- Meet the Mentors
- Get Involved
- Get the T-Shirt
- Life Science Marketing
- Community Marketing
- Custom Marketing
Join Us Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.
- Genomics & Epigenetics
- DNA / RNA Manipulation and Analysis
- Protein Expression & Analysis
- PCR & Real-time PCR
- Flow Cytometry
- Microscopy & Imaging
- Cells and Model Organisms
- Analytical Chemistry and Chromatography Techniques
- Chemistry for Biologists
- Basic Lab Skills & Know-how
- Equipment Mastery & Hacks
- Managing the Scientific Literature
- Career Development and Networking
- Dealing with Fellow Scientists
- Getting Funded
- Lab Statistics & Math
- Organization & Productivity
- Personal Development
- PhD Survival
- Soft Skills & Tools
- Software & Online Tools
- Survive & Thrive
- Taming the Literature
- Writing, Publishing & Presenting
- Writing, Publishing and Presenting

Journal Club: How to Prepare Effectively and Smash Your Presentation
Journal Club. So much more than reading a paper aloud. So many ways to mess it up. Got to present one? Then read our journal club toolkit.
Published September 14, 2022

I have a Master’s Degree in Chemistry and a Ph.D. in Structural Biology. I am interested in how the shape and connectivity of molecules relate to their reactivity and function.

Journal club. It’s so much more than orally dictating a paper to your peers.
It’s an opportunity to get a bunch of intelligent people in one place to share ideas. It’s a means to expand the scientific vocabulary of you and the audience. It’s a way to stimulate inventive research design.
But there are so many ways it can go wrong.
Poorly explained papers dictated blandly to an unengaged audience. Confusing heaps of data shoehorned into long presentations. Everybody stood awkwardly outside a meeting room you thought would be free.
Whether you are unsure what journal club is, are thinking of starting one, or simply want to up your presentation game—you’ve landed on the ultimate journal club guide.
The whats, the whys, and the hows, all in one place.
What Is a Journal Club in Science?
A journal club is a series of meetings in which somebody is elected to present a research paper, its methods, and findings to a group of colleagues.
The broad goal is to stimulate discussion and ideas that the attendees may apply to their own work. Alternatively, someone may choose a paper because it’s particularly impactful or ingenious.
Usually, the presenter alternates per a rota, and attendance may be optional or compulsory.
The presenter is expected to choose, analyze, and present the paper to the attendees with accompanying slides.
The presentation is then followed by a discussion of the paper by the attendees. This is usually in the form of a series of questions and answers directed toward the presenter. Ergo , the presenter is expected to know and understand the paper and subject area to a moderate extent.
Why Have a Journal Club?
I get it. You’re a busy person. There’s a difficult research problem standing between you and your next tenure.
Why bother spending the time and energy participating in a series of meetings that don’t get you closer to achieving your scientific goals?
The answer: journal club does get you closer to achieving your scientific goals!
But it does this in indirect ways that subtly make you a better scientist. For example:
- It probably takes you out of your comfort zone.
- It makes you a better communicator.
- It makes you better at analyzing data.
- It improves your ability to critique research.
- It makes you survey relevant literature.
- It exposes you and your audience to new concepts.
- It exposes your audience to relevant literature.
- It improves the reading habits of you and your audience.
- It gets clever people talking to each other.
- It gives people a break from practical science.
It also provides a platform for people to share ideas based on their collective scientific experience. And every participant has a unique set of skills. So every participant has the potential to provide valuable insight.
This is what a good journal club should illicit.
Think of journal club as reading a book. It’s going to enrich you and add beneficially to the sum of your mental furniture, but you won’t know how until you’ve read it.
Need empirical evidence to convince you? Okay!
In 1988 a group of medical interns was split into two groups. One received journal club teaching and the other received a series of seminars. Approximately 86% of the journal club group reported improved reading habits. This compares to 0% in the group who received seminar-based teaching. [1]
Journal Club Template Structure
So now you know what journal club is, you might wonder, “how is it organized and structured?”
That’s what the rest of this article delves into. If you’re in a rush and need to head back to the lab, here’s a graphical summary (Figure 1).

Nobody likes meetings that flounder around and run over time. And while I have no data to prove it, I reckon people take less away from such meetings. Here’s a basic journal club template that assumes you are the presenter.
Introduce the Paper, Topic, Journal, and Authors
Let your audience know what you will be talking about before diving right in. Remember that repetition (of the important bits) can be a good thing.
Introducing the journal in which the paper is published will give your audience a rough idea of the prestige of the work.
And introducing the authors and their respective institutes gives your audience the option of stowing this information away and following it up with further reading in their own time.
Provide a Reason Why You Chose the Paper
Have the authors managed to circumvent sacrificing animals to achieve a goal that traditionally necessitated animal harm? Have the authors repurposed a method and applied it to a problem it’s not traditionally associated with? Is it simply a monumental feat of work and success?
People are probably more likely to listen and engage with you if they know why, in all politeness, you have chosen to use their time to talk about a given paper.
It also helps them focus on the relevant bits of your presentation and form cogent questions.
Orally Present Key Findings and Methods of the Paper
Simple. Read the paper. Understand it. Make some slides. Present.
Okay, there are a lot of ways you can get this wrong and make a hash of it. We’ll tell you how to avoid these pitfalls later on.
But for now, acknowledge that a journal club meeting starts with a presentation that sets up the main bit of it—the discussion.
Invite Your Audience to Participate in a Discussion
The discussion is the primary and arguably most beneficial component of journal club since it gives the audience a platform to share ideas. Ideas formulated by their previous experience.
And I’ve said already that these contributions are unique and have the potential to be valuable to your work.
That’s why the discussion element is important.
Their questions might concur and elaborate on the contents of the paper and your presentation of it.
Alternatively, they might disagree with the methods and/or conclusions. They might even disagree with your presentation of technical topics.
Try not to be daunted, however, as all of this ultimately adds to your knowledge, and it should all be conducted in a constructive spirit.
Summarize the Meeting and Thank Your Audience for Attending
There’s no particularly enlightening reason as to why to do these things. Summarizing helps people come away from the meeting feeling like it was a positive and rewarding thing to attend.
And thanking people for their time is a simple courtesy.
How Do You Organize It?
Basic steps if you are the organizer.
Okay, we’ve just learned what goes into speaking at the journal club. But presenter or not, the responsibility of organizing it might fall to you.
So, logistically , how do you prepare a journal club? Simply follow these 5 steps:
- Distribute copies of the research article to potential participants.
- Arrange a meeting time and location.
- Organize a speaker.
- Hold the journal club.
- Seek feedback on the quality of the meeting.
Apart from point 5, these are fairly self-explanatory. Regarding point 5, feedback is essential to growing as a scientist and presenter. The easiest way to seek feedback is simply to ask.
Alternatively, you could create a form for all the meetings in the series and ask the audience to complete and return it to you.
Basic Steps If You Are the Speaker
If somebody has done all the logistics for you, great! Don’t get complacent, however.
Why not use the time to elevate your presentation to make your journal club contribution memorable and beneficial?
Don’t worry about the “hows” because we’re going to elaborate on these points, but here are 5 things you can do to ace your presentation:
- Don’t leave it to the last minute.
- Know your audience.
- Keep your presentation slides simple.
- Keep your audience engaged.
- Be open to questions and critiques.
Regarding point 1, giving yourself sufficient time to thoroughly read the article you have chosen to present ensures you are familiar with the material in it. This is essential because you will be asked questions about it. A confident reply is the foundation of an enlightening discussion.
Regarding point 3, we’re going to tell you exactly how to prepare effective slides in its own section later. But if you are in a rush, minimize the use of excessive text. And if you provide background information, stick to diagrams that give an overview of results from previous work. Remember: a picture speaks louder than a thousand words.
Regarding point 4, engagement is critical. So carry out a practice run to make sure you are happy with the flow of your presentation and to give you an idea of your timing. It is important to stick to the time that is allotted for you.
This provides good practice for more formal conference settings where you will be stopped if you run over time. It’s also good manners and shows consideration for the attendees.
And regarding point 5, as the presenter, questions are likely to be directed toward you. So anticipate questions from the outset and prepare for the obvious ones to the best of your ability.
There’s a limit to everyone’s knowledge, but being unable to provide any sort of response will be embarrassing and make you seem unprepared.
Anticipate that people might also disagree with any definitions you make and even with your presentation of other people’s data. Whether or not you agree is a different matter, but present your reasons in a calm and professional manner.
If someone is rude, don’t rise to it and respond calmly and courteously. This shouldn’t happen too often, but we all have “those people” around us.
How Do You Choose a Journal Club Paper?
Consider the quality of the journal.
Just to be clear, I don’t mean the paper itself but the journal it’s published in.
An obscure journal is more likely to contain science that’s either boring, sloppy, wrong, or all three.
And people are giving up their time and hope to be stimulated. So oblige them!
Journal impact factor and rejection rate (the ratio of accepted to rejected articles) can help you decide whether a paper is worth discussing.
Consider the Impact and Scope of the Paper
Similar to the above, but remember, dross gets published in high-impact journals too. Hopefully, you’ve read the paper you want to present. But ask yourself what makes this particular paper stand out from the millions of others to be worth presenting.
Keep It Relevant and Keep It Interesting
When choosing a paper to present, keep your audience in mind. Choose something that is relevant to the particular group you are presenting to. If only you and a few other people understand the topic, it can come off as elitist.
How Do You Break Down and Present the Paper?
Know and provide the background material.
Before you dive into the data, spend a few minutes talking about the context of the paper. What did the authors know before they started this work? How did they formulate their hypothesis? Why did they choose to address it in this way?
You may want to reference an earlier paper from the same group if the paper represents a continuation of it, but keep it brief.
Try to explain how this paper tackles an unanswered question in the field.
Understand the Hypothesis and Methods of the Paper
Make a point of stating the hypothesis or main question of the paper, so everyone understands the goal of the study and has a foundation for the presentation and discussion.
Everyone needs to start on the same foot and remain on the same page as the meeting progresses.
Turn the Paper into a Progression of Scientific Questions
Present the data as a logical series of questions and answers. A well-written paper will already have done the hard work for you. It will be organized carefully so that each figure answers a specific question, and each new question builds on the answer from the previous figure.
If you’re having trouble grasping the flow of the paper, try writing up a brief outline of the main points. Try putting the experiments and conclusions in your own words, too.
Feel free to leave out parts of the figures that you think are unnecessary, or pull extra data from the supplemental figures if it will help you explain the paper better.
Ask Yourself Questions about the Paper Before You Present
We’ve touched on this already. This is to prepare you for any questions that are likely to be asked of you. When you read the paper, what bits didn’t you understand?
Simplify Unfamiliar and Difficult Concepts
Not everyone will be familiar with the same concepts. For example, most biologists will not have a rigorous definition of entropy committed to memory or know its units. The concept of entropy might crop up in a biophysics paper, however.
Put yourself in the audience’s shoes and anticipate what they might not fully understand given their respective backgrounds.
If you are unsure, ask them if they need a definition or include a short definition in your slides.
Sum Up Important Conclusions
After you’ve finished explaining the nitty-gritty details of the paper, conclude your presentation of the data with a list of significant findings.
Every conclusion will tie in directly to proving the major conclusion of the paper. It should be clear at this point how the data answers the main question.
How Do You Present a Journal Club Powerpoint?
Okay, so we’ve just gone through the steps required to break down a paper to present it effectively at journal club. But this needs to be paired with a PowerPoint presentation, and the two bridged orally by your talk. How do you ace this?
Provide Broad Context to the Research
We are all bogged down by minutia and reagents out of necessity.
Being bogged down is research. But it helps to come up for air. Ultimately, how will the research you are about to discuss benefit the Earth and its inhabitants when said research is translated into actual products?
Science can be for its own sake, but funded science rarely is. Reminding the journal club audience of the widest aims of the nominated field provides a clear starting point for the discussion and shows that you understand the efficacy of the research at its most basic level.
The Golden Rule: A Slide per Minute
Remember during lectures when the lecturer would open PowerPoint, and you would see, with dismay, that their slides went up to 90 or something daft? Then the last 20 get rushed through, but that’s what the exam question ends up being based on.
Don’t be that person!
A 10-15 minute talk should be accompanied by? 10-15 slides! Less is more.
Be Judicious about the Information You Choose to Present
If you are present everything in the paper, people might as well just read it in their own time, and we can call journal club off.
Try to abstract only the key findings. Sometimes technical data is necessary for what you are speaking about because their value affects the efficacy of the data and validity of the conclusions.
Most of the time, however, the exact experimental conditions can be left out and given on request. It’s good practice to put all the technical data that you anticipate being asked for in a few slides at the end of your talk.
Use your judgment.
Keep the Amount of Information per Slide Low for Clarity
Your audience is already listening to you and looking at the slides, so they have a limited capacity for what they can absorb. Overwhelming them with visual queues and talking to them will disengage them.
Have only a few clearly related images that apply directly to what you speaking about at the time. Annotate them with the only key facts from your talk and develop the bigger picture verbally.
This will be hard at first because you must be on the ball and confident with your subject area and speaking to an audience.
And definitely use circles, boxes, and arrows to highlight important parts of figures, and add a flowchart or diagram to explain an unfamiliar method.
Keep It Short Overall
The exact length of your meeting is up to you or the organizer. A 15-minute talk followed by a 30-minute discussion is about the right length, Add in tea and coffee and hellos, and you get to an hour.
We tend to speak at 125-150 words per minute. All these words should not be on your slides, however. So, commit a rough script to memory and rehearse it.
You’ll find that the main points you need to mention start to stand out and fall into place naturally. Plus, your slides will serve as visual queue cards.
How Do You Ask a Question in Journal Club?
A well-organized journal club will have clear expectations of whether or not questions should be asked only during the discussion, or whether interruptions during the presentation are allowed.
And I don’t mean literally how do you soliloquize, but rather how do you get an effective discussion going.
Presenters: Ask Questions to the Audience
We all know how it goes. “Any questions?” Silence.
Scientists, by their very nature, are usually introverted. Any ideas they might want to contribute to a discussion are typically outweighed by the fear of looking silly in front of their peers. Or they think everyone already knows the item they wish to contribute. Or don’t want to be publicly disproven. And so on.
Prepare some questions to ask the audience in advance. As soon as a few people speak, everyone tends to loosen up. Take advantage of this.
Audience: Think About Topics to Praise or Critique
Aside from seeking clarification on any unclear topics, you could ask questions on:
- Does the data support the conclusions?
- Are the conclusions relevant?
- Are the methods valid?
- What are the drawbacks and limitations of the conclusions?
- Are there better methods to test the hypothesis?
- How will the research be translated into real-world benefits?
- Are there obvious follow-up experiments?
- How well is the burden of proof met?
- Is the data physiologically relevant?
- Do you agree with the conclusions?
How to Keep It Fun
Make it interactive.
Quizzes and polls are a great way to do this! And QR codes make it really easy to do on-the-fly. Remember, scientists, are shy. So why not seek their participation in an anonymized form?
You could poll your audience on the quality of the work. You could make a fun quiz based on the material you’ve covered. You could do a live “what happened next?” You could even get your feedback this way. Here’s what to do:
- Create your quiz or poll using Google forms .
- Make a shareable link.
- Paste the link into a free QR code generator .
- Put the QR code in the appropriate bit of your talk.
Use Multimedia
Talking to your audience without anything to break it up is a guaranteed way of sending them all to sleep.
Consider embedding demonstration videos and animations in your talk. Or even just pausing to interject with your own anecdotes will keep everyone concentrated on you.
Keep It Informal
At the end of the day, we’re all scientists. Perhaps at different stages of our careers, but we’ve all had similar-ish trajectories. So there’s no need for haughtiness.
And research institutes are usually aggressively casual in terms of dress code, coffee breaks, and impromptu chats. Asking everyone to don a suit won’t add any value to a journal club.
Your Journal Club Toolkit in Summary
Anyone can read a paper, but the value lies in understanding it and applying it to your own research and thought process.
Remember, journal club is about extracting wisdom from your colleagues in the form of a discussion while disseminating wisdom to them in a digestible format.
Need some inspiration for your journal club? Check out the online repositories hosted by PNAS and NASPAG to get your juices flowing.
We’ve covered a lot of information, from parsing papers to organizational logistics, and effective presentation. So why not bookmark this page so you can come back to it all when it’s your turn to present?
While you’re here, why not ensure you’re always prepared for your next journal club and download bitesize bio’s free journal club checklist ?
And if you present at journal club and realize we’ve left something obvious out. Get in touch and let us know. We’ll add it to the article!
- Linzer M et al . (1988) Impact of a medical journal club on house-staff reading habits, knowledge, and critical appraisal skills . JAMA 260 :2537–41
Share this article:
More 'Writing, Publishing and Presenting' articles

The Practical Guide to Running a Perfect Homemade SDS-PAGE Gel
As biochemists, we routinely run SDS-PAGE to analyze our proteins. Imagine the time and effort you are going to save when you can run every gel to perfection.

What is the H-index, and Does it Matter?
How do you measure how good you are as a scientist? One way is the h-index. Discover what this is, and learn about the pros and cons of using it to assess your scientific career.
5 Ways to Delay The Publication of Your Manuscript
Most scientists I know approach the publication process with fear and trembling: the endless discussions about what journal to submit to, the agonized consideration of impact factors, comparing the all-important “time to first decision”, etc. Now that I’ve been working for a scientific publisher for a few months, I’m surprised at how many manuscripts still…

Five Simple Tips to Break Your Dissertation up into Manageable Parts
You’ve got an advisor, you’re done with classes, you’ve finally passed your qualifying exams and your dissertation project is underway. Life is looking good, but it’s not too early to start thinking about how to tackle your dissertation. Chances are this is the biggest writing project you have ever undertaken, so breaking it up into…

How to Check the Accuracy of Your Pipette in 7 Easy Steps
I’d bet that your trusty pipette is probably one the the most often used tools in the lab. But do you have any idea how to check the accuracy of your pipette? We’ll take you though how to do this in just 7 easy steps.

A poster presentation at a conference: a to-do list
People go to conferences to get feedback on their work, to learn about recent findings, and to meet colleagues (both new and old). I advise not to concentrate only on your work, but also on on your goals. Here is my algorithm for attending conferences.
Raise your Research Game with Bitesize Bio
Sign up for our feature-packed newsletter today to ensure you get the latest expert help and advice to level up your lab work.
You’ll stay up-to-date with our podcasts, webinars, workshops, downloadables, and more, delivered to your inbox every fortnight.
Don’t delay! Sign up now
Newsletters
All emails contain an unsubscribe link. You can review our privacy policy , cookie policy and terms and conditions online.
- Technical Skills
- More Skills
Bitesize Bio Powered
- Microscopy Focus
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
Advertisement
How to Prepare an Outstanding Journal Club Presentation
- Request Permissions
Rishi Sawhney; How to Prepare an Outstanding Journal Club Presentation. The Hematologist 2006; 3 (1): No Pagination Specified. doi: https://doi.org/10.1182/hem.V3.1.1308
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
Dr. Sawhney is a member of the ASH Trainee Council and a Fellow at the Medical University of South Carolina.
Journal club presentations provide a forum through which hematology trainees keep abreast of new developments in hematology and engage in informal discussion and interaction. Furthermore, honing presentation skills and mastering the ability to critically appraise the evidence add to our armamentarium as clinicians. Outlined here is a systematic approach to preparing a journal club presentation, with emphasis on key elements of the talk and references for electronic resources. Use of these tools and techniques will contribute to the success of your presentation.
I. ARTICLE SELECTION:
The foundation of an outstanding journal club presentation rests on the choice of an interesting and well-written paper for discussion. Several resources are available to help you select important and timely research, including the American College of Physicians (ACP) Journal Club and the Diffusion section of The Hematologist . McMaster University has created the McMaster Online Rating of Evidence (MORE) system to identify the highest-quality published research. In fact, the ACP Journal Club uses the MORE system to select their articles 1 . Specific inclusion criteria have been delineated in order to distinguish papers with the highest scientific merit 2 . Articles that have passed this screening are then rated by clinicians on their clinical relevance and newsworthiness, using a graded scale 3 . With the help of your mentors and colleagues, you can use these criteria and the rating scale as informal guidelines to ensure that your chosen article merits presentation.
II. ARTICLE PRESENTATION:
Study Background: This section provides your audience with the necessary information and context for a thoughtful and critical evaluation of the article's significance. The goals are 1) to describe the rationale for and clinical relevance of the study question, and 2) to highlight the preclinical and clinical research that led to the current trial. Review the papers referenced in the study's "Background" section as well as previous work by the study's authors. It also may be helpful to discuss data supporting the current standard of care against which the study intervention is being measured.
Study Methodology and Results: Clearly describe the study population, including inclusion/exclusion criteria. A diagrammatic schema is easy to construct using PowerPoint software and will help to clearly illustrate treatment arms in complex trials. Explain the statistical methods, obtaining assistance from a statistician if needed. Take this opportunity to verbally and graphically highlight key results from the study, with plans to expand on their significance later in your presentation.
Author's Discussion: Present the authors' conclusions and their perspective on the study results, including explanations of inconsistent or unexpected results. Consider whether the conclusions drawn are supported by the data presented.
III. ARTICLE CRITIQUE:
This component of your presentation will define the success of your journal club. A useful and widely accepted approach to this analysis has been published in JAMA's series "User's guide to the medical literature." The Centre for Health Evidence in Canada has made the complete full-text set of these user's guides available online 4 . This site offers review guidelines for a menu of article types, and it is an excellent, comprehensive resource to focus your study critique. A practical, user-friendly approach to literature evaluation that includes a worksheet is also available on the ASH Web site for your use 5 .
While a comprehensive discussion of scientific literature appraisal is beyond the scope of this discussion, several helpful tips warrant mention here. In assessing the validity of the study, it is important to assess for potential sources of bias, including the funding sources and authors' affiliations. It is also helpful to look for accompanying editorial commentary, which can provide a unique perspective on the article and highlight controversial issues. You should plan to discuss the trade-offs between potential benefits of the study intervention versus potential risks and the cost. By utilizing the concept of number needed to treat (NNT), one can assess the true impact of the study intervention on clinical practice. Furthermore, by incorporating the incidence rates of clinically significant toxicities with the financial costs into the NNT, you can generate a rather sophisticated analysis of the study's impact on practice.
IV. CONCLUSIONS, IMPLICATIONS, AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS:
Restate the authors' take-home message followed by your own interpretation of the study. Provide a personal perspective, detailing why you find this paper interesting or important. Then, look forward and use this opportunity to "think outside the box." Do you envision these study results changing the landscape of clinical practice or redirecting research in this field? If so, how? In articles about therapy, future directions may include moving the therapy up to first-line setting, assessing the drug in combination regimens or other disease states, or developing same-class novel compounds in the pipeline. Searching for related clinical trials on the NIH Web site 6 can prove helpful, as can consultation with an expert in this field.
Good journal club discussions are integral to the educational experience of hematology trainees. Following the above approach, while utilizing the resources available, will lay the groundwork for an outstanding presentation.
WEB BASED REFERENCES
www.acpjc.org
hiru.mcmaster.ca/more/InclusionCriteria.htm
hiru.mcmaster.ca/more/RatingFormSample.htm
www.cche.net/main.asp
www.hematology.org/Trainees
www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials
- Previous Article
- Next Article
Email alerts
Affiliations.
- Current Issue
- About The Hematologist
- Advertising in The Hematologist
- Editorial Board
- Permissions
- Submissions
- Email Alerts
- ASH Publications App
American Society of Hematology
- 2021 L Street NW, Suite 900
- Washington, DC 20036
- TEL +1 202-776-0544
- FAX +1 202-776-0545
ASH Publications
- Blood Advances
- Blood Neoplasia
- Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis
- Hematology, ASH Education Program
- ASH Clinical News
- The Hematologist
- Publications
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to prepare and...
How to prepare and deliver an effective oral presentation
- Related content
- Peer review
- Lucia Hartigan , registrar 1 ,
- Fionnuala Mone , fellow in maternal fetal medicine 1 ,
- Mary Higgins , consultant obstetrician 2
- 1 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin, Ireland
- 2 National Maternity Hospital, Dublin; Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Medicine and Medical Sciences, University College Dublin
- luciahartigan{at}hotmail.com
The success of an oral presentation lies in the speaker’s ability to transmit information to the audience. Lucia Hartigan and colleagues describe what they have learnt about delivering an effective scientific oral presentation from their own experiences, and their mistakes
The objective of an oral presentation is to portray large amounts of often complex information in a clear, bite sized fashion. Although some of the success lies in the content, the rest lies in the speaker’s skills in transmitting the information to the audience. 1
Preparation
It is important to be as well prepared as possible. Look at the venue in person, and find out the time allowed for your presentation and for questions, and the size of the audience and their backgrounds, which will allow the presentation to be pitched at the appropriate level.
See what the ambience and temperature are like and check that the format of your presentation is compatible with the available computer. This is particularly important when embedding videos. Before you begin, look at the video on stand-by and make sure the lights are dimmed and the speakers are functioning.
For visual aids, Microsoft PowerPoint or Apple Mac Keynote programmes are usual, although Prezi is increasing in popularity. Save the presentation on a USB stick, with email or cloud storage backup to avoid last minute disasters.
When preparing the presentation, start with an opening slide containing the title of the study, your name, and the date. Begin by addressing and thanking the audience and the organisation that has invited you to speak. Typically, the format includes background, study aims, methodology, results, strengths and weaknesses of the study, and conclusions.
If the study takes a lecturing format, consider including “any questions?” on a slide before you conclude, which will allow the audience to remember the take home messages. Ideally, the audience should remember three of the main points from the presentation. 2
Have a maximum of four short points per slide. If you can display something as a diagram, video, or a graph, use this instead of text and talk around it.
Animation is available in both Microsoft PowerPoint and the Apple Mac Keynote programme, and its use in presentations has been demonstrated to assist in the retention and recall of facts. 3 Do not overuse it, though, as it could make you appear unprofessional. If you show a video or diagram don’t just sit back—use a laser pointer to explain what is happening.
Rehearse your presentation in front of at least one person. Request feedback and amend accordingly. If possible, practise in the venue itself so things will not be unfamiliar on the day. If you appear comfortable, the audience will feel comfortable. Ask colleagues and seniors what questions they would ask and prepare responses to these questions.
It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don’t have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
Try to present slides at the rate of around one slide a minute. If you talk too much, you will lose your audience’s attention. The slides or videos should be an adjunct to your presentation, so do not hide behind them, and be proud of the work you are presenting. You should avoid reading the wording on the slides, but instead talk around the content on them.
Maintain eye contact with the audience and remember to smile and pause after each comment, giving your nerves time to settle. Speak slowly and concisely, highlighting key points.
Do not assume that the audience is completely familiar with the topic you are passionate about, but don’t patronise them either. Use every presentation as an opportunity to teach, even your seniors. The information you are presenting may be new to them, but it is always important to know your audience’s background. You can then ensure you do not patronise world experts.
To maintain the audience’s attention, vary the tone and inflection of your voice. If appropriate, use humour, though you should run any comments or jokes past others beforehand and make sure they are culturally appropriate. Check every now and again that the audience is following and offer them the opportunity to ask questions.
Finishing up is the most important part, as this is when you send your take home message with the audience. Slow down, even though time is important at this stage. Conclude with the three key points from the study and leave the slide up for a further few seconds. Do not ramble on. Give the audience a chance to digest the presentation. Conclude by acknowledging those who assisted you in the study, and thank the audience and organisation. If you are presenting in North America, it is usual practice to conclude with an image of the team. If you wish to show references, insert a text box on the appropriate slide with the primary author, year, and paper, although this is not always required.
Answering questions can often feel like the most daunting part, but don’t look upon this as negative. Assume that the audience has listened and is interested in your research. Listen carefully, and if you are unsure about what someone is saying, ask for the question to be rephrased. Thank the audience member for asking the question and keep responses brief and concise. If you are unsure of the answer you can say that the questioner has raised an interesting point that you will have to investigate further. Have someone in the audience who will write down the questions for you, and remember that this is effectively free peer review.
Be proud of your achievements and try to do justice to the work that you and the rest of your group have done. You deserve to be up on that stage, so show off what you have achieved.
Competing interests: We have read and understood the BMJ Group policy on declaration of interests and declare the following interests: None.
- ↵ Rovira A, Auger C, Naidich TP. How to prepare an oral presentation and a conference. Radiologica 2013 ; 55 (suppl 1): 2 -7S. OpenUrl
- ↵ Bourne PE. Ten simple rules for making good oral presentations. PLos Comput Biol 2007 ; 3 : e77 . OpenUrl PubMed
- ↵ Naqvi SH, Mobasher F, Afzal MA, Umair M, Kohli AN, Bukhari MH. Effectiveness of teaching methods in a medical institute: perceptions of medical students to teaching aids. J Pak Med Assoc 2013 ; 63 : 859 -64. OpenUrl
Loading metrics
Open Access
Ten Simple Rules for Making Good Oral Presentations
- Philip E Bourne

Published: April 27, 2007
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030077
- Reader Comments
Citation: Bourne PE (2007) Ten Simple Rules for Making Good Oral Presentations. PLoS Comput Biol 3(4): e77. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030077
Copyright: © 2007 Philip E. Bourne. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Funding: The author received no specific funding for this article.
Competing interests: The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Continuing our “Ten Simple Rules” series [ 1 – 5 ], we consider here what it takes to make a good oral presentation. While the rules apply broadly across disciplines, they are certainly important from the perspective of this readership. Clear and logical delivery of your ideas and scientific results is an important component of a successful scientific career. Presentations encourage broader dissemination of your work and highlight work that may not receive attention in written form.
Rule 1: Talk to the Audience
We do not mean face the audience, although gaining eye contact with as many people as possible when you present is important since it adds a level of intimacy and comfort to the presentation. We mean prepare presentations that address the target audience. Be sure you know who your audience is—what are their backgrounds and knowledge level of the material you are presenting and what they are hoping to get out of the presentation? Off-topic presentations are usually boring and will not endear you to the audience. Deliver what the audience wants to hear.
Rule 2: Less is More
A common mistake of inexperienced presenters is to try to say too much. They feel the need to prove themselves by proving to the audience that they know a lot. As a result, the main message is often lost, and valuable question time is usually curtailed. Your knowledge of the subject is best expressed through a clear and concise presentation that is provocative and leads to a dialog during the question-and-answer session when the audience becomes active participants. At that point, your knowledge of the material will likely become clear. If you do not get any questions, then you have not been following the other rules. Most likely, your presentation was either incomprehensible or trite. A side effect of too much material is that you talk too quickly, another ingredient of a lost message.
Rule 3: Only Talk When You Have Something to Say
Do not be overzealous about what you think you will have available to present when the time comes. Research never goes as fast as you would like. Remember the audience's time is precious and should not be abused by presentation of uninteresting preliminary material.
Rule 4: Make the Take-Home Message Persistent
A good rule of thumb would seem to be that if you ask a member of the audience a week later about your presentation, they should be able to remember three points. If these are the key points you were trying to get across, you have done a good job. If they can remember any three points, but not the key points, then your emphasis was wrong. It is obvious what it means if they cannot recall three points!
Rule 5: Be Logical
Think of the presentation as a story. There is a logical flow—a clear beginning, middle, and an end. You set the stage (beginning), you tell the story (middle), and you have a big finish (the end) where the take-home message is clearly understood.
Rule 6: Treat the Floor as a Stage
Presentations should be entertaining, but do not overdo it and do know your limits. If you are not humorous by nature, do not try and be humorous. If you are not good at telling anecdotes, do not try and tell anecdotes, and so on. A good entertainer will captivate the audience and increase the likelihood of obeying Rule 4.
Rule 7: Practice and Time Your Presentation
This is particularly important for inexperienced presenters. Even more important, when you give the presentation, stick to what you practice. It is common to deviate, and even worse to start presenting material that you know less about than the audience does. The more you practice, the less likely you will be to go off on tangents. Visual cues help here. The more presentations you give, the better you are going to get. In a scientific environment, take every opportunity to do journal club and become a teaching assistant if it allows you to present. An important talk should not be given for the first time to an audience of peers. You should have delivered it to your research collaborators who will be kinder and gentler but still point out obvious discrepancies. Laboratory group meetings are a fine forum for this.
Rule 8: Use Visuals Sparingly but Effectively
Presenters have different styles of presenting. Some can captivate the audience with no visuals (rare); others require visual cues and in addition, depending on the material, may not be able to present a particular topic well without the appropriate visuals such as graphs and charts. Preparing good visual materials will be the subject of a further Ten Simple Rules. Rule 7 will help you to define the right number of visuals for a particular presentation. A useful rule of thumb for us is if you have more than one visual for each minute you are talking, you have too many and you will run over time. Obviously some visuals are quick, others take time to get the message across; again Rule 7 will help. Avoid reading the visual unless you wish to emphasize the point explicitly, the audience can read, too! The visual should support what you are saying either for emphasis or with data to prove the verbal point. Finally, do not overload the visual. Make the points few and clear.
Rule 9: Review Audio and/or Video of Your Presentations
There is nothing more effective than listening to, or listening to and viewing, a presentation you have made. Violations of the other rules will become obvious. Seeing what is wrong is easy, correcting it the next time around is not. You will likely need to break bad habits that lead to the violation of the other rules. Work hard on breaking bad habits; it is important.
Rule 10: Provide Appropriate Acknowledgments
People love to be acknowledged for their contributions. Having many gratuitous acknowledgements degrades the people who actually contributed. If you defy Rule 7, then you will not be able to acknowledge people and organizations appropriately, as you will run out of time. It is often appropriate to acknowledge people at the beginning or at the point of their contribution so that their contributions are very clear.
As a final word of caution, we have found that even in following the Ten Simple Rules (or perhaps thinking we are following them), the outcome of a presentation is not always guaranteed. Audience–presenter dynamics are hard to predict even though the metric of depth and intensity of questions and off-line followup provide excellent indicators. Sometimes you are sure a presentation will go well, and afterward you feel it did not go well. Other times you dread what the audience will think, and you come away pleased as punch. Such is life. As always, we welcome your comments on these Ten Simple Rules by Reader Response.
Acknowledgments
The idea for this particular Ten Simple Rules was inspired by a conversation with Fiona Addison.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
Research Communities by Springer Nature
How to make a good (and interesting) presentation in journal club.
Share this post
Choose a social network to share with, or copy the shortened URL to share elsewhere
Share with...
...or copy the link.

communities.springernature.com
Who says science needs to be hard and dry?
When I give presentation in journal club, I always select the kind of papers that tell a "fun" story- I believe we can learn more by discussing "how the author(s) come up with such idea?" question. Over the years, the topics of my selected papers have ranged from how bugs determine the color of laid eggs to whether getting cancer is just bad luck. Many people have told me that they like how the papers I selected arouse interest and discussion from the audience in journal club. Here I'd like to explain how we all can benefit our research by reading and interpreting research papers from a different perspective.
To begin with, we have to understand that the purpose of scientific research is very different from that of scientific publication, and the latter can facilitate but does not achieve the former. Therefore, it is important for a career scientist to be able to distinguish these from each other, get to know the structural elements of both, and identify what can be learned from them for her/his own research.
First of all, we don’t only study cancer. We study the natural history of life. Ultimately, all biological studies address different perspectives of life. Keeping in mind the quote "Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution" (Theodosius Dobzhansky, 1973), any paper is relevant.
Second, in most studies, the authors observe the world through the lens of the contemporary paradigm or prevailing models. Many papers in top-tier journals attempt to find the “last piece” of the puzzle in the established model (and many “elite” authors are very good at this). An idea that does not fit into any of the paradigms will have a hard time getting published. A good example is Carl Woese. He single-handedly redefined the history of life but was mostly ignored until his later years because people of his time did not know where his idea should be placed (if you don’t know who he is, please Google him).
Third, we have to understand how a paper is written. Running a study is like constructing a skyscraper. You dig ground to make a foundation, lift pillars, construct floor by floor. Finally, you reach the top and finish the roof. When the construction is completed, you remove all the scaffolds and auxiliaries, clean up all the garbage, and decorate the environment. Now a brand new, beautiful building stands in front of people. But when someone asks you how such a marvelous building is constructed, you say: "I started constructing it from the roof, followed by the top floor, and floor by floor built down until the first floor touched the ground. This is a perfect plan, isn’t it?” Unfortunately, this is often how a study is presented at publication nowadays. If you follow the authors’ plans, most papers are over-decorated in a similar fashion, making them quite indistinguishable, with everything arranged perfectly and logically, even though the study hadn’t truly evolved in that way, sacrificing many critical elements that may give implications or insights to the field. For example, a discovery made by chance is described as a process following a logical design without mentioning the accident, thus the critical elements involved in the discovering circumstances may be lost forever, resulting in low reproducibility. Alternatively, following a “perfect” plan, a paper may be over-decorated with mechanism studies, and the real drivers of the phenomenon are overlooked.
The route out of these “conceptual traps”, I believe, comes from a genuine observation or curious question that can catch people by surprise. For example, one of my all-time favorite papers is “Genetic Variations Associated with Red Hair Color and Fear of Dental Pain, Anxiety Regarding Dental Care and Avoidance of Dental Care” - yes, this is the real title. The study was initiated by an urban legend circulating among dentists: redheads have a worse response to anesthesia and terrible tooth conditions. The author - a dentist - wanted to test if it was true. What would you think if you heard such a rumor as a dentist? As you can imagine, this study is not high-profile journal material (it was published in a dental house journal, J. Am. Dental Assoc., 2009, 140:896-905). Because I study pigment cells, the results gave me a “think-out-of-the-box” moment: pigment variation and neural response are intertwined together evolutionarily.
With these thoughts in mind, I would like to share a few “tips” for selecting a paper and preparing a presentation for journal club:
● Select a paper with a subject that might interest both scientists and non-scientists. A genuine question out of curiosity is always intriguing. Studies in lifestyle and behavior are fun because the audience can connect with them personally.
● In many cases, why the researcher asked the question and how she/he solved it are more valuable - and interesting - than the discovery itself. Even a wrong question can lead to a good observation.
● Discuss what led the authors to the current study in the historic and/or conceptual (paradigm) perspective. This is necessary, in my opinion. For example, Joan Masague copied the in vivo cycling methodology from Isaiah J. Fidler, who got the idea from Luria-Delbruck distribution in bacterial resistance to phage. From here, we can easily see how studies of bacterial resistance heavily impacted the concept of clonal selection in cancer research. It would be very interesting to discuss the extent/limit of this concept in cancer research. Digging into the history of the research field can bring implications beyond the imagination.
● Figure out if the question and the hypothesis are the “roof” or the “foundation” of the study. This will also arouse fun discussion.
● Examine whether the “mechanism” is required or decorative for the conclusion. Here is one of my favorite examples. In 1846, Hungarian clinician Ignaz Semmelweis published his findings in Vienna that washing deliverers’ hands with chlorinated lime solutions could effectively reduce maternal mortality in obstetrical clinics. Although the experimental data was solid, the idea was rejected by the most renowned doctors at the time, including Rudolf Virchow. The reason? Semmelweis could not offer an explanation fitting the contemporary scientific concept (i.e., “mechanism”) for his findings. The practice of hand disinfection did not prevail until Pasteur’s germ theory emerged in 1880, 15 years after Semmelweis had died in a mental institute. During this period, more women died unnecessarily because elite doctors demanded mechanisms in a scientific paper.
● Try to discuss how the findings can be applied to other fields. For example, after discovery of immune checkpoints, many immunologists tried to activate them to cure autoimmunity. Imagine this: if you read such a paper in those years, how would you think about its implication in cancer research?
Actually, all the statements above involve only two factors: zooming out and then zooming in on the question. Believe me, doing this will easily facilitate many fun discussions.
Here are some more practical, step-by-step suggestions for the slides for journal club:
1. Start with a brief background of the field: a historic account to explain “how we got here”, and/or introduction to the current and alternative paradigms. Do these paradigms make sense in terms of biological evolution or life history?
2. Summarize the model system and focused pathway/process being used and studied that is related to the paper. What is the scope of the model being used, and how relevant is it to the real world?
3. What is the author’s question? Why did she/he ask it? Is the question derived from the current model, or from an unexpected observation?
4. What are the key claims in the paper? (We put this first so we can hang all the data against their claims. Ironically, the hypothesis in the paper may already give a good clue since it is often added after all the results were generated.)
5. A summary of the study design is helpful, especially for complicated projects.
6. Pick and choose key data that support the central conclusion, summarize everything else.
7. How much could the results answer the question? Alternatively, what is the paradigm-shifting discovery?
8. What is the implication of the results? How can we make use of the information in the paper in our own work? In what ways could the results impact other fields? What are the unanswered questions?
All the questions here can be asked during your presentation to arouse questions or discussion from the audience.
Case Study: Ising C., et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature (2019).
Conclusion: 1. fibrillar amyloid-beta -> NLRP3 inflammasome -> tau kinase/phosphatase -> tau pathology 2. Neurofibrillary tangles develop downstream of amyloid-beta-induced microglial activation.
Historic context: What is the “driver” of Alzheimer disease (AD) identified by pathological and genetic studies in the history of research?
Evolutionary context: Why is there neurodegeneration disease? 1. Do other animals get neurodegeneration disease? Are the genes involved in AD conserved in other animals? What are the functions of the conserved and divergent genes? 2. “Why would we have in our brains proteins such as α-synuclein or tau that, without substantive modification appears to be able to accumulate and cause some rather distressing diseases?” (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4662249/) 3. What is the common cause of microglia activation? Is neurodegeneration disease the price we pay to prevent parasite infection in brain? 4. Does the conclusion of this study fit in any evolutionary biology explanation? If so, is the explanation supported by any epidemiological data worldwide?
Results: 1. How much in pathology can the identified mechanism explain? 2. Can boundary condition of the model be mapped to human data?
Biomedical relevance: 1. Is there any study in diet and life style related to the conclusion, so a preventive/diagnostic measure can be suggested? 2. Disease of aging and cancer are two extreme ends in the same spectrum. Is the activation of microglia relevant to the occurrence or suppression of brain tumors?
The author would like to thank Dr. Sarah Spaeh for her editorial assistance.
Please sign in or register for FREE
If you are a registered user on Research Communities by Springer Nature, please sign in
This is an excellent article, not only about how to present but where adn what to look for. Most big findings are serendipitous, and boggles our mind. Keeping an open mind, looking for crazy connections everywhere, not just in high tier journals, is a w3onderful suggestion. Thank you
Hi, Sarawati,
I am glad that this article is helpful for you! There are so many interesting and important papers out there, not necessarily in the top-tier journals. For example, Luria-Delbruck distribution was published in the journal Gene in 1943. The work, which won them Nobel Prize, is the foundation of research in the evolution of cells, but the modern impact factor of the journal was like 4.0.
Subscribe to the Topic
Recommended content, career transition in my 50s, in memory of a young postdoc, supernova, wow signal, and reproducibility, the rise and fall of a paradigm, the journey with max delbrück.
We use cookies to ensure the functionality of our website, to personalize content and advertising, to provide social media features, and to analyze our traffic. If you allow us to do so, we also inform our social media, advertising and analysis partners about your use of our website. You can decide for yourself which categories you want to deny or allow. Please note that based on your settings not all functionalities of the site are available.
Further information can be found in our privacy policy .
Cookie Control
Customise your preferences for any tracking technology
The following allows you to customize your consent preferences for any tracking technology used to help us achieve the features and activities described below. To learn more about how these trackers help us and how they work, refer to the cookie policy. You may review and change your preferences at any time.
These trackers are used for activities that are strictly necessary to operate or deliver the service you requested from us and, therefore, do not require you to consent.
These trackers help us to deliver personalized marketing content and to operate, serve and track ads.
These trackers help us to deliver personalized marketing content to you based on your behaviour and to operate, serve and track social advertising.
These trackers help us to measure traffic and analyze your behaviour with the goal of improving our service.
These trackers help us to provide a personalized user experience by improving the quality of your preference management options, and by enabling the interaction with external networks and platforms.
The Scientific Hypothesis
The Key to Understanding How Science Works
How to Give a Great Journal Club Presentation
A lot of advanced science education takes place in the more-or-less formal setting of a journal club where one member of a group presents a paper from the scientific literature to the whole group. giving a good presentation is a learned skill; here are some tips on how to do it well..
- Pick a good paper. (Don’t get all neurotic about this. If you find it interesting and significant, then it will almost certainly benefit your group. If you’re in doubt, ask a colleague or mentor.) Read it. Two or three times. Skimming quickly may be enough to tell you whether or not there is something to it, but getting down to the level of detail that you’ll want to have under control for the actual presentation can easily take more time and effort than you first think it will. Is it clearly written and understandable? If you find it too difficult, or poorly written to get the message, chances are that others will struggle too. You might want to pick a different paper.
- Ask yourself why the authors did the research. What did they hope to learn? The abstract and conclusion of a paper generally express the essence of the work. Read them carefully even before going over the rest of the paper in depth. It often helps you to figure out the big picture, especially when the authors seem to take it for granted that all readers will see what it is. Authors often start off by saying that some subject, X, “is not well-understood.” Well, of course it’s not! That’s why they got a paper out of studying X. The statement usually just gives you a general idea of what the about and is only rarely the level of information that you want.
- Find the hypothesis in the paper; most have one, but a great many papers that are based on hypotheses don’t say so explicitly (BTW, some authors say they’re testing a “model;” occasionally they are referring to an “animal model” such as a mouse, but usually a model that’s being tested is the same as a hypothesis).
- The most important thing for your audience is to trace the logical flow of the paper. How do the experiments in the paper test the hypothesis? Is each result truly relevant to the hypothesis: that is, does it support or contradict it, or is it irrelevant to the truth of the hypothesis (this is more common than you might think)?
- With practice you can make a smooth and informative narrative out of any average paper. When transitioning from one figure to the next, avoid the trite and deadly-boring phrase “… and then they wanted to look at…” The authors certainly had a reason for “wanting to look at” whatever they looked at. Tell the audience what it was! Why did they do what the authors did and why that experiment followed at that point. What did they learn by doing it?
- Be able to go over the important figures, tables or other displayed items in enough detail to make the main point(s) clear.
- You should understand the methods used by the authors well enough to explain them generally to a group, and say why the authors chose them. You are not expected to become a technical expert in the field represented by the paper, however. Be aware of notable advantages and limitations of the methods in case questions about them arise.
- Try to anticipate the kinds of questions that may come up, but if you can’t answer one, it is perfectly ok to say, “I don’t know.” We’ve all been there. Maybe someone else in the group does know, in any case an honest statement of ignorance is preferable than trying to fake it.
- You must be scrupulously fair to the authors, but you are not their advocate; your job is to discuss their paper in a critical and insightful way. After presenting their reasoning and results as the authors would want them to be presented, feel free to point out shortcomings if you disagree with them or think that they have made a mistake in reasoning, execution, etc.. But be a bit cautious: if you think that the authors made a bone-headed error, try extra hard to understand what they were doing. It is possible that they did err somehow, but it is possible that you’ve missed something. Hopefully, your audience will be engaged and following right along and they will raise critical questions as well. It is important to keep in mind that an attack on the paper is not an attack on you! Your reputation is not on the line here, the authors’ reputations are. Of course, if you wind up completely trashing the paper, it may appear that you didn’t follow rule number 1.
- Be aware that you may be the only person in the room who has actually read the paper. You are the authority on it. A common mistake is to assume that everyone else already knows full well what you just spent a week learning; after all, they showed up expecting to be enlightened. There might be one or two experts in the audience, but you should assume that most people aren’t experts. And even experts are rarely offended by hearing a concise review of the basics: they know full well that the audience needs it. So don’t assume too much and do give enough detail. Your main task is to educate your colleagues about a piece of work that you think is interesting and valuable.
- Plan to finalize your talk at least a day or so in advance. Practice going through the slides out loud (ideally with a couple of friends), indicating the major points of each one, but do not try to memorize or read your talk! It’s nice to know your transition to the next slide, but if you forget it, don’t panic – just advance the slide and pick up from there. (Some people like to have a card with a few notes on it as a security blanket in case of a public brain freeze. Ordinarily, having a card handy is enough to guarantee that they won’t need it.)
- On the day of the talk show up early, get into the room, get your presentation loaded. and flip through the slides in advance. Every experienced presenter has nightmare stories of last minute computer crashes, software incompatibilities, missing pointers, unfamiliar set-ups. These problems are not fun, and not what you want to have to cope with after you’ve been introduced. If you find a glitch during your run-through, you’ll have time to fix it.
1 thought on “ How to Give a Great Journal Club Presentation ”
I have encouraged students to study Brad’s tips on giving a great journal club presentation for 20 years. I plan to continue doing so!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Expert Consult
Journal Club: How to Build One and Why
By Michelle Sharp, MD; Hunter Young, MD, MHS
Published April 6, 2022
Journal clubs are a longstanding tradition in residency training, dating back to William Osler in 1875. The original goal of the journal club in Osler’s day was to share expensive texts and to review literature as a group. Over time, the goals of journal clubs have evolved to include discussion and review of current literature and development of skills for evaluating medical literature. The ultimate goal of a journal club is to improve patient care by incorporating evidence into practice.
Why are journal clubs important?
In 2004, Alper et al . reported that it would take more than 600 hours per month to stay current with the medical literature. That leaves residents with less than 5 hours a day to eat, sleep, and care for patients if they want to stay current, and it’s simply impossible. Journal clubs offer the opportunity for residents to review the literature and stay current. Furthermore, Lee et al . showed that journal clubs improve residents’ critical appraisal of the literature.
How do you get started?
The first step to starting a journal club is to decide on the initial goal. A good initial goal is to lay the foundation for critical thinking skills using literature that is interesting to residents. An introductory lecture series or primer on study design is a valuable way to start the journal club experience. The goal of the primer is not for each resident to become a statistician, but rather to lay the foundation for understanding basic study designs and the strengths and weaknesses of each design.
The next step is to decide on the time, frequency, and duration of the journal club. This depends on the size of your residency program and leadership support. Our journal club at Johns Hopkins is scheduled monthly during the lunch hour instead of a noon conference lecture. It is essential to pick a time when most residents in your program will be available to attend and a frequency that is sustainable.
How do you get residents to come?
Generally, if you feed them, they will come. In a cross-sectional analysis of journal clubs in U.S. internal medicine residencies, Sidorov found that providing food was associated with long-lasting journal clubs. Factors associated with higher resident attendance were fewer house staff, mandatory attendance, formal teaching, and an independent journal club (separate from faculty journal clubs).
The design or format of your journal club is also a key factor for attendance. Not all residents will have time during each rotation to read the assigned article, but you want to encourage these residents to attend nonetheless. One way to engage all residents is to assign one or two residents to lead each journal club, with the goal of assigning every resident at least one journal club during the year. If possible, pick residents who are on lighter rotations, so they have more time outside of clinical duties to dissect the article. To enhance engagement, allow the assigned residents to pick an article on a topic that they find interesting.
Faculty leadership should collaborate with residents on article selection and dissection and preparation of the presentation. Start each journal club with a 10- to 20-minute presentation by the assigned residents to describe the article (as detailed below) to help residents who did not have time to read the article to participate.
What are the nuts and bolts of a journal club?
To prepare a successful journal club presentation, it helps for the structure of the presentation to mirror the structure of the article as follows:
Background: Start by briefly describing the background of the study, prior literature, and the question the paper was intended to address.
Methods: Review the paper’s methods, emphasizing the study design, analysis, and other key points that address the validity and generalizability of the results (e.g., participant selection, treatment of potential confounders, and other issues that are specific to each study design).
Results: Discuss the results, focusing on the paper’s tables and figures.
Discussion: Restate the research question, summarize the key findings, and focus on factors that can affect the validity of the findings. What are potential biases, confounders, and other issues that affect the validity or generalizability of the findings to clinical practice? The study results should also be discussed in the context of prior literature and current clinical practice. Addressing the questions that remain unanswered and potential next steps can also be useful.
Faculty participation: At our institution, the faculty sponsor meets with the assigned residents to address their questions about the paper and guide the development of the presentation, ensuring that the key points are addressed. Faculty sponsors also attend the journal club to answer questions, emphasize key elements of the paper, and facilitate the open discussion after the resident’s presentation.
How do you measure impact?
One way to evaluate your journal club is to assess the evidence-based practice skills of the residents before and after the implementation of the journal club with a tool such as the Berlin questionnaire — a validated 15-question survey that assesses evidence-based practice skills. You can also conduct a resident satisfaction survey to evaluate the residents’ perception of the implementation of the journal club and areas for improvement. Finally, you can develop a rubric for evaluation of the resident presenters in each journal club session, and allow faculty to provide feedback on critical assessment of the literature and presentation skills.
Journal clubs are a great tradition in medical training and continue to be a valued educational resource. Set your goal. Consider starting with a primer on study design. Engage and empower residents to be part of the journal club. Enlist faculty involvement for guidance and mentorship. Measure the impact.
JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
- Compare Products
Have a question? +1 604 877 0713 or Email Us at [email protected]
Your cart has an existing quote
Your shopping cart contains an active quote order and cannot be modified. To modify your shopping cart, please remove the current quote order before making changes to your cart. If you require changes to the quote, please contact your local sales representative.
- Sign In Email Address Password Sign In Forgot your password?
Register for an account to quickly and easily purchase products online and for one-click access to all educational content.
- 10 Journal Club Tips: How to Run, Lead, and Present Like a Pro
Ten Tips for Scientific Journal Clubs: How to Organize, Lead, and Participate Well

What is a journal club? A scientific journal club is a dedicated meeting where researchers gather to discuss publications from peer-reviewed journals. These meetings help researchers keep up with current findings, exercise their critical thinking skills, and improve their presentation and debate abilities.
Journal club formats vary depending on the preferences of organizers and participants. Online journal clubs organized using virtual meeting platforms (e.g. Zoom, Google Meets, Webex) are increasing in popularity with research labs and institutions.
In a well-run journal club, participants engage in lively discussions, while critically and honestly evaluating a study's strengths and weaknesses. They take away insights on what to do—and what not to do—in their own work. They feel inspired by new findings and walk away with ideas for their own research. On the contrary, ineffective journal clubs lack active participation. There may be a fear of openly voicing thoughts and opinions, or attendees may just be there for the free refreshments. In the end, the attendees take away nothing useful and think it's a waste of time. Whether you’re an organizer or a participant, follow these tips to run and lead a successful journal club, and to create engaging journal club presentations.
1. Make It a Routine
Schedule the journal club at a recurring time and location, so that it becomes a regular part of everyone's schedule. Choose a time that will be the least disruptive to everyone's experiments. Perhaps host it during lunchtime and invite people to eat while the presenter is speaking. Or perhaps host it in late afternoon with coffee and snacks provided.
We try and make the meeting times agreeable to most people and at times that are conducive to the work day of a grad student. We hold our journal clubs after seminars or presentations so it doesn’t interrupt experiments.
Shan Kasal, Graduate Student, The University of Chicago
2. Designate a Leader
A designated leader(s) who can take ownership of running the journal club will contribute tremendously to its success. The responsibilities of a leader may include organizing the journal club (see below) and facilitating the meeting (e.g., starting and ending meetings on time, making speaker introductions and announcements, and moderating discussions). Skilled journal club leaders make it safe for members to openly voice their thoughts and opinions. They work to generate excitement and encourage active participation. They also provide opportunities for members to join them in organizing and leading the journal club. Great leaders inspire personal and professional growth in others within their journal club community. Download this journal club preparation checklist to help you stay organized as a leader and ensure all necessary tasks are completed before each journal club meeting.
3. Get Organized
Staying organized is key to running a successful journal club. Here are some ways that can help you organize a journal club:
- Set a consistent format and make sure members are aware of it.
- Create and share schedules so participants know it's their turn to present, facilitate, pre-read, or provide refreshments.
- Develop a communication rhythm to make sure announcements and reminders are sent out in a timely manner.
- Provide guidelines and/or a template for presenters.
- Bring attendance sheets to track member turnouts. Depending on the institute, keeping track of attendance can help with budget requests and approvals.
- Provide feedback forms to the audience to help identify areas for improvement.
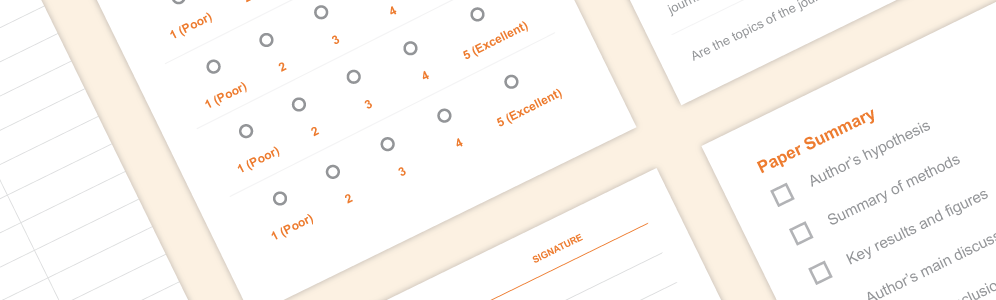
Journal Club ToolKit
Get organized with these downloadable tools, including a journal club preparation checklist, attendance sheet template, presentation checklist, feedback form template, and presenter evaluation forms.
4. Pre-Read Papers
Pre-reading is a great way to ensure that you have sufficient background information to participate in journal club discussions. In an ideal world, everyone in the journal club will read the paper prior to the meeting. But due to the high demands of research , members may not have the time to pre-read before every single meeting. Journal club leaders can encourage pre-reading or even make it mandatory. Some journal clubs ask for different members to present different figures. Using this format, several individuals have to pre-read the paper and actively participate during each meeting. Other journal clubs designate one or two individuals, in addition to the presenter, to thoroughly pre-read the paper each week. The pre-readers are asked to help promote discussion by asking questions during the meetings. Organizers can set a schedule so that members know when it's their turn to pre-read.
5. Build a Community
You need to have students that are interested in the club in the first place, and I would also say, interested in hanging out with each other. Our journal club format is informal, which allows us to at least enjoy the company of each other.
Journal club organizers and leaders should aim to create a community where the members feel safe enough to share their thoughts and ask questions. Fostering community encourages active participation and the exchange of ideas, and can increase participant satisfaction and collaborations.
Successful journal clubs always come with food!!
Serena Chang, Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Stanford University
A great way to foster community is, simply, to serve food and drinks. Eating and drinking together can create a friendly, informal atmosphere conducive to open discussions, which will help encourage the flow of ideas and thoughts on the journal club paper. In addition, refreshments help to incentivize members to continue attending the journal club.


Immunology Journal Club Sponsorship Contest
Enter for a chance to win a $500 USD sponsorship budget for your immunology journal club. Use it to fund food and drinks. Be a hero and win it for your journal club community.
6. Choose Relevant Papers
Consider the composition of your journal club community when choosing a paper. A journal club may have a broad group of researchers (e.g., a general immunology journal club), or it may only involve one or two labs specifically working on immune tolerance or a particular immune cell type. Papers discussed should be be on topics relevant to the participants’ research areas so that they remain interested.
We encourage people to select papers they are not already reading to try and expand our understanding of immunology and theirs. Too many times I feel like people select papers they already have read or will read and gain nothing from it, so there is no incentive to invest more.
As a busy researcher, the additional task of preparing for a journal club can feel like an extra burden. It’s easy to choose a paper that you are already reading for your research project. But choosing a paper that is outside of your research specialty can help you and others gain new perspectives and broaden your knowledge.
7. Make Engaging Presentations
You’ve likely suffered through boring lectures with text-heavy slides, or a monotonous presentation. How can this be avoided in your journal club?
I have a one page suggestion list of things to include in the presentation, including criticisms for the methods, hypothesis, whether the results are valid/strong enough to support the hypothesis, etc. This helps keep everyone on track.
As a journal club organizer or leader, you can provide presenters with a suggested list of presentation content and best practices:
- Start with why. Capture everyone’s interest by sharing why you chose that paper or why the paper is important to discuss.
- Prepare a concise presentation. Summarize only the key points of the paper. Include enough background information but avoid the urge to include every single detail. You can provide technical details when needed during the discussion period.
- Simplify complex information. Create simple visual representations of complex ideas, pathways, or techniques to help your audience understand the information. Avoid writing out complex information in text-heavy slides that nobody will read.
- Give it more space. Make your slides easier to read by avoiding having too much text in small fonts or too many figures on one slide. If a figure is too large, you can break it up into a few slides.
- Include discussion starters. Instead of simply summarizing, include your thoughts and opinions on all aspects of the paper to initiate a discussion. What were the strengths and weaknesses? What questions did you have when reading the paper?
Download this journal club presentation checklist to help your presentation preparation.
8. Keep It Exciting
Break out of the routine once in a while to keep the journal club fresh and exciting. For example, you could invite external speakers to your journal club:
- Invite a visiting scientist to present their work.
- Ask a biotech company to present their technologies.
- Find a speaker who can discuss scientific careers.
- Ask a science communication expert to give tips.
9. Look for Ways to Improve
You’ve taken the first step towards improving your journal club by reading this article, but improvement is a continual process. What does your journal club community think? Perform regular audits of the journal club by asking for feedback every few months. Distribute feedback forms that attendees can fill out at the end of a journal club meeting. Download a journal club feedback form template > In addition to asking for feedback, pay attention to what happens during journal club meetings. Do members generally appear awake and engaged during presentations? Are you constantly running out of discussion time? You can gain a lot of insights by simply being observant in the meeting.
10. Make Time for It
Understandably, the demands of research can prevent you from making the choice to take on this additional task of leading or participating in a journal club. Adopt smart practices so you can use your time more efficiently. Working smart will help free up your time for other beneficial activities, including journal clubs. One of the ways to work smarter is to make the switch to more efficient technologies that can help you get your results in less time. For example, you can switch to a smarter way to isolate cells.

Efficient Tools and Technologies for Life Science Research
Accomplish more in less time and with less effort by making smarter choices for the tools you use in the lab, including cell isolation and cell culture technologies.
Share This Article:
Tweet Share
Watch Our Virtual Journal Club Presentations
Choose one of the titles below to see a recording of our online journal club presentations.
- Viral Exploitation of Extracellular Vesicles to Spread Infection
- Mechanisms of Glioblastoma Resistance
- New Strategies to Target Macrophages in Cancer
- Patient-Derived Alzheimer’s Disease Modeling
- Cerebral Organoids for Human-Specific Infection Modeling
- Human In Vitro T Cell Development
- Expanding the Therapeutic Tool Kit for CAR T Cells
- NK Cell Expansion or Differentiation from Progenitors for Cell Therapy
- The Potential of Antibody-Producing B Cells for Modelling and Therapy
- Advances in Live-Attenuated Vaccine Development for Zika Virus
- Evaluating Functional Immune Responses in the Next Generation of Humanized Mice
Related Resources
Watch live virtual events.
Register for upcoming digital experiences hosted by STEMCELL, including online journal clubs and live webinars.
Browse Events >

Visit Virtual Conference Exhibitions
Attend scientific talks, browse posters, and join discussions on immunology, pluripotent stem cells, and organoids.
Explore Now >
- Organize Lab Bench
- Manage Inventory
- Organize Notebooks
- Share Duties
- Choose Technologies
- Productivity Habits
- Staying Motivated
- Productive Commute
- Mentor Effectively
- Successful Journal Club
- Immunologists to Follow
- Attending Conferences
- Effective Presentations
- Networking Tips
- Habits to Break
- Optimizing Value
- Thriving in Research
- Information Overload
- Storing and Preserving Data
- Poster Presentations
- Efficient Technologies
- Return to Lab
- Managing Projects
- Reopening the Lab
- Lab Coats & Life™ Podcast
- Increase Your Productivity
- Get Organized
- Communicate Effectively
- Advance Your Career
- Move from Academia to Industry

- Cookie Preferences
- Terms & Conditions
- Current Country/Region
How to make a great presentation
Stressed about an upcoming presentation? These talks are full of helpful tips on how to get up in front of an audience and make a lasting impression.

The secret structure of great talks

The beauty of data visualization

TED's secret to great public speaking

How to speak so that people want to listen

How great leaders inspire action

- Publication Recognition
How to Make a PowerPoint Presentation of Your Research Paper
- 4 minute read
- 129.4K views
Table of Contents
A research paper presentation is often used at conferences and in other settings where you have an opportunity to share your research, and get feedback from your colleagues. Although it may seem as simple as summarizing your research and sharing your knowledge, successful research paper PowerPoint presentation examples show us that there’s a little bit more than that involved.
In this article, we’ll highlight how to make a PowerPoint presentation from a research paper, and what to include (as well as what NOT to include). We’ll also touch on how to present a research paper at a conference.
Purpose of a Research Paper Presentation
The purpose of presenting your paper at a conference or forum is different from the purpose of conducting your research and writing up your paper. In this setting, you want to highlight your work instead of including every detail of your research. Likewise, a presentation is an excellent opportunity to get direct feedback from your colleagues in the field. But, perhaps the main reason for presenting your research is to spark interest in your work, and entice the audience to read your research paper.
So, yes, your presentation should summarize your work, but it needs to do so in a way that encourages your audience to seek out your work, and share their interest in your work with others. It’s not enough just to present your research dryly, to get information out there. More important is to encourage engagement with you, your research, and your work.
Tips for Creating Your Research Paper Presentation
In addition to basic PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, think about the following when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Know your audience : First and foremost, who are you presenting to? Students? Experts in your field? Potential funders? Non-experts? The truth is that your audience will probably have a bit of a mix of all of the above. So, make sure you keep that in mind as you prepare your presentation.
Know more about: Discover the Target Audience .
- Your audience is human : In other words, they may be tired, they might be wondering why they’re there, and they will, at some point, be tuning out. So, take steps to help them stay interested in your presentation. You can do that by utilizing effective visuals, summarize your conclusions early, and keep your research easy to understand.
- Running outline : It’s not IF your audience will drift off, or get lost…it’s WHEN. Keep a running outline, either within the presentation or via a handout. Use visual and verbal clues to highlight where you are in the presentation.
- Where does your research fit in? You should know of work related to your research, but you don’t have to cite every example. In addition, keep references in your presentation to the end, or in the handout. Your audience is there to hear about your work.
- Plan B : Anticipate possible questions for your presentation, and prepare slides that answer those specific questions in more detail, but have them at the END of your presentation. You can then jump to them, IF needed.
What Makes a PowerPoint Presentation Effective?
You’ve probably attended a presentation where the presenter reads off of their PowerPoint outline, word for word. Or where the presentation is busy, disorganized, or includes too much information. Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation.
- Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon.
- Clean and professional : Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font changes, animations, and too many words. Instead of whole paragraphs, bullet points with just a few words to summarize and highlight are best.
- Know your real-estate : Each slide has a limited amount of space. Use it wisely. Typically one, no more than two points per slide. Balance each slide visually. Utilize illustrations when needed; not extraneously.
- Keep things visual : Remember, a PowerPoint presentation is a powerful tool to present things visually. Use visual graphs over tables and scientific illustrations over long text. Keep your visuals clean and professional, just like any text you include in your presentation.
Know more about our Scientific Illustrations Services .
Another key to an effective presentation is to practice, practice, and then practice some more. When you’re done with your PowerPoint, go through it with friends and colleagues to see if you need to add (or delete excessive) information. Double and triple check for typos and errors. Know the presentation inside and out, so when you’re in front of your audience, you’ll feel confident and comfortable.
How to Present a Research Paper
If your PowerPoint presentation is solid, and you’ve practiced your presentation, that’s half the battle. Follow the basic advice to keep your audience engaged and interested by making eye contact, encouraging questions, and presenting your information with enthusiasm.
We encourage you to read our articles on how to present a scientific journal article and tips on giving good scientific presentations .
Language Editing Plus
Improve the flow and writing of your research paper with Language Editing Plus. This service includes unlimited editing, manuscript formatting for the journal of your choice, reference check and even a customized cover letter. Learn more here , and get started today!

- Manuscript Preparation
Know How to Structure Your PhD Thesis

- Research Process
Systematic Literature Review or Literature Review?
You may also like.

What is a Good H-index?

What is a Corresponding Author?

How to Submit a Paper for Publication in a Journal
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Lippincott Open Access

How to deliver an oral presentation
Georgina wellstead.
a Lister Hospital, East and North Hertfordshire NHS Trust
Katharine Whitehurst
b Royal Devon and Exeter Hospital
Buket Gundogan
c University College London
d Guy's St Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK
Delivering an oral presentation in conferences and meetings can seem daunting. However, if delivered effectively, it can be an invaluable opportunity to showcase your work in front of peers as well as receive feedback on your project. In this “How to” article, we demonstrate how one can plan and successfully deliver an engaging oral presentation.
Giving an oral presentation at a scientific conference is an almost inevitable task at some point during your medical career. The prospect of presenting your original work to colleagues and peers, however, may be intimidating, and it can be difficult to know how to approach it. Nonetheless, it is important to remember that although daunting, an oral presentation is one of the best ways to get your work out there, and so should be looked upon as an exciting and invaluable opportunity.
Slide content
Although things may vary slightly depending on the type of research you are presenting, the typical structure is as follows:
- Opening slide (title of study, authors, institutions, and date)
- Methodology
- Discussion (including strengths and weaknesses of the study)
Conclusions
Picking out only the most important findings to include in your presentation is key and will keep it concise and easy to follow. This in turn will keep your viewers engaged, and more likely to understand and remember your presentation.
Psychological analysis of PowerPoint presentations, finds that 8 psychological principles are often violated 1 . One of these was the limited capacity of working memory, which can hold 4 units of information at any 1 time in most circumstances. Hence, too many points or concepts on a slide could be detrimental to the presenter’s desire to give information.
You can also help keep your audience engaged with images, which you can talk around, rather than lots of text. Video can also be useful, for example, a surgical procedure. However, be warned that IT can let you down when you need it most and you need to have a backup plan if the video fails. It’s worth coming to the venue early and testing it and resolving issues beforehand with the AV support staff if speaking at a conference.
Slide design and layout
It is important not to clutter your slides with too much text or too many pictures. An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
It is best to keep the slide design simple, as busy backgrounds and loud color schemes are distracting. Ensure that you use a uniform font and stick to the same color scheme throughout. As a general rule, a light-colored background with dark-colored text is easier to read than light-colored text on a dark-colored background. If you can use an image instead of text, this is even better.
A systematic review study of expert opinion papers demonstrates several key recommendations on how to effectively deliver medical research presentations 2 . These include:
- Keeping your slides simple
- Knowing your audience (pitching to the right level)
- Making eye contact
- Rehearsing the presentation
- Do not read from the slides
- Limiting the number of lines per slide
- Sticking to the allotted time
You should practice your presentation before the conference, making sure that you stick to the allocated time given to you. Oral presentations are usually short (around 8–10 min maximum), and it is, therefore, easy to go under or over time if you have not rehearsed. Aiming to spend around 1 minute per slide is usually a good guide. It is useful to present to your colleagues and seniors, allowing them to ask you questions afterwards so that you can be prepared for the sort of questions you may get asked at the conference. Knowing your research inside out and reading around the subject is advisable, as there may be experts watching you at the conference with more challenging questions! Make sure you re-read your paper the day before, or on the day of the conference to refresh your memory.
It is useful to bring along handouts of your presentation for those who may be interested. Rather than printing out miniature versions of your power point slides, it is better to condense your findings into a brief word document. Not only will this be easier to read, but you will also save a lot of paper by doing this!
Delivering the presentation
Having rehearsed your presentation beforehand, the most important thing to do when you get to the conference is to keep calm and be confident. Remember that you know your own research better than anyone else in the room! Be sure to take some deep breaths and speak at an appropriate pace and volume, making good eye contact with your viewers. If there is a microphone, don’t keep turning away from it as the audience will get frustrated if your voice keeps cutting in and out. Gesturing and using pointers when appropriate can be a really useful tool, and will enable you to emphasize your important findings.
Presenting tips
- Do not hide behind the computer. Come out to the center or side and present there.
- Maintain eye contact with the audience, especially the judges.
- Remember to pause every so often.
- Don’t clutter your presentation with verbal noise such as “umm,” “like,” or “so.” You will look more slick if you avoid this.
- Rhetorical questions once in a while can be useful in maintaining the audience’s attention.
When reaching the end of your presentation, you should slow down in order to clearly convey your key points. Using phases such as “in summary” and “to conclude” often prompts those who have drifted off slightly during your presentation start paying attention again, so it is a critical time to make sure that your work is understood and remembered. Leaving up your conclusions/summary slide for a short while after stopping speaking will give the audience time to digest the information. Conclude by acknowledging any fellow authors or assistants before thanking the audience for their attention and inviting any questions (as long as you have left sufficient time).
If asked a question, firstly thank the audience member, then repeat what they have asked to the rest of the listeners in case they didn’t hear the first time. Keep your answers short and succinct, and if unsure say that the questioner has raised a good point and that you will have to look into it further. Having someone else in the audience write down the question is useful for this.
The key points to remember when preparing for an oral presentation are:
- Keep your slides simple and concise using the 5×5 rule and images.
- When appropriate; rehearse timings; prepare answers to questions; speak slowly and use gestures/ pointers where appropriate; make eye contact with the audience; emphasize your key points at the end; make acknowledgments and thank the audience; invite questions and be confident but not arrogant.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflict of interest with regard to the content of this report.
Sponsorships or competing interests that may be relevant to content are disclosed at the end of this article.
Published online 8 June 2017
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
What It Takes to Give a Great Presentation
- Carmine Gallo

Five tips to set yourself apart.
Never underestimate the power of great communication. It can help you land the job of your dreams, attract investors to back your idea, or elevate your stature within your organization. But while there are plenty of good speakers in the world, you can set yourself apart out by being the person who can deliver something great over and over. Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired together are more memorable); don’t underestimate the power of your voice (raise and lower it for emphasis); give your audience something extra (unexpected moments will grab their attention); rehearse (the best speakers are the best because they practice — a lot).
I was sitting across the table from a Silicon Valley CEO who had pioneered a technology that touches many of our lives — the flash memory that stores data on smartphones, digital cameras, and computers. He was a frequent guest on CNBC and had been delivering business presentations for at least 20 years before we met. And yet, the CEO wanted to sharpen his public speaking skills.
- Carmine Gallo is a Harvard University instructor, keynote speaker, and author of 10 books translated into 40 languages. Gallo is the author of The Bezos Blueprint: Communication Secrets of the World’s Greatest Salesman (St. Martin’s Press).
Partner Center

Reference Examples
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual . Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual .
To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of work (e.g., journal article ) and follow the relevant example.
When selecting a category, use the webpages and websites category only when a work does not fit better within another category. For example, a report from a government website would use the reports category, whereas a page on a government website that is not a report or other work would use the webpages and websites category.
Also note that print and electronic references are largely the same. For example, to cite both print books and ebooks, use the books and reference works category and then choose the appropriate type of work (i.e., book ) and follow the relevant example (e.g., whole authored book ).
Examples on these pages illustrate the details of reference formats. We make every attempt to show examples that are in keeping with APA Style’s guiding principles of inclusivity and bias-free language. These examples are presented out of context only to demonstrate formatting issues (e.g., which elements to italicize, where punctuation is needed, placement of parentheses). References, including these examples, are not inherently endorsements for the ideas or content of the works themselves. An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers .
Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10
Related handouts
- Common Reference Examples Guide (PDF, 147KB)
- Reference Quick Guide (PDF, 225KB)
Textual Works
Textual works are covered in Sections 10.1–10.8 of the Publication Manual . The most common categories and examples are presented here. For the reviews of other works category, see Section 10.7.
- Journal Article References
- Magazine Article References
- Newspaper Article References
- Blog Post and Blog Comment References
- UpToDate Article References
- Book/Ebook References
- Diagnostic Manual References
- Children’s Book or Other Illustrated Book References
- Classroom Course Pack Material References
- Religious Work References
- Chapter in an Edited Book/Ebook References
- Dictionary Entry References
- Wikipedia Entry References
- Report by a Government Agency References
- Report with Individual Authors References
- Brochure References
- Ethics Code References
- Fact Sheet References
- ISO Standard References
- Press Release References
- White Paper References
- Conference Presentation References
- Conference Proceeding References
- Published Dissertation or Thesis References
- Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
- ERIC Database References
- Preprint Article References
Data and Assessments
Data sets are covered in Section 10.9 of the Publication Manual . For the software and tests categories, see Sections 10.10 and 10.11.
- Data Set References
- Toolbox References
Audiovisual Media
Audiovisual media are covered in Sections 10.12–10.14 of the Publication Manual . The most common examples are presented together here. In the manual, these examples and more are separated into categories for audiovisual, audio, and visual media.
- Artwork References
- Clip Art or Stock Image References
- Film and Television References
- Musical Score References
- Online Course or MOOC References
- Podcast References
- PowerPoint Slide or Lecture Note References
- Radio Broadcast References
- TED Talk References
- Transcript of an Audiovisual Work References
- YouTube Video References
Online Media
Online media are covered in Sections 10.15 and 10.16 of the Publication Manual . Please note that blog posts are part of the periodicals category.
- Facebook References
- Instagram References
- LinkedIn References
- Online Forum (e.g., Reddit) References
- TikTok References
- X References
- Webpage on a Website References
- Clinical Practice References
- Open Educational Resource References
- Whole Website References
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
CRediT author statement
CRediT (Contributor Roles Taxonomy) was introduced with the intention of recognizing individual author contributions, reducing authorship disputes and facilitating collaboration. The idea came about following a 2012 collaborative workshop led by Harvard University and the Wellcome Trust, with input from researchers, the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) and publishers, including Elsevier, represented by Cell Press.
CRediT offers authors the opportunity to share an accurate and detailed description of their diverse contributions to the published work.
The corresponding author is responsible for ensuring that the descriptions are accurate and agreed by all authors
The role(s) of all authors should be listed, using the relevant above categories
Authors may have contributed in multiple roles
CRediT in no way changes the journal’s criteria to qualify for authorship
CRediT statements should be provided during the submission process and will appear above the acknowledgment section of the published paper as shown further below.
Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Conceptualization | Ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims |
Methodology | Development or design of methodology; creation of models |
Software | Programming, software development; designing computer programs; implementation of the computer code and supporting algorithms; testing of existing code components |
Validation | Verification, whether as a part of the activity or separate, of the overall replication/ reproducibility of results/experiments and other research outputs |
Formal analysis | Application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data |
Investigation | Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection |
Resources | Provision of study materials, reagents, materials, patients, laboratory samples, animals, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools |
Data Curation | Management activities to annotate (produce metadata), scrub data and maintain research data (including software code, where it is necessary for interpreting the data itself) for initial use and later reuse |
Writing - Original Draft | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation) |
Writing - Review & Editing | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary or revision – including pre-or postpublication stages |
Visualization | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/ data presentation |
Supervision | Oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution, including mentorship external to the core team |
Project administration | Management and coordination responsibility for the research activity planning and execution |
Funding acquisition | Acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication |
*Reproduced from Brand et al. (2015), Learned Publishing 28(2), with permission of the authors.
Sample CRediT author statement
Zhang San: Conceptualization, Methodology, Software Priya Singh. : Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation. Wang Wu : Visualization, Investigation. Jan Jansen : Supervision. : Ajay Kumar : Software, Validation.: Sun Qi: Writing- Reviewing and Editing,
Read more about CRediT here opens in new tab/window or check out this article from Authors' Updat e: CRediT where credit's due .
Change Password
Your password must have 6 characters or more:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character
Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
Create your account
Forget yout password.
Enter your email address below and we will send you the reset instructions
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to reset your password
Forgot your Username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username

- June 5, 2024 | VOL. 19, NO. 4 CURRENT ISSUE pp.2-9
- March 1, 2024 | VOL. 19, NO. 3 pp.2-13
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) has updated its Privacy Policy and Terms of Use , including with new information specifically addressed to individuals in the European Economic Area. As described in the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, this website utilizes cookies, including for the purpose of offering an optimal online experience and services tailored to your preferences.
Please read the entire Privacy Policy and Terms of Use. By closing this message, browsing this website, continuing the navigation, or otherwise continuing to use the APA's websites, you confirm that you understand and accept the terms of the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, including the utilization of cookies.
Repeated Suicide Attempts in a Patient With Stiff Person Syndrome
- Diane Mathew , M.D. ,
- Akshay Muttath , B.S.
Search for more papers by this author
Stiff person syndrome (SPS) is a rare neurological disorder with large functional impacts ( 1 ). The physical manifestations of SPS include rigidity, stiffness, unpredictable spasms, frequent falls, and pain ( 1 ). Psychiatric comorbidities often include anxiety, depression, and phobias ( 1 ). A study conducted in the United Kingdom showed that SPS affected 1–2 people per million over a 5-year span. Among patients with SPS, 60%–80% have the presence of antibodies against glutamic acid decarboxylase ( 1 ). The exact role of autoantibodies in SPS pathogenesis is still under investigation, although all these antibodies target inhibitory synaptic transmission through gamma-aminobutyric acid, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, in the brain and spinal cord ( 1 ).
It is important for clinicians to recognize the signs and symptoms of SPS because there have been past occurrences of misdiagnosis. Case reports from the literature and a systematic review of articles published before May 2020 show how initial signs of SPS have often been misdiagnosed as primary psychiatric disorders, leading to potential delay in care ( 2 , 3 ). In one case, although the patient had progressive stiffness and spasms for 11 years, he was treated for phobic symptoms before neurological evaluation ( 3 ). Early detection of psychiatric comorbidity in the context of SPS could provide great benefit for patients.
A systematic review revealed that the rate of psychiatric comorbidities among patients with SPS was greater than that of the general population, with relative risk estimates of 6.09–11.25, although the study reported small sample sizes ( 2 ). The prognosis of SPS is variable, and many patients have disability despite immunological and symptomatic treatment ( 4 ).
Here, we present a case of severe depression leading to multiple suicide attempts in a patient who was diagnosed with SPS along with other medical comorbid conditions.
Case Presentation
A 46-year-old female patient with a history of depression and no previously documented suicide attempts or psychiatric hospitalizations presented to the emergency department with multiple self-inflicted stab wounds. She reported that she had attempted suicide and expressed regret that her suicidal behaviors were nonfatal. Her wounds, inflicted by a knife, were 2-cm lacerations of the right neck, right chest, right abdomen, and right groin; 1-cm lacerations of the left chest and upper-left thigh; and a 6-cm laceration of the left abdomen. No signs of damage to large blood vessels, airways, or other vital organs were seen on computed tomography. Her serum ethyl alcohol level was negative.
The patient had a history of SPS, first diagnosed at the age of 38. At age 44, she suddenly developed blindness; there was concern that this may have been the result of a suicide attempt by ingestion of methanol, but the etiology was never elucidated. Her medical history included adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, seizure disorders, meningioma, and decreased gastric motility. Her psychiatric history included insomnia, anxiety, and depression. In the year before presentation to the emergency department, she had multiple hospitalizations for seizures, worsening symptoms of SPS, and adrenal insufficiency.
Prior to admission, the patient was taking clonazepam (2 mg) and diazepam (5 mg) three times a day, escitalopram (15 mg) and levothyroxine (112 µ g) daily, levetiracetam (1,250 mg) twice a day, hydrocortisone (20 mg in the morning and 10 mg in the afternoon), intravenous immunoglobulin therapy (1,280 mL monthly), botulinum toxin injections every 4 months, and rituximab (100 mg/10 mL) injections every 6 months. The patient did not have a relevant family psychiatric history. She lived at home with her husband and two children. Of note, her previous psychiatric management was escitalopram, which she was taking at the time of admission, and outpatient therapy, although the type of therapy was not specified.
Because the patient required further care for self-inflicted lacerations, for which she required 12 sutures (including repair of a deep wound in the left abdomen), she was admitted to the trauma surgery service. She refused treatment for her lacerations early in admission but later consented.
While in the emergency department, psychiatry was consulted. The patient reported intent to end her life by stabbing herself. She shared her struggles living with multiple medical conditions and expressed frustration about her reliance on her family. Her overall health declined steadily after the diagnosis of SPS. She reported having suicidal ideation two weeks prior to this hospitalization and had attempted to end her life by swallowing a handful of benzodiazepines. She aborted the attempt by vomiting because she thought about her children. The disposition recommendation from psychiatry was admission to an inpatient psychiatric unit once the patient was medically cleared, with criteria met for involuntary hospitalization.
The psychiatry consultation-liaison service followed the patient during her admission to trauma surgery service and recommended an increase in escitalopram to 20 mg daily. During initial follow-up interviews, the patient reported improved mood and less burdensomeness but was regretful that her suicidal behaviors were nonfatal. Four days after her initial encounter, she began to deny suicidal ideations. She was eventually medically cleared but was boarding on the surgery unit awaiting bed placement in the psychiatry unit where there was a shortage of inpatient beds. As her symptoms continued to improve, with consistent denials of suicidal ideation, she no longer met criteria for involuntary inpatient psychiatric hospitalization because she was not at imminent risk of harm to herself. The psychiatry consultation-liaison service recommended intensive outpatient care because she might have had difficulty acclimating to the acute psychiatry unit as a result of comorbid blindness, SPS spasticity, and overall frailty, but voluntary admission was presented as an option. Her husband was supportive of her choice and could provide supervision if needed. She expressed interest in inpatient psychiatric services. Two weeks after the initial presentation, with the availability of a bed, she was transferred to an inpatient psychiatry unit.
On the first day of psychiatric admission, the patient endorsed a depressed mood and decreased energy but denied further symptoms of depression. Brief inpatient cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) was utilized to target feelings of hopelessness and burdensomeness. The patient declined medication adjustments. The following day, she expressed a desire for discharge because of overall symptom improvement, along with perceived inaccessibility of therapeutic activities due to blindness and cold sensitivity. CBT was continued, and she was receptive to this treatment, focusing on thinking patterns and behaviors in her life. Through this therapy, she gained insight into the role SPS played in worsening her depressive symptoms.
On day 3, the treatment team recommended additional inpatient care for continued intervention with CBT, but the patient requested discharge. By telephone, the husband indicated that he felt comfortable with the patient being discharged and was supportive of outpatient treatment, agreeing to assist in maintaining a safe environment. After careful consideration of her current symptoms and requests, she was discharged home. Referral was made for intensive outpatient care on discharge.
Although SPS is a rare condition, treatment options for depression among patients with comorbid SPS are important to investigate. In this case, a short trial of CBT showed positive initial results. Research has demonstrated the positive impact of CBT for anxiety and stiffness in SPS ( 5 , 6 ). However, there is limited information on the impact of CBT on comorbid depression in the context of this disorder.
Aspects of life with SPS had a large impact on the patient’s mental health. A study exploring quality of life among 24 individuals with SPS showed lower quality-of-life scores in all domains, with markedly lower scores in physical and social functioning ( 7 ). The patient in our report engaged in therapy while on the unit and expressed a sense of isolation because of her diagnosis; few others understood her experience. She shared concerns of unforeseen functional decline, the rate at which she could deteriorate, and the burden it might place on her family. During CBT sessions, the technique of reframing was used to pose alternative perspectives, such as her family’s desire to care for her rather than the thought that she was a burden. Through reframing, she began to grieve the loss of mobility she faced in her life, having once been an athlete. Mindfulness was also used to nonjudgmentally appraise cognitive distortions, such as catastrophizing, with the emphasis to choose not to listen to these thoughts. With these positive initial advancements, CBT showed promise in addressing her depressive symptoms.
Although the CBT intervention was brief as a result of the patient’s desire for discharge, there were initial signs of improvement indicating the potential of this intervention. There is a need to balance specialization and generalization of CBT to allow for incorporation of this intervention in medical settings such as consultation-liaison service. Identifying commonalities in CBT modalities, such as psychoeducation and behavioral activation, rather than focusing on unique methods of delivery in specialized settings can reduce barriers to utilizing CBT ( 8 ). With this generalization, use of CBT in the consultation-liaison setting may have proved to be beneficial for this patient early in admission. One noteworthy limitation to this study is the uncertainty of the patient’s survival following hospitalization. Early screening of psychiatric comorbidity in SPS and direction regarding treatment may have prevented progression of depression in this case. Furthering awareness of the association of these comorbid conditions may allow clinicians, patients, and families to detect early indications that psychiatric treatment should begin.
Key Points/Clinical Pearls
Comorbid psychiatric illnesses are common among people with stiff person syndrome (SPS) and can pose challenges in their treatments.
Early recognition of psychiatric comorbidity in SPS and appropriate psychoeducation can limit dysfunction and disability.
Intervention with brief cognitive-behavioral therapy showed promise for treatment of depression for a patient who had comorbid SPS.
The patient in this case provided informed consent. The authors have confirmed that details of the case have been disguised to protect patient privacy.
The authors thank Muslim Khan, M.D., SUNY Upstate Medical University, for supervision of the case.
1. Hadavi S, Noyce AJ, Leslie RD, et al. : Stiff person syndrome . Pract Neurol 2011 ; 11:272–282 Crossref , Google Scholar
2. Caffrey D, Finn CT, Song SM, et al. : Stiff-person syndrome and psychiatric comorbidities: a systematic review . J Acad Consultat Liaison Psychiatry 2021 ; 62:3–13 Crossref , Google Scholar
3. Souissi MA, Bellakhal S, Gharbi E, et al. : A stiff person syndrome misdiagnosed as a psychiatric illness: a case report . Curr Rheumatol Rev 2020 ; 16:343–345 Crossref , Google Scholar
4. Baizabal-Carvallo JF, Jankovic J : Stiff-person syndrome: insights into a complex autoimmune disorder . J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2015 ; 86:840–848 Crossref , Google Scholar
5. Bhatti AB, Gazali ZA : Recent advances and review on treatment of stiff person syndrome in adults and pediatric patients . Curēus 2015 ; 7(12):e427 Google Scholar
6. Morris LL, Dysch L, Salkovskis PM, et al. : Reducing excess stiffness in stiff person syndrome using CBT: a case study . NeuroRehabilitation 2014 ; 35(3):627–631 Crossref , Google Scholar
7. Gerschlager W, Schrag A, Brown P : Quality of life in stiff person syndrome . Mov Disord 2002 ; 17:1064–1067 Crossref , Google Scholar
8. Magidson JF, Weisberg RB : Implementing cognitive behavioral therapy in specialty medical settings . Cogn Behav Pract 2014 ; 21(4):367–371 Crossref , Google Scholar
- Cited by None

Here’s how you know
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
- National Institutes of Health
Melatonin: What You Need To Know

.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} What is melatonin and how does it work?
Melatonin is a hormone that your brain produces in response to darkness. It helps with the timing of your circadian rhythms (24-hour internal clock) and with sleep. Being exposed to light at night can block melatonin production.
Research suggests that melatonin plays other important roles in the body beyond sleep. However, these effects are not fully understood.
Melatonin dietary supplements can be made from animals or microorganisms, but most often they’re made synthetically. The information below is about melatonin dietary supplements.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} What are the health benefits of taking melatonin?
Melatonin supplements may help with certain conditions, such as jet lag, delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, some sleep disorders in children, and anxiety before and after surgery.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Jet lag
Jet lag affects people when they travel by air across multiple time zones. With jet lag, you may not feel well overall and you may have disturbed sleep, daytime tiredness, impaired functioning, and digestive problems.
Research suggests that melatonin supplements may help with jet lag. This is based on medium-sized reviews from 2010 and 2014.
- Four studies that included a total of 142 travelers showed that melatonin may be better than a placebo (an inactive substance) in reducing overall symptoms of jet lag after eastward flights. Another study of 234 travelers on eastward flights looked at only sleep quality and found low-quality evidence that melatonin may be better than placebo for improving sleep quality.
- Two studies that included a total of 90 travelers showed that melatonin may be better than a placebo in reducing symptoms of jet lag after westward flights.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Delayed sleep-wake phase disorder (DSWPD)
People with DSWPD have trouble falling asleep at the usual times and waking up in the morning. They typically have difficulty getting to sleep before 2 to 6 a.m. and would prefer to wake up between 10 a.m. and 1 p.m.
Melatonin supplements appear to help with sleep in people with DSWPD, but it’s uncertain whether the benefits outweigh the possible harms. This is based on a clinical practice guideline, a small review, and a more recent study.
- In 2015, the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommended melatonin supplements given at specific times for DSWPD. The recommendation was a weak one, and it came with uncertainty about whether the benefits of melatonin outweigh its potential harms.
- A 2016 review that looked at a small number of people (52) from two studies showed that melatonin supplements reduced the time it took for people with DSWPD to fall asleep when compared to placebo. On average, it took about 22 minutes less for them to fall asleep.
- A 2018 randomized controlled trial that lasted 4 weeks and included 307 people with DSWPD found that taking melatonin 1 hour before the desired bedtime combined with going to bed at a set time led to several improvements. Those improvements included falling asleep an average of 34 minutes earlier, better sleep during the first third of the night, and better daytime functioning.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Some sleep disorders in children
Sleep problems in children can have undesirable effects on their behavior, daytime functioning, and quality of life. Children with certain conditions, such as atopic dermatitis, asthma, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), or autism spectrum disorder (ASD), are more prone to sleep problems than other children.
There are no overall guidelines on the best approach to improving sleep in children. However, guidelines for specific conditions recommend behavioral treatments, such as good bedtime habits and parent education, as an initial treatment that may be supplemented with medicines.
The list below shows the review’s results on melatonin’s short-term effects for children with specific conditions.
- Children with ASD fell asleep 37 minutes earlier and slept 48 minutes longer.
- Children with ADHD fell asleep 20 minutes earlier and slept 33 minutes longer.
- Children with atopic dermatitis fell asleep 6.8 minutes earlier and slept 35 minutes longer.
- Children with chronic sleep-onset insomnia fell asleep 24 minutes earlier and slept 25 minutes longer.
Because there aren’t many studies on children and melatonin supplements, there is a lot we don’t know about the use of melatonin in children. For example, there are uncertainties about what dose to use and when to give it, the effects of melatonin use over long periods of time, and whether melatonin’s benefits outweigh its possible risks. Because melatonin is a hormone, it’s possible that melatonin supplements could affect hormonal development, including puberty, menstrual cycles, and overproduction of the hormone prolactin, but we don’t know for sure.
Because of these uncertainties, it’s best to work with a health care provider if you’re considering giving a child melatonin for sleep problems.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Anxiety before and after surgery
Anxiety before and after surgery happens in up to 80 percent of patients.
Melatonin supplements appear to be helpful in reducing anxiety before surgery, but it’s unclear if it helps to lower anxiety after surgery. This is a based on a 2015 review.
- The 2015 review looked at 12 studies that involved 774 people and assessed melatonin supplements for treating anxiety before surgery, anxiety after surgery, or both. The review found strong evidence that melatonin is better than placebo at reducing anxiety before surgery. Melatonin supplements may be as effective as standard treatment (the antianxiety medicine midazolam). However, the results on melatonin’s benefits for reducing anxiety after surgery were mixed.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Is melatonin helpful for preventing or treating COVID-19?
Current research looking at the effects of melatonin on COVID-19 is only in the early stages. There are a few randomized controlled trials (studies evaluating melatonin in people) in progress. At this point, it is too soon to reach conclusions on whether melatonin is helpful for COVID-19.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Does melatonin help with cancer symptoms?
Studies of the effect of melatonin supplements on cancer symptoms or treatment-related side effects have been small and have had mixed results.
Keep in mind that unproven products should not be used to replace or delay conventional medical treatment for cancer. Also, some products can interfere with standard cancer treatments or have special risks for people who’ve been diagnosed with cancer. Before using any complementary health approach, including melatonin, people who’ve been diagnosed with cancer should talk with their health care providers to make sure that all aspects of their care work together.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Can melatonin help with insomnia?
People with insomnia have trouble falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. When symptoms last a month or longer, it’s called chronic insomnia.
According to practice guidelines from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine (2017) and the American College of Physicians (2016), there’s not enough strong evidence on the effectiveness or safety of melatonin supplementation for chronic insomnia to recommend its use. The American College of Physicians guidelines strongly recommend the use of cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) as an initial treatment for insomnia.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Does melatonin work for shift workers?
Shift work that involves night shifts may cause people to feel sleepy at work and make it difficult to sleep during the daytime after a shift ends.
According to two 2014 research reviews, studies on whether melatonin supplements help shift workers were generally small or inconclusive.
- The first review looked at 7 studies that included a total of 263 participants. The results suggested that (1) people taking melatonin may sleep about 24 minutes longer during the daytime, but (2) other aspects of sleep, such as time needed to fall asleep, may not change. The evidence, however, was considered to be of low quality.
- The other review looked at 8 studies (5 of which were also in the first review), with a total of 300 participants, to see whether melatonin helped promote sleep in shift workers. Six of the studies were high quality, and they had inconclusive results. The review did not make any recommendations for melatonin use in shift workers.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Is it safe to take melatonin?
For melatonin supplements, particularly at doses higher than what the body normally produces, there’s not enough information yet about possible side effects to have a clear picture of overall safety. Short-term use of melatonin supplements appears to be safe for most people, but information on the long-term safety of supplementing with melatonin is lacking.
Also keep in mind:
Interactions with medicines
- As with all dietary supplements, people who are taking medicine should consult their health care providers before using melatonin. In particular, people with epilepsy and those taking blood thinner medications need to be under medical supervision when taking melatonin supplements.
Possible allergic reaction risk
- There may be a risk of allergic reactions to melatonin supplements.
Safety concerns for pregnant and breastfeeding women
- There’s been a lack of research on the safety of melatonin use in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Safety concerns for older people
- The 2015 guidelines by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommend against melatonin use by people with dementia.
- Melatonin may stay active in older people longer than in younger people and cause daytime drowsiness.
Melatonin is regulated as a dietary supplement
- In the United States, melatonin is considered a dietary supplement. This means that it’s regulated less strictly by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) than a prescription or over-the-counter drug would be. In several other countries, melatonin is available only with a prescription and is considered a drug.
Products may not contain what’s listed on the label
- Some melatonin supplements may not contain what’s listed on the product label. A 2017 study tested 31 different melatonin supplements bought from grocery stores and pharmacies. For most of the supplements, the amount of melatonin in the product didn’t match what was listed on the product label. Also, 26 percent of the supplements contained serotonin, a hormone that can have harmful effects even at relatively low levels.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Is melatonin safe for children?
In addition to issues mentioned above, there are some things to consider regarding melatonin’s safety in children.
- Parents considering giving their children melatonin should first speak with a health care provider about melatonin use in children.
- A 2023 study found that 22 out of 25 over-the-counter melatonin gummy products were inaccurately labeled. One product did not contain detectable levels of melatonin. In the remaining products, the melatonin levels ranged from 74 to 347 percent of the labeled quantity (i.e., up to almost 3.5 times more melatonin than reported on the label). Most had more than the label said, with the majority containing between 1.2 to 1.7 times more melatonin than the amount listed.
- Parents need to ensure safe storage and appropriate use of melatonin supplements. Based on case surveillance data, a 2024 report by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimated that from 2019 to 2022, 11,000 emergency department visits were for unsupervised melatonin ingestion by children 5 years and younger. The report noted that many of the incidents involved ingestion of flavored products such as gummies and emphasized the importance of keeping medications and supplements out of children’s reach and sight.
- A 2022 study indicated that U.S. sales of melatonin—which is widely available in tablet, capsule, liquid, and gummy formulations—increased by about 150 percent between 2016 and 2020. The study authors said that the increase in sales, availability, and widespread use of melatonin in the United States has likely resulted in increased access to melatonin among children in the home.
- The 2022 study also showed that the number of reports to U.S. poison control centers about people 19 years and younger who took melatonin increased from 8,337 in 2012 to 52,563 in 2021. Over the 10-year period, the number of reports increased each year. Hospitalizations and serious outcomes from melatonin ingestion by people 19 years and younger also increased over the 10 years. Most hospitalizations involved teenagers who had intentionally taken melatonin overdoses, and the largest increase in hospitalizations occurred in children 5 years and younger.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} More Information
- Most of the calls to poison control centers—94.3 percent—were for children 5 years and younger who accidentally consumed melatonin products in their homes.
- Data from the calls show that most of the people who had taken melatonin—82.8 percent—did not have any symptoms. Among those who did have symptoms, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, or symptoms related to the central nervous system were the most common.
- Of the 4,097 people who were hospitalized over the 10-year period, 287 needed intensive care.
- Five individuals required mechanical ventilation, and two children younger than age 2 died, but the data from the poison control centers did not show whether the two deaths were caused by a melatonin overdose or another cause.
Melatonin supplements at normal doses appear to be safe for most children for short-term use, but there aren’t many studies on children and melatonin. Also, there’s little information on the long-term effects of melatonin use in children. Because melatonin is a hormone, it’s possible that melatonin supplements could affect hormonal development, including puberty, menstrual cycles, and overproduction of the hormone prolactin, but we don’t know for sure.
Possible melatonin supplement side effects reported in children have usually been mild and have included:
- Increased bedwetting or urination in the evening
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} What are the side effects of melatonin?
A 2015 review on the safety of melatonin supplements indicated that only mild side effects were reported in various short-term studies that involved adults, surgical patients, and critically ill patients. Some of the mild side effects that were reported in the studies included:
The possible long-term side effects of melatonin use are unclear.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Tips To Consider
- Remember that even though the FDA regulates dietary supplements, such as melatonin, the regulations for dietary supplements are different and less strict than those for prescription or over-the-counter drugs.
- Some dietary supplements may interact with medicines or pose risks if you have medical problems or are going to have surgery.
- If you’re pregnant or nursing a child, it’s especially important to see your health care provider before taking any medicine or supplement, including melatonin.
- If you use dietary supplements, such as melatonin, read and follow label instructions. “Natural” doesn’t always mean “safe.” For more information, see Using Dietary Supplements Wisely .
- Take charge of your health—talk with your health care providers about any complementary health approaches you use. Together, you can make shared, well-informed decisions.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} For More Information
Nccih clearinghouse.
The NCCIH Clearinghouse provides information on NCCIH and complementary and integrative health approaches, including publications and searches of Federal databases of scientific and medical literature. The Clearinghouse does not provide medical advice, treatment recommendations, or referrals to practitioners.
Toll-free in the U.S.: 1-888-644-6226
Telecommunications relay service (TRS): 7-1-1
Website: https://www.nccih.nih.gov
Email: [email protected] (link sends email)
Know the Science
NCCIH and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) provide tools to help you understand the basics and terminology of scientific research so you can make well-informed decisions about your health. Know the Science features a variety of materials, including interactive modules, quizzes, and videos, as well as links to informative content from Federal resources designed to help consumers make sense of health information.
Explaining How Research Works (NIH)
Know the Science: How To Make Sense of a Scientific Journal Article
Understanding Clinical Studies (NIH)
A service of the National Library of Medicine, PubMed® contains publication information and (in most cases) brief summaries of articles from scientific and medical journals. For guidance from NCCIH on using PubMed, see How To Find Information About Complementary Health Approaches on PubMed .
Website: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
NIH Clinical Research Trials and You
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has created a website, NIH Clinical Research Trials and You, to help people learn about clinical trials, why they matter, and how to participate. The site includes questions and answers about clinical trials, guidance on how to find clinical trials through ClinicalTrials.gov and other resources, and stories about the personal experiences of clinical trial participants. Clinical trials are necessary to find better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases.
Website: https://www.nih.gov/health-information/nih-clinical-research-trials-you
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
The NHLBI Health Information Center provides information to health professionals, patients, and the public about heart, lung, and blood diseases and sleep disorders and accepts orders for publications.
P.O. Box 30105 Bethesda, MD 20824-0105
Toll-free in the U.S.: 1-877-NHLBI4U (1-877-645-2448)
Website: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov
Email: [email protected] (link sends email)
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Key References
- Acuña-Castroviejo D, Escames G, Figueira JC, et al. Clinical trial to test the efficacy of melatonin in COVID-19. Journal of Pineal Research. 2020;69(3):e12683.
- Andersen LP, Gögenur I, Rosenberg J, et al. The safety of melatonin in humans. Clinical Drug Investigation . 2016;36(3):169-175.
- Artigas L, Coma M, Matos-Filipe P, et al. In-silico drug repurposing study predicts the combination of pirfenidone and melatonin as a promising candidate therapy to reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection progression and respiratory distress caused by cytokine storm. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0240149.
- Auger RR, Burgess HJ, Emens JS, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the treatment of intrinsic circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders: advanced sleep-wake phase disorder (ASWPD), delayed sleep-wake phase disorder (DSWPD), non-24-hour sleep-wake rhythm disorder (N24SWD), and irregular sleep-wake rhythm disorder (ISWRD). An update for 2015. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine . 2015;11(10):1199-1236.
- Auld F, Maschauer EL, Morrison I, et al. Evidence for the efficacy of melatonin in the treatment of primary adult sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine Reviews . 2017;34:10-22.
- Bahrampour Juybari K, Pourhanifeh MH, Hosseinzadeh A, et al. Melatonin potentials against viral infections including COVID-19: current evidence and new findings. Virus Research. 2020;287:198108.
- Cohen PA, Avula B, Wang Y-H, et al. Quantity of melatonin and CBD in melatonin gummies sold in the US . JAMA . 2023;329(16):1401-1402.
- Costello RB, Lentino CV, Boyd CC, et al. The effectiveness of melatonin for promoting healthy sleep: a rapid evidence assessment of the literature. Nutrition Journal . 2014;13:106.
- Esposito S, Laino D, D’Alonzo R, et al. Pediatric sleep disturbances and treatment with melatonin. Journal of Translational Medicine . 2019;17:77.
- Freeman DI, Lind JN, Weidle NJ, et al. Notes from the field: emergency department visits for unsupervised pediatric melatonin ingestion - United States, 2019-2022 . MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report . 2024;73(9):215-217.
- García IG, Rodriguez-Rubio M, Mariblanca AR, et al. A randomized multicenter clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy of melatonin in the prophylaxis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in high-risk contacts (MeCOVID Trial): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):466.
- Hansen MV, Halladin NL, Rosenberg J, et al. Melatonin for pre- and postoperative anxiety in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . 2015;(4):CD009861. Accessed at www.cochranelibrary.com on October 10, 2019.
- Hazra S, Chaudhuri AG, Tiwary BK, et al. Matrix metallopeptidase 9 as a host protein target of chloroquine and melatonin for immunoregulation in COVID-19: a network-based meta-analysis. Life Sciences. 2020;257:118096.
- Herxheimer A. Jet lag. Clinical Evidence . 2014;2014:2303.
- Kennaway D. Potential safety issues in the use of the hormone melatonin in paediatrics. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health . 2015;51(6):584-589.
- Lelak K, Vohra V, Neuman MI, et al. Pediatric melatonin ingestions - United States, 2012–2021 . MMWR Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report . 2022;71(22):725-729.
- Liira J, Verbeek JH, Costa G, et al. Pharmacological interventions for sleepiness and sleep disturbances caused by shift work. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . 2014;(8):CD009776. Accessed at www.cochranelibrary.com on October 10, 2019.
- McDonagh MS, Holmes R, Hsu F. Pharmacologic treatments for sleep disorders in children: a systematic review. Journal of Child Neurology . 2019;34(5):237-247.
- Miller MA, Cappuccio FP. A systematic review of COVID-19 and obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Medicine Reviews. 2020;55:101382.
- Öztürk G, Akbulut KG, Güney Ş. Melatonin, aging, and COVID-19: Melatonin, aging, and COVID-19: Could melatonin be beneficial for COVID-19 treatment in the elderly? Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences. 2020;50(6):1504-1512.
- Qaseem A, Kansagara D, Forciea MA, et al. Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Management of chronic insomnia disorder in adults: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine . 2016;165(2):125-133.
- Sateia MJ, Buysse DJ, Krystal AD, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the pharmacologic treatment of chronic insomnia in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine . 2017;13(2):307-349.
- Sehirli AO, Sayiner S, Serakinci N. Role of melatonin in the treatment of COVID-19; as an adjuvant through cluster differentiation 147 (CD147). Molecular Biological Reports. 2020;47(10):8229-8233.
- Tan D-X, Hardeland R. Targeting host defense system and rescuing compromised mitochondria to increase tolerance against pathogens by melatonin may impact outcome of deadly virus infection pertinent to COVID-19. Molecules. 2020;25(19):4410.
- Zhou Y, Hou Y, Shen J, et al. A network medicine approach to investigation and population-based validation of disease manifestations and drug repurposing for COVID-19. PLoS Biology. 2020;18(11):e3000970.
- Ziaei A, Davoodian P, Dadvand H, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of melatonin in moderately ill patients with COVID-19: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2020;21(1):882.
.header_greentext{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_bluetext{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_redtext{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_purpletext{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_yellowtext{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_blacktext{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_whitetext{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.header_darkred{color:#803d2f!important;}.Green_Header{color:green!important;font-size:24px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Blue_Header{color:blue!important;font-size:18px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Red_Header{color:red!important;font-size:28px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Purple_Header{color:purple!important;font-size:31px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Yellow_Header{color:yellow!important;font-size:20px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.Black_Header{color:black!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;}.White_Header{color:white!important;font-size:22px!important;font-weight:500!important;} Other References
- Barion A, Zee PC. A clinical approach to circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine . 2007;8(6):566-577.
- Brasure M, MacDonald R, Fuchs E, et al. Management of insomnia disorder . Comparative Effectiveness Reviews no. 159. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; 2015. AHRQ publication no. 15(16)-EHC027-EF.
- Bruni O, Alonso-Alconada, Besag F, et al. Current role of melatonin in pediatric neurology: clinical recommendations. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology . 2015;19(2):122-133.
- Chen WY, Giobbie-Hurder A, Gantman K, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of melatonin on breast cancer survivors: impact on sleep, mood, and hot flashes. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment . 2014;145(2):381-388.
- Del Fabbro E, Dev R, Hui D, et al. Effects of melatonin on appetite and other symptoms in patients with advanced cancer and cachexia: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology . 2013;31(10):1271-1276.
- Erland LAE, Saxena PK. Melatonin natural health products and supplements: presence of serotonin and significant variability of melatonin content. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine . 2017;13(2):275-281.
- Grigg-Damberger MM, Ianakieva D. Poor quality control of over-the-counter melatonin: what they say is often not what you get. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine . 2017;13(2);163-165.
- Hansen MV, Andersen LT, Madsen MT, et al. Effect of melatonin on depressive symptoms and anxiety in patients undergoing breast cancer surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment . 2014;145(3);683-695.
- Herxheimer A, Petrie KJ. Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of jet lag (review). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews . 2010;(1):CD001520. Accessed at www.cochranelibrary.com on October 10, 2019.
- Madsen MT, Hansen MV, Andersen LT, et al. Effect of melatonin on sleep in the perioperative period after breast cancer surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine . 2016;12(2):225-233.
- Masters A, Pandi-Perumal SR, Seixas A, et al. Melatonin, the hormone of darkness: from sleep promotion to Ebola treatment. Brain Disorders & Therapy . 2014;4(1):1000151.
- Posadzki P, Bajpai R, Kyaw BM, et al. Melatonin and health: an umbrella review of health outcomes and biological mechanisms of action. BMC Medicine . 2018;16(1):18.
- Rasmussen CL, Olsen MK, Johnsen AT, et al. Effects of melatonin on physical fatigue and other symptoms in patients with advanced cancer receiving palliative care: a double-blind placebo-controlled crossover trial. Cancer . 2015;121(20):3727-3736.
- Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Tan D-X, et al. Melatonin, a full service anti-cancer agent: inhibition of initiation, progression and metastasis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences . 2017;18(4):E843.
- Sletten TL, Magee M, Murray JM, et al. Efficacy of melatonin with behavioural sleep-wake scheduling for delayed sleep-wake phase disorder: a double-blind, randomised clinical trial. PLoS Medicine . 2018;15(6):e1002587.
- Tordjman S, Chokron S, Delorme R, et al. Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Current Neuropharmacology . 2017;15(3):434-443.
- Vural EMS, van Munster BC, de Rooij SE. Optimal dosages for melatonin supplementation therapy in older adults: a systematic review of current literature. Drugs & Aging . 2014;31(6):441-451.
- Wilt TJ, MacDonald R, Brasure M, et al. Pharmacologic treatment of insomnia disorder: an evidence report for a clinical practice guideline by the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine . 2016;165(2):103-113.
Acknowledgments
NCCIH thanks D. Craig Hopp, Ph.D., and David Shurtleff, Ph.D., NCCIH, for their review of this publication.
This publication is not copyrighted and is in the public domain. Duplication is encouraged.
NCCIH has provided this material for your information. It is not intended to substitute for the medical expertise and advice of your health care provider(s). We encourage you to discuss any decisions about treatment or care with your health care provider. The mention of any product, service, or therapy is not an endorsement by NCCIH.
For Consumers
Know the Science: 9 Questions To Help You Make Sense of Health Research
For Health Care Providers
Use of Natural Products by Children
Related Fact Sheets
Using Dietary Supplements Wisely
Anxiety at a Glance
Sleep Disorders: What You Need To Know
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Biden takes a big swing at hostage-for-truce deal, puts onus on Israeli, Hamas officials to step up
President Joe Biden delivers remarks on the verdict in former President Donald Trump’s hush money trial and on the Middle East, from the State Dining Room of the White House, Friday, May 31, 2024, in Washington. (AP Photo/Evan Vucci)
Israeli police remove a person protesting against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s government as demonstrators call for the release of hostages held in the Gaza Strip by the Hamas militant group, in Tel Aviv, Israel, Saturday, June 1, 2024. (AP Photo/Maya Alleruzzo)
- Copy Link copied
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Joe Biden is looking past resistance from key Israeli officials as he presses Israel and Hamas to agree to a three-phase agreement that could immediately bring home dozens of Israeli hostages, free Palestinian prisoners and perhaps even lead to an endgame in the nearly eight-month-old Gaza war.
Biden’s big swing — during a tough reelection battle — could also demonstrate to a significant slice of his political base demoralized by his handling of the conflict that he’s doing his part to end the war that has killed more than 36,000 Palestinians and left hundreds of thousands struggling to meet basic needs.
White House officials on Monday said Biden’s decision to make public what it describes as an Israeli proposal — just one day after it was delivered to Hamas — was driven by a desire to put Hamas on the spot. The move diverged from the U.S. administration’s position throughout the conflict to allow the Israelis to speak for themselves about hostage negotiations.
“The president felt that where we are in this war, where we are in the negotiations to get the hostages out, that it was time for a different approach and a time to make the proposal public, to try to energize the process here and catalyze a different outcome,” White House national security spokesman John Kirby said.
Almost immediately after Biden detailed the proposal — which includes a cease-fire and phased Israeli troop withdrawal from Gaza if Hamas releases all hostages — Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office said it would continue its war until Hamas was destroyed.
NETANYAHU FACING PRESSURE FROM FAR-RIGHT
Netanyahu’s political survival depends on a far-right coalition that is adamant about eradicating Hamas. He sowed further doubt about proposal’s viability Monday when he told an Israeli parliament committee that there are certain “gaps” in how Biden laid out the proposal. The prime minister said Israelis “reserve the right to return to war.”
Kirby played down differences between Biden and Netanyahu and underscored that the proposal was an Israeli one. He added that Biden agrees with Israelis that Hamas should not govern postwar Gaza nor does he “expect that Israel should have to live next door to that kind of a terrorist threat.”
“This wasn’t about jamming the prime minister, the war cabinet,” Kirby said. “This was about laying bare for the public to see how well and how faithfully and how assertively the Israelis came up with a new proposal. It shows how much they really want to get this done.”
But even if Hamas agreed to terms, it would require Netanyahu to make some difficult political calculations. Two leading members of his far-right coalition — National Security Minister Itamar Ben-Gvir and Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich — have threatened to leave Netanyahu’s government if he signs off on the proposal. That would cause the coalition to collapse.
Smotrich said Monday that agreeing to a cease-fire would amount to a humiliation of Israel and a surrender. Increased military pressure, he said, is “the only language understood in the Middle East.”
Biden last week expressed concern about those in the Israeli government who “want to keep fighting for years” and don’t see freeing the hostages as a “priority.” Administration officials on Monday warned Israeli officials that getting bogged down in Gaza could be detrimental to Israel’s national security.
“Endless conflict in Gaza in pursuit of some idea of total victory is not going to make Israel safer,” said State Department spokesman Matthew Miller.
Netanyahu has also faced pressure from families of hostages — officials say about 80 people captured by militants i n the Oct. 7 attack are still alive and Hamas is holding the bodies of 43 others — to reach an agreement to free their loved ones. Opposition leader Yair Lapid, however, vowed over the weekend to provide a political safety net to Netanyahu, ensuring his government would not fall over the deal.
OPTIMISM DESPITE HEADWINDS
Even as the proposal faces stiff headwinds, the Biden administration said it was cautiously optimistic that a deal could be reached.
White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan urged world leaders to rally behind the proposal.
“They need to train their eyes on Hamas this week and say it’s time to come to the table to do this deal,” Sullivan said in an appearance at the U.S. Global Leadership Coalition conference in Washington.
To that end, Biden on Monday spoke with Sheikh Tamim bin Hamad Al Thani of Qatar, a key Hamas interlocutor, and said it was “the best possible opportunity for an agreement,” the White House said.
Ambassador Linda Thomas-Greenfield, the U.S. envoy to the United Nations, said the U.S. circulated a draft resolution seeking support for the proposal from the 14 other members of the U.N. Security Council.
Sullivan, meanwhile, spoke to his Turkish counterpart, Akif Cagatay Kilic, about Turkey using its influence with Hamas to get them to accept the proposal. Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has defended Hamas and hosted the group’s political leader, Ismail Haniyeh, for talks in April.
Group of Seven leaders on Monday also endorsed the deal.
“We call on Hamas to accept this deal, that Israel is ready to move forward with, and we urge countries with influence over Hamas to help ensure that it does so,” the G7 leaders said in a statement.
EVEN GETTING TO PHASE ONE IS A CHALLENGE
Biden acknowledged last week that getting beyond the first phase of the proposal would be difficult.
The first phase would last for six weeks and would include a cease-fire, a withdrawal of Israeli forces from all densely populated areas of Gaza and the release of a number of hostages, including women, the elderly and the wounded, in exchange for the release of hundreds of Palestinian prisoners.
The Israelis, under the proposal, would also allow 600 humanitarian aid trucks into Gaza each day during the first phase. The second phase would include the release of all remaining living hostages, including male soldiers, and Israeli forces would withdraw from Gaza.
Hamas is likely to make enormous demands about which Palestinian prisoners will be released and call on Israel to assure that it won’t continue to target top Hamas leaders.
Aaron David Miller, a former U.S. Middle East peace negotiator, said even getting to phase one — and the six-week pause in fighting — would bring about a “downshift in the escalation of the military campaign, fewer people dying.”
“I’m not sure they can expect much more,” said Miller, now a senior fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. “Negotiations work in the end only if the parties feel sufficient pain accompanied by the prospects of gain, and that generates urgency. The only party that is in a hurry here is the Biden administration.”
Indeed, Israeli officials view the conflict on a far longer timeline.
Just last week, Israeli national security adviser Tzachi Hanegbi said he expected the war to drag on for another seven months, in order to destroy the military and governing capabilities of Hamas and the smaller Islamic Jihad militant group.
But with Election Day in the U.S. now just over five months away, Biden faces tightening pressure to more quickly resolve the Mideast conflict that’s left him bleeding support.
AP writers Edith M. Lederer at the United Nations and Matthew Lee contributed reporting.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Published September 14, 2022. I have a Master's Degree in Chemistry and a Ph.D. in Structural Biology. I am interested in how the shape and connectivity of molecules relate to their reactivity and function. Journal Club. So much more than reading a paper aloud. So many ways to mess it up.
In this video, I will show you how to create a research article or journal article presentation quickly in PowerPoint.Get the 30-day Research Jumpstart Guide...
The foundation of an outstanding journal club presentation rests on the choice of an interesting and well-written paper for discussion. Several resources are available to help you select important and timely research, including the American College of Physicians (ACP) Journal Club and the Diffusion section of The Hematologist.McMaster University has created the McMaster Online Rating of ...
Rule 2: Spend only 1 minute per slide. When you present your slide in the talk, it should take 1 minute or less to discuss. This rule is really helpful for planning purposes—a 20-minute presentation should have somewhere around 20 slides. Also, frequently giving your audience new information to feast on helps keep them engaged.
Delivery. It is important to dress appropriately, stand up straight, and project your voice towards the back of the room. Practise using a microphone, or any other presentation aids, in advance. If you don't have your own presenting style, think of the style of inspirational scientific speakers you have seen and imitate it.
What is a journal club? How do your prepare for it? And how do you present it? In this video, I will guide you on how to prepare a journal club presentation....
With 5 identical slides, work backwards and remove 1 item from the preceding slide. If you must animate a slide, make sure it works and in the right order! Avoid the use of complicated images of which you will use only a small part. A simpler diagram will make the point more forcefully and in a less distracting way. 9.2.
Rule 3: Only Talk When You Have Something to Say. Do not be overzealous about what you think you will have available to present when the time comes. Research never goes as fast as you would like. Remember the audience's time is precious and should not be abused by presentation of uninteresting preliminary material.
With these thoughts in mind, I would like to share a few "tips" for selecting a paper and preparing a presentation for journal club: Select a paper with a subject that might interest both scientists and non-scientists. A genuine question out of curiosity is always intriguing. Studies in lifestyle and behavior are fun because the audience ...
Giving a good presentation is a learned skill; here are some tips on how to do it well. Pick a good paper. (Don't get all neurotic about this. If you find it interesting and significant, then it will almost certainly benefit your group. If you're in doubt, ask a colleague or mentor.)
Journal clubs are a longstanding tradition in residency training, dating back to William Osler in 1875. The original goal of the journal club in Osler's day was to share expensive texts and to review literature as a group. ... To prepare a successful journal club presentation, it helps for the structure of the presentation to mirror the ...
A Template for Journal Club Presentations, Celia M. Elliott If you feel compelled to provide an outline, make it content‐rich Today we'll discuss Majorana fermions (MFs), theory background InSb nanowires used as "colliders" Zero‐energy peaks observed; believed to be electrons scattering off MFs
Frame your story (figure out where to start and where to end). Plan your delivery (decide whether to memorize your speech word for word or develop bullet points and then rehearse it—over and ...
1. Make It a Routine. Schedule the journal club at a recurring time and location, so that it becomes a regular part of everyone's schedule. Choose a time that will be the least disruptive to everyone's experiments. Perhaps host it during lunchtime and invite people to eat while the presenter is speaking.
Make sure to ask the residents how they usually do journal club in their department. Some programs do not use powerpoints or want your presentation under 5 mins. Regardless of the timing and format, every journal club presentation can be approached in this general format: Step 1: Introduction
The secret structure of great talks. From the "I have a dream" speech to Steve Jobs' iPhone launch, many great talks have a common structure that helps their message resonate with listeners. In this talk, presentation expert Nancy Duarte shares practical lessons on how to make a powerful call-to-action. 18:00.
Here are some simple tips for creating an effective PowerPoint Presentation. Less is more: You want to give enough information to make your audience want to read your paper. So include details, but not too many, and avoid too many formulas and technical jargon. Clean and professional: Avoid excessive colors, distracting backgrounds, font ...
Chosen well, trigger videos can present a thought-provoking dilemma that encourages discussion and debate. 4 They can alter the dynamics of a presentation. Success requires careful linking or embedding the videos into the presentation, making sure they play on the computer and projector, and confirming appropriate loudness of the audio settings.
When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences. As an ...
An easy way to do this is by using the 5×5 rule. This means using no more than 5 bullet points per slide, with no more than 5 words per bullet point. It is also good to break up the text-heavy slides with ones including diagrams or graphs. This can also help to convey your results in a more visual and easy-to-understand way.
Creating the Visual. Stick with 1 to 3 learning objectives, and focus the talk on them. The key is to know the message of the presentation upfront. Build the visuals of the lecture to include the background, evidence, and conclusions for those specific messages. Too much text is overwhelming.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
PROOFREADING / ACADEMIC ESSAY SERVICE (£/$)For all academic proofreading and mentoring services, send a request on https://www.thepagedoctor.comChapter Times...
Abridged Science for High School Students. The Nuclear Research Foundation School Certificate Integrated, Volume 2. Book. • 1966. Abschlusskurs Sonografie der Bewegungsorgane First Edition. Book. • 2024. Absolute Radiometry. Electrically Calibrated Thermal Detectors of Optical Radiation.
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual.Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual.. To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of ...
Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary or revision - including pre-or postpublication stages. Visualization. Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/ data presentation. Supervision
Case Presentation. A 46-year-old female patient with a history of depression and no previously documented suicide attempts or psychiatric hospitalizations presented to the emergency department with multiple self-inflicted stab wounds. She reported that she had attempted suicide and expressed regret that her suicidal behaviors were nonfatal.
Melatonin is a hormone that your brain produces in response to darkness. It helps with the timing of your circadian rhythms (24-hour internal clock) and with sleep. Being exposed to light at night can block melatonin production. Research suggests that melatonin plays other important roles in the body beyond sleep.
Biden takes a big swing at hostage-for-truce deal, puts onus on Israeli, Hamas officials to step up. President Joe Biden delivers remarks on the verdict in former President Donald Trump's hush money trial and on the Middle East, from the State Dining Room of the White House, Friday, May 31, 2024, in Washington.
Presentation of Case. Dr. Kevin S. Oh (Radiation Oncology): A 45-year-old woman was evaluated in the oncology clinic of this hospital because of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. The ...