
Home » Education » What is the Difference Between Assignment and Assessment

What is the Difference Between Assignment and Assessment
The main difference between assignment and assessment is that assignments refer to the allocation of a task or set of tasks that are marked and graded while a ssessment refers to methods for establishing if students have achieved a learning outcome, or are on their way toward a learning objective.
Assignments and assessment are two important concepts in modern education. Although these two words are similar, they have different meanings. Assignments are the pieces of coursework or homework students are expected to complete. Assessment, on the other hand, refer to the method of assessing the progress of students. Sometimes, assignments can act as tools of assessment.
Key Areas Covered
1. What is an Assignment – Definition, Goals, Characteristics 2. What is an Assessment – Definition, Characteristics 3. Difference Between Assignment and Assessment – Comparison of Key Differences

What is an Assignment
Assignments are the pieces of coursework or homework given to the students by teachers at school or professors at university. In other words, assignments refer to the allocation of a task or set of tasks that are marked and graded. Assignments are essential components in primary, secondary and tertiary education.
Assignments have several goals, as described below:
– gives students a better understanding of the topic being studied
– develops learning and understanding skills of students
– helps students in self-study
– develops research and analytical skills
– teaches students time management and organization
– clear students’ problems or ambiguities regarding any subject
– enhance the creativity of students

Generally, educators assign such tasks to complete at home and submit to school after a certain period of time. The time period assigned may depend on the nature of the task. Essays, posters, presentation, annotated bibliography, review of a book, summary, charts and graphs are some examples of assignments. Writing assignments develop the writing skills of students while creative assignments like creating posters, graphs and charts and making presentation enhance the creativity of students. Ultimately, assignments help to assess the knowledge and skills, as well as the students’ understanding of the topic.
What is an Assessment
Assessment refers to methods for establishing if students have achieved a learning outcome, or are on their way toward a learning objective. In other words, it is the method of assessing the progress of students. Assessment helps the educators to determine what students are learning and how well they are learning it, especially in relation to the expected learning outcomes of a lesson. Therefore, it helps the educator to understand how the students understand the lesson, and to determine what changes need to be made to the teaching process. Moreover, assessment focuses on both learning as well as teaching and can be termed as an interactive process. Sometimes, assignments can act as tools of assessment.

There are two main types of assessment as formative and summative assessment . Formative assessments occur during the learning process, whereas summative assessments occur at the end of a learning unit. Quizzes, discussions, and making students write summaries of the lesson are examples of formative assessment while end of unit tests, term tests and final projects are examples of summative assessment. Moreover, formative assessments aim to monitor student learning while summative assessments aim to evaluate student learning.
Difference Between Assignment and Assessment
Assignments refer to the allocation of a task or set of tasks that are marked and graded while assessment refers to methods for establishing if students have achieved a learning outcome, or are on their way toward a learning objective.
Assignments are the pieces of coursework or homework students have to complete while assessment is the method of assessing the progress of students
Goal
Moreover, assignments aim to give students a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being studied and develop learning and understanding skills of students. However, the main goal of assessment is monitoring and evaluating student learning and progress.
Assignments are the pieces of coursework or homework students have to complete while assessment refers to the method of assessing the progress of students. This is the main difference between assignment and assessment. Sometimes, assignments can also act as tools of assessment.
Image Courtesy:
1. “Focused schoolgirl doing homework and sitting at table” (CC0) via Pexels 2. “Assessment” By Nick Youngson (CC BY-SA 3.0) Alpha Stock Images
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Types of Assignments and Assessments
Assignments and assessments are much the same thing: an instructor is unlikely to give students an assignment that does not receive some sort of assessment, whether formal or informal, formative or summative; and an assessment must be assigned, whether it is an essay, case study, or final exam. When the two terms are distinquished, "assignment" tends to refer to a learning activity that is primarily intended to foster or consolidate learning, while "assessment" tends to refer to an activity that is primarily intended to measure how well a student has learned.
In the list below, some attempt has been made to put the assignments/assessments in into logical categories. However, many of them could appear in multiple categories, so to prevent the list from becoming needlessly long, each item has been allocated to just one category.
Written Assignments:
- Annotated Bibliography : An annotated bibliography is a list of citations or references to sources such as books, articles, websites, etc., along with brief descriptions or annotations that summarize, evaluate, and explain the content, relevance, and quality of each source. These annotations provide readers with insights into the source's content and its potential usefulness for research or reference.
- Summary/Abstract : A summary or abstract is a concise and condensed version of a longer document or research article, presenting the main points, key findings, and essential information in a clear and brief manner. It allows readers to quickly grasp the main ideas and determine whether the full document is relevant to their needs or interests. Abstracts are commonly found at the beginning of academic papers, research articles, and reports, providing a snapshot of the entire content.
- Case Analysis : Case analysis refers to a systematic examination and evaluation of a particular situation, problem, or scenario. It involves gathering relevant information, identifying key factors, analyzing various aspects, and formulating conclusions or recommendations based on the findings. Case analysis is commonly used in business, law, and other fields to make informed decisions and solve complex problems.
- Definition : A definition is a clear and concise explanation that describes the meaning of a specific term, concept, or object. It aims to provide a precise understanding of the item being defined, often by using words, phrases, or context that distinguish it from other similar or related things.
- Description of a Process : A description of a process is a step-by-step account or narrative that outlines the sequence of actions, tasks, or events involved in completing a particular activity or achieving a specific goal. Process descriptions are commonly used in various industries to document procedures, guide employees, and ensure consistent and efficient workflows.
- Executive Summary : An executive summary is a condensed version of a longer document or report that provides an overview of the main points, key findings, and major recommendations. It is typically aimed at busy executives or decision-makers who need a quick understanding of the content without delving into the full details. Executive summaries are commonly used in business proposals, project reports, and research papers to present essential information concisely.
- Proposal/Plan : A piece of writing that explains how a future problem or project will be approached.
- Laboratory or Field Notes: Laboratory/field notes are detailed and systematic written records taken by scientists, researchers, or students during experiments, observations, or fieldwork. These notes document the procedures, observations, data, and any unexpected findings encountered during the scientific investigation. They serve as a vital reference for later analysis, replication, and communication of the research process and results.
- Research Paper : A research paper is a more extensive and in-depth academic work that involves original research, data collection from multiple sources, and analysis. It aims to contribute new insights to the existing body of knowledge on a specific subject. Compare to "essay" below.
- Essay : A composition that calls for exposition of a thesis and is composed of several paragraphs including an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. It is different from a research paper in that the synthesis of bibliographic sources is not required. Compare to "Research Paper" above.
- Memo : A memo, short for memorandum, is a brief written message or communication used within an organization or business. It is often used to convey information, provide updates, make announcements, or request actions from colleagues or team members.
- Micro-theme : A micro-theme refers to a concise and focused piece of writing that addresses a specific topic or question. It is usually shorter than a traditional essay or research paper and requires the writer to present their ideas clearly and concisely.
- Notes on Reading : Notes on reading are annotations, comments, or summaries taken while reading a book, article, or any other written material. They serve as aids for understanding, retention, and later reference, helping the reader recall essential points and ideas from the text.
- Outline : An outline is a structured and organized plan that lays out the main points and structure of a written work, such as an essay, research paper, or presentation. It provides a roadmap for the writer, ensuring logical flow and coherence in the final piece.
- Plan for Conducting a Project : A plan for conducting a project outlines the steps, resources, timelines, and objectives for successfully completing a specific project. It includes details on how tasks will be executed and managed to achieve the desired outcomes.
- Poem : A poem is a literary work written in verse, using poetic devices like rhythm, rhyme, and imagery to convey emotions, ideas, and experiences.
- Play : A play is a form of literature written for performance, typically involving dialogue and actions by characters to tell a story or convey a message on stage.
- Choreography : Choreography refers to the art of designing dance sequences or movements, often for performances in various dance styles.
- Article/Book Review : An article or book review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, such as an article or a book. It typically includes a summary of the content and the reviewer's assessment of its strengths, weaknesses, and overall value.
- Review of Literature : A review of literature is a comprehensive summary and analysis of existing research and scholarly writings on a particular topic. It aims to provide an overview of the current state of knowledge in a specific field and may be a part of academic research or a standalone piece.
- Essay-based Exam : An essay-based exam is an assessment format where students are required to respond to questions or prompts with written, structured responses. It involves expressing ideas, arguments, and explanations in a coherent and organized manner, often requiring critical thinking and analysis.
- "Start" : In the context of academic writing, "start" refers to the initial phase of organizing and planning a piece of writing. It involves formulating a clear and focused thesis statement, which presents the main argument or central idea of the work, and creating an outline or list of ideas that will support and develop the thesis throughout the writing process.
- Statement of Assumptions : A statement of assumptions is a declaration or acknowledgment made at the beginning of a document or research paper, highlighting the underlying beliefs, conditions, or premises on which the work is based. It helps readers understand the foundation of the writer's perspective and the context in which the content is presented.
- Summary or Precis : A summary or precis is a concise and condensed version of a longer piece of writing, such as an article, book, or research paper. It captures the main points, key arguments, and essential information in a succinct manner, enabling readers to grasp the content without reading the full text.
- Unstructured Writing : Unstructured writing refers to the process of writing without following a specific plan, outline, or organizational structure. It allows the writer to freely explore ideas, thoughts, and creativity without the constraints of a predefined format or order. Unstructured writing is often used for brainstorming, creative expression, or personal reflection.
- Rough Draft or Freewrite : A rough draft or freewrite is an initial version of a piece of writing that is not polished or edited. It serves as an early attempt by the writer to get ideas on paper without worrying about perfection, allowing for exploration and creativity before revising and refining the final version.
- Technical or Scientific Report : A technical or scientific report is a document that presents detailed information about a specific technical or scientific project, research study, experiment, or investigation. It follows a structured format and includes sections like abstract, introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion to communicate findings and insights in a clear and systematic manner.
- Journal article : A formal article reporting original research that could be submitted to an academic journal. Rather than a format dictated by the professor, the writer must use the conventional form of academic journals in the relevant discipline.
- Thesis statement : A clear and concise sentence or two that presents the main argument or central claim of an essay, research paper, or any written piece. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, outlining the writer's stance on the topic and the key points that will be discussed and supported in the rest of the work. The thesis statement provides focus and direction to the paper, guiding the writer's approach to the subject matter and helping to maintain coherence throughout the writing.
Visual Representation
- Brochure : A brochure is a printed or digital document used for advertising, providing information, or promoting a product, service, or event. It typically contains a combination of text and visuals, such as images or graphics, arranged in a visually appealing layout to convey a message effectively.
- Poster : A poster is a large printed visual display intended to catch the attention of an audience. It often contains a combination of text, images, and graphics to communicate information or promote a particular message, event, or cause.
- Chart : A chart is a visual representation of data or information using various formats such as pie charts, bar charts, line charts, or tables. It helps to illustrate relationships, trends, and comparisons in a concise and easy-to-understand manner.
- Graph : A graph is a visual representation of numerical data, usually presented using lines, bars, points, or other symbols on a coordinate plane. Graphs are commonly used to show trends, patterns, and relationships between variables.
- Concept Map : A concept map is a graphical tool used to organize and represent the connections and relationships between different concepts or ideas. It typically uses nodes or boxes to represent concepts and lines or arrows to show the connections or links between them, helping to visualize the relationships and hierarchy of ideas.
- Diagram : A diagram is a visual representation of a process, system, or structure using labeled symbols, shapes, or lines. Diagrams are used to explain complex concepts or procedures in a simplified and easy-to-understand manner.
- Table : A table is a systematic arrangement of data or information in rows and columns, allowing for easy comparison and reference. It is commonly used to present numerical data or detailed information in an organized format.
- Flowchart : A flowchart is a graphical representation of a process, workflow, or algorithm, using various shapes and arrows to show the sequence of steps or decisions involved. It helps visualize the logical flow and decision points, making it easier to understand and analyze complex processes.
- Multimedia or Slide Presentation : A multimedia or slide presentation is a visual communication tool that combines text, images, audio, video, and other media elements to deliver information or a message to an audience. It is often used for educational, business, or informational purposes and can be presented in person or virtually using software like Microsoft PowerPoint or Google Slides.
- ePortfolio : An ePortfolio, short for electronic portfolio, is a digital collection of an individual's work, accomplishments, skills, and reflections. It typically includes a variety of multimedia artifacts such as documents, presentations, videos, images, and links to showcase a person's academic, professional, or personal achievements. Eportfolios are used for self-reflection, professional development, and showcasing one's abilities to potential employers, educators, or peers. They provide a comprehensive and organized way to present evidence of learning, growth, and accomplishments over time.
Multiple-Choice Questions : These questions present a statement or question with several possible answer options, of which one or more may be correct. Test-takers must select the most appropriate choice(s). See CTE's Teaching Tip "Designing Multiple-Choice Questions."
True or False Questions : These questions require test-takers to determine whether a given statement is true or false based on their knowledge of the subject.
Short-Answer Questions : Test-takers are asked to provide brief written responses to questions or prompts. These responses are usually a few sentences or a paragraph in length.
Essay Questions : Essay questions require test-takers to provide longer, more detailed written responses to a specific topic or question. They may involve analysis, critical thinking, and the development of coherent arguments.
Matching Questions : In matching questions, test-takers are asked to pair related items from two lists. They must correctly match the items based on their associations.
Fill-in-the-Blank Questions : Test-takers must complete sentences or passages by filling in the missing words or phrases. This type of question tests recall and understanding of specific information.
Multiple-Response Questions : Similar to multiple-choice questions, but with multiple correct options. Test-takers must select all the correct choices to receive full credit.
Diagram or Image-Based Questions : These questions require test-takers to analyze or interpret diagrams, charts, graphs, or images to answer specific queries.
Problem-Solving Questions : These questions present real-world or theoretical problems that require test-takers to apply their knowledge and skills to arrive at a solution.
Vignettes or Case-Based Questions : In these questions, test-takers are presented with a scenario or case study and must analyze the information to answer related questions.
Sequencing or Order Questions : Test-takers are asked to arrange items or events in a particular order or sequence based on their understanding of the subject matter.
Projects intended for a specific audience :
- Advertisement : An advertisement is a promotional message or communication aimed at promoting a product, service, event, or idea to a target audience. It often uses persuasive techniques, visuals, and compelling language to attract attention and encourage consumers to take specific actions, such as making a purchase or seeking more information.
- Client Report for an Agency : A client report for an agency is a formal document prepared by a service provider or agency to communicate the results, progress, or recommendations of their work to their client. It typically includes an analysis of data, achievements, challenges, and future plans related to the project or services provided.
- News or Feature Story : A news story is a journalistic piece that reports on current events or recent developments, providing objective information in a factual and unbiased manner. A feature story, on the other hand, is a more in-depth and creative piece that explores human interest topics, profiles individuals, or delves into issues from a unique perspective.
- Instructional Manual : An instructional manual is a detailed document that provides step-by-step guidance, explanations, and procedures on how to use, assemble, operate, or perform specific tasks with a product or system. It aims to help users understand and utilize the item effectively and safely.
- Letter to the Editor : A letter to the editor is a written communication submitted by a reader to a newspaper, magazine, or online publication, expressing their opinion, feedback, or comments on a particular article, topic, or issue. It is intended for publication and allows individuals to share their perspectives with a broader audience.
Problem-Solving and Analysis :
- Taxonomy : Taxonomy is the science of classification, categorization, and naming of organisms, objects, or concepts based on their characteristics, similarities, and differences. It involves creating hierarchical systems that group related items together, facilitating organization and understanding within a particular domain.
- Budget with Rationale : A budget with rationale is a financial plan that outlines projected income and expenses for a specific period, such as a month or a year. The rationale provides explanations or justifications for each budget item, explaining the purpose and reasoning behind the allocated funds.
- Case Analysis : Case analysis refers to a methodical examination of a particular situation, scenario, or problem. It involves gathering relevant data, identifying key issues, analyzing different factors, and formulating conclusions or recommendations based on the findings. Case analysis is commonly used in various fields, such as business, law, and education, to make informed decisions and solve complex problems.
- Case Study : A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific individual, group, organization, or situation. It involves thorough research, data collection, and detailed examination to understand the context, challenges, and outcomes associated with the subject of study. Case studies are widely used in academic research and professional contexts to gain insights into real-world scenarios.
- Word Problem : A word problem is a type of mathematical or logical question presented in a contextual format using words rather than purely numerical or symbolic representations. It challenges students to apply their knowledge and problem-solving skills to real-life situations.
Collaborative Activities
- Debate : A debate is a structured discussion between two or more individuals or teams with differing viewpoints on a specific topic or issue. Participants present arguments and counterarguments to support their positions, aiming to persuade the audience and ultimately reach a resolution or conclusion. Debates are commonly used in academic settings, public forums, and formal competitions to foster critical thinking, communication skills, and understanding of diverse perspectives.
- Group Discussion : A group discussion is an interactive conversation involving several individuals who come together to exchange ideas, opinions, and information on a particular subject. The discussion is typically moderated to ensure that everyone has an opportunity to participate, and it encourages active listening, collaboration, and problem-solving. Group discussions are commonly used in educational settings, team meetings, and decision-making processes to promote dialogue and collective decision-making.
- An oral report is a form of communication in which a person or group of persons present information, findings, or ideas verbally to an audience. It involves speaking in front of others, often in a formal setting, and delivering a structured presentation that may include visual aids, such as slides or props, to support the content. Oral reports are commonly used in academic settings, business environments, and various professional settings to share knowledge, research findings, project updates, or persuasive arguments. Effective oral reports require clear organization, articulation, and engaging delivery to effectively convey the intended message to the listeners.
Planning and Organization
- Inventory : An inventory involves systematically listing and categorizing items or resources to assess their availability, quantity, and condition. In an educational context, students might conduct an inventory of books in a library, equipment in a lab, or supplies in a classroom, enhancing their organizational and data collection skills.
- Materials and Methods Plan : A materials and methods plan involves developing a structured outline or description of the materials, tools, and procedures to be used in a specific experiment, research project, or practical task. It helps learners understand the importance of proper planning and documentation in scientific and research endeavors.
- Plan for Conducting a Project : This learning activity requires students to create a detailed roadmap for executing a project. It includes defining the project's objectives, identifying tasks and timelines, allocating resources, and setting milestones to monitor progress. It enhances students' project management and organizational abilities.
- Research Proposal Addressed to a Granting Agency : A formal document requesting financial support for a research project from a granting agency or organization. The proposal outlines the research questions, objectives, methodology, budget, and potential outcomes. It familiarizes learners with the process of seeking funding and strengthens their research and persuasive writing skills.
- Mathematical Problem : A mathematical problem is a task or question that requires the application of mathematical principles, formulas, or operations to find a solution. It could involve arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, or other branches of mathematics, challenging individuals to solve the problem logically and accurately.
- Question : A question is a sentence or phrase used to elicit information, seek clarification, or provoke thought from someone else. Questions can be open-ended, closed-ended, or leading, depending on their purpose, and they play a crucial role in communication, problem-solving, and learning.
More Resources
CTE Teaching Tips
- Personal Response Systems
- Designing Multiple-Choice Questions
- Aligning Outcomes, Assessments, and Instruction
Other Resources
- Types of Assignments . University of Queensland.
If you would like support applying these tips to your own teaching, CTE staff members are here to help. View the CTE Support page to find the most relevant staff member to contact.
Catalog search
Teaching tip categories.
- Assessment and feedback
- Blended Learning and Educational Technologies
- Career Development
- Course Design
- Course Implementation
- Inclusive Teaching and Learning
- Learning activities
- Support for Student Learning
- Support for TAs
- Assessment and feedback ,

Assessment Help
Assessment Help Online For Students

What Is The Difference Between Assignments And Assessments?
The two central ideas of contemporary education are assignment and assessment. Assignments and assessments are essential components of a student’s academic career. However, a lot of students are unaware of the fundamental distinction between an assignment and an assessment. Assignment refers to the distribution of the numerous tasks that students must do to receive the best grades in their academic curriculums. In comparison, a teacher will assess students by giving them a variety of assessment tasks that may be of different types and observing what information and skills they have learned. A student can get to know various outcomes of their learning and how they are progressing with learning objectives by completing the assessment activity.
For the best results in their academic work, students pursuing a variety of courses at various colleges must deal with assignments and assessments. Therefore, they must complete these two tasks using the right format and procedure. Assessments include writing assignments, class exercises, quizzes, case studies, and group activities, whereas assignments consist of writing tasks like case studies, reports, essays, etc. As a result, both are equally important but approached in different ways.
Let’s have a look at this in detail!
What Is An Assignment?
Assignments are pieces of writing paper or homework that a lecturer or university gives to assess your knowledge and abilities. It may also be referred to as writing assignments that must be finished and submit in before the deadlines. This is a requirement for their academic work; thus, you must conduct extensive research to finish the assignment. Numerous tasks require you to select a topic before you begin writing on it, including essays, reports, a thesis, case study assignments, and many more. It aids in the development of your comprehension and learning abilities, and you can conduct your research to finish these assignments. Additionally, it develops research and analytical skills, which will help the students in the future.
What Is An Assessment?
Assessment refers to the process by which a teacher evaluates the scholars’ knowledge and learning outcomes. In other words, multiple assessment assignments can be used to evaluate your academic development. It aids the professor in determining a student’s aptitude and degree of curricular compliance. Because of this, an assessment is an interactive process that focuses on both teaching and learning. An assignment may occasionally serve as an assessment tool.
Formative and summative assessments are the two main types of assessment. Summative evaluation takes place after each learning unit, whereas formative evaluation is undertaken throughout the learning process. Assessment includes tests, assignments, group projects, quizzes, and summaries.
What Is The Format Of An Assignment?
Understanding the right format and structure is essential before beginning any work. The format is crucial in capturing the reader’s interest. You’ll be able to compose the assignment extremely precisely if you follow the right format for an assignment. As a result, the most crucial assignment writing format must be used.
- Executive summary: The executive summary is crucial for making a good first impression on the reader; therefore, when a student begins writing an assignment, he needs to focus on it. It briefly describes an academic topic, such as a project proposal or business strategy. It provides a synopsis of the case study or reports writing and a solid structure for the writing techniques you’ll employ later on.
- Table of content: Each subsection in this section must be listed together with the relevant page number. It will surely be helpful for the reader to skip straight to the topic’s intriguing parts. Also, they can directly jump to that topic according to their interest.
- Introduction: The first section of your assignment must contain all of the crucial information related to the topic you have chosen for the assignment. In this section, you have to be very precise and clear while framing it. You need to mention all those details that you are going to explain in the further assignment. Therefore an introduction must create an impact on the reader’s mind and develop an interest in reading the whole assignment.
- Body section: After the introduction is complete, you must start on the body section. All of the crucial information should be mentioned in the assignment’s central section. When you reach this part, you need to be familiar with the major ideas, illustrations, and statistics.
- Conclusion: In conclusion, you must be able to present a summary of all the data once the primary steps have been completed. Never provide extra information for the assignment.
What Are The Major Steps To Complete An Assessment Task?
- Know the purpose of evaluation: This stage clarifies the aim of the meeting to everyone in attendance. Additionally, it establishes the meeting’s objectives and tone. It also makes it clear how questions and remarks that should be shorter for the meeting’s format will be addressed. Use our recommended introduction in the description below, or write your own.
- Determine the work provided to you: In this phase, the learner and you will review the pertinent responses you both filled out on your assessment form. The Educator should have gone over these in advance and taken any necessary notes.
- Discuss all your work and start writing it: Items for homework are tasks that must be finished at home. To allow the learner and Educator enough time to complete the work, they are assigned homework. To answer questions from the learner and to make expectations clear, homework is discussed in this stage so that you can get the best answers for your assessment questions.
If you are enrolled in a course or program offered by a reputable university, you must understand the assignment and assessment differences. Since you will be dealing with both tasks during your curriculum, it will aid you in writing them correctly. You can seek assistance from our assessment help services if you still need help understanding the difference and are unable to complete the assignment or assessment activity. Our most experienced expert will help you correctly write your assignment or assessment work. Our highly qualified experts are skilled at assessment and assignment help and finishing them before the deadlines.
- ← How To Get The Most Out Of Your Research Paper Help
- CHCPRP001 Assessment Answers →
6. Assessment
6.1 assessment and evaluation.
Assessment, as defined by www.edglossary.org , “ refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.” It is analogous to evaluation, judgment, rating, appraisal, and analysis. (Great Schools Partnership, 2015)
Although the terms assessment and evaluation are often used synonymously, they are in fact distinctive and different. The intent of assessment is to measure effectiveness; evaluation adds a value component to the process. A teacher may assess a student to ascertain how well the individual successfully met the learning target. If, however, the measurement is used to determine program placement, for example with a special education program, honors club, or for Individual Educational Program documentation, the assessment constitutes an evaluation.

Goals of Assessment
Assessment is two-fold in nature. It enables the teacher to gather information and to then determine what the learner knows or does not know and concurrently drives the planning phase. In order to meet the needs of all learners, the teacher may need to differentiate the instruction.
The teacher is then responsible for providing positive feedback in a timely manner to the student. This feedback should include specifically whether the student met the learning target, specifically what needs to be improved upon, and who and how these goals will be met.
The intent of assessment has traditionally been to determine what the learner has learned. Today, the emphasis is on authentic assessment. While the former typically employed recall methods, the latter encourages learners to demonstrate greater comprehension. (Wiggins, 1990)
7 Keys to Effective Feedback
Methods to assess .
Within an academic setting, assessment may include “the process of observing learning; describing, collecting, recording, scoring, and interpreting information about a student’s or one’s own learning http://www.k12.hi.us/atr/evaluation/glossary.htm .”
It can occur by observations, interviews, tests, projects or any other information gathering method. Within the early childhood and early primary elementary grades, observations are used frequently to assess learners. Teachers may use a checklist to note areas of proficiency or readiness and may opt to use checkmarks or some other consistent means for record-keeping.

It is helpful for a teacher to include the date, day, and time. This record-keeping may result in emerging patterns. Does the learner exhibit certain behaviors or respond to learning activities because of proximity to lunchtime, or morning or afternoon? The aspect of understanding how individuals learn can be noted within the affective domain. (Kirk, N/D) This may influence how a student learns and behaves within a classroom setting. Seating, natural and artificial lighting, noise, and temperature all influence how a student feels and interacts within the environment and can have effect cognitive behaviors.
Interviews can be used on the elementary or secondary levels as an assessment tool. Like any other well- planned assessment tool, they necessitate careful planning and development of questions, positive rapport with the student, and an environment that is free from distractions, outside noise, and time constraints. Interviews may or may not be audiotaped or videotaped and scoring rubrics may be used to assess (Southerland, ND).
Tests offer yet another venue for assessment purposes. They may take the form of essay or short response, fill-in-the-blank, matching, or true or false formats. Like any of the other methods, they should be valid and reliable. Carefully thought out test questions need to be tied to learning standards and a clear and fair scoring measure needs to be in place.
Typically, assessment has been viewed as the result; the letter or point assigned at the end of an assignment; however, assessment can and should come at the beginning, end and throughout the teaching and learning process. While assessment should drive instruction, it often falls short when determining instructional decisions

Danielle Stein eagerly anticipated the upcoming parent-teacher conferences of the day. She had studied hard as a Childhood Education major and had worked diligently in her first year as a third-grade teacher at Maplewood Elementary School. Danielle had planned interdisciplinary lessons, employed inquiry-based learning centers, and met regularly with individual students to ensure that they had mastered the skills as determined by the state standards.
Each student had a portfolio filled with dated representations of their work. Ms. Stein understood the importance of specific and timely feedback and had painstakingly provided detailed written feedback on each work sample. She meticulously arranged the portfolios along with anecdotal notes and looked forward to sharing the accomplishments of the students with their family members.
As last-minute jitters began to set in, Danielle realized that she had no grades for any of the students. Despite doing all the right things, she had no way to assign a grade to any of the work the students had done. How would she respond when guardians asked what grade their child would earn on the first report card? How would she accurately tell them how they compared with their peers in reading? In math? In social studies and science?
Danielle quickly realized she was not as prepared as she had anticipated.
Discussion Questions
How do teachers assess student work? Is there a certain number of assignments that should be graded within a 9-week session? Are there alternatives to letter grades? Reflect on how you were graded as a student.
- Foundations of Education. Authored by : SUNY Oneonta Education Department. License : CC BY: Attribution

Privacy Policy

Assignment vs. Assessment — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Assignment and Assessment
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, action vs. judgment, individual vs. group, compare with definitions, common curiosities, is every assignment followed by an assessment, what's the purpose of an assignment, how do teachers benefit from assessments, can an assignment be collaborative, what forms can assessments take, are assignments exclusive to academic settings, what is an assignment in an educational context, how does assessment differ from grading, can assessments be biased, is feedback essential after an assessment, can one forgo an assignment, do all assignments need a deadline, why are assessments integral in the learning process, how do assignments and assessments relate to real-world skills, can an assignment be both written and oral, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »

In education, the term assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.
While assessments are often equated with traditional tests—especially the standardized tests developed by testing companies and administered to large populations of students—educators use a diverse array of assessment tools and methods to measure everything from a four-year-old’s readiness for kindergarten to a twelfth-grade student’s comprehension of advanced physics. Just as academic lessons have different functions, assessments are typically designed to measure specific elements of learning—e.g., the level of knowledge a student already has about the concept or skill the teacher is planning to teach or the ability to comprehend and analyze different types of texts and readings. Assessments also are used to identify individual student weaknesses and strengths so that educators can provide specialized academic support , educational programming, or social services. In addition, assessments are developed by a wide array of groups and individuals, including teachers, district administrators, universities, private companies, state departments of education, and groups that include a combination of these individuals and institutions.
While assessment can take a wide variety of forms in education, the following descriptions provide a representative overview of a few major forms of educational assessment.
Assessments are used for a wide variety of purposes in schools and education systems :
- High-stakes assessments are typically standardized tests used for the purposes of accountability—i.e., any attempt by federal, state, or local government agencies to ensure that students are enrolled in effective schools and being taught by effective teachers. In general, “high stakes” means that important decisions about students, teachers, schools, or districts are based on the scores students achieve on a high-stakes test, and either punishments (sanctions, penalties, reduced funding, negative publicity, not being promoted to the next grade, not being allowed to graduate) or accolades (awards, public celebration, positive publicity, bonuses, grade promotion, diplomas) result from those scores. For a more detailed discussion, see high-stakes test .
- Pre-assessments are administered before students begin a lesson, unit, course, or academic program. Students are not necessarily expected to know most, or even any, of the material evaluated by pre-assessments—they are generally used to (1) establish a baseline against which educators measure learning progress over the duration of a program, course, or instructional period, or (2) determine general academic readiness for a course, program, grade level, or new academic program that student may be transferring into.
- Formative assessments are in-process evaluations of student learning that are typically administered multiple times during a unit, course, or academic program. The general purpose of formative assessment is to give educators in-process feedback about what students are learning or not learning so that instructional approaches, teaching materials, and academic support can be modified accordingly. Formative assessments are usually not scored or graded, and they may take a variety of forms, from more formal quizzes and assignments to informal questioning techniques and in-class discussions with students.
Formative assessments are commonly said to be for learning because educators use the results to modify and improve teaching techniques during an instructional period, while summative assessments are said to be of learning because they evaluate academic achievement at the conclusion of an instructional period. Or as assessment expert Paul Black put it, “When the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When the customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.”
- Interim assessments are used to evaluate where students are in their learning progress and determine whether they are on track to performing well on future assessments, such as standardized tests, end-of-course exams, and other forms of “summative” assessment. Interim assessments are usually administered periodically during a course or school year (for example, every six or eight weeks) and separately from the process of instructing students (i.e., unlike formative assessments, which are integrated into the instructional process).
- Placement assessments are used to “place” students into a course, course level, or academic program. For example, an assessment may be used to determine whether a student is ready for Algebra I or a higher-level algebra course, such as an honors-level course. For this reason, placement assessments are administered before a course or program begins, and the basic intent is to match students with appropriate learning experiences that address their distinct learning needs.
- Screening assessments are used to determine whether students may need specialized assistance or services, or whether they are ready to begin a course, grade level, or academic program. Screening assessments may take a wide variety of forms in educational settings, and they may be developmental, physical, cognitive, or academic. A preschool screening test, for example, may be used to determine whether a young child is physically, emotionally, socially, and intellectually ready to begin preschool, while other screening tests may be used to evaluate health, potential learning disabilities, and other student attributes.
Assessments are also designed in a variety of ways for different purposes:
- Standardized assessments are designed, administered, and scored in a standard, or consistent, manner. They often use a multiple-choice format, though some include open-ended, short-answer questions. Historically, standardized tests featured rows of ovals that students filled in with a number-two pencil, but increasingly the tests are computer-based. Standardized tests can be administered to large student populations of the same age or grade level in a state, region, or country, and results can be compared across individuals and groups of students. For a more detailed discussion, see standardized test .
- Standards-referenced or standards-based assessments are designed to measure how well students have mastered the specific knowledge and skills described in local, state, or national learning standards . Standardized tests and high-stakes tests may or may not be based on specific learning standards, and individual schools and teachers may develop their own standards-referenced or standards-based assessments. For a more detailed discussion, see proficiency-based learning .
- Common assessments are used in a school or district to ensure that all teachers are evaluating student performance in a more consistent, reliable, and effective manner. Common assessments are used to encourage greater consistency in teaching and assessment among teachers who are responsible for teaching the same content, e.g. within a grade level, department, or content area . They allow educators to compare performance results across multiple classrooms, courses, schools, and/or learning experiences (which is not possible when educators teach different material and individually develop their own distinct assessments). Common assessments share the same format and are administered in consistent ways—e.g., teachers give students the same instructions and the same amount of time to complete the assessment, or they use the same scoring guides to interpret results. Common assessments may be “formative” or “summative .” For more detailed discussions, see coherent curriculum and rubric .
- Performance assessments typically require students to complete a complex task, such as a writing assignment, science experiment, speech, presentation, performance, or long-term project, for example. Educators will often use collaboratively developed common assessments, scoring guides, rubrics, and other methods to evaluate whether the work produced by students shows that they have learned what they were expected to learn. Performance assessments may also be called “authentic assessments,” since they are considered by some educators to be more accurate and meaningful evaluations of learning achievement than traditional tests. For more detailed discussions, see authentic learning , demonstration of learning , and exhibition .
- Portfolio-based assessments are collections of academic work—for example, assignments, lab results, writing samples, speeches, student-created films, or art projects—that are compiled by students and assessed by teachers in consistent ways. Portfolio-based assessments are often used to evaluate a “body of knowledge”—i.e., the acquisition of diverse knowledge and skills over a period of time. Portfolio materials can be collected in physical or digital formats, and they are often evaluated to determine whether students have met required learning standards . For a more detailed discussion, see portfolio .
The purpose of an assessment generally drives the way it is designed, and there are many ways in which assessments can be used. A standardized assessment can be a high-stakes assessment, for example, but so can other forms of assessment that are not standardized tests. A portfolio of student work can be a used as both a “formative” and “summative” form of assessment. Teacher-created assessments, which may also be created by teams of teachers, are commonly used in a single course or grade level in a school, and these assessments are almost never “high-stakes.” Screening assessments may be produced by universities that have conducted research on a specific area of child development, such as the skills and attributes that a student should have when entering kindergarten to increase the likelihood that he or she will be successful, or the pattern of behaviors, strengths, and challenges that suggest a child has a particular learning disability. In short, assessments are usually created for highly specialized purposes.
While educational assessments and tests have been around since the days of the one-room schoolhouse, they have increasingly assumed a central role in efforts to improve the effectiveness of public schools and teaching. Standardized-test scores, for example, are arguably the dominant measure of educational achievement in the United States, and they are also the most commonly reported indicator of school, teacher, and school-system performance.
As schools become increasingly equipped with computers, tablets, and wireless internet access, a growing proportion of the assessments now administered in schools are either computer-based or online assessments—though paper-based tests and assessments are still common and widely used in schools. New technologies and software applications are also changing the nature and use of assessments in innumerable ways, given that digital-assessment systems typically offer an array of features that traditional paper-based tests and assignments cannot. For example, online-assessment systems may allow students to log in and take assessments during out-of-class time or they may make performance results available to students and teachers immediately after an assessment has been completed (historically, it might have taken hours, days, or weeks for teachers to review, score, and grade all assessments for a class). In addition, digital and online assessments typically include features, or “analytics,” that give educators more detailed information about student performance. For example, teachers may be able to see how long it took students to answer particular questions or how many times a student failed to answer a question correctly before getting the right answer. Many advocates of digital and online assessments tend to argue that such systems, if used properly, could help teachers “ personalize ” instruction—because many digital and online systems can provide far more detailed information about the academic performance of students, educators can use this information to modify educational programs, learning experiences , instructional approaches, and academic-support strategies in ways that address the distinct learning needs, interests, aspirations, or cultural backgrounds of individual students. In addition, many large-scale standardized tests are now administered online, though states typically allow students to take paper-based tests if computers are unavailable, if students prefer the paper-based option, or if students don’t have the technological skills and literacy required to perform well on an online assessment.
Given that assessments come in so many forms and serve so many diverse functions, a thorough discussion of the purpose and use of assessments could fill a lengthy book. The following descriptions, however, provide a brief, illustrative overview of a few of the major ways in which assessments—especially assessment results—are used in an attempt to improve schools and teaching:
- System and school accountability : Assessments, particularly standardized tests, have played an increasingly central role in efforts to hold schools, districts, and state public-school systems “accountable” for improving the academic achievement of students. The most widely discussed and far-reaching example, the 2001 federal law commonly known as the No Child Left Behind Act, strengthened federal expectations from the 1990s and required each state develop learning standards to govern what teachers should teach and students should learn. Under No Child Left Behind, standards are required in every grade level and content area from kindergarten through high school. The law also requires that students be tested annually in grades 3-8 and at least once in grades 10-12 in reading and mathematics. Since the law’s passage, standardized tests have been developed and implemented to measure how well students were meeting the standards, and scores have been reported publicly by state departments of education. The law also required that test results be tracked and reported separately for different “subgroups” of students, such as minority students, students from low-income households, students with special needs, and students with limited proficiency in English . By publicly reporting the test scores achieved by different schools and student groups, and by tying those scores to penalties and funding, the law has aimed to close achievement gaps and improve schools that were deemed to be underperforming. While the No Child Left Behind Act is one of the most controversial and contentious educational policies in recent history, and the technicalities of the legislation are highly complex, it is one example of how assessment results are being used as an accountability measure.
- Teacher evaluation and compensation : In recent years, a growing number of elected officials, policy makers, and education reformers have argued that the best way to improve educational results is to ensure that students have effective teachers, and that one way to ensure effective teaching is to evaluate and compensate educators, at least in part, based on the test scores their students achieve. By basing a teacher’s income and job security on assessment results, the reasoning goes, administrators can identify and reward high-performing teachers or take steps to either help low-performing teachers improve or remove them from schools. Growing political pressure, coupled with the promise of federal grants, prompted many states to begin using student test results in teacher evaluations. This controversial and highly contentious reform strategy generally requires fairly complicated statistical techniques—known as value-added measures or growth measures —to determine how much of a positive or negative effect individual teachers have on the academic achievement of their students, based primarily on student assessment results.
- Instructional improvement : Assessment results are often used as a mechanism for improving instructional quality and student achievement. Because assessments are designed to measure the acquisition of specific knowledge or skills, the design of an assessment can determine or influence what gets taught in the classroom (“teaching to the test” is a common, and often derogatory, phrase used to describe this general phenomenon). Formative assessments, for example, give teachers in-process feedback on student learning, which can help them make instructional adjustments during the teaching process, instead of having to wait until the end of a unit or course to find out how well students are learning the material. Other forms of assessment, such as standards-based assessments or common assessments, encourage educators to teach similar material and evaluate student performance in more consistent, reliable, or comparable ways.
- Learning-needs identification : Educators use a wide range of assessments and assessment methods to identify specific student learning needs, diagnose learning disabilities (such as autism, dyslexia, or nonverbal learning disabilities), evaluate language ability, or determine eligibility for specialized educational services. In recent years, the early identification of specialized learning needs and disabilities, and the proactive provision of educational support services to students, has been a major focus of numerous educational reform strategies. For a related discussion, see academic support .
In education, there is widespread agreement that assessment is an integral part of any effective educational system or program. Educators, parents, elected officials, policy makers, employers, and the public all want to know whether students are learning successfully and progressing academically in school. The debates—many of which are a complex, wide ranging, and frequently contentious—typically center on how assessments are used, including how frequently they are being administered and whether assessments are beneficial or harmful to students and the teaching process. While a comprehensive discussion of these debates is beyond the scope of this resource, the following is a representative selection of a few major issues being debated:
- Is high-stakes testing, as an accountability measure, the best way to improve schools, teaching quality, and student achievement? Or do the potential consequences—such as teachers focusing mainly on test preparation and a narrow range of knowledge at the expense of other important skills, or increased incentives to cheat and manipulate test results—undermine the benefits of using test scores as a way to hold schools and educators more accountable and improve educational results?
- Are standardized assessments truly objective measures of academic achievement? Or do they reflect intrinsic biases—in their design or content—that favor some students over others, such wealthier white students from more-educated households over minority and low-income students from less-educated households? For more detailed discussions, see measurement error and test bias .
- Are “one-size-fits-all” standardized tests a fair way to evaluate the learning achievement of all students, given that some students may be better test-takers than others? Or should students be given a variety of assessment options and multiple opportunities to demonstrate what they have learned?
- Will more challenging and rigorous assessments lead to higher educational achievement for all students? Or will they end up penalizing certain students who come from disadvantaged backgrounds? And, conversely, will less-advantaged students be at an even greater disadvantage if they are not held to the same high educational standards as other students (because lowering educational standards for certain students, such as students of color, will only further disadvantage them and perpetuate the same cycle of low expectations that historically contributed to racial and socioeconomic achievement gaps )?
- Do the costs—in money, time, and human resources—outweigh the benefits of widespread, large-scale testing? Would the funding and resources invested in testing and accountability be better spent on higher-quality educational materials, more training and support for teachers, and other resources that might improve schools and teaching more effectively? And is the pervasive use of tests providing valuable information that educators can use to improve instructional quality and student learning? Or are the tests actually taking up time that might be better spent on teaching students more knowledge and skills?
- Are technological learning applications, including digital and online assessments, improving learning experiences for students, teaching them technological skills and literacy, or generally making learning experiences more interesting and engaging? Or are digital learning applications adding to the cost of education, introducing unwanted distractions in schools, or undermining the value of teachers and the teaching process?

Alphabetical Search
- 1300 364 499
- [email protected]

The Difference Between an Assessment and an Assignment
Posted 4 jun '20.
.jpg)
Every school has a unique method of setting work, tasks and assessing the level their students are at, but mostly these tests come in the forms of an assessment or an assignment. However, the difference between the two of these can be hard to spot - both receive task sheets, both can usually be worked on at home, they can contain some of the same content. So, how do we tell the difference and how can this help your child?
The Assignment
So, your child has come home brandishing an assignment task sheet. What does this mean exactly? An assignment is all in the name; it is the act of assigning. It is an allocation of a task or set of tasks that are marked and graded for the report card (but does not have to be). The purpose of an assignment is to give your child a more comprehensive understanding of the topic being studied and can include questions, long-form writing tasks or a more tactile and interactive activity. An assignment is usually completed at home and submitted to the school after a certain period.
The Assessment
An assessment may not come in a much different form to the assignment, but they are usually considered more important. This is because an assessment is the act of assessing the progress of your child. The assessment may be a take-home task, an exam/test, speech or something more hands-on. An assessment can be both in-class or at home. Usually, your child will get an assessment notification that is given approximately 2 weeks before the assessment is due. Particularly for Year 12s, assessments are incredibly important as they contribute to their overall internal mark.
Why It Is Important To Know The Difference
With this information, you are now able to help your child prioritise their work. Although the tasks given can look similar, knowing the weighted importance of both can help you help them to plan out when they will complete these tasks.
If you or your child require further assistance in completing schoolwork, visit www.fsedu.com.au where you can be provided personalised, one-on-one education with an experienced, dedicated teacher with an in-depth understanding of the Australian curriculum.
Written by Ben Maher - Founder and Director of Education at Full Spectrum Education
Related Articles
Happy Mothers Day

Blackhawks Ice Hockey Club

Lest we forget. 🌹
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
In the Instructional Design process model, the Course Design section includes consideration of assessment strategies as an integral part of the overall course concept.
There is plenty of educational research that describe different philosophical approaches to assessment and there are innumerable models of assessment that you could embrace as the basis of your instruction.
Rather than trying to cover everything that is possible in domain of assessment strategy, this chapter will provide an overview so that you can be prepared for a meaningful discussion with your ID partner that is tailored to your course’s needs.
What is an assessment strategy?
There is a difference between grading and an assessment strategy . Before you can grade student work, you will need to determine the overarching perspective by which student work would be judged. There are a variety of ways that student work can be assessed depending on a few factors:
- The purpose or role of the course within a degree program
- The philosophy of the degree program itself (academic advancement or competency)
- The mission of the college (research or workforce readiness)
For example, a student can produce a project plan comprised of a paper, an oral presentation, and an accompanying slideshow. Overall, this work could be assessed according to:
- Standards for professional proficiency, such as indicators as described in performance statements in a set of competencies.
- The criteria set by the Program Director/Department, lead faculty, or the instructors themselves.
- A set of ideals of the embodied learner, such as in Jesuit eduction .
- The criteria created, curated, and agreed to by students .
In simplest terms, an assessment strategy reflects a decision (or a set of decisions) that identify what is important in student work worth making judgments about .
These decisions invariably reflect the values of the professional field, college, program, or instructor as well as the values that are associated with each individual discipline or area of subject matter. For example, the values and assessment criteria for social services programs may be different from project management or leadership programs.
Why does an assessment strategy matter?
When you are in a position to present the basis of assessment for your course, you are making a statement to your students about what matters in their work and, in a way, modeling what you believe matters in the community of professional or scholarly practice.
Your syllabus and assignment briefs should explain the basis of your assessment strategy so that students are certain about how their work will be judged and the perspective of your feedback.
Approaches to developing an assessment strategy
Some academic programs already include guidelines for how student work will be assessed.
If you have the liberty to design your own assessment strategy, then think about the following guiding principles:
What are the criteria that matter according to the scope of the assignment? While there may be many possible criteria you could use, be certain that the ones you select can actually be demonstrated or indicated within the scope and expectations of the assignment .
What are reasonable levels of assessment? For each criterion, you will need to determine how many levels there ought to be (usually no more than four or five) and what ought to be the verbiage you use to differentiate between one level and another. (See the chapter on Rubric Development).
What are the indicators associated with an exemplary assignment submission? Some subject matter can be more complex to assess than others. For example, assessing a student’s watercolor painting can be more challenging than assessing a mathematics exercise since there is no particular “solution” in creating a work of art. This is why assessing certain kinds of subject matter may need a list of well-crafted indicator statements that can be used to seek the presence or absence of them in assessing student work.
Introduction to the Instructional Design Process Copyright © 2018 by UNH-CPS (USNH) is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Assignments vs Assessments: When to Use Them

- Discussions
- Announcements

Blackbaud's Academics product offers educators plenty of ways to create new work for students. However, it may not always be clear which option is best suited to accomplish what you need. Let's talk about Assignments versus Assessments.
Leave a Comment
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Shield Notice
- Terms of Use
- Acceptable Use Policy
- General Data Protection Regulations
- Blackbaud Customer Support
- Knowledgebase
- © 2024 Blackbaud
- Powered by Personify Community
All Categories > Assessments > What is the difference between an Assessment and an Assignment?
What is the difference between an Assessment and an Assignment?

How did we do?
- Try for free
Assessment vs. Evaluation: What's the Difference?

Successful teachers know the difference. Do you?
Assessment vs. evaluation.
Assessment is, most likely, not a new concept for you; however, in most previous assessment situations, you were probably the one being tested. As you move into your teaching position, you will assume the responsibilities of an evaluator and an assessor. You will be required to determine how well your students are learning, gauge their performance, and measure the appropriateness of the content and the effectiveness of the methods and techniques utilized in your classroom.
Jabberwocky
When you assess your individual students, you gather information about their level of performance or achievement. Evaluation is comparing a student's achievement with other students or with a set of standards.
Effective assessment is a continuous process. It's not simply something that's done at the conclusion of a unit of study or at the end of a lesson. Effective assessment and evaluation are integrated into all aspects of the curriculum, providing both teachers and students with relevant and useful data to gauge progress and determine the effectiveness of materials and procedures.
Here are some criteria to consider for your own classroom:
Effective evaluation is a continuous, on-going process. Much more than determining the outcome of learning, it is rather a way of gauging learning over time. Learning and evaluation are never completed; they are always evolving and developing.
A variety of evaluative tools is necessary to provide the most accurate assessment of students' learning and progress. Dependence on one type of tool to the exclusion of others deprives students of valuable learning opportunities and robs you of measures that help both students and the overall program grow.
Evaluation must be a collaborative activity between teachers and students. Students must be able to assume an active role in evaluation so they can begin to develop individual responsibilities for development and self-monitoring.
Evaluation needs to be authentic. It must be based on the natural activities and processes students do both in the classroom and in their everyday lives. For example, relying solely on formalized testing procedures might send a signal to children that learning is simply a search for “right answers.”
Evaluation is intrinsically more complex than writing a test, giving it to a group of students, scoring it, and handing it back with some sort of letter grade. Indeed, it involves a combination of procedures and designs that not only gauge students' work but also help them grow in the process.
Featured High School Resources

Related Resources

About the author

TeacherVision Editorial Staff
The TeacherVision editorial team is comprised of teachers, experts, and content professionals dedicated to bringing you the most accurate and relevant information in the teaching space.


Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what is the difference between assessment and grading.
Assessment and grading are not the same.
Generally, the goal of grading is to evaluate individual students’ learning and performance. Although grades are sometimes treated as a proxy for student learning, they are not always a reliable measure. Moreover, they may incorporate criteria – such as attendance, participation, and effort – that are not direct measures of learning.
The goal of assessment is to improve student learning. Although grading can play a role in assessment, assessment also involves many ungraded measures of student learning (such as concept maps and CATS ). Moreover, assessment goes beyond grading by systematically examining patterns of student learning across courses and programs and using this information to improve educational practices.
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons
Difference Between Assessment and Evaluation

The basic difference between assessment and evaluation lies in the orientation, i.e. while the assessment is process oriented, evaluation is product oriented. The article presented to you describes all the distinguishing points between these two.
Content: Assessment Vs Evaluation
Comparison chart, definition of assessment.
Assessment is defined as a methodical way of acquiring, reviewing and using information about someone or something, so as to make improvement where necessary. The term is interpreted in a variety of ways, i.e. educational, psychological, financial, taxation, human resource and so on.
In general, assessment is an ongoing interactive process, in which two parties (assessor and assessee) are involved. The assessor is someone who assesses the performance based on the defined standards, while assessee is someone who is being assessed. The process aims at determining the effectiveness of the overall performance of the assessee and the areas of improvement. The process involves, setting up goals, collecting information (qualitative and quantitative) and using the information for increasing quality.
Definition of Evaluation
The term ‘evaluation’ is derived from the word ‘value’ which refers to ‘usefulness of something’. Therefore, evaluation is an examination of something to measure its utility.
Simply put, evaluation is a systematic and objective process of measuring or observing someone or something, with an aim of drawing conclusions, using criteria, usually governed by set standards or by making a comparison. It gauges the performance of a person, completed project, process or product, to determine its worth or significance.
The evaluation includes both quantitative and qualitative analysis of data and undertaken once in a while. It ascertains whether the standards or goals established are met or not. If they are met successfully, then it identifies the difference between actual and intended outcomes.
Key Differences Between Assessment and Evaluation
The significant differences between assessment and evaluation are discussed in the points given below:
- The process of collecting, reviewing and using data, for the purpose of improvement in the current performance, is called assessment. A process of passing judgment, on the basis of defined criteria and evidence is called evaluation.
- Assessment is diagnostic in nature as it tends to identify areas of improvement. On the other hand, evaluation is judgemental, because it aims at providing an overall grade.
- The assessment provides feedback on performance and ways to enhance performance in future. As against this, evaluation ascertains whether the standards are met or not.
- The purpose of assessment is formative, i.e. to increase quality whereas evaluation is all about judging quality, therefore the purpose is summative.
- Assessment is concerned with process, while evaluation focuses on product.
- In an assessment, the feedback is based on observation and positive & negative points. In contrast to evaluation, in which the feedback relies on the level of quality as per set standard.
- In an assessment, the relationship between assessor and assessee is reflective, i.e. the criteria are defined internally. On the contrary, the evaluator and evaluatee share a prescriptive relationship, wherein the standards are imposed externally.
- The criteria for assessment are set by both the parties jointly. As opposed to evaluation, wherein the criteria are set by the evaluator.
- The measurement standards for assessment are absolute, which seeks to achieve the quintessential outcome. As against this, standards of measurement for evaluation are comparative, that makes a distinction between better and worse.
So, after reviewing the points above, it would be clear that assessment and evaluation are completely different. While evaluation involves making judgments, assessment is concerned with correcting the deficiencies in one’s performance. Although, they play a crucial role in analysing and refining the performance of a person, product, project or process.
You Might Also Like:

October 28, 2016 at 1:55 am
Thanks for sharing
Narendra says
January 29, 2017 at 6:23 am
Precise and useful.
Musaed says
October 9, 2017 at 10:00 pm
I would never be confused again about the difference between assessment and evaluation. Thanks.
Kelly Mokashi says
June 14, 2018 at 8:58 pm
Can we use this article educationally, is there a copyright issue?
Surbhi S says
June 15, 2018 at 9:40 am
You can use the article, subject to proper references are given to keydifferences.com
Naijil George says
June 19, 2018 at 6:56 pm
I thought, both are very much same. This article is an eye opener.
Mehr.a.zadeh says
July 11, 2018 at 10:39 pm
Hi, your contents are excellent. Thanx
mohammed says
August 27, 2018 at 11:34 am
very detail message with concise note
Mfanelo Siziba says
September 3, 2018 at 3:56 pm
This is wonderful, well researched. Where can I get more references on this?
September 6, 2018 at 11:14 pm
Really great summary; however, I’d appreciate it if you could add some book references.
Maryam Talebi says
December 12, 2018 at 12:22 am
I really appreciate it
Augustine B says
April 10, 2019 at 11:55 am
Thanks very much for the information which is precise and helpful.
MUGABI S.R says
September 16, 2019 at 3:37 pm
Thank you very much,I now get the difference
March 13, 2020 at 9:52 am
Thanks for the piece. Could you please distinguish the three? (measurement, assessment and evaluation)
NIMUSIIMA IVAN says
September 21, 2019 at 8:14 pm
Wonderful!! Am humbled
zulfiaqar Ali says
February 18, 2020 at 10:43 am
Thank you so much for this valuable information
May 26, 2020 at 5:11 am
thanks for help
February 12, 2021 at 5:18 am
Thanks so much for the important message and I think that it will be helpful in doing my second assignment… Cheers…
February 19, 2021 at 10:54 am
Wonderful answer
Paul King Ayinde says
February 19, 2021 at 8:49 pm
Thank you immensely for these explicit explanations. They have really helped me.
saliha belhacene says
February 20, 2021 at 1:18 am
It’s so useful. Thanks
Mansharam says
February 21, 2021 at 10:58 pm
It is a base of understanding the difference between them
Lubega paul says
March 3, 2021 at 4:08 pm
Thanks for the wonderful and precise information I have learnt a lot from your information
Munyope Joseph says
March 17, 2021 at 3:48 pm
Yes maximum appreciation for the wonderful message indeed I have learnt the distinction between these two concepts.
Nakasumba GORRET says
March 26, 2021 at 6:50 am
I thought these words are the same but l realized that there is a big difference between them thanks alot
Ainomugisha Emily says
March 28, 2021 at 11:44 am
Really helpful
Faith hajara Barack says
April 2, 2021 at 10:38 pm
Thanks a lot for the clarification
Kakaire Joseph says
April 8, 2021 at 12:27 pm
Thanks for the message have really learnt about assessment and evaluation and their comparisons
Agaba Ashraf says
April 9, 2021 at 3:03 am
Thanx i have managed to understand and learnt how to distinguish between evaluation and assessment and they cannot confuse me at all in applying them as a teacher.
Kamuhanda William says
April 14, 2021 at 3:44 pm
Thanks for the useful information about the differences between Assessment and Evaluation I used to think that they are the same but they are not similar
Ahaisibwe micheal says
April 16, 2021 at 10:31 pm
Vital information about the differences between assessment and evaluation.
Dr.Dilip Chaudhari says
April 17, 2021 at 12:51 pm
Really, very good explain the difference between assessment and evaluation
Halliru Sule says
December 7, 2021 at 11:19 am
Thank you for differentiate all this information.
haron chemutai says
February 7, 2022 at 7:54 pm
Thank you for the great work
Chitra Rodrigo says
March 9, 2022 at 4:59 pm
I had a doubt on the difference between assignment and evaluation. NOW I ‘m confident. Thank you very much!
fajar mag says
August 13, 2022 at 6:59 pm
Such a brilliant information
Ada Morrison says
February 2, 2023 at 11:15 am
Thank you for the information.
Musana Elias says
February 28, 2023 at 8:29 am
Your work has cleared the misconceptions l had about the two Now clear thanks for your research
Mohanraj Sathuvalli says
April 6, 2023 at 4:32 pm
I found the article extremely useful It is precise and helps a reader understand the two terms without any ambiguity. Makes useful reading materials for teachers.
Farhana says
June 13, 2023 at 1:19 pm
want to know full name of Surbhi as I have to write reference in my assignment.
June 16, 2023 at 6:35 pm
This informative article clearly explains the difference between assessment and evaluation
El-Med says
September 9, 2023 at 10:48 pm
Thanks for your effort about those two concepts, I really understand their differences now
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- English Difference Between
- Difference Between Project and Assignment
Difference between Project and Assignment | Assignment vs Project
It is paramount that we use good English grammar, regardless of whether it is for academics or business. Inaccurate grammar usage could lead to misinterpretation of concepts and in some cases, it can be considered a lack of professionalism.
What is the Difference between Project and Assignment?
Project and assignment are two words that are often used interchangeably. However, they have their differences.
Table of Content
- Table Summarising the Difference between Project and Assignment
- The Meanings of Assignment and Project
- Examples for Project and Assignment
- Assignment vs. Project – Conclusion
Mastering English grammar is not easy. One of the biggest reasons is that there are many rules in English grammar as well as countless exceptions in the way that words are used. Moreover, the English language has a vocabulary of over 170,000 words, and therefore, learning English grammar can quickly become daunting. Regardless, adding a few words to your vocabulary each day can make a big difference. In this article, we shall explore the difference between project and assignment, their meanings and usage.
Table Summarising the Difference between Project and Assignment:
The meanings of project and assignment.
As already summarised above, the meanings of ‘project’ and ‘assignment’ are quite different, and they vary according to their usage.
- ‘Project’ meaning – The word project can be used either as a verb or a noun. Its meaning varies accordingly.
- Give an estimate or a projection based on current data
A specific plan or design
- Assignment meaning – The word assignment can only be used as a noun, and it refers to allocation of work or individuals.
Examples for Assignment and Project:
We shall explore some examples:
- Global average temperatures are projected to reach 25 degrees celsius by the year 2030.
- I noticed scaly growths projecting from his skin after exposure to the chemical.
- The image was projected on the wall.
She was captivated by the findings of the project .
- Assignment – The deadline for the assignment is next week.
Project vs. Assignment – Conclusion
As a verb, the word assignment refers to something that you are given to do by someone else. Alternatively, it could also refer to the assignment of individuals to work. A project, on the other hand, can be used as a verb as well as a noun and its meaning varies accordingly. As a verb, the word refers to the process of giving an estimate or a projection. Alternatively, it can also mean ‘to protrude’. As a noun, the word ‘project’ refers to a specific plan or design. To explore more differences between ‘project’ and ‘assignment’, register at BYJU’S. You can also find other important concepts in grammar, as well as resources for your studies here.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Should you give job applicants an assignment during the interview process? Be thoughtful about the ask

Hiring is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor. Companies need candidates who offer the right skills and experience for a given role, and who align with their organization’s vision and mission.
To find the best fit, many companies still lean on a strategy that continues to generate debate : the assignment. Some candidates believe their experience and interviews should give prospective employers enough information to determine whether they will fit the role. Employers have to ask themselves whether they are willing to turn off a strong candidate by asking them to do additional work.
Is the assignment valuable enough to the evaluation process that they cannot move someone forward without it? Sometimes it is—sometimes they help an employer decide between two strong candidates. And if they are necessary, how can employers make assignments fair and equitable for the candidate or candidates?
When done right, assignments help assess practical skills and problem-solving abilities, giving a clearer picture of a candidate beyond what their resume or interview reveals. But employers should be thoughtful about the ask. While it may make sense for roles that require specific technical expertise or creative thinking, it isn’t appropriate for all roles—so assignments should always be given with a clear reason for why they are needed.
Plus, they don’t just benefit the employer. For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail. Remember that the candidate should be interviewing the company, too. Having a test run of the work they’d be asked to do is a great way to see whether they believe the role is a fit.
However, there is a rift in how people perceive the assignment as part of the interview process. Workers today span many generations, each with unique values and expectations. Whereas older workers often prioritize stability and loyalty, younger millennials and Gen Zers are more focused on flexibility and work well-being, Indeed data shows .
This mindset impacts the amount of time and energy a candidate is willing to devote to each application. After multiple rounds of interviews and prep, taking on an in-depth assignment may feel like a bridge too far—especially if the expectations for the assignment are not clearly communicated ahead of time.
Some candidates are wary of providing free labor to a company that may use their work and not hire them. Hiring managers should be clear about how the work will be used. They may also consider offering compensation if the assignment requires more than a couple hours of someone’s time, or if they plan to use the work without hiring the candidate.
The key for early career candidates in particular is to ensure their time and efforts are respected. This is a win-win for employers: By providing clarity and transparency, they not only elicit the additional information they want from candidates, but they demonstrate that the organization is transparent and fair.
Equity is also imperative: Which candidates are being asked to complete assignments? Is the hiring team consistent in giving out assignments across ages, experience levels, and roles? There should always be a process and clear evaluation criteria in place to ensure fairness.
As we adapt to the rapidly evolving world of work, we must continue to think critically about each step in the hiring process. Candidate assignments can be a valuable tool, but only with appropriate respect for job seekers’ time and contributions.
With the right strategy, we can bridge the gap between generations in the workplace and build a hiring culture that values efficiency, talent, and integrity.
Eoin Driver is the global vice president of talent at Indeed.
More must-read commentary:
- Fannie Mae CEO: Beyoncé is right. Climate change has already hit the housing market—and homeowners aren’t prepared
Congress could soon spell the end of employment arbitration—but it’s not all good news for American workers
- Outdated laws prevent gig economy workers from getting benefits. This pilot program shows the path forward
- No, combustion engines won’t be supplanted by electric vehicles—and they’re critical for sustainable transport
The opinions expressed in Fortune.com commentary pieces are solely the views of their authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions and beliefs of Fortune .
Latest in Commentary

Birthing mothers’ near-death experience rates are 100 times higher than maternal mortality—and we don’t even know exactly why

Shark Tank entrepreneur: E-commerce giants are eating my sister’s lunch—and destroying the American Dream

I’m the CTO of Canada’s biggest airport. AI isn’t destroying jobs in aviation—it’s giving us superpowers to improve air travel

Ask Andy: I’m a founder struggling with mental-health issues. How can I step away from my startup?
Most popular.

Meet the boomers who’d rather spend $100k to renovate their homes than risk the frozen housing market: ‘It would be too hard to purchase anything else’

Hedge fund billionaire Ken Griffin says college protests are the result of a ‘cultural revolution’ and Harvard should ’embrace our Western values’

‘Housing has hit rock bottom’: Top real estate CEO says high home prices are shutting people out of the market

Apple cofounder Steve Wozniak was expelled from the school where he just delivered his commencement speech—’be leaders, not followers’

Meet the 81-year-old CEO who built a $10.4 billion luxury cruise line tailored just for baby boomers: ‘They’re the richest group we have around’

China’s economy is headed for a ‘dead-end,’ and Beijing won’t do anything to stop it, scholar says
- Open access
- Published: 06 May 2024
Effectiveness of digital and analog learning methods for learning anatomical structures in physiotherapy education
- Larissa Pagels ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3850-9454 1 ,
- Robert-Christopher Eschke ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1698-3334 1 &
- Kerstin Luedtke ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7308-5469 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 500 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
143 Accesses
Metrics details
According to the German Physiotherapy Education and Qualification Regulations, teaching of anatomical structures is one of the fundamental subjects of physiotherapy education. Besides exhibits and models, anatomy atlases are usually used as teaching and learning tools. These are available in both analog form such as printed books or in digital form as a mobile application. Furthermore, the use of digital teaching and learning tools is steadily increasing within the education of health professionals.
To assess the efficacy of a digital educational tool in contrast to an analog anatomical atlas in acquiring knowledge about anatomical structures.
Material and method
The data collection took place in the context of an anatomy tutorial for students of the bachelor’s degree program in physiotherapy. In a cross-over design, the students completed two learning assignments, each, with different learning materials provided, either with an anatomy app on a tablet or with an anatomy atlas as a book. The tests to assess the newly acquired knowledge immediately after the task, consisted of questions about the anatomical structures of the knee as well as the shoulder. In addition, the students’ satisfaction with the learning materials provided was surveyed using a questionnaire. The survey assessed their satisfaction, their assessment of learning success, and their affinity to digital learning materials. This was done using a 5-point Likert scale and a free-text field. The data was analyzed descriptively, and group differences were calculated using a t-tests.
Thirty students participated. The group comparison showed a significantly better outcome for the group that prepared with the analog anatomy atlas for the questions on the knee than the comparison group that used the anatomy app (t(28) = 2.6; p = 0.007). For the questions concerning the shoulder, there was no significant difference between the digital and analog groups (t(28) = 1.14; p = 0.26). The questionnaire revealed that satisfaction with the analog anatomy atlas was significantly higher than with the anatomy app. A total of 93.34% rated their experience with the analog learning tool at least “somewhat satisfied”. In contrast, 72.67% of students partially or fully agreed that they “enjoyed learning with digital learning tools”.
Learning anatomical structures with the Human Anatomy Atlas 2023 + app did not show a clear advantage when compared to an anatomy book in these two cohorts of physiotherapy students. The results of the questionnaire also showed greater satisfaction with the analog anatomy atlas than with the anatomy app, whereas most students stated that they frequently use digital learning tools, including some for anatomical structures. Satisfaction with the learning tool seems to play a central role in their effectiveness. In addition, sufficient time must be provided for users to familiarize themselves with the user interface of digital applications to use them effectively.
Registration
Diese klinische Studie wurde nicht in einem Studienregister registriert.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The desire for digital teaching is growing in all areas of university teaching. Due to the Sars-CoV-2 pandemic, teaching has experienced a major boost in digitalization since March 2020 [ 1 ]. A substantial number of digital teaching and learning tools are already available for this purpose. Especially in the of basic education in health sciences, the use of various teaching and learning tools can promote student motivation [ 2 ].
As part of the “HySkiLabs project - Teaching and learning health in hybrid skills labs”, education in the health sciences at the University of Luebeck is being enriched with digital teaching and learning tools. The project not only aims to transfer classroom teaching approaches to digital and hybrid teaching-learning environments, but also to systematically investigate their effectiveness. Previous surveys have shown a positive attitude of students towards digital teaching [ 3 ].
Over the last few years, the availability of digital learning tools has also increased considerably. There are various softwares and apps that students can use to organize their time in self-study or that are used as complementary teaching methods in anatomy lectures. An early study by Keedy et al. (2011) compared a 3D digital application to a 2D form for learning the anatomy of the liver and gall bladder by medical students [ 1 ]. No significant difference between the two visually different teaching methods was found for the knowledge of anatomical structures at the end of their study. Nevertheless, students’ satisfaction with the 3D digital application was very high. Two years later, Noguera et al. (2013) analyzed the effect of a digital 3D anatomy app in comparison to traditional teaching (lectures) in a physiotherapy degree program [ 2 ]. They found significantly better results in musculoskeletal anatomical knowledge among those students who used the digital anatomy app. More recently, Browne et al. (2019) analyzed the effect of online quizzes to learn anatomical structures complementing traditional learning in laboratory sessions (with wet and dry specimen, plastic models, histological slides etc.) and lectures [ 3 ]. Questions using images of anatomical structures and multiple-choice questions were provided in the online quizzes that were subsequently completed by students during self-study periods. The experiences of the students were evaluated and indicated a high level of engagement and satisfaction with the supplementary online material. Another study from 2014 used online discussion forums as an addition to their traditional learning (laboratory sessions and lectures) as an option for the students to interact and help each other in the learning process [ 4 ]. This digital learning method showed good effects on the students grades at the end of the module. In 2023, a study used Kahoot! quizzes to promote the learning of anatomical structures with a game-based learning method [ 5 ]. The quizzes contained questions about anatomical structures with four response options and were presented at the end of each lecture. An open-book technique was used, giving the students only 20s to answer the questions. A significant increase of short-term knowledge retention and an increase in the frequencies of correctly answered responses was found, compared to the traditional teaching method (lectures without Kahoot! quizzes). Additionally, all students perceived that the use of the interactive quiz improved their anatomy short-term knowledge retention.
Innovative computer-based learning tools can improve the learning of the complex spatial relationships of the musculoskeletal system and facilitate the transfer of anatomical knowledge to patients [ 5 ]. Inaccurate identification of anatomical structures is a common source of error in the assessment and treatment of musculoskeletal conditions, therefore, accurate learning of these, is essential for clinical practice [ 5 ]. From an educational perspective, interactive learning with 3D visualizations also offers several potential advantages over traditional methods of teaching anatomy: (1) a directly recognizable visualization of anatomical structures, (2) a reduction in cognitive load as students do not need to build their own mental visualization of the model, (3) many different anatomical perspectives and the ability to move the model interactively, and (4) the ability to incorporate 3D models obtained from live human imaging datasets − 2D drawings of anatomical structures are potentially inaccurate [ 5 , 6 ].
In this study, a digital 3D anatomy atlas was used to promote the short-term learning retention of physiotherapy students. To create a comparison between an analog and digital learning tool in this study, the app Human Anatomy Atlas 2023 + by Visible Body® (further referred to as “digital anatomy app”) was chosen.
There are currently no studies to indicate how effective this digital teaching and learning tool (digital anatomy app) is compared to traditional methods (analog anatomy atlas), hence, this study investigated the effect of using the Human Anatomy Atlas 2023 + on physiotherapy students’ learning of anatomical structures compared to learning with the Prometheus Atlas of Anatomy (further referred to as “analog anatomy atlas”) .
The study was designed as an empirical cross-sectional study. The data collection took place in the context of a tutorial in which students were able to intensively study anatomical structures of the musculoskeletal system and peripheral nervous system. For this purpose, they were using work assignments, as well as teaching and learning tools provided by the supervisor.
The students were randomized into two groups (“digital/analog” or “analog/digital” depending on the order of learning tools that were provided) and allocated by one of the supervisors of the tutorial in two different rooms before the beginning of the study. The groups attended the tutorials in these two different rooms and were both given the same tasks but with different teaching and learning materials (Fig. 1 ).
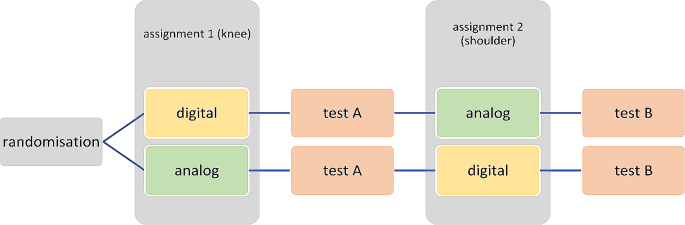
Study design
Participants
All students of the bachelor’s degree program in physiotherapy at the University of Luebeck were invited to participate in the study. At the University of Luebeck the anatomy module is taught as face-to-face lectures, practice sessions in the dissection room and 50% self-study time. In the latter, the students deepen their knowledge independently - typically this is done with the help of anatomy atlases. These can be analog (2D) and digital (2D or 3D). As a rule, the collective work “Prometheus- Atlas of Anatomy” [ 4 ] serves as an analog anatomy atlas. Previous knowledge of anatomical structures was mandatory for the participation in this study, but it had to be assumed that the knowledge was rather heterogenous due to different levels of studying of the participants. The students were informed about the data collection at the beginning of the tutorial and written consent was obtained. Participation was voluntary and had no influence on the tutorial procedure, further study program or examination results.
Application used in this study
There are several applications to learn anatomical structures with different learning modes. Some show theoretical descriptions, as well as drawings (2D) of anatomical structures, and additional skill related content as placing of ultrasound probes or manual palpation techniques (Ecofisio app; [ 6 , 7 ]). Other applications use vision-based augmented reality to display anatomical structures on human models [ 8 ] or in the room, with the option to move around the augmented reality simulated anatomical structure [ 8 , 9 ]. In addition to augmented reality 3D visualizations of anatomical structures, there are also applications that use three-dimensional images to display their content interactively [ 2 , 9 ].
The digital anatomy app used for the purpose of this study (Human Anatomy Atlas 2023+), provides various options to learn anatomical structures, and physiological processes using 3D models (by option as augmented reality simulation). The learning content is presented as a 3D model, which is interactive and can be used individually by the students. Thereby, various information on the anatomical structures and common pathologies can be accessed and learned. Additionally, short videoclips of functional anatomy (e.g. showing the muscles that are required to bend the knee while an animated skeleton is bending the knee), or rather complex functions as swallowing food, are part of the content of the app. The app does not provide options for self-testing of knowledge. This app was chosen after screening different options as it is already known by some of the students and the teaching staff and it offers interactive 3D models that have been proven to facilitate knowledge gain and satisfaction of the students when learning anatomical structures [ 2 , 8 ]. Next to being the most practicable option (as it needs time to familiarize with the interface of new applications) this app provides all functions needed to operate with the work assignments in this study. The costs of the app were covered by the “Stiftung Innovation in der Hochschullehre” as part of the HySkiLabs project.
Material and procedure
Work assignments were prepared by the supervisor of the tutorial. These contained questions about structures of the knee (ligaments, bone and joint structures) including surrounding muscles and their innervation (assignment 1). Assignment 2 focused on the shoulder joint. The supervisor was a physiotherapist with experience in teaching and good knowledge of anatomical structures. Both work assignments were double-checked by faculty members of the physiotherapy degree program of the University of Luebeck for comprehensibility.
The knowledge of the students after each learning session, was assessed via written tests that contained open ended questions about the previously repeated learning content (e.g. “name all the ligaments of the knee joint and their special features.“). The number of points to be achieved were displayed next to each question, so that the students knew about the expected scope of the answers.
In the group “analog/digital”, each participant received an analog anatomy atlas (Prometheus), while in the group “digital/analog”, each participant received the digital anatomy app on a tablet device (Human Anatomy Atlas 2023+). All students were given an initial 45-minute work assignment, which was identical in both groups and related to structures of the knee joint. A supervisor was available in each room to answer questions.
to familiarize themselves with their learning tool. Merely a verbal suggestion was given to the users of the anatomy app to use the search function of the app. After the first assignment, the participants completed the first test (maximum score 41 points) on the teaching content. During the test, no books or apps were allowed. Afterwards, the teaching and learning materials were exchanged in the rooms and the participants thus received the respective teaching and learning tool. With the new teaching and learning tool, the participants worked on another 45-minute assignment (on structures of the shoulder joint) and completed the subsequent test (maximum score 47 points).
Subsequently, the students filled out a questionnaire in which their name, age, gender and satisfaction with the teaching/learning tool offered (0 = not at all satisfied − 5 = very satisfied) were asked. The teaching/learning tool used privately by the students (free response option) and the desire for similar teaching units as exam preparation (0 = not at all − 5 = absolutely) on a 5-point Likert scale were also part of the questionnaire.
In addition, the following sub-questions were formulated for secondary analyses and assessed as a survey by students after the completion of the tasks:
How satisfied are students with the analog or digital teaching and learning tools measured on a 5-point Likert scale?
How do students rate their learning success in relation to the teaching and learning tools available on a 5-point Likert scale?
Are the teaching and learning tools offered known and have they already been used by the students (open ended question)?
Data analysis
The collected data were tabulated and analyzed using Stata (Student Version BE 17, Mac).
The null hypothesis for the analysis was:
H0 = there is no difference between the group using an analog anatomy atlas and the group using a digital anatomy app.
H1 = the respective group that learns with the digital anatomy app shows better results in the tests.
Socio-demographic data, answers from the questionnaire and the evaluation of the work assignments were analyzed descriptively with regard to frequencies (mode, median, mean) as well as dispersion measures ((interquartile) range, standard deviation) and shape measures (kurtosis, skewness) for the groups “analog/digital” and “digital/analog”.
Normal distribution of the data was tested using Shapiro-Wilk tests and group differences were calculated using t-tests.
The assessment of the group differences took place on the basis of the calculated Cohen’s d. Thus, the effect size of the use of digital vs. analog teaching and learning aids (here: anatomy atlases) was determined.
Thirty students from the semesters 2–8 of the physiotherapy degree program of the University of Luebeck participated in the study. The demographic analysis revealed an asymmetric data set for the variable semester in the analog/digital group and the variable age in the digital/analog group. The detailed results can be found in Table 1 . The majority of participants identified as female ( n = 25; 83.3%). The groups analog/digital and digital/analog differed significantly in the distribution of male and female participants (t(28)=-2.43; p = 0.01).
The results of test A (knee) unveiled a significant group difference (t(28) = 2.6; p = 0.01) and a Cohen’s d of 0.95 (Fig. 2 ). with a higher score for the group that completed the task using an analog anatomy atlas. No significant group difference was found for test B (shoulder) (t(28) = 1.14; p = 0.26). In that analysis the effect size was a Cohen’s d of 0.42 (Fig. 3 ; Table 2 ).
The evaluation of the questionnaire (Table 3 ) showed that satisfaction with the analog anatomy atlas is significantly higher than with the anatomy app. In the question about the analog learning tool 93.34% selected “somewhat satisfied” to “very satisfied”. On the other hand, 43.33% of the participants were “somewhat dissatisfied” with the digital anatomy atlas offered. In contrast, 72.67% of the students partially or fully agreed that they generally “enjoy learning with digital learning tools”.
Twenty of the students stated that they learn privately with the analog anatomy atlas used in the study (Table 4 ). In addition, the students mainly use the notes from the anatomy lectures ( n = 12), and the lecture material ( n = 10). Apps and software for learning anatomical structures, on the other hand, were mentioned less frequently. Only 10 of the students stated that they used additional software (Visible Body, Anvil, etc.) for independent learning of anatomical structures. It was frequently mentioned that the Prometheus atlas was used digitally and recordings from the lectures and other teaching videos were used.
Boxplot of the results of test A
This study analyzed the effect of learning anatomical structures with a digital anatomy app in comparison to the use of an analog anatomy atlas in the context of a physiotherapy students’ tutorial. The test results showed that the group which prepared with the analog anatomy atlas for the first test (A; knee) performed significantly better than the digital group. This could not be confirmed with the second test (B; shoulder). Hence, the results of this study about the effect of the digital anatomy app on knowledge gain is ambivalent.
Two-thirds of the participants ( n = 20) reported that they used the analog Prometheus Anatomy Atlas for studying at home and expressed satisfaction with it as a learning tool during the tutorial. Interestingly, the questionnaire also revealed that the students enjoy working with digital learning tools, but not with the one they used during the study. This might explain the difference in the first test results because it insinuates that the students had a better learning experience with the familiar learning tool. This can be supported with the results of a study from 2016, that was able to show that familiarities improve the acquisition of new knowledge. This can also be supported by the fact that the app can be used more effectively if the user interface is known beforehand and operation are clear because less working memory is devoted to understand the interface [ 10 , 11 ].
Research has shown that students’ dissatisfaction with a learning tool plays a role in its effectiveness and learning success [ 2 ]. As the participants in this study were not satisfied with the digital anatomy app provided (Table 2 ), this presents a valid explanation for the poor results of the digital learning outcomes. Moreover, many students of this sample still prefer to use analog learning materials (e.g. index cards, lecture notes, Prometheus atlas) or combine both by supplementing their analog learning materials with information from the internet (e.g. DocCheck, learning videos), further explaining the results.
The main functions of the digital anatomy app used in this study are of interactive nature and it is assumed, that active learning took place when students used the app. Interactive learning has been shown to lead to greater learning progress [ 12 ]. There is evidence for a significant better knowledge gain and student satisfaction when learning anatomical structures with mobile applications compared to traditional learning (2D images, textbook learning) [ 2 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. The fact that the test results did not show a superiority of the digital learning tool compared to the analog anatomy atlas could be, amongst other things, that the students had too little time to learn the body regions tested digitally. But according to Noguera et al. (2013), it is necessary that students have enough time to internalize anatomical structures learned in 2 dimensions and to convert them into a 3D understanding as well [ 2 ].
Previous studies have found divergent results when comparing digital vs. analog learning tools for learning anatomical structures. Keedy et al. already showed in 2011 that there was no significant difference in learning anatomical structures (liver and gall bladder) with a 3D digital application or a 2D application [ 1 ]. In contrast to the present study, the students’ satisfaction with the 3D digital application was very high [ 1 ]. One reason might be that in 2011 there were fewer alternative digital learning tools available and the comparison between several digital learning tools was therefore low.
Contradicting tothe present results Noguera et al. (2013) found a significantly better result in musculoskeletal anatomical knowledge among physiotherapy students who used a digital (3D) anatomy app than among students who received traditional teaching [ 2 ]. This difference may be attributed to their utilization of a different, more rudimentary application, characterized by a reduced set of functions compared to the alternative. Presumably, this helped students to familiarize themselves with the digital application more quickly leading to better learning effects. Furthermore, anatomical knowledge was tested witha multiple-choice questionnaire, which means that the mere probability of correct answers is higher than in this study.
Limitations
In this current study, only the students’ ability to acquire knowledge in a short time and to recall it immediately, is tested. No conclusion can be drawn about how well the students can recall the knowledge acquired after a longer period of time. Likewise, it is not possible to say how good the students’ knowledge was in advance of the tutorial, so that the learning gain through the work assignments cannot be precisely mapped. Since it was announced in advance of the tutorial that the test results would have no effect on the further course of studies, students might not have taken the test seriously. However, this effect would have been comparable in both groups.
The survey used in this study was only checked by faculty members for comprehensibility, relevance, expected acceptance of the students as well as feasibility. It has not been pilot-tested in the target population (physiotherapy students), therefore no conclusion can be drawn to its content validity.
Conclusions
This study highlights that the analog and familiar learning tools are superior if the user-friendliness and simplicity of the digital tool are not on a comparable level. Regarding the “HySkiLabs” framework project, it can be deduced from the results that the students enjoy working with digital learning tools, but a higher effectiveness of these tools could not be shown.
Further research should investigate, whether additional teaching and learning methods like discussion forums, or interactive quizzing situations might be more beneficial for knowledge retention of anatomical structures and enjoyment of learning than the mere tool itself [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Through digitalization, technical solutions are increasingly emerging with the potential to positively effect students’ motivation to learn and provide an effective learning environment [ 13 , 14 ].
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Keedy AW, Durack JC, Sandhu P, et al. Comparison of traditional methods with 3D computer models in the instruction of hepatobiliary anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2011;4:84–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.212 .
Article Google Scholar
Noguera JM, Jiménez JJ, Osuna-Pérez MC. Development and evaluation of a 3D mobile application for learning manual therapy in the physiotherapy laboratory. Comput Educ. 2013;69:96–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.07.007 .
Browne CJ. Assessing the engagement rates and satisfaction levels of various clinical health science student sub-groups using supplementary eLearning resources in an introductory anatomy and physiology unit. Health Educ. 2019;119:2–17. https://doi.org/10.1108/HE-04-2018-0020 .
Green RA, Farchione D, Hughes DL, et al. Participation in asynchronous online discussion forums does improve student learning of gross anatomy: discussion forums improve Student Learning. Anat Sci Educ. 2014;7:71–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1376 .
Cuschieri S, Narnaware Y. Improving physiotherapy students’ anatomy learning experience and short-term knowledge retention—An observational study in Malta. Anat Sci Educ. 2023;16:1134–43. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.2307 .
Fernández-Lao C, Cantarero-Villanueva I, Galiano-Castillo N, et al. The effectiveness of a mobile application for the development of palpation and ultrasound imaging skills to supplement the traditional learning of physiotherapy students. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:274. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0775-1 .
Lozano-Lozano M, Galiano-Castillo N, Fernández-Lao C, et al. The Ecofisio Mobile App for Assessment and Diagnosis Using Ultrasound Imaging for Undergraduate Health Science Students: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22:e16258. https://doi.org/10.2196/16258 .
Kandasamy G, Bettany-Saltikov J, Cordry J, et al. Use of vision-based augmented reality to improve student learning of the spine and spinal deformities. An exploratory study. South Afr J Physiother. 2021;77. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajp.v77i2.1579 .
Visible Body. Anatomy and physiology apps. 2024.
Reder LM, Liu XL, Keinath A, et al. Building knowledge requires bricks, not sand: the critical role of familiar constituents in learning. Psychon Bull Rev. 2016;23:271–7. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-015-0889-1 .
Perrig SAC, Ueffing D, Opwis K, et al. Smartphone app aesthetics influence users’ experience and performance. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1113842. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1113842 .
Langfield T, Colthorpe K, Ainscough L. Online instructional anatomy videos: student usage, self-efficacy, and performance in upper limb regional anatomy assessment: videos, anatomy Self-Efficacy, and performance. Anat Sci Educ. 2018;11:461–70. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1756 .
Kelly D, Hoang TN, Reinoso M, et al. Augmented reality learning environment for physiotherapy education. Phys Ther Rev. 2018;23:21–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/10833196.2018.1447256 .
Rasmussen K, Belisario JM, Wark PA, et al. Offline eLearning for undergraduates in health professions: a systematic review of the impact on knowledge, skills, attitudes and satisfaction. J Glob Health. 2014;4. https://doi.org/10.7189/jogh.04.010405 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
The HySkiLabs project is supported by the “Stiftung Innovation in der Hochschullehre”.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Pain and Exercise Research Luebeck, Institution of Health Sciences, University of Luebeck, Luebeck, Deutschland
Larissa Pagels, Robert-Christopher Eschke & Kerstin Luedtke
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conception or design of the work: LP, KLCollection of data: LP, RCEAnalysis of the data: LPInterpretation of the data: LP, RCE, KLDrafting the manuscript: LP, RCE, KLCritical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: LP, RCE, KL All authors give final approval of the version to be published. All authors declare that they are responsible for all aspects of the work and ensure that issues relating to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are adequately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Larissa Pagels .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study received a positive ethical approval from the ethics committee of the University of Lübeck. The students were informed about the course of the study at the beginning of the tutorial and informed consent to participate was obtained. Participation was voluntary and had no influence on the tutorial procedure or further study program or examination aspects.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pagels, L., Eschke, RC. & Luedtke, K. Effectiveness of digital and analog learning methods for learning anatomical structures in physiotherapy education. BMC Med Educ 24 , 500 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05484-1
Download citation
Received : 15 September 2023
Accepted : 29 April 2024
Published : 06 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05484-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Physiotherapy
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Understanding the differences between assignment and assessment can help educators make informed decisions about which to use in different situations. Assignments. Assignments are tasks given to students to complete outside of class time. They are typically designed to help students develop specific skills or knowledge and may be graded or ...
The main difference between assignment and assessment is that assignments refer to the allocation of a task or set of tasks that are marked and graded while assessment refers to methods for establishing if students have achieved a learning outcome, or are on their way toward a learning objective. Assignments and assessment are two important ...
Assignments and assessments are much the same thing: an instructor is unlikely to give students an assignment that does not receive some sort of assessment, whether formal or informal, formative or summative; and an assessment must be assigned, whether it is an essay, case study, or final exam.
Assignments and assessments are essential components of a student's academic career. However, a lot of students are unaware of the fundamental distinction between an assignment and an assessment. Assignment refers to the distribution of the numerous tasks that students must do to receive the best grades in their academic curriculums.
6.1 Assessment and Evaluation. Assessment, as defined by www.edglossary.org, "refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students.". It is analogous to evaluation, judgment, rating, appraisal, and ...
The purpose of an assessment is to help the teacher evaluate a student's ability and level of curriculum compliance. As a result, an evaluation is a collaborative process focusing on learning and teaching. Sometimes, assignments can be used as a tool for assessment. The types of assessment are summative and formative.
An assignment typically refers to a task, project, or duty given to someone, usually within an educational or work context. An assessment, conversely, is the act of evaluating or appraising someone's performance, skills, knowledge, or capabilities. Teachers often give students an assignment as part of their coursework, which they are expected ...
Noun. ( wikipedia assessment ) ( en noun ) The act of assessing or an amount (of tax, levy or duty etc) assessed. An appraisal or evaluation. As nouns the difference between assignment and assessment is that assignment is the act of assigning; the allocation of a job or a set of tasks while assessment is...
In education, the term assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students. While assessments are often equated with traditional tests—especially the standardized tests developed by testing companies and administered to large populations ...
An assessment may not come in a much different form to the assignment, but they are usually considered more important. This is because an assessment is the act of assessing the progress of your child. The assessment may be a take-home task, an exam/test, speech or something more hands-on. An assessment can be both in-class or at home.
There is a difference between grading and an assessment strategy. Before you can grade student work, you will need to determine the overarching perspective by which student work would be judged. There are a variety of ways that student work can be assessed depending on a few factors:
Assignment Types play a key role when creating a new Assignment. Defined Assignment types are necessary for the Gradebook as you can assign specific weights to each one. Through Assignment types, you could create a Test assignment to represent work handed in and graded manually outside of the in-app assessment feature. Assessments.
Assessments for learning - also described as assessments as learning - assess a student's comprehension and understanding of a skill or lesson during the learning and teaching process. According to the Eberly Center at Carnegie Mellon, this provides educators with ongoing feedback and allows them to: Identify at-risk students early.
Conclusion. Assignments are the bits of coursework or homework that students are required to complete, whereas Assessment refers to the process of determining how well students are progressing. This is the most significant distinction between an assignment and an assessment.
Assignments. Those campuses choosing to use our Rubrics LMS Integration will link the rubric with an Assignment rather than an Assessment. These individuals have the ability to: Create a rubric in Baseline. Associate the rubric with an Assignment that lives in the LMS course gradebook. Evaluate students in Baseline using the rubric.
The purpose of the assessment is for the teacher to have an understanding of the student's skill level so they can create the best study plan for the student. An assignment is a free feature and works as either classwork or homework. It has a due date and the student will know their score immediately. The score is also added to the student's ...
Assignments can be comprised of Assessments you have created or things such as Practice Tests, Video Lessons, and Practice Questions. The assignment builder is also the vehicle that you'll use to deliver your assessments to your students. Once you've created an assessment, you'll use the assignment builder to assign it to your students.
Jabberwocky. When you assess your individual students, you gather information about their level of performance or achievement. Evaluation is comparing a student's achievement with other students or with a set of standards. Effective assessment is a continuous process. It's not simply something that's done at the conclusion of a unit of study or ...
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark. Summative assessments are often high stakes, which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include: a midterm exam. a final project. a paper. a senior recital.
The goal of assessment is to improve student learning. Although grading can play a role in assessment, assessment also involves many ungraded measures of student learning (such as concept maps and CATS ). Moreover, assessment goes beyond grading by systematically examining patterns of student learning across courses and programs and using this ...
Assessment is made to identify the level of performance of an individual, whereas evaluation is performed to determine the degree to which goals are attained. The basic difference between assessment and evaluation lies in the orientation, i.e. while the assessment is process oriented, evaluation is product oriented.
Project vs. Assignment - Conclusion. As a verb, the word assignment refers to something that you are given to do by someone else. Alternatively, it could also refer to the assignment of individuals to work. A project, on the other hand, can be used as a verb as well as a noun and its meaning varies accordingly.
For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail ...
The survey assessed their satisfaction, their assessment of learning success, and their affinity to digital learning materials. This was done using a 5-point Likert scale and a free-text field. The data was analyzed descriptively, and group differences were calculated using a t-tests. Thirty students participated.