UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Admit-a-bull // official admissions blog, why a college education is important.
By Joe Emerson | Last Updated: Jul 15, 2022

Defining why a college education is important involves more than just identifying the superficial benefits of more career opportunities. At a deeper level, college is where you will map a path through life that can take you to places you never expected to go.
The beauty of postsecondary education is that college can yield tangible and intangible benefits for you that in turn benefit others – even if school doesn’t awaken your sleeping Pablo Picasso, Stephen Hawking, or Bill Gates.

Tangible Benefits of a College Education
It’s well established that a college education delivers measurable material benefits. If you were to rattle off the list of reasons you’re attending school, chances are these are the first ones you’ll mention.
College Education and Wages
A handful of money definitely qualifies as a tangible benefit, and research has matched levels of education to payroll expectations and the ability to find a job:
- In 2015, bachelor’s degree holders earned 64 percent more than those with a high school diploma.
- Bachelor’s degree recipients can expect to earn about $1 million more over a lifetime than a person who doesn’t go to college.
- A postsecondary education is expected to be required for about two-thirds of available jobs by 2020.
A recent study broke the higher education benefits down even further, finding among other things, that a bachelor’s degree now means the holder will earn 84 percent more than someone with no postsecondary education. The report went even further, projecting lifetime earnings based on virtually all education levels:
- Lifetime wages of a high school dropout – $973,000
- Lifetime wages of a high school graduate – $1.3 million
- Lifetime wages of someone with some college but no degree – $1.5 million
- Lifetime wages of an associate degree holder – $1.7 million
- Lifetime wages of a bachelor’s degree holder – $2.3 million
- Lifetime wages of a master’s degree holder – $2.7 million
- Lifetime wages of a person with a doctorate – $3.3 million
- Lifetime wages of a professional degree holder –$3.6 million
Based on U.S. Census Bureau data , the usual median weekly earnings in 2017 for people of varying education levels was:
- Doctoral degree holder’s median weekly earnings – $1,743
- Professional degree holder’s median weekly earnings – $1,836
- Master’s degree holder’s median weekly earnings – $1,401
- Bachelor’s degree holder’s median weekly earnings – $1,173
- Associate degree holder’s median weekly earnings – $836
- Person with some college (no degree) median weekly earnings – $774
- High school diploma (only) holder’s median weekly earnings – $712
- Person without high school diploma median weekly earnings – $520
The unemployment rates in 2017 for people in those education categories was 1.5 percent for doctoral degree holders, 1.5 percent for professional degree holders, 2.2 percent for master’s degree holders, 2.5 percent for bachelor’s degree holders, 3.4 percent for associate degree holders, 4 percent for people with some college, 4.6 percent for people with a high school diploma, and 6.5 percent for people without a high school diploma.
Better Jobs Equal Better Benefits, Perks
A college education also usually translates to great benefits and perks as well:
- Typical white-collar benefits: health insurance, eyecare insurance, vacation and other paid time off, dental insurance, maternity/paternity leave, pension plan, 401(k)
- Potential white-collar perks: transportation and parking reimbursement and/or company car, free food and beverages, flexible schedules and freedom to work from home (or elsewhere), concierge services, golden parachutes (high-dollar severance packages)
For Some, College Is the First Real Adventure
College takes you out of familiar surroundings and presents new challenges. But college doesn’t only pave the way for intangible experiences. Adapting to new faces in a fresh place is just the start. The education process can mean internships, overseas travel, exciting research opportunities, and exploration of multiple career paths, all of which can lead to some very tangible results when you start working.
And academic success opens doors to careers where, quite literally in some cases, even the sky and moon aren’t the limits. Think aerospace engineering.
Connections that Can Last a Lifetime
The thousands of people you meet, study with, and work alongside in college will range from peers to mentors, along with power players in your chosen field and others. These are connections you will make note of and potentially use to advance yourself and your ideas.
And as far as relationships go, the only romantic label as common as “high school sweetheart” is “college sweetheart.”

Intangible Benefits of a College Education
A college education can open doors for your career and your own personal growth. For example, college helps develop many important skills, such as self-awareness, global-mindedness, critical thinking, and more.
People by Nature Desire Knowledge
That is a paraphrase of a premise that the Greek philosopher Aristotle states in his Metaphysics . It is affirmed by the connection of head and heart when the study of history helps you forecast the future, when math adds up to real-life solutions, and when the development of skills allows you to produce a masterpiece worthy of the Library of Congress, Metropolitan Museum of Art, or U.S. Patent Office.
In Pursuit of Critical Thinking
Results are in on colleges and critical thinking. During one recent study , researchers began with the notion that everyone wants colleges to teach critical-thinking skills and that the challenge routinely is accepted. Here’s a key finding: Data show that a student who begins college with critical thinking skills in the 50 th percentile can expect to be in the 72 nd percentile after four years.
Critical thinking is, according to the Foundation for Critical Thinking , “that mode of thinking — about any subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully analyzing, assessing, and reconstructing it.” Developing that skill yields endless opportunities to enrich your life both personally and professionally.
College Advances Self-Realization
A college education, if pursued honestly and earnestly, gives you the knowledge and skills needed to pursue a career and your passions. The degree also can bring hard-to-match personal satisfaction. A huge part of ensuring that self-realization process is finding a school that is right for you , where you’ll feel safe and comfortable enough to let yourself grow and explore.
Our USF admissions advisors are happy to answer your questions about the USF admissions process, so contact us online or by phone at 813-974-3350 .

About Joe Emerson
Joe Emerson, former reporter and editor with 30 years of experience, turned to freelancing in 2016. Writing valuable information remains his passion.
Previous Post

What's the Difference in On-Campus and Off-Campus Housing?

How to Finish the College Process
The New York Times
Advertisement
College Is the Goal. Will These Three Teenagers Get There?
By ANEMONA HARTOCOLLIS
The Times followed three teenagers in Topeka, Kan., as they decided where to apply to college – and even whether college was the right choice for them. Here’s a look at their journey: Senior Year at Topeka High * The Pros and Cons of Delaying College * The Allure of Leaving Kansas * ‘I’m Panicking’ * College Is Not the Only Option * The First in the Family to Go to College * Two Different Paths to College * Is Higher Education the Cure-All? * Imagining Life Away From Home * Mind-Sets Are the Barrier * The Pitch for Technical School * One Student’s Calculation * Confronting Debt * Getting Motivated * What Is a College Education Worth? * Missed Deadlines * Chat: Navigating a Path
What Is a College Education Worth?
As they look to graduation, many Topeka High seniors are debating the value of a college education. Is it worth their while to go to a four-year institution? Or should they choose a two-year degree, technical school or the work force instead?
From an economic point of view, studies show there is little contest: The pay gap between people with four-year college degrees and everyone else is bigger than ever.
That gap has been growing since the 1980s, according to an analysis by the Economic Policy Institute, not so much because wages for college graduates have risen, but because the average wage for everyone else has fallen.
“If there is class mobility in America, it exists through the vehicle of education,” Sean C. Bird, an associate dean at Washburn University, a public university in Topeka, said the other day. Mr. Bird focuses on retaining first-generation and disadvantaged students at the college.
College is transformational, he added. “They walk differently, they dress differently, they think differently, they talk differently,” after going to college, he said.
Beyond the economics, proponents of college education point out that there is value in loving to learn, and in knowing how to learn. The market value of a college degree may be less tangible than the value of technical certification in a field like welding or auto mechanics, but college advocates say there is strength in versatility.
“You will be employable on the day you graduate, but it’s impossible to say what you’re going to do,” said E. Whitney Soule, dean of admissions and financial aid at Bowdoin College, a small, highly selective liberal arts college in Brunswick, Me. “Because the exposure in those four years is so broad that the possibilities will be incredibly broad. It will take the student’s experience and motivation to nail down what this will look like.”
But, she added, “It can feel insecure if it doesn’t have a salary attachment and a guarantee of a particular job.”
That conflict between knowing right away what the future holds and being willing — and perhaps able — to assume some risk is exactly what the Topeka seniors are facing. Many of the best students will take that risk, move to more vibrant urban areas and never look back.
“On the whole, Kansas is facing a brain drain,” said Alan Bearman, a Washburn dean who works with Mr. Bird in helping keep students in college. “Some of our very top-achieving students leave after high school, and they don’t come back.”
For those who stay, the goal after high school can be very practical. “We’re looking at the next generation of Topeka police officers, attorneys and teachers,” Mr. Bird said.
In mid-October, some of the students here attended a fair given by Washburn Institute of Technology, the tech school in town. The parking lot was full of pickup trucks and 4x4s. Each presentation, in fields like construction, technology and health care, was crafted to give prospective students a precise sense of the wages they would make on the day they graduated, and the companies that would be likely to hire them.
In computer science, for instance, the teacher told them they would make $15 to $20 an hour in their first year after graduation. If they learned to operate an excavator, they were told, they could make up to $22 an hour. For a machinist, common starting wages ranged from $12 to $17. For masons, $15, “If you’re union,” the teacher said, adding, “It’s a little bit labor intensive, but not like you’re out bucking bales of hay. That’s work. This is fun.”
Data show that the average hourly wage for college graduates rose slightly to about $32.60 over the last decade, double the wage for everyone else.
A few days later, the seniors took WorkKeys, a test to measure basic job readiness skills, and then filed into the auditorium for a mandatory manufacturing presentation. They were told that local factories for companies like Mars chocolate and Frito-Lay were looking for people who were at least 18 with a high school diploma and who could “show up to work on time” and be “part of a team.”
“Does making between $13 and $19 an hour sound good to you?” one of the presenters asked.
But an edge of near-desperation often crept into the presenters’ voices. They knew it was an uphill battle to attract students who could show up to work on time, let alone the best and brightest.
“Sometimes young kids think about manufacturing as a last resort,” Michelle Waggoner, a human resources manager at Mars, said after the presentation. “We don’t want them to view it as a last resort.”
Join the Discussion
Senior year at topeka high.
Nearly all high school students want to go to college these days, studies show, but many never make it. Of those who do, many fail to earn their degrees. Researchers call this the “aspirations-attainment gap.”
What stops kids from getting a college degree? Poor academic preparation, rising college costs, the declining value of financial aid and, not least, just managing the process. Applying to college requires a huge amount of social capital — the support of family, friends, mentors and teachers — as well as personal drive and initiative.
In the last month, I have been visiting Topeka High School, talking with seniors, and their parents and guidance counselors, about their college plans as they take standardized tests, decide where to apply, write essays, fill out financial aid forms and send in their applications. I’ve followed their successes and mishaps along the way and will look in again in a few months to see where they end up, whether in college, vocational school, a job or at home.
Why Topeka?
Topeka High is in many ways an all-American school, the largest public high school in this sprawling low-rise city of about 127,000 people. The school has a strong racial, ethnic and economic mix among its 1,800 students. As in many American schools, black students are often the most disadvantaged, despite integration.
But Topeka High also has many poor and struggling white students, as well as students of Mexican descent and children of migrant farmworkers, some undocumented. A handful of students, mainly affluent ones, will go to the Ivy League. But the graduation rate hovers in the low 70 percent range, the principal said; 45 percent of graduates go to a four-year college, and 17 percent go to a two-year college. More than half the students are poor by federal standards.
Topeka High is also where I went to high school, before going on to college on the East Coast. Many of my friends stayed closer to home or chose not to go to college, saying they did not see the value in it. Has that pattern changed or stayed the same? How did the Great Recession affect the ambitions and dreams of students here? I set out to get to know some of the kids and find the answers.
The Pros and Cons of Delaying College
He is Nate in the country and Nathan in the city, torn between two worlds.
Nathan Triggs lives with his mother in Topeka on weekdays. On weekends, he drives his scruffy Chevy S-10 pickup truck to his father’s farm outside Holton, population 3,300, about 45 minutes to the north.
In the country, what matters is what you can do with your hands: baling hay, hunting or fixing a broken U-joint. In the city, what matters is what you can do with your brain, whether it’s understanding the difference between kinetic and potential energy in physics class or being able to explain the meaning of social capital in government class.
Nathan/Nate can do both. That push and pull between these worlds is working on him now as he tries to decide, amid conflicting advice from family and friends, whether to go to college or to trade school. But are the life of the farm and the life of the mind mutually exclusive?
The college decision is a critical turning point and a central point of satisfaction in life, economists say. That’s why college admissions directors say everything matters — not just grades, but also life experience.
Nate, who is about to turn 18, sees a number of gates ahead of him, all attractive. Which one will he choose to go through?
To get to Nate’s father’s farm, you drive north from Topeka on U.S. 75, past the ubiquitous grain elevators and a sign advertising Goodyear, one of Topeka’s largest employers. The landscape undulates from a gritty urban setting to more idyllic cornfields, sunflowers and church spires. About a half-hour on, Holton flashes by in two stoplights.
The gravel driveway to the farm is marked by stars and stripes painted on boards, like a Jasper Johns painting, with a baby’s footprints where the stars should be. Its whimsy hints at the affectionate family life inside. In the kitchen, the grocery list on the chalkboard shows requisitions, in different handwriting, for “man soap” and “sanity.” Well-seasoned cast iron pans hang on the wall, and in a freewheeling spirit, nobody minds that the bathroom has no door.
At school in town, Nathan is the quiet boy in the back of the classroom, whom nobody notices.
The student government leaders and the high school principal have to think for a couple of minutes before he gradually swims into view — lanky, in jeans and cowboy boots. Oh yes, they say, the farm boy. What is he doing at Topeka High? He does not seem to belong.
In Holton, Nate has learned skills that are not clearly measured on a college application. He even speaks differently, mixing his tenses and sprinkling in some ain’ts. In Topeka, he is a committed student who eagerly signed up for a college-prep program when he was still in seventh grade.
“Is that why you’re in all those honors classes?” his grandmother Ann Matthews asked the other day when she heard him talking about his schoolwork. Nate nodded shyly.
His grandfather Al Matthews, a retired insurance claims manager who, like his wife, has a college degree, is pushing the military, saying Nate can find himself in the service before making a life-changing decision like going to college.
“Does one go to college, and run the risk of spending four years and a lot of money and getting out and there’s no jobs?” Mr. Matthews said, sitting on his comfortable front porch in nearby Netawaka, Kan., as Nate listened quietly. “Use the military as an intermediate step while you can see what is going on with the economy.”
Or, he said, “lay out for a year” and work. To which Nate instantly replied, “I don’t want to lay out for a year.”
The Allure of Leaving Kansas
A few years ago, TaTy’Terria Gary and her mother made a pact. After TaTy finished at Topeka High School, her mother would move out of Kansas, and TaTy would consider leaving the state to go to college.
“She feels like Topeka is not a good place for people who have dreams,” TaTy said. “Go where your heart is. There’s 49 other states. Why stay in this one?”
That deadline is approaching, and TaTy, 17, a senior, is one of the few students in the college-prep program here who want to go to college out of state. Not much seems to intimidate her. She is tall and full-bodied. She wears her hair swept up and has learned to look camera-ready through her job selling cosmetics at a beauty store. Teachers sometimes criticize her for being sassy.
She may not always fit feminine stereotypes of being agreeable, but she has steel.
TaTy’s life seems tailor-made for a college application. She has a clear, long-term ambition: to be an obstetrician and gynecologist. She has an instinct to help people that she traces to her childhood, when she helped her grandmother shop for groceries. She has been doing volunteer jobs since seventh grade, like serving food at a nursing home and helping out at a preschool. She does it because the college-prep program requires it, but she has found that “honestly, it’s better than sitting in the house.”
Even with her job and her responsibilities as captain of the school step team, she has a grade point average of about 3.7, she said, with an 87 in human anatomy.
Change has been a theme of her life lately. To escape the jangling police and ambulance sirens of central Topeka, her family moved last year to rural Pauline. “I like seeing the stars at night,” she said. She drives a half-hour to school each morning, sometimes taking her younger brother and sister to school first, which adds another half-hour.
Her mother was turning 18 when she had TaTy, dashing her own hopes of going to college. She now works at a group home for abused and abandoned children, and she is studying for a bachelor’s degree in criminal justice at Washburn University, a public institution in Topeka.
TaTy avoids her father, who, she said, has been in and out of jail. “He likes to blame everyone else for his problems,” she said.
TaTy does not want to have children, she said, so she does not expect to repeat her mother’s experience of becoming pregnant at a young age. For her 16th birthday, she asked for a “purity ring,” a silver ring symbolizing a pledge that she will abstain from sex before marriage, or until she is ready.
She embraces the role of the independent woman. The step team that she leads, a kind of stomp-dancing group, has become a bonding experience for its mostly black and Hispanic members, many of them girls who are not the cheerleader type: too heavy or not popular enough.
She wants to be an OB-GYN partly so she can help young women understand their bodies. “I definitely think that women are so much stronger than they know,” she said.
A Familiar Feeling at 18: ‘I’m Panicking’
Zachary Shaner was truant when other marching band members received their dress uniforms, so the other night he was rummaging around the empty band room, hoping to find one that fit in time for the next game. Then he went down to the cafeteria, where teachers were sitting behind rows of tables for parent-teacher conferences.
“I’ll take that,” said Eric Bradshaw, the band director, snatching the marching band hat out of Zac’s hand as he walked up to the table with his mother for their conference. It is the wrong color hat, and it has a broken black feather plume on top. He can’t wear it.
At that moment, the broken plume seems symbolic of the wounded spirit that is Zac’s senior year at Topeka High School. He is the gifted boy everyone complains is not living up to his potential.
Zac, 18, has been raised by a single mother on disability insurance in a poor part of Topeka. He transferred from his neighborhood’s sports-oriented high school to Topeka High in search of a better education. He sings, composes music and makes his own puppets for puppet shows. He plays so many instruments that when people ask him which ones, he just says, “All of them.”
By all rights, Zac should be a find for an artsy college like Bard or Bennington.
Everyone has known someone like him in high school: the exceptionally smart, glib kid destined for great things despite a troubled background. But in time, that trouble seems to catch up, and the dreams to turn to dust.
Zac may be at that pressure point.
His teachers say that he has chosen easy courses he can glide through with minimal effort, and that he is often late or absent. Zac admits he stays up late at night, composing and recording music, and then has power struggles with his mother over getting to school. He has no license or car, so she has to drive him.
He took the ACT college admissions test without practice and got a 27, about the 86th percentile, a high score for having taken it cold. But he knows that to really stand out, he has to nudge up his score. “I’m panicking,” Zac said this fall, a few weeks before he was supposed to take the ACT for the second time.
The truancy began junior year, when he decided he needed an after-school job to make money to buy musical equipment.
He put on a collared shirt, a tie and dress shoes for an interview to bag groceries at Mike’s IGA, three blocks from his house. “I can’t believe I was worried that I wouldn’t get the job,” he said, laughing.
He earned $7.25 an hour after school, and a dollar more on Sundays. But he was taking hard courses like honors precalculus and trig, and his grades dropped.
He stopped working at the supermarket this fall to concentrate on his studies. But he sees himself falling into the same pattern as his older brother, Chris, 20, who became so depressed in high school that he barely graduated. Chris lives at home, drifting through part-time minimum-wage jobs, contemplating a factory job.
Zac craves success yet fears failure.
He plays bass in the school orchestra, bass guitar in jazz band and saxophone in marching band. He can imitate Johnny Cash’s testosterone-filled growl in “Folsom Prison Blues,” or Art Garfunkel’s angelic high notes in “The Sounds of Silence.”
Broad-shouldered, with a hangdog stoop and long dirty-blond hair, he was once a misfit, teased for using big words. But playing music with his big brother and their band, Pegasi, at Topeka venues like a dive bar called the Boobie Trap has brought him out of his shell.
“My fantasy job would be making it big as a musician,“ he said. “I don’t know what a more realistic option would be.”
At the parent-teacher conference, his band teacher, Mr. Bradshaw, asked Zac what his plans were after graduation. To study sound engineering, Zac replied.
You need to show up, the teacher told him: “The thing about college is, there’s no grade recovery. You get one shot.”
‘College Is Not the Only Option’
In late September, Topeka High held a senior parent information night, encouraged by the new superintendent, Tiffany Anderson, who has made college attendance a priority. The guidance counselors were startled — and pleased — to find a line of parents stretching down the main hallway of the school.
The parents were told that to be assured admission to most of the big state universities in Kansas, students had to have at least a 21 on the ACT, the average at Topeka High, or be in the top third of their class. Scholarships, a counselor warned the parents, are harder to get than they might think.
But the counselors did not assume that all students aspired to go to college. “College is not the only option,” Angela Locke, a guidance counselor, told the audience. “Sometimes it’s not even the best option.”
While the counselors “firmly believe the philosophy that college is great,” Ms. Locke told the parents, “Our world is a different place than when most of us were going to school.”
She added, “I know when I was going to school, if you were going to college, you probably were going to get a very good job.” A very good job could no longer be taken for granted, she implied.
Last year, she said, Washburn Institute of Technology, once the vocational arm of the Topeka public schools and now a division of Washburn University, had added a phlebotomy program. “How cool would it be to be able to work my way through college as a phlebotomist?” Ms. Locke said.
This year, Washburn Tech added cosmetology, which is “wonderful for Topeka,” she added. “We feel pretty confident that they’re not going to take a lot of tuition money from our students and disappear.”
Ms. Locke went on to extol Topeka High’s R.O.T.C. program and the benefits of an apprenticeship or a union. “We are going to help students get from Point A to Point B, and it’s not always going to be college, and that’s O.K.,” she said.
There was little talk of how to prepare for standardized tests like the ACT or the SAT. At the very end, responding to a question from the audience, a counselor said that “a lady from Manhattan” would be offering one session of ACT prep during the school day in the week before the test, and that it would cost $40. The session had been arranged by the school’s gifted facilitator, and people were told that for further details, they could go to the counseling center and pick up a flier. They were also told to go to a website, Number2.com , for free online test prep.
“We do have some study materials for you, practice test booklets” and links to online resources, said Kayla Banzhaf, the testing coordinator.
A parent asked about the deadline to sign up for the ACT. “Last Friday,” a counselor replied. “There is a late fee.“
How to Become the First in the Family to Go to College
For Nathan Triggs’s mother, Tera, Topeka High was the bright light of her life. She hung out at the mall; worked at Bobo’s, a local diner; and performed with the flag team. She loved French class, because it was easy for her and she liked the teacher’s accent. She learned to make crepes in French club. After passing home economics, she took interior design, and fantasized about becoming an interior designer.
But she is also an object lesson in how elusive college can be, and how hard it often is to get there without role models and help from a wealth of people, including parents, teachers and tutors.
Ms. Triggs, 39, graduated in 1995 and wanted to go to college, but somehow the opportunity passed her by and she never applied. “I wasn’t a very good student,” she said, apologetically. “I only made the honor roll a couple of times.”
Soon she was pregnant with Nathan’s brother, “and then I was a mom,” she said.
Now she works in a center for people with developmental disabilities, and was recently promoted from aide to secretary.
As she spoke, Ms. Triggs sat in her cozy living room in a small bungalow on a red-brick street, in a part of Topeka where a real estate agent warned me to watch my back. But on a street without public street lights, the Triggs house is strung with twinkling white decorative lights that blink out a welcome.
As the memories of high school came flooding back, she dashed upstairs to her bedroom. On the bureau, under a pile of clean clothes, was a pale blue-glazed ceramic vase, decorated with rosettes. She had made it in high school art class and saved it for more than 20 years.
It would be “awesome,” she said, for Nathan to go to college.
But Ms. Triggs’s inexperience means she does not know how to help put him through the paces of applying. His father, Tim Sturgeon, never went to college either. His older brother dropped out of high school.
Has Ms. Triggs looked at Nathan’s college choices? “No,” she said.
Has she looked at his essay? “What essay?” she asked, softly, as Nathan sat across from her in their living room, petting his black dog, Lucky.
“I am a very determined person. I have always found a way to get the job done, no matter the level of difficulty the task may hold. I developed this trait at a young age by working for everything that I have by earning money doing farm work. On a farm, nothing comes easy enough.” – from Nathan’s first draft of his college essay.
Two Generations, Two Different Paths to College
“She knows what she needs to do,” Jennifer Womack, a college-prep teacher, told TaTy’Terria Gary’s mother at a recent parent-teacher conference night at Topeka High School. “She knows what she wants to do, and she’s taking care of it.”
The glowing comments from one teacher after another came to sound like a broken record, though with a happy tune.
But TaTy, whose teachers have encouraged her long-term plans to go to medical school, was not the only one on the receiving end. Her mother, Tracy Gary, 35, came in for some of the credit.
“She’s defying that whole stereotype that a single mother cannot raise a child successfully — pshaw!” said Teresa Leslie-Canty, the teacher in a class where TaTy mentors younger students, as mother and daughter sat across from her in the high school gymnasium.
Teenage pregnancy can be part of the high school experience at schools across America, and Topeka High is no exception. Several girls here told me that they had classmates who had become pregnant, and that they felt sorry for them because life was suddenly much harder, and they were stigmatized.
“So many girls are looked down upon because of it,” said one of TaTy’s classmates, Mya McFadden, whose mother was a student at Topeka High when she had Mya and her twin sister, Deja, 17 years ago.
The twins’ mother and father were high school sweethearts, a dream couple, so good-looking that they turned heads as they walked through the halls holding hands. But the gloss quickly wore off when their father, Michael McFadden, had to join the Army to support his children and was posted to the war in Iraq.
He came back with severe post-traumatic stress disorder. The couple split, and the girls went to live with him. Like TaTy, they have taken their family history as a warning, and they are determined to go to college.
Tracy Gary was a senior at Topeka High when she gave birth to TaTy, her oldest child. She turned 18 two weeks after giving birth. Though she was allowed to walk in her high school graduation, she had half a credit left to earn, she said, and did not receive her diploma until more than two years later.
TaTy was not planned, Ms. Gary said, “She was a rebellion against my family.”
But Ms. Gary was also repeating history. Her mother was 15 or 16 when she had a son. Ms. Gary’s sister had her son at about 15 or 16, too. Ms. Gary was raised mainly by her grandmother, because her own mother, she said, had other interests. “My mother cared more about the men,” she said.
She resisted her mother’s pressure to have an abortion, and being a mother forced her to mature. “When I had her, I started to grow up,” Ms. Gary said. “I knew I was responsible.”
Ms. Gary has two other children, a 10-year-old girl and a boy about to turn 14. But as TaTy’s teacher said, Ms. Gary broke the cycle. She worked at fast-food jobs, advancing into management, to support her children, then realized she wanted more out of a career.
So she enrolled at Washburn University, a public institution in Topeka with a neatly groomed campus and a serious atmosphere. She is close to a degree in criminal justice, a field she chose because she always wanted to be lawyer, and this comes close.
Ms. Gary was ambitious in high school but not academically focused. She was a manager for track and basketball teams and spent four years in the Marine Corps R.O.T.C. because she liked the structure and having “somewhere to go, something to do.” She thought about going into the Marines, until she became pregnant, but she did not consider college an option.
She is proud of TaTy for being more committed to her studies than her mother was. She attributes much of her daughter’s success to the guidance of her college-prep teachers. “I didn’t have anybody telling me, ‘Hey, you’re good in English, so you should take those A.P. classes,’ ” Ms. Gary said.
Last year, Ms. Gary moved TaTy and her two younger siblings to Pauline, on the outskirts of Topeka, where the city gives way to antique stores, gas stations and car dealerships, then finally to railroad tracks and cows. The family lives in a ranch house in a subdivision of similar houses. “I’m real big on stability,” she said.
Ms. Gary works taking care of children at the Villages, a group home for children who have been abandoned, abused or in trouble with the law. So she relies on TaTy to help take care of her younger sister and brother.
When it comes to college, Ms. Gary said, she will support TaTy in whatever she decides to do. But she hopes her daughter will go far enough from Topeka that she will not be able to return home on weekends, even if she feels homesick. “I don’t want her to ever think about quitting,” Ms. Gary said. “I don’t want her to walk in my shoes.”
Wondering if Higher Education Is the Cure-All
When Charla Shaner appeared at a recent parent-teacher conference with Zac, she looked immaculate in pressed coral blouse, skirt and smooth blond hair. Few of the teachers realized how much effort went into maintaining that middle-class facade.
Ms. Shaner’s intense focus on her two sons helped steer them into the Topeka public school system’s gifted track, based on their exceptionally high IQ’s in elementary school. She has a bachelor’s degree in early childhood education and for some years ran a daycare center out of her house.
But Zac’s family is downwardly mobile. Ms. Shaner, 51, and her two sons are barely making ends meet, surviving mainly on government benefits. They are emotionally overwhelmed by the day-to-day tasks of life and school.
Zac and his brother wonder whether the American dream of a college education is still attainable for them, and if it is, whether they can afford to go to a college where they will blossom.
About seven years ago, Ms. Shaner lost her daycare license after dropping a 6-month-old on the head while she tried to hold the baby, talk on the phone and watch out for a pot of boiling water in the kitchen.
She attributes the accident to a traumatic brain injury she suffered in a childhood car crash, which left her in a coma. She still has damaged peripheral vision and a squint in her right eye. She misses taking care of babies. But she has not tried to renew her daycare license or find another job in her field, because, she said, the accident made her realize that she should not be taking care of other people’s children.
So she supports the family largely on her disability payments, in addition to small amounts in child support from her ex-husband, which she expects to run out now that Zac is older.
The family lives in Oakland, in northeast Topeka, a neighborhood of small houses, porch ornaments, chain-link fences and barking guard dogs. Ms. Shaner’s parents grew up in the same predominantly white, working-class enclave in its golden era, but the community ties have frayed since then. She rents her house at a discount from her father, Charles Wray, 78, who has worked as a pastor, a Goodyear tire maker and a salesman of church directories. In retirement, he is a self-taught Norman Rockwell-style painter of portraits. Both he and Ms. Shaner’s mother have college educations.
Ms. Shaner sometimes quarrels with her Puritanical father about overdue rent. But she has made paying the water and electric bills a priority. She has seen other houses in the neighborhood go dark, and people without running water who have had to wear donated clothes until they are dirty and then throw them away. She does not want that to happen to them.
She volunteers at her Nazarene church’s food pantry and used clothing bank, partly from the goodness of her heart and partly out of necessity. In exchange, she takes home extra food and clothing for her family.
The food selection can be arbitrary; one week, they ate a lot of pepperoni and tomato sandwiches. The suit jacket that Zac wears in the orchestra came from the charity.
Ms. Shaner’s sons see that going to college – as she did – is not a panacea. She still needs food from the food pantry.
As he considers college, Zac alternates between optimism and anxiety. He has received many fliers in the mail saying he is a “priority candidate” for community college, but he is determined to go to a four-year college despite his spotty school record. “I know it sounds like blown opportunities, but I know what I want,” he said.
Is it living or just existing
If living means a mask
Is it dying or is it trying
If dying means taking it off
— lyrics by Zac Shaner, a.k.a. Shane Wray
For Some Students, It's Hard to Imagine Life Away From Home
Topeka High’s principal, Rebecca Morrisey, understands how hard it is for kids to visualize going to college out of state, or even leaving Topeka.
Ms. Morrisey, who took over as principal this year, grew up on a farm in Atwood, a city of 1,200 people in northwest Kansas. When she first arrived in Topeka, many years ago, it struck her as “a metropolis.”
The first thing you notice when she walks into a room is how tall she is, six feet in flats. Being so tall was her ticket to becoming a basketball player and coach, and a first-generation college graduate. Her coaches helped her figure out how to apply to college.
She cobbled together academic and athletic scholarships and low-income grants to go to St. Mary of the Plains College in Dodge City, Kan. (The college has since closed.) Her three children did not stay close to home. One runs a cytogenetic lab at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., another is in Boston training to be an architect and the third is a nurse-anesthetist in Kansas City, Kan.
“I have kids on the east side who have never been to the mall on the west side,” Ms. Morrisey said. “I grew up that way. My grandparents were six miles and 10 miles from us. I didn’t get to Oklahoma until I was an adult. I didn’t get west of Denver.”
Just persuading students that going away might be an option can be hard. To nudge them, Ms. Morrisey and Phillip Wrigley, one of the college prep teachers, arranged a trip the other week to Rockhurst University, a Jesuit institution in Kansas City, Mo., where Ms. Morrisey coached basketball and Mr. Wrigley earned his master’s degree.
As they walked through the lush, green campus, one of the seniors, Mya McFadden, a petite, spunky twin, told her teacher why she wanted to be a midwife. “I have a soft spot for teenage girls because my mom was 15 when she had me and her,” she said, gesturing toward her twin sister, Deja, walking next to them.
Mr. Wrigley urged her to consider leaving Topeka. Being in Kansas City, at a place like Rockhurst, would open the door to practicing medicine in some of the most sophisticated academic medical centers in the country. “I’m going to say something snobby,” he said. “Stormont Vail is a good hospital, but it’s in Topeka.”
“But I like Topeka,” Mya said.
Topeka Schools Chief: ‘Our Mind-Sets Are the Barrier’
Topeka High was authorized during the Roaring Twenties and opened in 1931, in defiance of the Wall Street crash. Designed as a Gothic temple to education, it is still a high school out of Hollywood casting, so prized by its graduates that it has an on-site archivist, Joan Barker, a 1971 graduate, whose salary is paid by donations.
Yet its record of achievement does not match its lofty architecture. The percentage of students who graduate from high school hovers in the low 70s, compared with about 10 points higher nationally. After graduation, about 45 percent enroll in four-year colleges, and 17 percent in community colleges, in line with the national average for urban schools.
The new superintendent of city schools, Tiffany Anderson, wants to change that.
She arrived in Topeka this summer from Missouri, where she was the superintendent of the Jennings School District. That district adjoins Ferguson, where the killing of an unarmed black man by a police officer who said the man had fought for his gun propelled the Black Lives Matter movement to the national stage. (A grand jury declined to indict the officer.) She was hailed as Topeka’s first African-American female schools superintendent.
When Dr. Anderson began working here, she found that the school system was using a popular program, Advancement Via Individual Determination, or AVID, to identify middle school students with college potential, and to groom them for college by encouraging them to take honors courses and then advising them on the application process. The program has had mixed results across the country.
She said she was bringing a tracking system to Topeka from Jennings, which will follow every senior by name and document whether they have applied to college or the military, how many applications they have filed, whether they filled out a financial aid form, their highest standardized test score, and whether they were ultimately accepted.
In Missouri, Dr. Anderson became known for community-building innovations like installing washers and dryers in school buildings so families could do their laundry. She has already made an impression in Topeka for rushing around in suits paired with white sneakers, accessorizing to match school colors, and refueling with Dr Pepper, a popular drink among Kansans, who pride themselves on being nonconformist.
Dr. Anderson keeps an apartment in Topeka, but drives home most nights to Overland Park, where her husband is an OB/GYN and surgeon. But the commute has shrunk to an hour, as opposed to four hours from Jennings.
She is the general to the troops, issuing inspirational declarations like: “Money’s no barrier, because it’s really not. Our mind-sets are the barrier.”
The Pitch for Technical School Over a Four-Year College
The wood shop and the metal shop have been closed, but if you want to learn how to fix cars, Topeka High School’s legendary auto mechanics class is for you.
The shop is a car addict’s paradise. At the moment, students are cutting a car in half as part of a project to build a homemade electronics trainer, a learning tool for mechanics. They are also overhauling a go-kart and practicing their painting skills on a bus that will be redone in black and gold, the school colors, and paraded at football games.
At the beginning of senior year, the teacher, Dean Fairweather, a blues guitar player who looks like a Hells Angel and speaks with a strong British accent, brought in a pitchman from Universal Technical Institute to speak to the students, so they could see, Mr. Fairweather said, “that there’s more to life than flipping burgers.”
It was a slick exposition, one of the most persuasive the students will hear on the pros and cons of technical school compared with a four-year college.
The pitchman, in fancy cowboy boots and belt buckle, presented the technical institute as, effectively, the Harvard of what he called the transportation industry. After graduation, he told the students, they would be in demand everywhere from Porsche to Nascar.
He did the math. The average rent in Topeka is close to $600, he said. A minimum-wage job brings in, he figured, about $15,000 a year, $1,000 a month after taxes. After paying rent, you still need a phone, a car, utilities, groceries, food, fuel, furniture. “What are your options?”
“Get a better job,” one boy replied. Bingo.
But a high school diploma is not enough, the representative said. “Having just a diploma is like telling an employer you can brush your own teeth.”
The military is a “phenomenal choice,” if you make a career out of it, he added.
A traditional college degree is one approach. “You will never learn too much,” he said. “You will never be too smart.”
But, he argued, if you feel at home in the shop and want to go right into a job, “do not waste your money.”
Americans are overeducated for the jobs available, he told them. “If everybody went to college, there’s going to be a lot of unemployed people like there is — there is going to be a lot of people not working in their fields.”
Nathan Triggs, one of the class stars, was in the front row, listening carefully. He took the trouble to talk to the rep, and they bonded over trucks. Nate signed up for a personal interview — to keep his options open, he said.
One Student’s Calculation: College vs. Trade School
The knowledge Nate Triggs has gained from the farm may not be from books, but it is shaping his vision of his future, and of what he could do after graduating from Topeka High if he gets a college education.
He works construction with his father. One of his favorite projects was the hip roof that they built for his grandfather’s house. I had never heard of a hip roof , but when he took me to see it, I thought it looked like the kind of roof that Frank Lloyd Wright put on his celebrated prairie houses.
Nate had never heard of Frank Lloyd Wright. But he nodded appreciatively at the concept of a prairie house. His father’s farm, outside Holton, Kan., is prairie country. Nate’s experience working construction makes him think that if he goes to a four-year college, he would like to become an architect. He has done the research, and found that Kansas State University has a good architecture and engineering program. He is good at math, so he would like to try there.
Or maybe he will become a game warden, he said. As a hunter, he has seen animals horrifically mutilated by other hunters. He would like to prevent that. In his family, they never kill wild animals wantonly, and they always eat what they kill.
But he is also a good auto mechanic, and can envision working at the Ford dealership in town.
Nate has been hunting and fishing for as long as he can remember – catfish, bass, rabbits, raccoons, coyotes, deer, quail, turkeys, doves. He knows all their quirks and habits.
One recent morning, he loaded his Mossberg shotgun, put on his camouflage vest and headed out through his 80-acre family property with his hunting buddy, Tyler, to the cedar copse where the doves roost.
Two dogs followed: his black dog, Lucky, who commutes with him from Topeka each weekend in his Chevy S-10 truck, and a yellow Labrador trained as a bird dog. It was near dawn. On the horizon, Tyler saw a truck passing slowly on the highway and waved. “It’s loaded down with corn,” Tyler said. “It’s harvest time.”
They could tell the doves by their distinctively angled wings, their quickness and their flight pattern, more soaring than flapping. Tyler took three shots, but Nate never raised his gun. He reminisced about how he once let three male turkeys strut right past him down a creek bed as he sat behind a ground blind, because he was holding out for deer. “I coulda smoked ’em,” he said. “I didn’t think they was quite big enough.”
It is a character trait, this perseverance, this willingness to wait. Isn’t that what college is all about? Delayed gratification.
College or trade school?
He is weighing the benefits of each. “With technical school, you go in for what you go in for,” he said. “With four years of college, you expand your interests.”
His grandmother Ann Matthews, a retired teacher, said it should be up to him. “He’s analytical, so I think he’ll make a good choice,” she said.

Confronting College Debt
“Everyone’s going to have crisp and nice new pants this year,” TaTy’Terria Gary told the group of about 20 girls gathered around her in the second-floor hallway at Topeka High.
They are members of the step team, a dance group that performs at basketball games, and TaTy is speaking to them as their captain.
“From now on, you are upstanding citizens,” TaTy said. “Don’t talk back to your teachers. Don’t be starting fights. Don’t be causing drama. And y’all better be on time.”
She sees herself empowering girls who probably wouldn’t make the cheerleading squad. She does not ask the girls for more than she asks of herself. When something needs to be done, TaTy does it, and it is that ability to put one foot in front of the other and keep moving forward, ignoring any obstacles, that seems to be moving her toward college. When she needs help, she asks for it.
Last Saturday, Oct. 22, was the day for college-bound Topeka High seniors to take the ACT, the standardized test favored by Midwestern colleges and universities. That day, TaTy got herself up, dressed and went to McDonald’s for a breakfast of sausage and cheese on a biscuit with grape jelly and hash browns. She drove herself the half-hour to school in her used 1999 Chevrolet Tracker, and had enough time to socialize with classmates before the test.
The science section was hard, she said; English was easier. She’ll find out her score in about two weeks. Meanwhile, she has filled out the Fafsa, the financial aid form, putting down parental income of under $18,000. She was excited when the financial aid calculator estimated that she could be entitled to nearly $11,000 a year in financial aid.
“If I go to Oklahoma Baptist University, that will cover one-third of everything,” she said gleefully, naming one of the schools she is applying to.
Her college-prep teacher, Jennifer Womack, has tried to give the seniors a sense of the cost of college beyond tuition, including extras like “Walmart runs,” drugstore supplies, gas, parking, and room and board. TaTy has absorbed this lesson. One of the colleges she is interested in has free laundry, she said.
But she is not worried about college debt. She is certain that education is a good investment. She is counting on making enough money eventually as an obstetrician-gynecologist to pay off her college loans. “Let’s say I go into private practice and earn $5,000 a kid,” she said. “That’s very profitable.”
Getting Motivated to Seek That Degree
It was Saturday night, and Zac Shaner’s four-man band, Pegasi, was setting up at the Boobie Trap, a small, dark cave of a bar on a sketchy stretch of Sixth Avenue in central Topeka.
Zac plays bass guitar and sings in the band. This night, his drummer, a finance major at Washburn University who wants to go into bankruptcy law, is the first person in the door, and begins setting up.
“I can tell a lot about someone’s playing just by their attitude,” the drummer said. “How they carry themselves. How they act around people.”
He joined the band because he was touched by Zac’s gentle personality. “I don’t really sense any form of ego with him,” he said.
That sweetness and humility come across in Zac’s interactions with teachers, as well, and have endeared him to them even as they worry that he is not living up to his potential. Is it fear of failure? Perfectionism? They aren’t sure, but they want to help.
He has so much charm and talent, they say. He is college material – good college material – if only he could be more consistent in his schoolwork.
“Talk to me, Zac,” Murray Moore, his business teacher, said to him at parent-teacher conferences the other day.
Zac is taking business class in the hope that he can use the knowledge he gains to promote his music and help his band. His grades range from strings of 100s one week, when he is coming to school, to rows of zeros the next, when he is not.
“He will pass,” Mr. Moore said.
But he could be a star. Zac explained that he goes through “cycles of motivation.” Part of his problem is psychological, he said: “When everybody’s on my back and forcing me to do things, I want not to do it. When people say it’s up to me, I want to succeed.”
Mr. Moore listened, then told Zac’s worried mother, Charla, “He has to help himself.”
Clearly uncomfortable with the discussion, Zac tried to change the subject. “Is that a Jerry Garcia tie?” he asked, looking at his teacher’s neckwear. He has one at home, he said.
“It’s Stacy Adams,” Mr. Moore replied. Then warming to the subject, he tried to turn the question into a homily on positive thinking.
Mr. Moore was an assistant basketball coach for a losing team, he said. He told himself that every time the team won, he would treat himself to a new tie. The team turned itself around and was 19-4. “That got expensive,” he said, but he persisted.
The moral of the story: “You’ve got to invest in you and in what you do.”
“He likes ties,” Ms. Shaner said.
“It’s not about the tie,” Mr. Moore said. “You could buy a new set of picks. Reward yourself. What you need is a Yates banjo or a Scheerhorn dobro.”
Zac grinned shyly.
Missed Deadlines Complicate the Quest for Higher Education
Was it perfectionism? Fear of failure? Or just teenage disorganization?
It could have been any or all of those things, but the bottom line was that somehow, both Zac Shaner and Nathan Triggs flubbed taking the ACT test for college admission in October.
Zac, the musician, who has a habit of staying up late, managed to overcome his problem of oversleeping. At 6:30 a.m. on test day, he popped up from the living room couch where he usually sleeps, and woke his mother, Charla.
She made him breakfast. But an hour later, just as they should have been leaving for Topeka High, where the test was being given, he had a sneezing attack. When he couldn’t stop, he decided not to take the test, for fear of disturbing other students and hurting their scores.
“Right as we were about to leave, I started getting really bad allergies,” Zac said the next day. “Even after I took some allergy pills, I was still sneezing. I felt it wouldn’t be responsible for me to go sneezing like that. People would be distracted.”
So ignoring his mother’s entreaties, he went back to sleep.
Nathan’s problem was different. A few days before the test, he was closing some tabs on his computer screen when he realized that he had never pressed the final button to register for the ACT. He had filled out the form, but never submitted the payment – in his case a waiver allowing him to take the test free because of financial need.
“It was a freak accident,” he said later.
It was too late even to pay the late fee. So he registered to take the test in December.
“It kinda sucks,” Nathan said.
Their classmate TaTy’Terria Gary woke up, got breakfast at McDonald’s and arrived at Topeka High in time to take the test, a sign of her disciplined approach to life. She is the captain of the step team, holds down an after-school job and has a 3.7 grade point average. Her top college choice at the moment is Oklahoma Baptist University, because she wants to go somewhere with a spiritual component.
TaTy, who hopes to become a doctor, said she believed spirituality was important for mental and physical health.
“I can’t really make it to church on Sundays because I work,” she said. “I like to be around people who have faith. One of my pet peeves is that you have to believe in something, even if you believe that we were birthed from the stars and the moon. I feel like believing in something helps you strive, helps you be a better person, because you are working toward a goal. Even if you believe in yourself, that’s O.K.”
TaTy’s belief in herself has helped her stay organized throughout the college search. And what happened to the boys shows how indecision, passivity and self-doubt can make an extraordinarily complex process even more daunting. Students must meet all sorts of deadlines for tests and applications, as well as make decisions about a future that may be hard to imagine, not to mention pay application fees and begin to come to terms with the ultimate cost.
Nathan has support from his college-prep teacher, and Zac from a sympathetic counselor. Still, with parents who are cheerleaders but do not have the experience, time and money to drag them through the process, it was easy for things to go wrong.
Such mistakes are fairly common, and the boys can still recover, said Paul Weeks, senior vice president of client relations at ACT and a former admissions dean at Ripon College in Wisconsin. He added that Zac’s “really strong score” of 27 the first time he took the test (without any commercial test prep) and other qualities, like his musical talent and his writing ability – he had a 33 out of 36 on the English section of the test – could propel him into all but the most selective colleges.
A little over half of students who retake the test improve their scores, but by just one point on average, Mr. Weeks said.
His advice to Nathan was to call the colleges he is most interested in and explain what happened. “My advice is always to contact the schools rather than speculate or make assumptions” about how they would react to a delayed ACT score, Mr. Weeks said.
Zac consoled himself that it was just as well that he did not take the test, because he hadn’t studied for it. But he knows that raising his score would help his chances of receiving scholarship aid.
Both boys have somewhat solidified their plans. Zac said he would aim to go to Washburn University, a public institution in Topeka, for the first year or so, where his family’s low income might qualify him for a free ride. He would live at home and return to work at Mike’s IGA – stocking, bagging groceries and running the cash register. Once he had enough money saved, he would transfer to the University of Denver or the University of Central Missouri to study sound engineering. But he would still want to stay fairly close to home, in case his mother or older brother needed him.
“I want to get out and explore,” Zac said. “But I don’t want to be too far, so I could come back in an emergency.”
In English class, Zac wrote a college essay about rebelling against his mother’s religious beliefs, and against his conservative upbringing. “The day I denounced my religion, the day I made my mother cry, was the day I decided to live,” he wrote. His teacher called it “powerful” in a margin note. But Washburn does not require an essay. He has filled out the Common Application, but that also seems like an empty exercise.
“They say that more than 700 colleges accept the Common App,” he said, quoting the website. “But it seems like not the ones I’m interested in.”
None of the people he knows at Topeka High are applying to private universities. “There’s always the kids who get 4.0s and perfect ACT scores, and numerous letters and accolades,” Zac said. “I’m not sure what their plans are, college-wise. I think some of them might go straight for the Ivy League.”
His teachers all say he has spark. Did he ever think of trying to get into a small, liberal arts college out of state? “I look at a lot of these schools that are out of reach right now, and my spark is intimidated,” he replied.
Nathan is thinking of Allen Community College, a short drive from Topeka, as his “safety” application; Washburn University as his “best fit,” because his stepmother works there and could get him a tuition discount; and Kansas State as his “stretch,” because, he said, it is known for its engineering and architecture programs. He does not have any brand-name colleges outside Kansas on his list, and neither do most of his classmates.
Today, Phillip Wrigley and Jennifer Womack, who teach the college prep classes that TaTy and Nathan are in (Zac is in a gifted track), will be asking them for proof that they have filed some college applications by the priority deadline of Nov. 1 – perhaps a screenshot of a confirmation email.
Soon they will be buffing their essays, because even if they are not needed to apply to most local colleges, they will be needed to apply for scholarships. The kids will also be learning the intricacies of financial aid.
Mr. Wrigley said the students thought about college in a practical way. “I think they are thinking about cost,” he said. “They are thinking about feasibility, about what’s going to fit for me. They’re very much pragmatists when it comes to college.”
Yet the other day in class, Nathan was pondering an intangible benefit that college could offer.
He asked his study group to help him understand the concept of social capital, which had come up in government, his favorite class.
“What’s a network?” the teacher, Mr. Wrigley, asked, as Nathan wrote the word on a whiteboard.
“A community,” Nathan replied.
“What defines a community?”
“I have no clue of the definition,” Nathan said. “But I can tell when something is.”
Eventually, the students arrived at the concept of building social capital through dinner parties, mentors, knowledge and connections. The teacher told them that was what they were doing in class.
It’s also something they would do in college.
College: What It's All About and Why It Matters
You might think that college is just high school continued, but it’s not. College opens doors for you that high school doesn’t. And college can change you and shape you in ways that you might not imagine.
Unlock Opportunities
Thanks to all the knowledge, skills and experience you’ll gain in college, you’ll be able to adapt to a greater variety of jobs and careers. Statistics show that a college diploma can help you:
- Make more money
Become More Independent
College work will challenge and inspire you. In college, you will:
- Explore subjects in greater depth than you did in high school
- Choose your own courses and class schedule
- Decide which extracurricular activities you’ll focus on — and how much time you’ll give them
College helps students develop into mature, responsible and independent adults. But you’re not entirely on your own: colleges offer students many kinds of help making this transition, such as tutoring and academic advising as well as counseling and other support .

Explore Your Options
One of the great things about being able to choose your own courses is that you get the opportunity to explore. You can try classes in a lot of different subjects, or you can dive right into a favorite subject. You may choose to begin training for a career right away. Or you may pick a major after taking some time to check out your options. Colleges offer classes and majors in subjects you’ve studied in high school — plus many more that you haven’t.
Explore Outside the Classroom
College is about much more than just course work. A campus is its own world, and students have the chance to experience a wide range of activities. For example, college students may be able to:
- Publish newspapers
- Create TV and radio broadcasts
- Run their own government
- Stage performances
- Play sports
- Volunteer to improve their communities
The list goes on. And you don’t have to live on campus to experience campus life.
Invest in Yourself
As you take on college work and participate in college life, you’ll encounter new ideas and challenges. Along the way, you’ll:
- Build knowledge, skills and brainpower
- Discover new passions
- Follow and satisfy your curiosity
- Learn more about yourself
- Bond with new friends
- Prepare for a future in which you’re better equipped to give back
Whatever your destination, college can help you get there — even if you don’t know where “there” is yet. Whether you’ve mapped out a long-term plan or you see new possibilities every day, college can help you become your future self.
Find the right college for you.
Related articles.
U.S. News Best Colleges

Expert advice, rankings and data to help you navigate your education journey and find the best college for you.
National Universities
Liberal Arts Colleges
More Rankings & Lists
Latest College Advice
Schools in the National Universities category offer a full range of undergraduate majors, plus master's and Ph.D. programs.

Princeton University

Massachusetts Institute of Technology

Harvard University
See All the Data With College Compass
See expanded profiles and advanced search for more than 1,800 schools, all entering class stats, including SAT scores and GPAs and financial aid packages given to students by schools.
Liberal Arts Colleges emphasize undergraduate education and award at least half of their degrees in the liberal arts fields of study.

Williams College

Amherst College

Swarthmore College
Best Value Schools
The higher the quality of the program and the lower the cost, the better the deal.
- # 1 Princeton University
- # 2 Harvard University
- # 3 Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Other Rankings & Lists
- Regional Universities
- Regional Colleges
- Engineering Programs
- Historically Black Colleges and Universities
- A-Plus Schools for B Students
- Business Programs
- Top Public Schools
- Ivy League Schools
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
U.S. News College Compass
Unlock our comprehensive data, rankings and interactive tools to help you and your child choose the right college.
Expanded Profiles
There are more than 500,000 data points available exclusively to College Compass subscribers.
Test Scores
We break down the SAT/ACT scores and high school GPAs for each college's freshman class.
Financial Aid
Discover how many students receive need-based and merit-based scholarships and grants.
Pick the Perfect Major
Discover the perfect major for you based on your innate wiring. The Innate Assessment sets you up for success by pairing you with majors, colleges and careers that fit your unique skills and abilities.
Colleges By State
- Connecticut
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia
Colleges By Metro Area
- Abilene, TX
- Asheville, NC
- Atlanta, GA
- Augusta, GA
- Baltimore, MD
- Baton Rouge, LA
- Birmingham, AL
- Buffalo, NY
- Charleston, SC
- Charlotte, NC
- Cleveland, OH
- Columbus, OH
- Des Moines, IA
- Detroit, MI
- Gainesville, FL
- Grand Rapids, MI
- Greensboro, NC
- Greenville, SC
- Houston, TX
- Huntsville, AL
- Indianapolis, IN
- Jackson, MS
- Jacksonville, FL
- Kansas City, MO
- Knoxville, TN
- Lakeland, FL
- Lancaster, PA
- Las Vegas, NV
- Los Angeles, CA
- Louisville, KY
- Lynchburg, VA
- Madison, WI
- Memphis, TN
- Milwaukee, WI
- Minneapolis, MN
- Montgomery, AL
- Nashville, TN
- New Orleans, LA
- Orlando, FL
- Pensacola, FL
- Philadelphia, PA
- Phoenix, AZ
- Pittsburgh, PA
- Portland, OR
- Raleigh, NC
- Richmond, VA
- Rochester, NY
- Salt Lake City, UT
- San Antonio, TX
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Savannah, GA
- Seattle, WA
- Spokane, WA
- Springfield, MO
- St. Louis, MO
- Virginia Beach, VA
- Wilmington, DE
- Worcester, MA
Search U.S. News Best Colleges
Whether you're looking for a small campus in Boston or an engineering program in Albuquerque, we'll help you find the best college for you.
Applying To College
Apply to College

Colleges That Enroll the Most Transfers
Best Value Out-of-State Public Schools
Backing Out of Early Decision
Having a Service Animal in College
Paying For College
Overlooked Ways to Pay for College

Colleges With Cheap Out-of-State Tuition
See Average Student Loan Debt Change
Scholarships for BIPOC Students
Most Recent
What Not to Wear on Halloween in College

How to Study Real Estate Online
Top Schools for Internships, Co-Ops
College Students and Natural Disasters
What to Know About HSIs
Choosing The Right College Or University
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Is College Worth It?
As economic outcomes for young adults with and without degrees have improved, americans hold mixed views on the value of college, table of contents.
- Labor force trends and economic outcomes for young adults
- Economic outcomes for young men
- Economic outcomes for young women
- Wealth trends for households headed by a young adult
- The importance of a four-year college degree
- Getting a high-paying job without a college degree
- Do Americans think their education prepared them for the workplace?
- Is college worth the cost?
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
- Current Population Survey methodology
- Survey of Consumer Finances methodology

Pew Research Center conducted this study to better understand public views on the importance of a four-year college degree. The study also explores key trends in the economic outcomes of young adults among those who have and have not completed a four-year college degree.
The analysis in this report is based on three data sources. The labor force, earnings, hours, household income and poverty characteristics come from the U.S. Census Bureau’s Annual Social and Economic Supplement of the Current Population Survey. The findings on net worth are based on the Federal Reserve’s Survey of Consumer Finances.
The data on public views on the value of a college degree was collected as part of a Center survey of 5,203 U.S. adults conducted Nov. 27 to Dec. 3, 2023. Everyone who took part in the survey is a member of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. Address-based sampling ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this report , along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
Young adults refers to Americans ages 25 to 34.
Noncollege adults include those who have some college education as well as those who graduated from high school but did not attend college. Adults who have not completed high school are not included in the analysis of noncollege adults. About 6% of young adults have not completed high school. Trends in some labor market outcomes for those who have not finished high school are impacted by changes in the foreign-born share of the U.S. population. The Census data used in this analysis did not collect information on nativity before 1994.
Some college includes those with an associate degree and those who attended college but did not obtain a degree.
The some college or less population refers to adults who have some college education, those with a high school diploma only and those who did not graduate high school.
A full-time, full-year worker works at least 50 weeks per year and usually 35 hours a week or more.
The labor force includes all who are employed and those who are unemployed but looking for work.
The labor force participation rate is the share of a population that is in the labor force.
Young adults living independently refers to those who are not living in the home of either of their parents.
Household income is the sum of incomes received by all members of the household ages 15 and older. Income is the sum of earnings from work, capital income such as interest and dividends, rental income, retirement income, and transfer income (such as government assistance) before payments for such things as personal income taxes, Social Security and Medicare taxes, union dues, etc. Non-cash transfers such as food stamps, health benefits, subsidized housing and energy assistance are not included. As household income is pretax, it does not include stimulus payments or tax credits for earned income and children/dependent care.
Net worth, or wealth, is the difference between the value of what a household owns (assets) and what it owes (debts).
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and those who say they lean toward the Republican Party. Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and those who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
At a time when many Americans are questioning the value of a four-year college degree, economic outcomes for young adults without a degree are improving.
After decades of falling wages, young U.S. workers (ages 25 to 34) without a bachelor’s degree have seen their earnings increase over the past 10 years. Their overall wealth has gone up too, and fewer are living in poverty today.
Things have also improved for young college graduates over this period. As a result, the gap in earnings between young adults with and without a college degree has not narrowed.
The public has mixed views on the importance of having a college degree, and many have doubts about whether the cost is worth it, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.
- Only one-in-four U.S. adults say it’s extremely or very important to have a four-year college degree in order to get a well-paying job in today’s economy. About a third (35%) say a college degree is somewhat important, while 40% say it’s not too or not at all important.
- Roughly half (49%) say it’s less important to have a four-year college degree today in order to get a well-paying job than it was 20 years ago; 32% say it’s more important, and 17% say it’s about as important as it was 20 years ago.
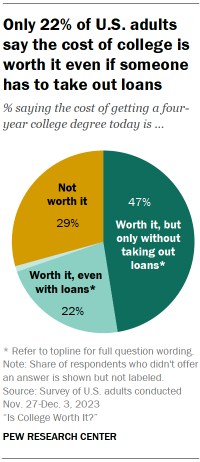
- Only 22% say the cost of getting a four-year college degree today is worth it even if someone has to take out loans. Some 47% say the cost is worth it only if someone doesn’t have to take out loans. And 29% say the cost is not worth it.
These findings come amid rising tuition costs and mounting student debt . Views on the cost of college differ by Americans’ level of education. But even among four-year college graduates, only about a third (32%) say college is worth the cost even if someone has to take out loans – though they are more likely than those without a degree to say this.
Four-year college graduates (58%) are much more likely than those without a college degree (26%) to say their education was extremely or very useful in giving them the skills and knowledge they needed to get a well-paying job. (This finding excludes the 9% of respondents who said this question did not apply to them.)
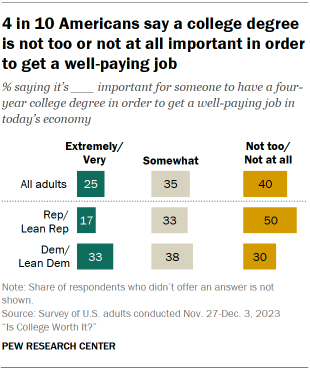
Views on the importance of college differ widely by partisanship. Republicans and Republican-leaning independents are more likely than Democrats and Democratic leaners to say:
- It’s not too or not at all important to have a four-year college degree in order to get a well-paying job (50% of Republicans vs. 30% of Democrats)
- A college degree is less important now than it was 20 years ago (57% vs. 43%)
- It’s extremely or very likely someone without a four-year college degree can get a well-paying job (42% vs. 26%)
At the same time that the public is expressing doubts about the value of college, a new Center analysis of government data finds young adults without a college degree are doing better on some key measures than they have in recent years.
A narrow majority of workers ages 25 to 34 do not have a four-year college degree (54% in 2023). Earnings for these young workers mostly trended downward from the mid-1970s until roughly a decade ago.
Outcomes have been especially poor for young men without a college degree. Other research has shown that this group saw falling labor force participation and sagging earnings starting in the early 1970s , but the last decade has marked a turning point.
This analysis looks at young men and young women separately because of their different experiences in the labor force.
Trends for young men
- Labor force participation: The share of young men without a college degree who were working or looking for work dropped steadily from 1970 until about 2014. Our new analysis suggests things have stabilized somewhat for this group over the past decade. Meanwhile, labor force participation among young men with a four-year degree has remained mostly flat.
- Full-time, full-year employment: The share of employed young men without a college degree who are working full time and year-round has varied somewhat over the years – trending downward during recessions. It’s risen significantly since the Great Recession of 2007-09, with the exception of a sharp dip in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. For employed young men with a college degree, the share working full time, full year has remained more stable over the years.
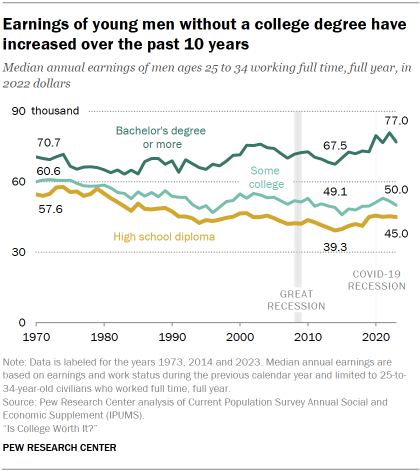
- Median annual earnings: Since 2014, earnings have risen for young men with some college education and for those whose highest attainment is a high school diploma. Even so, earnings for these groups remain below where they were in the early 1970s. Earnings for young men with a bachelor’s degree have also trended up, for the most part, over the past 10 years.
- Poverty: Among young men without a college degree who are living independently from their parents, the share in poverty has fallen significantly over the last decade. For example, 12% of young men with a high school diploma were living in poverty in 2023, down from a peak of 17% in 2011. The share of young men with a four-year college degree who are in poverty has also fallen and remains below that of noncollege young men.
Trends for young women
- Labor force participation: The shares of young women with and without a college degree in the labor force grew steadily from 1970 to about 1990. Among those without a college degree, the share fell after 2000, and the drop-off was especially sharp for young women with a high school diploma. Since 2014, labor force participation for both groups of young women has increased.
- Full-time, full-year employment: The shares of employed young women working full time and year-round, regardless of their educational attainment, have steadily increased over the decades. There was a decline during and after the Great Recession and again (briefly) in 2021 due to the pandemic. Today, the shares of women working full time, full year are the highest they’ve ever been across education levels.
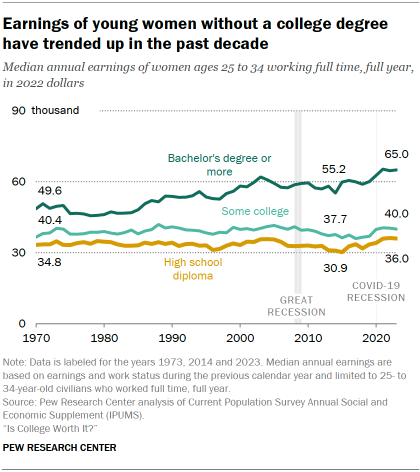
- Median annual earnings: Median earnings for young women without a college degree were relatively flat from 1970 until about a decade ago. These women did not experience the steady decline in earnings that noncollege young men did over this period. By contrast, earnings have grown over the decades for young women with a college degree. In the past 10 years, earnings for women both with and without a college degree have risen.
- Poverty: As is the case for young men without a college degree, the share of noncollege young women living in poverty has fallen substantially over the past decade. In 2014, 31% of women with a high school diploma who lived independently from their parents were in poverty. By 2023, that share had fallen to 21%. Young women with a college degree remain much less likely to be in poverty than their counterparts with less education.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Business & Workplace
- Economic Conditions
- Higher Education
- Income & Wages
- Recessions & Recoveries
- Student Loans
A look at historically Black colleges and universities in the U.S.
5 facts about student loans, half of latinas say hispanic women’s situation has improved in the past decade and expect more gains, from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, fewer young men are in college, especially at 4-year schools, most popular, report materials.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center
