Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Research: Where to Begin

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Research isn't something that only scientists and professors do. Any time you use sources to investigate claims or reach new conclusions, you are performing research. Research happens in virtually all fields, so it’s vitally important to know how to conduct research and navigate through source material regardless of your professional or academic role.
Choosing and Narrowing Your Research Topic
Before beginning the process of looking for sources, it’s important to choose a research topic that is specific enough to explore in-depth. If your focus is too broad, it will be difficult to find sources that back up what you’re trying to say.
If your instructor gives you the flexibility to choose your own research topic, you might begin by brainstorming a list of topics that interest you ( click here to visit an OWL page that can help you get started brainstorming or prewriting ). Once you find something that grabs your attention, the next step is to narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Some ways to narrow your focus are by sub-topic, demographic, or time period.
For example, suppose that you want to research cancer treatments. Cancer treatment is a fairly broad topic, so you would be wise to at least consider narrowing your scope. For example, you could focus on a sub-topic of cancer treatment, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy. However, these are still broad topics, so you might also narrow your topic to a narrower sub-topic or even examine how these topics relate to a specific demographic or time period. In the end, you might decide to research how radiation therapy for women over fifty has changed in the past twenty years. In sum, having a specific idea of what you want to research helps you find a topic that feels more manageable.
Writing Your Research Question
Writing your research topic as a question helps you focus your topic in a clear and concise way. It ensure that your topic is arguable. While not all research papers have to offer an explicit argument, many do.
For the above example, you might phrase your research question like this: "How has radiation therapy changed in the past twenty years for women over fifty?" Of course, phrasing this topic as a question assumes that the research has, in fact, changed. Reading your sources (or, to begin with, at least summaries and abstracts of those sources) will help you formulate a research question that makes sense.
Knowing What Types of Sources You Need
Depending on the type of research you’re doing, you may need to use different types of sources. Research is usually divided into scholarly and popular, and primary and secondary. For more information on specific details about these types of sources, visit our "Where to Begin" page in our "Evaluating Sources" subsection. This subsection contains additional pages that explore various kinds of sources (like, e.g., internet sources) in more detail.
Asking Productive Questions
Before you begin your research, you should ask yourself questions that help narrow your search parameters.
What kind of information are you looking for?
Different types of research will require different sources. It’s important to know what kinds of sources your research demands. Ask whether you need facts or opinions, news reports, research studies, statistics and data, personal reflections, archival research, etc. Restricting yourself to only the most relevant kinds of sources will make the research process seem less daunting.
Where do you need to look for your research?
Your research topic will also dictate where you find your sources. This extends beyond simply whether you use the internet or a print source. For example, if you are searching for information on a current event, a well-regarded newspaper like the New York Times or Wall Street Journal could be a useful source. If you are searching for statistics on some aspect of the U.S. population, then you might want to start with government documents, such as census reports. While much high-level academic research relies mainly on the sorts of academic journal articles and scholarly books that can be found in university libraries, depending the nature of your research project, you may need to look elsewhere.
How much information do you need?
Different research projects require different numbers of sources. For example, if you need to address both sides of a controversial issue, you may need to find more sources than if you were pursuing a non-controversial topic. Be sure to speak with your instructor if you are unclear on how many sources you will be expected to use.
How timely does your research need to be?
Depending on your research topic, the timeliness of your source may or may not matter. For example, if you are looking into recent changes in a specific scientific field, you would want the most up-to-date research. However, if you were researching the War of 1812, you might benefit from finding primary sources written during that time period.
How to Do Research: A Step-By-Step Guide: Get Started
- Get Started
- 1a. Select a Topic
- 1b. Develop Research Questions
- 1c. Identify Keywords
- 1d. Find Background Information
- 1e. Refine a Topic
- 2a. Search Strategies
- 2d. Articles
- 2e. Videos & Images
- 2f. Databases
- 2g. Websites
- 2h. Grey Literature
- 2i. Open Access Materials
- 3a. Evaluate Sources
- 3b. Primary vs. Secondary
- 3c. Types of Periodicals
- 4a. Take Notes
- 4b. Outline the Paper
- 4c. Incorporate Source Material
- 5a. Avoid Plagiarism
- 5b. Zotero & MyBib
- 5c. MLA Formatting
- 5d. MLA Citation Examples
- 5e. APA Formatting
- 5f. APA Citation Examples
- 5g. Annotated Bibliographies
Research Essentials Video Tutorials
Related guides.
- Elmira College Writing Center Get one-on-one assistance for all types of writing.
Recommended Websites
- Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL)
Research Process Overview
Step 1. Develop a topic Select a Topic | Develop Research Questions | Identify Keywords | Find Background Information | Refine a Topic
Step 2. Locate information Search Strategies | Books | eBooks | Articles | Videos & Images | Databases | Websites | Grey Literature
Step 3. Evaluate and analyze information Evaluate Sources | Primary vs Secondary | Types of Periodicals
Step 4. Write, organize, and communicate information Take Notes | Outline the Paper | Incorporate Source Material
Step 5. Cite sources Avoid Plagiarism | Zotero & MyBib | MLA | APA | Chicago Style | Annotated Bibliographies
For research help, use one of the following options:
Ask the GTL

- Next: Step 1: Develop a Topic >>
- Last Updated: May 29, 2024 1:53 PM
- URL: https://libguides.elmira.edu/research
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services

- Virtual Tour
- Staff Directory
- En Español
You are here
Science, health, and public trust.
September 8, 2021
Explaining How Research Works
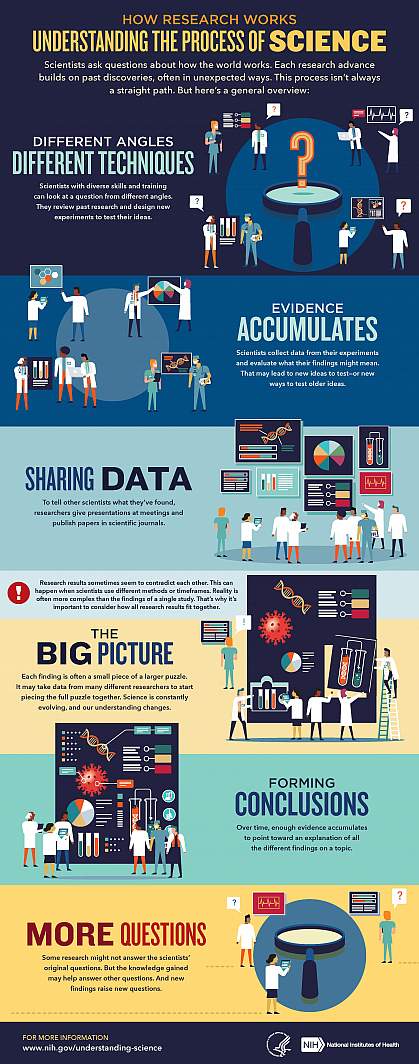
We’ve heard “follow the science” a lot during the pandemic. But it seems science has taken us on a long and winding road filled with twists and turns, even changing directions at times. That’s led some people to feel they can’t trust science. But when what we know changes, it often means science is working.

Explaining the scientific process may be one way that science communicators can help maintain public trust in science. Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle.
Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels. For example, scientists can look at the different atoms in a molecule, cells in a tissue, or how different tissues or systems affect each other. Researchers often must choose one or a finite number of ways to investigate a question. It can take many different studies using different approaches to start piecing the whole picture together.
Sometimes it might seem like research results contradict each other. But often, studies are just looking at different aspects of the same problem. Researchers can also investigate a question using different techniques or timeframes. That may lead them to arrive at different conclusions from the same data.
Using the data available at the time of their study, scientists develop different explanations, or models. New information may mean that a novel model needs to be developed to account for it. The models that prevail are those that can withstand the test of time and incorporate new information. Science is a constantly evolving and self-correcting process.
Scientists gain more confidence about a model through the scientific process. They replicate each other’s work. They present at conferences. And papers undergo peer review, in which experts in the field review the work before it can be published in scientific journals. This helps ensure that the study is up to current scientific standards and maintains a level of integrity. Peer reviewers may find problems with the experiments or think different experiments are needed to justify the conclusions. They might even offer new ways to interpret the data.
It’s important for science communicators to consider which stage a study is at in the scientific process when deciding whether to cover it. Some studies are posted on preprint servers for other scientists to start weighing in on and haven’t yet been fully vetted. Results that haven't yet been subjected to scientific scrutiny should be reported on with care and context to avoid confusion or frustration from readers.
We’ve developed a one-page guide, "How Research Works: Understanding the Process of Science" to help communicators put the process of science into perspective. We hope it can serve as a useful resource to help explain why science changes—and why it’s important to expect that change. Please take a look and share your thoughts with us by sending an email to [email protected].
Below are some additional resources:
- Discoveries in Basic Science: A Perfectly Imperfect Process
- When Clinical Research Is in the News
- What is Basic Science and Why is it Important?
- What is a Research Organism?
- What Are Clinical Trials and Studies?
- Basic Research – Digital Media Kit
- Decoding Science: How Does Science Know What It Knows? (NAS)
- Can Science Help People Make Decisions ? (NAS)
Connect with Us
- More Social Media from NIH

Research Basics
- What Is Research?
- Types of Research
- Secondary Research | Literature Review
- Developing Your Topic
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Responsible Conduct of Research
- More Information

A good working definition of research might be:
Research is the deliberate, purposeful, and systematic gathering of data, information, facts, and/or opinions for the advancement of personal, societal, or overall human knowledge.
Based on this definition, we all do research all the time. Most of this research is casual research. Asking friends what they think of different restaurants, looking up reviews of various products online, learning more about celebrities; these are all research.
Formal research includes the type of research most people think of when they hear the term “research”: scientists in white coats working in a fully equipped laboratory. But formal research is a much broader category that just this. Most people will never do laboratory research after graduating from college, but almost everybody will have to do some sort of formal research at some point in their careers.
So What Do We Mean By “Formal Research?”
Casual research is inward facing: it’s done to satisfy our own curiosity or meet our own needs, whether that’s choosing a reliable car or figuring out what to watch on TV. Formal research is outward facing. While it may satisfy our own curiosity, it’s primarily intended to be shared in order to achieve some purpose. That purpose could be anything: finding a cure for cancer, securing funding for a new business, improving some process at your workplace, proving the latest theory in quantum physics, or even just getting a good grade in your Humanities 200 class.
What sets formal research apart from casual research is the documentation of where you gathered your information from. This is done in the form of “citations” and “bibliographies.” Citing sources is covered in the section "Citing Your Sources."
Formal research also follows certain common patterns depending on what the research is trying to show or prove. These are covered in the section “Types of Research.”
- Next: Types of Research >>
- Last Updated: May 21, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.iit.edu/research_basics
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Do Research
Last Updated: March 13, 2023 References
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Jennifer Mueller, JD . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. This article has been viewed 227,421 times.
The idea of doing research may seem daunting, but as long as you keep yourself organized and focus on the question you want to answer, you'll be fine. If you're curious and interested in the topic, you might even find it fun! We here at wikiHow have gathered answers to all your most common questions about how to do research, from finding a good topic to identifying the best sources and writing your final paper.
How do I find a topic to research?

- For example, if you're researching in the political science field, you might be interested in determining what leads people to believe that the 2020 US presidential election was illegitimate.
How do I get started on my research?

- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might find that "absentee ballots" and "voting by mail" come up frequently. Those are issues you could look into further to figure out how they impacted the final election results.
- You don't necessarily have to use the overview articles you look at as resources in your actual paper. Even Wikipedia articles can be a good way to learn more about a topic and you can check the references for more reputable sources that might work for your paper.
What's the best way to keep track of my sources?

- Research papers typically discuss 2 or 3 separate things that work together to answer the research question. You might also want to make a note on the front of which thing that source relates to. That'll make it easier for you to organize your sources later.
- For example, if you're researching the 2020 election, you might have a section of your paper discussing voting by mail. For the sources that directly address that issue, write "voting by mail" in the corner.
What kind of notes should I be taking as I research?

- If you find something that you think would make a good quote, copy it out exactly with quote marks around it, then add the page number where it appears so you can correctly cite it in your paper without having to go back and hunt for it again.
How do I evaluate the quality of a source?

- Does the article discuss or reference another article? (If so, use that article instead.)
- What expertise or authority does the author have?
- When was the material written? (Is it the most up-to-date reference you could use?)
- Why was the article published? (Is it trying to sell you something or persuade you to adopt a certain viewpoint?)
- Are the research methods used consistent and reliable? (Appropriate research methods depend on what was studied.)
What if I'm having a hard time finding good sources?

- For example, if you're writing about the 2020 election, you might find tons of stories online, but very little that is reputable enough for you to use in your paper. Because the election happened so recently, it might be too soon for there to be a lot of solid academic research on it. Instead, you might focus on the 2016 election.
- You can also ask for help. Your instructor might be able to point you toward good sources. Research librarians are also happy to help you.
How do I organize my research for my paper?

- For example, if you're researching the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the 2020 election, you might have sections on social distancing and cleaning at in-person voting locations, the accessibility of mail-in ballots, and early voting.
What's the best way to start writing my paper?

- Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft. That'll help you make sure that you don't inadvertently misattribute or fail to cite something as you work your way through substantive drafts.
- Write your introduction and conclusion only after you're satisfied that the body of your paper is essentially what you want to turn in. Then, you can polish everything up for the final draft.
How can I make sure I'm not plagiarizing?

- If you have any doubt over whether you should cite something, go ahead and do it. You're better off to err on the side of over-citing than to look like you're taking credit for an idea that isn't yours.
- ↑ https://www.nhcc.edu/student-resources/library/doinglibraryresearch/basic-steps-in-the-research-process
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Sociology Professor, Stanford University. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
- ↑ https://library.taylor.edu/eng-212/research-paper
- ↑ http://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/research/research_paper.html
- ↑ https://www.potsdam.edu/sites/default/files/documents/support/tutoring/cwc/6-Simple-Steps-for-Writing-a-Research-Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.umgc.edu/current-students/learning-resources/writing-center/online-guide-to-writing/tutorial/chapter4/ch4-05.html
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

About This Article

If you need to do research on a particular topic, start by searching the internet for any information you can find on the subject. In particular, look for sites that are sourced by universities, scientists, academic journals, and government agencies. Next, visit your local library and use the electric card catalog to research which books, magazines, and journals will have information on your topic. Take notes as you read, and write down all of the information you’ll need to cite your sources in your final project. To learn how interviewing a first-hand source can help you during your research, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Shenuka Ranawaka
Sep 16, 2016
Did this article help you?
Ismail El Omari
Mar 3, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
College Info Geek
How to Do Research in 7 Simple Steps
C.I.G. is supported in part by its readers. If you buy through our links, we may earn an affiliate commission. Read more here.

It’s 2 am, and you’re on your fifth cup of coffee (or was it your sixth?). You’re crouched at a table in some dark corner of the library surrounded by fifteen open books. Equally as many tabs are open on your laptop, and you still haven’t written a word of the paper that’s due in 7 hours.
Many things can explain how you got to this point, including procrastination , poor organization , and a messy schedule .
Very often, however, the problem is a lack of research skills .
And it’s not your fault. High school does a poor job of teaching you how to do research, and most college classes do little better. It feels like you’re expected to figure it out through trial and error.
I think we can do better than that, however. In this guide, I’m going to show you the 7-step process for researching everything from a 10-page term paper to a final presentation. Not only will you learn how to do better research; you’ll also learn how to research more efficiently.
What Is Research?
Before we go any further, what is research?
At its core, research is an attempt to answer a question. This could be anything from “How can we reduce infant mortality rates?” to “Why does salt make food taste good?”
To answer your question, you consult books, academic papers, newspaper articles, historical records, or anything else that could be helpful. The broad term for these things is “sources.”
And, usually, once you’ve done the research, you present or summarize it in some way. In many cases, this means writing an essay or another type of scholarly paper, but it could also mean giving a presentation or even creating a YouTube video.
Even if you have no interest in academia, research is an extremely useful skill to learn. When you know how to do research, it’s much easier to improve your life and work more effectively . Instead of having to ask someone every time you have a question, research will help you solve problems yourself (and help others in turn).
Note: Research can also mean conducting surveys, performing experiments, or going on archaeological digs. While these activities are crucial for advancing human knowledge, I won’t be discussing them here. This article focuses on the research you can do with only a library and an internet connection.
The 7 Steps of the Research Process
Research can feel overwhelming, but it’s more manageable when you break it down into steps. In my experience, the research process has seven main steps:
- Find a topic
- Refine your topic
- Find key sources
- Take notes on your sources
- Create your paper or presentation
- Do additional research as necessary
- Cite your sources
Let’s look at each of these steps in more detail.
1. Find a Topic
If you don’t have a topic, your research will be undirected and inefficient. You’ll spend hours reading dozens of sources, all because you didn’t take a few minutes to develop a topic.
How do you come up with a topic? My number one suggestion is to create a mind map.
A mind map is a visual way to generate ideas. Here’s how it works:
- Get a piece of paper and a pen. Make sure the paper isn’t too small — you want lots of room for your ideas.
- Draw an oval in the center of the paper.
- Inside that oval, write a super vague topic. Start with whatever your professor has assigned you.
- Draw lines from the oval towards the edges of the paper.
- Draw smaller ovals connected to each of these lines.
- Inside the smaller ovals, write more specific ideas/topics related to the central one.
- Repeat until you’ve found 3-5 topic ideas.
When I write it out step by step, it sounds kind of strange. But trust me, it works . Anytime I’m stuck on a writing assignment, this method is my go-to. It’s basically magic.
To see what mind mapping looks like in practice, check out this clip:
Want to create a digital mind map like the one Thomas uses in the video? Check out Coggle .
2. Refine Your Topic
Okay, so now you have a list of 3-5 topics. They’re all still pretty general, and you need to narrow them down to one topic that you can research in depth.
To do this, spend 15 minutes doing some general research on each topic. Specifically, take each topic and plug it into your library’s catalog and database search tools.
The details of this process will vary from library to library. This is where consulting a librarian can be super helpful. They can show you how to use the tools I mentioned, as well as point you to some you probably don’t know about.
Furthermore, I suggest you ask your professor for recommendations. In some cases, they may even have created a resource page specifically for your assignment.
Once you’ve found out where to search, type in your topic. I like to use a mixture of the library catalog, a general academic database like EBSCO Host , and a search on Google Scholar .
What exactly are you trying to find? Basically, you’re trying to find a topic with a sufficient quantity and variety of sources.
Ideally, you want something with both journal articles and books, as this demonstrates that lots of scholars are seriously engaging with the topic.
Of course, in some cases (if the topic is very cutting edge, for example), you may be only able to find journal articles. That’s fine, so long as there are enough perspectives available.
Using this technique, you’ll be able to quickly eliminate some topics. Be ruthless. If you’re not finding anything after 15 minutes, move on. And don’t get attached to a topic.
Tip: If you find two topics with equal numbers of sources available, ask your professor to help you break the tie. They can give you insight into which topic is super common (and thus difficult to write about originally), as well as which they find more interesting.
Now that you have your topic, it’s time to narrow down your sources.
3. Find Key Sources
If you’ve picked a good topic, then you probably have lots of sources to work with. This is both a blessing and a curse. A variety of sources shows that there’s something worth saying about your topic, and it also gives you plenty of material to cite.
But this abundance can quickly turn into a nightmare in which you spend hours reading dense, mind-numbing material without getting any closer to actually producing a paper.
How do you keep this from happening? Choose 3–5 key sources and focus on them intently. Sure, you may end up needing more sources, especially if this is a long paper or if the professor requires it. But if you start out trying to read 15 sources, you’re likely to get overwhelmed and frustrated.
Focusing on a few key sources is powerful because it:
- Lets you engage deeply with each source.
- Gives you a variety of perspectives.
- Points you to further resources.
- Keeps you focused.
4. Read and Take Notes
But what do you do with these sources, exactly? You need to read them the right way . Follow these steps to effectively read academic books and articles:
Go through the article and look at the section headings. If any words or terms jump out at you, make note of them. Also, glance at the beginning sentences of each section and paragraph to get an overall idea of the author’s argument.
The goal here isn’t to comprehend deeply, but to prime your mind for effective reading .
Write down any questions you have after skimming the article, as well as any general questions you hope the article can answer. Always keep your topic in mind.
Read Actively
Now, start reading. But don’t just passively go through the information like you’re scrolling through Tumblr. Read with a pen or pencil in hand , underlining any unfamiliar terms or interesting ideas.
Make notes in the margins about other sources or concepts that come to mind. If you’re reading a library book, you can make notes on a separate piece of paper.
Once you’ve finished reading, take a short break. Have a cup of tea or coffee. Go for a walk around the library. Stretch. Just get your mind away from the research for a moment without resorting to distracting, low-density fun .
Now come back to the article and look at the things you underlined or noted. Gather these notes and transfer them to a program like Evernote .
If you need to look up a term, do that, and then add that definition to your notes. Also, make note of any sources the author cites that look helpful.
But what if I’m reading a book? Won’t this take forever? No, because you’re not going to read the entire book.
For most research you’ll do in college, reading a whole academic book is overkill . Just skim the table of contents and the book itself to find chapters or sections that look relevant.
Then, read each of those in the same way you would read an article. Also, be sure to glance at the book’s bibliography, which is a goldmine for finding additional sources.
Note: The above method is a variation on the classic SQ3R method , adapted slightly since we’re not interested in taking notes from textbooks .
5. Create Your Paper or Presentation
“You can’t turn in raw research.”
Research is crucial to crafting a great paper or presentation, but it’s also a great way to procrastinate. I had classmates in college who would spend 8 hours researching a 5-page paper. That’s way too much!
At some point, you need to stop researching and start writing (or whatever method you’re using to present your research).
How do you decide when to stop researching? There’s no strict rule, but in general I wouldn’t spend more than 30 minutes per page of the final paper.
So if the final paper is supposed to be 10 pages, don’t spend more than 5 hours researching it.
6. Do Additional Research (As Necessary)
Once you’ve started writing the draft of your paper, you’ll probably find a few gaps. Maybe you realize that one scholar’s argument isn’t relevant to your paper, or that you need more information for a particular section. In this case, you are free to return to researching as necessary.
But again, beware the trap of procrastination masquerading as productivity! Only do as much additional research as you need to answer your question. Don’t get pulled into rabbit holes or dragged off on tangents. Get in there, do your research, and get back to writing .
To keep yourself focused, I suggest keeping a separate document or piece of paper nearby to note points that need additional research.
Every time you encounter such a point, make note of it in the document and then keep writing. Only stop when you can’t get any further without additional research.
It’s much better to get a full draft done first. Otherwise, you risk suffering a cognitive switching penalty , making it harder to regain your focus.
7. Cite Your Sources
Whether you’re creating an oral presentation, essay, or video, you’ll need to cite your sources. Plagiarism is a serious offense, so don’t take any chances.
How to cite your sources depends on the subject and the professor’s expectations. Chicago, MLA, and APA are the most common citation formats to use in college, but there are thousands more.
Luckily, you don’t need to painstakingly type each of your citations by hand or slog through a style manual. Instead, you can use a tool like Zotero to track and generate your citations. To make things even easier, install the Zotero Connector browser extension. It can automatically pull citation information from entries in an online library catalog.
Once you’ve collected all of your sources, Zotero can generate a properly formatted works cited page or bibliography at just the click of a button.
For help setting up and using Zotero, read this guide . If you need further assistance, ask a librarian.
Go Research With Confidence
I hope you now understand how to do research with more confidence. If you follow the procedures I’ve covered in this article, you’ll waste less time, perform more effective research, and ultimately have the material for a winning essay.
Curious about how to use your research to write a great research paper? Check out this guide .
Image Credits: picking book from shelf
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?
- Open Access
- First Online: 03 December 2022
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- James Hiebert 6 ,
- Jinfa Cai 7 ,
- Stephen Hwang 7 ,
- Anne K Morris 6 &
- Charles Hohensee 6
Part of the book series: Research in Mathematics Education ((RME))
18k Accesses
Abstractspiepr Abs1
Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain, and by its commitment to learn from everyone else seriously engaged in research. We call this kind of research scientific inquiry and define it as “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses.” By “hypotheses” we do not mean the hypotheses you encounter in statistics courses. We mean predictions about what you expect to find and rationales for why you made these predictions. Throughout this and the remaining chapters we make clear that the process of scientific inquiry applies to all kinds of research studies and data, both qualitative and quantitative.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF

Part I. What Is Research?
Have you ever studied something carefully because you wanted to know more about it? Maybe you wanted to know more about your grandmother’s life when she was younger so you asked her to tell you stories from her childhood, or maybe you wanted to know more about a fertilizer you were about to use in your garden so you read the ingredients on the package and looked them up online. According to the dictionary definition, you were doing research.
Recall your high school assignments asking you to “research” a topic. The assignment likely included consulting a variety of sources that discussed the topic, perhaps including some “original” sources. Often, the teacher referred to your product as a “research paper.”
Were you conducting research when you interviewed your grandmother or wrote high school papers reviewing a particular topic? Our view is that you were engaged in part of the research process, but only a small part. In this book, we reserve the word “research” for what it means in the scientific world, that is, for scientific research or, more pointedly, for scientific inquiry .
Exercise 1.1
Before you read any further, write a definition of what you think scientific inquiry is. Keep it short—Two to three sentences. You will periodically update this definition as you read this chapter and the remainder of the book.
This book is about scientific inquiry—what it is and how to do it. For starters, scientific inquiry is a process, a particular way of finding out about something that involves a number of phases. Each phase of the process constitutes one aspect of scientific inquiry. You are doing scientific inquiry as you engage in each phase, but you have not done scientific inquiry until you complete the full process. Each phase is necessary but not sufficient.
In this chapter, we set the stage by defining scientific inquiry—describing what it is and what it is not—and by discussing what it is good for and why people do it. The remaining chapters build directly on the ideas presented in this chapter.
A first thing to know is that scientific inquiry is not all or nothing. “Scientificness” is a continuum. Inquiries can be more scientific or less scientific. What makes an inquiry more scientific? You might be surprised there is no universally agreed upon answer to this question. None of the descriptors we know of are sufficient by themselves to define scientific inquiry. But all of them give you a way of thinking about some aspects of the process of scientific inquiry. Each one gives you different insights.

Exercise 1.2
As you read about each descriptor below, think about what would make an inquiry more or less scientific. If you think a descriptor is important, use it to revise your definition of scientific inquiry.
Creating an Image of Scientific Inquiry
We will present three descriptors of scientific inquiry. Each provides a different perspective and emphasizes a different aspect of scientific inquiry. We will draw on all three descriptors to compose our definition of scientific inquiry.
Descriptor 1. Experience Carefully Planned in Advance
Sir Ronald Fisher, often called the father of modern statistical design, once referred to research as “experience carefully planned in advance” (1935, p. 8). He said that humans are always learning from experience, from interacting with the world around them. Usually, this learning is haphazard rather than the result of a deliberate process carried out over an extended period of time. Research, Fisher said, was learning from experience, but experience carefully planned in advance.
This phrase can be fully appreciated by looking at each word. The fact that scientific inquiry is based on experience means that it is based on interacting with the world. These interactions could be thought of as the stuff of scientific inquiry. In addition, it is not just any experience that counts. The experience must be carefully planned . The interactions with the world must be conducted with an explicit, describable purpose, and steps must be taken to make the intended learning as likely as possible. This planning is an integral part of scientific inquiry; it is not just a preparation phase. It is one of the things that distinguishes scientific inquiry from many everyday learning experiences. Finally, these steps must be taken beforehand and the purpose of the inquiry must be articulated in advance of the experience. Clearly, scientific inquiry does not happen by accident, by just stumbling into something. Stumbling into something unexpected and interesting can happen while engaged in scientific inquiry, but learning does not depend on it and serendipity does not make the inquiry scientific.
Descriptor 2. Observing Something and Trying to Explain Why It Is the Way It Is
When we were writing this chapter and googled “scientific inquiry,” the first entry was: “Scientific inquiry refers to the diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on the evidence derived from their work.” The emphasis is on studying, or observing, and then explaining . This descriptor takes the image of scientific inquiry beyond carefully planned experience and includes explaining what was experienced.
According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary, “explain” means “(a) to make known, (b) to make plain or understandable, (c) to give the reason or cause of, and (d) to show the logical development or relations of” (Merriam-Webster, n.d. ). We will use all these definitions. Taken together, they suggest that to explain an observation means to understand it by finding reasons (or causes) for why it is as it is. In this sense of scientific inquiry, the following are synonyms: explaining why, understanding why, and reasoning about causes and effects. Our image of scientific inquiry now includes planning, observing, and explaining why.

We need to add a final note about this descriptor. We have phrased it in a way that suggests “observing something” means you are observing something in real time—observing the way things are or the way things are changing. This is often true. But, observing could mean observing data that already have been collected, maybe by someone else making the original observations (e.g., secondary analysis of NAEP data or analysis of existing video recordings of classroom instruction). We will address secondary analyses more fully in Chap. 4 . For now, what is important is that the process requires explaining why the data look like they do.
We must note that for us, the term “data” is not limited to numerical or quantitative data such as test scores. Data can also take many nonquantitative forms, including written survey responses, interview transcripts, journal entries, video recordings of students, teachers, and classrooms, text messages, and so forth.

Exercise 1.3
What are the implications of the statement that just “observing” is not enough to count as scientific inquiry? Does this mean that a detailed description of a phenomenon is not scientific inquiry?
Find sources that define research in education that differ with our position, that say description alone, without explanation, counts as scientific research. Identify the precise points where the opinions differ. What are the best arguments for each of the positions? Which do you prefer? Why?
Descriptor 3. Updating Everyone’s Thinking in Response to More and Better Information
This descriptor focuses on a third aspect of scientific inquiry: updating and advancing the field’s understanding of phenomena that are investigated. This descriptor foregrounds a powerful characteristic of scientific inquiry: the reliability (or trustworthiness) of what is learned and the ultimate inevitability of this learning to advance human understanding of phenomena. Humans might choose not to learn from scientific inquiry, but history suggests that scientific inquiry always has the potential to advance understanding and that, eventually, humans take advantage of these new understandings.
Before exploring these bold claims a bit further, note that this descriptor uses “information” in the same way the previous two descriptors used “experience” and “observations.” These are the stuff of scientific inquiry and we will use them often, sometimes interchangeably. Frequently, we will use the term “data” to stand for all these terms.
An overriding goal of scientific inquiry is for everyone to learn from what one scientist does. Much of this book is about the methods you need to use so others have faith in what you report and can learn the same things you learned. This aspect of scientific inquiry has many implications.
One implication is that scientific inquiry is not a private practice. It is a public practice available for others to see and learn from. Notice how different this is from everyday learning. When you happen to learn something from your everyday experience, often only you gain from the experience. The fact that research is a public practice means it is also a social one. It is best conducted by interacting with others along the way: soliciting feedback at each phase, taking opportunities to present work-in-progress, and benefitting from the advice of others.
A second implication is that you, as the researcher, must be committed to sharing what you are doing and what you are learning in an open and transparent way. This allows all phases of your work to be scrutinized and critiqued. This is what gives your work credibility. The reliability or trustworthiness of your findings depends on your colleagues recognizing that you have used all appropriate methods to maximize the chances that your claims are justified by the data.
A third implication of viewing scientific inquiry as a collective enterprise is the reverse of the second—you must be committed to receiving comments from others. You must treat your colleagues as fair and honest critics even though it might sometimes feel otherwise. You must appreciate their job, which is to remain skeptical while scrutinizing what you have done in considerable detail. To provide the best help to you, they must remain skeptical about your conclusions (when, for example, the data are difficult for them to interpret) until you offer a convincing logical argument based on the information you share. A rather harsh but good-to-remember statement of the role of your friendly critics was voiced by Karl Popper, a well-known twentieth century philosopher of science: “. . . if you are interested in the problem which I tried to solve by my tentative assertion, you may help me by criticizing it as severely as you can” (Popper, 1968, p. 27).
A final implication of this third descriptor is that, as someone engaged in scientific inquiry, you have no choice but to update your thinking when the data support a different conclusion. This applies to your own data as well as to those of others. When data clearly point to a specific claim, even one that is quite different than you expected, you must reconsider your position. If the outcome is replicated multiple times, you need to adjust your thinking accordingly. Scientific inquiry does not let you pick and choose which data to believe; it mandates that everyone update their thinking when the data warrant an update.
Doing Scientific Inquiry
We define scientific inquiry in an operational sense—what does it mean to do scientific inquiry? What kind of process would satisfy all three descriptors: carefully planning an experience in advance; observing and trying to explain what you see; and, contributing to updating everyone’s thinking about an important phenomenon?
We define scientific inquiry as formulating , testing , and revising hypotheses about phenomena of interest.
Of course, we are not the only ones who define it in this way. The definition for the scientific method posted by the editors of Britannica is: “a researcher develops a hypothesis, tests it through various means, and then modifies the hypothesis on the basis of the outcome of the tests and experiments” (Britannica, n.d. ).

Notice how defining scientific inquiry this way satisfies each of the descriptors. “Carefully planning an experience in advance” is exactly what happens when formulating a hypothesis about a phenomenon of interest and thinking about how to test it. “ Observing a phenomenon” occurs when testing a hypothesis, and “ explaining ” what is found is required when revising a hypothesis based on the data. Finally, “updating everyone’s thinking” comes from comparing publicly the original with the revised hypothesis.
Doing scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, underscores the value of accumulating knowledge rather than generating random bits of knowledge. Formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is an ongoing process, with each revised hypothesis begging for another test, whether by the same researcher or by new researchers. The editors of Britannica signaled this cyclic process by adding the following phrase to their definition of the scientific method: “The modified hypothesis is then retested, further modified, and tested again.” Scientific inquiry creates a process that encourages each study to build on the studies that have gone before. Through collective engagement in this process of building study on top of study, the scientific community works together to update its thinking.
Before exploring more fully the meaning of “formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses,” we need to acknowledge that this is not the only way researchers define research. Some researchers prefer a less formal definition, one that includes more serendipity, less planning, less explanation. You might have come across more open definitions such as “research is finding out about something.” We prefer the tighter hypothesis formulation, testing, and revision definition because we believe it provides a single, coherent map for conducting research that addresses many of the thorny problems educational researchers encounter. We believe it is the most useful orientation toward research and the most helpful to learn as a beginning researcher.
A final clarification of our definition is that it applies equally to qualitative and quantitative research. This is a familiar distinction in education that has generated much discussion. You might think our definition favors quantitative methods over qualitative methods because the language of hypothesis formulation and testing is often associated with quantitative methods. In fact, we do not favor one method over another. In Chap. 4 , we will illustrate how our definition fits research using a range of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Exercise 1.4
Look for ways to extend what the field knows in an area that has already received attention by other researchers. Specifically, you can search for a program of research carried out by more experienced researchers that has some revised hypotheses that remain untested. Identify a revised hypothesis that you might like to test.
Unpacking the Terms Formulating, Testing, and Revising Hypotheses
To get a full sense of the definition of scientific inquiry we will use throughout this book, it is helpful to spend a little time with each of the key terms.
We first want to make clear that we use the term “hypothesis” as it is defined in most dictionaries and as it used in many scientific fields rather than as it is usually defined in educational statistics courses. By “hypothesis,” we do not mean a null hypothesis that is accepted or rejected by statistical analysis. Rather, we use “hypothesis” in the sense conveyed by the following definitions: “An idea or explanation for something that is based on known facts but has not yet been proved” (Cambridge University Press, n.d. ), and “An unproved theory, proposition, or supposition, tentatively accepted to explain certain facts and to provide a basis for further investigation or argument” (Agnes & Guralnik, 2008 ).
We distinguish two parts to “hypotheses.” Hypotheses consist of predictions and rationales . Predictions are statements about what you expect to find when you inquire about something. Rationales are explanations for why you made the predictions you did, why you believe your predictions are correct. So, for us “formulating hypotheses” means making explicit predictions and developing rationales for the predictions.
“Testing hypotheses” means making observations that allow you to assess in what ways your predictions were correct and in what ways they were incorrect. In education research, it is rarely useful to think of your predictions as either right or wrong. Because of the complexity of most issues you will investigate, most predictions will be right in some ways and wrong in others.
By studying the observations you make (data you collect) to test your hypotheses, you can revise your hypotheses to better align with the observations. This means revising your predictions plus revising your rationales to justify your adjusted predictions. Even though you might not run another test, formulating revised hypotheses is an essential part of conducting a research study. Comparing your original and revised hypotheses informs everyone of what you learned by conducting your study. In addition, a revised hypothesis sets the stage for you or someone else to extend your study and accumulate more knowledge of the phenomenon.
We should note that not everyone makes a clear distinction between predictions and rationales as two aspects of hypotheses. In fact, common, non-scientific uses of the word “hypothesis” may limit it to only a prediction or only an explanation (or rationale). We choose to explicitly include both prediction and rationale in our definition of hypothesis, not because we assert this should be the universal definition, but because we want to foreground the importance of both parts acting in concert. Using “hypothesis” to represent both prediction and rationale could hide the two aspects, but we make them explicit because they provide different kinds of information. It is usually easier to make predictions than develop rationales because predictions can be guesses, hunches, or gut feelings about which you have little confidence. Developing a compelling rationale requires careful thought plus reading what other researchers have found plus talking with your colleagues. Often, while you are developing your rationale you will find good reasons to change your predictions. Developing good rationales is the engine that drives scientific inquiry. Rationales are essentially descriptions of how much you know about the phenomenon you are studying. Throughout this guide, we will elaborate on how developing good rationales drives scientific inquiry. For now, we simply note that it can sharpen your predictions and help you to interpret your data as you test your hypotheses.

Hypotheses in education research take a variety of forms or types. This is because there are a variety of phenomena that can be investigated. Investigating educational phenomena is sometimes best done using qualitative methods, sometimes using quantitative methods, and most often using mixed methods (e.g., Hay, 2016 ; Weis et al. 2019a ; Weisner, 2005 ). This means that, given our definition, hypotheses are equally applicable to qualitative and quantitative investigations.
Hypotheses take different forms when they are used to investigate different kinds of phenomena. Two very different activities in education could be labeled conducting experiments and descriptions. In an experiment, a hypothesis makes a prediction about anticipated changes, say the changes that occur when a treatment or intervention is applied. You might investigate how students’ thinking changes during a particular kind of instruction.
A second type of hypothesis, relevant for descriptive research, makes a prediction about what you will find when you investigate and describe the nature of a situation. The goal is to understand a situation as it exists rather than to understand a change from one situation to another. In this case, your prediction is what you expect to observe. Your rationale is the set of reasons for making this prediction; it is your current explanation for why the situation will look like it does.
You will probably read, if you have not already, that some researchers say you do not need a prediction to conduct a descriptive study. We will discuss this point of view in Chap. 2 . For now, we simply claim that scientific inquiry, as we have defined it, applies to all kinds of research studies. Descriptive studies, like others, not only benefit from formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, but also need hypothesis formulating, testing, and revising.
One reason we define research as formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses is that if you think of research in this way you are less likely to go wrong. It is a useful guide for the entire process, as we will describe in detail in the chapters ahead. For example, as you build the rationale for your predictions, you are constructing the theoretical framework for your study (Chap. 3 ). As you work out the methods you will use to test your hypothesis, every decision you make will be based on asking, “Will this help me formulate or test or revise my hypothesis?” (Chap. 4 ). As you interpret the results of testing your predictions, you will compare them to what you predicted and examine the differences, focusing on how you must revise your hypotheses (Chap. 5 ). By anchoring the process to formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses, you will make smart decisions that yield a coherent and well-designed study.
Exercise 1.5
Compare the concept of formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses with the descriptions of scientific inquiry contained in Scientific Research in Education (NRC, 2002 ). How are they similar or different?
Exercise 1.6
Provide an example to illustrate and emphasize the differences between everyday learning/thinking and scientific inquiry.
Learning from Doing Scientific Inquiry
We noted earlier that a measure of what you have learned by conducting a research study is found in the differences between your original hypothesis and your revised hypothesis based on the data you collected to test your hypothesis. We will elaborate this statement in later chapters, but we preview our argument here.
Even before collecting data, scientific inquiry requires cycles of making a prediction, developing a rationale, refining your predictions, reading and studying more to strengthen your rationale, refining your predictions again, and so forth. And, even if you have run through several such cycles, you still will likely find that when you test your prediction you will be partly right and partly wrong. The results will support some parts of your predictions but not others, or the results will “kind of” support your predictions. A critical part of scientific inquiry is making sense of your results by interpreting them against your predictions. Carefully describing what aspects of your data supported your predictions, what aspects did not, and what data fell outside of any predictions is not an easy task, but you cannot learn from your study without doing this analysis.

Analyzing the matches and mismatches between your predictions and your data allows you to formulate different rationales that would have accounted for more of the data. The best revised rationale is the one that accounts for the most data. Once you have revised your rationales, you can think about the predictions they best justify or explain. It is by comparing your original rationales to your new rationales that you can sort out what you learned from your study.
Suppose your study was an experiment. Maybe you were investigating the effects of a new instructional intervention on students’ learning. Your original rationale was your explanation for why the intervention would change the learning outcomes in a particular way. Your revised rationale explained why the changes that you observed occurred like they did and why your revised predictions are better. Maybe your original rationale focused on the potential of the activities if they were implemented in ideal ways and your revised rationale included the factors that are likely to affect how teachers implement them. By comparing the before and after rationales, you are describing what you learned—what you can explain now that you could not before. Another way of saying this is that you are describing how much more you understand now than before you conducted your study.
Revised predictions based on carefully planned and collected data usually exhibit some of the following features compared with the originals: more precision, more completeness, and broader scope. Revised rationales have more explanatory power and become more complete, more aligned with the new predictions, sharper, and overall more convincing.
Part II. Why Do Educators Do Research?
Doing scientific inquiry is a lot of work. Each phase of the process takes time, and you will often cycle back to improve earlier phases as you engage in later phases. Because of the significant effort required, you should make sure your study is worth it. So, from the beginning, you should think about the purpose of your study. Why do you want to do it? And, because research is a social practice, you should also think about whether the results of your study are likely to be important and significant to the education community.
If you are doing research in the way we have described—as scientific inquiry—then one purpose of your study is to understand , not just to describe or evaluate or report. As we noted earlier, when you formulate hypotheses, you are developing rationales that explain why things might be like they are. In our view, trying to understand and explain is what separates research from other kinds of activities, like evaluating or describing.
One reason understanding is so important is that it allows researchers to see how or why something works like it does. When you see how something works, you are better able to predict how it might work in other contexts, under other conditions. And, because conditions, or contextual factors, matter a lot in education, gaining insights into applying your findings to other contexts increases the contributions of your work and its importance to the broader education community.
Consequently, the purposes of research studies in education often include the more specific aim of identifying and understanding the conditions under which the phenomena being studied work like the observations suggest. A classic example of this kind of study in mathematics education was reported by William Brownell and Harold Moser in 1949 . They were trying to establish which method of subtracting whole numbers could be taught most effectively—the regrouping method or the equal additions method. However, they realized that effectiveness might depend on the conditions under which the methods were taught—“meaningfully” versus “mechanically.” So, they designed a study that crossed the two instructional approaches with the two different methods (regrouping and equal additions). Among other results, they found that these conditions did matter. The regrouping method was more effective under the meaningful condition than the mechanical condition, but the same was not true for the equal additions algorithm.
What do education researchers want to understand? In our view, the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. So, we believe the ultimate purpose of scientific inquiry in education is to develop understanding that supports the improvement of learning opportunities for all students. We say “ultimate” because there are lots of issues that must be understood to improve learning opportunities for all students. Hypotheses about many aspects of education are connected, ultimately, to students’ learning. For example, formulating and testing a hypothesis that preservice teachers need to engage in particular kinds of activities in their coursework in order to teach particular topics well is, ultimately, connected to improving students’ learning opportunities. So is hypothesizing that school districts often devote relatively few resources to instructional leadership training or hypothesizing that positioning mathematics as a tool students can use to combat social injustice can help students see the relevance of mathematics to their lives.
We do not exclude the importance of research on educational issues more removed from improving students’ learning opportunities, but we do think the argument for their importance will be more difficult to make. If there is no way to imagine a connection between your hypothesis and improving learning opportunities for students, even a distant connection, we recommend you reconsider whether it is an important hypothesis within the education community.
Notice that we said the ultimate goal of education is to offer all students the best possible learning opportunities. For too long, educators have been satisfied with a goal of offering rich learning opportunities for lots of students, sometimes even for just the majority of students, but not necessarily for all students. Evaluations of success often are based on outcomes that show high averages. In other words, if many students have learned something, or even a smaller number have learned a lot, educators may have been satisfied. The problem is that there is usually a pattern in the groups of students who receive lower quality opportunities—students of color and students who live in poor areas, urban and rural. This is not acceptable. Consequently, we emphasize the premise that the purpose of education research is to offer rich learning opportunities to all students.
One way to make sure you will be able to convince others of the importance of your study is to consider investigating some aspect of teachers’ shared instructional problems. Historically, researchers in education have set their own research agendas, regardless of the problems teachers are facing in schools. It is increasingly recognized that teachers have had trouble applying to their own classrooms what researchers find. To address this problem, a researcher could partner with a teacher—better yet, a small group of teachers—and talk with them about instructional problems they all share. These discussions can create a rich pool of problems researchers can consider. If researchers pursued one of these problems (preferably alongside teachers), the connection to improving learning opportunities for all students could be direct and immediate. “Grounding a research question in instructional problems that are experienced across multiple teachers’ classrooms helps to ensure that the answer to the question will be of sufficient scope to be relevant and significant beyond the local context” (Cai et al., 2019b , p. 115).
As a beginning researcher, determining the relevance and importance of a research problem is especially challenging. We recommend talking with advisors, other experienced researchers, and peers to test the educational importance of possible research problems and topics of study. You will also learn much more about the issue of research importance when you read Chap. 5 .
Exercise 1.7
Identify a problem in education that is closely connected to improving learning opportunities and a problem that has a less close connection. For each problem, write a brief argument (like a logical sequence of if-then statements) that connects the problem to all students’ learning opportunities.
Part III. Conducting Research as a Practice of Failing Productively
Scientific inquiry involves formulating hypotheses about phenomena that are not fully understood—by you or anyone else. Even if you are able to inform your hypotheses with lots of knowledge that has already been accumulated, you are likely to find that your prediction is not entirely accurate. This is normal. Remember, scientific inquiry is a process of constantly updating your thinking. More and better information means revising your thinking, again, and again, and again. Because you never fully understand a complicated phenomenon and your hypotheses never produce completely accurate predictions, it is easy to believe you are somehow failing.
The trick is to fail upward, to fail to predict accurately in ways that inform your next hypothesis so you can make a better prediction. Some of the best-known researchers in education have been open and honest about the many times their predictions were wrong and, based on the results of their studies and those of others, they continuously updated their thinking and changed their hypotheses.
A striking example of publicly revising (actually reversing) hypotheses due to incorrect predictions is found in the work of Lee J. Cronbach, one of the most distinguished educational psychologists of the twentieth century. In 1955, Cronbach delivered his presidential address to the American Psychological Association. Titling it “Two Disciplines of Scientific Psychology,” Cronbach proposed a rapprochement between two research approaches—correlational studies that focused on individual differences and experimental studies that focused on instructional treatments controlling for individual differences. (We will examine different research approaches in Chap. 4 ). If these approaches could be brought together, reasoned Cronbach ( 1957 ), researchers could find interactions between individual characteristics and treatments (aptitude-treatment interactions or ATIs), fitting the best treatments to different individuals.
In 1975, after years of research by many researchers looking for ATIs, Cronbach acknowledged the evidence for simple, useful ATIs had not been found. Even when trying to find interactions between a few variables that could provide instructional guidance, the analysis, said Cronbach, creates “a hall of mirrors that extends to infinity, tormenting even the boldest investigators and defeating even ambitious designs” (Cronbach, 1975 , p. 119).
As he was reflecting back on his work, Cronbach ( 1986 ) recommended moving away from documenting instructional effects through statistical inference (an approach he had championed for much of his career) and toward approaches that probe the reasons for these effects, approaches that provide a “full account of events in a time, place, and context” (Cronbach, 1986 , p. 104). This is a remarkable change in hypotheses, a change based on data and made fully transparent. Cronbach understood the value of failing productively.
Closer to home, in a less dramatic example, one of us began a line of scientific inquiry into how to prepare elementary preservice teachers to teach early algebra. Teaching early algebra meant engaging elementary students in early forms of algebraic reasoning. Such reasoning should help them transition from arithmetic to algebra. To begin this line of inquiry, a set of activities for preservice teachers were developed. Even though the activities were based on well-supported hypotheses, they largely failed to engage preservice teachers as predicted because of unanticipated challenges the preservice teachers faced. To capitalize on this failure, follow-up studies were conducted, first to better understand elementary preservice teachers’ challenges with preparing to teach early algebra, and then to better support preservice teachers in navigating these challenges. In this example, the initial failure was a necessary step in the researchers’ scientific inquiry and furthered the researchers’ understanding of this issue.
We present another example of failing productively in Chap. 2 . That example emerges from recounting the history of a well-known research program in mathematics education.
Making mistakes is an inherent part of doing scientific research. Conducting a study is rarely a smooth path from beginning to end. We recommend that you keep the following things in mind as you begin a career of conducting research in education.
First, do not get discouraged when you make mistakes; do not fall into the trap of feeling like you are not capable of doing research because you make too many errors.
Second, learn from your mistakes. Do not ignore your mistakes or treat them as errors that you simply need to forget and move past. Mistakes are rich sites for learning—in research just as in other fields of study.
Third, by reflecting on your mistakes, you can learn to make better mistakes, mistakes that inform you about a productive next step. You will not be able to eliminate your mistakes, but you can set a goal of making better and better mistakes.
Exercise 1.8
How does scientific inquiry differ from everyday learning in giving you the tools to fail upward? You may find helpful perspectives on this question in other resources on science and scientific inquiry (e.g., Failure: Why Science is So Successful by Firestein, 2015).
Exercise 1.9
Use what you have learned in this chapter to write a new definition of scientific inquiry. Compare this definition with the one you wrote before reading this chapter. If you are reading this book as part of a course, compare your definition with your colleagues’ definitions. Develop a consensus definition with everyone in the course.
Part IV. Preview of Chap. 2
Now that you have a good idea of what research is, at least of what we believe research is, the next step is to think about how to actually begin doing research. This means how to begin formulating, testing, and revising hypotheses. As for all phases of scientific inquiry, there are lots of things to think about. Because it is critical to start well, we devote Chap. 2 to getting started with formulating hypotheses.
Agnes, M., & Guralnik, D. B. (Eds.). (2008). Hypothesis. In Webster’s new world college dictionary (4th ed.). Wiley.
Google Scholar
Britannica. (n.d.). Scientific method. In Encyclopaedia Britannica . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://www.britannica.com/science/scientific-method
Brownell, W. A., & Moser, H. E. (1949). Meaningful vs. mechanical learning: A study in grade III subtraction . Duke University Press..
Cai, J., Morris, A., Hohensee, C., Hwang, S., Robison, V., Cirillo, M., Kramer, S. L., & Hiebert, J. (2019b). Posing significant research questions. Journal for Research in Mathematics Education, 50 (2), 114–120. https://doi.org/10.5951/jresematheduc.50.2.0114
Article Google Scholar
Cambridge University Press. (n.d.). Hypothesis. In Cambridge dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022 from https://dictionary.cambridge.org/us/dictionary/english/hypothesis
Cronbach, J. L. (1957). The two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 12 , 671–684.
Cronbach, L. J. (1975). Beyond the two disciplines of scientific psychology. American Psychologist, 30 , 116–127.
Cronbach, L. J. (1986). Social inquiry by and for earthlings. In D. W. Fiske & R. A. Shweder (Eds.), Metatheory in social science: Pluralisms and subjectivities (pp. 83–107). University of Chicago Press.
Hay, C. M. (Ed.). (2016). Methods that matter: Integrating mixed methods for more effective social science research . University of Chicago Press.
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Explain. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved July 15, 2022, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/explain
National Research Council. (2002). Scientific research in education . National Academy Press.
Weis, L., Eisenhart, M., Duncan, G. J., Albro, E., Bueschel, A. C., Cobb, P., Eccles, J., Mendenhall, R., Moss, P., Penuel, W., Ream, R. K., Rumbaut, R. G., Sloane, F., Weisner, T. S., & Wilson, J. (2019a). Mixed methods for studies that address broad and enduring issues in education research. Teachers College Record, 121 , 100307.
Weisner, T. S. (Ed.). (2005). Discovering successful pathways in children’s development: Mixed methods in the study of childhood and family life . University of Chicago Press.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Education, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
James Hiebert, Anne K Morris & Charles Hohensee
Department of Mathematical Sciences, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, USA
Jinfa Cai & Stephen Hwang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Hiebert, J., Cai, J., Hwang, S., Morris, A.K., Hohensee, C. (2023). What Is Research, and Why Do People Do It?. In: Doing Research: A New Researcher’s Guide. Research in Mathematics Education. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19078-0_1
Published : 03 December 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-19077-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-19078-0
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
What is Research: Definition, Methods, Types & Examples

The search for knowledge is closely linked to the object of study; that is, to the reconstruction of the facts that will provide an explanation to an observed event and that at first sight can be considered as a problem. It is very human to seek answers and satisfy our curiosity. Let’s talk about research.
Content Index
What is Research?
What are the characteristics of research.
- Comparative analysis chart
Qualitative methods
Quantitative methods, 8 tips for conducting accurate research.
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, “research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.”
Inductive methods analyze an observed event, while deductive methods verify the observed event. Inductive approaches are associated with qualitative research , and deductive methods are more commonly associated with quantitative analysis .
Research is conducted with a purpose to:
- Identify potential and new customers
- Understand existing customers
- Set pragmatic goals
- Develop productive market strategies
- Address business challenges
- Put together a business expansion plan
- Identify new business opportunities
- Good research follows a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers need to practice ethics and a code of conduct while making observations or drawing conclusions.
- The analysis is based on logical reasoning and involves both inductive and deductive methods.
- Real-time data and knowledge is derived from actual observations in natural settings.
- There is an in-depth analysis of all data collected so that there are no anomalies associated with it.
- It creates a path for generating new questions. Existing data helps create more research opportunities.
- It is analytical and uses all the available data so that there is no ambiguity in inference.
- Accuracy is one of the most critical aspects of research. The information must be accurate and correct. For example, laboratories provide a controlled environment to collect data. Accuracy is measured in the instruments used, the calibrations of instruments or tools, and the experiment’s final result.
What is the purpose of research?
There are three main purposes:
- Exploratory: As the name suggests, researchers conduct exploratory studies to explore a group of questions. The answers and analytics may not offer a conclusion to the perceived problem. It is undertaken to handle new problem areas that haven’t been explored before. This exploratory data analysis process lays the foundation for more conclusive data collection and analysis.
LEARN ABOUT: Descriptive Analysis
- Descriptive: It focuses on expanding knowledge on current issues through a process of data collection. Descriptive research describe the behavior of a sample population. Only one variable is required to conduct the study. The three primary purposes of descriptive studies are describing, explaining, and validating the findings. For example, a study conducted to know if top-level management leaders in the 21st century possess the moral right to receive a considerable sum of money from the company profit.
LEARN ABOUT: Best Data Collection Tools
- Explanatory: Causal research or explanatory research is conducted to understand the impact of specific changes in existing standard procedures. Running experiments is the most popular form. For example, a study that is conducted to understand the effect of rebranding on customer loyalty.
Here is a comparative analysis chart for a better understanding:
It begins by asking the right questions and choosing an appropriate method to investigate the problem. After collecting answers to your questions, you can analyze the findings or observations to draw reasonable conclusions.
When it comes to customers and market studies, the more thorough your questions, the better the analysis. You get essential insights into brand perception and product needs by thoroughly collecting customer data through surveys and questionnaires . You can use this data to make smart decisions about your marketing strategies to position your business effectively.
To make sense of your study and get insights faster, it helps to use a research repository as a single source of truth in your organization and manage your research data in one centralized data repository .
Types of research methods and Examples

Research methods are broadly classified as Qualitative and Quantitative .
Both methods have distinctive properties and data collection methods .
Qualitative research is a method that collects data using conversational methods, usually open-ended questions . The responses collected are essentially non-numerical. This method helps a researcher understand what participants think and why they think in a particular way.
Types of qualitative methods include:
- One-to-one Interview
- Focus Groups
- Ethnographic studies
- Text Analysis
Quantitative methods deal with numbers and measurable forms . It uses a systematic way of investigating events or data. It answers questions to justify relationships with measurable variables to either explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
Types of quantitative methods include:
- Survey research
- Descriptive research
- Correlational research
LEARN MORE: Descriptive Research vs Correlational Research
Remember, it is only valuable and useful when it is valid, accurate, and reliable. Incorrect results can lead to customer churn and a decrease in sales.
It is essential to ensure that your data is:
- Valid – founded, logical, rigorous, and impartial.
- Accurate – free of errors and including required details.
- Reliable – other people who investigate in the same way can produce similar results.
- Timely – current and collected within an appropriate time frame.
- Complete – includes all the data you need to support your business decisions.
Gather insights

- Identify the main trends and issues, opportunities, and problems you observe. Write a sentence describing each one.
- Keep track of the frequency with which each of the main findings appears.
- Make a list of your findings from the most common to the least common.
- Evaluate a list of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats identified in a SWOT analysis .
- Prepare conclusions and recommendations about your study.
- Act on your strategies
- Look for gaps in the information, and consider doing additional inquiry if necessary
- Plan to review the results and consider efficient methods to analyze and interpret results.
Review your goals before making any conclusions about your study. Remember how the process you have completed and the data you have gathered help answer your questions. Ask yourself if what your analysis revealed facilitates the identification of your conclusions and recommendations.
LEARN MORE ABOUT OUR SOFTWARE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Trend Report: Guide for Market Dynamics & Strategic Analysis
May 29, 2024

Cannabis Industry Business Intelligence: Impact on Research
May 28, 2024
Top 10 Dynata Alternatives & Competitors
May 27, 2024
What Are My Employees Really Thinking? The Power of Open-ended Survey Analysis
May 24, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Breaking News
Q&A: These researchers examined 20 years of data on same-sex marriage. They didn’t find any harms

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
Twenty years ago this month, Marcia Kadish and Tanya McCloskey exchanged wedding vows at Cambridge City Hall in Massachusetts and became the first same-sex couple to legally marry in the United States .
The couple had been together since 1986, but their decision to wed was radical for its time. In 2004, only 31% of Americans supported same-sex marriage, while 60% were opposed , according to a Pew Research Center poll.
Much of that opposition was fueled by fears that expanding the definition of marriage beyond the traditional union of a man and a women would undermine the institution and be destabilizing to families. Researchers at the Rand Corp. decided to find out if those predictions turned out to be true.
A team from the Santa Monica-based think tank spent a year poring over the data. The result is a 186-page report that should be reassuring to supporters of marriage equality.
“If there were negative consequences in the last 20 years of the decision to legalize marriage for same-sex couples, no one has yet been able to measure them,” said Benjamin Karney , an adjunct behavioral scientist at Rand.
Karney, who is also a social psychologist at UCLA, led the report with Melanie Zaber , a labor economist and economic demographer at Rand. They spoke with The Times about what they learned.
Does marriage make people better off?
Benjamin Karney: On average, yes. People who are married experience fewer health problems , they live years longer , they make more money , and they accumulate more wealth than people who marry and divorce or who don’t marry at all. People who are married also experience more stable and positive psychological health , and they have sex more frequently than people who are not married.
All those benefits accrue primarily to people who are in happy marriages. Unhappy marriage is very, very harmful. But most people who are married are happy — that’s why they stay married.
What prompted you to examine same-sex marriage now?
BK: At the time that these policies were changing, there were a lot of arguments on both sides about whether the consequences would be positive or negative. Twenty years is a long time, and during that time, a lot of research has been conducted. It seemed like a good time to ask the question: What did happen as a consequence of legalizing marriage for same-sex couples? So that’s one reason.
The second reason is that in the Dobbs decision that overturned Roe vs. Wade , Justice Clarence Thomas in his concurring opinion said explicitly that this Supreme Court should consider reviewing and potentially overturning other decisions , and he named the 2015 Obergefell vs. Hodges decision that legalized marriage for same-sex couples by name. Given that people may be wondering about the merits of that decision, it seemed like a good time to evaluate the consequences of that decision, and that’s what we’ve done.
What did you find?
BK: We found 96 studies across a range of disciplines. Some are in economics. Some are in psychology. Some are in medicine. Some are in public health.
Melanie Zaber: We wanted it to be research that actually measured something. There were a number of more qualitative or theoretical or legal arguments that we excluded.
BK: What I found most notable is that all of the studies drew the same conclusions: There was either no effect or beneficial effects on any outcome you could look at. That’s 20 years of research, 96 studies, and no harms.

On same-sex marriage, ‘the country has caught up with California’
Gov. Gavin Newsom and Vice President Kamala Harris were at the vanguard in pushing for marriage equality, which will soon be signed into federal law.
Dec. 12, 2022
Does it seem plausible that the results could be so one-sided?
BK: I was not surprised. There’s a lot of good theory in family science and relationship science to argue that if you extend rights to a group that’s been stigmatized, that group should do better, and the majority group should not be affected. Indeed, that’s what we found.
MZ: I don’t find it particularly surprising. When we say there are no harms, that doesn’t mean everything’s coming up sunshine and roses — it means sunshine and roses or nothing. In this case, where the prediction was something negative, then nothing still feels like sunshine and roses.
What sorts of things did these studies measure?
BK: There were three general categories. The largest group was looking at outcomes for LGBT individuals and same-sex couples. The second bucket looked at the children of same-sex parents. And the third bucket was the effect on everybody else.
There was no evidence of harms anywhere.
That’s interesting because opponents of these policy changes very strongly — and very explicitly — predicted there would be harms. They predicted it in front of the Supreme Court , arguing that if we allow same-sex couples to marry, the consequences for the country will be negative and severe and unavoidable and irreversible.

Who benefits the most from legalizing same-sex marriage?
BK: Same-sex couples. Their relationships last longer when they are able to marry and cement their commitment. Their incomes go up. Their mental health improves.
That mental health improvement extends to LGBT individuals whether or not they are married. Even if you’re not married , if you’re a member of a sexual minority and live in a world that validates same-sex relationships, that relieves a stressor and has measurable benefits on physical and mental health.
What’s behind these improvements?
BK: The effects on health seem like they operate partly through employer-based health insurance being extended to spouses.
The mechanisms for mental health have been described by minority stress theory . Living in a society that is constantly sending you a message that you are less worthy of equal treatment is stressful, partly because it leads to discrimination. Being the target of discrimination is stressful , and that stress has real mental and physical consequences .
You found 96 studies about gay marriage. Why did you conduct your own research as well?
MZ: Some of those studies were conducted when only a few states had marriage for same-sex couples. A state like West Virginia or Wyoming might say, “Well that’s all well and good that you have evidence from Massachusetts or Vermont, but New England isn’t the center of the universe.”
By looking at a broader range of years, we’re better able to capture some of those states that did allow same-sex couples to marry but weren’t among the first to do so. We have reason to think those states may be very different environments. Our approach was to use each state as a quasi-experiment.
What did all that data tell you?
MZ: The headline from our new analysis is no negative impacts and some positive ones.
We see an increase in marriage, and that increase is driven not just by newly marrying same-sex couples, but also by an increase in marriage among different-sex couples. That was a bit surprising to us.

World & Nation
Hearing threat to Roe vs. Wade, I thought of my gay marriage — and Jim Obergefell’s fight
Like LGBTQ people nationwide, I can’t help but worry that the legal logic that might topple Roe will be used against my marriage.
May 16, 2022
What do you think was going on?
MZ: There are a few different mechanisms for this, none of which we can explicitly test.
One could be allyship . There are individuals who identify as cisgender straight individuals, but they want to show their allyship so they delay marriage until everyone’s able to marry.
There’s an increasing number of individuals who identify as bisexual in the United States. Even if they’re marrying a different-sex partner, they may be trying to have validation of their broader identity.
The argument we find most compelling is that having people loudly clamoring for all the great things that come along with marriage made people in the broader population say, “Oh hey, getting married means people can go visit me in the hospital, and that if I’m in an accident there’s no concern about who my property will go to, and we have more access to health insurance.” Talking about that may have made some people realize, “You know, marriage actually is pretty helpful.”
BK: If you hear about a restaurant that everyone’s trying to get into, you want to eat at that restaurant.
MZ: That is an excellent way of putting it!
Do you think this research will persuade those who were concerned that same-sex marriage would have terrible consequences?
MZ: That’s our goal — to put evidence out to the public so policymakers can make informed choices.
BK: I’d like to believe so. At the time those arguments were made, they were speculative. People were trying to predict the future. Now we don’t have to predict the future. Twenty years have passed and we have the data. We can document what has happened.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
More to Read

Patt Morrison: California settled no-fault divorce decades ago. Why is it back in the news?
May 24, 2024

Can straight married men and women be friends? I went on a quest to find out
April 30, 2024

Commentary: ‘The Golden Bachelor’ divorce turns a TV success story into a cautionary tale
April 16, 2024

Karen Kaplan covers science and medical research for the Los Angeles Times. She has been a member of the science team since 2005, including 13 years as an editor. Her first decade at The Times was spent covering technology in the Business section as both a reporter and editor. She grew up in San Diego and is a graduate of MIT and Columbia University.
More From the Los Angeles Times
Scott Peterson suffers big setback in effort to prove he did not kill wife, unborn son

San José State professor suspended over pro-Palestinian work
Climate & Environment
Can satellites combat wildfires? Inside the booming ‘space race’ to fight the flames
May 30, 2024

Are pet dogs and cats the weak link in bird flu surveillance?

I want to keep my child safe from abuse − but research tells me I’m doing it wrong
Founder and Executive Director, Center for Violence Prevention Research; Affiliate Faculty with the Crimes Against Children Research Center, University of New Hampshire
Disclosure statement
Melissa Bright receives funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the World Childhood Foundation (via work with Stop it Now!).
View all partners
Child sexual abuse is uncomfortable to think about, much less talk about. The idea of an adult engaging in sexual behaviors with a child feels sickening. It’s easiest to believe that it rarely happens, and when it does, that it’s only to children whose parents aren’t protecting them.
This belief stayed with me during my early days as a parent. I kept an eye out for creepy men at the playground and was skeptical of men who worked with young children, such as teachers and coaches. When my kids were old enough, I taught them what a “good touch” was, like a hug from a family member, and what a “bad touch” was, like someone touching their private parts.
But after nearly a quarter-century of conducting research – 15 years on family violence, another eight on child abuse prevention, including sexual abuse – I realized that many people, including me, were using antiquated strategies to protect our children .
As the founder of the Center for Violence Prevention Research , I work with organizations that educate their communities and provide direct services to survivors of child sexual abuse. From them, I have learned much about the everyday actions all of us can take to help keep our children safe. Some of it may surprise you.
Wrong assumptions
First, my view of what constitutes child sexual abuse was too narrow. Certainly, all sexual activities between adults and children are a form of abuse.
But child sexual abuse also includes nonconsensual sexual contact between two children. It includes noncontact offenses such as sexual harassment, exhibitionism and using children to produce imagery of sexual abuse. Technology-based child sexual abuse is rising quickly with the rapid evolution of internet-based games, social media, and content generated by artificial intelligence. Reports to the National Center for Missing & Exploited Children of online enticements increased 300% from 2021 to 2023 .
My assumption that child sexual abuse didn’t happen in my community was wrong too. The latest data shows that at least 1 in 10 children, but likely closer to 1 in 5, experience sexual abuse . Statistically, that’s at least two children in my son’s kindergarten class.
Child sexual abuse happens across all ethnoracial groups, socioeconomic statuses and all gender identities. Reports of female victims outnumber males , but male victimization is likely underreported because of stigma and cultural norms about masculinity .
I’ve learned that identifying the “creepy man” at the playground is not an effective strategy. At least 90% of child sexual abusers know their victims or the victims’ family prior to offending. Usually, the abuser is a trusted member of the community; sometimes, it’s a family member .
In other words, rather than search for a predator in the park, parents need to look at the circle of people they invite into their home.
To be clear, abuse by strangers does happen, and teaching our kids to be wary of strangers is necessary. But it’s the exception, not the norm , for child sexual abuse offenses.
Most of the time, it’s not even adults causing the harm. The latest data shows more than 70% of self-reported child sexual abuse is committed by other juveniles . Nearly 1 in 10 young people say they caused some type of sexual harm to another child . Their average age at the time of causing harm is between 14 and 16.
Now for a bit of good news: The belief that people who sexually abuse children are innately evil is an oversimplification. In reality, only about 13% of adults and approximately 5% of adolescents who sexually harm children commit another sexual offense after five years . The recidivism rate is even lower for those who receive therapeutic help .
By contrast, approximately 44% of adults who commit a felony of any kind will commit another offense within a year of prison release .
What parents can do
The latest research says uncomfortable conversations are necessary to keep kids safe. Here are some recommended strategies:
Avoid confusing language. “Good touches” and “bad touches” are no longer appropriate descriptors of abuse . Harmful touches can feel physically good, rather than painful or “bad.” Abusers can also manipulate children to believe their touches are acts of love.
The research shows that it’s better to talk to children about touches that are “OK” or “not OK,” based on who does the touching and where they touch. This dissipates the confusion of something being bad but feeling good.
These conversations require clear identification of all body parts, from head and shoulders to penis and vagina. Using accurate anatomical labels teaches children that all body parts can be discussed openly with safe adults. Also, when children use accurate labels to disclose abuse, they are more likely to be understood and believed.
Encourage bodily autonomy. Telling my children that hugs from family members were universally good touches was also wrong . If children think they have to give hugs on demand, it conveys the message they do not have authority over their body.
Instead, I watch when my child is asked for a hug at family gatherings – if he hesitates, I advocate for him. I tell family members that physical touch is not mandatory and explain why – something like: “He prefers a bit more personal space, and we’re working on teaching him that he can decide who touches him and when. He really likes to give high-fives to show affection.” A heads-up: Often, the adults are put off, at least initially.
In my family, we also don’t allow the use of guilt to encourage affection. That includes phrases like: “You’ll make me sad if you don’t give me a hug.”
Promote empowerment. Research on adult sexual offenders found the greatest deterrence to completing the act was a vocal child – one who expressed their desire to stop, or said they would tell others.
Monitor your child’s social media. Multiple studies show that monitoring guards against sexting or viewing of pornography , both of which are risk factors for child sexual abuse. Monitoring can also reveal permissive or dangerous sexual attitudes the child might have.
Talk to the adults in your circle. Ask those watching your child how they plan to keep your child safe when in their care. Admittedly, this can be an awkward conversation. I might say, “Hey, I have a few questions that might sound weird, but I think they’re important for parents to ask. I’m sure my child will be safe with you, but I’m trying to talk about these things regularly, so this is good practice for me.” You may need to educate them on what the research shows.
Ask your child’s school what they’re doing to educate students and staff about child sexual abuse. Many states require schools to provide prevention education; recent research suggests these programs help children protect themselves from sexual abuse .
Talk to your child’s sports or activity organization. Ask what procedures are in place to keep children safe . This includes their screening and hiring practices, how they train and educate staff, and their guidelines for reporting abuse. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides a guide for organizations on keeping children safe .
Rely on updated research. Finally, when searching online for information, look for research that’s relatively recent – dated within the past five years. These studies should be published in peer-reviewed journals .
And then be prepared for a jolt. You may discover the conventional wisdom you’ve clung to all these years may be based on outdated – and even harmful – information.
- Child sexual abuse
- Child sexual abuse prevention
- Child safety

Data Manager

Director, Social Policy

Communications Coordinator

Head, School of Psychology

Senior Research Fellow - Women's Health Services
Cars for sale
Sell my car, car research, sign in, android auto not working with uconnect here's what to do, these tips can make fixing the connection between your smartphone and your vehicle easier..

QuickTakes:
- Do you have an Android Auto-compatible phone and vehicle?
- Check the connection if you're having problems
- Uconnect-specific tips and tricks
Android Auto is one of the most popular tools drivers use to pair their smartphones with a vehicle's infotainment system. In effect, it duplicates many of a personal device's entertainment, navigation, and communication apps and much of its user interface onto an automobile's touchscreen. Like all technologies, however, when used regularly, there can be issues.
Here's how to troubleshoot your Android Auto connection when using the Uconnect infotainment system found in many Alfa Romeo, Chrysler, Dodge, Fiat, Jeep, Maserati, and Ram vehicles.
Do You Have an Android Auto-Compatible Phone and Vehicle?
One of the first suggestions Google — the company behind the Android Auto software — makes to users who are having problems connecting is to ensure that both their vehicle and smartphone are compatible with the software.
Phones that use Android versions 6 through 9 can use the technology, but you'll need to download the Android Auto app first. From Android 10 and up, it's included as part of the device's operating system. Ensure your phone software is up to date to have the most seamless connection experience.
Vehicles such as the Dodge Challenger and Charger , the Chrysler 300 , the Jeep Renegade and Compass , and the entire Fiat and Alfa Romeo lineups feature Uconnect compatible with Android Auto from the 2017 model year onward. For Ram trucks, the Dodge Durango , the Jeep Grand Cherokee and Wrangler , and the Chrysler Pacifica , it's 2018 and newer. Maserati vehicles also offer Uconnect (branded as Maserati Touch Control), with availability split between the 2017 and 2018 model years. All Jeep Wagoneer models offer Android Auto.
Check the Connection Between Your Phone and the Car
If your Android Auto connection is through a USB cable, it should be the next suspect in your troubleshooting. Swap in a different cable, then make sure that it's capable of carrying data and isn't just a charging cable.
There are several troubleshooting steps if your vehicle allows a wireless phone connection. First, turn your phone's Bluetooth off then on, and reconnect to Uconnect. If that doesn't help, you can restart the car (including opening and closing the vehicle's door). Finally, reboot your phone before attempting to connect again.
It might sound strange, but connecting your smartphone to more than one vehicle using Android Auto can sometimes make it difficult to establish a fresh connection. Google lists a series of steps you can take in the settings under Connected Devices in Android that will allow you to delete previously connected vehicles from Android Auto's memory. You can also clear your past Bluetooth connections if you have trouble getting Uconnect to link up with your device.
Uconnect-Specific Tips and Tricks
While the above advice will work on most Android Auto setups, there are some Uconnect-specific problem solvers you can try if all else fails.
On 2019 and older Chrysler Pacifica models, it may be possible to reboot the Uconnect system by pulling fuse 76 under the hood. This might be something that could help in more extreme cases where no other options have worked to pair a device with Android Auto.
You may also have issues connecting if the "only connect to known cars" setting is checked in the Android Auto app settings itself.

Related Articles

Fresh styling, innovative new features, and class-leading towing and hauling highlight Ford's updated full-size pickup.

A fun look at the popular muscle car's history.

With sportier looks, fewer seats, and exclusive colors, the 2025 CX-70 aims at a different audience than the CX-90's.
Research Our Records

World War II Japanese Americans Incarceration: Search the Database
The Records About Japanese Americans Removed During World War II database provides basic information about Japanese and Japanese Americans who were incarcerated in War Relocation Authority (WRA) camps beginning in May 1942. This information can help you request an individual's WRA case file .
This database is available online through the National Archives' Access to Archival Databases (AAD) . Before you can effectively find a person in the AAD database, you need to know:
The individual's name (including all names used while at the WRA camp) . Some individuals are listed by their Japanese name, and others are listed by their English name. Many younger internees had both Japanese and English names.
Note: The AAD database generally does not include records of individuals who were born in the WRA camps. For these individuals, please proceed to the WRA Case File Request form , provide us with the requested information, and send it to the email address or mailing address listed on the form.
For more information about this database, please see the Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
On This Page

Individuals of Japanese ancestry at the Santa Anita Assembly Center in April 1942 before removal to WRA camps. (National Archives Identifier: 537040 )
Basic Search Steps
- Navigate to Records About Japanese Americans Removed During World War II .
- Enter the name of the person you are looking for in the box under "Search this file," and click on "Search."
- Enter the person's last name, first name, year of birth, or other information in the boxes under "Enter Values." Then click on "Search."
- If a record is found for a search under that name, click on "View Record" to determine if it is the right person.
- You can sort the search results by "last permanent address" by clicking on the arrow just below the column name. You can also sort by "individual number." The individual number groups family members together. (For more information, see the FAQs .)
- You can search the 1930 Census if you know the name of a family member who was born before 1930. Once you find that person in the 1930 Census, it may lead you to the head of household who accompanied the person to the WRA camp.
Search Results
Positive search result (you find an entry in the aad for the person.).
If you find your person, write down the following information as it appears in the AAD entry:
- Name of the internee (include all names used while in a WRA camp)
- Year of birth
- Name of the WRA camp (also known as a center or project)
Then proceed to Accessing WRA Case Files for information about requesting a case file.
You may also want to check the Department of Justice (DOJ) Internee Cards and Case Files to see if the person had an Alien Enemy hearing.
Negative Search Result (You do not find an entry in the AAD for the person.)
If you do not find your person, proceed to search the Department of Justice (DOJ) Internee Cards and Case Files to see if the person had an Alien Enemy hearing.
To illustrate the above, we will search for two individuals in the AAD database who we believe were incarcerated in a WRA camp.
Example 1: Positive Search Result
First we look for Eitaro Baba.
- Proceed to Accessing WRA Case Files .
Example 2: Negative Search Result
Next we look for Choichi Ito.
- Proceed to look for Chiochi Ito in the Department of Justice (DOJ) Internee Cards and Case Files .
Are you moving? What to know to protect your belongings and have a smooth experience

After 25 years in their Long Island, New York, house, Michael and Deirdre Kupka decided to move to Charleston, South Carolina, to be closer to their youngest grandchildren.
The lifelong New York residents thought they did everything right when shopping for a mover for their life’s belongings, including a large number of family antiques.
But instead of a smooth moving experience out of their four-bedroom house, the Kupkas’ move is a cautionary tale for others to protect themselves. Many pieces of their antique furniture were cracked or severely damaged and the couple had to pay nearly $5,000 above their original agreement when the moving company refused to deliver their furniture, instead drastically changing the price from their original “flat-rate booking" fee.
Since the couple refused to sign a document presented by the moving company after they saw all the damage to their furniture, the movers are now saying they have no claim to insurance to cover what the Kupkas estimate would take thousands of dollars to fix and refurbish.
Though USA TODAY made multiple attempts to reach the Kupkas' moving company, and it said via email that it would respond, USA TODAY never received a comment.
How to find a good mover
May is not only National Moving Month, it’s also the start of the busy summer moving season, said Ryan Bowley, the American Trucking Associations’ moving and storage executive director.
Most moving companies book 70% of their business between May and September, said Bowley. The trucking association is the largest national trade association for the trucking industry with more than 34,000 trucking and moving company members.
While a majority of those moves go smoothly and most professional moving companies are reputable, consumers do run into problems, he said,
More than 6,200 complaints were filed with the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration’s National Consumer Complaint Database in 2023. It is important to properly research a moving company, make sure you have a contract and understand your rights, said Bowley. The complaint database also has educational information on its website, www.protectyourmove.gov
There are unscrupulous companies who bait and switch consumers with low-ball estimates, then raise the prices, holding furniture until consumers pay, in what the industry calls a "hostage shipment." he said. Some scammers never deliver the goods and instead auction them off, he added.
There are also fraudulent companies that put up fancy websites or use a name that is similar to a long-standing, reputable company, posting what looks like legitimate reviews and endorsements, Bowley said.
But “if you look a little bit closer ... it doesn’t quite look right,” he said. Photos of trucks may be photoshopped or the promises by the company don’t line up with standard practices of reputable businesses, Bowley said.
Any company that moves goods over state lines must have a registration number with the Department of Transportation. That can be found on the www.protectyourmove.gov site, said Bowley.
Bowley said it did not appear that the Kupka’s moving company, Call My Mover, was registered with the DOT.
What happened to the Kupkas?
The Kupkas had a short window of time to coordinate the closing dates of their New York house and one being built in South Carolina. They were looking for a company that could store their furniture on the truck and not mingle their goods with those of another family.
They called four moving companies. Michael Kupka also received a cold call from a local moving company, Call My Mover.
Michael said he assumed the company got his contact information from listings of recent home sales.
The moving estimates from the other companies were about $13,500 while Call My Mover came in with a “flat booking price” of $8,603.75 after a salesperson came out to the house to see their belongings.
While price played a role in choosing the company, Deirdre said, it wasn’t the only reason.
The other movers said the couple would have to pay for storage while Call My Mover said it would be free and they did not need an exact closing date. The movers also said they would wrap all of the couple’s fragile mirrors and pictures.
“It sort of all fell into place with this wonderful salesman that we had with Call My Mover,” Deirdre Kupka said. “Everything I asked him, he said yes, and I believed him.”
The Kupkas now say they should have done some internet research on the company. They would have seen negative customer reviews and an F rating with the local Better Business Bureau for Call My Mover in Plainview, New York, which also does business as Tri-State Relocation Inc.
“That would be the first thing I would tell everybody,” Michael Kupka said. “These people prey mainly on older people that don’t have the knowledge of going on the internet and investigating these people.”
He also went to the office of the local mover twice to pick up boxes and sat down with the owner, who said “don’t worry about anything." That in-person connection helped him feel better about the upcoming move.
The couple agreed to use Call My Mover. They now know they didn’t sign a contract, but rather a spreadsheet of their home's contents that the salesperson put together.
What happened on moving day
When the foreman arrived on moving day, he said in 22 years, he’d never once had the quoted price be what the customer would ultimately pay. Usually, it was more, he said.
That was not what the Kupkas expected.
One of the movers also had Deirdre Kupka sign her name on a phone, saying it was to confirm the insurance plan she chose and that there were movers on site to complete the move. There was nothing for her to review, but with the stress of moving day, she signed.
By the end of the day, there would be two truckloads and a van that came for excess items though their original verbal agreement was that all of their belongings would be on one truck and not transferred,
“That’s when they started shoving things into the truck, which is when I’m sure half of it broke,” Deirdre Kupka said.
The foreman then showed her husband five written pages listing furniture not on the original spreadsheet. He signed but said there was no indication that there would be extra charges. The moving truck left.
A few days later as the truck was in transit, the Kupkas were told the new total was $13,763.59 – over $5,000 more than what the couple originally agreed to pay. They were also told the payment must be by certified check, not a credit card like the original $100 deposit the couple put down.
Michael Kupka argued with the company, saying he wanted to see a detailed report. He then received what he said were several threatening phone calls from the company saying the truck would not arrive unless the full amount was paid and that the truck’s driver would be told to return to New York with the Kupkas financially responsible for the fuel and additional storage.
The Kupkas finally gave the company a certified check for $885.85 as "a good faith gesture.” The company wasn't satisfied.
That evening, Michael Kupka said he got a phone call from a woman at the company using “language that a truck driver couldn’t even imagine.” She was upset that the full amount had not been paid. When he hung up, he was unsure if the truck would arrive the next morning.
It did, but the driver said he could not unload until the remaining $4,273.99 was paid.
The Kupkas were shown a contract with Deirdre’s signature on it, though she said the couple had never seen a copy of it. It also had a signature certifying “no damage had been done to any of the furniture.”
After more verbal threats during a phone call with the moving company, the couple felt they had no choice but to pay the money.
“They were holding our furniture hostage,” Deirdre Kupka said.
The furniture finally began to be unloaded, after about a 2 ½ hour delay. That's when she noticed that many of her family’s antique heirlooms were damaged.
“I’m crying because my antique furniture has got dents that it’s never had,” she said. Some furniture was more than 150 years old.
The damage included a China cabinet with the legs broken off and her dining room chairs, one of which was completely destroyed. A couch Deirdre's mother bought her at an antique store has broken legs and arms.
“You can’t sit on the couch on either end without it falling,” she said.
“Every single piece of furniture they packaged up had something wrong with it,” including screws loose, scratches, or broken," added Michael.
The driver wanted the Kupkas to sign a document after the truck was emptied, but they refused. They complained about the damaged items and the driver took pictures before leaving.
“There was too much emotion at that point to argue with him or do anything more,” Michael Kupka said.
An hour later, the Kupkas received an email saying since they refused to sign the document, they had no claim to the insurance they'd originally agreed to – $250,000.
Adult daughter tries to help resolve issues
The Kupkas' daughter, Rebecca Overton, tried to communicate with the company on behalf of her parents after she found out what happened.
The family has sent a letter from an attorney demanding the $5,159.84 they say they were forced to overpay and full reimbursement for their repairs or they will seek relief from the courts. The family has received no return communication.
How to make a safe move: Don't want to lug that couch down the stairs yourself? Here's how to find safe movers
Call My Mover did not respond with comment to three requests by USA TODAY. A phone message was left with an employee who answered the phone on a Tuesday and an email was sent. USA TODAY received a reply saying the company would respond by the end of the day Wednesday, but the company sent no follow-up to that email or another sent the following Monday.
The Kupkas don’t know how much the final cost to repair the damaged antiques will be, though they estimate it to be thousands of dollars. Deirdre Kupka said she has glued together as many of the cracked pieces as she can.
“A lot of this stuff is irreplaceable,” her husband said.
Housing report: Want to live near your state's top schools? Prepare to pay $300,000 more for your house.
Do your research before moving, couple advises
The Kupkas are the victims, said BBB spokeswoman Melanie McGovern.
“It sounds like they asked all of the questions they needed to ask, but they (the company) knew how to answer them” telling the Kupkas what they wanted to hear McGovern said.
“A lot of people would have been in the same situation," McGovern said.
Neither Bowley nor McGovern had ever heard of a moving company cold-calling a new home seller. Both said that concerned them and they would be alerting their organizations about the potential new tactic.
The cold-calling itself isn’t troublesome, they said, unless the company is then not following up with good customer service. They worry that the practice could become like “storm chasers” who go door-to-door in neighborhoods after storms offering new roofs or “extra asphalt” and other materials and not providing consumers with quality workmanship.
It’s difficult once a move is happening to do much to resolve issues if things go south, said Bowley. Consumers who call the local police will probably be told it’s a contract dispute and something the police can’t intercede in, he said. Consumers would then need to go to the state attorney general or the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration.
So do your research and follow these tips before you make a deal, Bowley said.
Betty Lin-Fisher is a consumer reporter for USA TODAY. Reach her at [email protected] or follow her on X, Facebook, or Instagram @blinfisher . Sign up for our free The Daily Money newsletter, which will include consumer news on Fridays, here.
Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge

You are exiting the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service website
You are being directed to
We do not guarantee that the websites we link to comply with Section 508 (Accessibility Requirements) of the Rehabilitation Act. Links also do not constitute endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
- Skip to content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Lifeway Research
Enlightening today’s church with relevant research and insights
Practical Help for Building a Thriving Ministry to Women in Your Church
Insights | Church Life & Ministry | May 29, 2024

Whether your church is launching a women’s ministry or has a rich history of ministry to women, you can cultivate a thriving ministry.
By Marissa Postell Sullivan
According to the State of Ministry to Women report from Lifeway Research, having an organized ministry to women benefits not only the women in the church but also the church as a whole. But for churches that don’t already have a women’s ministry, knowing how to get started can be challenging. And many with an organized ministry to women can take steps to better equip their women’s ministry leaders and support ministry to women in and through the church.
In her book A Short Guide to Women’s Ministry , long-time director of women’s ministry, Nora Allison, helps pastors and women’s ministry leaders navigate ministry to women—whether in a church launching a women’s ministry for the first time or a church with a rich history of ministry to women. Allison calls leaders to develop relationships that help women build community and grow in their walk with God. Here’s a look at a recent conversation with Allison on how pastors can champion ministry to women in their congregations.
Why is it good for the church if women are part of an organized ministry to women?
Nora Allison: I think it’s vital because women make up at least half the church . And as image bearers, they need to be discipled; they need to be trained. They’re going to give advice and input to lots of other people in the church. And it will either be theologically-sound, good, God-honoring advice and input or not. So, it’s important they are trained in theology, in knowing how to study their Bibles, and in knowing how to glean the truth from their Bibles about who God is and who He made them to be. It’s a disservice to the whole church if we’re not making sure all its members are built up and encouraged.
In your book, you say there are two starting places for building a ministry to women: where you are and where you want to go. Why do these starting places that may sound conflicting go hand-in-hand?
We have to know what the purpose is of women’s ministry, of discipling people—where we want to take them. We need to know what God’s goal is for all of us—that we would know Him well, that we would become like Him, that we would be good ambassadors for Him, that we would spread His fame. And we need to make sure everybody knows that’s what we’re aiming for.
But if we don’t realize where our starting point is, we can falsely adopt all sorts of programs and classes. And sometimes that’s not where God wants us to start, because that’s not the people He has at our church. The programs that worked somewhere else might not be the particular needs of your church, or it might not be the gifting He has in your church that He wants to use to build the ministry. We need to know where we need to go. But we also need to know where we’re starting—what our resources are, who we’re dealing with, and the particular needs of that church.
What advice would you give a pastor looking for someone to lead an organized ministry to women in the church?
God always looks at character. You have to find a woman who’s walking with the Lord in a way that’s a model for the other women in the church. They can look up to her and see not that she’s perfect and certainly not that she’s sinless but that she goes to the Lord. She’s dependent on Him for all her needs. She goes to Him and readily confesses and realizes when she falls short.

Then, it comes down to gifting and calling. And it’s a matter of the pastor’s discernment in speaking to women and trying to see if God might be calling them to take a leadership role. Pray and take some time to get to know some of the women. See who other women in the church are responding to, who they look up to. Then approach that woman and see if she would be interested in taking on that role. Sometimes, especially if it’s new, it’s good to see if there’s a woman or two who might want to work together. But ultimately, you need someone who’s in charge.
What other practical tips do you have for pastors looking to start a ministry to women in their churches?
It’s important he sees the ministry as a vital ministry to the church—that it’s not sidelined. The pastor should work with the women’s ministry leader to bring that ministry under the umbrella of the church. So, he would constantly communicate what the vision is for the church and how this ministry fits into that vision. Too often, there will be some passion on the part of women but not buy-in from the pastors or elders. So, it’s like a two-ring circus going on.
Since some of women’s needs and where they’re going is a little different, it’s important to have a women’s ministry. But it needs to be incorporated into the big picture of the church. Schedule meetings and reports with the women’s ministry leader to see how things are progressing and how the church’s leadership can serve the women’s ministry as well. A women’s ministry director should be at the staff meetings if at all possible. She should be invited and welcome. I invited myself when I was volunteering. I was going to be a part to know where we’re going, to be a part of the vision, and to be able to represent women.
What ideas do you have for collaborating with a women’s ministry director who can’t attend regular staff meetings?
If she can’t go to the scheduled staff meeting, she should meet with a staff member. She should have someone she reports to. It should be clear to her who she’s responsible to, and she should meet regularly with that person. This allows them to talk about where they’re going, what struggles she might be having, and what upcoming things are happening. This way, if she’s not in the staff meeting, she can at least be represented by someone else.
And if possible, if there are announcements during the service, she should be the one to give them for the women’s events or courses, because she can best communicate her heart for women’s ministry and what the event or course would be about.
How can churches provide training for those leading women’s ministry?
There are a lot of things women can do to be trained online. Online training resources should be made available and encouraged for the women’s director and any other women interested. Wherever there are gaps in her training, it’s the role of the pastor and the elders to help fill that. We want to build people up to be more and more like Christ. That entails helping them know how to study the Bible and pray, helping them know theology and doctrine and how to communicate that, and helping them counsel people better.
There are so many conferences, books, schools, and online classes. I don’t think we have an excuse for not being able to provide that sort of thing for women. If we have any kind of discipleship training for men, we should also have it for women.
What do you wish more pastors understood about ministry to women?
As image bearers and co-laborers, we need to recognize that women are an essential part of the church. And as such, their shoulders need to be tapped to use their gifts, abilities, and influence in the church.
They need to realize all kinds of training—and especially theological training—is a necessity for women, not just men. It can’t be an afterthought. Pastors need to do all they can to make sure women are built up to feel comfortable in leadership roles and are challenged to grow into greater responsibility in their churches.
Too often, we have thought of women’s ministry as programs or social events to get the women together, and that’s not what women’s ministry’s about at all. It’s about helping people see where God wants them to be and get there. It’s about discipleship of our women. We’re not trying to build strong ministry programs for women. We’re trying to build strong women who can minister to other women. Programs can be useful, but they’re only a means. The key is focusing on the women and then using various means to disciple them and build them up.
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
For permission to republish this article, contact Marissa Postell Sullivan .

Marissa Postell Sullivan
@marissapostell
Marissa is the managing editor for LifewayResearch.com.

A Short Guide to Women’s Ministry
Related posts:.

Looking for valuable insights for your church?
Get practical insights and the latest data relevant to your church delivered to your inbox:
- Select Frequency Daily Insights (Every Weekday) Weekly Update (Every Friday) Daily Insights and Weekly Update
- Hidden postKey
- Hidden subscription
- Hidden formName
- Hidden formBrand
- Hidden formPage
- Hidden postKey_insights
- Hidden subscription_insights
- Hidden formName_insights
- Hidden formBrand_insights
- Hidden formPage_insights
- Hidden postKey_dual
- Hidden subscription_dual
- Hidden formName_dual
- Hidden formBrand_dual
- Hidden formPage_dual
Leader Resources


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
How to Research: 5 Steps in the Research Process. Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Mar 18, 2022 • 3 min read. Research is an essential process to keep yourself informed on any topic with reliable sources of information. Research is an essential process to keep yourself informed on any topic with reliable sources of information.
Research: Where to Begin. Research isn't something that only scientists and professors do. Any time you use sources to investigate claims or reach new conclusions, you are performing research. Research happens in virtually all fields, so it's vitally important to know how to conduct research and navigate through source material regardless of ...
For research help, use one of the following options: Ask the GTL General Information & Research Help Phone: (607) 735-1862 Research Help Email: [email protected] For help registering a device, password reset and more: EC IT Resources and Services
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
Placing research in the bigger context of its field and where it fits into the scientific process can help people better understand and interpret new findings as they emerge. A single study usually uncovers only a piece of a larger puzzle. Questions about how the world works are often investigated on many different levels.
Research is the deliberate, purposeful, and systematic gathering of data, information, facts, and/or opinions for the advancement of personal, societal, or overall human knowledge. Based on this definition, we all do research all the time. Most of this research is casual research. Asking friends what they think of different restaurants, looking ...
Start writing the middle, or body, of your paper. Get your ideas down, then see if you need to do any research. Since your introduction and conclusion summarize your paper, it's best to write those last. [8] Include an in-text citation for everything that needs one, even in your initial rough draft.
Research is defined as a meticulous and systematic inquiry process designed to explore and unravel specific subjects or issues with precision. This methodical approach encompasses the thorough collection, rigorous analysis, and insightful interpretation of information, aiming to delve deep into the nuances of a chosen field of study.
Do additional research as necessary. Cite your sources. Let's look at each of these steps in more detail. 1. Find a Topic. If you don't have a topic, your research will be undirected and inefficient. You'll spend hours reading dozens of sources, all because you didn't take a few minutes to develop a topic.
Qualitative Research Methodology. This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Judge the scope of the project. Reevaluate the research question based on the nature and extent of information available and the parameters of the research project. Select the most appropriate investigative methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) and research tools (periodical indexes, databases, websites). Plan the research project.
Abstractspiepr Abs1. Every day people do research as they gather information to learn about something of interest. In the scientific world, however, research means something different than simply gathering information. Scientific research is characterized by its careful planning and observing, by its relentless efforts to understand and explain ...
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
Twenty years is a long time, and during that time, a lot of research has been conducted. It seemed like a good time to ask the question: What did happen as a consequence of legalizing marriage for ...
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
A Swedish study has found a potential link between tattoos and a type of cancer called malignant lymphoma, but it ultimately calls for more research on the topic, and cancer experts say the ...
Research on adult sexual offenders found the greatest deterrence to completing the act was a vocal child - one who expressed their desire to stop, or said they would tell others.
There are several troubleshooting steps if your vehicle allows a wireless phone connection. First, turn your phone's Bluetooth off then on, and reconnect to Uconnect. If that doesn't help, you can restart the car (including opening and closing the vehicle's door). Finally, reboot your phone before attempting to connect again.
Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article. You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation.
Sullivan hopes that research into extraterrestrial visitations to the Earth can be shifted away from Japan's military, which has traditionally overseen the issue, and be centred on scientists ...
Basic Search Steps. Navigate to Records About Japanese Americans Removed During World War II. Search for the individual you are looking for. There are two options for a search: Enter the name of the person you are looking for in the box under "Search this file," and click on "Search." Enter the person's last name, first name, year of birth, or ...
It is important to properly research a moving company, make sure you have a contract and understand your rights, said Bowley. The FMCSA also has educational information on its website, www ...
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions. The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions. 2.
Welcome to Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge! Part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument, Johnston Atoll is home to a variety of wildlife, which includes one of the largest known nesting populations of red-tailed tropicbirds, more than 300 species of fish, and a shallow coral reef that encompasses approximately 32,000 acres. The Monument boundary is a complete 200 mile ...
According to the State of Ministry to Women report from Lifeway Research, having an organized ministry to women benefits not only the women in the church but also the church as a whole. But for churches that don't already have a women's ministry, knowing how to get started can be challenging. And many with an organized ministry to women can ...
For artists, writers, gamemasters, musicians, programmers, philosophers and scientists alike! The creation of new worlds and new universes has long been a key element of speculative fiction, from the fantasy works of Tolkien and Le Guin, to the science-fiction universes of Delany and Asimov, to the tabletop realm of Gygax and Barker, and beyond.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.