

How to Write a Case Study - All You Wanted to Know

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

| 📝 Step | 📌 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Draft Structure | 🖋️ Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references. |
| 2. Introduction | 📚 In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research. |
| 3. Research Process | 🔍 Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world. |
| 4. Quotes and Data | 💬 Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case. |
| 5. Offer Solutions | 💡 At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself. |
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
Bringing Stories to Your Essay: Introducing a Case Study the Right Way!
Table of contents
Ever found yourself immersed in a story, hanging onto every detail, eager to know what happens next? That, my friend, is the magic of a case study when sprinkled into an essay.
Just as a dash of spice can elevate a dish, a well-placed case study can take your essay from 'meh' to 'marvelous'. It's not just about showcasing real-world examples; it's about making your arguments relatable, tangible, and above all, memorable.
But hold on, before you dive headfirst into weaving in that intriguing case study you found, let’s chat about the art of introducing it. You see, dropping it in without context is like telling a joke without a punchline.
In this post, we'll guide you through the craft of smoothly and effectively introducing a case study into your essay, ensuring it's not just a detour but a meaningful journey for your readers. So, are you ready to give your essay that extra oomph?
Why Use Case Studies in Essays
You know those moments when you're explaining a theory or a concept, and you see those blank stares? Yup, we’ve all been there. That’s where real-world examples come into play. By weaving a case study into your essay, you're essentially turning on a light in a dim room. Suddenly, that complex theory has color, depth, and context. It's no longer just words on paper; it's a story, a lesson, a real-world incident that breathes life into your arguments.
And let's talk about the brownie points. When you toss a well-researched case study into the mix, it's like handing your readers proof that you've rolled up your sleeves and delved deep into your subject. It's a signal: you're not just skimming the surface; you're diving into the depths, bringing out treasures of knowledge.
Lastly, an apt case study is like the secret sauce to winning trust. Readers lean in, believing in your words, connecting with your narrative. It’s not just about flashing your research chops; it’s about creating a bond, engaging them, making them think, "Hey, this writer really knows their stuff!"
In a nutshell? Case studies? They're your essay's best friend.
Choosing the Right Case Study
Before you jump onto the Internet's vast ocean and fish out the first case study that sorta-kinda fits, let’s have a quick heart-to-heart. Not all case studies are created equal. And while it might be tempting to pick that dramatic, headline-grabbing one, it's essential to remember a few golden rules.
Firstly, it's all about alignment. Think of your essay as a puzzle. Every piece, every argument, every citation should fit just right. Your chosen case study? It's that central piece, setting the tone, connecting dots. So, make sure it's directly related to your topic. No square pegs in round holes, okay?
Next, reputation is everything. Dive into journals, accredited institutions, and renowned publications. Trustworthy sources not only boost your essay's credibility but save you from those cringe-worthy moments when someone points out a glaring error or bias in your chosen study.
Quick tip from the pros : Some case studies are like that popular song on the radio - overplayed and heard by everyone. Unless you’re bringing a fresh, unheard angle or a unique perspective to the table, steer clear of the overly popular ones. It's always more impressive to introduce your readers to a gem they haven't encountered before.
Introducing a Case Study: The Art of the Hook
Picture this : You're at a party, and someone starts a story with, "You won't believe what happened to me yesterday!" Chances are, you're all ears. That's the power of a good essay hook . Now, let's bring that energy to your essay!
Starting with a compelling fact or statement is your ticket to gripping your readers. Imagine leading with, "In a village where electricity was once a dream, solar panels changed everything." Instantly, your readers are curious. They want to know more about this village, the change, the story behind it all.
Once you've got their attention, lay down the problem. Paint a picture of the challenges, the obstacles, the scenario before the solution came into play. This sets the stage for your case study. By presenting the problem, you're essentially saying, "Hey, here's a situation. Stick around to see how it unraveled."
Quick Checklist: Crafting That Perfect Hook
- Relevance : Ensure it ties back to your main essay topic.
- Emotion : Strike a chord, whether it's curiosity, empathy, or even surprise.
- Simplicity : Keep it straightforward. No need for jargon or over-the-top language.
- Authenticity : Stay true to the essence of your case study. No embellishing facts!
Remember, the aim is to draw readers in, making them eager to delve into the heart of your case study. With a killer hook, you're not just starting an essay; you're beginning a journey they'll want to join.
MLA Citation: Giving Credit Where It's Due
Alright, let's chat about something we often overlook in our writing excitement: citation. I get it; it may not be the most thrilling part of essay writing, but think of it as the unsung hero, quietly ensuring your work stands tall with authenticity and respect.
First off, why the fuss about proper citation ? Well, citing your sources isn't just about avoiding the scary plagiarism monster. It's about acknowledging the hard work of others. It's a nod to fellow researchers, saying, "Hey, I see your efforts, and they've helped shape mine."
How to cite a case study in MLA format
Author's Last Name, First Name . "Title of the Case Study." Title of the Journal or Publication , vol. number, no. issue number, Year of Publication, page range.
For example: Smith, John. "Solar Power in Remote Villages." Energy Research Journal , vol. 5, no. 2, 2020, pp. 45-59.
If found online: Add the website name, the URL, and the access date at the end.
Smith, John. "Solar Power in Remote Villages." Energy Research Journal , vol. 5, no. 2, 2020, pp. 45-59. ERJ Online, www.erjonline123.com , Accessed 5 June 2022.
Avoid these mistakes
- Forgetting the access date: Especially for online sources, this one's crucial!
- Overlooking the punctuation: Note the periods, commas, and italics. They're all essential in MLA.
Quick Tip : If this feels a tad overwhelming, online citation tools are here to rescue! Platforms like EasyBib or Citation Machine can churn out MLA citations in a snap. Just feed in your source details, and voila!
In the end, think of citations as your essay's backstage crew, working behind the scenes to ensure your masterpiece gets a standing ovation.
Weaving the Case Study into Your Essay Narrative
Alright, so you've got this shiny case study and you’re all set to embed it into your essay. But here's the catch – it's not about just dropping it in; it's about stitching it seamlessly into your narrative fabric.
Make It Relevant : Think of your essay and case study as dance partners. They need to move in harmony. Ensure that your case study doesn't just stand alone; it should back up your arguments, add depth to them, or even offer a contrasting perspective. It’s about making the dance memorable.
Build a Logical Flow : Your readers are on a journey with you. Introduce your case study at a point where it feels natural, leading them from one idea to the next. It’s like following breadcrumbs; one leading to another, ensuring they never get lost in the woods.
Pacing is Key : Imagine watching a movie where the climax is revealed in the first ten minutes. Boring, right? Similarly, don’t spill all the beans about your case study right away. Tease a little, build intrigue, let it unfold gradually, keeping your readers hooked.
In essence, introducing a case study is an art. It’s not about making it fit, but about ensuring it belongs, enriching your essay's narrative and making it truly unforgettable.
Concluding Your Case Study Introduction
As you wrap up the intro to your case study, think of it as putting a bow on a gift. First, make a promise to your readers: assure them that venturing deeper into this case study will shed light, offer insights, or challenge perspectives. Maybe it's a promise of a lesson learned or an innovative solution unveiled. Then, seamlessly pave the way for what's next: your main arguments. Like a skilled guide, hint at the journey ahead, ensuring your readers are not only invested but also eager to embark on the exploration with you.
Final Thoughts & Wrap-up
Introducing a case study in an essay is much like mastering a dance step; at first, it might feel a tad awkward, maybe even a little forced. But with practice? Ah, that’s when the magic happens. Just as dancers become one with the music, with time, you'll find that blending case studies into your essays becomes second nature. The beauty lies in the richness they add, turning plain text into tapestries of real-life stories, insights, and revelations.
But what if you're pressed for time or feeling a tad overwhelmed? Here's a lifesaver: Writers Per Hour offers impeccable custom case study writing services tailored to your needs. They're the backstage crew ensuring your essay shines under the spotlight.
Now, with or without help, here's a challenge for you, dear readers: In your next essay, venture out, find that perfect case study, and weave it in. Experience the transformation it brings. And when you do, remember that every story you tell, every example you cite, adds depth and dimension to your narrative. Ready to give it a whirl?
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
- Basics of Research Process
- Methodology
- How to Write a Case Study: Definition, Outline, Steps & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Case Study: Definition, Outline, Steps & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination of a particular subject, often a person, group, event, or organization. It's used to explore complex issues in real-world contexts. A case study can provide insights that might not be achieved with other research methods.
Are you struggling with writing a case study and don't know where to begin? You are not alone. Most students involved in the Psychology or Sociology field often find this task challenging. Especially if they are new to this research method. However, with the right structure and preparation, creating a case study paper will be a piece of cake.
After reading this article, you will be armed with all essential details including:
- Definition
- Case study types
- Basic structure
- Steps on how to write a case study
- Examples that worked.
Let’s dive right in!
What Is a Case Study: Definition
A case study is a research method that involves examining a specific instance to let researchers learn more about an individual, event, organization or concept. It is like a magnifying glass for studying real-life situations. By looking at a single example, we can learn more about complex issues and understand patterns.
Case studies are used in the fields like Psychology, Business, Statistics or Nursing. As a rule, students apply this research method when writing a dissertation or thesis .
Depending on the research question and the data needed to address a problem, case studies can involve various research methods.
Research Methods Applied in Case Studies
|
|
Interviews | Surveys |
Observations | Statistical analysis |
Document analysis |
Case Study Example
Let's recap the main points.

What Is the Purpose of a Case Study?
The primary purpose of a case study is to gain insight into the real-world situations through the investigation and analysis of a single instance. This research design is often applied to meet such goals:
- Develop a better understanding of complex issues or phenomena
- Identify patterns and relationships
- Test hypotheses and theories in natural settings
- Provide practical solutions
- Illustrate best practices or successful strategies.
Every case study writer can customize their work to fit the needs of a specific discipline, as shown below.
Use of Case Studies
|
|
|
|
| ✓ Analyze successful marketing campaigns✓ Evaluate customer satisfaction✓ Assess brand loyalty |
| ✓ Understand complex legal issues✓ Prepare for trials✓ Make decisions based on previous court cases |
| ✓ Examine individual behavior✓ Develop treatment plans✓ Test hypotheses |
| ✓ Understand social structures✓ Analyze group dynamics✓ Explore societal issues |
| ✓ Evaluate patient care✓ Diagnose rare conditions✓ Offer treatment |
Looking for expert case study help ? Don't hesitate to contact our academic writers today to get the assistance you need. Our team of experts is ready to provide you with top-notch writings to help you achieve your academic or professional goals
Types of Case Studies
There are different types of case studies that scholars or students can bring into play. Each approach has its own focus and is chosen based on research objectives.
- Descriptive case studies This approach involves a detailed examination of a particular situation or phenomenon to understand it better. Here, researchers see the context, events, and processes that led to a particular outcome, and get a comprehensive picture of the situation.
- Explanatory case studies Explanatory method allows us to understand the "why" and “how” behind a particular event or phenomenon. As the name suggests, this type of case study seeks to test and explain the causal relationship between independent and dependent variables .
- Exploratory case studies Imagine being a detective and investigating a mystery or problem in its early stages. This is the main idea of an exploratory investigation. It helps to recognize key questions, potential patterns, and areas for further research. It's like peeling back the layers of an onion, revealing new insights and uncovering possible solutions.
- Intrinsic case studies Unlike other case study methods, an intrinsic approach is used to explore a unique instance. Here, researchers focus on a particular scenario in its own right, rather than trying to apply the outcomes to a broader population.
- Instrumental case studies This type of study examines one instance to shed light on a larger group or phenomenon. Instrumental technique is a good choice if you want to develop theoretical frameworks and obtain generalizable findings.
- Cumulative case studies While conducting cumulative research, students compile and synthesize information from multiple similar instances. Here, you combine the results of multiple studies to draw more generalized conclusions.
- Collective case reports Think of several individual instances being studied together to provide a broader understanding of a specific phenomenon. These instances are often connected by a common theme. This enables researchers to compare and contrast cases and uncover tendencies.
- Critical case studies Researchers use this method to explore exceptional instances that are particularly interesting or thought-provoking. Critical approach helps to analyze why a specific situation occurred and what could have been done differently.
Case Study Structure: Main Parts
When investigating any phenomenon, it’s important to organize your sections in a logical manner. A structure of a case study usually includes such components:
- Introduction This section is a place to present a case. Provide a brief overview of your instance, introduce your key research objectives and prepare the readers for further analysis.
- Problem identification By laying out a problem, you will be able to show the scope and significance of your topic. Identify the main issue that will be examined and build a clear statement of the problem.
- Background A properly established context sets the stage for research and lays a foundation for case evaluation. Offer relevant background information on the instance. This can be a historical, geographical or cultural context.
- Methodology Describe your methodology in research – approach, data collection methods and analysis techniques used in your investigation.
- Solution Now is the time to determine potential solutions to address the problem, and evaluate the pros and cons of each resolution. Make sure solutions are realistic.
- Results Once a case study is conducted, you should share your key findings. Mention any data or evidence that was collected and analyzed.
- Discussion This part of a case study is a perfect opportunity for analysis. Discuss the implications of your outcomes and draw conclusions
- Conclusion Summarize your main points, restate a problem and solutions, and offer final recommendations or next steps.

Case Study Outline
Before you create a case study, it’s a good idea to prepare an outline. It serves as a skeleton of your project. A well-structured outline of a case study helps organize your thoughts in a logical manner.
Below you can see an example of a basic template. Feel free to use it for inspiration.
General Outline
- Brief subject introduction
- Research purpose and objectives
- Necessary context
- Problem/issue
- Problem significance
- Subject/idea history
- Setting or environment description
- Key challenges, opportunities, or turning points
- Research methods used to gather information
- Data analysis methods
- Possible strategies
- Assessment of solutions
- Recommended solvents
- Major discoveries from the data analysis
- Implications
- Limitations/challenges
- Summary of key points
- Restatement of the problem and solution
- Final suggestions or next steps
Based on the sample template shown above, arrange your key ideas and highlight critical information. You may change the blocks to meet your assignment’s unique requirements.
Before You Start Writing a Case Study
Preparation is the key to success. To make your case study flawless, you need to establish your goal and plan. This will lay the foundation of the whole process before you begin writing.
Ensure you follow these 3 crucial steps before moving further.
1. Carefully Read the Instructions
Your professor may provide you with special requirements, case study rubric or exemplary works. The instructions may include details on preferred format, structure, word count, writing style or analysis techniques. Read given material attentively and make sure you fully understand the guidelines.
Get expertly crafted works to meet your academic needs. Buy case study from certified professionals and ace your assignments with ease.
2. Conduct Research
Researching is the most time-consuming part of writing a case study. Review relevant studies on the research topic to gain a deeper understanding of your subject. You may want to go through different sources and identify their strengths and limitations. Strive to build a bridge between your case study report and existing gaps.
Make sure to jot down all your ideas, opinions, notes or questions related to your research. This approach will help you build an outline and write a case study accordingly.
3. Gather Data
Now you are all set for the data collection process. Identify the most relevant type of information pertinent to your research question.
Consider using primary sources such as interviews, surveys or questionnaires. Secondary resources may include books, articles, case studies and public documents.
Your data must be accurate and reliable so double-check your research results before integrating them into your project.

How to Write a Case Study in 7 Steps?
Now that you are familiar with the preparation stages, it's time to dive into the writing process. Writing case studies can be challenging. But by following a structured approach, you can produce a clear and engaging work.
To create a strong project, it's important to carefully plan and execute each step of your flow, from identifying the research question to presenting your conclusions. Below we have prepared detailed guidelines on how to write a case study paper.

1. Introduce a Case Study
Start your case study introduction by presenting your subject and providing a brief overview of the research objectives. It's important to highlight the significance of your case and explain why it warrants examination. One way to do this is to focus on innovative aspects, such as a novel approach to a problem or a new technology. You can also emphasize the broader implications.
You should also preview a structure. This will give readers an idea of what to expect. Briefly describe your main points or provide a rough outline.
Case Study Introduction Example
2. Describe a Problem
Before you get to the problem, provide context that explains the issue at hand. Identify the scope and impact of this problem. One efficient strategy of creating case studies that trigger attention is integrating examples or statistics. This helps to understand how severe this situation is.
Additionally, you may want to highlight any challenges or obstacles that have prevented a problem from being solved.
Example of Problem Description in a Case Study
>> Read more: How to Write a Problem Statement
3. Discuss Research Methods
Research methods you apply will define how to make a case study. There are multiple ways to collect data. So your primary task here is to figure out what kind of information you want to obtain.
Your research strategy should align with your objectives. For instance, interviews can help capture detailed information from a small sample of people. On the other hand, surveys involve large groups of individuals. If you are using interviews or surveys, provide a list of questions participants were asked.
You can also do experiments to test out different theories or conduct document analysis to identify trends.
>> Learn more: What Is Experimental Design
Example of How to Describe Research Methods
4. Offer Solutions to the Problem
The next stage involves coming up with potential solutions. Explain what strategies could be used to address the problem.
For example, if you write a case study on a business-related problem, solutions may involve implementing procedures to improve efficiency. Alternatively, in a healthcare niche, you will offer a new medication or therapy.
Be sure to provide evidence from your research or expert opinions to support your suggestions.
Here’s how to do a case study solutions section.
Example of Solution
5. Present Your Key Results
Most scholars judge case study reports by research outcomes. You need to show that your solution works. Analyze collected data and share your most significant findings in your results section . This can be an increase in profits or a patient's health improvement.
When you write your case study outcomes, it is important to organize the information in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs and charts to illustrate your data visually.
Provide a short summary of your results and their implications. But don’t just tell. You need to back up your research with evidence. If you used interviews, be sure to include any statistical analysis done for those results.
Example of Case Study Research Results
6. Conclude with Recommendations
A conclusion of a case study is where you wrap everything up and provide recommendations for further research. Sum up your key points and explain how they could be used to solve similar problems. You can also highlight any unexpected findings or insights that emerged during the study. Don’t forget to discuss any ethical considerations or limitations.
You need to create a lasting impression. For this, end a case study with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
Case Study Conclusion Example
7. Proofread Your Case Study
Once you are done with writing a case study, you need to carefully review it. Keep an eye on these things when checking your work:
- Grammar mistakes Proofread your writing for typos and grammar errors. Feel free to use our Grammar Checker to make sure you got everything right.
- Clarity Check whether your work is readable and concise. Avoid long sentences and complex structures.
- Sources accuracy Make sure to check all sources for accuracy. It is also important to ensure that all reported data is up-to-date.
- Citations Ascertain whether all sources are properly cited and the same style is used consistently throughout your paper.
Case Study Format
Besides the content, it is also important to stick to a specific case study paper format. The layout of your paper should follow guidelines of the chosen citation style.
There are different ways to format a case study. Commonly used styles include APA, MLA, Chicago and Harvard. Each format presents specific requirements for formatting your text and references.
Check out our detailed guides listed below to learn more about each style.
>> How to Write a Paper in APA Format?
>> How to Do MLA Format?
>> How to Write a Chicago Style Paper?
Case Study Examples
Getting actual examples of case studies can be a great way to learn and understand how to write one. To help you out, we have collected several sample case study paper examples for different disciplines. Feel free to use these samples as inspiration when writing your own paper.
Case Study Writing Tips
With the right approach, your effort will reward you with an A+. In this section, we will list some actionable tips on how to write a good case study:
- Planning your work ahead Planning your work ahead Make sure to create an outline before you start writing and stick to it throughout the entire process.
- Arranging your data logically Break down complex information into chunks and use visual elements (tables, graphs, diagrams) to present it.
- Structuring your writing Use headings and subheadings to organize your content and make key points easy to access.
- Keeping your text simple Write your case study in an easy-to-read language and refrain from complex sentence structures.
- Remaining impartial Be objective in your analysis and avoid personal biases.
Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Case Study
Even a small mistake can undermine your whole work. Here are some common pitfalls students fail to account for in their case studies:
- Focusing too much on the background Provide enough space for analysis of your problem and solution.
- Stuffing with direct quotes Quotes can be used as evidence in your paper. But relying on them too much will make it sound overly repetitive.
- Not referring to all sources Always cite your sources correctly and use only reliable data in your paper.
- Being vague Avoid general statements and be more specific while discussing your results and solutions.
- Failing to mention possible gaps Always consider ethical considerations or limitations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Case Study
Using a case study approach as your research method has its own pros and cons. On one hand, it is an effective way to explore a particular issue in detail. On the other, there are certain limitations that come with this approach. Below we will cover both strengths and limitations of case studies.
Benefits of Case Study
A case study is like a seed that can grow into a fruitful tree, providing resolutions to intricate problems. Here are the biggest case study benefits you can use to your advantage:
- In-depth analysis Researchers can gather a lot of information on a specific topic or issue.
- Insights into elaborate issues Allows researchers to examine complex issues in a controlled manner.
- Real-life situations You are able to test theories or hypotheses in real-world settings.
- Comprehensive approach Researchers can collect both quantitative and qualitative data.
- Unique revelations This method can enlight on previously unexplored or understudied areas.
Limitations of Case Study
As with any research method, case studies have their fair share of drawbacks. Let's take a closer look at some of the most prevalent issues that can arise when using this approach.
- Limited generalizability Due to the small sample size and unique nature of each case, it can be difficult to generalize findings to a larger population.
- Observer bias Researchers may bring their own biases and perspectives, which can influence their results and interpretations.
- Time-consuming and expensive This approach requires significant time and resources to conduct, making it less feasible for some research questions.
- Lack of control In contrast to experimental research, case studies lack control over extraneous variables. This can make it difficult to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Subjectivity Collected data is often subjective and open to interpretation, which can introduce potential errors.
Case Study Paper Writing Checklist
Before you write a case study assignment, make sure to recap all the information you have learnt today. Refer to this checklist to ensure you are on the right track.
Bottom Line on How to Write a Case Study
Writing a case study can be an incredibly challenging task for any student. However, with the right approach and tips, you can easily turn this daunting task into a pleasant experience.
We hope this article helped you understand how to write a case study. Remember to focus on the practical part and avoid overgeneralizing or cherry-picking data.
Our paper writing service is your best choice. We have helped thousands of students with their projects and would be glad to assist you, too. Our team of skilled writers is ready to help you complete your work upon ‘ write my case study ’ request.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what is a case study in research.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth analysis of a particular subject. This approach most often focuses on a single event, person or group. It provides insight into the context of a problem and can be used to explore solutions to intricate issues.
2. What is the difference between a case study and a research paper?
The main difference between a case study and a research paper is in their scope. A case study explores a limited number of subjects, while research papers investigate multiple variables and/or draw conclusions from larger data sets. While both works contain evidence-based information, the focus and approach taken are quite different. Research papers are more general in nature, while case studies focus on narrow problems.
3. How long should a case study be?
The length of a case study varies depending on the type of assignment. Case studies intended for scholarly articles range from 3,000 to 4,0000 words or more. Meanwhile, if it’s a separate chapter in your MA or PhD dissertation, you will need to keep it between 8,000-15,000 words. Follow specific guidelines provided by your professor or institution.
4. Why is a case study important?
Case studies are an important research tool, as they provide detailed information on a particular issue. By exploring a single instance from multiple angles, researchers can uncover solutions to complicated problems that may not be immediately apparent. Using this method, scientists also test hypotheses and generate new theories.
5. What makes a good case study?
A good case study should be organized, well-researched, and contain evidence. Some characteristics of a case study include:
- Precise subject overview
- Thorough analysis that goes beyond surface-level information
- Examination of a single scenario from various perspectives
- Fact-based arguments
- Validated findings.
6. How to start a case study?
To start a case study, begin by carefully reading requirements and identifying the main problem to be addressed. Don't jump to conclusions or make assumptions – take it one step at a time. Once you have a clear understanding of your goal, gather relevant data. This includes doing research, interviewing people, and analyzing relevant documents.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.

You may also like

- checkbox I thoroughly researched my topic and gathered relevant information.
- checkbox A problem/issue is clearly defined.
- checkbox My case study structure is well-organized.
- checkbox I used appropriate research methods to gather data.
- checkbox My findings are well-supported by analysis and evidence.
- checkbox I discussed possible limitations and ethical considerations.
- checkbox The work offers recommendations for further research.
- checkbox My paper adheres to formatting guidelines required by my instructor.
A researcher is interested in studying the effects of a newly implemented teaching method on student performance. To find out, they observe a class of 30 students over one semester. The researcher compares the test scores from before and after the method was used, documenting its effectiveness. The study results showed that academic performance had improved by 11.5% since the new teaching method was implemented. The researcher concluded that this approach works well and can be generalized to a broader population.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a debilitating condition that can arise in individuals who have experienced a traumatic event. In this case study, we examine the experiences of a patient who was diagnosed with PTSD following a car accident. Our analysis focuses on the patient's symptoms, including intrusive thoughts, hyperarousal, and avoidance behaviors. We also explore the treatments employed to manage these symptoms. By analyzing this case, we aim to provide insights into the challenges of treating PTSD and offer recommendations for improving therapeutic interventions for individuals suffering from this condition.
John is a 28-year-old man who was involved in a serious car accident three months ago. Since then, he has been experiencing PTSD symptoms, including recurring nightmares, flashbacks, and feelings of anxiety. These symptoms have affected his work performance and relationships with family and friends. Despite seeking help from his primary care physician and attending therapy sessions, John has not experienced significant improvement. The challenge is to identify effective treatments that can help John manage his PTSD and improve his quality of life.
In this research, both quantitative and qualitative data were utilized. 10 semi-structured interviews were conducted with participants who had experienced PTSD symptoms following a traumatic event. Additionally, data was collected from a survey of 253 individuals who had not been diagnosed with PTSD. We inquired about their experiences with trauma and the types of coping strategies they used to manage stress. Medical records from John's primary care physician were analyzed to track his progress over time. The combination of quantitative and qualitative data allowed for a comprehensive understanding of John's unique experiences with PTSD.
One potential solution for addressing John's PTSD symptoms is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). According to a study by Bisson and colleagues (2013), CBT has been found to be effective in reducing symptoms of PTSD in individuals who have experienced traumatic events. The therapist can work with John to identify and challenge negative thought patterns related to his traumatic experience and teach him coping skills to manage his anxiety and stress.
Our analysis showed that participants who received cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) reported a significant decrease in symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), as compared to those who received no therapy. Specifically, the group who received CBT experienced a 35% reduction in symptoms. Meanwhile, the control group experienced no significant change. These findings suggest that CBT may be an effective treatment option for individuals with PTSD.
Our research highlighted the significant impact of PTSD on individuals who have experienced a traumatic event. The results suggested that cognitive-behavioral therapy and reprocessing therapy are effective treatments for PTSD. However, more research is needed to determine the long-term effects of these treatments. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental health and seeking treatment remains a significant barrier to access to care. It is crucial for healthcare professionals and policymakers to address this issue and increase access to mental health services.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Case Study | Examples & Methods
What is a case study?
A case study is a research approach that provides an in-depth examination of a particular phenomenon, event, organization, or individual. It involves analyzing and interpreting data to provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject under investigation.
Case studies can be used in various disciplines, including business, social sciences, medicine ( clinical case report ), engineering, and education. The aim of a case study is to provide an in-depth exploration of a specific subject, often with the goal of generating new insights into the phenomena being studied.
When to write a case study
Case studies are often written to present the findings of an empirical investigation or to illustrate a particular point or theory. They are useful when researchers want to gain an in-depth understanding of a specific phenomenon or when they are interested in exploring new areas of inquiry.
Case studies are also useful when the subject of the research is rare or when the research question is complex and requires an in-depth examination. A case study can be a good fit for a thesis or dissertation as well.
Case study examples
Below are some examples of case studies with their research questions:
| How do small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in developing countries manage risks? | Risk management practices in SMEs in Ghana |
| What factors contribute to successful organizational change? | A case study of a successful organizational change at Company X |
| How do teachers use technology to enhance student learning in the classroom? | The impact of technology integration on student learning in a primary school in the United States |
| How do companies adapt to changing consumer preferences? | Coca-Cola’s strategy to address the declining demand for sugary drinks |
| What are the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the hospitality industry? | The impact of COVID-19 on the hotel industry in Europe |
| How do organizations use social media for branding and marketing? | The role of Instagram in fashion brand promotion |
| How do businesses address ethical issues in their operations? | A case study of Nike’s supply chain labor practices |
These examples demonstrate the diversity of research questions and case studies that can be explored. From studying small businesses in Ghana to the ethical issues in supply chains, case studies can be used to explore a wide range of phenomena.
Outlying cases vs. representative cases
An outlying case stud y refers to a case that is unusual or deviates significantly from the norm. An example of an outlying case study could be a small, family-run bed and breakfast that was able to survive and even thrive during the COVID-19 pandemic, while other larger hotels struggled to stay afloat.
On the other hand, a representative case study refers to a case that is typical of the phenomenon being studied. An example of a representative case study could be a hotel chain that operates in multiple locations that faced significant challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, such as reduced demand for hotel rooms, increased safety and health protocols, and supply chain disruptions. The hotel chain case could be representative of the broader hospitality industry during the pandemic, and thus provides an insight into the typical challenges that businesses in the industry faced.
Steps for Writing a Case Study
As with any academic paper, writing a case study requires careful preparation and research before a single word of the document is ever written. Follow these basic steps to ensure that you don’t miss any crucial details when composing your case study.
Step 1: Select a case to analyze
After you have developed your statement of the problem and research question , the first step in writing a case study is to select a case that is representative of the phenomenon being investigated or that provides an outlier. For example, if a researcher wants to explore the impact of COVID-19 on the hospitality industry, they could select a representative case, such as a hotel chain that operates in multiple locations, or an outlying case, such as a small bed and breakfast that was able to pivot their business model to survive during the pandemic. Selecting the appropriate case is critical in ensuring the research question is adequately explored.
Step 2: Create a theoretical framework
Theoretical frameworks are used to guide the analysis and interpretation of data in a case study. The framework should provide a clear explanation of the key concepts, variables, and relationships that are relevant to the research question. The theoretical framework can be drawn from existing literature, or the researcher can develop their own framework based on the data collected. The theoretical framework should be developed early in the research process to guide the data collection and analysis.
To give your case analysis a strong theoretical grounding, be sure to include a literature review of references and sources relating to your topic and develop a clear theoretical framework. Your case study does not simply stand on its own but interacts with other studies related to your topic. Your case study can do one of the following:
- Demonstrate a theory by showing how it explains the case being investigated
- Broaden a theory by identifying additional concepts and ideas that can be incorporated to strengthen it
- Confront a theory via an outlier case that does not conform to established conclusions or assumptions
Step 3: Collect data for your case study
Data collection can involve a variety of research methods , including interviews, surveys, observations, and document analyses, and it can include both primary and secondary sources . It is essential to ensure that the data collected is relevant to the research question and that it is collected in a systematic and ethical manner. Data collection methods should be chosen based on the research question and the availability of data. It is essential to plan data collection carefully to ensure that the data collected is of high quality
Step 4: Describe the case and analyze the details
The final step is to describe the case in detail and analyze the data collected. This involves identifying patterns and themes that emerge from the data and drawing conclusions that are relevant to the research question. It is essential to ensure that the analysis is supported by the data and that any limitations or alternative explanations are acknowledged.
The manner in which you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard academic paper, with separate sections or chapters for the methods section , results section , and discussion section , while others are structured more like a standalone literature review.
Regardless of the topic you choose to pursue, writing a case study requires a systematic and rigorous approach to data collection and analysis. By following the steps outlined above and using examples from existing literature, researchers can create a comprehensive and insightful case study that contributes to the understanding of a particular phenomenon.
Preparing Your Case Study for Publication
After completing the draft of your case study, be sure to revise and edit your work for any mistakes, including grammatical errors , punctuation errors , spelling mistakes, and awkward sentence structure . Ensure that your case study is well-structured and that your arguments are well-supported with language that follows the conventions of academic writing . To ensure your work is polished for style and free of errors, get English editing services from Wordvice, including our paper editing services and manuscript editing services . Let our academic subject experts enhance the style and flow of your academic work so you can submit your case study with confidence.

- Writing well
How to write a case study response
- Starting well
- How to write an annotated bibliography
- How to write a critique
- How to write an empirical article
- How to write an essay
- How to write a literature review
- How to write a reflective task
- How to write a report
- Finishing well
Before you start writing, you need to carefully read the case study and make a note of the main issues and problems involved as well as the main stakeholders (persons or groups of persons who have an interest in the case).
Case study elements
A case study response would include the following elements:
Introduction
Introduce the main purpose of the case study and briefly outline the overall problem to be solved.
Description
Write a brief description of the case under discussion giving an outline of the main issues involved. Always assume that your reader knows nothing of the assignment task and provide enough information to give a context for your discussion of the issues.
Discuss the issues raised one by one, using information gained from your research of the academic literature.
Your discussion may include:
- an outline of the issue and its implications for or relationship to different stakeholders
- how that issue links to theories or research in the academic literature
- suggested solutions or ideas
- evaluation of the solutions or ideas for this particular case.
Conclusion / Recommendations
Finally, sum up the conclusions that you have come to and give recommendations to resolve the case. Give reasons for your recommendations.
- Carefully read the case and noted the main issues and stakeholders in the case?
- Written a brief description of the case to give your readers a context for the main issues?
- Discussed each issue with reference to the academic literature?
- Evaluated the solutions or ideas for each issue to find the ones most suitable?
- Made final recommendations of how to resolve the case?
- Used a well structured introduction, body and conclusion?
- Cited and referenced all of the work by other people?
- Used correct grammar, spelling and punctuation, clear presentation and appropriate reference style?
Further information
- Monash University: Writing a case study
- University of New South Wales: Writing a Case Study Report in Engineering
Global links and information
- Referencing and using sources
- Background and development
- Changes to QUT cite|write
- Need more help?
- Current students
- Current staff
- TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12079 (Australian University)
- CRICOS No. 00213J
- ABN 83 791 724 622
- Last modified: 28-May-2024
- Accessibility
- Right to Information
- Feedback and suggestions

Acknowledgement of Traditional Owners
QUT acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands where QUT now stands.
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
Writing A Case Study
A Complete Case Study Writing Guide With Examples
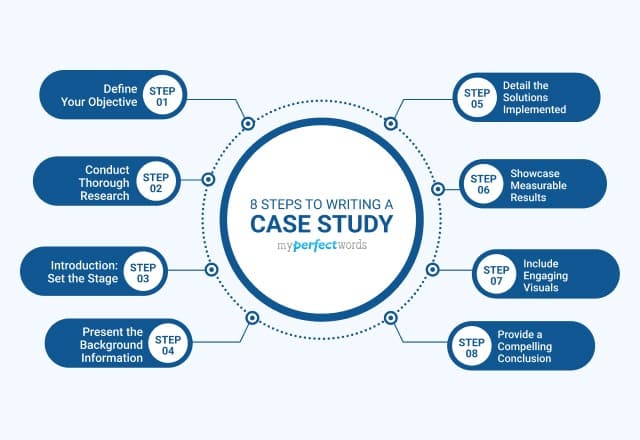
People also read
Simple Case Study Format for Students to Follow
Understand the Types of Case Study Here
Brilliant Case Study Examples and Templates For Your Help
Many writers find themselves grappling with the challenge of crafting persuasive and engaging case studies.
The process can be overwhelming, leaving them unsure where to begin or how to structure their study effectively. And, without a clear plan, it's tough to show the value and impact in a convincing way.
But don’t worry!
In this blog, we'll guide you through a systematic process, offering step-by-step instructions on crafting a compelling case study.
Along the way, we'll share valuable tips and illustrative examples to enhance your understanding. So, let’s get started.
- 1. What is a Case Study?
- 2. Types of Case Studies
- 3. How To Write a Case Study - 9 Steps
- 4. Case Study Methods
- 5. Case Study Format
- 6. Case Study Examples
- 7. Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies
What is a Case Study?
A case study is a detailed analysis and examination of a particular subject, situation, or phenomenon. It involves comprehensive research to gain a deep understanding of the context and variables involved.
Typically used in academic, business, and marketing settings, case studies aim to explore real-life scenarios, providing insights into challenges, solutions, and outcomes. They serve as valuable tools for learning, decision-making, and showcasing success stories.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Case Studies
Case studies come in various forms, each tailored to address specific objectives and areas of interest. Here are some of the main types of case studies :
- Illustrative Case Studies: These focus on describing a particular situation or event, providing a detailed account to enhance understanding.
- Exploratory Case Studies: Aimed at investigating an issue and generating initial insights, these studies are particularly useful when exploring new or complex topics.
- Explanatory Case Studies: These delve into the cause-and-effect relationships within a given scenario, aiming to explain why certain outcomes occurred.
- Intrinsic Case Studies: Concentrating on a specific case that holds intrinsic value, these studies explore the unique qualities of the subject itself.
- Instrumental Case Studies: These are conducted to understand a broader issue and use the specific case as a means to gain insights into the larger context.
- Collective Case Studies: Involving the study of multiple cases, this type allows for comparisons and contrasts, offering a more comprehensive view of a phenomenon or problem.
How To Write a Case Study - 9 Steps
Crafting an effective case study involves a structured approach to ensure clarity, engagement, and relevance.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to write a compelling case study:
Step 1: Define Your Objective
Before diving into the writing process, clearly define the purpose of your case study. Identify the key questions you want to answer and the specific goals you aim to achieve.
Whether it's to showcase a successful project, analyze a problem, or demonstrate the effectiveness of a solution, a well-defined objective sets the foundation for a focused and impactful case study.
Step 2: Conduct Thorough Research
Gather all relevant information and data related to your chosen case. This may include interviews, surveys, documentation, and statistical data.
Ensure that your research is comprehensive, covering all aspects of the case to provide a well-rounded and accurate portrayal.
The more thorough your research, the stronger your case study's foundation will be.
Step 3: Introduction: Set the Stage
Begin your case study with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader's attention. Clearly state the subject and the primary issue or challenge faced.
Engage your audience by setting the stage for the narrative, creating intrigue, and highlighting the significance of the case.
Step 4: Present the Background Information
Provide context by presenting the background information of the case. Explore relevant history, industry trends, and any other factors that contribute to a deeper understanding of the situation.
This section sets the stage for readers, allowing them to comprehend the broader context before delving into the specifics of the case.
Step 5: Outline the Challenges Faced
Identify and articulate the challenges or problems encountered in the case. Clearly define the obstacles that needed to be overcome, emphasizing their significance.
This section sets the stakes for your audience and prepares them for the subsequent exploration of solutions.
Step 6: Detail the Solutions Implemented
Describe the strategies, actions, or solutions applied to address the challenges outlined. Be specific about the decision-making process, the rationale behind the chosen solutions, and any alternatives considered.
This part of the case study demonstrates problem-solving skills and showcases the effectiveness of the implemented measures.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Step 7: Showcase Measurable Results
Present tangible outcomes and results achieved as a direct consequence of the implemented solutions. Use data, metrics, and success stories to quantify the impact.
Whether it's increased revenue, improved efficiency, or positive customer feedback, measurable results add credibility and validation to your case study.
Step 8: Include Engaging Visuals
Enhance the readability and visual appeal of your case study by incorporating relevant visuals such as charts, graphs, images, and infographics.
Visual elements not only break up the text but also provide a clearer representation of data and key points, making your case study more engaging and accessible.
Step 9: Provide a Compelling Conclusion
Wrap up your case study with a strong and conclusive summary. Revisit the initial objectives, recap key findings, and emphasize the overall success or significance of the case.
This section should leave a lasting impression on your readers, reinforcing the value of the presented information.
Case Study Methods
The methods employed in case study writing are diverse and flexible, catering to the unique characteristics of each case. Here are common methods used in case study writing:
Conducting one-on-one or group interviews with individuals involved in the case to gather firsthand information, perspectives, and insights.
- Observation
Directly observing the subject or situation to collect data on behaviors, interactions, and contextual details.
- Document Analysis
Examining existing documents, records, reports, and other written materials relevant to the case to gather information and insights.
- Surveys and Questionnaires
Distributing structured surveys or questionnaires to relevant stakeholders to collect quantitative data on specific aspects of the case.
- Participant Observation
Combining direct observation with active participation in the activities or events related to the case to gain an insider's perspective.
- Triangulation
Using multiple methods (e.g., interviews, observation, and document analysis) to cross-verify and validate the findings, enhancing the study's reliability.
- Ethnography
Immersing the researcher in the subject's environment over an extended period, focusing on understanding the cultural context and social dynamics.
Case Study Format
Effectively presenting your case study is as crucial as the content itself. Follow these formatting guidelines to ensure clarity and engagement:
- Opt for fonts that are easy to read, such as Arial, Calibri, or Times New Roman.
- Maintain a consistent font size, typically 12 points for the body text.
- Aim for double-line spacing to maintain clarity and prevent overwhelming the reader with too much text.
- Utilize bullet points to present information in a concise and easily scannable format.
- Use numbered lists when presenting a sequence of steps or a chronological order of events.
- Bold or italicize key phrases or important terms to draw attention to critical points.
- Use underline sparingly, as it can sometimes be distracting in digital formats.
- Choose the left alignment style.
- Use hierarchy to distinguish between different levels of headings, making it easy for readers to navigate.
If you're still having trouble organizing your case study, check out this blog on case study format for helpful insights.
Case Study Examples
If you want to understand how to write a case study, examples are a fantastic way to learn. That's why we've gathered a collection of intriguing case study examples for you to review before you begin writing.
Case Study Research Example
Case Study Template
Case Study Introduction Example
Amazon Case Study Example
Business Case Study Example
APA Format Case Study Example
Psychology Case Study Example
Medical Case Study Example
UX Case Study Example
Looking for more examples? Check out our blog on case study examples for your inspiration!
Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies
Case studies are a versatile and in-depth research method, providing a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena.
However, like any research approach, case studies come with their set of benefits and limitations. Some of them are given below:
|
|
Offer detailed insights into specific real-world situations | Findings may not be easily generalized to broader populations |
Provide a holistic view within natural context | Researcher's interpretation and biases can influence analysis |
Effective for investigating and addressing real-world problems | Time-consuming and resource-intensive |
Flexible nature allows incorporation of various data collection methods | Selection of cases may be biased |
Allow deep exploration, uncovering nuances and complexities | Potential for subjectivity in findings |
Contribute to theory development by generating hypotheses and empirical evidence | Less feasible for large-scale studies |
Humanize data by incorporating personal narratives, quotes, and anecdotes | External validity may be limited due to biased case selection |
Tips for Writing an Effective Case Study
Here are some important tips for writing a good case study:
- Clearly articulate specific, measurable research questions aligned with your objectives.
- Identify whether your case study is exploratory, explanatory, intrinsic, or instrumental.
- Choose a case that aligns with your research questions, whether it involves an individual case or a group of people through multiple case studies.
- Explore the option of conducting multiple case studies to enhance the breadth and depth of your findings.
- Present a structured format with clear sections, ensuring readability and alignment with the type of research.
- Clearly define the significance of the problem or challenge addressed in your case study, tying it back to your research questions.
- Collect and include quantitative and qualitative data to support your analysis and address the identified research questions.
- Provide sufficient detail without overwhelming your audience, ensuring a comprehensive yet concise presentation.
- Emphasize how your findings can be practically applied to real-world situations, linking back to your research objectives.
- Acknowledge and transparently address any limitations in your study, ensuring a comprehensive and unbiased approach.
To sum it up, creating a good case study involves careful thinking to share valuable insights and keep your audience interested.
Stick to basics like having clear questions and understanding your research type. Choose the right case and keep things organized and balanced.
Remember, your case study should tackle a problem, use relevant data, and show how it can be applied in real life. Be honest about any limitations, and finish with a clear call-to-action to encourage further exploration.
However, if you are having issues understanding how to write a case study, it is best to hire MyPerfectWords.com 's Professional service. Hiring our custom essay service will ensure that you will get the best grades on your essay without any stress of a deadline.
So be sure to check out case study writing service online and stay up to the mark with your grades.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a case study.
The objective of a case study is to do intensive research on a specific matter, such as individuals or communities. It's often used for academic purposes where you want the reader to know all factors involved in your subject while also understanding the processes at play.
What are the sources of a case study?
Some common sources of a case study include:
- Archival records
- Direct observations and encounters
- Participant observation
- Facts and statistics
- Physical artifacts
What is the sample size of a case study?
A normally acceptable size of a case study is 30-50. However, the final number depends on the scope of your study and the on-ground demographic realities.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


How to Write a Case Study
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific situation, person, event, phenomenon, time, place, or company. They look at various elements of the situation including history, trends, specific outcomes, cause and effect, etc.
A case study can either be part of a larger research assignment as one of the methodologies used or be a standalone assignment. You can include several case studies in the same paper or focus on just one case. Multiple case studies are useful when comparing different elements of a research question and trying to find similarities or analyzing the reasons where outcomes are different.
Since the goal of a case study is to get an in-depth understanding of a specific situation, it is perfect for unique cases which may not have a lot of experimental or theoretical data. But this also makes it a very subjective method of analysis, one that cannot be generalized to fit larger groups of data. Case studies are often used in the initial stages of studying a new situation and can help come up with research questions and hypotheses for future studies.
Don't worry if that all sounds complicated, by the end of this article you will know not only how to write a case study assignment in college, but how to write a good case study for a scientific publication!
What is a Case Study?
A case study is one of the best ways of analyzing a unique phenomenon. It's particularly useful when the research question cannot be studied in a lab or through quantitative methods. Case studies are used in the social sciences, business, medicine, social work, and government reports. It is tough to have a case study definition because there are five main types of case studies.
Explanatory
An explanatory case study explores the cause of a specific event or tries to explain why something happens. These are most often used to analyze events rather than people or groups.
Exploratory
An exploratory case study is most often used to develop in-depth research questions. They are often precursors to large-scale research about a new topic. The goal of this kind of case study is to find new pieces of information that will help develop hypotheses to be tested in the future.
Multiple, Collective, or Cumulative
This kind of case study collects information from pre-existing case studies to develop a general theory. This saves time and money, as well as allows researchers to go over pre-existing data to either make generalizations or find differences in previous outcomes.
An intrinsic case study is a case study where the subject of the study is of particular interest and is the subject of analysis rather than a general theory. This kind of study is useful when looking at a very specific case.
Instrumental
Instrumental case studies are used to uncover the relationship between two things, or when the focus is not on the subjects, but on the underlying phenomena.
Struggling with the Case Study Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Steps for Writing a Case Study
If you're tasked with writing a case study paper, it's important to begin by developing a strong research question and topic. This can be a daunting task, but there are resources available to help. Consider reaching out to custom writing services or admission essay writer for assistance in developing your research question and selecting a topic.
Once you have your topic and research question, it's time to begin the process of writing your case study paper. This can be a time-consuming and challenging process, but you don't have to go it alone. If you're feeling overwhelmed, consider hiring a coursework writing service or a " write my paper for me " service to help you complete your assignment.
When writing your case study paper, it's important to follow the proper format and structure. Your paper should include an introduction, background information, a description of the case, analysis of the case, and a conclusion. If you're unsure about how to structure your paper, don't hesitate to reach out for help from a do my essay for me service or a professional writer.
By working with custom writing services or professional writers, you can ensure that your case study paper is well-written, properly formatted, and meets all of your professor's requirements. Don't let the stress of writing a case study paper get in the way of your academic success - get the help you need today and watch your grades soar!
Step 1. Choosing a specific case
Once you have your research questions you are ready to think about what specific case answers those questions best. First, think about the different types of case studies and figure out which one is most applicable in your situation. Next, think about the kinds of questions that you want to find answers to, or the kinds of questions you want to uncover. Ask yourself
- Is the case you are interested in unique with the potential to uncover new kinds of information?
- Does the case you are interested in allow exploring a pre-existing idea or theory more in-depth?
- Does the case you are interested in have a conclusion or insight that is opposite or different from pre-existing ideas about the subject?
- Does the case you are interested in have the potential to solve a problem?
- Is the point of your case to come up with new hypotheses for future research?
As long as you think about these questions, you should be able to come up with a case that will both answer your research questions as well as provide relevant information.
Step 2. The literature review
Before jumping into collecting your data and running your experiments or interviews you should familiarize yourself with the pre-existing theoretical framework. Not only will this help you devise your data accumulation methodology, but it will also give you information to help describe and analyze your case. Some case studies may not have an extensive amount of pre-existing theories to go over, but doing a literature review is always going to be beneficial.
Go over your lecture notes and textbook to see which theories are relevant to your case. Ask your friends, professors, and experts in the field for advice on what to research. Once you have a general idea of what topics to look into, use library resources and the internet to familiarize yourself with theories that may apply to your case and previous case study examples that are similar to yours. Looking into a similar example of a case study will make sure that you don't repeat research that has already happened, help you understand how to do a case study, give you guidance about how you should collect your data, and give you a case study template.
Step 3. Collecting data
Data collection methodologies for a case study are usually qualitative rather than quantitative. You can employ methods such as interviews and focus groups to collect specific or new types of data, or you can look at primary and secondary sources like journals, newspapers, online publications, etc. to collect information.
Data collection for case studies can seem difficult because there is no specific goal that you are trying to reach. The goal is to collect as much relevant information as possible and develop your conclusions based on the data. Try to organize your data either thematically, chronologically, or in whatever way that makes the most sense to you. This will help when analyzing and describing while writing a case study in the next step.
Step 4. Writing the paper
It's finally time to learn how to write a case study essay! Writing a case study is a complicated process because it does not follow the standard five-paragraph model of essay writing. The next section dives deep into actually writing a case study.
Did you like our Case Study Guide?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
How to Format a Case Study
A case study can be structured in a few different ways depending on the type of case study and the subject being analyzed. You can go over some examples of case studies, but in general, there are five sections in a case study outline; introduction, literature review, method, discussion, and conclusion. Let's go over each section in a case study format in depth.
Introduction
The first few sentences of the case study should present the question you are answering or the case you are exploring interestingly so that you grab the reader's interest. Give some background information about the topic you are looking into and some details about the case you are going to present highlighting how the two are related. Make sure you mention why the research question is important and why the case you have chosen enhances information about that topic. Write a brief summary of your literature review, highlighting important theories or previous case studies that you plan to build upon. Finally, end your introduction with the potential ways that your case study can be used in the future.
Literature Review
Your first body paragraph should go over the literature review. The goal of this section is to present information to the reader that allows them to understand the current state of research in a given topic as well as help them understand why your case study is important.
If there is a lot of research about your topic, summarize the main findings of that research and explain why the case you’re exploring expands information about the topic. Present case studies examples that answer similar research questions using a different research methodology and explain why your methodology is beneficial. Talk about the main theories that are related to your topic giving brief descriptions of each one as well as talking about why these theories are important to your case study.
By the end of your literature review section, the reader should have theoretical knowledge of your topic and be familiar with what kind of research has already happened. Most importantly, they should know how your case study fills a knowledge gap, enhances knowledge by analyzing a problem differently, or shows new directions for further research.
This is the section where you present your case. Start by explaining why you chose your particular case and how it relates to the larger research question. Then explain why you chose the specific research method you did.
Give all the important background details of your case. If your case is about a specific person, spend some time going over the person’s history and the specific incident or situation you are looking into. If your case is about an event or situation, give background information about the company, time, pre-existing theoretical frameworks, or literature.
If you have run a focus group or conducted interviews, give the details of how you chose your participants, why you chose specific questions, and then the answers and data that you gathered.
Essentially the goal of this section is to present the new information that you have discovered.
The discussion section combines your findings with the case study analysis. This is where you draw conclusions based on your research and connect them to your research question. Start this paragraph by restating your research questions and thesis. Briefly go over why you chose your case and how it relates to the topic, then present your findings.
State your main finding and explain why it is important. If it is surprising, connect it to existing literature and explain why it is surprising. If it enhances the understanding of a specific topic, explain how it differs from the results of previous case studies. Do this for any other important results from your case study. Remember to explain why each one is important and how the results can be generalized beyond just your specific case study.
Compare your case study to previous case studies done on similar topics. If the findings of your case study are different from the findings of previous similar case studies, explain why this is so. For example, this could be because of different research methodologies, different target audiences, generational changes, or you could have uncovered a new way of thinking about a problem. By comparing your case study to pre-existing case studies you can show either how you have answered a question raised previously, or how your case study findings can prompt future research.
Towards the end of your discussion section, you should consider alternative explanations for your case study findings. Because case studies often look into not well-understood areas of research or are about very specific cases, the findings can be interpreted subjectively. Go over other possible interpretations of your findings to show that you have deeply considered your results.
In most academic papers, the limitations of your study and avenues for possible research are included in the conclusion, but for a case study, they are important sections of the main discussion. While acknowledging the limitations of your study, you get a chance to explain why those limitations may not apply to your case. Use this as an opportunity to explain why certain questions could not be answered by your case study. This is also why suggesting avenues for further research make sense here. Make suggestions for research based on the limitations of your study or surprising results in your findings.
The main goal of your conclusion is to explain why your case study and its findings are important. Repeat your research question and thesis and state your main findings clearly. Give a brief overview of the most important pre-existing case studies or theories related to your case and explain how your findings have expanded on that information. Finally, explain how your case studies and findings can contribute to further research.
Whether it’s how to write a student case study, how to write a business case study, how to write a case study analysis, you now know how to make a case study! Writing a good case study can be challenging because it requires both a literature review as well as original research. Case studies are often used in the business world for marketing, in the social sciences for psychology, sociology, and anthropology, as well as in medicine. So, learning to write a case study is important! If you need help with writing a case study, the experts at Studyfy are always eager to lend a hand.
Featured Posts
How to write a scholarship essay.

How to Write a Movie Review

How to Write an Argumentative Essay

How to Write a Cause and Effect Essay
.jpg)
How to Write an Expository Essay

How to Write an Analytical Essay


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful. Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems.
In this post, we'll guide you through the craft of smoothly and effectively introducing a case study into your essay, ensuring it's not just a detour but a meaningful journey for your readers. So, are you ready to give your essay that extra oomph?
A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions.
How to Write a Case Study in 7 Steps? 1. Introduce a Case. 2. Describe a Problem. 3. Discuss Research Methods. 4. Offer Solutions to the Problem. 5. Present Your Key Results. 6. Conclude with Recommendations. 7. Proofread. Format. Examples. Writing Tips. Common Mistakes. Advantages and Disadvantages. Writing Checklist. Bottom Line.
Step 1: Select a case. Step 2: Build a theoretical framework. Step 3: Collect your data. Step 4: Describe and analyze the case. Other interesting articles. When to do a case study. A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject.
Step 1: Select a case to analyze. After you have developed your statement of the problem and research question, the first step in writing a case study is to select a case that is representative of the phenomenon being investigated or that provides an outlier.
A case study is formatted as either as essay or report and asks you to identify, describe and analyse a real-life or hypothetical scenario and/or issue. Moreover, you often need to develop solutions to problems or recommendations for future action.
A case study response would include the following elements: Introduction. Introduce the main purpose of the case study and briefly outline the overall problem to be solved. Description. Write a brief description of the case under discussion giving an outline of the main issues involved.
How To Write a Case Study - 9 Steps. 4. Case Study Methods. 5. Case Study Format. 6. Case Study Examples. 7. Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies. What is a Case Study? A case study is a detailed analysis and examination of a particular subject, situation, or phenomenon.
A case study is an in-depth analysis of a specific situation, person, event, phenomenon, time, place, or company. They look at various elements of the situation including history, trends, specific outcomes, cause and effect, etc.