👀 Turn any prompt into captivating visuals in seconds with our AI-powered design generator ✨ Try Piktochart AI!

How to Write a Case Study

You’re not the first person to feel like you’re drowning in data and information while planning for a case study. The good news is that it’s not as complex as you think.
This guide on how to write a case study breaks down the process into easy-to-follow steps — from information-gathering to writing to design. Pro tip : Get your free Piktochart account before you scroll down. This way, you can immediately put our tips to practice as you read along. Alternatively, you can hop over to our AI case study generator and find more examples of professional case study templates.
Why case studies matter across industries
A case study is not just a school assignment or an item on your marketing checklist. They are persuasive stories that demonstrate your expertise and build credibility. A well-crafted business case study can sway potential clients, as demonstrated by HubSpot’s study on the Lean Discovery Group , which helped increase deal value fivefold. Even in the social sciences, case studies like the “ Bobo doll experiment ” yield powerful insights, such as revealing the impact of media violence on children. It’s clear that case studies remain highly effective. Content Marketing Institute’s 2025 outlook even ranks them second only to video in terms of content effectiveness.
For these reasons, investing time and resources in crafting a unique and insightful case study that resonates with your target readers makes sense. This brings us to the next section!
Preparing your case study
Before you start writing your first case study, remember that a compelling case study requires careful preparation and research as your foundation for success..
1. Choose the right subject
Pick a case study subject that resonates with your target audience. A SaaS company aiming for enterprise clients, for example, might showcase a large corporation that saw major efficiency gains after using their software. Don’t forget to get consent before featuring any story.
2. Define your case study’s purpose
Purpose matters too. Joanna Knight, founding director at merl and developer of impact case studies for the Humanitarian Innovation Fund (HIF), explains , “Although many case studies have more than one purpose (e.g. for learning and communication), to maximize their effectiveness it is important to be clear about what we want to achieve with the case study.”
3. Gather information
Gathering relevant information might involve interviews, data analysis, and understanding the “why” behind the numbers.
A business case study might examine business proposals , financial reports, customer interviews, and marketing materials. On the other hand, academic case studies may pore over archival records, interviews, written observations, and artifacts. Recommended resource : How to Transcribe an Interview Quickly with Tips and Tool Hacks
4. Decide on the format
While the traditional lengthy case study can be effective, don’t be afraid to think outside the box. Consider your goals and audience – how can you best capture their attention and deliver your message?
Here are case study format alternatives you can try aside from the overly long ones:
- Interactive web pages
- Infographics
- Podcast episode
- Short blog post
Outside of a long-form text-based written case study, you can repurpose the content in several formats to share across your business’s distribution channels. You can combine visuals, interviews, and various elements for high-impact content.
You’ll find examples of these case study formats as you scroll down below.
5. Create an outline and structure
A clear structure ensures your case study narrative flows logically and effectively communicates your key message. The following frameworks are good starting points when planning for your case study’s structure:
The Problem-Hypothesis-Solution-Impact framework
The Problem-Hypothesis-Solution-Impact framework guides case studies with a clear narrative flow: define the problem, propose a hypothesis, outline the solution, and analyze the impact. For example, Jon Knuston, Head of Core IT Services at Rockwell Automation, used Gartner’s insights to accelerate digital transformation and achieved results within 90 days of starting his role (as detailed in this Gartner case study ). This structure is adaptable to your needs. Feel free to:
- Expand where needed: If your solution involves a complex process, dedicate more space to explaining each step.
- Highlight unique elements: Showcase unexpected innovations or surprising outcomes.
The MEAL framework
Incorporating frameworks relevant to your industry adds depth and credibility to your case study. The MEAL (Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning) framework is a good example.
This framework is commonly used by NGOs (non-government organizations) to assess the effectiveness of their projects. It provides a structured approach to:
- Monitoring: Tracking progress towards project goals.
- Evaluation: Assessing the impact and effectiveness of interventions.
- Accountability: Ensuring transparency and responsibility in project implementation.
- Learning: Using data and insights to improve future projects and strategies.
Read about the MEAL framework’s role in writing effective case studies .
Other case study frameworks worth exploring are:
- SWOT analysis : This model examines strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the case study subject.
- Porter’s Five Forces analysis : This framework helps analyze competition in a case study. It looks at rivalry, new competitors, supplier and buyer power, and substitutes to understand how profitable an industry is.
- Customer journey map : For this framework, you’ll illustrate the customer’s experience with the product or service.
With your groundwork laid, it’s time to bring your case study to life and start writing!
Writing your case study
You’re halfway done! Keep these best practices in mind when writing your case study:
1. Use your chosen framework as a guide when writing
The framework you’ve picked during the preparation phase creates a logical flow. Make sure each section builds the story and supports your main point.
2. Be mindful of your headlines
Use clear, concise headlines that allow readers to skim and easily find the information they need. Intriguing headlines can also pique their curiosity and encourage them to read further.
Instead of a bland headline like “Project Overview,” try something more specific and engaging like “How We Increased Website Traffic by 40% in 3 Months.” This immediately tells the reader about the case study and highlights a key achievement.
3. Have a consistent narrative
Maintain a consistent tone and style throughout your case study. Whether you choose a formal or informal approach, make sure it aligns with your brand guidelines.
A brand style guide can be incredibly helpful for this. It provides clear guidelines for voice, tone, and visual elements to ensure every part of your case study feels cohesive. This consistency reinforces your brand identity and makes the information easier to digest. Need help with your brand style guide? We’ve got 11 amazing brand style guideline examples and ideas you can copy .
4. Include data to support claims
Back up your claims with real results, including both quantitative data and customer quotes.
For instance, don’t just write that your new marketing campaign was successful. Instead, include specific numbers like “The campaign generated a 15% increase in leads, a 10% rise in website traffic, and a 5% boost in sales.” Follow this up with a quote from a satisfied customer praising the campaign’s creativity and effectiveness. This combination of data and customer feedback paints a convincing picture of your success.
5. Show, don’t tell with visuals
Incorporate infographics, charts, and other visuals to make your case study more engaging, memorable, and persuasive.
Let’s say you’re writing a case study about a website redesign. Instead of just describing the changes, include:
- Before and after screenshots to visually demonstrate the improved user interface and design elements.
- Charts or graphs to show how the bounce rate decreased and conversion rates increased after the redesign.
- An infographic to summarize key results, such as improved page load speed and mobile responsiveness.
6. Focus on value, not on sales
While the ultimate goal might be to promote your product or service, avoid overt selling. Instead, focus on demonstrating your value by showcasing the customer’s success story.
7. Wrap it up with a memorable conclusion
A memorable conclusion is just as important as a strong introduction. It’s your last chance to leave a lasting impression on the reader and reinforce the key takeaways of your case study.
Here’s how to make it count:
- Summarize the key takeaways of your case study.
- Use a powerful quote or anecdote highlighting your solution’s positive impact.
- End with a call to action . Encourage readers to learn more about your company or product, download a resource, or contact you for a consultation.
Want to see these case study writing best practices come to life? Check out the case study examples below. In the next section, let’s explore how thoughtful design can transform your content into a visually compelling and persuasive experience.
Designing your case study
A well-designed case study is more than just words on a page. You can also use visuals to get attention in seconds and communicate your information quickly.
The good news is you don’t have to design your case studies from scratch if you use Piktochart templates . These professionally-designed templates provide a solid framework you can use for visually engaging content.
Here’s how to use Piktochart for case studies in 3 easy steps:
Step 1: Start with a template
Pick a template that aligns with your industry, brand, and the overall tone of your case study.
Step 2: Customize your design
Adapt the template to fit your specific content and style. Change the colors, fonts, and layout to match your brand identity.

Step 3: Add the final touches
Whether you use a template or start from scratch, these best practices will help you create a case study that looks as good as it reads:
High-quality visuals
Incorporate images, icons, and illustrations to break up the text and enhance your case study’s visual appeal. Use high-quality images that are relevant to your content and visually appealing.

Data visualization
Use data visualization to highlight key findings and trends in your case study. Piktochart offers a range of charts and graphs to present data in a clear and compelling way.
Visual hierarchy
Use headings, subheadings, and visual cues to guide the reader’s eye and emphasize key information. This creates a clear and consistent visual hierarchy to make your case study easy to read and understand.

Color palette
Pick a color palette that reflects your brand and complements the overall design of your case study. Use color consistently throughout your case study to create a cohesive look and feel.

White space
Don’t overcrowd the page. Use white space effectively to improve readability and create a more modern look.

Opt for fonts that are easy to read and visually appealing. Stick to two or three fonts to avoid visual clutter.

Proofreading
Typos and grammatical errors can undermine your case study’s credibility. Proofread your case study carefully before publishing it.
Recommended resources when designing your case study:
- Fonts and Colors for the Retail, Healthcare, and Financial Industries
- 4 Things You Need to Know to Pair Fonts Well
Get your free Piktochart account and start designing your case study. Now that you’ve got the case study design basics down, let’s see these principles in action with some inspiring case study examples below.
Real-word case study examples to learn from
Need inspiration for your next case study? Here’s how others are doing (and nailing!) it!
1. How to reduce your SLA by 99.9% (Breadcrumbs)
Breadcrumbs, an AI-powered lead scoring platform, excels at demonstrating the value of its product in this case study for Thinkific. Here’s why it works:
- Impactful storytelling: The case study uses a clear problem-solution-impact format and backs it up with compelling data (like a 99% SLA reduction) to show the power of lead scoring.
- Credibility and clarity: A direct quote from Thinkific’s CMO adds credibility, while concise explanations make the information accessible to any reader. Plus, they offer a convenient downloadable version.
2. How SupportLogic AI-proofed and 5x its organic traffic in 12 Months (Animalz)
This Animalz case study tells a clear and compelling story about how SupportLogic overcame the challenge of AI-generated search results through content diversification. Here’s what makes it stand out:
- The case study uses visuals , including screenshots and charts to break up the text and make it more engaging.
- Detailed explanations of the different types of solutions that Animalz created for SupportLogic such as 101, 201, and 301 content.
3. Helping Calm make work a better place to be with a new positioning and optimized content (Velocity Partners)

Calm partnered with Velocity Partners to solidify its position as the leader in B2B wellness solutions. This case study stands out because:
- Crystal-clear purpose: In just two sentences, it establishes the challenge, the players, and the goal.
- Simple, direct language: It reads like a story as it avoids jargon and gets straight to the point.
- Focus on “how” and “why”: It effectively explains both the content deliverables and how they connect to Calm’s larger business goals.
4. How Portland Medical Center is saving GP time despite increased demand (Klinik Healthcare Solutions)
Klinik Healthcare Solutions, a provider of intelligent healthcare software, created a visually engaging case study that’s as easy to digest as an infographic. Here’s what makes it stand out :

- Infographic-style summary: The last page uses visuals and minimal text to highlight key achievements, making it easy to grasp the impact at a glance.
- Visual cues: Icons and color-coded sections guide the reader’s eye to important information.
- Prominent call to action: A dedicated CTA section with photos and contact details encourages engagement.
5. The Wall brings design at the Hyundai America Technical Center to life (Samsung)
This video case study effectively showcases how Samsung’s The Wall display transforms Hyundai’s design process. It captures your attention because of:
- Visual storytelling: The video format brings The Wall’s impact to life, showcasing the immersive design environment and designers at work.
- Designer testimonials: Firsthand accounts from Hyundai designers add credibility and demonstrate the improved workflow.
6. A new day for the night shift (Deloitte)

This Deloitte case tells the story of how they helped Kroger improve the employee experience for night shift workers. Here’s why it works:
- Relatable challenge: It starts by highlighting the complexities of overnight stocking, a challenge that many retailers face.
- Humanizing the team: Instead of just names and titles, they feature photos and quotes from individual team members which makes them relatable and approachable.
7. Speed is nothing without reliability (Verizon)
This Verizon case study featuring a major US bank proves that sometimes less is more. Here’s a breakdown of its key strengths:

- The entire case study is condensed to a single page which makes it incredibly digestible for busy readers. It delivers key information without overwhelming the audience.
- Attention-grabbing headline . “Speed Is Nothing Without Reliability” immediately grabs attention.
- The copy uses clear. vivid language to paint a picture of the challenges and solutions. It avoids jargon and focuses on the impact.
Want to see more examples of case studies? Head on over to 8 Amazing Case Study Examples & Ideas to Copy
Use Piktochart to create case studies that leave a lasting impression
Whether you’re a student, marketer, or researcher, keep in mind that a truly compelling case study isn’t just about the data – it’s about weaving a narrative that informs and resonates with your readers.
Piktochart has everything you need to bring your case studies to life visually. From customizable templates to our AI case study generator , you can bring your case studies to life and make your research findings stand out.
Get your Piktochart free plan if you haven’t yet!

Other Posts
Mastering the Craft: Presentation Design Strategies From a Pro

How to Make a Presentation (Guide With Tips & Templates)
Presentation Design: A Step-by-Step Guide
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics


How to Write a Case Study: A Complete Guide with Templates

Writing compelling and insightful case studies is a marketer’s biggest job, yet most get frustrated with this content. The challenge? Figuring out how to write a case study that not only highlights the company’s strongest suit but engages new clients with strategic information. If you often struggle with making case studies as more than just dry facts and figures, you’re leading your efforts to missed opportunities.
How to Write a Case Study Step-by-Step
- Craft a Compelling Headline: Highlight the main success with a clear, direct title.
- Start with a Strong Introduction: Provide a broad overview and hook the reader.
- Discuss Unique Client Challenges: Highlight specific industry-related challenges.
- Highlight the Solution: Showcase your strategies and key results.
- Present Quantifiable Results: Use data and visuals to demonstrate impact.
- Be Clear and Concise: Stick to the point and support claims with data.
- Treat Your Case Study Like a Story: Focus on the customer’s journey and success.
- Use Direct Quotes from the Client: Add authenticity with client testimonials.
- Make the Key Takeaway Clear: Reinforce your expertise and the solution’s value.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): Guide the reader on what to do next.
- Make It Readable: Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points.
- Finalize and Proofread: Review for errors and ensure a smooth flow.
In this blog, you’ll discover a step-by-step guide that simplifies the process, making it easier to create interesting case studies. From planning to writing, I’ve got you covered. So, let’s start with some basics.
Table of Contents
What is the format of a case study.
- How to Plan a Case Study
How to Write a Case Study
How to summarize a case study, how to cite a case study.
A well-structured case study isn’t just a collection of facts—it’s a powerful marketing tool that tells a compelling story. Using the right format for a case study ensures that your message is clear, engaging, and impactful.
The proper format guides readers through the narrative with hierarchy and scannability, helping them connect with your brand on a deeper level. Most importantly, it empowers you as a marketer to set clear goals for presenting your case studies and ensures you deliver the correct information effectively!

Case studies format helps you to plan and write the case study for your clients. With this outline in mind, you can create steps to complete the process of writing and publishing your case study research. There are eight components of a case study that are essential for building a layout of information in the correct order that makes sense to the viewers.
Start with a catchy “Title” that grabs attention and an “Overview” that sets the stage. Clearly define the “Problem” your client faced, and then showcase your “Solution” in detail. Highlight the success with “Results” that are measurable and impactful. Add authenticity with “Testimonials and Quotes” from satisfied clients. Wrap it up with a firm “Conclusion” and a compelling “Call to Action” in the “About Us” section that guides the reader on what to do next.
By following this format, you create a case study design that resonates with your audience and effectively showcases your brand’s value.
Check out the marketing case study template I’ve included below—it has a clear outline that makes it easy to see how sticking to a format can help you plan and write the entire thing.

How to Plan a Case Study
Now comes the big part! Understanding what to include in a case study outline is just the starting point for beginners. The real challenge lies in creating a step-by-step plan to craft that outline and filling it in with the right information!

1. Set Clear Goals for Your Case Study
Before diving into how to write a case study, defining your ultimate objective is essential. Think about it—what do you want your audience to take away from this case study? For example, your goal is to showcase how your SEO strategies boosted a client’s organic traffic by 150% in just six months. This clear goal will shape your entire narrative and ensure that your case study is laser-focused on demonstrating your expertise and the value you bring.
2. Select a Client that Highlights Your Strongest Suit
Choosing the right client or subject is vital while creating case studies. Imagine you’ve worked with a small e-commerce brand struggling to rank for competitive keywords. Your strategies helped them rank on the first page and increase conversions. This is the perfect client for your case study because their success story directly showcases your SEO prowess.
By picking a client whose experience aligns with your goals, you’ll create a case study that resonates with your target audience.
3. Reach Out to Your Client for Collaboration
Now that you’ve identified the ideal client, it’s time to reach out. Let’s say you contact your client and explain how a case study can highlight their remarkable success story. It’s a great way to spotlight a mutual collaboration based on credibility. Their buy-in is crucial; their insights and data will authenticate your case study.
4. Gather Comprehensive Data and Insights
Data is the lifeblood of any compelling case study. For instance, in your SEO case study, you’ll need to gather data on key metrics like keyword rankings, organic traffic, and conversion rates before and after implementing your strategies. Let’s say your client saw a 50% increase in organic traffic within three months of optimizing their website. Collecting this data will help you build a robust, evidence-based narrative highlighting your impact.
It’s essential to monitor the before-and-after data to track the effectiveness of implementing your strategies.
5. Prepare Insightful Questions and Conduct Interviews
It would be best to ask the right questions to get the most out of your client interviews. Imagine asking your client, “What specific challenges were you facing with your organic search rankings before we started working together?” or “How did our SEO strategies help you achieve your business goals?” These questions will lead to detailed responses that add depth to your case study, making it more than just numbers on a page.
Always ask questions that uncover the key challenges your clients face. This way, your prospects will know when to turn to you to navigate or overcome similar obstacles in their business.
Since I’m giving an example of an SEO case study in marketing, you can try these questions to interview your existing client. Obviously, you can modify the sentences according to your industry basics, but these types of questions are fundamental for collecting structured data from your clients.
- What were your business’s main SEO challenges before we started working together?
- Can you describe your initial expectations for implementing our SEO strategies?
- What specific SEO tactics did we implement that you found most effective?
- How did you monitor and measure the impact of these strategies on your organic traffic?
- What were the key metrics or results that stood out to you after the first three months?
6. Ask Questions That Drive the Story Forward
Impactful questions are the backbone of a strong case study. They allow you to highlight the unique value you delivered to your clients. You can effortlessly showcase your USPs within the case study by asking the right questions.
Focus on inquiring about the effectiveness of your services and strategies, their impact, and which aspects of the solution were most beneficial. This insight will be your key to demonstrating the tangible benefits you offer your clients.
Consider asking questions like:
- Can you share a moment when you first noticed a significant improvement in your website’s organic traffic?
- How did the increase in organic traffic impact other business areas, such as lead generation or sales?
- What feedback did your team or customers receive regarding the changes in your site’s performance?
- Looking back, what do you believe was the most critical factor in achieving these results?
- How has this success with SEO influenced your overall marketing strategy moving forward?
These types of questions encourage clients to share their experiences in a way that paints a vivid picture for your readers, making the case study more relatable and engaging.
7. Draft a Clear and Organized Outline
With all the data and insights gathered, it’s time to create a well-structured case study outline. Let’s say you start with a brief overview of your client’s business and its challenges, followed by a detailed account of the SEO strategies you implemented. Then, you showcase the results with hard data and close with client testimonials and a solid call to action.
As mentioned above, organizing your content in a logical, easy-to-follow format will help you write a case study that not only informs but also captivates your audience.
These steps are the cornerstones of designing a case study. Once you complete this checklist, you can proceed to the next step, which is writing a case study. Since I discussed planning an SEO case study extensively, here is a case study template that perfectly illustrates the process.

You want to create an informative case study for your prospects. But how do you make sure it’s done right? Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write a case study that drives results.
1. Craft a Compelling Headline
Your headline is the first thing readers see, so make it count! It should grab attention and hint at the success story you’re about to share.
How to Write a Case Study Title:
1. Highlight the Result: Showcase the critical success, like “Increased Sales by 200%.”
2. Be Clear and Direct: Make sure the headline is straightforward to grasp.
3. Use Action Words: Start with strong verbs like “How We” or “Achieved.”
4. Mention Client or Industry: Include relevant details for specificity.
5. Keep It Short: Make it concise and attention-grabbing.
2. Start with a Strong Introduction
Kick off your case study with a broad overview that sets the stage. Provide the big picture and construct a clear narrative that draws readers in, making them eager to learn more about how you solved a significant challenge.
Look at the consulting case study template , which includes a stunning overview description and precise instructions for writing a short and compelling introduction. You can add every little detail to hook the reader.

Get This Template and More
3. Discuss Specific Challenges of Your Client
This is where your prospect can truly connect. By highlighting unique yet specific challenges to their industry, you give them insight into issues they might not have encountered yet—or ones they’ve already faced. This way, they’ll know exactly who to turn to when similar challenges arise.
The following financial case study template provides a brief flow of the company’s common challenges in the financial analysis process. The template is almost ready to use with this domain-specific content, requiring minimal adjustments to design your case study.

4. Highlight the Solution
Now, dive into the heart of the story. Highlight the solution you provided, and make sure to include a notable achievement or key result. This is your chance to shine!
Check out the format for presenting the implications of your service on your client’s business. The benefits should be well-written and data-driven to convince your upcoming clients. This graphic design case study format helps you understand the specific impacts a company seeks from a reputable graphic design firm.

5. Present Quantifiable Results
When sharing the outcome, numbers speak louder than words. Present quantifiable results that clearly demonstrate the impact of your solution. Use graphs or charts to make the data easy to digest and visually appealing.
6. Be Clear and Concise
Less is more. Stick to the point and offer just the right amount of detail to keep your readers engaged. Include data that supports your claims, but avoid overwhelming them with too much information.
Here’s a stunning sales consulting case study that uses a simple case study layout and details written in readable, plain language to gauge more utility.

7. Treat Your Case Study Like a Story
Focus on your customer’s journey. Think of your case study as a story in which your client is the hero, and your solution is the tool that helped them succeed. This approach will make your case study relatable and compelling.
8. Be as Specific as Possible
Don’t be vague—details matter. Mention the specific company and its industry to let your audience know that the challenge and solution are relevant to them. The more precise you are, the more credible and trustworthy your case study will be.
Check out the sample case study below for payroll accounting. The details are clearly organized and grouped to emphasize the type of case study.

Also, the next case study template displays very specific problems that a company faces when it lacks digital marketing expertise.

These templates make it a breeze to craft a case study that’s perfect for your niche.
9. Use Direct Quotes from the Client
Quotes from your client add authenticity and credibility. They give readers insight into the client’s perspective and make your case study more relatable. Plus, a glowing testimonial is always a nice touch!
The following inbound marketing case study has a prominent client testimonial. With the brief instructions on this template, it’s easier for you to understand how to capture the golden words of your client and use them as a word-of-mouth strategy within the case study.

10. Pick an Interesting Angle
Find a unique angle that makes your case study stand out. Maybe it’s an unexpected challenge you overcame, or perhaps it’s a particularly innovative solution. Whatever it is, make it intriguing.
11. Make the Key Takeaway Crystal Clear
Your readers should walk away with a clear understanding of the main point of your case study. This takeaway should reinforce your expertise and the value of your solution.
12. Include a Call to Action (CTA)
Don’t leave your readers hanging—tell them what to do next! Include a compelling summary about your company, showcase your happy client base, and conclude the journey with a strong CTA, whether to contact you for a consultation, download a related resource, or learn more about your services on social media, like the following case study template design.

12. Format Professionally
The design of the case study is just as important as the content. A well-formatted, visually appealing document makes a great impression and enhances readability. With ready-to-use niche-oriented templates, you can easily create a professional-looking case study that impresses and converts. Here is an eye-catching template for an AI assistant software case study that displays a sleek and well-navigated format.

13. Make It Readable
Easy readability is key. Use simple language, short paragraphs, and bullet points where appropriate. Your case study should be easy to scan and digest. Follow the thirteen design principles to create a standout piece that enhances your marketing efforts.
To understand this, take a look at the following consulting case study template.

14. Finalize and Proofread Your Case Study
In order to excel in how to write case studies, give your case study a final review before you hit publish. Proofread carefully to catch any typos or errors, and make sure everything flows smoothly. A polished case study reflects your attention to detail and professionalism.
To effectively summarize a case study, start by completing all sections, including the introduction, challenges, solutions, and results. This approach helps marketers identify key points to highlight, making it easier to craft a succinct and engaging summary.
One tricky thing is the length of the case study summary. So, how long should a case study summary be?
The length of a case study summary can vary depending on the details you’re covering. Generally, it should be kept concise, usually spanning a couple of lines or up to a single page with several paragraphs. If you’re crafting a customer case study and want to flex your storytelling muscles, it’s perfectly fine for the summary to stretch to a full page.
If summarizing a case study seems daunting, try DocHipo’s advanced AI Writer tool, which effortlessly creates a crisp and concise summary.
Watch this short video to use it.
This is the last step in writing a case study analysis. Citation in a case study is the practice of giving proper credit to the sources you reference or use in your research. It helps validate your work, shows the depth of your research, and avoids plagiarism. Follow the below steps to cite a case study:
- Identify the Source: Gather details like the author, title, publication year, and where the case study was published.
- Choose a Citation Style: Follow the specific formatting style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) required for your work.
- Format the Citation: Arrange the details according to the chosen citation style.
- Include In-Text Citations: Place citations within the text or paragraphs for the case study.
- Create a References List: At the end of your case study, compile all your sources in a bibliography or reference list.
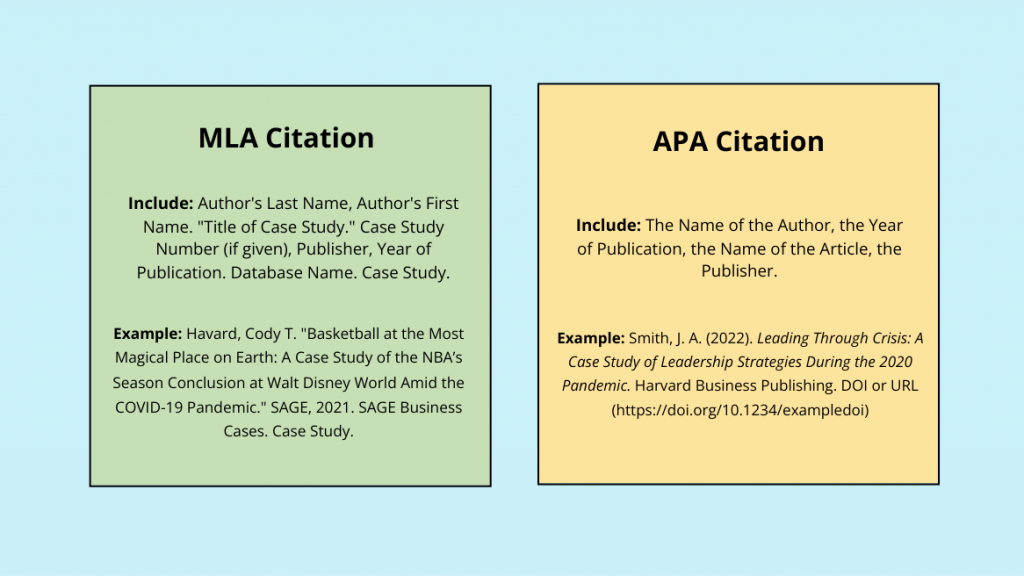
For case studies, citations in APA and MLA styles are very common. If you are just beginning, then you might be confused about these case study citation formats.
Hence, take a look at the picture below, which easily comprehends the APA vs MLA citation features.
Still feeling overwhelmed about case studies? Be stress-free with the most convenient case study maker, which saves time and allows you to present data in the most attention-grabbing way.
Watch the video to create case studies in minutes with DocHipo’s case study maker.
Conclusion
To summarize, if you want to write a case study, start with a proper case study format, plan the case study, and finally write it with all the information in hand. Then, write a summary to provide an overview of your case study, and finally, add citations for reference.
Meanwhile, if you want to design a case study, Try DocHipo templates. Sign up to explore all the case study templates.
What is the structure of a case study?
A case study typically includes the following sections: Title, Introduction, Background, Problem Statement, Solutions, Results, and Conclusion. Each section serves to tell a comprehensive story of the business, from the issue at hand to the resolution and outcomes.
What are the 5 essential elements of a great case study?
The 5 essential elements are: 1) Clear Objective, 2) Detailed Background, 3) Specific Challenges, 4) Effective Solutions, and 5) Measurable Results. These components provide a compelling narrative that highlights the value delivered.
How to begin a case study?
Start a case study by defining the purpose and scope of the study. Introduce the subject, outline the problem, and provide background information to give readers context. This sets the stage for the detailed analysis that follows.
How to make an introduction in case study?
To craft a compelling introduction, briefly describe the subject, outline the problem they faced, and explain why the study is relevant. This section should grab the reader’s attention and make them interested in the rest of the study.
How to make a business case study?
A business case study should begin with a clear objective and background information. Identify the problem, explain the solutions implemented, and conclude with the results achieved. Use real data and quotes from stakeholders to enhance credibility.
How to write a case study step by step?
To write a case study step by step, start by identifying the case you want to explore and gathering relevant data on the subject. Outline the structure of your case study, then craft an engaging Introduction to set the context. Next, detail the Background and Challenges faced, followed by the Solutions applied. Share the Results and Conclusion to highlight the impact. Finally, edit and proofread your case study to ensure clarity and accuracy.

Turn your ideas into beautiful design
No prior design skill required

Talk to Sales
Wherever you are on your Dochipo journey, you can always get in touch.

Talk to Support
How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Updated: July 18, 2024
Published: June 13, 2012
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a major challenge. Before you can expect to earn their business, you’ll need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on the promises of your product or service. The best way to win new business is with cold, hard proof.

A great way to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. HubSpot’s 2024 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so captivating that they were the fifth most commonly used type of content that marketers relied on.
That statistic still holds true in Forbes Advisor’s 2024 study, which adds that 78% of B2B businesses report using case studies and customer stories because they are “ crucial for demonstrating real-world value. ”
Having written these ever more frequently over the past ten years, I hope to serve as your guide through a process that can feel daunting, but I promise is worth the effort. Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic.
Table of Contents
Case Study Definition
- Why Write a Case Study?
- How Long Should a Case Study Be?
Case Study Templates
How to write a case study, case study format, business case study examples.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A case study is coverage of a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it‘s common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client.
Perhaps the success you’re highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers, helping you attract new clients.

Why write a case study?
I know, it sounds like a huge endeavor — is it really worth it?
The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples.
Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain complex topics or concepts.
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies, showing how they can be applied in a practical way.
You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that demonstrates how your product solved their issue. Most importantly, it explains how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar, successful results.
2. Show expertise.
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build trust and credibility.
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework.
A robust case study instills confidence in the solutions you present because the reader has now vicariously experienced the problem — and they followed, step-by-step, what it took to solve it. These elements work together, enabling you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create social proof.
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof .
People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — put your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes play together like an orchestra to help you gain more clients. Afterward, the case study acts as a reference. You can pull quotes from customers that were featured in these studies to repurpose them in other marketing content.
How long should a case study be?
Now that you’re more acquainted with the benefits of producing a case study, let’s explore how long these documents should be.
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved.
This may be easier said than done, but it‘s important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader’s interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Make it attractive to dive into by using headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers.
I’ve also seen more and more brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience, which is highly recommended given that video is currently the best performing marketing content format.
In terms of the interview structure, I recommend categorizing the questions in a way that the answers flow into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, plus how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context that helps match the customer's needs with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes.
Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
It’s a smart idea to send a copy of your interview questions to your subject ahead of time so they can prepare strong answers and collect the numerical data you need from them.
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you‘ve collected and actually turn it into something useful, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. I always do, but I also know that it works out in the end, so I just jump on in and work it through.
So where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
It‘s important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study.
They can be very visual, which you’ll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated through video or photos with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections I’d suggest, and I'll cover these in more detail after #11 below:
- Title. Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle. Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary . A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject. An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives. A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped. A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results. A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes. Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans. Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call-to-Action (CTA). Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible.
Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you‘ve completed your case study, it’s time to publish and promote it.
Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas.
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF.
To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client‘s success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they’d like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people to it from your homepage with a “Case Studies” or “Testimonials” button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

27 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![writing in case study 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![writing in case study How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![writing in case study What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
The weekly email to help take your career to the next level. No fluff, only first-hand expert advice & useful marketing trends.
Must enter a valid email
We're committed to your privacy. HubSpot uses the information you provide to us to contact you about our relevant content, products, and services. You may unsubscribe from these communications at any time. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
You've been subscribed
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
5 Steps for Writing a Case Study for Business (+Templates)
Get professional tips for writing a case study that drives business impact. Learn the best format and research method to use alongside examples & templates.
5 minute read

helped business professionals at:

SHORT ANSWER
What are the 5 steps to write a case study.
- Open with an introductory overview
- Explain the problem in question
- Detail the solutions that solved the problem
- Refer to key results
- Finish with recommendations and next steps
Keep reading for a full breakdown ⤵
What is a case study?
In business, a case study , or customer success story, is a marketing tool that showcases how your product or service helped clients overcome business challenges. It uses statistics, quotes, and specific examples to convincingly highlight your ability to produce results.
What is the purpose of a case study?
The purpose of a case study, usually, is to provide your prospective clients with specific examples of how your products or services can help solve business problems they might be facing.
Case studies legitimize your business activities allowing you to go beyond explaining what you do and focus on how well you do it.
And, in case you were wondering just HOW important case studies are, here’s an item of data to ponder: according to a DemandGen report , 78% of B2B buyers want to review case studies before making a purchase decision.
Another study by Uplift found that at the end of 2023, for the third year in a row, marketers ranked case studies the #1 most effective marketing tactic to increase sales—ahead of general website content, SEO, blog posts, social media, paid ads and other tactics.
How to write a case study?
In business, everyone claims to be the next big thing, but a case study is how you prove it. It shows the real value of your product or service and backs up your claims with real results.
A well-written case study builds trust by showing you can deliver on what you promise and proving the impact your actions have on the bottom line. Here's how to write a case study that engages readers and makes them excited to work with you.
NOTE: If you don't want a slide-by-slide breakdown and just want to see real decks, check out the best case study presentation examples .
Effective case study outline
Introductory overview
The problem or challenge
The solution
Key results
Recommendations and next steps
1. Open with an introductory overview
People don’t usually read case studies. At least not immediately. First, they skim the contents to see if the subject is relevant enough.
How to make sure your case study sticks? At the beginning, place an introductory overview (also called an “executive summary”).
Provide an overview of the whole case. It’s not supposed to be a catchy intro but a full synopsis, detailing the problem at hand, your assumptions, the solutions implemented, and the results achieved.
How to write a case study introduction?
Introduce the company: Start by giving a brief overview of the company that’s the focus of the case study. Share who they are, what they do, and any relevant background.
Introduce the purpose of the case study —specify exactly what you were aiming to achieve.
Define the problem or the most significant challenge. For instance, low conversion rates, a technological issue or high costs. (It could also be a combination of such factors!)
Explain briefly what the solution to the problem was.
Share the most important results your actions produced. Don’t go into too much detail, a few key points will do. It’s best if you can quantify the results: numbers pop!
Keep it short. Usually, 2–4 paragraphs + a few bullet points with key results will do. Consider using an AI rewriter to help you break down complex sentences into clear and concise sentences that effectively convey your message.

While, as its name implies, this section comes at the beginning of your case study, write it last. First, craft the rest of your document, then pick the most important bits and compile them into the introductory overview.
2. Explain the problem in question
In the problem section of your case study, you want to put your reader in the shoes of your client, so that, later on, you can present your company as the miraculous savior.
Paint a clear picture of the challenge your product or service solves, and focus on how difficult the situation was for the client before your solution came along.
The goal is to create a sense of urgency and connection—making it easy for readers to relate and feel the weight of the problem. This emotional engagement is key to highlighting just how valuable your solution is.
How to write a “problem” section in a case study?
In a single sentence, describe your customer’s business challenges and objectives.
Explain the problem your customer faced that prevented them from achieving those objectives prior to working with you.
If that was the case, mention other solutions your client experimented with that didn’t work out and explain why.
Make it clear how the issue or problem impacted the client’s business results so that it’s easy to understand why a solution was badly needed.

3. Detail the solutions implemented to solve the problem
Here comes the moment to toot your own horn a bit (and also that moment when you can get slightly technical).
Present your solutions in reference to the issue your client was dealing with and make it obvious that those are easily replicable for all future cases. Of course, the exact formula for this section will depend on your industry and mode of operation.
Sometimes a 2–3 paragraph summary will be enough. In other cases, you’ll need to include more detailed technical specs regarding the solution you implemented.
How to write a "solution" section in a case study?
Focus on your customer’s experience in using your product or services.
Explain the process : say how long it took to get the solution up and running and what teams on your customer’s end were involved.
Highlight the features of your product or service that turned out to be the most beneficial to your customer.
If possible, attach or link to relevant assets that will work as real-life examples of your solution (unless, of course, the information is highly sensitive).
Always run your case study by your client’s marketing team before you go live. Even if you’re using direct quotes or verifiable results, it’s ultimately their decision whether or not to make certain information freely available.

4. Refer to key results
In business, nothing speaks louder than ROI and you know it.
Prospective customers reading your case study won’t be bothered to take notice of your state-of-the-art technology or innovative approach. Neither will they care about your past customers’ happiness. What they want to know is this: Will that help me save or make money? When writing a case study, your job is to present results in a way that answers the above question with a resounding YES.
Here’s how to write about results:
In a few bullet points, list numerical results your solution delivered to the client.
Ideally, you’ll want to include revenue-related data: increase in clients’ base, more demos booked, higher conversion rates, or optimized pricing.
If you can’t (or aren’t allowed to) share hard sales numbers, refer to softer KPIs: time saved, customer happiness scores, expanding the community, or enhancing brand visibility.
Make it blatantly obvious that such results are easily replicable.

If possible, by all means include quotes from your client. Results should speak for themselves, obviously, but showing the real human whose problems you solved makes for a much more powerful narrative. Plus, it further adds credibility to the case study. Start by preparing a list of powerful case study questions to guide your client interviews.
5. Finish with recommendations and next steps
Everyone enjoys a solid epilogue. To end on a high note, include a list of key findings from your case study.
Even if a given reader won’t decide to get in touch with you, at least you’ll provide them with a valuable source of knowledge—sometimes that’s enough to keep your company top of mind in the future. Now, not every case study requires a call to action (especially if your main purpose is to inform and educate rather than convert, which is okay, too), but for those more commercially-oriented ones, do add it. Make your CTA singular and clear —if the most desired action is to reach out to you, leave your contact details, if you’d rather direct prospects to a landing page or a welcome screen, add a button.
For your reference, here’s an example of our very own case study, showing how, at Storydoc, we helped the Spot company boost some of their key metrics: Learn How Spot by NetApp boosted their conversion rates 2x .
Interactive case study templates
No matter how great the contents of your case study might be, if you fail to present it in an eye-pleasing way, most likely, no one will really read it.
Interactive case study templates help bring your story to life with features like data visualization, clickable elements, and the option to add links or multimedia.
This makes it easier for your audience to follow along and understand your message and helps you stand out from the competition.
Just grab one.
Tips on preparing a case study
Before writing a case study, it’s important to take the time to prepare properly. It’s more than just sharing a success story—you want to gather the right details and present them in a way that really connects with your audience.
By doing this groundwork, you can ensure your case study demonstrates your value but also builds a sense of credibility and trust that sticks with potential clients.
Case study preparation tips:
Determine a customer use case
Go over existing clients
Reach out to the happy clients
Set success criteria
Set measurements
Set time period for observation
Conduct post interview to assess results
Get data from client
Get client approval
For more information, check out our guide on how to create a case study .

Hi, I'm John, Editor-in-chief at Storydoc. As a content marketer and digital writer specializing in B2B SaaS, my main goal is to provide you with up-to-date tips for effective business storytelling and equip you with all the right tools to enable your sales efforts.
Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.

Make your best case study to date.
Try Storydoc for free for 14 days (keep anything you make for ever!)

COMMENTS
In this article, we explore the concept of a case study, including its writing process, benefits, various types, challenges, and more.. How to write a case study. Understanding how to write a case study is an invaluable skill. You'll need to embrace decision-making - from deciding which customers to feature to designing the best format to make them as engaging as possible.
Let's say you're writing a case study about a website redesign. Instead of just describing the changes, include: Before and after screenshots to visually demonstrate the improved user interface and design elements. Charts or graphs to show how the bounce rate decreased and conversion rates increased after the redesign.
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. ... In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the ...
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
Most resources tell you that a case study should be 500-1500 words. We also encourage you to have a prominent snapshot section of 100 words or less. The results and benefits section should take the bulk of the word count. Don't use more words than you need. Let your data, images, and customers quotes do the talking.
To write a case study step by step, start by identifying the case you want to explore and gathering relevant data on the subject. Outline the structure of your case study, then craft an engaging Introduction to set the context. Next, detail the Background and Challenges faced, followed by the Solutions applied.
Written Case Study. Consider writing your case study in the form of an ebook and converting it to a downloadable PDF. Then, gate the PDF behind a landing page and form that your readers fill out before downloading the piece. This enables your case study to generate leads for your business. Video Case Study
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
While, as its name implies, this section comes at the beginning of your case study, write it last. First, craft the rest of your document, then pick the most important bits and compile them into the introductory overview. 2. Explain the problem in question.