

What is the Essay Method for Performance Appraisals?
While some would label it as the “grandfather” of performance appraisal methods, the essay method is still a commonly used appraisal method in a variety of business models. The essay method, sometimes known as the “free-form method,” is a performance review system where a superior creates a written review of the employee’s performance.
These essays are meant to describe and record an employee’s strengths and weaknesses in job performance, identifying problem areas and creating a plan of action to remedy them. Whether the essay is written by the appraiser alone, or in collaboration with the appraisee, essays provide supervisors the opportunity to assess behaviors and performance with greater complexity and attention to detail.
There are many reasons that the essay method--which was one of the first methods used to evaluate performance--is still effective today.
One of the most noteworthy aspects of essay appraisals is their free-form approach to performance reviews. Whereas some employers can feel limited by rigid performance appraisal criteria, the essay method takes a far less structured stance than typical rating scale methods. In so doing, the appraiser is able to examine any relevant issue or attribute of performance that is pertinent to an employee’s job description or overall company growth.
The essay method assumes that not all employee traits and behaviors can be neatly analyzed, dissected, and rated--instead, it allows appraisers to place varied degrees of emphasis on certain qualities, issues, or attributes that are appropriate. Rather than being locked into a fixed system, this open-ended method gives supervisors the freedom of expression and critical thought. For appraisers, there exist special services such as StudyCrumb , which help in writing accurate essays.
When preparing an essay, a supervisor may consider any of the following factors of an employee as they relate to the company and employee relationship: potential and job knowledge, understanding of the company’s policies, relationships with peers and supervisors, planning and organization, and general attitudes and perceptions. This thorough, non-quantitative assessment provides a good deal more information about an employee than most other performance appraisal techniques.
However, as with all performance appraisal methods, there are a few limitations that the essay method suffers from that are worth examining.
One of the major drawbacks of the essay method is its highly subjective nature--they are often subject to bias, and it can be difficult to separate the assessment of the employee from the bias of the evaluator. While the essay can provide a good deal of information about the employee, it tends to tell more about the evaluator than the one being evaluated.
Another element that essays leave out (that other appraisal methods rely heavily on) is comparative results. Instead of utilizing standardized, numeric questions, these appraisals rely only on open-ended questions. While the essay method gives managers the ability to provide detailed and circumstantial information on a specific employee’s performance, it removes the component of comparing performance with other employees. This often makes it difficult for HR to distinguish top performers.
Overall, the appraisal method’s greatest advantage--the freedom of expression for the evaluator--can also serve as its greatest handicap. Even the actual writing of the reviews can upset or distort the process of employee appraisals, as the introduction of inconsistent, unorganized, or poor writing styles can distort and upset the review process. An employee may be unfairly helped or harmed by an evaluator’s writing ability. An evaluator can also find themselves lacking sufficient time to prepare the essay, and can write an essay hurriedly without accurately assessing an employee’s performance.
What is the essay method best used for?
Appraisal by essay is generally most effective in performance reviews for employees with atypical job descriptions or non-numerical goals. While other appraisals work well in analyzing performance for jobs that are subject to goals based on numbers, essays offer a more subjective analysis of performance for employees with managerial or customer service positions.
When analyzing production, the essay method is most effective in combination with another appraisal method. Using a graphic rating scale along with essay appraisals allows one method to focus solely on numbers, while the essay portion can be used to analyze other performance goals.
Doing essay appraisals right
Here are 3 things to strive for in order to set your company up for success in essay performance appraisals:
- Consistency.
Keeping a standard for style and length of essay appraisals can make the biggest difference in ensuring that your reviews are effective. Essays that are unstructured and unnecessarily complex can be detrimental to an employee’s rating, as well as using unspecific, flowery language that is not relevant to the employee’s performance. In order to remain efficient and effective, today’s evaluators should focus on making appraisal essays short and specific, ensuring that the entire review reflects the performance of the employee.
The appraiser should also ensure that they are making sufficient time in their schedule to prepare the essay. A busy evaluator may compromise an employee’s performance rating by writing a hurried essay, or running out of time to thoroughly assess employee performance. It’s important for all participants of essay appraisals to take enough time to write a consistent, accurate, and succinct review in order to set employees up for success.
2. Proficiency.
If you’ve chosen to use essay appraisals in your organization, it’s important to ensure that your appraisers possess the ability to write well. Even if an essay contains detailed, circumstantial information, it becomes difficult to extract valuable data from a poorly written essay. To ensure that nothing stands between an HR professional’s ability to assess an employee’s performance, evaluators should be trained as well-equipped writers.
Giving writing assistant tools or tips to supervisors can make all the difference in the accuracy and efficiency of an employee’s performance review.
2. Objectivity.
Subjectivity is both a strength and a weakness in essay appraisals. Not only are essays themselves often biased, but the misinterpretation of essays can even further distance the main evaluator from an accurate portrayal of an employee’s performance. Including objective standards in a performance review results in a more balanced and productive review process, and helps to eliminate the forming of incorrect conclusions about an employee’s behavior and performance.
Organizations often implement this goal by pairing essay appraisals with another appraisal method, such as graphic scale ratings, to draw more accurate conclusions and performance data. In so doing, evaluators can utilize all of the free expression and open-ended characteristics of an essay appraisal, while still maintaining accurate, easily translated results that are effective for the overall organization.

Employee Core Competencies - Examples & Development Steps
.jpg)
6 Steps to Run a Talent Review That Actually Works

6 Examples of Positive Performance Review Phrases
- Our Partners
- HR Management Software
- Applicant Tracking System
- Performance Management Software
- Plans and features
- Integrations
The Pros and Cons of Different Performance Appraisal Methods

Morgane Lança
Employee performance management is not a walk in the park, and there are many evaluation methods and tools to choose from. If you want to choose the right type of assessment for your specific business goals, you need to know the pros and cons of each performance review process.
In this article, we’ll give you all the information you need on these methods, along with details on their pros and cons for your company! As a bonus, you’ll find evaluation questions and evaluation examples you can use as inspiration.
Performance Evaluation Methods
1. traditional performance review or checklist method.
Employees are evaluated according to a checklist of predetermined key performance indicators and strengths and weaknesses such as time management skills. Supervisors determine whether the evaluated employee’s performance meets these criteria and provide structured goals. Most of the time, these employee appraisals take place annually and workers are rated on a linear scale.

- Structure and formality : Traditional performance reviews provide a structured framework for evaluating and discussing employee performance. They often follow a set process and timeline, which can help ensure consistency across the organization.
- Learning and development : These reviews offer an opportunity for supervisors to provide feedback on an employee’s performance, strengths, and areas for improvement. They can be a platform for discussing career goals, development plans, and performance expectations.
- Compensation and rewards : Annual employee reviews often play a role in determining compensation, promotions, and rewards. They provide a basis for identifying high-performing employees who may be eligible for salary increases, bonuses, or advancement opportunities.
- Performance documentation and tracking : Formal performance reviews typically involve documentation of the evaluation process and its outcomes. This can help build a record of performance discussions, achievements, and areas needing improvement, which can be useful for future reference and decision-making processes.
- Infrequent feedback : Annual performance reviews often imply that feedback is not shared on a daily basis. This time gap can hinder timely feedback and limit opportunities for ongoing communication and performance improvement.
- Bias and subjectivity : Annual employee performance reviews can lead to subjectivity, as they solely rely on the opinions of supervisors. This can lead to biased assessments based on personal perceptions and negative experiences for employees.
- Focus on past performance : These reviews often emphasize past performance rather than real-time or future-oriented assessments. They may not capture recent accomplishments or changes in an employee’s performance since the last review meeting.
- Anxiety and stress : The anticipation of an annual performance review can create anxiety and stress for employees. This once-a-year process can make the evaluation feel high-stakes and put pressure on both supervisors and employees.
- Lack of continuous feedback : Traditional reviews do not provide the feedback loop necessary for ongoing feedback and coaching. Employees may miss out on regular opportunities to receive guidance, suggestions for improvement, support, and recognition for their work.
- Administrative burden : Conducting annual reviews for all employees can be time-consuming, especially in large organizations. This can divert resources from other important tasks and potentially delay the feedback process.
The manufacturing industry, warehouses and retail companies can get great results from traditional employee appraisal systems. Indeed, these evaluations often focus on quantitative evaluation criteria that fit with repetitive tasks.
2. 360-Degree System
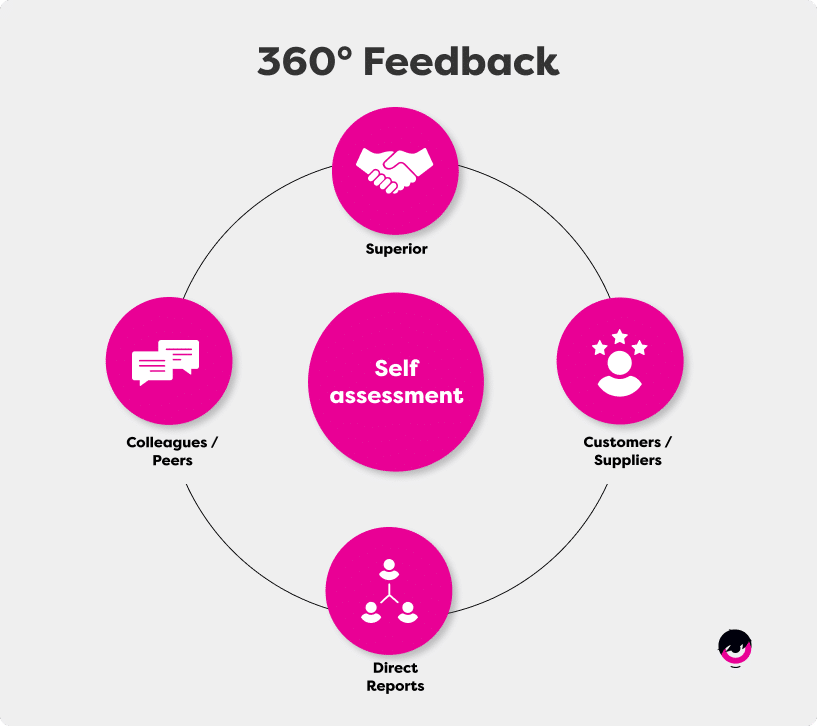
360-degree feedback consists of multi-rater feedback collected about an employee from their peers, their managers, and themselves. Obtaining constructive feedback coming from different perspectives helps gather comprehensive insights on employee performance strategies in the workplace.
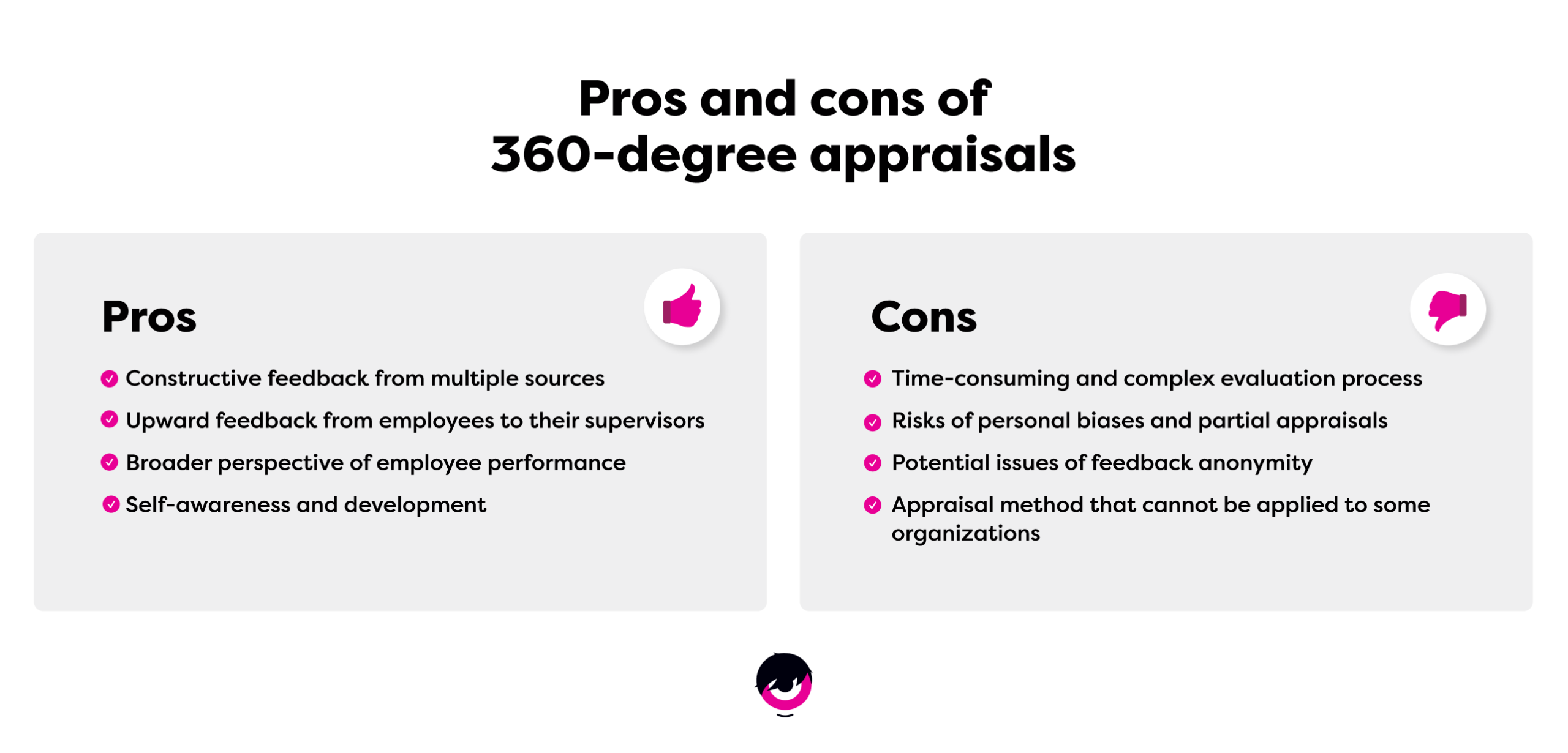
- Feedback from multiple sources : Collecting feedback from peers, employees, and supervisors helps build a comprehensive evaluation.
- Upward feedback : This method encourages feedback from teams regarding their supervisor and management, meaning that everyone is accountable for their own performance.
- Broader perspective on employee performance : When conducted right, these evaluations provide a general and fair perspective of employee performance throughout the entire company.
- Encourages self-awareness and development : Receiving constructive feedback from multiple raters encourages self-reflection and development. Moreover, 360-degree feedback includes a self-evaluation that further fosters professional growth.
- Time-consuming process : Gathering feedback from multiple raters takes time and this method might be difficult to implement in your business.
- Personal biases : Office conflicts and personal opinions might influence raters and cause partial appraisals.
- Issues of anonymity : Anonymity – or lack thereof – may affect the quality and honesty of feedback.
All companies can use 360-degree feedback – it more so depends on the job category. Managers can particularly benefit from this process and it can be adjusted depending on the industry (companies that provide services can use client feedback for the evaluation). The downside is that this method can be quite costly and time consuming depending on your business reality.
3. Management by Objectives (MBO)
This method defines clear and concrete goals that the employee and the organization aim to achieve. These objectives may be quantitative or qualitative, and tracking them often requires regular performance meetings.

- Goal-setting and alignment with organizational objectives : With a MBO approach, self-development objectives and organizational goals are aligned for better workflows and greater productivity.
- Employee participation and ownership : Employees participate in goal setting, which is proven to multiply their chances to be engaged by 3,6. They are also more likely to be proud of their performance and committed to improving it.
- Clear framework : This method provides a clear framework for evaluating performance based on measurable goals such as SMART goals . This means that everyone has a clear idea of what they have to do and can see the impact of their productivity on the company’s mission.
- Challenge of setting measurable goals : Although measurable goals are effective, they can be difficult to set up depending on the company’s roles. This performance appraisal method might be more efficient in some teams than others.
- Focus on short-term goals : Defining short-term objectives may result in a narrow focus that neglects broader aspects of performance and sets aside development opportunities.
- Reliance on goal attainment : Solely focusing on goal attainment might lead to a lack of recognition for smaller but valuable contributions.
This method is interesting for companies that work by project completion – consulting and professional services, for instance. A relationship of trust and providing autonomy to employees is crucial, so the evaluated team dynamic matters here.
4. Self-assessment Method
Employees evaluate their own performance based on predefined criteria or goals to further encourage their personal commitment to their performance and growth.

- Self-reflection : Employees who reflect on their own performance have a better understanding of the challenges they need to overcome to become high performers. They are also more likely to request growth opportunities and share their ambitions with their managers.
- Ownership : Owning up to your individual performance and the way it impacts the team and the organization at large encourages growth and renewal.
- Self-development : Self-assessment is one of the best drivers of individual development as employees are able to regularly analyze their performance and its evolution over time.
- Lack of objectivity and biases : Evaluating your own performance is not an easy feat. Employees might be tempted to positively rate themselves to avoid questioning their practices. Objectively rating your strengths and weaknesses is a method that requires training beforehand.
- Issues of self-worth : On the contrary, some employees might have issues recognizing their self-worth and underrate themselves, which undermines their self-assessment.
- Need more varied perspectives : Self-assessments are not enough on their own and they need to be implemented alongside another appraisal method to be efficient, which might be complicated and time-consuming for some companies.
Industries which typically focus on qualitative criteria such as behavior and people skills can greatly benefit from using this appraisal method. This is the case of service industries, for example.
Of course, other appraisal methods exist, such as the 9-box grid appraisal and many others. However, with the previous examples we introduced, you will get a strong idea of which performance appraisal process will be the most efficient for your reality.
Some of these methods’ limitations can be addressed by implementing a healthy feedback culture consisting of regular check-ins, ongoing performance management, and effective performance management software tools. Indeed, regular and actionable feedback optimizes employee performance management and fosters productivity and development.
25 Performance Review Questions
Here are some sample questions covering the essential points you need to address during a performance appraisal, sorted by evaluation method:
Traditional review questions
1) What technical skills have you acquired or developed this year?
2) How have these skills supported your day-to-day performance?
3) How would you describe your general attitude at work?
4) How do you react to feedback, whether positive or negative?
5) Can you share an example of how you have used feedback to improve your work?
6) How do you ensure that your actions are aligned with the company’s culture and objectives?
Self-assessment questions
7) What are your strengths and weaknesses, and how would you assess them?
8) Are you satisfied with your performance over the last period? Are there any tasks or projects you would have completed differently?
9) What are your plans for future professional development?
10) What skills have you acquired recently and which ones would like to acquire in the future?
11) What individual goals would you like to set for the next period?
12) What have been your favorite projects to work on? Were there any projects you didn’t like as much?
13) What could we do to improve your daily work?
Objective-based evaluation questions
14) What objectives have you achieved during this evaluation period?
15) Could you describe the results achieved in relation to the objectives we set?
16) What challenges did you encounter in achieving your objectives?
17) How did you overcome these obstacles?
18) What objectives would you like to work on for the next period, and how do you think you can achieve them?
19) Do you feel that your objectives and your work have a direct impact team and organizational performance?
20) Do you think the goals you set were realistic? Were there too ambitious, or not ambitious enough?
360-degree appraisal questions
21) How would you rate your collaboration with team members?
22) Did you receive feedback from your colleagues? Has it been helpful?
23) How do you support and coach your employees on a daily basis?
24) What comments have your employees shared about your leadership skills?
25) Do you have a healthy relationship with your direct supervisor? Do you find their feedback relevant?
Examples of Performance Appraisal Results
Once you’ve asked your questions during the performance interview, you can write up your assessment. Here are some sample results to help you in your writing and summarizing process:
Positive Results
“This employee has met all the criteria detailed in our assessment scale. Their positive attitude and their concern to meet all the individual objectives defined during the previous appraisal make all the difference to team and company success. I wish to underline their good understanding with team members and their ability to collaborate effectively with colleagues. I also noticed leadership skills that we could develop and that could lead to a promotion in the future. Therefore, I have added this element to the performance objectives for the next appraisal.”
Underlining Progress
“After experiencing a dip in performance over the last period, this employee challenged themselves and progressed in every respect. In addition to improving their performance level, they took my feedback into account to implement better practices on a daily basis. These changes have turned the situation around and optimized the employee’s potential. For the next quarterly appraisal, I’d like this employee to focus on maintaining a stable level of productivity while learning to use tools that will help them continuously improve.”
Negative Results
“Despite our previous exchanges, this employee has not considered the constructive feedback shared and has not implemented good work practices. What’s more, their negative attitude is impacting the workplace and the well-being of team members. I have therefore put performance improvement measures in place and communicated the importance of solving these issues as quickly as possible. A further assessment will be organized next month to quickly analyze the situation and make the appropriate follow-up decisions.”
Whatever the method you choose, a successful appraisal must focus on finding solutions to improve employee productivity and motivation, as well as promoting skills development. Good performance management is an integral part of effective human resources management practices, and directly supports your strategic objectives and the success of your organization.
Do you want to implement the best performance appraisal method in your organization?
Folks performance management tools let you customize your entire process!

Related articles

Exit Interviews Questions and Best Practices
Exit interviews are useful processes to get insights and employee feedback. Here are questions you should ask and tips to follow.

6 HR Marketing Trends You Need to Know in 2024
Here are current recruitment challenges and key trends you need to keep in mind to implement an effective HR marketing strategy.

HR Software: Benefits & Tips to Make the Right Choice
In this article, we present the benefits and different types of HR solutions, as well as best practices for choosing HR software that matches your company’s needs and reality.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Appraisal Methods
Learning objective.
- Be able to describe the various appraisal methods.
It probably goes without saying that different industries and jobs need different kinds of appraisal methods. For our purposes, we will discuss some of the main ways to assess performance in a performance evaluation form. Of course, these will change based upon the job specifications for each position within the company. In addition to industry-specific and job-specific methods, many organizations will use these methods in combination, as opposed to just one method. There are three main methods of determining performance. The first is the trait method , in which managers look at an employee’s specific traits in relation to the job, such as friendliness to the customer. The behavioral method looks at individual actions within a specific job. Comparative methods compare one employee with other employees. Results methods are focused on employee accomplishments, such as whether or not employees met a quota.
Within the categories of performance appraisals, there are two main aspects to appraisal methods. First, the criteria are the aspects the employee is actually being evaluated on, which should be tied directly to the employee᾿s job description. Second, the rating is the type of scale that will be used to rate each criterion in a performance evaluation: for example, scales of 1–5, essay ratings, or yes/no ratings. Tied to the rating and criteria is the weighting each item will be given. For example, if “communication” and “interaction with client” are two criteria, the interaction with the client may be weighted more than communication, depending on the job type. We will discuss the types of criteria and rating methods next.
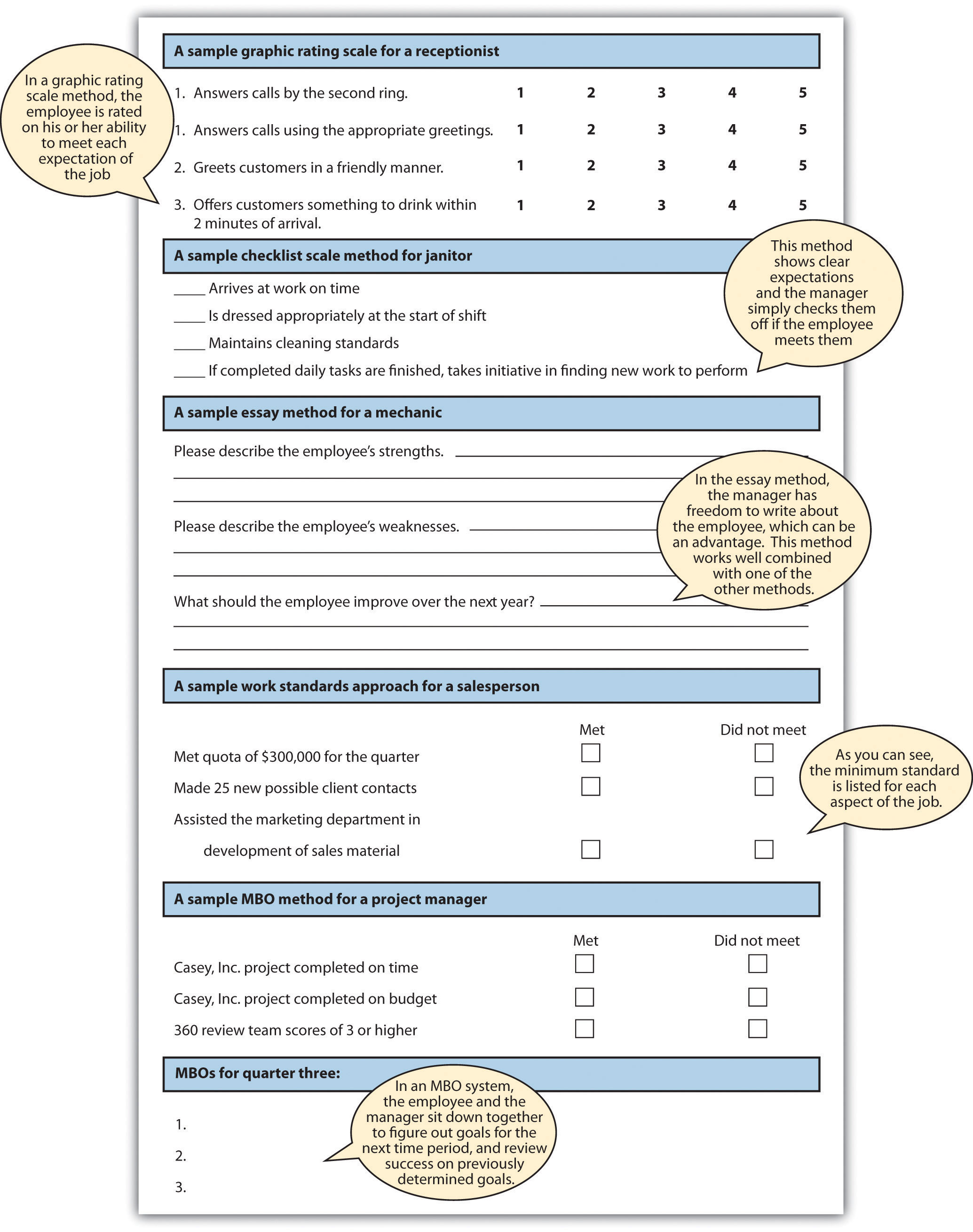
Graphic Rating Scale
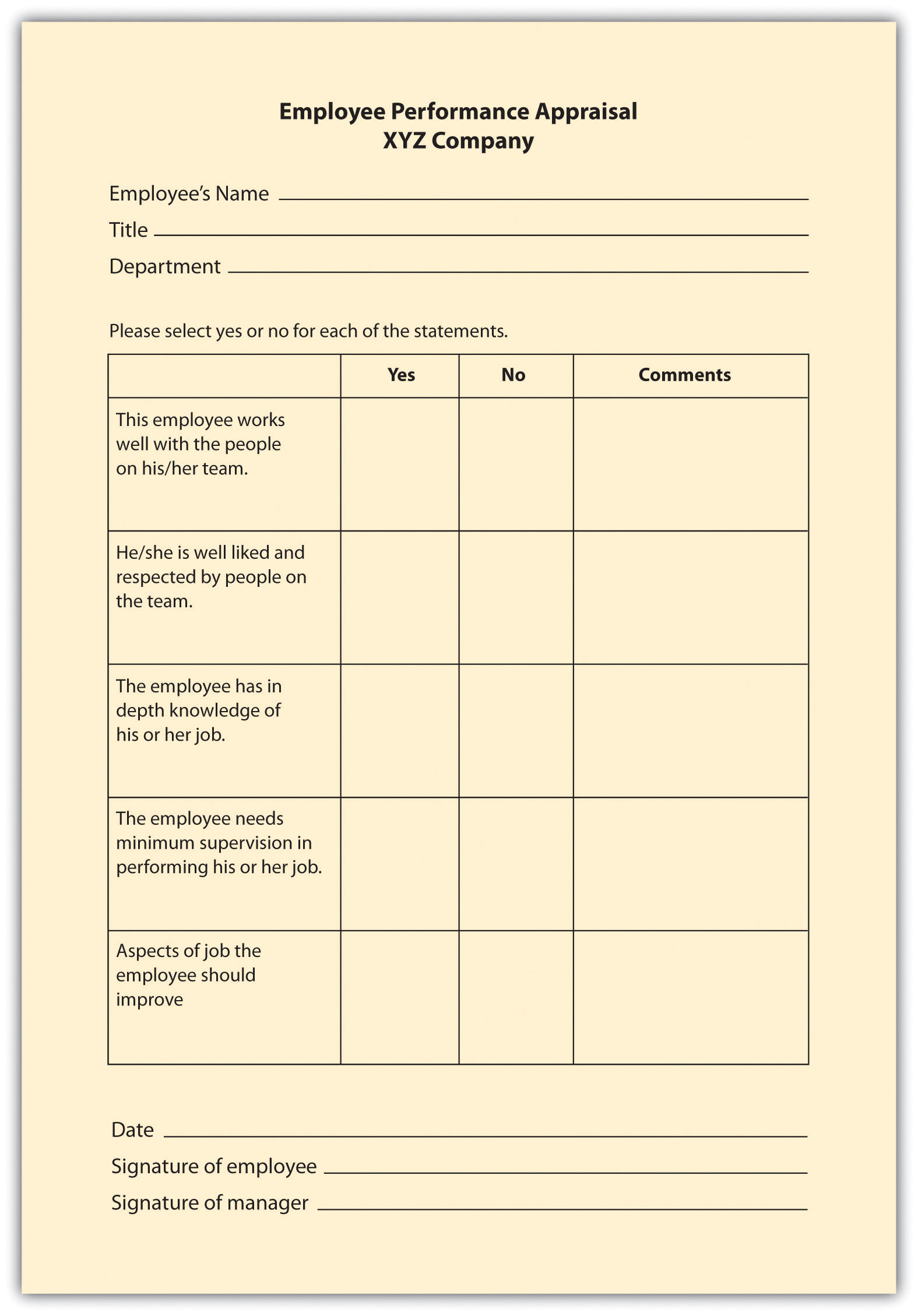
The graphic rating scale , a behavioral method, is perhaps the most popular choice for performance evaluations. This type of evaluation lists traits required for the job and asks the source to rate the individual on each attribute. A discrete scale is one that shows a number of different points. The ratings can include a scale of 1–10; excellent, average, or poor; or meets, exceeds, or doesn’t meet expectations, for example. A continuous scale shows a scale and the manager puts a mark on the continuum scale that best represents the employee’s performance. For example:
| Poor | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | Excellent |
The disadvantage of this type of scale is the subjectivity that can occur. This type of scale focuses on behavioral traits and is not specific enough to some jobs. Development of specific criteria can save an organization in legal costs. For example, in Thomas v. IBM , IBM was able to successfully defend accusations of age discrimination because of the objective criteria the employee (Thomas) had been rated on.
Many organizations use a graphic rating scale in conjunction with other appraisal methods to further solidify the tool’s validity. For example, some organizations use a mixed standard scale , which is similar to a graphic rating scale. This scale includes a series of mixed statements representing excellent, average, and poor performance, and the manager is asked to rate a “+” (performance is better than stated), “0” (performance is at stated level), or “−” (performance is below stated level). Mixed standard statements might include the following:
- The employee gets along with most coworkers and has had only a few interpersonal issues.
- This employee takes initiative.
- The employee consistently turns in below-average work.
- The employee always meets established deadlines.
An example of a graphic rating scale is shown in Figure 11.1 “Example of Graphic Rating Scale” .
Essay Appraisal
In an essay appraisal , the source answers a series of questions about the employee’s performance in essay form. This can be a trait method and/or a behavioral method, depending on how the manager writes the essay. These statements may include strengths and weaknesses about the employee or statements about past performance. They can also include specific examples of past performance. The disadvantage of this type of method (when not combined with other rating systems) is that the manager’s writing ability can contribute to the effectiveness of the evaluation. Also, managers may write less or more, which means less consistency between performance appraisals by various managers.
Checklist Scale
A checklist method for performance evaluations lessens the subjectivity, although subjectivity will still be present in this type of rating system. With a checklist scale , a series of questions is asked and the manager simply responds yes or no to the questions, which can fall into either the behavioral or the trait method, or both. Another variation to this scale is a check mark in the criteria the employee meets, and a blank in the areas the employee does not meet. The challenge with this format is that it doesn’t allow more detailed answers and analysis of the performance criteria, unless combined with another method, such as essay ratings. A sample of a checklist scale is provided in Figure 11.3 “Example of Checklist Scale” .
Figure 11.1 Example of Graphic Rating Scale
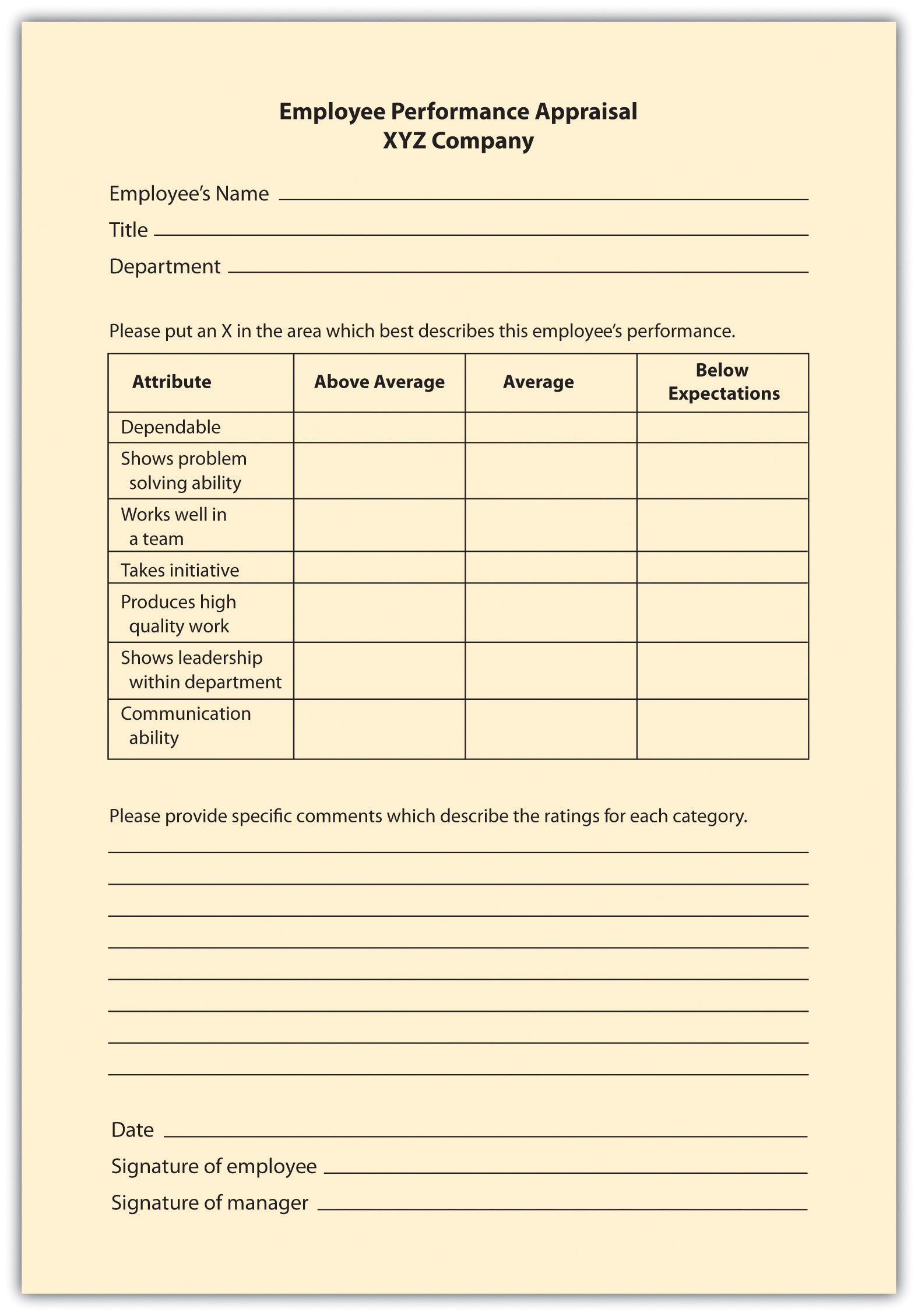
Figure 11.2 Example of Essay Rating
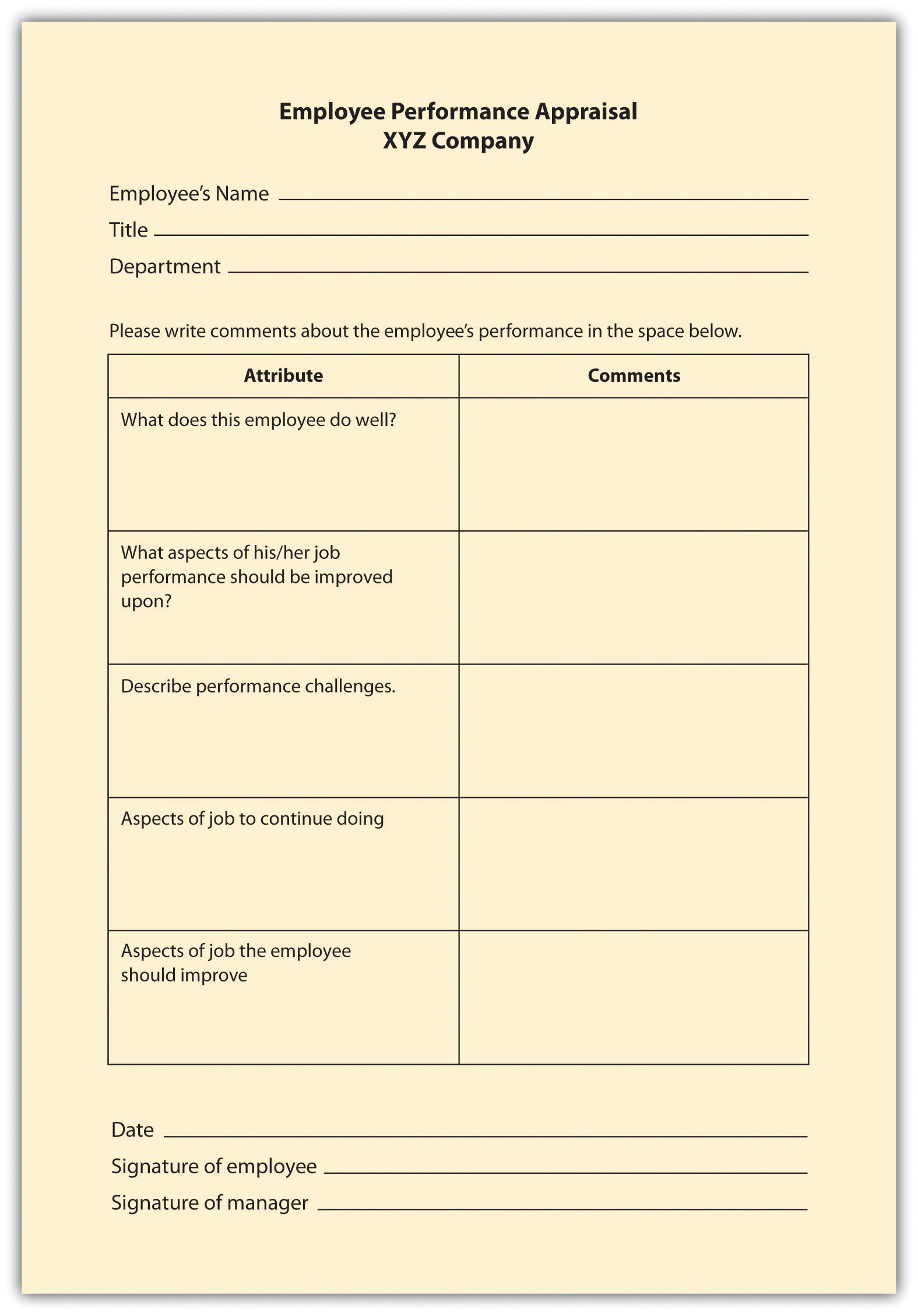
Figure 11.3 Example of Checklist Scale
Critical Incident Appraisals
This method of appraisal, while more time-consuming for the manager, can be effective at providing specific examples of behavior. With a critical incident appraisal , the manager records examples of the employee’s effective and ineffective behavior during the time period between evaluations, which is in the behavioral category. When it is time for the employee to be reviewed, the manager will pull out this file and formally record the incidents that occurred over the time period. The disadvantage of this method is the tendency to record only negative incidents instead of postive ones. However, this method can work well if the manager has the proper training to record incidents (perhaps by keeping a weekly diary) in a fair manner. This approach can also work well when specific jobs vary greatly from week to week, unlike, for example, a factory worker who routinely performs the same weekly tasks.
Work Standards Approach
For certain jobs in which productivity is most important, a work standards approach could be the more effective way of evaluating employees. With this results-focused approach, a minimum level is set and the employee’s performance evaluation is based on this level. For example, if a sales person does not meet a quota of $1 million, this would be recorded as nonperforming. The downside is that this method does not allow for reasonable deviations. For example, if the quota isn’t made, perhaps the employee just had a bad month but normally performs well. This approach works best in long-term situations, in which a reasonable measure of performance can be over a certain period of time. This method is also used in manufacuring situations where production is extremely important. For example, in an automotive assembly line, the focus is on how many cars are built in a specified period, and therefore, employee performance is measured this way, too. Since this approach is centered on production, it doesn’t allow for rating of other factors, such as ability to work on a team or communication skills, which can be an important part of the job, too.
Ranking Methods
In a ranking method system (also called stack ranking), employees in a particular department are ranked based on their value to the manager or supervisor. This system is a comparative method for performance evaluations.The manager will have a list of all employees and will first choose the most valuable employee and put that name at the top. Then he or she will choose the least valuable employee and put that name at the bottom of the list. With the remaining employees, this process would be repeated. Obviously, there is room for bias with this method, and it may not work well in a larger organization, where managers may not interact with each employee on a day-to-day basis.
To make this type of evaluation most valuable (and legal), each supervisor should use the same criteria to rank each individual. Otherwise, if criteria are not clearly developed, validity and halo effects could be present. The Roper v. Exxon Corp case illustrates the need for clear guidelines when using a ranking system. At Exxon, the legal department attorneys were annually evaluated and then ranked based on input from attorneys, supervisors, and clients. Based on the feedback, each attorney for Exxon was ranked based on their relative contribution and performance. Each attorney was given a group percentile rank (i.e., 99 percent was the best-performing attorney). When Roper was in the bottom 10 percent for three years and was informed of his separation with the company, he filed an age discrimination lawsuit. The courts found no correlation between age and the lowest-ranking individuals, and because Exxon had a set of established ranking criteria, they won the case (Grote, 2005).
Another consideration is the effect on employee morale should the rankings be made public. If they are not made public, morale issues may still exist, as the perception might be that management has “secret” documents.
Fortune 500 Focus
Critics have long said that a forced ranking system can be detrimental to morale; it focuses too much on individual performance as opposed to team performance. Some say a forced ranking system promotes too much competition in the workplace. However, many Fortune 500 companies use this system and have found it works for their culture. General Electric (GE) used perhaps one of the most well-known forced ranking systems. In this system, every year managers placed their employees into one of three categories: “A” employees are the top 20 percent, “B” employees are the middle 70 percent, and “C” performers are the bottom 10 percent. In GE’s system, the bottom 10 percent are usually either let go or put on a performance plan. The top 20 percent are given more responsibility and perhaps even promoted. However, even GE has reinvented this stringent forced ranking system. In 2006, it changed the system to remove references to the 20/70/10 split, and GE now presents the curve as a guideline. This gives more freedom for managers to distribute employees in a less stringent manner 1 .
The advantages of a forced ranking system include that it creates a high-performance work culture and establishes well-defined consequences for not meeting performance standards. In recent research, a forced ranking system seems to correlate well with return on investment to shareholders. For example, the study (Sprenkel, 2011) shows that companies who use individual criteria (as opposed to overall performance) to measure performance outperform those who measure performance based on overall company success. To make a ranking system work, it is key to ensure managers have a firm grasp on the criteria on which employees will be ranked. Companies using forced rankings without set criteria open themselves to lawsuits, because it would appear the rankings happen based on favoritism rather than quantifiable performance data. For example, Ford in the past used forced ranking systems but eliminated the system after settling class action lawsuits that claimed discrimination (Lowery, 2011). Conoco also has settled lawsuits over its forced ranking systems, as domestic employees claimed the system favored foreign workers (Lowery, 2011). To avoid these issues, the best way to develop and maintain a forced ranking system is to provide each employee with specific and measurable objectives, and also provide management training so the system is executed in a fair, quantifiable manner.
In a forced distribution system, like the one used by GE, employees are ranked in groups based on high performers, average performers, and nonperformers. The trouble with this system is that it does not consider that all employees could be in the top two categories, high or average performers, and requires that some employees be put in the nonperforming category.
In a paired comparison system, the manager must compare every employee with every other employee within the department or work group. Each employee is compared with another, and out of the two, the higher performer is given a score of 1. Once all the pairs are compared, the scores are added. This method takes a lot of time and, again, must have specific criteria attached to it when comparing employees.
Human Resource Recall
How can you make sure the performance appraisal ties into a specific job description?
Management by Objectives (MBO)
Management by objectives (MBOs) is a concept developed by Peter Drucker in his 1954 book The Practice of Management (Drucker, 2006). This method is results oriented and similar to the work standards approach, with a few differences. First, the manager and employee sit down together and develop objectives for the time period. Then when it is time for the performance evaluation, the manager and employee sit down to review the goals that were set and determine whether they were met. The advantage of this is the open communication between the manager and the employee. The employee also has “buy-in” since he or she helped set the goals, and the evaluation can be used as a method for further skill development. This method is best applied for positions that are not routine and require a higher level of thinking to perform the job. To be efficient at MBOs, the managers and employee should be able to write strong objectives. To write objectives, they should be SMART (Doran, 1981):
- Specific. There should be one key result for each MBO. What is the result that should be achieved?
- Measurable. At the end of the time period, it should be clear if the goal was met or not. Usually a number can be attached to an objective to make it measurable, for example “sell $1,000,000 of new business in the third quarter.”
- Attainable. The objective should not be impossible to attain. It should be challenging, but not impossible.
- Result oriented. The objective should be tied to the company’s mission and values. Once the objective is made, it should make a difference in the organization as a whole.
- Time limited. The objective should have a reasonable time to be accomplished, but not too much time.
Setting MBOs with Employees
(click to see video)
An example of how to work with an employee to set MBOs.
To make MBOs an effective performance evaluation tool, it is a good idea to train managers and determine which job positions could benefit most from this type of method. You may find that for some more routine positions, such as administrative assistants, another method could work better.
Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scale (BARS)
A BARS method first determines the main performance dimensions of the job, for example, interpersonal relationships. Then the tool utilizes narrative information, such as from a critical incidents file, and assigns quantified ranks to each expected behavior. In this system, there is a specific narrative outlining what exemplifies a “good” and “poor” behavior for each category. The advantage of this type of system is that it focuses on the desired behaviors that are important to complete a task or perform a specific job. This method combines a graphic rating scale with a critical incidents system. The US Army Research Institute (Phillips, et. al., 2006) developed a BARS scale to measure the abilities of tactical thinking skills for combat leaders. Figure 11.4 “Example of BARS” provides an example of how the Army measures these skills.
Figure 11.4 Example of BARS
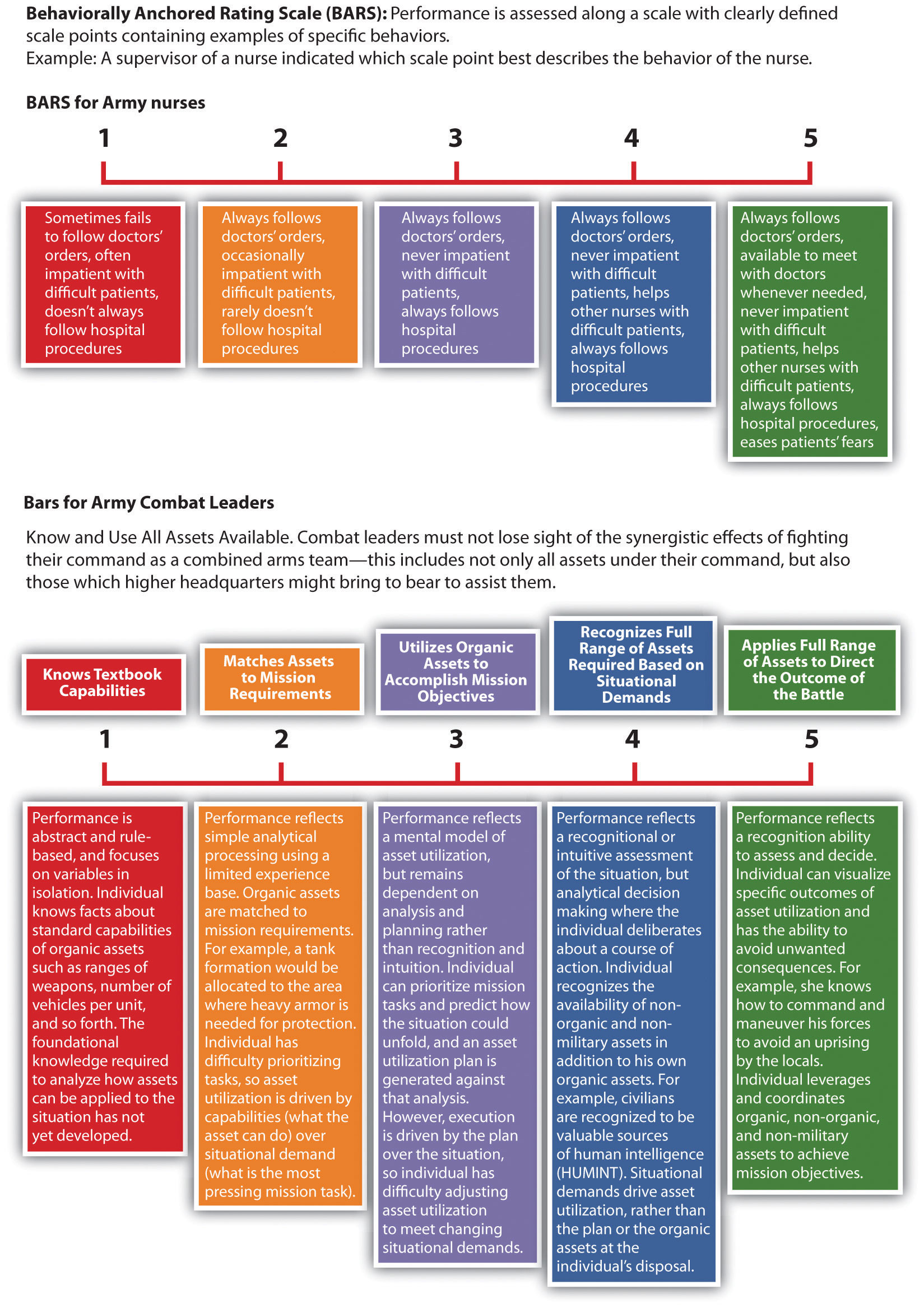
Figure 11.5 More Examples of Performance Appraisal Types
How Would You Handle This?
Playing Favorites
You were just promoted to manager of a high-end retail store. As you are sorting through your responsibilities, you receive an e-mail from HR outlining the process for performance evaluations. You are also notified that you must give two performance evaluations within the next two weeks. This concerns you, because you don’t know any of the employees and their abilities yet. You aren’t sure if you should base their performance on what you see in a short time period or if you should ask other employees for their thoughts on their peers’ performance. As you go through the files on the computer, you find a critical incident file left from the previous manager, and you think this might help. As you look through it, it is obvious the past manager had “favorite” employees and you aren’t sure if you should base the evaluations on this information. How would you handle this?
Table 11.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Performance Appraisal Method
| Type of Performance Appraisal Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Graphic Rating Scale | Inexpensive to develop | Subjectivity |
| Easily understood by employees and managers | Can be difficult to use in making compensation and promotion decisions | |
| Essay | Can easily provide feedback on the positive abilities of the employee | Subjectivity |
| Writing ability of reviewer impacts validity | ||
| Time consuming (if not combined with other methods) | ||
| Checklist scale | Measurable traits can point out specific behavioral expectations | Does not allow for detailed answers or explanations (unless combined with another method) |
| Critical Incidents | Provides specific examples | Tendency to report negative incidents |
| Time consuming for manager | ||
| Work Standards Approach | Ability to measure specific components of the job | Does not allow for deviations |
| Ranking | Can create a high-performance work culture | Possible bias |
| Validity depends on the amount of interaction between employees and manager | ||
| Can negatively affect teamwork | ||
| MBOs | Open communication | Many only work for some types of job titles |
| Employee may have more “buy-in” | ||
| BARS | Focus is on desired behaviors | Time consuming to set up |
| Scale is for each specific job | ||
| Desired behaviors are clearly outlined | ||
| No one performance appraisal is best, so most companies use a variety of methods to ensure the best results. | ||
Key Takeaways
- When developing performance appraisal criteria, it is important to remember the criteria should be job specific and industry specific.
- The performance appraisal criteria should be based on the job specifications of each specific job. General performance criteria are not an effective way to evaluate an employee.
- The rating is the scale that will be used to evaluate each criteria item. There are a number of different rating methods, including scales of 1–5, yes or no questions, and essay.
- In a graphic rating performance evaluation, employees are rated on certain desirable attributes. A variety of rating scales can be used with this method. The disadvantage is possible subjectivity.
- An essay performance evaluation will ask the manager to provide commentary on specific aspects of the employee’s job performance.
- A checklist utilizes a yes or no rating selection, and the criteria are focused on components of the employee’s job.
- Some managers keep a critical incidents file . These incidents serve as specific examples to be written about in a performance appraisal. The downside is the tendency to record only negative incidents and the time it can take to record this.
- The work standards performance appraisal approach looks at minimum standards of productivity and rates the employee performance based on minimum expectations. This method is often used for sales forces or manufacturing settings where productivity is an important aspect.
- In a ranking performance evaluation system, the manager ranks each employee from most valuable to least valuable. This can create morale issues within the workplace.
- An MBO or management by objectives system is where the manager and employee sit down together, determine objectives, then after a period of time, the manager assesses whether those objectives have been met. This can create great development opportunities for the employee and a good working relationship between the employee and manager.
- An MBO’s objectives should be SMART: specific, measurable, attainable, results oriented, and time limited.
- A BARS approach uses a rating scale but provides specific narratives on what constitutes good or poor performance.
Review each of the appraisal methods and discuss which one you might use for the following types of jobs, and discuss your choices.
- Administrative Assistant
- Chief Executive Officer
- Human Resource Manager
- Retail Store Assistant Manager
1 “The Struggle to Measure Performance,” BusinessWeek , January 9, 2006, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/content/06_02/b3966060.htm .
Doran, G. T., “There’s a S.M.A.R.T. Way to Write Management’s Goals and Objectives,” Management Review 70, no. 11 (1981): 35.
Drucker, P., The Practice of Management (New York: Harper, 2006).
Grote, R., Forced Ranking: Making Performance Management Work (Boston: Harvard Business School Press, 2005).
Lowery, M., “Forcing the Issue,” Human Resource Executive Online , n.d., accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.hrexecutive.com/HRE/story.jsp?storyId=4222111&query=ranks .
Phillips, J., Jennifer Shafter, Karol Ross, Donald Cox, and Scott Shadrick, Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scales for the Assessment of Tactical Thinking Mental Models (Research Report 1854), June 2006, US Army Research Institute for the Behavioral and Social Sciences, accessed August 15, 2011, http://www.hqda.army.mil/ari/pdf/RR1854.pdf .
Sprenkel, L., “Forced Ranking: A Good Thing for Business?” Workforce Management, n.d., accessed August 15, 2011, http://homepages.uwp.edu/crooker/790-iep-pm/Articles/meth-fd-workforce.pdf .
Human Resource Management Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

The Essay Method of Performance Appraisal
Master the Essay Method of Performance Appraisal! Explore its strengths, weaknesses, best practices, and discover how to craft effective essays for employee development.
In the ever-evolving landscape of performance management, selecting the right appraisal method is crucial for fostering employee growth and organizational success. among the various approaches, the essay method stands out for its flexibility and narrative-based evaluation. this comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the essay method, equipping managers and hr professionals with the knowledge to leverage its strengths and navigate its potential pitfalls., understanding the essay method.
The Essay Method, also known as the Free-Form Method, empowers supervisors to create a written evaluation of an employee's performance. This evaluation takes the form of a narrative essay, detailing the employee's strengths, weaknesses, accomplishments, and areas for improvement. Unlike structured methods with predetermined ratings, the Essay Method allows for a more nuanced and qualitative assessment.
Key Features of the Essay Method:
- Flexibility: The Essay Method isn't constrained by rigid formats or rating scales. It allows appraisers to tailor the evaluation to the specific role, accomplishments, and development needs of the employee.
- Narrative format: The essay format fosters a story-telling approach, enabling appraisers to provide context and specific examples to support their observations.
- Focus on strengths and weaknesses: The essay delves into both the employee's strengths, which contribute positively to performance, and identifies areas where improvement is necessary.
- Development-oriented: The Essay Method encourages a forward-looking perspective by incorporating suggestions for professional development and goal setting.
Advantages of the Essay Method
The Essay Method offers several benefits for both managers and employees:
- Rich and detailed feedback: The essay format allows for in-depth descriptions of an employee's performance, providing valuable insights beyond numerical scores.
- Customization: The Essay Method can be easily adapted to various job roles and departmental needs, ensuring a more relevant evaluation.
- Open communication: The narrative format fosters open communication between managers and employees, allowing for a two-way dialogue about performance and development.
- Identification of potential: The essay can go beyond immediate performance to identify an employee's potential for future growth and leadership roles.
Potential Challenges of the Essay Method
While the Essay Method offers distinct advantages, it also presents certain challenges:
- Subjectivity: The absence of standardized ratings can lead to subjectivity in evaluations. Mitigating this risk requires clear performance expectations and training for appraisers.
- Time-consuming: Crafting a well-written essay can be time-consuming for busy managers. Utilizing templates and focusing on key points can streamline the process.
- Inconsistent evaluations: Without a standardized format, evaluations might lack consistency across different managers. Training, performance standards, and peer review can help maintain consistency.
- Bias: Unconscious bias can creep into the appraisal process. Managers need to be aware of their biases and strive for objectivity in their evaluations.
Best Practices for Using the Essay Method
To maximize the effectiveness of the Essay Method, consider these best practices:
- Establish Clear Performance Standards: Define clear and measurable performance expectations for each role before conducting the evaluation. This provides a framework for the essay and ensures alignment with organizational goals.
- Focus on Specific Examples: Back up observations with concrete examples of the employee's behavior, achievements, and areas for improvement.
- Maintain Objectivity: Strive for a neutral and objective tone, avoiding subjective opinions and focusing on observable facts.
- Maintain a Balance: Present a balanced picture of the employee's performance, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and development opportunities.
- Set SMART Goals: Establish Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound goals for the employee's development based on the evaluation.
- Facilitate Open Dialogue: Schedule a meeting with the employee to discuss the evaluation, allowing for open communication and questions.
- Utilize Templates: Develop templates or outlines to guide the essay writing process and ensure consistency across evaluations.
- Training for Appraisers: Provide training for managers and supervisors on the Essay Method, including best practices for writing effective essays and minimizing bias.
Additional Tips:
- Maintain a professional tone throughout the essay.
- Use clear and concise language, avoiding jargon and technical terms.
- Proofread the essay carefully before finalizing it.
By following this structure and incorporating the best practices outlined earlier, you can craft an effective performance essay that provides valuable feedback and fosters employee development. Remember, the Essay Method, when used thoughtfully, can be a powerful tool for fostering open communication, setting clear expectations, and ultimately, driving employee and organizational success.
8 performance appraisal methods you should be aware of
Performance Reviews
Performance appraisals form an essential part of the HR department as they provide important and useful information for the assessment of employee’s performance, skill, knowledge, and overall ability. These appraisals are not only used to eliminate behavior and productivity issues, but also to motivate employees to contribute more. There are many modern performance appraisal methods that organisations can implement depending on their preference: most have their specific advantages as well as limitations. Let us have a look at some of them in more detail.
What are the different performance appraisal methods?
Graphic Rating scale:
A graphic rating scale lists the traits each employee should have and rates workers on a numbered scale for each trait. The scores are meant to separate employees into tiers of performers, which can play a role in determining promotions and salary adjustments. The method is easy to understand and quite user friendly. It allows behaviors to be quantified making appraisal systems much easier.
What are the methods of performance evaluation in Graphic rating scale?
However, the scale has disadvantages that make it difficult to use as an effective management tool. Even with intense training, some modern performance appraisal methods will be too strict. Some will be too lenient, and others may find it hard to screen out their personal agendas. Although it is good at identifying the best and poorest of employees, it does not help while differentiating between the average employees.
Analyse performance of employees working on Project A from April to June 2017

Essay Performance Appraisal method:
Essay Appraisal is a traditional form of Appraisal also known as “Free Form method.” It involves a description of the employee’s performance by his superior which needs to be based on facts and often includes examples to support the information. Under this method, the rater is asked to express the strengths and weaknesses of the employee’s performance.
What are the techniques of performance appraisal in the Essay Performance Appraisal method?
This technique is normally used with a combination of the graphic rating scale in one of the modern methods variants, because the rater or feedback giver can present the scale in more detail by also giving an explanation for his rating. While preparing the essay on the employee, the rater also needs to consider specific job knowledge, understanding of the company’s policies and objectives, relations with peers, ability to plan and organize, attitude and perception of employees in general.
The Essay performance appraisal methods are non-quantitative and highly subjective. While it provides a good deal of information about the employee, it takes a lot of time of the appraiser which is not always feasible.
| 1 | Does the employee pay attention to detail? | |
| 2 | Does the employee work well with the team? | |
| 3 | Is the employee capable of taking initiative? |
Checklist Scale performance appraisal method:
Under this method, a checklist of statements of traits of the employee in the form of Yes or No based questions is prepared. If the person giving the feedback believes strongly that the employee possesses a particular listed trait, he checks the item; otherwise, he leaves the item blank. Here the rater only does the reporting or checking and the HR department does the actual evaluation after observing details over a period of time – and it does not allow detailed analysis of the overall performance.
| Gives complete attention to detail | ||
| Has complete knowledge of the product | ||
| Works well with the team | ||
| Takes initiative | ||
| Has creative approach to solving problems |
Critical Incidents method:
In this method, managers prepare lists of statements of very effective and ineffective behavior of an employee. These critical incidents or events represent the outstanding or poor behavior of employees on the job. The manager maintains logs on each employee, whereby he periodically records critical incidents of the workers behavior.
What is a performance appraisal in Critical Incidents method
At the end of the rating period, these recorded critical incidents are used in the evaluation of the workers’ performance. It provides an objective basis for feedback and conducts a thorough discussion of an employee’s performance appraisal process – hence also known as cost accounting method.
Although this method avoids recency bias , there is a tendency for manager and employee both to focus more on the negative incidents than otherwise.
Work Standards performance appraisal method:
In this technique, management establishes the goals openly and sets targets against realistic output standards. These standards are incorporated into the organizational performance appraisal system . Thus each employee has a clear understanding of their duties and knows well what is expected of them. Performance appraisal and interview comments are related to these duties. This makes the appraisal process objective and more accurate. It works best in long-term situations for human resources teams, as it considers performances during that duration and eliminates time consuming processes.
However, it is difficult to compare individual ratings because standards for work may differ from job to job and from employee to employee. It does not allow for reasonable deviations.
Ranking Appraisal:
Here the manager compares an employee to other similar employees, rather than to a standard measurement predefined for employee productivity. The employees are ranked from the highest to the lowest or from the best to the worst. The problem here is that it does not tell how much better or worse one is than another. Also it cannot be used for a large number of employees, or feedback.
Attention to detail
| Poor | Average | Excellent |
Management by objectives (MBO) methods of performance review are results-oriented. That is, they seek to measure employee performance by examining the extent to which predetermined work objectives have been met. Usually the objectives are established jointly by the supervisor and subordinate. Once an objective is agreed, the employee is usually expected to self-audit; that is, to identify the skills needed to achieve the objective. Typically they do not rely on others to locate and specify their strengths and weaknesses. They are expected to monitor their own development and progress, and drive their future performance. The MBO method of performance review concentrates on actual outcomes.
What makes MBOs efficient is the ability to set SMART Goals i.e. set goals that are Specific, Measurable, Actionable, Relevant and Time-bound.
The problem of judgmental performance evaluation inherent in the traditional methods of employee performance appraisal process led to some organisations to go for objective evaluation by developing a technique known as “Behaviorally Anchored Rating Scale (BARS)” around the 1960s. This performance appraisal method is considered better than the traditional ones because it provides advantages like a more accurate gauge, clearer standards, 360 degree feedback, and consistency in evaluation.
The BARS method is designed to bring the benefits of both qualitative and quantitative data to the employee appraisal process. It compares an individual employee’s performance against specific examples of behaviour that are anchored to numerical ratings.
Although even this method has its limitations as it is often accused of being subject to unreliability and leniency error.
Performance appraisal process is already being considered a necessary evil . Thus companies need to be careful while selecting out of these appraisal methods and accept feedback on improving the process. The method should be able to provide value to the company starting from the review period as well as the employees and managers.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Blogs
Performance Reviews , Work Culture Mar 18, 2016
Recognition, the most powerful performance enhancer at the workplace, performance reviews may 11, 2016, 4 steps to make performance reviews insanely effective, feedback , goal setting , performance reviews jun 7, 2016, traditional vs agile performance management.
Stay Updated with latest news at UpRaise
Your email will be safe and secure in our database
Thanks for subscribing! Please check your email for further instructions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance Appraisals
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
The end of the year is quickly approaching, which typically means an evaluation of how the organization performed during the prior twelve months.
This year-end review can help an organization fine-tune its practices and work to create momentum for the next twelve months.
Often this review includes conducting performance appraisals for employees.
Why Is It Important To Conduct Performance Appraisals?
Employees, as well as managers, often question why organizations do employee performance appraisals .
Anyone who has ever been on the receiving end of a performance appraisal could argue why they perceive it to be ineffective and a complete waste of time.
Employees often feel unjustly assessed, and managers often go through a forced annual process to comply with job expectations.
This doesn’t make it easy for either party.
So what exactly is a performance appraisal?
A performance appraisal is an evaluation of an employee’s job performance over a specific period of time.
It is the equivalent of a report card on an employee and how their manager assessed their performance over the prior year.
Anyone who has worked in more than one department or at more than one organization can attest to the fact that not all performance appraisal processes are the same.
The varying systems and processes are all over the map.
Unfortunately, some are done so poorly that they are not only designed to fail but also to create a negative experience for both the manager as well as the employee.
Why do organizations do performance appraisals?
There are many varying opinions on the subject of performance appraisals and why they are done.
Some organizations do performance appraisals because they feel obligated to do them – because everyone else does.
Other organizations do performance appraisals to make sure they have a piece of paper in the employee’s file – in case they ever need to take corrective action .
However successful organizations understand the importance of incorporating performance appraisals into their performance management process and strategy.
They use this tool to encourage, engage, and develop their talent pool.
There are without a doubt some disadvantages to conducting performance appraisals, however, there are also important advantages to going through the process.
Let’s explore both the advantages and disadvantages of conducting performance appraisals.
Advantages of Performance Appraisals
Documentation : A PA provides a document of employee performance over a specific period of time. It’s a piece of paper that can be placed in an employee file. This document can be used as a resource that tells the story of an en employee and is used when there is a change in leadership.
Structure : This process creates a structure where a manager can meet and discuss performance with an employee. A structured process forces the uncomfortable conversations that often need to happen and may not without the formalization of the process.
Feedback : Employees crave feedback, and this process allows a manager the opportunity to provide the employee with feedback about their performance and discuss how well the employee g o als were accomplished. It also provides an opportunity to discuss employee development opportunities.
For instance, performance appraisals should identify areas of development for an employee so a manager can work to develop the employee for greater responsibility.
Clarify Expectations : Employees need to understand what is expected of them and the PA process allows for a manager to clarify expectations and discuss issues with their employees.
Annual Planning : It provides a structure for thinking through and planning the upcoming year and developing employee goals.
For instance, if a manager has departmental goals for the year, the performance appraisal time is a great time for developing employee goals that help a department reach its goals.
Motivation : The process should motivate employees by rewarding them with a merit increase and as part of a comprehensive compensation strategy .
For instance, employees who perform at higher levels should be rewarded with a higher percentage pay increase than employees who merely go through the motions.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisals
Creates Negative Experience : If not done right, the performance appraisal can create a negative experience for both the employee as well as the manager. Proper training on processes and techniques can help with this.
For instance, an untrained manager may fulfill the duty of conducting a performance appraisal without investing the time and thought into helping to develop an employee. Or, a manager may only focus on the negative and not reinforce positive employee behaviors.
Time-Consuming : Performance appraisals are very time-consuming and can be overwhelming to managers with many employees. I’ve known managers who were responsible for doing an annual PA on hundreds of employees.
Natural Biases : Human assessments are subject to natural biases that result in rater errors . Managers need to understand these biases to eliminate them from the process.
For instance, similar-to-me bias is one in which managers favor employees with similar personalities and work habits.
Waste of Time : The entire process can be a waste of time if not done appropriately. Think about the time investment when the end result is negative. It is time wasted on all fronts.
Stressful Workplace : Performance appraisals can create stressful work environments for both employees and managers. Proper training can help to reduce the stress involved in the process.
A Performance Management System Can Help
Finally, performance appraisals are only as good as the performance management system it operates within.
Organizations that only do performance appraisals for the sake of doing them are wasting their time.
However, organizations that incorporate performance appraisals into a comprehensive performance management system and use them to implement business goals have an advantage in accomplishing their goals and ultimately their strategic plan .
Patricia Lotich, MBA is a Certified Manager of Quality and Organizational Excellence through the American Society for Quality. She has a driving passion to help small businesses, nonprofits and churches fulfill their mission by managing their resources of - people, time and money.
Similar Posts
The 5 step process of strategic planning.
Facebook47Pin111 Strategic plans help identify what an organization is striving to achieve and maps out the necessary steps needed to be successful. It used to be that strategic plans would…
What is a Vision Statement?
Facebook0Pin2 People start businesses for a purpose. These entrepreneurs will create a product or service to meet an unmet need. Sometimes, a business owner has a passion for creating innovative…
Do You Know How To Write Business Goals?
Facebook17Pin174 Businesses need to plan to be successful. An important part of the business planning process is determining business objectives that are translated into actionable business goals. Goals should support the strategic…
3 Tips To Make Managing Employees Easier
Facebook21Pin19 Anyone who is responsible for managing others will attest to the fact that it can be one of the most challenging aspects of a supervisor’s job. However, it can…
How To Develop A Quality Management System
Facebook13Pin0 Successful organizations understand the importance of managing organizational quality. We can all provide an example of an experience with an organization with poor product or service quality. The experience…
What is Total Quality Management (TQM)?
Facebook51Pin9 The way organizations are managed not only determines the quality of their products and services – but, ultimately, their success. Businesses use a Total Quality Management approach to how…

Access to 13 certificate programs, courses and all future releases
Personal Coaching and Career Guidance
Community and live events
Resource and template library

- Graphic Rating Scale: Advantages, Limitations,...
Graphic Rating Scale: Advantages, Limitations, Examples, and Best Practices

What is a graphic rating scale in performance appraisals?

Graphic rating scale examples
- Very poor (always misses deadlines, is not punctual)
- Needs improvement (sometimes misses deadlines)
- Average (average at managing their time, neither good nor bad at time management)
- Good (is aware of deadlines and able to work to them fairly well)
- Excellent (very effective at managing their time, always meets deadlines)

- Extremely unlikely (does not work well in a team, sabotages colleagues, is difficult to work with)
- Quite unlikely (doesn’t particularly enjoy working in a group)
- Hard to say (hasn’t worked in many team situations, is neither good nor bad at working in a group)
- Quite likely (team player, enjoys working with colleagues, colleagues want to work with them)
- Extremely likely (always thrives in any team environment, exceeds expectations within a team).
Advantages of the graphic rating scale method
- Easy to understand and use
- Quantifying behaviors makes the appraisal system easier
- Inexpensive to develop
Limitations of the graphic rating scale method
- Subjectivity of different evaluators
- Different types of biases
- Difficult to understand employees’ strengths
Tips for using a graphic rating scale effectively
1. define your desired outcomes, 2. try to use questions that are as objective as possible, 3. use behavioral questions, 4. get answers to reflect the questions, 5. combine it with other appraisal methods, 6. train managers on how to use the graphic rating scale, a graphic rating scale can be a valuable tool.

Related articles

Free Workforce Planning Template (Plus 5 Practical Examples)

What is Skills Mapping? Your 11-Step Implementation Guide

CEO Succession Planning: Your 2024 Comprehensive Guide (+Free Template)
New articles.

Chief People Officer: All You Need To Know About the Role
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter, are you ready for the future of hr.
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online

- Performance Appraisal
Performance Appraisal Definition
Performance appraisal or performance review is a systematic process in which employee performance at work is evaluated in relation to the projects on which employee has worked and his contribution to the organisation. It is also known as an annual review or performance review.
Suggested Videos
It helps the managers place the right employees for the right jobs, depending on their skills. Often, employees are often curious to know about their performance details and compare it with their fellow colleagues and how they can improve upon it. So every company needs a good performance appraisal system.

(source-wisestep)
The basic purpose of performance appraisal is to identify employees worth and contribution to the company. Important factors include – attendance, efficiency, attitude, quality of work, amount of work are just a few important factors.
The physical or objective factors like attendance, amount of work, efficiency can be easily measured by the records maintained by the Human Resource Department Manager.
However, it gets a bit icky, when it comes to measuring subjective factors like attitude, behaviour, friendliness etc. But to properly evaluate an individual’s performance, appraisal of both subjective and objective factors needs to be done.
As Dale Yoder said, “Performance appraisal includes all formal procedures used to evaluate personalities and contributions and potential of group members in a working organisation. It is a continuous process to secure information necessary for making correct and objective decisions on employees.
Performance Appraisal Methods
There are various methods that are used by managers and employers to evaluate the performance of the employees, but they can be put into two categories:
- Traditional Methods
- Modern Methods

Performance Appraisal Components
(source – businesstopia)
Browse more Topics under Human Resource Management
- Features of HRM
- Importance and Limitations of HRM
- Role of Personnel Manager
- Qualities of the HR Manager
- Managerial Functions of HR Manager
- Operative Functions of HR Manager
- Recruitment Process
- Selection Procedure
- Training and Development
- Methods of Training
- Traditional Methods of Appraisal
- Modern Methods of Appraisal
- HR Forecasting
Performance Appraisal Process
- Setting performance standards
- Set up measurable goals
- Measure actual performance
- Compare with preset standards and goals
- Discuss with the employee – met the expectations, did not meet the expectations, exceeded the expectations
- Take corrective actions
- Set standards for next cycle

Advantages of Performance Appraisal
- A systematic appraisal system helps the managers to properly identify the performance of employees in a systematic manner and their areas of talent and areas where they are lacking.
- It helps the management to place the right employees for the perfect jobs depending on their skills in particular areas.
- It helps employees identify the areas in which they need to improve. The managers can also use this information to provide constructive criticism of the way employees perform their work.
- Potential employees are often given promotions on the basis of or the results of performance appraisals. People who have high ratings get promotions. They can also transfer or demote employees if they not performing up to the expectations of the managers.
- An appraisal is also useful in determining the effectiveness and results of training programmes. It can show managers how much employees have improved after taking the training programmes. This will give managers data on how to change and evolve the training programmes .
- It creates healthy competition among employees as they will try to improve their performance and score better than their colleagues.
- Managers use appraisal programmes to identify the grievances of employees and act upon them.
- Keeping extensive records of performance appraisal will give managers a very good idea of which employees have the highest growth rate and are which ones have a declining rate of performance.
Learn the Selection Process here.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal
- If the factors being used in the performance appraisal are incorrect or not relevant, the appraisal will fail to provide any useful or effective data.
- Sometimes, equal weightage is not given to important factors when performing an appraisal.
- Some objective factors are very vague and difficult to gauge like attitude and initiative. There is no scientific method to measure these factors.
- Managers are sometimes not qualified enough to correctly assess the employees and their abilities. Thus, these mistakes can be very detrimental to the growth of the company.
Solved Question on Performance Appraisal
List three ways performance appraisal helps an organisation.
Answer – Three ways performance appraisal helps an organisation mention as follows:
- A systematic performance appraisal system helps the managers to properly identify the performance of employees in a systematic manner and their areas of talent and areas where they are lacking.
- Performance appraisal helps employees identify the areas in which they need to improve. Furthermore, the managers can also use this information to provide constructive criticism of the way employees perform their work.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Human Resource Management
- Human Resource Forecasting
- Selection Process
2 responses to “Performance Appraisal”
I liked that you said that one thing to consider when you own a business is to conduct performance appraisals. I would imagine that this would help you to evaluate which areas of the business need improving. I would be sure to have performance appraisals in order to help my business to become more successful.
We at 9 links believe for performance appraisal to be done objectively…they should be assessed using psychometric assessments.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

12 Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance Appraisals
Managers, as well as, employees often wonder why organizations do performance appraisals. Anyone who has been given or received performance appraisal could possibly say that it is a complete waste of time as it is ineffective. So what is performance appraisal exactly? Performance appraisal is the evaluation done on employees in regard to their job performances over a certain period of time. It is like a report card showing how one has been performing during the past year. So, is it necessary? Below are advantages and disadvantages of performance appraisal
Advantages Of Performance Appraisals
1. Improves Performance. Performance appraisals major focus on improving employees performance as it analyses and evaluates the opportunity factors like social process and technology.
2. Employee Development. Performance appraisal helps determine who is in need of more training as it gives information regarding the strengths and potentials as well as weaknesses of the employees.
3. Corrects Deficiencies. Performance appraisal detects employee deficiency and suggests on corrective measures to be taken.
4. Career Growth. Appraisal serves as a tool for the employees’ career planning and development as it assists in preparing each employee’s SWOT analysis.
5. Promotion. Appraisals help the management determine which employee is to be promoted, transferred or rewarded.
6. Motivation. Appraisals motivate employees to work harder.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal
1. Prone To Biasness. Some raters may rate one depending on the general impression one gives. For instance, one might be rated high on all criteria even though he/she just performed well in a single area. The rater’s biases and prejudices also affect the process. These cases are seen when a one gets underrated because of sex, religion, favoritism, appearance, and race.
2. Contrast Error. Performance appraisal is always based specific standards, however, when one gets rated without taking the standards into account a contrast error occurs. This also can occur if the rater looks at an employee’s current performance based on the past performance.
3. Generalization Tendency Error. This occurs when a rater rates everyone within a narrow range because he/she thinks that the employees are all on the same level averagely.
4. Severity Or Leniency. Appraisals demand that an evaluator should objectively draw a conclusion regarding an employee’s performance.
5. Sampling Error. This occurs when a rater uses a small portion of an employee’s work to draw a conclusion.
6. Regency And Primary Errors. Employee behavior at the start of the appraisal period and at the end can affect the process a time. For instance, a salesperson’s performance varies with season, at times it can be low and a time high.
Overall, appraisals are good only if the management operating them stick with their standards otherwise it will pointless.
Your Article Library
Performance appraisal methods: traditional and modern methods (with example).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Performance Appraisal Methods: Traditional and Modern Methods!
Each method of performance appraisal has its strengths and weaknesses may be suitable for one organisation and non-suitable for another one. As such, there is no single appraisal method accepted and used by all organisations to measure their employees’ performance.
All the methods of appraisal devised so far have been classified differently by different authors. While DeCenzo and Robbins’^ have classified appraisal methods into three categories: absolute methods, relative methods and objective methods; Aswathappa has classified these into two categories past-oriented and future-oriented.
Michael R Carrell et. al. have classified all appraisal methods into as many as six categories: rating scales, comparative methods, critical incidents, 6ssay, MBO and combination methods. Rock and Levis” have classified the methods into two broad categories: narrow interpretation and broad interpretation. Beatty and Schneier have categorised various methods of appraisal into four groups: comparative methods, absolute methods, goal setting, and direct indices.
A more widely used classification of appraisal methods into two categories, viz., traditional methods and modem methods, is given by Strauss and Sayles”. While traditional methods lay emphasis on the rating of the individual’s personality traits, such as initiative, dependability, drive creativity, integrity, intelligence, leadership potential, etc.; the modem methods, on the other hand, place more emphasis on the evaluation of work results, i.e., job achievements than the personal traits! Modem methods tend to be more objective and worthwhile. The various methods included in each of the two categories are listed in Table 28.4.

In the discussion that follows, each method under both categories will be described briefly.
Traditional Methods :
Ranking method:.
It is the oldest and simplest formal systematic method of performance appraisal in which employee is compared with all others for the purpose of placing order of worth. The employees are ranked from the highest to the lowest or from the best to the worst.
In doing this the employee who is the highest on the characteristic being measured and also the one who is L lowest, are indicated. Then, the next highest and the next lowest between next highest and lowest until all the employees to be rated have been ranked. Thus, if there are ten employees to be appraised, there will be ten ranks from 1 to 10.
However, the greatest limitations of this appraisal method are that:
(i) It does not tell that how much better or worse one is than another,
(ii) The task of ranking individuals is difficult when a large number of employees are rated, and
(iii) It is very difficult to compare one individual with others having varying behavioural traits. To remedy these defects, the paired comparison method of performance appraisal has been evolved.
Paired Comparison:
In this method, each employee is compared with other employees on one- on one basis, usually based on one trait only. The rater is provided with a bunch of slips each coining pair of names, the rater puts a tick mark against the employee whom he insiders the better of the two. The number of times this employee is compared as better with others determines his or her final ranking.
The number of possible pairs for a given number of employees is ascertained by the following formula:
Where N = the total number of employees to be evaluated. Let this be exemplified with an imaginary example.
If the following five teachers have to be evaluated by the Vice Chanceller of a University:
(K), Mohapatra (M Raul (R), Venkat (V), and Barman (B), the above formula gives 5 (5 -1) / 2 or 10 pairs.

This method is good for measuring various job behaviours of an employee. However, it is also subjected to rater’s bias while rating employee’s behaviour at job. Occurrence of ambiguity in design- mg the graphic scale results in bias in appraising employee’s performance.
Essay Method:
Essay method is the simplest one among various appraisal methods available. In this method, the rater writes a narrative description on an employee’s strengths, weaknesses, past performance, potential and suggestions for improvement. Its positive point is that it is simple in use. It does not require complex formats and extensive/specific training to complete it.
However, essay method, like other methods, is not free from drawbacks. In the absence of any prescribed structure, the essays are likely to vary widely in terms of length and content. And, of course, the quality of appraisal depends more upon rater’s writing skill than the appraiser’s actual level of performance.
Moreover, because the essays are descriptive, the method provides only qualitative information about the employee. In the absence of quantitative data, the evaluation suffers from subjectivity problem. Nonetheless, the essay method is a good start and is beneficial also if used in conjunction with other appraisal methods.
Field Review Method:
When there is a reason to suspect rater’s biasedness or his or her rating appears to be quite higher than others, these are neutralised with the help of a review process. The review process is usually conducted by the personnel officer in the HR department.
The review process involves the following activities:
(a) Identify areas of inter-rater disagreement.
(b) Help the group arrive at a consensus.
(c) Ensure that each rater conceives of the standard similarity.
However, the process is a time-consuming one. The supervisors generally resent what they consider the staff interference. Hence, the method is not widely used.
Confidential Report:
It is the traditional way of appraising employees mainly in the Government Departments. Evaluation is made by the immediate boss or supervisor for giving effect to promotion and transfer. Usually a structured format is devised to collect information on employee’s strength weakness, intelligence, attitude, character, attendance, discipline, etc. report.
Modern Methods :
Management by objectives (mbo):.
Most of the traditional methods of performance appraisal are subject to the antagonistic judgments of the raters. It was to overcome this problem; Peter F. Drucker propounded a new concept, namely, management by objectives (MBO) way back in 1954 in his book.
The Practice of management. The concept of MBO as was conceived by Drucker, can be described as a “process whereby the superior and subordinate managers of an organization jointly identify its common goals, define each individual’s major areas of responsibility in terms of results expected of him and use these measures as guides for operating the unit and assessing the contribution of each its members”.
In other words, stripped to its essentials, MBO requires the manager to goals with each employee and then periodically discuss his or her progress toward these goals.
In fact, MBO is not only a method of performance evaluation. It is viewed by the Practicing managers and pedagogues as a philosophy of managerial practice because .t .s a method by wh.ch managers and subordinates plan, organise, communicate, control and debate.
An MBO programme consists of four main steps: goal setting, performance standard, comparison, and periodic review. In goal-setting, goals are set which each individual, s to attain. The superior and subordinate jointly establish these goals. The goals refer to the desired outcome to be achieved by each individual employee.
In performance standards, the standards are set for the employees as per the previously arranged time period. When the employees start performing their jobs, they come to know what is to be done, what has been done, and what remains to be done.
In the third step the actual level of goals attained are compared with the goals agreed upon. This enables the evaluator to find out the reasons variation between the actual and standard performance of the employees. Such a comparison helps devise training needs for increasing employees’ performance it can also explore the conditions having their bearings on employees’ performance but over which the employees have no control.
Finally, in the periodic review step, corrective measure is initiated when actual performance deviates from the slandered established in the first step-goal-setting stage. Consistent with the MBO philosophy periodic progress reviews are conducted in a constructive rather than punitive manner.
The purpose of conducting reviews is not to degrade the performer but to aid in his/her future performance. From a motivational point of view, this would be representative of McGregor’s theories.
Figure 28.4 present the MBO method of performance appraisal presently used by an engineering giant i.e., Larsen and Turbro Limited.

Limitation of MBO:
MBO is not a panacea, cure for all organisational problems.
As with other methods, it also suffers from some limitations as catalogued below:
(i) Setting Un-measurable Objectives:
One of the problems MBO suffers from is unclear and un-measurable objectives set for attainment. An objective such as “will do a better job of training” is useless as it is un-measurable. Instead, “well have four subordinates promoted during the year” is a clear and measurable objective.
(ii) Time-consuming:
The activities involved in an MBO programme such as setting goals, measuring progress, and providing feedback can take a great deal of time.
(iii) Tug of War:
Setting objectives with the subordinates sometimes turns into a tug of war in the sense that the manager pushes for higher quotas and the subordinates push for lower ones. As such, goals so set are likely to be unrealistic.
(iv) Lack of Trust:
MBO is likely to be ineffective in an environment where management has little trust in its employees. Or say, management makes decisions autocratically and relies heavily on external controls.
Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS):
The problem of judgmental performance evaluation inherent in the traditional methods of performance evaluation led to some organisations to go for objective evaluation by developing a technique known as “Behaviourally Anchored Rating Scales (BARS)” around 1960s. BARS are descriptions of various degrees of behaviour with regard to a specific performance dimension.
It combines the benefits of narratives, critical incidents, and quantified ratings by anchoring a quantified scale with specific behavioural examples of good or poor performance. The proponents of BARS claim that it offers better and more equitable appraisals than do the other techniques of performance appraisal we discussed so far.
Developing BARS typically involves five steps:
1. Generating Critical Incidents:
Critical incidents (or say, behaviours) are those which are essential for the performance of the job effectively Persons who are knowledgeable of the job in question (jobholders and/or supervisors) are asked to describe specific critical incidents of effective and ineffective performance. These critical incidents may be described in a few short sentences or phrases using the terminology.
2. Developing Performance Dimensions:
The critical incidents are then clustered into a smaller set of performance dimensions, usually five to ten. Each cluster, or say, dimension is then defined.
3. Reallocating Incidents:
Various critical incidents are reallocated dimensions by another group of people who also know the job in question. Various critical incidents so reallocated to original dimensions are clustered into various categories, with each cluster showing similar critical incidents. Those critical incidents are retained which meet 50 to 80% of agreement with the cluster as classified in step 2.
4. Scaling Incidents:
The same second group as in step 3 rates the behaviour described in each incident in terms of effectiveness or ineffectiveness on the appropriate dimension by using seven to nine points scale. Then, average effectiveness ratings for each incident are determined to decide which incidents will be included in the final anchored scales.
5. Developing Final BARS Instrument:
A subset of the incidents (usually six or seven per cluster) is used as a behavioural anchor for the final performance dimensions. Finally, a BARS instrument with vertical scales is drawn to be used for performance appraisal, as in Figure 27-5.
How BARS is developed can be exemplified with an example of grocery checkout clerks working in a large grocery chain.
A number of critical incidents involved in checking out of grocery can be clustered into seven performance dimensions:
1. Knowledge and Judgment
2. Conscientiousness
3. Skill in Human Relations
4. Skill in Operation of Register
5. Skill in Bagging
6. Organisational Ability of Check stand Work
7. Skill in Monetary Transactions
8. Observational Ability
Now, a BARS for one of these performance dimensions, namely, “knowledge and judgment” can be developed, as in Figure 28-5. Notice how the typical BARS is behaviourally anchored with specific critical incidents.
BARS method of performance appraisal is considered better than the traditional ones because it provides advantages like a more accurate gauge, clearer standards, better feedback, and consistency in evaluation. However, BARS is not free from limitations.
The research on BARS indicates that it too suffers from distortions inherent in most rating scales. The research study concluded that “it is clear that research on BARS to date does not support the high promise regarding scale independence In short, while BARS may outperform conventional rating techniques, it is clear that they are not a panacea for obtaining high interrater reliability”
Assessment Centres:
The introduction of the concept of assessment centres as a method of performance method is traced back in 1930s in the Germany used to appraise its army officers. The concept gradually spread to the US and the UK in 1940s and to the Britain in 1960s.
The concept, then, traversed from the army to business arena during 1960s. The concept of assessment centre is, of course, of a recent origin in India. In India, Crompton Greaves, Eicher, Hindustan Lever and Modi Xerox have adopted this technique of performance evaluation.
In business field, assessment centres are mainly used for evaluating executive or supervisory potential. By definition, an assessment centre is a central location where managers come together to participate in well-designed simulated exercises. They are assessed by senior managers supplemented by the psychologists and the HR specialists for 2-3 days.
Assessee is asked to participate in in-basket exercises, work groups, simulations, and role playing which are essential for successful performance of actual job. Having recorded the assessee’s behaviour the raters meet to discuss their pooled information and observations and, based on it, they give their assessment about the assesee. At the end of the process, feedback in terms of strengths and weaknesses is also provided to the assesees.
The distinct advantages the assessment centres provide include more accurate evaluation, minimum biasedness, right selection and promotion of executives, and so on. Nonetheless, the technique of assessment centres is also plagued by certain limitations and problems. The technique is relatively costly and time consuming, causes suffocation to the solid performers, discourages to the poor performers (rejected), breeds unhealthy competition among the assessees, and bears adverse effects on those not selected for assessment.
360 – Degree Appraisal:
Yet another method used to appraise the employee’s performance is 360 – degree appraisal. This method was first developed and formally used by General Electric Company of USA in 1992. Then, it travelled to other countries including India. In India, companies like Reliance Industries, Wipro Corporation, Infosys Technologies, Thermax, Thomas Cook etc., have been using this method for appraising the performance of their employees. This feedback based method is generally used for ascertaining training and development requirements, rather than for pay increases.
Under 360 – degree appraisal, performance information such as employee’s skills, abilities and behaviours, is collected “all around” an employee, i.e., from his/her supervisors, subordinates, peers and even customers and clients.
In other worlds, in 360-degree feedback appraisal system, an employee is appraised by his supervisor, subordinates, peers, and customers with whom he interacts in the course of his job performance. All these appraisers provide information or feedback on an employee by completing survey questionnaires designed for this purpose.
All information so gathered is then compiled through the computerized system to prepare individualized reports. These reports are presented to me employees being rated. They then meet me appraiser—be it one’s superior, subordinates or peers—and share the information they feel as pertinent and useful for developing a self-improvement plan.
In 360 – degree feedback, performance appraisal being based on feedback “all around”, an employee is likely to be more correct and realistic. Nonetheless, like other traditional methods, this method is also subject to suffer from the subjectivity on the part of the appraiser. For example, while supervisor may penalise the employee by providing negative feedback, a peer, being influenced by ‘give and take feeling’ may give a rave review on his/her colleague.
Cost Accounting Method:
This method evaluates an employee’s performance from the monetary benefits the employee yields to his/her organisation. This is ascertained by establishing a relationship between the costs involved in retaining the employee, and the benefits an organisation derives from Him/her.
While evaluating an employee’s performance under this method, the following factors are also taken into consideration:
1. Unit wise average value of production or service.
2. Quality of product produced or service rendered.
3. Overhead cost incurred.
4. Accidents, damages, errors, spoilage, wastage caused through unusual wear and tear.
5. Human relationship with others.
6. Cost of the time supervisor spent in appraising the employee.
Related Articles:
- Top 15 Methods used for Performance Appraisal of Employees
- Performance Appraisal: Meaning, Features, Needs and Methods
Performance Appraisal
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
The Advantages & Disadvantages of the Basic Checklist Method in Performance Appraisals
by Barbara Bean-Mellinger
Published on 25 Oct 2018
Chances are everyone who has ever worked for someone else has memories of awkward performance reviews. Your manager was unprepared. You were caught off-guard by some of his comments. He was surprised you were surprised. Many different types of performance reviews have become standards designed to make reviews meaningful for both managers and employees. The basic checklist appraisal method is one of the most popular because everything you need is there in black and white. What could go wrong with a checklist, right?
Functions of Effective Performance Appraisals
Since they are so awkward, why are performance appraisals done? Many employees are convinced their purpose is to justify a paltry raise. If you're a manager, you know one reason for appraisals is to put inferior workers on notice for areas in need of improvement. While you hope they will improve, you are also setting the groundwork of proof in case you need to terminate their employment in the future.
Effective performance appraisals, however, can serve better purposes. They can be an excellent means for providing feedback for the employee about his performance of job tasks, and for the manager as to her effectiveness and how her employees perceive her management style. Reviews can separate skills an employee has now and skills still emerging, note areas where extra training would be helpful and set goals to accomplish by his next performance appraisal. The most effective evaluations are a checkpoint for both the manager and the employee, of where things stand now and where to go from here.
The Checklist Appraisal Method
The checklist appraisal method also goes by similar names, such as the behavioral checklist or checklist scale. The key word is "checklist" because the appraisal form is, literally, a checklist. Instead of an essay or descriptions or rating employees against one another, the checklist appraisal method consists of a series of statements, both positive and negative, that the evaluator answers "yes" or "no," checks if the employee exhibits that behavior or leaves it unchecked if she does not.
The checklist includes statements about workplace habits in general, and about the employee's specific job skills. For example, workplace habits for all employees could include:
- ____ Reports for work on time most days.
- ____ Exhibits a pleasant demeanor toward colleagues.
- ____ Stays at work until important tasks of the day are completed.
- ____ Tends to take criticisms personally.
You can see that the first three statements are positive attributes, while the fourth is negative.
Statements about skills and job tasks for a receptionist/secretary in a "yes" and "no" checklist could include:
- Displays a pleasant attitude as the first face a visitor sees. _ Yes _ No
- Is able to multitask between greeting visitors and answering phones. _ Yes _ No
- Often overlooks errors when proofreading. _Yes _ No
- Maintains track of co-workers' comings and goings. _Yes _ No
The appropriate checklists are prepared in advance and approved for each job title. The manager completes the checklist before the employee's performance appraisal meeting. When discussing performance with the employee, the manager goes through the checklist item-by-item. She may group some, such as saying, "I've noticed that you are very good at meeting deadlines and being on time." It's important that each question is addressed, however, and that emphasis isn't placed solely on the areas where the employee needs improvement.
Advantages of Checklist Appraisal Method
There are both pros and cons to the checklist appraisal method. Some have to do with the pros and cons of checklists in general.
Promotes objectivity: On the plus side, a checklist helps the manager to be objective. He can read each statement and honestly answer whether or not the employee's behavior fits that statement. Even if the employee is one of his best salespersons, a top producer with a good attitude, the manager can readily see that he's late every morning, so he leaves that statement unchecked.
Prevents memory lapses: People can naturally be forgetful, especially in stressful situations or when they feel rushed. With a different type of appraisal, the manager might have forgotten to mention the tardiness. Once an appraisal is concluded, it's difficult and unprofessional to say, "Oh, by the way, I forgot to mention that your tardiness needs to stop." That negative comment will then be what the employee remembers.
Improves organization : Using a checklist helps even disorganized people stay on task. Following the checklist in order, you make sure you don't miss any details. Even interruptions can't ruin the process, because you just go right back to the checklist and pick up where you left off, easily found by the checkmarks.
Increases productivity : There's something almost fun about checking items off a list. You can see what you've accomplished, which motivates you to keep on going. Don't stop now; you have more to accomplish before the day's out! For tasks that don't have a tangible product to show for your efforts, you can look at the checklist for proof.
Disadvantages of Checklist Appraisal Method
No appraisal method is perfect. The checklist appraisal method does have some disadvantages:
Doesn't allow explanations: Since it is a checklist only, the checklist appraisal method doesn't allow for explanations. Sometimes answers are more complex than either/or, or yes/no. When too many answers are really "yes, except when...," the checklist may not be the ideal method to use.
Time-consuming/costly to prepare: Someone has to make the checklist to begin with. Doing it well, with a lot of thought, takes time; and that means it could cost the company money. Human Resources might be able to find a standard checklist to use, but it's likely some questions won't apply, and others are not addressed so that the company will need to customize it anyway.
Easy to overlook what isn't there: There's a tendency to equate the checklist to gold. Even subconsciously, a manager may feel that if it isn't on the checklist, it isn't important. But maybe some tasks that matter to your company and your department should be on the checklist for a performance appraisal. Nevertheless, if it's not on the checklist, it isn't brought up. Ideally, if something has been omitted from the checklist, you should add it but then ask HR to revise the checklist. If you start having additional pages for things not on the checklist, you're not using the checklist method as intended.
Other Methods of Performance Evaluation
There are many other types of performance evaluation methods:
Behaviorally anchored rating scale: BARS compares performance against numerical standards, such as sales volume or average daily output.
Critical incidents: The manager lists notable incidents, both positive and negative.
Essay: The manager answers questions in a few sentences or a short paragraph.
Forced ranking: This method ranks all employees of the same job title from best to worst.
Graphics rating scale: This method rates an employee on a scale for each behavior or action.
Management by objectives: MBO measures whether goals from the previous appraisal have been met.
Self Appraisal: The employee writes an essay or answers questions about what she believes her accomplishments are and where she can improve.
Work standards: This evaluation method establishes realistic goals and sets target dates.
There are pros and cons of performance appraisal rating systems of all types. After all, if there were one with no disadvantages, everyone would opt to use it. All are valid appraisal methods, and each has its fans. The checklist appraisal method is an excellent place to start because you just read each question, consider it carefully and mark it yes or no. If you feel you have more to say after completing the checklist, look further at the other methods. One of them might be more suited to your management style.
29 Performance Appraisal Methods Explained

Performance Appraisal is a systematic approach to evaluating the performance of employees to understand the capability of the employees’ and ascertain the training and development needs.
Performance Appraisals helps in improving employer-employee relations in the workplace. It initiates a continuous flow of communication between employer and employees.
In this article, we give an overview of 29 different methods of performance appraisal , where are they applicable, the advantages and disadvantages.
There is no best method since each one of them has advantages and disadvantages. Make sure you pick well for your organization based on its culture, and strategy.
Trait-Focused Performance Appraisal
What it is.
Employees are assessed on key personality/work traits such as Discipline, Reliability, Ownership etc by their Supervisors. The evaluation is based on a simple rating scale, ranging from Outstanding to Needs Improvement. Typically, all employees are evaluated on the same set of attributes.
Example of assessment
“Does John reply to a customer complaint within time with the right tone and actionable response?”
Where is this applicable?
This type of performance appraisal is effective in teams/departments where employees are required to do a similar set of tasks with high efficiency like a BPO or a Customer Support department. This is also an effective tool in organizations where employees are expected to align to a set of values or work traits.
It’s a simple evaluation format and helps communicate to employees on what are the key attributes they need to possess to do well in their work. It also helps in putting forth a spirit of competitiveness amongst employees, as they strive to belong and deliver better results.
Disadvantages
The evaluation is completely based on a qualitative assessment by the Supervisor and thus exposed to risks of all bias related to subjectivity, recency and personal relationships.
Behavior-Focused Performance Appraisal
This type of performance appraisal assesses employee actions to evaluate key behavior.
Various rating scale options are available – (a) sliding rating (ranging from poor to excellent), (b) forced choice (With options like poor, average, good, etc), (c) forced choice with comments allowing for Supervisor descriptive inputs, and (d) behaviorally anchored where supervisors rate Pass or Fail on specific employee actions.
This appraisal type is applicable where job descriptions are typically well defined and employees are required to deliver as per expected service levels. This may not be very effective where job responsibilities are dynamic and employees are expected to play multiple roles across functions and teams.
With descriptions of various behavior properly defined for a specific performance aspect, supervisors can be more accurate in terms of their assessment rather than in a completely subjective and generic rating system approach. Further, with the opportunity to add narratives, Supervisors are required to articulate the assessment and thus provides more clarity in the performance appraisal.
Research has shown that this rating system is not devoid of the disadvantages of the common appraisal types.
Unstructured Method
This type of performance appraisal is completely based on narratives, without any specific attributes to be assessed or objective rating scales. Questions are asked in an open-ended format and the Supervisor is required to respond as per his/her subjective assessment.
“How is John as an employee?”
This appraisal type can be applicable in organization setups that either do not or cannot have any appraisal process in place. In such organizations, this appraisal type can be introduced as a soft option.
It is the simplest to design and implement and can also be useful to evaluate the assessment capabilities of the Supervisor.
Since the assessment is completely subjective, the method may not be reliable as it’s exposed to risks of all bias related to subjectivity, recency and personal relationships.
Straight Ranking
This type of performance appraisal compares employees and ranks them from top to bottom.
“Rank employees on a resolution of customer complaints”
This appraisal type can be applicable in departments/functions where all employees are performing a specific task for which the key performance indicators are standard across the board.
It is a quick and simple method to find the best and worst performers in a team.
It is difficult to rank employees that are in the middle. This is again a subjective assessment type open to the risks of bias of the Supervisor/Manager.
Paired Comparison
This type of performance appraisal compares employees on a one on one basis on a specific trait. The number of times an employee is chosen better decides the final ranking.
“Between John and Jane, who is more reliable?”
This appraisal type can be applicable in deciding on which employees to promote amongst a set of potential candidates.
It is a systematic approach to evaluation and helps rank employees uniformly.
If the number of employees to compare is high, then this method may become too exhausting for the assessor and thus evaluation may be prone to human errors.
Grading Method
This type of performance appraisal has specific grades defined with characteristics that need to be demonstrated for an employee to be allocated that grade.
“Grade employees across Outstanding, Satisfactory and Needs Improvement wherein the employee may be graded Outstanding if he/she has demonstrated the following characteristics ….”
This appraisal type can be applied in government/semi-government organizations where performance is assessed based on a holistic perspective.
With clear definitions for each grade, the Supervisor is provided enough guidance to be able to grade an employee judiciously.
The evaluator may rate most employees high.
Checklist Method
This type of performance appraisal has Yes/No questions for appraisers with questions pertaining to the employee’s work and behavior. Each question has weightage based on the priority of the aspect being assessed. There are no rating scales to be used by the Supervisor. On completion of the assessment, the responses are collated by HR and an overall performance score is calculated for each employee. To ensure appraiser consistency, similar but worded differently questions are sometimes asked twice as part of the assessment.
“Is John interested in his job role?”
This appraisal type can be applicable in organizations that have a simple structure with few job roles and well defined job-competency maps.
It definitely eases the burden on the appraiser to rate or grade based on a scale. The appraiser can rather focus on the question and the related attribute to be evaluated for the employee. Thus, appraiser bias or human errors may be reduced.
If there are a large number of job roles in an organization, creating questionnaires specific to each role, defining the scoring rules, maintaining consistency in scoring to ensure comparable scores across job roles, etc become quite a tedious planning and operational overhead.
Management By Objective
This type of performance appraisal was formulated by Peter Drucker. In this process, the first step is a collaborative Goal Setting exercise between employee & Supervisor with clear definitions of responsibilities and expected results. There is a periodic review to track progress , identify performance gaps, training needs, and course corrections.
“Hire 25 graduate engineers for the Production department by July 2018”
This appraisal type can be applicable in organizations where employees perform varied job roles and require a collaborative approach with Supervisors to attain their work objectives.
If followed in the right spirit, MBO can be quite effective in employee engagement as it helps the employees know what is expected of them and how their contribution leads to overall success for the organization. With the periodic review, the Manager also gets an opportunity to communicate regularly with the employee in a constructive setup that eliminates expectation mismatch and promotes organizational alignment.
There are several disadvantages – MBO can be quite time-consuming. Moreover, there is the possibility of conflict with Managers setting exceedingly high goals while employees aiming for lower targets. Also, if objectives are not measurable, then the process fails as progress review and assessment will be extremely subjective.
Psychological Appraisals
This type of performance appraisal assesses the employee’s aptitude, emotional balance, analytical skills, and other psychological attributes. The appraisal is done in the form of detailed interviews, tests and supervisor discussions.
This appraisal type is best applicable to identify employees for fast track or future leaders for the Management Cadre.
These types of appraisal are useful to identify training & development needs of and suitable job roles for employees.
Since the approach is in-depth, the process can be time-consuming and costly in terms of organizational resources.
360-Degree Appraisal
This type of performance appraisal involves inputs from seniors, colleagues, juniors and also, customers and partners. It is used to assess an employee’s competencies, aptitude & behavior.
This appraisal type is best applicable to identify development & training needs for employees.
Since this type of appraisal collects inputs from all key work associates of an employee, the accuracy of the feedback is expectedly higher compared to other performance appraisal types.
The method is still a subjective assessment and open to the risks of bias based on personal rapport, recency or competition.
Numerical Rating Scale
What is it.
This type of performance appraisal assesses an employee’s performance by taking specific job-related behavior such as attendance, punctuality, discipline, readiness etc. into account. A numeric score is given for each of the criteria. If employees do not meet a minimum score, they are sent for training.
This type of appraisal is best suited for new employees/freshers where the organization wants to find out the training needs for newcomers.
This method is quite easy to use and can be implemented in any type of organization irrespective of size, job function etc. It requires very less effort to set up and requires no formal training.
The rater can be biased with some of his favorite employees.
Critical Incidents
In this method, critical incidents that an employee was engaged with are listed, prioritized and then rated based on a checklist, indicating good or bad.
This type of appraisal is best suited where employees are subject to responding to critical emergencies and crisis, like a Hospital or Fire Department.
When things are normal, employees can be expected to operate quite similarly. But in a crisis or criticality, its how the employee responds to it and performs the expected duties is what determines the effectiveness of performance.
This method is completely subjective and thus open to the risks of bias and prejudice. Also, it is extremely time taking as the evaluators have to write down the critical incidents regularly.
Job Results
In this method, the expected results of a job are compared with actual performance. Typically, there will be an expected target to achieve or maintain and this will be benchmarked against the actual numbers.
This type of appraisal is useful in appraising measurable goals like say, No of Units sold, Volume of manufactured units etc.
With clear-cut expected job results and simple comparison with actual performance, there is very little left to the subjectivity of the evaluator’s opinions.
Not all work that an employee does can be determined to have job results that can be quantitatively measured, like say, improve interdepartmental communication or employee happiness.
Essay Method
In this method, the rater describes the performance of an employee by writing a descriptive essay where he describes the strengths, weakness, capability etc. of an employee.
This type of appraisal is useful in appraising employees in the academic industry, where the research that a faculty does is being appraised by the evaluator.
This method is free from complex structures and formats hence easy to implement.
This method may be time-consuming since the rater has to write a description for each employee. It also lacks quantitative data and the length of the description may vary for each employee.
General Performance Appraisal
This type of performance appraisal is based on constant communication between employee and manager, right through the review period. In the end, the actual performance is tracked against the goals that were set, feedback is exchanged and goals for the next session are set.
This type of appraisal is best suited where employee and manager work in close coordination, the Manager is responsible for a smaller team and possibilities of One-on-One between employee and manager is quite high.
Since communication is at the basis of this appraisal, it results in very effective performance discussions between employee and manager right through the year without any chance for misunderstanding or expectations mismatch.
This may be overwhelming for the Manager if he/she is responsible for a large team of people.
Technological/Administrative Performance Appraisal
This type of performance appraisal assesses the technical performance aspects of an employee.
This is applicable to assess the performance of the technical department of an organization.
The rater can focus on a specific skill set, rather than open-ended performance parameters
This method is restrictive and cannot be applied uniformly across the organization.
Manager Performance Appraisal
In this method, the employees who are Managers are appraised of their managerial performance. This type of appraisal assesses job skills and well as people skills because the Manager not only is responsible for the overall work deliverables but also keep the employees motivated and happy.
A Manager Appraisal is most applicable in a knowledge-based services industries where employees and Managers need to engage collaboratively and thus need to feed on each other’s feedback to improve and perform better.
Managers getting feedback from those who actually work with them on a day to day basis helps tremendously.
Reportees may not be completely honest in their feedback to the Managers for the fear of spoiling the relationship.
Employee Self-Assessment
In this method, the employees are given the opportunity to scrutinize their own performance and assess their own strengths and weaknesses. In this way, they can find out their areas of improvement and make a list of their accomplishments over the year.
A Self Assessment is typically applicable in any organization as the employee’s voice must be heard as part of the evaluation process.
When employees are given the opportunity to self-evaluate they feel empowered. They realize that their opinions do matter and are taken into consideration during performance review discussions.
An employee may not be able to evaluate himself effectively. He/she may overemphasize their contributions or downplay their success.
Project Evaluation Review
In this method, job evaluation is done at the end of each project. After the assigned task is completed, employees are evaluated based on the performance of the latest task.
This is relevant in project-based organizations where employees shift from one project to another and it makes sense to evaluate at the completion of the project, rather than at the end of the review period.
This method helps to instill a regular feedback culture in the organization. Regular reviews allow to identify and address any deviation in work and deal with it before it gets out of control.
Since there is no single Manager, feedback from one project manager does not always flow to the next project manager.
Sales Performance Appraisal
In this method, sales targets are compared with actual performance. Typically, there will be an expected set of goals to achieve or maintain and this will be benchmarked against the actual numbers.
This type of appraisal is useful in a sales-based organization where the main activity is selling.
With clear-cut goals set and simple comparison with actual performance, there is very little left to the subjectivity of the evaluator’s opinions.
Not all work that a Sales representative does can be linked to sales or financial performance.
Human Asset Accounting Method
In this method, the individual employee’s performance is linked to the amount of revenue being generated, new deals won or average business size growth per customer.
This type of appraisal is employed in startups where the imperative is to deliver or die.
With a single point focus on financial performance, there is no room for misunderstanding between employee and management on what is expected. It helps to identify employees for promotion or exit.
It may not be conducive to creating a good work environment, where employees are always on the pressure to deliver results or lose their job.
In this method, an employee is expected to maintain a document trail of his achievements throughout the year. This document is used in annual reviews.
This type of appraisal is useful in appraising employees in the academic industry, where the research that employee does requires detailed journaling to be assessed by the evaluator.
Well documented accounts of employee performance are more useful than performance reports leading up to only a couple of months before the review.
This method is becoming outdated since automated feedback tools are preferred over traditional documentation.
Field review technique
In this method, if a rater is suspected to be biased or higher than others, a review process is conducted to identify inter-rater differences, discuss and arrive at a common rating.
This is not widely used by can be considered for evaluation of mission-critical positions or in decisions that are related to promotion or termination.
The main advantage is the elimination of rating bias through human dialog.
This method is extremely time taking & Managers can feel disturbed by other peers’ interventions.
Confidential records
In this method, the assessment is done by the Supervisor with the objective to recommend for transfer and promotion. A structured form that collects information on employee’s strengths, weaknesses, achievements etc form the basis of this evaluation.
This is typically how performance evaluations happen in govt agencies.
There is no specific advantage as there are possibilities for manipulation and deceit.
This method is completely subjective and thus open to the risks of bias and prejudice.
Cost accounting technique
In this method, the individual employee’s performance is linked to the monetary value being generated. Here, the costs to maintain the employee and the value that the employee brings are compared.
With a single point focus on monetary performance, there is no room for misunderstanding between employee and management on what is expected. It helps to identify employees for promotion or exit.
Work Standards Approach
In this method, a results-focused approach is employed to evaluate actual performance. Typically, a minimum is set that has to be achieved for an employee to be considered performing.
This type of appraisal is useful in a sales or manufacturing based organization where evaluation targets can be set on quantities sold or produced.
Not all work that an employee does can be linked to volumes sold or produced. Aspects like communication, team skills do not get covered here.
Assessment Centers
In this method, an offsite location brings together the employees to participate in simulations and games that will help assess managerial potential. Other than company senior executives, external consultants and psychologists are involved in this process.
This type of appraisal is typically used to assess organizational leadership
This method allows for accurate assessment, reduced bias and better approach towards identifying candidates for promotion and transfer.
Other than being time taking and costly, it promotes an unhealthy atmosphere of competitiveness and insecurity.
Forced choice method
In this method, a group of statements is to be rated by evaluators to be most applicable for the employee. Statements include both positive and negative ones that provide the perspectives for the rater to evaluate both these opposite aspects. Each statement has a weightage that is not revealed to the evaluator.
This type of appraisal can be applicable to work positions where clear definitions of expected positive and negative performance can be defined.
This method allows for objective assessment of employee performance, as the evaluator is asked to choose the statement most reflecting the employee’s performance.
The real issue is that constructing a sequence of statements to be used for the evaluation of each of the employee performance aspects is extremely time-consuming.
Forced Distribution method
In this method, Tiffin tried to eliminate the bias of managers to rate high on rating scales.
This type of appraisal is useful wherever there has been past history of rating distortions.
This method was brought about to take care of the bias of evaluators to mark employees on the higher end of the rating scale with the core objective of removing rater bias.
Since rating statements have to be crafted that will let evaluators choose, that’s why there is the possibility of the statements being fundamentally wrongly constructed.
So, are you ready with the best method for your organization?
If not you can combine two or three methods from the above list to suit your organization.
Have more methods in mind? Let us know
Also, let us know in the comment section if you already have some combinations in mind.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Very comprehensive and informative list. This will serve as a great ready reckoner.
[…] performance evaluation is expected to be binary based on whether targets were achieved or […]
[…] 29 Types of Performance Appraisal Method Explained October 2, 2018 […]
[…] of review. We have already compiled a list explaining 29 Types of Performance Appraisal Method. Click to view. Performance appraisal forms make the whole process of Performance Review less engaging and […]
[…] stated that performance appraisals are not effective at all. Its losing relevance to employees and […]
[…] many organizations, HR departments still rely on outdated employee evaluation techniques. They are mostly centered around year-end reviews and categorized under performance management. To […]
[…] are many pre-established performance appraisal methods available today, each with its own benefits. Take a look at some the options below to figure out […]
[…] the effectiveness of the Performance Management System, the first thing that comes to our mind is performance reviews or the annual […]
[…] performance appraisal is the ideal chance to address long term career aspirations of the employee that get lost in the […]
Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Should Performance Appraisals Be Eliminated
Recommendations to managers.
The topic of performance appraisal has been lately put under significant scrutiny within the corporate environment. As the requirements and the demands of clients change, businesses are forced to adapt and make improvements following such changes. Consequently, the environment in the workplace also changes, calling for more efficiency in performing assigned tasks. Performance appraisal interviews have been criticised for being ineffective in evaluating the actual accomplishments of employees.
Furthermore, performance appraisals are conducted once or twice a year while employees that want to achieve something in a company need feedback on a weekly basis (Bersin, 2013). Many successful companies like Microsoft are currently trying to overcome the burden of performance appraisals and focus on in-time feedback for employees, as mentioned by Kaine and Johns (2015). Appraisal interviews can be particularly stressful for workers when the results depend on the pay rises and bonuses for excellent performance. Adding together all of the points mentioned above and the hard costs of performance management (Buckingham & Goodall, 2015), and the image of performance appraisal interviews is not as pristine as it could have been.
Therefore, to answer the question of whether the days of performance appraisal should be numbered, it is important to account for its pros and cons. As for the pros, the aim of performance appraisals is assessing employees’ effectiveness as well as setting goals for the future (Sandlund, Olin-Scheller, Nyroos, & Nahnfeldt, 2011), which cannot be considered an unimportant task. Another advantage is directly associated with managers’ inability to spend more time with employees and engage into a conversation with them.
Performance appraisals offer managers an opportunity to have one-on-ones with workers, giving a better understanding of who feels great working in the company. Moreover, appraisals allow managers to give a formal positive feedback to those employees who feel confident in their abilities and want to identify their future areas for improvement. Lastly, interviews about employees’ performance identify opportunities, which may be discovered in the course of the appraisal. As a result of this, the manager can assign and reassign projects in agreement with the interests of workers. Overall, if done correctly, performance appraisals can motivate, direct, and positively impact the performance of separate individuals or a company as a whole.
The cons of performance appraisals interviews overweigh the advantages. As discussed in multiple articles, especially the authoritative resources such as Forbes and Harvard Business Review , the majority of performance appraisals do much more damage than good. Among the damages is the wasting of time on the lower end of the spectrum and the alienation of employees on the other end, which is the most troublesome (Lawler, 2014).
Many can agree that the process of performance management itself is uncomfortable for both workers and managers. A manager can often be uncomfortable in his or her ‘judgement seat’, having to provide constructive criticism and make sure that the interviewee does not respond with a defensive remark (Heathfield, 2016). Therefore, there is an immense amount of pressure put on the manager, who should not only conduct an objective performance appraisal but also identify the consequences of the interview. Otherwise, if there are no clear results of the evaluation, it can be considered a complete waste of time, funds, and effort (Daoanis, 2012).
Having advantages and disadvantages, performance appraisal interviews have been said to influence employees both negatively and positively. For example, worker’s loyalty and efficiency can be significantly increased after a performance appraisal. On the other hand, some employees do not experience positive outcomes and are unwilling to dedicate more of their extra time to completing an assignment if they are not financially rewarded for it. This means that the majority of workers in a company put their interests first, and are only willing to dedicate extra effort if their payment increases.
It can be concluded that the majority of performance appraisals require much more effort on the part of the manager and the employee compared to the value they offer. As seen from the role-playing exercises that were targeted to find out the benefits of performance appraisals, employees are usually forced to take a defensive position and make sure that the manager agrees with them.
Managers may also be put under great pressure since they usually do not spend much time interacting with employees on a daily basis, but at the performance appraisal, they should act like they know everything about the relationships within the company as well as the effectiveness of employees in completing their assignments. Therefore, the days of yearly performance appraisals are long gone, and managers should start paying more attention to giving workers feedback in real time. Such a strategy will be more effective since there will be a chance to fix mistakes, regroup, set new objectives, and act upon them. There is no point for an employee to wait a year to get feedback from the manager when there is an option to go to his or her office and ask straightforward questions.
The process of performance management is one of the weakest points for the vast majority of companies. Comprised of employee development and performance appraisal, performance management is often called the “Achille’s heel of human resource management” (Pulakos, 2004, p. 1). Moreover, as discussed previously, there is only a small portion of employees in a company who think that performance appraisals bring positive outcomes for their professional development. This suggests that the majority of appraisal interviews are poorly designed, and managers contribute to their ineffectiveness with the reluctance of providing constructive feedback and discuss relevant topics with employees on honest terms.
Lastly, performance appraisals may be very cumbersome for the company as to the financial aspect. Therefore, it is high time for managers to improve their performance management skills to facilitate conversation within the corporate environment, make sure that employees do their work, and establish trusting relationships that will become a basis for success in accomplishing assignments. Effective performance management will correlate with the enhancement of individual and group productivity, creating behaviors that align with the company’s strategy and providing a ground for making human capital decisions (Pulakos, 2004).
The key advice one may give to a manager to improve his or her performance management is associated with the notion of ongoing feedback. It has already been discussed that yearly performance appraisals rarely bring any benefits because they are conducted once in a long period of time. Similar to the way coaches train athletes, managers can also give their employees feedback in real time, so there is a possibility to improve quickly.
Moreover, ongoing feedback improves productivity within the company because managers can share their ideas instantly and give employees an opportunity to develop new skills. Apart from improving productivity, ongoing feedback influences the development of strong corporate relationships and increases retention in a position (Reynolds, 2016). Therefore, there is a variety of advantages ongoing feedback brings to the workplace ranging from maintaining engagement to eliminating any surprises during the review period. It is strongly recommended for managers to start giving employees feedback in real time and experience its positive impact.
The second recommendation that can be given to any manager in a company is measuring employee engagement. Many workers may be unsatisfied with their job, but the manager may have no idea about it. Employee engagement is a crucial component of performance management that is very often overlooked. It is advised for the manager to develop employee surveys that will act as “two-way communication tools” (McMullen, 2013, p. 25). The results of the surveys should be shared with the senior management as well as employees to cooperatively develop a cohesive plan for action. If managers never address the challenges identified in employee engagement surveys, workers will continue doing their work at minimum capacity just to get paid each month. It is crucial for managers to act upon the identified challenges and make sure that workers are emotionally engaged in the job they do (Markos & Sridevi, 2010).
The last recommendation that can be given to managers is trying to answer the question of ‘What makes a good employer?’ So many managers are currently stuck in a rut and have no idea how to progress and effectively lead employees towards achieving success. A good employer is the one that supports the unique company culture, focuses on growing talent within the company, has a strong sense of responsibility, and inspires others through leadership (Looi, Marusarz, & Baumruk, 2004). As mentioned in the article by Gillian White (2014), it is often not money that endears workers to their employers. It is the action an employer takes to make sure that the company is on the right track, that employees feel secure in their position, and that there are benefits such as health packages provided to all workers. Despite the fact that it is difficult to account for all requirements of employees, a manager should think outside the box and establish strong relationships to become a truly successful leader.
Bersin, J. (2013). Time to scrap performance appraisals? Web.
Buckingham, M., & Goodall, A. (2015). Reinventing performance management. Web.
Daoanis. L. (2012). Performance appraisal system: It’s implication to employee performance. International Journal of Economics and Management Sciences, 2 (3), 55-62.
Heathfield, S. (2016). Performance appraisals don’t work . Web.
Kaine, S., & Johns, R. (2015). Why the days of performance appraisals should be numbered. Web.
Lawler, E. (2014). Eliminating performance appraisals . Web.
Looi, P., Marusarz, T., & Baumruk, R. (2004). What makes a best employer? Insights and findings from Hewitt’s Global Best Employers study. Web.
Markos, S., & Sridevi, S. (2010). Employee engagement: The key to improving performance. International Journal of Business and Management, 5 (12), 89-96.
McMullen, T. (2013). Reward strategy and practice: Eight recommendations to improve employee engagement. Journal of Compensation and Benefits, 3 (7), 23-29.
Pulakos, E. (2004). Performance management: A roadmap for developing, implementing, and evaluating performance management systems. Alexandria, VA: SHRM Foundation.
Reynolds, J. (2016). The importance of ongoing feedback . Web.
Sandlund, E., Olin-Scheller, C., Nyroos, L., & Nahnfeldt, C. (2011). The performance appraisal interview – An arena for the reinforcement of norms for employees. Nordic Journal of Working Life Studies, 1 (2), 59-75.
White, G. (2014). What makes a good employer? Web.
- Attitudes, Their Types, Formation, and Components
- Mental Health Strategies at the Workplace
- Performance Management and Appraisal
- Type of Performance Appraisals
- The Various Types of Performance Appraisals
- Employee Empowerment: Influential Factors
- Quanchi Retailer's Management: Problems and Solutions
- Mechanistic vs Human Relations Management
- Ideal Hotels: Management Development
- Power Sources in the Working Environment
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, August 2). Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks. https://ivypanda.com/essays/performance-appraisal-its-benefits-and-drawbacks/
"Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks." IvyPanda , 2 Aug. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/performance-appraisal-its-benefits-and-drawbacks/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks'. 2 August.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks." August 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/performance-appraisal-its-benefits-and-drawbacks/.
1. IvyPanda . "Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks." August 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/performance-appraisal-its-benefits-and-drawbacks/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Performance Appraisal, Its Benefits and Drawbacks." August 2, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/performance-appraisal-its-benefits-and-drawbacks/.
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal
Everything you need to know about the advantages and disadvantages of performance appraisal. Performance appraisal may be viewed as a systematic and objective process of assessing an individual employee’s job performance and productivity at specified intervals of time in relation to certain pre-established criteria and the organisation’s objectives.
Performance appraisal always involves the following –
1. setting work standards, 2. assessing employee’s actual performance relative to those standards and 3. providing feedback to the employee with the aim of motivating him or her to eliminate performance deficiencies.
Performance appraisal also seeks to assess employee’s behaviour, accomplishments and potentials for future improvement, and points of his strength and weakness.
Although performance appraisal lays emphasis on the assessment of individual employee’s performance, the process may also be made applicable to a group of employees or a team.
In this article we will discuss about the advantages and disadvantages of employee performance appraisal.
Learn about the Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal of Employees
Advantages and disadvantages of performance appraisal of employees.
Performance appraisal means evaluating an employee’s current and/or past performance relative to his or her performance standards. It is designed to help employees understand their roles, objectives, expectations and performance success. Appraising performance assumes that performance standards have been set and feedback is given to the employees to help them eliminate performance deficiencies or continue to perform above par. It is an integrated process of setting goals, training and developing employees, appraising their performance and rewarding them.
Advantages of Performance Appraisal : Top 9 Benefits
Advantages of the performance appraisal are as follows:
1. Right Placement:
Performance appraisal is beneficial for assessing strengths and weaknesses of an employee. It enables to find out areas / tasks in which the employee is competent. Basically, the process is useful for identifying true potential and interests of the employees. Such analysis helps HR Department to assign right jobs according to the skill and competencies of employees.
2. Assistance to Improve Performance :
The manager / team head shares evaluation result with the respective employees. Such feedback is useful as it enables employees to focus on improving their strengths. The managers also suggest ideas and methods through which employees can overcome their weaknesses. Thus, the process helps in personal & career development of employees.
3. Acts as a Motivator :
The process involves recognizing & rewarding employee’s efforts and performance. It boosts their morale and confidence. Further, greater awareness of one’s true potential motivates employees to give their best performance. The organization acknowledges efforts of employees by giving higher salary, higher responsibilities, certificates and other monetary and non-monetary benefits. These benefits and recognition also motivates other employees to perform better at their job.
4. Planning and Designing Training Programmes :
The assessment of strengths and weaknesses of employees is useful for HR department to plan and design training programmes. The employees are provided with right training at right time to overcome their weaknesses and to develop their strengths. The content and method of training can be modified according to the human resource requirements.
5. Improves Employee and Management Relationship :
Performance appraisal is also an opportunity for the employees to discuss work related problems with their superiors & to find out ways to resolve them. Promotions and transfers are done on the basis of performance of employees. The fair promotion and transfer policies improve relationship between employees & management. It also facilitates good work atmosphere which directly benefits the final output.
6. Human Resource Planning and Development :
Performance appraisal is useful for taking inventory of quality of human resources available in the organization. This information helps in future planning and development of human resources. As per the assessment, the HRD can plan to recruit new employees or develop the quality of existing workforce in the organization. This ensures that organization has required quality and quantity of manpower to carry out its activities.
7. Improves Employee Communication with Managers :
Performance appraisal is also an opportunity for the employees to convey their needs and expectations to superiors. Further, employee can seek guidance of their managers to improve performance and also for career advancement. In short, the process gives a platform to improve employee communication.
8. Personal Development :
Appraisal facilitates acknowledgement of employee’s efforts and achievements. This motivates employees to learn and acquire new skills that aid them in personal and career development. This process boosts employees’ confidence and encourages them to take challenging tasks. During appraisal, managers also suggest ideas and methods to improve their attitude, behaviour, mental ability, emotional stability and so on.
9. Promotion and Transfers :
Performance appraisal is beneficial for identifying talented employees in the organization. This information helps the organization in grooming and developing competent employees. The organization acknowledges the efforts and achievement of employees through promotion, deputation, transfer etc. Performance appraisal ensures that promotion and transfer is only offered to employees based on merit and experience, not on the basis of seniority and favouritism.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal: Top 11 Disadvantages
Disadvantages of the performance appraisal are as follows:
1. Time Consuming Process :
Every manager or supervisor is responsible for preparing performance report for his team members. He is required to fill up an appraisal form for every team member and note down strengths, achievements, weaknesses and other observations of his team members. The process includes lot of procedures and is a time consuming process.
2. Inexperienced Evaluators :
Sometimes, appraisal may not be conducted by skilled or trained managers. The evaluation process may not be carried out properly owing to lack of knowledge and experience of evaluator.
3. Defective Rating or Personal Bias :
Managers avoid giving negative remarks or poor ratings as employees may not always view feedback in a positive manner. The managers try to avoid possible future conflicts or arguments with employees. Moreover, they also fear non- cooperation from employees in future.
It results in managers giving favourable ratings, so that work environment and relationships are not affected. Moreover, the evaluator’s personal relation with the employee also affects the process. Sometimes, managers may give higher ratings to favorite’s employees. They may also give low rating to deserving employees due to jealousy or fear that such employees might replace them.
4. Difficulty in Selection of Appraisal Method :
There are number of techniques to evaluate performance of employees. The appraisal technique must be selected on basis of the nature of organization, number of employees, work policies, budget etc. However, evaluators may not always select appraisal method that is suitable for the organization. They select appraisal method that is simple, less time consuming in order to reduce workload.
5. Central Tendency :
Managers have the tendency to give average rating to employees irrespective of their actual performance. It means average rating is given to both, the underperformers as well as the over performers. Generally, managers resort to this kind of behaviour in order to avoid displeasing other employees, future conflicts, jealousy and tension in the team. However, it is unfair for those employees who actually deserve high ratings but are given average score.
6. Horn & Halo Effect :
The behaviour to look only on negative aspects and ignore the positive aspects of a person is called as horn effect. It occurs when an appraiser makes his decision only on the basis of employee’s negative attributes. For instance, the appraiser gives overall low rating to an employee because he is overly focused on employee’s lack of communication and presentation skills.
He totally overlooks the fact that the employee is proficient in his job and completes tasks within the specified time. Halo effect is the opposite of Horn effect. In this, positive qualities of the employee are overshadowed by negative qualities of the employee. It means the appraiser gives high rating to employees also in those areas where he is not proficient.
7. Lack of Participation from Employees :
Employees resist performance appraisal system because they consider that the whole process of appraisal is only for pointing out their mistakes and criticizing their performance. Thus, they may not be actively involved in the evaluation process.
8. Spill Over Effect :
The behaviour to ignore employee’s current performance and to make decision on the basis of past performance and overall impression of the employee is termed as spillover effect. For instance, if the employee had a good performance during the last year, the supervisor by default rates him high even in the current year without considering his actual performance.
9. Attitude of Evaluator :
Mind set of manager also affects the evaluation process. The managers who are strict and have high expectations from his employees may give low ratings to all employees in spite, of good performance from employees. The lenient managers give high rating to all employees irrespective of their performance. Such evaluations are not valuable to the organization or the employees.
10. Inadequate Attention to Human Resource Development :
The main aim of appraisal system is to assess the performance of employees at current job so that they can be motivated and developed further. However, the performance reports may not be actually used by the managers to achieve this goal. The managers prepare these reports only to fulfil their duties and obligation of company policy. They may not always find time to evaluate actual performances of employees and to develop their abilities.
11. Expensive :
The organization has to allot huge funds for setting up assessment centres. Further, technical experts are to be hired to plan and design evaluation techniques. Sometimes, organizations also have to hire professional experts from outside to conduct the evaluation process.
Advantages of Performance Appraisal:
Following are the advantages of performance appraisal:
1. This system provides information of great assistance in making and enforcing decisions about promotions, pay increase, layoffs and transfers.
2. It serves as a guide for employee’s development.
3. Performance appraisal puts a psychological pressure on workers to improve their performance on the job.
4. This serves to maintain fair relationship in groups.
5. This system avoids errors of nepotism, self-interest and discrimination while promoting and enhancing wages and salaries.
6. Personnel decision can be taken on the basis of this performance appraisal system
7. It is an efficient device for rating their personnel as it enhances proper control on sub-ordinates.
8. Timely, systematically, up to date, honestly and sincerely performance appraisal creates mutual understanding, trust and confidence among the supervisor – sub – ordinate relationship.
Thus, it has been seen that performance appraisal is an important tool of personnel management.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal:
The most problems involved in performance appraisal are as follows:
1. Errors in Rating:
Performance appraisal may not be valid indicator of performance and potential of employees due to the following types of errors:
(a) Halo Effect – It is the tendency to rate an employee consistently high or low on the basis of overall impression.
(b) Stereotyping – It implies forming a mental picture of a person on the basis of his age, sex, caste or religion.
(c) Central Tendency – It means assigning average ratings to all the employees in order to avoid commitment or involvement
(d) Constant Error – This tendency may be avoided by holding meetings so that the raters understand what is required of them.
(e) Personal Bias – Performance appraisal may become invalid because the rater dislikes an employee,
(f) Spillover effect – This arises when post- performance affects assessment of present performance. For instance, recent behaviour or performance of an employee may be used to judge him.
2. Lack of Reliability:
Reliability implies stability and consistency in the measurement. Inconsistent use of measuring standards and lack of training in appraisal techniques may also reduce reliability. Factors like initiative are highly subjective and cannot be quantified.
3. Incompetence:
Raters may fail to evaluate performance accurately due to lack of knowledge and experience. Past appraisal interview is often handled ineffectively.
4. Negative Approach:
Performance appraisal loses most of its value when the focus of management is on punishment rather than on development of employees.
5. Multiple Objectives:
Raters may get confused due to too many objectives or unclear objectives of performance appraisal.
6. Resistance:
Trade unions may resist performance appraisal on the ground that it involves discrimination among its members. Negative ratings may affect interpersonal relations and industrial relations particularly when employees or unions do not have faith in the system of performance appraisal.
7. Lack of Knowledge:
The staff appraising performance of employees might not be trained and experienced enough to make correct appraisal.
These include the benefits to the organization, to the supervisor, and to the employee himself or herself.
Organization:
1. Communicates corporate goals
2. Provides management with decision-making information on human resources
3. Provides objective basis for raises, promotions, training, and other personnel actions
4. Builds stronger working relationships
5. Improves overall organizational productivity
6. Provides documentation for inquiries on general promotion policies or individual claims of discrimination
Supervisor:
1. Builds management skills
2. Develops and improves rapport with employees
3. Identifies and rewards high performers
4. Identifies performers needing improvement for coaching/training
5. Improves individual employee productivity
6. Identifies general training needs
7. Demonstrates fairness to employees Improves group morale
1. Finds out how they’re doing
2. Provides recognition for accomplishments
3. Allows for two-way communication on goals and performance
4. Encourages taking responsibility for their performance and progress
5. Helps set goals and direct efforts
6. Provides opportunities for career development and improvement
7. Assures fair individual evaluations
1. There will be an objective analysis of traits of both the superior and subordinate.
2. There will be a chance for the subordinate to express his views even after performance appraisal.
3» An employee shall express his emotional needs and his value system which is considered taboo till today.
4. It overcomes the communication barrier.
5. It will remove the inherent weakness of the appraisal system i.e., subjective assessment of vague and abstract performance targets, unclear guidelines for appraisal, etc.
Disadvantages of Performance Appraisal :
Though the performance appraisal is a very useful technique, it suffers from serious limitations too.
Some of its limitations are as follows:
1. Though it is a useful technique of efficiency rating but there are certain personal characteristics which cannot be expressed either in figures or in any other measures.
2. However systematic and objective system of performance appraisal is used in the organisation, it is impossible to eliminate personal and subjective element from it.
3. Generally, there is the presence of ‘a halo’ effect which leads to a tendency to rate the same individual first, which once have stood first.
4. Some people are more distinct while some are very liberal in assigning the factors, points or number to the employees. They are unable to maintain a fair distinction between two individuals. It also nullifies the utility of this system.
5. Sometimes the results of performance appraisals are not confirmed by other techniques of motivation, incentive wages plans and so on. Factors are introduced in the managerial appraisal because of a fact or bias in the person concerned conducting the appraisal.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Performance Appraisa l of Employees
Performance appraisal may be viewed as a systematic and objective process of assessing an individual employee’s job performance and productivity at specified intervals of time in relation to certain pre-established criteria and the organisation’s objectives. Performance appraisal always involves the following – “1. setting work standards, 2. assessing employee’s actual performance relative to those standards and 3. providing feedback to the employee with the aim of motivating him or her to eliminate performance deficiencies.”
Performance appraisal also seeks to assess employee’s behaviour, accomplishments and potentials for future improvement, and points of his strength and weakness. Although performance appraisal lays emphasis on the assessment of individual employee’s performance, the process may also be made applicable to a group of employees or a team.
Advantages of Performance Appraisal :
Apart from contributing to the overall performance of the enterprise, performance appraisal is useful in various areas of organisation’s HR activities.
Some of the major HR areas in which advantages of performance appraisal can be obviously discerned are as follows:
1. Production and Productivity:
Where targets of performance or production per unit of time have been specified, employees try their best to achieve these and even go beyond within the specified time in expectation of consequential rewards. The employees usually also develop a spirit of competition, which ultimately results in enhancement of their productivity, thus assuring the organisation a minimum level of production. Similar phenomenon applies also to the processes where the piece-rate system is prevalent.
2. Employees’ Capabilities and Competence:
Performance appraisal makes it possible to identify the points of strength and weaknesses of employees. The organisation can conveniently adopt measures to rectify their deficiencies through suitable training and development programmes. Performance appraisal can also be helpful to employees in their career planning and development.
3. Promotions and Transfers:
The potentials of employees revealed through performance appraisal enable the management to take objective decision about the employees deserving promotion and those who are unsuitable. The employees also become aware that their level of performance will be a deciding factor in their future advancement. Even where unions pressurise for adopting seniority criterion as the basis for promotion, it is conceded that there must be a certain level of efficiency in deciding promotion cases.
Performance appraisal also makes it possible for the HR professionals to identify the employees whose services could be more fruitfully utilised by their transfer to some other suitable jobs. Habitual low performing employees may, however, have to face termination of their services.
4. Compensation:
In many organisations, various categories of employees including supervisors, managers and executives are paid handsome additional compensation packages for their high level of performance as revealed by the appraisal. The additional compensation packages for high performing employees usually comprise performance-based lump sum bonus, enhanced annual increment and improved fringe benefits.
Such inducements act as a potential motivational factor not only for the high performing employees, but also for those whose level of performance is not up to the mark. The low performing employees start making efforts to improve their performance in expectation of higher earnings and improved facilities.
5. Selection:
Performance appraisal also enables the organisation to identify those employees whose potentials could be more fruitfully utilised for higher positions. It also reveals the unavailability of suitable candidates from internal sources, with the only option to look to the external supply.
6. HR Planning:
Information about points of strength and weaknesses of existing employees as revealed by performance appraisal is also useful while making plans in regard to human resources requirements of the organisation.
Such information will be helpful to the organisation in framing workable plans in regard to the present and future requirements of the organisation, adoption of an appropriate T&D programme for developing needed skills and capabilities of employees, determination of compensation packages and incentives, adjustments of workforce and taking decisions on other related issues.
7. Communication:
Performance appraisal is also useful in ensuring useful communication in the organisation. When the employees are convinced about the objectivity of their performance appraisals, they generally feel free in communicating with their superiors and peers about their strength and weaknesses.
Performance appraisals are also useful in making the process of identifying, measuring and developing the performance of individuals and teams and aligning their performance with the organisation’s goals more effective and acceptable.
For the sake of easy understandability, it is desirable to give special attention to the major problems experienced in the course of application of the performance appraisal in a wider perspective.
These are briefly described below:
1. Lack of Clarity in Norms :
In some methods such as rating scales, employees may be rated as “poor”, “fair”, “good” or “excellent” in respect of each trait, for instance, “job knowledge”, “creativity”, “adaptability” and so on, but different raters often interpret the same degree on the scale and also the specific traits differently. Such a situation arises mainly on the account of ambiguity in the standards set. This often results in distorted ratings.
Appraisals laying emphasis on personal traits are more vulnerable to such a situation. The problem can be minimised by setting clear standards which can easily be understood by the raters.
2. Elements of Bias and Subjectivity :
Performance appraisals are done by human beings who may have their own biases and prejudices. In India, there have been numerous examples to show prejudicial approaches of the supervisors, managers and even executives in evaluating their subordinates’ performance based on considerations of caste, tribe, religion, language and region.
The bias may be positive in the sense of unreasonably helping a particular employee, and negative in the sense of harming an employee not liked by the appraiser. Appraisals may also be influenced by many other subjective considerations. As such, there is the need to adopt objective standards in every area of evaluation.
3. Leniency and Strictness :
Like lenient and strict examiners evaluating answer books in educational institutions, there are too lenient and too strict appraisers also in the business and industrial settings. Many of them develop such traits rather naturally. Thus, there is a great probability that too lenient appraisers rate even “average” employees as “very good”, whereas too strict appraisers may keep even “highly efficient” employees in the relegated “average” category.
More lenient appraisers may provide undue protection to inefficient employees at the cost of rightful claims of high performing ones. Too much strictness may also generate a demoralising effect on the motivation and morale of high performing employees.
There are also evidences to show the general impression about a particular employee influencing the ratings of the appraiser on all traits being evaluated. This is known as “halo effect.” This means that an employee about whom the rater has formed an unfavourable impression may be ranked very low on every trait even though he possesses potentials to be rated high.
On the other hand, a favourable impression about an employee may result in rating the performance of even an “average” employee as “excellent.” Objectively laid down standards will minimise the scope for too much leniency and too much strictness in appraisals and also reduce the scope of “halo effect.”
4. Central Tendency :
In many cases, the raters tend to avoid possible controversy or criticism by awarding middle level or average ratings. This tendency results in distorted ratings and especially denies the rightful claims of high performing employees in regard to enhanced compensation and benefits.
5. Element of Manipulation :
There are instances where managers and supervisors dominate over the entire process of performance appraisal and are in a position to manipulate things with a view to favouring employees of their own liking. On the other hand, there may be dominant employees, such as group or union leaders who exert undue pressure on the appraiser to accommodate them even when their performance has been consistently poor. In such cases, the option left before the raters is either to decline to be a rater or to manipulate things to accommodate them.
Related Articles:
- Performance Appraisal: Meaning, Characteristics and Advantages
- Performance Appraisal: Need and Features of Performance Appraisal
- Project Report on Performance Appraisal | Personnel Management
We use cookies
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |

COMMENTS
The essay method, sometimes known as the "free-form method," is a performance review system where a superior creates a written review of the employee's performance. These essays are meant to describe and record an employee's strengths and weaknesses in job performance, identifying problem areas and creating a plan of action to remedy them.
Pros. Structure and formality: Traditional performance reviews provide a structured framework for evaluating and discussing employee performance. They often follow a set process and timeline, which can help ensure consistency across the organization. Learning and development: These reviews offer an opportunity for supervisors to provide feedback on an employee's performance, strengths, and ...
The essay appraisal. The appraiser, usually the manager, writes an essay about the employee being evaluated. Then, the evaluator describes the employee's performance, giving examples to support this description. Key idea. Also known as the free-form method, it's considered one of the easiest and most forward performance appraisal methods.
The Essay Method, also known as the Free-Form Method, is a qualitative performance appraisal approach where the manager writes a narrative description of the employee's performance during the review period. This description typically focuses on the employee's strengths, weaknesses, achievements, contributions, and areas for improvement.
In an essay appraisal, the source answers a series of questions about the employee's performance in essay form. This can be a trait method and/or a behavioral method, depending on how the manager writes the essay. ... Type of Performance Appraisal Method Advantages Disadvantages; Graphic Rating Scale: Inexpensive to develop: Subjectivity ...
Essay Method. I n the essay method approach, the appraiser prepares a written statement about the employee being appraised. The statement usually concentrates on describing specific strengths and weaknesses in job performance. It also suggests courses of action to remedy the identified problem areas. The statement may be written and edited by ...
This evaluation takes the form of a narrative essay, detailing the employee's strengths, weaknesses, accomplishments, and areas for improvement. Unlike structured methods with predetermined ratings, the Essay Method allows for a more nuanced and qualitative assessment. Key Features of the Essay Method: Flexibility: The Essay Method isn't ...
Essay Evaluation Method. The essay method is a fairly straightforward approach in which the manager or evaluator writes a descriptive essay about each employee. The essay would cover the employees' achievements throughout the evaluation period as well as their strengths and weaknesses. The essay format gives the evaluators the flexibility to ...
Checklist Scale performance appraisal method: Under this method, a checklist of statements of traits of the employee in the form of Yes or No based questions is prepared. If the person giving the feedback believes strongly that the employee possesses a particular listed trait, he checks the item; otherwise, he leaves the item blank.
Time-Consuming: Performance appraisals are very time-consuming and can be overwhelming to managers with many employees. I've known managers who were responsible for doing an annual PA on hundreds of employees. Natural Biases: Human assessments are subject to natural biases that result in rater errors.
There are some of the employee's performance appraisal methods that are framed taking into consideration all the contemporary aspect of modern day business workflow. Management by objectives mbo. 360-degree appraisal method. Cost accounting method. behaviorally anchored rating scale bars.
Advantages of the graphic rating scale method. ... Combining this appraisal method with others, such as an essay performance appraisal method, checklist scale, ranking appraisal, etc., helps minimize limitations and provides a more accurate insight into an employee's performance. 6. Train managers on how to use the graphic rating scale
Advantages of Performance Appraisal. A systematic appraisal system helps the managers to properly identify the performance of employees in a systematic manner and their areas of talent and areas where they are lacking. It helps the management to place the right employees for the perfect jobs depending on their skills in particular areas.
3. Corrects Deficiencies. Performance appraisal detects employee deficiency and suggests on corrective measures to be taken. 4. Career Growth. Appraisal serves as a tool for the employees' career planning and development as it assists in preparing each employee's SWOT analysis. 5. Promotion.
Essay Method: Essay method is the simplest one among various appraisal methods available. In this method, the rater writes a narrative description on an employee's strengths, weaknesses, past performance, potential and suggestions for improvement. Its positive point is that it is simple in use.
Self Appraisal: The employee writes an essay or answers questions about what she believes her accomplishments are and where she can improve. Work standards: This evaluation method establishes realistic goals and sets target dates. There are pros and cons of performance appraisal rating systems of all types.
Table 11.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Performance Appraisal Method. Type of Performance Appraisal Method. Advantages. Disadvantages. Graphic Rating Scale. Inexpensive to develop. Subjectivity. Easily understood by employees and managers. Can be difficult to use in making compensation and promotion decisions.
Forced Distribution. This method is a comparative method of performance appraisal. It requires managers to spread their employees on certain rating distribution. They place employees in classification ranging from poor to outstanding whereby 10% of the employees are rated as poor, 20% below average, 40% satisfactory, 20% above average and 10% ...
Performance Appraisals helps in improving employer-employee relations in the workplace. It initiates a continuous flow of communication between employer and employees. In this article, we give an overview of 29 different methods of performance appraisal, where are they applicable, the advantages and disadvantages.
Furthermore, performance appraisals are conducted once or twice a year while employees that want to achieve something in a company need feedback on a weekly basis (Bersin, 2013). Many successful companies like Microsoft are currently trying to overcome the burden of performance appraisals and focus on in-time feedback for employees, as ...
Everything you need to know about the advantages and disadvantages of performance appraisal. Performance appraisal may be viewed as a systematic and objective process of assessing an individual employee's job performance and productivity at specified intervals of time in relation to certain pre-established criteria and the organisation's objectives. Performance appraisal always involves the ...
Performance appraisals offer a business with the methods to gather data and share business and specific objectives to each employee. These appraisals are methods that can make all employee's more beneficial and involved in their work and thus make the business more prosperous. References. Youssef, C. (2015). Human resource management. (2nd ed.).
Decoding Method: Pair the letters in the ciphertext. Convert each letter to its numerical position in the alphabet (A=1, B=2, …, Z=26). Sum the numerical values of each pair. Compute the average of the sum (divide by 2). Convert the average back to a letter (1=A, 2=B, …, 26=Z). Apply this method to the given ciphertext: