Students & Educators —Menu
- Educational Resources
- Educators & Faculty
- College Planning
- ACS ChemClub
- Project SEED
- U.S. National Chemistry Olympiad
- Student Chapters
- ACS Meeting Information
- Undergraduate Research
- Internships, Summer Jobs & Coops
- Study Abroad Programs
- Finding a Mentor
- Two Year/Community College Students
- Social Distancing Socials
- Planning for Graduate School
- Grants & Fellowships
- Career Planning
- International Students
- Planning for Graduate Work in Chemistry
- ACS Bridge Project
- Graduate Student Organizations (GSOs)
- Schedule-at-a-Glance
- Standards & Guidelines
- Explore Chemistry
- Science Outreach
- Publications
- ACS Student Communities
- You are here:
- American Chemical Society
- Students & Educators

Writing the Research Plan for Your Academic Job Application
By Jason G. Gillmore, Ph.D., Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, Hope College, Holland, MI
A research plan is more than a to-do list for this week in lab, or a manila folder full of ideas for maybe someday—at least if you are thinking of a tenure-track academic career in chemistry at virtually any bachelor’s or higher degree–granting institution in the country. A perusal of the academic job ads in C&EN every August–October will quickly reveal that most schools expect a cover letter (whether they say so or not), a CV, a teaching statement, and a research plan, along with reference letters and transcripts. So what is this document supposed to be, and why worry about it now when those job ads are still months away?
What Is a Research Plan?
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation. It must be a document that people at the department you hope to join will (a) read, and (b) be suitably excited about to invite you for an interview.
That much I knew when I was asked to write this article. More specifics I only really knew for my own institution, Hope College (a research intensive undergraduate liberal arts college with no graduate program), and even there you might get a dozen nuanced opinions among my dozen colleagues. So I polled a broad cross-section of my network, spanning chemical subdisciplines at institutions ranging from small, teaching-centered liberal arts colleges to our nation’s elite research programs, such as Scripps and MIT. The responses certainly varied, but they did center on a few main themes, or illustrate a trend across institution types. In this article I’ll share those commonalities, while also encouraging you to be unafraid to contact a search committee chair with a few specific questions, especially for the institutions you are particularly excited about and feel might be the best fit for you.
How Many Projects Should You Have?

While more senior advisors and members of search committees may have gotten their jobs with a single research project, conventional wisdom these days is that you need two to three distinct but related projects. How closely related to one another they should be is a matter of debate, but almost everyone I asked felt that there should be some unifying technique, problem or theme to them. However, the projects should be sufficiently disparate that a failure of one key idea, strategy, or technique will not hamstring your other projects.
For this reason, many applicants wisely choose to identify:
- One project that is a safe bet—doable, fundable, publishable, good but not earthshaking science.
- A second project that is pie-in-the-sky with high risks and rewards.
- A third project that fits somewhere in the middle.
Having more than three projects is probably unrealistic. But even the safest project must be worth doing, and even the riskiest must appear to have a reasonable chance of working.
How Closely Connected Should Your Research Be with Your Past?
Your proposed research must do more than extend what you have already done. In most subdisciplines, you must be sufficiently removed from your postdoctoral or graduate work that you will not be lambasted for clinging to an advisor’s apron strings. After all, if it is such a good idea in their immediate area of interest, why aren’t they pursuing it?!?
But you also must be able to make the case for why your training makes this a good problem for you to study—how you bring a unique skill set as well as unique ideas to this research. The five years you will have to do, fund, and publish the research before crafting your tenure package will go by too fast for you to break into something entirely outside your realm of expertise.
Biochemistry is a partial exception to this advice—in this subdiscipline it is quite common to bring a project with you from a postdoc (or more rarely your Ph.D.) to start your independent career. However, you should still articulate your original contribution to, and unique angle on the work. It is also wise to be sure your advisor tells that same story in his or her letter and articulates support of your pursuing this research in your career as a genuinely independent scientist (and not merely someone who could be perceived as his or her latest "flunky" of a collaborator.)
Should You Discuss Potential Collaborators?
Regarding collaboration, tread lightly as a young scientist seeking or starting an independent career. Being someone with whom others can collaborate in the future is great. Relying on collaborators for the success of your projects is unwise. Be cautious about proposing to continue collaborations you already have (especially with past advisors) and about starting new ones where you might not be perceived as the lead PI. Also beware of presuming you can help advance the research of someone already in a department. Are they still there? Are they still doing that research? Do they actually want that help—or will they feel like you are criticizing or condescending to them, trying to scoop them, or seeking to ride their coattails? Some places will view collaboration very favorably, but the safest route is to cautiously float such ideas during interviews while presenting research plans that are exciting and achievable on your own.
How Do You Show Your Fit?
Some faculty advise tailoring every application packet document to every institution to which you apply, while others suggest tweaking only the cover letter. Certainly the cover letter is the document most suited to introducing yourself and making the case for how you are the perfect fit for the advertised position at that institution. So save your greatest degree of tailoring for your cover letter. It is nice if you can tweak a few sentences of other documents to highlight your fit to a specific school, so long as it is not contrived.
Now, if you are applying to widely different types of institutions, a few different sets of documents will certainly be necessary. The research plan that you target in the middle to get you a job at both Harvard University and Hope College will not get you an interview at either! There are different realities of resources, scope, scale, and timeline. Not that my colleagues and I at Hope cannot tackle research that is just as exciting as Harvard’s. However, we need to have enough of a niche or a unique angle both to endure the longer timeframe necessitated by smaller groups of undergraduate researchers and to ensure that we still stand out. Furthermore, we generally need to be able to do it with more limited resources. If you do not demonstrate that understanding, you will be dismissed out of hand. But at many large Ph.D. programs, any consideration of "niche" can be inferred as a lack of confidence or ambition.
Also, be aware that department Web pages (especially those several pages deep in the site, or maintained by individual faculty) can be woefully out-of-date. If something you are planning to say is contingent on something you read on their Web site, find a way to confirm it!
While the research plan is not the place to articulate start-up needs, you should consider instrumentation and other resources that will be necessary to get started, and where you will go for funding or resources down the road. This will come up in interviews, and hopefully you will eventually need these details to negotiate a start-up package.
Who Is Your Audience?
Your research plan should show the big picture clearly and excite a broad audience of chemists across your sub-discipline. At many educational institutions, everyone in the department will read the proposal critically, at least if you make the short list to interview. Even at departments that leave it all to a committee of the subdiscipline, subdisciplines can be broad and might even still have an outside member on the committee. And the committee needs to justify their actions to the department at large, as well as to deans, provosts, and others. So having at least the introduction and executive summaries of your projects comprehensible and compelling to those outside your discipline is highly advantageous.
Good science, written well, makes a good research plan. As you craft and refine your research plan, keep the following strategies, as well as your audience in mind:
- Begin the document with an abstract or executive summary that engages a broad audience and shows synergies among your projects. This should be one page or less, and you should probably write it last. This page is something you could manageably consider tailoring to each institution.
- Provide sufficient details and references to convince the experts you know your stuff and actually have a plan for what your group will be doing in the lab. Give details of first and key experiments, and backup plans or fallback positions for their riskiest aspects.
- Hook your readers with your own ideas fairly early in the document, then strike a balance between your own new ideas and the necessary well referenced background, precedents, and justification throughout. Propose a reasonable tentative timeline, if you can do so in no more than a paragraph or two, which shows how you envision spacing out the experiments within and among your projects. This may fit well into your executive summary
- Show how you will involve students (whether undergraduates, graduate students, an eventual postdoc or two, possibly even high schoolers if the school has that sort of outreach, depending on the institutions to which you are applying) and divide the projects among students.
- Highlight how your work will contribute to the education of these students. While this is especially important at schools with greater teaching missions, it can help set you apart even at research intensive institutions. After all, we all have to demonstrate “broader impacts” to our funding agencies!
- Include where you will pursue funding, as well as publication, if you can smoothly work it in. This is especially true if there is doubt about how you plan to target or "market" your research. Otherwise, it is appropriate to hold off until the interview to discuss this strategy.
So, How Long Should Your Research Plan Be?

Learn more on the Blog
Here is where the answers diverged the most and without a unifying trend across institutions. Bottom line, you need space to make your case, but even more, you need people to read what you write.
A single page abstract or executive summary of all your projects together provides you an opportunity to make the case for unifying themes yet distinct projects. It may also provide space to articulate a timeline. Indeed, many readers will only read this single page in each application, at least until winnowing down to a more manageable list of potential candidates. At the most elite institutions, there may be literally hundreds of applicants, scores of them entirely well-suited to the job.
While three to five pages per proposal was a common response (single spaced, in 11-point Arial or 12-point Times with one inch margins), including references (which should be accurate, appropriate, and current!), some of my busiest colleagues have said they will not read more than about three pages total. Only a few actually indicated they would read up to 12-15 pages for three projects. In my opinion, ten pages total for your research plans should be a fairly firm upper limit unless you are specifically told otherwise by a search committee, and then only if you have two to three distinct proposals.
Why Start Now?
Hopefully, this question has answered itself already! Your research plan needs to be a well thought out document that is an integrated part of applications tailored to each institution to which you apply. It must represent mature ideas that you have had time to refine through multiple revisions and a great deal of critical review from everyone you can get to read them. Moreover, you may need a few different sets of these, especially if you will be applying to a broad range of institutions. So add “write research plans” to this week’s to do list (and every week’s for the next few months) and start writing up the ideas in that manila folder into some genuine research plans. See which ones survive the process and rise to the top and you should be well prepared when the job ads begin to appear in C&EN in August!

Jason G. Gillmore , Ph.D., is an Associate Professor of Chemistry at Hope College in Holland, MI. A native of New Jersey, he earned his B.S. (’96) and M.S. (’98) degrees in chemistry from Virginia Tech, and his Ph.D. (’03) in organic chemistry from the University of Rochester. After a short postdoctoral traineeship at Vanderbilt University, he joined the faculty at Hope in 2004. He has received the Dreyfus Start-up Award, Research Corporation Cottrell College Science Award, and NSF CAREER Award, and is currently on sabbatical as a Visiting Research Professor at Arizona State University. Professor Gillmore is the organizer of the Biennial Midwest Postdoc to PUI Professor (P3) Workshop co-sponsored by ACS, and a frequent panelist at the annual ACS Postdoc to Faculty (P2F) Workshops.
Other tips to help engage (or at least not turn off) your readers include:
- Avoid two-column formats.
- Avoid too-small fonts that hinder readability, especially as many will view the documents online rather than in print!
- Use good figures that are readable and broadly understandable!
- Use color as necessary but not gratuitously.
Accept & Close The ACS takes your privacy seriously as it relates to cookies. We use cookies to remember users, better understand ways to serve them, improve our value proposition, and optimize their experience. Learn more about managing your cookies at Cookies Policy .
1155 Sixteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20036, USA | service@acs.org | 1-800-333-9511 (US and Canada) | 614-447-3776 (outside North America)
- Terms of Use
- Accessibility
Copyright © 2024 American Chemical Society
Digital Job Searching and Recruitment Platforms: A Semi-systematic Literature Review
- Conference paper
- First Online: 29 August 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Chiara Signore 15 ,
- Bice Della Piana 15 &
- Francesco Di Vincenzo 15
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems ((LNNS,volume 769))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference in Methodologies and intelligent Systems for Techhnology Enhanced Learning
301 Accesses
1 Citations
The purpose of this paper is to shed light on the new E-recruitment trend that is pervading the lives of job seekers, included students, and job offers. A semi-systematic literature review on digital job searching and recruiting platform in the last five years was conducted with the aim to develop a preliminary conceptual framework. Following a replicable research process, a final sample of 37 publications was located in five subdimensions - Web Application Framework, Use of Artificial Intelligence technologies, Use of Blockchain Technologies, Type of User, User Experience - grouped by two dimensions of analysis: “Technical implementation of the platform”, “Platform usability analysis”. From our findings it emerges that the first one received strong attention, specifically with regards to subdimensions Web Application Framework and Use of the Artificial Intelligence Technologies; the subdimension Use of the Blockchain Technologies started to attract scholarly attention only from 2020. The second dimension of analysis has received a fair amount of attention over the last five years, but it seems that in 2021 the sub-dimension Type of User is perceived as the most attractive from scholars from different field of studies.
The contribution of this work is twofold. Firstly, it tries to shed lights on the main characteristics of the studies about the job searching and recruiting platforms as derived from the publications included in our review identifying appropriate dimensions and sub-dimensions of analysis that could be useful to analyze these platforms in the future. Secondly, for each sub-dimensions we identified the major challenges that authors have set out to address. This specific aspect will be helpful to identify the future research agenda for the topic investigated.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Adamovic, M.: Organizational justice research: a review, synthesis, and research agenda. Eur. Manag. Rev. (2023)
Google Scholar
Afnan, T., Rabaan, H., Jones, K.M.L., Dombrowski, L.: Asymmetries in online job-seeking: a case study of Muslim-American women. Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact. 5 (CSCW2), 1–29 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3479548
Ahamad, F.: Impact of online job search and job reviews on job decision. In: Paper Presented at the WSDM 2020 - Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, pp. 909–910 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3336191.3372184
Alben, L.: Defining the Criteria for Effective Interaction Design, vol. 5 (1996)
Awaji, B., Solaiman, E., Marshall, L.: Blockchain-based trusted achievement record system design. In: Paper Presented at the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series, pp. 46–51 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1145/3411681.3411689
McElrath, B.: Braiding the blockchain. Presentation at Scaling Bitcoin Hong Kong, 7 December 2015 (2015). https://scalingbitcoin.org/hongkong2015/presentations/DAY2/2breakingthechain1-mcelrath.pdf
Basri, W., Siam, M.R.: E-recruitment adoption strategy in the universities of Saudi Arabia. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 8 (33), 32–43 (2016)
Behaneck, M.: Employment websites: personnel by mouse click. [Online-Jobborsen: Personal per Mausklick]. Betonwerk Und Fertigteil-Technik/Concrete Plant Precast Technol. 84 (1), 42–51 (2019)
Brown, J., Matsa, D.A.: Locked in by leverage: job search during the housing crisis. J. Financ. Econ. 136 (3), 623–648 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2019.11.001
Article Google Scholar
Cao, H., Do, D., Tran, V., Cao, T., Song, Y.: Synonym prediction for Vietnamese occupational skills (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-08530-7_29
Chamakiotis, P., Panteli, N., Davison, R.M.: Reimagining e-leadership for reconfigured virtual teams due to Covid-19. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 60 , 102381 (2021)
Choi, K.: Gender differences in the use of social contacts in the job search process. In: Paper Presented at the 81st Annual Meeting of the Academy of Management 2021: Bringing the Manager Back in Management, AoM 2021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.5465/AMBPP.2021.181
Chou, C., Lu, T.: A hybrid-feedback recommender system for employment websites. J. Ambient Intell. Human. Comput. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-020-01772-y
Chou, Y., Wongso, F.R., Chao, C., Yu, H.: An AI mock-interview platform for interview performance analysis. In: Paper Presented at the 2022 10th International Conference on Information and Education Technology, ICIET 2022, pp. 37–41 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIET55102.2022.9778999
Dabić, M., Obradović, T., Vlačić, B., Sahasranamam, S., Paul, J.: Frugal innovations: a multidisciplinary review & agenda for future research. J. Bus. Res. 142 , 914–929 (2022)
Dagnino, G.B., Picone, P.M., Ferrigno, G.: Temporary competitive advantage: a state-of-the-art literature review and research directions. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 23 (1), 85–115 (2021)
Della Piana, B., Griffith, R., Milosevic, M., Scymcyk, J.M.: Reviewing culture–innovation relationships: trends and themes from selected management journals. J. Int. Counc. Small Bus. 4 , 1–29 (2022)
Dillahunt, T.R., Israni, A., Lu, A.J.: Examining the use of online platforms for employment: a survey of U.S. job seekers. In: Paper Presented at the Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems - Proceedings (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3411764.3445350
Dubovitskaya, A., Mazzola, L., Denzler, A.: Towards a trusted support platform for the job placement task (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-48340-1_16
Gasparėnienė, L., Matulienė, S., Žemaitis, E.: Opportunities of job search through social media platforms and its development in Lithuania. Bus.: Theory Pract. 22 (2), 330–339 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3846/btp.2021.11055
Grant, M.J., Booth, A.: A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 26 (2), 91–108 (2009)
Gusdorf, M.: Recruitment and selection: hiring the right person (2008)
Hassan, H.M., Galal-Edeen, G.H.: From usability to user experience. In: 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Informatics and Biomedical Sciences (ICIIBMS), Okinawa, Japan, pp. 216–222 (2017)
Hamdane, A., Belhaj, N., El Hamdaoui, H., Aissaoui, K., El Bekkali, M., El Houda Chaoui, N.: Big data based architecture to bringing together graduates and recruiters: case of Moroccan University. Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 26 (3), 1701–1709 (2022). https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v26.i3.pp1701-1709
Hassenzahl, M., Law, E.L.C., Hvannberg, E.T.: User Experience-towards a unified view. Ux Ws Nordichi 6 , 1–3 (2006)
Heggo, I.A., Abdelbaki, N.: Hybrid information filtering engine for personalized job recommender system (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-74690-6_54
Henry, C., Lewis, K.V.: The art of dramatic construction: enhancing the context dimension in women’s entrepreneurship research. J. Bus. Res. 155 , 113440 (2023)
Javed, Z., Qazi, H., Khoja, S.A.: An ontology-based knowledge management model for e-recruitment utilizing MOOCs data. In: Paper Presented at the 2019 8th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies, ICICT 2019, pp. 124–128 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICT47744.2019.9001911
Kamaru Zaman, E.A., Ahmad Kamal, A.F., Mohamed, A., Ahmad, A., Raja Mohd Zamri, R.A.Z.: Staff employment platform (StEP) using job profiling analytics (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3441-2_30
Kaur, D., Kaur, R.: Does electronic word-of-mouth influence e-recruitment adoption? A mediation analysis using the PLS-SEM approach. Manag. Res. Rev. 46 (2), 223–244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-04-2021-0322
Kim, J., Heo, W.: Artificial intelligence video interviewing for employment: perspectives from applicants, companies, developer and academicians. Inf. Technol. People 35 (3), 861–878 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1108/ITP-04-2019-0173
Kişi, N.: Exploratory research on the use of blockchain technology in recruitment. Sustainability 14 (16), 10098 (2022)
Kolekar, A.: SKYNET: a platform for maximizing career opportunities. In: Paper Presented at the 2021 International Conference on Nascent Technologies in Engineering, ICNET 2021 - Proceedings (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNTE51185.2021.9487581
Lee, D., Ahn, C.: Industrial human resource management optimization based on skills and characteristics. Comput. Ind. Eng. 144 , 106463 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106463
Li, L., Peltsverger, S., Zheng, J., Le, L., Handlin, M.: Retrieving and classifying LinkedIn job titles for alumni career analysis. In: Paper Presented at the SIGITE 2021 - Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference on Information Technology Education, pp. 85–90 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1145/3450329.3476858
Lakhani, A.: Recommendations for recruiters with sentiment detection. In: Paper Presented at the CEUR Workshop Proceedings, vol. 2967 (2021)
Liu, H., Ge, Y.: Job and employee embeddings: a joint deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 35 , 1–12 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2022.3180593
Ma, H., Xu, Y., Ma, W., Lin, Z., Jiang, K.: A multi-field feature interaction convolutional neural network for resume recommendation. In: Paper Presented at the 2020 International Symposium on Autonomous Systems, ISAS 2020, pp. 186–191 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISAS49493.2020.9378849
Martins, N., Dominique-Ferreira, S., Lopes, C.: Design and development of a digital platform for seasonal jobs: improving the hiring process. J. Glob. Sch. Mark. Sci.: Bridg. Asia World 32 (3), 452–469 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1080/21639159.2020.1808851
Mat Saad, M.F., Listyo Nugro, A.W., Thinakaran, R., Baijed, M.: A review of artificial intelligence based platform in human resource recruitment process. In: Paper Presented at the 2021 6th IEEE International Conference on Recent Advances and Innovations in Engineering, ICRAIE 2021 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRAIE52900.2021.9704023
Mehboob, M., Ali, M.S., Ul Islam, S., Sarmad Ali, S.: Evaluating automatic CV shortlisting tool for job recruitment based on machine learning techniques. In: Paper Presented at the Proceedings of the 2022 Mohammad Ali Jinnah University International Conference on Computing, MAJICC 2022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/MAJICC56935.2022.9994112
Mehta, M., et al.: A service-oriented human capital management recommendation platform. In: Paper Presented at the SysCon 2019 - 13th Annual IEEE International Systems Conference, Proceedings (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/SYSCON.2019.8836842
Norman, D., Miller, J., Henderson, A.: What you see, some of what’s in the future, and how we go about doing it: HI at Apple Computer. In: Conference Companion on Human Factors in Computing Systems, p. 155 (1995)
Okolie, U.C., Irabor, I.E.: E-recruitment: practices, opportunities and challenges. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 9 (11), 116–122 (2017)
Saini, A., Rusu, F., Johnston, A.: PrivateJobMatch: a privacy-oriented deferred multi-match recommender system for stable employment. In: Paper Presented at the RecSys 2019 - 13th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems, pp. 87–95 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3298689.3346983
Sarath, C., Sandhya, G.: A qualitative approach to study the perception of job seekers towards digital job portals. Int. J. Bus. Innov. Res. 29 (1), 32–46 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1504/ijbir.2022.125668
Salehi, B., Kazimipour, B., Baldwin, T.: Differences in language use: insights from job and talent search. In: Paper Presented at the ACM International Conference Proceeding Series (2019). https://doi.org/10.1145/3372124.3372127
Shan, T.C., Hua, W.W.: Taxonomy of Java web application frameworks. In: 2006 IEEE International Conference on e-Business Engineering (ICEBE 2006), Shanghai, China, pp. 378–385 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEBE.2006.98
Smaldone, F., Ippolito, A., Lagger, J., Pellicano, M.: Employability skills: profiling data scientists in the digital labour market. Eur. Manag. J. 40 (5), 671–684 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emj.2022.05.005
Snyder, H.: Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 104 , 333–339 (2019)
Verschuere, B., Brandsen, T., Pestoff, V.: Co-production: the state of the art in research and the future agenda. VOLUNTAS: Int. J. Voluntary Nonprofit Org. 23 , 1083–1101 (2012)
Wickramasinghe, H.C.P., Thebuwana, T.D., Wijesinghe, G.K.H.S., Dissanayake, U.N., Kodagoda, N., Suriyawansa, K.: Digital platform to empower the self-employment in Sri Lanka. In: Paper Presented at the Proceedings of 6th International Conference on Information Technology Research: Digital Resilience and Reinvention, ICITR 2021 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITR54349.2021.9657410
Xu, C., Mewburn, I., Grant, W.J., Suominen, H.: PostAc®: a visual interactive search, exploration, and analysis platform for Ph.D. intensive job postings. In: Paper Presented at the ACL 2019 - 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Proceedings of System Demonstrations, pp. 43–48 (2019)
Yujun, Y., Yimei, Y., Wang, Z., Wei, L., Liyun, L., Debin, H.: Research on high-quality employment of college students based on big data technology and artificial intelligence. In: Paper Presented at the 2022 19th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing, ICCWAMTIP 2022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCWAMTIP56608.2022.10016596
Yazdanian, R., West, R., Dillenbourg, P.: Keeping up with the trends: analyzing the dynamics of online learning and hiring platforms in the software programming domain. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 31 (4), 896–939 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-020-00231-1
Vermeeren, A.P., Law, E.L.C., Roto, V., Obrist, M., Hoonhout, J., Väänänen-Vainio-Mattila, K.: User experience evaluation methods: current state and development needs. In: Proceedings of the 6th Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction: Extending Boundaries, pp. 521–530 (2010)
Zhang, Z., Luo, Y., Wen, Y., Zhang, X.: CycleResume: a cycle learning framework with Hybrid attention for Fine-grained talent-job fit (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-20503-3_21
Zhang, W., Hu, F., Xie, Q.: Design, development and application of big data platform on provision of job information search services for students in vocational college. In: Paper presented at the Proceedings - 2018 7th International Conference of Educational Innovation through Technology, EITT 2018, pp. 180–183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/EITT.2018.00043
Zhou, Z., Zhou, X., Li, M., Song, Y., Zhang, T., Yan, R.: Personalized query suggestion with searching dynamic flow for online recruitment. In: Paper Presented at the International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Proceedings, pp. 2773–2783 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3511808.3557416
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
3CLab-Cross Cultural Competence Learning and Education, Department of Management and Innovation Systems, University of Salerno, Via Giovanni Paolo II, 132, Fisciano, Italy
Chiara Signore, Bice Della Piana & Francesco Di Vincenzo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chiara Signore .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Mathematics, Physics and Informatics, Comenius University, Bratislava, Slovakia
Zuzana Kubincová
University of L'Aquila, L'Aquila, Italy
Federica Caruso
Universitetet i Tromsø (UiT) – Norges arktiske universitet, Tromsø, Norway
Tae-eun Kim
Technical University of Sofia , Sofia, Bulgaria
Malinka Ivanova
Department of Life, Health and Environmental Sciences, University of L'Aquila, Coppito, Italy
Loreto Lancia
Department of Computer Science, University of Salerno, FISCIANO, Salerno, Italy
Maria Angela Pellegrino
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Signore, C., Della Piana, B., Di Vincenzo, F. (2023). Digital Job Searching and Recruitment Platforms: A Semi-systematic Literature Review. In: Kubincová, Z., Caruso, F., Kim, Te., Ivanova, M., Lancia, L., Pellegrino, M.A. (eds) Methodologies and Intelligent Systems for Technology Enhanced Learning, Workshops - 13th International Conference. MIS4TEL 2023. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 769. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42134-1_31
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-42134-1_31
Published : 29 August 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-42133-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-42134-1
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Understanding and solving intractable resource governance problems.
- In the Press
- Conferences and Talks
- Exploring models of electronic wastes governance in the United States and Mexico: Recycling, risk and environmental justice
- The Collaborative Resource Governance Lab (CoReGovLab)
- Water Conflicts in Mexico: A Multi-Method Approach
- Past projects
- Publications and scholarly output
- Research Interests
- Higher education and academia
- Public administration, public policy and public management research
- Research-oriented blog posts
- Stuff about research methods
- Research trajectory
- Publications
- Developing a Writing Practice
- Outlining Papers
- Publishing strategies
- Writing a book manuscript
- Writing a research paper, book chapter or dissertation/thesis chapter
- Everything Notebook
- Literature Reviews
- Note-Taking Techniques
- Organization and Time Management
- Planning Methods and Approaches
- Qualitative Methods, Qualitative Research, Qualitative Analysis
- Reading Notes of Books
- Reading Strategies
- Teaching Public Policy, Public Administration and Public Management
- My Reading Notes of Books on How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation/How to Conduct PhD Research
- Writing a Thesis (Undergraduate or Masters) or a Dissertation (PhD)
- Reading strategies for undergraduates
- Social Media in Academia
- Resources for Job Seekers in the Academic Market
- Writing Groups and Retreats
- Regional Development (Fall 2015)
- State and Local Government (Fall 2015)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2016)
- Regional Development (Fall 2016)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2018)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2019)
- Public Policy Analysis (Spring 2016)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Summer Session 2011)
- POLI 352 Comparative Politics of Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 2)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Term 1)
- POLI 332 Latin American Environmental Politics (Term 2, Spring 2012)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
Preparing a research statement for an academic job application
This is not my first blog post on research statements (this one on research statements and research trajectories and this other on research pipelines, research trajectories and research programmes are quite related), but this is perhaps the first time I write about and address the Research Statement as a key component of job applications for tenure-track or post-doctoral positions. We all know how angry and upset I feel about the dismal state of the academic job market(s). However, let us assume that you still want to apply for tenure-track (TT) jobs. I do have some experience applying for (and landing) TT jobs, as well as chairing search committees for these positions. I have also sat on search committees, and have read hundreds of applications. These are thus a few pointers that I think might help potential applicants write their statements.

We all know the huge role that luck, connections, institutional “pedigree” and other factors play, but for purposes of helping those who want to apply, some ideas that you all may want to consider in crafting your Research Statements. This blog post started as a Twitter thread so I’ve pulled from there too.
One way to write your research statement is to follow a similar model to the blog post I wrote here https://t.co/A3FaGQkeCU DO NOTE: In this post, I wrote about writing a Research Statement and crafting a Research Trajectory. This was not by chance. There’s a logic to this. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
Personally, I think that when departments and universities hire you, they want to see how you develop your work through time . In that sense, the Research Statement that you arrive with (at the time of application) is STATIC . You present a SNAPSHOT of what you’ve done so far.
In my personal view (please don’t take my suggestions as dogma or guidelines!), I think that there is value in developing both a Research Statement and a Research Trajectory (this one is worth considering in both ex-ante and ex-post modes)
A Research Trajectory can one (or both) of two things:
1) it can present a narrative in timeline form of how your thinking has evolved.
2) it can present your Research Plan for the next 5-6 years (pandemics and life will obviously derail that plan!)
So what I have done with my own Research Statements is to present how my research interests have evolved through time. In that sense, my Research Statement is a STATIC snapshot at a certain point in time (at the time of writing, of course!) of how my different research strands have evolved through time (that is, of my Research Trajectory ). Below is an example of how I have done self-reflection about my own Research Statement.
Last year I was invited to participate in a global workshop of a few selected scholars on the future of environmental policy, which surprised a couple of people. Well, here’s the thing: at the beginning of my career, I *was* a specialist in environmental policy instruments.
Now, my own thinking about the importance, value, structure and content of the Research Plan, Research Trajectory, Research Pipeline and Research Statement has evolved (most recent iteration can be found here https://t.co/nNMDnKa3Gm ) What must be clear from my blog is that… — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
… to observe and read many Research Statements (or research narratives, as you may want to call them), but I recently came across @paullagunes ‘ revamped website, and I really, really liked how he narrates his work https://t.co/dWdYJbHjvT Paul explains his projects through time — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
Paul also explains very well how his work contributes to theoretical debates and the empirical literature. Paul is an excellent writer and you may consider reading through his website and published work to see how he crafts his narratives.
If people want to learn more about how to craft a Research Statement, I think one strategy would be to poke around and read the “Research” pages of various scholars’ websites to find patterns. That is how I have learned much of what I now write about, by looking at many scholars’ strategies, distilling them and adapting them into something that works FOR ME.
I said I had two pieces of advice. But in reality, I think it’s just that one: for me, a Research Statement of a candidate tells me what they’ve done, if/where it is published or under review, and how those pieces of work fit a coherent, cohesive narrative of their research .
As someone with interdisciplinary training who continues to do interdisciplinary work, I often struggle when people want to categorize me (am I a geographer, a political scientist, a public administration scholar, a sociologist?). Truth be told, the way I have made peace with this challenge of being interdisciplinary when being in disciplinary departments (who say they want interdisciplinarity but judge you by their disciplinary norms) is to show how my work speaks to the debates of their discipline.
Also, my work (though it cuts through different disciplines and methods), is centred around ONE key question that has puzzled me my entire life: what drives agents to cooperate and collaborate? ?
Studying collaborative behaviour has led me to write on environmental activism and transnational coalitions.
And yes, I study cooperation and collaboration, but often times there are factors that preclude these and lead to disputes, which is why I ALSO study protests, activist mobilization and conflict: https://t.co/cwOJ6mkrcO Studying water conflict has led me to study this resource. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
… the study of cooperation and conflict for the governance of orthodox and unorthodox commons (or common pool resources). Anyhow, just my two cents in hopes this thread may help those crafting their research statements. </end thread> — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) July 25, 2020
You can share this blog post on the following social networks by clicking on their icon.
Posted in academia .
Tagged with research pipeline , research plan , research statement , research trajectory .
No comments
By Raul Pacheco-Vega – July 31, 2020
0 Responses
Stay in touch with the conversation, subscribe to the RSS feed for comments on this post .
Leave a Reply Cancel Some HTML is OK
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
or, reply to this post via trackback .
About Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
Find me online.
My Research Output
- Google Scholar Profile
- Academia.Edu
- ResearchGate
My Social Networks
- Polycentricity Network
Recent Posts
- “State-Sponsored Activism: Bureaucrats and Social Movements in Brazil” – Jessica Rich – my reading notes
- Reading Like a Writer – Francine Prose – my reading notes
- Using the Pacheco-Vega workflows and frameworks to write and/or revise a scholarly book
- On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- The Abstract Decomposition Matrix Technique to find a gap in the literature
Recent Comments
- Hazera on On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- Kipi Fidelis on A sequential framework for teaching how to write good research questions
- Razib Paul on On framing, the value of narrative and storytelling in scholarly research, and the importance of asking the “what is this a story of” question
- Jonathan Wilcox on An improved version of the Drafts Review Matrix – responding to reviewers and editors’ comments
- Catherine Franz on What’s the difference between the Everything Notebook and the Commonplace Book?
Follow me on Twitter:
Proudly powered by WordPress and Carrington .
Carrington Theme by Crowd Favorite
At home, abroad, working, interning? Wherever you are this summer, contact OCS or make an appointment for a virtual advising session. We are available all summer!
- Undergraduates
- Ph.Ds & Postdocs
- Prospective Students & Guests
- What is a Community?
- Student Athletes
- First Generation and/or Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Student Veterans
- Exploring Careers
- Advertising, Marketing & PR
- Finance, Insurance & Real Estate
- General Management & Leadership Development Programs
- Law & Legal Services
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelance Work
- Environment, Sustainability & Energy
- Media & Communications
- Policy & Think Tanks
- Engineering
- Healthcare, Biotech & Global Public Health
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Programming & Data Science
- Graduate School
- Health Professions
- Business School
- Meet with OCS
- Student Organizations Workshop Request
- OCS Podcast Series
- Office of Fellowships
- Navigating AI in the Job Search Process
- Cover Letters & Correspondence
- Job Market Insights
- Professional Conduct & Etiquette
- Professional Online Identity
- Interview Preparation
- Resource Database
- Yale Career Link
- Jobs, Internships & Other Experiences
- Gap Year & Short-Term Opportunities
- Planning an International Internship
- Funding Your Experience
- Career Fairs/Networking Events
- On-Campus Recruiting
- Job Offers & Salary Negotiation
- Informational Interviewing
- Peer Networking Lists
- Building Your LinkedIn Profile
- YC First Destinations
- YC Four-Year Out
- GSAS Program Statistics
- Statistics & Reports
- Contact OCS
- OCS Mission & Policies
- Additional Yale Career Offices
Writing Samples
- Share This: Share Writing Samples on Facebook Share Writing Samples on LinkedIn Share Writing Samples on X
Guide to Submitting a Writing Sample
Source: https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/interviewing/guide-to-submitting-a-writing-sample
Writing samples are used by employers to evaluate your writing skills, tone and style. If you are applying for positions that require strong writing skills, you might be asked to submit a writing sample.
While some employers might ask you to email or upload your writing sample as part of your application, others might ask you to bring it to your interview or possibly email it after your interviews to help employers make a decision. In this guide, we discuss what employers look for in a writing sample, how to choose a writing sample, how to write one and how to submit it.
What is a writing sample?
A writing sample is a supplemental document for a job application often requested for jobs that include a significant amount of writing, like those in journalism, marketing, public relations and research. Employers might also ask for a writing sample if you will be responsible for writing and communicating important information or correspondences. For example, if you are applying for a job in HR at a small company, you might be responsible for sending company-wide information. In this case, the employer will look for candidates with strong writing skills who can clearly communicate important information across the company.
What do employers look for in a writing sample?
Different employers look for different details in your writing sample depending on the job, company and industry. Every employer, however, will look for tone, style and writing skills including content, grammar, spelling and punctuation. While the specific writing style of the company can often be learned on the job, employers might be looking to hire someone with a certain level of writing skills at their first day on the job.
How long should a writing sample be?
In most cases, your writing sample should be around 750 words or between one and two pages. Like your resume, employers have a limited amount of time to review your writing sample. A brief, impactful writing sample is better than a long, less impressive one. Often times, employers will provide a specific page or word count they require from your sample. If you decide to submit a research paper or other lengthy document, you can make it shorter for the employer by selecting a certain passage or section.
How do I choose a writing sample?
While some employers might give you a writing assignment with a specific prompt, others might simply ask you to provide a sample from your past work. Choose a writing sample that is relevant for the job you’re applying for. Here are some examples you may want to consider:
- Research papers from a job or class
- Narrative papers from a job or class
- Other writing assignments
- Press releases
- Articles or other contributions
When deciding which piece of writing you should submit, consider the following ideas:
Follow the employer’s instruction
The employer might ask for a specific type of writing like a research paper or a piece covering a certain topic. Read the employer’s instructions carefully before making a writing sample selection.
Consider relevant writing samples
When deciding on a writing sample, you should consider only those writing pieces that are relevant to the position. For example, if you are applying for a scientific research position, you should select a research paper from your most recent position or highest level of schooling. If you are applying for a position in PR, you should submit a press release or other relevant documents.
Find relatable topics
Along with selecting a relevant writing style, you should try to find a sample that also relates to the subject matter of the position. Submitting a sample with content similar to what you’ll be writing about on the job will help employers relate your writing skills directly to the job.
Align your writing with the company’s tone
You should select a piece of writing that is relatable for the company. For example, you should not submit a sarcastic, irreverent writing sample for a company with a professional, helpful brand image. Alternatively, you might not submit a modest, simple writing sample to a company that’s sole focus is risk and creativity. You can find clues about a company’s tone by researching their website, Company Page and recent news articles or press releases.
You should also read several pieces of writing that the company has already published. This could include reading their company blog, website or research papers.
Make sure it is up to date
Selecting a writing sample that is older than one year might contain out of date or irrelevant content. If you are selecting an old writing sample, be sure to carefully review and update it to reflect the most recent ideas. You also want to demonstrate that you have recently had to use your writing skills—if you send an employer a writing sample from several years ago, they may assume that you have not done any writing since then.
Avoid sensitive subject matter
Unless specifically requested by the employer, you should avoid sensitive content like politics, religion or personal information. You should also review your writing sample to exclude any confidential information like third-party contact information or private company information like financial or other data.
What if I don’t have a writing sample?
You might not have a writing sample if you have no professional experience or have not previously held a job where you produced applicable pieces of writing. If this is the case, it is acceptable to write a new sample for the employer. This way, you’ll be able to write a fresh, relevant passage that is specific to the position you’re applying for.
Pay close attention to the employer’s direction regarding the writing sample, research the company for clues on tone and style and review your document carefully for grammar, spelling and punctuation mistakes.
How to submit a writing sample
Before submitting a writing sample, you should proofread it several times to ensure it is free of errors. It is critical to achieve as close to perfection as possible in a writing sample, as your writing skills are the key focus of this document. It might be helpful to read your document backward—doing so presents the words in a new order and makes it easier to catch mistakes. You might also consider asking trusted friends or family to review your writing sample.
Whether you submit an entire piece or part of a writing sample, it can be helpful to write a short introductory paragraph for context. You might include it directly on your sample, on a cover page or in your email. For example:
“Please find my writing sample for the Sr. Product Research position attached to this email. This sample is a passage from a larger study about how product simplicity impacts consumers. I believe it showcases my ability to clearly communicate results from an important project that lead to key achievements for the company.”
After you’ve polished your writing sample, you should follow the employer’s instructions when submitting it. You might be asked to upload your sample on an online application, email it or bring it to your interview. If you are bringing your sample to an interview, you should bring at least five hard copies in case you have multiple interviewers. If you are applying to several writing jobs, you might consider creating an online writing portfolio that you can easily send to employers.
Visitors to this website should refer to our terms of use policy .
Office of Career Strategy
Visiting yale.

- Appointments

- Resume Reviews

- Undergraduates
- PhDs & Postdocs
- Faculty & Staff
- Prospective Students
- Online Students
- Career Champions
- I’m Exploring
- Architecture & Design
- Education & Academia
- Engineering
- Fashion, Retail & Consumer Products
- Fellowships & Gap Year
- Fine Arts, Performing Arts, & Music
- Government, Law & Public Policy
- Healthcare & Public Health
- International Relations & NGOs
- Life & Physical Sciences
- Marketing, Advertising & Public Relations
- Media, Journalism & Entertainment
- Non-Profits
- Pre-Health, Pre-Law and Pre-Grad
- Real Estate, Accounting, & Insurance
- Social Work & Human Services
- Sports & Hospitality
- Startups, Entrepreneurship & Freelancing
- Sustainability, Energy & Conservation
- Technology, Data & Analytics
- DACA and Undocumented Students
- First Generation and Low Income Students
- International Students
- LGBTQ+ Students
- Transfer Students
- Students of Color
- Students with Disabilities
- Explore Careers & Industries
- Make Connections & Network
- Search for a Job or Internship
- Write a Resume/CV
- Write a Cover Letter
- Engage with Employers
- Research Salaries & Negotiate Offers
- Find Funding
- Develop Professional and Leadership Skills
- Apply to Graduate School
- Apply to Health Professions School
- Apply to Law School
- Self-Assessment
- Experiences
- Post-Graduate
- Jobs & Internships
- Career Fairs
- For Employers
- Meet the Team
- Peer Career Advisors
- Social Media
- Career Services Policies
- Walk-Ins & Pop-Ins
- Strategic Plan 2022-2025
Research statements for faculty job applications
The purpose of a research statement.
The main goal of a research statement is to walk the search committee through the evolution of your research, to highlight your research accomplishments, and to show where your research will be taking you next. To a certain extent, the next steps that you identify within your statement will also need to touch on how your research could benefit the institution to which you are applying. This might be in terms of grant money, faculty collaborations, involving students in your research, or developing new courses. Your CV will usually show a search committee where you have done your research, who your mentors have been, the titles of your various research projects, a list of your papers, and it may provide a very brief summary of what some of this research involves. However, there can be certain points of interest that a CV may not always address in enough detail.
- What got you interested in this research?
- What was the burning question that you set out to answer?
- What challenges did you encounter along the way, and how did you overcome these challenges?
- How can your research be applied?
- Why is your research important within your field?
- What direction will your research take you in next, and what new questions do you have?
While you may not have a good sense of where your research will ultimately lead you, you should have a sense of some of the possible destinations along the way. You want to be able to show a search committee that your research is moving forward and that you are moving forward along with it in terms of developing new skills and knowledge. Ultimately, your research statement should complement your cover letter, CV, and teaching philosophy to illustrate what makes you an ideal candidate for the job. The more clearly you can articulate the path your research has taken, and where it will take you in the future, the more convincing and interesting it will be to read.
Separate research statements are usually requested from researchers in engineering, social, physical, and life sciences, but can also be requested for researchers in the humanities. In many cases, however, the same information that is covered in the research statement is often integrated into the cover letter for many disciplines within the humanities and no separate research statement is requested within the job advertisement. Seek advice from current faculty and new hires about the conventions of your discipline if you are in doubt.
Timeline: Getting Started with your Research Statement
You can think of a research statement as having three distinct parts. The first part will focus on your past research, and can include the reasons you started your research, an explanation as to why the questions you originally asked are important in your field, and a summary some of the work you did to answer some of these early questions.
The middle part of the research statement focuses on your current research. How is this research different from previous work you have done, and what brought you to where you are today? You should still explain the questions you are trying to ask, and it is very important that you focus on some of the findings that you have (and cite some of the publications associated with these findings). In other words, do not talk about your research in abstract terms, make sure that you explain your actual results and findings (even if these may not be entirely complete when you are applying for faculty positions), and mention why these results are significant.
The final part of your research statement should build on the first two parts. Yes, you have asked good questions, and used good methods to find some answers, but how will you now use this foundation to take you into your future? Since you are hoping that your future will be at one of the institutions to which you are applying, you should provide some convincing reasons why your future research will be possible at each institution, and why it will be beneficial to that institution, or to the students at that institution.
While you are focusing on the past, present, and future or your research, and tailoring it to each institution, you should also think about the length of your statement and how detailed or specific you make the descriptions of your research. Think about who will be reading it. Will they all understand the jargon you are using? Are they experts in the subject, or experts in a range of related subjects? Can you go into very specific detail, or do you need to talk about your research in broader terms that make sense to people outside of your research field focusing on the common ground that might exist? Additionally, you should make sure that your future research plans differ from those of your PI or advisor, as you need to be seen as an independent researcher. Identify 4-5 specific aims that can be divided into short-term and long-term goals. You can give some idea of a 5-year research plan that includes the studies you want to perform, but also mention your long-term plans, so that the search committee knows that this is not a finite project.
Another important consideration when writing about your research is realizing that you do not perform research in a vacuum. When doing your research you may have worked within a team environment at some point, or sought out specific collaborations. You may have faced some serious challenges that required some creative problem-solving to overcome. While these aspects are not necessarily as important as your results and your papers or patents, they can help paint a picture of you as a well-rounded researcher who is likely to be successful in the future even if new problems arise, for example.
Follow these general steps to begin developing an effective research statement:
Step 1: Think about how and why you got started with your research. What motivated you to spend so much time on answering the questions you developed? If you can illustrate some of the enthusiasm you have for your subject, the search committee will likely assume that students and other faculty members will see this in you as well. People like to work with passionate and enthusiastic colleagues. Remember to focus on what you found, what questions you answered, and why your findings are significant. The research you completed in the past will have brought you to where you are today; also be sure to show how your research past and research present are connected. Explore some of the techniques and approaches you have successfully used in your research, and describe some of the challenges you overcame. What makes people interested in what you do, and how have you used your research as a tool for teaching or mentoring students? Integrating students into your research may be an important part of your future research at your target institutions. Conclude describing your current research by focusing on your findings, their importance, and what new questions they generate.
Step 2: Think about how you can tailor your research statement for each application. Familiarize yourself with the faculty at each institution, and explore the research that they have been performing. You should think about your future research in terms of the students at the institution. What opportunities can you imagine that would allow students to get involved in what you do to serve as a tool for teaching and training them, and to get them excited about your subject? Do not talk about your desire to work with graduate students if the institution only has undergraduates! You will also need to think about what equipment or resources that you might need to do your future research. Again, mention any resources that specific institutions have that you would be interested in utilizing (e.g., print materials, super electron microscopes, archived artwork). You can also mention what you hope to do with your current and future research in terms of publication (whether in journals or as a book), try to be as specific and honest as possible. Finally, be prepared to talk about how your future research can help bring in grants and other sources of funding, especially if you have a good track record of receiving awards and fellowships. Mention some grants that you know have been awarded to similar research, and state your intention to seek this type of funding.
Step 3: Ask faculty in your department if they are willing to share their own research statements with you. To a certain extent, there will be some subject-specific differences in what is expected from a research statement, and so it is always a good idea to see how others in your field have done it. You should try to draft your own research statement first before you review any statements shared with you. Your goal is to create a unique research statement that clearly highlights your abilities as a researcher.
Step 4: The research statement is typically a few (2-3) pages in length, depending on the number of images, illustrations, or graphs included. Once you have completed the steps above, schedule an appointment with a career advisor to get feedback on your draft. You should also try to get faculty in your department to review your document if they are willing to do so.
Explore other application documents:

More From Forbes
How important is research for bs/md programs.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Direct medical programs, often referred to as BS/MD programs, are some of the most competitive programs in the country. With programs at Baylor University, Brown University and Case Western Reserve University accepting less than 3% of all its applicants, these programs are often more competitive than the Ivy League. They are looking for exceptional students who are completely committed to becoming physicians. That means the students have spent the better part of their high school career pursuing STEM-focused activities, including physician shadowing, volunteering in healthcare settings and leadership positions in clubs.
Many BS/MD hopefuls pursue research as a way to build their resume.
Numerous BS/MD programs like Rensselaer Polytechnic University, like to see students with extensive research experience. Its program, aptly named the Physician-Scientist Program, wants to see students who will not only participate in research during their tenure in the program but also lead and create their own research projects. The University of South Carolina’s Accelerated Undergraduate to M.D. program has an extensive research and thesis component that is required throughout the student’s academic career. The University of Rochester offers funding for summer research for its BS/MD students. Similarly, the University of Illinois at Chicago looks for students who can demonstrate their “research aptitude.”
What Type Of Research Do BS/MD Programs Accept?
High school students have access to a wide array of research opportunities. School-related options could include science fair projects or AP Seminar and AP Research. Students might also choose to pursue camps or programs over the summer, which allows them to dedicate more time to research. Other students find independent research projects with a local professor. Alternatively, others opt to write a literature review paper to get published.
When BS/MD admission officers review applications, they don’t pit one type of experience against another. They know not every student will be able to find a local professor who allows them to research with them or can afford to do a paid summer program that spans numerous weeks or months. Consequently, they typically will consider holistically the depth of a student’s research experience, irrespective of the type of research the student completes.
Virtual Or In-Person Programs?
Both virtual and in-person experiences can add value to a BS/MD application. However, it depends on the program’s learning objectives and deliverables. Some students don’t have the flexibility to travel to an in-person camp and spend multiple weeks or months there. The University of Pittsburgh’s Guaranteed Admission Program says that “while in-person experiences are encouraged, virtual or remote experiences will be considered when evaluating the applicant.” For those students who have other obligations, a virtual camp might be the perfect fit and still offer a valuable experience.
Apple iOS 17 5 Major iPhone Software Release Should You Upgrade
Baby reindeer piers morgan seeks richard gadd for interview after real martha segment, tyson fury vs oleksandr usyk results winner scorecard and reaction, does the research topic matter.
The research experience doesn’t necessarily have to align with the student’s research interests, but it can often be helpful if it does. However, BS/MD admission officers know that high school students are still exploring their interests, which will likely evolve over the years. An opportunity that doesn’t align with the student’s interest will still be valuable because it allows the student to gain valuable skills that they can leverage to other research experiences in the future.
Summer programs might give students a chance to explore dual interests. Some students interested in medicine might also want to explore computer science or Artificial Intelligence, so finding an opportunity that allows them to blend those interests might be ideal. For example, Rising Researchers , a sister company of Moon Prep, is hosting two five-week summer camps that allow students to practice AI and Machine Learning to study human diseases. Other camps, like Penn Summer Academies, allow students to apply coding skills to other areas of study.

How Long Should The Research Experience Be?
The typical length of a research experience, especially one in the summer, can vary from as short as one week to up to eight weeks. A longer research experience can give students a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter and, importantly, the opportunity to build meaningful relationships with their mentor and fellow students. However, the duration is not the sole determinant of a meaningful experience. Students should also look to see what the tangible outcomes of the program, such as a research paper, skills gained, letter of recommendation and more.
For students who find an independent research experience, the relationship might span several months or even years. Those experiences might result in more fruitful research results and a strong relationship between the student and the mentor.
Are Publications Required?
An experience resulting in a research publication is an added bonus, but it isn’t a requirement. If a student writes a research paper, even if not published, can still demonstrate the student’s scientific writing ability and add value to their college application.
Every BS/MD program is different, and the admission officers' value of research might vary from program to program. Ultimately, BS/MD programs are looking for students who are passionate about medicine and have had extensive experiences to affirm that passion. The College of New Jersey stated in an interview with Moon Prep that they are looking for passionate students, be it a deep involvement in Boy Scouts, Taekwondo or music. Therefore, students should never feel obligated to research if it does not align with their interests. Being genuine in their activities and demonstrating their passions is how to build a resume that stands out to BS/MD admission officers.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Peer To Peer Confidentiality in Social Applications
Ieee account.
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Using ideas from game theory to improve the reliability of language models
Press contact :.
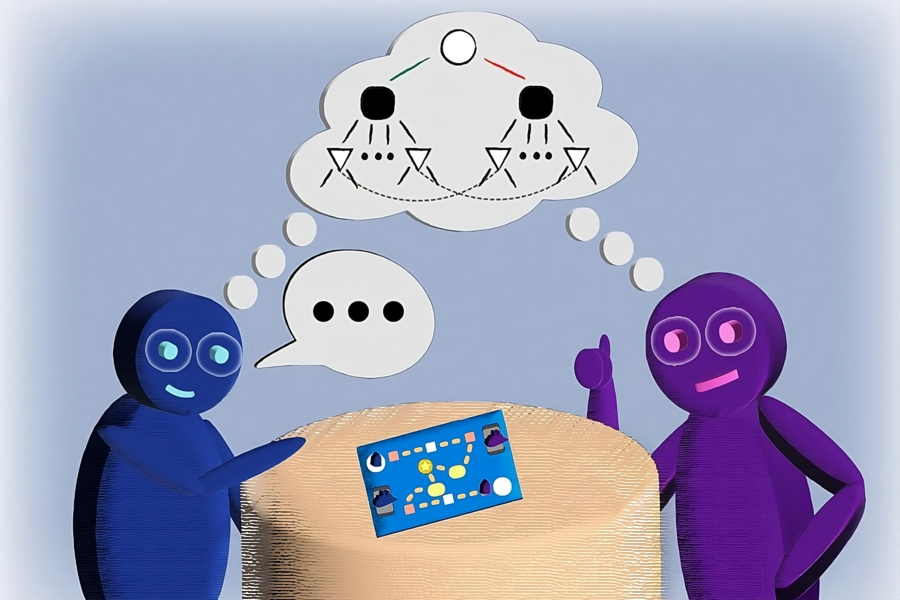

Previous image Next image
Imagine you and a friend are playing a game where your goal is to communicate secret messages to each other using only cryptic sentences. Your friend's job is to guess the secret message behind your sentences. Sometimes, you give clues directly, and other times, your friend has to guess the message by asking yes-or-no questions about the clues you've given. The challenge is that both of you want to make sure you're understanding each other correctly and agreeing on the secret message.
MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) researchers have created a similar "game" to help improve how AI understands and generates text. It is known as a “consensus game” and it involves two parts of an AI system — one part tries to generate sentences (like giving clues), and the other part tries to understand and evaluate those sentences (like guessing the secret message).
The researchers discovered that by treating this interaction as a game, where both parts of the AI work together under specific rules to agree on the right message, they could significantly improve the AI's ability to give correct and coherent answers to questions. They tested this new game-like approach on a variety of tasks, such as reading comprehension, solving math problems, and carrying on conversations, and found that it helped the AI perform better across the board.
Traditionally, large language models answer one of two ways: generating answers directly from the model (generative querying) or using the model to score a set of predefined answers (discriminative querying), which can lead to differing and sometimes incompatible results. With the generative approach, "Who is the president of the United States?" might yield a straightforward answer like "Joe Biden." However, a discriminative query could incorrectly dispute this fact when evaluating the same answer, such as "Barack Obama."
So, how do we reconcile mutually incompatible scoring procedures to achieve coherent, efficient predictions?
"Imagine a new way to help language models understand and generate text, like a game. We've developed a training-free, game-theoretic method that treats the whole process as a complex game of clues and signals, where a generator tries to send the right message to a discriminator using natural language. Instead of chess pieces, they're using words and sentences," says Athul Jacob, an MIT PhD student in electrical engineering and computer science and CSAIL affiliate. "Our way to navigate this game is finding the 'approximate equilibria,' leading to a new decoding algorithm called 'equilibrium ranking.' It's a pretty exciting demonstration of how bringing game-theoretic strategies into the mix can tackle some big challenges in making language models more reliable and consistent."
When tested across many tasks, like reading comprehension, commonsense reasoning, math problem-solving, and dialogue, the team's algorithm consistently improved how well these models performed. Using the ER algorithm with the LLaMA-7B model even outshone the results from much larger models. "Given that they are already competitive, that people have been working on it for a while, but the level of improvements we saw being able to outperform a model that's 10 times the size was a pleasant surprise," says Jacob.
"Diplomacy," a strategic board game set in pre-World War I Europe, where players negotiate alliances, betray friends, and conquer territories without the use of dice — relying purely on skill, strategy, and interpersonal manipulation — recently had a second coming. In November 2022, computer scientists, including Jacob, developed “Cicero,” an AI agent that achieves human-level capabilities in the mixed-motive seven-player game, which requires the same aforementioned skills, but with natural language. The math behind this partially inspired the Consensus Game.
While the history of AI agents long predates when OpenAI's software entered the chat in November 2022, it's well documented that they can still cosplay as your well-meaning, yet pathological friend.
The consensus game system reaches equilibrium as an agreement, ensuring accuracy and fidelity to the model's original insights. To achieve this, the method iteratively adjusts the interactions between the generative and discriminative components until they reach a consensus on an answer that accurately reflects reality and aligns with their initial beliefs. This approach effectively bridges the gap between the two querying methods.
In practice, implementing the consensus game approach to language model querying, especially for question-answering tasks, does involve significant computational challenges. For example, when using datasets like MMLU, which have thousands of questions and multiple-choice answers, the model must apply the mechanism to each query. Then, it must reach a consensus between the generative and discriminative components for every question and its possible answers.
The system did struggle with a grade school right of passage: math word problems. It couldn't generate wrong answers, which is a critical component of understanding the process of coming up with the right one.
“The last few years have seen really impressive progress in both strategic decision-making and language generation from AI systems, but we’re just starting to figure out how to put the two together. Equilibrium ranking is a first step in this direction, but I think there’s a lot we’ll be able to do to scale this up to more complex problems,” says Jacob.
An avenue of future work involves enhancing the base model by integrating the outputs of the current method. This is particularly promising since it can yield more factual and consistent answers across various tasks, including factuality and open-ended generation. The potential for such a method to significantly improve the base model's performance is high, which could result in more reliable and factual outputs from ChatGPT and similar language models that people use daily.
"Even though modern language models, such as ChatGPT and Gemini, have led to solving various tasks through chat interfaces, the statistical decoding process that generates a response from such models has remained unchanged for decades," says Google Research Scientist Ahmad Beirami, who was not involved in the work. "The proposal by the MIT researchers is an innovative game-theoretic framework for decoding from language models through solving the equilibrium of a consensus game. The significant performance gains reported in the research paper are promising, opening the door to a potential paradigm shift in language model decoding that may fuel a flurry of new applications."
Jacob wrote the paper with MIT-IBM Watson Lab researcher Yikang Shen and MIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science assistant professors Gabriele Farina and Jacob Andreas, who is also a CSAIL member. They presented their work at the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) earlier this month, where it was highlighted as a "spotlight paper." The research also received a “best paper award” at the NeurIPS R0-FoMo Workshop in December 2023.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions, quanta magazine.
MIT researchers have developed a new procedure that uses game theory to improve the accuracy and consistency of large language models (LLMs), reports Steve Nadis for Quanta Magazine . “The new work, which uses games to improve AI, stands in contrast to past approaches, which measured an AI program’s success via its mastery of games,” explains Nadis.
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Article: "Game Theory Can Make AI More Correct and Efficient"
- Jacob Andreas
- Athul Paul Jacob
- Language & Intelligence @ MIT
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
- MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab
Related Topics
- Computer science and technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Human-computer interaction
- Natural language processing
- Game theory
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Reasoning and reliability in AI

Explained: Generative AI

Synthetic imagery sets new bar in AI training efficiency

Simulating discrimination in virtual reality
More mit news.

Q&A: A graduating student looks back on his MIT experience
Read full story →

Eleven from MIT awarded 2024 Fulbright fellowships

Robotic palm mimics human touch

Trying to make the grade
Janabel Xia: Algorithms, dance rhythms, and the drive to succeed

Jonathan Byrnes, MIT Center for Transportation and Logistics senior lecturer and visionary in supply chain management, dies at 75
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: indus: effective and efficient language models for scientific applications.
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) trained on general domain corpora showed remarkable results on natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, previous research demonstrated LLMs trained using domain-focused corpora perform better on specialized tasks. Inspired by this pivotal insight, we developed INDUS, a comprehensive suite of LLMs tailored for the Earth science, biology, physics, heliophysics, planetary sciences and astrophysics domains and trained using curated scientific corpora drawn from diverse data sources. The suite of models include: (1) an encoder model trained using domain-specific vocabulary and corpora to address natural language understanding tasks, (2) a contrastive-learning-based general text embedding model trained using a diverse set of datasets drawn from multiple sources to address information retrieval tasks and (3) smaller versions of these models created using knowledge distillation techniques to address applications which have latency or resource constraints. We also created three new scientific benchmark datasets namely, CLIMATE-CHANGE-NER (entity-recognition), NASA-QA (extractive QA) and NASA-IR (IR) to accelerate research in these multi-disciplinary fields. Finally, we show that our models outperform both general-purpose encoders (RoBERTa) and existing domain-specific encoders (SciBERT) on these new tasks as well as existing benchmark tasks in the domains of interest.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
- College of Engineering and Computing
- Location Location
- Contact Contact
- Colleges and Schools
- News and Events
- 2024 News Archive
Jamshidi earns recognition for most influential paper

When someone in academia publishes a research paper, one of the goals is to have the paper cited by other professors and researchers. A paper published 10 years ago by Computer Science and Engineering Assistant Professor Pooyan Jamshidi was recently recognized for its significant impact.
Jamshidi received the Most Influential Paper Award in April at the 19th International Conference on Software Engineering for Adaptive and Self-Managing Systems (SEAMS) in Lisbon, Portugal. Jamshidi’s paper, “ Autonomic Resource Provision for Cloud-based Software ,” was submitted, accepted and published just prior to earning his Ph.D. from Dublin City University in Ireland in 2014. It was presented at the 2014 SEAMS Conference in India.
For the most influential paper award, a select committee considers conference publications published approximately 10 years previously and selects those that have made the most impact according to several criteria, including the number of citations, practical applications and industry adoption, and influence on subsequent research. The most influential award is selected from this short list.
“I wanted to publish the most important part of my Ph.D. research at SEAMS because it was a special community, and their work was close to mine,” Jamshidi says. “Receiving this award is important because this was my first paper with the community. I kept publishing with SEAMS and remained engaged.”
The paper’s title referred to a groundbreaking approach to fundamentally transform how resources are managed and allocated in cloud environments. The key innovation was to enable multiple tenants to describe their adaptation rules for cloud and multi-cloud resource provisioning using a specific language that enables the incorporation of reasoning, inference and resolution of conflicting adaptation rules.
Since the paper was published, it has received 188 citations according to Google Scholar . In addition, the autonomic resource provision technique has been integrated with Microsoft Azure and OpenStack . The concepts and methods introduced in the paper have also led to follow-up research in cloud autoscaling, Edge-and-Internet of Things resource scaling, and networking and autonomous driving.
The paper has impacted the field of software engineering, especially in the context of adaptive and self-managing systems in the cloud, research, industry practices and the broader technological landscape.
While Jamshidi admits that autonomous autoscaling system for cloud-based software is not as a hot topic as it was when his paper was published, it is still a relevant research area that is leading to new ideas, methods, and approaches.
“The most exciting direction in cloud auto-scaling and resource provisioning overall is sustainability-aware approaches to enable sustainable computer usage for modern applications, such as AI systems,” Jamshidi says. “We plan to continue this line of research. For example, thanks to funds provided by the National Science Foundation and collaborators from Carnegie Mellon University and Rochester Institute of Technology, we are investigating software-driven sustainability.”
Challenge the conventional. Create the exceptional. No Limits.
Main Navigation
- Contact NeurIPS
- Code of Ethics
- Code of Conduct
- Create Profile
- Journal To Conference Track
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Proceedings
- Future Meetings
- Exhibitor Information
- Privacy Policy
Call for High School Projects
Machine learning for social impact .
The Thirty-Eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024) is an interdisciplinary conference that brings together researchers in machine learning, neuroscience, statistics, optimization, computer vision, natural language processing, life sciences, natural sciences, social sciences, and other adjacent fields.
This year, we invite high school students to submit research papers on the topic of machine learning for social impact. A subset of finalists will be selected to present their projects virtually and will have their work spotlighted on the NeurIPS homepage. In addition, the leading authors of up to five winning projects will be invited to attend an award ceremony at NeurIPS 2024 in Vancouver.
Each submission must describe independent work wholly performed by the high school student authors. We expect each submission to highlight either demonstrated positive social impact or the potential for positive social impact using machine learning. Application areas may include but are not limited to the following:
- Agriculture
- Climate change
- Homelessness
- Food security
- Mental health
- Water quality
Authors will be asked to confirm that their submissions accord with the NeurIPS code of conduct and the NeurIPS code of ethics .
Submission deadline: All submissions must be made by June 27th, 4pm EDT. The system will close after this time, and no further submissions will be possible.
We are using OpenReview to manage submissions. Papers should be submitted here . Submission will open June 1st. Submissions under review will be visible only to their assigned program committee. We will not be soliciting comments from the general public during the reviewing process. Anyone who plans to submit a paper as an author or a co-author will need to create (or update) their OpenReview profile by the full paper submission deadline.
Formatting instructions: All submissions must be in PDF format. Submissions are limited to four content pages , including all figures and tables; additional pages containing only references are allowed. You must format your submission using the NeurIPS 2024 LaTeX style file using the “preprint” option for non-anonymous submission. The maximum file size for submissions is 50MB. Submissions that violate the NeurIPS style (e.g., by decreasing margins or font sizes) or page limits may be rejected without further review. Papers may be rejected without consideration of their merits if they fail to meet the submission requirements, as described in this document.
Mentorship and collaboration: The submitted research can be a component of a larger research endeavor involving external collaborators, but the submission should describe only the authors’ contributions. The authors can also have external mentors but must disclose the nature of the mentorship. At the time of submission, the authors will be asked to describe the involvement of any mentors or external collaborators and to distinguish mentor and collaborator contributions from those of the authors. In addition, the authors may (optionally) include an acknowledgements section acknowledging the contributions of others following the content sections of the submission. The acknowledgements section will not count toward the submission page limit.
Proof of high school attendance: Submitting authors will also be asked to upload a signed letter, on school letterhead, from each author’s high school confirming that the author was enrolled in high school during the 2023-2024 academic year.
Supplementary artifacts: In their submission, authors may link to supplementary artifacts including videos, working demonstrations, digital posters, websites, or source code. Please do not link to additional text. All such supplementary material should be wholly created by the authors and should directly support the submission content.
Review process: Each submission will be reviewed by anonymous referees. The authors, however, should not be anonymous. No written feedback will be provided to the authors.
Use of Large Language Models (LLMs): We welcome authors to use any tool that is suitable for preparing high-quality papers and research. However, we ask authors to keep in mind two important criteria. First, we expect papers to fully describe their methodology. Any tool that is important to that methodology, including the use of LLMs, should be described also. For example, authors should mention tools (including LLMs) that were used for data processing or filtering, visualization, facilitating or running experiments, or proving theorems. It may also be advisable to describe the use of LLMs in implementing the method (if this corresponds to an important, original, or non-standard component of the approach). Second, authors are responsible for the entire content of the paper, including all text and figures, so while authors are welcome to use any tool they wish for writing the paper, they must ensure that all text is correct and original.
Dual submissions: Submissions that are substantially similar to papers that the authors have previously published or submitted in parallel to other peer-reviewed venues with proceedings or journals may not be submitted to NeurIPS. Papers previously presented at workshops or science fairs are permitted, so long as they did not appear in a conference proceedings (e.g., CVPRW proceedings), a journal, or a book. However, submissions will not be published in formal proceedings, so work submitted to this call may be published elsewhere in the future. Plagiarism is prohibited by the NeurIPS Code of Conduct .
Paper checklist: In order to improve the rigor and transparency of research submitted to and published at NeurIPS, authors are required to complete a paper checklist . The paper checklist is intended to help authors reflect on a wide variety of issues relating to responsible machine learning research, including reproducibility, transparency, research ethics, and societal impact. The checklist does not count towards the page limit and will be entered in OpenReview.
Contact: [email protected]
Better Siri is coming: what Apple’s research says about its AI plans
Apple hasn’t talked too much about ai so far — but it’s been working on stuff. a lot of stuff..
By David Pierce , editor-at-large and Vergecast co-host with over a decade of experience covering consumer tech. Previously, at Protocol, The Wall Street Journal, and Wired.
Share this story
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25430195/247097_Apple__AI__CVirginia_B2B.jpg)
It would be easy to think that Apple is late to the game on AI. Since late 2022, when ChatGPT took the world by storm, most of Apple’s competitors have fallen over themselves to catch up. While Apple has certainly talked about AI and even released some products with AI in mind, it seemed to be dipping a toe in rather than diving in headfirst.
But over the last few months, rumors and reports have suggested that Apple has, in fact, just been biding its time, waiting to make its move. There have been reports in recent weeks that Apple is talking to both OpenAI and Google about powering some of its AI features, and the company has also been working on its own model, called Ajax .
If you look through Apple’s published AI research, a picture starts to develop of how Apple’s approach to AI might come to life. Now, obviously, making product assumptions based on research papers is a deeply inexact science — the line from research to store shelves is windy and full of potholes. But you can at least get a sense of what the company is thinking about — and how its AI features might work when Apple starts to talk about them at its annual developer conference, WWDC, in June.
Smaller, more efficient models
I suspect you and I are hoping for the same thing here: Better Siri. And it looks very much like Better Siri is coming! There’s an assumption in a lot of Apple’s research (and in a lot of the tech industry, the world, and everywhere) that large language models will immediately make virtual assistants better and smarter. For Apple, getting to Better Siri means making those models as fast as possible — and making sure they’re everywhere.
In iOS 18, Apple plans to have all its AI features running on an on-device, fully offline model, Bloomberg recently reported . It’s tough to build a good multipurpose model even when you have a network of data centers and thousands of state-of-the-art GPUs — it’s drastically harder to do it with only the guts inside your smartphone. So Apple’s having to get creative.
In a paper called “ LLM in a flash: Efficient Large Language Model Inference with Limited Memory ” (all these papers have really boring titles but are really interesting, I promise!), researchers devised a system for storing a model’s data, which is usually stored on your device’s RAM, on the SSD instead. “We have demonstrated the ability to run LLMs up to twice the size of available DRAM [on the SSD],” the researchers wrote, “achieving an acceleration in inference speed by 4-5x compared to traditional loading methods in CPU, and 20-25x in GPU.” By taking advantage of the most inexpensive and available storage on your device, they found, the models can run faster and more efficiently.
Apple’s researchers also created a system called EELBERT that can essentially compress an LLM into a much smaller size without making it meaningfully worse. Their compressed take on Google’s Bert model was 15 times smaller — only 1.2 megabytes — and saw only a 4 percent reduction in quality. It did come with some latency tradeoffs, though.
In general, Apple is pushing to solve a core tension in the model world: the bigger a model gets, the better and more useful it can be, but also the more unwieldy, power-hungry, and slow it can become. Like so many others, the company is trying to find the right balance between all those things while also looking for a way to have it all.
Siri, but good
A lot of what we talk about when we talk about AI products is virtual assistants — assistants that know things, that can remind us of things, that can answer questions, and get stuff done on our behalf. So it’s not exactly shocking that a lot of Apple’s AI research boils down to a single question: what if Siri was really, really, really good?
A group of Apple researchers has been working on a way to use Siri without needing to use a wake word at all; instead of listening for “Hey Siri” or “Siri,” the device might be able to simply intuit whether you’re talking to it. “This problem is significantly more challenging than voice trigger detection,” the researchers did acknowledge, “since there might not be a leading trigger phrase that marks the beginning of a voice command.” That might be why another group of researchers developed a system to more accurately detect wake words . Another paper trained a model to better understand rare words, which are often not well understood by assistants.
In both cases, the appeal of an LLM is that it can, in theory, process much more information much more quickly. In the wake-word paper, for instance, the researchers found that by not trying to discard all unnecessary sound but, instead, feeding it all to the model and letting it process what does and doesn’t matter, the wake word worked far more reliably.
Once Siri hears you, Apple’s doing a bunch of work to make sure it understands and communicates better. In one paper, it developed a system called STEER (which stands for Semantic Turn Extension-Expansion Recognition, so we’ll go with STEER) that aims to improve your back-and-forth communication with an assistant by trying to figure out when you’re asking a follow-up question and when you’re asking a new one. In another, it uses LLMs to better understand “ambiguous queries” to figure out what you mean no matter how you say it. “In uncertain circumstances,” they wrote, “intelligent conversational agents may need to take the initiative to reduce their uncertainty by asking good questions proactively, thereby solving problems more effectively.” Another paper aims to help with that, too: researchers used LLMs to make assistants less verbose and more understandable when they’re generating answers.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431587/CleanShot_2024_05_03_at_09.50.52.png)
AI in health, image editors, in your Memojis
Whenever Apple does talk publicly about AI, it tends to focus less on raw technological might and more on the day-to-day stuff AI can actually do for you. So, while there’s a lot of focus on Siri — especially as Apple looks to compete with devices like the Humane AI Pin, the Rabbit R1, and Google’s ongoing smashing of Gemini into all of Android — there are plenty of other ways Apple seems to see AI being useful.
One obvious place for Apple to focus is on health: LLMs could, in theory, help wade through the oceans of biometric data collected by your various devices and help you make sense of it all. So, Apple has been researching how to collect and collate all of your motion data, how to use gait recognition and your headphones to identify you, and how to track and understand your heart rate data. Apple also created and released “the largest multi-device multi-location sensor-based human activity dataset” available after collecting data from 50 participants with multiple on-body sensors.
Apple also seems to imagine AI as a creative tool. For one paper, researchers interviewed a bunch of animators, designers, and engineers and built a system called Keyframer that “enable[s] users to iteratively construct and refine generated designs.” Instead of typing in a prompt and getting an image, then typing another prompt to get another image, you start with a prompt but then get a toolkit to tweak and refine parts of the image to your liking. You could imagine this kind of back-and-forth artistic process showing up anywhere from the Memoji creator to some of Apple’s more professional artistic tools.
In another paper , Apple describes a tool called MGIE that lets you edit an image just by describing the edits you want to make. (“Make the sky more blue,” “make my face less weird,” “add some rocks,” that sort of thing.) “Instead of brief but ambiguous guidance, MGIE derives explicit visual-aware intention and leads to reasonable image editing,” the researchers wrote. Its initial experiments weren’t perfect, but they were impressive.
We might even get some AI in Apple Music: for a paper called “ Resource-constrained Stereo Singing Voice Cancellation ,” researchers explored ways to separate voices from instruments in songs — which could come in handy if Apple wants to give people tools to, say, remix songs the way you can on TikTok or Instagram.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431565/CleanShot_2024_05_03_at_09.36.28.png)
Over time, I’d bet this is the kind of stuff you’ll see Apple lean into, especially on iOS. Some of it Apple will build into its own apps; some it will offer to third-party developers as APIs. (The recent Journaling Suggestions feature is probably a good guide to how that might work.) Apple has always trumpeted its hardware capabilities, particularly compared to your average Android device; pairing all that horsepower with on-device, privacy-focused AI could be a big differentiator.
But if you want to see the biggest, most ambitious AI thing going at Apple, you need to know about Ferret . Ferret is a multi-modal large language model that can take instructions, focus on something specific you’ve circled or otherwise selected, and understand the world around it. It’s designed for the now-normal AI use case of asking a device about the world around you, but it might also be able to understand what’s on your screen. In the Ferret paper, researchers show that it could help you navigate apps, answer questions about App Store ratings, describe what you’re looking at, and more. This has really exciting implications for accessibility but could also completely change the way you use your phone — and your Vision Pro and / or smart glasses someday.
We’re getting way ahead of ourselves here, but you can imagine how this would work with some of the other stuff Apple is working on. A Siri that can understand what you want, paired with a device that can see and understand everything that’s happening on your display, is a phone that can literally use itself. Apple wouldn’t need deep integrations with everything; it could simply run the apps and tap the right buttons automatically.
Again, all this is just research, and for all of it to work well starting this spring would be a legitimately unheard-of technical achievement. (I mean, you’ve tried chatbots — you know they’re not great.) But I’d bet you anything we’re going to get some big AI announcements at WWDC. Apple CEO Tim Cook even teased as much in February, and basically promised it on this week’s earnings call. And two things are very clear: Apple is very much in the AI race, and it might amount to a total overhaul of the iPhone. Heck, you might even start willingly using Siri! And that would be quite the accomplishment.
Sonos is teasing its ‘most requested product ever’ on Tuesday
Inside microsoft’s mission to take down the macbook air, two students find security bug that could let millions do laundry for free, microsoft’s surface and windows ai event live blog: it’s arm time, the new, faster surface pro is microsoft’s all-purpose ai pc.
More from Apple
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25432052/installer.png)
The best new browser for Windows
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24205851/HT015_S_Haddad_ios_iphone_14_slideshow.jpg)
How to make the most of Apple Notes
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24401980/STK071_ACastro_apple_0003.jpg)
More details emerge about Apple’s plans for AI in iOS 18
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25431511/VST_0503_Site.jpg)
On The Vergecast: AI gadgets, iPads, and antitrust
Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
At michigan state university, international research team uses wavefunction matching to solve quantum many-body problems, new approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possible.
FRIB researchers are part of an international research team solving challenging computational problems in quantum physics using a new method called wavefunction matching. The new approach has applications to fields such as nuclear physics, where it is enabling theoretical calculations of atomic nuclei that were previously not possible. The details are published in Nature (“Wavefunction matching for solving quantum many-body problems”) .
Ab initio methods and their computational challenges
An ab initio method describes a complex system by starting from a description of its elementary components and their interactions. For the case of nuclear physics, the elementary components are protons and neutrons. Some key questions that ab initio calculations can help address are the binding energies and properties of atomic nuclei not yet observed and linking nuclear structure to the underlying interactions among protons and neutrons.
Yet, some ab initio methods struggle to produce reliable calculations for systems with complex interactions. One such method is quantum Monte Carlo simulations. In quantum Monte Carlo simulations, quantities are computed using random or stochastic processes. While quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be efficient and powerful, they have a significant weakness: the sign problem. The sign problem develops when positive and negative weight contributions cancel each other out. This cancellation results in inaccurate final predictions. It is often the case that quantum Monte Carlo simulations can be performed for an approximate or simplified interaction, but the corresponding simulations for realistic interactions produce severe sign problems and are therefore not possible.
Using ‘plastic surgery’ to make calculations possible
The new wavefunction-matching approach is designed to solve such computational problems. The research team—from Gaziantep Islam Science and Technology University in Turkey; University of Bonn, Ruhr University Bochum, and Forschungszentrum Jülich in Germany; Institute for Basic Science in South Korea; South China Normal University, Sun Yat-Sen University, and Graduate School of China Academy of Engineering Physics in China; Tbilisi State University in Georgia; CEA Paris-Saclay and Université Paris-Saclay in France; and Mississippi State University and the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State University (MSU)—includes Dean Lee , professor of physics at FRIB and in MSU’s Department of Physics and Astronomy and head of the Theoretical Nuclear Science department at FRIB, and Yuan-Zhuo Ma , postdoctoral research associate at FRIB.
“We are often faced with the situation that we can perform calculations using a simple approximate interaction, but realistic high-fidelity interactions cause severe computational problems,” said Lee. “Wavefunction matching solves this problem by doing plastic surgery. It removes the short-distance part of the high-fidelity interaction, and replaces it with the short-distance part of an easily computable interaction.”
This transformation is done in a way that preserves all of the important properties of the original realistic interaction. Since the new wavefunctions look similar to that of the easily computable interaction, researchers can now perform calculations using the easily computable interaction and apply a standard procedure for handling small corrections called perturbation theory. A team effort
The research team applied this new method to lattice quantum Monte Carlo simulations for light nuclei, medium-mass nuclei, neutron matter, and nuclear matter. Using precise ab initio calculations, the results closely matched real-world data on nuclear properties such as size, structure, and binding energies. Calculations that were once impossible due to the sign problem can now be performed using wavefunction matching.
“It is a fantastic project and an excellent opportunity to work with the brightest nuclear scientist s in FRIB and around the globe,” said Ma. “As a theorist , I'm also very excited about programming and conducting research on the world's most powerful exascale supercomputers, such as Frontier , which allows us to implement wavefunction matching to explore the mysteries of nuclear physics.”
While the research team focused solely on quantum Monte Carlo simulations, wavefunction matching should be useful for many different ab initio approaches, including both classical and quantum computing calculations. The researchers at FRIB worked with collaborators at institutions in China, France, Germany, South Korea, Turkey, and United States.
“The work is the culmination of effort over many years to handle the computational problems associated with realistic high-fidelity nuclear interactions,” said Lee. “It is very satisfying to see that the computational problems are cleanly resolved with this new approach. We are grateful to all of the collaboration members who contributed to this project, in particular, the lead author, Serdar Elhatisari.”
This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, the U.S. National Science Foundation, the German Research Foundation, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences President’s International Fellowship Initiative, Volkswagen Stiftung, the European Research Council, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Security Academic Fund, the Rare Isotope Science Project of the Institute for Basic Science, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science, and the Espace de Structure et de réactions Nucléaires Théorique.
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC), supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics. Hosting what is designed to be the most powerful heavy-ion accelerator, FRIB enables scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security, and industry.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of today’s most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This review distills available empirical research about the process and experience of looking for a job. Job search varies according to several dimensions, including intensity, content, and ...
We provide examples of the relevance of context to job search (i.e., the job seeker's geographical region, country, and culture; the economy; the job seeker's current or past employment situation; and employer behaviors and preferences) and review research on bias in the job search.
Summary of key research findings in recruitment and selection. A systematic, fully comprehensive literature review of extent selection and recruitment literature is beyond the scope of this paper - rather, we focus our effort on recent meta-analyses as well as conceptual and literature review papers to identify the meta-trends in the recruitment and selection research.
Job Search and Employment Success: A Quantitative Review and Future Research Agenda. July 2020. Journal of Applied Psychology. DOI: 10.1037/apl0000675. Authors: Edwin van Hooft. University of ...
job-search quality as promising constructs for future research, as these predicted both quantitative employment success outcomes and employment quality. Based on the results of the theoretical and quantitative synthesis, we map out an agenda for future research. Keywords: job search, self-regulation, meta-analysis, unemployment, turnover
Conceptualizing job search systematicity. Kanfer et al. (Citation 2001) conceptualized job search behaviour as referring to a pattern of thinking, affect, and behaviour that can be evaluated along three different dimensions: (a) intensity-effort (frequency and effort with which job seekers engage in job search activities), (b) content-direction (the activities job seekers engage in and the ...
A research plan is a thoughtful, compelling, well-written document that outlines your exciting, unique research ideas that you and your students will pursue over the next half decade or so to advance knowledge in your discipline and earn you grants, papers, speaking invitations, tenure, promotion, and a national reputation.
didate reaction to recruiting research [78, 79] and candidate employment choice research [8 , 15, 55]. Attraction and t theories argue, and the related research has found, that the more attractive the job application pro-cess, the job, and the organization, the more likely the can-didate is to apply for the job and join the company [46].
This paper adopts a semi-systematic approach to the literature review. Although less structured and rigorous than the fully systematic literature review method, the semi-systematic one allows scholars to include their perspectives in the analysis [11, 15, 16, 21, 27, 51].This methodological choice makes it possible to develop new perspectives on the issue at hand and highlight future research ...
Paragraph 1: A brief sketch of the main themes and topics of your research as well as how it relates to your field. Paragraph 2: A summary of your dissertation research. This may be similar to the paragraph on the dissertation in your cover letter, but it must have more detail about the methods, the theoretical foundations, and most of all, the ...
A Research Trajectory can one (or both) of two things: 1) it can present a narrative in timeline form of how your thinking has evolved. 2) it can present your Research Plan for the next 5-6 years (pandemics and life will obviously derail that plan!) So what I have done with my own Research Statements is to present how my research interests have ...
in-person applications for local positions may continue, job search activities, such as creating a resume, finding a job posting, filling out an application, and contacting employers, have become significantly more efficient with the use of job search engines (Arora & Kumari, 2021; Wanberg et al., 2020).
A writing sample is a supplemental document for a job application often requested for jobs that include a significant amount of writing, like those in journalism, marketing, public relations and research. ... The employer might ask for a specific type of writing like a research paper or a piece covering a certain topic. Read the employer's ...
Building from a PhD to a first postdoctoral research/teaching position This section is aimed at those who are in the final stages of their PhD or have submitted their thesis and/or had their viva. The posts you may be applying for could have a number of job titles e.g. Research Assistant, Research Associate, Research Fellow, Teaching Fellow.
Step 4: The research statement is typically a few (2-3) pages in length, depending on the number of images, illustrations, or graphs included. Once you have completed the steps above, schedule an appointment with a career advisor to get feedback on your draft. You should also try to get faculty in your department to review your document if they ...
The research outcomes through this paper will be a portal that is entirely based on a survey that we have conducted among various job- seekers, students, current employees, various kinds of freelancers, employers, and ... applications. A skill showcasing dashboard can be a great feature in which the user or the job seekers can show off their ...
How to fill out a paper job application. You can follow this step-by-step guide to complete a paper job application: 1. Include your personal information. Start by providing your personal information, including your name, address and phone number, in the correct fields. Be sure that all of your information is accurate and up to date.
6.CONCLUSION. A resume builder web application is a valuable tool that simplifies and streamlines the process of creating professional resumes. It offers a user-friendly interface for users to input their information, select desired templates and layouts, and generate well-formatted resumes in various formats.
What Type Of Research Do BS/MD Programs Accept? High school students have access to a wide array of research opportunities. School-related options could include science fair projects or AP Seminar ...
This research paper investigates peer-to-peer (P2P) confidentiality within social apps, addressing the need for effective and user-friendly privacy methods in today's digital age. With the increasing emphasis on peer-to-peer communication in social networking, user privacy has become critical. This research looks into many aspects of P2P confidentiality in social applications, including ...
Abstract. The introduction of AlphaFold 2 1 has spurred a revolution in modelling the structure of proteins and their interactions, enabling a huge range of applications in protein modelling and ...
The significant performance gains reported in the research paper are promising, opening the door to a potential paradigm shift in language model decoding that may fuel a flurry of new applications." Jacob wrote the paper with MIT-IBM Watson Lab researcher Yikang Shen and MIT Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science assistant ...
Large language models (LLMs) trained on general domain corpora showed remarkable results on natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, previous research demonstrated LLMs trained using domain-focused corpora perform better on specialized tasks. Inspired by this pivotal insight, we developed INDUS, a comprehensive suite of LLMs tailored for the Earth science, biology, physics ...
For the most influential paper award, a select committee considers conference publications published approximately 10 years previously and selects those that have made the most impact according to several criteria, including the number of citations, practical applications and industry adoption, and influence on subsequent research.
Papers may be rejected without consideration of their merits if they fail to meet the submission requirements, as described in this document. Mentorship and collaboration: The submitted research can be a component of a larger research endeavor involving external collaborators, but the submission should describe only the authors' contributions ...
Better Siri is coming: what Apple's research says about its AI plans. Apple hasn't talked too much about AI so far — but it's been working on stuff. A lot of stuff. By David Pierce, editor ...
What is a writing sample? A writing sample is a supplemental document for a job application often requested for jobs that include a significant amount of writing, like those in journalism, marketing, public relations and research. Employers might also ask for a writing sample if you will be responsible for writing and communicating important information or correspondences.
New approach makes calculations with realistic interactions possibleFRIB researchers are part of an international research team solving challenging computational problems in quantum physics using a new method called wavefunction matching. The new approach has applications to fields such as nuclear physics, where it is enabling theoretical calculations of atomic nuclei that were previously not ...