- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

How to Structure the Table of Contents for a Research Paper

4-minute read
- 16th July 2023
So you’ve made it to the important step of writing the table of contents for your paper. Congratulations on making it this far! Whether you’re writing a research paper or a dissertation , the table of contents not only provides the reader with guidance on where to find the sections of your paper, but it also signals that a quality piece of research is to follow. Here, we will provide detailed instructions on how to structure the table of contents for your research paper.
Steps to Create a Table of Contents
- Insert the table of contents after the title page.
Within the structure of your research paper , you should place the table of contents after the title page but before the introduction or the beginning of the content. If your research paper includes an abstract or an acknowledgements section , place the table of contents after it.
- List all the paper’s sections and subsections in chronological order.
Depending on the complexity of your paper, this list will include chapters (first-level headings), chapter sections (second-level headings), and perhaps subsections (third-level headings). If you have a chapter outline , it will come in handy during this step. You should include the bibliography and all appendices in your table of contents. If you have more than a few charts and figures (more often the case in a dissertation than in a research paper), you should add them to a separate list of charts and figures that immediately follows the table of contents. (Check out our FAQs below for additional guidance on items that should not be in your table of contents.)
- Paginate each section.
Label each section and subsection with the page number it begins on. Be sure to do a check after you’ve made your final edits to ensure that you don’t need to update the page numbers.
- Format your table of contents.
The way you format your table of contents will depend on the style guide you use for the rest of your paper. For example, there are table of contents formatting guidelines for Turabian/Chicago and MLA styles, and although the APA recommends checking with your instructor for formatting instructions (always a good rule of thumb), you can also create a table of contents for a research paper that follows APA style .
- Add hyperlinks if you like.
Depending on the word processing software you’re using, you may also be able to hyperlink the sections of your table of contents for easier navigation through your paper. (Instructions for this feature are available for both Microsoft Word and Google Docs .)
To summarize, the following steps will help you create a clear and concise table of contents to guide readers through your research paper:
1. Insert the table of contents after the title page.
2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order.
3. Paginate each section.
4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide.
5. Add optional hyperlinks.
If you’d like help formatting and proofreading your research paper , check out some of our services. You can even submit a sample for free . Best of luck writing your research paper table of contents!
What is a table of contents?
A table of contents is a listing of each section of a document in chronological order, accompanied by the page number where the section begins. A table of contents gives the reader an overview of the contents of a document, as well as providing guidance on where to find each section.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
What should I include in my table of contents?
If your paper contains any of the following sections, they should be included in your table of contents:
● Chapters, chapter sections, and subsections
● Introduction
● Conclusion
● Appendices
● Bibliography
Although recommendations may differ among institutions, you generally should not include the following in your table of contents:
● Title page
● Abstract
● Acknowledgements
● Forward or preface
If you have several charts, figures, or tables, consider creating a separate list for them that will immediately follow the table of contents. Also, you don’t need to include the table of contents itself in your table of contents.
Is there more than one way to format a table of contents?
Yes! In addition to following any recommendations from your instructor or institution, you should follow the stipulations of your style guide .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.
Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
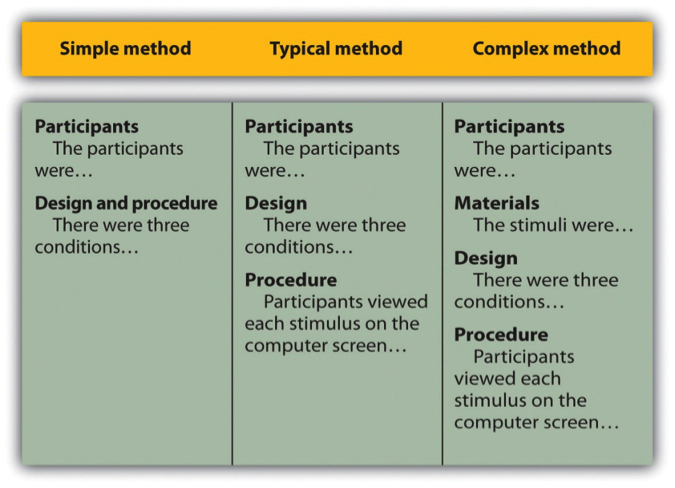
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Published on 15 May 2022 by Tegan George .
The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers. A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality paper will follow.
The table of contents (TOC) should be placed between the abstract and the introduction. The maximum length should be two pages. Depending on the nature of your thesis, dissertation, or paper, there are a few formatting options you can choose from.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What to include in your table of contents, what not to include in your table of contents, creating a table of contents in microsoft word, table of contents examples, updating a table of contents in microsoft word, other lists in your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, frequently asked questions about the table of contents.
Depending on the length of your document, you can choose between a single-level, subdivided, or multi-level table of contents.
- A single-level table of contents only includes ‘level 1’ headings, or chapters. This is the simplest option, but it may be too broad for a long document like a dissertation.
- A subdivided table of contents includes chapters as well as ‘level 2’ headings, or sections. These show your reader what each chapter contains.
- A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into ‘level 3’ headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
Examples of level 1 headings are Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, and Bibliography. Subsections of each of these would be level 2 headings, further describing the contents of each chapter or large section. Any further subsections would be level 3.
In these introductory sections, less is often more. As you decide which sections to include, narrow it down to only the most essential.
Including appendices and tables
You should include all appendices in your table of contents. Whether or not you include tables and figures depends largely on how many there are in your document.
If there are more than three figures and tables, you might consider listing them on a separate page. Otherwise, you can include each one in the table of contents.
- Theses and dissertations often have a separate list of figures and tables.
- Research papers generally don’t have a separate list of figures and tables.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
All level 1 and level 2 headings should be included in your table of contents, with level 3 headings used very sparingly.
The following things should never be included in a table of contents:
- Your acknowledgements page
- Your abstract
- The table of contents itself
The acknowledgements and abstract always precede the table of contents, so there’s no need to include them. This goes for any sections that precede the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, be sure to first apply the correct heading styles throughout the document, as shown below.
- Choose which headings are heading 1 and which are heading 2 (or 3!
- For example, if all level 1 headings should be Times New Roman, 12-point font, and bold, add this formatting to the first level 1 heading.
- Highlight the level 1 heading.
- Right-click the style that says ‘Heading 1’.
- Select ‘Update Heading 1 to Match Selection’.
- Allocate the formatting for each heading throughout your document by highlighting the heading in question and clicking the style you wish to apply.
Once that’s all set, follow these steps:
- Add a title to your table of contents. Be sure to check if your citation style or university has guidelines for this.
- Place your cursor where you would like your table of contents to go.
- In the ‘References’ section at the top, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Here, you can select which levels of headings you would like to include. You can also make manual adjustments to each level by clicking the Modify button.
- When you are ready to insert the table of contents, click ‘OK’ and it will be automatically generated, as shown below.
The key features of a table of contents are:
- Clear headings and subheadings
- Corresponding page numbers
Check with your educational institution to see if they have any specific formatting or design requirements.
Write yourself a reminder to update your table of contents as one of your final tasks before submitting your dissertation or paper. It’s normal for your text to shift a bit as you input your final edits, and it’s crucial that your page numbers correspond correctly.
It’s easy to update your page numbers automatically in Microsoft Word. Simply right-click the table of contents and select ‘Update Field’. You can choose either to update page numbers only or to update all information in your table of contents.
In addition to a table of contents, you might also want to include a list of figures and tables, a list of abbreviations and a glossary in your thesis or dissertation. You can use the following guides to do so:
- List of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
It is less common to include these lists in a research paper.
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Apply heading styles throughout the document.
- In the references section in the ribbon, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents.
- Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents.
Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The table of contents in a thesis or dissertation always goes between your abstract and your introduction.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, May 15). Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/contents-page/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation title page, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
- Formatting Guides
APA Table of Contents Writing Guide (+ example)
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker

You may also like

Today we are going to learn how to make a proper APA table of contents. However, let’s start with some backstory to understand the formatting standards according to the latest APA 7th edition .
In an APA style paper , a table of contents is commonly used in longer research papers or dissertations to provide an organized outline of the document's structure. It helps to increase readability and navigation greatly. Even though a table of contents is not officially required by the APA guide, you may be asked by the instructor to include one. That’s why we compiled this guide on how to format a table of contents in APA style. Read our detailed instructions to arrange a contents page. Or you can always ask StudyCrumb to " write my paper for me " and get comprehensive help with your work, including assistance with formatting.
Whether it is an APA-style paper or an opinion essay, be sure it will be delivered timely and composed with skill and diligence. Check out the writing service and give yourself a little break from writing! Contact us when you are ready.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. is there a size limit for a table of contents in apa style.
Yes, your table of contents should not be bigger than two pages long. If it is larger, consider deleting it entirely or some of the headlines to fit in.
2. Where in the text is the table of contents located in APA style paper?
The table of contents is located after the Acknowledgment but before the Introduction paragraph.
3. How many heading levels is it required to have in a table of contents?
You need to include at least 2 levels and not more than 5 levels of headings. Just analyze the text and come up with the right format for your paper.
Emma Flores knows all about formatting standards. She shares with StudyCrumb readers tips on creating academic papers that will meet high-quality standards.
In the present APA table of contents guide, we will show the most convenient and recommendable format for an APA paper. The first thing that you need to remember — it can not exceed two pages in size. So if the table is a must according to the instructor, you may have to exclude some section headings to fit in. It is good to optimize your paper with subheadings, but don’t get obsessed with it. Here are some of the major formatting rules according to APA Style:
In all other regards, your formatting sticks to the plain text format. Don’t include any unnecessary formatting or highlighting. And don't be afraid to ask your instructor about it if you have any doubts or questions. At any time, you can buy essay quickly, remember about it.
Nevertheless, there is nothing more representative than a proper APA table of contents sample. Pay attention to the length of indents for different heading levels. Check out our sample right below.
Note, there is no fixed standard for the length of indents that you make to highlight every level of headlines. Make sure that your headlines look readable and easy to distinguish.
Looking for annotated bibliography example APA ? We have got you covered! Open one more of our blogs.
Microsoft Word is the most likely software for formatting APA style tables of content. That’s why right now, we will learn how to generate automated ones. It is a very simple operation, and you only have to remember easy 3 steps:
And now, look closer at each individual step, so it will be much easier to remember. So, let’s go! Buy APA format paper entirely from scratch if you have troubles at this point.
Before starting working with headings, make sure that all of them are in line with the general formatting style. Normally, the table of contents is generated after the text is finished and proofread. So don’t be in a hurry, even though the contents are located in the very beginning of the text. Make sure that your piece is flawless and doesn’t contain misspellings. Try an online typing test to hone your typing skills quickly. Formatting headings is easy — just highlight the heading first. Then, find a top panel featuring heading styles and make a right click on the one you want to choose. After it, select Please update Heading X to match selection. Do it with every heading that you have. Assign each one with Heading 1 — Heading 5 roles.
One more step and our APA paper with table of contents is as good as ready. From the very beginning, type the page name, keep it centered and aligned to the top. Remember about 1-inch long indents. Make the heading bold to increase readability and navigation. Then choose the “ Table of Contents ” option from the “References” menu that is located on the top panel. In the new window, choose the number of heading levels that will be displayed. As you remember, you need at least 2 and not more than 5 levels of headings.
From this point, all the highlighted headings will be automatically synchronized with your table of contents. In case if you make changes to the actual heading, you may also change it in your list in one click. Just make a right click on it and choose the “Update Field” option. In Microsoft Word, you can choose to update either one element or all elements at a time. We recommend updating all the elements to keep your paper consistent and good-looking. Hiring a bibliography writer to work on your table of contents might be helpful as well.
We hope our blog explained all those formatting tricks in a most understandable way. Check out other articles if you have any other questions about academic writing. Good luck with your writing!
- Include at least 2 levels of headings — level 1 and level 2.
- Use up to 5 levels of headings if it fits the structure.
- Apply indents to highlight different levels of headings.
- Locate it right after the abstract, before the intro part. (Read more information if you still wonder on how to write an abstract APA .)
- Use a 12 pt Times New Roman font.
- Keep the headings in the table left-aligned.
- Capitalize all the headlines.
- Make sure that margins from all sides are 1 inch long.
- Format the headings first
- Apply an APA style format
- Keep your table updated.
Table of Contents APA: Basics
Apa table of contents example, how to make apa table of contents in word, format your headings, create table of contents in apa formats, keep table of contents consistent.

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
A Table of Contents in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Adah Chung is a fact checker, writer, researcher, and occupational therapist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Adah-Chung-1000-df54540455394e3ab797f6fce238d785.jpg)
General Guidelines
- Table of Contents
APA style does not require a table of contents, but there are cases where you may need to include one. For example, your instructor may specify that your paper must be submitted with a table of contents. A table of contents can be particularly helpful in cases where your paper is lengthy or covers a lot of material, such as a thesis paper or dissertation. Research papers, in particular, may benefit from the addition of a table of contents.
APA style is the official publication style of the American Psychological Association. APA style is used in psychology courses as well as other social science classes including those in social science, behavioral sciences, and education.
The table of contents serves as a basic roadmap of your paper. It should list all of the major headings and subheadings within the body of your paper. For a standard psychology paper, it might include listings for the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections of your paper.
While the APA may not specify guidelines for a table of contents, you should use the basic APA format for formatting your table of contents:
- Use one-inch margins on all sides
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font
- Double-space
Since APA does not require a table of contents, you should always refer to your instructor’s guidelines when deciding whether or not to include one.
It is also important to note that the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association was published in 2020, and included updated guidelines on many topics.
For example, while the previous edition of the style manual required a running head on each page of a paper, the 7th edition has eliminated that requirement on student papers unless your instructor specifies to include it. Always ask first.
If you are using a standard APA paper format, your table of contents should include the following sections:
- Introduction
The above format may work well for a standard lab report or research paper. However, your table of contents will look much different if you are writing something such as a critique, essay, or case study.
Notice, that the table of contents does not include the abstract or acknowledgments pages. When applicable, it should list the appendices and the lists of tables and figures.
The exact order of your paper depends largely on the type of paper you are writing. In general, your paper should be presented in the following order:
- Main Body of Paper
Table of Contents Format
Because there is no standard format for a table of contents in APA style, you should always defer to the provided guidelines for your assignment.
If your instructor does not have a preferred format, consider using the following:
- Title the page “Table of Contents” and center the title at the top of the page.
- Most papers should include at least two levels of headings, up to five levels.
- Level one headings will be for main topics, such as chapter titles like "Chapter One; Name of Chapter," or research sections like "Method," "Results," and "Discussion."
- All level-one headings should be flush-left and sub-headings should be indented five spaces deeper than the last.
- All heading levels should be in title case, capitalizing the first letter of each word. The font type, style, and size stay the same for each level.
- The page number for each heading is formatted flush-right. Include dot leaders between the headings and the page number to improve readability.
While you might not think that following APA format is important, it is one of those areas where students can lose points for making small errors. It pays to spend a little extra time and attention making sure that your paper is formatted in proper APA style.
- If you need help, you can get assistance from your school's writing lab.
- Getting your own copy of the latest edition of the APA publication manual can be very helpful.
- Always refer to any instructions or guidelines that were provided by your course instructor.
- There is a helpful feature in most word processors that you can use to pre-format your paper in APA style. It takes a little effort to set it up, but well worth it in the end, especially for longer documents. You can save the style to apply to your future papers saving you the effort next time.
For those writing a paper to submit for publication, check with the publisher for any specific formatting requirements that they may have.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) ; 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
6.4: Formal Report—Table of Contents and List of Figures
Learning objectives.
- Identify the role and format of a table of contents and list of figures
What Is a Table of Contents?
The table of contents shows readers what topics are covered in the report, how those topics are discussed (the subtopics), and on which page numbers those sections and subsections start.
In creating a table of contents, you have a number of design decisions:
- Levels of headings to include: In longer reports, consider including only the top two levels of headings. This keeps the table of contents from becoming long and unwieldy. The table of contents should provide an at-a-glance way of finding information in the report quickly.
- Indentation, spacing, and capitalization: Notice in the illustration below that items in each of the levels of headings are aligned with each other. Although you can’t see it in the illustration, page numbers are right-aligned with each other.
- Vertical spacing: Notice that the first-level sections have extra space above and below, which increases readability.
Using the automatic table of contents creator in Word can help you produce a clean, professional document. Make sure the words in the table of contents are the same as they are in the text. As you write and revise, you might change some of the headings—don’t forget to change the table of contents accordingly.
Example: Table of Contents
What Is a List of Figures?
If your document has more than two figures or tables, create a separate list of figures. The list of figures has many of the same design considerations as the table of contents. Readers use the list of figures to quickly find the illustrations, diagrams, tables, and charts in your report.
Complications arise when you have both tables and figures. Strictly speaking, figures are illustrations, drawings, photographs, graphs, and charts. Tables are rows and columns of words and numbers; they are not considered figures.
For longer reports that contain dozens of figures and tables each, create separate lists of figures and tables. Put them together on the same page if they fit, as shown in the illustration below. You can combine the two lists under the heading, “List of Figures and Tables,” and identify the items as figure or table as is done in the illustration below.
Example: List of Figures
References & Attributions
Attributions
Content is adapted from Technical Writing by Allison Gross, Annemarie Hamlin, Billy Merck, Chris Rubio, Jodi Naas, Megan Savage, and Michele DeSilva, which is is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Original content for this page was derived by Annemarie Hamlin, Chris Rubio, and Michele DeSilva, Central Oregon Community College from Online Technical Writing by David McMurrey – CC: BY 4.0
Writing in a Technical Environment (First Edition) Copyright © 2022 by Centennial College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Share This Book

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Example for Table of Contents
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition
- 3 Examples for Your Thesis
- 4 Master’s Thesis Examples
- 5 Microsoft Word Tutorial
- 6 In a Nutshell
Definition
A table of contents example will help structure a long academic manuscript and a table of contents page is necessary for academic submission. The table of contents contains an organised listing of your manuscript’s chapters and sections with clearly marked (and accurate) page numbers. The aim of the table of contents is to allow the reader to flip easily to the section they require and to get a feel of your argument’s structure.
What comes first, table of contents or abstract?
If you are writing an academic paper, you have to take the order of your paper into account. Usually, the first sections of your thesis are the title page, cover page, acknowledgements and the abstract . After these pages, you place the table of contents. Be sure to check that all of the page numbers in your table of contents are correct.
What variations of table of content examples exist?
The table of contents can be displayed in the following formats:
- Single level table of contents
- Subdivided table of contents
- Multi-level table of contents
- Academic table of contents
You will find further details about what needs to be included inside of the table of contents on our blog.
Are references included in table of contents?
Yes. The references are included in the table of contents. You add them in as you would any other section of your thesis. Simply write the section in the table of contents with the corresponding page number. However, the acknowledgement for thesis and the abstract are usually not included in the table of contents. However, check with your institution as this could be dependent upon the formatting that you’re required to follow.
How can I make a table of contents in Microsoft Word?
On Microsoft Word, you will find the function to create a table of contents under the ‘references’ tab. Click on the tab and select ‘table of contents’. You can use one that has been designed by Microsoft Word, or you can create a custom one by yourself. Scroll down for a full tutorial on Microsoft Word and creating a table of contents.
Examples for Your Thesis
Below, you will find different examples for table of contents, including a
- Single level table of contents example
- Subdivided table of contents example
- Multi-level table of contents example
We will also show you with an example how the table of contents for a bachelor’s thesis could look like, as well as for a master’s thesis.
Advice for creating a good table of contents: A good table of contents must be easy to read and formatted accurately, containing quick reference pages for all figures and illustrations. A table of contents example will help you structure your own thesis, but remember to make it relevant to your discipline. Table of contents example structures can be created for different disciplines, such as social sciences, humanities and engineering.
The type and length of a table of contents example will depend on the manuscript. Some thesis’ are short, containing just several chapters, whilst others (like a PhD thesis) are as lengthy as a book. This length will dictate the amount of detail that goes into forming a table of contents example page and the amount of “levels” (or subdivisions) in each chapter.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
Single Level Table of Contents Example
For shorter documents, a single level table of contents example can be used. This is a short and succinct table of contents example which utilises only single-level entries on sections or chapters. Remember, you’ll need to include properly formatted dots to lead the reader’s eye to the page number on the far right. The following table of contents example explores this basic structure:
Subdivided Table of Contents E xample
A subdivided table of contents example is required for more lengthy papers, offering a subdivision of chapters and sections within chapters. These are more detailed and are recommended for higher-level dissertations like masters or PhD thesis’ (as well as some more detailed bachelor’s dissertations).
When formating subdivided table of contents example, ensure that chapters are listed in bold font and that subsections are not. It’s common (though not necessary) to denote each subsection by a number (1.1, etc.). You’ll also want to indent the subsections so that they can be read easily. The following table of contents example explores this structure:

Multi-level Table of Contents E xample
Adding additional levels to your table of contents is known as a multi-level table of contents example. These would be numbered onwards at 1.1.1, etc. Be aware that although you want to guide your reader through your manuscript, you should only highlight important areas of your manuscript, like sections and sub-sections, rather than random areas or thoughts in your manuscript. Creating too many levels will make your table of contents unnecessarily busy and too complex.

Academic Table of Contents
All of the above can be used as an academic table of contents example. Often, each separate heading in an academic work needs to be both numbered and labelled in accordance with your preferred reference style (consult your department). The following table of contents example sections will illustrate a table of contents example for a bachelor thesis and a table of contents example for a master thesis.
Table of Contents Example: Bachelor’s Thesis
A bachelor’s degree thesis has no set word or page limit nationwide and will depend entirely on your university or department’s guidelines. However, you can expect a thesis under 60 pages of length at between 10,000 – 15,000 words. As such, you won’t be expected to produce a long and detailed table of contents example with multiple levels and subsections. This is because your main body is more limited in terms of word count. At most, you may find yourself using a subdivided table of contents similar to the table of contents example above.
A bachelor’s thesis table of contents example may be structured like so:

This table of contents example may change depending on your discipline and thesis structure, but note that a single-level structure will often suffice. Subdivided structures like the table of contents example listed earlier will only be necessary when writing several chapters, like in a Master’s thesis.
Master’s Thesis Examples
A master’s table of contents example is more complex than a bachelor’s thesis. This is because they average at about 80 pages with up to 40,000 words. Because this work is produced at a higher academic level, it normally includes a subdivision of chapters and subheadings, with a separate introduction and conclusion, as well as an abstract.
A table of contents example for a master’s thesis may then look something like this:

Microsoft Word Tutorial
Creating a table of contents page with Microsoft Word is simple.
In a Nutshell
- All theses are different. Various departments and disciplines follow different structures and rules. The table of contents example pages here will help you in general to format your document, but remember to consult your university guidelines
- Consistency and accuracy are the most important things to remember. You need the correct page number and the same layout for each chapter. It’s no good combining single-level table of contents with a multi-level table of contents
- Simply put, bachelor’s thesis’ generally follow a single-level table of contents example unless otherwise specified
- Postgraduate thesis’ like master and PhD-level work generally require a more detailed subdivision table of contents example. This is because they deal with both more complex arguments and more words
- Remember to include all aspects of your thesis within the table of contents. Pre-thesis material needs to be listed in Roman numerals and you need to include all back-matter as well, such as References and Bibliography
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Recalls, Outbreaks & Emergencies
- Outbreaks of Foodborne Illness
Investigations of Foodborne Illness Outbreaks

Note: Not all recalls and alerts result in an outbreak of foodborne illness . Check recent Food Recalls and Safety Alerts .
The following is a list of outbreak and adverse event investigations primarily being managed by FDA’s CORE Response Teams . The investigations are in a variety of stages, meaning that some have limited information, while others may be near completion. If you think you have symptoms of foodborne illness, talk to your healthcare provider and public health officials to provide them with details of what you ate before becoming sick. This often aids in helping solve emerging or ongoing outbreaks.
A public health advisory will be issued for investigations that have resulted in specific, actionable steps for consumers to take to protect themselves. Please direct your attention to those pages for the most up to date information on the investigation and for consumer protection information.
Outbreak and adverse event investigations that do not result in specific, actionable steps for consumers may or may not conclusively identify a source or reveal any contributing factors. Adverse event investigations rely on self-reported data. Although these reports may name a particular product, FDA will only indicate a product category in the table and will not publicly name a specific product until there is sufficient evidence to implicate that product as a cause of illnesses or adverse events. If a cause and/or contributing factors are identified that could inform future prevention, FDA commits to providing a summary of those findings.
- An outbreak of Salmonella Africana illnesses (ref # 1227) linked to a not yet identified product has been added to the table. FDA has initiated traceback.
- For the outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 (ref # 1221) linked to bulk organic walnuts, FDA has initiated an onsite inspection and sample collection and analysis.
Active Investigations
Closed investigations, 2024 investigations, 2023 investigations.
title="2022 Investigations" icon="fa fa-angle-down" open="no"
2022 Investigations
1 This cluster represents a subset of the total number of domestically-acquired cases of cyclosporiasis cases in the U.S.
2 Based on CDC’s epidemiological investigation of two large multistate outbreaks of cyclosporiasis , ill people reported eating a variety of leafy greens before becoming sick. For both investigations, CDC, FDA, and state and local partners conducted epidemiologic and traceback investigations and collected and analyzed product and environmental samples. All samples collected were reported as negative for Cyclospora . Due to the lack of additional detail in the epidemiological data and the absence of supporting evidence collected from traceback and sample collection, FDA could not identify a specific product as the source of either outbreak.
2020 Investigations
Related links.
CDC Investigations
FSIS Investigations
Table Definitions
Date Posted : Date the investigation is posted to the table. This happens once CORE begins to actively coordinate an investigation. In collaboration with federal and state partners, CORE initiates response activities to control the outbreak or adverse events.
Reference Number : This number is assigned to incidents that CORE is working on. Each foodborne illness investigation on the table will have a unique reference number and this is provided to help users of this table differentiate between investigations. Those reference numbers beginning with an “E” have carried over from an older numbering system that will not be used by CORE in the future.
Pathogen or Cause of Illness : A bacterium, virus, other microorganism, toxin, or other contaminant that can cause disease.
Product(s) Linked to Illnesses (if any) : During an outbreak or adverse event investigation, the FDA and CDC, along with state and local authorities collect and analyze three types of information: epidemiological information, laboratory analyses of food and/or samples taken from food production environments, and traceback investigation findings. Each outbreak or adverse event is unique and the information available to investigators varies from outbreak to outbreak – however, through rigorous analysis of the information collected, investigators are often able to identify a likely or confirmed food source of an outbreak or adverse events. Additionally, adverse event investigations rely on self-reported data, which may not include all necessary information to fully investigate the product or event. It is important to note that before a specific food is linked to an outbreak or adverse events, the investigation of a commodity or a specific food by the FDA, CDC and state and local partners does not mean that the food is the cause of an outbreak or adverse events. In many cases the investigation is also looking to rule out specific foods even as it identifies the particular suspect. If there is evidence that a specific food is linked to illnesses, it will be reflected here and health authorities will warn the public about that food.
Total Case Count : Updated weekly. For outbreak investigations, the case count is provided to the FDA by the CDC. Case counts are dynamic and the exact number of illnesses constantly changes during an investigation. This number is provided in order to provide an estimate of the size of an outbreak each week. In the case of adverse event investigations, FDA will provide the number of adverse events that have been self-reported by consumers to FDA consumer complaint coordinators and the CFSAN Adverse Event Reporting System (CAERS), which could include duplicate reports. More formalized data will be published in CDC Investigation Notices or in FDA and CDC advisories, should they be posted.
Investigation Status : Communicates whether this outbreak is still under investigation by CORE or the investigational activities have ended. Options for this column would be either “Active” or “Closed”. At times an FDA investigation may be active after an outbreak has ended.
Outbreak/Event Status : Communicates whether this outbreak or series of adverse event reports is ongoing or has ended.
Recall Initiated : A recall occurs when a firm takes a product off the market because there is reason to believe that it may cause consumers to become ill. In some situations, FDA may request the company recall a potentially contaminated food. In other situations, FDA may issue a mandatory recall if there is a reasonable probability that the food is adulterated under certain FDA authorities, and that the food could cause serious illnesses or death.
FDA Traceback Initiated : Used to identify the source and distribution of the implicated food and remove the contaminated product from the marketplace, to distinguish between two or more implicated food products, and to determine potential routes and/or sources of contamination in order to help prevent future illnesses. For additional information, see How the FDA Uses Traceback to Respond to Foodborne Illness Outbreaks .
FDA Inspection Initiated : An official examination by FDA of the operational processes of a facility to determine its compliance with federal law, which may include, among other things, record and sample collection. Activities reported on the table are limited to those conducted by FDA; however, state and local partners work in coordination with FDA and may also conduct inspectional activities. Additional information on the different types of inspections conducted by FDA can be found on the FDA website .
FDA Sampling Initiated : Collection of samples for the presence or absence of a pathogen in a food or in the environment surrounding the food. Samples reported on the table include those collected by the FDA or state collected samples that are analyzed by the FDA. Significant sample findings are reviewed by FDA and are reported in Public Health Advisories .
Who to Contact if you Have Symptoms of Foodborne Illness
Consumers who have symptoms of foodborne illness should contact their health care provider to report their symptoms and receive care.
To report a complaint or adverse event (illness or serious allergic reaction), you have three choices:
- Call an FDA Consumer Complaint Coordinator if you wish to speak directly to a person about your problem.
- Complete an electronic Voluntary MedWatch form online.
- Complete a paper Voluntary MedWatch form that can be mailed to FDA.
Visit www.fda.gov/fcic for additional consumer and industry assistance.
Get email updates delivered to your inbox.
Get regular FDA email updates delivered on this topic to your inbox.

External UK validation of the ENDPAC model to predict pancreatic cancer risk: A registered report protocol
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Claire A Price
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- ORCID record for Hugh Claridge
- ORCID record for Simon de Lusignan
- ORCID record for Natalia Khalaf
- ORCID record for Freda Mold
- ORCID record for Nadia A S Smith
- ORCID record for Martyn Winn
- ORCID record for Agnieszka Lemanska
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Introduction Overall cancer survival has increased over recent decades, but the very low survival rates of pancreatic cancer have hardly changed in the last 50 years. This is attributed to late diagnosis. Pancreatic cancer symptoms are non-specific which makes early diagnosis challenging. Data-driven approaches, including algorithms using combinations of symptoms to predict cancer risk, can aid clinicians. A simple but effective algorithm called Enriching New-Onset Diabetes for Pancreatic Cancer (ENDPAC) has been developed in the United States (US). ENDPAC has not yet been used in the United Kingdom (UK), our aim is to translate ENDPAC into the UK setting. The objectives are to validate ENDPAC and report its predictive utility within primary care. Methods A retrospective cohort study of people with new-onset diabetes using the nationally representative Oxford-Royal College of General Practitioners Clinical Informatics Digital Hub (ORCHID) database. ORCHID holds over 10 million primary care electronic healthcare records. ENDPAC scores will be calculated for eligible people along with positive predictive value, negative predictive value, sensitivity and specificity of the algorithm. We will evaluate the optimal cut-off for defining people with high-risk of having pancreatic cancer. Discussion Once validated within the UK, ENDPAC could be implemented in practice to improve early pancreatic cancer diagnosis by using routine data. ENDPAC is currently being tested in the US in a clinical trial to evaluate its effectiveness. ENDPAC offers an automatable and inexpensive way to improve early diagnosis as part of a sequential approach to identify individuals at high-risk of having undiagnosed pancreatic cancer.
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Funding Statement
This project was funded as part of an EPSRC iCase studentship undertaken by CP. The work of NPL co-authors was funded by the UK Governments Department for Science, Innovation & Technology through the UKs National Measurement System programmes.
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
The Ethics Committee of University of Surrey gave ethical approval for this work (reference number: FHMS 21-22 269 EGA). Access to ORCHID data has been approved by Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP) Research and Surveillance Centre (RSC) under data request RSC_0420.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
Data will remain under the control of the Oxford-Royal College of General Practitioners Clinical Informatics Digital Hub (ORCHID, orchid.phc.ox.ac.uk) and can be accessed following all necessary approvals.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (324)
- Allergy and Immunology (629)
- Anesthesia (166)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2391)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (289)
- Dermatology (207)
- Emergency Medicine (380)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (843)
- Epidemiology (11786)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (703)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3759)
- Geriatric Medicine (350)
- Health Economics (636)
- Health Informatics (2403)
- Health Policy (935)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (902)
- Hematology (341)
- HIV/AIDS (783)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13330)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (769)
- Medical Education (366)
- Medical Ethics (105)
- Nephrology (400)
- Neurology (3517)
- Nursing (199)
- Nutrition (528)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (677)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (665)
- Oncology (1828)
- Ophthalmology (538)
- Orthopedics (219)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (234)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (447)
- Pediatrics (1035)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (423)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3186)
- Public and Global Health (6161)
- Radiology and Imaging (1283)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (750)
- Respiratory Medicine (830)
- Rheumatology (379)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (372)
- Sports Medicine (324)
- Surgery (402)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (146)
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
An Early Look at Black Voters’ Views on Biden, Trump and Election 2024
- Acknowledgments
Table of Contents
- Black voters consistently align with the Democratic Party
- Black voters prefer Biden in 2024 election, but some would replace both candidates
- Black voters’ views on Biden and Trump as presidents
- Black Americans’ policy priorities
- Methodology
This report was written by Kiana Cox, senior researcher.
Editorial guidance was provided by Mark Hugo Lopez, director, race and ethnicity research; Jocelyn Kiley, associate director, political research; and Carroll Doherty, director, political research.
Guidance on the communications strategy and outreach was provided by Tanya Arditi, senior communications manager.
The report was number-checked by Shanay Gracia, research assistant. Sara Atske, digital producer, produced the report. David Kent, senior copy editor, copy edited the report. Charts were designed by Cox and Mohamad Moslimani, research assistant.
Find related reports online at our topic page on Black Americans .
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Black Americans
- Donald Trump
- Election 2024
- Race, Ethnicity & Politics
- U.S. Elections & Voters
- Voter Demographics
- Voters & Voting
More than 80% of Americans believe elected officials don’t care what people like them think
Voters’ views of trump and biden differ sharply by religion, in tight presidential race, voters are broadly critical of both biden and trump, changing partisan coalitions in a politically divided nation, about 1 in 4 americans have unfavorable views of both biden and trump, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Guidelines and Guidance Library
- Core Practices
- Isolation Precautions Guideline
- Disinfection and Sterilization Guideline
- Environmental Infection Control Guidelines
- Hand Hygiene Guidelines
- Multidrug-resistant Organisms (MDRO) Management Guidelines
- Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infections (CAUTI) Prevention Guideline
- Tools and resources
- Evaluating Environmental Cleaning
Infection Control Basics
- Infection control prevents or stops the spread of infections in healthcare settings.
- Healthcare workers can reduce the risk of healthcare-associated infections and protect themselves, patients and visitors by following CDC guidelines.
Germs are a part of everyday life. Germs live in our air, soil, water and in and on our bodies. Some germs are helpful, others are harmful.
An infection occurs when germs enter the body, increase in number and the body reacts. Only a small portion of germs can cause infection.
Terms to know
- Sources : places where infectious agents (germs) live (e.g., sinks, surfaces, human skin). Sources are also called reservoirs.
- Susceptible person: someone who is not vaccinated or otherwise immune. For example, a person with a weakened immune system who has a way for the germs to enter the body.
- Transmission: a way germs move to the susceptible person. Germs depend on people, the environment and/or medical equipment to move in healthcare settings. Transmission is also called a pathway.
- Colonization: when someone has germs on or in their body but does not have symptoms of an infection. Colonized people can still transmit the germs they carry.
For an infection to occur, germs must transmit to a person from a source, enter their body, invade tissues, multiply and cause a reaction.
How it works in healthcare settings
Sources can be:.
- People such as patients, healthcare workers and visitors.
- Dry surfaces in patient care areas such as bed rails, medical equipment, countertops and tables).
- Wet surfaces, moist environments and biofilms (collections of microorganisms that stick to each other and surfaces in moist environments, like the insides of pipes).
- Cooling towers, faucets and sinks, and equipment such as ventilators.
- Indwelling medical devices such as catheters and IV lines.
- Dust or decaying debris such as construction dust or wet materials from water leaks.
Transmission can happen through activities such as:
- Physical contact, like when a healthcare provider touches medical equipment that has germs on it and then touches a patient before cleaning their hands.
- Sprays and splashes when an infected person coughs or sneezes. This creates droplets containing the germs, and the droplets land on a person's eyes, nose or mouth.
- Inhalation when infected patients cough or talk, or construction zones kick up dirt and dust containing germs, which another person breathes in.
- Sharps injuries such as when someone is accidentally stuck with a used needle.
A person can become more susceptible to infection when:
- They have underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, cancer or organ transplantation. These can decrease the immune system's ability to fight infection.
- They take medications such as antibiotics, steroids and certain cancer fighting medications. These can decrease the body's ability to fight infection.
- They receive treatments or procedures such as urinary catheters, tubes and surgery, which can provide additional ways for germs to enter the body.
Recommendations
Healthcare providers.
Healthcare providers can perform basic infection prevention measures to prevent infection.
There are 2 tiers of recommended precautions to prevent the spread of infections in healthcare settings:
- Standard Precautions , used for all patient care.
- Transmission-based Precautions , used for patients who may be infected or colonized with certain germs.
There are also transmission- and germ-specific guidelines providers can follow to prevent transmission and healthcare-associated infections from happening.
Learn more about how to protect yourself from infections in healthcare settings.
For healthcare providers and settings
- Project Firstline : infection control education for all frontline healthcare workers.
- Infection prevention, control and response resources for outbreak investigations, the infection control assessment and response (ICAR) tool and more.
- Infection control specifically for surfaces and water management programs in healthcare settings.
- Preventing multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs).
Infection Control
CDC provides information on infection control and clinical safety to help reduce the risk of infections among healthcare workers, patients, and visitors.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

COMMENTS
The table of contents is usually located at the beginning of the document or book, after the title page and any front matter, such as a preface or introduction. Table of Contents in Research. In Research, A Table of Contents (TOC) is a structured list of the main sections or chapters of a research paper, Thesis and Dissertation. It provides ...
Now you can generate your table of contents. First write the title "Contents" (in the style of a level 1 heading). Then place your cursor two lines below this and go to the References tab. Click on Table of Contents and select Custom Table of Contents…. In the popup window, select how many levels of heading you wish to include (at least ...
In the "References" section at the top, locate the Table of Contents group. Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select "Custom Table of Contents.". Here, you can select which levels of headings you would like to include. You can also make manual adjustments to each level by clicking the Modify button.
To summarize, the following steps will help you create a clear and concise table of contents to guide readers through your research paper: 1. Insert the table of contents after the title page. 2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order. 3. Paginate each section. 4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide. 5.
Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section. ... and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles. ... ("Table 1," "Table 2," and so on). Figures are numbered the same way ("Figure 1 ...
A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into 'level 3' headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
Create Table of Contents in APA Formats. One more step and our APA paper with table of contents is as good as ready. From the very beginning, type the page name, keep it centered and aligned to the top. Remember about 1-inch long indents. Make the heading bold to increase readability and navigation.
For a standard psychology paper, it might include listings for the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections of your paper. While the APA may not specify guidelines for a table of contents, you should use the basic APA format for formatting your table of contents: Use one-inch margins on all sides. Use 12-point Times New Roman font.
The table of contents forms an essential part of any academic paper. Through the use of headings, sub-headings, and page numbers, we can construct an accurate road map to assist reviewers, evaluators, tutors, and general readers. The table of contents shows how effective the writer is at dividing the thesis into relevant and manageable sections.
A report is typically made up of three main divisions: (1) preliminary material, (2) body and (3) supplementary material. Each of the sections contains a different kind of content. Refer to the tables below: Table 1: Divisions and sections of a report Broad Divisions Individual Sections (1) Preliminary material Title of Report Table of Contents
The table of contents shows readers what topics are covered in the report, how those topics are discussed (the subtopics), and on which page numbers those sections and subsections start. In creating a table of contents, you have a number of design decisions: Levels of headings to include: In longer reports, consider including only the top two ...
Microsoft Word - sample-table-of-contents.doc Created Date: 10/2/2014 3:53:13 PM ...
Sample results of several t tests table. Sample correlation table. Sample analysis of variance (ANOVA) table. Sample factor analysis table. Sample regression table. Sample qualitative table with variable descriptions. Sample mixed methods table. These sample tables are also available as a downloadable Word file (DOCX, 37KB).
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
A table of contents is a list, usually on a page at the beginning of a piece of academic writing, which outlines the chapters or sections names with their corresponding page numbers. In addition to chapter names, it includes bullet points of the sub-chapter headings or subsection headings. It usually comes right after the title page of a ...
MS Word is equally as useful, but creating a table of contents in Google Docs is a really straightforward process. Choose your preferred location for your table of contents on the document. Click 'Insert' and choose 'Table of contents.'. Decide on your chosen table of contents format.
A table of contents example will help structure a long academic manuscript and a table of contents page is necessary for academic submission. The table of contents contains an organised listing of your manuscript's chapters and sections with clearly marked (and accurate) page numbers. The aim of the table of contents is to allow the reader to ...
Tables and figures are each numbered separately, in the order they are referred to in your text. For example, the first table you refer to is Table 1; the fourth figure you refer to is Figure 4. The title should clearly and straightforwardly describe the content of the table or figure. Omit articles to keep it concise.
Step 4: Click the arrow that is next to the TOC icon and select Custom Table of Contents. Here, select the level of heading that you would like to include in your table and also make the necessary adjustments to each level by clicking the modify button. Click on Custom table of contents.
The content must then reinforce or counter the thesis. The sample report below is about the idea that going to university isn't for everyone. The slides are in a modern creative style and will look great with any content. Customize this analysis report template and make it your own! Edit and Download.
Investigation Status: Communicates whether this outbreak is still under investigation by CORE or the investigational activities have ended. Options for this column would be either "Active" or ...
The fourth was conducted among 8,709 adults from April 8 to April 14, 2024 on Pew Research Center's ATP. There was an oversample of non-Hispanic Black adults, for a total of 1,372 Black adults in the sample. This survey provided the data on Black voters' views on Joe Biden, Donald Trump and the 2024 presidential election discussed in this ...
The heritability of human diseases is extremely enriched in candidate regulatory elements (cRE) from disease-relevant cell types. Critical next steps are to infer which and how many cell types are truly causal for a disease (after accounting for co-regulation across cell types), and to understand how individual variants impact disease risk through single or multiple causal cell types.
Introduction Overall cancer survival has increased over recent decades, but the very low survival rates of pancreatic cancer have hardly changed in the last 50 years. This is attributed to late diagnosis. Pancreatic cancer symptoms are non-specific which makes early diagnosis challenging. Data-driven approaches, including algorithms using combinations of symptoms to predict cancer risk, can ...
Browse a list of every CMI research report (including archive of past years' reports) Research by Topic. Go directly to the latest report on each of these subjects. ... Use this table of contents to go directly to the sections you're most interested in, or dive in and read it all. Table of contents. Video use, types, production, and challenges.
Acknowledgments. Methodology. This report was written by Kiana Cox, senior researcher. Editorial guidance was provided by Mark Hugo Lopez, director, race and ethnicity research; Jocelyn Kiley, associate director, political research; and Carroll Doherty, director, political research. Guidance on the communications strategy and outreach was ...
Infection prevention, control and response resources for outbreak investigations, the infection control assessment and response (ICAR) tool and more. Infection control specifically for surfaces and water management programs in healthcare settings. Preventing multi-drug resistant organisms (MDROs). Sources. Infection control prevents or stops ...