

APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.)
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Powerpoint Presentations
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: Oct 14, 2024 1:11 PM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th

AI Generator

The scientific method requires researchers or scholars to follow a specific set of guidelines and structure. After they have obtained the data, the researchers or scholars will need to create a structured research paper that will introduce and explain the finding to interested parties. The title page is the first part of the research paper the reader will encounter.
1. Title Page Template

Size: 28 KB
2. Formatting Title Page Abstract

Size: 92 KB
3. Sample Title Page in APA Style

Size: 24 KB
4. Title Page APA Checklist
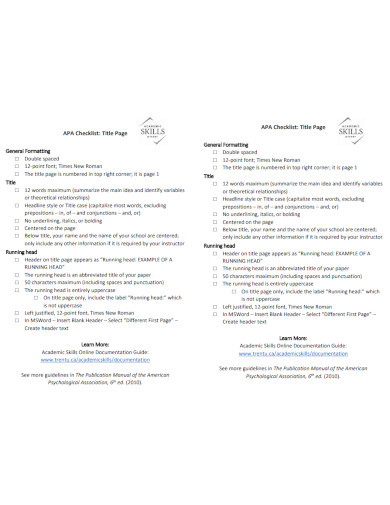
Size: 41 KB
5. Sample APA Title Page
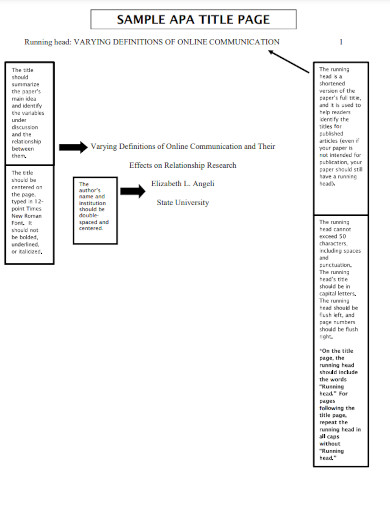
Size: 31 KB
6. Sample Title Page for MS Thesis

Size: 14 KB
7. Scholarly Paper Title Page

Size: 15 KB
8. Formatting an APA Style Title Page in OpenOffice

Size: 74 KB
9. Manuscript Title Page Instructions

Size: 46 KB
10. Final Project Title Page

Size: 26 KB
11. Sample Traditional Title Page

What Is a Title Page?
The title page or the cover page is a single part of the research paper that will hold the title or label of the research paper. Not only that, but the title page will also list the significant people who have mainly contributed to the writing of the whole research paper.
How to Create an APA Title Page
The APA title page is very easy to make as it follows an easy-to-use APA format . The most recent variation of the title page follows the guidelines the APA 7 th edition has proposed.
Step 1: Ensure Proper Margin
The APA title page requires a 1-inch margin on all sides of the paper. This margin will be present throughout the whole research paper. You may also opt to use an outline or an APA outline format to help with the margins and the spacing of the APA title page.
Step 2: Write the Title of The Study
You must write down the title of the study at the beginning of the title page. Ensure that the title is centered, bold, and in Times New Roman with proper APA capitalization.
Step 3: List Out the Author/s’ Names and Institutional Affiliations
After you have written down the title of the study, you must list all of the authors’ names below the title with a double-spaced gap. The authors’ names must be alphabetically ordered. Afterward, you will need to write the authors’ institutional affiliation and their professor’s full name. Note that this portion of the title page is written in Times New Roman, with a font size of 12, and is centered below the title.
Step 4: Write Down the Date of Submission
You will also need to write down the date of submission below the name of the professor. Be sure that the date is the same day you will have to send and submit your research paper.
Step 5: Insert the Title Header
The APA format requires the person to add a running head with the title on the top part of the page. Said header will have the title of the paper on it following the APA capitalization rules.
What are the elements of an APA title page?
The APA title page follows a very stringent format or template that will always have or consist of five distinct elements or parts. The first and most prominent element of the APA title page is the title, which is the name of the label or the name of the whole research paper. The running head is the second element of an APA title page and is the title listed in the header. The next is the name of the institute or the institutional affiliation, which indicates the academic affiliation of the researcher/s. The last element of the APA title page is called the author’s note. These are the five elements that compose the APA title page.
MLA vs. APA Title Page; what is the difference between an MLA and an APA title page?
In the MLA style of writing the title page or cover page is fused with the introduction of the whole research paper. This means that the MLA title page is a single paragraph that will preface the paper. The only caveat is if one of the requirements for the MLA paper is a title page. The APA title page on the other hand is a single entity or element in the whole research paper eliciting its page. If one were to make an APA title page due to it being a requirement then one should make it similar to the APA title page.
Should an essay have a title page?
The presence of a title page entirely depends on whether or not the professors demand it. Unlike the bibliography or the APA format reference page , most essays do not have a title page and will instead follow the MLA format of having the title over the initial paragraph. If the essay is required to have a title page, then one should follow either a format given to them by their school or educator or use the format of an APA title page,
The title page is a single page that will list the whole title of the research paper alongside the author’s name and institutional affiliation. The main purpose of the title page is to provide the reader with small amounts of pertinent information about the research study and give a title to said the study. In conclusion, if one wants to make an APA research paper, then one will need to know how to create a properly formatted title page.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like


Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Methodology – Types, Examples and...
- The Complete Guide to APA Format in 2020
APA Title Page / Cover Page
- Headings and Subheadings
- Discussion Section
- Websites and Online Sources
- Journals and Periodicals
- Other Print Sources
- Other Non-Print Sources
- In-text Citations
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Using MyBib Responsibly
- Miscellaneous Questions

Details to include
The title page (also known as the cover page) is the front page of your paper. It should contain:
- The running head , a header at the top of the page.
- The first page number .
- The title of the paper
- The institution for which you writing.
Running head
The running head should be in the top-left corner of the page in uppercase. It should include a shortened title of your paper. On the front page only, it should also be prepended with "Running head:".
First page number
The first page number -- generally page 1 -- should be in the top-right corner of the page. Both the page number and the running head should be a half inch from the top of the page.
The title of the paper can contain upper and lowercase letters, and ideally should be no more than 12 words in length. It should be direct, and should not contain abbreviations or other unnecessary words. It should not span longer than 2 lines. The first letter of each word should be uppercase, except for articles (a, an, the), and conjunctions (and, but, for, or, yet).
Underneath the title should be your name (or the author's name if you're not the author). It should be displayed as the first name , middle initial , and last name . Do not add titles (such as Dr.) to the beginning, or qualifications (such as PhD) to the end of an author's name.
Your institution
Finally, underneath the author's name, state the full name of the institution or school you're writing the paper for.
The font for all text on the title page should be Times New Roman, size 12pt, with double line-spacing.
A correct title page will look like the below image:

After completing your title page you will move on to writing an abstract of your paper.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Example

Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
Published on: Jun 12, 2021
Last updated on: Jul 19, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
350+ Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
Writing a research paper is the most challenging task in a student's academic life. researchers face similar writing process hardships, whether the research paper is to be written for graduate or masters.
A research paper is a writing type in which a detailed analysis, interpretation, and evaluation are made on the topic. It requires not only time but also effort and skills to be drafted correctly.
If you are working on your research paper for the first time, here is a collection of examples that you will need to understand the paper’s format and how its different parts are drafted. Continue reading the article to get free research paper examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
A research paper typically consists of several key parts, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and annotated bibliography .
When writing a research paper (whether quantitative research or qualitative research ), it is essential to know which format to use to structure your content. Depending on the requirements of the institution, there are mainly four format styles in which a writer drafts a research paper:
Letâs look into each format in detail to understand the fundamental differences and similarities.
Research Paper Example APA
If your instructor asks you to provide a research paper in an APA format, go through the example given below and understand the basic structure. Make sure to follow the format throughout the paper.
APA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example MLA
Another widespread research paper format is MLA. A few institutes require this format style as well for your research paper. Look at the example provided of this format style to learn the basics.
MLA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Chicago
Unlike MLA and APA styles, Chicago is not very common. Very few institutions require this formatting style research paper, but it is essential to learn it. Look at the example given below to understand the formatting of the content and citations in the research paper.
Chicago Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Harvard
Learn how a research paper through Harvard formatting style is written through this example. Carefully examine how the cover page and other pages are structured.
Harvard Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper is based on different parts. Each part plays a significant role in the overall success of the paper. So each chapter of the paper must be drafted correctly according to a format and structure.
Below are examples of how different sections of the research paper are drafted.
Research Proposal Example
A research proposal is a plan that describes what you will investigate, its significance, and how you will conduct the study.
Research Proposal Sample (PDF)
Abstract Research Paper Example
An abstract is an executive summary of the research paper that includes the purpose of the research, the design of the study, and significant research findings.
It is a small section that is based on a few paragraphs. Following is an example of the abstract to help you draft yours professionally.
Abstract Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Literature Review Research Paper Example
A literature review in a research paper is a comprehensive summary of the previous research on your topic. It studies sources like books, articles, journals, and papers on the relevant research problem to form the basis of the new research.
Writing this section of the research paper perfectly is as important as any part of it.
Literature Review in Research Sample (PDF)
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
The method section comes after the introduction of the research paper that presents the process of collecting data. Basically, in this section, a researcher presents the details of how your research was conducted.
Methods Section in Research Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Conclusion Example
The conclusion is the last part of your research paper that sums up the writerâs discussion for the audience and leaves an impression. This is how it should be drafted:
Research Paper Conclusion Sample
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
The research papers are not limited to a particular field. They can be written for any discipline or subject that needs a detailed study.
In the following section, various research paper examples are given to show how they are drafted for different subjects.
Science Research Paper Example
Are you a science student that has to conduct research? Here is an example for you to draft a compelling research paper for the field of science.
Science Research Paper Sample (PDF)
History Research Paper Example
Conducting research and drafting a paper is not only bound to science subjects. Other subjects like history and arts require a research paper to be written as well. Observe how research papers related to history are drafted.
History Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Psychology Research Paper Example
If you are a psychology student, look into the example provided in the research paper to help you draft yours professionally.
Psychology Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for Different Levels
Writing a research paper is based on a list of elements. If the writer is not aware of the basic elements, the process of writing the paper will become daunting. Start writing your research paper taking the following steps:
- Choose a topic
- Form a strong thesis statement
- Conduct research
- Develop a research paper outline
Once you have a plan in your hand, the actual writing procedure will become a piece of cake for you.
No matter which level you are writing a research paper for, it has to be well structured and written to guarantee you better grades.
If you are a college or a high school student, the examples in the following section will be of great help.
Research Paper Outline (PDF)
Research Paper Example for College
Pay attention to the research paper example provided below. If you are a college student, this sample will help you understand how a winning paper is written.
College Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for High School
Expert writers of CollegeEssay.org have provided an excellent example of a research paper for high school students. If you are struggling to draft an exceptional paper, go through the example provided.
High School Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples are essential when it comes to academic assignments. If you are a student and aim to achieve good grades in your assignments, it is suggested to get help from CollegeEssay.org .
We are the best writing company that delivers essay help for students by providing free samples and writing assistance.
Professional writers have your back, whether you are looking for guidance in writing a lab report, college essay, or research paper.
Simply hire a writer by placing your order at the most reasonable price. You can also take advantage of our essay writer to enhance your writing skills.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Need Help With Your Essay?
Also get FREE title page, Turnitin report, unlimited revisions, and more!
Keep reading

OFF ON CUSTOM ESSAYS
Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Paper and report design and layout templates
Pen perfect looking papers and reports every time when you start your assignment with a customizable design and layout template. whether you want your paper to pop off the page or you need your report to represent your data in the best light, you'll find the right template for your next paper..

Perfect your papers and reports with customizable templates
Your papers and reports will look as professional and well put together as they sound when you compose them using customizable Word templates . Whether you're writing a research paper for your university course or putting together a high priority presentation , designer-created templates are here to help you get started. First impressions are important, even for papers, and layout can make or break someone's interest in your content. Don't risk it by freestyling, start with a tried-and-true template. Remember, though: Papers and reports don't have to be boring. Professional can still pop. Tweak your favorite layout template to match your unique aesthetic for a grade A package.

COMMENTS
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader. Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication).
The title page (or cover page) of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper should contain all the key information about your document. It usually includes: Dissertation or thesis title; Your name; The type of document (e.g., dissertation, research paper) The department and institution; The degree program (e.g., Master of Arts) The date of ...
This page contains sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style. The sample papers show the format that authors should use to submit a manuscript for publication in a professional journal and that students should use to submit a paper to an instructor for a course assignment. ... 750 First St. NE, Washington, DC 20002-4242. Telephone ...
included in academic papers. This sample paper is very detailed and includes visual application of many formatting aspects of APA-7. Please use the searchable features to look for answers here ...
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. • Page numbers:Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
The page number goes in the upper-right corner of the title page, as part of the running head. This should be flush right with the page margin (1 inch). Because the title page comes first, this page number is always 1. 2 Title. The first line of text on the title page is, appropriately, the title. It follows these formatting guidelines: The ...
Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing! Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
The APA title page is the first page of your academic paper that provides information on the title, author(s), professors, and institutions affiliated with your research paper. There are separate APA cover page formats for student and professional papers. An APA 7 title page consists of the following components: Student paper. Page number ...
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example. ... the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any ...
This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to ... Research paper introduction examples. Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper. ...
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on January 20, 2023. The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you're following. In addition to citations, APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the ...
After they have obtained the data, the researchers or scholars will need to create a structured research paper that will introduce and explain the finding to interested parties. The title page is the first part of the research paper the reader will encounter. 1. Title Page Template
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. ... Research Paper - Structure, Examples and Writing Guide. March 26, 2024. by Muhammad Hassan. Table of Contents. ... The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field ...
First page number. The first page number-- generally page 1 -- should be in the top-right corner of the page. Both the page number and the running head should be a half inch from the top of the page. Title. The title of the paper can contain upper and lowercase letters, and ideally should be no more than 12 words in length.
papers (a change from APA 6). Page numbers begin on the first page and follow on every subsequent page without interruption. No other information (e.g., authors' last names) is required. Note: your instructor may ask for a running head or your last name before the page number. You can look at the APA professional sample paper for guidelines on ...
Title Page. The title page of your paper includes the following information: Title of the paper; Author's name; Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated; Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
Running Head with Page Numbers. Placement of the List of Works Cited. Tables and Illustrations. Paper and Printing. Corrections and Insertions on Printouts. Binding a Printed Paper. Electronic Submission. fig. 1
Reading Time: 13 minutes In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper.. The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within ...
Repeat the paper title at the top of the first page of text. Begin the paper with an introduction to provide background on the topic, cite related studies, and contextualize the paper. Use descriptive headings to identify other sections as needed (e.g., Method, Results, Discussion for quantitative research papers).
Research Paper Example for Different Formats. A research paper typically consists of several key parts, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and annotated bibliography.. When writing a research paper (whether quantitative research or qualitative research), it is essential to know which format to use to structure your content.
Write a first draft of the research paper. Your first draft won't be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows: Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later. Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second ...
Your papers and reports will look as professional and well put together as they sound when you compose them using customizable Word templates.Whether you're writing a research paper for your university course or putting together a high priority presentation, designer-created templates are here to help you get started.First impressions are important, even for papers, and layout can make or ...