

Products & Services Section in a Business Plan (+ Examples)
- March 21, 2024
- Business Plan , How to Write

In this blog post, we’ll guide you through writing the products and services section of your business plan. We’ll cover how to describe what you’re selling and why it’s important in your business plan.
Whether you’re launching a new startup or creating a business plan for an existing business, this section is crucial for showing the value you bring to customers. Let’s get started!
Why do we include them in a business plan?
The products and services section of a business plan is more than just a list of what a company sells; it’s a vital narrative that tells the story of the business’s core offerings and their significance to the market.
This section is paramount for readers (especially potential investors) to grasp the essence of what the business is about, the unique problems it solves, or the specific needs it addresses.
A meticulously crafted products and services segment does much more than describe offerings. Indeed, it lays the groundwork for comprehensive marketing strategies , informs operational planning, and financial projections.
Moreover, understanding the business’s offerings in depth enables stakeholders to envision the company’s value proposition and competitive edge.
Where should you include them?
In a business plan, the Products and Services section is typically included within the business overview section.
This allows you to first introduce the business model and what it offers to customers. Only after this you can provide more details of the products and services.
The Products and Services section should clearly detail what you are selling, highlight the unique value proposition . It should also ideally explain how it meets the needs of your target market if it isn’t obvious. T
What to include: 2 Examples
Begin with a clear, engaging description of each product or service you offer. For services, describe the process, customer experience, and outcome. For products, discuss the materials, technology, and any unique features.
Services example: a Cryotherapy business plan

Products example: a Brewery business plan

Related Posts

Pro One Janitorial Franchise Costs $9K – $76K (2024 Fees & Profits)
- July 5, 2024

Dance Studio Business Plan PDF Example
- June 17, 2024
- Business Plan

Carpet and Upholstery Cleaning Business Plan PDF Example
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
How to describe your product and service in a business plan like a pro
It’s deceiving.
You’d think that this part of a business plan does exactly what it says on the tin–describe your product & service offering– right ?
And yes, you are partially right.
But there’s a very specific way in which this description should be written to make sure that your business has the best chance of succeeding – in real life and under the eagle eye of a potential backer (if you’re preparing a business plan for external financing purposes).
Keep reading to find out the secret sauce to writing a winning product and service description:
WHAT is the Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
This business plan section is also known as:
- Product and/or Service Overview
HOW Do You Write a Product and Service Description in a Business Plan?
So, what should a good product/service overview contain?
Here are some items to consider including into this section:
1. Portfolio:
The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers.
2. Features and benefits (value proposition):
Explain what the product/service does and how it works.
3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.):
The problem(s) the product or service solves. Every business needs to solve a problem that its customers face. Explain what the problem is and how the product or service solves it.
4. Innovation:
If the company is doing something new and different, explain why the world needs the innovation.
5. Proprietary advantages:
Any proprietary features that contribute to a competitive advantage. This could include: intellectual property (e.g., copyright, trademark, patent filings, trade secret), exclusive agreements with suppliers or vendors, exclusive licenses (e.g., for a product, service or technology), company’s own research and development activities.
6. Development stage:
Current stage of development of the product / service (e.g., idea, development, testing, prototype, already on the market).
7. Product life-cycle:
Estimate the life span of the product or service.
Specify whether the product or service under consideration is a short-lived fad or has a long-term potential.
8. Future:
Mention plans for changes and new additions to the current portfolio of products / services.
Describe any plans to move into new markets in the future (e.g., serving different types or sizes of customers, industries, geographic areas).
Make your best guess at when the business will be ready to address these markets and what it needs to do first to be ready.
9. Limitations:
If applicable, explain any risks or limitations associated with the product (e.g., liability issues like guarantees or returns), along with any legal advice received regarding these issues.
10. Visual aids:
Use photos, images, diagrams and other graphics to help the reader visualize and learn about the products / services.
If the business is tackling several distinct problems through different products / services, describe the solutions individually .
However, for a large line of products / services, there is no need to list each one, just identifying the general categories will suffice.
How LONG Is the Product and Service Chapter of a Business Plan?
This part of a business plan can be very short, just a couple of paragraphs, or it can spread over multiple pages, depending on how many products/services you offer and how much explanation they require.
If your products or services are particularly complex , technical , innovative , or proprietary , you will want to provide more information and spend considerable time describing them.
This is especially true if you are seeking funding for a new product or service, particularly one that is not immediately understandable to the business plan readers, and if potential funders are likely to be motivated by the specifics.
In any case, when describing a product or service, provide just enough information to paint a clear picture of what it is and does . A brief explanation of what you will be making, selling or doing is appropriate here.
Excessive detail makes this section cumbersome for a reader to wade through. Reserve detailed descriptions (e.g., production processes) for the Appendix.
In any case, it is a good idea to first summarize the value proposition of each product or service into a one short sentence, and only then continue with a more detailed description of the product or service.
If any images or graphics are available that would contribute to the understanding of the product or service, the writers of a business plan should use them.
Otherwise, include any product or service details , such as technical specifications, drawings, photos, patent documents and other support information, in the Appendix section of the business plan document.
TOP 4 TIPS for Writing a Product and Service Overview
Tip #1: features v. benefits.
Don’t just list the features of the product / service.
Instead, describe the specific benefits it will offer to customers – from their perspective.
Make it clear what your customers will gain through buying your product or service. Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service – from your customers’ perspective.
Features are not the same thing as benefits. And you need to understand both.
Confused? Let’s clarify:
What Is the Difference Between Features and Benefits?
| Difference: Features v. Benefits | Features | Benefits | Descriptive, factual, and often technical, aspects of a product or service, describing what something is and does. | The positive impact of what consumers can accomplish with the product or service to solve a problem and improve their lives. |
|---|---|---|
| Why is it important? | Give customer facts to rationalize a purchase | Give customers a reason to buy |
| Example: iPhone camera | Technical specifications for lens aperture, optical zoom, image stabilization, etc. | Users can capture beautiful photos and video in any location or setting |
| Questions in customer’s mind | What does it do? | So what? |
| How does it work? | Why should I care? | |
| What are the specs? | What can it do for me? |
Tip #2: Problem v. Solution
If at all possible, present the information in the Problem >> Solution format.
Start by describing the key problem that your customers have, immediately followed by the solution with which you will address this need for your target market.
| Step | Action | Question to Answer | List your customers' top 1-3 problems, capturing their central frustration. | What is the crucial problem faced by your consumers? |
|---|---|---|
| 2. Solution | Each problem should be matched by a solution. | What are you going to do to solve the problems of your customers? |
Tip #3: Competitive Advantage
You should also comment on your ability to meet consumers’ key problems or unmet needs in a way that brings your product or service advantages over the competition.
For example:
- If you have a common business, such as a restaurant:
Explain why your customers need your particular restaurant. Do you offer lower prices? More convenient hours? A better location? A different concept, such as a vegan ice-cream pop up store? A specialty that is not otherwise available in your area, such as a Peruvian ceviche or Hungarian goulash?
- If your company is doing something new and innovative :
What is it about the existing solutions that is subpar? Maybe you are improving on a mediocre product category, such as creating better medical uniforms for healthcare workers (e.g., more flattering cut, trendy designs, sustainable materials). Or perhaps your new blockchain solution has the potential to entirely eliminate the middle-men in an entire industry.
Although the subject of competitive advantage regarding the business as a whole will be fully explored in the Market and Competitor Analysis part of a business plan, it is advisable to touch on it here also – in the context of the company’s products and service.
Tip #4: Validating the Problem and Solution
Speaking of which, when you are doing market research and analysis for your business plan, remember to validate the problem and solution your product or service is addressing.
There is a plethora of minor issues out there that people are perfectly fine with just tolerating. To build a solid business, though, you need a problem that a sufficient number of people are motivated to solve. That is, that they recognize it as a problem that’s worth paying you to solve. Even if they didn’t realize it was solvable until they were presented with your solution.
So, how do you get evidence that prospects are willing to pay for your solution?
Validation of Problem
Describe what you’ve done so far to confirm that the problem you are focused on is a real problem for your customers.
- Existing Business:
For an established business, this is probably just a matter of recapping your success in the marketplace. Your customers have already voted with their wallets.
- New Business:
For a startup, it is important to survey and have conversations with as many potential customers as possible about where they are having problems, how they solve them today, and validate that they are interested enough in addressing those problems to pay for a good solution.
Validation of Solution
Describe how you have tested your ideas with existing or potential customers to confirm that there is a good market for the products or services you plan to offer. Summarize the positive customer feedback or market traction that you have achieved with your solution so far.
For an established business, the answers probably lie in your paying customer base – their existence itself, combined with their repeat business, word-of-mouth referrals, follow-up customer surveys, and other indicators of customer satisfaction.
For a new business, you can start validating your solution immediately by trying it out with potential customers, even informally or at no charge, to get their opinion. If your product or service does not exist yet, talk to prospects about what you plan to offer and measure their feedback.
In summary, this section should answer the million dollar question:
What makes you think that people will buy, be satisfied with, and recommend your products or services?
Related Questions
What are products and services.
Products and services are items that businesses offer for sale to a market. While services are intangible, meaning that they do not exist in a physical form, products are of tangible nature, in other words – you can touch them.
What is a Product Line?
Product line is a group of related products that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
What is a Service Line?
Service line is a group of related services that are all produced or sold by one entity and typically marketed under one brand name.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
How To Write the Products and Services of a Business Plan
Crucial to business plans designed to secure funding or partnerships, your products and services section needs to showcase the quality, value, and benefits your business offers.
It’s not just a list of what your business is going to produce or provide. Instead, it outlines what you make or do, why your market needs your products or services, how you will compete with other companies selling the same or similar products or services, and what you will charge.
What To Include In The Products and Services Section
When looking at how to write the Products and Services section of your plan, be sure to include:
- A description of the products or services you offer or plan to offer
- A pricing model for your products or service, including how you set your prices and how you will make a profit. Include a breakdown of your Costs of Goods (COG) and Costs of Services (COS), what your contingency plan is in the event of a shift in market conditions, changes to laws, or availability of supplies, and your markup strategy.
- A comparison of your competitors’ products or services against yours, including a survey of what your competitors charge for similar items, along with a discussion explaining your pricing strategy
- Any sales literature or marketing materials you will use, including your website’s role in your sales efforts.
- An outline of how your orders will be processed or fulfilled.
- Any needs required to create or deliver your products (for example, up-to-date computer equipment)
- Any intellectual property (trademarks) or legal issues needing to be addressed.
- Future product or services
How to Make The Products & Service Section Appealing
Ideally, this section should elicit excitement in your reader and entice them to fund your business or work with you.
Here are few ways to accomplish this when deciding how to write the Products and Services section of your business plan:
- Showcase why there is a need for your product or service. Doing so is especially important if you’re introducing a new concept or invention or introducing your product or service into a place where there is currently no market for it.
- Emphasize the features of your product or service. How does it differ from that of your competitors in terms of make, shape, form, or appearance? Or price point? Or the level of service? What makes it unique?
- Focus on benefits. Once you’ve identified what features make your product unique, it’s vital to show how those features provide value to consumers. Is your product cheaper? Is your service faster? You want to clearly indicate how your product or service will fix a problem or improve a client or customer’s life.
- Be clear and concise and talk in layman’s terms. Avoid getting bogged down in lengthy descriptions or unnecessary details. Use bullet points and numbered lists to highlight important information. Don’t assume that your potential funders, partners, or customers have the same level of knowledge. Instead, consider the reader doesn’t know as much as you do when explaining your offering. Stay away from acronyms, jargon, industry buzzwords, and aim to be customer-oriented. If you have to use acronyms or jargon, always provide a definition.
- “ Why are you the best person to provide your products and services?”
- “What education or experience do you have that makes you qualified to provide them?”
Have Questions? Looking To Get Started?
- Your Name *
- Email Address *
- Phone Number
Don’t forget to include any testimonials, awards, or accolades you’ve received as well as any patents, copyrights, or trademarks you own or have applications for. Have you had the product tested or certified? Gotten approvals from industry experts? Including these details adds credibility to your overall business plan.
- Identify any liability issues: A liability lawsuit can significantly change the landscape of your business. Even if you don’t foresee any liability issues, include a statement to that effect rather than not address it at all. If there is a liability issue, real or apparent, acknowledge it and describe how you’ll deal with it. Let the reader know you will take all necessary steps to protect your business, your products, and yourself from litigation.
- Be precise in your product or service descriptions. For example, you don’t want only to say, “I sell shoes.” You want instead to say, “I sell leather boots targeted at women aged 16 – 25 who buy online”. Wherever possible, also include pictures of your products.
Questions to Answer in Your Products & Services Section
- Are your products or services in development or existing and on the market?
- If they currently aren’t on the market, what is the timeline for bringing them to it? Do you have a prototype?
- What makes your product or service different? What are your competitive advantages? What are your competitive disadvantages, and how will you overcome them?
- Is your pricing an issue? Are your operating costs low enough to allow for a reasonable profit margin?
- Where are you acquiring your products? Do you manufacture them, or do you assemble them using third-party components? Do you purchase from suppliers or wholesalers? If demand increases, do you have a steady supply of products available?
- How are you going to sell your product or service? Will it be available online or in retail stores? Do you have any vendors lined up?
Once you’ve answered these questions, stop and reread the section. Ask yourself if you’ve tried to answer why a client would want your product or service. Consider whether your offering will make your customers’ lives better or more accretive.
Examine the need you are fulfilling or the problem you are solving. More importantly, does the section give the reader a clear understanding of why you’re in business, what you sell, and how you differ from your competitors?
After completing this exercise, if you’re still unsure or would like more support about how to write the Products and Services section of your business plan, we invite you to reach out to our team at Bsbcon.
We are available to help small-medium-sized enterprises worldwide tackle their most critical challenges and capture their most significant opportunities. We make a point to understand new trends, digital options, and partnerships that help our clients today and tomorrow. Call us toll-free at 1(888) 880-1898, write [email protected] , or fill out our contact form here .
Let's Get Started!
How can we help you.
Get in touch with us or visit our office
- United States
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
The fourth in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
In the Products and Services section of your business plan, you will clearly describe--yep--the products and services your business will provide.
Keep in mind that highly detailed or technical descriptions are not necessary and definitely not recommended. Use simple terms and avoid industry buzzwords so your readers can easily understand.
On the other hand, describing how the company's products and services will differ from the competition is critical. So is describing why your products and services are needed if no market currently exists. (For example, before there was Federal Express, overnight delivery was a niche business served by small companies. FedEx had to define the opportunity for a new, large-scale service and justify why customers needed--and would actually use --that service.)
Patents, copyrights, and trademarks you own or have applied for should also be listed in this section.
Depending on the nature of your business, your Products and Services section could be very long or relatively short. If your business is product-focused, you will want to spend more time describing those products.
If you plan to sell a commodity item and the key to your success lies in, say, competitive pricing, you probably don't need to provide significant product detail. Or if you plan to sell a commodity readily available in a variety of outlets, the key to your business may not be the commodity itself but your ability to market in a more cost-effective way than your competition.
But if you're creating a new product (or service), make sure you thoroughly explain the nature of the product, its uses, and its value, etc.--otherwise your readers will not have enough information to evaluate your business.
Key questions to answer:
- Are products or services in development or existing (and on the market)?
- What is the timeline for bringing new products and services to market?
- What makes your products or services different? Are there competitive advantages compared with offerings from other competitors? Are there competitive disadvantages you will need to overcome? (And if so, how?)
- Is price an issue? Will your operating costs be low enough to allow a reasonable profit margin?
- How will you acquire your products? Are you the manufacturer? Do you assemble products using components provided by others? Do you purchase products from suppliers or wholesalers? If your business takes off, is a steady supply of products available?
In the cycling rental business example we've been using, products and services could be a relatively simple section to complete or it could be fairly involved. It depends on the nature of the products the company plans to rent to customers.
If Blue Mountain Cycling Rentals plans to market itself as a provider of high-end bikes, describing those bikes--and the sources for those bikes--is important, since "high-end cycling rentals" is intended to be a market differentiation. If the company plans to be the low-cost provider, then describing specific brands of equipment is probably not necessary.
Also, keep in mind that if a supplier runs out of capacity--or goes out of business altogether--you may not have a sufficient supply to meet your demand. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships, and describe those relationships fully.
Remember, the primary goal of your business plan is to convince you that the business is viable--and to create a road map for you to follow.
The Products and Services section for our cycling rental business could start something like this:
Product Description
Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will provide a comprehensive line of bicycles and cycling equipment for all ages and levels of ability. Since the typical customer seeks medium-quality equipment and excellent services at competitive prices, we will focus on providing brands like Trek bikes, Shimano footwear, and Giro helmets. These manufacturers have a widespread reputation as mid- to high-level quality, unlike equipment typically found in the rental market.
The following is a breakdown of anticipated rental price points, per day and per week:
Bicycle $30 $120
Helmet $6 $30
- Customers can extend the rental term online without visiting the store.
- A grace period of two hours will be applied to all rentals; customers who return equipment within that two-hour period will not be charged an additional fee.
Competition
Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will have clear advantages over its primary competitors, the bike shops located in Harrisonburg, Virginia:
- Newer equipment inventory with higher perceived quality
- Price points 15 percent below the competition
- Online renewals offering greater convenience
- A liberal return grace period that will reinforce our reputation as a customer-friendly rental experience
Future Products
Expansion will allow us to move product offerings into new equipment sales. We will also explore maintenance and fitting services, leveraging our existing maintenance staff to provide value-added services at a premium price.
(And so on...)
When you draft your Products and Services section, think of your reader as a person who knows little to nothing about your business. Be clear and to the point.
Think of it this way: The Products and Services section answers the "what" question for your business. Make sure you fully understand the "what" factor; you may run the business, but your products and services are its lifeblood.
Now let's take a look at the next major section of your business plan: the Market Opportunities .
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

How to Write Products and Services Section of Business Plan
Business plan products and services section gives details of your product or service, how it is different and if you have a reliable manufacturing or sourcing system for the product.
Show competitive advantages of your product or service. Convince investors or lenders that you can outperform competition; you’ll likely get the funding you need.
Use this article as a guide when writing the product and service section of your business plan.
Hire business plan writer now!
How do you write the business plan products and services section.

Your goal in writing the business plan products and services section should be to explain your offering in simple, layman’s terms.
Anyone reading about your products or services should be able to understand:
- what you are offering
- what is the unique value you are offering
- how will you do quality assurance
- How will you meet the increased demand?
The product service plan section should include the following.
Explain Your Products or Services
Explain your product or service in detail. Try to include a brief about all the aspects of your product or service that will improve the consumers’ lives or increase business efficiency.
Show why your Product is Unique
Talk about the distinctive features of your product. Show what competitors are offering and explain how your offer is unique and better.
Emphasize the Benefits
Your hopes of capturing a share of the market depend on the benefits your product or service provides. Describe the benefits in terms customers can relate to.
For example, if you are offering the same features as the competitors but at a low price, highlight the low price.
Manufacturing, Sourcing, and Fulfillment
Explain if you will manufacture your products or you’ll source. If you are going to source the product from a manufacturer, how will you select the manufacturer?
Also, briefly explain the product supply chain and fulfillment process. Potential lenders may want to know if your supply chain and fulfillment system can handle high demand.
Be Short and Concise
Keep to the point. The Product service section in a business plan is about introducing your offering with a fair amount of detail. However, don’t make it lengthy.
You will discuss your product or service in every section of the business plan one way or another.
Show your Expertise
A product coming from an acknowledged expert gets more acceptance in the market.
Show your education or experience with the offering. If your business has any patents, trademarks, or special permits, make sure you showcase them. That way, you can establish yourself as an authority.
For a sole proprietor, you can include your experience or education. For example, when an athlete starts a fitness brand, it becomes a quick success. However, other similar businesses face struggles at the start.
Explain in Simple Language
Make a detailed plan of product service but explain everything in simple language.
Every industry has its jargon and buzzwords. People familiar with your product can understand the technical details, but the lenders or investors may not know much about your industry.
Here is a pro tip for this. When you have written the product or service description, ask a trusted friend or family member to read it and explain your product to you. That way, you can know if your product service part of the business plan is generally understandable.
What is your Exclusive Advantage?
Your exclusive advantage is what makes you stand out. You spotted your exclusive advantage when you developed your product or service offering. Explain that exclusive advantage here.
If you think there is no exclusive advantage, see if you can lower your price or provide better after-sale support. Even if your exclusive advantage is indirectly related to your product, it can help you get ahead fast.
Assume you are talking to the customer
When you walk into the customer’s shoes, you can understand their needs better.
Assume you are talking to an actual customer and convincing them to buy from you. They know your competition and they know what they need. You will have to talk in layman’s terms without missing any important details. You will need to focus on your competitive advantage.
You will write an excellent product or service section when you think you are explaining it to a potential customer.
Key Questions to Answer in the Business Plan Products and Services Section
- Do you have a ready product or an under-development product?
- When will you bring new products or services to the market?
- What is the unique advantage of your product or service?
- What are the competitive advantages of your product or service?
- Does your product or service have any competitive disadvantages?
- Are you bound to charge a price in a short range, or can you charge a different price with a better offer?
- Are your business operating costs reasonable?
- Will you manufacture your products or buy from a supplier?
- Do you sub-contract the parts of your product to different manufacturers and assemble the product at your facility?
- Will you be able to keep a steady and reliable supply chain for your product when demand rises?
WiseBusinessPlans is one of the best business plan writing companies !
In the products and services section, describe your offerings in detail, including their features, benefits, and uniqueness. Include information on pricing, any proprietary technology or intellectual property, and how your products or services meet customer needs.
Differentiate your products or services from competitors by highlighting their unique selling points, such as superior quality, innovative features, customizable options, or exceptional customer service. Explain how these differentiators give you a competitive advantage.
Yes, it’s important to outline your pricing strategy in the products and services section. Explain your pricing model, whether it’s based on cost-plus, value-based, or market-based pricing. Justify your pricing strategy by considering factors such as market demand, competitors’ pricing, and perceived value.
Demonstrate the market need for your products or services by providing market research and analysis. Include data on customer demographics, target market size, and any trends or consumer preferences that support the demand for your offerings.
Yes, you can mention future product or service expansion plans in the products and services section. Briefly outline your growth strategy, such as introducing new product lines, expanding into new markets, or offering additional services. However, focus primarily on your current offerings and their value proposition.
Access our free business plan examples now!
Quick links.

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Write Products and Services Section of a Business Plan
Product and Service Description Workbook
- June 3, 2024

The products and services section of your business plan is much more than a list of products or services you will offer.
It includes a detailed description of the problem you solve, the pricing you charge, and the intellectual properties you own. Moreover, it also offers insight into your marketing and order fulfillment process.
Well, that’s not it.
There’s a lot more to the products and services in a business plan and we shall discuss that in this blog post. Also, we will share a few creative tips to make this section informative.
So, let’s get started.
What is the products and services section?
The products and services section of your business plan is where you mention and elaborate on your product range, product descriptions, pricing strategies, and other relevant details.
If you’re looking for partners or investors, this section plays a crucial role in persuading them. What you include in this section and how you write it can deeply impact whether or not your investors will seal the deal with you.
What to include in the products and services section?
The products and services section is the most important component when you write your business plan .
It includes everything a prospective reader needs to understand the products you sell—its unique selling proposition (USP), pricing, marketing tactics, delivery, and order fulfillment process. In short, a complete detailed guide about your business’s product and services.
Let’s explore this section in more detail as we dive further.
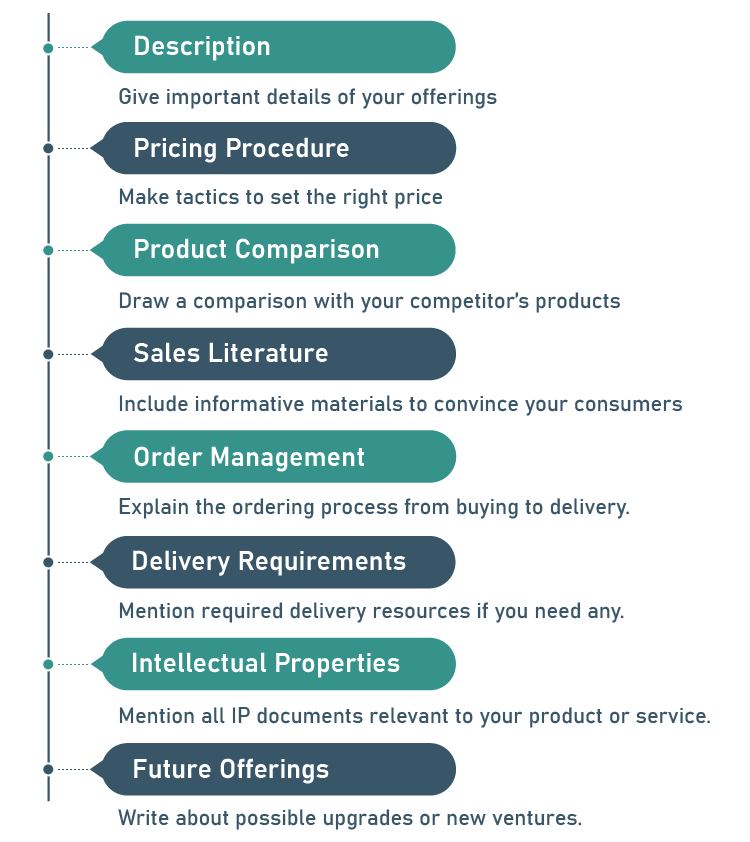
1. Description
In this part, include all the important details of your offerings. To write an accurate description, use the 5W2H(who, what, when, where, why, how and how much) method and answer these questions:
- Who can use this product? Mention the details of your ideal customer.
- What are the fundamental aspects of your product? These may include features, materials, ingredients, costs, dimensions, etc.
- When should someone use this product? Mention the occasion, or the season if it’s a seasonal product. You can also mention if it’s designed for a specific purpose.
- Where should your customers use the product? Is it used indoors or outdoors? Specify these details.
- Why should your customers use your product? Mention how the product fulfills their needs.
- How should they use your product? Mention if there are any important user instructions.
- How much should they use it? Mention the ideal frequency of usage that’s essential to follow while using your product.
2. Pricing procedure
A pricing strategy refers to the tactics you use to set a price for your products and services. While there are various strategies to choose from, conducting a price analysis will help you determine the pricing strategy that works best for your business model.
Follow this step-by-step procedure to conduct a pricing analysis:
Determine cost of goods sold (COGS)
To calculate the total cost of your products and services, add all the expenses that you incurred before the sale. This will include costs such as manufacturing, labor, warehousing, distributing, packaging and labeling, marketing, etc.
Also, determine your profit markup and add that to the COGS to set the final price for your products.
Collect data about the price preferences of your customers
Study your target customer’s opinions regarding pricing through surveys and questionnaires. This helps you know your customers’ price sensitivity.
Using this data, you can set an equilibrium price that’s low enough to sustain demand and high enough to secure profits.
Study your competitors’ prices
Perhaps the best way to tell whether a price works is by looking at the prices of your direct competitors.
Direct competitors are those who sell the same products as you do. Analyzing their pricing strategy helps you understand the price range for similar products in the current market.
With this information, you can modify your prices to set a competitive price.
Consider all the legal and ethical aspects
Setting a price that induces sales is essential.
However, ensure that you don’t set a price so low that it cuts off the competition. Such practice, often regarded as predatory pricing, is considered illegal in certain industries.
To avoid such troubles, be aware of the laws applicable to your business.
After conducting a pricing analysis, you can look at these pricing strategies to choose one for your business.
3. Product Comparison
Regardless of what you’re selling, someone in the market might already be selling it. Unlike direct competitors, indirect competitors sell similar products with slight variations.
Looking at your competitors can help you draw a comparison. To do that, examine their products and services and list down the similarities and differences.
Categorize this information into qualitative and quantitative aspects and organize it in tables. Finally, summarize it by including your advantages over competitors. Also, include how you will leverage them to balance your drawbacks.
4. Sales Literature
Sales literature refers to the promotional and informative materials you use to inform, clarify, and convince your customers to make buying decisions. These include brochures, catalogs, newsletters, price lists, customer testimonials, and case studies.
List out all the sales literature you use to market your products and services and briefly outline the information it conveys. Another integral part of your sales literature is your website; explain how it contributes to your sales.
Perhaps you run a blog to promote your products and inform your customers about new releases. Maybe you sell your products and services directly from your website; in that case, your sales literature material will go there.
5. Order management
From the moment a customer places an order to the delivery, followed by after-sales services—order processing constitutes everything.
Here, you explain how customers will order or buy the products and detail your delivery process.
For instance, for an online retail store, the order processing may include stages like:
- Order placement
- Order processing
- Picking inventory
- Product delivery
- Customer support
Depending on your offerings, your order processing workflow can have several stages. Describe each step and provide elaborate details about the execution.
6. Delivery Requirements
If the delivery or creation of your products and services needs any resources, mention them here. These can include equipment, vehicles, technology, and software.
For instance, a cafe owner will need kitchen equipment and IT solutions to run and provide its services. Mention these things in this part of the products and services section.
To cite another example, a consumer electronics company needs an IT infrastructure and production facility to create its products. For delivery, it needs vehicles and an online portal for customers to place and receive orders. All these are mentioned here.
7. Intellectual Properties
Mention all the Intellectual Property (IP) documents that are related to your products and services. These include trademarks, seller permits, patents, other licenses, etc.
Here you can also include any legal issues you’re currently facing and explain how you’re dealing with them.
Further, mention the issues that might occur in the future and the counteractive measures you will take to prevent them. These include adding safety labels, and disclaimers, opting for insurance policies, etc.
8. Future Offerings
This is a chance to impress your investors or partners by briefing them about your future products or services.
If your future products are an extension of the current products, offer an outline of the improvements you will make and clarify if the products are under development or ready for launch.
You can alter the products and services section as you wish to fit your product ideas the best. However, we have some practical tips that can help you make this section enriching.
6 Tips on Writing a Good Products and Services Section

Bear these tips for the business plans products and services section in mind when you start writing. Remember, this is just a list. You can always find other little tactics most unique to your product, service or industry.
1. Opt for a customer-centric approach
Your goal is to cater to the needs of your customers through your products or services. Hence, write as if you’re talking to your customers and directly addressing their issues. Point out how your product will make their lives better and easier.
2. Keep it simple
Clearly represent the information. Use bullet points and lists to convey your message. You can also use tables and charts to display product comparisons, strengths, etc.
3. Ditch buzzwords and industrial jargon
Everyone who reads your business plan may not understand the industrial jargon and buzzwords. Therefore, it’s best to skip the complicated lingo and use layman’s terms.
4. Specify market pain points
Elaborate on the problems your target audience is facing. You can gather this data by conducting a market analysis. Mention the various pain points and the features of your product that address them. Consider citing examples and relevant statistics to display how your product solves a customer problem.
5. Emphasize your USP
Highlight the benefits and the unique features of your products and services. Mention the things you do differently than your competitors and how you offer more value in comparison.
6. Flaunt your achievements
Make sure to show off the business milestones you’ve achieved such as awards, news articles, customer reviews, etc. You can also include your past sales numbers, your customer base, and the projects you fulfilled. These instill trust and help potential investors, clients, and partners to make decisions.
Persuade interest with a product and service section
Your products and services are the lifeblood of your business. Its accurate representation in a business plan is essential to instill investors’ faith in your ability to achieve growth and secure funding.
Ensure that this section communicates the value of your product offerings and highlights your strategies to market, sell, and deliver customer orders.
Now, kickstart writing this section. However, remember that you need to complete other sections of your business plan, as well.
Using a business planning app like Upmetrics could be a smart choice to streamline your entire plan writing process. Its AI business plan generator uses the information you offer to create detailed plans in less than just 10 minutes.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much detail should i include about my products or services.
The answer depends on the purpose and type of business plan you intend to write. While this section in a comprehensive traditional plan includes details about products, it also includes an in-depth detailing about how you plan to market, sell, and deliver your orders. However, this much detailing is not essential if you are writing a lean plan.
What are the key components of a products and services business plan?
Here are the key essentials a products and services section should include:
- Product Description
- Pricing strategies
- Product USPs
- Marketing materials
- Intellectual properties
- Future offerings
- Order management
- Delivery Process
Do I need to include pricing information in the Products and Services section?
It’s ideally preferable to add pricing information to the products section of a business plan. This will help prospective readers understand your pricing strategy and revenue potential. It can assist them in calculating your profit margins and assess the competitive position of your business.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning


The products and services section of a business plan is a critical component that outlines what your company offers, how it meets customer needs , and what sets it apart from competitors. This section provides an opportunity to showcase the value and uniqueness of your offerings, helping investors and stakeholders understand the core of your business. In this article, we will explore how to write an effective products and services section in a business plan, providing valuable insights and tips to help you create a compelling and informative segment.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Your Target Audience: Tailor your descriptions and language to your specific target audience. Use terminology and explanations that resonate with them and highlight how your offerings meet their specific needs.
- Focus on Benefits, Not Just Features: While it’s important to outline the features of your products or services, it’s equally crucial to emphasize the benefits they bring to customers. Clearly communicate the value proposition and the positive impact on customers’ lives or businesses.
- Highlight Competitive Advantages: Identify and emphasize what sets your offerings apart from competitors. Whether it’s pricing, quality, convenience, customization, or any other aspect, highlight your strengths and differentiators.
- Be Clear and Concise: Use clear and concise language to ensure easy understanding. Avoid technical jargon or complex explanations that may confuse readers.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate visuals such as images, charts, or diagrams to enhance understanding and showcase your products or services visually.
- Include Relevant Legal Considerations: If applicable, discuss any patents, copyrights, or trademarks associated with your products or services, demonstrating the measures you have taken to protect your intellectual property.
Understanding the Importance of the Products and Services Section
The products and services section of your business plan plays a vital role in conveying the essence of your offerings. It helps potential investors, lenders, and partners understand what you offer, its benefits, and how it satisfies customer demands. This section serves as a platform to demonstrate your understanding of the market, highlight your competitive advantages, and differentiate your products or services from others in the industry. It should inspire confidence and showcase your ability to deliver value to your target audience.
Developing an authentic and compelling products and services section in your business plan is essential for effectively communicating the value and differentiation of your offerings. By following the steps and tips outlined in this article, you can create a standout section that captivates readers and instills confidence in your business.
Customer-Centric Approach:
When crafting the products and services section, it’s crucial to adopt a customer-centric approach. Understand your target audience and their pain points, desires, and preferences. This understanding will guide you in tailoring your offerings and messaging to address their specific needs effectively. Consider conducting market research, surveys, or focus groups to gather insights into customer preferences, which can inform the development and positioning of your products or services.
Clear Communication of Benefits:
While it’s important to describe the features of your offerings, it’s the benefits that truly resonate with customers. Clearly articulate how your products or services improve their lives, solve their problems, or fulfill their desires. Use language that is relatable and engaging , focusing on the outcomes and positive impact your offerings bring. Whether it’s saving time, increasing efficiency, enhancing productivity, or providing cost savings, highlight these benefits in a concise and compelling manner.
Addressing Objections and Concerns:
Anticipate potential objections or concerns that customers may have about your products or services. Address these directly in the products and services section to instill confidence and overcome any hesitations. Whether it’s addressing quality, scalability, support, or any other concerns, provide reassurances and explanations that demonstrate your commitment to customer satisfaction.
Incorporating Testimonials and Case Studies:
To strengthen the credibility of your offerings, consider incorporating testimonials or case studies from satisfied customers. Real-life examples and success stories help build trust and provide social proof. Highlight the positive experiences and outcomes of customers who have benefited from your products or services, showcasing the value they have derived.
Competitive Analysis:
A comprehensive products and services section should include a competitive analysis. Identify your main competitors and analyze their offerings, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Highlight how your products or services differentiate from the competition and offer a superior value proposition. This analysis demonstrates your market awareness and positions your business as a viable and compelling option in the industry.
Continuous Improvement:
Emphasize your commitment to continuous improvement in the products and services section. Discuss how you gather customer feedback, analyze market trends, and use these insights to enhance your offerings. This conveys that your business is adaptable and responsive to changing customer needs and preferences, further reinforcing your competitive advantage.
By expanding on these key points, you can create a products and services section that effectively communicates the value, benefits, and differentiation of your offerings. Remember to maintain a customer-centric focus, utilize clear and engaging language, address potential concerns, and incorporate evidence of customer satisfaction. A well-crafted products and services section will showcase your business’s understanding of the market and its ability to deliver exceptional value to customers.
Structuring the Products and Services Section
Start with an overview:.
Begin by providing a brief overview of your products or services. Clearly state what you offer and how it fulfills customer needs or solves their problems. Capture the attention of your readers with a compelling introduction.
Describe Your Offerings:
Provide a detailed description of each product or service you offer. Highlight their key features, functionalities, and specifications. Use clear and concise language, avoiding technical jargon that may confuse readers who are not familiar with your industry.
Explain the Benefits:
Clearly articulate the benefits and advantages your offerings provide to customers. Focus on how your products or services address pain points, enhance efficiency, save costs, improve outcomes, or bring unique value to the market.
Illustrate the Unique Selling Proposition (USP):
Differentiate your offerings by highlighting what sets them apart from competitors. Identify your USP, which could be a distinctive feature, superior quality, innovative technology, exceptional customer service, or any other factor that gives you a competitive edge.
Provide Supporting Evidence:
Back up your claims with evidence and data. Include testimonials from satisfied customers, case studies, market research findings, or any other relevant information that showcases the credibility and value of your products or services.
Discuss Product Development or Service Expansion:
If applicable, outline your plans for future product development or service expansion. This demonstrates your vision for growth and adaptation to evolving market needs.
Crafting an effective products and services section in your business plan is crucial for capturing the attention of investors, lenders, and stakeholders. It is an opportunity to showcase the value, benefits, and unique selling propositions of your offerings. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can create a compelling and informative products and services section that effectively communicates the essence of your business.
Remember to tailor your descriptions to your target audience, focusing on the benefits your offerings bring to customers. Highlight your competitive advantages and provide supporting evidence to back up your claims. Clear and concise language, along with visuals, can enhance understanding and engagement.
The products and services section is your chance to demonstrate your market understanding, differentiation, and value proposition. Use this section to paint a compelling picture of how your offerings meet customer needs and pave the way for success in your industry.
- Apply as a Writer
- Privacy policy
- Terms of use
- SBA business plans
- Non-profit business plans
- Startup business plans
All rights reserved by MovaslearningOU @2023

Business Plan Products and Services Section: How to Write Guide .
Sep 17, 2023 | Business Consulting , Business Growth , Business Plan , Business Strategy Development , Products and Services , Starting a Business , Strategy

How to Write the Business Plan Products and Services Section
The business plan products and services section provides a comprehensive overview of your business, including your business model, product and service offerings, target market, and sales forecast.
“You’ve got to start with the customer experience and work back toward the technology – not the other way around.” – Steve Jobs
In this, the fifth installment in our” Creating your business plan” article series, we will discuss the information you should include regarding your products and services, how they contribute to your unique value proposition, and what sets you apart from your peer group.
Most companies either sell a range of products or offer several services to their customers, sometimes both, especially as you grow and scale up your business operations.

This section of your business plan should excite potential investors or partners. Here are some tips to create a compelling products and services section.
The products and services section should not just list your business offers in your business plan. It should provide comprehensive information on the pricing of your products and services, how you intend to fulfill orders, and other relevant details that investors require to make funding decisions. Find out more below.
Why you need a products and services section in a business plan
The section on products and services in your business plan is the focal point of your entire plan. Although other areas are significant, this section is the core of your business and serves as the foundation for the rest of your plan.
Describe your b usiness plan p roduct or service offerings
Firstly, within this section of your business plan, you want to include a description of your products or services. These should be reasonably detailed to give your reader a strong understanding of how they fit into your overall business plan.
You should discuss the general categories under which your products or services fall and then describe the relevant characteristics of your offerings. It’s important to remember that, while offering a detailed review, you shouldn’t get too technical. It would help if you avoided buzzwords, acronyms, and dense industry jargon.
There’s a good chance that some of your readers won’t be familiar with these terms, and using them could confuse them. Instead, write for someone who doesn’t know anything about your business. That guarantees that your descriptions are clear and understandable.
Remember the following questions as you sculpt each entry’s product and service description.
- What is the current status of the product or service offering in the marketplace?
- Is the offering an existing product or service or one in development?
- How will you offer the product or services?
- What are the ideal price point and profit margins?
- What are your innovation plans for this product or service?
For the former, discuss how long it has been a part of your company, any significant historical developments, industry awards, or the use of technology or advanced sustainability elements that differentiate you.
For the pricing, you can list the product category or individual SKUs (items). If you use Point of Sale (POS) software, like Shopify , you can include information from the system.
- Item 1 = $4.99
- Item 2 = $7.99
- Item 3 = $15.95
If it’s a new product or service, give your business plan readers information about where it is in its development, what else is required to bring it to completion (and ready to sell), and when you expect to roll it out.
Develop strategic priorities for your business plan
Whether your offerings are currently in the market or under development, to remain competitive, you need a strategic roadmap plan to guide their continued innovation over time, offering customers thoughtful and innovative new solutions to delight and introduce them to your broader product and service offering.
Ideally, you would want to include an innovation roadmap for each product or service you offer customers.
For each overarching category, describe how this helps your customers articulate how your product offering or services fit into the marketplace and how you plan to develop it to stay ahead of your competitors.
Your strategy roadmap describes how you’ll remain competitive in the future, but you also need to discuss how your products and services are currently differentiated.
- What are the characteristics, design innovations, and features set your offering apart from the rest of the market?
- How do they fit in general, and where do they shine?
- Where do your prices fall relative to your competitors?
- Is price a distinguishing feature?
- Are you catering to value-conscious or price-sensitive consumers, or do you charge more than the competition because your products and services warrant it?
Affordability is a relative term. High-end products aren’t affordable to most people, but affordability isn’t generally a concern if your market strategy targets wealthy consumers.
You can also talk about product and service shortcomings if any exist. Describe how your three-to-five-year forward-focusing strategy and innovation plans will help to rectify the situation. Other than providing enrichment, this will demonstrate to your business plan readers that you’re open, transparent, honest, and proactive in seeking solutions.
Unique value proposition for your b usiness plan products and services section
Your value proposition is a declaration from you about the benefits your customers receive by using your service or the challenges they will overcome by using your product versus an alternative in the marketplace.
Discuss why your target market prefers or should prefer your offerings over the competition.
- What is your value proposition, and what does this mean for your customers?
- How does your product or service offering solve/ improve problems?
- What benefits do you provide that are lacking from other market contenders?
- What is the product and service difference that you selected for marketing purposes that will drive customer adoption?
Your value propositions should focus on your customer needs, and answering these questions will give your business plan readers a robust understanding of everything you offer and your future aspirations for business growth.
You may have different value propositions for each of the target core customer groups. As your business grows, you will likely have to revisit your value proposition for each product and service to safeguard your competitiveness and relevance in the marketplace.
Be strategic. You can’t leave change up to chance. You will need a strategy development process to oversee your decisions and focus your efforts. Otherwise, you run the risk of stagnation, ultimately impacting your business growth and cash flow.
Why is the b usiness plan products and services section important?
In the products and services section of your business plan, you can explain the purpose behind your business. This can include detailed information about your products or services, such as pricing, and more personal aspects like your mission statement.
The goal is to create a compelling and well-rounded description of what you offer, how it operates, and why it is beneficial. This section should be able to stand alone and be supported by the other areas of your plan.
For example, have a look at Bplans , US-SBA , or Upmetrics have some valuable insights/
Get in Touch
Are you looking to grow your business but unsure where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We’ll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let’s get started!
Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868.
Recent posts .

Project Portfolio Management (PPM)
Jun 30, 2024
Project portfolio management (PPM) is a systematic process by project managers and project management organizations (PMOs) to evaluate the potential advantages of initiating a project. In this process, project managers play a crucial role in providing companies with predictive and business analyses for potential project investments. They do this by collating and structuring all pertinent information about proposed and ongoing projects, and by facilitating communication between team members and stakeholders.
Project portfolio management (PPM) empowers organizations and managers by providing comprehensive insights. This wealth of information allows executives to discern which project managers to engage with, and enables project managers to easily access team members. It facilitates improved communication with leadership and colleagues for team members, and ensures that stakeholders are continually informed with reliable and consistent feedback, making everyone feel informed and knowledgeable.

Setting Up a PMO (Project Management Office)
May 25, 2024
Project management plays a crucial role in every business, and establishing a project management office is essential for maintaining consistency and achieving successful results. Many companies create a project management office (PMO) to ensure that projects are finished on time and within budget. But what exactly does this involve? This article will furnish you with all the essential information for setting up a PMO, covering everything from the fundamentals of a PMO to selecting the appropriate tools and procedures for your business.

What is Program Management?
Apr 2, 2024
Program management is a vital component of organizational success, as it enables the coordinated execution of interdependent projects that yield benefits beyond the scope of individual project management. It involves the judicious application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to meet specific program requirements. Our experience has demonstrated that organizations with well-developed program management and program management offices (PMOs) consistently outperform those that lack such structures. Therefore, it is imperative that organizations prioritize the establishment of robust program management frameworks to achieve their strategic objectives.
Happy clients .
Trevor mcomber, us.
I recently worked with Zoe@Noirwolf, who provided me with an outstanding 5-year business plan. The expertise in financial planning, market research, SWOT analysis, and consulting was exceptional. Zoe provided me with a comprehensive and well-researched plan tailored to my business. The entire process was professional, timely, and communicative.
Bill Walton, Leeds
Zoe provided first-rate work and is an excellent business consultant. I was trying to figure out my cash flow forecast for my startup. Zoe gave me an interactive consultation session over MS teams, which was valuable and saved me a lot of time. She is super quick in excel and knowledgeable about what to include in your estimates. She was able to offer me ideas & choices that I hadn't considered. Highly recommended.
Jeendanie Lorthe, US
Warren kim, us, oscar sinclair, london, get in touch ..
Looking to grow your business but feeling unsure about where to start? Our small business consulting and leadership coaching services are here to help! We'll work with you to scale your operations and achieve your goals. Plus, we offer a free one-hour consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started!
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Products or Services Section
Learn about this essential part of a business plan
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
Describe and Compare
Price points, order fulfillment, tips for writing the products or services section.
The products or services section of your business plan should clearly describe what you are selling with an emphasis on the value you're providing to your customers or clients. Include an in-depth look at all of the elements related to what you are selling.
The section needs to explain exactly what you are selling and how it fits in the marketplace. It's easier to describe the value provided if you are the only business in the area selling the product or service in question, but it is likely competitors are doing something similar.
Provide information about your competitors' offerings, how they are similar to yours, and how they are different. It's possible your business has a slightly different take on the product or service or is targeting a slightly different audience. It's also possible what you are offering is almost identical to what your competitors are offering, but demand in the marketplace is high enough to support multiple businesses doing the same thing. Explain your situation.
In addition to describing the actual products or services, break down how much they will cost. Products may come in different sizes, quantities, or varieties that will impact price, and services might be more or less extensive depending on the price being charged.
Address what competitors are doing in this regard as well. Perhaps you are offering higher or lower quality for a different demographic, but be clear about the cost and who can afford it.
Explain what happens once someone purchases what you are selling. If it is a product, they might buy it from a retail store, have it delivered from your online shop, or perhaps they submit a custom order in advance and pick it up at a later date.
If you are offering a service, it might be something that involves clients coming to you, or you might go to them. Whatever the details, make sure the process is clear.
If special technology is involved, outline what it entails. This could be specific technology you need in order to provide your services, or it might be technology clients or customers need in order to take advantage of what you're selling.
For example, if signing up clients for a training seminar, you might need specific hardware and software for a presentation. Perhaps you are selling software that requires the latest version of a particular operating system. Be sure these details are provided.
Make your description of available products or services an effective part of your business plan by following these tips:
- Focus on the customer: The purpose of the products or services section is to clearly express the benefits you're providing to your customers or clients. Focus on that goal by addressing how what you are selling benefits your customers. Show how it makes their lives better, easier, or more profitable.
- Get to the point: State the value upfront, then elaborate throughout the rest of the section while providing supporting materials. For example, if the primary benefit of what you are offering is that it saves time, state as much right away. Follow this statement with details about how it saves time and data to support the claim.
- Keep It simple: Assume the reader has little to no understanding of your industry and product or service. You're the expert in the industry, but the basics may not be as clear to those reading your business plan.
- Show what makes you unique: While describing similar products and services that are already in existence, take some time in your description to express how your product or service stands out as something different.
- Include the fine print: While the bulk of your products or services section should focus on the end result, you also should include information about your pricing and how you arrived at that price point.
Business Plan Offering Example: Everything You Need to Know
A small business plan offering example revolves around the goods or services you plan to offer to the public or other businesses. 3 min read updated on January 01, 2024
A small business plan offering example revolves around the goods or services you plan to offer to the public or other businesses. It's important to understand what your company is offering in order to engage in the proper marketing efforts.
It's also important to understand how that offering will compare to the competition in your marketplace. Of course, the end goal is to influence a customer to purchase from you over the competition.
Some businesses offer multiple goods and/or services. For example, a car dealership might sell cars, but it can also offer services to repair and maintain cars. The term "product mix" refers to the entire line of products and services offered by such a business.
Product Depth
The product lines of companies have varying depths. Varying depth refers to the number of products or services a company plans to offer in each product line.
The depth of a product line also refers to the customer segments, or the various kinds of customers, that the product line will satisfy. For example, a car dealership might sell luxury, sport, economy, and utility vehicles in an effort to cater to a wide variety of customers. This may also help the dealership quash other competitors in the marketplace.
Product Width
Along with product depth, businesses may also want to consider "product width." Product width refers to the number of product lines being offered.
Product width can help a company increase its sales and marketing efforts. This may make its profits less susceptible to market fluctuations in the demand for each type of product.
For example, if a company sells hot chocolate and ice cream, it will withstand the market fluctuations that come with an increase in hot chocolate sales in the winter and a plummet in the summer.
Products or Services Section
In the Products or Services Section of your business plan , you'll describe the products or services you're offering and explain the concept for your business (including manufacturing, purchasing, packaging, and distribution). This is also the time to annotate suppliers and fees. You should also indicate how your offerings will fit into the current marketplace and size up against the competition.
This section provides a clear understanding of your motivations, what you plan to sell, how you will compete, and how you can find a niche that no one else is filling.
The Products or Services section must emphasize the value you will be providing to your clients or customers.
How to Write the Products or Services Section
This is the opportunity to provide an in-depth look at every element pertaining to the products and/or services you're selling. The Products or Services section can be broken down into the following parts:
- A description of your products and/or services
- A comparison to other products and/or services currently on the market
- A list of all your price points
- An explanation of how your product and/or service orders will be filled
- An overview of specialized equipment, software, supplies, or technology required to produce your products and/or services
- An outline of planned future offerings
In every part, you must maintain a focus on the benefits of your products and/or services to the public.
Explain your offerings in layman's terms so that even someone who's unfamiliar with those products or services may become excited about them. Always keep the reader in mind. Be aware of any elements you might take for granted because you know the industry inside out but that might not be common knowledge to your investors or lenders.
Avoid technical knowledge, acronyms, and buzzwords. Never make assumptions about the knowledge level of your readers. To make sure you've hit the mark, ask someone who's not in the industry to proofread this section. See if they can paraphrase the section for you in their own words and state the benefits of your products and/or services.
Other Considerations for the Products or Services Section
You may also want to include any pertinent accreditations or intellectual property in this section. Was your product tested or certified? Did you copyright, patent, or trademark your product? Each of these elements can add credibility and substance to your business plan.
Photos or brochures will also provide a visual representation of your offerings. Although these are typically found in the business plan's appendix, you could refer to them in this section as well.
If you need help with a business plan offering example, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- What Is Service Product?
- Service Business Plan
- Is a Service a Product? Everything You Need to Know
- Parts of Business Plan and Definition
- What Are Product and Services Examples?
- Business Plan Outline: Everything You Need To Know
- What Is a Product or Service Description?
- How to Make a Business Plan Format
- Creating a Business Plan
- Business Description Outline
Business Plan Section 4: Products and Services
To give others a clear understanding of the value your product or service provides, read about 11 important things to include in this section of your plan.

This is the part of your business plan where you will describe the specific products and services you’re going to offer. You’ll fully explain the concept for your business, along with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. You’ll go over suppliers, costs, and how what you’re offering fits into the current market and stacks up against your competitors.
How do you write the Products and Services section of a business plan?
While your product may be technical, don’t get caught up in complicated industry jargon. Explain and describe what you’re offering in layman’s terms, so someone who isn’t familiar with your business will understand and be excited about it. It may be necessary to give some basic background if this is an area or industry people are unfamiliar with.
While you write up the Products and Services section of your business plan, keep your reader in mind. Things that you might take for granted or know inside-out might not be common knowledge to potential lenders or investors. As you write, avoid being too technical, assuming too much knowledge from your readers, and using buzzwords.
You don’t want to come off as condescending, but you do want to make sure everyone understands what you’re talking about. To see if you’ve succeeded, have some trusted people who aren’t in your industry proof-read this section for you, and ask them to explain your product or service in their own words, along with the benefits to using them.
Here are the points you want to write up in the Products and Services section of your business plan:
The Product or Service Description
What is your product and service, and how does it work? How does it benefit customers? How do you make it or how will you get it made?
Product Comparison
What makes this product or service unique or better than what’s already available in the market? Why would someone choose to buy your product or do business with you over someone else?
Accreditations/Intellectual Property
Have you had the product tested or certified? Gotten approvals from industry experts? Did you trademark, copyright, or patent your product ? These can add substance and credibility, so be sure to mention them.
Where are you currently with this product or service? Is it in the idea stage or do you have a prototype? Have you produced some and are looking to expand? Have you started offering this service already or are you still in the planning stages ?
How much will you charge for the products or services you’re offering? Where does this fit in with what’s currently available?
Sales and Distribution Strategy
How will you sell it? Will you market it online or in retail stores? Have you lined up any vendors? How will you distribute it or deliver the service you’re providing?
Fulfillment
How will you fill orders or deliver the service? Will you manufacture items yourself or outsource to someone else? Who will handle distribution, and how?
Requirements
Will you need any special equipment or technology to provide your product or service?
Do you envision future products or services as an extension of the business once it’s successfully launched?
Photos or Brochures
It’s beneficial to include a visual representation of your offering. Photos or brochures would generally get put in the plan’s appendix, but you would refer to them in this section.
How Do You Stand Out?
Perhaps most importantly, emphasize how and why you are competitive. How do you stand out, and why does this business have such a terrific chance at succeeding? In talking about your product or service, always try to answer why a client would want it. How will your offering make your customers’ lives better or more profitable? What need are you fulfilling or what problem are you solving?
To sum up, the product and services section of your business plan gives the reader a clear understanding of why you’re in business, what you sell, how you compete with what’s already available, or how you fill a niche that no one else is meeting.
Next > Business Plan Section 5: Market Analysis
Apply for a loan, get started.
Loans from $5,000 - $100,000 with transparent terms and no prepayment penalty. Tell us a little about yourself, your business and receive your quote in minutes without impacting your credit score.
Thanks for applying!
Loans are originated and funded through our lending arm, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development. By clicking “Continue to Application,” you consent to, Accion Opportunity Fund Community Development’s Terms of Use and Privacy Policy ; and to receive emails, calls and texts , potentially for marketing purposes, including autodialed or pre-recorded calls. You may opt out of receiving certain communications as provided in our Privacy Policy .
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?
- How To Write An Effective Business Proposal

What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

7 Business Plan Examples to Inspire Your Own (2024)
Need support creating your business plan? Check out these business plan examples for inspiration.

Any aspiring entrepreneur researching how to start a business will likely be advised to write a business plan. But few resources provide business plan examples to really guide you through writing one of your own.
Here are some real-world and illustrative business plan examples to help you craft your business plan .
7 business plan examples: section by section
The business plan examples in this article follow this template:
- Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business.
- Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists.
- Market analysis. Research-based information about the industry and your target market.
- Products and services. What you plan to offer in exchange for money.
- Marketing plan. The promotional strategy to introduce your business to the world and drive sales.
- Logistics and operations plan. Everything that happens in the background to make your business function properly.
- Financial plan. A breakdown of your numbers to show what you need to get started as well as to prove viability of profitability.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary is a page that gives a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. It’s easiest to save this section for last.
In this free business plan template , the executive summary is four paragraphs and takes a little over half a page:

- Company description
You might repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, social media profile pages, or other properties that require a boilerplate description of your small business.
Soap brand ORRIS has a blurb on its About page that could easily be repurposed for the company description section of its business plan.

You can also go more in-depth with your company overview and include the following sections, like in the example for Paw Print Post:
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your business —as an LLC , sole proprietorship, corporation, or other business type . “Paw Print Post will operate as a sole proprietorship run by the owner, Jane Matthews.”
- Nature of the business. “Paw Print Post sells unique, one-of-a-kind digitally printed cards that are customized with a pet’s unique paw prints.”
- Industry. “Paw Print Post operates primarily in the pet industry and sells goods that could also be categorized as part of the greeting card industry.”
- Background information. “Jane Matthews, the founder of Paw Print Post, has a long history in the pet industry and working with animals, and was recently trained as a graphic designer. She’s combining those two loves to capture a niche in the market: unique greeting cards customized with a pet’s paw prints, without needing to resort to the traditional (and messy) options of casting your pet’s prints in plaster or using pet-safe ink to have them stamp their ‘signature.’”
- Business objectives. “Jane will have Paw Print Post ready to launch at the Big Important Pet Expo in Toronto to get the word out among industry players and consumers alike. After two years in business, Jane aims to drive $150,000 in annual revenue from the sale of Paw Print Post’s signature greeting cards and have expanded into two new product categories.”
- Team. “Jane Matthews is the sole full-time employee of Paw Print Post but hires contractors as needed to support her workflow and fill gaps in her skill set. Notably, Paw Print Post has a standing contract for five hours a week of virtual assistant support with Virtual Assistants Pro.”
Your mission statement may also make an appearance here. Passionfruit shares its mission statement on its company website, and it would also work well in its example business plan.
- Market analysis
The market analysis consists of research about supply and demand, your target demographics, industry trends, and the competitive landscape. You might run a SWOT analysis and include that in your business plan.
Here’s an example SWOT analysis for an online tailored-shirt business:
You’ll also want to do a competitive analysis as part of the market research component of your business plan. This will tell you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to differentiate your brand. A broad competitive analysis might include:
- Target customers
- Unique value add or what sets their products apart
- Sales pitch
- Price points for products
- Shipping policy
- Products and services
This section of your business plan describes your offerings—which products and services do you sell to your customers? Here’s an example for Paw Print Post:

- Marketing plan
It’s always a good idea to develop a marketing plan before you launch your business. Your marketing plan shows how you’ll get the word out about your business, and it’s an essential component of your business plan as well.
The Paw Print Post focuses on four Ps: price, product, promotion, and place. However, you can take a different approach with your marketing plan. Maybe you can pull from your existing marketing strategy , or maybe you break it down by the different marketing channels. Whatever approach you take, your marketing plan should describe how you intend to promote your business and offerings to potential customers.
- Logistics and operations plan
The Paw Print Post example considered suppliers, production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan provides a breakdown of sales, revenue, profit, expenses, and other relevant financial metrics related to funding and profiting from your business.
Ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy’s financial plan breaks down predicted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
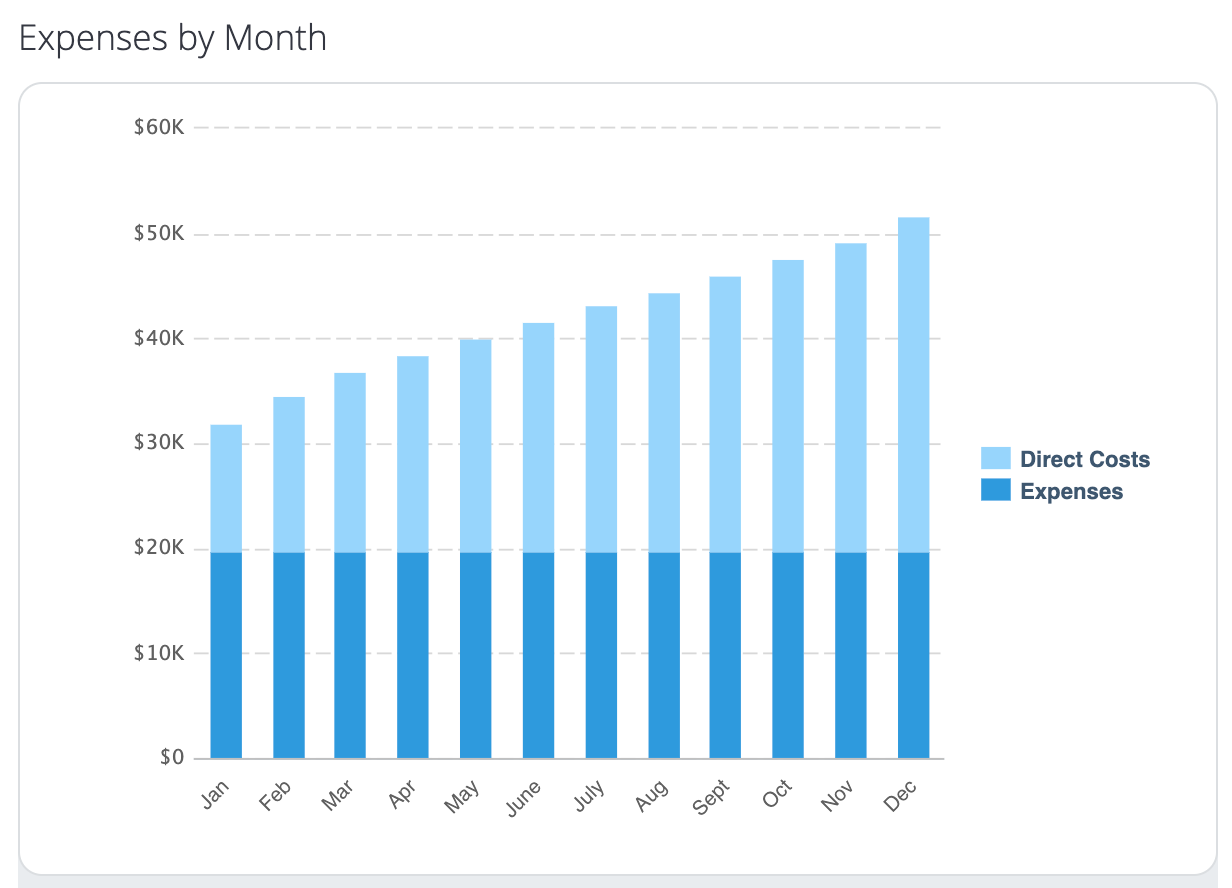
It then dives deeper into the financials to include:
- Funding needs
- Projected profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Projected cash-flow statement
You can use this financial plan spreadsheet to build your own financial statements, including income statement, balance sheet, and cash-flow statement.
Types of business plans, and what to include for each
A one-page business plan is meant to be high level and easy to understand at a glance. You’ll want to include all of the sections, but make sure they’re truncated and summarized:
- Executive summary: truncated
- Market analysis: summarized
- Products and services: summarized
- Marketing plan: summarized
- Logistics and operations plan: summarized
- Financials: summarized
A startup business plan is for a new business. Typically, these plans are developed and shared to secure outside funding . As such, there’s a bigger focus on the financials, as well as on other sections that determine viability of your business idea—market research, for example.
- Market analysis: in-depth
- Financials: in-depth
Your internal business plan is meant to keep your team on the same page and aligned toward the same goal.
A strategic, or growth, business plan is a bigger picture, more-long-term look at your business. As such, the forecasts tend to look further into the future, and growth and revenue goals may be higher. Essentially, you want to use all the sections you would in a normal business plan and build upon each.
- Market analysis: comprehensive outlook
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Marketing plan: comprehensive outlook
- Logistics and operations plan: comprehensive outlook
- Financials: comprehensive outlook
Feasibility
Your feasibility business plan is sort of a pre-business plan—many refer to it as simply a feasibility study. This plan essentially lays the groundwork and validates that it’s worth the effort to make a full business plan for your idea. As such, it’s mostly centered around research.

Set yourself up for success as a business owner
Building a good business plan serves as a roadmap you can use for your ecommerce business at launch and as you reach each of your business goals. Business plans create accountability for entrepreneurs and synergy among teams, regardless of your business model .
Kickstart your ecommerce business and set yourself up for success with an intentional business planning process—and with the sample business plans above to guide your own path.
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- The 13 Best Dropshipping Suppliers in 2024
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- 25+ Ideas for Online Businesses To Start Now (2024)
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Build a Business Website for Beginners
- 7 Inspiring Marketing Plan Examples (and How You Can Implement Them)
- 10 Ways to Write Product Descriptions That Persuade (2024)
- Get Guidance- 6 Business Plan Software to Help Write Your Future
- Business Valuation- Learn the Value of Your Business
Business plan examples FAQ
How do i write a simple business plan, what is the best format to write a business plan, what are the 4 key elements of a business plan.
- Executive summary: A concise overview of the company's mission, goals, target audience, and financial objectives.
- Business description: A description of the company's purpose, operations, products and services, target markets, and competitive landscape.
- Market analysis: An analysis of the industry, market trends, potential customers, and competitors.
- Financial plan: A detailed description of the company's financial forecasts and strategies.
What are the 3 main points of a business plan?
- Concept: Your concept should explain the purpose of your business and provide an overall summary of what you intend to accomplish.
- Contents: Your content should include details about the products and services you provide, your target market, and your competition.
- Cashflow: Your cash flow section should include information about your expected cash inflows and outflows, such as capital investments, operating costs, and revenue projections.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 22, 2024
Aug 21, 2024
Aug 20, 2024
Aug 19, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
How to Write a Product or Service Strategy in a Business Plan
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Write a Business Plan
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Customer Characteristics for Marketing
How to stop realplayer at startup, how to apply a segmentation, targeting, and positioning approach to marketing.
- Types of Marketing Communication Concepts
- Rationales for Marketing Strategies
For a small business to succeed, it must offer products and services that provide superior benefits when customers compare them side-by-side to the benefits provided by competitors’ products or services. The strategy element of the business plan describes how your products or services will be sold, the target markets you will sell to, the marketing message you intend to use to convince customers to purchase from you, and the methods you will use to deliver this message.
Distribution Channels
Describe how you will get your products or services in front of target customers. Growing the company’s revenues will be easier if the company can expand its distribution channels over time. For example, a gourmet candy maker could start out by marketing at gourmet food fairs as well as selling the products through the company’s website. As the products become more popular and the brand name better known, the owner could begin wholesaling the products to specialty food stores or upscale grocery markets.
Target Markets
Present a clear picture of who your best customers are or will be. Don’t limit your description of target markets in your business plan to basic demographic characteristics, such as age or income level. The more you know about what actually motivates them to purchase, the more precise your marketing message can be. A car repair shop owner may see that his loyal, repeat customers are those who seek to take extra good care of their vehicles. These would be individuals who regard automobiles as more than transportation, but rather as a source of pride and an integral part of their lifestyle.
Positioning Versus Competitors
When choosing among vendors of a product or service, potential customers compare their perceptions of the advantages and disadvantages of each company’s products and services. They consider the features or benefits that are important to them and try to identify the company that most closely meets their needs. In your business plan this is called positioning -- describing where your company stacks up versus competitors in delivering what is important to customers. How your products are priced relative to competitors is one aspect of positioning, but other features are important to customers’ decision making as well. A golf course for example could position itself as having the best practice and training facility in the region, the facility that caters to golfers who are truly serious about improving their games.
Marketing Message
In your business plan you describe why the benefits of your products and services are powerful enough to give you a competitive advantage. Part of devising your marketing strategy is determining how best to communicate these compelling benefits to your target customers. This is your marketing message. Strive for a consistent message than can be delivered in a concise manner. Communicate this message across all the platforms you will use to reach out to customers.
Media and Methods
Explain the reasoning behind the platforms you chose to deliver your marketing message. Choosing poorly can mean wasting precious marketing dollars and losing opportunities to acquire customers. Your choices include print, radio and TV advertising, online advertising, direct mail, your website or blog, attending trade shows and establishing a sales force to directly call upon potential customers. As you write this section of your plan, look at what methods work best for your most successful competitors. Don’t be afraid to try new methods, but start with a modest dollar commitment. You may find, for example, that your target markets respond well to receiving email notifications of specials or discounts you are offering.
- Entrepreneur: How to Design a Marketing Strategy
Brian Hill is the author of four popular business and finance books: "The Making of a Bestseller," "Inside Secrets to Venture Capital," "Attracting Capital from Angels" and his latest book, published in 2013, "The Pocket Small Business Owner's Guide to Business Plans."
Related Articles
What is a competitive climate in marketing, marketing strategy for beginners, how to start a passenger transportation company, marketing plan for a logistic business, how do companies market to their target market, the importance of ad slogans, what is a strategic business plan, differentiation in product marketing strategy, how to plan & grow a business venture, most popular.
- 1 What is a Competitive Climate in Marketing?
- 2 Marketing Strategy for Beginners
- 3 How to Start a Passenger Transportation Company
- 4 Marketing Plan for a Logistic Business
Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Small Business Trends
How to create a business plan: examples & free template.
Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or launching your very first startup, the guide will give you the insights, tools, and confidence you need to create a solid foundation for your business.
Table of Contents
How to Write a Business Plan
Executive summary.
It’s crucial to include a clear mission statement, a brief description of your primary products or services, an overview of your target market, and key financial projections or achievements.
Our target market includes environmentally conscious consumers and businesses seeking to reduce their carbon footprint. We project a 200% increase in revenue within the first three years of operation.
Overview and Business Objectives
Example: EcoTech’s primary objective is to become a market leader in sustainable technology products within the next five years. Our key objectives include:
Company Description
Example: EcoTech is committed to developing cutting-edge sustainable technology products that benefit both the environment and our customers. Our unique combination of innovative solutions and eco-friendly design sets us apart from the competition. We envision a future where technology and sustainability go hand in hand, leading to a greener planet.
Define Your Target Market
Market analysis.
The Market Analysis section requires thorough research and a keen understanding of the industry. It involves examining the current trends within your industry, understanding the needs and preferences of your customers, and analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors.
Our research indicates a gap in the market for high-quality, innovative eco-friendly technology products that cater to both individual and business clients.
SWOT Analysis
Including a SWOT analysis demonstrates to stakeholders that you have a balanced and realistic understanding of your business in its operational context.
Competitive Analysis
Organization and management team.
Provide an overview of your company’s organizational structure, including key roles and responsibilities. Introduce your management team, highlighting their expertise and experience to demonstrate that your team is capable of executing the business plan successfully.
Products and Services Offered
This section should emphasize the value you provide to customers, demonstrating that your business has a deep understanding of customer needs and is well-positioned to deliver innovative solutions that address those needs and set your company apart from competitors.
Marketing and Sales Strategy
Discuss how these marketing and sales efforts will work together to attract and retain customers, generate leads, and ultimately contribute to achieving your business’s revenue goals.
Logistics and Operations Plan
Inventory control is another crucial aspect, where you explain strategies for inventory management to ensure efficiency and reduce wastage. The section should also describe your production processes, emphasizing scalability and adaptability to meet changing market demands.
We also prioritize efficient distribution through various channels, including online platforms and retail partners, to deliver products to our customers in a timely manner.
Financial Projections Plan
This forward-looking financial plan is crucial for demonstrating that you have a firm grasp of the financial nuances of your business and are prepared to manage its financial health effectively.
Income Statement
Cash flow statement.
A cash flow statement is a crucial part of a financial business plan that shows the inflows and outflows of cash within your business. It helps you monitor your company’s liquidity, ensuring you have enough cash on hand to cover operating expenses, pay debts, and invest in growth opportunities.
| Section | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Brief overview of the business plan | Overview of EcoTech and its mission |
| Overview & Objectives | Outline of company's goals and strategies | Market leadership in sustainable technology |
| Company Description | Detailed explanation of the company and its unique selling proposition | EcoTech's history, mission, and vision |
| Target Market | Description of ideal customers and their needs | Environmentally conscious consumers and businesses |
| Market Analysis | Examination of industry trends, customer needs, and competitors | Trends in eco-friendly technology market |
| SWOT Analysis | Evaluation of Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats | Strengths and weaknesses of EcoTech |
| Competitive Analysis | In-depth analysis of competitors and their strategies | Analysis of GreenTech and EarthSolutions |
| Organization & Management | Overview of the company's structure and management team | Key roles and team members at EcoTech |
| Products & Services | Description of offerings and their unique features | Energy-efficient lighting solutions, solar chargers |
| Marketing & Sales | Outline of marketing channels and sales strategies | Digital advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships |
| Logistics & Operations | Details about daily operations, supply chain, inventory, and quality control | Partnerships with manufacturers, quality control |
| Financial Projections | Forecast of revenue, expenses, and profit for the next 3-5 years | Projected growth in revenue and net profit |
| Income Statement | Summary of company's revenues and expenses over a specified period | Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold, Gross Profit, Net Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Overview of cash inflows and outflows within the business | Net Cash from Operating Activities, Investing Activities, Financing Activities |
Tips on Writing a Business Plan
4. Focus on your unique selling proposition (USP): Clearly articulate what sets your business apart from the competition. Emphasize your USP throughout your business plan to showcase your company’s value and potential for success.
FREE Business Plan Template
To help you get started on your business plan, we have created a template that includes all the essential components discussed in the “How to Write a Business Plan” section. This easy-to-use template will guide you through each step of the process, ensuring you don’t miss any critical details.
What is a Business Plan?
Why you should write a business plan.
Understanding the importance of a business plan in today’s competitive environment is crucial for entrepreneurs and business owners. Here are five compelling reasons to write a business plan:
What are the Different Types of Business Plans?
| Type of Business Plan | Purpose | Key Components | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Business Plan | Outlines the company's mission, objectives, target market, competition, marketing strategies, and financial projections. | Mission Statement, Company Description, Market Analysis, Competitive Analysis, Organizational Structure, Marketing and Sales Strategy, Financial Projections. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Internal Business Plan | Serves as a management tool for guiding the company's growth, evaluating its progress, and ensuring that all departments are aligned with the overall vision. | Strategies, Milestones, Deadlines, Resource Allocation. | Internal Team Members |
| Strategic Business Plan | Outlines long-term goals and the steps to achieve them. | SWOT Analysis, Market Research, Competitive Analysis, Long-Term Goals. | Executives, Managers, Investors |
| Feasibility Business Plan | Assesses the viability of a business idea. | Market Demand, Competition, Financial Projections, Potential Obstacles. | Entrepreneurs, Investors |
| Growth Business Plan | Focuses on strategies for scaling up an existing business. | Market Analysis, New Product/Service Offerings, Financial Projections. | Business Owners, Investors |
| Operational Business Plan | Outlines the company's day-to-day operations. | Processes, Procedures, Organizational Structure. | Managers, Employees |
| Lean Business Plan | A simplified, agile version of a traditional plan, focusing on key elements. | Value Proposition, Customer Segments, Revenue Streams, Cost Structure. | Entrepreneurs, Startups |
| One-Page Business Plan | A concise summary of your company's key objectives, strategies, and milestones. | Key Objectives, Strategies, Milestones. | Entrepreneurs, Investors, Partners |
| Nonprofit Business Plan | Outlines the mission, goals, target audience, fundraising strategies, and budget allocation for nonprofit organizations. | Mission Statement, Goals, Target Audience, Fundraising Strategies, Budget. | Nonprofit Leaders, Board Members, Donors |
| Franchise Business Plan | Focuses on the franchisor's requirements, as well as the franchisee's goals, strategies, and financial projections. | Franchise Agreement, Brand Standards, Marketing Efforts, Operational Procedures, Financial Projections. | Franchisors, Franchisees, Investors |
Using Business Plan Software
Upmetrics provides a simple and intuitive platform for creating a well-structured business plan. It features customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, and collaboration capabilities, allowing you to work with team members and advisors. Upmetrics also offers a library of resources to guide you through the business planning process.
| Software | Key Features | User Interface | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| LivePlan | Over 500 sample plans, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking against KPIs | User-friendly, visually appealing | Allows creation of professional-looking business plans |
| Upmetrics | Customizable templates, financial forecasting tools, collaboration capabilities | Simple and intuitive | Provides a resource library for business planning |
| Bizplan | Drag-and-drop builder, modular sections, financial forecasting tools, progress tracking | Simple, visually engaging | Designed to simplify the business planning process |
| Enloop | Industry-specific templates, financial forecasting tools, automatic business plan generation, unique performance score | Robust, user-friendly | Offers a free version, making it accessible for businesses on a budget |
| Tarkenton GoSmallBiz | Guided business plan builder, customizable templates, financial projection tools | User-friendly | Offers CRM tools, legal document templates, and additional resources for small businesses |
Business Plan FAQs
What is a good business plan.
A good business plan is a well-researched, clear, and concise document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies, target market, competitive advantages, and financial projections. It should be adaptable to change and provide a roadmap for achieving success.
What are the 3 main purposes of a business plan?
Can i write a business plan by myself, is it possible to create a one-page business plan.
Yes, a one-page business plan is a condensed version that highlights the most essential elements, including the company’s mission, target market, unique selling proposition, and financial goals.
How long should a business plan be?
What is a business plan outline, what are the 5 most common business plan mistakes, what questions should be asked in a business plan.
A business plan should address questions such as: What problem does the business solve? Who is the specific target market ? What is the unique selling proposition? What are the company’s objectives? How will it achieve those objectives?
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
How is business planning for a nonprofit different.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Service Business

Noah Parsons
10 min. read
Updated July 29, 2024

Free Download: Sample Administrative Services Business Plan Templates
If you’re starting a business that sells a service, writing a business plan is one of the first steps you need to take. Whether you are starting a consulting business, a car repair shop, or a construction firm, a business plan will help you figure out your strategy, develop your marketing plan and figure out the all-important financial forecasts so that you can be successful.
Writing a business plan can seem complicated at first. There are multiple topics you have to cover and you want to impress your readers with a complete plan. Whether it’s a loan officer reading your business plan or a potential business partner, you need to make sure you get your plan right.
That’s why we put this guide together. Business planning doesn’t have to be intimidating and we’ll guide you through the process of pulling everything together for your new service business.
- What is a service business?
A service business typically focuses on selling services to customers instead of products. For example, a consultant or lawyer typically sells their time and expertise to customers. A repair business typically is selling the service of fixing broken equipment and appliances. Event planners are selling the service of planning and managing events such as weddings and corporate retreats.
Service businesses don’t just have to sell services. Many service businesses sell a mix of products and services. Take a car repair shop, for example. They’ll sell the service of repairing your car in addition to the parts required to get your car serviced. Even though the repair shop sells parts, it’s different from an auto parts store that only sells parts and doesn’t sell any repair services.
- Why you should write a business plan for a service business
It’s tempting to just dive right in and start building your business. A business plan can seem like a waste of time and it’s certainly more fun to start working on things like logos, business cards, and finding office space. But, it’s important to remember that a business plan is a vital step in the process that will prevent you from wasting precious time and money as you get your business up and running.
Taking a little time to plan now can save you from making critical mistakes and prevent you from wasting thousands of dollars. Even though it may not be as “fun”, it’s worth every minute. Here’s why you’ll want to plan:
1. Clearly define your offering
Although you may have a good idea in your head for the services you’ll be offering, it’s important to write down exactly what you plan to offer to your customers and what you plan to charge. Especially for service businesses where you may be selling your time, it can be tempting to take on any job. That can lead to distractions and lead you away from your core business. You also want to ensure that business partners are on the same page as you and that you agree on the services you are providing, what you’re going to charge, and how you are going to deliver those services.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
2. Create a marketing plan
A clear marketing plan is crucial for getting your service business up and running. You’ll need to know not only how you plan on landing your first customers, but also your hundredth customer. Taking the time to describe your ideal customer and craft a marketing plan to reach them in a smart and cost-effective way is the key to a business that can grow efficiently over time.
3. Know your numbers
Before you start any business, understanding what it’s going to take to make money is a crucial first step. As you create a sales forecast and expense budget, you’ll be able to see what it will take to become profitable. Understanding how much it’s going to cost to start your business is also a critical number to know. For some service businesses, startup costs can be high. Looking back at our car repair service business example, startup costs may be significant. This business will need to purchase a workspace, tools, and other equipment before it can offer any services. In contrast, a consulting business may not have many startup costs. You may be able to simply work from home and offer your services online , avoiding the need for any physical overhead costs. Regardless of whether your startup costs are low or high, understanding what level of sales you’ll need to make money is something a business plan will tell you.
4. Build your business strategy
A business plan helps you outline your business strategy . Knowing your strategy before you start helps you focus on building your business the right way from the beginning. Figuring out your strategy while you’re trying to build your business is somewhat like building an airplane while you’re headed down the runway. It’s potentially possible but very difficult to do.
Your business plan will force you to think through and answer the questions you need to answer to have a successful business.
- How is a business plan for a service business different from a product business plan?
Although business plans for service businesses are fairly similar to plans for product businesses, there are a few key differences.
Often, service businesses have fairly low cost of goods sold . This is how much it costs you in parts, products, or other tangible items to make a sale. Most service businesses have low costs to deliver the service and therefore have fairly high-profit margins. Software-as-a-service businesses are a perfect example of this because the incremental cost of a new customer is so low.
Service businesses often have little or no inventory as they are focused on selling their service, not a product. That said, this isn’t always the case. Any kind of repair service usually has to have replacement parts on hand. But, lawyers and accountants almost never have any kind of physical inventory.
For some service businesses, overhead expenses can also be very low. Many service businesses don’t need storefronts, warehouses, or other expensive real estate.
- What you should include in your business plan
A good business plan includes six key chapters. Following this business plan outline will ensure that you have a complete and effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
Every business plan should have a short executive summary . Your executive summary is an overview of your entire business and a preview of the rest of your plan. Ideally, your executive summary can be used as a stand-alone document that you can use to introduce your business to investors who don’t have the time to read a complete business plan. Your executive summary should describe the services that you are offering, who your target market is, and provide a snapshot of your sales goals and profit projections for the coming year. If you’re raising money to launch your business, be sure to include how much money you need to get the business launched. Write your executive summary last, after you’ve written the rest of your plan. Because it’s just a brief summary – two or three pages at most – writing it last will ensure that you cover all the key points in the rest of your plan.
2. Problem and Solution
The first major chapter of your business plan will cover the problem that you solve for your clients and describe the services that you provide. If you’re starting a landscaping service, the problem you’re solving is your customers’ desire for a well maintained, beautiful lawn and garden when they don’t have the time to do it themselves. A headhunting firm helps businesses find and recruit new employees without having to have a large HR department. When you describe the services you provide, make sure to describe your pricing and how you stack up against the competition. What makes your services better than other businesses that provide similar services? What sets you apart?
3. Target Market
The target market chapter of your business plan focuses on the customers that you are selling to. A good business plan describes your business’s ideal customer very specifically. No business sells to “everyone”. Instead, good businesses know the type of customer that they are after and where to find them. For example, a financial planning service business might target millennials that work in technology companies who like to communicate mostly online. When you describe your target market, make sure to indicate how large the market is . You’ll want to make sure that there are enough potential customers for your services out there so that you can grow your business.
4. Marketing and Sales
Once you’ve defined the problem you are solving for people, how you solve that problem for them and described exactly who your customer is, you’ll have a great platform for creating a marketing and sales plan . With your target market information, you should know where and how to reach your ideal customer so that you can come up with a marketing plan to reach them. If your business is local, focusing on local advertising and social media groups might be a good idea. If your services are expensive, you’ll also want to describe your sales plan since customers most likely won’t just sign up for your services immediately after hearing about you. You’ll most likely need to deliver information about your services, create bids, and have a follow-up strategy for closing deals. Use this chapter of your business plan to create your marketing and sales roadmap so that you can start executing on your marketing plan when your business is up and running and have sales processes in place so you make sure that you maximize your marketing efforts.
5. Company & Team
Your idea is surprisingly not the most important part of your business. It’s actually the people that build the business and run it that are the most important. Even the best idea that’s poorly executed is likely to fail, so it’s critical that you assemble the right people to make your business a success. In this chapter of your business plan, describe who is behind the business and why this team is the right team to build it. Investors often focus more on the team than the idea because they assume that a smart and motivated team will adjust and refine an idea to make it successful, even if the first iteration isn’t perfect.
6. Financial Plan
Finally, your business plan needs a financial plan . This plan should include:
- Sales forecast
- Profit and Loss
- Cash Flow Forecast
- Balance Sheet
If you’re starting a subscription service, include a forecast for subscriptions, renewals, and cancellations — otherwise known as “churn”. Your Profit and Loss statement will show your sales and expenses so that you can calculate your predicted profits. The Cash Flow Forecast will predict how cash moves in and out of your business and will help you identify potential cash flow problems that may occur in the future. The Balance Sheet will detail the assets and liabilities that your business is predicted to have over time.
- Free business plan examples & templates
It might be helpful to explore how other service-based businesses have written their business plans. Check out our free library of sample plans and templates for service businesses . You can download any of these along with our detailed business plan template in Word format and get some structure for your own plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

11 Min. Read
How to Write a Business Plan for a SaaS Startup

5 Min. Read
How to Write an Agritourism Business Plan + Example Templates

8 Min. Read
How to Write a Home Health Care Business Plan

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Cleaning Service Business Plan + Free Sample Plan PDF
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Business Plans
How to Describe your Product in a Business Plan

The product or products your business intends to produce or offer will have to be described in the product description section of your business plan. This section of your business plan is meant to explain how your product will stand out from comparable items in the market.
You have to clearly explain its concept, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. You should also identify your suppliers, costs, and how the product you are offering fits into the current market.
Note that the product description in your business plan is more than a simple listing of product features. In this section, you will need to highlight your product’s most unique characteristics that will ensure it stands out in the marketplace and attract buyers who won’t mind paying your price.
Note that a properly written product description in your business plan can entice investors and help your business grow. Make sure you describe what you are offering in layman’s terms, to guarantee that someone who isn’t conversant with your business will grasp and be excited about it.
It may also be necessary to provide some basic background if this is an area or industry that people are not so familiar with. While you write up the Products and Services description section of your business plan, always keep your reader in mind.
What to Include in the Products and Services Description Section of Your Business Plan
Just as was noted above, the products and services section of your business plan will have to explain in detail your product or service, its demand in your market, and how it intends to compete with other businesses selling the same or similar products or services. Nonetheless, the product and services description section of your business plan is expected to include:
The Product or Service Description
It is important the product description section of your business plan clearly explains the concept of your product, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. What are your product and service, and how does it work? How will this product benefit your customers? How do you plan to make it or how do you intend to get it made?
Product Comparison
This section of your business plan will also have to explain how your product compares with similar products in the market. What makes this product or service unique or better than what’s already obtainable in the market? Why would anyone prefer your product or do business with you?
You will need to describe how and why you are competitive. How do you stand out, and why do your business and everything it offers have such a viable chance at succeeding? In talking about your product or service, always try to answer why a client would want it and how it can make their lives better or more profitable?
Accreditations/Intellectual Property
For businesses that have had their product tested by industry experts, you must include this information when describing your product. Don’t forget to highlight any certifications, trademarks, copyrights, or patents.
Have it in mind that these added advantages or achievements can give you and your product an upper hand. Verified patents and trademarks can also heighten the value of your product especially since it shows that only your company can manufacture the product for the life of the patent.
Have it in mind that a product’s life cycle includes the idea, prototype, and expansion stages. If you are still in the idea stage, you must buttress in your description how you intend to get the product made and why your product matters.
If you maybe already have a prototype, outline your plans for evaluating the prototype and manufacturing your product. If your business has been making the product but is looking to expand to keep up with demand, ensure you explain this when describing your product in your business plan.
You will also want to include the cost of your product and how that cost aligns with other comparable products on the market. In very concise detail, explain how you came to this price, including the cost to manufacture, selling price, and profit margin.
Sales and Distribution Strategy
Also, take your time to explain how and where you will sell your product. Have in mind that your options may include online stores, brick-and-mortar locations, and vendors. If you already have vendors selling your product, ensure to note who they are and their locations in this section of your business plan.
Fulfillment
When describing your product in your business plan, it is also important you describe your plan to ensure your product gets to the intended customers. This should include manufacturing details and delivery specifics. If you plan to outsource the production of your goods, don’t forget to note manufacturer specifics such as location and production time. Also, remember to include the approximate delivery times and methods.
Requirements
Will you require any special equipment or technology to provide your product or service? Also explain if any specialized technology, materials, or equipment will be required to manufacture your product.
You will also have to explain your plans for product development and introduction especially as your business grows.
Photos or Brochures
Also, make sure that your potential investors can get a good insight into your product through photos and brochures. Don’t forget that your business plan is expected to have an appendix for photos and brochures. Also, don’t forget to refer to them in the product description section.
Tips for Writing a Product Description
To ensure you describe your product thoroughly, here are some vital tips to guide you;
- Always remember the reader. The product description section of your business plan must note your product’s most vital information. Always remember to make this section very easy to read and understand. Consider making it better by leveraging numbered lists and bullets.
- Focus on benefits. When describing your product, you must explain how its features can provide value to consumers. Translate your features into benefits, and remember that the aim is to describe how your product or service will be a solution to a problem or improve a client or customer’s life.
- Highlight the features of your product or service. To attain substantial success in any business, your business will need the ability to set itself apart from other businesses that offer or sell the same products and services. Take your time to analyze key features, such as price point or level of service, or anything that makes your product unique in the market.
- Show off a little. Don’t forget that you are selling a product and also selling yourself as the most viable provider of that product. Ensure to include all vital educational or industry-specific experiences and awards in this section. If you have endorsements or testimonials specific to your product, include them as well.
- Show the need for your product. Also make sure you explain how your product will cater to a need or improve life, showing why your product is very necessary to the consumer. This is very pertinent if your product has no current market.
The product and services description section of your business plan is meant to provide the reader with an explicit understanding of why you are in business, what you sell, how you will compete with what’s already available, or how you intend to fill a niche that no one else is currently meeting. Noted above are things you need to consider when creating the product description section of your business plan to ensure that it will indeed grab your readers’ attention.
More on Business Plans
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Crafting an Impactful Sample Company Description for Business Plan

Crafting an impactful company description is a pivotal step in developing a successful business plan. This section serves as the initial introduction to your company, setting the stage for potential investors, partners, and stakeholders. An effective company description should encapsulate your company’s core values, mission, and the unique value proposition it offers. It must provide a clear and compelling overview of what your business does, its target market, and how it stands out from competitors. By highlighting the company’s history, achievements, and strategic goals, you create a narrative that engages readers and provides a foundation for understanding the business’s purpose and vision.
In addition to outlining your company’s mission and vision, the description should delve into the specifics of your products or services, market positioning, and operational structure. It’s essential to convey the scale of your operations, your business model, and the market needs you address. This segment not only offers insight into your company’s current standing but also showcases its potential for growth and scalability. A well-crafted company description combines clarity with enthusiasm, ensuring that readers grasp the significance of your business and its potential to succeed in a competitive landscape.
Creating a Winning Business Plan: The Importance of a Company Description
Creating a winning business plan is an essential step for entrepreneurs seeking to steer their startups towards success. At the heart of this plan is the company description, a concise yet comprehensive portrayal of your venture. This section serves as the reader’s first glimpse into your business, painting a picture of who you are, what you do, and what sets you apart in the market.
The company description is not merely a formality but a cornerstone that resonates with various stakeholders, including investors, partners, and potential customers. It allows them to grasp the essence of your business in a snapshot, which is particularly crucial in high-stakes documents like business plans.
Here’s why a strong company description is indispensable for different stakeholders:
- Investors: Investors need to understand the core of your business quickly. A well-defined company description highlights your value proposition, unique selling points, and market potential, helping to secure their interest and investment.
- Partners: Potential business partners look for synergy. A detailed description illustrates your mission and vision, operational scope, and strategic fit with their own goals.
- Customers: Customers and clients want to know who they are dealing with. A clear and persuasive company description helps build trust and establishes credibility, detailing why your business is the right choice for their needs.
- Employees: Future employees and current team members can align better with your company’s goals. The description sets the tone for your organizational culture and objectives, helping to attract talent that resonates with your mission.
By breaking down the primary purposes of a company description into these key points, you can see how vital this section is to articulate clearly and compellingly. It is not just about filling a page but about crafting a narrative that drives engagement and interest across a spectrum of audiences.
To help you structure an impactful company description, consider the following essential components. Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring that your description is both informative and engaging:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| A brief introduction that includes the name, location, and nature of your business. It should provide a snapshot of your company at a glance. | |
| A succinct declaration of your business’s purpose and values, outlining what you aim to achieve in the long term. | |
| A forward-looking statement that describes where you see your company in the future. It should inspire and guide strategic planning. | |
| ) | Details what sets your business apart from competitors and why customers should choose you. This is essential for capturing investor interest. |
| A brief history of your company, including key milestones, achievements, and lessons learned that contribute to your current position. | |
| An overview of what you offer, highlighting the features and benefits of your products or services. | |
| Information about your market, including target customers, market size, and competitive landscape. This insight substantiates your business strategy. | |
| A brief introduction to your leadership team. Highlight their qualifications and experience, which add credibility to your business plan. |
Incorporating these components into your company description ensures that it is thorough, engaging, and informative. Each section not only adds depth to your narrative but also helps build a robust, convincing business plan that can draw in investors, partners, customers, and employees alike.
By following this guide, you will be well-equipped to draft a stellar company description that does more than just describe your business—it will set the tone for the rest of your business plan and pave the way for your entrepreneurial success.
Company Description: Key Elements for a Comprehensive Overview
When drafting a company description, it is crucial to cover all the fundamental aspects to provide a clear and compelling snapshot of your business. Investors and stakeholders rely on this information to understand the essence of your company and its strategic positioning. The following table outlines the core elements that should be included:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Name | Start by stating the name of your business. It’s the identity that your audience will remember. |
| Location | Mention where your business operates from. This may include the main office, branches, or areas served. |
| Business Structure | Clarify the legal structure of your company (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership, Limited Liability Company, corporation). |
| Vision and Mission | Briefly state your company’s overarching vision and core mission. This helps convey your aims and values. |
| Products or Services | Describe the primary products or services you offer, emphasizing how they benefit your target market. |
| Market Position | Provide insights into your market niche, target demographics, and competitive advantages. |
Each of these elements plays a vital role in painting a comprehensive picture of your business to potential investors. The business name serves as the identifier and brand for your business, while location details inform stakeholders about your operational base and reach. Describing the business structure helps clarify legal and organizational setups which are crucial for investment decisions.
Similarly, including your vision and mission statements provides a glimpse into your company’s forward-looking goals and core principles. Describing your products or services not only showcases what you offer but also how these offerings meet the needs of your target market. Lastly, detailing your market position allows investors to understand your competitive edge and market demographics.
Ensuring that these elements are well articulated aligns your company description with investor expectations and demonstrates your preparedness and clarity about your business operations and long-term ambitions. This alignment can be pivotal in fostering investor confidence and securing potential funding opportunities.
Understanding Effective Company Descriptions: Examples
To craft a compelling company description, examining effective examples provides valuable insights. Each example outlined below demonstrates unique elements that contribute to a successful company profile. Through detailed analysis, you can decipher why these descriptions resonate with their intended audience, be it investors or potential customers.
Example 1: Tech Startup
This example outlines a Tech Startup’s company description, illuminating the factors that make it impactful and memorable. By breaking it down into specific components, you can better understand what elements to include in your own company description to achieve similar effectiveness.
- Clear Vision: The Tech Startup articulates a clear vision for changing the industry.
- Solution-Oriented: It addresses a particular problem faced by the target market and provides an innovative solution.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): The description highlights what sets the startup apart from competitors.
- Specific Market: A defined target audience is clearly mentioned.
- Future Plans: Insight into future growth and development plans is provided.
Each element mentioned above contributes to a comprehensive and compelling company description. The clear vision sets the tone and direction for the startup, while addressing a specific problem ensures relevance to potential clients or investors. Highlighting the Unique Selling Proposition differentiates the startup in a crowded market. Clarifying the target audience ensures the message is directed at the right recipients. Finally, discussing future plans gives an exciting peek into the company’s growth trajectory, fostering investor confidence.
Preface and Example Instructions
This section is pivotal as it explains the relevance of the example to the overall context of financial modeling, which is crucial for entrepreneurs and finance professionals alike. By detailing the example in bullet points, it becomes easier to follow and understand. Here, we highlight the step-by-step instructions provided, ensuring that no detail is left out and each point is clear and concise.
Example Breakdown
We will break down the example into digestible bullet points. This will help you to grasp each element with clarity and precision, avoiding any potential confusion:
- Identify the primary objective of your financial model.
- Determine what you intend to achieve with your analysis (e.g., raising funds, forecasting, or investment analysis).
- Collect at least three to five years of historical financial data.
- Ensure the data includes income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Make educated assumptions about future performance metrics.
- Include revenue growth rates, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and capital expenditures.
- Create the structure of your financial model in Excel.
- Input the historical data and future assumptions into the model.
- Ensure all financial statements are interconnected and dynamically linked.
- Validate the model by checking for errors and inconsistencies.
- Test different scenarios to see how changes in assumptions impact the financial forecast.
Each of these steps provides a foundational approach to financial modeling, which is essential for reliable and accurate financial forecasting. By following these detailed steps, entrepreneurs and finance professionals can develop robust financial models that aid in making informed business decisions. It is important to continuously refine the model as more data becomes available and as assumptions change.
Collection of Necessary Inputs
Another critical aspect of financial modeling is collecting the necessary inputs for the model. The table below summarizes the key inputs required for an effective financial model:
| Input Category | Details | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Financial Data | Income Statements, Balance Sheets, Cash Flow Statements | High |
| Market Analysis | Market Trends, Competitor Analysis, Customer Demographics | Medium |
| Business Assumptions | Revenue Growth Rates, Cost of Goods Sold, Operating Expenses | High |
| Capital Expenditure Plans | Details on Future Investments in Capital Assets | Medium |
Ensuring the collection of accurate and comprehensive inputs is imperative for building a reliable financial model. Each category of input has its importance, and collectively they form the foundation of the financial projections. Neglecting to gather complete data can lead to inaccuracies in the modeling process and result in misguided business decisions.
Tips to Enhance Your Company Description
A compelling company description is crucial for making a lasting impression on investors, customers, and potential partners. It is not merely about covering the basics but about presenting the information in an engaging and informative manner. Below are some key strategies to elevate the quality of your company description:
- Be Concise but Informative: Striking a balance between brevity and detail is essential. Your description should be clear and concise while still providing all necessary information. This ensures readers can quickly grasp the core of your business without feeling overwhelmed.
- Use Engaging Language: The tone and choice of words can make a significant impact. Utilize dynamic language that not only conveys your message effectively but also demonstrates your enthusiasm and passion for your business. This can inspire confidence and interest in your audience.
- Highlight Unique Selling Points: Identifying what sets your business apart is critical. Clearly articulate your unique selling points to distinguish your company from competitors. This makes your business more appealing by showcasing the particular advantages you offer.
- Customize for Your Audience: Tailoring your description to suit different audiences is a strategic approach. Adjust your tone and content based on whether you are addressing investors, customers, or partners to better align with their specific interests and expectations.
By focusing on these aspects, you can craft a company description that is both engaging and informative. This approach not only fits the needs of various stakeholders but also adds credibility and appeal to your business narrative. Ensuring your description speaks directly to your intended audience helps cultivate stronger connections and fosters trust, which is fundamental to business success.
Writing an Impactful Sample Company Description for a Business Plan
Writing an impactful sample company description for a business plan is a pivotal step towards showcasing your business’s potential. By focusing on the core elements, drawing inspiration from practical examples, and incorporating effective enhancement tips, you can craft a description that is both informative and captivating.
Key Points to Remember
A high-quality company description should:
- Clearly define the core elements of your business.
- Draw from practical and relevant examples.
- Include tips and strategies for impactful writing.
- Be concise, ensuring that the essential information is easily digestible.
- Engage your audience while highlighting what makes your business unique.
When you integrate these elements into your company description, you ensure that your message is clear and compelling. This makes a significant difference in how your business is perceived by potential investors and partners.
The Importance of a Well-Crafted Company Description
A well-crafted company description serves as the cornerstone of your business plan. It is often the first piece of content that potential investors and partners will read, thus setting the tone for the rest of your document. By being precise and engaging, you:
- Create a strong first impression.
- Make your business stand out in a competitive landscape.
- Build trust and credibility with your audience.
- Highlight the key aspects that differentiate your business from others.
Taking the time to develop a robust company description pays off by establishing a solid foundation for your entire business plan, thereby increasing the likelihood of gaining investor interest and support.
Application of Learned Concepts
Encouraging readers to apply the learned concepts from the article can significantly elevate the quality of their business plan. By implementing these strategies in crafting your company description, you lay the groundwork for a compelling business narrative.
Consider the following steps:
- Reflect on the unique elements of your business.
- Utilize practical examples for inspiration.
- Incorporate strategic writing tips to enhance readability and engagement.
- Revise and refine your draft to ensure conciseness and clarity.
By following these steps, you can create a company description that not only informs but also captivates your audience, making a memorable impression that paves the way for your business’s success. Remember, a compelling company description is your first opportunity to make a lasting impact on potential investors and partners.
What is the purpose of a company description in a business plan?
The company description serves as a foundational component of your business plan, offering a thorough overview of your company. This section outlines your business’s fundamental aspects, including its primary objectives, strategic goals, and current market position. By providing essential information about your company in this part, you set the stage for the rest of the business plan, enabling potential investors, partners, and stakeholders to understand your business’s core premise right from the start.
The Importance of a Company Description
Including a well-crafted company description in your business plan is crucial for several reasons:
- First Impressions: This section serves as the first touchpoint for readers, often determining whether they will continue to engage with the rest of your plan.
- Clarity and Direction: It defines your business’s purpose, scope, and unique value proposition, offering clear insights into what your business aims to achieve.
- Alignment: Sets the tone and direction for the entire business plan, ensuring all other sections resonate with the overall vision and goals of the company.
A well-constructed company description effectively captures the essence of your business, establishing a robust framework for the rest of your business plan. By presenting a clear snapshot of your business, it helps build credibility and sets a positive tone for the forthcoming sections.
Key Elements to Include
To create an impactful company description, include the following key elements:
- Business Name and Location: Clearly state the official name of your business and where it is headquartered.
- Mission Statement: Outline the core purpose of your business, reflecting its fundamental goals and values.
- Business Model: Briefly describe how your business operates and generates revenue. This can include the type of business (e.g., service-based, product-focused) and its operating structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership).
- Market Overview: Provide a snapshot of the industry landscape, highlighting your business’s position within the market.
- Products or Services Offered: List the primary products or services your business provides, emphasizing what sets them apart from competitors.
- Long-term Goals: Mention your business’s long-term vision and specific objectives it aims to achieve over time.
These elements collectively contribute to crafting a comprehensive yet concise company description, effectively communicating the essence and aspirations of your business.
In conclusion, crafting an impactful sample company description for a business plan is a critical step in defining your business’s identity and conveying its value proposition. An effective company description should succinctly capture the essence of your business, highlighting its mission, vision, and unique selling points. By clearly articulating the core values and goals of your company, you provide potential investors, partners, and stakeholders with a compelling overview that demonstrates your business’s potential for success and growth.
Moreover, a well-crafted company description not only sets the stage for the rest of your business plan but also establishes a solid foundation for your brand’s narrative. It should resonate with your target audience and reflect the strategic direction of your business, making it clear why your company stands out in the marketplace. By focusing on clarity, relevance, and differentiation, you create a strong initial impression that can drive interest and confidence in your business’s potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long should the company description be?
Typically, a company description should be one to two paragraphs long. It needs to be concise yet comprehensive enough to convey all the core elements of your business.
- What should I avoid in my company description?
Avoid jargon, overly technical language, and excessive detail. The aim is to provide a clear, understandable snapshot of your business that anyone can grasp quickly.
- Can I update the company description over time?
Absolutely! As your business evolves, you should update your company description to reflect new objectives, products, or market positions. Keeping it current ensures it remains relevant and accurate.
A succinct and well-organized company description lays a strong foundation for your business plan, ensuring all stakeholders gain instant clarity about your business’s core aspects. By updating it regularly, you keep information accurate and relevant, enhancing the overall value of your business plan.

Google Sheets Project Plan Template
This Project Plan Template in Google Sheet allows you to quickly develop a project plan and plot a Gantt chart. Enjoy all the benefits of Google Docs ... read more

All My Financial Models, Spreadsheets, Templates, and Tools: 120+
Lifetime access to all future templates as well! Here is a set of spreadsheets that have some of the most valuable logic in the world. I have been thr... read more
- All My Excel Tools – $999.00 Version 1

Payable and Receivable Tracking (Google Sheets)
This is a Google Sheets version of the financial model template for tracking accounts payable and accounts receivable
- Google Sheet Version – $45.00
- Excel Version – $45.00

Price Volume Mix Charts and Analysis – On revenue and Gross Profit by Product
Best practice model for a complete Price Volume Mix (PVM) analysis on revenue and on gross profit by product.

Accounting Financial Model Bundle
Simply open the files using MS Excel
- Template Bundle – $249.00 Version 1

3 Statement Financial Modeling with DCF & Relative Valuation – Self Learning Kit
Financial Modeling Tutorial guides user via step by step approach on how to build financial models with DCF valuation

Prepaid Expense and Unearned Income Calculator
Prepaid Expense and Unearned Income amortization calculator with accounting entries

1 year Budget vs. Actual (Google Sheets)
Enter your expected annual budget by month and compare that against your actuals. Variance by line item and aggregates. Visualizations included.

Bookkeeping Agency Financial Model Excel Template
Try Bookkeeping Agency Financial Plan. Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help Five year bookkeeping agency 3 way financia... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Financial Advisors Agency Financial Model Excel Template
Shop Financial Advisors Agency Pro-forma Template. Creates 5-year financial projection and financial ratios in GAAP or IFRS formats on the fly. Five-y... read more

Accounting Firm Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup or existing Accounting Firm.
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $89.00
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $119.00
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00

General Financial Model Bundle
Take advantage of these free, high-quality Excel financial model templates to enhance your financial analysis and decision-making process. Download ou... read more

Auditor Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Auditor Pro-forma Template. Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help Creates 5-year auditor financial projection m... read more
Commercial Bank Valuation Model
This Commercial Banking Valuation Model values any bank of your choice using a wide range of industry valuation methods, including Discount Dividend M... read more
- Full Excel Model – $39.95
- Free Demo PDF – $0.00

Depreciation Schedule Calculator
CALCULATE DEPRECIATION OF A TANGIBLE ASSET USING 4 OF THE MOST POPULAR DEPRECIATION METHODS. This excel tool will calculate the depreciation expense o... read more
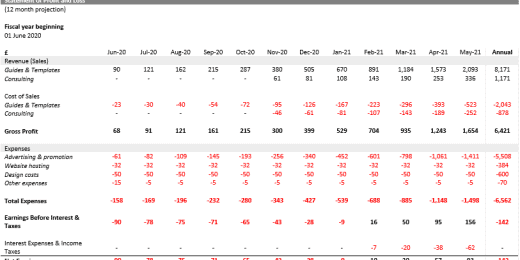
1 Year P&L, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow, and Breakeven Analysis
This excel template is great for those starting out as a small business, or looking at the financials of a potential business venture. You can customi... read more
- Excel Model – $20.00
- PDF Demo – $0.00

Accounts Payable Template | Receivable | Tracking
A simple template to keep track of the amount of money you owe other companies and how much other companies owe you.

How to Track Important SaaS Metrics: CaC, LTV, and LTV to CaC Ratio Plus More
This is a financial model template for SaaS business models that help to calculate the key metrics of relevance to a SaaS company such as Lifetime Val... read more

Management Accounting and Corporate Budget Report
This template enables users to compile comprehensive monthly management accounts based on any chart of account structure. The management accounts are ... read more
- Full Excel Model – $30.00
- Free PDF DEMO – $0.00

Accounting Software Financial Model Excel Template
Order Your Accounting Software Pro Forma Projection. Sources & Uses, Profit & Loss, Cash Flow statements, KPIs and 30+ graphs Inside Fiv... read more
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PACKAGE (2023 RELEASE)
FULLY FLEDGED FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND ACCOUNTING SYSTEM, DEVELOPED ENTIRELY IN EXCEL. ONE-OF-THE KIND. Technical assistance available. A comprehensiv... read more
- Excel Model – $15.00 Version 3
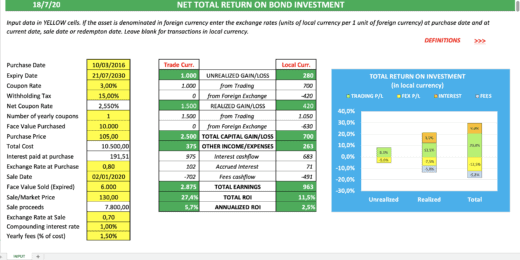
NET TOTAL RETURN ON BOND INVESTMENT CALCULATOR
CALCULATE NET TOTAL RETURN ON BOND INVESTMENT DENOMINATED IN ANY CURRENCY, broken-down by: Capital Gain/Loss (Realized & Unrealized), Foreign Exch... read more
- Protected Version – $5.00 Version 2

Consultancy Startup/Existing Business Financial Projection 3 Statement Excel Model
User-friendly 3 statement 5 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a startup or existing Consultancy business
- Excel Model – $59.00
- PDF Example – $0.00

Data Entry Business Financial Model Excel Template
Data Entry Business Pro Forma Template Allows you to start planning with no fuss and maximum of help . Shop Now Highly versatile and user-friendly Dat... read more

Financial Statement Analyzer – Excel Template
All the ratios and metrics you could ever think of to dive deeper into financial statements. Includes tracking module.

Tax Preparation Financial Model Excel Template
Tax Preparation Financial Plan Enhance your pitches and impress potential investors with the expected financial metrics. Buy Now Five-year Tax Prepara... read more

3-in-1 Templates: Accounting System in Excel
This is an easy financial statement creator based on various transaction types entered by the user. Logic works for accrual as well as cash-basis acco... read more

Descriptive Statistics for Grouped (Weighted) Data
Excel has a powerful set of tools to perform statistical analysis, but they apply only to ungrouped data. This review compiles the formulas to perform... read more
- Free Excel Template + PDF Guide – $0.00 Version 1

Bookkeeping Agency Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Bookkeeping services finances, including yearly Online and Offline Marketing % Opportuniti... read more
- Excel Model – $90.00 Version 1

Profit and Loss Excel Dashboard
Manage your monthly budget through the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement and easily obtain a Dashboard with all the information you need to plan you... read more
- Excel Template – $39.00 Version 1
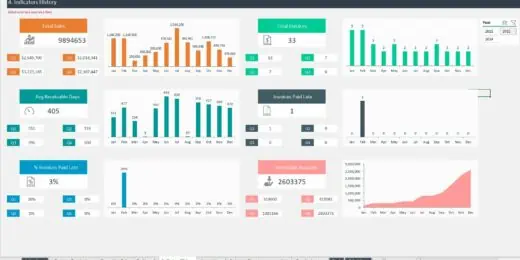
Accounts Receivable Dashboard
Enhance Accounts Receivable Management with Excel Spreadsheet Template
- Excel Template – $49.00 Version 1

CMBS/ABS Securitization Excel Model
The CMBS/ABS Securitization Excel Model is a powerful tool designed to simplify the complex process of asset-backed securitization. With its intuitive... read more
- Excel Model – $175.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Marketboats Blog
Master the art of b2b lead generation with valuable tips and tricks, the complete guide to service marketing mix: understanding the 7 p’s.
Home / The Complete Guide to Service Marketing Mix: Understanding the 7 P’s
Table of Contents
Marketing plays a vital role in any company’s success. A well-researched marketing plan can help your company reach its target audience and achieve overall business goals. In our previous blog on service marketing , we covered the basics – the types, characteristics, and advantages of service marketing. In this blog, we discuss the service marketing mix and the 7P’s of service marketing mix, along with a few practical examples. Additionally, we provide tips on how to incorporate the marketing mix into your marketing plan. Stick around until the end to gain a clear understanding of how to use the marketing mix to enhance your business strategy.
What is the Service Marketing Mix?
The Service Marketing mix is an extension to the traditional marketing mix and an important aspect to consider while creating your marketing strategy. It includes seven components: the 4Ps are from the product marketing (Product, Pricing, Place, Promotion) and 3 additional Ps (People, Process, and Physical Evidence). This extended marketing mix allows marketers to develop a detailed strategy that addresses the core of their business and aids them in conveying their brand and organizational message to customers.
7 P’s of the Service Marketing Mix with Examples:
Product refers to the main service that you provide to your customers. It includes both tangible and intangible aspects of your service.
It is good to regularly monitor and adapt your offerings to changing market trends, customer preferences, and technological refinements. Understanding this approach can help you deliver services that meet or even exceed your customer expectations resulting in customer satisfaction, loyalty, and long-term success.
For example, A spa might offer a variety of massage therapies (products), ensuring high-quality service (quality), personalized treatments (customization), and a relaxing atmosphere (intangible aspect). This approach considers the overall experience provided to the customer.
Price is the charge that customers pay for your service. Unlike products where you have fixed price structures, the pricing for services can be more complex.
Key considerations in service pricing include the expertise and experience of the service you provide, the costs associated with the service delivery, and the value that customers get when they pay for your service. Building a reputation plays a significant role in justifying higher prices, as customers will pay a premium if they can feel the quality and reliability of your offering. Additionally, factors such as market competition and economic conditions must be carefully evaluated when creating your pricing strategy.
For example, A high-end restaurant might set its price based on the quality of ingredients (Inputs), the expertise of the chefs (Staff experience), the prime location (Location expenses), and the reputation it has built over time (Customer trust).
Place refers to the channel through which your service is distributed to reach your customer. It could be a physical location, an online platform, or a combination of both, which makes achieving this aspect crucial among the 7Ps of the marketing mix.
The selection of distribution channels for service can play a factor in your business’s growth. When considering distribution channels, it’s important to evaluate factors like customer preferences, target market demographics, and the nature of your service. Additionally, assuring a smooth customer experience across all touchpoints is prominent. A consistent brand presence and efficient delivery can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
For example, An online tutoring service must have a physical centre where the classes are conducted (Physical Location) and an accessible app (Online platform) for additional support with the study material.
A Promotion consists of the actions you take to communicate your service and its values to your potential customers.
Promotion includes a wide range of activities such as advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and digital marketing. By leveraging these tools, you can build brand awareness , generate interest, and drive customer acquisition. In the service industry, where differentiation can be difficult, promotion plays an essential role in shaping customer perceptions. By highlighting unique selling points, focusing on customer satisfaction, and addressing concerns, you can position yourself as the preferred choice for your target audience.
For example, A fitness centre might use social media campaigns to highlight its unique training programs and success stories, to attract more clients, and set itself apart from competitors.
The people aspect of the mix refers to the “folks” you see in the front helping customers with your offering.
Your employees are the face of your company, interacting directly with customers and shaping their experiences. Investing in your team’s development is crucial for the success of your business. By providing training and growth opportunities, you groom your employees to deliver service that exceeds customer expectations.
A well-trained and motivated workforce can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. When employees feel valued and are equipped with the necessary skillset, they are more likely to go above and beyond to provide personalized and memorable experiences. This, in turn, strengthens your brand reputation and attracts new customers. Remember, your people are your most valuable asset, and their dedication and expertise are the foundation upon which your business is built.
For example, A hotel that invests in customer service training for its staff is more likely to see higher guest satisfaction and repeat bookings.
The process consists of the steps, procedures, and interactions involved in delivering the service to your customers. A well-defined process contributes to consistent and high-quality customer experience.
By carefully designing and implementing a process, you can minimize errors, reduce operational costs, and optimize resource allocation. Technology plays an essential role in enhancing process efficiency, automating tasks, and providing real-time data for analysis.
Continuously evaluating and refining the process is crucial for staying relevant among your audience and adapting to their changing needs. By seeking feedback and implementing improvements, you can optimize your service delivery and create a lasting impression on your customers.
For example, A restaurant might streamline its order-taking to food preparation time ratio (Process) to ensure that customers receive their meals quickly every time, enhancing their dining experience and listing you as their go-to destination.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence refers to cues that contribute to their overall perception of your offering. Since services are intangible, the environment, customer interactions, and supporting physical elements are vital in creating a satisfying experience.
By carefully curating the physical evidence surrounding a service, you can create a strong brand identity and differentiate yourself from your competitors.
For example, Visualize yourself sitting in a cafe. The cozy sofas, aroma of freshly brewed coffee, music in the background, and a friendly barista are the first few things that come to your mind. These elements will help you determine the best cafe that matches your description ideal chilling spot.

Tips for Implementing Service Marketing Mix
Here are some tips from Marketboats for you to consider while implementing the service marketing mix in your marketing strategy:
Consider your Target Audience
- Understand Your Customers: Keep your target audience at the centre of your marketing efforts. Customize your strategies to meet their needs and preferences.
- Adapt Your Approach: Always stay prepared to adjust your marketing strategies to market dynamics to keep your target audience happy.
Take the Company and Industry into Account
- Align with Business Goals: Ensure your service marketing mix aligns with your company’s overall objectives and industry standards.
- Stay Relevant: Always stay updated on industry trends and competitor activities to stay competitive and relevant.
Perform In-Depth Research
- Gather Insights: Conduct comprehensive research to understand your market, competitors, as well as your target audience.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Use this data to make detailed decisions and refine your marketing strategies.
Leverage Customer Feedback
- Listen to Your Customers: Regularly collect and analyze customer feedback to understand their needs.
- Continuous Improvement: Use this feedback to continuously improve your services & meet their needs.
Embrace Technology
- Use Marketing Automation: Implement marketing automation tools to streamline your campaigns and improve efficiency.
- Analyze Performance: Use analytics tools to monitor the performance of your marketing efforts and make data-driven adjustments.
Conduct a SWOT Analysis
- Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: Analyze your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats by conducting a SWOT analysis.
- Strategic Planning: Use this analysis to create tactics that leverage your organization’s strengths and prioritize improving the areas of weakness.
Foster Cross-Department Collaboration
- Work Together: Collaborate with other departments like sales, R&D, and customer service to ensure you have a robust marketing strategy.
- Unified Goals: Align your marketing goals with the overall business strategy for better results.
These tips will surely help you create a dynamic and effective service marketing mix that not only meets but exceeds your business objectives.
Mastering the service marketing mix is like building a strong foundation for your business. By understanding and effectively using the 7 P’s, you can create a powerful marketing strategy to attract and retain customers. Remember, it’s not just about selling a service; it’s about delivering an exceptional experience; and crafting a marketing plan that sets your business apart.
Invest in your business’s future! Marketboats can help you generate high-quality B2B leads. Let us handle the lead generation while you focus on delivering exceptional service. Contact us today to learn more about our customized lead-generation solutions.
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to write one.
Share the Post:
Frequently asked questions:, what does marketboats do.
MarketBoats Consulting is a lead supply agency that specializes in lead generation for B2B companies. We use a combination of best practices and technology to deliver high-quality sales opportunities to our clients worldwide.
What sets MarketBoats apart from other lead generation agencies?
MarketBoats Consulting differentiates itself through its technology-led processes and proprietary lead generation engine. Our advanced technology enables us to provide verified, validated, and enriched leads to our clients. We also offer a 90% accuracy guarantee, ensuring the quality and reliability of the leads we deliver.
How does MarketBoats generate leads?
We employ a combination of lead generation best practices and cutting-edge technology to generate leads for our clients. Our proprietary lead generation engine utilizes various data sources, targeting techniques, and validation processes to identify and qualify potential leads.
How accurate are the leads generated by MarketBoats?
We offer a 90% accuracy guarantee on our leads. Our technology-driven processes, combined with rigorous verification and validation techniques, ensure that the leads we deliver meet high-quality standards.
Related Posts

Top 10 B2B Lead Generation Companies to Watch for in 2024

How to Measure the ROI of Email Marketing Campaigns

A Complete Guide to Service Marketing: Boost Your Business and Build the Trust

Measuring the ROI of Content Syndication: Metrics and Tools You Need

- Database Development
- Lead Generation
- Lead Development
- Account Profiling
- Privacy Policy
- Do not sell my information
- Case Studies

IMAGES
COMMENTS
What to include: 2 Examples. Begin with a clear, engaging description of each product or service you offer. For services, describe the process, customer experience, and outcome. For products, discuss the materials, technology, and any unique features. Services example: a Cryotherapy business plan.
Business plans include details about the products and services you'll offer, including exactly how you plan to market, sell, and deliver on customer orders. The best business plans are clear and concise. The products and services section of your plan should show why your product or service is needed.
1. Portfolio: The range of products and/or services that a business offers to potential and current customers. 2. Features and benefits (value proposition): Explain what the product/service does and how it works. 3. Problem and solution (value proposition cont.): The problem (s) the product or service solves.
Updated January 3, 2024. A complete business plan describes what you sell: either products, services, or both. This section needs to be more than a simple list of what you provide. It should detail the problem you're solving, the value you provide, how it compares to the competition, and logistical information like pricing and distribution.
A description of the products or services you offer or plan to offer A pricing model for your products or service, including how you set your prices and how you will make a profit. Include a breakdown of your Costs of Goods (COG) and Costs of Services (COS), what your contingency plan is in the event of a shift in market conditions, changes to ...
Apr 6, 2015. Shutterstock. This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan. In the Products and Services section of your business plan, you will clearly describe--yep--the ...
In a Business Plan Products and Services Section, you will explain your product or service, competitive advantage, manufacturing or sourcing, and fulfillment. ... For example, if you are offering the same features as the competitors but at a low price, highlight the low price.
The products and services section is the most important component when you write your business plan. It includes everything a prospective reader needs to understand the products you sell—its unique selling proposition (USP), pricing, marketing tactics, delivery, and order fulfillment process. In short, a complete detailed guide about your ...
Below is an example of how the products and services section of your business plan might look like. It includes a list of the services provided by the business and how each one is structured in terms of the processes. This example was taken from one of our business plan templates.
A comprehensive products and services section should include a competitive analysis. Identify your main competitors and analyze their offerings, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning. Highlight how your products or services differentiate from the competition and offer a superior value proposition. This analysis demonstrates your market ...
Plus, we offer a free 30-minute consultation to ensure we fit your needs correctly. Let's get started! Contact Noirwolf Consulting today using the website contact form or by emailing [email protected] or call us at +44 113 328 0868. The business plan products and services section is the focal point of your entire plan and serves as the ...
Focus on the customer: The purpose of the products or services section is to clearly express the benefits you're providing to your customers or clients. Focus on that goal by addressing how what you are selling benefits your customers. Show how it makes their lives better, easier, or more profitable. Get to the point: State the value upfront ...
In the Products or Services Section of your business plan, you'll describe the products or services you're offering and explain the concept for your business (including manufacturing, purchasing, packaging, and distribution). This is also the time to annotate suppliers and fees. You should also indicate how your offerings will fit into the ...
This is the part of your business plan where you will describe the specific products and services you're going to offer. You'll fully explain the concept for your business, along with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. You'll go over suppliers, costs, and how what you're offering fits into the current ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
7 business plan examples: section by section. The business plan examples in this article follow this template: Executive summary. An introductory overview of your business. Company description. A more in-depth and detailed description of your business and why it exists. Market analysis.
Marketing Message. In your business plan you describe why the benefits of your products and services are powerful enough to give you a competitive advantage. Part of devising your marketing ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Tips on Writing a Business Plan. 1. Be clear and concise: Keep your language simple and straightforward. Avoid jargon and overly technical terms. A clear and concise business plan is easier for investors and stakeholders to understand and demonstrates your ability to communicate effectively. 2.
Product Offering refers to the combination of products, services, and experiences a company offers its customers. Key Components of a Product Offering include the product or service itself, pricing, marketing, and customer service. Developing and testing product offerings is an ongoing process that requires market analysis, customer feedback ...
Following this business plan outline will ensure that you have a complete and effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. Every business plan should have a short executive summary. Your executive summary is an overview of your entire business and a preview of the rest of your plan. Ideally, your executive summary can be used as a stand-alone ...
A DESCRIPTION OF YOUR PRODUCT / SERVICE. Include information about the specific benefits of your product or service, from your customers' perspective. You should also write about your product or service's ability to meet consumer needs, any advantages your product has over that of the competition, and the current development stage your ...
This section of your business plan is meant to explain how your product will stand out from comparable items in the market. You have to clearly explain its concept, coupled with all aspects of purchasing, manufacturing, packaging, and distribution. You should also identify your suppliers, costs, and how the product you are offering fits into ...
Describe the primary products or services you offer, emphasizing how they benefit your target market. Market Position: Provide insights into your market niche, target demographics, and competitive advantages. ... Writing an Impactful Sample Company Description for a Business Plan. Writing an impactful sample company description for a business ...
For example, A spa might offer a variety of massage therapies (products), ensuring high-quality service (quality), personalized treatments (customization), and a relaxing atmosphere (intangible aspect). This approach considers the overall experience provided to the customer. Price. Price is the charge that customers pay for your service.