

Lean Business Plan Template & How-To Guide
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Historically, business owners have devoted months to constructing a detailed plan to establish strategy, executive, and financial numbers for their business. Although a strategic plan is often created, these entrepreneurs often miss a big piece: gathering feedback from potential customers.
Without collecting data and insight from target customers, the detailed business plan becomes a document of assumptions and guesses rather than a proven success blueprint.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
Lean business planning allows you to more quickly and accurately develop your business plan based on actual customer feedback and interactions.
On this page:
Key benefits of lean startup business planning, can you use a lean plan to raise funding, key elements of a lean business plan.
- Lean Planning Process
- Putting The Lean Plan Into Action
Review Your Results & Revise Your Plan
Lean business plan faqs, other helpful business plan articles & templates.

The lean startup business model is supported by a one-page business plan that does not require extensive financial forecasting or long-term market research and development plans. While the traditional business plan details every aspect of your company’s operations, the lean business plan focuses on key factors that present immediate opportunities for new companies to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors. This approach allows you to maintain company focus on your core mission and avoid adding unnecessary information that can weigh down your final document.
The lean startup movement has encouraged entrepreneurs to shorten their plans down from hundreds of pages to a one-page business plan or less – essentially eliminating the need for small businesses to create traditional plans at all. Rather than spending time creating lengthy reports, owners can simply list their core values, mission statement, market analysis, marketing strategies, and projected financial statements – all on one page.
Some companies even document their entire value proposition on a single sheet of paper which serves as both the foundation for further market research and development to improve its product or service offering. By having this type of information readily available to share with investors or clients, your company will appear more professional and prepared without taking up too much time creating unnecessary documentation.
Developing a lean business plan is a critical step in launching or growing your business. However, it’s important to note that if you’re seeking VC funding , bank funding, or angel investors , a traditional business plan is required. Such a plan includes additional research, strategy, and financial forecasts to give investors and lenders the information they need to determine whether they will receive an adequate ROI (return on investment) if they provide funding to you.
Below are nine key elements of a lean business plan example:
Business overview
Describe what the business does.
Value propositions
Detail the value your business brings to the market and the industry.
Key partnerships
List the key partners, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, vendors, or software firms, with whom your business will work.
Key activities
List the key activities your business will perform to gain a competitive advantage, grow market share, and fuel profits.
Key resources
List the resources that your business has at its disposal to create maximum value. This could include human capital (your own experience or that of your core team), intellectual property, patents, funding, etc.
Customer relationships
Describe how your customers will interact with your business. Will you have personal or automated channels of communication available? Chart out the end-to-end customer experience journey and how you intend on building customer relationships.
Customer segments and channels
Specify your target audience, what requirements of theirs you cater to, how you reach out to them, and, most importantly, the steps you are taking to generate a customer experience that will result in long-term loyalty.
Cost structure
Define your key costs and variable costs, and how they represent a competitive advantage if applicable. A lean startup business plan (versus a lean business plan for an existing company), needs to also include key startup costs you anticipate in launching your company.
Revenue streams
Describe how your business generates money. What are your revenue streams or sources, for example, selling advertising space on your app or publication, membership fees, direct sales, etc? List all your revenue sources in this section, starting with the source that delivers the largest revenue.
Download Your Free Lean Business Plan Template
Lean Business Planning Process
To create your lean business plan, follow these 4 steps:
Create the Plan
Your lean business plan will start with you, your business idea, and one sheet of paper. Yes, one sheet is all you will need.
Business Strategy
You will first begin by explaining your business strategy. This is simply a summary of what you are planning to do, who your customers are, and who your competitors are.
Identify the problem you are trying to solve along with your solution and potential alternative solutions. Then, describe your target customers. Focus on defining and describing the audience you expect to serve, who they are, where they live, etc. Lastly, explain who your competitors are. Describe what they’re doing and how they’re doing it.
Easy enough, that is all you need for your plan. With lean business planning, you simply create a business strategy that focuses on the essence and function of your business: what you’re doing and who it’s for.
Course of Action
The next piece of your lean business plan is laying out an outline of your course of action. This section will illustrate how you’re going to make your strategy happen. Here, you will focus on sales, marketing, your team members, and any potential key partners or future relationships in the business world.
Sales Strategy
It is important to first begin creating your course of action by establishing just what your sales strategy is. Will you be selling in a physical store or online? Or both? Consider whether or not your product will be sold in stores owned by other companies, and who these companies would be.
Marketing Strategy
Next up is creating your marketing strategy. Think about how you will effectively and attractively reach your potential customers. Here, consider the following:
- Target market
- Online presence
- Advertising
- Public relations
- Special promotions
Team Members
The success of your course of action will be dependent on the team members who execute it. If you need to build a team, think about who the key people are that you will need to hire. What are their qualifications and characteristics? If you already have an existing business, highlight the key members that help run your company and accomplish strategy and success.
Partners and Business Resources
Begin to think of the other businesses that you might want to work with. Most likely there are other companies that you will have to work with to make your strategy work. Brainstorm all key resources, business partners, distributors, and key suppliers that you will need to have relationships with.
After constructing your Course of Action, it’s time to create your schedule. Since lean business planning is centered around efficiency, designing an organized schedule is key.
For startups:
If you’re starting a new business, you should begin with getting to know your customers. For you to grow a viable business, you must understand your customers’ views, wants, and needs. Your goal here will be to ensure that you’ve developed a strategic, organized strategy. A startup’s schedule will often include sending out surveys, interviewing customers, and researching locations.
For established businesses:
For most businesses that have been around, your schedule should be focused on achieving the business goals you have identified. Your schedule should have specific actions with names, dates, and even times. The schedule you create should hold your business and its employees accountable for their work and progress.
The final part of scheduling is to make time to regularly review your Lean Business Plan. As your business progresses, so will your Lean Business Plan. Setting a regular review time is critical to get your business moving in the right direction and your team members on board.
Forecast and Budget
Even if you have the best business idea in the world, if the numbers aren’t there, it won’t work out. The final section of your Lean Business Plan should depict a business model that forecasts and budgets for the future.
Here, all you have to do is create basic bottom-up sales forecasts and a basic budget for expenses. Do not try to sugarcoat here, these numbers should be as practical as possible. With this, you will be able to identify just what will and won’t work for your business.
By taking on this pragmatic sense, you may begin to feel like your business will not be able to succeed unless you are flooding with customers or getting daily news coverage. You may need to alter your business model here and adjust your pricing and expenses to ensure that you can turn a profit. Also, keep in mind any funding options for large-scale marketing and PR campaigns. Keep a realistic view, but also be sure to acknowledge offers that may be available to help you out.
Putting The Lean Business Plan Into Action
After you have completed your lean business plan, it’s time to put it into action. Your main goal here should be to get a deeper understanding of your customers. Is your product solving their problem? Are they willing to pay for it? Do they want something else?
Reaching out to your customers early on will help you get a grasp on their wants and needs to make the necessary alterations to your Lean Business Plan for ultimate success. It will also provide you with some insight as to what products you may want to produce in the future.

As earlier mentioned, your lean plan should be reviewed regularly to discern just what is working and what isn’t. Compare your results with your lean plan. Are sales growing according to plan? Does the plan need to be changed?
For startups who have little to no metrics to track, review your customer interviews, surveys, or any other information that you have gathered about the industry. Here, you can begin to continually refine your plan and strategy if necessary.
If you are an established business, review your recent results with those from the past. Take note of your key metrics as well as foot traffic in stores, website visits, and any other critical units of measure for your business success.
After analyzing your results, it’s time to revise your plan. Remember that your Lean Business Plan is a process rather than a finalized document, and it is made for continuous improvements. Don’t be afraid to make any necessary changes to aid in your business’s success.
Lean business planning might just be the key to your company’s ultimate success. This simple method of business planning has helped many startups and existing businesses advance and flourish such as Google, Facebook, YouTube, and Amazon. By focusing on reviewing, revising, and business management, lean planning allows you to test out different strategies to find the best one to create a successful business.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
What is a lean business plan?
A lean business plan is a compact, single-page document typically for internal use. Lean planning is a short-term business plan strategy for making small changes and measuring the results to improve the efficiency of the business. This compares to the formal business plan which is typically very detailed, includes 10 key components , and can be up to 15-25 pages in length.
What is the purpose of a lean business plan?
The lean business plan is primarily for internal use, so it doesn’t have to be a fancy document. The purpose of this plan is for you to document the changes you’ve made to your business so that you can analyze their effectiveness in improving business operations, marketing, and/or sales over a short period.
How long is a lean business plan?
The lean business plan is typically a one-page document to describe your business strategy including your goals, targeted audience, your business model, and how your sales and marketing strategies work to support your business goals.
How do you create a lean business plan?
Refer to our article on ‘ Lean Business Plan: How-To Guide & Template ’ for the 4 steps in creating a lean business plan or a lean startup business plan template . You can also download our free lean plan template to help you get started.

Fundamentals of Lean Planning Explained

Noah Parsons
11 min. read
Updated April 15, 2024

Let’s face facts: Writing a traditional business plan is a hassle.
- A traditional business plan takes too long to write.
- Most people won’t even read it from cover-to-cover.
- It’s often outdated by the time you finish writing it.
- It doesn’t lend itself to frequent and easy updating—and that’s the core of the problem.
Historically, entrepreneurs have taken months to craft detailed plans without even gathering feedback from potential customers. They’ve viewed business planning as a single hurdle to get their business up and running or a thick wad of paper to shove across a banker’s desk in order to get the funding they need.
These business plans end up as just a collection of guesses and assumptions, instead of a proven roadmap for growth.
But planning is still critical, even if the business plan might be broken. Studies have shown that businesses that set goals and track their progress grow 30 percent faster than those who “just wing it.” Furthermore, even established businesses grow faster when they have a plan .
So what if I told you there was a better way to do business planning? One that lets you adjust and refine your plan as you gather more information about your business and customers.
A method known as Lean Planning.
- Welcome to the Lean Planning method
Lean Planning is a 4-step process that helps you discover a business model that works and manage your company successfully.
Here’s the Lean Planning process:
- Create a one-page plan
- Test the plan
- Review your results
- Revise your plan
These 4-steps replace the traditionally lengthy business plan with a 20-minute planning process. This ensures that you are taking small steps, reviewing your results, and creating incremental improvements—all while reducing your risk of failure.
It’s also simpler and faster than writing a traditional business plan. And, possibly, the greatest benefit is that this method can benefit both startups and established businesses.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
If you’re a startup
Lean Planning helps you quickly figure out if your idea is any good and what you need to change to build a viable business.
If you’re an established business
Lean Planning works even if you’re already up and running. It helps you continually refine and tweak your strategy while measuring your progress toward your goals. After all, planning is about making better management decisions, not about producing a thick document that sits in a drawer.
Read on to learn how to make the lean model work by creating your own one-page business plan .
- Step 1: Create a one-page plan
The Lean Planning methodology starts with a one-page plan you can create in 20 minutes .
That’s right—one page. Lean Planning is a simple methodology and your one-page plan should be simple, too. You can download a lean planning template and fill it in as you follow the steps below.
What to include in your one-page plan
- Strategy: What you’re going to do
- Tactics: How you’re going to do it
- Business model: How you’re going to make money
- Schedule: Who is doing what and when
Let’s dive into each section.
Your business strategy
Your business strategy is simply an overview of what you want to do and who your customers and competitors are. Start by identifying the problem you are solving for people and follow up by explaining your solution to this problem.
The problem you’re solving
Businesses exist to solve problems for customers. Their products and services fill a need or satiate a desire. If all you have is a solution that is in search of a problem, you’re going to have a hard time building a successful business. So, start with the other side of the equation and focus on how you can help your customers solve a problem.
Start small with just one or two sentences or a few bullet points to identify the problem you are solving. Do the same thing to describe your solution.
Your ideal customer
Now, quickly describe your target market. Who is your ideal customer? If you know how many potential customers are out there, great. If you’re in the early stages of fleshing out your business idea, don’t worry too much about detailed market research . Instead, focus on defining your ideal customer —who are they, and what are their key attributes?
Your competition
Finally, create a shortlist of your competition . How do your potential customers solve their problems today?
That’s it. A business strategy doesn’t have to be complicated with Lean Planning. It’s just a few bullets points that describe the essence of your business: what you’re doing and who you’re doing it for.
The next section of your one-page plan is a short outline of your business tactics. This is just an outline of how you will make your strategy happen. You’ll be thinking about sales, marketing, the team you might need , and any partners or outside resources you’ll need to leverage.
Your sales strategy
Start by thinking through your sales strategy. Are you selling online or building a physical store? Maybe both? Or, perhaps your product will be sold in stores owned by other companies.
Your marketing strategy
Next comes your marketing strategy. How are you going to reach your customers? How do they find out that you exist and that you solve their problem?
If you need to build a team to grow your business, who are the key people that you’ll need to hire? If you’re an existing business, who are the critical employees that run the company and execute your strategy?
Key partners and resources
Finally, think about other businesses that you might need to work with to make your strategy happen. Are their key suppliers or distributors that you’ll need to have relationships with?
Remember, this is on a single page, so each of these sections should just be three to five bullet points each.
Now it’s time to build a schedule. Lean Planning is all about getting things done, so you need a timeline to follow.
Your next step is to get out from behind your desk and go talk to your potential customers (I’ll go into more detail on this in a moment). Your goal will be to verify that you’ve defined a solid strategy . To that end, a startup’s schedule should include things like conducting customer interviews, sending out surveys, researching physical locations, interviewing potential suppliers, and so on.
Your schedule will probably be focused on specific business milestones that are related to executing your strategy and implementing your tactics.
It’s critical to have accountability here. Your schedule should have dates and people responsible for completing each task.
Finally, make sure to include a time to regularly review your plan. You’ll want to review and revise this plan frequently, so having a regular review point is critical. I recommend a monthly review cycle, but reviewing more frequently is fine, too.
Business model
Even if you have a problem that’s worth solving, a solid solution to the problem, and a target market that needs your solution, you don’t have a business unless the numbers work out. You need a business model that works. The last component of your one-page plan is a basic forecast and budget to ensure that a great idea can actually lead to a great business.
Yes, forecasting and budgeting do mean looking into the future, and no one knows the future (at least I don’t!). But, it doesn’t have to be as difficult as it sounds.
Putting together some basic, bottom-up sales forecasts and a basic budget for expenses will quickly tell you if you have a business model that works—one that can create a viable business that will pay the bills.
At this stage, it’s important not to paint an incredibly rosy picture of your financial prospects. Instead, the sales forecasts should be as realistic as possible. Assume that not nearly as many people as you think will show up in your store. Assume that your website won’t get mainstream press coverage.
With this “realistic” forecast, do you still have a viable business? Can you turn a profit ? If you can only be successful with incredibly high volumes of customers, you may need to take a second look at your pricing, expenses, and other aspects of your business model. Or, make sure that you get the kind of funding that’s needed for large marketing and PR campaigns.
You can get started on your one-page plan right away by downloading our free template . You should be able to complete an initial draft in under an hour—that’s much faster than writing a traditional business plan.
- Step 2: Test the plan
Now that you have your one-page plan in hand, you’re ready to start putting the plan into action to see if your ideas will work.
Depending on your business stage, you’ll do this in different ways. If you’re a startup with an unproven idea or an existing business that’s considering a new strategic direction—your next step is to validate them.
Your one-page plan is just a set of assumptions about a business. Ask yourself:
- Do the target customers actually have the problem that you think they have?
- Does the solution you’re proposing actually solve their problem?
- Do your target customers want to pay for your solution? How much?
Reducing risk is your goal in the early stages of starting a business
Starting a business is full of risks . There are just so many unknowns, and it’s incredibly risky to just build your business based on a set of assumptions about your target market, their problems, and how they’ll react to your solution.
Your plan is a really just a set of educated guesses that need to be answered and then revised on a continuous basis until most unknowns are removed. That’s how you reduce risk.
So, you need to take the very simple, but very challenging step of actually talking to your potential customers .
Look at your first version of your plan as a set of assumptions that need to be proven true or false and then go back and revise your assumptions as you go. Refining your plan so that it’s a collection of facts instead of guesses can be the difference between a successful business and a failure.
If your business is up and running, focus on implementation
For more mature businesses that already know a lot about their target customers, the goal of the plan is to help guide implementation. In this situation, use a one-page plan to get everyone on the same page, set goals, and manage the business.
- Step 3: Review your results
Both Silicon Valley startups and Main Street small businesses need to know how they are doing. Which means Are they growing according to plan? Why or why not? If not, what changes need to be made? Should the plan change?
For new startups
If you’re just getting started and don’t have many (or any) metrics to track yet, you should be reviewing the results of your customer interviews and any other information that you’ve gathered that would change your strategy. Perhaps you’ll be refining your solution or even tweaking the definition of the problem you are solving. Perhaps you’ll refine your marketing and sales strategy.
For established businesses
Beyond tracking key financial metrics such as cash , sales, expenses, accounts receivable, and accounts payable, businesses must track the other key metrics that are critical to their success. These other key metrics might be website visits, foot traffic in the store, tables turned in a restaurant or any other core number that drives business success.
Reviewing your results regularly is key to better management and success. These metrics should be reviewed at least monthly in a regular plan review meeting with key business partners and employees. This is when you refine your plan and your pitch if necessary and track your ongoing action plan.
- Step 4: Revise your plan
Lean Planning is a process, not just a document. It’s is all about continuous improvement. You’re quickly defining a strategy, experimenting to see if that strategy works, reviewing the results, and revising the plan before you start again.
Lean Planning is never finished. It’s simply a process for running your business better, more efficiently, and setting you and your team up for success.
What if you need a more detailed business plan?
There may be a time when you need a more detailed business plan. There’s nothing wrong with that. Some people might want to read it, you may need to submit a full plan for funding and you might even want to document your strategy in more detail.
Your detailed business plan will be born from your one-page plan. The ideas will transfer from bulleted lists to sentences and paragraphs. You’ll add more detail to your sales and marketing strategy, your pricing strategy, and perhaps your manufacturing plans and distribution strategy.
For a step-by-step guide to creating a detailed business plan, check out our guide .
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

8 Min. Read
What Type of Business Plan Do You Need?

5 Min. Read
How to Write a Growth-Oriented Business Plan

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan

14 Min. Read
How to Write a Five-Year Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- > Benefits, Tools, & Examples of the Lean Business Model
Benefits, Tools, & Examples of the Lean Business Model
Posted by JJ Puentes
Jun 2, 2022 10:36:00 AM

The Lean approach is sometimes referred to as operational excellence or continuous improvement. No matter what you call it, the model is focused on identifying the areas that are hindering business growth and addressing them effectively. This requires demonstrating respect for employees and fully understanding the customer journey. Achieving these objectives brings significant advantages to both the organization and its customers.
What are the benefits of building a Lean business?
Augmented leadership skills.
From C-level leaders to directors, middle managers, and supervisors, the Lean business model encourages a more proactive and thoughtful approach to management. As a result, leaders become more adept at finding and minimizing non-beneficial practices.
When the Lean model takes hold, all managers begin to identify how their business area could implement improvements to achieve better efficiency, higher quality, and maximum profitability. Clear goals add clarity to every management role and help individuals develop their skills in building a more united and effective team.
Engaged Employees
The Lean business model emphasizes each employee's value to the organization. It demands their attention and encourages increased participation in positive change. Employees who feel connected to the organization's purpose and their team's immediate goals are more apt to expend effort to achieve the organization's strategic goals and short-term targets. Employee engagement is enhanced when a broad cross-section of team members can participate in business planning.
Accelerated Growth
Because Lean businesses expend effort only on essential activities, companies use the model function more holistically. As a result, lean gives a more complete insight into the organization's operational effectiveness, allowing people to better optimize what is working and eliminate what is not. As a result, lean organizations continuously grow through improved leadership skills, increased employee engagement, individual efficiency, and enhanced customer value.
Customer Satisfaction
Lean leaders put customers first by understanding their point of view and what matters to them. The customer journey becomes the center of everything the business does. Nothing is more valuable than customer feedback and opinions. Lean businesses don't just gather this information; they act on it and frequently iterate to meet customer needs.
hbspt.cta._relativeUrls=true;hbspt.cta.load(326641, 'eb5ac7b8-b040-48b7-810e-1589561ffff9', {"useNewLoader":"true","region":"na1"});
Plan, do, study, adjust (pdsa).
While there are many tools and techniques that help leaders build a Lean business, one of the most fundamental is the PDSA improvement cycle. PDSA offers a structured and consistent method of problem-solving and implementing positive change. It can be repeated as often as needed to move each process or activity closer to perfection.
During the planning phase of an improvement project, the team asks the following questions:
- What are our goals for this project?
- What is the current situation?
- How will we define and measure improvement?
- Who should participate in this project?
- What are the key dates and milestones?
After these questions are answered, the team can agree on what change should be implemented to reach the goals.
This is the experimentation phase in which the proposed improvements are implemented. It is essential not to implement too many changes at once so that you can be clear about what is impacting the outcomes. It is OK to be patient because the cycle can be started again very quickly if additional changes are needed. Keep in mind that, like with any scientific experiment, careful observation and data collection are as crucial as the implementation itself.
This phase compares the actual results with what the team expected would happen. While it is often overlooked in non-Lean organizations, it is essential for lasting success. Observations are helpful, but objective data should be the deciding factor whenever possible.
If the study phase indicates that a positive change has resulted from the experiment, the new process becomes the standard. The Standard Work documentation and any supporting materials, instructions, or signs are adjusted. The next improvement cycle will be performed against this new best practice.
Supporting Tools and Techniques
While PDSA forms the basis for change in Lean businesses, there are several tools and techniques that teams use to support it, including:
Control Charts
Control charts are graphs used to visualize how a process performs over time. Data points are charted in time order in a graph with a center line for the average, an upper control limit, and a lower control limit. Visualizing the information this way helps leaders avoid reacting to every up and down movement. They also help prevent the common mistake of looking only at the average results instead of process variation.
Kanban Boards
Kanban boards are another visualization technique for optimizing the flow of work-in-progress or raw materials. They help achieve a pull system in which work-in-progress, raw materials, or parts are only moved within the process when they are needed. Toyota developed the approach using physical inventory cards, but today, Kanban is managed digitally by organizations of all types.
A3 reports are a method for structured problem-solving. They get their name from the size of paper used in the days before Lean business software. An A3 report captures the information produced in a PDSA cycle in organizations that use them. A3 reports provide a standard planning, problem-solving, innovation, and knowledge transfer process.
Examples of Lean Businesses
Any size or type of business can become a Lean business by applying the principles of respect for people, continuous improvement, and waste reduction. Therefore, you'll find Lean being practiced in almost every sector.
Lean in healthcare aims to look carefully at every step in a process, such as an office appointment, and identify which actions add value, which do not, and what can be improved. As a result, the people closest to the patient, physicians, nurses, medical assistants, and front office staff, are in the driver's seat to create better patient experiences and outcomes.
Targets for improvement in Lean healthcare organizations are waiting, unnecessary tests, missed diagnosis, overly complex paperwork, and unused medications or supplies.
Construction
The popularity of Lean in the construction business is increasing. The method is well suited to meet the needs of an industry in which budgets, safety, and timelines are all critical. In addition, the Lean approach to construction unifies all stakeholders, including the owner, engineers, architect, general contractor, subcontractors, and suppliers.
Common causes of waste in construction include unnecessary movement of equipment, inspection failures, waiting, and underutilized talent.
Software Development
Businesses that build software solutions have turned to Lean to help better meet customer needs and accelerate time to market. The PDSA approach fits nicely with the rapid development cycles of most software development organizations. Kanban boards are an excellent fit for controlling work in progress as a software project moves from requirements development through coding and QA.
Targets for waste reduction in software include bugs, underutilized product features, unclear or unnecessary documentation, and ineffective resource utilization.
If there is one group of folks who are constantly asked to do more with less, it's teachers. Budgets are tight, and expectations for student achievement are high. Lean helps educators focus on what activities will benefit students and minimize all of the other required but non-value-adding activities. Lean isn't only applicable in the classroom; it can help optimize related functions such as food service, office administration, transportation, and facility maintenance.
Educational organizations find waste in outdated or unused books or other materials, disorganized classrooms or other workspaces, too many or too few consumable supplies, and underutilized creativity and passion.

These are just some types of organizations that have discovered the benefits of the Lean way of thinking. If you'd like to learn more about how it might help yours, our team can share how our customers have transformed theirs with Lean.
Topics: Lean , Improvement Process , Improvement Methodology
Add a Comment
Subscribe via email, recent posts.

- Our Customers
Why KaiNexus
- Collaboration
- Standardization
- Customer Success Manager
- Lean Strategy
- Solutions Engineering
- Customer Marketing
- Configuration
- Continuous Enhancements
- Employee Driven
- Leader Driven
- Strategy Development
- Process Driven
- Daily Huddles
- Idea Generation
- Standard Work
- Visual Management
- Advanced ROI
- Notifications
- Universal Badges
- Case Studies
- Education Videos
Copyright © 2024 Privacy Policy
A Guide to Creating a Lean Business Plan (2022)
Don’t have the time to develop a formal business plan for your startup? Here’s how to create a lean business plan to put things into motion.

Vivienne Chen
Vivienne is a Product Marketer at Bubble. She is a storyteller and is passionate about meaningful ways technology can help foster social solidarity.
More posts by Vivienne Chen.
The dramatic increase of small businesses in the United States during the last five years prompted the business community to rekindle the concept of Lean Business Plans. While having all these start-ups is laudable, 45% of them fail after five years.
The key to having a successful business, small or large, is having the right idea at the right time and crafting a viable business plan to fill that market niche . However, many entrepreneurs don't write business plans because they recoil at writing a voluminous traditional or formal business plan that spans 30 pages and has multi-year income statements and layers of operational complexity.
A lean business plan is the perfect solution for that problem.
Traditional Business Plan vs. Lean Business Plan
Traditional business plans tend to be written for start-ups that have multi-million-dollar revenue objectives and require large amounts of seed funding for a large staff and large office spaces that keep the enterprise running until it turns a profit. Investors want to know how their money will get spent, the potential market share, and the founders' experience. Hence, the 30-page masterwork loaded with numbers, graphs, and charts takes three months to create.
A lean business plan, however, is more effective for a small- to medium-sized business (SMB) because it concentrates on the key elements of the company. You’ll give a traditional plan a big haircut by writing a lean plan that outlines your business idea, what market problem you’re solving, how you’ll solve it, how much money you need, and when you’ll break even.
Why Lean Business Plan Methodology Is Gaining in Popularity
The Small Business Association (SBA) encourages entrepreneurs to develop a lean business plan first , even when contemplating writing a traditional plan later. This approach helps lean startups organize their concepts without getting bogged down with unwieldy traditional plans that often discourage writing a plan in the first place.
Start-ups commonly fail for six reasons . However, entrepreneurs today have access to a greater variety of resources than ever. Web-based apps, digital libraries, government agencies like the SBA, and mobile solutions provide a robust ecosystem for new companies.
These invaluable support systems often mitigate the need to write traditional plans for SMB start-ups because vast data stores are but a click away that can help entrepreneurs and potential investors validate any business model.
Benefits of a Lean Business Plan
Lean Business Plans continue to grow in popularity for these important reasons:
- Accessibility: Lean plans are relatively easy to conceive, formulate, and understand. Anyone with basic business sense can discern the unique value proposition (UVP) and unique selling proposition (USP) without being a former CEO.
- Speed: A lean business plan only takes two to four days to write and requires only three to five pages to complete. Compared to a traditional plan, this lean approach moves at light speed.
- Flexibility: A lean plan allows you to organize the business concept and summarize the UVP and USP in short, easy-to-digest thoughts, which can be modified when new information or investor inputs are presented. And it can be upgraded to a traditional plan later if needed.
The Major Components of a Lean Business Plan
Since you’re writing a lean business plan, you’ll be pleased to learn that such plans still have all the key elements of a traditional plan (again, making it a great foundation to build on later as you grow your business).
- Business Model : There’s no way around this essential requirement. Everyone, especially you, must understand the business model you’re starting to make a profit (e.g., retail, manufacturing, fee-for-service, etc.).
- Strategy: This describes how your company will solve a problem or addresses a market need and how it differs from competitors (aka the differentiator).
- Tactics: Outlines the operational steps needed to manage marketing, sales, and business objectives.
- Schedule: Explains when your business starts operations, where it’s located, when it expects to break even, and when it’s profitable.
- Income/Expense Statement: Summarizes revenues, sales, and expense projections for one year.
What to Include in a Lean Business Plan
The value of “lean” means describing these elements in a few short and clear sentences; write only one paragraph per subject.
- Overview: Describes your company’s mission
- Problem: Shows what problem you’ll solve or market need
- Solution: Outlines how you solve the problem
- Target Market: Defines your customers and the market
- Competition: Identifies competitors and what differentiates your company
- Marketing: Explains how you’ll reach customers
- Sales Channels/POS : Outlines where you’ll meet customer needs
- Revenue: Shows how you’ll make money
- Expenses: Summarizes start-up costs and ongoing expenses
- Milestones/Growth: Projects timelines for attaining business goals
- Partners/Resources: Indicates your business connections and other professional assets
- Talent/Roles: Identifies the team, relevant experience, and type of expertise you still need
How to Write a Lean Business Plan
Since you now understand the requisite elements of a good lean business plan, these links provide excellent resources and apps to help you write a lean business plan document.
- Hoshin Planning Process : Outlines a step-by-step thought process needed to develop a lean business plan.
- SBA Guide to Lean Business Plans : Shows how to write a lean business plan.
- What It Costs to Start a Business in 2022 : The Bubble community offers excellent tips on what it costs to start a business.
- Emerald Insight : Provides insights on what kind of business plan to use.
- Startly : A one-stop service that provides enhanced time and expense solutions.
Important Next Steps
- Add an MVP Summary. A start-up that plans to sell a new version of an existing product should consider adding a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) summary. The MVP protocol is an important testing and engineering process that ensures a prototype gets the proper development and testing prior to release.
The MVP methodology plays well with the lean business philosophy because it enhances the development of existing products rather than starting from square one.
- Get Funding. Once you have a solid lean business plan, you'll be in an excellent position to look for funding. The Bubble community can show you how to get seed funding .
- Getting Started. There is no time like the present to start building your dream. This is your Call to Action (CTA): wake up, get up, and start-up. Today.
How a No-Code Solution Like Bubble Can Help
Bubble’s numerous no-code platform solutions are invaluable tools that help entrepreneurs start new businesses. In addition to saving considerable time and money during the development phase, the Bubble community offers a wealth of know-how and support tools that guide entrepreneurs during the daunting start-up process.
These support structures complement the lean business plan approach because Bubble eliminates many infrastructure costs and operational hurdles a new company must overcome.
About Bubble
Bubble is a leader in the no-code movement. Bubble offers a powerful point-and-click web editor and cloud hosting platform that allows users to build fully customizable web applications and workflows, ranging from simple prototypes to complex marketplaces, SaaS products, and more.
Millions of users are building and launching businesses on Bubble — many have gone on to participate in top accelerator programs, such as Y Combinator, and even raised $365M in venture funding. Bubble is more than just a product. We are a strong community of builders and entrepreneurs who are united by the belief that everyone should be able to create technology.
Start building with a free account

Build the next big thing with Bubble
- How to build
- Responsive design
- Version control
- Feature index
- Integrations
- Marketplace
- Partnerships
- Brand guidelines
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to content

- Try Tactyqal

The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Lean Startup Business Plan
Starting a business can be both thrilling and terrifying. On one hand, you have this brilliant idea and can’t wait to bring it into the world. But there’s also the nagging fear that your amazing concept might fall flat or fail to gain traction.
So how do you make sure your startup succeeds? The answer is charting out a solid business plan.
I know, I know. Just hearing the phrase “business plan” brings back bad memories of dry, long-winded documents from business school. But for startups, there’s a better way to plan out your venture – something called the lean startup business plan.
The lean startup approach focuses on streamlining the business planning process so you can start testing your idea faster, without getting bogged down with lengthy sections and financial projections you can’t possibly predict accurately at such an early stage.
In this beginner’s guide, I’ll walk you through exactly how to create a lean startup business plan template that helps you quickly validate your business idea with real-life customers.
What is a Lean Startup Business Plan?
First things first – let’s define what exactly the lean methodology means when applied to an entrepreneur’s business plan.
Put simply, a lean startup business plan is a streamlined, no-fluff version of a traditional business plan. It’s designed for speed and adaptability rather than comprehensiveness.
The lean startup movement first became popular around 2008. It emphasizes testing a product or service idea quickly, using a minimum viable product (MVP), and getting real user feedback before committing to long development and release cycles.
The key principles of lean startup are:
- Rapid build-test-learn loops
- Scientific testing with real customers from day one
- Iterating based on validated learning
Most new companies that take the lean approach never reach an official launch stage. Instead, they continuously test with and adapt to real customers – refining their MVP and pivoting directions based on evidence of what does or doesn’t get market traction.
So how does that tie in with writing a business plan?
Well, the traditional business plan model doesn’t fit the lean paradigm shift.
Lengthy, complex, intricate business plans take too much time to write. Attempting to project multiple years of expenses, sales, hiring, growth rates etc…..it’s all just guesswork when you haven’t started selling anything yet.
The lean startup business plan tosses unnecessary details out the window and instead focuses only on critical hypotheses and assumptions that must be tested as quickly as possible.
Investors like this approach because it shows you:
- Know what assumptions make or break your business
- Can test them quickly at low cost
- Will adapt based on real data
So if you’re an early stage startup looking for funding or entering an accelerator program like Y Combinator, a lean business plan is likely your best bet to showcase your entrepreneurial abilities.
Now the big question….
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup template pares down the typical business plan format to just the essential elements early-stage investors care about:
- Problem – What pain points will your product address? Why are those needs not being met?
- Solution – How will your product alleviate that pain better than alternatives? Why will customers buy from you over other options?
- Target market — Who has that specific problem and will buy your solution? ( Note: Be specific! “Everyone” is never the right answer.)
- Competition — Who else is tackling that customer problem? How is your solution fundamentally better or different?
- Key features – What’s the minimum feature set to address target customers’ needs on day one and provide value?
- Marketing & sales – What tactics will you use to reach early adopters? ( Note: For most startups, digital sales & marketing channels rule supreme. )
- Operations – Outline your core business processes. Don’t go into granular detail, just highlight how you’ll deliver value to customers.
- Milestones – What big assumptions will you test? Include timelines + costs to conduct experiments so you can demonstrate a logical thought process.
- Financials – Optional Breakdown high-level estimates only if useful. For the lean startup plan, elaborate projections are unnecessary and speculative. Focus everything on testing key assumptions.
You may have noticed one conspicuously absent item – the Executive Summary. We’re skipping it because unlike traditional business plans sent to various stakeholders, your lean startup plan has just one audience – startup investors.
And remember, the lean methodology is all about using real-life data instead of guesses and best-case scenarios. So even if some assumptions in your original lean business plan don’t pan out, that’s actually great news! It gives you hard evidence to adapt intelligently while developing your MVP.
Now that you know what the lean startup template includes at a high-level, let’s go through each of the core sections in more detail.
First and foremost, you need to spell out exactly what customer problem your startup aims to solve. (And yes, it needs to be an actual must-solve problem, not a nice-to-have).
Start by broadly describing the pain points your target customers face. Get tactical by including stats, data or quotes that showcase why this issue is so urgent for them.
Then explain how the problem ties into a larger trend in your target industry. Paint a big picture view of why common solutions up until now have failed to address this pain sufficiently.
Essentially, convincingly convey that there’s a pressing customer need ready for innovation.
You need to display beyond any doubt that you:
- Deeply understand your target customers’ challenges
- Can explain why those problems exist in the first place
- Will provide a compelling solution tailored to fix them
This sets the stage for why launching a startup to address this issue makes so much sense.
2. Solution
Now that you’ve framed the problem, shift gears into explaining your startup’s solution. Start by providing an overview of your product and how it alleviates target customer pains better than alternatives already on the market.
Then embellish with details on:
Product Benefits
How specifically will your product make customers’ lives easier? Don’t just describe product features or functionality. Speak directly to how you’ll empower them to achieve something that’s currently difficult, inconvenient or even impossible for them to accomplish on their own.
Competitive Advantage
What specifically sets your solution apart from potential competitor offerings and substitutes? Is it higher quality, better convenience, lower cost, less hassle, faster performance – or perhaps an innovative model that’s never been seen before in the market?
Highlight your startup’s special sauce that no one else can easily replicate. Explain barriers to entry that will hinder copycats.
Customer Incentive
Why will target users’ purchase from your brand over chasing other options? It usually comes down to believing you can deliver significantly MORE value than alternatives or solve an urgent pain nothing else currently satisfies. Make your case for why you fit one or both scenarios.
Scalability
Particularly if you are pursuing venture capital investors, explain how your business can rapidly scale up to tap a very large global market with your solution. Outline a blueprint for how you realistically grow from thousands to millions of customers in the coming years.
Remember, don’t drown potential investors in intricate details about every single product feature and technical specification. They care most about how your solution nails the value proposition trifecta:
- Targets an urgent customer problem
- Provides 10x+ better value over existing options
- Can scale to a very large market long term
If you can compellingly check all three boxes, you’ll spark investor interest even with limited hard evidence at such an early phase.
Of course, that doesn’t mean you won’t eventually need to back up your claims. However, the lean startup plan is more about framing hypotheses than definitive proof. We’ll cover how to demonstrate enough evidence to warrant launching experiments soon.
For now, stick to crafting an intriguing startup story that sets you up to start testing fundamental assumptions very soon after funding. There will be plenty of time to figure out minor product details once you validate solving a pressing problem for real paying customers.
3. Target Market
Up until now, I’ve used the term “target customer” quite loosely. But it’s time to get very specific on who those real-world people actually are for your startup.
Venture capital investors want to quantify the population size and traits of target buyer personas in precise detail. So you need to describe exact psychographic and demographic qualities of your beachhead market – the subset of overall customers you tackle first to gain a foothold quickly.
Start by explaining your total addressable market (TAM) – the entire population who could plausibly need and want your solution for the core problem it tackles. Depending on the ubiquity of that issue for consumers and/or businesses, the TAM could be very narrow or encompass hundreds of millions globally.
Then segment down from that full market to identify your specific beachhead target customer population. The ideal beachhead often has these characteristics:
- Suffers from the problem much more painfully than casual groups
- Has already tried existing solutions without sufficient success
- Has disposable income to purchase a premium solution for relief
- Is easy to access and serve operationally in early phases
- Isn’t incredibly price sensitive
- Can provide extensive feedback on the product
- Has influencer qualities to attract wider market segments
Nail down quantifiable population size estimates for this core beachhead subset. Combine publicly accessible data from existing market research reports with reasonable inferences or assumptions from adjacent industries.
But resist the founder’s tendency towards magical thinking – “If we nailed even just 1% of the market…!” Generic hypotheticals don’t sway experienced investors focused on tangible traction signals.
Paint a detailed demographic picture of exactly who fits the mold of a hot prospect customer for you in the beginning.
For B2C startups , call out relevant attributes like:
- Marital/family status
- Home ownership
For B2B startups , highlight qualities like:
- Industry vertical
- Company size
- Title seniority
- Annual revenue
- Tech adoption habits
Then outline statistical commonalities across your core beachhead buyers – what key similarities unite this subgroup vs. the entire population facing the problem?
Finally, convey TAM expansion opportunities once you solidify solutions tailored for that first niche. But defer outlining detailed ways to extend your reach right now since nailing product/market fit with just one segment is the critical prerequisite to win over adjacent groups.
Position your solution as optimized for an underserved niche ripe for disruption based on competitors failing to deliver adequate solutions. Then segue into how your distribution plan concentrated on this “low-hanging fruit” beachhead will purposefully evolve later to expand TAM reach long term.
4. Competition
What the competition section lacks by traditional business plan standards in length, it more than makes up for in strategic rigor.
The core question competitive analysis must answer:
Why are current solutions in the market failing to adequately alleviate your target customers’ pain?
Start by inventorying existing competitor products/services currently used by prospects experiencing this problem. List out the main options your target persona has for solving their struggles today, even if those solutions don’t perfectly fix the issue or fully satisfy them.
Then contrast point-by-point specifics on why your solution beats competitors, especially on the metrics most important to your target niche. Show how you will “disrupt the disruptors” because even pioneering products have limitations needing innovation.
Criteria to call out where you claim competitive advantage:
- Convenience
- Scale potential
- Business model innovation
Back up any bold claims of superiority with limited initial evidence beyond conjecture — data from beta user testing prototype versions, customer quotes from initial beachhead outreach, or precedents from analogs in adjacent markets.
Take care to focus specifically on competitors targeting the same early adopter beachhead market segment though. Details contrasting solutions for other peripherical segments are unnecessary right now.
Round out competitor analysis by itemizing macro trends almost certain to diminish prospects for legacy products over the next 5-10 years. These should make the rationale behind your startup now abundantly clear even to skeptics.
5. Key Features
Thus far you’ve made a case for:
- A pressing customer problem inadequately solved
- Your startup’s superior solution
- Quantified target beachhead market
Now it’s time to shift to specifics on the crucial product and feature details enabling your entire value proposition.
Remember – only include what’s absolutely necessary for launch based on addressing revealed target customer needs!
Err on the side of a minimal feature set early on. Describe additional functionality prospects request once you start serving initial customers.
Outline the critical set of features required to deploy a minimum viable product (MVP) with just enough core attributes to satisfy early adopters on day one.
Organize by:
Must-Have Features
What feature absolute “must-haves” must be ready for early adopters to provide enough value converting from current solutions?
Nice-To-Have Features
What would enhance perceived value but aren’t imperative to activate paying users? Defer these to later product milestones.
Future Features
Briefly mention functionality on the long-term roadmap to showcase platform potential.
Think of must-have features as the “walking version” of your product – unscalable manual processes providing baseline value perfect for testing with friendly early adopters.
Then nice-to-haves represent the “jogging version” – automating more of the workflow via technology – while future functionality serves as the “running version” enhanced for steep vertical scaling.
In conjunction with digital tools, brainstorm creative ways to manually deliver MVP experiences centered around must-haves. This showcases your determination to activate solutions for that first tiny niche even sans a fully built production-grade product.
Emphasize with investors that you respect their money enough to not waste it on premature optimizations. Your plan ensures you build and roadmap additional functionality responsibly IF AND ONLY IF initial feature experimentation proves substantial product/market fit warranting doubling down.
6. Marketing & Sales
Thus far you’ve covered the key value proposition and functionality your startup will offer. Now shift to tactical specifics on how you’ll connect your novel solution with that clearly defined target beachhead.
Start by breaking down your blended omni-channel market blueprint to cut through the noise and achieve conversion lift.
Here is an ideal framework pairing both scalable and targeted elements for seed-stage ventures:
Paid Digital Marketing
- Targeted Facebook/Instagram/TikTok Ads
- Search/Display Retargeting
- Streaming Radio Spots
- Industry Forum Sponsorships
- Highly-Targeted Content Marketing
Grassroots Outreach
- Beachhead Email Outreach
- Beachhead Calls/Texts
- Industry Event Networking
- Local University Campus Reps
- Early Adopter Referral Programs
Earned Media
- Contributed Articles
- Podcast Interviews
- Reviews / Testimonials
- Referral Partnerships
- PR Launches & Press Releases
The glaring omission? Sales team headcount.
Early on, founders must handle sales themselves to economize cash burn. Hiring reps too early risks overextending finances before ensuring product viability.
So spotlight your personal founder sales fit first. Play up hands-on selling experience within the specific market context you’re pursuing with this venture.
Then convey a scaling plan centered on refining and automating conversion funnel elements that empirically guide qualified leads to become delighted long-term customers.
The core funnel methodology goes:
- Broad-based brand awareness marketing → Baits wide audience
- Lead capturing mechanisms → Filters for buyers
- Consultative selling touchpoints → Focuses high-potential targets
- Frictionless conversion → Delivers ROI proof
If your business model doesn’t fit this framework, adapt concepts accordingly while sticking to the seed stage constraints of capital efficiency and lean experimentation.
7. Operations
By this point you’ve described WHAT your startup does and WHO it serves. Now it’s time to explain HOW you’ll deliver on ambitious promises to customers.
Start by simply framing core business processes required to get your product or service from raw inputs all the way through to solving target user pain points.
For physical products, that could involve flows like:
- Design concepts → Engineering specifications → Prototyping → Manufacturing → Quality assurance → Packaging → Distributing → Support
For software platforms:
- Product requisites → Cloud infrastructure → Coding → Version control → Usage analytics → Onboarding → Technical support
For services:
- Prospecting → Onboarding → Account Management → Delivery capacity → Quality control → Supplemental services → Support
You get the idea. Just define macro processes without diving into granular details. Those come through experimentation!
Primarily, concentrate operational details on two crucial pillars:
- Proprietary unfair advantages that supercharge efficiency to delight customers while maintaining profit margins despite tight costs. Common examples include algorithms, datasets, novel business model frameworks, or embedded industry experts.
- Partnerships or platforms enabling you to deliver baseline functionality matching incumbent competitors on day one. Don’t attempt to build everything end-to-end or innovate across every dimension from the start! Leverage existing commoditized solutions while you test differentiated value propositions focused on solving target customer problems 10x better.
Essentially, convey you grasp the key 20% inputs that drive 80% of customer value. If the processes seem complex, find ingenious ways to simplify. Position enhanced intricacies as optional add-ons once baseline product/market fit is proven vs. overbuilding the wrong advanced solution.
8. Milestones
The milestones section represents the culmination of everything you’ve documented thus far. Here, outline the step-by-step process for methodically testing the riskiest assumptions underlying your startup.
In conjunction with the experiment design, detail concrete metrics or signals indicating whether hypotheses prove true or false. Then estimate costs, durations, and resource requirements for rapid experiments.
Frame assumptions through statements structured like:
We believe [this capability] will result in [this customer reaction]
Then design tests around the ability to measure:
- behavioral changes
- sentiment improvements
- usage increases
- revenue lift
Common milestone tests to consider:
- Solution Viability – Manual then automated demonstrations quantifying interest
- Demand Validation – Willingness to prepay as a signal
- Market Sizing Accuracy – Applying proxies from analogous use cases
- Business Model Fit – Contrasting pricing sensitivity across customer segments
- Feature Prioritization – Gauging reactions to mockups or limited functionality
- Operational Scalability – Maximizing utilization before adding overhead
Combine testing both internally-facing operations and externally-visible customer experiences. But concentrate on product/solution related hypotheses first.
Beating competitors takes precedence over backend experimentation. Optimize business operations AFTER establishing winning customer value propositions.
The key is conveying to investors an empirical, metrics-driven approach centered on turning critical assumptions into facts or disproving them faster than incumbents hampered by legacies and red tape.
Cement belief you’ll double down on evidence proving repeatable formulas to acquire and monetize target niche segments. And quickly cut losses spending minimal capital if data suggests limited viability.
9. Financials
We’ve made it clear that traditional multi-year financial projections typical of standard business plans are counterproductive guesses for early stage startups.
However, seed investors still want to see back-of-napkin math you’ve done to quantify potential venture scale. So mock up top level metrics more as directional guidelines than definitive targets.
Take utmost care however NOT to pull imaginary hockey stick numbers from thin air. Founders claiming $100 million valuations on basic eCommerce stores face extreme investor skepticism…and deserve to!
Baseline financial model components should include:
- Estimated Customer Acquisition Costs Per Beachhead Channel
- Willingness-To-Pay Price Range For Target Personas
- Logical Volume Estimates Based On Analog Use Cases
- Assumed Conversion Rates Each Funnel Stage
- Operational Unit Economics At Various Scale Points
Use inherently bottom-up thinking grounded in realities of what combination of inputs would need to scale to hit specific 8-figure outcomes. Top-down abstract number picking lacks validity.
And remember, early-stage startup financial models serve more as instruments of learning than definitive targets. Adapt projections based on empirical evidence once live.
Concentrate everything on validating customer demand first. Defer advanced modeling of operational minutiae or elaborating hockey stick projections.
Getting REAL buyers is all that matters initially.
Bringing It All Together
Despite extending 3k+ words at this point, the lean startup methodology boils down to an elementary formula:
- Start by deeply understanding a pressing customer problem
- Design an innovative solution specifically addressing root causes
- Concentrate on dominating an underserved niche beachhead market segment
- Validate demand empirically through rapid testing
- Scale up deliberately only once achieving initial product/market fit
In that sense, think of the lean business plan format as more of an exercise in startup soul searching than a stuffy document.
It pushes founders to pressure test their value proposition, business model, and operational viability through the lens of target customers rather than theoretical academic assumptions.
You can’t survive let alone thrive in the brutally competitive startup game without getting inside the hearts and minds of actual buyers needing your solutions.
So escape the temptation to overly complicate initial planning with intricate spreadsheets and 40-page reports professional managers expect.
Instead, concentrate efforts on distilling explanations of the crucial assumptions requiring testing above all else before launch.
Then close your lean startup business plan with next step calls-to-action so readers clearly understand how you’ll leverage funding to start rapidly experimenting using the scientific method.
Now…go show the world what your brilliance is made of!
Related Posts

Partha Chakraborty
Partha Chakraborty is a venture capitalist turned entrepreneur with 17 years of experience. He has worked across India, China & Singapore. He is the founder of Tactyqal.com, a startup that guides other startup founders to find success. He loves to brainstorm new business ideas, and talk about growth hacking, and venture capital. In his spare time, he mentors young entrepreneurs to build successful startups.
You may also like

What is Smart Money Vs Dumb Money?
- Startup funding

35 Tips to Raise Funds for Your Startup
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How to make a lean business model canvas
Imagine that you have an idea for a new product or business. Yet, as enthusiastic as you are about the potential for this nugget of inspiration, you’re also plagued by this question: Will it work? Is it actually a viable idea?
A lean business model canvas is a one-page business plan that helps you break down your product or business model, question and test your assumptions, and determine if your idea actually has legs.
Lean business model canvas explained: What is a lean canvas?
You might also hear a lean business model canvas referred to as a variety of other, similar terms like a lean business canvas, lean business plan, or even simply a lean canvas.
This tool was created by Ash Maurya and is an adaptation of the original business model canvas by Alex Osterwalder .
You can think of a lean business model canvas as a straightforward business plan that skips the fluff and gets to the most important elements you need to identify or evaluate (primarily, the problem you’re solving).
When you have an idea for a product or business, you’ll use a lean business model canvas template to fill in the various sections (more on those in a minute) and validate your idea.
The lean canvas is most frequently used by lean startups, which use a lean startup methodology to deliver products to customers faster and determine whether or not the business model itself is viable. In short, lean startups and lean canvases are all about moving fast, testing, and iterating.
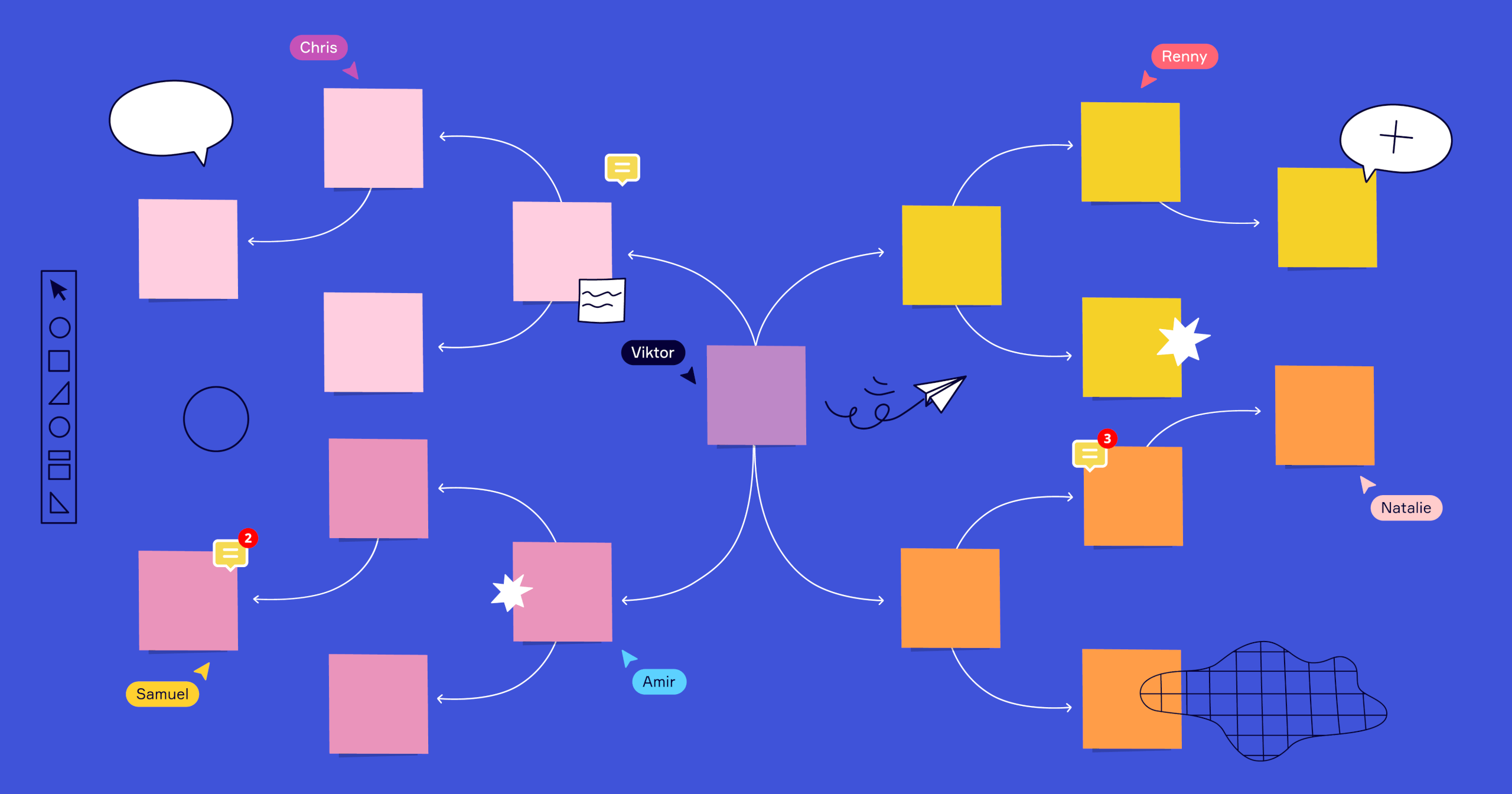
Lean canvas example
One of the best ways to understand a lean business model canvas is to see one. So, let’s set up a lean canvas as an example.
Perhaps you have an idea for a business: You want to create an app or a website that’s essentially a database of parks and playgrounds, which parents can search and filter using location, features (splash pad, baby swings, etc.), and more.
You want to dig into your idea even further using a lean business model canvas. Here’s a simple peek at what that could look like after jotting your initial notes down:

Lean canvas vs. business model canvas
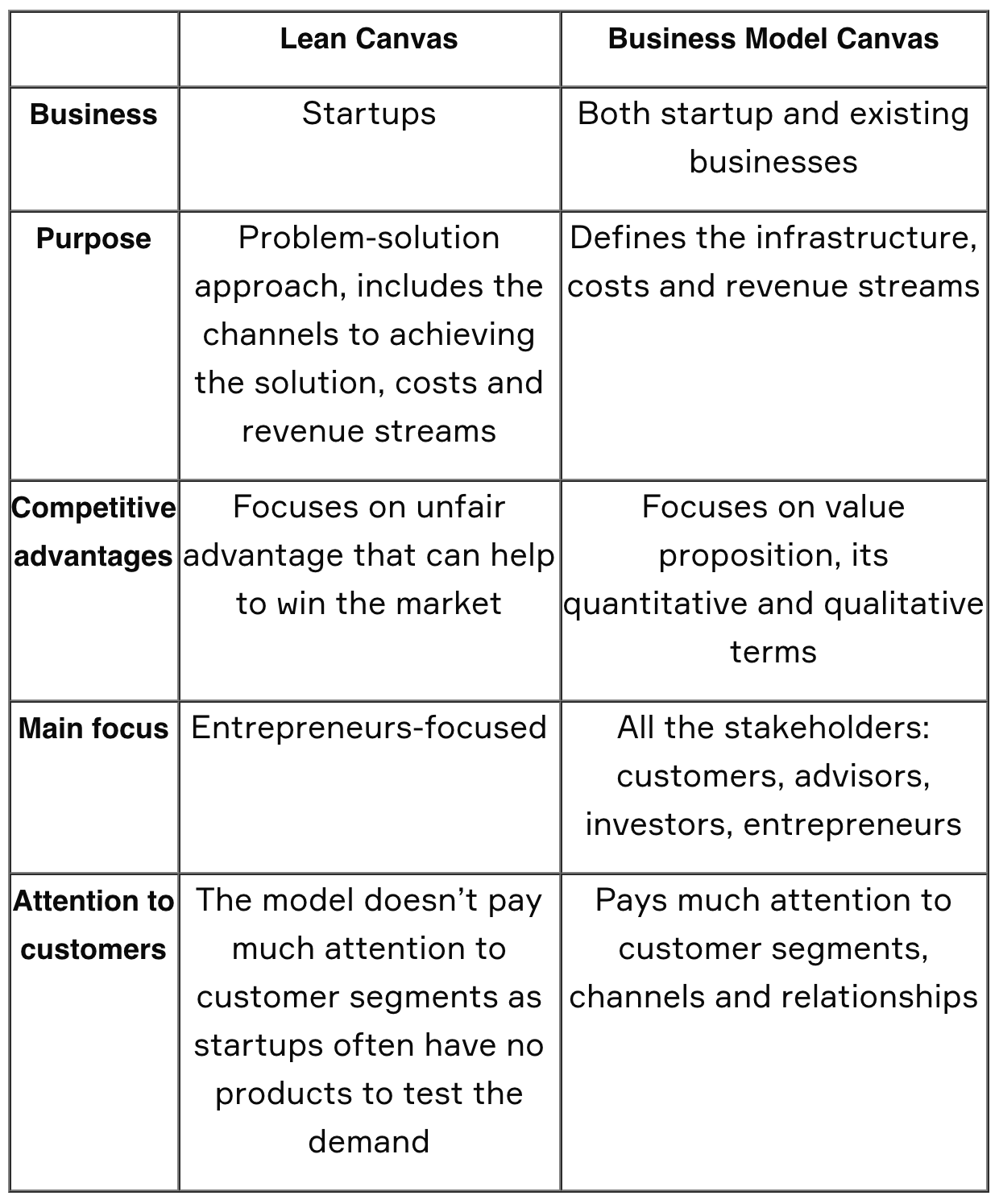
There’s a lean business model canvas and then simply a business model canvas . The two terms are often confused, as they have a lot in common — and the lean canvas is an adaptation of the business model canvas.
However, the biggest difference is that a business model canvas is focused on a specific product while a lean canvas focuses on a specific problem.
This means that the business model canvas has a few blocks that you won’t see on a lean canvas. These are:
- Key partners (lean canvas replaced with problem)
- Key activities (lean canvas replaced with solution)
- Key resources (lean canvas replaced with key metrics)
- Customer relationships (lean canvas replaced with unfair advantage)
That’s the gist, but here’s a chart that digs even more into the difference between a business model canvas and a lean canvas:
What is included in a lean canvas?
Now that you have a better grip on what exactly a lean canvas is let’s break it down even further. The typical lean business model canvas has nine elements or quadrants. These are:
- Problem: A brief description of the top three problems you’re addressing.
- Solution: The proposed fix for the problem you’ve identified.
- Unique value proposition: Why your solution is different and what will make people buy.
- Unfair advantage: Something you have that can’t be easily copied or bought.
- Customer segments: Who your target customers or users are and if they can be further segmented.
- Key metrics: The important numbers that will indicate how your business is doing.
- Channels: The free and paid channels you’ll use to reach your customers.
- Cost structure: All of your fixed and variable costs.
- Revenue streams: How your business model will earn income.
However, our lean canvas template here at Miro dives even deeper with the addition of a few more elements, including:
- Existing alternatives: How these problems are currently solved today.
- High-level concept: A simple X for Y analogy (e.g., “Zillow for playgrounds”).
- Early adopters: Characteristics of your ideal customers who will jump right on the bandwagon.
How to make a lean canvas in Miro
A lean canvas can provide a lot of clarity about a business model or a product idea. Ready to create one with your own team? Getting started is easy.
- Grab our lean business model canvas template and create a new Miro board . You can put as many canvases on one board as you need.
- Define the product or business idea you’re working on, and then fill in the blocks with different types of content. You don’t just have to use text — you can also use pictures, videos, and more.
- Invite your team and/or advisors to the board so you can brainstorm , collect feedback, and collaborate in real-time.
- Come back to the board regularly to make necessary changes, add new information, and discuss progress.
And that’s it! Once you’ve created your own lean business model canvas, you can move forward with a product or business idea with more strategy — and a lot more confidence too.
Get started on your own lean business model canvas with Miro
Miro is your team's visual platform to connect, collaborate, and create — together..
Join millions of users that collaborate from all over the planet using Miro.
Keep reading
How to make a concept map – with examples.
Learn Miro basics with new template pack
5 insights from leaders transitioning teams back to the office

AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
Quickbooks Sync and compare with your quickbooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how it works →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth and investor readiness
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Lean Business Plan Template

Free Lean Canvas Template
- Vinay Kevadia
- April 27, 2024
Are you too struggling to figure out how to write a lean business plan?
Well, you’re not alone—many entrepreneurs do! A lean business plan is the first document that introduces your business to potential investors or partners.
So, it has to be appealing to persuade potential investors or partners!
Making a plan visually appealing with all the essential information about your business can get overwhelming. Worry not—here is a guide on writing a lean business plan with all the sections and an example.
Thus, don’t wait any longer and dive right in.
What is a Lean Business Plan?
A lean business plan is a short, one-page document that acts as a roadmap for your business.
It focuses on the most important aspects like what your business does, who it is for, what makes it unique, and how it helps you make money.
Unlike traditional business plans that are lengthy and complex, a lean business plan is simple to understand.
It also provides a foundation for creating a more detailed business plan later.
Writing a lean business plan follows a customer-centric approach. So, let’s begin by understanding a lean business plan outline.
Components of a Lean Business Plan
- Customer Segment
- Unique Value Proposition
- Cost Structure
- Revenue Streams
- Key Metrics
- Unfair Advantages
The problem statement talks about what problems your business aims to solve for potential customers.
First, try to understand what top problems are your product or service solving for your target market. Know that your business idea is not viable enough if it isn’t solving any practical problem.
Along with it, mention your customers’ pain points. The most efficient way is to figure out your ideal customer profile first, and then understand their pain points.
Discuss what are the solutions your customers are looking for and how your idea fits in their requirements.
While doing so, try avoiding jargon and any technical terms that will be hard to understand. Also, back your problem statement with evidence and facts instead of assumptions.
Existing alternatives
This is the second part of the problem section. In this section, mention the existing alternatives that are solving your potential customers’ problems.
The businesses solving the same problems are your current competitors. These alternatives are what customers are using or considering as of now.
Understanding these existing alternatives helps you identify how your solution can stand out and provide greater value to customers.
2. Customer segment
The key to writing this chapter is to understand your target market and separate them into various customer groups. Consider demographics, psychographics, and consumer behavior while bifurcating.
To identify target customers, ask yourself the following questions:
- Who are we creating value for in our business model?
- Who are our most important customers?
This way, you will be able to identify your most profitable segments too.
Once you’ve your customers, here are the various components to include in this chapter:
- Types of Customer Segments
- Mass Market
- Niche Market
- Diversified
- Multi-sided platforms/ markets
Creating a customer profile
The customer profile defines the customer segment more clearly for your company by assessing the customer’s pains and gains.
To understand customer pain points better, we can categorize them as follows:
- Undesired outcomes, problems, and characteristics
- Pain severity
Customer Gains: Customer gains are the results or benefits that customers want. Ideally, this is what your product or solution must provide. This is how we can categorize gains:
- Required Gains
- Expected Gains
- Desired Gains
- Unexpected Gains
- Gain relevance
Early Adopters
Early adopters are the customer section that is among the first customers to try out your product or services.
Since they are more in need than others of something to solve their problems, they will forgive the imperfections or flaws of the early releases. This would help you better test and collect the actual feedback for your solutions.

Want to create a Customer Persona in Easy Steps?
Generate valuable customer insights in minutes with Free Customer Persona Generator .
3. Unique Value Proposition
Once you’ve identified your target audience, you should also pinpoint the strengths of your product or service that attract them.
In other words, how would you describe your business to target customers in just ONE sentence (possibly less than 200 characters long)?
A Unique Value Proposition is a sentence that tells why what you do is different from competitors and why that difference matters to customers.
This is a critical parameter in your plan and is hard to get right. It might take years of experience and a lot more market analysis to make that one sentence.
It usually combines:
- The target segment
- The key problem
- The key benefits the customers are going to get after having the product/service.
- The special and unique way you will deliver it
For example, Google’s USP is “Organizing the world’s information and making it universally accessible and useful” .
4. Solution
How would you solve customers’ problems? Outline a possible solution for each problem.
Describe your business idea briefly and in concise sentences that explain what the customer experience is going to be. Make sure you don’t go with the technical words here and keep it all simple.
We have already written a problem chapter. Now match your every solution with its associated problem from the problem chapter. Make a one-to-one association between the problem and the solution, keeping your product offering in mind.
Need help in preparing a lean business plan?
Create an appealing lean business plan using Upmetrics
Plans starting from $7/month

5. Channels
Once you know the solution, it is time to attract customers. List your inbound or outbound marketing strategy to spread your reach: How are you going to acquire your customers?
When your product is ready to solve customers’ problems uniquely, you need to speak loud so customers know that you have the solution for their problems.
Here are examples of some marketing channels: social media, paid online advertising, TV ads, PR, cold calls, Google Ads etc.
List all the possible channels you are going to use for your business, and how will you leverage them to spread the reach.
6. Cost structure
Now, this is one of the most important sections, as your potential investors or business partners will want to know about the costs.
Costs are necessary as they help you to identify how many customers you need to cover your costs.
The accuracy of costs depends on whether you have an existing business or the business is in just the idea stage. If your business is at the idea stage, you will have to make assumptions regarding cost structures.
Write this section last. At an early stage, you don’t even need to write down these numbers. You’ll have more clarity on cost figures once you implement your ideas.
7. Revenue streams
This slide of the lean startup plan template outlines how you will generate income for your business.
Start by listing all the sources of revenue. It could include the way you will charge as in through product sales, service fees, subscription model, or any other mode.
8. Key metrics
Identify the key numbers that indicate your business’s performance: these are the metrics you’ll use to monitor your progress.
Every business, regardless of its industry or size, relies on key performance metrics.
Define the customer actions you’ll track to measure your progress and evaluate your business performance. For example, some of the metrics you can track are:
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
- Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
- Customer churn rate
- Gross profit
- Conversion rate
- Website traffic
9. Unfair Advantages
The “unfair advantage” is a single, clear, and compelling statement that states why you are different from your competitors and worth paying attention to. Do you have more resources, access to more patents, or better brand recognition?
This section is a little hard to describe. Many entrepreneurs make mistakes while defining this section.
It has to be about something that you already have, which cannot be copied or bought and would require a considerable amount of time for anyone else to build.
To understand your unfair advantage, ask yourself: why do I believe I have more chances to be successful than anyone else in my chosen business vertical?
For example: Tesla’s technological innovation in electric vehicles (EVs) and battery technology is a key unfair advantage. The company’s EVs offer superior performance, range, and charging infrastructure compared to traditional automakers.
Now as we know what all sections to include in a lean business plan, let us go further and see an example.
Lean business plan example
Below is an example of a restaurant lean business plan to have clarity:
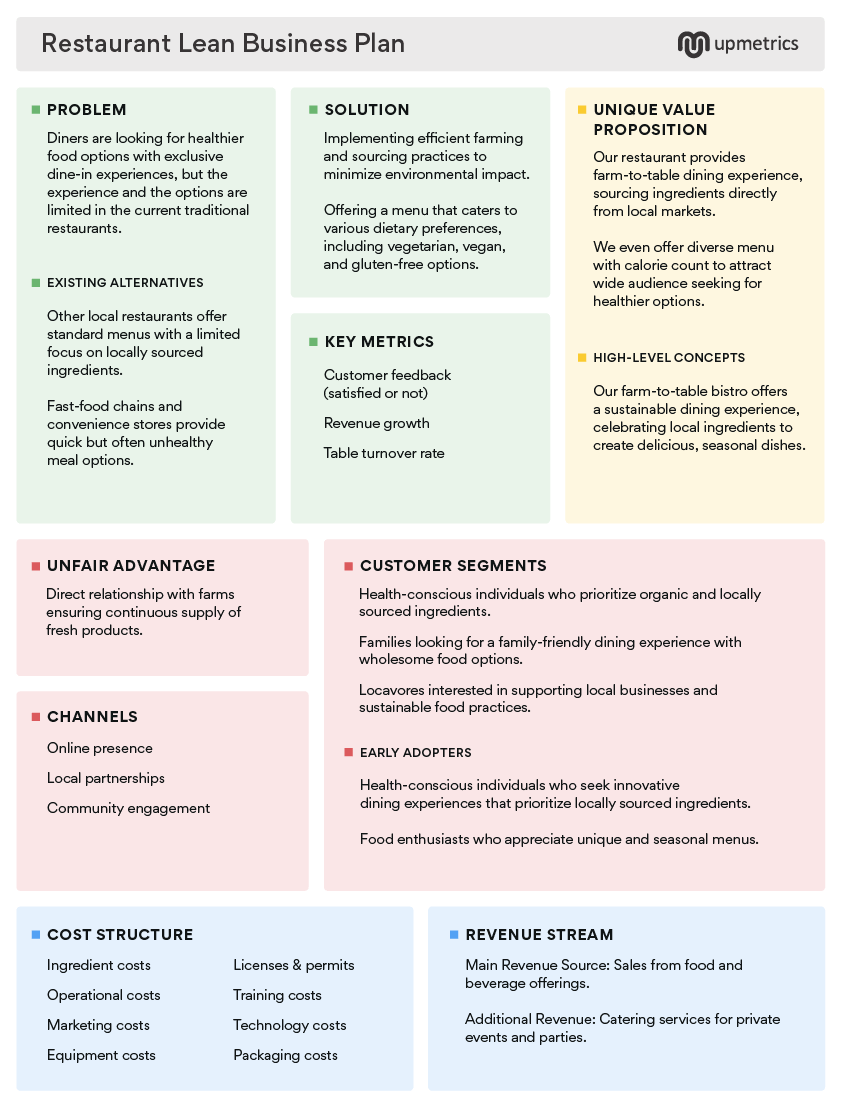
Benefits of a Lean Business Plan
A lean business plan is an efficient and condensed business plan to draw investors’ attention to your business in its initial stage.
Some of the advantages of a lean business plan include:
- Simplicity: Only the main elements of a business are focused on a lean business plan, which makes it simple for readers to understand.
- Efficiency: A lean plan writing takes less time and resources than a traditional business plan.
- Actionable insights: It helps you track key metrics and performance indicators at one glance.
That’s it for today. We hope you found this lean business plan writing guide helpful. If you are still confused, you can always use a business planning software like Upmetrics, for both your lean and traditional business plan.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
How many pages should a lean business plan be.
A lean startup business plan is also known as a one-page plan. So, as the name suggests, it should be one page only covering the main elements of a business.
What is the difference between a traditional business plan and a lean business plan?
A business plan is a detailed document showcasing everything about a business, including its goals, revenue streams, financial projections, funding ask, call to action, target market, and a lot more.
On the other hand, a lean plan is short, focusing on the most important parts of the business.
Where can I find free templates and resources for creating a lean business plan?
There are several options from where you can find a free lean business plan template. Here are some options:
- Upmetrics: It offers a free lean canvas that is easy to customize and provides other resources too for your business plan.
- Score: SCORE offers a variety of business planning templates, including lean plan templates, that you can download for free.
- SBA: The SBA website offers resources for small business owners, including business planning templates and guides.
About the Author

Vinay Kevadiya
Vinay Kevadiya is the founder and CEO of Upmetrics, the #1 business planning software. His ultimate goal with Upmetrics is to revolutionize how entrepreneurs create, manage, and execute their business plans. He enjoys sharing his insights on business planning and other relevant topics through his articles and blog posts. Read more
Related Articles

Lean Business Planning: The Modern approach to Business Plan Writing

SBA Business Plan Template Essentials: The Complete Guide

How to Prepare a Financial Plan for Startup Business (w/ example)
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

How to Write a Lean Business Plan

A lean business plan is a tool used by startup companies to validate their business idea and drum up funding from investors. Unlike a traditional business plan, which can be hundreds of pages long, a lean business plan is typically only 10-20 pages.
The advantage of using a lean business plan is that it forces you to focus on the key aspects of your business, such as your value proposition and target market. This makes it easier to communicate your business idea to potential investors.
Tips for Writing a Lean Startup Business Plan
If you’re thinking about writing lean startup business plans , here are a few tips to help you get started:
Keep it short and sweet
Remember, the whole point of a lean startup business plan is to be concise as you try to propose to business partners. So, don’t try to cram too much information into your 10-20 pages. Stick to the essentials and cut out any fluff.
Focus on your value proposition
Your value proposition is what sets your business apart from the competition. It’s what makes your customers want to buy from you instead of someone else.
When crafting your value proposition, think about what benefit your product or service provides for your customers. For example, if you’re selling a new type of toothbrush that is more effective at preventing cavities, then your value proposition might be “The toothbrush that prevents cavities better than any other.”
Know your target market
Your target market is the group of people who are most likely to buy your product or service, sometimes referred to as customer segments. When writing your lean business plan, be sure to include information on who your target market is and how you plan to reach them.
Describe your business model
Your business model is how you plan to make money. There are a variety of different business models, so it’s important to choose the one that makes the most sense for your particular business and is in line with your business strategy.
For example, if you’re selling a physical product, your business model might be “retail” or “direct-to-consumer.” But if you’re selling a service, your business model might be “subscription” or “pay-per-use.”
Outline your go-to-market strategy
Your go-to-market strategy is how you plan to get your product or service into the hands of your target customers. There are several different channels you can use to reach your target markets, such as online advertising, PR, or direct sales.
When outlining your go-to-market strategy, be sure to include information on which channels you plan to use and why you think they will be effective.
Create financial projections
One of the most important parts of your lean business plan is your financial projections . This is where you estimate how much revenue your business will generate and what your expenses will be.
Creating realistic financial projections is crucial for convincing investors to give you funding. But it can also be one of the most challenging parts of writing a lean business plan.
If you’re not sure where to start, there are some online templates and calculators that can help you generate financial projections for your business.
Get feedback from others
Once you’ve completed a draft of your lean business plan, it’s a good idea to get feedback from other people. This can help you identify any areas that need clarification or further development.
You can get feedback from friends, family, mentors, or even potential investors. Just be sure to take all feedback with a grain of salt and use your best judgment to decide what changes, if any, you should make to your plan.
Keep it updated
As your business grows and changes, so too should your lean business plan. Be sure to review and update your plan regularly to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
Benefits of a Lean Business Plan
Many benefits come with using a lean business plan:
- You can get started quickly : Because they’re shorter and less detailed, lean business plans are much easier to write than traditional business plans. This means you can get started on your business faster.
- You can save time and money : Writing a lean business plan will take less time and money than writing a traditional business plan. This is because you won’t need to do as much research or hire someone to help you write it.
- You can raise funding more easily : Investors are more likely to give you funding if you have a lean business plan. This is because they can see that you’ve thought through your business and have a clear idea of what you’re doing.
- You can adapt more easily : Because they’re shorter and less detailed, lean business plans are much easier to change than traditional business plans. This means you can quickly adapt your plan as your business changes.
Using a Lean Business Plan to Raise Funding
If you’re looking to raise funding for your business, a lean business plan is a great way to do it. Investors are more likely to give you funding if you have a lean business plan because they can see that you’ve thought through your business and have a clear idea of what you’re doing.
To increase your chances of getting funding, be sure to include information on your business model, go-to-market strategy, and financial projections in your lean business plan. You should also get feedback from others to ensure your plan is clear and concise.
Sections of a Lean Business Plan Template
There are some different sections you can include in your lean business plan, but the most important ones are your executive summary, business model, go-to-market strategy, and financial projections.
- Your executive summary should give a brief overview of your business. This is where you can talk about what you’re selling and why it’s different from what’s already on the market.
- Your business model should explain how you plan on making money. This is important for investors to see so they know your business is viable.
- Your go-to-market strategy should outline how you plan on getting your product or service into the hands of your customers. This is important for investors to see so they know you have a growth plan.
- Your financial projections should show how much money you think your business will make in the future. This is important for investors to see so they know your business is a good investment.

Resources needed to Write a Lean Business Plan
The resources you need to write a business plan vary depending on the type of plan you’re writing. If you’re writing a lean business plan, you won’t need as much information as you would if you were writing a traditional business plan.
That said, there are a few resources you should always have handy when writing a business plan:
- Your business idea: You need to have a clear idea of what your business is before you can write a business plan.
- Your target market: You need to know who your target market is so you can create a marketing strategy that reaches them.
- Your financials: You need to know your financials so you can create realistic projections for your business.
Getting Feedback on Your Business Plan
When you’re finished writing your business plan, be sure to get feedback from other people. Ask them if it’s easy to understand and if they have any suggestions for changes. Remember, not everyone will have the same opinion, so it’s important to take all feedback with a grain of salt and use your best judgment to decide what changes, if any, you should make to your plan.”
Actioning Your Lean Business Plan
Once you have your lean business plan written, it’s time to start taking action. This is where you’ll put your plan into motion and start working towards your goals.
Create the Plan
The first step is to create a plan. This means outlining what you need to do to achieve your goals. Write down each task you need to complete, and then create a timeline for when you plan on completing it.
Make sure your timeline is realistic, and don’t be afraid to adjust it as needed. You may find that some tasks take longer than you thought, or that you can complete some tasks faster than you expected.
Get Started
Once you have your plan created, it’s time to get started. Begin working on the tasks you’ve outlined, and make sure you’re staying on track. If you find yourself falling behind, don’t be afraid to adjust your timeline.
Remember, a lean business plan is meant to be flexible. As your business grows and changes, so too will your plan. Be sure to review and revise your plan regularly to ensure it’s still relevant and accurate.
Course of Action
There are a few different courses of action you can take when writing your lean business plan. You can choose to write the plan yourself, or you can hire someone to help you. You can also use a template, or create your own from scratch.
If you’re not sure where to start, we recommend using a lean business plan template. This will give you a solid foundation to work from, and it will make the writing process easier.
Once you have your template, you can start filling in the blanks. If you get stuck, don’t hesitate to reach out to a business consultant for help. They can provide guidance and feedback to ensure your plan is on track.
Forecast and Budget
To get started, create a timeline of when you want to achieve each goal. Then, break down each goal into smaller tasks that you can complete. As you complete each task, check it off your list.
It’s also important to track your progress along the way. This will help you see how well your lean business planning is working and make adjustments as needed.
Reviewing & Revising Your Lean Business Plan
To review and revise your lean business plan, you’ll need to:
- Check your progress against your original timeline using all key resources
- Make changes as needed
- Review your financials, revenue streams, and other vital metrics regularly
- Update your plan as your customer relationships and business planning change
- Get feedback from other people
- Take action on your plan
- Celebrate your successes!
As you can see, there’s a lot that goes into writing and revising a lean business plan. But don’t worry, we’re here to help. Our team of experts can provide guidance and feedback to ensure your plan is on track.
A lean business plan is a great way to get your business off the ground. It’s important to remember that your plan is meant to be flexible, so don’t hesitate to make changes as needed. Be sure to review and revise your plan regularly to ensure it’s still relevant and accurate.
If you need help writing or revising your lean business plan, our team of experts can help. We offer a wide range of services to suit your needs, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Lean Business Plan FAQs
What is a lean business plan.
A lean business plan is a concise and effective way to outline your business goals, strategies, and progress. It’s a flexible and adaptable plan that can be updated as your business grows and changes.
Why should I use a lean business plan?
There are many benefits to using a lean business plan, including:
- It’s a great way to get your business off the ground.
- It helps you focus on what’s important.
- It can be updated as your business grows and changes.
- It’s a great way to raise funding.
- It’s a great way to track your progress and ensure you’re on track.
How do I write a lean business plan?
There are a few different ways you can write a lean business plan. You can use a template, hire someone to help you, or create your own from scratch.
How often should I review my lean business plan?
You should review and revise your lean business plan regularly to ensure it’s still relevant and accurate. We recommend reviewing it at least once a year.

- Business Planning
- Venture Funding
- Project management
Lean management: the pros, cons, and everything in-between
Georgina Guthrie
February 14, 2020
Waste is never a good thing — whether that’s resources, time, or money — and that’s exactly what Lean management is about: creating a culture that is as efficient as possible.
Toyota originally developed the Lean methodology back in the ‘80s to minimize waste on their production line. Needless to say, it worked for them, and since then, a huge range of industries have adopted it, from marketing and manufacturing to design, management, and beyond.
If you want to work more effectively with your team, then Lean could be your new favorite tool. Read on to find out exactly what this popular methodology involves.
What are the main principles of Lean?
Lean management is shaped around five core principles, as described by the Lean Management Institute .
1. Identify your value. Always satisfy your customers’ needs by only providing services that add value . Any activity that doesn’t add value is considered waste.
2. Map the value stream. Analyze your workflow from start to finish, including all the activities of everyone on your team (and potentially beyond). Once you’ve done this, you’ll be able to see which activities add value, and which don’t.
3. Create flow. Refine and streamline your workflow , highlighting things like bottlenecks or unnecessary approval stages that could slow things down. Remember: if it doesn’t add value (or causes problems), then get rid of it.
4. Establish pull. This is a way of working that requires people to ‘pull’ jobs to work on when there’s demand, and only when there’s demand.
To use a real-life example, say you’re working behind a bar. You’d pull a drink for someone when they step up and order one — you wouldn’t pour beers in advance when the bar is empty. It’s the same for Lean working.
5. Seek perfection. Lean isn’t something that has an endpoint; it’s about continuous improvement . Tasks and workforces change, which is why it’s important to revisit and refine the workflow. And even if nothing’s changed, assess anyway — there’s almost always room for improvement.
What are the benefits of Lean management?
Lean principles are designed to continually improve productivity. It’s popular because, when done properly, it works. Here are some of the benefits:
- Less waste. Continually refining your workflow means you can iron out productivity-sapping issues and tasks that don’t add anything.
- More focus. By cutting out activities that don’t add value, your team can apply more focus to those that do.
- Better motivation. When employees are able to focus on meaningful and impactful work, rather than valueless busy work, they have a greater sense of purpose.
- A smarter way of working. Using the pull system means the team will only work on tasks when there’s demand. They can spend any spare time on either preparation or training.
- More value for the customer. By cutting out tasks that don’t add value, you’ll be able to commit more time to those that do, ensuring a higher-quality product.
Are there any disadvantages to Lean management?
As with all things, there are downsides. However, as with all downsides, there are steps you can take to minimize the chance of occurrence. Here are the main things to look out for:
- Lack of time. Lean requires some planning and time upfront: you’ll need to take a deep dive into your current workflow and team activities, which could include tracking things over a period of time (if you’re not already), as well as talking to team members and heads of other teams. You’ll also need to encourage your team to meet regularly (many Lean teams hold a daily standup ) to discuss the work that’s been completed, what needs to be done, and any problems that could get in the way.
- A lack of strategy. Some organizations get so focused on Lean tactics that they lose sight of the bigger picture. One way to get around this is to create a project charter for each project, as well as an overall mission statement.
- Not enough buy-in. Lean is considered a radical way of working that requires complete buy-in from teams. They’ll need to work independently without too much direction, which might not work if your team is inexperienced. Implementing a new strategy can also cause stress, especially if it’s a particularly results-oriented methodology — which Lean is. Brush up on your organizational communication skills so you can effectively tell everyone why they are shifting to this way of working. You may also need to invest in training to get less experienced (or resistant) workers up to speed.
- Cutting things too fine. Lean follows a ‘pull’ style of working which means work is delivered as needed, and not preemptively. However, if there’s a bottleneck or your resources are low (for example, someone’s off sick), then delays can start adding up quickly. Having a contingency plan in place can help provide leeway, while smart planning using project management software will help you track tasks in real time, helping you plan ahead.
Lean management tools
Lean’s enduring popularity is a testament to its potential. As with all management methodologies though, there are pros and cons — but being aware of the potential pitfalls is your best line of defense. Here are three things to keep in mind:
- Understand the potential problems, and take steps towards mitigating these.
- Always keep your overarching company goal in mind.
- Track and monitor progress as you go, both through project management software and daily team standups.
If you use these three points as your guiding star, you’ll be able to build an efficient project that evolves and improves each day. You’ll also have a team that’s working to their greatest potential.

A comprehensive guide to creating your first SIPOC diagram

Everything you need to know about heijunka, a Lean management essential
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Learn with Nulab to bring your best ideas to life
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Lean Strategy
- David J. Collis

Strategy and entrepreneurship are often seen as polar opposites. Strategy means rigorously defining and pursuing one clear path, while entrepreneurship involves continually changing direction to take advantage of new opportunities. Yet the two desperately need each other: Strategy without entrepreneurship is central planning; entrepreneurship without strategy leads to chaos.
There is a way to reconcile the two, through the lean strategy process. It ensures that start-ups innovate in a disciplined fashion so that they make the most of their limited resources. Lean strategy helps company builders choose viable opportunities, stay focused, and align the entire organization.
The process begins with setting the venture’s vision, or ultimate purpose—perhaps the only aspect of strategy that should be permanent. To deliver on it, senior executives agree on a deliberate strategy, defining the firm’s objective (the near-term goal that describes success), scope (what the firm will and will not do), and competitive advantage (how it will win). The deliberate strategy sets the bounds within which experiments will take place and guides daily decisions. But the results of those experiments and decisions lead to learning that reshapes the strategy. Though priorities evolve, at each point in time it’s clear to everyone in the firm which ones take precedence.
Start-ups need both agility and direction.
Idea in Brief
Leaders of start-ups often see strategy, the pursuit of a clearly defined path that is systematically identified in advance, as the enemy of entrepreneurship, which requires ventures to be opportunistic and quickly shift course as they learn what customers want.
The Reality
Entrepreneurs badly need strategies that articulate what their ventures will and will not do. Such boundaries are crucial for making the most of scarce resources, deciding which ideas to pursue, and evaluating experiments. But a rigid, fixed strategy is dangerous.
The Solution
The lean strategy process integrates the bottom-up approach of the lean start-up with the top-down orientation of strategic management. In an iterative fashion, the venture builds new capabilities and revises the original strategy in response to what it learns.
Strategy and entrepreneurship are often viewed as polar opposites. Strategy is seen as the pursuit of a clearly defined path—one systematically identified in advance—through a carefully chosen set of activities. Entrepreneurship is seen as the epitome of opportunism—requiring ventures to pivot in new directions continually, as information comes in and markets shift rapidly. Yet the two desperately need each other. Strategy without entrepreneurship is central planning. Entrepreneurship without strategy leads to chaos.
- David J. Collis is an adjunct professor of business administration at Harvard Business School and the winner of the McKinsey Award for the best HBR article of 2008.
Partner Center

- Can a Lean Canvas Replace a Traditional Business Plan?
B-School Search
For the 2023-2024 academic year, we have 118 schools in our BSchools.org database and those that advertise with us are labeled “sponsor”. When you click on a sponsoring school or program, or fill out a form to request information from a sponsoring school, we may earn a commission. View our advertising disclosure for more details.
More than many other MBA students and graduates, entrepreneurs love possibilities. And only within roughly the past 15 years have new kinds of business plan possibilities captured the imagination of entrepreneurs. Some of these planning approaches—which embody radical departures from the process of drafting traditional business plans—appear to be gaining momentum.
What entrepreneur wouldn’t love to dispense with the lengthy and often tedious process of spending months drafting a traditional business plan—a document that Stanford entrepreneurship professor Steve Blank characterizes as one that “investors make you write that they don’t read.”
Business plans customarily include five years’ worth of financial forecasts and 12 to 18 months’ worth of new product marketing plans. That’s a hefty volume of speculation entrepreneurs often need to estimate under extremely uncertain conditions that can render accuracy virtually impossible.
Moreover, what entrepreneur wouldn’t love to replace their typical 40-page-plus business plan with a single-page document—if for no other reason than investors could no longer dodge meeting requests through spurious excuses that they “haven’t yet found time to read” a document they expected in the first place?
A one-page document of this kind may not satisfy every potential investor at every financing stage. But many investors will consider a document like this to be more than adequate. Read on for an analysis of one viable alternative to traditional business plans.
How Lean Startups Encouraged Lean Business Plans
One newer business planning approach for startups aligns with the now-common “lean” startup principles that earlier in this decade gained popularity in Silicon Valley and form the topics of some recent business books we’ve showcased here on BSchools . Lean methodologies such as agile development grew out of struggles in the software industry to manage product creation cycles that had become unmanageable because they now had to operate continuously in response to changes prompted by aggressive competitive threats. In particular, the agile approach saves time and resources by building new products through iterative, incremental steps that produce only the most essential functionality.
This classic Harvard Business Review article by Blank, “Why the Lean Start-Up Changes Everything,” explains how concepts borrowed from lean methodologies influenced a rethinking of traditional business plans. For example, in contrast to generally accepted business plan development methods, the lean approach encourages entrepreneurs to only conduct minimal research.
Instead, lean methods encourage entrepreneurs to talk directly with potential initial customers. That way, they gain a more accurate and complete understanding of the needs of such early adopters, as well as the opportunity to build relationships with likely first customers.
Lean methodology also encourages the faster development of minimum viable product prototypes, or MVPs, that don’t require substantial development time or budgets because they only offer the most critical features. If the MVP doesn’t win validation from customer reviewers, the lean approach applauds “pivoting.” Currently, in vogue in Silicon Valley, that term denotes quick course corrections based on revised initial assumptions that better suit customer needs.
In other words, the approach rewards chasing customers and markets instead of funding. If entrepreneurs receive enough validation from their customer reviewer panel, the arguments in favor of funding start to seem so overwhelmingly compelling to investors that access to startup capital ceases to pose such a challenging obstacle. Accelerated launch schedules and rapid scaling then flow naturally as an outcome of this process.
The Lean Canvas Framework: Advantages Over a Traditional Business Plan
First conceptualized by business model expert and author Ash Maurya in 2010, the platform for this approach comprises a framework known as “ lean canvas .” As Blank notes, this diagram depicts how a firm creates value. The canvas compares key characteristics of both the product and the market through an analysis of essential elements known as “building blocks.” Nine building blocks are used to describe every conceivable business model, whether the model belongs to Apple, Amazon, or Starbucks. The same nine components also allow for the design of any new business model imaginable.
Building Block Topics: Focused Essentials
The building blocks compare in some ways with the more general sections of a traditional business plan, such as the latter’s Opportunity, Execution, Company Overview, Executive Team, and Financial Forecasts sections.
However, that’s where the similarities end. For one thing, the topics of the building blocks comprise more focused and targeted essentials , which we interpret in these ways:
- The Problem – The marketplace obstacles or challenges that the new product, service, or venture plans to address.
- The Solution – The action mechanisms or methods through which the new product, service, or venture will solve the marketplace challenges.
- Key Metrics – These are performance indications that measure progress, such as market share against competitors, or an individual product’s contribution margin towards the overall profitability of a product line or division.
- Unique Selling or Value Proposition – The exclusive competitive advantages that the product, service, or venture offers and entices customers to buy despite competing alternatives in the marketplace.
- Unfair Advantages – The overwhelming advantages the product, service, or venture exerts in the marketplace that competitors cannot match or surpass in the short run.
- Channels – Maurya specifies a very different definition than those typically appearing in MBA marketing management textbooks for this building block. He defines channels simply as “paths to customers, whether inbound or outbound.” This is a broader interpretation than the means that exist through which the business can distribute the product or solution. These channels include intermediaries like distributors of physical goods in brick-and-mortar marketplaces. Channels also include search engine optimization (or SEO) and other techniques that enable customers to find sellers online.
- Customer Segments – These are specific categories of customers to which the business appeals, or “targets.”
- Cost Structure – The costs the business must pay in order to bring the product or service to market, like the costs of direct materials and labor in manufacturing processes, or for online businesses, computer server leasing within data centers.
- Revenue Streams – The earnings cash flows, expressed over time, from specific products or services.
Emphasizing “Big Picture” Relationships Among Building Blocks
Furthermore, unlike the narrative format of a business plan, the diagram displays all these elements side-by-side on a page, poster, or computer screen—that is, within a single visual framework. That way, the canvas offers a substantial advantage because it emphasizes the big-picture synergies and interrelationships among the building blocks in a way that a traditional business plan narrative cannot.
Swiss startup strategy expert Alexander Osterwalder said , “the combination between great products and a great business model is going to keep you ahead [of] competition in the coming decade.” So what you really want to understand is how all these pieces fit together and what the best business model could be for your idea.
Adapting Business Models
Also, unlike a business plan, the canvas allows one to experiment with and adapt existing business models for new purposes. For example, Osterwalder points out that the business model of Nestle’s Nespresso coffee system, which prominently features high-end retail “boutiques,” is nothing but a recycling of Apple’s Apple Store retail concept. Because both companies built their own stores to create high-end consumer brands, the stylized depictions of their business models on lean canvases display similar diagrams. Visually representing the models in such ways enables model designers to more easily recognize the advantages and drawbacks of repurposing a venerable model to serve the innovative purposes of a new startup.
How the Lean Canvas Expedites Drafting and Revisions
When finalized, the one-page format is faster and simpler for entrepreneurs to write than a lengthy and complex business plan which could take months to draft and revise. And when printed, the canvas becomes a one-page document that investors are much more likely to read. Moreover, instead of a PowerPoint slide deck, the canvas can also form the foundation for entrepreneurs’ succinct investor pitches.
Business Model Competitions
Because the lean methodology provides in many ways a superior means of presenting the business model narrative that appears within most typical business plans, increasing numbers of entrepreneurs and investors began to rally around the lean business model methodology. This movement led to the staging of business model competitions requiring contestants to apply the lean business model framework during their presentations before judging panels. Some events, like the International Business Model Competition , offer prize pools as large as $200,000.
But What About the Numbers? Extensions to the Lean Canvas Model
In January 2018, Maurya acknowledged a deficiency in the lean canvas framework. He conceded that the lean canvas framework alone could not replace more complete business plans for stakeholders who required financial forecasts and product introduction roadmaps.
Maurya’s team then introduced two diagrams that complement the lean business model framework. Similar in principle to the lean canvas, the first, which he named the “ customer factory blueprint ,” applies only seven key metrics “to replace all the numbers in a typical financial forecast spreadsheet.”
The customer factory blueprint specifies a “minimum success criteria,” or MSC. Other metrics include:
- Revenue (the pricing model)
- Retention (the drivers of repeat purchases)
- Acquisition (how the firm identifies new customers)
- Activation (the initial value experience)
- Referrals (the drivers that encourage customers to tell others about the product or firm)
- The annual growth rate
Maurya calls the second diagram the “ traction roadmap ,” or TR. The TR’s purpose is to illustrate a product roll-out’s objectives and milestones to stakeholders. Some milestones might assess the fit between the problem and the solution, or the fit between the product and the market; others might indicate when the firm’s objective shifts to rapid scaling after testing has assured the management team of the product’s marketplace success.
It might seem too early to tell whether these two complementary quantitative tools will win acceptance comparable to the lean canvas framework. However, one effect seems apparent. These two additional frameworks help remove some of the remaining roadblocks to the widespread adoption of the lean canvas methodology as a replacement for traditional business plans.
Douglas Mark
While a partner in a San Francisco marketing and design firm, for over 20 years Douglas Mark wrote online and print content for the world’s biggest brands , including United Airlines, Union Bank, Ziff Davis, Sebastiani, and AT&T. Since his first magazine article appeared in MacUser in 1995, he’s also written on finance and graduate business education in addition to mobile online devices, apps, and technology. Doug graduated in the top 1 percent of his class with a business administration degree from the University of Illinois and studied computer science at Stanford University.
Related Programs
- 1 MBA in Sales & Sales Leadership 2">
- 2 AACSB-Accredited Online MBA Programs 1">
- 3 MBA in Data Analytics & Business Intelligence 1">
- 4 MBA in Digital Marketing & Social Media 1">
- 5 MBA in Economics 1">
- 6 MBA in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) 1">
- 7 MBA in Entrepreneurship 1">
Related FAQs
- 1 How Do I Become a Construction Manager?
- 2 How Do I Become a Supply Chain Manager?
- 3 How Do I Secure an MBA Internship?
- 4 What Can I Do with an MBA Degree?
- 5 What is the Best MBA Program for Creatives & Designers?
- 6 Finance vs. Accounting vs. Taxation Programs
- 7 How Do I Become a Certified Business Process Professional (CBPP)?
Related Posts
Guide to mba careers – business administration career paths.
Over the last couple of years, the technology industry has begun to chip away at the share of MBA graduates joining the finance world, and more specifically, investment banking. Some studies even suggest that tech has already, or soon will, become the top recruiter of MBA graduates.
List of MBA Associations and Organizations (2024)
Students should not limit themselves by relying exclusively on their school’s clubs for networking opportunities. Compelling arguments exist for joining local chapters of global, national, and regional professional organizations while students are still in business school.
MBA Alternatives: Business Fundamental MOOCs (DIY MBA)
Through MOOCs, outstanding coverage of MBA core topics is available online from some of the best business schools in the world.
MBA Salary Guide: Starting Salaries & Highest Paying MBA Concentrations (2023)
Specializations amount to critical choices in an MBA student’s career. They permit students to immediately deliver highly marketable skills to an employer upon graduation, the value for which most employers will gladly pay handsome salaries.
Best Business Schools for Environmentalists (2023-2024)
Five business schools, in particular, are outstanding for environmentalists: the Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s MIT Sloan School of Management, University of Vermont’s Grossman School of Business, Georgia Institute of Technology’s Scheller College of Business, Fordham University’s Gabelli School of Business, and the University of California at Berkeley’s Haas School of Business.
List of MBA Conferences for 2023-2024
MBA fairs are all about personal connections. School gatekeepers travel to these events to meet well-qualified applicants. Moreover, the savviest candidates understand that connecting in a personal way with a school's admissions team can award those applicants with their most critical advantage in the admissions process: a great lasting impression.
Harvard Professor Sues University for Defamation Over Misconduct Allegations
A superstar Harvard Business School professor accused of research misconduct has filed a defamation lawsuit against Harvard University, the school’s dean, and the three blog authors who levied the allegations. Tenured faculty member Dr. Francesca Gino—a famous leadership expert and author of two books plus more than 100 scholarly research papers—filed the suit in the U.S. District Court for the District of Massachusetts on August 2 after HBS had placed her on administrative leave.

Deconstruct Your Big Idea on 1-Page
Business plans take too long to write, are seldom updated, and almost never read by others. You need dynamic models, not static plans, when going fast and under extreme uncertainty. The Lean Canvas replaces long and boring business plans with a 1-page business model that takes 20 minutes to create and gets read.

Lean Canvas is used by over a million people that span startups, universities, and large enterprises.

What is a Lean Canvas?
Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan template created by Ash Maurya that helps you deconstruct your idea using twelve business modeling building blocks.
A Lean Canvas can describe a business model, a product release, or even a single feature, making it a highly popular business model innovation and product management tool used by millions worldwide.
If you have ever written a business plan or created a slide deck for investors, you’ll immediately recognize most of the building blocks on the canvas.

Lean Canvas helps you communicate your idea clearly and concisely to key stakeholders.
You can outline multiple business models on a Lean Canvas in one afternoon instead of writing a business plan, which can take several weeks or months. More importantly, a single-page business model is much easier to share with others, so it will be read by more people and updated more frequently.
Lean Canvas helps you systematically build and launch successful products.
When taking on a complex project, like, say, building a house, you wouldn’t start by putting up walls. You’d probably start with an architectural plan or blueprint — even if it’s just a sketch.
Building and launching an idea is no different.
Most entrepreneurs start with a strong initial vision and a Plan A to realize that vision. Unfortunately, most Plan As don’t work.
It has statistically been shown that two-thirds of successful startups report drastically changing (or pivoting) their plans along the way.
So, what separates successful startups then isn’t necessarily starting with a better initial plan (or Plan A) but finding a plan that works before running out of resources .
Until now, finding this better Plan B or C or Z has been based largely on gut, intuition, and luck. There has been no systematic process for rigorously stress testing a Plan A.
The first step to iterating your Plan A is gaining clarity on your Plan A.
This is what the Lean Canvas helps you do.
What is the difference between Lean Canvas and Business Model Canvas?
Lean Canvas was adapted from Alex Osterwalder's Business Model Canvas and optimized for the Lean Startup methodology.
The motivation behind Lean Canvas was creating a more founder-focused business modeling tool better suited for early-stage products.
It replaces these boxes on the Business Model Canvas: key partners, key resources, key activities, and customer relationships with these boxes: problem, solution, key metrics (KPIs), and unfair advantage (a defensible competitive advantage).

See what's different
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Free Business Plan Template for Small Businesses (2024)
Use this free business plan template to write your business plan quickly and efficiently.
A good business plan is essential to successfully starting your business — and the easiest way to simplify the work of writing a business plan is to start with a business plan template.
You’re already investing time and energy in refining your business model and planning your launch—there’s no need to reinvent the wheel when it comes to writing a business plan. Instead, to help build a complete and effective plan, lean on time-tested structures created by other entrepreneurs and startups.
Ahead, learn what it takes to create a solid business plan and download Shopify's free business plan template to get started on your dream today.
What this free business plan template includes
- Executive summary
- Company overview
- Products or services offered
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financial plan
This business plan outline is designed to ensure you’re thinking through all of the important facets of starting a new business. It’s intended to help new business owners and entrepreneurs consider the full scope of running a business and identify functional areas they may not have considered or where they may need to level up their skills as they grow.
That said, it may not include the specific details or structure preferred by a potential investor or lender. If your goal with a business plan is to secure funding , check with your target organizations—typically banks or investors—to see if they have business plan templates you can follow to maximize your chances of success.
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format:
1. Executive summary
This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business objectives and strategy, and other background information about the brand.
2. Company overview
This section of your business plan will answer two fundamental questions: “Who are you?” and “What do you plan to do?” Answering these questions clarifies why your company exists, what sets it apart from others, and why it’s a good investment opportunity. This section will detail the reasons for your business’s existence, its goals, and its guiding principles.
3. Products or services offered
What you sell and the most important features of your products or services. It also includes any plans for intellectual property, like patent filings or copyright. If you do market research for new product lines, it will show up in this section of your business plan.
4. Market analysis
This section includes everything from estimated market size to your target markets and competitive advantage. It’ll include a competitive analysis of your industry to address competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Market research is an important part of ensuring you have a viable idea.
5. Marketing plan
How you intend to get the word out about your business, and what strategic decisions you’ve made about things like your pricing strategy. It also covers potential customers’ demographics, your sales plan, and your metrics and milestones for success.
6. Logistics and operations plan
Everything that needs to happen to turn your raw materials into products and get them into the hands of your customers.
7. Financial plan
It’s important to include a look at your financial projections, including both revenue and expense projections. This section includes templates for three key financial statements: an income statement, a balance sheet, and a cash-flow statement . You can also include whether or not you need a business loan and how much you’ll need.
Business plan examples
What do financial projections look like on paper? How do you write an executive summary? What should your company description include? Business plan examples can help answer some of these questions and transform your business idea into an actionable plan.
Professional business plan example
Inside our template, we’ve filled out a sample business plan featuring a fictional ecommerce business .
The sample is set up to help you get a sense of each section and understand how they apply to the planning and evaluation stages of a business plan. If you’re looking for funding, this example won’t be a complete or formal look at business plans, but it will give you a great place to start and notes about where to expand.

Lean business plan example
A lean business plan format is a shortened version of your more detailed business plan. It’s helpful when modifying your plan for a specific audience, like investors or new hires.
Also known as a one-page business plan, it includes only the most important, need-to-know information, such as:
- Company description
- Key members of your team
- Customer segments
💡 Tip: For a step-by-step guide to creating a lean business plan (including a sample business plan), read our guide on how to create a lean business plan .

Benefits of writing a solid business plan
It’s tempting to dive right into execution when you’re excited about a new business or side project, but taking the time to write a thorough business plan and get your thoughts on paper allows you to do a number of beneficial things:
- Test the viability of your business idea. Whether you’ve got one business idea or many, business plans can make an idea more tangible, helping you see if it’s truly viable and ensure you’ve found a target market.
- Plan for your next phase. Whether your goal is to start a new business or scale an existing business to the next level, a business plan can help you understand what needs to happen and identify gaps to address.
- Clarify marketing strategy, goals, and tactics. Writing a business plan can show you the actionable next steps to take on a big, abstract idea. It can also help you narrow your strategy and identify clear-cut tactics that will support it.
- Scope the necessary work. Without a concrete plan, cost overruns and delays are all but certain. A business plan can help you see the full scope of work to be done and adjust your investment of time and money accordingly.
- Hire and build partnerships. When you need buy-in from potential employees and business partners, especially in the early stages of your business, a clearly written business plan is one of the best tools at your disposal. A business plan provides a refined look at your goals for the business, letting partners judge for themselves whether or not they agree with your vision.
- Secure funds. Seeking financing for your business—whether from venture capital, financial institutions, or Shopify Capital —is one of the most common reasons to create a business plan.
Why you should you use a template for a business plan
A business plan can be as informal or formal as your situation calls for, but even if you’re a fan of the back-of-the-napkin approach to planning, there are some key benefits to starting your plan from an existing outline or simple business plan template.
No blank-page paralysis
A blank page can be intimidating to even the most seasoned writers. Using an established business planning process and template can help you get past the inertia of starting your business plan, and it allows you to skip the work of building an outline from scratch. You can always adjust a template to suit your needs.
Guidance on what to include in each section
If you’ve never sat through a business class, you might never have created a SWOT analysis or financial projections. Templates that offer guidance—in plain language—about how to fill in each section can help you navigate sometimes-daunting business jargon and create a complete and effective plan.
Knowing you’ve considered every section
In some cases, you may not need to complete every section of a startup business plan template, but its initial structure shows you you’re choosing to omit a section as opposed to forgetting to include it in the first place.
Tips for creating a successful business plan
There are some high-level strategic guidelines beyond the advice included in this free business plan template that can help you write an effective, complete plan while minimizing busywork.
Understand the audience for your plan
If you’re writing a business plan for yourself in order to get clarity on your ideas and your industry as a whole, you may not need to include the same level of detail or polish you would with a business plan you want to send to potential investors. Knowing who will read your plan will help you decide how much time to spend on it.
Know your goals
Understanding the goals of your plan can help you set the right scope. If your goal is to use the plan as a roadmap for growth, you may invest more time in it than if your goal is to understand the competitive landscape of a new industry.
Take it step by step
Writing a 10- to 15-page document can feel daunting, so try to tackle one section at a time. Select a couple of sections you feel most confident writing and start there—you can start on the next few sections once those are complete. Jot down bullet-point notes in each section before you start writing to organize your thoughts and streamline the writing process.
Maximize your business planning efforts
Planning is key to the financial success of any type of business , whether you’re a startup, non-profit, or corporation.
To make sure your efforts are focused on the highest-value parts of your own business planning, like clarifying your goals, setting a strategy, and understanding the target market and competitive landscape, lean on a business plan outline to handle the structure and format for you. Even if you eventually omit sections, you’ll save yourself time and energy by starting with a framework already in place.
- How to Start an Online Boutique- A Complete Playbook
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- 6 Creative Ways to Start a Business With No Money in 2024
- What is Shopify and How Does it Work?
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- How to Price Your Products in 3 Simple Steps
- 10 Common Small Business Mistakes to Avoid
- How to Turn a Hobby into a Business in 8 Steps
Business plan template FAQ
What is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of your business plan is to describe a new business opportunity or an existing one. It clarifies the business strategy, marketing plan, financial forecasts, potential providers, and more information about the company.
How do I write a simple business plan?
- Choose a business plan format, such as a traditional or a one-page business plan.
- Find a business plan template.
- Read through a business plan sample.
- Fill in the sections of your business plan.
What is the best business plan template?
If you need help writing a business plan, Shopify’s template is one of the most beginner-friendly options you’ll find. It’s comprehensive, well-written, and helps you fill out every section.
What are the 5 essential parts of a business plan?
The five essential parts of a traditional business plan include:
- Executive summary: This is a brief overview of the business plan, summarizing the key points and highlighting the main points of the plan.
- Business description: This section outlines the business concept and how it will be executed.
- Market analysis: This section provides an in-depth look at the target market and how the business will compete in the marketplace.
- Financial plan: This section details the financial projections for the business, including sales forecasts, capital requirements, and a break-even analysis.
- Management and organization: This section describes the management team and the organizational structure of the business.
Are there any free business plan templates?
There are several free templates for business plans for small business owners available online, including Shopify’s own version. Download a copy for your business.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Jun 9, 2024
Jun 8, 2024
Jun 7, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
- Agile project management
- Lean Methodology
What is Lean methodology?
Browse topics.
Like NASA mission control specialists, project managers must track numerous aspects to ensure their team delivers projects without incident. But while NASA manages spacecraft, project managers monitor deliverables.
Lean methodologies can help prevent project management disasters akin to the Apollo 13 catastrophe, allowing you to deliver projects on time and within budget.
Lean methodology facilitates an ongoing process of incremental adjustment, significantly accelerating product delivery by optimizing resources and effort and allowing teams to work efficiently and effectively.
In this article, you will learn more about Lean methodology, its benefits, and how Jira can help your software team implement its principles.
History of Lean methodology
Lean methodology aims to fully optimize your team’s process and output through continuous improvements. When done well, Lean allows teams to deliver customer value efficiently.
Toyota Founder Kiichiro Toyoda developed the Lean methodology after World War II to conserve resources and eliminate waste. After observing the purchasing and restocking of items at a supermarket, he conceived the just-in-time concept, which focuses on making products exactly when customers need them.
Toyoda's concept morphed into the Toyota Production System , which eventually became the Lean methodology. From these small beginnings, Lean evolved into the foundation of Agile project management —several industries, including software development, construction, and healthcare, now use Lean methodology.
Overview of Lean methodology
Lean methodology rests on two pillars that provide a framework for all Lean projects: Continuous improvement and respect for people.
- Continuous improvement : An ongoing feedback loop helps teams make progressive changes to processes, products, and personnel to improve systems continuously. By identifying, evaluating, and modifying existing processes or systems – one cog at a time – teams can eliminate waste and improve efficiency on the whole.
- Respect : Managers recognize the value of team contributions and customer feedback, and take those insights and ideas seriously. Lean managers distribute work throughout the workflow in the most efficient manner to encourage close collaboration and maximize value to customers.
The core principles of Lean methodology have been developed with both of these factors.
Principles of Lean methodology
It’s essential to consider the impact your work will have on the customer experience. Lean’s five core principles help teams organize tasks and provide project managers with oversight. These five core principles include:
1. Identify value
To deliver value to your customers, you must first understand their needs. You can do this by:
- Engaging directly with customers to learn about their pain points.
- Identifying how your product helps mitigate those pain points.
Next, you need to define your product’s value in meeting customer needs and communicate this with your team. You can do this by framing the team’s work around how it impacts the customer experience and researching the best tools to help your team deliver value to your customers.
Identifying value saves time and money by ensuring your team builds only features that add value for your customers.
2. Map the value stream
The activities needed to deliver quality customer experiences form part of the value stream. Value stream mapping uses diagrams to help visualize the project process, aiding in value stream management , which is critical to eliminating waste.
Value stream mapping involves the following activities:
- Identify the problem and choose the right team : Identify your customers’ main pain points, and then choose a team with the skills to solve these problems.
- Bound and map the process : Limit the project's scope to necessary activities. You can then map the process using the Scrum board template in Jira and set dates for each deliverable.
- Collect data : Understand what resources are needed by tracking data such as the hours the team spends working on the project.
- Assess and adjust : To ensure continuous process improvement, constantly assess processes and ask the question, “Is there a better way to do this?”
3. Create a flow
A flow state is when the team is in a groove and work is moving smoothly, so much so that we don’t notice the passage of time. Creating a flow state increases team engagement and performance.
Team flow reflects the efficiency of the value stream, which you can continuously fine-tune using the ongoing feedback loop. Lean methodology requires a smooth and continuous flow to reduce delays and minimize handoff times.
“When implementing Lean, focus on flow,” says Atlassian’s Modern Work Coach Mark Cruth. “Flow is at the center of each element of Lean, whether it’s reducing waste, eliminating silos, or continuously improving…all elements come back to flow!”
You can improve your team’s flow by implementing the following:
- Cross-functional collaboration : Silos are the kryptonite of Lean. Your team should participate in the entire process and collaborate with other teams, if necessary, to accomplish their tasks. For example, this might involve looping in customer success teams and getting their input on customer pain points. Moreover, your team can deepen their knowledge of how other departments operate.
Task tracking : Kanban boards , or the Kanban template in Jira, can help you assign tasks, visualize work, and coordinate your team. These cards help teams track the progress of tasks throughout the project lifecycle .
4. Establish pull
With a pull system, teams only work on what the customer needs when they need it, producing according to actual customer demand, not forecasted projections.
To accurately assess customer needs, the team must talk to customers and seek their input.
5. Seek perfection
Lean requires a growth mindset and strives for perfection through continuous improvement, using an ongoing feedback loop to help the project manager, team, and company reduce waste and enhance efficiency.
Benefits of Lean methodology
As a project manager, you’ve probably encountered a project hiccup or two, such as waiting for stakeholder feedback. If the feedback comes too late, the entire project stalls. Lean methodology has many benefits that alleviate such roadblocks, such as:
- Increased efficiency : By mapping the value stream, you can center work around customer needs, eliminating unnecessary work on products and services customers do not want.
- Fewer issues : Lean mitigates issues, such as lack of communication and unrealistic deadlines, before they become larger problems. In the case of communication, Lean provides tracking and transparency so everyone is clear on tasks, responsibilities, and deadlines. Since the team participates more closely in the process, they can also push back on any unreasonable timelines.
- Reduced costs : By creating a clear plan and eliminating roadblocks, you can save money by producing just enough to meet customer demand. That way, you’re not producing more stock than necessary, which is especially important for physical products.
- Improved customer relationships : By focusing on customer value, you create stronger customer relationships, which is crucial to a business.
- Continuous improvement : Lean’s ongoing feedback loop helps refine and continually improve processes to deliver value efficiently.
- Team investment : Because Lean requires more involvement upfront from your team, they’ll be more engaged with the outcome. They’ll have a say on what they’re working on and when they expect to complete it. An empowered team is an engaged one.
Potential challenges of Lean methodology
Despite its numerous benefits, practicing Lean may present some challenges that project managers should recognize and learn to overcome. These challenges include:
- Fix : Get the team’s buy-in as early as possible and show them how Lean can help.
- Fix : When onboarding the team, provide adequate training in Lean methodology. You can enroll your team in a Lean certification program that will provide hands-on training. With a certification, you’ll be confident that they have the proper knowledge of Lean methods.
Focus on tools rather than culture : Putting tools before people decreases team engagement. An emphasis on tools in Lean may dehumanize and devalue your team and their work. When a team doesn’t feel valued, they’re less likely to give their best.
Fix : Build a culture of trust using Lean's philosophy of continuous improvement . Providing continuous feedback and opportunities for growth shows that you, as a manager, are interested in your team’s career development.
- Fix : Pay attention to the metrics to measure project success and look for improvement areas to develop your team.
Use Jira for project management
Lean accelerates your project management and keeps team agile by eliminating waste and continually streamlining processes.
Jira can help software teams stay lean and deliver more customer value. Contextual insights empower teams to build and train muscles to continuously learn and improve their way of working. Scrum and Kanban boards give your team full visibility into what’s next so you can continuously deliver maximum output in minimal time. With Jira as the backbone of collaboration, all teams can stay in lockstep with each other and the rest of the organization.
Jira also enables enterprises to visualize value streams. With this, your enterprise can:
- Set up process flow automation . Give your teams time back and reduce manual work with Jira’s powerful automation engine.Align work with business needs. See how day-to-day work ladders up to the strategic objectives and keeps important stakeholders informed with ready-made agile reports.
- Track investments . Understand what resources are being used and the time invested in any project so you can allocate efforts appropriate for the next.
- Uncover roadblocks . Identify potential roadblocks and prevent them before they happen.
- Deliver continuous value . With more clarity and insight, your team will be able to consistently deliver value to customers and the company as a whole.
This solution also works well for other methods such as Agile, Open DevOps , and value stream management.
Lean methodology: frequently asked questions
What is the difference between agile and lean.
At first glance, it seems challenging to distinguish between Lean methodology vs. Agile. While both focus on efficiency and customer value, they emphasize different aspects of project management. Lean focuses on waste elimination, process, and delivering value, whereas Agile focuses on customers, mitigating uncertainty, and delivering working software.
Let’s break that down:
- Focus : As a top-down approach, Lean is concerned with process improvements. However, Agile is a bottom-up approach where work is broken down into smaller iteration loops.
- Product delivery : Both Lean and Agile teams work fast to deliver products as soon as possible. However, Agile is less concerned with speed than it is with feedback. So Agile teams build smaller, get feedback, and iterate. Lean is focused on improving the overall process to deliver faster.
- Frameworks : Lean doesn't have specific frameworks, whereas Agile does. Scrum and Kanban are two Agile project management frameworks that allow you to apply Agile principles. Jira offers a Scrum template and a Kanban template to help project managers get started with the Agile methodology.
What is the difference between DevOps and Lean?
DevOps creates functional collaboration between development and operational teams, allowing for faster software delivery. This is the core philosophy of DevOps: Continually deliver value to the business through a culture of understanding and collaboration.
In contrast, Lean’s core philosophy is to deliver value through process improvements and waste elimination.
Lean and DevOps are customer-centric methodologies, but they differ in two main areas:
- Customer value: DevOps creates customer empathy image maps, framing business goals into customer value. Lean chooses customer value activities based on need.
- Focus : DevOps integrates development and operations with documentation and collaboration. Lean optimizes processes, resources, and effort.
In addition, DevOps automates mundane tasks, such as pull requests—which the DevOps beginner's guide delves more deeply into.
If you already use DevOps, Open DevOps —an out-of-the-box DevOps foundation powered by Jira with an open-tool approach and automation—can help your Agile team focus on shipping and operating quality software and ensure the "you build it, you run it" practice associated with DevOps principles.
Can you use Agile, Lean, and DevOps at the same time?
Yes! These methodologies complement each other in their aim to deliver quality and value to customers. DevOps breaks down silos to integrate the development and operations teams. Agile encourages continuous improvement. Lean puts continuous improvement ideals into practice.
Using all three can speed up product delivery and customer value. For example, your company might be using all three but not in concert. Lean can help improve your Agile process. And Agile’s iterative approach can help with Lean’s continuous improvement. With DevOps, you can improve your cross-collaboration.
Using all three, your company would become a powerhouse, delivering customer value through more efficient practices.
You can connect these methodologies using Atlassian’s suite of project management tools.
Lean principles: advancing DevOps efficiency
Explore the power of Lean Principles and DevOps in streamlining project management, enhancing efficiency, and delivering value faster.
Lean Process Improvement [What is it & How to Implement]
Eliminate waste with lean process improvement. Explore how lean process improvement techniques can work with other principles for better project management
JavaScript is disabled in your browser. To view the website properly, please enable JavaScript in your browser settings and refresh the page.
Apply for and manage a grant or program for your business.
Manage your interactions with the R&D Tax Incentive program.
- Business plans
Develop your business plan
On this page
Why you need a business plan
Use our business plan tool, download a detailed business plan template, tips to help you write your business plan.
Whether you've just started out or have been running your business for years, business planning can be the key to your success. Having a business plan:
- helps you to prioritise – it gives your business direction, defines your objectives, maps out how you'll achieve your goals and helps you to manage possible bumps in the road
- gives you control over your business – the planning process helps you learn about the different things that could affect your success. If you're already in business, it helps you to step back and look at what's working and what you can improve on
- helps you seek finance – if you're seeking finance for your business, you'll need to show banks and investors why they should invest in your business.
It will help you to develop a shorter business plan to:
- evaluate a new business idea
- set some goals for the year ahead
- keep your business on track.
Use this template if you are seeking finance for your business or want to include more detail in your business plan.
Business plan template
1. Determine what your plan is for
Does your business plan have more than one purpose? Will you use it internally, or will you share it externally, for example with potential investors or banks?
Deciding what the purpose is, can help you develop your plan for the right audience. If the plan has been developed for third parties, you will need to determine what they’ll be most interested in.
2. Prepare your finances
Use our detailed business plan template if you are seeking finance.
Lenders and investors will want to know if your finances are in order and your business is in a strong financial position. They'll want to know how much money you currently have, how much money you need and how much you expect to make in the near future. While a bit of extra funding will help you ensure you’re covered for unexpected costs, be realistic and avoid asking for more than you need.
If you're starting out and don't have financial information yet, our template provides resources to help you get your finances ready.
3. Write your summary last
Summarise the main points of your business plan using as few words as possible. You want to get to the point but not overlook important facts. This is your opportunity to sell yourself, but don't overdo it. The summary should include details about your business, market, goals and what makes you different from other businesses.
4. Get help
Don't leave your business plan to the last minute. It takes time, research and careful preparation to develop an effective business plan.
If you aren't confident in completing the plan yourself, consider getting a professional to look over it and provide advice.
There are a number of government services available to help you plan, start or grow your business. These services can provide general advice, workshops, seminars and networking events, and can even match you with a mentor or business coach.
Get expert help from a business adviser in your area .
5. Review your plan regularly
As your business changes, your plan will need to change to ensure your business is still heading in the right direction. Having your plan up-to-date can keep you focused on where you are heading.
It's a good idea to keep a record of each version of your business plan.
6. Protect your plan
Having an understanding with third parties when distributing a plan could be enough protection for some businesses. But if you have innovative business practices, products or services, you may want people to sign a confidentiality agreement to protect your innovations.
It may also be a good idea to include some words in your plan asking the reader not to disclose the details of your plan.
Start writing and developing your marketing strategy.
Find out what you need to register for when starting a business., was this page helpful, thanks for sharing your feedback with us..
Our live chat service is open from 8am - 8pm, Monday to Friday, across Australia (excluding national public holidays ).
Learn about the other ways you can contact us .
All our experts are busy now. Please try again later or contact us another way
We're open from 8am - 8pm, Monday to Friday, across Australia (excluding national public holidays ).
We use cookies to give you a better experience on our website. Learn more about how we use cookies and how you can select your preferences.

Despite AI enthusiasm, Workforce Index reveals workers aren’t yet unlocking its benefits
By the team at Slack June 3rd, 2024
Quick take: Using AI tools at work is associated with a host of positive outcomes, from improved productivity to higher employee satisfaction. But executive urgency to incorporate AI is outpacing its use among employees. A new global survey of desk workers from the Workforce Lab at Slack, a Salesforce company, finds that two-thirds of workers have still not tried AI tools and 93% do not consider AI outputs completely trustworthy for work-related tasks.
Read on to learn about the top AI blockers for workers, the surprising AI gender gap emerging among Gen Z, and why we believe the AI hype cycle is just beginning.
Key findings
- Executive urgency to incorporate AI tools into business operations has increased 7x over the past six months and is now a top concern, above inflation or the broader economy.
- Among desk workers who use AI tools, 81% say it’s improving their productivity. And those who use AI show higher employee engagement and experience scores across the board, including 22% higher overall satisfaction.
- And yet more than two-thirds of desk workers have never used AI at work, and nearly 2 in 5 say their company has no AI usage guidelines.
- Just 7% of desk workers consider the outputs of AI completely trustworthy for work-related tasks , with 35% of desk workers saying AI results are only slightly or not at all trustworthy.
- There’s an AI gender gap emerging, and it’s largest among Gen Z. While young people are most likely to have experimented with AI tools, Gen Z men are 25% more likely to have tried AI tools compared with Gen Z women.
- Desk workers report spending a third of their day on average on tasks they consider low-value. But troublingly, instead of allocating the time saved by AI toward strategic or high-value activities like learning and skill building, employees are likely to spend 37% more of their time on routine administrative tasks.
- Even so, the AI hype cycle shows no signs of slowing. Seventy-three percent of desk workers say that AI hype is warranted and the technology “will have a big impact,” and those who have used AI tools are even more convinced.

See the data: June 2024 Workforce Index
In its latest survey of more than 10,000 desk workers around the globe, the Workforce Lab from Slack, a Salesforce company, finds that nearly all executives (96%) now feel an urgency to incorporate AI into business operations. The share of leaders aiming to do this “in the next 18 months” has grown 7x since September 2023, rising from 5% to 35% of all executives. And AI innovation now tops the list of executives ’ external concerns, above inflation or the broader economy.
At the same time, AI use among desk workers is up 23% since January and 60% since September. Thirty-two percent of desk workers have now experimented with AI tools and half of that group is using AI at work at least weekly.
Most AI users (81%) report that AI tools are improving their productivity. And notably, those using AI show higher scores across the board on all measures of employee engagement and experience, including:
- +13% Level of access to relevant people, files and resources
- +18% Work-life balance
- +23% Ability to manage stress
- +24% Overall satisfaction with work
- +25% Flexibility
- +29% more likely to say they feel highly passionate about their work

“The data shows that employees using AI are having an all-around markedly better time on the job. They’re not just more productive; they’re experiencing greater excitement, fulfillment and pride in their work,” says Christina Janzer, head of the Workforce Lab. “Leaders should take note that using AI at work is correlated with a host of positive associations.”
That said, the data also shows that there’s a gap between executives’ urgency to incorporate AI tools and actual AI use among employees: the majority of desk workers —more than two-thirds—have still not tried AI for work.
So what’s stopping more employees from experimenting with AI tools? Concerns about privacy and data security followed by mistrust of data quality and accuracy top the list of blockers that desk workers cite as limiting factors. Just 7% of desk workers consider the outputs of AI completely trustworthy for work-related tasks, with 35% of desk workers saying AI results are only slightly or not at all trustworthy.
“Companies have urgent, ambitious goals for AI in the enterprise and our research shows there are huge productivity benefits to be gained—but many leaders are still figuring out how to kickstart adoption among employees,” says Denise Dresser, CEO of Slack. “While this is truly a seismic shift in the future of work, there are simple steps every business can take starting today to help onboard employees on AI while maintaining trust.”
What should leaders do to encourage uptake? The PET plan: Permission, education, training
Step one to boost workplace AI use is to clarify permission by establishing clear usage guidelines. This may sound obvious, yet nearly 2 in 5 desk workers (37%) say their company has no AI policy. Desk workers at companies that have established permissions for AI use are nearly 6x as likely to have experimented with AI tools.
The next step is education and training . Only a small percentage of global desk workers (15%) strongly agree that they have the education and training necessary to use AI effectively. Unsurprisingly, the more training and education workers have, the more likely they are to use AI tools, and those who are trained to use AI are up to 19x as likely to report that AI is improving their productivity.

Education and training are fundamental to building trust in AI tools; desk workers who are well trained in AI are 7x as likely to trust AI tools to assist them with work-related tasks compared with desk workers lacking AI training.
Another significant factor in a desk worker’s likelihood to try AI and to consider it trustworthy is whether that worker feels their manager trusts them as an employee. Desk workers who feel trusted by their employers are 94% more likely to have tried AI for work-related tasks, and they’re also more trusting of AI’s accuracy and reliability.
Forecasting the AI future: Three predictions for leaders
The ai hype cycle is far from peaking—it’s just gearing up..
You might think AI couldn’t possibly garner more hype. But sentiment from global desk workers indicates the buzz is just getting started. Today, 47% of global desk workers express enthusiasm for AI to handle tasks from their job (compared with 42% at the start of the year). The majority of desk workers—73%—believe the fanfare around AI is justified, saying they expect it to have a substantial impact on their work lives. This sentiment is even stronger among those who have firsthand experience using AI tools.
This trend is set to intensify as Gen Z and Gen Alpha enter the workforce. The youngest workers show the most enthusiasm for AI, with 55% of workers ages 18 to 29 saying they’re excited for AI and automation to handle parts of their work, compared with 33% of workers over age 60.
Our take: “AI fervor shows no signs of stopping,” says Nathalie Scardino, Salesforce’s Chief People Officer. “At Salesforce, we’ve seen how integrating AI into our workforce strategies can have massive benefits for employees and companies alike. Freeing up employees to focus on more impactful work is good for morale and for business.”
Mind the gap: AI could further marginalize women in the workforce—or give them a competitive edge.
There remains a small but stubborn gender gap in AI uptake, with more men trying AI for work (35% of respondents) compared with women (29% of respondents). Even though younger workers are most likely to have experimented with AI tools, the AI gender gap is largest among Gen Z, with men ages 18 to 29 25% more likely to have tried AI tools compared with women in the same age group.
One bright spot is that AI use is accelerating at a faster clip among workers of color, with 43% of Hispanic/Latinx desk workers, 42% of Black desk workers and 36% of Asian American desk workers having tried AI tools at work, compared with 29% of white desk workers. And there’s little to no gender gap among Hispanic/Latinx or Asian American employees.
Our take: “As we embrace our future with AI, it’s imperative that we continue to provide access to those who have historically been left out of technology shifts,” says Alexandra Legend Siegel, Salesforce’s Chief Equality Officer. “It is encouraging to see some of the findings on workplace AI tools and we’re committed to continuing to upskill and empower every community to leverage this technology for good in their workplace, careers and lives.”

AI is at risk of increasing busywork rather than reducing it.
AI promises to transform our work lives, and the latest Workforce Index survey shows there’s room for improvement: the majority of desk workers (64%) experience burnout once a month or more, about a third say they regularly feel stress about work, and 30% do not feel passion for their job. At the same time, desk workers estimate they spend about a third of their day, on average, on tasks they consider “low-value” and “not meaningful to their job.”
The top three most commonly cited low-value tasks are unnecessary meetings or work events, managing low-value emails, and excessive paperwork or data entry. In a perfect world, we’d minimize these tasks with the help of AI, creating more time to focus on more meaningful work.
But when asked how they would prioritize the time they get back from AI, “more admin” topped the list, while innovating and creating, learning and skill-building, and networking with colleagues fell to the bottom.

Our take: “AI could really open up a lot of time for workers, but it would be a shame if we waste that time on more busywork,” says Janzer. “If we want to make the most of what AI can offer, it’s up to us as leaders to help our people prioritize the most rewarding work.”
AI fast facts

Methodology
The survey included 10,045 workers in the U.S., Australia, France, Germany, Japan and the U.K. between March 6 and March 22, 2024.
The survey was administered by Qualtrics and did not target Slack or Salesforce employees or customers. Respondents were all desk workers, defined as employed full-time (30 or more hours per week) and either having one of the roles listed below or saying they “work with data, analyze information or think creatively”: executive management (e.g. president/partner, CEO, CFO, C-suite), senior management (e.g. executive VP, senior VP), middle management (e.g. department/group manager, VP), junior management (e.g. manager, team leader), senior staff (i.e. non-management), skilled office worker (e.g. analyst, graphic designer).
For brevity, we refer to the survey population as “desk-based” or “desk workers.”
Was this post useful?
Thanks so much for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback.
Oops! We're having trouble. Please try again later!
Try Slack with your team for free
- Best for customer satisfaction
- Best for older adults
- Best for long-term care
- Best for high returns
- Best for agent support
- Best for term life
- Why you should trust us
Best Life Insurance of June 2024
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate insurance products to write unbiased product reviews.
Life insurance is as complicated as the policyholders and beneficiaries who use it. That means there's no single "best" life insurance company. Instead, you can find the best option based on what you want or what you prioritize.
Summary of the Best Life Insurance Companies
- Best for customer satisfaction: State Farm Life Insurance
- Best for older adults: Prudential Life Insurance
- Best for agent support: New York Life Insurance
- Best for long-term care: Columbus Life
- Best for high returns: Allianz Life
- Best for term life: North American Company
Best Life Insurance Companies of 2024
While there is no such thing as the objective best life insurance policy, you will be able to find the best insurance policy for your specific needs. Here are our picks for the best life insurance companies, whether you want to use your life insurance policy to build wealth through cash value or you're just looking for a term life insurance policy .
Best Life Insurance for Customer Satisfaction: State Farm Life Insurance
Bundling is standard, and agents often quote with multiple discounts.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Best in JD Power customer service ratings
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Company offers a range of different insurance products to meet buyer needs
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Agents are knowledgeable about its products
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Life insurance products are conservative and limited
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Buyers may be subject to multi-year waiting periods before they qualify for full payouts on life insurance policies
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. State Farm agents cannot offer alternative options if State Farm is unable to bind a life insurance policy
State Farm is one of the insurance industry's most prominent insurers offering auto, home, and other insurance. Bundling is standard, and agents often quote with multiple discounts. Its term, universal, and whole life insurance products are no exception.
- Life insurance products include term and permanent life
- Ranks highly for customer satisfaction
State Farm Life Insurance gets the best life insurance ranking in J.D Power's Individual Life Insurance Study, with a score of 843/1,000. The company is also ranked A++ with AM Best for its financial stability with term, universal, and whole life insurance options.
All State Farm policies have to be purchased through a State Farm agent. Your agent can help you bundle and save or buy one policy. State Farm is also among the companies offering "survivorship universal life insurance ," which means the policy covers two people, and it kicks in after the second person dies. Couples looking to maximize their death benefit for beneficiaries with one premium payment each month may enjoy lower overall costs.
State Farm agents can run quotes and compare options to find the right plans for each applicant. The range of options, discounts, and familiar name all contribute to the popularity of State Farm's life insurance.
Read our State Farm Life Insurance review here.
Best Life Insurance for Older Adults: Prudential VUL Protector Life Insurance
Offers aggressive financial plans.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Available in all 50 states (New York residents may have different plans)
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Buyers can withdraw money to pay for nursing home bills due to severe illness or disability
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Knowledgeable agents who can walk you through your options
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Financial returns are limited
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Limited policy options for seniors and other groups who might struggle to find life insurance
The aggressive financial plans offered by Prudential may appeal to many younger buyers and those with a stable income. However, those with lower income or buyers who aren't sure about the financial system may be more hesitant to engage with Prudential. Like many other industry giants, Prudential is working to change this perception.
Prudential Life Insurance is available in all states except New York. New York residents can buy the Pruco Life of New Jersey VUL Protector plan. This plan allows buyers to pull money out of their plan to pay for nursing home expenses. Cash value policy premiums are fixed, so you won't have to worry about extra costs later on. Internal costs are low, which minimizes risk. Due to age, many older adults want a safe investment option for their money. Prudential VUL Protector invests to avoid loss. That also means you're not as likely to see big increases in your available funds outside of what you deposit.
Read our Prudential Life Insurance review here.
Best Life Insurance for Long-Term Care: Columbus Life Insurance
Offers lien method to makes it easier to calculate the financial impact of pulling money out early.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Buyers can pull money out for medical and other bills in the event of disease or disability
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Columbus uses lien method to simplify accelerated death payments
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Company offers a wide range of riders to customize policies
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Premiums may be higher than competitors
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Term policies are not guaranteed to be converted to whole
Best for long-term care and accelerated death benefits.
Columbus Life offers a wide range of riders to customize your policy with affordable premiums. The company also allows you to convert term policies to whole life insurance policies until the end of your term (generally around age 70). For this and many other reasons, customer satisfaction is high.
When using living health benefits (otherwise known as accelerated death benefits), buyers are allowed to pull money from policies early to pay for medical bills, living costs, etc. under certain circumstances. Most companies use a discounted death benefit, which reduces your final payout using two models. Columbus uses the lien method, which makes it easier to calculate the financial impact of pulling money out early.
Best Life Insurance for High Returns on Income: Allianz Life Insurance
Offers life insurance policies for foreign nationals with H-1B visas.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Plans offer high returns on investment
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Great for investment and long-term retirement planning
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. May increase your income by as much as 20%
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Allianz offers plans for foreign nationals including H-1B visas
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Plans are meant specifically for high-income adults, alternatives may not be offered
Best for investing and high returns on income.
Allianz Life plans are geared towards high-income adults looking for more tax-free income. Allianz offers a 40% multiplier bonus with a 1% annual assets charge. In short, the professionals managing your investments take 10%. Overall, your investments would pull in an extra 14%-1% asset charge. This means you end up with 3% more than what you deposit every year your life policy is active. This plan offers strong returns when using a life policy to supplement your retirement savings. Allianz also offers specialized plans to grow your income by as much as 20% according to some estimates.
Of note: Allianz also offers plans for foreign nationals, including those with H-1B visas.
Best Life Insurance for Agent Support: New York Life Insurance
Offers aggressive financial products and extensively trained agents.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Strong life insurance options for financial planning and wealth building
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Policies available nationwide
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Knowledgeable life insurance agents
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. May require a medical exam
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Buyers looking for more modest policies may not find the most competitive pricing
If you're preparing for a comfortable retirement or looking to build generational wealth, New York Life is one of the strongest options. If you have questions or genuinely want to understand your life insurance options, New York Life agents are among the most qualified professionals in the business.
- Life insurance provider with policies available across the US
New York Life Insurance agents go through extensive training before they ever hit the sales floor. What does this get you? Policies vary widely, and New York Life offers both large and small payouts. Some policies have significant penalties for early withdrawal, but taking a loan offers more options. Whatever your questions, New York Life agents are trained to offer comprehensive support giving you accurate information about its policies every time. The company comes in at position eight in J.D. Power's latest life insurance customer satisfaction study.
Read our New York Life Insurance review here.
Best Life Insurance for Term Life: North American Life Insurance
Offers term policies alongside accelerated death benefits for critical, chronic, and terminal illnesses and more.
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Offers accelerated death benefits for critical, chronic, and terminal illnesses
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Offers conversion for life policies up to 70 years old
- Check mark icon A check mark. It indicates a confirmation of your intended interaction. Term policies can be renewed up to age 95 for qualifying applicants
- con icon Two crossed lines that form an 'X'. Not all term policies qualify for renewal or conversion
Best Term Policy.
North American Company offers term policies alongside accelerated death benefits for critical, chronic, and terminal illnesses and more. The company allows one conversion on a 20-year policy at 15 years or 70 years old (whichever is earlier). The conversion cannot happen later than the five-year marker regardless of which policy you choose or the length. North American Company also offers a term policy with a lower premium renewable up to the age of 95 for qualifying insureds.
Types of Life Insurance
While there's many different types of life insurance policies , broadly speaking, there are two types of life insurance: temporary and permanent. Let's go over each in detail.
Temporary life insurance
Temporary life insurance is often called term life insurance. This type of policy covers you for a set amount of time before expiring, usually between 10-30 years. If you pass away after your policy expires, your family won't receive any benefits. Additionally, your policy won't accrue cash value like a permanent policy. That said, some term life insurance policies offer a conversion from term to whole life insurance, so you can extend your coverage.
Because its benefits aren't guaranteed, term life policies are generally cheaper than permanent life insurance. That said, the vast majority of term life insurance policies never pay out. on
Permanent life insurance
Permanent life insurance is an umbrella term for a variety of life insurance policies that will insure you indefinitely and guarantee a payout as long as you maintain your policy. Policy types that fall under permanent life insurance includes:
- Whole life insurance
- Universal life insurance
- Variable life insurance
- Variable universal life insurance
- Simplified life insurance
- Guaranteed issue life insurance
These policies vary widely in purpose and intended buyers, but all guarantee death benefits to your loved ones. Some permanent life insurance policies, like whole, universal, and variable have a cash value component , which you can use as a savings tool or to leave your heirs a larger death benefit.
How to Pick the Best Life Insurance Policy for You
Finding the right fit in life insurance starts with finding a trusted insurance agent. Because there are so many state regulations, shopping for homeowners or auto insurance can be easily done online. Life insurance is not required. So it's a voluntary purchase. Many buyers don't know what they need or when they need it. Before making your selection, consider a few things:
Some companies will sell you a policy for your child as soon as they're born. While this may seem morbid, early sign-up means lower rates for a policy your child could enjoy in the future. Regardless, early sign-up equates to more policy for lower premiums and a higher likelihood of acceptance. At 20, you may be healthier and be able to pay into the policy for a longer period compared to when you're 50 with more age-related conditions.
As a general rule, never agree to more than you can afford. For the average life insurance agent, their job is to sell you a large policy with a large commission. Consider not only how much you make now, but how likely your current income is to continue. If you work on a project basis and your project is scheduled to end in 12 months, you may want to reconsider a policy premium outside your monthly savings.
How much are you prepared to buy? Some people only want a small policy to cover funerals and other end-of-life expenses. Others build a life policy into their retirement plan. Whatever direction you're going, involving a financial planner could help you make the right decisions. Depending on the carrier, customers can also compare set limits with index universal life policies, which set no limit. These policies never expire, and the value builds over the entirety of your life.
Living Benefits
Life happens unexpectedly. You could be healthy one day and in the hospital the next. Many life policies offer living benefits. These allow you to draw a limited amount out of your policy to cover medical and other bills you cannot pay while sick.
Much like a 401(k), many life insurance policies have penalties for early withdrawal. No matter what policy you want, this question is critical to an informed decision. It's a question of how early you can withdraw and how much you'll lose from the total to have the money in 10 years instead of 30 or after death.
Some policies require insured parties to pay premiums for at least one year before any significant payout would be available. Suicide exclusions are common. Even with no medical exam policies, the company may still do a check for known conditions. An insurance company has to mitigate its risk.
Flexibility
Once you've been denied a life insurance policy, a mark goes on your record. No matter the reasons, other insurance companies may deny you coverage based on the first denial. So consider your whole situation and choose your policy carefully before you submit any applications. Some policies have greater flexibility if you lose your job or otherwise can't make payments. Others will lapse if you miss even one payment.
Payment Type
Even within whole life or term life insurance policies, customers have the option to choose guaranteed fixed or variable rates. Some have guaranteed payouts, but you'll need to ask your agent for details.
What is your intended use? Why are you shopping for a life insurance policy in the first place, and what are your goals? Many successful financial planners also have a background in life insurance. So while they may not be able to find you a specific life insurance policy, financial planners can help you set out a blueprint for your purchase.
Why You Should Trust Us: How We Reviewed the Best Life Insurance Companies
In life insurance, it's easy to get "sold a bill of goods." Many life insurance agents pass a state test to be thrown into the deep end. Agents sell the company product, but not all know the products. In this vein, we look at the products each company offers. We also look at agent training.
A good life insurance agent may not volunteer all facts upfront. But a company's agents should answer questions about its products accurately and in a way the average consumer can digest. Agents should be able to inform you about the long-term benefits and limitations. This will help customers find the right policy for their long-term plan.
We consider affordability, policy sizes available, and performance for a comprehensive assessment in our insurance rating methodology . If you can, we recommend also working with a financial advisor to make a plan for your future with life insurance.
Our Expert Panel for The Best Life Insurance Companies
To inform our choices for the best life insurance companies, we spoke with the following experts:
- Paul LaPiana , head of product at MassMutual
- Barbara Pietrangelo , CFP, CLU, and chair of the nonprofit Life Happens
- Wykeeta Peel , Corporate Vice President and Market Manager, African American Market Unit at New York Life
The Experts' Advice on Choosing The Best Life Insurance for You
How much life insurance coverage do you believe the average buyer should have.
Paul LaPiana, Head of Product at MassMutual
"There are different approaches to determining how much life insurance you need. One is the 'human life' approach, which estimates the current value of your future earning potential. Another is securing specific coverage to pay off debts such as a mortgage or provide for the education of children. A comprehensive protection plan should provide the right amount of coverage over the course of your working life and into retirement."
Barbara A. Pietrangelo, Chair of Life Happens
"There is no one-size-fits-all life insurance policy because everyone is different. One way to get a rough estimate is to multiply your income by 10 to 15; another is adding $100,00 to that amount, should you have a child and anticipate college education expenses.
Your best bet is to talk to a financial professional or use the Life Insurance Needs Calculator on LifeHappens.org to analyze what's right for you."
Wykeeta Peel, Corporate Vice President & Market Manager African American Market Unit at New York Life
"As you consider what policy best meets your needs, it can help to answer four key questions: First, how much death benefit do you need? Second, how long will you need that coverage? Third, what is your budget (or how much monthly premium can you afford to pay?), and finally, what is your investment risk tolerance?
To determine how much death benefit makes sense, it's helpful to think beyond using life insurance to cover funeral expenses and consider whether anyone is relying on the policy owner's income to maintain a lifestyle, pay rent or a mortgage, or fund a child's education and for how long.
There are various rules of thumb regarding the right amount of Life insurance coverage. Some tips can be found online, but they only provide an estimate and don't necessarily factor in an individual's specific needs. In my opinion, human guidance, powered by technology, is required. Basically, it comes down to how much money your loved ones would need to remain on firm financial ground if your earnings were no longer in the picture and that is different for everyone."
What is the biggest opportunity you see for improvement in the life insurance industry?
"Increased accessibility through digital and other channels as well as through underwriting enhancements. Increased tailoring of products and features. And an increased emphasis on health and wellness programs."
"Having enough qualified insurance professionals to walk potential buyers through the multiple benefits of life insurance will be pivotal to the growth of the industry. Education is a key factor here, as professional agents also need to be able to explain life insurance and its benefits in an easy, digestible way, especially when there are so many misconceptions about life insurance."
"The need for life insurance is greater than ever. In fact, a recent New York Life Wealth Watch survey found that 37% of adults have been thinking about life insurance more often these days – and half of adults report that financial products that provide protection (50%) and reliability (50%) are more important now compared to last year. This may be especially true for middle-market and Cultural Market families.
Our organizational structure of having Cultural Market agents embedded in the communities where we live and work allows us to understand the needs of diverse communities and develop solutions that resonate with them."
What advice would you give to buyers who are debating whether or not to buy life insurance?
"It is difficult to say with any certainty how healthy you will be years from now. That's why securing life insurance, and insuring your insurability, today, when you are the youngest you'll ever be again, and perhaps your healthiest is a wise decision."
"Do you love someone? If the answer is yes, then life insurance is certainly something you should consider. Many buy gifts and experiences to express their love, but haven't considered that life insurance is just another way to say I love you. Nothing says support like ensuring your family's financial security and peace of mind."
"If you have someone depending on your income, you should consider purchasing life insurance. A death benefit from a life insurance policy can replace income from the loss of a breadwinner, ensure a family can stay in their home, fund educational or retirement expenses, address debt and so much more.
A life insurance policy can also help you grow your family's wealth over time. Once the risk of an unexpected loss has been managed, you can begin to think more broadly about your family's financial future. Life insurance can enable your mindset to shift from death to growth."
What's the most important thing buyers should look for when choosing a life insurance agent/company to buy from?
"With life insurance, you are securing a future commitment that may be decades away. Research the company behind the policy to ensure it has high financial strength ratings, longevity, and an excellent track record of paying claims."
"When looking for an insurance agent or company, be sure to do your research. When comparing companies, be sure to remember that the policy features that fit you and your loved ones best is the most important factor. Don't automatically assume you should buy from the higher-rated company.
If the policy from the other company has more of what you're looking for, it might be the better choice. If you're unsure where to start, try the Life Happens Agent Locator to find an insurance professional in your area."
- "The insurers' track record: At its core, life insurance is protection - a hedge against the unexpected - and you are paying premiums in exchange for the promise that the insurer will be there when you need them, so the financial strength and track record of the company backing your policy is critical.
- Customer service: Are service professionals available by phone and digital channels? Is there is an online dashboard where you can manage your policy? Beyond ensuring assistance is available after you purchase a policy, it's also critical to ensure you have access to trusted advice and guidance before you buy.
- Flexibility in conversion: How easy is it to change? Life can be unpredictable and while term insurance can cover your loved ones through a critical period of time, you may decide that access to cash value is an important piece of your strategy.
- Accelerated online applications : Online applications are convenient but don't replace human guidance. Keep in mind that accelerated online applications may have a maximum coverage amount, meaning that you may not be able to get all the coverage you may need exclusively through an online process.
- A range of payment options: It's important to understand how often you're required to make premium payments and whether and how often you can change the frequency of payments."
Best Life Insurance FAQs
According to JD Power's 2023 life insurance study, State Farm is the highest-rated life insurance company when it comes to overall customer satisfaction. However, you still may want to shop around for quotes from various insurers if you're looking to purchase a new policy.
There isn't one best life insurance company, because the best option for you will depend on the type of policy you're looking for. It's best to work with a qualified insurance agent to help you find the best coverage. If you're deciding between multiple similar options, it's also worth consulting J.D. Power's life insurance customer satisfaction study . The latest study ranks State Farm as the top pick for individual life insurance, outpacing Nationwide by three points.
The best type of life insurance policy for you will differ from someone else's, as your policy should be tailored to your needs. The best policy for you will be affordable and will offer the benefits best suited to your situation. For example, some policies are only meant to cover end-of-life expenses such as burial and funeral arrangements, whereas others include living benefits like a cash value insurance plan , which you can borrow against during your lifetime.
Some life insurance policies are advertised as "no medical exam." This doesn't mean the insurer won't ask you about known conditions or look at medical records. Policies with no medical exam also tend to offer lower benefits with higher premiums. Most companies have a network of medical examiners, some of whom can come to your home. You can find our guide on the best no exam life insurance here.
Each situation is different and requires a knowledgeable life insurance agent to assess your best options. Bring all your questions and the coverage you're looking for to an insurance agent near you to explore your options.
Editorial Note: Any opinions, analyses, reviews, or recommendations expressed in this article are the author’s alone, and have not been reviewed, approved, or otherwise endorsed by any card issuer. Read our editorial standards .
Please note: While the offers mentioned above are accurate at the time of publication, they're subject to change at any time and may have changed, or may no longer be available.
**Enrollment required.

- Main content
- Manage your subscription
- Manage payment method
- Renew your subscription
- Turn recurring billing on or off
- When subscription expires
- Cancel Microsoft 365
- Microsoft 365 subscription refunds
- Share Microsoft 365 Family
- Stop sharing Microsoft 365 Family
- You received an invitation to share
- Switch between Microsoft 365 subscriptions
- Switch to a business subscription
- Transfer to a different Microsoft account
- About accounts
- Sign in to Microsoft 365
- Why you need to sign in
- Forgot account or password
- Get started at Microsoft 365.com
- Meet the Microsoft 365 app launcher
- Check version
- Microsoft 365 for home or business
- What business product do I have?
- Difference between Microsoft 365 and Office 2021
- Difference between home and business plans
- Difference between Microsoft 365 and free web apps
- Troubleshoot

What's the difference between Microsoft 365 plans for home or business
Microsoft 365 is a subscription service that makes sure you always have the most up-to-date modern productivity tools. If you're looking to buy Microsoft 365, but not sure which plan is right for you, use the information below to help guide your decision.
Watch: Business plans versus personal and family plans

Business plans versus personal and family plans
Microsoft 365 business subscriptions
Microsoft 365 business subscriptions can help you grow your business, no matter if you're a team of one or more.
Microsoft 365 Family and Personal
Personal and family subscriptions are ideal for personal use like home, personal, or family projects and school related activities.
The right plan for you will depend on what your needs are. Let's explore the options.
|
|
| |
|---|---|---|
|
| ||
|
| premium desktop apps like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint which you can download and install on multiple PCs, Macs, tablets, and phones. | |
If you're leaning towards a business plan, deciding which one can depend on your specific business needs. The Microsoft 365 plan chooser is designed to help you with this. The chooser will make recommendations based on your answers to questions such as the size of your business, your field of work, the devices you use, and what kind of features, IT support, and security you're looking for. See Find the right plan for your business .
Looking for more product details and prices? Check out the comparison tables: Compare Microsoft 365 for business plans
Buy or try Microsoft 365:
For business For personal and family
Do you need both a business plan and a personal plan?
In some cases, a single Microsoft 365 plan will suit all your needs, but there might be instances when having both plans is the correct decision for you.
For example, you may want to keep your personal files, photos, and other documents separate from your business, having two plans will allow you to do this.
Additionally, if you already have Microsoft 365 Family that you're sharing with friends and family who aren't part of your business, keeping that personal subscription might be the best thing for everyone. This means you don't have to move anyone off that plan, and you don't have to worry about any personal files you already have associated with that subscription and your personal account.
Switch from a personal Microsoft 365 subscription to Microsoft 365 for business
Have you already been using Microsoft 365 Family or Personal for your business and now you're ready to switch your business to Microsoft 365 for business? It's possible to transfer your business documents and files to your new business plan. Learn more about your options to help you with this process.
Follow the steps in Switch from Microsoft 365 for home to a business subscription .
Work with a Microsoft 365 business partner in your area: Find the right partner for you .
Our product experts are available to help you with this free of charge: Contact product experts online. Note: Help from Microsoft business consultants isn't available in all markets.

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Follow these steps to create your lean business plan: 1. Define your business. Start with a brief high-level description of your business. Write a single sentence about what your business does. Focus your answer on your value proposition and how you're unique from other options on the market. 2.
Lean business planning adopts the ideas of small steps, constant tracking, and frequent course corrections to planning. It includes only what adds value, without waste. It starts with a core business plan for internal use only, just big enough for optimizing the business. A lean business plan has four essential parts:
The lean plan contains four essentials every business needs, and nothing else. It's a streamlined core plan for running the business, not a document or detailed plan, full of descriptions, to be presented to investors or lenders. It's to optimize management. Here's what the lean business plan includes. The principles apply to every ...
Define your key costs and variable costs, and how they represent a competitive advantage if applicable. A lean startup business plan (versus a lean business plan for an existing company), needs to also include key startup costs you anticipate in launching your company. Revenue streams; Describe how your business generates money.
List your company's key points: name, business model, product/service, USP. Identify the target market and financial highlights. Use bullet points to organize these details in a concise manner. Write a draft of your executive summary, ensuring it's compelling and brief.
Step 4: Revise your plan. Lean Planning is a process, not just a document. It's is all about continuous improvement. You're quickly defining a strategy, experimenting to see if that strategy works, reviewing the results, and revising the plan before you start again. Lean Planning is never finished.
From C-level leaders to directors, middle managers, and supervisors, the Lean business model encourages a more proactive and thoughtful approach to management. As a result, leaders become more adept at finding and minimizing non-beneficial practices. When the Lean model takes hold, all managers begin to identify how their business area could ...
Benefits of a Lean Business Plan. Lean Business Plans continue to grow in popularity for these important reasons: Accessibility: Lean plans are relatively easy to conceive, formulate, and understand. Anyone with basic business sense can discern the unique value proposition (UVP) and unique selling proposition (USP) without being a former CEO.
The lean startup movement first became popular around 2008. It emphasizes testing a product or service idea quickly, using a minimum viable product (MVP), and getting real user feedback before committing to long development and release cycles. The key principles of lean startup are: Rapid build-test-learn loops.
Process efficiency and cost reduction are the most direct benefits of a Lean business model. But the benefits of a Lean business extend far beyond the obvious. Here are some of the top advantages of operating as a Lean business: ... which stands for Plan, Do, Check, Act. This model encourages teams to perform incremental tests and document ...
A lean business plan is essentially a one-page business plan for companies to kickstart their businesses. Contrary to traditional business plans which are often bulky and complex documents, a lean business plan is a simple, reader-friendly, and easy-to-make document. It is a streamlined core plan that acts as a basis for a more elaborate one.
You might also hear a lean business model canvas referred to as a variety of other, similar terms like a lean business canvas, lean business plan, or even simply a lean canvas. ... Customer relationships (lean canvas replaced with unfair advantage) That's the gist, but here's a chart that digs even more into the difference between a ...
The Lean Business Model Canvas is defined as a visual tool and framework that helps entrepreneurs and business professionals plan and communicate their business ideas, strategies, and models in a concise and structured format. Learn more about lean business model canvas benefits.
A lean business plan is an efficient and condensed business plan to draw investors' attention to your business in its initial stage. Some of the advantages of a lean business plan include: Simplicity: Only the main elements of a business are focused on a lean business plan, which makes it simple for readers to understand.
First Step: A Lean Business Plan. The lean business planning method is about taking small steps, consistent tracking, and frequent course corrections. The lean plan itself only includes what adds value to management, without waste. The plan itself is lean, small, streamlined for internal use only, just big enough for optimizing the business.
That's what is called lean. The benefits are obvious. Consider how the pace of change is constantly increasing. Technology ... It Starts with a Lean Business Plan . Lean business planning adopts the ideas of small steps, constant tracking, and frequent course corrections to planning. It includes only what adds value, without waste.
Unlike a traditional business plan, which can be hundreds of pages long, a lean business plan is typically only 10-20 pages. The advantage of using a lean business plan is that it forces you to focus on the key aspects of your business, such as your value proposition and target market.
Lean principles are designed to continually improve productivity. It's popular because, when done properly, it works. Here are some of the benefits: Less waste. Continually refining your workflow means you can iron out productivity-sapping issues and tasks that don't add anything. More focus.
Lean Strategy. Start-ups need both agility and direction. Summary. Strategy and entrepreneurship are often seen as polar opposites. Strategy means rigorously defining and pursuing one clear path ...
A Lean Canvas is an ideal way to display this information, and in this article, we will outline some of the essential Lean Canvas advantages. Having a manual thick business plan may help while pitching for funds but offers no help when it comes to testing out your ideas in the early stages of your business. Nor does a conventional business model.
An unfair advantage might include proprietary technology, exclusive partnerships, or other unique attributes not easily replicated by competitors. ... Creating a Lean Business Plan using Ash Maurya's LEANSTACK methodology is more than just a task; it's a transformative process that equips you with the clarity and focus necessary for startup ...
The Lean Canvas Framework: Advantages Over a Traditional Business Plan. First conceptualized by business model expert and author Ash Maurya in 2010, the platform for this approach comprises a framework known as " lean canvas .". As Blank notes, this diagram depicts how a firm creates value. The canvas compares key characteristics of both ...
Lean Canvas is a 1-page business plan template created by Ash Maurya that helps you deconstruct your idea using twelve business modeling building blocks. A Lean Canvas can describe a business model, a product release, or even a single feature, making it a highly popular business model innovation and product management tool used by millions ...
Our free business plan template includes seven key elements typically found in the traditional business plan format: 1. Executive summary. This is a one-page summary of your whole plan, typically written after the rest of the plan is completed. The description section of your executive summary will also cover your management team, business ...
Lean methodology rests on two pillars that provide a framework for all Lean projects: Continuous improvement and respect for people. Continuous improvement: An ongoing feedback loop helps teams make progressive changes to processes, products, and personnel to improve systems continuously.By identifying, evaluating, and modifying existing processes or systems - one cog at a time - teams can ...
Tips to help you write your business plan. Open all. 1. Determine what your plan is for. 2. Prepare your finances. 3. Write your summary last. 4.
In its latest survey of more than 10,000 desk workers around the globe, the Workforce Lab from Slack, a Salesforce company, finds that nearly all executives (96%) now feel an urgency to incorporate AI into business operations. The share of leaders aiming to do this "in the next 18 months" has grown 7x since September 2023, rising from 5% to 35% of all executives.
Summary of the Best Life Insurance Companies. Best for customer satisfaction: State Farm Life Insurance. Best for older adults: Prudential Life Insurance. Best for agent support: New York Life ...
Microsoft 365 personal plans. What's different. Get a branded email address for your business or bring an existing one. Create branded templates in Word, Excel, and PowerPoint. Let customers schedule appointments with you online and share calendars across individuals. Use a central location for all work files.
Plus get unlimited 5G and 4G LTE data with 5GB of hotspot data to share for only $20/mo. Order now. With 24 monthly bill credits when you add a line on a qualifying plan.. For well-qualified customers; plus tax. During congestion, heavy data users (>50GB/mo. for most plans) and customers choosing lower-prioritized plans may notice lower speeds ...