Key Arguments From Both Sides of the Abortion Debate
Mark Wilson / Staff / Getty Images
- Reproductive Rights
- The U. S. Government
- U.S. Foreign Policy
- U.S. Liberal Politics
- U.S. Conservative Politics
- Civil Liberties
- The Middle East
- Race Relations
- Immigration
- Crime & Punishment
- Canadian Government
- Understanding Types of Government
- B.A., English Language and Literature, Well College
Many points come up in the abortion debate . Here's a look at abortion from both sides : 10 arguments for abortion and 10 arguments against abortion, for a total of 20 statements that represent a range of topics as seen from both sides.

Pro-Life Arguments
- Since life begins at conception, abortion is akin to murder as it is the act of taking human life. Abortion is in direct defiance of the commonly accepted idea of the sanctity of human life.
- No civilized society permits one human to intentionally harm or take the life of another human without punishment, and abortion is no different.
- Adoption is a viable alternative to abortion and accomplishes the same result. And with 1.5 million American families wanting to adopt a child, there is no such thing as an unwanted child.
- An abortion can result in medical complications later in life; the risk of ectopic pregnancies is increased if other factors such as smoking are present, the chance of a miscarriage increases in some cases, and pelvic inflammatory disease also increases.
- In the instance of rape and incest, taking certain drugs soon after the event can ensure that a woman will not get pregnant. Abortion punishes the unborn child who committed no crime; instead, it is the perpetrator who should be punished.
- Abortion should not be used as another form of contraception.
- For women who demand complete control of their body, control should include preventing the risk of unwanted pregnancy through the responsible use of contraception or, if that is not possible, through abstinence .
- Many Americans who pay taxes are opposed to abortion, therefore it's morally wrong to use tax dollars to fund abortion.
- Those who choose abortions are often minors or young women with insufficient life experience to understand fully what they are doing. Many have lifelong regrets afterward.
- Abortion sometimes causes psychological pain and stress.
Pro-Choice Arguments
- Nearly all abortions take place in the first trimester when a fetus is attached by the placenta and umbilical cord to the mother. As such, its health is dependent on her health, and cannot be regarded as a separate entity as it cannot exist outside her womb.
- The concept of personhood is different from the concept of human life. Human life occurs at conception, but fertilized eggs used for in vitro fertilization are also human lives and those not implanted are routinely thrown away. Is this murder, and if not, then how is abortion murder?
- Adoption is not an alternative to abortion because it remains the woman's choice whether or not to give her child up for adoption. Statistics show that very few women who give birth choose to give up their babies; less than 3% of White unmarried women and less than 2% of Black unmarried women.
- Abortion is a safe medical procedure. The vast majority of women who have an abortion do so in their first trimester. Medical abortions have a very low risk of serious complications and do not affect a woman's health or future ability to become pregnant or give birth.
- In the case of rape or incest, forcing a woman made pregnant by this violent act would cause further psychological harm to the victim. Often a woman is too afraid to speak up or is unaware she is pregnant, thus the morning after pill is ineffective in these situations.
- Abortion is not used as a form of contraception . Pregnancy can occur even with contraceptive use. Few women who have abortions do not use any form of birth control, and that is due more to individual carelessness than to the availability of abortion.
- The ability of a woman to have control of her body is critical to civil rights. Take away her reproductive choice and you step onto a slippery slope. If the government can force a woman to continue a pregnancy, what about forcing a woman to use contraception or undergo sterilization?
- Taxpayer dollars are used to enable poor women to access the same medical services as rich women, and abortion is one of these services. Funding abortion is no different from funding a war in the Mideast. For those who are opposed, the place to express outrage is in the voting booth.
- Teenagers who become mothers have grim prospects for the future. They are much more likely to leave school; receive inadequate prenatal care; or develop mental health problems.
- Like any other difficult situation, abortion creates stress. Yet the American Psychological Association found that stress was greatest prior to an abortion and that there was no evidence of post-abortion syndrome.
Additional References
- Alvarez, R. Michael, and John Brehm. " American Ambivalence Towards Abortion Policy: Development of a Heteroskedastic Probit Model of Competing Values ." American Journal of Political Science 39.4 (1995): 1055–82. Print.
- Armitage, Hannah. " Political Language, Uses and Abuses: How the Term 'Partial Birth' Changed the Abortion Debate in the United States ." Australasian Journal of American Studies 29.1 (2010): 15–35. Print.
- Gillette, Meg. " Modern American Abortion Narratives and the Century of Silence ." Twentieth Century Literature 58.4 (2012): 663–87. Print.
- Kumar, Anuradha. " Disgust, Stigma, and the Politics of Abortion ." Feminism & Psychology 28.4 (2018): 530–38. Print.
- Ziegler, Mary. " The Framing of a Right to Choose: Roe V. Wade and the Changing Debate on Abortion Law ." Law and History Review 27.2 (2009): 281–330. Print.
“ Life Begins at Fertilization with the Embryo's Conception .” Princeton University , The Trustees of Princeton University.
“ Long-Term Risks of Surgical Abortion .” GLOWM, doi:10.3843/GLOWM.10441
Patel, Sangita V, et al. “ Association between Pelvic Inflammatory Disease and Abortions .” Indian Journal of Sexually Transmitted Diseases and AIDS , Medknow Publications, July 2010, doi:10.4103/2589-0557.75030
Raviele, Kathleen Mary. “ Levonorgestrel in Cases of Rape: How Does It Work? ” The Linacre Quarterly , Maney Publishing, May 2014, doi:10.1179/2050854914Y.0000000017
Reardon, David C. “ The Abortion and Mental Health Controversy: A Comprehensive Literature Review of Common Ground Agreements, Disagreements, Actionable Recommendations, and Research Opportunities .” SAGE Open Medicine , SAGE Publications, 29 Oct. 2018, doi:10.1177/2050312118807624
“ CDCs Abortion Surveillance System FAQs .” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 25 Nov. 2019.
Bixby Center for Reproductive Health. “ Complications of Surgical Abortion : Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology .” LWW , doi:10.1097/GRF.0b013e3181a2b756
" Sexual Violence: Prevalence, Dynamics and Consequences ." World Health Organizaion.
Homco, Juell B, et al. “ Reasons for Ineffective Pre-Pregnancy Contraception Use in Patients Seeking Abortion Services .” Contraception , U.S. National Library of Medicine, Dec. 2009, doi:10.1016/j.contraception.2009.05.127
" Working With Pregnant & Parenting Teens Tip Sheet ." U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Major, Brenda, et al. " Abortion and Mental Health: Evaluating the Evidence ." American Psychological Association, doi:10.1037/a0017497
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- The Pro-Life vs Pro-Choice Debate
- Abortion on Demand: A Second Wave Feminist Demand
- Abortion Facts and Statistics in the 21st Century
- The 1969 Redstockings Abortion Speakout
- The Roe v. Wade Supreme Court Decision
- Biography of Margaret Sanger
- Is Abortion Legal in Every State?
- Biography of Norma McCorvey, 'Roe' in the Roe v. Wade Case
- Pro-Choice Quotes
- Supreme Court Decisions and Women's Reproductive Rights
- Oppression and Women's History
- Roe v. Wade
- 8 Major Issues Facing Women Today
- 1970s Feminism Timeline
- Understanding Why Abortion Is Legal in the United States

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1: Arguments Against Abortion
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 35918

- Nathan Nobis & Kristina Grob
- Morehouse College & University of South Carolina Sumter via Open Philosophy Press
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
We will begin with arguments for the conclusion that abortion is generally wrong , perhaps nearly always wrong . These can be seen as reasons to believe fetuses have the “right to life” or are otherwise seriously wrong to kill.
5.1.1 Fetuses are human
First, there is the claim that fetuses are “human” and so abortion is wrong. People sometimes debate whether fetuses are human , but fetuses found in (human) women clearly are biologically human : they aren’t cats or dogs. And so we have this argument, with a clearly true first premise:
Fetuses are biologically human.
All things that are biologically human are wrong to kill.
Therefore, fetuses are wrong to kill.
The second premise, however, is false, as easy counterexamples show. Consider some random living biologically human cells or tissues in a petri dish. It wouldn’t be wrong at all to wash those cells or tissues down the drain, killing them; scratching yourself or shaving might kill some biologically human skin cells, but that’s not wrong; a tumor might be biologically human, but not wrong to kill. So just because something is biologically human, that does not at all mean it’s wrong to kill that thing. We saw this same point about what’s merely biologically alive.
This suggests a deficiency in some common understandings of the important idea of “human rights.” “Human rights” are sometimes described as rights someone has just because they are human or simply in virtue of being human .
But the human cells in the petri dish above don’t have “human rights” and a human heart wouldn’t have “human rights” either. Many examples would make it clear that merely being biologically human doesn’t give something human rights. And many human rights advocates do not think that abortion is wrong, despite recognizing that (human) fetuses are biologically human.
The problem about what is often said about human rights is that people often do not think about what makes human beings have rights or why we have them, when we have them. The common explanation, that we have (human) rights just because we are (biologically) human , is incorrect, as the above discussion makes clear. This misunderstanding of the basis or foundation of human rights is problematic because it leads to a widespread, misplaced fixation on whether fetuses are merely biologically “human” and the mistaken thought that if they are, they have “human rights.” To address this problem, we need to identify better, more fundamental, explanations why we have rights, or why killing us is generally wrong, and see how those explanations might apply to fetuses, as we are doing here.
It might be that when people appeal to the importance and value of being “human,” the concern isn’t our biology itself, but the psychological characteristics that many human beings have: consciousness, awareness, feelings and so on. We will discuss this different meaning of “human” below. This meaning of “human” might be better expressed as conscious being , or “person,” or human person. This might be what people have in mind when they argue that fetuses aren’t even “human.”
Human rights are vitally important, and we would do better if we spoke in terms of “conscious-being rights” or “person-rights,” not “human rights.” This more accurate and informed understanding and terminology would help address human rights issues in general, and help us better think through ethical questions about biologically human embryos and fetuses.
5.1.2 Fetuses are human beings
Some respond to the arguments above—against the significance of being merely biologically human—by observing that fetuses aren’t just mere human cells, but are organized in ways that make them beings or organisms . (A kidney is part of a “being,” but the “being” is the whole organism.) That suggests this argument:
Fetuses are human beings or organisms .
All human beings or organisms are wrong to kill.
Therefore, fetuses are wrong to kill, so abortion is wrong.
The first premise is true: fetuses are dependent beings, but dependent beings are still beings.
The second premise, however, is the challenge, in terms of providing good reasons to accept it. Clearly many human beings or organisms are wrong to kill, or wrong to kill unless there’s a good reason that would justify that killing, e.g., self-defense. (This is often described by philosophers as us being prima facie wrong to kill, in contrast to absolutely or necessarily wrong to kill.) Why is this though? What makes us wrong to kill? And do these answers suggest that all human beings or organisms are wrong to kill?
Above it was argued that we are wrong to kill because we are conscious and feeling: we are aware of the world, have feelings and our perspectives can go better or worse for us —we can be harmed— and that’s what makes killing us wrong. It may also sometimes be not wrong to let us die, and perhaps even kill us, if we come to completely and permanently lacking consciousness, say from major brain damage or a coma, since we can’t be harmed by death anymore: we might even be described as dead in the sense of being “brain dead.” 10
So, on this explanation, human beings are wrong to kill, when they are wrong to kill, not because they are human beings (a circular explanation), but because we have psychological, mental or emotional characteristics like these. This explains why we have rights in a simple, common-sense way: it also simply explains why rocks, microorganisms and plants don’t have rights. The challenge then is explaining why fetuses that have never been conscious or had any feeling or awareness would be wrong to kill. How then can the second premise above, general to all human organisms, be supported, especially when applied to early fetuses?
One common attempt is to argue that early fetuses are wrong to kill because there is continuous development from fetuses to us, and since we are wrong to kill now , fetuses are also wrong to kill, since we’ve been the “same being” all along. 11 But this can’t be good reasoning, since we have many physical, cognitive, emotional and moral characteristics now that we lacked as fetuses (and as children). So even if we are the “same being” over time, even if we were once early fetuses, that doesn’t show that fetuses have the moral rights that babies, children and adults have: we, our bodies and our rights sometimes change.
A second attempt proposes that rights are essential to human organisms: they have them whenever they exist. This perspective sees having rights, or the characteristics that make someone have rights, as essential to living human organisms. The claim is that “having rights” is an essential property of human beings or organisms, and so whenever there’s a living human organism, there’s someone with rights, even if that organism totally lacks consciousness, like an early fetus. (In contrast, the proposal we advocate for about what makes us have rights understands rights as “accidental” to our bodies but “essential” to our minds or awareness, since our bodies haven’t always “contained” a conscious being, so to speak.)
Such a view supports the premise above; maybe it just is that premise above. But why believe that rights are essential to human organisms? Some argue this is because of what “kind” of beings we are, which is often presumed to be “rational beings.” The reasoning seems to be this: first, that rights come from being a rational being: this is part of our “nature.” Second, that all human organisms, including fetuses, are the “kind” of being that is a “rational being,” so every being of the “kind” rational being has rights. 12
In response, this explanation might seem question-begging: it might amount to just asserting that all human beings have rights. This explanation is, at least, abstract. It seems to involve some categorization and a claim that everyone who is in a certain category has some of the same moral characteristics that others in that category have, but because of a characteristic (actual rationality) that only these others have: so, these others profoundly define what everyone else is . If this makes sense, why not also categorize us all as not rational beings , if we are the same kind of beings as fetuses that are actually not rational?
This explanation might seem to involve thinking that rights somehow “trickle down” from later rationality to our embryonic origins, and so what we have later we also have earlier , because we are the same being or the same “kind” of being. But this idea is, in general, doubtful: we are now responsible beings, in part because we are rational beings, but fetuses aren’t responsible for anything. And we are now able to engage in moral reasoning since we are rational beings, but fetuses don’t have the “rights” that uniquely depend on moral reasoning abilities. So that an individual is a member of some general group or kind doesn’t tell us much about their rights: that depends on the actual details about that individual, beyond their being members of a group or kind.
To make this more concrete, return to the permanently comatose individuals mentioned above: are we the same kind of beings, of the same “essence,” as these human beings? If so, then it seems that some human beings can be not wrong to let die or kill, when they have lost consciousness. Therefore, perhaps some other human beings, like early fetuses, are also not wrong to kill before they have gained consciousness . And if we are not the same “kind” of beings, or have different essences, then perhaps we also aren’t the same kind of beings as fetuses either.
Similar questions arise concerning anencephalic babies, tragically born without most of their brains: are they the same “kind” of beings as “regular” babies or us? If so, then—since such babies are arguably morally permissible to let die, even when they could be kept alive, since being alive does them no good—then being of our “kind” doesn’t mean the individual has the same rights as us, since letting us die would be wrong. But if such babies are a different “kind” of beings than us, then pre-conscious fetuses might be of a relevantly different kind also.
So, in general, this proposal that early fetuses essentially have rights is suspect, if we evaluate the reasons given in its support. Even if fetuses and us are the same “kind” of beings (which perhaps we are not!) that doesn’t immediately tell us what rights fetuses would have, if any. And we might even reasonably think that, despite our being the same kind of beings as fetuses (e.g., the same kind of biology), we are also importantly different kinds of beings (e.g., one kind with a mental life and another kind which has never had it). This photograph of a 6-week old fetus might help bring out the ambiguity in what kinds of beings we all are:
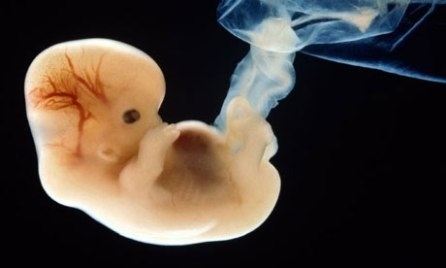
In sum, the abstract view that all human organisms have rights essentially needs to be plausibly explained and defended. We need to understand how it really works. We need to be shown why it’s a better explanation, all things considered, than a consciousness and feelings-based theory of rights that simply explains why we, and babies, have rights, why racism, sexism and other forms of clearly wrongful discrimination are wrong, and , importantly, how we might lose rights in irreversible coma cases (if people always retained the right to life in these circumstances, presumably, it would be wrong to let anyone die), and more.
5.1.3 Fetuses are persons
Finally, we get to what some see as the core issue here, namely whether fetuses are persons , and an argument like this:
Fetuses are persons, perhaps from conception.
Persons have the right to life and are wrong to kill.
So, abortion is wrong, as it involves killing persons.
The second premise seems very plausible, but there are some important complications about it that will be discussed later. So let’s focus on the idea of personhood and whether any fetuses are persons. What is it to be a person ? One answer that everyone can agree on is that persons are beings with rights and value . That’s a fine answer, but it takes us back to the initial question: OK, who or what has the rights and value of persons? What makes someone or something a person?
Answers here are often merely asserted , but these answers need to be tested: definitions can be judged in terms of whether they fit how a word is used. We might begin by thinking about what makes us persons. Consider this:
We are persons now. Either we will always be persons or we will cease being persons. If we will cease to be persons, what can end our personhood? If we will always be persons, how could that be?
Both options yield insight into personhood. Many people think that their personhood ends at death or if they were to go into a permanent coma: their body is (biologically) alive but the person is gone: that is why other people are sad. And if we continue to exist after the death of our bodies, as some religions maintain, what continues to exist? The person , perhaps even without a body, some think! Both responses suggest that personhood is defined by a rough and vague set of psychological or mental, rational and emotional characteristics: consciousness, knowledge, memories, and ways of communicating, all psychologically unified by a unique personality.
A second activity supports this understanding:
Make a list of things that are definitely not persons . Make a list of individuals who definitely are persons . Make a list of imaginary or fictional personified beings which, if existed, would be persons: these beings that fit or display the concept of person, even if they don’t exist. What explains the patterns of the lists?
Rocks, carrots, cups and dead gnats are clearly not persons. We are persons. Science fiction gives us ideas of personified beings: to give something the traits of a person is to indicate what the traits of persons are, so personified beings give insights into what it is to be a person. Even though the non-human characters from, say, Star Wars don’t exist, they fit the concept of person: we could befriend them, work with them, and so on, and we could only do that with persons. A common idea of God is that of an immaterial person who has exceptional power, knowledge, and goodness: you couldn’t pray to a rock and hope that rock would respond: you could only pray to a person. Are conscious and feeling animals, like chimpanzees, dolphins, cats, dogs, chickens, pigs, and cows more relevantly like us, as persons, or are they more like rocks and cabbages, non-persons? Conscious and feeling animals seem to be closer to persons than not. 13 So, this classificatory and explanatory activity further supports a psychological understanding of personhood: persons are, at root, conscious, aware and feeling beings.
Concerning abortion, early fetuses would not be persons on this account: they are not yet conscious or aware since their brains and nervous systems are either non-existent or insufficiently developed. Consciousness emerges in fetuses much later in pregnancy, likely after the first trimester or a bit beyond. This is after when most abortions occur. Most abortions, then, do not involve killing a person , since the fetus has not developed the characteristics for personhood. We will briefly discuss later abortions, that potentially affect fetuses who are persons or close to it, below.
It is perhaps worthwhile to notice though that if someone believed that fetuses are persons and thought this makes abortion wrong, it’s unclear how they could coherently believe that a pregnancy resulting from rape or incest could permissibly be ended by an abortion. Some who oppose abortion argue that, since you are a person, it would be wrong to kill you now even if you were conceived because of a rape, and so it’s wrong to kill any fetus who is a person, even if they exist because of a rape: whether someone is a person or not doesn’t depend on their origins: it would make no sense to think that, for two otherwise identical fetuses, one is a person but the other isn’t, because that one was conceived by rape. Therefore, those who accept a “personhood argument” against abortion, yet think that abortions in cases of rape are acceptable, seem to have an inconsistent view.
5.1.4 Fetuses are potential persons
If fetuses aren’t persons, they are at least potential persons, meaning they could and would become persons. This is true. This, however, doesn’t mean that they currently have the rights of persons because, in general, potential things of a kind don’t have the rights of actual things of that kind : potential doctors, lawyers, judges, presidents, voters, veterans, adults, parents, spouses, graduates, moral reasoners and more don’t have the rights of actual individuals of those kinds.
Some respond that potential gives the right to at least try to become something. But that trying sometimes involves the cooperation of others: if your friend is a potential medical student, but only if you tutor her for many hours a day, are you obligated to tutor her? If my child is a potential NASCAR champion, am I obligated to buy her a race car to practice? ‘No’ to both and so it is unclear that a pregnant woman would be obligated to provide what’s necessary to bring about a fetus’s potential. (More on that below, concerning the what obligations the right to life imposes on others, in terms of obligations to assist other people.)
5.1.5 Abortion prevents fetuses from experiencing their valuable futures
The argument against abortion that is likely most-discussed by philosophers comes from philosopher Don Marquis. 14 He argues that it is wrong to kill us, typical adults and children, because it deprives us from experiencing our (expected to be) valuable futures, which is a great loss to us . He argues that since fetuses also have valuable futures (“futures like ours” he calls them), they are also wrong to kill. His argument has much to recommend it, but there are reasons to doubt it as well.
First, fetuses don’t seem to have futures like our futures , since—as they are pre-conscious—they are entirely psychologically disconnected from any future experiences: there is no (even broken) chain of experiences from the fetus to that future person’s experiences. Babies are, at least, aware of the current moment, which leads to the next moment; children and adults think about and plan for their futures, but fetuses cannot do these things, being completely unconscious and without a mind.
Second, this fact might even mean that the early fetus doesn’t literally have a future: if your future couldn’t include you being a merely physical, non-conscious object (e.g., you couldn’t be a corpse: if there’s a corpse, you are gone), then non-conscious physical objects, like a fetus, couldn’t literally be a future person. 15 If this is correct, early fetuses don’t even have futures, much less futures like ours. Something would have a future, like ours, only when there is someone there to be psychologically connected to that future: that someone arrives later in pregnancy, after when most abortions occur.
A third objection is more abstract and depends on the “metaphysics” of objects. It begins with the observation that there are single objects with parts with space between them . Indeed almost every object is like this, if you could look close enough: it’s not just single dinette sets, since there is literally some space between the parts of most physical objects. From this, it follows that there seem to be single objects such as an-egg-and-the-sperm-that-would-fertilize-it . And these would also seem to have a future of value, given how Marquis describes this concept. (It should be made clear that sperm and eggs alone do not have futures of value, and Marquis does not claim they do: this is not the objection here). The problem is that contraception, even by abstinence , prevents that thing’s future of value from materializing, and so seems to be wrong when we use Marquis’s reasoning. Since contraception is not wrong, but his general premise suggests that it is , it seems that preventing something from experiencing its valuable future isn’t always wrong and so Marquis’s argument appears to be unsound. 16
In sum, these are some of the most influential arguments against abortion. Our discussion was brief, but these arguments do not appear to be successful: they do not show that abortion is wrong, much less make it clear and obvious that abortion is wrong.
Four pro-life philosophers make the case against abortion

To put it mildly, the American Philosophical Association is not a bastion of pro-life sentiment. Hence, I was surprised to discover that the A.P.A. had organized a pro-life symposium, “New Pro-Life Bioethics,” at our annual conference this month in Philadelphia. Hosted by Jorge Garcia (Boston College), the panel featured the philosophers Celia Wolf-Devine (Stonehill College), Anthony McCarthy (Bios Centre in London) and Francis Beckwith (Baylor University), all of whom presented the case against abortion in terms of current political and academic values.
Recognizing the omnipresent call for a “welcoming” society, Ms. Wolf-Devine explored contemporary society’s emphasis on the virtue of inclusion and the vice of exclusion. The call for inclusion emphasizes the need to pay special attention to the more vulnerable members of society, who can easily be treated as non-persons in society’s commerce. She argued that our national practice of abortion, comparatively one of the most extreme in terms of legal permissiveness, contradicts the good of inclusion by condemning an entire category of human beings to death, often on the slightest of grounds. There is something contradictory in a society that claims to be welcoming and protective of the vulnerable but that shows a callous indifference to the fate of human beings before the moment of birth.
There is something contradictory in a society that claims to be protective of the vulnerable but shows a callous indifference to the fate of human beings before the moment of birth.
Mr. McCarthy’s paper tackled the question of abortion from the perspective of equality. A common egalitarian argument in favor of abortion and the funding thereof goes something like this: If a woman has an unwanted pregnancy and is denied access to abortion, she might be required to sacrifice educational and work opportunities. Since men do not become pregnant, they face no such obstacles to pursuing their professional goals. Restrictions to abortion access thus places women in a position of inequality with men.
Mr. McCarthy counter-argued that, in fact, the practice of abortion creates a certain inequality between men and women since it does not respect the experiences, such as pregnancy, which are unique to women. Some proponents of abortion deride pregnancy as a malign condition. A disgruntled audience member referred to pregnant women as “incubators.” Mr. McCarthy argued that authentic gender equality involves respect for what makes women different, including support for the well-being of both women and children through pregnancy, childbirth and beyond. He pointed out that in his native England, pregnant women acting as surrogates are given a certain amount of time after birth to decide whether to keep the child they bore and not fulfill the conditions of the surrogacy contract. This is done out of acknowledgment of the gender-specific biological and emotional changes undergone by a woman who has nurtured a child in the womb.
The most compelling argument against abortion remains what it has been for decades: Directly killing innocent human beings is gravely unjust.
Mr. Beckwith explored the question of abortion in light of the longstanding philosophical dispute concerning the “criteria of personhood.” The question of which human beings count as persons is closely yoked to the political question of which human beings will receive civil protection and which can be killed without legal penalty. The personhood criteria range from the most inclusive (genetic identity as a member of the species Homo sapiens ) to the more restrictive (evidence of consciousness) to the most exclusionary (evidence of rationality and self-motivating behavior).

Mr. Beckwith has long used the argument from personal identity (the continuity between my mature, conscious self and my embryonic, fetal and childhood self and my future older, possibly demented self) to make the case against abortion, infanticide and euthanasia. To draw the line between personhood and non-personhood after conception or before natural death is to make an arbitrary distinction—and a lethal one at that. Mr. Beckwith noted, however, that none of the usual candidates for a criterion of personhood is completely satisfying. Even the common pro-life argument from species membership could, unamended, smack of a certain materialism.
The most compelling argument against abortion remains what it has been for decades: Directly killing innocent human beings is gravely unjust. Abortion is the direct killing of innocent human beings. But political debate rarely proceeds by such crystalline syllogisms. The aim of the A.P.A.’s pro-life symposium was to amplify the argument by showing how our practice of abortion brutally violates the values of inclusion, equality and personhood that contemporary society claims to cherish. In the very month we grimly commemorate Roe v. Wade, such new philosophical directions are welcome winter light.

John J. Conley, S.J., is a Jesuit of the Maryland Province and a regular columnist for America . He is the current Francis J. Knott Chair of Philosophy and Theology at Loyola University, Maryland.
Most popular

Your source for jobs, books, retreats, and much more.
The latest from america

Arguments against Abortion
This essay about the arguments against abortion explores the complex moral, ethical, and societal considerations surrounding the issue. It examines perspectives rooted in the sanctity of human life, bodily autonomy, and the potential harm to women’s physical and psychological well-being. Additionally, it discusses how the normalization of abortion may contribute to a culture of death and perpetuate discrimination through selective practices. Ultimately, the essay emphasizes the need for thoughtful engagement with these diverse viewpoints and a commitment to upholding the dignity and rights of all individuals involved.
How it works
Abortion is an issue that continues to spark intense debate and controversy across societies worldwide. It is a topic entrenched in moral, ethical, and legal complexities, with advocates and opponents presenting divergent viewpoints shaped by various philosophical, religious, and cultural perspectives. While proponents of abortion rights champion the importance of reproductive autonomy and women’s rights, opponents of abortion articulate compelling arguments grounded in notions of morality, the sanctity of life, and societal well-being. In this essay, I will delve into several distinct arguments against abortion, offering a nuanced exploration of their underlying principles and implications.
One of the foremost arguments against abortion stems from the belief in the inherent value and sanctity of human life. Many individuals, often guided by religious or philosophical convictions, assert that life begins at conception and that every embryo possesses intrinsic worth deserving of protection. From this perspective, abortion is viewed as an act of unjustifiable violence against an innocent human being, denying them the opportunity to fulfill their potential and contribute to society. Proponents of this argument advocate for the recognition of the unborn as moral subjects entitled to the same rights and protections afforded to born individuals.
Furthermore, opponents of abortion raise concerns about the ethical implications of terminating a pregnancy on the grounds of bodily autonomy alone. While women undoubtedly have the right to make decisions about their bodies, critics argue that this right must be balanced against the rights of the unborn child. They contend that abortion represents a violation of the unborn’s fundamental right to life, emphasizing the ethical responsibility that comes with engaging in activities that may result in pregnancy. Rather than resorting to abortion as a solution to unplanned or unwanted pregnancies, opponents advocate for alternatives such as adoption, which prioritize the preservation of life while respecting women’s autonomy.
Another compelling argument against abortion centers on the potential physical and psychological harm it can inflict upon women. Critics point to a range of adverse outcomes associated with abortion, including medical complications, emotional distress, and long-term psychological trauma. While advocates for abortion rights often emphasize the importance of safe and legal access to abortion, opponents caution against overlooking the risks and consequences that women may face. They argue that a more holistic approach to reproductive healthcare should prioritize the well-being of both women and unborn children, promoting alternatives that address the underlying reasons for seeking abortion while mitigating potential harms.
Moreover, opponents of abortion contend that its widespread acceptance contributes to a culture of death and devalues the sanctity of human life. They argue that the normalization of abortion erodes societal attitudes towards the inherent value and dignity of every individual, fostering a climate in which the taking of human life is increasingly viewed as permissible. From this perspective, abortion not only threatens the lives of the unborn but also undermines the moral fabric of society, perpetuating a culture of indifference towards human suffering and injustice.
Critics of abortion also raise concerns about the discriminatory practices that can arise from selective abortions based on factors such as gender, disability, or socioeconomic status. They argue that the widespread availability of abortion perpetuates harmful stereotypes and inequalities, reinforcing existing prejudices against vulnerable populations. Additionally, they contend that selective abortion perpetuates a eugenic mindset, wherein certain lives are deemed less valuable or worthy of protection based on arbitrary criteria, further exacerbating social injustices and inequities.
In conclusion, the arguments against abortion encompass a spectrum of ethical, religious, and social considerations, reflecting the complex nature of this contentious issue. From the assertion of the sanctity of life to concerns about bodily autonomy and societal implications, opponents of abortion present diverse perspectives that challenge prevailing narratives surrounding reproductive rights. Engaging with these arguments fosters a deeper understanding of the ethical dilemmas at play and underscores the need for thoughtful and compassionate approaches to addressing the complexities of abortion. Ultimately, navigating this fraught terrain requires a commitment to upholding the dignity and worth of all individuals, born and unborn, while striving to promote the well-being and autonomy of women within a framework of respect and justice.
Cite this page
Arguments Against Abortion. (2024, Apr 07). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/
"Arguments Against Abortion." PapersOwl.com , 7 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Arguments Against Abortion . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/ [Accessed: 8 Jun. 2024]
"Arguments Against Abortion." PapersOwl.com, Apr 07, 2024. Accessed June 8, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/
"Arguments Against Abortion," PapersOwl.com , 07-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/. [Accessed: 8-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Arguments Against Abortion . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/arguments-against-abortion/ [Accessed: 8-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
How To Win Any Argument About Abortion

So you're talking to someone who says something ignorant . And while you know that they're in the wrong, your words escape you. To make sure that doesn't happen, we've compiled a series of reference guides with the most common arguments — and your counter-arguments — for the most hot-button issues. Ahead, how to argue the pro-choice position .
Common Argument #1: A fetus is a human being, and human beings have the right to life, so abortion is murder.
The Pro-Choice Argument: I'm probably not going to convince you that a fetus isn't a life, as that's basically the most intractable part of this whole debate, so I'll be brief:
- A fetus can't survive on its own. It is fully dependent on its mother's body, unlike born human beings.
- Even if a fetus was alive, the "right to life" doesn't imply a right to use somebody else's body. People have the right to refuse to donate their organs , for example, even if doing so would save somebody else's life.
- The "right to life" also doesn't imply a right to live by threatening somebody else's life. Bearing children is always a threat the life of the mother (see below).
- A "right to life" is, at the end of the day, a right to not have somebody else's will imposed upon your body. Do women not have this right as well?
Common Argument #2: If a woman is willing to have sex, she's knowingly taking the risk of getting pregnant, and should be responsible for her actions.
The Pro-Choice Argument: You're asserting that giving birth is the "responsible" choice in the event of a pregnancy, but that's just your opinion. I'd argue that if a mother knows she won't be able to provide for her child, it's actually more responsible to have an abortion, and in doing so prevent a whole lot of undue suffering and misery.
But let's look at this argument a bit further. If you think getting an abortion is "avoiding responsibility," that implies that it's a woman's responsibility to bear a child if she chooses to have sex. That sounds suspiciously like you're dictating what a woman's role and purpose is, and a lot less like you're making an argument about the life of a child.
Common Reply : No, because women can practice safe sex and avoid getting pregnant. If she refuses to use contraception and gets pregnant as a result, that's her fault, and her responsibility.
Your Rebuttal: Not everyone has easy access to contraception , nor does everyone have a good enough sex education class to know how to use it or where to obtain it. But let's just suppose, for the sake of argument, that everyone had access to free contraception and knew how to use it correctly.
Even then, no contraception is 100% effective. Presumably, you oppose abortions even in cases where contraception fails (and it does sometimes fail, even when used perfectly). If that's true, you're saying that, by merely choosing to have sex — with or without a condom — a woman becomes responsible for having a child. And that's a belief that has everything to do with judging a woman's behavior, and nothing to do with the value of life.
Common Argument #3: But I'm OK with abortions in cases of rape .
The Pro-Choice Argument: Why only in those cases? Are the lives of children who were conceived by rape worth less than the lives of children who were willfully conceived? If preserving the life of the child takes primacy over the desires of the mother — which is what you're saying if you if you oppose any legal abortions — then it shouldn't matter how that life was conceived.
Common Argument #4: "If it's a legitimate rape, the female body has ways to try to shut that whole thing down."
Your Response: Go home, Todd Akin , you're drunk.
Common Argument #5: Adoption is a viable alternative to abortion.
The Pro-Choice Argument: This implies that the only reason a woman would want to get an abortion is to avoid raising a child, and that isn't the case. Depending on the circumstances, the mere act of having a child in a hospital can cost between $3,000 and $37,000 in the United States. Giving birth is dangerous, too: In the United States, pregnancy complications are the sixth most common cause of death for women between the ages of 20 and 34.
Even before birth, there are costs to pregnancy. In addition to the whole "carrying another human being around in your stomach for nine months" thing, many women, particularly teens, are shunned and shamed for their pregnancies — not only by friends, families, employers, and classmates, but also by advertisements in the subway . There's also the risk of violent retribution from abusive partners and parents.
In short, there are a lot of reasons a woman might seek an abortion. Adoption doesn't address all of them.
Common Argument #6: When abortion is legal, women just use it as a form of birth control.
The Pro-Choice Argument: Do you have evidence of this? Considering that contraceptives are cheaper, easier, less painful, less time-consuming, less emotionally taxing, and more readily available than abortions, it seems odd to suggest that women who've already decided to use birth control would select abortion as their preferred method. It's more likely the opposite: Historical and contemporary data suggests that women will seek abortions regardless of whether or not they're legal, but that when birth control and contraceptives are more widely accessible, abortion rates go down.
Common Argument #7: Abortions are dangerous.
The Pro-Choice Argument: When performed by trained professionals, abortions are one of the safest procedures in medicine, with a death rate of less than 0.01%. The risk of dying while giving birth is roughly 13 times higher. Abortions performed by people without the requisite skills and training, however, are extremely unsafe. An estimated 68,000 women die every year from back alley abortions, which are generally most common when abortion is illegal and/or inaccessible.
If you'd like to examine the health impact of banning abortion, consider Romania, which banned abortions in 1966. That policy remained in place for about 23 years, during which time over 9,000 women died from unsafe abortions , and countless others were permanently injured. That's around two women dying every day. When the policy was reversed, maternal mortality rate plummeted to one-eighth of what it was at its peak under the no-abortion policy.
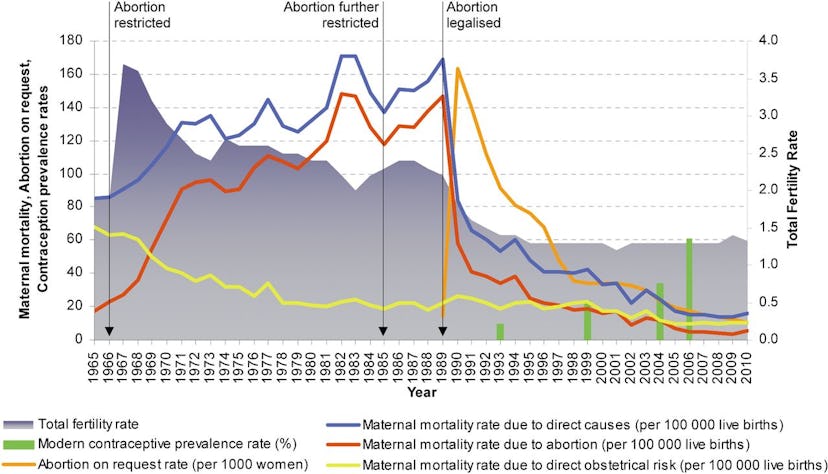
Abortions and maternal death rates in Romania, 1965-2010. Image credit: BMJ Group
The negative health effects of prohibiting abortion don't end with the mothers. Romania's abortion ban sparked a nationwide orphan crisis, as roughly 150,000 unwanted newborns were placed in nightmarish state-run orphanages . Many of those orphans now suffer from severe mental and physical health problems, including reduced brain size, schizoaffective disorder, and sociopathy.
When abortion is illegal, it becomes exponentially more unsafe for both women and their children. You may not like the fact that women will seek abortions even when they're illegal, but it is undeniably a fact nonetheless.
Common Argument #8: What if Winston Churchill or Martin Luther King had been aborted?
Your Response: Are you saying abortion policy should be influenced by how good of a person a fetus ends up becoming? If that's the case, what if Joseph Stalin or Pol Pot had been aborted?
Common Argument #9: Many women who get abortions regret their decision later on.
The Pro-Choice Argument: This is a pretty common argument. As with shaming of teen moms, it pops up in subway ads.
This is a bad argument. Should the government ban people from doing things they sometimes regret? Think of everything you've ever regretted — not moving after college, dating the wrong person — and ask yourself if you wish there had been a law to prevent you from doing that thing. You probably don't, because you probably believe people should be able to choose their own paths in life regardless of whether they regret those choices later on. I agree, which is part of why I'm pro-choice .
Common Argument #10: Taxpayers shouldn't be forced to pay for things they find morally disagreeable.
The Pro-Choice Argument: By that rationale, America also shouldn't have a military, since that's funded by taxes, and many taxpayers find American foreign policy morally disagreeable. Also, the Hyde Amendment prevents most public funds from going toward abortions. But that's a moot point, because these are two separate arguments. Believing that abortion should be legal doesn't require you to also believe that taxpayer dollars should fund abortions.
Common Argument #11: What if your mother had aborted you?
The Pro-Choice Argument: Well, if I'd never come into existence in the first place, I probably wouldn't have any strong feelings on the matter. Anyway, I love my mother very much and respect her right to make whatever decisions are right for her body and life.
The best pro-choice arguments , in summary:
- A "right to life" doesn't imply a right to use someone else's body to sustain a life.
- Women do not have a "responsibility" to have children, and certainly don't assume such a responsibility by virtue of deciding to have sex.
- Outlawing abortion is very dangerous, both for women and their children.
- Adoption still requires women to carry a baby to term and then give birth, both of which are also inherently dangerous.
- Abortions, on the other hand, are quite safe.
- Banning abortion violates a woman's right to control her own body.
This article was originally published on March 5, 2014

- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
Pro and Con: Abortion

To access extended pro and con arguments, sources, and discussion questions about whether abortion should be legal, go to ProCon.org .
The debate over whether abortion should be a legal option has long divided people around the world. Split into two groups, pro-choice and pro-life, the two sides frequently clash in protests.
A June 2, 2022 Gallup poll , 55% of Americans identified as “pro-choice,” the highest percentage since 1995. 39% identified as “pro-life,” and 5% were neither or unsure. For the first time in the history of the poll question (since 2001), 52% of Americans believe abortion is morally acceptable. 38% believed the procedure to be morally wrong, and 10% answered that it depended on the situation or they were unsure.
Surgical abortion (aka suction curettage or vacuum curettage) is the most common type of abortion procedure. It involves using a suction device to remove the contents of a pregnant woman’s uterus. Surgical abortion performed later in pregnancy (after 12-16 weeks) is called D&E (dilation and evacuation). The second most common abortion procedure, a medical abortion (aka an “abortion pill”), involves taking medications, usually mifepristone and misoprostol (aka RU-486), within the first seven to nine weeks of pregnancy to induce an abortion. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) found that 67% of abortions performed in 2014 were performed at or less than eight weeks’ gestation, and 91.5% were performed at or less than 13 weeks’ gestation. 77.3% were performed by surgical procedure, while 22.6% were medical abortions. An abortion can cost from $500 to over $1,000 depending on where it is performed and how long into the pregnancy it is.
- Abortion is a safe medical procedure that protects lives.
- Abortion bans endangers healthcare for those not seeking abortions.
- Abortion bans deny bodily autonomy, creating wide-ranging repercussions.
- Life begins at conception, making abortion murder.
- Legal abortion promotes a culture in which life is disposable.
- Increased access to birth control, health insurance, and sexual education would make abortion unnecessary.
This article was published on June 24, 2022, at Britannica’s ProCon.org , a nonpartisan issue-information source.
Home — Essay Samples — Philosophy — Ethics — Ethical Issues on Abortion
Ethical Issues on Abortion
- Categories: Abortion Ethics
About this sample

Words: 841 |
Published: Jun 6, 2024
Words: 841 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues Philosophy

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1020 words
6 pages / 2770 words
5 pages / 2147 words
1 pages / 552 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Ethics
Utilitarianism is a prominent ethical theory that has influenced moral philosophy for centuries. In this essay, we will explore the definition and history of utilitarianism, examining its association with renowned philosophers [...]
Being a responsible person means taking the necessary steps to ensure that one is doing the right thing in the right way. It involves being accountable for one's actions and making wise considerations when faced with difficult [...]
In Harper Lee's novel "To Kill a Mockingbird," one of the most memorable characters is Atticus Finch, a lawyer who defends Tom Robinson, a black man falsely accused of raping a white woman. Atticus's decision to take on this [...]
Ethics and values are foundational principles that guide human behavior and shape the moral fabric of society. They define what is right and wrong, influence decision-making, and determine the standards by which individuals and [...]
Revenge is a complex and controversial topic that has been debated for centuries. Some argue that revenge is a natural human instinct, while others believe it is never justified. In this essay, we will explore the various [...]
Overview of the author's moral and ethical stance based on Levinas' theory Connection to biblical passage "Thou shalt not kill" Discussion of how scripture and Catholic teachings inform the author's conscience [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Most Important Study in the Abortion Debate
Researchers rigorously tested the persistent notion that abortion wounds the women who seek it.
The demographer Diana Greene Foster was in Orlando last month, preparing for the end of Roe v. Wade , when Politico published a leaked draft of a majority Supreme Court opinion striking down the landmark ruling. The opinion, written by Justice Samuel Alito, would revoke the constitutional right to abortion and thus give states the ability to ban the medical procedure.
Foster, the director of the Bixby Population Sciences Research Unit at UC San Francisco, was at a meeting of abortion providers, seeking their help recruiting people for a new study . And she was racing against time. She wanted to look, she told me, “at the last person served in, say, Nebraska, compared to the first person turned away in Nebraska.” Nearly two dozen red and purple states are expected to enact stringent limits or even bans on abortion as soon as the Supreme Court strikes down Roe v. Wade , as it is poised to do. Foster intends to study women with unwanted pregnancies just before and just after the right to an abortion vanishes.
Read: When a right becomes a privilege
When Alito’s draft surfaced, Foster told me, “I was struck by how little it considered the people who would be affected. The experience of someone who’s pregnant when they do not want to be and what happens to their life is absolutely not considered in that document.” Foster’s earlier work provides detailed insight into what does happen. The landmark Turnaway Study , which she led, is a crystal ball into our post- Roe future and, I would argue, the single most important piece of academic research in American life at this moment.
The legal and political debate about abortion in recent decades has tended to focus more on the rights and experience of embryos and fetuses than the people who gestate them. And some commentators—including ones seated on the Supreme Court—have speculated that termination is not just a cruel convenience, but one that harms women too . Foster and her colleagues rigorously tested that notion. Their research demonstrates that, in general, abortion does not wound women physically, psychologically, or financially. Carrying an unwanted pregnancy to term does.
In a 2007 decision , Gonzales v. Carhart , the Supreme Court upheld a ban on one specific, uncommon abortion procedure. In his majority opinion , Justice Anthony Kennedy ventured a guess about abortion’s effect on women’s lives: “While we find no reliable data to measure the phenomenon, it seems unexceptionable to conclude some women come to regret their choice to abort the infant life they once created and sustained,” he wrote. “Severe depression and loss of esteem can follow.”
Was that really true? Activists insisted so, but social scientists were not sure . Indeed, they were not sure about a lot of things when it came to the effect of the termination of a pregnancy on a person’s life. Many papers compared individuals who had an abortion with people who carried a pregnancy to term. The problem is that those are two different groups of people; to state the obvious, most people seeking an abortion are experiencing an unplanned pregnancy, while a majority of people carrying to term intended to get pregnant.
Foster and her co-authors figured out a way to isolate the impact of abortion itself. Nearly all states bar the procedure after a certain gestational age or after the point that a fetus is considered viable outside the womb . The researchers could compare people who were “turned away” by a provider because they were too far along with people who had an abortion at the same clinics. (They did not include people who ended a pregnancy for medical reasons.) The women who got an abortion would be similar, in terms of demographics and socioeconomics, to those who were turned away; what would separate the two groups was only that some women got to the clinic on time, and some didn’t.
In time, 30 abortion providers—ones that had the latest gestational limit of any clinic within 150 miles, meaning that a person could not easily access an abortion if they were turned away—agreed to work with the researchers. They recruited nearly 1,000 women to be interviewed every six months for five years. The findings were voluminous, resulting in 50 publications and counting. They were also clear. Kennedy’s speculation was wrong: Women, as a general point, do not regret having an abortion at all.
Researchers found, among other things, that women who were denied abortions were more likely to end up living in poverty. They had worse credit scores and, even years later, were more likely to not have enough money for the basics, such as food and gas. They were more likely to be unemployed. They were more likely to go through bankruptcy or eviction. “The two groups were economically the same when they sought an abortion,” Foster told me. “One became poorer.”
Read: The calamity of unwanted motherhood
In addition, those denied a termination were more likely to be with a partner who abused them. They were more likely to end up as a single parent. They had more trouble bonding with their infants, were less likely to agree with the statement “I feel happy when my child laughs or smiles,” and were more likely to say they “feel trapped as a mother.” They experienced more anxiety and had lower self-esteem, though those effects faded in time. They were half as likely to be in a “very good” romantic relationship at two years. They were less likely to have “aspirational” life plans.
Their bodies were different too. The ones denied an abortion were in worse health, experiencing more hypertension and chronic pain. None of the women who had an abortion died from it. This is unsurprising; other research shows that the procedure has extremely low complication rates , as well as no known negative health or fertility effects . Yet in the Turnaway sample, pregnancy ended up killing two of the women who wanted a termination and did not get one.
The Turnaway Study also showed that abortion is a choice that women often make in order to take care of their family. Most of the women seeking an abortion were already mothers. In the years after they terminated a pregnancy, their kids were better off; they were more likely to hit their developmental milestones and less likely to live in poverty. Moreover, many women who had an abortion went on to have more children. Those pregnancies were much more likely to be planned, and those kids had better outcomes too.
The interviews made clear that women, far from taking a casual view of abortion, took the decision seriously. Most reported using contraception when they got pregnant, and most of the people who sought an abortion after their state’s limit simply did not realize they were pregnant until it was too late. (Many women have irregular periods, do not experience morning sickness, and do not feel fetal movement until late in the second trimester.) The women gave nuanced, compelling reasons for wanting to end their pregnancies.
Afterward, nearly all said that termination had been the right decision. At five years, only 14 percent felt any sadness about having an abortion; two in three ended up having no or very few emotions about it at all. “Relief” was the most common feeling, and an abiding one.
From the May 2022 issue: The future of abortion in a post- Roe America
The policy impact of the Turnaway research has been significant, even though it was published during a period when states have been restricting abortion access. In 2018, the Iowa Supreme Court struck down a law requiring a 72-hour waiting period between when a person seeks and has an abortion, noting that “the vast majority of abortion patients do not regret the procedure, even years later, and instead feel relief and acceptance”—a Turnaway finding. That same finding was cited by members of Chile’s constitutional court as they allowed for the decriminalization of abortion in certain circumstances.
Yet the research has not swayed many people who advocate for abortion bans, believing that life begins at conception and that the law must prioritize the needs of the fetus. Other activists have argued that Turnaway is methodologically flawed; some women approached in the clinic waiting room declined to participate, and not all participating women completed all interviews . “The women who anticipate and experience the most negative reactions to abortion are the least likely to want to participate in interviews,” the activist David Reardon argued in a 2018 article in a Catholic Medical Association journal.
Still, four dozen papers analyzing the Turnaway Study’s findings have been published in peer-reviewed journals; the research is “the gold standard,” Emily M. Johnston, an Urban Institute health-policy expert who wasn’t involved with the project, told me. In the trajectories of women who received an abortion and those who were denied one, “we can understand the impact of abortion on women’s lives,” Foster told me. “They don’t have to represent all women seeking abortion for the findings to be valid.” And her work has been buttressed by other surveys, showing that women fear the repercussions of unplanned pregnancies for good reason and do not tend to regret having a termination. “Among the women we spoke with, they did not regret either choice,” whether that was having an abortion or carrying to term, Johnston told me. “These women were thinking about their desires for themselves, but also were thinking very thoughtfully about what kind of life they could provide for a child.”
The Turnaway study , for Foster, underscored that nobody needs the government to decide whether they need an abortion. If and when America’s highest court overturns Roe , though, an estimated 34 million women of reproductive age will lose some or all access to the procedure in the state where they live. Some people will travel to an out-of-state clinic to terminate a pregnancy; some will get pills by mail to manage their abortions at home; some will “try and do things that are less safe,” as Foster put it. Many will carry to term: The Guttmacher Institute has estimated that there will be roughly 100,000 fewer legal abortions per year post- Roe . “The question now is who is able to circumvent the law, what that costs, and who suffers from these bans,” Foster told me. “The burden of this will be disproportionately put on people who are least able to support a pregnancy and to support a child.”
Ellen Gruber Garvey: I helped women get abortions in pre- Roe America
Foster said that there is a lot we still do not know about how the end of Roe might alter the course of people’s lives—the topic of her new research. “In the Turnaway Study, people were too late to get an abortion, but they didn’t have to feel like the police were going to knock on their door,” she told me. “Now, if you’re able to find an abortion somewhere and you have a complication, do you get health care? Do you seek health care out if you’re having a miscarriage, or are you too scared? If you’re going to travel across state lines, can you tell your mother or your boss what you’re doing?”
In addition, she said that she was uncertain about the role that abortion funds —local, on-the-ground organizations that help people find, travel to, and pay for terminations—might play. “We really don’t know who is calling these hotlines,” she said. “When people call, what support do they need? What is enough, and who falls through the cracks?” She added that many people are unaware that such services exist, and might have trouble accessing them.
People are resourceful when seeking a termination and resilient when denied an abortion, Foster told me. But looking into the post- Roe future, she predicted, “There’s going to be some widespread and scary consequences just from the fact that we’ve made this common health-care practice against the law.” Foster, to her dismay, is about to have a lot more research to do.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Reproductive rights in America
7 persistent claims about abortion, fact-checked.

Jaclyn Diaz
Koko Nakajima
Nick Underwood

Anti-abortion demonstrators watch as abortion rights protestors chant in front of the U.S. Supreme Court in Washington, D.C., on May 5. Jim Watson/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Anti-abortion demonstrators watch as abortion rights protestors chant in front of the U.S. Supreme Court in Washington, D.C., on May 5.
Since the Supreme Court's 1973 Roe v. Wade decision ruled that women have a constitutional right to end their pregnancies, proponents and opponents of abortion rights have worked to own the conversation over the issue.
In 2019, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported that 629,898 legal induced abortions were reported across the United States.
Lingering claims circulate about abortion, including about the safety of it, who gets abortions and even who supports or opposes access to abortion.
Below, seven popular claims surrounding abortion get fact-checked.
According to the Pew Research Center's polls , 37% of Americans want abortion illegal in all or most cases.
But an even bigger fraction — around 6 in 10 Americans — think abortion should be legal in all or most cases.
Current abortion rates are lower than what they were in 1973 and are now less than half what they were at their peak in the early 1980s, according to the Guttmacher Institute , a reproductive health research organization that supports abortion rights.
In 2017, pregnancy rates for females age 24 or below hit their lowest recorded levels, reflecting a long-term decline in pregnancy rates among females 24 or below.
Overall, in 2017, pregnancy rates for females of reproductive age hit their lowest recorded levels, with 87 pregnancies per 1,000 females ages 15 to 44, according to the Guttmacher Institute.
The annual number of deaths related to legal induced abortion has fluctuated from year to year since 1973, according to the CDC.
An analysis of data from 2013 to 2018 showed the national case-fatality rate for legal induced abortion was 0.41 deaths per 100,000 legal induced abortions, lower than in the previous five years.
The World Health Organization said people obtaining unsafe abortions are at a higher risk of death. Annually, 4.7% to 13.2% "of maternal deaths can be attributed to unsafe abortion," the WHO said. In developing regions of the world, there are 220 deaths per 100,000 unsafe abortions.
Trans and nonbinary people have undergone abortions as well.
The Guttmacher Institute estimates in 2017 an estimated 462 to 530 transgender or nonbinary individuals in the U.S. had abortions. That same year, the CDC said, 609,095 total abortions were carried out in the country.
The Abortion Out Loud campaign has collected stories from thousands of people who have had an abortion. Included are stories from trans and nonbinary people who have had an abortion — such as Jae, who spoke their experience.
"Most abortions in 2019 took place early in gestation," according to the CDC . Nearly 93% of abortions were performed at less than 13 weeks' gestation.
Abortion pills, which can typically be used up to 10 weeks into a pregnancy, made up 54% of abortions in 2020. These pills were the primary choice in the U.S. for the first time since the Food and Drug Administration approved the abortion drug mifepristone more than 20 years ago.
State legislatures have been moving to adopt 20-week abortion bans, with abortion opponents claiming fetuses can feel pain at that point. Roughly a third of states have implemented an abortion ban around 20 weeks .
But this contradicts widely accepted medical research from 2005. This study , published in the Journal of the American Medical Association , concluded that a fetus is not capable of experiencing pain until somewhere between 29 or 30 weeks.
Researchers wrote that fetal awareness of pain requires "functional thalamocortical connections." Those thalamocortical fibers begin appearing between 23 and 30 weeks' gestational age, but the capacity for pain perception comes later.
The argument against abortion has frequently been based on religion.
Data shows that the majority of people who get an abortion have some sort of religious affiliation, according to the most recent Guttmacher Institute data , from 2014.
The Pew Research Center also shows that attitudes on whether abortion should be legal vary among evangelical Protestants, mainline Protestants and Catholics.


Roe v. Wade and the future of reproductive rights in America
Here's what could happen now that roe v. wade is overturned.
- Supreme Court
- Roe v. Wade

Princeton Legal Journal

The First Amendment and the Abortion Rights Debate
Sofia Cipriano
4 Prin.L.J.F. 12
Following Dobbs v. Jackson ’s (2022) reversal of Roe v. Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are protected by various state constitutions’ free exercise clauses — and, by extension, the First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution. While reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is undoubtedly strategic, the Free Exercise Clause is not the only place to locate abortion rights: the Establishment Clause also warrants further investigation.
Roe anchored abortion rights in the right to privacy — an unenumerated right with a long history of legal recognition. In various cases spanning the past two centuries, t he Supreme Court located the right to privacy in the First, Fourth, Fifth, Ninth, and Fourteenth Amendments . Roe classified abortion as a fundamental right protected by strict scrutiny, meaning that states could only regulate abortion in the face of a “compelling government interest” and must narrowly tailor legislation to that end. As such, Roe ’s trimester framework prevented states from placing burdens on abortion access in the first few months of pregnancy. After the fetus crosses the viability line — the point at which the fetus can survive outside the womb — states could pass laws regulating abortion, as the Court found that “the potentiality of human life” constitutes a “compelling” interest. Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v. Casey (1992) later replaced strict scrutiny with the weaker “undue burden” standard, giving states greater leeway to restrict abortion access. Dobbs v. Jackson overturned both Roe and Casey , leaving abortion regulations up to individual states.
While Roe constituted an essential step forward in terms of abortion rights, weaknesses in its argumentation made it more susceptible to attacks by skeptics of substantive due process. Roe argues that the unenumerated right to abortion is implied by the unenumerated right to privacy — a chain of logic which twice removes abortion rights from the Constitution’s language. Moreover, Roe’s trimester framework was unclear and flawed from the beginning, lacking substantial scientific rationale. As medicine becomes more and more advanced, the arbitrariness of the viability line has grown increasingly apparent.
As abortion rights supporters have looked for alternative constitutional justifications for abortion rights, the First Amendment has become increasingly more visible. Certain religious groups — particularly Jewish groups — have argued that they have a right to abortion care. In Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida , a religious rights group argued that Florida’s abortion ban (HB 5) constituted a violation of the Florida State Constitution: “In Jewish law, abortion is required if necessary to protect the health, mental or physical well-being of the woman, or for many other reasons not permitted under the Act. As such, the Act prohibits Jewish women from practicing their faith free of government intrusion and thus violates their privacy rights and religious freedom.” Similar cases have arisen in Indiana and Texas. Absent constitutional protection of abortion rights, the Christian religious majorities in many states may unjustly impose their moral and ethical code on other groups, implying an unconstitutional religious hierarchy.
Cases like Generation to Generation Inc v. Florida may also trigger heightened scrutiny status in higher courts; The Religious Freedom Restoration Act (1993) places strict scrutiny on cases which “burden any aspect of religious observance or practice.”
But framing the issue as one of Free Exercise does not interact with major objections to abortion rights. Anti-abortion advocates contend that abortion is tantamount to murder. An anti-abortion advocate may argue that just as religious rituals involving human sacrifice are illegal, so abortion ought to be illegal. Anti-abortion advocates may be able to argue that abortion bans hold up against strict scrutiny since “preserving potential life” constitutes a “compelling interest.”
The question of when life begins—which is fundamentally a moral and religious question—is both essential to the abortion debate and often ignored by left-leaning activists. For select Christian advocacy groups (as well as other anti-abortion groups) who believe that life begins at conception, abortion bans are a deeply moral issue. Abortion bans which operate under the logic that abortion is murder essentially legislate a definition of when life begins, which is problematic from a First Amendment perspective; the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment prevents the government from intervening in religious debates. While numerous legal thinkers have associated the abortion debate with the First Amendment, this argument has not been fully litigated. As an amicus brief filed in Dobbs by the Freedom From Religion Foundation, Center for Inquiry, and American Atheists points out, anti-abortion rhetoric is explicitly religious: “There is hardly a secular veil to the religious intent and positions of individuals, churches, and state actors in their attempts to limit access to abortion.” Justice Stevens located a similar issue with anti-abortion rhetoric in his concurring opinion in Webster v. Reproductive Health Services (1989) , stating: “I am persuaded that the absence of any secular purpose for the legislative declarations that life begins at conception and that conception occurs at fertilization makes the relevant portion of the preamble invalid under the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the Federal Constitution.” Judges who justify their judicial decisions on abortion using similar rhetoric blur the line between church and state.
Framing the abortion debate around religious freedom would thus address the two main categories of arguments made by anti-abortion activists: arguments centered around issues with substantive due process and moral objections to abortion.
Conservatives may maintain, however, that legalizing abortion on the federal level is an Establishment Clause violation to begin with, since the government would essentially be imposing a federal position on abortion. Many anti-abortion advocates favor leaving abortion rights up to individual states. However, in the absence of recognized federal, constitutional protection of abortion rights, states will ban abortion. Protecting religious freedom of the individual is of the utmost importance — the United States government must actively intervene in order to uphold the line between church and state. Protecting abortion rights would allow everyone in the United States to act in accordance with their own moral and religious perspectives on abortion.
Reframing the abortion rights debate as a question of religious freedom is the most viable path forward. Anchoring abortion rights in the Establishment Clause would ensure Americans have the right to maintain their own personal and religious beliefs regarding the question of when life begins. In the short term, however, litigants could take advantage of Establishment Clauses in state constitutions. Yet, given the swing of the Court towards expanding religious freedom protections at the time of writing, Free Exercise arguments may prove better at securing citizens a right to an abortion.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Asian Bioeth Rev
- v.14(1); 2022 Jan
The Moral Significance of Abortion Inconsistency Arguments
William simkulet.
1 Park University, Parkville, MO USA
2 Dodge City Community College, Dodge City, KS USA
Most opponents of abortion (OA) believe fetuses matter . Critics argue that OA act inconsistently with regards to fetal life, seeking to restrict access to induced abortion, but largely ignoring spontaneous abortion and the creation of surplus embryos by IVF. Nicholas Colgrove, Bruce Blackshaw, and Daniel Rodger call such arguments inconsistency arguments and contend they do not matter. They present three objections to these arguments — the other beliefs, other actions, and hypocrisy objection. Previously, I argued these objections fail and threaten to undermine ethical inquiry. Colgrove et al. have recently replied, but here, I argue their reply fails as well and raises a new criticism of the other actions’ objection. This essay sets out to show, as well as any philosophical argument can, that inconsistency arguments are morally significant.
Introduction
Nicholas Colgrove, Bruce Blackshaw, and Daniel Rodger ( 2020 ) set out to show that inconsistency arguments “do not matter”; by inconsistency argument , they mean to pick out a variety (Fleck 1979 ; Murphy 1985 ; Ord 2008 ; Lovering 2013 , 2014 , 2017 , 2020 ; Berg 2017 ; Simkulet 2016 , 2017 , 2019a , b , c , 2020 ; Bovens 2006 ; Schlumpf 2019 ) of disparate criticisms identifying apparent inconsistencies in how opponents of abortion (OA) treat fetuses. Unfortunately, this term is misleading, as practically all philosophical arguments involve identifying some form of inconsistency, confusion, or misunderstanding.
Critics of the prolife anti-abortion position argue that OA hold inconsistent moral beliefs; they claim to believe that fetuses are persons from conception, but they neglect the welfare of fetuses who are spontaneously aborted by natural causes, and overlook the well-being of the surplus frozen human embryos created for IVF. Perhaps the strangest argument that Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) label as an inconsistency argument comes from Sister Joan Chittister (Schlumpf 2019 ), who chastises those who call themselves “pro-life” for neglecting the welfare of born persons. Proponents of inconsistency arguments argue that OA hold inconsistent moral beliefs, arguing that upon revision, they will conclude that they either (i) need to do more, or (ii) need not oppose abortion.
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) contend that such arguments “do not matter.” This paper interprets this as the claim that inconsistency arguments are morally irrelevant for any (widely held) OA view. This paper will show that such arguments are morally relevant to the most widely held OA position.
Another way to read Colgrove et al. is as claiming they “do not matter” because they cannot show that OA need to adopt (ii) over (i). They say, “Inconsistency arguments simply are not equipped to undermine OAs’ views; at most, they reveal what OAs should do (or believe).” (Colgrove et al. 2020 ) This is uncharitable. First, while some inconsistency theorists (Ord 2008 ; Berg 2017 ) might believe that OA do not really believe fetuses are persons from conception, these arguments identify apparent inconsistency, but need not take a stance on how OA ought to resolve this inconsistency. Second, even if OA choose (i) and conclude they ought to do more to prevent spontaneous abortion (education, research, increased access to healthcare (Simkulet 2017 , 2020 ), and perhaps a major shift in social priorities (Ord 2008 ; Berg 2017 ), and more for surplus IVF embryos (adoption, and gestation (Lovering 2020 ; Blackshaw and Colgrove 2020 ; Blackshaw 2021 ), this matters . Colgrove et al. jest that if OA embrace option (i) it would “make the world a (much) worse place (from the critic’s perspective)”; but fail to note that it would make the world a much better place from the perspective of OA!
Complicating matters, there seems to be disagreement among Colgrove, Blackshaw, and Rodger regarding what opposition to abortion requires. Notably, Bruce Blackshaw ( 2021 , 166) contends that Christians ought to act as neighbors, and offers a robust, clear account of what this requires:
Treating frozen embryos as neighbors requires securing them a life like ours through adoption and gestation, and as well as opposing abortion, Christians must work toward this goal for the vast numbers of frozen embryos that would otherwise be discarded.
Blackshaw and Rodger ( 2019 ) attempt to justify OA disinterest in spontaneous abortion, claiming that most cases of spontaneous abortion are not currently preventable; but Blackshaw ( 2021 ) notes that “if we regard all human life as equally valuable, we have at least some obligation toward helping reduce deaths from spontaneous abortion where possible”.
This paper argues that inconsistency arguments matter. It is divided into three main sections. The first draws a distinction between restrictivist and moralist views on abortion, arguing only restrictivist views are OA. The second sets out to defend my earlier criticism (Simkulet 2021 ) of the other beliefs, other actions, and hypocrisy objections from Blackshaw et al.’s ( 2021 ) recent response. The third offers a new argument against the other actions objection; I argue that if this objection were to succeed, it would undermine restrictivist opposition to abortion.
Opposition to Abortion
On miscarriage.
Before his collaboration (Colgrove et al. 2020 ) with Blackshaw and Rodger, Colgrove ( 2019 ) raised a different criticism of Berg’s ( 2017 ) inconsistency argument. Berg argues that because miscarriage is so common, if we believe fetuses matter , we ought to devote more medical resources to protecting them. Colgrove replies that “miscarriage is not a cause of death,” but rather “it is an outcome.” Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) accuse me of the same error.
This is rather uncharitable, but it also misses two key points common in inconsistency arguments. First, if OA believe that fetuses matter, one would expect them to be concerned with both spontaneous and induced abortion, as both are tragic. Second, even if spontaneous abortion has many disparate causes, there may be a common solution. For example, Aspirin can treat a wide variety of conditions, from scraped knee to eye strain to migraine. Many proposals inconsistency theorists discuss (for example, education, gene therapy, and ectogenesis technology) would prevent spontaneous abortion by many different causes. In short, even if miscarriage is not a single cause of death, there is good reason to think a single solution might address many different cases, saving many fetal lives.
On Opposition to Abortion
To play on Colgrove, note that opposition to abortion is not a moral theory, it is an action or stance one can take toward abortion. There are many reasons why one might oppose abortion; one might merely find the word “abortion” to be distasteful, might oppose abortion on teleological grounds, argue that it is outside the scope of medicine, or that it violates the Hippocratic Oath.
However, most opposition to abortion rests on a single belief. Judith Jarvis Thomson ( 1972 ) says, “Most opposition to abortion relies on the premise that the fetus is a human being, a person, from the moment of conception.” Don Marquis ( 1989 ) says “Many of the most insightful and careful writers on the ethics of abortion… believe that whether or not abortion is morally permissible stands or falls on whether or not a fetus is the sort of being whose life it is seriously wrong to end.”
In short, most opposition to abortion turns on the belief that a fetus matters from conception (or soon afterwards (Marquis 2007 , 2013 ); that the fetus is morally comparable to an adult human person. This view is usually abbreviated as the view that fetuses are persons, broadly construed to mean one of many disparate theories about moral status; that human fetuses are human organisms (Mulder 2013 ), rational substances (Lee and George 2005 ; Beckwith 2007 ; George and Tollefsen 2008 ; Friberg-Fernros 2015 ), have a possible future it would be wrong to deprive them of Marquis 1989 ; Stone 1987 ), etc.
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) seek to show that inconsistency arguments are morally irrelevant for any (widely held) anti-abortion view, and there seems to be widespread consensus the most widely held anti-abortion view claims fetuses are persons, broadly construed, from conception (PAC). This paper defends the position that inconsistency arguments are morally relevant to the PAC view.
Restrictivism and Moralism
It will be practical to distinguish between two groups of anti-abortion positions — Restrictivism (Davis 1984 ; Carroll and Crutchfield Forthcoming ), the view that we should adopt social policies that restrict a woman’s access to induced abortion, and Moralism , the view that abortion is merely immoral, but that we do not need adopt Restrictivist social policies.
It is not hard to see why PAC theorists might embrace restrictivism. On this view, fetuses are comparable to adult human persons, and society has adopted policies aimed at protecting the rights of adult human persons, so it is prima facie plausible that we should adopt similar social policies regarding fetuses. However, Thomson ( 1972 ) demonstrates that it is not enough to show that fetuses merely have a right to life by way of the violinist case:
Violinist: The Society of Music Lovers kidnaps you and attaches your circulatory system to a famous, innocent, unconscious violinist suffering from a kidney ailment that will kill him unless he remains connected to your kidneys for nine months. (Adapted)
The violinist obviously has a right to life, but Thomson argues that the right to life does not give him the right to use your body; it is morally permissible for you to disconnect yourself from the violinist. Thomson says it would be a “great kindness” to stay attached to the violinist but that you do not have to accede to this.
Disconnecting the violinist from your body is comparable to disconnecting a patient from life support to let him die. Restrictivists might argue that induced abortion is not a matter of letting die; but of killing; but this will not do, as one can terminate a pregnancy without killing the fetus by severing the umbilical cord or removing the uterus, “merely” letting the fetus die. If this distinction mattered, restrictivists would not be anti-abortion, they would merely oppose how most abortions are currently performed.
Thomson shows it is not enough for restrictivists to believe fetuses are persons with a right to life, they must also believe something more , that (a) the fetus’s right to life is a positive right to assistance, or (b) the gestational mother somehow comes to have a special obligation to provide assistance to the fetus. She argues that this special obligation cannot be explained by merely risking the chance of pregnancy, as this would imply any woman who leaves the house without a hysterectomy has consented to pregnancy, even by rape. Furthermore, David Boonin ( 2002 ) argues that even if one consents to provide aid, one can withdraw consent.
Bone Marrow: Your neighbor is diagnosed with a condition that will kill him unless he receives monthly bone marrow transplants over the course of nine months from a match. You are a match and you agree to donate. However, it soon becomes clear that these surgeries ask more than you are willing to give, and you refuse to go in for the second surgery. (Adapted)
These thought experiments demonstrate that restrictivists must do more than argue fetuses are persons, they must argue that the fetus has a positive right to assistance.
However, one can believe abortion is immoral without believing we ought to adopt restrictivist social policies. There are many prima facie immoral things that it would be inappropriate to restrict by law. For example, I think most of us would agree that it is prima facie immoral to waste scarce resources, but that individuals might have a right to do so in some cases. One might hold that it is wrong to waste food without holding that throwing away leftovers should be illegal. Similarly, one might hold that adultery outside of an open marriage is immoral, but that adopting social policies that restrict such behavior would be undesirable, in part, because they are difficult to enforce, and in part because it might incentivize other immoral behavior, such as murdering one’s spouse to keep one’s adultery secret.
Moralism is the view that abortion is often, all things considered, immoral, but does not require that we adopt social policies that restrict woman’s access to abortion. There are many reasons why moralists might reject restrictivism independent of Thomson and Boonin-style concerns.
For example, restrictivist views have a hard time making exceptions for rape cases, despite the fact that many restrictivists believe such exceptions should be made. Rape victims are often reluctant to report rape and reluctant to take medical exams. Convictions in rape cases are difficult to obtain, especially within the short window in which inducing abortion would be medically preferable. As such, restrictivists face a dilemma – (a) if they require proof of rape, then few rape victims are allowed to abort; while (b) if they do not require proof of rape, they encourage women to merely say they were raped (whether true or not), failing to prevent most induced abortions and encouraging deception.
Restrictivists face a similar challenge with regards to self-defense, as all pregnancies are medically risky. The prospect of drawing a nonarbitrary line with regards to legally obligatory medical risk is dubious, but even if such a task could be achieved, those physicians sympathetic to abortion might overestimate risk and those opposing abortion might underestimate or ignore risk. Furthermore, medical risk of abortion increases with malnutrition and other medical emergencies, so those seeking abortion on medical grounds are incentivized to harm themselves to pass this threshold.
In light of these, and other, difficulties, many people who believe abortion are immoral reject restrictivism and adopt moralism. Notably, moralists need not hold that fetuses have a positive right to assistance, like restrictivists. I have contended (Simkulet 2021 ) that most OA believe fetuses have a positive right to assistance — that most OA are restrictivists. Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) claim that I miss “the target,” as one can be an OA without being committed to the belief that fetuses have a positive right to assistance.
Perhaps Colgrove et al. wish OA to pick out both restrictivist and moralist positions, but this will not do. Although moralists believe induced abortion is immoral, they are prochoice, while Colgrove et al. identify OA as prolife. Perhaps Colgrove et al. mean to say restrictivism does not require the belief that fetuses have a positive right to assistance, but this would merely introduce greater inconsistency regarding medical and legal ethics, as illustrated by Thomson ( 1972 ) and Boonin ( 2002 ).
Do Inconsistency Arguments Matter?
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) raise three objections to inconsistency arguments — the other beliefs, other actions, and hypocrisy objections. I contend (Simkulet 2021 ) these objections threaten to undermine moral analysis completely; opposing parties could always claim to have other beliefs, other actions, or interpret criticism as an ad hominem attack impinging their character.
This section is divided into four subsections. The first looks at two inconsistency arguments. The next three subsections briefly summarize Colgrove et al.’s objections, and my criticisms (Simkulet 2021 ) of these arguments.
Inconsistency Arguments
OA often point to high numbers of induced abortion as a call to action. Upwards of 60% (Boklage 1990 ; Léridon 1977 ) of human pregnancies end in spontaneous abortion, prompting critics to ask why OA do not see spontaneous abortion as a call to action. Toby Ord ( 2008 ) compares spontaneous abortion to a scourge that kills over half of humanity. Berg ( 2017 ) compares it to Heart Disease, Cancer, and Stroke. Faced with these overwhelming numbers, inconsistency theorists conclude that if fetuses matter, then the problem of spontaneous abortion calls for a massive shift in our social and political priorities. I have noted (Simkulet 2021 ) that we recently underwent such a shift to address the COVID-19 pandemic.
Henrik Friberg-Fernros ( 2015 , 2019 , 2018 ) challenges this position, contending that while fetal death is always tragic, not all fetal deaths are equally tragic; that killing is worse than letting die, and even that fetal lives are worth less than adult human lives because they lack time relative interests (Friberg-Fernros 2019 )! However, inconsistency arguments do not assume that all fetal deaths are equally tragic, merely that if fetuses matter, their deaths are tragic.
OA face a dilemma — either they (i) need to do more to prevent fetal death, or (ii) should withdraw opposition to induced abortion. Some proponents think OA should choose (ii) — that the argument demonstrates they do not really believe fetuses are persons. However, others propose a wide variety of methods by which OA might reasonably seek to confront the problem of fetal death, from increased education and better access to healthcare, to technologies like ectogenesis and gene therapy that those on both sides of the abortion debate could reasonably support (Simkulet 2020 ).
While many inconsistency arguments focus on unaddressed fetal loss, Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) also categorize Chittister's tweet (Schlumpf 2019 ) as an inconsistency argument. She asks whether it makes sense to call OA “pro-life” merely because they oppose abortion, noting all OA seem to be concerned with is ensuring the child is born, not fed, educated, or housed; asserting “That’s not pro-life. That’s pro-birth.”
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) contend that Chittister is using the term “pro-birth” pejoratively, but this is rather uncharitable. The term “pro-life” carries with it a positive emotive context, and when OA present their view as “pro-life,” they may mislead their audience about their position. In contrast, the term “pro-birth” seems to capture the one unifying feature of OA.
Even if Chittister is angry or disappointed that OA misrepresent their position, neglect their moral obligations, or the like… so what? That is how moral judgements work. If you think Φing is wrong, and you see someone Φing, it makes sense to be angry or disappointed. Colgrove et al. speak as though this, and accusations of pro-life hypocrisy are ad hominem attacks on OA; not so. An ad hominem fallacy occurs when one attacks person rather than their argument or view. Inconsistency arguments do not do this; they identify apparent inconsistency within the OA view, and call for change, as Chittister does when she concludes, “We need a much broader conversation on what the morality of pro-life is.”
Other Beliefs Objection and Response
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) raise three objections to inconsistency arguments. In the first, they contend that inconsistency arguments do not matter because there is a diversity of beliefs among OA, suggesting that no one inconsistency argument undermine them all; “This diversity makes broad accusations of inconsistency problematic.” Following this, one might argue that when an OA is confronted with apparent inconsistency within one view, they can jump ship to another OA view. But moral analysis is not a shell game. If inconsistency arguments identify a problem within even one OA position, they matter; and if they threaten the most widely held OA position, it seems they matter quite a bit.
Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) suggest that OA may have other beliefs which explain away apparent inconsistency and justify their inaction with regards to spontaneous abortion; for example they ask us to consider someone who both opposes induced abortion and opposes universal healthcare; noting these beliefs would justify rejecting the conclusion that we should adopt universal health care to help address the problem of induced and spontaneous abortion (and suffering and death due to lack of medical care, more broadly). To this, I reply (Simkulet 2021 ):
It is not enough to show that some [OA] have some beliefs that are prima facie at odds with some [inconsistency theorist] proposals; they must show that the current level of apparent indifference that many [OA] show is justified by their other beliefs; and it is not clear what set of other beliefs would be both internally consistent and justify the conclusion that while persons [matter], this right requires very little in the way of sacrifice from anyone but gestational mothers.
Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) contend that I argue “this [apparent] indifference must be justified by their other beliefs…” continuing “there is an obvious belief that justifies [OA]’s actions and priorities —… [OA] believe that induced abortion is a more important priority than these other issues.” However, this misses the point. As we have seen above, inconsistency theorists do not claim that OA need to treat the problem of spontaneous abortion as equally important to the problem of induced abortion, but rather they must consistently recognize both are tragic.
Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) continue “induced abortion is the leading preventable cause of death of human beings, as spontaneous abortions are largely unpreventable.” However, they seem to understand “preventable” in an opportunistically narrow way — as preventable with our current technology — to disregard the problem of spontaneous abortion. Amy Berg ( 2017 ) challenges this opportunistically narrow caveat:
But imagine throwing up our hands about a horrible disease… Imagine saying that we should let AIDS, or cancer, or heart disease take its course, rather than expending more effort researching how we might prevent that disease or treat people who contract it. That’s not what we do.
Berg ( 2017 ) notes that just because spontaneous abortion is medically intractable now does not mean it will be in the future, comparing to the AIDs epidemic, “In just a couple of decades, AIDS went from a mysterious underground disease, to a devastating and fatal epidemic, to a relatively manageable chronic condition.”
Perhaps more troublingly, Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) say, “If OAs sincerely believe these claims, then they are acting consistently with their beliefs, and the Other Beliefs Objection succeeds.” Above I have argued that even if one sees one form of abortion as a greater priority than another, this does not justify apparent indifference OAs show with regards to spontaneous abortion.
The real challenge here is “sincerity,” most people have inconsistent beliefs of one form or another and do not realize it; but it is possible that one can realize that they hold two sincere beliefs while also sincerely believing those beliefs to be inconsistent. Consider the problem of evil; one might sincerely believe that God exists, that evil exists, and that God would not allow evil to exist. This belief set is inconsistent, but does not necessarily yield conflicting implications for how we ought to live our lives.
But what if an OA sincerely believes the following?
- All human death is morally tragic.
- Not all human death is morally tragic.
- Propositions (a) and (b) are apparently a contradiction.
It is easy to imagine a Socratic dialogue in which Socrates helps an OA to express position (a) and proposition (b), prompting them to reconsider their position; what’s less easy to imagine is what would happen if an OA freely admits proposition (c), but refuses to reconsider. Moral agency requires some degree of reason-responsiveness, and at least with regards to the topic at hand, it is not clear such an OA would be able to function as a moral agent without rejecting one of these three propositions.
Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) end their reply as follows “If critics of [OA] want to change the subject – to examining whether the things [OA] believe are true or false, rather than fixating on [OA’s] alleged inconstancy — then [our] essay has succeeded.” Here, they again miss the point of inconsistency arguments, as these arguments do set out to examine whether the things [OA] believe are true or false; if the principle of non-contradiction is true, and OA hold contradictory beliefs, then at least one of their beliefs are false !
Why do they miss this point? I cannot be sure, but at times Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) and Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) talk as though inconsistency theorists are uniformly prochoice and hope to convince OA to abandon restrictivism; however, inconsistency arguments might just as easily lead one to believe they ought to do more to prevent spontaneous abortion, address surplus frozen human embryos, and the like. Some inconsistency theorists believe both would lead to less restrictivist opposition to abortion, but this is irrelevant.
What matters is that inconsistency arguments share the same form as the Socratic method, highlighting apparent inconsistency and prompting introspection. Perhaps Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) would also conclude that the Socratic method does not matter , but I hope not.
Other Actions Objection and Response
Colgrove et al.’s second criticism of inconsistency arguments is that they are too specific with their recommendations, suggesting OA can address problems raised by these arguments with different actions than those proposed by inconsistency theorists. For example, rather than adopt and gestate frozen human Embryos, as Lovering ( 2020 ) (and Blackshaw 2021 !) advocate, Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) suggest OA might fight “to change public perception of the status of embryos,” or lobby to change IVF laws.
There are three problems here. First, although inconsistency theorists propose a variety of recommendations, these recommendations are not meant to be exhaustive, but rather representative of the kinds of changes an OA would need to adopt to resolve their apparent inconsistency. Remember, inconsistency theorists argue that OA face a dilemma — either (i) do more, or (ii) abandon their opposition to abortion; to say that an OA can perform other actions to address the problem just is to embrace the first horn of the dilemma.
Second, I have pointed out (Simkulet 2021 ) that the other actions Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) propose are not necessarily mutually exclusive; one might both lobby to change IVF laws and adopt and gestate frozen human embryos. The fact that one lobbies to change IVF laws may reduce the number of surplus embryos created and frozen in the future; but it fails to address the needs of currently existing frozen human embryos, highlighting a third problem, that many of Colgrove et al.’s “other actions” are simply not enough. I illustrate (Simkulet 2021 ) this with a case inspired by James Rachels ( 1979 ):
Jack 2 finds himself in a room with a starving child, surplus sandwich in hand. He receives a call… The caller asks, “Will you donate your sandwich?” and he replies, “I’ll do you one better; I’m going to fight to change the public perception of the status of such starving children and raise awareness!” He proceeds to tweet about the starving child, sets up a donation page to help spread awareness, and posts pictures and videos of the child’s deteriorating state. Jack 2 , an expert in such things, narrates as the child slowly dies.
Jack 2 ’s claim to act to raise awareness pokes fun at Colgrove et al.’s ( 2020 ) proposal to protect frozen embryos by fighting to change public perception. Despite his tweeting, it is clear Jack 2 fails morally — he lets a child starve to death when he could have easily saved that child’s life.
Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) argue that this case is disanalogous to OA (in)action, arguing that OA “live in a world where there are many important issues clamoring for their attention,” and suggest the following case is more analogous:
Jack 100 finds himself in a room with 100 needy children and only enough resources to save 1 child, which he does.
There are three substantive problems with this response. First, the case of Jack 2 is not meant to be analogous to OA inaction (despite poking fun at it); it is meant to demonstrate that merely having other actions is not sufficient to show that inconsistency arguments fail.
Second, the case of Jack 100 begs the question by assuming Jack is saving as many people as possible. However, as Lovering ( 2020 ) and Blackshaw ( 2021 ) seem to show, this simply is not how OA act. Inconsistency theorists argue that OA neglect to address the problems of spontaneous abortion, surplus frozen embryos, and even starving born children. Rather than save all they can, inconsistency theorists contend that OA act like Jack 2 , they do something , but fail to do everything they can.
Third, inconsistency theorists contend that most OA legislation and philosophical literature neglect to discuss the problems of spontaneous abortion, surplus frozen embryos, or starving born children. As such, perhaps the following case would be more analogous:
Jack 300 finds himself in a room with 300 needy children, and he says, “I see 100 needy children, but woe is me I can only save 1,” and so he saves 1 child.
It seems Jack 300 is unreliable; he says he sees 100 needy children in the room, but there are 300 needy children in the room. If we cannot trust Jack 300 to get an accurate headcount, it seems unreasonable to take his word that he is doing all he can.
With the Jack 100 case Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) seem to abandon the other actions objection, instead arguing that OA, like Jack 100 , do the “most good” they can. In short, Blackshaw et al. seem to treat the other actions’ objection as a surrogate for an argument from effective altruism, the view that we should try to do the most good we can. Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) claim that there are many different beliefs about what it means to do the “most good”, and suggest that objectively measuring options might be difficult, as though to claim that it does not matter what other actions OA take as long as they are trying to do the “most good.”
But this will not do. Effective altruism asks us to use reason and empirical evidence to maximize the amount of good we do, and inconsistency arguments seem to show that OA fail to do just this. Like Jack 2 , OA seem to ignore the easily preventable deaths of some with an unearned confidence that their current course of action is sufficient. If OA strive for effective altruism, they should be at least open to the prospect of embracing the first horn of the inconsistency theorist’s dilemma — that maybe should do more. Suppose Jill 100 finds herself in the locked room with Jack 100 , and promises to show Jack 100 how he can save 3 needy children, rather than just 1, with the resources at hand; if Jack 100 seeks to be an effective altruist, should he not at least listen, time permitting?
Effective altruism requires that we guide our choices by reason and evidence; it is not enough to have a sincere belief that one is doing all that one can, the evidence has to back this up. If inconsistency theorists can show that OA are not doing all they can, then they have been succeeding in showing that OA fall short of effective altruism.
Of course, this is exactly what proponents of inconsistency theorists purport to show. Take the aforementioned inconsistency theorist Lovering ( 2020 ) who, like OA restrictivist Blackshaw ( 2021 ), argues that OA should do more than merely fight to change public perception or lobby to change IVF laws, in many cases they ought to also adopt and gestate actually existing frozen human embryos. Of course, not every OA can gestate frozen human embryos — without effective ectogenesis technology and universal healthcare this burden seems to fall on wealthy, female OA alone. However, few OA argue that adopting and gestating these embryos are obligatory for those with the means to do so, and this omission at least appears to be inconsistent with their assertion that all fetuses matter from conception, let alone the position that OA are acting as effective altruists.
Furthermore, Blackshaw ( 2021 ) does not merely side with Lovering regarding OA’s obligations regarding frozen human embryos; he says:
[I]f we regard all human life as equally valuable, we have at least some obligation toward helping reduce deaths from spontaneous abortion where possible. The parable of the Good Samaritan reinforces the notion that Christians do have some responsibility toward this neglected group of human beings, who are also our neighbors.
Here Blackshaw ( 2021 ) contends that these groups — frozen human embryos and those fetuses who die from spontaneous abortion — matter , and that at least some OA — those inconsistency arguments seek to criticize — neglect them. In short, Blackshaw’s ( 2021 ) view seems at odd with the view he expresses in Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) and Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ). This is not meant as a criticism of Blackshaw; philosophers revise their views over time, articles are often published long after their initial submission, and many articles are written for blind review which could disincentivize the author from discussing their previous works.
Note, however, that Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) and Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) set out to argue that inconsistency arguments do not matter for any OA view and in doing so they bite off far more than they can chew. It is easy to contend that all OA have other possible actions – contra Frankfurt ( 1969 ), many philosophers believe alternate possibilities are required for moral agency and responsibility; but it is quite a different matter to argue that all OA are acting as effective altruists, or even that all OA merely sincerely believe they are acting as effective altruists, especially when confronted with criticism from inconsistency theorists. Blackshaw ( 2021 ) contends inconsistency arguments demonstrate that some OA neglect this group, and this alone seems sufficient to show inconsistency arguments are morally significant.
Hypocrisy Objection and Response
In their third objection, Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) contend that inconsistency arguments aim to show that OA are hypocrites, rather than demonstrate inconsistency. I note (Simkulet 2021 ) that Colgrove et al. equivocate between hypocrisy and inconsistency, and that they characterize hypocrisy as a moral failing. Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) say:
[OA] are often described as ’inconsistent’ (hypocrites) in terms of their beliefs, actions and/or priorities…These objections notwithstanding, perhaps some OAs do act in ways that can be shown to be inconsistent with their beliefs. If so, then they are hypocrites. Hypocrisy is a serious charge regarding the character of OAs, but it has nothing to say regarding the validity and consistency of their beliefs—and OAs’ beliefs are surely what critics should primarily be targeting.
In short, it seems that Colgrove et al. mischaracterize inconsistency arguments as ad hominem fallacies; but as we have already seen there is a difference. Inconsistency arguments are simply not aimed at showing OA are hypocrites; only that they have inconsistent beliefs.
In their reply to my previous work (Simkulet 2021 ), Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) say something bizarre “Simkulet offers no empirical evidence regarding [OA’s] supposed lack of interest in relevant issues.” But inconsistency theorists do this ; Lovering ( 2020 ) goes to great lengths to discuss OA who do go out of their way to address these concerns and provides evidence such altruism is rare . Still, it is difficult to take this call for empirical evidence seriously, as neither Colgrove et al. ( 2020 ) nor Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) provide such evidence on behalf of OA.
Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) also challenge my claim (Simkulet 2021 ) that legislation seeking to reduce the creation of surplus IVF embryos would be relatively easy to pass:
Not so. Italy, for example, passed a law in 2004 prohibiting the freezing of embryos, and requiring that all embryos be implanted. (Riezzo et al. 2016 ) The law was swiftly condemned, eventually overturned and, in one case, actions prescribed by the law were declared by the UN to have constituted a ‘human rights violation.’ (Scaffidi 2019 ) Thus, relevant laws would likely face international resistance. So, a central problem Simkulet puts forth as having an ‘easy’ solution does not.
There are two big problems here. First, I propose (Simkulet 2021 ) passing legislation to limit the creation of surplus embryos, not to force all created embryos to be implanted. The difference is obvious, my restrictivist proposal would limit the number of embryos created at a time, so it might take multiple tries before a successful embryo is created.
In contrast, the Italian law seems to place no limits on how many embryos can be created, rather it sets out to force women to undergo invasive, risky medical procedures. IVF has a relatively low chance of success; but imagine more attempts at fertilization succeed than expected; this law would compel physicians to perform, and women to undergo, dangerous medical procedures against their wills. This is hauntingly similar to forcing you to donate bone marrow even at the cost of your life in Boonin’s ( 2002 ) bone marrow case. In short, the Italian law threatens to harm citizens and undermine professional ethics by requiring medically risky and unnecessary interventions without the patient’s consent.
In contrast, my proposal (Simkulet 2021 ) would merely require physicians limit the number of embryos created at one time; not entirely dissimilar from legal limits on how many drugs a physician can prescribe within a period of time. Furthermore, I do not say such legislation would be easy, only “relatively easy” compared to restrictivist legislation – legislation that has far more in common with the Italian law than Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) acknowledge. Both restrictivist legislation and the Italian law seek to undermine women’s rights to control their body and force them to risk their lives for the sake of others. Meanwhile limiting the number of embryos created does not limit one’s reproductive freedom, nor compel them to take on additional medical risk.
Both OA restrictivist legislation and the Italian law seek to limit women’s reproductive choices and force women to take on additional medical risk. Legislation of this kind faces strong opposition from those seeking to protect women’s liberty and reproductive freedom. This kind of legislation also faces strong opposition from biomedical ethicists and medical professionals, as it threatens to violate patient autonomy and the Hippocratic Oath by forcing patient and physician to perform risky medical procedures to benefit a third party, not unlike forcing you to remain attached to the violinist in Thomson’s infamous violinist case (Thomson 1972 ).
In contrast, it is not clear that my proposed legislation (Simkulet 2021 ) to limit the number of embryos that can be created at a single time, would face much opposition at all. Perhaps eugenicists would oppose such legislation for limiting a parent’s right to choose the “best” fetus from the widest possible net, but this does not seem like a widely held position. Perhaps bioethicists and medical professionals would oppose such legislation believing it cumbersome and impractical, but this seems like a much weaker ground for opposition than the autonomy and professional ethics violations epitomized by OA restrictivist legislation and the Italian law.
The Prochoice Other Beliefs Objection
I have argued (Simkulet 2021 ) that if the other beliefs, other actions, and hypocrisy objections are not successful in showing inconsistency arguments “do not matter,” they threaten to undermine the discipline of ethics. No person has merely one moral belief, so if a diversity of beliefs invalidates moral analysis, ethics is impossible. In all cases in which a person acts morally responsibly (save maybe some interpretations of Frankfurt-style cases (Frankfurt 1969 ), agents have other possible actions, so if merely having other actions was sufficient to disregard moral analysis, ethics fails. Finally, if interpreting moral analysis as an ad hominem attack of hypocrisy was sufficient to rebuff criticism, one can shut down all moral debate merely by being thin-skinned. Here, I have argued that Blackshaw et al. ( 2021 ) fail to defend these objections, and fail to show that inconsistency arguments do not matter.
However, these are lofty claims about the discipline of ethics; let’s consider something a bit more down to Earth. Consider the following case:
Jacqueline is surprised to find herself pregnant, calling into question her school’s sexual education program. While discussing the matter with her physician, she learns that some people believe embryos are persons from conception! She finds this view intuitive and compelling, and outraged by her school’s poor sexual education program, she endeavors to work tirelessly to change the public perception of the status of embryos. Later, her physician expresses concern about her exertion, recommending that she puts her efforts to educate on hiatus during the pregnancy, fearing the worst. Jacqueline faces a choice — (i) continue with her pregnancy for the next 6 months, losing ground on her fight to change public perception of embryos or (ii) induce abortion (perhaps by hysterectomy) and continue the fight. When speaking with her physician, Jacqueline quotes an influential piece of literature (Colgrove et al. 2020 ), “It may be unclear, however, which option is superior. Many considerations apply to each, and they may be highly individualistic.” She continues “Objectively evaluating options to determine the most appropriate action for a particular belief held by a specific individual seems a very difficult task.” Upon careful and thoughtful reflection, she chooses (ii), judging that it will do the most good. After all, her embryo is but one embryo and while it is tragic to disconnect it from her body and let it die, her tireless efforts might do more good overall.
If the other actions objection shields OA from inconstancy arguments, it seems that it equally shields Jaqueline from restrictivist OA arguments that seek to restrict her freedom. Therefore, it seems that Blackshaw et al. face a dilemma — (i) reject the position that merely having other actions, beliefs, etc. is sufficient to shield a position from criticism, or (ii) abandon their opposition to induced abortion. If (i), then inconsistency arguments matter. Then again, if (ii), then it seems as though no ethical arguments matter.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Beckwith, Francis J. 2007. Defending life: A moral and legal case against abortion choice . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
- Berg Amy. Abortion and miscarriage. Philosophical Studies. 2017; 174 (5):1217–1226. doi: 10.1007/s11098-016-0750-z. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blackshaw, Bruce Philip. 2021. Is pregnancy really a Good Samaritan act? Christian Bioethics 7(2): 158–168. 10.1093/cb/cbab004.
- Blackshaw, Bruce Philip, and Daniel Rodger. 2019. The problem of spontaneous abortion: is the pro-life position morally monstrous? New Bioethics 25(2): 103–120. 10.1080/20502877.2019.1602376. [ PubMed ]
- Blackshaw Bruce Philip, Colgrove Nicholas. Frozen embryos and the obligation to adopt. Bioethics. 2020; 34 (8):857–861. doi: 10.1111/bioe.12733. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blackshaw, Bruce Philip, Nicholas Colgrove, Daniel Rodger. 2021. Inconsistency arguments still do not matter. Journal of Medical Ethics . 10.1136/medethics-2021-107644. [ PubMed ]
- Boklage, C.E. 1990. Survival probability of human conceptions from fertilization to term. International Journal of Fertility 35(2): 75–94. [ PubMed ]
- Boonin, David. 2002. A defense of abortion . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. 10.1017/CBO9780511610172.
- Bovens Luc. The rhythm method and embryonic death. Journal of Medical Ethics. 2006; 32 (6):355–356. doi: 10.1136/jme.2005.013920. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carroll, Emily, and Parker Crutchfield. Forthcoming. The duty to protect, abortion, and organ donation. Cambridge Quarterly of Healthcare Ethics . [ PubMed ]
- Colgrove, Nicholas. 2019. Miscarriage is not a cause of death: a response to Berg’s “abortion and miscarriage”. Journal of Medicine and Philosophy 46(4): 394–413. 10.1093/jmp/jhab010. [ PubMed ]
- Colgrove, Nicholas, Bruce Philip Blackshaw, Daniel Rodger. 2020. Prolife hypocrisy: why inconsistency arguments do not matter. Journal of Medical Ethics . 10.1136/medethics-2020-106633. [ PubMed ]
- Davis, Nancy. 1984. Abortion and self-defense. Philosophy and Public Affairs 13(3): 175–207. [ PubMed ]
- Fleck, Leonard M. 1979. Abortion, deformed fetuses, and the Omega pill. Philosophical Studies 36(3): 271–283. 10.1007/BF00372631. [ PubMed ]
- Frankfurt, Harry G. 1969. Alternate possibilities and moral responsibility. Journal of Philosophy 66(23): 829–839. 10.2307/2023833.
- Friberg-Fernros, Henrik. 2015. A critique of Rob Lovering’s criticism of the substance view. Bioethics 29(3): 211–216. 10.1111/bioe.12080. [ PubMed ]
- Friberg-Fernros, Henrik. 2018. Within the limits of the defensible: A response to Simkulet’s argument against the pro-life view on the basis of spontaneous abortion. Journal of Medical Ethics 44(11): 743–745. 10.1136/medethics-2017-104688. [ PubMed ]
- Friberg-Fernros, Henrik. 2019. Defending the two tragedies argument: A response to Simkulet. Journal of Medical Ethics 45(6): 417–418. 10.1136/medethics-2019-105489. [ PubMed ]
- George Robert P, Tollefsen Christopher. Embryo: A defense of human life. New York, NY: Doubleday; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee, Patrick, and Robert P. George. 2005. The Wrong of Abortion. In Contemporary Debates in Applied Ethics , ed. Andrew I. Cohen, and Christopher Heath Wellman. Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Léridon, Henri. 1977. Human fertility: The basic components . Translated by Judith F. Helzner. Chicago, Il: University of Chicago Press.
- Lovering, Rob. 2013. The Substance View: A Critique. Bioethics 27(5): 263–270. 10.1111/j.1467-8519.2011.01954.x. [ PubMed ]
- Lovering, Rob. 2014. The Substance View: A Critique (Part 2). Bioethics 28(7): 378–386. 10.1111/j.1467-8519.2012.02006.x. [ PubMed ]
- Lovering, Rob. 2017. The Substance View: A Critique (Part 3). Bioethics 31(4): 305–312. 10.1111/bioe.12330. [ PubMed ]
- Lovering Rob. A moral argument for frozen human embryo adoption. Bioethics. 2020; 34 (3):242–251. doi: 10.1111/bioe.12671. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marquis, Don. 1989. Why abortion is immoral. Journal of Philosophy 86(4): 183–202. 10.2307/2026961. [ PubMed ]
- Marquis, Don. 2007. The moral-principle objection to human embryonic stem cell research. Metaphilosophy 38(2–3): 190–206. 10.1111/j.1467-9973.2007.00481.x.
- Marquis Don. An argument that abortion is wrong. In: Shafer-Landau Russ., editor. Ethical theory: an anthology. 2. Oxford: Blackwell; 2013. pp. 400–409. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mulder, Jack. 2013. A short argument against abortion rights. Think 12(34): 57–68. 10.1017/S1477175613000080.
- Murphy, Timothy F. 1985. The moral significance of spontaneous abortion. Journal of Medical Ethics 11(2): 79–83. 10.1136/jme.11.2.79. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Ord, Toby. 2008. The scourge: Moral implications of natural embryo loss. American Journal of Bioethics 8(7): 12–19. 10.1080/15265160802248146. [ PubMed ]
- Rachels, James. 1979. Killing and starving to death. Philosophy 54(208): 159–171. 10.1017/S0031819100048415. [ PubMed ]
- Riezzo, Irene, Margherita Neri, Stefania Bello, Cristoforo Pomara, and Emanuela Turillazzi. 2016. Italian law on medically assisted reproduction: Do women’s autonomy and health matter? BMC Women’s Health 16: 44. 10.1186/s12905-016-0324-4. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ]
- Scaffidi, Sarah. 2019. Forced pregnancy in Italy violated ‘woman’s human right to health’, UN experts rule. UN News , 27 March 2019. https://news.un.org/en/story/2019/03/1035601 . Accessed 11 July 2021.
- Schlumpf, Heidi. 2019. Sr. Joan Chittister’s 2004 quote on ’pro-life’ versus ’pro-birth’ goes viral. National Catholic Reporter , 23 May 2019. https://www.ncronline.org/news/politics/sr-joan-chittisters-2004-quote-pro-life-versus-pro-birth-goes-viral. Accessed 11 July 2021.
- Simkulet William. A critique of Henrik Friberg-Fernros’s defense of the substance view. Bioethics. 2016; 30 (9):767–773. doi: 10.1111/bioe.12289. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simkulet, William. 2017. Cursed lamp: The problem of spontaneous abortion. Journal of Medical Ethics 43(11): 784–791. 10.1136/medethics-2016-104018. [ PubMed ]
- Simkulet William. Substance, rights, value, and abortion. Bioethics. 2019; 33 (9):1002–1011. doi: 10.1111/bioe.12616. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simkulet William. The two tragedies argument. Journal of Medical Ethics. 2019; 45 (5):304–308. doi: 10.1136/medethics-2018-105145. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simkulet, William. 2019c. Two tragedies argument: Two mistakes. Journal of Medical Ethics 45(8): 562–564. 10.1136/medethics-2019-105587. [ PubMed ]
- Simkulet William. Abortion and ectogenesis: Moral compromise. Journal of Medical Ethics. 2020; 46 (2):93–98. doi: 10.1136/medethics-2019-105676. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simkulet, William. 2021. The inconsistency argument: why apparent pro-life inconsistency undermines opposition to induced abortion. Journal of Medical Ethics . 10.1136/medethics-2020-107207. [ PubMed ]
- Stone, Jim. 1987. Why potentiality matters. Canadian Journal of Philosophy 17(4): 815–830. 10.1080/00455091.1987.10715920.
- Stone, Jim. 1994. Why potentiality still matters. Canadian Journal of Philosophy 24(2): 281–293. 10.1080/00455091.1994.10717370.
- Thomson, Judith Jarvis. 1972. A Defense of Abortion. Philosophy & Public Affairs 1(1): 47–66.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
The Study That Debunks Most Anti-Abortion Arguments
By Margaret Talbot

There is a kind of social experiment you might think of as a What if? study. It would start with people who are similar in certain basic demographic ways and who are standing at the same significant fork in the road. Researchers could not assign participants to take one path or another—that would be wildly unethical. But let’s say that some more or less arbitrary rule in the world did the assigning for them. In such circumstances, researchers could follow the resulting two groups of people over time, sliding-doors style, to see how their lives panned out differently. It would be like speculative fiction, only true, and with statistical significance.
A remarkable piece of research called the Turnaway Study, which began in 2007, is essentially that sort of experiment. Over three years, a team of researchers, led by a demographer named Diana Greene Foster, at the University of California, San Francisco, recruited 1,132 women from the waiting rooms of thirty abortion clinics in twenty-one states. Some of the women would go on to have abortions, but others would be turned away, because they had missed the fetal gestational limit set by the clinic. Foster and her colleagues decided to compare the women in the two groups—those who received the abortion they sought and those who were compelled to carry their unwanted pregnancy to term—on a variety of measures over time, interviewing them twice a year for up to five years.
The study is important, in part, because of its ingenious design. It included only women whose pregnancies were unwanted enough that they were actively seeking an abortion, which meant the researchers were not making the mistake that some previous studies of unplanned conceptions had—“lumping the happy surprises in with the total disasters,” as Foster puts it. In terms of age, race, income level, and health status, the two groups of women closely resembled each other, as well as abortion patients nationwide. (Foster refers to the study’s participants as women because, to her knowledge, there were no trans men or non-binary people among them.) Seventy per cent of the women who were denied abortions at the first clinic where they sought them carried the unwanted pregnancies to term. Others miscarried or were able to obtain late abortions elsewhere, and Foster and her colleagues followed the trajectories of those in the latter group as well.
While you might guess that those who were turned away had messier lives—after all, they were getting to the clinic later than the seemingly more proactive women who made the deadline—that did not turn out to be the case. Some of the women who got their abortions (half of the total participants) did so just under the wire; among the women in the study who were denied abortions (a quarter of the total), some had missed the limit by a matter of only a few days. (The remaining quarter terminated their pregnancies in the first trimester, which is when ninety per cent of abortions in the United States occur.) The women who were denied abortions were on average more likely to live below the poverty line than the women who managed to get them. (One of the main reasons that people seek abortions later in pregnancy is the need to raise money to pay for the procedure and for travel expenses.) But, in general, Foster writes, the two groups “were remarkably similar at the first interview. Their lives diverged thereafter in ways that were directly attributable to whether they received an abortion.”
Over the past several years, findings from the Turnaway Study have come out in scholarly journals and, on a few occasions, gotten splashy media coverage. Now Foster has published a patiently expository precis of all the findings in a new book, “ The Turnaway Study: Ten Years, a Thousand Women, and the Consequences of Having—or Being Denied—an Abortion .” The over-all impression it leaves is that abortion, far from harming most women, helps them in measurable ways. Moreover, when people assess what will happen in their lives if they have to carry an unwanted pregnancy to term, they are quite often proven right. That might seem like an obvious point, but much of contemporary anti-abortion legislation is predicated on the idea that competent adults can’t really know what’s at stake in deciding whether to bear a child or not. Instead, they must be subjected to waiting periods to think it over (as though they can’t be trusted to have done so already), presented with (often misleading) information about the supposed medical risks and emotional fallout of the procedure, and obliged to look at ultrasounds of the embryo or fetus. And such scans are often framed, with breathtaking disingenuousness, as a right extended to people—what the legal scholar Carol Sanger calls “the right to be persuaded against exercising the right you came in with.”
Maybe the first and most fundamental question for a study like this to consider is how women feel afterward about their decisions to have an abortion. In the Turnaway Study, over ninety-five per cent of the women who received an abortion and did an interview five years out said that it had been the right choice for them. It’s possible that the women who remained in the study that long were disproportionately inclined to see things that way—maybe if you were feeling shame or remorse about an abortion you’d be less up for talking about it every six months in a phone interview with a researcher. (Foster suggests that people experiencing regrets might actually be more inclined to participate, but, to me, the first scenario makes more psychological sense.) Still, ninety-five per cent is a striking figure. And it’s especially salient, again, in light of anti-choice arguments, which often stress the notion that many of the quarter to third of all American women who have an abortion will be wracked with guilt about their decision. (That’s an awful lot of abject contrition.) You can pick at the study for its retention rate—and some critics, particularly on the anti-abortion side, have. Nine hundred and fifty-six of the original thousand-plus women who were recruited did the first interview. Fifty-eight per cent of them did the final interview. But, as Foster pointed out in an e-mail to me, on average, the women in the study completed an impressive 8.4 of the eleven interviews, and some of the data in the study—death records and credit reports—cover all 1,132 women who were originally enrolled.
To the former Supreme Court Justice Anthony Kennedy, among others, it seemed “unexceptionable to conclude some women come to regret their choice to abort the infant life they once created and sustained.” In a 2007 abortion-case ruling, he wrote that “severe depression and loss of esteem can follow.” It can , but the epidemiologists, psychologists, statisticians, and other researchers who evaluated the Turnaway Study found it was not likely. “Some events do cause lifetime damage”—childhood abuse is one of them—“but abortion is not common among these,” Foster writes. In the short term, the women who were denied abortions had worse mental health—higher anxiety and lower self-esteem. In the longer run, the researchers found “no long-term differences between women who receive and women who are denied an abortion in depression, anxiety, PTSD, self-esteem, life satisfaction, drug abuse, or alcohol abuse.” Abortion didn’t weigh heavily in determining mental health one way or the other. Foster and her co-authors note, in an earlier article, that “relief remained the most commonly felt emotion” among women who got the abortions they sought. That relief persisted, but its intensity dissipated over time.
Other positive impacts were more lasting. Women in the study who received the abortion they sought were more likely to be in a relationship they described as “very good.” (After two years, the figure was forty-seven per cent, vs. twenty-eight per cent for the women turned away.) If they had been involved with a physically abusive man at the time of the unwanted pregnancy, they were less likely to still be experiencing violence, for the simple reason that they were less likely to be in contact with him. (Several of the participants interviewed for the book talk about not wanting to be tethered to a terrible partner by having a child together.) Women who got the abortion were more likely to become pregnant intentionally in the next five years than women who did not. They were less likely to be on public assistance and to report that they did not have enough money to pay for food, housing, and transportation. When they had children at home already, those children were less likely to be living in poverty. Based on self-reports, their physical health was somewhat better. Two of the women in the study who were denied abortions died from childbirth-related complications; none of the women who received abortions died as a result. That is in keeping with other data attesting to the general safety of abortion. One of Foster’s colleagues, Ushma Upadhyay, analyzed complications after abortions in California’s state Medicaid program, for example, and found that they occurred in two per cent of the cases—a lower percentage than for wisdom-tooth extraction (seven per cent) and certainly for childbirth (twenty-nine per cent). Indeed, maternal mortality has been rising in the U.S.—it’s now more than twice as high as it was in 1987, and has risen even more steeply for Black women, due, in part, to racial disparities in prenatal care and the quality of hospitals where women deliver.
Yet, as Foster points out, many of the new state laws restricting abortion suggest that it is a uniquely dangerous procedure, one for which layers of regulation must be concocted, allegedly to protect women. The Louisiana law that the Supreme Court struck down last Monday imposed just such a rule—namely, a requirement that doctors performing abortions hold admitting privileges at a hospital no more than thirty miles away. As Justice Stephen Breyer’s majority opinion noted, “The evidence shows, among other things, that the fact that hospital admissions for abortion are vanishingly rare means that, unless they also maintain active OB/GYN practices, abortion providers in Louisiana are unlikely to have any recent in-hospital experience.” Since hospitals often require such experience in order to issue admitting privileges, abortion providers would be caught in a Catch-22, unable to obtain the privileges because, on actual medical grounds, they didn’t need them. The result of such a law, had it gone into effect, would have been exactly what was intended: a drastic reduction in the number of doctors legally offering abortions in the state.
The Turnaway Study’s findings are welcome ones for anyone who supports reproductive justice. But they shouldn’t be necessary for it. The overwhelming majority of women who received abortions and stayed in the study for the full five years did not regret their decision. But the vast majority of women who’d been denied abortions reported that they no longer wished that they’d been able to end the pregnancy, after an actual child of four or five was in the world. And that’s good, too—you’d hope they would love that child wholeheartedly, and you’d root for their resilience and happiness.
None of that changes the fundamental principle of human autonomy: people have to be able to make their own decisions in matters that profoundly and intimately affect their own bodies and the course of their lives. Regret and ambivalence, the ways that one decision necessarily precludes others, are inextricable facts of life, and they are also fluid and personal. Guessing the extent to which individuals may feel such emotions, hypothetically, in the future, is not a basis for legislative bans and restrictions.
The Turnaway Study will be understood, criticized, and used politically, however carefully conceived and painstakingly executed the research was. Given that inevitability, it’s worth underlining the most helpful political work that the study does. In light of its findings, the rationale for so many recent abortion restrictions—namely, that abortion is uniquely harmful to the people who choose it—simply topples.
Books & Fiction
By signing up, you agree to our User Agreement and Privacy Policy & Cookie Statement . This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

By Eliza Griswold

By Jay Caspian Kang
- DOI: 10.1093/jmp/jhae023
- Corpus ID: 269755422
Impairment Arguments, Interests, and Circularity.
- Stephen Napier
- Published in Journal of Medicine and… 13 May 2024
- Philosophy, Law
21 References
Abortion, time-relative interests, and futures like ours, even if the fetus is not a person, abortion is immoral: the impairment argument, the impairment argument for the immorality of abortion: a reply, paradoxes of abortion and prenatal injury*, on the moral and legal status of abortion., a defense of abortion, abortion and moral risk1, morality, potential persons and abortion., against the strengthened impairment argument: never-born fetuses have no flo to deprive, killing and the time-relative interest account, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- America’s Abortion Quandary
2. Social and moral considerations on abortion
Table of contents.
- Abortion at various stages of pregnancy
- Abortion and circumstances of pregnancy
- Parental notification for minors seeking abortion
- Penalties for abortions performed illegally
- Public views of what would change the number of abortions in the U.S.
- A majority of Americans say women should have more say in setting abortion policy in the U.S.
- How do certain arguments about abortion resonate with Americans?
- In their own words: How Americans feel about abortion
- Personal connections to abortion
- Religion’s impact on views about abortion
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms: Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is morally acceptable most of the time. About an additional one-in-five do not consider abortion a moral issue.
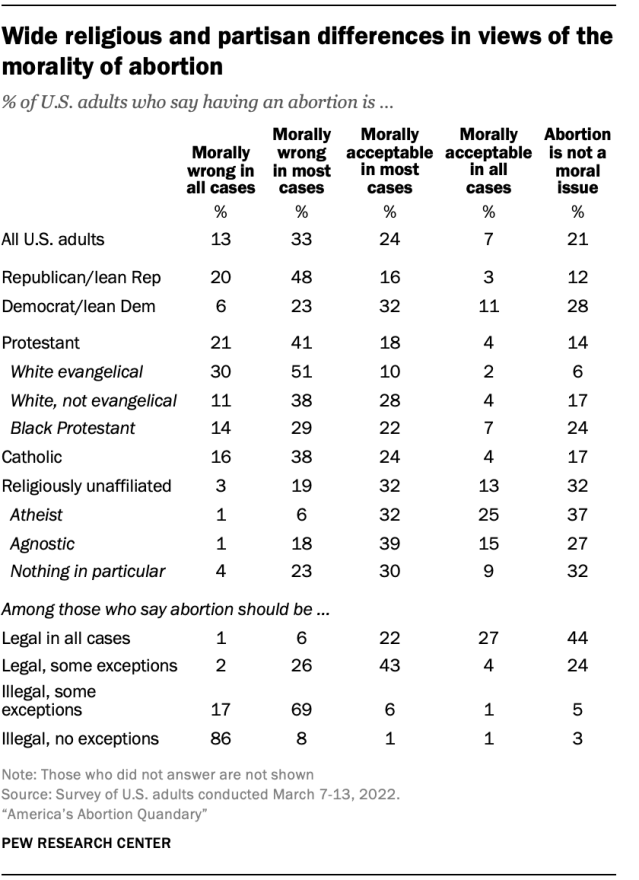
There are wide differences on this question by political party and religious affiliation. Among Republicans and independents who lean toward the Republican Party, most say that abortion is morally wrong either in most (48%) or all cases (20%). Among Democrats and Democratic leaners, meanwhile, only about three-in-ten (29%) hold a similar view. About four-in-ten Democrats say abortion is morally acceptable in most (32%) or all (11%) cases, while an additional 28% say abortion is not a moral issue.
White evangelical Protestants overwhelmingly say abortion is morally wrong in most (51%) or all cases (30%). A slim majority of Catholics (53%) also view abortion as morally wrong, but many also say it is morally acceptable in most (24%) or all cases (4%), or that it is not a moral issue (17%). And among religiously unaffiliated Americans, about three-quarters see abortion as morally acceptable (45%) or not a moral issue (32%).
There is strong alignment between people’s views of whether abortion is morally wrong and whether it should be illegal. For example, among U.S. adults who take the view that abortion should be illegal in all cases without exception, fully 86% also say abortion is always morally wrong. The prevailing view among adults who say abortion should be legal in all circumstances is that abortion is not a moral issue (44%), though notable shares of this group also say it is morally acceptable in all (27%) or most (22%) cases.
Most Americans who say abortion should be illegal with some exceptions take the view that abortion is morally wrong in most cases (69%). Those who say abortion should be legal with some exceptions are somewhat more conflicted, with 43% deeming abortion morally acceptable in most cases and 26% saying it is morally wrong in most cases; an additional 24% say it is not a moral issue.
The survey also asked respondents who said abortion is morally wrong in at least some cases whether there are situations where abortion should still be legal despite being morally wrong. Roughly half of U.S. adults (48%) say that there are, in fact, situations where abortion is morally wrong but should still be legal, while just 22% say that whenever abortion is morally wrong, it should also be illegal. An additional 28% either said abortion is morally acceptable in all cases or not a moral issue, and thus did not receive the follow-up question.
Across both political parties and all major Christian subgroups – including Republicans and White evangelicals – there are substantially more people who say that there are situations where abortion should still be legal despite being morally wrong than there are who say that abortion should always be illegal when it is morally wrong.

Asked about the impact a number of policy changes would have on the number of abortions in the U.S., nearly two-thirds of Americans (65%) say “more support for women during pregnancy, such as financial assistance or employment protections” would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S. Six-in-ten say the same about expanding sex education and similar shares say more support for parents (58%), making it easier to place children for adoption in good homes (57%) and passing stricter abortion laws (57%) would have this effect.
While about three-quarters of White evangelical Protestants (74%) say passing stricter abortion laws would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S., about half of religiously unaffiliated Americans (48%) hold this view. Similarly, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say this (67% vs. 49%, respectively). By contrast, while about seven-in-ten unaffiliated adults (69%) say expanding sex education would reduce the number of abortions in the U.S., only about half of White evangelicals (48%) say this. Democrats also are substantially more likely than Republicans to hold this view (70% vs. 50%).
Democrats are somewhat more likely than Republicans to say support for parents – such as paid family leave or more child care options – would reduce the number of abortions in the country (64% vs. 53%, respectively), while Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say making adoption into good homes easier would reduce abortions (64% vs. 52%).
Majorities across both parties and other subgroups analyzed in this report say that more support for women during pregnancy would reduce the number of abortions in America.
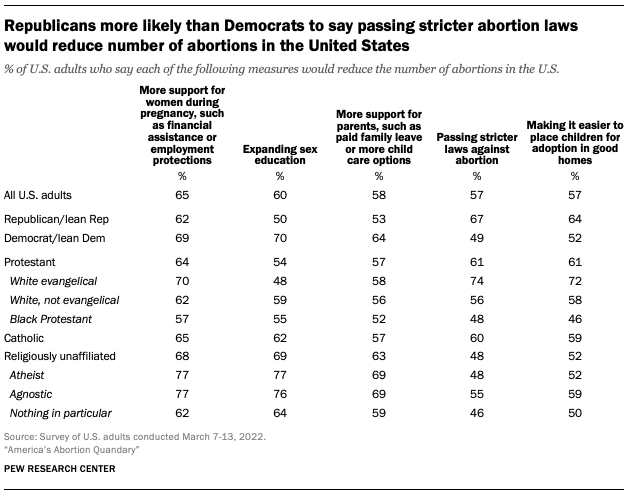
More than half of U.S. adults (56%) say women should have more say than men when it comes to setting policies around abortion in this country – including 42% who say women should have “a lot” more say. About four-in-ten (39%) say men and women should have equal say in abortion policies, and 3% say men should have more say than women.
Six-in-ten women and about half of men (51%) say that women should have more say on this policy issue.
Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to say women should have more say than men in setting abortion policy (70% vs. 41%). Similar shares of Protestants (48%) and Catholics (51%) say women should have more say than men on this issue, while the share of religiously unaffiliated Americans who say this is much higher (70%).
Seeking to gauge Americans’ reactions to several common arguments related to abortion, the survey presented respondents with six statements and asked them to rate how well each statement reflects their views on a five-point scale ranging from “extremely well” to “not at all well.”
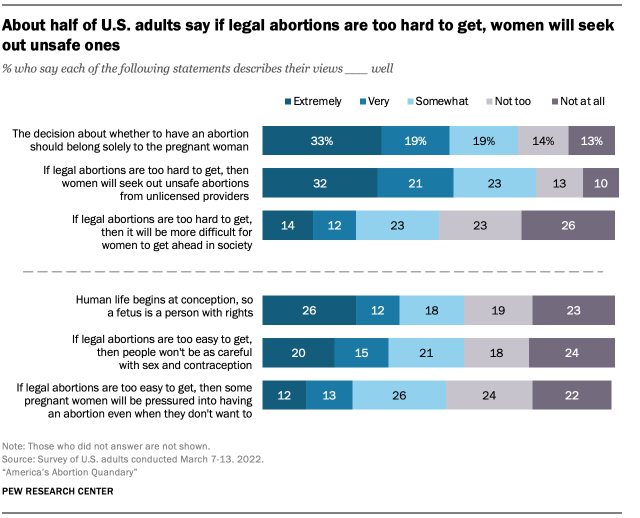
The list included three statements sometimes cited by individuals wishing to protect a right to abortion: “The decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman,” “If legal abortions are too hard to get, then women will seek out unsafe abortions from unlicensed providers,” and “If legal abortions are too hard to get, then it will be more difficult for women to get ahead in society.” The first two of these resonate with the greatest number of Americans, with about half (53%) saying each describes their views “extremely” or “very” well. In other words, among the statements presented in the survey, U.S. adults are most likely to say that women alone should decide whether to have an abortion, and that making abortion illegal will lead women into unsafe situations.
The three other statements are similar to arguments sometimes made by those who wish to restrict access to abortions: “Human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights,” “If legal abortions are too easy to get, then people won’t be as careful with sex and contraception,” and “If legal abortions are too easy to get, then some pregnant women will be pressured into having an abortion even when they don’t want to.”
Fewer than half of Americans say each of these statements describes their views extremely or very well. Nearly four-in-ten endorse the notion that “human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights” (26% say this describes their views extremely well, 12% very well), while about a third say that “if legal abortions are too easy to get, then people won’t be as careful with sex and contraception” (20% extremely well, 15% very well).
When it comes to statements cited by proponents of abortion rights, Democrats are much more likely than Republicans to identify with all three of these statements, as are religiously unaffiliated Americans compared with Catholics and Protestants. Women also are more likely than men to express these views – and especially more likely to say that decisions about abortion should fall solely to pregnant women and that restrictions on abortion will put women in unsafe situations. Younger adults under 30 are particularly likely to express the view that if legal abortions are too hard to get, then it will be difficult for women to get ahead in society.
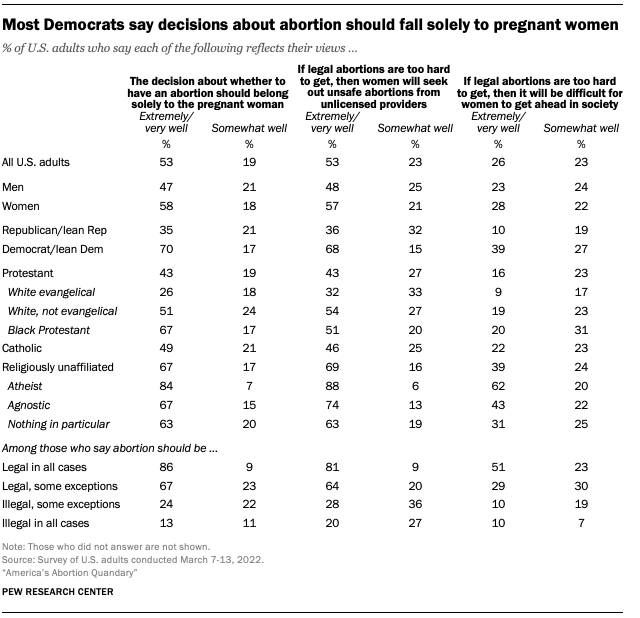
In the case of the three statements sometimes cited by opponents of abortion, the patterns generally go in the opposite direction. Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say each statement reflects their views “extremely” or “very” well, as are Protestants (especially White evangelical Protestants) and Catholics compared with the religiously unaffiliated. In addition, older Americans are more likely than young adults to say that human life begins at conception and that easy access to abortion encourages unsafe sex.
Gender differences on these questions, however, are muted. In fact, women are just as likely as men to say that human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights (39% and 38%, respectively).
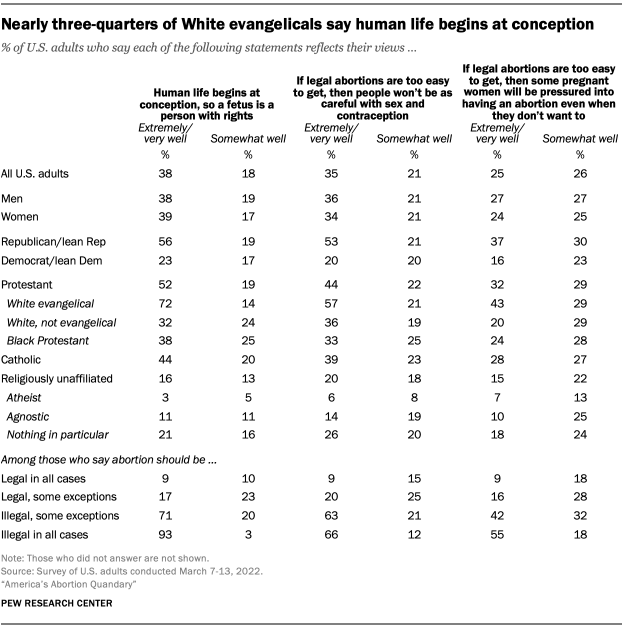
Analyzing certain statements together allows for an examination of the extent to which individuals can simultaneously hold two views that may seem to some as in conflict. For instance, overall, one-in-three U.S. adults say that both the statement “the decision about whether to have an abortion should belong solely to the pregnant woman” and the statement “human life begins at conception, so the fetus is a person with rights” reflect their own views at least somewhat well. This includes 12% of adults who say both statements reflect their views “extremely” or “very” well.
Republicans are slightly more likely than Democrats to say both statements reflect their own views at least somewhat well (36% vs. 30%), although Republicans are much more likely to say only the statement about the fetus being a person with rights reflects their views at least somewhat well (39% vs. 9%) and Democrats are much more likely to say only the statement about the decision to have an abortion belonging solely to the pregnant woman reflects their views at least somewhat well (55% vs. 19%).
Additionally, those who take the stance that abortion should be legal in all cases with no exceptions are overwhelmingly likely (76%) to say only the statement about the decision belonging solely to the pregnant woman reflects their views extremely, very or somewhat well, while a nearly identical share (73%) of those who say abortion should be illegal in all cases with no exceptions say only the statement about human life beginning at conception reflects their views at least somewhat well.
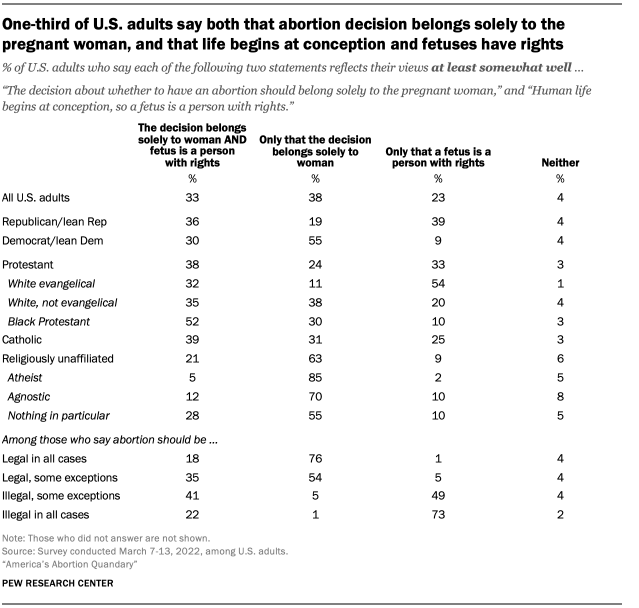
When asked to describe whether they had any other additional views or feelings about abortion, adults shared a range of strong or complex views about the topic. In many cases, Americans reiterated their strong support – or opposition to – abortion in the U.S. Others reflected on how difficult or nuanced the issue was, offering emotional responses or personal experiences to one of two open-ended questions asked on the survey.
One open-ended question asked respondents if they wanted to share any other views or feelings about abortion overall. The other open-ended question asked respondents about their feelings or views regarding abortion restrictions. The responses to both questions were similar.
Overall, about three-in-ten adults offered a response to either of the open-ended questions. There was little difference in the likelihood to respond by party, religion or gender, though people who say they have given a “lot” of thought to the issue were more likely to respond than people who have not.
Of those who did offer additional comments, about a third of respondents said something in support of legal abortion. By far the most common sentiment expressed was that the decision to have an abortion should be solely a personal decision, or a decision made jointly with a woman and her health care provider, with some saying simply that it “should be between a woman and her doctor.” Others made a more general point, such as one woman who said, “A woman’s body and health should not be subject to legislation.”
About one-in-five of the people who responded to the question expressed disapproval of abortion – the most common reason being a belief that a fetus is a person or that abortion is murder. As one woman said, “It is my belief that life begins at conception and as much as is humanly possible, we as a society need to support, protect and defend each one of those little lives.” Others in this group pointed to the fact that they felt abortion was too often used as a form of birth control. For example, one man said, “Abortions are too easy to obtain these days. It seems more women are using it as a way of birth control.”
About a quarter of respondents who opted to answer one of the open-ended questions said that their views about abortion were complex; many described having mixed feelings about the issue or otherwise expressed sympathy for both sides of the issue. One woman said, “I am personally opposed to abortion in most cases, but I think it would be detrimental to society to make it illegal. I was alive before the pill and before legal abortions. Many women died.” And one man said, “While I might feel abortion may be wrong in some cases, it is never my place as a man to tell a woman what to do with her body.”
The remaining responses were either not related to the topic or were difficult to interpret.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Christianity
- Evangelicalism
- Political Issues
- Politics & Policy
- Protestantism
- Religion & Abortion
- Religion & Politics
- Religion & Social Values
Cultural Issues and the 2024 Election
How americans and israelis view one another and the u.s. role in the israel-hamas war, more than half of americans are following election news closely, and many are already worn out, public’s positive economic ratings slip; inflation still widely viewed as major problem, americans have mixed views about how the news media cover biden’s, trump’s ages, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Texas professors sue to fail students who seek abortions
Men are using abortion bans to control and abuse women in their lives for "consensual sexual intercourse", by amanda marcotte.
A pair of Texas professors figured out that their female students have sex and, boy, they do not like it. So now the philosophy professor and finance professor are suing for the right to punish their students who, outside of class, have abortions.
"Pregnancy is not a disease, and elective abortions are not 'health care,'" University of Texas at Austin professor Daniel Bonevac sneers in a federal court filing with professor John Hatfield. Instead, Bonevac writes, because pregnancy is the result of "voluntary and consensual sexual intercourse," students should not be allowed time off to get abortions. If the students disobey and miss class for abortion care, the filing continues, the professors should be allowed to flunk students. Additionally, Bonevac asserts that he has a right to refuse to employ a teaching assistant who has had an abortion, calling such women "criminals."
The sexual hang-ups of abortion opponents are rarely far from the surface, but even by those low standards, the unjustified male grievance on display in this new Texas lawsuit is a doozy. At issue are federal regulations, called Title IX, first signed into law by President Richard Nixon in 1972. They currently bar publicly funded schools from discriminating on the basis of sex or gender. This means that schools cannot penalize students for health care based on sex. As a male student would be granted leave if he had to travel for surgery, so must a female student, the federal statute requires. The two men argue that granting students an excused absence in such cases violates their First Amendment rights.
Even though the plaintiffs suing for the right to flunk female students for abortion include boilerplate arguments in which they feign concern that abortion is "killing," the legal filing makes it clear that what really outrages Bonevac and Hatfield is that Title IX prevents them from controlling the private lives of students. Along with their anger about abortion, they grouse about not being allowed to punish students "for being homosexual or transgender." They also argue they should be able to penalize teaching assistants for "cross-dressing," by which they appear to mean allowing trans women to wear skirts.
Want more Amanda Marcotte on politics? Subscribe to her newsletter Standing Room Only .
As Jessica Valenti at Abortion, Every Day wrote , the language of the legal complaint is "downright petulant." The picture painted is of two men obsessed with controlling student lives based on what they're packing inside their underwear. It should be common sense that college students should be graded on their performance in class, not whether or not their professor resents their sex life or sexual identity. Alas, because the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade and Texas banned abortion, it's created a pretext for every busybody who wants to spend less time grading papers and more time working himself into an angry froth over the imagined sexual exploits of his students.
Even though Bonevac and Hatfield work in Austin, Texas, they filed their lawsuit 486 miles away in Amarillo, Texas . The reason for this is not mysterious: Donald Trump-appointed judge Matthew Kacsmaryk. The right-wing judge has a long and frankly unhinged history of screeching at top volume about the evils of "sexual revolutionaries." (Yes, that does sound like a compliment, but he doesn't mean it as such.) It takes very little to draw Kacsmaryk's sexualized condemnation . Premarital sex, for instance, makes one a "sexual revolutionary." Using contraception within marriage also makes one an irredeemable pervert. In his legal writings, Kacsmaryk is very clear that sex is only for procreation within marriage, and anything outside of that should draw legal sanction. He has not weighed in on whether there should be restrictions on what sexual positions are legally permissible within the procreation-only marital sex, but give him time.
Unfortunately, the Dobbs decision, which ended abortion rights, didn't just empower professors who are overly preoccupied with the sex lives of undergraduates. Texas has swiftly turned into a case study in how abortion bans aren't really about "life" at all, but about giving abusive misogynists a whole new set of tools to use in controlling women. As Melissa Gira Grant at the New Republic wrote earlier this month, domestic "[a]busers have noticed and taken advantage" of how abortion bans mean the "legal system itself" is now "an instrument of abuse." Operators at domestic violence hotlines have seen a surge in calls from victims whose abusers who "use state anti-abortion laws to intimidate and threaten partners" who have had or are considering an abortion.
One would think the Republicans who wrote the abortion bans might want to distance themselves from terrible men using the laws as leverage to force women into sexual relationships. Instead, Republicans are embracing the cause of men who believe coercion is an acceptable substitute for romance. Jonathan Mitchell, the former Texas solicitor general who wrote one of the two major Texas abortion bans, has been representing men who don't even bother to hide that they are motivated by a belief that women simply don't have a right to say no to them.
We've covered the first case, of Marcus Silva, extensively at Salon. Court filings accuse Silva of extensive abuse of his ex-wife, including getting drunk at her work party and calling her misogynist names in front of colleagues. Her friends document how he reportedly knew his ex-wife was going to abort a pregnancy, but didn't try to stop her. Instead, he wanted to use her abortion as leverage. Text messages show him threatening to turn her and her friends into the law after her abortion unless she returned to do his laundry and have sex with him. Mitchell is representing Silva in a lawsuit against his ex-wife's friends for "aiding and abetting" an abortion that made it easier for her to leave him.
Turns out Mitchell is quickly creating a cottage industry of using the Texas law to help men harass ex-girlfriends. As the Texas Tribune reported earlier this month , Mitchell is representing two more men who want to use legal action to punish their ex-girlfriends for traveling out of state to get a legal abortion. In one case, the woman's lawyers argued it was part of a "scheme to harass an ex-girlfriend who has moved on from her relationship with him." Even if Mitchell never moves to sue the women, their providers, or their friends who helped, by filing legal motions, a legal expert told the Tribune, Mitchell can put "the woman in front of a court reporter and force her to answer questions." Making a woman sit through humiliating questioning at the hands of an abusive ex-boyfriend is clearly a punishment in and of itself. And, again, for using her legal and moral right to terminate an unwanted relationship.
We need your help to stay independent
In the decades after Roe v. Wade, the Christian right insisted stridently that their opposition to abortion was about "protecting life," and was not about restoring male dominance over women. That this was a lie was always evident to those willing to look even a centimeter below the surface. These same forces also organized against sex education and affordable contraception, both far more effective at preventing abortion than abortion bans. But in the aftermath of Dobbs, there can be no doubt. After red states started banning abortion, the abortion rate rose , fitting the pattern seen in other countries with severe abortion restrictions , because anti-abortion states also tend to be hostile to pregnancy prevention.
These series of legal maneuvers in Texas further flesh out what's really going on here. Nosy right-wing professors and angry ex-boyfriends are not, despite their feeble protestations to the contrary, just really into babies. For people who actually care about children, there are plenty of volunteer opportunities that aid real kids who need food to eat and opportunities to grow. Instead, the throughline is anger at women, whether students in their classrooms or ex-girlfriends who don't return their calls, for living their lives outside of the control of the men who feel entitled to dominate them.
about this topic
- Texas Supreme Court rules against women who say their lives were endangered by state abortion ban
- Reproductive rights advocates: Texas GOP wishlist includes death penalty for abortion patients
- Forcing Kate Cox to travel out of state for an abortion is cruel, and shows exceptions don't work
Amanda Marcotte is a senior politics writer at Salon and the author of " Troll Nation: How The Right Became Trump-Worshipping Monsters Set On Rat-F*cking Liberals, America, and Truth Itself ." Follow her on Twitter @AmandaMarcotte and sign up for her biweekly politics newsletter, Standing Room Only .
Related Topics ------------------------------------------
Related articles.
Advertisement
Supported by
Texas Supreme Court Rejects Challenge on Exceptions to Abortion Ban
The court on Friday unanimously reversed a ruling that had expanded the definition of what counts as a medical emergency under the state’s strict abortion ban.
- Share full article

By Kate Zernike
Kate Zernike covers abortion for The Times.
The Texas Supreme Court on Friday unanimously rejected a challenge to the state’s strict abortion ban, ruling against a group of 22 women and abortion providers who sought to expand the exceptions for medical emergencies under the law.
While the challenge will continue in trial court, the state’s attorney general, Ken Paxton, would almost certainly appeal any loss there, and the high court’s decision Friday made clear that he would ultimately prevail.
“I will continue to defend the laws enacted by the Legislature and uphold the values of the people of Texas by doing everything in my power to protect mothers and babies,” Mr. Paxton said in a statement.
The lawsuit, filed by the Center for Reproductive Rights, was the first on behalf of women denied abortions after the United States Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade two years ago. While the case revolves around the question of what counts as an exception — unlike other lawsuits, it did not seek to overturn a state ban — it has changed the political debate around abortion by underscoring the potentially devastating medical consequences of abortion bans even for women who were not seeking to end unwanted pregnancies.
The court’s 38-page decision on Friday agreed that the experiences the women had recounted in testimony — some so painful that a judge ordered the court into recess — were “filled with immense personal heartbreak.” But it said that Texas law allowed abortions for any woman who faces a life-threatening condition, “before death or serious physical impairment are imminent.”
Echoing arguments from the state and anti-abortion groups, the court blamed doctors for misinterpreting the law.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Case Against Abortion. Nov. 30, 2021. Crosses representing abortions in Lindale, Tex. Tamir Kalifa for The New York Times. Share full article. 3367. By Ross Douthat. Opinion Columnist. A ...
Pro-Life Arguments. abortion is akin to murder as it is the act of taking human life. Abortion is in direct defiance of the commonly accepted idea of the sanctity of human life. No civilized society permits one human to intentionally harm or take the life of another human without punishment, and abortion is no different.
5.1.5 Abortion prevents fetuses from experiencing their valuable futures. We will begin with arguments for the conclusion that abortion is generally wrong, perhaps nearly always wrong. These can be seen as reasons to believe fetuses have the "right to life" or are otherwise seriously wrong to kill.
The most compelling argument against abortion remains what it has been for decades: Directly killing innocent human beings is gravely unjust. Abortion is the direct killing of innocent human ...
This essay about the arguments against abortion explores the complex moral, ethical, and societal considerations surrounding the issue. It examines perspectives rooted in the sanctity of human life, bodily autonomy, and the potential harm to women's physical and psychological well-being. Additionally, it discusses how the normalization of ...
Common Argument #4: "If it's a legitimate rape, the female body has ways to try to shut that whole thing down." Your Response: Go home, Todd Akin, you're drunk. Common Argument #5: Adoption is a ...
There's a Better Way to Debate Abortion. Caution and epistemic humility can guide our approach. If Justice Samuel Alito's draft majority opinion in Dobbs v. Jackson Women's Health ...
Legal abortion promotes a culture in which life is disposable. Increased access to birth control, health insurance, and sexual education would make abortion unnecessary. This article was published on June 24, 2022, at Britannica's ProCon.org, a nonpartisan issue-information source. Some argue that believe abortion is a safe medical procedure ...
Since the Supreme Court's historic 1973 decision in Roe v. Wade, the issue of a woman's right to an abortion has fostered one of the most contentious moral and political debates in America.Opponents of abortion rights argue that life begins at conception - making abortion tantamount to homicide.
Abortion does not free women. Some argue that abortion does not liberate women, but allows society not to cater to women's needs. They say that what women need for equality is not free access to ...
The wider gap has been largely driven by Democrats: Today, 84% of Democrats say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, up from 72% in 2016 and 63% in 2007. Republicans' views have shown far less change over time: Currently, 38% of Republicans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, nearly identical to the 39% who said this ...
These religious perspectives often shape the policies and laws of countries where these faiths are predominant. However, secular arguments also play a crucial role in the abortion debate. Secular pro-life advocates often base their arguments on scientific premises, such as the presence of a heartbeat or the capacity for pain in the fetus.
The Turnaway study, for Foster, underscored that nobody needs the government to decide whether they need an abortion. If and when America's highest court overturns Roe, though, an estimated 34 ...
The argument against abortion has frequently been based on religion. Data shows that the majority of people who get an abortion have some sort of religious affiliation, according to the most ...
By David Leonhardt. May 19, 2021. For nearly 50 years, public opinion has had only a limited effect on abortion policy. The Roe v. Wade decision, which the Supreme Court issued in 1973 ...
4 Prin.L.J.F. 12. Following Dobbs v.Jackson's (2022) reversal of Roe v.Wade (1973) — and the subsequent revocation of federal abortion protection — activists and scholars have begun to reconsider how to best ground abortion rights in the Constitution. In the past year, numerous Jewish rights groups have attempted to overturn state abortion bans by arguing that abortion rights are ...
Abortion is often talked about as a grave act. But bringing a new life into the world can feel like the decision that more clearly risks being a moral mistake. By Jia Tolentino. July 16, 2022 ...
Abortion could therefore be the lesser of two evils. Some of the arguments against abortion Roman Catholics believe that life begins at conception and therefore abortion is morally wrong.
July 3, 2022. DALLAS — The rollback of abortion rights has been received by many American women with a sense of shock and fear, and warnings about an ominous decline in women's status as full ...
This essay sets out to show, as well as any philosophical argument can, that inconsistency arguments are morally significant. Keywords: Abortion, Reproductive ethics, Spontaneous ... Mulder, Jack. 2013. A short argument against abortion rights. Think 12(34): 57-68. 10.1017/S1477175613000080. Murphy, Timothy F. 1985. The moral significance of ...
An Argument Against Abortion. means "a very young child, especially one newly or recently born." (Google) So when people say abortion is wrong because you're killing a baby, it would be incorrect. What you would be killing is called a fetus. The thing you would be killing wouldn't have a recollection (memories) of life, let alone miss it.
Margaret Talbot writes about "The Turnaway Study: Ten Years, a Thousand Women, and the Consequences of Having—or Being Denied—an Abortion," a book about the results of a study that asked ...
A common justification for abortion rights is that the death of the fetus does not violate any of the fetus's time-relative interests. The time-relative interest account (TRIA) of harm and wrongdoing tells us that a necessary condition for harming someone is that his or her time-relative interests are frustrated. Regarding the justification for abortion, this account falls prey to impairment ...
As the long-running debate over abortion reaches another key moment at the Supreme Court and in state legislatures across the country, a majority of U.S. adults continue to say that abortion should be legal in all or most cases.About six-in-ten Americans (61%) say abortion should be legal in "all" or "most" cases, while 37% think abortion should be illegal in all or most cases.
Social and moral considerations on abortion. Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms: Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is ...
"The scientific arguments that CLI is making," she said, "are just one more arrow in the quiver of legislators who already think abortion is contrary to God's law."
Wade and Texas banned abortion, it's created a pretext for every busybody who wants to spend less time grading papers and more time working himself into an angry froth over the imagined sexual ...
BY NEELAM PATEL*. One of the most common arguments levied against a woman's right to choose is the idea that abortion is "murder," and the killing of an innocent fetus is the most heinous sin a woman can partake in.1 This view is supposedly grounded in a deep reverence for human life.2 However, the origin of this belief is less humanistic ...
The Texas Supreme Court on Friday unanimously rejected a challenge to the state's strict abortion ban, ruling against a group of 22 women and abortion providers who sought to expand the ...