ratios The...
Revision Notes on Congruence of Triangles...
Revision Notes on Rational Numbers Natural Numbers...
Revision Notes on Visualising Solid Shapes Plane...
Revision Notes on Data Handling Data Any raw...
Revision Notes on Lines and Angles Point A point...
Revision Notes on Exponents and Powers...
Revision Notes on Perimeter and Area Perimeter It...
Revision Notes on The Triangle and its Properties...
Revision Notes on Algebraic Expressions Algebraic...
Revision Notes on Symmetry Symmetry If two or more...

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 7th Maths 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
Class 7th Maths Question Bank for 2023 Exams includes new aptitude-based questions which will cover the full syllabus in 2022 -23 Board Exams.
These competency-based practice question resources are most recommended by experts for the comprehensive chapter-wise practice of these moderate to high difficulty questions.
Here, you can find chapter-wise self practice paper solutions and solutions in PDF form. These PDFs are absolutely free to download.
| 1. Integers | |
| 2. Fractions and Decimals | |
| 3. Data Handling | |
| 4. Simple Equations | |
| 5. Lines and Angles | |
| 6. The Triangle and its Properties | |
| 7. Congruency in Triangles | |
| 8. Comparing Quantities | |
| 9. Rational Numbers | |
| 10. Practical Geometry | |
| 11. Perimeter and Area | |
| 12. Algebraic Expressions | |
| 13. Exponents and Power | |
| 14. Symmetry | |
| 15. Visualising Solid Shapes |
CBSE Class 7 Study Material

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 7th English 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 4 January, 2023, 6:42 pm
- CBSE Class 7th Science 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 2 January, 2023, 6:21 pm
- CBSE Class 7th Maths 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF 30 December, 2022, 3:59 pm
- CBSE Class 7th Mathematics 2023 : Competency-Based Practice Question Sets with Answers; Download PDF 29 December, 2022, 1:36 pm
- CBSE Class 7th Science 2023 : Competency-Based Practice Question Sets with Answers; Download PDF 26 December, 2022, 4:15 pm
- CBSE Class 7th : All Subject Syllabus 2020-2021 29 August, 2020, 8:16 pm
- Class 7th Science : Foundation & Olympiad Explorer 28 May, 2020, 8:56 pm

CBSE Class 7th English 2023 : Chapter-wise Competency-Based Test Items with Answers; Download PDF

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
Ncert solutions for class 7 maths chapter 1 integers| pdf download.

- Exercise 1.1 Chapter 1 Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 1.2 Chapter 1 Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 1.3 Chapter 1 Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions
- Exercise 1.4 Chapter 1 Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapters:
How many exercises are there in Chapter 1 Integers Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions?
Evaluate: (a) (–1) × (–2) × (–3) × (–4) × (–5), find 2 consecutive numbers whose sum is 129., what is associative property of integers, contact form.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths comprises solutions and analysis of all NCERT textbook sums based on triangles, area, and perimeter of different shapes, data handling, integers, etc. These class 7 maths NCERT solutions are prepared by math geniuses to cater to students of all intelligence levels. Thus, helping CBSE students to develop auxiliary skills and mathematical acumen.
NCERT solutions class 7 maths are extremely helpful for students preparing for home as well as competitive exams. These solutions provide an opportunity for students to develop a robust understanding of mathematics in grade 7. CBSE NCERT solutions for class 7 maths can also be referred to by students belonging to a different board who want to have ironclad mathematical concepts.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for class 7 maths are explained using the best and most precise techniques. These chapter-wise analysis of questions are available for free pdf download. Depending on whatever topic you are studying, the links to all the solutions are given below.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 to 15
| Download NCERT Solutions of Class 7 Maths Chapter-wise PDF | |
|---|---|
To ensure that you are well-versed with all topics at the time of an examination, it is imperative to revisit the solutions periodically. These class 7 maths NCERT solutions aid students in developing a better understanding of the topic at hand. You can download the NCERT textbook given below and find exemplary questions on fractions, solid shapes, triangles, and so on.
☛ Download Class 7 Maths NCERT Book
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 1 integers teach young minds how to work with number lines while performing mathematical operations on signed integers. The most important concepts falling under this chapter are the properties of arithmetic operations such as the addition of two numbers.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 1 Exercises |
|---|
| - 10 Questions - 4 Questions - 9 Questions - 7 Questions |
Important Formulas:
- Commutative Property: a + b = b + a; a × b = b × a
- Associative Property: (a + b) + c = a + (b + c); (a × b) × c = a × (b × c)
- Distributive Property: a × (b + c) = a × b + a × c
- Multiplicative Identity: 1 × a = a × 1 = a
- Additive Identity: a + 0 = 0 + a = a
Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
Topics Covered: Class 7 maths NCERT solutions cover problem sums on integer operations, closure property, commutative property, distributive property, associativity, and additive identity. It also encompasses the multiplication and division of two or more signed integers. The chapter has a total of 30 questions out of which 12 are easy, 8 are moderate and 10 are difficult.
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 2
NCERT solutions class 7 maths chapter 2 fractions and decimals are designed to understand the different categories of fractions and how to work with them. Students are further taught the methods of multiplying fractions and dividing fractions . The succeeding sections deal with decimals and performing arithmetic operations on them.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 2 Exercises |
|---|
| - 8 Questions - 8 Questions - 8 Questions - 4 Questions - 9 Questions - 5 Questions - 6 Questions |
Chapter 2 Preparation Tips:
NCERT solutions class 7 maths chapter 2 fractions and decimals form the basis for several sister topics hence, students need to build a strong understanding of this topic. For this purpose, they can follow the given tips to streamline their studying process.
- Try to apply the concepts to daily-life problems.
- Revise theories taught in previous grades.
- Regularly practice questions.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals
Topics Covered: Multiplication and division of fractions by various kinds of numbers such as fractions or whole numbers, along with simplifying fractions to their lowest form fall under this chapter. Other important topics include comparing decimals, multiplication, and division of decimals as well as associated word problems.
Total Questions: Chapter 2 has 48 questions in total which are categorized as 23 easy sums, 17 medium level, and 8 tough problems.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3
Class 7 maths NCERT solutions chapter 3 data handling teach students how to organize data before performing computations on it and graphically representing it. Arithmetic mean , range, mode, and median are measures of central tendency that students have the opportunity to learn from these solutions.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Exercises |
|---|
| - 9 Questions - 5 Questions - 6 Questions - 4 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 3 Data Handling
Topics Covered: Determining the arithmetic mean, range, mode, median are the major statistical topics covered under class 7 maths NCERT solutions . Furthermore, the representation of data using bar graphs and double bar graphs is also included in this chapter.
Total Questions: There are 24 questions in class 7 maths chapter 3 data handling out of which 5 are simple problems, 15 are of moderate difficulty and 4 are tough.
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 3 provides a bird’s eye view of how to collect and organize data using tables. It also aids students in understanding the tools required to perform computations on data, presenting it in a graphical format, and drawing conclusions from it.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 4
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 4 simple equations give an insight into how to interpret statements, convert them into the form of an equation, and subsequently solve it. Thus, students get a good idea of how to apply simple equations to practical situations.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 4 Exercises |
|---|
| - 6 Questions - 4 Questions - 4 Questions - 4 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 4 Simple Equations
Topics Covered: Converting a statement to an equation, finding the value of an equation by addition and subtraction on both sides, or transposing terms and corresponding word problems fall under the scope of class 7 maths NCERT solutions. The chapter has 18 questions with 6 long answer type sums, 5 medium, and 7 easy problems.
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 5
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 5 lines and angles introduce young minds to the formation of different types of angles and their properties, the intersection of lines and the pairs of angles formed as well as the relationship between such angles.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 5 Exercises |
|---|
| - 14 Questions - 6 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Lines and Angles
Topics Covered: Identifying complementary angles , supplementary angles , adjacent angles , linear pairs, and vertically opposite angles . Furthermore, transversal and pairs of lines are essential topics within this chapter. It consists of 20 questions. 3 are easy, 9 are long answer-type and 8 are moderately challenging problems.
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 5 Summary:
The chapter gives a quick recap of line segments, ray, and a line. This chapter also teaches students about transversals, categorizes the different types of angles, and gives a relationship among these angles.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 6
Class 7 maths NCERT solutions chapter 6 the triangle and its properties give students an in-depth knowledge of the elements of a triangle. It presents students with the important angle sum property of a triangle and the Pythagoras theorem . Moreover, this chapter also includes an explanation of the isosceles and equilateral triangles .
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 Exercises |
|---|
| - 3 Questions - 2 Questions - 2 Questions - 6 Questions - 8 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 6 Triangle and its Properties
Topics Covered: Drawing the median and altitude of triangles, determining the exterior angles, and finding the value of unknown angles using the angle sum property. Finally, topics associated with equilateral, isosceles, and right-angled triangle is also covered in this chapter.
Total Questions: Class 7 maths chapter 6 has 21 well-research sums that can be split into 4 tough problems, 9 moderately complex, and 8 easy questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 7
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 7 congruence of triangles starts with giving an introduction to the meaning of congruence between any two figures. Besides this, the chapter discusses the different criteria of congruence between triangles and how to apply them effectively.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 7 Exercises |
|---|
| - 4 Questions - 10 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles
Topics Covered: The congruence of triangles using SSS, SAS, ASA, and RHS criteria is the most important topic covered in this chapter. The chapter has 14 questions. 9 are simple sums based on the congruence theorems, 2 are moderately tough and 3 are complex problems.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8
Class 7 maths NCERT solutions chapter 8 comparing quantities give students the tools required to draw comparisons between two or more quantities and make inferences about them using equivalent ratios . This chapter also includes various concepts based on percentages and how to apply them to real-life problems.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 8 Exercises |
|---|
| - 3 Questions - 10 Questions - 11 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 8 Comparing Quantities
Topics Covered: Using equivalent ratios to determine the value of unknown quantities, converting fractional numbers and decimals to percentages , finding the percent increase or percent decrease , as well as profit and loss and annual interest questions.
Total Questions: Students can find a total of 24 questions in class 7 maths chapter 8 comparing quantities out of which 8 are effortless, 5 are of medium level and 11 require a certain degree of skill from a student. Studying NCERT solutions class 7 maths chapter 8 students will be adept at dealing with converting ratios to percentages, computing interest, and using different mechanisms to compare quantities.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 9
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 9 rational numbers establish a foundation for the concept of rational numbers. Students have the opportunity to learn about the representation of rationals on a number line , comparison, and reduction of rationals to their standard form, plus performing operations on rational numbers.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 9 Exercises |
|---|
| - 10 Questions - 4 Questions |
NCERT solutions class 7 maths chapter 9 can be best learned by following the tips given below.
- Revising concepts of HCF and LCM from previous classes for reduction of rationals to the standard form.
- Improving calculation speed by regular practice so as to power through questions based on arithmetic operations
Class 7 Maths Chapter 9 Rational Numbers
Topics Covered: Finding rationals between two rational numbers, number line representation and comparison of rationals, as well as multiplying, dividing, adding, and subtracting rational numbers. A set of 14 questions comprise chapter 9 rational numbers. 5 are fairly straightforward, 7 are intermediate, and 2 are difficult problems.
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths Chapter 10
NCERT solutions class 7 chapter 10 maths practical geometry edifies students on how to properly use geometrical instruments to construct transversals and parallel lines . Additionally, building triangles using the SSS, SAS, ASA, and RHS criteria are also part of this chapter.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 10 Exercises |
|---|
| - 3 Questions - 4 Questions - 3 Questions - 3 Questions - 3 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 10 Practical Geometry
Topics Covered: Class 7 maths NCERT solutions incorporate vital topics such as constructing parallel lines and the transversals through them, as well as using the constraints given by the SSS, SAS, ASA, and RHS criteria to construct triangles . Chapter 10 practical geometry has 16 sums on the construction of figures out of which 7 are straightforward questions, 5 are complex and 4 are medium level.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 11
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 11 perimeter and area educate on the steps required to find the area and perimeter of 2D shapes using different parameters. Moreover, students are given a step-wise explanation on how to employ these concepts while solving word problems.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 11 Exercises |
|---|
| - 8 Questions - 8 Questions - 17 Questions - 11 Questions |
- Perimeter of a square = 4 × side
- Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 × (length + breadth)
- Area of a square = side × side
- Area of a rectangle = length × breadth
- Area of a parallelogram = base × height
- Area of a triangle = ½ × base × height
- Circumference of a circle = 2πr
- Area of a circle = πr2
Class 7 Maths Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area
Topics Covered: Determining the area and perimeter of squares , rectangles , triangles, parallelograms , and circles . This chapter also covers converting units and applying the concepts mentioned above to real-life problems.
Total Questions: Chapter 11 perimeter and area has 44 well-curated questions. 18 are straightforward formula-based sums, 20 are of moderate complexity, and 6 high-level problems.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 12
Class 7 maths NCERT solutions chapter 12 algebraic expressions give an idea of what an expression means and the components that make up an algebraic expression. Students can use these solutions to grasp concepts such as solving polynomials , categorizing, and performing arithmetic operations on them.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 12 Exercises |
|---|
| - 7 Questions - 6 Questions - 10 Questions - 2 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions
Topics Covered: Using algebra formulas to find their value, along with performing addition and subtraction on general expressions of algebra . The chapter consists of 25 sums with 8 simple questions, 10 are slightly tougher and 7 complex problems.
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 12 covers a plethora of concepts such as the types of polynomials , addition, and subtraction of like terms as well as finding the value of given algebraic identities .
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 13
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 13 exponents and powers describe how to convert an exponent into a number and vice versa. These solutions give the procedure of using laws of exponents and applying them to problems. In addition to this, using exponents to express large numbers is also detailed in this chapter.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 13 Exercises |
|---|
| - 8 Questions - 5 Questions - 4 Questions |
Class 7 Maths Chapter 13 Exponents and Powers
Topics Covered: Expressing a number in the form of an exponent, various exponentiation laws, and showing how very large or small numbers can be converted into a standard form using exponents. Chapter 13 exponents and powers cover a total of 17 exemplar problems that be divided into 6 easy sums based on the laws, 7 are challenging and 4 are medium-level questions.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 14
NCERT solutions class 7 maths chapter 14 symmetry provides students with the best possible explanation of concepts related to symmetry such as line of symmetry, rotational symmetry, and how to use them to create designs in our day-to-day lives.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 14 Exercises |
|---|
| - 10 Questions - 2 Questions - 7 Questions |
Topics Covered: Questions based on lines of symmetry, identifying rotational symmetry, and a combination of these topics forms a part of class 7 maths NCERT solutions.
Total Questions: Chapter 14 symmetry has a total of 19 sums. 4 are long answer types, 10 are moderately difficult and 5 are simple problems.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 15 visualizing solid shapes help students instill the foundation required in higher grades to solve sister topics such as mensuration. It teaches students how to identify the different elements of a solid figure.
| Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 15 Exercises |
|---|
| - 5 Questions - 5 Questions - 1 Question - 3 Questions |
NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 15 is of great use especially in the upcoming classes. Students can follow the tips given below to enhance their learning.
- Try to apply the methods used in the textbook to real-life objects.
- Solve numerous questions for practice to develop a strong understanding of the subject.
Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 Visualising Solid Shapes
Topics Covered: Identifying nets with their corresponding solids, isometric and oblique sketches as well as viewing different sections of a solid using various techniques.
Total Questions: Chapter 15 visualizing solid shapes has 14 well-researched questions. 9 are very simple, 3 are slightly difficult while 2 are complex sums.
Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions Important Formulas
Formulas are some of the most important expressions in mathematics as they serve to increase the speed and accuracy of solving questions. It gives a concise way of conveying vital information using symbolic representations. Thus, students need to understand and memorize several formulas to successfully solve problems. The important formulas covered in NCERT solutions for class 7 maths are listed below .
Proportion Formulas:
- Addition: a/b + c/d = (ad + bc)/bd
- Subtraction: a/b - c/d = (ad - bc)/bd
- Area of Circle = πr 2
- Area of Rectangle = l × b
- Simple Interest, S.I = PTR/100, where P = Principal amount, T = Time, R = Rate of interest per annum
Importance of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
Class 7 Maths NCERT solutions are extremely helpful for CBSE students as they get an overview of the best techniques that can be used to solve any NCERT questions. The benefits of NCERT solutions for class 7th maths are given below:
- Exam Preparation: During examination days it becomes very difficult for students to solve every question. As every sum is equally important students need a quick run-through of all problems. NCERT solutions for class 7 maths are the perfect way to achieve this goal. They provide a step-wise and detailed analysis of all problems. Students can skim through them and do a quick revision on how to solve each question.
- Time-management: As there are a lot of chapters that are encompassed in the class 7th syllabus hence, students must manage their time well. These class 7 maths NCERT solutions help in completing the coursework well within the given limit. It also leaves enough time for revision.
- Solving Doubts: Many times when a student is attempting a textbook sum he might not be able to solve it completely. This could be due to a careless mistake or a shaky concept. NCERT solutions class 7th maths are precise and well explained thus, clearing any doubts that a student might have.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
Why are ncert solutions for class 7 maths important.
Young minds need to have reliable guides while studying the class 7 maths syllabus. The NCERT solutions for class 7 maths provide an excellent way to accomplish this goal. Students can not only cross-check their answers but also build a sound understanding of the subject. Students can use these well-researched class 7 maths NCERT solutions to improve their foundational knowledge of class 7 mathematics.
How Students can Utilize Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions?
To get the most out of the class 7 maths NCERT solutions it is advisable to first ensure that the student understands the theoretical concepts properly. Only after they build their knowledge base consisting of the important theories and formulas for that topic they should proceed to use these NCERT solutions class 7 maths and attempt problems.
Do I Need to Practice all Questions Provided in NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths?
Every topic within the scope of mathematics is interlinked. Thus, students must practice every question in the NCERT solutions class 7 maths to ensure that there is no gap in learning. The best results can only be obtained through due diligence and constant revision.
Do I Need to Make Notes while Referring to NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths?
Students make notes to remember certain points related to a question of concept. Thus, while revising NCERT solutions for class 7 maths students can use these as references and speed up the learning process. Thus, it is always recommended to consult your notes while studying.
Where Can I Get Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths?
Students have full access to easy-to-use exercise-wise NCERT solutions for class 7 maths in the links mentioned above. Moreover, these pdfs are free to download and are compatible with mobile screens.
What are the Important Topics Covered in Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions?
While learning a subject like math, as a thumb rule, no chapter should be skipped. Thus, all topics within the lessons covered by class 7 maths NCERT solutions are equally important. It is necessary to be well-versed with all topics to score the best possible marks in any examination.
Can We Use Different Methods to Solve Problems Apart From Those Mentioned in NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths?
Students are free to follow any method apart from the ones used in the NCERT solutions class 7 maths. However, they need to be universally recognized and simple tricks used to solve questions in competitive exams cannot be used.
Why Should I Practice NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Regularly?
The only way to master a subject is by practicing it regularly. Similarly, students should practice NCERT solutions class 7 maths routinely as it helps them stay in touch with the subject. This ensures that students do not forget any concept. Additionally, it also helps students to memorize math formulas easily.
What are the Benefits of NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths for CBSE Students?
NCERT solutions Class 7 maths help CBSE students to prepare for their exams as the syllabus is based on the NCERT textbooks. Apart from this, these solutions instill a deep-seated knowledge of the subject and help students clear their doubts immediately if they hit a roadblock while solving some problems.
Why Choose Cuemath for Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions?
Cuemath is the best website available for class 7 Maths NCERT solutions as they have been hand-picked and prepared by math experts such as IITians. These math wizards do proper research to find the most precise and accurate method to solve any question. A student is sure to excel in any exam by using these solutions as references.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers
- Last modified on: 12 months ago
- Reading Time: 7 Minutes

Here in this article, we are providing case study questions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers.
Maths Class 7 Chapter List
Latest chapter list (2023-24).
There is total 13 chapters.
Chapter 1 Integers Case Study Questions Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Case Study Questions Chapter 3 Data Handling Case Study Questions Chapter 4 Simple Equations Case Study Questions Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Case Study Questions Chapter 6 The Triangles and its Properties Case Study Questions Chapter 7 Comparing Quantities Case Study Questions Chapter 8 Rational Numbers Case Study Questions Chapter 9 Perimeter and Area Case Study Questions Chapter 10 Algebraic Expressions Case Study Questions Chapter 11 Exponents and Powers Case Study Questions Chapter 12 Symmetry Case Study Questions Chapter 13 Visualising Solid Shapes Case Study Questions
Old Chapter List
Chapter 1 Integers Chapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Chapter 3 Data Handling Chapter 4 Simple Equations Chapter 5 Lines and Angles Chapter 6 The Triangles and its Properties Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles Chapter 8 Comparing Quantities Chapter 9 Rational Numbers Chapter 10 Practical Geometry Chapter 11 Perimeter and Area Chapter 12 Algebraic Expressions Chapter 13 Exponents and Powers Chapter 14 Symmetry Chapter 15 Visualising Solid Shapes
Deleted Chapter:
- Chapter 7 Congruence of Triangles
- Chapter 10 Practical Geometry
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths in Exam

1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution.
2. Relevance Identification: Pinpoint pertinent mathematical concepts applicable to the case study. By doing so, you can streamline your thinking process and apply appropriate methods with precision.
3. Deconstruction of the Problem: Break down the complex problem into manageable components or steps. This approach enhances clarity and facilitates organized problem-solving.
4. Highlighting Key Data: Emphasize critical information and data supplied within the case study. This practice aids quick referencing during the problem-solving process.
5. Application of Formulas: Leverage pertinent mathematical formulas, theorems, and principles to solve the case study. Accuracy in formula selection and unit usage is paramount.
6. Transparent Workflow Display: Document your solution with transparency, showcasing intermediate calculations and steps taken. This not only helps track progress but also offers insight into your analytical process.
7. Variable Labeling and Definition: For introduced variables or unknowns, offer clear labels and definitions. This eliminates ambiguity and reinforces a structured solution approach.
8. Step Explanation: Accompany each step with an explanatory note. This reinforces your grasp of concepts and demonstrates effective application.
9. Realistic Application: When the case study pertains to real-world scenarios, infuse practical reasoning and logic into your solution. This ensures alignment with real-life implications.
10. Thorough Answer Review: Post-solving, meticulously review your answer for accuracy and coherence. Assess its compatibility with the case study’s context.
11. Solution Recap: Before submission, revisit your solution to guarantee comprehensive coverage of the problem and a well-organized response.
12. Previous Case Study Practice: Boost your confidence by practicing with past case study questions from exams or textbooks. This familiarity enhances your readiness for the question format.
13. Efficient Time Management: Strategically allocate time for each case study question based on its complexity and the overall exam duration.
14. Maintain Composure and Confidence: Approach questions with poise and self-assurance. Your preparation equips you to conquer the challenges presented.
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths cased study question bank for chapter 1 - real numbers is available here. this question bank is very useful to prepare for the class 10 maths exam 2021-2022..

The Central Board of Secondary Education has introduced the case study questions in class 10 exam pattern 2021-2022. The CBSE Class 10 questions papers of Board Exam 2022 will have questions based on case study. Therefore, students should get familiarised with these questions to do well in their board exam.
We have provided here case study questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers. These questions have been published by the CBSE board itself. Students must solve all these questions at the same time they finish with the chapter - Real numbers.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 - Real Numbers
To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of your friends to set up a class library. There are two sections- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students in section A and 36 students in section B.

1. What is the minimum number of books you will acquire for the class library, so that they can be distributed equally among students of Section A or Section B?
Answer: c) 288
2. If the product of two positive integers is equal to the product of their HCF and LCM is true then, the HCF (32 , 36) is
Answer: b) 4
3. 36 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 2 × 3 2
b) 2 1 × 3 3
c) 2 3 × 3 1
d) 2 0 × 3 0
Answer: a) 2 2 × 3 2
4. 7 × 11 × 13 × 15 + 15 is a
a) Prime number
b) Composite number
c) Neither prime nor composite
d) None of the above
Answer: b) Composite number
5. If p and q are positive integers such that p = ab 2 and q= a 2 b, where a , b are prime numbers, then the LCM (p, q) is
Answer: b) a 2 b 2
CASE STUDY 2:
A seminar is being conducted by an Educational Organisation, where the participants will be educators of different subjects. The number of participants in Hindi, English and Mathematics are 60, 84 and 108 respectively.

1. In each room the same number of participants are to be seated and all of them being in the same subject, hence maximum number participants that can accommodated in each room are
Answer: b) 12
2. What is the minimum number of rooms required during the event?
Answer: d) 21
3. The LCM of 60, 84 and 108 is
Answer: a) 3780
4. The product of HCF and LCM of 60,84 and 108 is
Answer: d) 45360
5. 108 can be expressed as a product of its primes as
a) 2 3 × 3 2
b) 2 3 × 3 3
c) 2 2 × 3 2
d) 2 2 × 3 3
Answer: d) 2 2 × 3 3
CASE STUDY 3:
A Mathematics Exhibition is being conducted in your School and one of your friends is making a model of a factor tree. He has some difficulty and asks for your help in completing a quiz for the audience.
Observe the following factor tree and answer the following:
1. What will be the value of x?
Answer: b) 13915
2. What will be the value of y?
Answer: c) 11
3. What will be the value of z?
Answer: b) 23
4. According to Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic 13915 is a
a) Composite number
b) Prime number
d) Even number
Answer: a) Composite number
5. The prime factorisation of 13915 is
a) 5 × 11 3 × 13 2
b) 5 × 11 3 × 23 2
c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
d) 5 × 11 2 × 13 2
Answer: c) 5 × 11 2 × 23
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- India Post GDS Merit List 2024
- NDA Question Paper 2024
- RBI Grade B Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Admit Card 2024
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Question Paper 2024 PDF
- CDS Question Paper 2024
- UP Police Exam Analysis 2024 Live Updates
- Sri Krishna
- Janmashtami Wishes in Hindi
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
Brain Teaser: Which Line is Longer? Only 1% Geniuses Answer It Correctly In 6 Seconds!
NDA 2 Answer Key 2024: Download Unofficial Maths and GAT Solutions
Today’s School Assembly News Headlines (2nd September): Heavy rains lash Andhra Pradesh, Telangana; train services disrupted, schools closed, First Vande Bharat Prototype Sleeper Train Unveiled
MJPRU Result 2024 OUT: यहां देखें MSc, BA, BCom, MBA, MA,BSc, BTech, BCA, MCom सहित अन्य UG, PG Annual & Semester मार्कशीट PDF
Find 3 differences between the farmer and his cow pictures in 16 seconds!
NDA 2 Question Paper 2024: Download Maths and GAT Set Wise Paper PDF Here
NDA Exam Analysis 2024: Check Today's Maths & GAT Paper Review, Difficulty Level, Good Attempts, and Questions Asked
CDS Exam Analysis 2024: Check Today's GK, Maths and English Paper Difficulty Level, Good Attempts
CDS Question Paper 2024: Download Set Wise English, Maths, GK Papers PDF Here
उत्तर प्रदेश के 8 रेलवे स्टेशनों को मिले नए नाम, यहां देखें नई लिस्ट
India's First Vande Bharat Sleeper Train: पहली वंदे भारत स्लीपर ट्रेन कब और किसी रूट पर दौड़ेगी? जानें
Vande Bharat Trains: वंदे भारत ट्रेन नेटवर्क में आते है उत्तर प्रदेश के कितने शहर? पढ़ें सबके नाम
You Can Score High In Exam: Weekly Current Affairs Quiz 27 Aug to 01 Sep 2024
Visual Skill Test: Find the odd emoji out in the picture in 4 seconds!
CDS Answer Key 2024: Download Maths, GK, English, Paper SET A, B, C, D PDF (Unofficial)
National Teachers Award 2024: ये हैं देश के सर्वश्रेष्ठ शिक्षक, जिन्हें मिलेगा राष्ट्रीय पुरस्कार
यह है भारत की सबसे लंबी बस यात्रा, जानें
Upcoming Government Jobs 2024 LIVE: Employment News (Aug 31-Sept 06) 2024, Notifications, Admit Card and much more
Word Search Puzzle: Only true heroes can find the word “hero” in 5 seconds!
ट्रेन का टिकट खोने या फटने पर क्या करें, यहां पढ़ें
- Algebraic Expressions and Identities Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 8

Last Updated on August 25, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 8 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 8 Algebraic Expressions and Identities. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths Series.
| Algebraic Expressions and Identities | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 8 | |
| Maths | |
| Class 8 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Algebraic Expressions and Identities
A playground is in shape of a square. The area of the square PQRS is 256 m 2 with each side (x + 2) m. One day Suraj along with his two friends Ajay and Aman went to play there with bicycle. Someone stole Suraj bicycle, but Ajay and Aman helped him by contributing ₹(4a + 60) and ₹(6a + 10) respectively, to buy a new bicycle. The cost of bicycle was ₹4200.
On basis of this information given in passage answer following questions.
Q. 1. Find the value of x. (a) 16 (b) 18 (c) 14 (d) 12
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Area of square = 256 m 2 (x + 2) 2 = 162 x + 2 = 16 x = 16 – 2 x = 14
Q. 2. Find the side of square quare-shaped ground? (a) 19 (b) 12 (c) 18 (d) 16
Ans. Option (d) is correct. Explanation: x = 14 Therefore, side of square = (x + 2) = 14 + 2 = 16
Q. 3. What is the value of a? (a) 410 (b) 403 (c) 413 (d) 423
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (C) is correct. Explanation: (4a + 60) + (6a + 10) = 4200 4a + 60 + 6a + 10 = 4200 10a + 70 = 4200 10a = 4130 Hence, a = 413
Q. 4. What was the amount given by Ajay and Aman to Suraj?
Sol. Money contributed by Ajay = (4a + 60) Money contributed by Aman = (6a + 10) Total amount = ₹4200 4a + 60 + 6a + 10 = 4200 10a + 70 = 4200 a = 413 Money contributed by Ajay = 4 × 413 + 60 = 1652 + 60 = ₹1712 Money contributed by Aman = 6 × 413 + 10 = 2478 + 10 = ₹2488
Q. 5. What is the perimeter of the playground?
Sol. Perimeter of square shaped playground = 4 × (x + 2) x = 14 Substituting value of x inside, we get = 4 × (14 + 2) Perimeter = 4 × 16 = 64 m
- Comparing Quantities Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 7
- Cube and Cube Roots Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 6
- Square and Square Roots Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 5
- Data Handling Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
- Understanding Quadrilaterals Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2
Rational numbers class 8 case study questions maths chapter 1, download ebooks for cbse class 8 maths.
- Rational Numbers Topicwise Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Linear Equations in One Variable Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Understanding Quadrilaterals Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Data Handling Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Squares and Square Roots Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Cube and Cube Roots Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Comparing Quantities Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Algebraic Expressions and Identities Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions
- Multiplying a Monomial by a Polynomial
- Multiplying a Polynomial by a Polynomial
Addition and Subtraction of Algebraic Expressions: While adding or subtracting polynomials, first look for like terms and then add or subtract these terms, then handle the unlike terms.
Multiplication of Algebraic Expressions (i) Multiplying two monomials (ii) Multiplying three or more monomials
Multiplying a monomial by a polynomial (i) Multiplying a monomial by a binomial (ii) Multiplying a monomial by a trinomial
Multiplying a polynomial by a polynomial (i) Multiplying a binomial by a binomial (ii) Multiplying a binomial by a trinomial.
Subtraction of a number is the same as addition of its additive inverse.
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Important Keywords
Like term: Terms having same literal factors are called like terms e.g., 7ab 2 , 2ab 2 , 3b 2 a are like terms. Monomial: An algebraic expression that contains only one term is called monomial. e.g., –6abc, 5xy etc Binomial: An algebraic expression that contains two terms are called Binomial. e.g., x + 5 etc Trinomial: An algebraic expression that contains three terms are called trinomial. e.g., 2x – 7y + 4 etc Polynomial: An algebraic expression that contains one or more terms are called Polynomial. e.g., 7xy + 2z + 3y + 4a
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Algebraic Expressions and Identities Case Study
Q1: what are algebraic expressions.
A1: Algebraic expressions are mathematical phrases that include numbers, variables (like x, y), and operations (like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division). They represent a quantity and can include constants, coefficients, and variables. For example, 3x+4 is an algebraic expression.
Q2: What is the difference between a term and a coefficient in an algebraic expression?
A2: A term in an algebraic expression is a single part of the expression separated by addition or subtraction signs. A coefficient is the numerical factor of a term.
Q3: What are like and unlike terms?
A3: Like terms in an algebraic expression are those that have the same variables raised to the same powers. Unlike terms have different variables or different powers.
Q4: What is an identity in algebra, and how is it different from an equation?
A4: An identity is an equation that is true for all values of the variables involved. An equation, on the other hand, is true only for specific values of the variables.
Q5: How do you add and subtract algebraic expressions?
A5: To add or subtract algebraic expressions, first identify and group like terms. Then, add or subtract the coefficients of these like terms while keeping the variables and their powers the same.
Q6: How are algebraic identities useful in simplifying expressions?
A6: Algebraic identities are useful in simplifying complex algebraic expressions by allowing us to replace complicated expressions with simpler, equivalent forms. This makes it easier to perform calculations and solve problems efficiently.
Q7: What is factorization of algebraic expressions, and why is it important?
A7: Factorization is the process of breaking down an algebraic expression into a product of its factors. It is important because it simplifies expressions and is essential in solving equations, especially quadratic equations.
Q8: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing comparing quantities case study questions?
A8: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths on our website . Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.

Related Posts

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 - Visualising Solid Shapes

NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 Visualising Solid Shapes PDF Download
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 PDF is available for students on the official website of Vedantu. Chapter 15 of Visualising Solid Shapes for class 7 as per the NCERT syllabus explains the concepts of drawing 3-D figures. It also describes the methods to identify and count vertices, edges, and faces. This is the basic concept of how to visualize solid shapes and how we can use this concept in our day-to-day life. Register Online for NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in CBSE board examination. Students can also download NCERT Solution PDF for all subjects to prepare for their forthcoming Exams. We assure you to offer the best assistance and guidance.
Class: |
|
Subject: |
|
Chapter Name: | Chapter 15 - Visualising Solid Shapes |
Content-Type: | Text, Videos, Images and PDF Format |
Academic Year: | 2024-25 |
Medium: | English and Hindi |
Available Materials: | |
Other Materials |
Access NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 – Visualising Solid Shapes
1. Identify the nets which can be used to make cubes (cut out copies of the nets and try it):
Ans: Cube's nets are \[\left( {ii} \right),{\text{ }}\left( {iii} \right),{\text{ }}\left( {iv} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {vi} \right).\]
2. Dice are cubes with dots on each face. Opposite faces of a die always
have a total of seven dots on them.
(Image will be uploaded soon)
Here are two nets to make dice (cubes); the numbers inserted in each square indicate
the number of dots in that box.
Insert suitable numbers in the blanks, remembering that the number on the
opposite faces should total to \[7.\]
3. Can this be a net for a die? Explain your answer.
Ans: one pair of opposite faces will have \[1{\text{ and }}4\] on them and another pair of opposite faces will have \[3{\text{ and }}6\] on them whose total is not equal to \[7.\]
Therefore, this cannot be a net for a die.
4. Here is an incomplete net for making a cube. Complete it in at least two different
ways. Remember that a cube has six faces. How many faces are there in the net here?
(Give two separate diagrams. If you like, you may use a squared sheet for easy
manipulation.)
Ans: In the given net there are \[3\] faces.
It can be completed as,
5. Match the nets with appropriate solids:
Exercise 15.2
1. Use isometric dot paper and make an isometric sketch for each one of the given
2. The dimensions of a cuboid are \[5\] cm, \[3\]cm and \[2\] cm. Draw three different isometric
sketches of this cuboid.
Ans: The dimensions of given cuboid are $5\;{\text{cm}},\,\,3\;{\text{cm}}$ and $2\;{\text{cm}}$
Three different isometric sketches are,
3. Three cubes each with $2\;{\text{cm}}$ edge are placed side by side to form a cuboid. Sketch an
oblique or isometric sketch of this cuboid.
Ans: Oblique sketch is,
Isometric sketch is,
4. Make an oblique sketch for each one of the given isometric shapes:
Ans: Oblique sketches are,
5. Give (i) an oblique sketch and (ii) an isometric sketch for each of the following:
(a) A cuboid of dimensions $5\;{\text{cm}},\,\,3\;{\text{cm}}$ and $2\;{\text{cm}}$. (Is your sketch unique?)
(i) Oblique sketch (ii) Isometric sketch
(Images will be uploaded soon)
(b) A cube with an edge $4\;{\text{cm}}$ long.
(i) Oblique sketch (ii) Isometric sketch
(Images will be uploaded soon)
6. An isometric sheet is attached at the end of the book. You could try to make on it
some cubes or cuboids of dimensions specified by your friend.
Ans: Cubes and cuboids shapes on isometric sheet is,
Exercise 15.3
1. What cross-sections do you get when you give a:
(i) vertical cut (ii) horizontal cut to the following solids?
(a) A brick
(b) A round apple
(d) A circular pipe
(e) An ice-cream cone.
Exercise 15.4
1. A bulb is kept burning just right above the following solids. Name the shape of the
shadows obtained in each case. Attempt to give a rough sketch of the shadow. (You
may try to experiment first and then answer these questions)
2. Here are the shadows of some \[{\text{3 - D}}\] objects, when seen under the lamp of the
overhead projector. Identify the solid (s) that match each shadow. (There may be
multiple answers for these!)
3. Examine if the following are true statements:
(i) The cube can cast a shadow in the shape of a rectangle.
Ans: The statement is true.
(ii) The cube can cast a shadow in the shape of a hexagon.
Ans: The statement is false.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 – Free PDF Download
Class 7 chapter 15 includes:.
Exercise 15.1 Solutions: 5 Questions (2 Short Questions and 3 Long Questions).
Exercise 15.2 Solutions: 5 Questions (1 Short question and 4 Long questions).
Exercise 15.3 Solutions: 1 question (MCQ).
Exercise 15.4 Solutions: 3 questions (1 short question and 2 long questions).
Introduction
Solid Shapes or figures are very common in our surroundings. We come across these solid shapes in the form of laptops, mobile phones, computers, ice-cream cones, tin cans, and so many other things. These solid shapes have length, breadth, and height.
Figures that are drawn on a paper are called plane figures, such as circle, triangle, square, cube, rectangle, etc.
The solid figures that occupy space are spheres, cones, cylinders, cuboids, cubes, etc.
The plane figures are 2-dimensional and solid-shapes are 3-dimensional.
The corners of a solid are called its vertices, the line segments joining its vertices are called its edges, and its surfaces are called faces.
3-D solids can be represented in 2-D by drawing their oblique sketches or isometric sketches.
A net is a skeleton-outline of a 2-D solid which when folded results in a 3-D shape. A solid can have more than one net.
Different sections of a solid are viewed either by slicing it or by observing its 2-D shadow. It can also be viewed from the front, top, or side.
The following are examples of 2-Dimensional Shapes.
Properties of 2 - Dimensional Shapes
1. A two-dimensional solid has two dimensions length and breadth.
2. The shape of a 2-D solid will always depend on two coordinates.
The following are examples of 3-Dimensional Shapes.
Properties of 3 - Dimensional Shapes
A three-dimensional shape has length, breadth, and height.
It has depth.
All things that we see and touch in our environment are three-dimensional solids.
The inside and outside of a 3-D solid are separated by a surface.
3-D solids have faces, vertices, edges, and volume. This property helps you to differentiate between 2-D and 3-D solids.
Some examples are pyramids, cones, spheres, cylinders, prisms, etc.
Faces, Edges, and Vertices
Face: The flat surface of a solid is called a face.
Edge: A line that joins two corners of a solid is an edge.
Vertices: The corners of a solid are its vertices.
Example: A cube has 8 vertices, 12 edges, and 6 faces.
Formula: If F, E, and V denote the number of faces, edges, and vertices of a cube respectively, then we have:
F – E + V = 2
Description of Some Basic Shapes
Square: It has four sides and four corners. All the sides of a square are of the same length. For example, a sandwich, napkin, chessboard, etc.
Rectangle: A rectangle has four sides and four corners. The opposite sides of a rectangle are of the same length. For example, a table, laptop, mobile phone, etc.
Triangle: A triangle has three sides and three vertices. For example, traffic lights, etc.
Cuboid: A cuboid has six flat surfaces, twelve straight edges, and eight vertices. For example, book, lunch box, cabinet, cubicles, etc.
Cube: A cube has six flat faces, eight vertices, and 12 straight edges. For example, dice, sugar cube, etc.
Cylinder: A cylinder has three faces: 1 curved face and 2 flat faces. It has two curved edges. For example, a gas cylinder, tin-can, pipes, candle, etc.
Cone: A cone has two faces, one slant face, and one flat face. For example, ice-cream cone, funnel, etc.
Solid Shape
A solid can be sketched in two ways.
An oblique sketch is drawn on a squared paper and does not indicate exact measurement but conveys all important aspects of the appearance of the solid.
An isometric sketch is drawn on a 3-D drawing paper and has proportional measurements of the solid.
Note: In the case of an isometric sketch the measurements are exact whereas it is not so for an oblique sketch.
We can view different sections of a solid in many ways:
When we slice the shape, it results in the cross-section of the solid.
We can observe a 2-D shadow of a 3-D shape.
We can look at the shape from different angles, i.e., the front-view, the side-view, and the top-view.
Description of Some More Solid Shapes
Triangular Prism: A triangular prism resembles a kaleidoscope. It has triangular bases. There are five faces, nine edges, and six vertices in a triangular prism.
Triangular Pyramid: A triangular pyramid is also called a tetrahedron. It has a triangular base. There are four faces, six edges, and four vertices in a triangular pyramid.
Square Pyramid: A square pyramid has a square base. It has five faces, eight edges, and five vertices.
Sphere: A sphere has no flat face. It has only a spherical face. A sphere has one face, no edges, and no vertices.
Polyhedrons
A solid made up of polygon regions is called a polyhedron. For example, cubes, cuboids, prisms, and pyramids are polyhedrons. Please note that spheres, cylinders, and cones are not polyhedrons because they are not made up of polygon regions.
There are two types of polyhedrons: Convex polyhedrons and Regular polyhedrons.
Convex Polyhedrons
When a line segment joining any two points on the surface of a polygon lies inside or on the polygon, the polygon is called a convex polyhedron.
Regular Polyhedrons
Regular polygons whose faces are regular and they meet at each vertex, are called regular polyhedrons.
A prism is a polyhedron shape whose base and top are congruent and the lateral faces are parallelograms.
Types of Prism
Triangular prism
Rectangular prism
Pentagonal prism
Hexagonal prism
Triangular pyramid
Rectangular pyramid
Square pyramid
Pentagonal pyramid
Hexagonal pyramid
Nets for Building a 3 - D Shape
Geometry net is a skeleton-outline of a 2-D solid which when folded results in a 3-D shape. A net can be used in order to find the surface area of an object.
Net is a 2-D representation of a 3-D object that is unfolded along its edges. A three-dimensional shape may have different nets.
Why Should You Use Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths?
Key Features of NCERT Solutions: These solutions are designed to help students achieve proficiency in their studies. They are crafted by experienced educators who excel in teaching Class 7 Maths. Some of the features include:
Comprehensive explanations for each exercise and questions, promoting a deeper understanding of the subject.
Clear and structured presentation for easy comprehension.
Accurate answers aligned with the curriculum, boosting students' confidence in their knowledge.
Visual aids like diagrams and illustrations to simplify complex concepts.
Additional tips and insights to enhance students' performance.
Chapter summaries for quick revision.
Online accessibility and downloadable resources for flexible study and revision.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 - Visualising Solid Shapes, provided by Vedantu, is a valuable tool for Class 7 students. It helps introduce Maths concepts in an accessible manner. The provided solutions and explanations simplify complex ideas, making it easier for Class 7 students to understand the material. By using Vedantu's resources, Students can develop a deeper understanding of NCERT concepts. These solutions are a helpful aid for grade 7 students, empowering them to excel in their studies and develop a genuine appreciation for “ Visualising Solid Shapes ”.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 - Visualising Solid Shapes
1. How many sums are there in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes?
There are four exercises in the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes. In the first exercise, Ex.-15.1, there are 5 sums. In the second exercise, Ex.-15.2, there are 6 sums. In the third exercise, Ex.- 15.3, there is 1 sum that will enhance your practical knowledge of solid shapes. In the last exercise, Ex.-15.4 there are 3 sums. Most of the sums in these exercises have sub-questions.
2. Is the Class 7 NCERT Maths Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes difficult to understand?
No, the Class 7 NCERT Maths Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes is not difficult to understand. The basic solid shapes of geometry are explained in this chapter. The concepts of isometric shapes, cubes, cuboids, cylinders, etc are discussed in this chapter. In short, this chapter is an introduction to the basic solid shapes in geometry. So, students will be able to understand the concepts covered in this chapter easily. Also, a thorough revision will enable them to solve all the sums of this chapter correctly, in their examination.
3. Can I get reliable NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes online?
Yes, you can get reliable NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes on Vedantu. The solutions for this chapter are prepared by the subject matter experts at Vedantu, as per the guidelines of NCERT for Class 7. These NCERT Solutions are among the most reliable study resources available online for Visualising Solid Shapes. So, you can rely on these NCERT Solutions for your exam preparation. Every sum is solved in a stepwise manner to facilitate an easy understanding of all students. You can download the PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15- Visualising Solid Shapes from Vedantu for free, for practicing the sums offline.
4. What is the difference between a cube and a cuboid?
A cube and a cuboid both are solid shapes, that is, both the shapes have three dimensions, length, breadth, and height. For a cube, all the dimensions are of equal length, whereas, for a cuboid, the length, breadth, and height all are of different measures.
5. How is Vedantu Going to Help you Prepare for Your Exams?
Vedantu provides a comprehensive study of NCERT subjects. These studies will clarify all your doubts about the topics and develop your conceptual foundation. These concepts are self-explanatory but you can still approach the team of experts in Vedantu for further understanding.
6. Mention the topics that are covered in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 15 of Class 7 Maths?
Geometry is the study of two-dimensional and three-dimensional forms and objects in our environment, as they all have length, breadth, and height. Chapter 15 of the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Visualising Solid Shapes begins with an explanation of concepts such as 2D and 3D, as well as why they are referred to by their appropriate names. Diagrams are used to clarify terms such as vertices, edges, and faces.
7. How will this chapter help students in their daily life?
In NCERT Solutions for Chapter 15 of Class 7 Maths, certain activities will help students comprehend three-dimensional space and how objects may be formed in three dimensions. They are instructed to create frames or nets of the desired shapes and then attempt to construct those shapes using the prepared cuttings or frames. This will aid in the development of visualizing abilities required for the exercise questions and this is how this chapter will help students in their daily life.
8. What topics are covered in Chapter 15 of Class 7 Maths?
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 15 of Class 7 Maths begins with an introduction to forms and objects in 2D and 3D space. The fundamentals of terminology like edges, faces, and vertices of shapes are reviewed in Chapter 15. The concept of perceiving solid objects and how to observe their different sections are described, as well as how to draw solids on a flat surface, oblique sketches, and isometric sketches. The chapter concludes with a discussion of shadow play as a technique of observing three-dimensional objects in two-dimensional space.
9. What are all things students should consider while studying this chapter?
10. List some important facts in Chapter 15 of Class 7 Maths.
Plane and Solid Shapes: Plane shapes have only length and breadth, such as square, rectangle, hexagon, and so on, but solid shapes have height in addition to length and breadth, such as cuboid, cube, sphere, cone, and so on.
2D representation of a 3D solid: This can be accomplished by drawing the solid's image on paper, and there are two methods for doing so. The first is an oblique drawing, and the second is an isometric drawing.
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths
Ncert solutions for class 7.

COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths Here in this article, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths. Maths Class 7 Chapter List Latest Chapter List (2023-24) There is total 13 chapters. Chapter 1 Integers Case Study QuestionsChapter 2 Fractions and Decimals Case Study QuestionsChapter 3 Data Handling Case Study QuestionsChapter 4 … Continue reading Case Study Questions for ...
Case Study Questions Class 7 Maths - Fractions. CBSE Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Fractions. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Fractions. Case Study 1: Karan, an electrician, undertook the writing job of a building. He bought 8 1/3 bundles of an electric ...
CBSE Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Decimals. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Decimals. Case Study 1: Miraya is calling a few friends to her home. She wanted to purchase a few bakery items for them. She prepared a list of all the items that she had to buy.
CBSE 7th Standard CBSE Mathematics English medium question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 7th Standard CBSE Mathematics books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place
Thus, the Important Questions Class 7 Mathematics Chapter 1 will help students to score better in exams. The questions are-. Question 1. Following number line given below shows the temperature present in degree celsius at different places on a particular day. Image Source: Internet / NCERT Textbook.
Here 1 is the multiplicative identity for integers. Associative property of Multiplication. For every integer a, b and c, (a×b)×c=a×(b×c) Distributive Property of Integers. Under addition and multiplication, integers show the distributive property. i.e., For every integer a, b and c, a×(b+c)=a×b+a×c. These properties make calculations ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers are available here. When students feel stressed about searching for the most comprehensive and detailed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths, we at BYJU'S have prepared step-by-step solutions with detailed explanations.We advise students who want to score good marks in Maths, to go through these solutions and strengthen their knowledge.
Also, check CBSE Class 7 Maths Important Questions for other chapters. CBSE Class 7 Maths Important Questions Chapter Wise. Chapter 1 - Integer. Chapter 2 - Fractions and Decimals. Chapter 3 - Data Handling. Chapter 4 - Simple Equations. Chapter 5 - Lines and Angles. Chapter 8 - Comparing Quantities.
Chapter 1 of the CBSE Class 7 syllabus includes three exercises on Integers. Each exercise contains problems that aim to help students understand the concept of Integers and their practical applications in solving various word problems. Exercise 1.1 - This Exercise contains 4 problems, with multiple parts.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Maths, Science, Social Science for Class Class 6, 7, 8, 9,10, 11 and 12 by Experienced Subject Teachers. ... DAV Class 5 Math Solution Chapter 4 Fractional Numbers. August 30, 2024. You Might Also Like. Case Study Question. Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Fibre to Fabric. August 28, 2024.
Below we have listed NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers Exercise 1.1, Ex 1.2, Ex 1.3 and Ex 1.4. These materials are prepared based on Class 7 NCERT syllabus, taking the types of questions asked in the NCERT textbook into consideration. Further, all the CBSE Class 7 Solutions Maths Chapter 1 Integers are in accordance with the ...
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT CBSE Book guidelines. ... Maths, English will become easy to study if you have access to NCERT Solution for ... the total number of questions is 25. So, this case is not possible. So, the possible ways are: • 22 correct, 0 incorrect ...
on April 12, 2024, 6:28 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Integers and Class 7 Maths Chapter 1 Try These Solutions in Hindi and English Medium modified and updated for academic year 2024-25. According to new syllabus and latest textbooks for new session 2024-25, there are only three exercises in chapter 1 of class 7th mathematics.
For any two integers p and q. p + q = q + p. Example. 23 + (-30) = - 7. (-30) + 23 = - 7. There is no difference in answer after changing the order of the numbers. b. If we change the order of the integers while subtracting then the result is not the same so subtraction is not commutative for integers. For any two integers p and q.
A10: A9: We provide assertion reason questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths on our website. Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.
Case Study Questions: Question 1: The top of a table is shown in the figure given below: (i) The coordinates of the points H and G are respectively(a) (1, 5), (5, 1) (b) (0, 5), (5, 0) (c) (1, 5), (5, 0) (d) (5, 1), (1, 5) (ii) The distance between the points A and … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
These competency-based practice question resources are most recommended by experts for the comprehensive chapter-wise practice of these moderate to high difficulty questions. Here, you can find chapter-wise self practice paper solutions and solutions in PDF form. These PDFs are absolutely free to download. 1. Integers. 2. Fractions and Decimals.
REAL NUMBERS- CASE STUDYCASE STUDY 1.To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of. our friends to set up a class library. There are two sectio. s- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students. ection A and 36 students in sectionB.What is the minimum number of books you will acquire for the ...
Chapter 1 Integers NCERT Solutions PDF Download available here will give good experience and provide opportunities to learn new things. Chapter 1 Class 7 Maths NCERT Solutions will help you in getting command over the problems present in the exercises. Through the help of NCERT Solutions for Class 7, you can also complete your homework on time ...
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 9 maths. ... Number Systems Class 9 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 1; Topics from which case study questions may be asked.
Total Questions: Class 7 maths chapter 6 has 21 well-research sums that can be split into 4 tough problems, 9 moderately complex, and 8 easy questions. NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 7. NCERT solutions for class 7 maths chapter 7 congruence of triangles starts with giving an introduction to the meaning of congruence between any two ...
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 7 Maths in Exam. 1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution. 2.
a) Prime number. b) Composite number. c) Neither prime nor composite. d) None of the above. Answer: b) Composite number. 5. If p and q are positive integers such that p = ab2 and q= a2b, where a ...
Reading Time: 8 minutes Last Updated on August 25, 2024 by XAM CONTENT. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 8 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board.
NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Maths Book PDF Download Chapter 8 Rational Numbers Solutions. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) Question 1: A rational number is defined as a number that can be expressed in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and (a) q = 0 (b) q = 1 (c) q ≠ 1 (d) q ≠ 0 Solution : (d) By definition, a number that can be expressed in the form of p/q, where p and q are integers and ...
Select and buy. Study Important Questions for Class7 Mathematics Chapter 3 - Data Handling. 1 Mark. 1. Insert a number between 1 4 and 1 7 . Ans. To insert a number between two numbers, first we add both numbers and divide the sum by two. 1 4 + 1 7 2 = 7 + 4 28 2.
#sslconamexam #examwinnersslc #onamexamrevision #sslcmathsE_SAT NEE PHASE 1 Register Now : https://form.jotform.com/242213502063441E_SAT JEE PHASE 1 Register...
The NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Maths Chapter 15 - Visualising Solid Shapes, provided by Vedantu, is a valuable tool for Class 7 students. It helps introduce Maths concepts in an accessible manner. The provided solutions and explanations simplify complex ideas, making it easier for Class 7 students to understand the material.