What does 2023 hold for the Philippines’ economy?
The COVID-19 pandemic and other geopolitical events have caused a global crisis over the past couple of years. Major upheavals of this scale are not unknown—in the 20th century, various significant events shook the world, like both World Wars and the Cold War. Between these periods of disruption, global events played out across three “eras”: the Post-War Boom after the Second World War, the Era of Contention from 1972 to 1974, and the Era of Markets from 1989 to 1992, each of which had distinct characteristics and opportunities.
The effects of the current crisis, both humanitarian and economic, cannot be underestimated. However, as the world continues to emerge from the pandemic, business leaders can take advantage of these upheavals, and shape innovation and growth—as evidenced in previous eras—by anticipating future disruptions and shaping strategies accordingly. This kind of “era thinking” is particularly valuable in the Philippines, where disruptions caused by the conflict in Ukraine and international supply-chain crises have had a clear impact.
Looking ahead into 2023, the economic forecast for the Philippines remains a moving target. After a record 10 percent contraction in 2020, the country may bounce back in 2023 with projected growth of around 5.3 percent, though it will hardly rise above preCOVID-19 levels (exhibit).
Key challenges face the country: significantly high unemployment numbers; a high inflation rate (forecast to reach 5.1 percent in 2023); rising policy rates; import and export bottlenecks; and the declining strength of the Philippine peso against the American dollar. 1 “2023 inflation seen topping official target,” Manila Times , January 13, 2023.

The state of the Philippines’ economy in seven major sectors
This article analyzes seven key sectors that offer a detailed insight into the state of the Philippines’ economy in 2023 and beyond. As the data shows, the outlook is complex—there are serious issues to address, but also reasons for optimism.
Real estate and construction
Several global and macroeconomic shocks will likely impact the Philippines’ post-pandemic economic recovery in the real estate and construction sectors. Policy rates may reach 6.25 percent in the first half of 2023, which would negatively impact home lending rates and increase the strain on a sector that must also address the increased costs of construction and logistics caused by supply-chain issues.
Nonetheless, more optimistic projections include an expansion in real estate investment opportunities and the emergence of green real estate, a promising step toward the Philippines’ goal to reduce carbon emissions by 75 percent by 2030. 1 “Philippines raises carbon emissions target to 75 percent by 2030,” Reuters, April 16, 2021.
Much of the sector is expected to recover to pre-pandemic levels by the end of 2023, and construction by the end of 2024. Much of this growth will likely be driven by residential building construction, predicted to grow by 12 percent. Non-residential construction, by contrast, has yet to recover to pre-pandemic levels.
There will likely be an increased demand for office space, caused by companies introducing return-to-office policies, as well as a resurgence in the need for industrial, retail, and leisure spaces, both of which would boost sector-wide growth.
Another consideration is hybrid working—this is in fact higher in the Philippines than the global norm. 1 Vaughn Alviar, “Hybrid work is the future,” Philippines Daily Inquirer , March 11, 2022. Office spaces may need to be reinvented as companies look to adopt more hybrid ways of working. This could result in vacancy rates persisting, however the growth of coworking facilities and the desire for sustainable buildings will necessitate innovations in construction techniques and leasing agreements, thus encouraging sector-wide growth.
Travel and hospitality
The outlook for the travel and hospitality sector is strong, with a full recovery to pre-pandemic levels expected by 2024. Outbound and inbound travel may be sluggish due to remaining international travel restrictions and further health and safety concerns: 71 percent of Asian countries still impose travel restrictions to varying degrees; Europe is more lenient with 50 percent of countries imposing no restrictions at all.
Despite this, hotel occupancy is expected to rise as more foreign tourists visit the Philippines. China’s removal of quarantine on arrival from January 8, 2023, and Hong Kong’s withdrawal of mandatory quarantine on arrival in September 2022, are both reasons for optimism. If mainland China’s air travel were to recover at the same pace as Hong Kong’s, four million air passengers a month out of China can be expected by the second quarter of 2023, pushing air travel back up to 40 percent of pre-COVID-19 levels.
Several key trends are expected to influence economic recovery in the sector, the impacts of which may be both positive and negative. High inflation, for example, has increased airlines’ operating expenses. The weakening peso, by contrast, could have a positive effect by encouraging locals to travel and spend within the country rather than abroad. In fact, local air travel is already on the rise and is expected to reach preCOVID-19 levels in the second half of 2023. 1 Katlene O. Cacho, “Air travel approaches pre-pandemic levels,” SunStar, December 20, 2022
The growth of “revenge travel” (travelling widely and often to make up for time and opportunities lost during the COVID-19 pandemic and attendant travel restrictions) also contributes to the robust growth of leisure travel, while business travel is recovering more slowly. This is largely due to the inconsistent travel restrictions between countries, and remote working tools that do away with the necessity of meeting in person.
Sustainable tourism and increased awareness of eco-friendly travel options may not negatively affect the number of tourists visiting the Philippines, but they will likely change how visitors and locals arrive in, and travel through, the country. The fact that the hospitality industry has recovered more significantly than airlines shows this. Other contributing factors include the increase in domestic travel and the popularity of the “digital-nomad” lifestyle, which allows travelers to live and work for extended periods in their destinations of choice, rather than flying between destinations frequently.
Financial services
The strength of the Philippines’ financial services sector in 2023 will likely be subject to two key factors: interest rate hikes and rising inflation. Interest rate hikes could have a positive effect by widening the net-interest margin, but macrovolatility could cause a slowdown in new loans. Rising inflation will likely increase the pressure on wages and increase operational costs.
The financial sector is already responding to these challenges. It is prioritizing the interoperability and digitization in top banks, and the country’s central bank, Bangko Sentral ng Philipinas, is expected to increase interest rate hikes to keep up with inflation. 1 Lawrence Agcaoili, “More BSP rate hikes boom as inflation spikes,” Philstar Global, January 6, 2023.
Banks have taken additional steps. These include recovering nonperforming loans, reducing loan loss provisions with an outlook on improved credit status, and the emergence of digital neobanks, which offer higher savings interest rates and faster customer acquisition. Perhaps most crucially, there are growing efforts to make banking more accessible and inclusive. The growth of digital banking is significant: in 2021, 60 percent of Filipinos used digital banking (a sharp increase from 17 percent in 2019), and growth is expected to accelerate in 2023. 2 “2021 financial inclusion survey,” Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, 2021.
Growth in the Philippines’ energy sector contracted to 4.8 percent in 2022 and is expected to rebound to 5.5 percent in 2023. However, the sector needs to ensure that this growth target can be met given looming supply constraints and while accelerating the transition to green energy.
Due to a growing population, an economy coupled with the depletion of domestic gas from the Malampaya gas field, and a heavy reliance on imported fuel, a power supply shortage is expected closer to 2024 to 2025. 1 “Malampaya depletion expected by 1st quarter of 2027,” BusinessWorld, May 19, 2021. This will put sustained upward pressure on prices and an urgency to bring greenfield capacity online.
On the energy transition, major players are addressing the challenge by diversifying energy assets across the board, with investments in cleaner technologies such as solar, hydro, and battery energy storage systems. These efforts are underway in both the private and public sectors. For example, the Philippine government has introduced measures to improve the availability and sustainability of energy. Legislation has been passed to reduce fuel and power costs via subsidies for transport operators, boost investments in indigenous energy resources such as coal, and strengthen electric cooperatives for broader access to electrification. 2 Philippine energy plan 2020–2040, Department of Energy, Republic of the Philippines.
The Philippines may generate enough energy to cover its consumption needs, but the supply-demand balance will remain tight, with clear downside risks. Threats to the energy supply include rising oil and gas prices, supply-chain disruptions, and currency depreciation.
The healthcare sector experienced strong growth during the COVID-19 pandemic: in 2021, healthcare services increased by 14.1 percent and pharmaceutical manufacturing by 12.9 percent. Growth stalled in 2022 (3.9 percent and 8.25 percent for healthcare services and pharmaceuticals respectively), and this trend is expected to continue in 2023. While demand will continue to grow, the sector will have to address three major challenges.
First, rising inflation will impact costs for service providers and manufacturers, though prices will initially lag due to procurement contracts being set in advance. One of the biggest drivers of inflation is an increase in healthcare wages, especially of hospital staff such as nurses, who are in short supply locally and globally. Second, supply-chain disruptions will drive up medicine price variations and production inefficiencies, particularly as the Philippines is a net importer of pharmaceuticals. And third, turnover levels for health workers are expected to remain high, straining the capacity of service providers and potentially resulting in a poor quality of healthcare.
To address these challenges, the sector is renewing the emphasis on universal healthcare and building robust healthcare ecosystems. The Department of Health aims to close the supply-demand gap in healthcare by increasing facilities in areas outside Metro Manila and making medicines more affordable. 1 “Universal health care,” Department of Health, Republic of the Philippines.
In the private sector, key players are investing strategically to cover the healthcare value chain, and making concerted efforts to tap into growing online markets through electronic medical records, all-in-one telemedicine and consultation apps, and other ancillary services.
The Philippines’ healthcare sector is so vast that broad, sector-wide forecasts can sometimes obscure as much as they reveal. The outlook becomes clearer when subsectors are evaluated on their own terms, as they diverge widely in market size, are subject to different trends, and experience different rates of growth. The healthcare providers subsector, for example, boasts a larger market size than the products and payors subsectors combined.
Despite significant growth in 2022, the Philippines still has some catching up to do. There is no doubt that it faces global macroeconomic headwinds in 2023, however big pockets of opportunity exist within each of its biggest sectors. To grasp these as soon as possible, companies need to rethink how they deliver to customers and operate their businesses. With such strategies in place for possible future disruptions, the Philippines can stand strong and continue to grow its economy in the year ahead.
Jon Canto is a partner in the Manila office, where Kristine Romano is a partner and Danice Parel and Vicah Villanueva are consultants.
The authors wish to thank Aaron Ong, Ryan Delos Reyes, and Jeongmin Seong for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Philippines economic outlook 2022

The Philippines Growth Dialogues
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Philippines records strongest economic growth in more than 40 years
To read this article for free, register now.
Once registered, you can: • Read free articles • Get our Editor's Digest and other newsletters • Follow topics and set up personalised events • Access Alphaville: our popular markets and finance blog
Explore more offers.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism. Cancel anytime during your trial.
FT Digital Edition
Today's FT newspaper for easy reading on any device. This does not include ft.com or FT App access.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
Standard Digital
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FT Edit app
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
World Bank Philippines Economic Update December 2021
12/7/2021 12:11:00 PM
Chua, Kevin C.,Cruz, Kevin Thomas,Cho, Yoonyoung
Economic & Sector Work
Philippines
East Asia and Pacific (EAP)
The economic rebound gained momentum in the third quarter of 2021 despite another COVID-19 wave. The Philippines has, so far, faced its worst infection wave in September when the 7-day daily average reached about 21,000 cases due to the Delta variant. In response, the authorities reimposed stringent mobility restrictions in Metro Manila and other key metropolitan areas. Nonetheless, compared with previous waves, domestic activity has been less sensitive to infections. Public containment measures constrained overall mobility less, while households and firms have learned to cope with infections and diminished mobility. As a result, the growth momentum was not severely hampered, and the third quarter growth surprised on the upside, exceeding market expectations. The economy expanded by 4.9 percent in the first three quarters of 2021, rebounding from a 10.1 percent contraction over the same period in 2020. Although partially driven by base effects, the growth expansion also reflected an increase in economic activity despite the implementation of several lockdowns. Growth was supported by the industry sector, driven by double-digit growth in manufacturing and robust public construction activity. The services sector posted a more moderate expansion as some key services were subdued by mobility restriction measures. The agriculture sector contracted as farm and livestock outputs were impacted by typhoons and ongoing outbreak of African Swine Fever. Meanwhile, domestic demand improved, supported by a resurgence in public construction spending. Private consumption picked up but still tempered by elevated inflation and unemployment, mobility restrictions, and low consumer confidence. Public consumption growth eased, in part due to the base effects from the swift disbursement of fiscal support a year ago. The global economic recovery strengthened exports, although services trade remained weak. The fiscal stance remains supportive of economic recovery, but the policy space is narrowing. Public spending accelerated from 23.6 percent of GDP in the first three quarters of 2020 to 24.6 percent of GDP in the same period in 2021, in line with the recovery in public investment and ongoing fiscal support. Infrastructure outlays increased from 3.5 percent of GDP to 4.7 percent of GDP in the first three quarters of 2021, a result of the government’s push on investment spending as part of its recovery program. Meanwhile, public revenues fell from 16.8 percent of GDP in the first three quarters of 2020 to 16.3 percent of GDP over the same period in 2021. Tax revenues rebounded due to strong tax and customs collections, but non-tax revenue contracted following the significant dividend remittances to the Bureau of the Treasury (BTr) in the beginning of the pandemic. The fiscal deficit widened from 6.9 percent of GDP in Q1-Q3 2020 to 8.3 percent of GDP in Q1-Q3 2021. The wider fiscal deficit has resulted in higher financing needs, which have been met by increased public borrowing. Public debt increased from 54.6 percent of GDP at end-2020 to 63.1 percent of GDP at end-September 2021.
MAIN DOCUMENT
World-Bank-Philippines-Economic-Update-December-2021.pdf
Download statistics
Total Downloads** :
Download Stats
**Download statistics measured since January 1st, 2014.
Licence or Product Purchase Required
You have reached the limit of premium articles you can view for free.
Already have an account? Login here
Get expert, on-the-ground insights into the latest business and economic trends in more than 30 high-growth global markets. Produced by a dedicated team of in-country analysts, our research provides the in-depth business intelligence you need to evaluate, enter and excel in these exciting markets.
View licence options
Suitable for
- Executives and entrepreneurs
- Bankers and hedge fund managers
- Journalists and communications professionals
- Consultants and advisors of all kinds
- Academics and students
- Government and policy-research delegations
- Diplomats and expatriates
This article also features in The Report: Philippines 2021 . Read more about this report and view purchase options in our online store.

Economy From The Report: Philippines 2021 View in Online Reader

The Philippines is one of the fastest-growing economies of the past decade, averaging 6.4% growth per year over 2010-19. Indeed, an expanding and youthful population, combined with reforms and an ambitious infrastructure programme, have made it an enticing investment destination. Nevertheless, as is often the case in emerging markets, challenges regarding inequality – particularly the distribution of wealth and services – remain barriers to growth. The Covid-19 pandemic tested the country’s resilience in 2020, impacting major sectors. The Philippine government launched a four-pillar socio-economic strategy to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and aid the national recovery effort. The framework aims to provide emergency support for vulnerable groups and individuals; expand medical resources to fight Covid-19 and ensure the safety of health workers; implement fiscal and monetary initiatives to keep the economy afloat; and launch an economic recovery plan to create jobs and sustain growth. This chapter contains interviews with Carlos Dominguez, Secretary of Finance; and Shinichi Kitaoka, President, Japan International Cooperation Agency.

Articles from this Chapter
A new normal: positioning the economy to emerge from the pandemic with the ability to generate knowledge-based, inclusive growth obg plus.
The Philippines is one of the fastest-growing economies of the past decade, averaging 6.4% growth per year in 2010-19. Indeed, an expanding and youthful population, combined with reforms and an ambitious infrastructure programme, have made it an enticing investment destination. Nevertheless, as is often the case in emerging markets, challenges regarding inequality – particularly the distribution of wealth and services – remain barriers to growth. The Covid-19 pandemic tested the country’s…
Strategic support: A blend of policy options seeks to kick-start economic recovery OBG plus
The Philippine government launched a four-pillar socio-economic strategy to mitigate the impact of the pandemic and aid the national recovery effort. The framework aims to provide emergency support for vulnerable groups and individuals; expand medical resources to fight Covid-19 and ensure the safety of health workers; implement fiscal and monetary initiatives to keep the economy afloat; and launch an economic recovery plan to create jobs and sustain growth. Bayanihan 1 & 2 The government…
Strong fundamentals: Carlos Dominguez, Secretary of Finance, on fiscal policies and tax reforms to facilitate economic recovery from the pandemic OBG plus
Interview:Carlos Dominguez To what extent has the country’s fiscal strategy prepared it for the planned P6trn ($119.3bn) worth of borrowings in 2020-21 to address the crisis? CARLOS DOMINGUEZ: The core of our strategy has been to protect both lives and livelihoods. This, of course, comes with significant economic costs at a time when revenue collection is understandably lower because of the pandemic-induced economic downturn. Fortunately, when Covid-19 struck, the Philippines was financially…
Better together: Shinichi Kitaoka, President, Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA), on nurturing regional ties OBG plus
Interview:Shinichi Kitaoka How can the Philippines create more favourable conditions for Japanese investment? SHINICHI KITAOKA: Japan is a major source of foreign direct investment in the Philippines and was formerly the country’s second-largest trade partner. With its growing population and relatively inexpensive labour, Japanese companies view the Philippines as a promising investment destination. However, Japanese investors remain concerned about the Philippines’ security conditions,…
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
The Philippine economy under the pandemic: From Asian tiger to sick man again?
Subscribe to the center for asia policy studies bulletin, ronald u. mendoza ronald u. mendoza dean and professor, ateneo school of government - ateneo de manila university.
August 2, 2021
In 2019, the Philippines was one of the fastest growing economies in the world. It finally shed its “sick man of Asia” reputation obtained during the economic collapse towards the end of the Ferdinand Marcos regime in the mid-1980s. After decades of painstaking reform — not to mention paying back debts incurred under the dictatorship — the country’s economic renaissance took root in the decade prior to the pandemic. Posting over 6 percent average annual growth between 2010 and 2019 (computed from the Philippine Statistics Authority data on GDP growth rates at constant 2018 prices), the Philippines was touted as the next Asian tiger economy .
That was prior to COVID-19.
The rude awakening from the pandemic was that a services- and remittances-led growth model doesn’t do too well in a global disease outbreak. The Philippines’ economic growth faltered in 2020 — entering negative territory for the first time since 1999 — and the country experienced one of the deepest contractions in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) that year (Figure 1).
Figure 1: GDP growth for selected ASEAN countries

And while the government forecasts a slight rebound in 2021, some analysts are concerned over an uncertain and weak recovery, due to the country’s protracted lockdown and inability to shift to a more efficient containment strategy. The Philippines has relied instead on draconian mobility restrictions across large sections of the country’s key cities and growth hubs every time a COVID-19 surge threatens to overwhelm the country’s health system.
What went wrong?
How does one of the fastest growing economies in Asia falter? It would be too simplistic to blame this all on the pandemic.
First, the Philippines’ economic model itself appears more vulnerable to disease outbreak. It is built around the mobility of people, yet tourism, services, and remittances-fed growth are all vulnerable to pandemic-induced lockdowns and consumer confidence decline. International travel plunged, tourism came to a grinding halt, and domestic lockdowns and mobility restrictions crippled the retail sector, restaurants, and hospitality industry. Fortunately, the country’s business process outsourcing (BPO) sector is demonstrating some resilience — yet its main markets have been hit heavily by the pandemic, forcing the sector to rapidly upskill and adjust to emerging opportunities under the new normal.
Related Books
Thomas Wright, Colin Kahl
August 24, 2021
Jonathan Stromseth
February 16, 2021
Tarun Chhabra, Rush Doshi, Ryan Hass, Emilie Kimball
June 22, 2021
Second, pandemic handling was also problematic. Lockdown is useful if it buys a country time to strengthen health systems and test-trace-treat systems. These are the building blocks of more efficient containment of the disease. However, if a country fails to strengthen these systems, then it squanders the time that lockdown affords it. This seems to be the case for the Philippines, which made global headlines for implementing one of the world’s longest lockdowns during the pandemic, yet failed to flatten its COVID-19 curve.
At the time of writing, the Philippines is again headed for another hard lockdown and it is still trying to graduate to a more efficient containment strategy amidst rising concerns over the delta variant which has spread across Southeast Asia . It seems stuck with on-again, off-again lockdowns, which are severely damaging to the economy, and will likely create negative expectations for future COVID-19 surges (Figure 2).
Figure 2 clarifies how the Philippine government resorted to stricter lockdowns to temper each surge in COVID-19 in the country so far.
Figure 2: Community quarantine regimes during the COVID-19 pandemic, Philippine National Capital Region (NCR ), March 2020 to June 2021

If the delta variant and other possible variants are near-term threats, then the lack of efficient containment can be expected to force the country back to draconian mobility restrictions as a last resort. Meanwhile, only two months of social transfers ( ayuda ) were provided by the central government during 16 months of lockdown by mid-2021. All this puts more pressure on an already weary population reeling from deep recession, job displacement, and long-term risks on human development . Low social transfers support in the midst of joblessness and rising hunger is also likely to weaken compliance with mobility restriction policies.
Third, the Philippines suffered from delays in its vaccination rollout which was initially hobbled by implementation and supply issues, and later affected by lingering vaccine hesitancy . These are all likely to delay recovery in the Philippines.
By now there are many clear lessons both from the Philippine experience and from emerging international best practices. In order to mount a more successful economic recovery, the Philippines must address the following key policy issues:
- Build a more efficient containment strategy particularly against the threat of possible new variants principally by strengthening the test-trace-treat system. Based on lessons from other countries, test-trace-treat systems usually also involve comprehensive mass-testing strategies to better inform both the public and private sectors on the true state of infections among the population. In addition, integrated mobility databases (not fragmented city-based ones) also capacitate more effective and timely tracing. This kind of detailed and timely data allows for government and the private sector to better coordinate on nuanced containment strategies that target areas and communities that need help due to outbreak risk. And unlike a generalized lockdown, this targeted and data-informed strategy could allow other parts of the economy to remain more open than otherwise.
- Strengthen the sufficiency and transparency of direct social protection in order to give immediate relief to poor and low-income households already severely impacted by the mishandling of the pandemic. This requires a rebalancing of the budget in favor of education, health, and social protection spending, in lieu of an over-emphasis on build-build-build infrastructure projects. This is also an opportunity to enhance the social protection system to create a safety net and concurrent database that covers not just the poor but also the vulnerable low- and lower-middle- income population. The chief concern here would be to introduce social protection innovations that prevent middle income Filipinos from sliding into poverty during a pandemic or other crisis.
- Ramp-up vaccination to cover at least 70 percent of the population as soon as possible, and enlist the further support of the private sector and civil society in order to keep improving vaccine rollout. An effective communications campaign needs to be launched to counteract vaccine hesitancy, building on trustworthy institutions (like academia, the Catholic Church, civil society and certain private sector partners) in order to better protect the population against the threat of delta or another variant affecting the Philippines. It will also help if parts of government could stop the politically-motivated fearmongering on vaccines, as had occurred with the dengue fever vaccine, Dengvaxia, which continues to sow doubts and fears among parts of the population .
- Create a build-back-better strategy anchored on universal and inclusive healthcare. Among other things, such a strategy should a) acknowledge the critically important role of the private sector and civil society in pandemic response and healthcare sector cooperation, and b) underpin pandemic response around lasting investments in institutions and technology that enhance contact tracing (e-platforms), testing (labs), and universal healthcare with lower out-of-pocket costs and higher inclusivity. The latter requires a more inclusive, well-funded, and better-governed health insurance system.
As much of ASEAN reels from the spread of the delta variant, it is critical that the Philippines takes these steps to help allay concerns over the country’s preparedness to handle new variants emerging, while also recalibrating expectations in favor of resuscitating its economy. Only then can the Philippines avoid becoming the sick man of Asia again, and return to the rapid and steady growth of the pre-pandemic decade.
Related Content
Emma Willoughby
June 29, 2021
Adrien Chorn, Jonathan Stromseth
May 19, 2021
Thomas Pepinsky
January 26, 2021
Adrien Chorn provided editing assistance on this piece. The author thanks Jurel Yap and Kier J. Ballar for their research assistance. All views expressed herein are the author’s and do not necessarily reflect the views and policies of his institution.
Foreign Policy
Southeast Asia
Center for Asia Policy Studies
The Brookings Institution, Washington DC
10:00 am - 12:00 pm EDT
Online Only
3:00 pm - 4:00 pm EDT
The Brookings Institution, Washington D.C.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 04 April 2022
Economic losses from COVID-19 cases in the Philippines: a dynamic model of health and economic policy trade-offs
- Elvira P. de Lara-Tuprio 1 ,
- Maria Regina Justina E. Estuar 2 ,
- Joselito T. Sescon 3 ,
- Cymon Kayle Lubangco ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1292-4687 3 ,
- Rolly Czar Joseph T. Castillo 3 ,
- Timothy Robin Y. Teng 1 ,
- Lenard Paulo V. Tamayo 2 ,
- Jay Michael R. Macalalag 4 &
- Gerome M. Vedeja 3
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 9 , Article number: 111 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
42k Accesses
12 Citations
19 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The COVID-19 pandemic forced governments globally to impose lockdown measures and mobility restrictions to curb the transmission of the virus. As economies slowly reopen, governments face a trade-off between implementing economic recovery and health policy measures to control the spread of the virus and to ensure it will not overwhelm the health system. We developed a mathematical model that measures the economic losses due to the spread of the disease and due to different lockdown policies. This is done by extending the subnational SEIR model to include two differential equations that capture economic losses due to COVID-19 infection and due to the lockdown measures imposed by the Philippine government. We then proceed to assess the trade-off policy space between health and economic measures faced by the Philippine government. The study simulates the cumulative economic losses for 3 months in 8 scenarios across 5 regions in the country, including the National Capital Region (NCR), to capture the trade-off mechanism. These scenarios present the various combinations of either retaining or easing lockdown policies in these regions. Per region, the trade-off policy space was assessed through minimising the 3-month cumulative economic losses subject to the constraint that the average health-care utilisation rate (HCUR) consistently falls below 70%, which is the threshold set by the government before declaring that the health system capacity is at high risk. The study finds that in NCR, a policy trade-off exists where the minimum cumulative economic losses comprise 10.66% of its Gross Regional Domestic Product. Meanwhile, for regions that are non-adjacent to NCR, a policy that hinges on trade-off analysis does not apply. Nevertheless, for all simulated regions, it is recommended to improve and expand the capacity of the health system to broaden the policy space for the government in easing lockdown measures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Modelling COVID-19 pandemic control strategies in metropolitan and rural health districts in New South Wales, Australia
Mathematical modeling of COVID-19 in 14.8 million individuals in Bahia, Brazil
Cost-effectiveness analysis of COVID-19 intervention policies using a mathematical model: an optimal control approach
Introduction.
The Philippine population of 110 million comprises a relatively young population. On May 22, 2021, the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases reported in the country is 1,171,403 with 55,531 active cases, 1,096,109 who recovered, and 19,763 who died. As a consequence of the pandemic, the real gross domestic product (GDP) contracted by 9.6% year-on-year in 2020—the sharpest decline since the Philippine Statistical Agency (PSA) started collecting data on annual growth rates in 1946 (Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, 2021 ). The strictest lockdown imposed from March to April 2020 had the most severe repercussions to the economy, but restrictions soon after have generally eased on economic activities all over the country. However, schools at all levels remain closed and minimum restrictions are still imposed in business operations particularly in customer accommodation capacity in service establishments.
The government is poised for a calibrated reopening of business, mass transportation, and the relaxation of age group restrictions. The government expects a strong recovery before the end of 2021, when enough vaccines have been rolled out against COVID-19. However, the economic recovery plan and growth targets at the end of the year are put in doubt with the first quarter of 2021 growth rate of GDP at -4.2%. This is exacerbated by the surge of cases in March 2021 that took the National Capital Region (NCR) and contiguous provinces by surprise, straining the hospital bed capacity of the region beyond its limits. The government had to reinforce stricter lockdown measures and curfew hours to stem the rapid spread of the virus. The country’s economic development authority proposes to ensure hospitals have enough capacity to allow the resumption of social and economic activities (National Economic and Development Authority, 2020 ). This is justified by pointing out that the majority of COVID-19 cases are mild and asymptomatic.
Efforts in monitoring and mitigating the spread of COVID-19 requires understanding the behaviour of the disease through the development of localised disease models operationalized as an ICT tool accessible to policymakers. FASSSTER is a scenario-based disease surveillance and modelling platform designed to accommodate multiple sources of data as input allowing for a variety of disease models and analytics to generate meaningful information to its stakeholders (FASSSTER, 2020 ). FASSSTER’s module on COVID-19 currently provides information and forecasts from national down to city/municipality level that are used for decision-making by individual local government units (LGUs) and also by key government agencies in charge of the pandemic response.
In this paper, we develop a mathematical model that measures the economic losses due to the spread of the disease and due to different lockdown policies to contain the disease. This is done by extending the FASSSTER subnational Susceptible-Exposed-Infectious-Recovered (SEIR) model to include two differential equations that capture economic losses due to COVID-19 infection and due to the lockdown measures imposed by the Philippine government. We then proceed to assess the trade-off policy space faced by the Philippine government given the policy that health-care utilisation rate must not be more than 70%, which is the threshold set by the government before declaring that the health system capacity is at high risk.
We simulate the cumulative economic losses for 3 months in 8 scenarios across 5 regions in the country, including the National Capital Region (NCR) to capture the trade-off mechanism. These 8 scenarios present the various combinations of either retaining or easing lockdown policies in these regions. Per region, the trade-off policy space was assessed through minimising the 3-month cumulative economic losses subject to the constraint that the average health-care utilisation rate (HCUR) consistently falls below 70%. The study finds that in NCR, a policy trade-off exists where the minimum economic losses below the 70% average HCUR comprise 10.66% of its Gross Regional Domestic Product. Meanwhile, for regions that are non-adjacent to NCR, a policy that hinges on trade-off analysis does not apply. Nevertheless, for all simulated regions, it is recommended to improve and expand the capacity of the health system to broaden the policy space for the government in easing lockdown measures.
The sections of the paper proceed as follows: the first section reviews the literature, the second section explains the FASSSTER SEIR model, the third section discusses the economic dynamic model, the fourth section specifically explains the parameters used in the economic model, the fifth section briefly lays out the policy trade-off model, the sixth discusses the methods used in implementing the model, the seventh section presents the results of the simulations, the eighth section discusses and interprets the results, and the final section presents the conclusion.
Review of related literature
Overview of the economic shocks of pandemics.
The onslaught of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic since 2020 has disrupted lifestyles and livelihoods as governments restrict mobility and economic activity in their respective countries. Unfortunately, this caused a –3.36% decline in the 2020 global economy (World Bank, 2022 ), which will have pushed 71 million people into extreme poverty (World Bank, 2020 ; 2021 ).
As an economic phenomenon, pandemics may be classified under the typologies of disaster economics. Particularly, a pandemic’s impacts may be classified according to the following (Benson and Clay, 2004 ; Noy et al., 2020 ; Keogh-Brown et al., 2010 ; 2020 ; McKibbin and Fernando, 2020 ; Verikios et al., 2012 ): (a) direct impacts, where pandemics cause direct labour supply shocks due to mortality and infection; (b) indirect impacts on productivity, firm revenue, household income, and other welfare effects, and; (c) macroeconomic impacts of a pandemic.
For most pandemic scenarios, social distancing and various forms of lockdowns imposed by countries around the world had led to substantial disruptions in the supply-side of the economy with mandatory business closures (Maital and Barzani, 2020 ; Keogh-Brown et al., 2010 ). Social distancing will have contracted labour supply as well, thus contributing to contractions in the macroeconomy (Geard et al., 2020 ; Keogh-Brown et al., 2010 ). Thus, in general, the literature points to a pandemic’s impacts on the supply- and demand-side, as well as the displacement of labour supply; thus, resulting in lower incomes (Genoni et al., 2020 ; Hupkau et al., 2020 ; United Nations Development Programme, 2021 ). Often, these shocks result from the lockdown measures; thus, a case of a trade-off condition between economic losses and the number of COVID-19 casualties.
Static simulations for the economic impacts of a pandemic
The typologies above are evident in the analyses and simulations on welfare and macroeconomic losses related to a pandemic. For instance, computable general equilibrium (CGE) and microsimulation analyses for the 2009 H1N1 pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic showed increases in inequities, welfare losses, and macroeconomic losses due to lockdown and public prevention strategies (Cereda et al., 2020 ; Keogh-Brown et al., 2020 ; Keogh-Brown et al., 2010 ). Public prevention-related labour losses also comprised at most 25% of the losses in GDP in contrast with health-related losses, which comprised only at most 17% of the losses in GDP.
Amidst the COVID-19 pandemic in Ghana, Amewu et al. ( 2020 ) find in a social accounting matrix-based analysis that the industry and services sectors will have declined by 26.8% and 33.1%, respectively. Other studies investigate the effects of the pandemic on other severely hit sectors such as the tourism sector. Pham et al. ( 2021 ) note that a reduction in tourism demand in Australia will have caused a reduction in income of tourism labourers. Meanwhile, in a static CGE-microsimulation model by Laborde, Martin, and Vos ( 2021 ), they show that as the global GDP will have contracted by 5% following the reduction in labour supply, this will have increased global poverty by 20%, global rural poverty by 15%, poverty in sub-Saharan Africa by 23%, and in South Asia by 15%.
However, due to the static nature of these analyses, the clear trade-off between economic and health costs under various lockdown scenarios is a policy message that remains unexplored, as the simulations above only explicitly tackle a pandemic’s macroeconomic effects. This gap is mostly due to these studies’ usage of static SAM- and CGE-based analyses.
Dynamic simulations for the economic impacts of a pandemic
An obvious advantage of dynamic models over static approaches in estimating the economic losses from the pandemic is the capacity to provide forward-looking insights that have practical use in policymaking. Epidemiological models based on systems of differential equations explicitly model disease spread and recovery as movements of population across different compartments. These compartmental models are useful in forecasting the number of infected individuals, critically ill patients, death toll, among others, and thus are valuable in determining the appropriate intervention to control epidemics.
To date, the Susceptible-Infectious-Recovered (SIR) and SEIR models are among the most popular compartmental models used to study the spread of diseases. In recent years, COVID-19 has become an important subject of more recent mathematical modelling studies. Many of these studies deal with both application and refinement of both SIR and SEIR to allow scenario-building, conduct evaluation of containment measures, and improve forecasts. These include the integration of geographical heterogeneities, the differentiation between isolated and non-isolated cases, and the integration of interventions such as reducing contact rate and isolation of active cases (Anand et al., 2020 ; Chen et al., 2020 ; Hou et al., 2020 ; Peng et al., 2020 ; Reno et al., 2020 ).
Typical epidemiological models may provide insight on the optimal lockdown measure to reduce the transmissibility of a virus. However, there is a need to derive calculations on economic impacts from the COVID-19 case projections to arrive at a conclusion on the optimal frontier from the trade-off between health and economic losses. In Goldsztejn, Schwartzman and Nehorai ( 2020 ), an economic model that measures lost economic productivity due to the pandemic, disease containment measures and economic policies is integrated into an SEIR model. The hybrid model generates important insight on the trade-offs between short-term economic gains in terms of productivity, and the continuous spread of the disease, which in turn informs policymakers on the appropriate containment policies to be implemented.
This approach was further improved by solving an optimal control of multiple group SIR model to find the best way to implement a lockdown (Acemoglu et al., 2020 ). Noting the trade-offs between economic outcomes and spread of disease implied in lockdown policies, Acemoglu et al. ( 2020 ) find that targeted lockdown yields the best result in terms of economic losses and saving lives. However, Acemoglu et al. ( 2020 ) only determine the optimal lockdown policy and their trade-off analysis through COVID-associated fatalities. Kashyap et al. ( 2020 ) note that hospitalisations may be better indicators for lockdown and, as a corollary, reopening policies.
Gaps in the literature
With the recency of the pandemic, there is an increasing but limited scholarship in terms of jointly analysing the losses brought about by the pandemic on health and the economy. On top of this, the literature clearly has gaps in terms of having a trade-off model that captures the context of low- and middle-income countries. Devising a trade-off model for said countries is an imperative given the structural and capability differences of these countries from developed ones in terms of responding to the pandemic. Furthermore, the literature has not explicitly looked into the trade-off between economic losses and health-care system capacities, both at a national and a subnational level.
With this, the paper aims to fill these gaps with the following. Firstly, we extend FASSSTER’s subnational SEIR model to capture the associated economic losses given various lockdown scenarios at a regional level. Then, we construct an optimal policy decision trade-off between the health system and the economy in the Philippines’ case at a regional level. From there, we analyse the policy implications across the different regions given the results of the simulations.
The FASSSTER SEIR model
The FASSSTER model for COVID-19 uses a compartmental model to describe the dynamics of disease transmission in a community, and it is expressed as a system of ordinary differential equations (Estadilla et al., 2021 ):
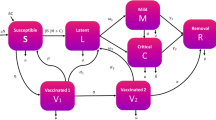
where β = β 0 (1– λ ), \(\alpha _a = \frac{c}{\tau }\) , \(\alpha _s = \frac{{1 - c}}{\tau }\) , and N ( t ) = S ( t ) = E ( t ) + I a ( t ) + I s ( t ) + C ( t ) + R ( t ).
The six compartments used to divide the entire population, namely, susceptible ( S ), exposed ( E ), infectious but asymptomatic ( I a ), infectious and symptomatic ( I s ), confirmed ( C ), and recovered ( R ), indicate the status of the individuals in relation to the disease. Compartment S consists of individuals who have not been infected with COVID-19 but may acquire the disease once exposed to infectious individuals. Compartment E consists of individuals who have been infected, but not yet capable of transmitting the disease to others. The infectious members of the population are split into two compartments, I a and I s , based on the presence of disease symptoms. These individuals may eventually transition to compartment C once they have been detected, in which case they will be quarantined and receive treatment. The individuals in the C compartment are commonly referred to as active cases. Finally, recovered individuals who have tested negative or have undergone the required number of days in isolation will move out to the R compartment. Given that there had only been rare instances of reinfection (Gousseff et al., 2020 ), the FASSSTER model assumes that recovered individuals have developed immunity from the disease. A description of the model parameters can be found in Supplementary Table S1 .
The model has several nonnegative parameters that govern the movement of individuals along the different compartments. The parameter β represents the effective transmission rate, and it is expressed as a product of the disease transmission rate β 0 and reduction factor 1 − λ . The rate β 0 is derived from an assumed reproduction number R 0 , which varies depending on the region. The parameter λ reflects the effect of mobility restrictions such as lockdowns and compliance of the members of the population to minimum health standards (such as social distancing, wearing of face masks etc.). In addition, the parameter ψ captures the relative infectiousness of asymptomatic individuals in relation to those who exhibit symptoms.
The incubation period τ and fraction of asymptomatic cases c are used to derive the transfer rates α α and α s from the exposed compartment to I a and I s compartments, respectively. Among those who are infectious and asymptomatic, a portion of them is considered pre-symptomatic, and hence will eventually develop symptoms of the disease; this is reflected in the parameter ω. The respective detection rates δ a and δ s of asymptomatic and symptomatic infectious individuals indicate the movement from the undetected infectious compartment to the confirmed compartment. These parameters capture the entire health system capacity to prevent-detect-isolate-treat-reintegrate (PDITR) COVID-19 cases; hence, they will henceforth be referred to as HSC parameters. The recoveries of infectious asymptomatic individuals and among the active cases occur at the corresponding rates θ and r . Death rates due to the disease, on the other hand, are given by ∈ I and ∈ T for the infectious symptomatic and confirmed cases, respectively.
Aside from the aforementioned parameters, the model also utilises parameters not associated with the COVID-19 disease, such as the recruitment rate A into the susceptible population. This parameter represents the birth rate of the population and is assumed to be constant. In addition, a natural death rate per unit of time is applied to all compartments in the model, incorporating the effect of non-COVID-19 related deaths in the entire population.
Economic dynamic model
The trade-off model aims to account for the incurred economic losses following the rise and fall of the number of COVID-19 cases in the country and the implementation of various lockdown measures. The model variables are estimated per day based on the SEIR model estimate of daily cases and are defined as follows. Let Y E ( t ) be the economic loss due to COVID-19 infections (hospitalisation, isolation, and death of infected individuals) and Y E ( t ) be the economic loss due to the implemented lockdown at time t . The dynamics of each economic variable through time is described by an ordinary differential equation. Since each equation depends only on the values of the state variables of the epidemiological model, then it is possible to obtain a closed form solution.
Economic loss due to COVID-19 infections (hospitalisation, isolation, and health)
The economic loss due to hospitalisation, isolation, and death Y E is described by the following differential equation:
where z = annual gross value added of each worker (assumed constant for all future years and for all ages), w = daily gross value added, ι i = % population with ages 0–14 ( i = 1), and labour force with ages 15–34 ( i = 2), 35–49 ( i = 3) and 50–64 ( i = 4), s r = social discount rate, κ = employed to population ratio, T i = average remaining productive years for people in age bracket i , i = 1, 2, 3, 4, and T 5 = average age of deaths from 0–14 years old age group. Note that the above formulation assumes that the young population 0–14 years old will start working at age 15, and that they will work for T 1 −15 years.
Solving Eq. ( 7 ), we obtain for t ≥ 0,
In this equation, the terms on the right-hand side are labelled as (A), (B), and (C). Term (A) is the present value of all future gross value added of 0–14 years old who died due to COVID-19 at time t . Similarly, term (B) is the present value of all future gross value added of people in the labour force who died due to COVID-19 at time t . Term (C) represents the total gross value added lost at time t due to sickness and isolation.
The discounting factors and the population age group shares in (A) and (B) can be simplified further into K 1 and K 2 , where \(K_1 = \iota _1\left( {\frac{{\left( {s_r + 1} \right)^{T_1 + T_5 - 13} - \left( {s_r + 1} \right)}}{{s_r\left( {s_r + 1} \right)^{T_1 + 1}}}} \right)\) and \(K_2 = \mathop {\sum}\nolimits_{i = 2}^4 {\iota _i\left( {\frac{{\left( {s_r + 1} \right)^{T_i + 2} - \left( {s_r + 1} \right)}}{{s_r\left( {s_r + 1} \right)^{T_i + 1}}}} \right)}\) . By letting L 1 = z( K 1 + K 2 ) ∈ I + κw (1 – ∈ I ) and L 2 = z( K 1 + K 2 ) ∈ T + κw (1 – ∈ T ), we have:
Economic losses due to lockdown policies
Equation ( 7 ) measures the losses due mainly to sickness and death from COVID-19. The values depend on the number of detected and undetected infected individuals, C and I s . The other losses sustained by the other part of the population are due to their inability to earn because of lockdown policies. This is what the next variable Y L represents, whose dynamics is given by the differential equation
where φ = the displacement rate, and κ and w are as defined previously.
Solving the differential equation, then
Note that [ S ( t ) + E ( t ) + I a ( t ) + R ( t )] is the rest of the population at time t , i.e., other than the active and infectious symptomatic cases. Multiplying this by κ and the displacement rate φ yields the number of employed people in this population who are displaced due to the lockdown policy. Thus, κwφ [ S ( t ) + E ( t ) + I a ( t ) + R ( t )] is the total foregone income due to the lockdown policy.
Economic model parameters
The values of the parameters were derived from a variety of sources. The parameters for employment and gross value added were computed based on the data from the Philippine Statistics Authority ( 2021 , 2020 , 2019a , 2019b ), the Department of Health’s Epidemiology Bureau (DOH-EB) ( 2020 ), the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) ( 2020a , 2020b ) and the National Economic Development Authority (NEDA) ( 2016 ) (See Supplementary Tables S2 and S3 for the summary of economic parameters).
Parameters determined from related literature
We used the number of deaths from the data of the DOH-EB ( 2020 ) to disaggregate the long-term economic costs of the COVID-related deaths into age groups. Specifically, the COVID-related deaths were divided according to the following age groups: (a) below 15 years old, (b) 15 to 34 years old, (c) 35 to 49 years old, and (d) 50 to 64 years old. The average remaining years for these groups were computed directly from the average age of death of the respective cluster. Finally, we used the social discount rate as determined by NEDA ( 2016 ) to get the present value of the stream of foregone incomes of those who died from the disease.
Parameters estimated from local data
The foregone value added due to labour displacement was estimated as the amount due to workers in a geographic area who were unable to work as a result of strict lockdown measures. It was expected to contribute to the total value added in a given year if the area they reside or work in has not been locked down.
The employed to population ratio κ i for each region i was computed as
where e i was total employment in region i , and Pi was the total population in the region. Both e i and Pi were obtained from the quarterly labour force survey and the census, respectively (Philippine Statistics Authority, 2020 , 2019a , 2019b ).
The annual gross value added per worker z i for region i was computed as
where g ji was the share of sector j in total gross value added of region i , GVA ji was the gross value added of sector j in region i (Philippine Statistics Authority, 2021 ), and e ji was the number of employed persons in sector j of region i . If individuals worked for an average of 22.5 days for each month for 12 months in a year, then the daily gross value added per worker in region i was given by
Apart from this, labour displacement rates were calculated at regional level. The rates are differentiated by economic reopening scenarios from March 2020 to September 2020, from October 2020 to February 2021, and from March 2021 onwards (Department of Trade and Industry, 2020a , 2020b , 2021 ). These were used to simulate the graduate reopening of the economy. From the country’s labour force survey, each representative observation j in a region i is designated with a numerical value in accordance with the percentage operating capacity of the sector where j works in. Given the probability weights p ji , the displacement rate φ i for region i was calculated by
where x ji served as the variable representing the maximum operating capacity designated for j ’s sector of work.
Policy trade-off model
The trade-off between economic losses and health measures gives the optimal policy subject to a socially determined constraint. From the literature, it was pointed out that the optimal policy option would be what minimises total economic losses subject to the number of deaths at a given time (Acemoglu et al., 2020 ). However, for the Philippines’ case, lockdown restrictions are decided based on the intensive care unit and health-care utilisation rate (HCUR). The health system is said to reach its critical levels if the HCUR breaches 70% of the total available bed capacity in intensive care units. Once breached, policymakers would opt to implement stricter quarantine measures.
Given these, a policy mix of various quarantine restrictions may be chosen for as long as it provides the lowest amount of economic losses subject to the constraint that the HCUR threshold is not breached. Since economic losses are adequately captured by the sum of infection-related and lockdown-related losses, Y E ( t ) + Y L ( t ), then policy option must satisfy the constrained minimisation below:
where the objective function is evaluated from the initial time value t 0 to T .
The COVID-19 case information data including the date, location transformed into the Philippine Standard Geographic Code (PSGC), case count, and date reported were used as input to the model. Imputation using predictive mean matching uses the mice package in the R programming language. It was performed to address data gaps including the date of onset, date of specimen collection, date of admission, date of result, and date of recovery. Population data was obtained from the country’s Census of Population and Housing of 2015. The scripts to implement the FASSSTER SEIR model were developed using core packages in R including optimParallel for parameter estimation and deSolve for solving the ordinary differential equations. The output of the model is fitted to historical data by finding the best value of the parameter lambda using the L-BFGS-B method under the optim function and the MSE as measure of fitness (Byrd et al., 1995 ). The best value of lambda is obtained by performing parameter fitting with several bootstraps for each region, having at least 50 iterations until a correlation threshold of at least 90% is achieved. The output generated from the code execution contains values of the different compartments at each point in time. From these, the economic variables Y E ( t ) and Y L ( t ) were evaluated using the formulas in Eq. ( 7 ) and ( 8 ) in their simplified forms, and the parameter and displacement rate values corresponding to the implemented lockdown scenario (Fig. 1 ).
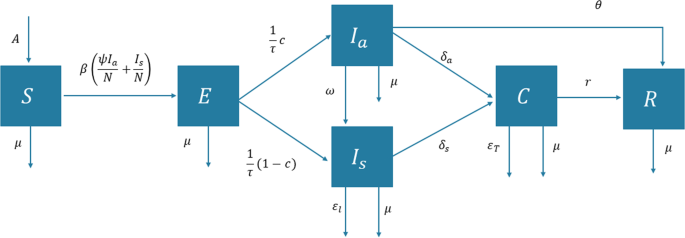
The different population states are represented by the compartments labelled as susceptible (S), exposed (E), infectious but asymptomatic ( I a ), infectious and symptomatic ( I s ), confirmed (C), and recovered (R).
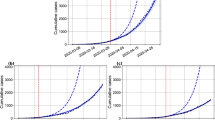
We simulate the economic losses and health-care utilisation capacity (HCUR) for the National Capital Region (NCR), Ilocos Region, Western Visayas, Soccsksargen, and for the Davao Region by implementing various combinations of lockdown restrictions for three months to capture one quarter of economic losses for these regions. The National Capital Region accounts for about half of the Philippines’ gross domestic product, while the inclusion of other regions aim to represent the various areas of the country. The policy easing simulations use the four lockdown policies that the Philippines uses, as seen in Table 1 .
Simulations for the National Capital Region
Table 2 shows the sequence of lockdown measures implemented for the NCR. Each lockdown measure is assumed to be implemented for one month. Two sets of simulations are implemented for the region. The first set assumes a health systems capacity (HSC) for the region at 17.99% (A), while the second is at 21.93% (B). A higher HSC means an improvement in testing and isolation strategies for the regions of concern.
From the sequence of lockdown measures in Table 2 , Fig. 2 shows the plot of the average HCUR as well as the corresponding total economic losses for the two sets of simulations for one quarter. For the scenario at 17.99% HSC (A), the highest loss is recorded at 16.58% of the annual gross regional domestic product (GRDP) while the lowest loss is at 12.19% of its GRDP. Lower average HCUR corresponds to more stringent scenarios starting with Scenario 1. Furthermore, under the scenarios with 21.93% HSC (B), losses and average HCUR are generally lower. Scenarios 1 to 4 from this set lie below the 70% threshold of the HCUR, with the lowest economic loss simulated to be at 9.11% of the GRDP.
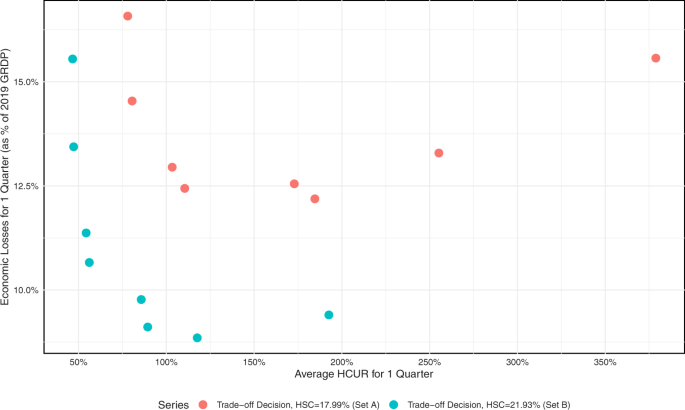
These include the set of trade-off decisions under a health system capacity equal to 17.99%, and another set equal to 21.93% (Source of basic data: Authors’ calculations).
Overall, the trend below shows a parabolic shape. The trend begins with an initial decrease in economic losses as restrictions loosen, but this comes at the expense of increasing HCUR. This is then followed by an increasing trend in losses as restrictions are further loosened. Notably, the subsequent marginal increases in losses in the simulation with 21.93% HSC are smaller relative to the marginal increases under the 17.99% HSC.
Simulations for the Regions Outside of NCR
Table 2 also shows the lockdown sequence for the Ilocos, Western Visayas, Soccsksargen, and Davao regions. The sequence begins with Level III only. Meanwhile, the lowest lockdown measure simulated for the regions is Level I. Two sets of simulations with differing health system capacities for each scenario are done as well.
With this lockdown sequence, Fig. 3 shows the panel of scatter plot between the average HCUR and total economic losses as percentage of the respective GRDP, with both parameters covering one quarter. Similar to the case of the NCR, the average HCUR for the simulations with higher health system capacity (B) is lower than the simulations with lower health system capacity (A). However, unlike in NCR, the regions’ simulations do not exhibit a parabolic shape.
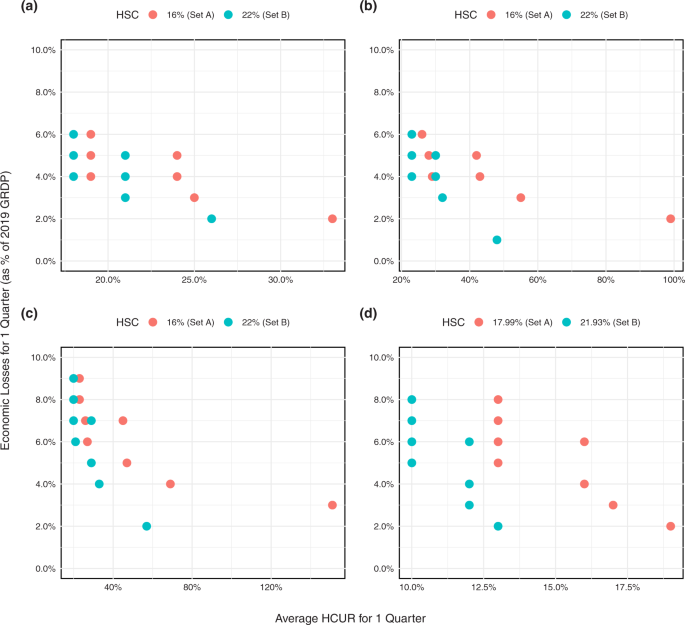
These include trade-offs for a Ilocos Region, b Western Visayas Region, c Soccsksargen Region, and d Davao Region (Source of basic data: Authors’ calculations).
Discussion and interpretation
The hypothetical simulations above clearly capture the losses associated with the pandemic and the corresponding lockdown interventions by the Philippine government. The trend of the simulations clearly shows the differences in the policy considerations for the National Capital Region (NCR) and the four other regions outside of NCR. Specifically, the parabolic trend of the former suggests an optimal strategy that can be attained through a trade-off policy even with the absence of any constraint in finding the said optimal strategy. This trend is borne from the countervailing effects between the economic losses due to COVID-19 infection ( Y E ) and the losses from the lockdown measures ( Y L ) implemented for the region. Specifically, Fig. 4(a), (b) show the composition of economic losses across all scenarios for the NCR simulation under a lower and higher health system capacity (HSC), respectively.
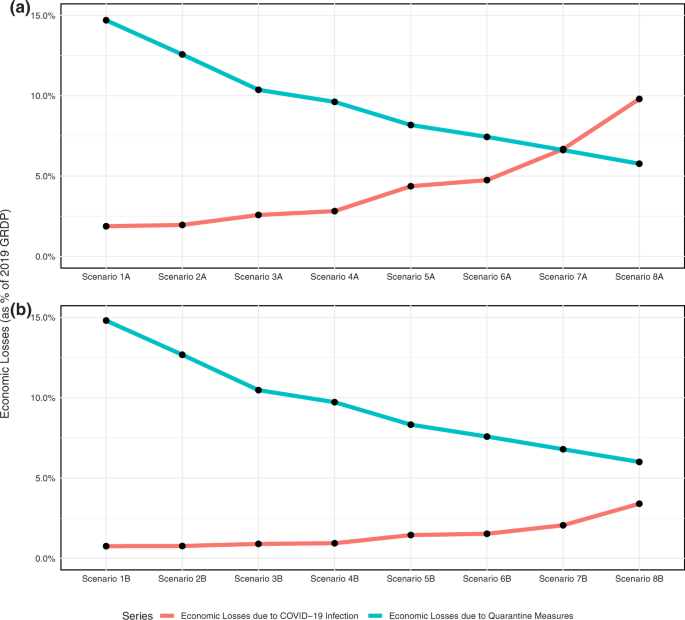
These include losses under a HSC = 17.99% and b HSC = 21.93% in the National Capital Region (Source of basic data: Authors’ calculations).
In both panels of Fig. 4 , as quarantine measures loosen, economic losses from infections ( Y E ) tend to increase while the converse holds for economic losses due to quarantine restrictions ( Y L ). The results are intuitive as loosening restrictions may lead to increased mobility, and therefore increased exposure and infections from the virus. In fact, economic losses from infections ( Y E ) take up about half of the economic losses for the region in Scenario 7A, Fig. 4(a) .
While the same trends can be observed for the scenarios with higher HSC at 21.93%, the economic losses from infections ( Y E ) do not overtake the losses simulated from lockdown restrictions ( Y L ) as seen in Fig. 4(b) . This may explain the slower upward trend of economic losses in Fig. 2 at HSC = 21.93%.
The output of the simulation for the Davao region shows that the economic losses from COVID-19 infections ( Y E ) remain low even as the lockdown restrictions ease down. At the same time, economic losses from lockdown restrictions ( Y L ) show a steady decline with less stringent lockdown measures. Overall, the region experiences a decreasing trend in total economic losses even as the least stringent lockdown measure is implemented for a longer period. This pattern is similar with the regions of Ilocos, Western Visayas, and Soccsksarkgen.
The results of the simulations from Figs. 2 and 3 also demonstrate differing levels of economic losses and health-care utilisation between the two sets of scenarios for NCR and the four other regions. Clearly, lower economic losses and health-care utilisation rates were recorded for the scenarios with higher HSC. Specifically, lower total economic losses can be attributed to a slower marginal increase in losses from infections ( Y E ) as seen in Fig. 4(b) . Thus, even while easing restrictions, economic losses may be tempered with an improvement in the health system.
With the above analysis, the policy trade-off as a constrained minimisation problem of economic losses subject to HCUR above appears to apply in NCR but not in regions outside of NCR. The latter is better off in enhancing prevention, detection, isolation, treatment, and reintegration (PDITR) strategy combined with targeted small area lockdowns, if necessary, without risking any increases in economic losses. But, in all scenarios and anywhere, the enhancement of the HSC through improved PDITR strategies remains vital to avoid having to deal with local infection surges and outbreaks. This also avoids forcing local authorities in a policy bind between health and economic measures to implement. Enhancing PDITR in congested urban centres (i.e., NCR) is difficult especially with the surge in new daily cases. People are forced to defy social distance rules and other minimum health standards in public transportation and in their workplaces that help spread the virus.
We extended the FASSSTER subnational SEIR model to include two differential equations that capture economic losses due to COVID-19 infection and due to the lockdown measures, respectively. The extended model aims to account for the incurred economic losses following the rise and fall of the number of active COVID-19 cases in the country and the implementation of various lockdown measures. In simulating eight different scenarios in each of the five selected regions in the country, we found a tight policy choice in the case of the National Capital Region (NCR) but not in the cases of four other regions far from NCR. This clearly demonstrates the difficult policy decision in the case of NCR in minimising economic losses given the constraint of its intensive care unit (ICU) bed capacity.
On the other hand, the regions far from the NCR have wider policy space towards economic reopening and recovery. However, in all scenarios, the primary significance of improving the health system capacity (HSC) to detect and control the spread of the disease remains in order to widen the trade-off policy space between public health and economic measures.
The policy trade-off simulation results imply different policy approaches in each region. This is also to consider the archipelagic nature of the country and the simultaneous concentration of economic output and COVID-19 cases in NCR and contiguous provinces compared to the rest of the country. Each local region in the country merits exploration of different policy combinations in economic and health measures depending on the number of active COVID-19 cases, strategic importance of economic activities and output specific in the area, the geographic spread of the local population and their places of work, and considering local health system capacities. However, we would like to caution that the actual number of cases could diverge from the results of our simulations. This is because the parameters of the model must be updated regularly driven generally by the behaviour of the population and the likely presence of variants of COVID-19. Given the constant variability of COVID-19 data, we recommend a shorter period of model projections from one to two months at the most.
In summary, this paper showed how mathematical modelling can be used to inform policymakers on the economic impact of lockdown policies and make decisions among the available policy options, taking into consideration the economic and health trade-offs of these policies. The proposed methodology provides a tool for enhanced policy decisions in other countries during the COVID-19 pandemic or similar circumstances in the future.

Data availability
The raw datasets used in this study are publicly available at the Department of Health COVID-19 Tracker Website: https://doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker . Datasets will be made available upon request after completing request form and signing non-disclosure agreement. Code and scripts will be made available upon request after completing request form and signing non-disclosure agreement.
Acemoglu D, Chernozhukov V, Werning I, Whinston M (2020) Optimal targeted lockdowns of a multi-group SIR model. In: National Bureau of Economic Research Working Papers. National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER). https://www.nber.org/system/files/working_papers/w27102/w27102.pdf . Accessed 16 Jun 2021
Amewu S, Asante S, Pauw K, Thurlow J (2020) The economic costs of COVID-19 in Sub-Saharan Africa: insights from a simulation exercise for Ghana. Eur J Dev Res 32(5):1353–1378. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41287-020-00332-6
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Anand N, Sabarinath A, Geetha S, Somanath S (2020) Predicting the spread of COVID-19 using SIR model augmented to incorporate quarantine and testing. Trans Indian Natl Acad Eng 5:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41403-020-00151-5
Article Google Scholar
Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (2021) 2021 Inflation Report First Quarter. https://www.bsp.gov.ph/Lists/Inflation%20Report/Attachments/22/IR1qtr_2021.pdf . Accessed 16 Jun 2021
Benson C, Clay E (2004) Understanding the economic and financial impacts of natural disasters. In: World Bank Disaster Risk Management Paper. World Bank. https://elibrary.worldbank.org/doi/abs/10.1596/0-8213-5685-2 . Accessed Jan 2022
Byrd R, Lu P, Nocedal J, Zhu C (1995) A limited memory algorithm for bound constrained optimization. SIAM J Sci Comput 16:1190–1208. https://doi.org/10.1137/0916069
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Cereda F, Rubião R, Sousa L (2020) COVID-19, Labor market shocks, and poverty in brazil: a microsimulation analysis. In: poverty and equity global practice. World Bank. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/34372/COVID-19-Labor-Market-Shocks-and-Poverty-in-Brazil-A-Microsimulation-Analysis.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y . Accessed 21 Feb 2021
Chen D, Lee S, Sang J (2020) The role of state-wide stay-at-home policies on confirmed COVID-19 cases in the United States: a deterministic SIR model. Health Informatics Int J 9(2/3):1–20. https://doi.org/10.5121/hiij.2020.9301
Article CAS Google Scholar
Department of Health-Epidemiology Bureau (2020) COVID-19 tracker Philippines. https://doh.gov.ph/covid19tracker . Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Department of Trade and Industry (2020a) Revised category I-IV business establishments or activities pursuant to the revised omnibus guidelines on community quarantine dated 22 May 2020 Amending for the purpose of memorandum circular 20-22s. https://dtiwebfiles.s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/COVID19Resources/COVID-19+Advisories/090620_MC2033.pdf . Accessed 09 Feb 2021
Department of Trade and Industry (2020b) Increasing the allowable operational capacity of certain business establishments of activities under categories II and III under general community quarantine. https://dtiwebfiles.s3-ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/COVID19Resources/COVID-19+Advisories/031020_MC2052.pdf . Accessed 09 Feb 2021
Department of Trade and Industry (2021) Prescribing the recategorization of certain business activities from category IV to category III. https://www.dti.gov.ph/sdm_downloads/memorandum-circular-no-21-08-s-2021/ . Accessed 15 Mar 2021
Estadilla C, Uyheng J, de Lara-Tuprio E, Teng T, Macalalag J, Estuar M (2021) Impact of vaccine supplies and delays on optimal control of the COVID-19 pandemic: mapping interventions for the Philippines. Infect Dis Poverty 10(107). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40249-021-00886-5
FASSSTER (2020) COVID-19 Philippines LGU Monitoring Platform. https://fassster.ehealth.ph/covid19/ . Accessed Dec 2020
Geard N, Giesecke J, Madden J, McBryde E, Moss R, Tran N (2020) Modelling the economic impacts of epidemics in developing countries under alternative intervention strategies. In: Madden J, Shibusawa H, Higano Y (eds) Environmental economics and computable general equilibrium analysis. Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd., Singapore, pp. 193–214
Chapter Google Scholar
Genoni M, Khan A, Krishnan N, Palaniswamy N, Raza W (2020) Losing livelihoods: the labor market impacts of COVID-19 in Bangladesh. In: Poverty and equity global practice. World Bank. https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/34449/Losing-Livelihoods-The-Labor-Market-Impacts-of-COVID-19-in-Bangladesh.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y . Accessed 21 Feb 2021
Goldsztejn U, Schwartzman D, Nehorai A (2020) Public policy and economic dynamics of COVID-19 spread: a mathematical modeling study. PLoS ONE 15(12):e0244174. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0244174
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gousseff M, Penot P, Gallay L, Batisse D, Benech N, Bouiller K, Collarino R, Conrad A, Slama D, Joseph C, Lemaignen A, Lescure F, Levy B, Mahevas M, Pozzetto B, Vignier N, Wyplosz B, Salmon D, Goehringer F, Botelho-Nevers E (2020) Clinical recurrences of COVID-19 symptoms after recovery: viral relapse, reinfection or inflammatory rebound? J Infect 81(5):816–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.073
Hou C, Chen J, Zhou Y, Hua L, Yuan J, He S, Guo Y, Zhang S, Jia Q, Zhang J, Xu G, Jia E (2020) The effectiveness of quarantine in Wuhan city against the Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A well-mixed SEIR model analysis. J Med Virol 92(7):841–848. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.25827
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Hupkau C, Isphording I, Machin S, Ruiz-Valenzuela J (2020) Labour market shocks during the Covid-19 pandemic: inequalities and child outcomes. In: Covid-19 analysis series. Center for Economic Performance. https://cep.lse.ac.uk/pubs/download/cepcovid-19-015.pdf . Accessed 21 Feb 2021
Inter-Agency Task Force for the Management of Emerging Infectious Diseases (2020) Omnibus Guidelines on the Implementation of Community Quarantine in the Philippines with Amendments as of June 3, 2020. https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/2020/06jun/20200603-omnibus-guidelines-on-the-implementation-of-community-quarantine-in-the-philippines.pdf . Accessed 09 Feb 2021
Kashyap S, Gombar S, Yadlowsky S, Callahan A, Fries J, Pinsky B, Shah N (2020) Measure what matters: counts of hospitalized patients are a better metric for health system capacity planning for a reopening. J Am Med Inform Assoc 27(7):1026–1131. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocaa076
Keogh-Brown M, Jensen H, Edmunds J, Smith R (2020) The impact of Covid-19, associated behaviours and policies on the UK economy: a computable general equilibrium model. SSM Popul Health 12:100651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssmph.2020.100651
Keogh-Brown M, Smith R, Edmunds J, Beutels P (2010) The macroeconomic impact of pandemic influenza: estimates from models of the United Kingdom, France, Belgium and The Netherlands. Eur J Health Econ 11:543–554. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10198-009-0210-1
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Laborde D, Martin W, Vos R (2021) Impacts of COVID-19 on global poverty, food security, and diets: insights from global model scenario analysis. Agri Econ (United Kingdom) 52(3):375–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/agec.12624
Maital S, Barzani E (2020) The global economic impact of COVID-19: a summary of research. https://www.neaman.org.il/en/Files/Global%20Economic%20Impact%20of%20COVID19.pdf . Accessed Jan 2022
McKibbin W, Fernando R (2020) The global macroeconomic impacts of COVID-19: seven scenarios. https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-global-macroeconomic-impacts-of-covid-19-seven-scenarios/ . Accessed Jan 2022
National Economic and Development Authority (2020) Impact of COVID-19 on the economy and the people, and the need to manage risk. https://www.sec.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/2020CG-Forum_Keynote_NEDA-Sec.-Chua_Impact-of-COVID19-on-the-Economy.pdf . Accessed Feb 2021
National Economic Development Authority-Investment Coordination Committee (2016) Revisions on ICC Guidelines and Procedures (Updated Social Discount Rate for the Philippines). http://www.neda.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Revisions-on-ICC-Guidelines-and-Procedures-Updated-Social-Discount-Rate-for-the-Philippines.pdf . Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Noy I, Doan N, Ferrarini B, Park D (2020) The economic risk of COVID-19 in developing countries: where is it highest? In: Djankov S, Panizza U (eds) COVID-19 in developing economies. Center for Economic Policy Research Press, London, pp. 38–52
Google Scholar
Peng T, Liu X, Ni H, Cui Z, Du L (2020) City lockdown and nationwide intensive community screening are effective in controlling the COVID-19 epidemic: analysis based on a modified SIR model. PLoS ONE 15(8):e0238411. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0238411
Pham T, Dwyer L, Su J, Ngo T (2021) COVID-19 impacts of inbound tourism on australian economy. Ann. Tourism Res. 88:103179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2021.103179
Philippine Statistics Authority (2019a) 2018 Labor Force Survey (Microdata). https://psa.gov.ph/content/2018-annual-estimates-tables . Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Philippine Statistics Authority (2019b) Updated population projections based on the results of 2015 POPCEN. https://psa.gov.ph/content/updated-population-projections-based-results-2015-popcen . Accessed 12 Feb 2021
Philippine Statistics Authority (2020) Census of population and housing. https://psa.gov.ph/population-and-housing . Accessed May 2020
Philippine Statistics Authority (2021) National Accounts Data Series. https://psa.gov.ph/national-accounts/base-2018/data-series . Accessed 05 Apr 2021
Reno C, Lenzi J, Navarra A, Barelli E, Gori D, Lanza A, Valentini R, Tang B, Fantini MP (2020) Forecasting COVID-19-associated hospitalizations under different levels of social distancing in Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna, Northern Italy: results from an extended SEIR compartmental model. J Clin Med 9(5):1492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051492
Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar
United Nations Development Programme (2021) The Socioeconomic Impact Assessment of COVID-19 in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao. UNDP in the Philippines. https://www.ph.undp.org/content/philippines/en/home/library/the-socioeconomic-impact-assessment-of-covid-19-on-the-bangsamor.html . Accessed Nov 2021.
Verikios G, McCaw J, McVernon J, Harris A (2012) H1N1 influenza and the Australian macroeconomy. J Asia Pac Econ 17(1):22–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/13547860.2012.639999
World Bank (2020) Projected Poverty Impacts of COVID-19 (Coronavirus). https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/poverty/brief/projected-poverty-impacts-of-COVID-19 . Accessed Jan 2022
World Bank (2021) Global economic perspectives. World Bank, Washington DC
World Bank (2022) GDP growth (annual %). https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/NY.GDP.MKTP.KD.ZG . Accessed Jan 2022
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Geoffrey M. Ducanes, Associate Professor, Ateneo de Manila University Department of Economics, for giving us valuable comments in the course of developing the economic model, and Mr. Jerome Patrick D. Cruz, current Ph.D. student, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, for initiating and leading the economic team in FASSSTER in the beginning of the project for their pitches in improving the model. We also thank Mr. John Carlo Pangyarihan for typesetting the manuscript. The project is supported by the Philippine Council for Health Research and Development, United Nations Development Programme and the Epidemiology Bureau of the Department of Health.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Mathematics, Ateneo de Manila University, Quezon City, Philippines
Elvira P. de Lara-Tuprio & Timothy Robin Y. Teng
Department of Information Systems and Computer Science, Ateneo de Manila University, Quezon City, Philippines
Maria Regina Justina E. Estuar & Lenard Paulo V. Tamayo
Department of Economics, Ateneo de Manila University, Quezon City, Philippines
Joselito T. Sescon, Cymon Kayle Lubangco, Rolly Czar Joseph T. Castillo & Gerome M. Vedeja
Department of Mathematics, Caraga State University, Butuan City, Philippines
Jay Michael R. Macalalag
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Model conceptualization, data collection and analysis were performed by EPdL-T, MRJEE, JTS, CKL, CJTC, TRYT, LPT, JMRM, and GMV. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript, and read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Cymon Kayle Lubangco .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
Proponents of the project are corresponding authors in the study. Research and corresponding publications are integral to the development of the models and systems. The authors declare no conflict nor competing interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
de Lara-Tuprio, E.P., Estuar, M.R.J.E., Sescon, J.T. et al. Economic losses from COVID-19 cases in the Philippines: a dynamic model of health and economic policy trade-offs. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 9 , 111 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01125-4
Download citation
Received : 06 August 2021
Accepted : 09 March 2022
Published : 04 April 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-022-01125-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Where We Work
- Philippines
Navigating a Challenging Recovery in the Philippines (Philippines Economic Update June 2021)

STORY HIGHLIGHTS
- The resurgence of COVID 19 cases and the reimposition of stringent quarantine measures held back early signs of an economic rebound.
- The economy is expected to recover over the forecast horizon, but there are significant downside risks.
- The key policy challenges are to manage the pandemic, effectively deliver social protection, and mobilize private sector participation in the recovery.
Recent Economic and Policy Developments
- The economy remained in recession, contracting by 4.2% year-on-year in the first quarter of 2021. The growth contraction was fueled by weak domestic demand, driven by the combination of containment measures, weak confidence, and rising inflation.
- Meanwhile, tepid external demand was driven by the sharp contraction in services exports amid lingering restrictions and weak demand for international tourism while goods exports recovered.
- The public sector was the main driver of growth with an expansionary budget.
- The impact of the recession is broad-based, affecting all sectors, i.e. industry, construction, manufacturing, services, trade, transportation, accommodation and food services.
- The Central Bank of the Philippines (Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas) maintained its key policy rate at 2.0% throughout the first four months of 2021 to support the economic recovery.
- The authorities also accelerated public spending. Stimulus spending and infrastructure investment drove public spending from 19.1% of GDP in the first quarter of 2020 to 23.4% of GDP in the same period in 2021.
- The unemployment rate decreased to 7.1% in March 2021 after remaining steady at 8.7-8.8% in the past five months.
Outlook and Risks
- The growth prospects hinge on the country’s ability to manage the COVID-19 health crisis.
- The economy is projected to expand at 4.7% in 2021, before accelerating to 5.9% in 2022 and 6.0% in 2023. The economic recovery will contribute to renewed progress in poverty reduction.
- A resurgence of infection due to the entry of new virus variants is the most significant risk, which may yet overwhelm the healthcare system.
- Ineffectively containing the virus or implementing the mass vaccination program may extend mobility restrictions, which could lead to further job and income losses, disrupt businesses, and delay economic recovery.
- External risks include a slower-than-expected global recovery, disruptions in international logistics and global value chains, and trade protectionism.
Policy Recommendations
- The key health policy response remains the management of the virus and roll out of the vaccination program.
- Effectively delivering social protection programs will help reduce the extent to which the crisis adversely affects long term human capital accumulation.
- Mobilizing greater private sector participation in public infrastructure projects will be important as the government faces limited fiscal space in the short term.
- Relaxing restrictions on FDI is expected to boost the economic recovery.
Special Focus on Subnational Finance
Local governments have played a crucial role at the front lines of the COVID crisis. A current lack of resources prevents local government units (LGUs) from fulfilling their devolved mandates.
- The Mandanas Ruling that will be implemented in 2022 is the first step towards strengthening decentralization and improving local service delivery.
- Large disparities in LGUs’ financial resources have led to persistent inequalities across LGUs.
- Implementation challenges can be addressed successfully through improved coordination and strategic planning and budgeting.
- Addressing the structural challenges of decentralization requires a long-term investment in designing institutional arrangements that will ensure the success of decentralization.
- Clearly define, communicate, and coordinate the re devolution of functions.
- Minimize inefficient allocation of LGU budgets by focusing on implementation ready programs and projects.
- Support capacity building in local government units.
- Reduce inequality by re devolving gradually and targeting national government support toward disadvantaged LGUs.
- Strengthen systems of monitoring and evaluation within government.
- Amend the Local Government Code to address fundamental challenges towards effective service delivery.
- Strengthen demand for transparency and accountability.

June 10, 2021 Report Launch Replay
- [FULL REPORT] Philippines Economic Update June 2021: Navigating a Challenging Recovery
- [PRESS RELEASE] Manila, June 10, 2021-Mandanas Ruling Provides Opportunities for Improving Service Delivery Through Enhanced Decentralization
- [SLIDE PRESENTATION] Mandanas Ruling: An Opportunity for Effective Decentralization
- [SLIDE PRESENTATION] Philippines Economic Update June 2021: Navigating a Challenging Recovery
- Get past issues of the Philippines Economic Update
Customer Logins
Obtain the data you need to make the most informed decisions by accessing our extensive portfolio of information, analytics, and expertise. Sign in to the product or service center of your choice.

- S&P Dow Jones Indices
- S&P Global Market Intelligence
- S&P Global Mobility
- S&P Global Commodity Insights
- S&P Global Ratings
- S&P Global Sustainable1
- Investor Relations Overview
- Investor Presentations
- Investor Fact Book
- News Releases
- Quarterly Earnings
- SEC Filings & Reports
- Executive Committee
- Corporate Governance
- Merger Information
- Stock & Dividends
- Shareholder Services
- Contact Investor Relations
- Email Subscription Center
- Media Center

Philippines on Track to Become One Trillion Dollar Economy by 2033

Executive Director and Asia-Pacific Chief Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
The Philippines economy grew at a pace of 7.6% in 2022, the fastest rate of economic growth recorded by the Philippines since 1976. With strong growth forecast over the medium-term outlook, the size of Philippines GDP measured in US Dollar nominal terms is set to reach USD one trillion by 2033.
This will make the Philippines one of the largest emerging markets in the Asia-Pacific as well as a leading emerging market globally. Average annual GDP per person has also risen dramatically over the past two decades, from below USD 1,000 per person in 2000 to USD 3,500 by 2022 and is projected to rise above USD 6,000 per person by 2030.
Philippines: One of World's Fastest Growing Emerging Markets
The strong rebound from the COVID-19 pandemic during 2022 helped to drive the pace of growth of the Philippines economy to the fastest rate since 1976. The Philippines GDP growth rate of 7.6% was comparable to some of the world's fastest growing large emerging markets in 2022, including the Gulf Co-operation Council oil exporting nations of Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates, as well as other rapidly growing Asian emerging economies such as Malaysia, Vietnam and India.
The Philippines has also shown a much-improved economic growth performance over the past decade, apart from during the peak period of the COVID-19 pandemic during 2020-21 when there was widespread global disruption to economic activity. During the period from 2012 to 2019, real GDP growth in the Philippines each year ranged between 6% to 7%. The economic rebound in 2022 pushed real economic growth to the highest pace recorded since 1976, with household final consumption expenditure growing by 8.3% y/y while gross capital formation grew by 16.8% y/y.
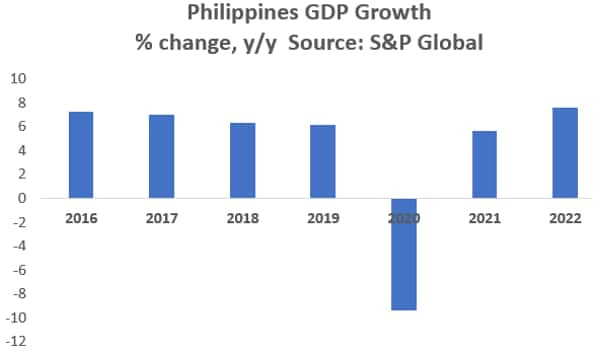
The S&P Global Philippines Manufacturing PMI survey reading of 52.5 in March continued to show expansionary conditions in the manufacturing sector, albeit somewhat lower than January's seven-month high of 53.5. Driving growth was a further expansion in output, which rose for the seventh consecutive month. The upturn in production was largely underpinned by the strong upturn in new orders.
However, supplier performance worsened further, as port congestion and material shortages meant a further lengthening of lead times. Delivery delays, in part, also resulted in a fresh rise in the levels of unfinished work.
Broader inflation pressures have remained a key concern for the near-term economic outlook. Although the headline CPI inflation rate moderated to 7.6% y/y in March compared with 8.6% y/y in February 2023, it still remains significantly above the Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas (BSP) inflation target range of 2% to 4%.
The BSP tightened monetary policy by a total of 350bps during 2022. Reflecting continued high inflation pressures, the Monetary Board of the BSP decided to further raise the interest rate on the BSP's overnight reverse repurchase facility by 50 basis points to 6.0 percent on 16 February 2023, with a further 25bp rate hike on 23 March 2023 pushing the overnight reverse repurchase facility rate to 6.25%. According to the BSP's latest assessment, average CPI inflation is projected to be above the upper end of the 2-4 percent target range at 6.0 percent in 2023, before returning to within target at 2.9 percent in 2024.
Deteriorating Current Account Deficit
Merchandise exports continued to record moderate expansion in 2022, rising by 5.6% y/y. The Philippines export sector showed resilience to the impact of the slowdown in mainland China, which is a key export market. Although exports to mainland China fell by 5.1% y/y in 2022, exports to a number of other key markets rose. Exports to the US were up by 4.2% y/y while exports to Singapore rose by 17% y/y and exports to South Korea rose by 21.5% y/y.
However, exports of electronics products, which comprises the largest share of the total merchandise exports of the Philippines at around 56% of the total, have weakened during the second half of 2022 as electronics demand in key export markets has slowed. In December 2022, exports of electronics products fell by 13.9% y/y, with semiconductors exports declining by 12.8% y/y.
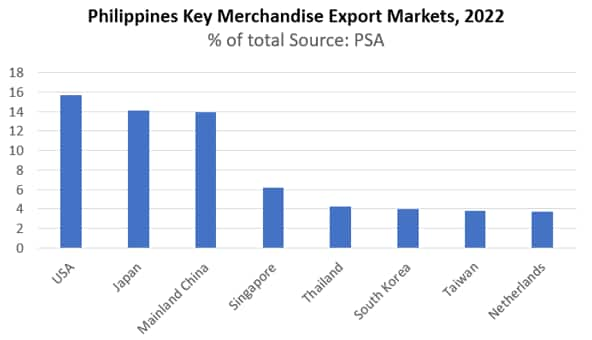
However, imports have shown even more rapid growth, rising by 17.3% y/y in 2022, reflecting sharply higher imports of energy products due to higher world prices for oil and gas. Consequently, the trade deficit for 2022 rose to USD 58.3 billion, compared with USD 37.1 billion in the same period of 2021.
The transmission effects from weaker growth in the US and Western Europe are a vulnerability for the Philippines export sector in 2023, but the rebound in economic growth in mainland China is expected to help to mitigate these effects.
In 2020, the current account surplus reached a record high of USD 11.6 billion or 3.2% of GDP, boosted by the sharp slump in imports due to the severe contraction in domestic demand. However, the current account shifted back to a deficit of USD 5.9 billion in 2021, or 1.5% of GDP, as growth recovery triggered higher domestic demand and rising imports.
Imports soared during 2022, with surging prices for world oil and gas being important factor contributing to a further sharp deterioration in the current account balance for calendar 2022. The current account for 2022 was in deficit of USD 17.8 billion or 4.4% of GDP due to a widening trade deficit, as the economic recovery and rising oil prices pushed up imports.
External debt as a share of GDP remains moderate, at an estimated 26.8% of GDP in September 2022, according to BSP data.
An important stabilizing factor for the Philippines economy has been overseas worker remittances by Filipinos working abroad, which remained quite stable during 2020 despite the COVID-19 pandemic, down only 0.8% y/y, and equivalent to around 10% of GDP. Remittances sent home by workers are an important factor supporting domestic consumer spending in the Philippines. Despite concerns about job losses for workers abroad due to the impact of the pandemic on many industries such as tourism and aviation, remittances data continues to show resilient remittance inflows for 2021. Remittances by workers abroad rose by 5.1% y/y in 2021, to a record high of USD 34.9 billion. In 2022, remittances by workers abroad rose by 3.6% y/y, to USD 36.1 billion.
Rapid growth in exports from the IT-BPO sector have also become an important boost for the Philippines economy and for total exports. IT-BPO exports have risen from USD 9.5 billion in 2010 to USD 25.1 billion by 2021, according to BSP estimates. Total estimated IT-BPO export revenues, consisting of computer and other business services, amounted to USD 27.4 billion in 2022, 9.1 percent higher in 2021.
Philippines Economic Outlook
Despite the impact of the COVID-19 Delta wave in the second half of 2021, GDP growth for calendar 2021 rebounded to 5.6% y/y. Strong growth momentum has continued in 2022, at a pace of over 7.6% y/y. Easing of pandemic-related travel restrictions during 2022 has also allowed a gradual reopening of domestic and international tourism travel. If sustained during 2023, this would provide an important boost to the economy. Prior to the pandemic, in 2019, gross direct tourism value added as a share of GDP was estimated at 12.7% of GDP, including both international and domestic tourism spending. International tourism spending was estimated at Peso 549 billion, while domestic tourism spending was estimated at Peso 3.1 trillion. Due to the importance of domestic tourism in the overall contribution of tourism to GDP, the recovery of domestic tourism could be a significant growth driver in 2023.
The near-term outlook for 2023 is for continued firm economic expansion. The latest S&P Global Philippines Manufacturing PMI survey results for March 2023 continue to signal expansionary conditions for manufacturing output and new orders. Sustained remittance inflows from workers abroad, fast-growing IT-BPO sector exports and the recovery of the tourism sector are also expected to support economic growth momentum during 2023.
According to the IT and Business Process Association of the Philippines, total IT-BPO headcount in the Philippines reached 1.57 million in 2022 with revenues for the sector rising to USD 32.5 billion.
The long-term outlook for the IT-BPO sector in the Philippines is for continued high growth, helped by key competitive advantages of a well-educated workforce and English language proficiency.
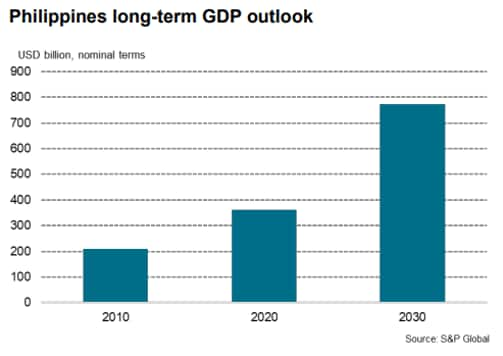
Continued rapid GDP growth of around 5.8% y/y is expected in 2023, helped by sustained strong private consumption spending, an upturn in government infrastructure spending and improving remittance inflows.
The Philippines economy is forecast to continue to grow rapidly, with total GDP doubling from USD 400 billion in 2022 to USD 800 billion in 2030. A key growth driver will be rapid growth in private consumption spending, buoyed by strong growth in urban household incomes.
By 2033, the Philippines is forecast to become one of the Asia-Pacific region's small group of one trillion-dollar economies, joining mainland China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Taiwan and Indonesia in this grouping of the largest economies in APAC. This strong growth in the size of the Philippines economy is also expected to drive rapidly rising per capita GDP, from USD 3,500 in 2022 to USD 6,200 by 2030. This will help to underpin the growth of the Philippines domestic consumer market, catalysing foreign and domestic investment into many sectors of the Philippines economy.
The Philippines will also benefit from its membership of the recently implemented RCEP trade deal, particularly due to its very favorable rules of origin treatment, which provide cumulative benefits that will help to build manufacturing supply chains within the RCEP region across different countries. This will help to attract foreign direct investment flows for a wide range of manufacturing and infrastructure projects into the RCEP member nations, particularly into low-cost manufacturing hubs such as the Philippines.
Consequently, the outlook for the Philippines economy over the next decade is very favourable, with significant progress in economic development expected. In 2021, the Family Income and Expenditure Survey of the Philippines government indicated that 20 million people, or around 18.1% of the total population, still live below the poverty threshold. Rapidly rising per capita GDP and standards of living will help to underpin a broad improvement in human development indicators and should deliver a significant reduction in the share of the population living in extreme poverty over the decade ahead.
Rajiv Biswas, Asia Pacific Chief Economist, S&P Global Market Intelligence
© 2023, S&P Global. All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
Purchasing Managers' Index™ (PMI ® ) data are compiled by S&P Global for more than 40 economies worldwide. The monthly data are derived from surveys of senior executives at private sector companies, and are available only via subscription. The PMI dataset features a headline number, which indicates the overall health of an economy, and sub-indices, which provide insights into other key economic drivers such as GDP, inflation, exports, capacity utilization, employment and inventories. The PMI data are used by financial and corporate professionals to better understand where economies and markets are headed, and to uncover opportunities.
Learn more about PMI data
Request a demo
This article was published by S&P Global Market Intelligence and not by S&P Global Ratings, which is a separately managed division of S&P Global.
Egyptian non-oil sector provides first glimpse of economic recovery after tumultuous start to the year
Week Ahead Economic Preview: Week of 9 September 2024
Global PMI selling price inflation close to four-year low in August
Philippine Review of Economics Journal

The Philippine Review of Economics is devoted to the publication of theoretical and empirical work in economic development. It welcomes papers about the Philippines and about other developing economics. It is also a forum for research findings that show the links of economics with other disciplines.
The PRE is a joint publication of the UP School of Economics (UPSE) and the Philippine Economic Society (PES).
PES members can access electronic copies of PRE issues.

ADB is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable Asia and the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty.
Established in 1966, it is owned by 68 members—49 from the region..

- Annual Reports
- Policies and Strategies
ORGANIZATION
- Board of Governors
- Board of Directors
- Departments and Country Offices
ACCOUNTABILITY
- Access to Information
- Accountability Mechanism
- ADB and Civil Society
- Anticorruption and Integrity
- Development Effectiveness
- Independent Evaluation
- Administrative Tribunal
- Ethics and Conduct
- Ombudsperson
Strategy 2030
Annual meetings, adb supports projects in developing member countries that create economic and development impact, delivered through both public and private sector operations, advisory services, and knowledge support..

ABOUT ADB PROJECTS
- Projects & Tenders
- Project Results and Case Studies
PRODUCTS AND SERVICES
- Public Sector Financing
- Private Sector Financing
- Financing Partnerships
- Funds and Resources
- Economic Forecasts
- Publications and Documents
- Data and Statistics
- Asia Pacific Tax Hub
- Development Asia
- ADB Data Library
- Agriculture and Food Security
- Climate Change
- Digital Technology
- Environment
- Finance Sector
- Fragility and Vulnerability
- Gender Equality
- Markets Development and Public-Private Partnerships
- Regional Cooperation
- Social Development
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Urban Development
REGIONAL OFFICES
- European Representative Office
- Japanese Representative Office | 日本語
- North America Representative Office
LIAISON OFFICES
- Pacific Liaison and Coordination Office
- Pacific Subregional Office
- Singapore Office
SUBREGIONAL PROGRAMS
- Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines East ASEAN Growth Area (BIMP-EAGA)
- Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC) Program
- Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) Program
- Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand Growth Triangle (IMT-GT)
- South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
With employees from more than 60 countries, ADB is a place of real diversity.
Work with us to find fulfillment in sharing your knowledge and skills, and be a part of our vision in achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient, and sustainable asia and the pacific., careers and scholarships.
- What We Look For
- Career Opportunities
- Young Professionals Program
- Visiting Fellow Program
- Internship Program
- Scholarship Program
FOR INVESTORS
- Investor Relations | 日本語
- ADB Green and Blue Bonds
- ADB Theme Bonds
INFORMATION ON WORKING WITH ADB FOR...
- Consultants
- Contractors and Suppliers
- Governments
- Executing and Implementing Agencies
- Development Institutions
- Private Sector Partners
- Civil Society/Non-government Organizations
PROCUREMENT AND OUTREACH
- Operational Procurement
- Institutional Procurement
- Business Opportunities Outreach
Philippines and ADB
ADB supports the Philippines in sustaining growth and steering the country’s development path toward greater inclusion, climate resilience, and increased competitiveness in the economy.
Economic forecasts for the Philippines
Share on social media.
- Philippines's GDP growth is expected at 6.0% in 2024 and 6.2% in 2025 – ADO April 2024
- Philippine inflation rates forecasted at 3.8% in 2024 and 3.4% in 2025 – ADO April 2024
- Per capita GDP growth for the Philippines is expected at 4.8% in 2024 and 5.1% in 2025 – ADO April 2024
Figures are based on the latest edition of ADB's Asian Development Outlook, which analyzes economic and development issues in Asia and the Pacific. This includes forecasting the inflation and gross domestic product growth rates of economies throughout the region.
Comparative economic forecasts
The latest available economic data for the Philippines compared to countries in Southeast Asia.
Policy Challenge—Promoting Greater Private Sector Participation
The private sector is an important engine of growth and productivity. It generates jobs, contributes to government revenues, drives innovation and improves efficiency through technology adoption. The Philippine Development Plan 2023-2028 underscores the need for greater private sector participation through stronger public–private collaboration along with the structural and regulatory reforms needed to enhance the policy environment.
Despite relatively strong GDP growth, investment in the Philippines lags behind its neighbors. While fixed investment has been over 20% of GDP since 2013, it remains lower than the 30% of GDP in neighbors such as Indonesia and Viet Nam. Similarly, foreign direct investment inflows remain lower than its neighbors, partly reflecting the country’s low global ranking as an investment destination. The Philippines ranked 52 out of 64 countries in the 2023 World Competitiveness Report by the International Institute for Management Development. It ranked 13 out of 14 countries included from the Asia and Pacific region. Infrastructure gaps remain among its key challenges, including in energy, transportation, and logistics. Poor connectivity limits access to factor and product markets, raises costs, and undermines the competitiveness of private firms.
A proactive reform agenda is making the country more attractive as an investment destination. Recent reforms have opened the country to more foreign investment and trade. Restrictions on foreign participation were eased in 2022, allowing full foreign ownership in sectors such as renewable energy, telecommunications, airports, shipping, railways, and expressways. Capitalization requirements for foreign investors in retail trade have also been lowered. The Corporate Recovery and Tax Incentives for Enterprises (CREATE) law, which reduced the corporate income tax rate from 30% to 25% (20% for MSMEs), is being refined to match incentives with investors and encourage investment in strategically important sectors. These reforms complement the country’s 2023 ratification of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership.
The enhanced public–private partnership (PPP) regulatory framework will help further mobilize private investment for infrastructure development. The PPP Code of the Philippines enacted in 2023 consolidates all legal frameworks and creates a unified system for investors involved in PPPs. Private sector participation in infrastructure helps reduce pressure on public finances and encourages greater expertise in designing and managing infrastructure projects, particularly complex projects such as long-span bridges and subways. The government’s infrastructure flagship program featured 185 big-ticket projects as of March 2024 worth ₱9.1 trillion (about $163 billion), 45 to be financed through PPPs. In February 2024, the rehabilitation, operation and maintenance of the Ninoy Aquino International Airport, the country’s main gateway, was awarded to the private sector—the largest solicited PPP project in nearly 25 years.
Further measures can enhance the investment climate. The private sector is dominated by a few large conglomerates. MSMEs constitute 99.5% of all enterprises and 63% of total employment. Yet they continue to face challenges in accessing finance and navigating red tape. High administrative burdens on startups, such as numerous permits and licenses, prevent ease of entry of small players. High trade costs also restrict competition and reduce opportunities for domestic firms to access larger markets. It is critical to strengthen market competition, including efforts across government to implement competition policy and deter anti-competitive practices. The Anti-Red Tape Authority has spearheaded efforts to streamline and automate government-related procedures to reduce the regulatory burden at both national and local government levels. Continuing capacity-building measures for local government units (LGUs) to make their localities more investor-friendly are vital While LGUs are mandated to implement electronic one-stop shops for business, some face capacity constraints. About 40% of LGUs as of February 2024 have adopted the system.
Accelerating private investment in key sectors including green and resilient energy, is critical for a better business environment. Coal and oil continue to dominate the energy mix, and the Philippines remains a net importer of fossil fuels. High energy costs are often cited as a key barrier to economic competitiveness. If current trends continue, energy self- sufficiency is expected to worsen as natural gas supplies from the Malampaya gas field dwindle. The government has sought to mobilize investment in renewable power generation to meet its 50% target share in the mix by 2040 (from a 22% share in 2022). The clean energy transition will require planning to replace and decommission fossil fuel-based power plants, and explore opportunities to develop geothermal, offshore wind, and floating solar capabilities. This also requires investment in energy storage, transmission, and grid resilience to accommodate the planned increase in renewable supply. The government has established the Energy Virtual One-Stop Shop System to streamline permits for new energy investments and assisting LGUs to adopt the system
The private sector can also play a greater role in expanding digital infrastructure. . Telecommunications face critical infrastructure gaps. In 2020, only 56.1% of households had internet access at home, with access largely concentrated in the capital, Metro Manila, nearby provinces, and in central Luzon. Most regions in the Visayas and Mindanao reported less than 50% access. Structural challenges of the local telecommunication industry and the archipelagic nature of the country have left poor tower coverage, the lowest among Association of Southeast Asian Nations members. Growing domestic demand cannot be met due to an industry dominated by only a few major players. To help attract private investment, the government issued a common telecommunications tower policy in 2020, with the initial wave of operator licensing and construction already underway. There is an accompanying need for more backhaul capacity and universal coverage which the National Broadband Plan seeks to address, with significant scope for private sector participation. The Open Access in Data Transmission Bill pending in Congress removes the legislative franchise requirement for telecommunications service providers and simplifies the licensing process to promote more competition.
A more inclusive and robust financial system is also vital. Relative to its peers, the Philippines must further deepen its capital markets, strengthen competition and technology adoption in banking, increase insurance penetration, and grow its mutual and pension fund ecosystem. These changes can potentially improve access to capital and the productivity of MSMEs. It will also facilitate more investment in productivity- enhancing innovation and entrepreneurship, disaster resilience projects including in agriculture, and enhance social protection.
More resources

Asian Development Bank and the Philippines: Fact Sheet
The Fact Sheets summarize ADB's partnerships with member economies, providing key facts and figures and an overview of activities and future directions.

Asian Development Outlook
The Asian Development Outlook analyzes economic and development issues in developing countries in Asia.

Key Indicators
The Key Indicators for Asia and the Pacific publication presents data regarding the economic, financial, social, and environmental situations in a broad range of countries across the region.

Basic Statistics
The Basic Statistics brochure presents data on selected social, economic, and SDG indicators such as population, poverty, annual growth rate of gross domestic product, inflation, and government finance for economies in Asia and the Pacific.
NEDA: Investment climate vital for Philippine economic growth
The long-term growth and development of the Philippines would depend on efforts to create a favorable investment environment that encourages economic diversification across multiple sectors, the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) said.
During the US-ASEAN Business Council’s (USABC) Third Quarterly Philippines Committee Call, NEDA Secretary Arsenio M. Balisacan emphasized the government's dedication to enhance the investment climate and align with advancements made by other Asian nations.
“Bolstering the economy's other growth pillars beyond consumption and services is crucial in ensuring sustainable and inclusive development,” Balisacan said in a statement.
“Nothing short of massive investments is necessary to crowd in even more investments that generate high-quality jobs and opportunities in increasingly higher value-added sectors,” he added.
Balisacan recognized the necessity of tackling several current economic challenges, including issues in the external sector, geographical inclusivity, and a chronic lack of investment in essential infrastructure.
In particular, he cited the insufficient infrastructure has led to a decrease in the country's competitiveness.
Despite these challenges, Balisacan pointed out various opportunities that could drive economic advancement, affirming that the Philippine economy remains one of Asia's most promising prospects.
He identified two trends likely to increase demand in the coming decades.
First, sustained economic growth, bolstered by strong fundamentals like moderate inflation and a dynamic labor market, has led to rising incomes and improved overall welfare.
Second, the country is experiencing a demographic “sweet spot,” with a growing working-age population outpacing the total population.
This presents a unique opportunity to boost economic growth if the country is able to invest in the supporting infrastructure enhancing the productivity of the expanding workforce, he said.
“The Marcos Administration has achieved much by creating an enabling investment ecosystem to help us carry out the strategies contained in the Philippine Development Plan 2023-2028,” Balisacan said.
“These actions are meant to ‘roll out the red carpet’ and make it easier for the private sector to invest in various sectors of the economy and accelerate the rollout of critical supporting infrastructure,” the government’s chief economic planner added.
Balisacan underscored the crucial role of public-private partnerships (PPPs) in the overall economic gameplan, with the private sector serving as a key partner in expanding both physical and social infrastructure projects.
Ambassador Brian McFeeters (ret.), the USABC’s Senior Vice President and Regional Managing Director, noted the marked increase in interest in the Philippines coming from U.S. companies and underscored the important role of continuing dialogues with the private sector.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Philippines ended 2023 on a high note, being the fastest growing economy across Southeast Asia with a growth rate of 5.6 percent—just shy of the government's target of 6.0 to 7.0 percent. 1 "National accounts," Philippine Statistics Authority, January 31, 2024; "Philippine economic updates," Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas, November 16, 2023. ...
Philippines Overview: Development news, research, data
The Philippine economy is forecast to accelerate to 5.8% growth in 2024 from 5.5% last year and to 5.9% in 2025. Growth is expected to be driven by strong household consumption, sustained strength in the services sector, and improved trade stemming from a rebound in global demand for goods and the continued recovery of services exports such as ...
The Philippines' economy in 2023
The south-east Asian economy grew at an annual rate of 7.2 per cent in the fourth quarter of 2022, beating economist expectations of about 6.5 per cent growth, according to Philippine Statistics ...
ADB's flagship economic publication Asian Development Outlook (ADO) April 2023 forecasts the Philippine economy to grow by 6.0% this year, climbing further by 6.2% in 2024. A recovery in employment and retail trade, sustained expansion in the manufacturing sector, and rising public infrastructure spending will support growth.
The Philippines Economic Update (PEU) summarizes key economic and social developments, important policy changes, and the evolution of external conditions over the past six months. It also presents findings from recent ... (Research Analyst), Ludigil Garces and Patrizia Benedicto (Consultants) from the MTI GP; Ou Nie (Financial Sector ...
Highlights of the Philippines Economic Update June 2023
The fiscal deficit widened from 6.9 percent of GDP in Q1-Q3 2020 to 8.3 percent of GDP in Q1-Q3 2021. The wider fiscal deficit has resulted in higher financing needs, which have been met by increased public borrowing. Public debt increased from 54.6 percent of GDP at end-2020 to 63.1 percent of GDP at end-September 2021.
The Philippines Economic Update (PEU) summarizes key economic and social developments, important policy changes, and the evolution of external conditions over the past six months. It also presents findings from recent World Bank analyses, ... (Research Analyst). Logistics and publication support were provided by Kristiana Rosario (Team ...
The Philippines economy has continued to show rapid expansion in early 2022, with first quarter GDP growth up 8.3% year-on-year (y/y). This followed a GDP growth rebound of 5.6% in 2021, despite the negative impact of the COVID-19 Delta wave that hit the nation in the second half of 2021. However, the Philippines is facing external headwinds ...
iii The Philippines Economic Update summarizes key economic and social developments, important policy changes, and the evolution of external conditions over the past six months. It also presents findings from recent World Bank analysis, situating them in the context of the country's long-term development trends and assessing their implications for the
The economy of the Philippines is an emerging market, and considered as a newly industrialized country in the Asia-Pacific region. [31] In 2024, the Philippine economy is estimated to be at ₱26.55 trillion ($471.5 billion), making it the world's 32nd largest by nominal GDP and 13th largest in Asia according to the International Monetary Fund.. The Philippine economy is transitioning from one ...
The economic rebound in 2022 pushed real economic growth to the highest pace recorded since 1976, with household final consumption expenditure growing by 8.3% y/y while gross capital formation grew by 16.8% y/y. Recent economic data has continued to show expansionary conditions in the Philippines economy during the fourth quarter of 2023.
Philippines economy shows strong expansion
EconomyFrom The Report: Philippines 2021View in Online Reader. Economy. The Philippines is one of the fastest-growing economies of the past decade, averaging 6.4% growth per year over 2010-19. Indeed, an expanding and youthful population, combined with reforms and an ambitious infrastructure programme, have made it an enticing investment ...
MANILA, December 7, 2021 —Rebounding from a deep contraction in 2020, the Philippine economy is forecast to grow 5.3 percent this year before accelerating to an average of 5.8 percent in 2022-23 on the road to recovery, according to the Philippines Economic Update (PEU) titled Regaining Lost Ground, Revitalizing the Filipino Workforce ...
The Philippine economy under the pandemic: From Asian ...
The Philippine population of 110 million comprises a relatively young population. On May 22, 2021, the number of confirmed COVID-19 cases reported in the country is 1,171,403 with 55,531 active ...
The June 2021 edition of the Philippines Economic Update analyzes the impact of COVID-19 on the economy and discusses short- and medium-term policy actions for speeding up recovery. The report also provides analysis and recommendations on enhancing decentralization and service delivery in view of the implementation of the Mandanas Ruling in 2022.
By 2033, the Philippines is forecast to become one of the Asia-Pacific region's small group of one trillion-dollar economies, joining mainland China, Japan, India, South Korea, Australia, Taiwan and Indonesia in this grouping of the largest economies in APAC. This strong growth in the size of the Philippines economy is also expected to drive ...
The Philippine Review of Economics is devoted to the publication of theoretical and empirical work in economic development. It welcomes papers about the Philippines and about other developing economics. It is also a forum for research findings that show the links of economics with other disciplines.
ADB supports the Philippines' recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic through its country partnership strategy 2018-2023 — focusing on infrastructure investment, local economic development, and social investments.
The long-term growth and development of the Philippines would depend on efforts to create a favorable investment environment that encourages economic diversification across multiple sectors, the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) said. ... affirming that the Philippine economy remains one of Asia's most promising prospects. He ...