

Essay Writing: A complete guide for students and teachers
P LANNING, PARAGRAPHING AND POLISHING: FINE-TUNING THE PERFECT ESSAY
Essay writing is an essential skill for every student. Whether writing a particular academic essay (such as persuasive, narrative, descriptive, or expository) or a timed exam essay, the key to getting good at writing is to write. Creating opportunities for our students to engage in extended writing activities will go a long way to helping them improve their skills as scribes.
But, putting the hours in alone will not be enough to attain the highest levels in essay writing. Practice must be meaningful. Once students have a broad overview of how to structure the various types of essays, they are ready to narrow in on the minor details that will enable them to fine-tune their work as a lean vehicle of their thoughts and ideas.

In this article, we will drill down to some aspects that will assist students in taking their essay writing skills up a notch. Many ideas and activities can be integrated into broader lesson plans based on essay writing. Often, though, they will work effectively in isolation – just as athletes isolate physical movements to drill that are relevant to their sport. When these movements become second nature, they can be repeated naturally in the context of the game or in our case, the writing of the essay.
THE ULTIMATE NONFICTION WRITING TEACHING RESOURCE

- 270 pages of the most effective teaching strategies
- 50+ digital tools ready right out of the box
- 75 editable resources for student differentiation
- Loads of tricks and tips to add to your teaching tool bag
- All explanations are reinforced with concrete examples.
- Links to high-quality video tutorials
- Clear objectives easy to match to the demands of your curriculum
Planning an essay

The Boys Scouts’ motto is famously ‘Be Prepared’. It’s a solid motto that can be applied to most aspects of life; essay writing is no different. Given the purpose of an essay is generally to present a logical and reasoned argument, investing time in organising arguments, ideas, and structure would seem to be time well spent.
Given that essays can take a wide range of forms and that we all have our own individual approaches to writing, it stands to reason that there will be no single best approach to the planning stage of essay writing. That said, there are several helpful hints and techniques we can share with our students to help them wrestle their ideas into a writable form. Let’s take a look at a few of the best of these:
BREAK THE QUESTION DOWN: UNDERSTAND YOUR ESSAY TOPIC.
Whether students are tackling an assignment that you have set for them in class or responding to an essay prompt in an exam situation, they should get into the habit of analyzing the nature of the task. To do this, they should unravel the question’s meaning or prompt. Students can practice this in class by responding to various essay titles, questions, and prompts, thereby gaining valuable experience breaking these down.
Have students work in groups to underline and dissect the keywords and phrases and discuss what exactly is being asked of them in the task. Are they being asked to discuss, describe, persuade, or explain? Understanding the exact nature of the task is crucial before going any further in the planning process, never mind the writing process .
BRAINSTORM AND MIND MAP WHAT YOU KNOW:
Once students have understood what the essay task asks them, they should consider what they know about the topic and, often, how they feel about it. When teaching essay writing, we so often emphasize that it is about expressing our opinions on things, but for our younger students what they think about something isn’t always obvious, even to themselves.
Brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about a topic offers them an opportunity to uncover not just what they already know about a topic, but also gives them a chance to reveal to themselves what they think about the topic. This will help guide them in structuring their research and, later, the essay they will write . When writing an essay in an exam context, this may be the only ‘research’ the student can undertake before the writing, so practicing this will be even more important.
RESEARCH YOUR ESSAY
The previous step above should reveal to students the general direction their research will take. With the ubiquitousness of the internet, gone are the days of students relying on a single well-thumbed encyclopaedia from the school library as their sole authoritative source in their essay. If anything, the real problem for our students today is narrowing down their sources to a manageable number. Students should use the information from the previous step to help here. At this stage, it is important that they:
● Ensure the research material is directly relevant to the essay task
● Record in detail the sources of the information that they will use in their essay
● Engage with the material personally by asking questions and challenging their own biases
● Identify the key points that will be made in their essay
● Group ideas, counterarguments, and opinions together
● Identify the overarching argument they will make in their own essay.
Once these stages have been completed the student is ready to organise their points into a logical order.
WRITING YOUR ESSAY
There are a number of ways for students to organize their points in preparation for writing. They can use graphic organizers , post-it notes, or any number of available writing apps. The important thing for them to consider here is that their points should follow a logical progression. This progression of their argument will be expressed in the form of body paragraphs that will inform the structure of their finished essay.
The number of paragraphs contained in an essay will depend on a number of factors such as word limits, time limits, the complexity of the question etc. Regardless of the essay’s length, students should ensure their essay follows the Rule of Three in that every essay they write contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Generally speaking, essay paragraphs will focus on one main idea that is usually expressed in a topic sentence that is followed by a series of supporting sentences that bolster that main idea. The first and final sentences are of the most significance here with the first sentence of a paragraph making the point to the reader and the final sentence of the paragraph making the overall relevance to the essay’s argument crystal clear.
Though students will most likely be familiar with the broad generic structure of essays, it is worth investing time to ensure they have a clear conception of how each part of the essay works, that is, of the exact nature of the task it performs. Let’s review:
Common Essay Structure
Introduction: Provides the reader with context for the essay. It states the broad argument that the essay will make and informs the reader of the writer’s general perspective and approach to the question.
Body Paragraphs: These are the ‘meat’ of the essay and lay out the argument stated in the introduction point by point with supporting evidence.
Conclusion: Usually, the conclusion will restate the central argument while summarising the essay’s main supporting reasons before linking everything back to the original question.
ESSAY WRITING PARAGRAPH WRITING TIPS

● Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea
● Paragraphs should follow a logical sequence; students should group similar ideas together to avoid incoherence
● Paragraphs should be denoted consistently; students should choose either to indent or skip a line
● Transition words and phrases such as alternatively , consequently , in contrast should be used to give flow and provide a bridge between paragraphs.
HOW TO EDIT AN ESSAY

Students shouldn’t expect their essays to emerge from the writing process perfectly formed. Except in exam situations and the like, thorough editing is an essential aspect in the writing process.
Often, students struggle with this aspect of the process the most. After spending hours of effort on planning, research, and writing the first draft, students can be reluctant to go back over the same terrain they have so recently travelled. It is important at this point to give them some helpful guidelines to help them to know what to look out for. The following tips will provide just such help:
One Piece at a Time: There is a lot to look out for in the editing process and often students overlook aspects as they try to juggle too many balls during the process. One effective strategy to combat this is for students to perform a number of rounds of editing with each focusing on a different aspect. For example, the first round could focus on content, the second round on looking out for word repetition (use a thesaurus to help here), with the third attending to spelling and grammar.
Sum It Up: When reviewing the paragraphs they have written, a good starting point is for students to read each paragraph and attempt to sum up its main point in a single line. If this is not possible, their readers will most likely have difficulty following their train of thought too and the paragraph needs to be overhauled.
Let It Breathe: When possible, encourage students to allow some time for their essay to ‘breathe’ before returning to it for editing purposes. This may require some skilful time management on the part of the student, for example, a student rush-writing the night before the deadline does not lend itself to effective editing. Fresh eyes are one of the sharpest tools in the writer’s toolbox.
Read It Aloud: This time-tested editing method is a great way for students to identify mistakes and typos in their work. We tend to read things more slowly when reading aloud giving us the time to spot errors. Also, when we read silently our minds can often fill in the gaps or gloss over the mistakes that will become apparent when we read out loud.
Phone a Friend: Peer editing is another great way to identify errors that our brains may miss when reading our own work. Encourage students to partner up for a little ‘you scratch my back, I scratch yours’.
Use Tech Tools: We need to ensure our students have the mental tools to edit their own work and for this they will need a good grasp of English grammar and punctuation. However, there are also a wealth of tech tools such as spellcheck and grammar checks that can offer a great once-over option to catch anything students may have missed in earlier editing rounds.

Putting the Jewels on Display: While some struggle to edit, others struggle to let go. There comes a point when it is time for students to release their work to the reader. They must learn to relinquish control after the creation is complete. This will be much easier to achieve if the student feels that they have done everything in their control to ensure their essay is representative of the best of their abilities and if they have followed the advice here, they should be confident they have done so.
WRITING CHECKLISTS FOR ALL TEXT TYPES

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
ESSAY WRITING video tutorials


- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend
- Copyright 2007-2021 пїЅ
- Submit a worksheet
- Mobile version
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Teach Essay Writing
Last Updated: June 26, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 89,664 times.
Teaching students how to write an essay is a big undertaking, but this is a crucial process for any high school or college student to learn. Start by assigning essays to read and then encourage students to choose an essay topic of their own. Spend class time helping students understand what makes a good essay. Then, use your assignments to guide students through writing their essays.
Choosing Genres and Topics

- Narrative, which is a non-fiction account of a personal experience. This is a good option if you want your students to share a story about something they did, such as a challenge they overcame or a favorite vacation they took. [2] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Expository , which is when you investigate an idea, discuss it at length, and make an argument about it. This might be a good option if you want students to explore a specific concept or a controversial subject. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Descriptive , which is when you describe a person, place, object, emotion, experience, or situation. This can be a good way to allow your students to express themselves creatively through writing. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Argumentative or persuasive essays require students to take a stance on a topic and make an argument to support that stance. This is different from an expository essay in that students won't be discussing a concept at length and then taking a position. The goal of an argumentative essay is to take a position right away and defend it with evidence. [5] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Make sure to select essays that are well-structured and interesting so that your students can model their own essays after these examples. Include essays written by former students, if you can, as well as professionally written essays.
Tip : Readers come in many forms. You can find readers that focus on a specific topic, such as food or pop culture. You can also find reader/handbook combos that will provide general information on writing along with the model essays.

- For example, for each of the essays you assign your students, you could ask them to identify the author's main point or focus, the structure of the essay, the author's use of sources, and the effect of the introduction and conclusion.
- Ask the students to create a reverse outline of the essay to help them understand how to construct a well-written essay. They'll identify the thesis, the main points of the body paragraphs, the supporting evidence, and the concluding statement. Then, they'll present this information in an outline. [8] X Research source

- For example, if you have assigned your students a narrative essay, then encourage them to choose a story that they love to tell or a story they have always wanted to tell but never have.
- If your students are writing argumentative essays, encourage them to select a topic that they feel strongly about or that they'd like to learn more about so that they can voice their opinion.
Explaining the Parts of an Essay

- For example, if you read an essay that begins with an interesting anecdote, highlight that in your class discussion of the essay. Ask students how they could integrate something like that into their own essays and have them write an anecdotal intro in class.
- Or, if you read an essay that starts with a shocking fact or statistic that grabs readers' attention, point this out to your students. Ask them to identify the most shocking fact or statistic related to their essay topic.

- For example, you could provide a few model thesis statements that students can use as templates and then ask them to write a thesis for their topic as an in-class activity or have them post it on an online discussion board.
Tip : Even though the thesis statement is only 1 sentence, this can be the most challenging part of writing an essay for some students. Plan to spend a full class session on writing thesis statements and review the information multiple times as well.

- For example, you could spend a class session going over topic sentences, and then look at how the authors of model essays have used topic sentences to introduce their claims. Then, identify where the author provides support for a claim and how they expand on the source.

- For example, you might direct students to a conclusion in a narrative essay that reflects on the significance of an author's experience. Ask students to write a paragraph where they reflect on the experience they are writing about and turn it in as homework or share it on class discussion board.
- For an expository or argumentative essay, you might show students conclusions that restate the most important aspect of a topic or that offer solutions for the future. Have students write their own conclusions that restate the most important parts of their subject or that outline some possible solutions to the problem.
Guiding Students Through the Writing Process

- Try giving students a sample timeline for how to work on their essays. For example, they might start brainstorming a topic, gathering sources (if required), and taking notes 4 weeks before the paper is due.
- Then, students might begin drafting 2 weeks before the paper is due with a goal of having a full draft 1 week before the essay's due date.
- Students could then plan to start revising their drafts 5 days before the essay is due. This will provide students with ample time to read through their papers a few times and make changes as needed.

- Freewriting, which is when you write freely about anything that comes to mind for a set amount of time, such as 10, 15, or 20 minutes.
- Clustering, which is when you write your topic or topic idea on a piece of paper and then use lines to connect that idea to others.
- Listing, which is when you make a list of any and all ideas related to a topic and ten read through it to find helpful information for your paper.
- Questioning, such as by answering the who, what, when, where, why, and how of their topic.
- Defining terms, such as identifying all of the key terms related to their topic and writing out definitions for each one.

- For example, if your students are writing narrative essays, then it might make the most sense for them to describe the events of a story chronologically.
- If students are writing expository or argumentative essays, then they might need to start by answering the most important questions about their topic and providing background information.
- For a descriptive essay, students might use spatial reasoning to describe something from top to bottom, or organize the descriptive paragraphs into categories for each of the 5 senses, such as sight, sound, smell, taste, and feel.

- For example, if you have just gone over different types of brainstorming strategies, you might ask students to choose 1 that they like and spend 10 minutes developing ideas for their essay.

- Try having students post a weekly response to a writing prompt or question that you assign.
- You may also want to create a separate discussion board where students can post ideas about their essay and get feedback from you and their classmates.

- You could also assign specific parts of the writing process as homework, such as requiring students to hand in a first draft as a homework assignment.

- For example, you might suggest reading the paper backward 1 sentence at a time or reading the paper out loud as a way to identify issues with organization and to weed out minor errors. [21] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Try peer-review workshops that ask students to review each others' work. Students can work in pairs or groups during the workshop. Provide them with a worksheet, graphic organizer, or copy of the assignment rubric to guide their peer-review.
Tip : Emphasize the importance of giving yourself at least a few hours away from the essay before you revise it. If possible, it is even better to wait a few days. After this time passes, it is often easier to spot errors and work out better ways of describing things.
Community Q&A
- Students often need to write essays as part of college applications, for assignments in other courses, and when applying for scholarships. Remind your students of all the ways that improving their essay writing skills can benefit them. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/index.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/narrative_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/expository_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/descriptive_essays.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://wac.colostate.edu/jbw/v1n2/petrie.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uww.edu/learn/restiptool/improve-student-writing
- ↑ https://twp.duke.edu/sites/twp.duke.edu/files/file-attachments/reverse-outline.original.pdf
- ↑ https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide/brainstorming.shtml
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/situating-student-writers/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/faculty-resources/tips-on-teaching-writing/in-class-writing-exercises/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Oct 13, 2017
Did this article help you?
Jul 11, 2017
Jan 26, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.
Four Strategies for Effective Writing Instruction

- Share article
(This is the first post in a two-part series.)
The new question-of-the-week is:
What is the single most effective instructional strategy you have used to teach writing?
Teaching and learning good writing can be a challenge to educators and students alike.
The topic is no stranger to this column—you can see many previous related posts at Writing Instruction .
But I don’t think any of us can get too much good instructional advice in this area.
Today, Jenny Vo, Michele Morgan, and Joy Hamm share wisdom gained from their teaching experience.
Before I turn over the column to them, though, I’d like to share my favorite tool(s).
Graphic organizers, including writing frames (which are basically more expansive sentence starters) and writing structures (which function more as guides and less as “fill-in-the-blanks”) are critical elements of my writing instruction.
You can see an example of how I incorporate them in my seven-week story-writing unit and in the adaptations I made in it for concurrent teaching.
You might also be interested in The Best Scaffolded Writing Frames For Students .
Now, to today’s guests:
‘Shared Writing’
Jenny Vo earned her B.A. in English from Rice University and her M.Ed. in educational leadership from Lamar University. She has worked with English-learners during all of her 24 years in education and is currently an ESL ISST in Katy ISD in Katy, Texas. Jenny is the president-elect of TexTESOL IV and works to advocate for all ELs:
The single most effective instructional strategy that I have used to teach writing is shared writing. Shared writing is when the teacher and students write collaboratively. In shared writing, the teacher is the primary holder of the pen, even though the process is a collaborative one. The teacher serves as the scribe, while also questioning and prompting the students.
The students engage in discussions with the teacher and their peers on what should be included in the text. Shared writing can be done with the whole class or as a small-group activity.
There are two reasons why I love using shared writing. One, it is a great opportunity for the teacher to model the structures and functions of different types of writing while also weaving in lessons on spelling, punctuation, and grammar.
It is a perfect activity to do at the beginning of the unit for a new genre. Use shared writing to introduce the students to the purpose of the genre. Model the writing process from beginning to end, taking the students from idea generation to planning to drafting to revising to publishing. As you are writing, make sure you refrain from making errors, as you want your finished product to serve as a high-quality model for the students to refer back to as they write independently.
Another reason why I love using shared writing is that it connects the writing process with oral language. As the students co-construct the writing piece with the teacher, they are orally expressing their ideas and listening to the ideas of their classmates. It gives them the opportunity to practice rehearsing what they are going to say before it is written down on paper. Shared writing gives the teacher many opportunities to encourage their quieter or more reluctant students to engage in the discussion with the types of questions the teacher asks.
Writing well is a skill that is developed over time with much practice. Shared writing allows students to engage in the writing process while observing the construction of a high-quality sample. It is a very effective instructional strategy used to teach writing.

‘Four Square’
Michele Morgan has been writing IEPs and behavior plans to help students be more successful for 17 years. She is a national-board-certified teacher, Utah Teacher Fellow with Hope Street Group, and a special education elementary new-teacher specialist with the Granite school district. Follow her @MicheleTMorgan1:
For many students, writing is the most dreaded part of the school day. Writing involves many complex processes that students have to engage in before they produce a product—they must determine what they will write about, they must organize their thoughts into a logical sequence, and they must do the actual writing, whether on a computer or by hand. Still they are not done—they must edit their writing and revise mistakes. With all of that, it’s no wonder that students struggle with writing assignments.
In my years working with elementary special education students, I have found that writing is the most difficult subject to teach. Not only do my students struggle with the writing process, but they often have the added difficulties of not knowing how to spell words and not understanding how to use punctuation correctly. That is why the single most effective strategy I use when teaching writing is the Four Square graphic organizer.
The Four Square instructional strategy was developed in 1999 by Judith S. Gould and Evan Jay Gould. When I first started teaching, a colleague allowed me to borrow the Goulds’ book about using the Four Square method, and I have used it ever since. The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of this instructional strategy is that it can be used by any student, in any grade level, for any writing assignment. These are some of the ways I have used this strategy successfully with my students:
* Writing sentences: Students can write the topic for the sentence in the middle box, and in each square, they can draw pictures of details they want to add to their writing.
* Writing paragraphs: Students write the topic sentence in the middle box. They write a sentence containing a supporting detail in three of the squares and they write a concluding sentence in the last square.
* Writing short essays: Students write what information goes in the topic paragraph in the middle box, then list details to include in supporting paragraphs in the squares.
When I gave students writing assignments, the first thing I had them do was create a Four Square. We did this so often that it became automatic. After filling in the Four Square, they wrote rough drafts by copying their work off of the graphic organizer and into the correct format, either on lined paper or in a Word document. This worked for all of my special education students!
I was able to modify tasks using the Four Square so that all of my students could participate, regardless of their disabilities. Even if they did not know what to write about, they knew how to start the assignment (which is often the hardest part of getting it done!) and they grew to be more confident in their writing abilities.
In addition, when it was time to take the high-stakes state writing tests at the end of the year, this was a strategy my students could use to help them do well on the tests. I was able to give them a sheet of blank paper, and they knew what to do with it. I have used many different curriculum materials and programs to teach writing in the last 16 years, but the Four Square is the one strategy that I have used with every writing assignment, no matter the grade level, because it is so effective.

‘Swift Structures’
Joy Hamm has taught 11 years in a variety of English-language settings, ranging from kindergarten to adult learners. The last few years working with middle and high school Newcomers and completing her M.Ed in TESOL have fostered stronger advocacy in her district and beyond:
A majority of secondary content assessments include open-ended essay questions. Many students falter (not just ELs) because they are unaware of how to quickly organize their thoughts into a cohesive argument. In fact, the WIDA CAN DO Descriptors list level 5 writing proficiency as “organizing details logically and cohesively.” Thus, the most effective cross-curricular secondary writing strategy I use with my intermediate LTELs (long-term English-learners) is what I call “Swift Structures.” This term simply means reading a prompt across any content area and quickly jotting down an outline to organize a strong response.
To implement Swift Structures, begin by displaying a prompt and modeling how to swiftly create a bubble map or outline beginning with a thesis/opinion, then connecting the three main topics, which are each supported by at least three details. Emphasize this is NOT the time for complete sentences, just bulleted words or phrases.
Once the outline is completed, show your ELs how easy it is to plug in transitions, expand the bullets into detailed sentences, and add a brief introduction and conclusion. After modeling and guided practice, set a 5-10 minute timer and have students practice independently. Swift Structures is one of my weekly bell ringers, so students build confidence and skill over time. It is best to start with easy prompts where students have preformed opinions and knowledge in order to focus their attention on the thesis-topics-supporting-details outline, not struggling with the rigor of a content prompt.
Here is one easy prompt example: “Should students be allowed to use their cellphones in class?”
Swift Structure outline:
Thesis - Students should be allowed to use cellphones because (1) higher engagement (2) learning tools/apps (3) gain 21st-century skills
Topic 1. Cellphones create higher engagement in students...
Details A. interactive (Flipgrid, Kahoot)
B. less tempted by distractions
C. teaches responsibility
Topic 2. Furthermore,...access to learning tools...
A. Google Translate description
B. language practice (Duolingo)
C. content tutorials (Kahn Academy)
Topic 3. In addition,...practice 21st-century skills…
Details A. prep for workforce
B. access to information
C. time-management support
This bare-bones outline is like the frame of a house. Get the structure right, and it’s easier to fill in the interior decorating (style, grammar), roof (introduction) and driveway (conclusion). Without the frame, the roof and walls will fall apart, and the reader is left confused by circuitous rubble.
Once LTELs have mastered creating simple Swift Structures in less than 10 minutes, it is time to introduce complex questions similar to prompts found on content assessments or essays. Students need to gain assurance that they can quickly and logically explain and justify their opinions on multiple content essays without freezing under pressure.

Thanks to Jenny, Michele, and Joy for their contributions!
Please feel free to leave a comment with your reactions to the topic or directly to anything that has been said in this post.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
Just a reminder; you can subscribe and receive updates from this blog via email (The RSS feed for this blog, and for all Ed Week articles, has been changed by the new redesign—new ones are not yet available). And if you missed any of the highlights from the first nine years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below.
- This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
- Race & Racism in Schools
- School Closures & the Coronavirus Crisis
- Classroom-Management Advice
- Best Ways to Begin the School Year
- Best Ways to End the School Year
- Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
- Implementing the Common Core
- Facing Gender Challenges in Education
- Teaching Social Studies
- Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
- Using Tech in the Classroom
- Student Voices
- Parent Engagement in Schools
- Teaching English-Language Learners
- Reading Instruction
- Writing Instruction
- Education Policy Issues
- Differentiating Instruction
- Math Instruction
- Science Instruction
- Advice for New Teachers
- Author Interviews
- Entering the Teaching Profession
- The Inclusive Classroom
- Learning & the Brain
- Administrator Leadership
- Teacher Leadership
- Relationships in Schools
- Professional Development
- Instructional Strategies
- Best of Classroom Q&A
- Professional Collaboration
- Classroom Organization
- Mistakes in Education
- Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


How to Teach Essay Writing in Secondary ELA

Teaching students how to write a multi-paragraph essay is a process, and it isn’t something that can be taught in one class period, nor is it a skill that we should expect our incoming students to know. Before I even assign my students a multi-paragraph essay, I first take several weeks to teach paragraph writing, and I typically do this with my short story unit.
However, once my students are ready to make the jump from paragraphs to an essay, I still continue to break down my writing instruction. When I teach essay writing in my high school English students, I break it down paragraph-by-paragraph to encourage them to be the best writer they can be. All of the lessons that I will refer to throughout this blog post are included in this print and digital essay writing teaching unit .
Teach Essay Writing in Middle School and High School ELA
Start with brainstorming.
I am a huge fan of group brainstorming, especially since I usually have some EL and SPED students mainstreamed in my college prep English classes. I usually dedicate an entire class period to brainstorming where students gather ideas, paragraph topics, and supporting quotes. You can read more about group brainstorming in this blog post where I discuss brainstorming with my students and I teach them how to brainstorm an essay.
Outline the essay
After brainstorming, I move my students to the outlining phase of the writing process. This step is essential because it helps students organize their papers and stay on topic. Ever since I started dedicating an entire class period to in-class essay outlining, I’ve noticed a significant improvement in my students’ essays. You can read more about how I teach essay outlining in this blog post . When we focus on outlining the essay, I make sure that we focus on all of the essential components of an essay: thesis statement, topic sentences, and evidence.
Write the thesis statement
After the class has completed the brainstorming and outlining, I then move on to direct instruction for essay writing. Since students have already outlined their main ideas, they can start working on their thesis statement. I use my introduction and thesis statement lesson to help students write a meaningful thesis statement. I also look at examples of good thesis statements with my students and have students turn in their draft thesis statements to me before moving on.

Write the introduction
Once students have a solid working thesis statement (and I say working because it is possible for it to change throughout this process), I then have them move on to the introduction. Using the same introduction and thesis writing lesson, I then have my students work on drafting a hook and background information to complete their introduction. Now that students are in high school, I don’t accept a question as an acceptable hook. However, if my students get stuck, especially some of my lower students, I have them write their questions and then help them turn them into a statement.
Also, I’ve noticed that students sometimes have a hard time jumping on the hook. They tend to get stuck there, and when this happens, I have them jump right into the background information. In doing so, students get started writing, and they can go back to the hook later.
Topic Sentences
When I complete essay outlining with my students before the drafting process, I typically have them outline each paragraph with a topic sentence and then the quotes they want to use. Once we move from the introduction to the body paragraphs, I have them work on their topic sentence first. I use my topic sentences and body paragraphs essay writing lesson with my students at this point in the essay. Once students have a good topic sentence for their body paragraph, they write the rest of their body paragraph.
Write the body paragraphs
The next step in the writing process, especially for the first essay of the school year, is for students to write out the rest of their body paragraphs. If they’ve done their outlining correctly, they have a good idea about what they want to include in their body paragraphs. In this step, I really emphasize that my students need to provide support and analysis. They should be providing more explanation than simply restating their quotes.
Write the conclusion
Once students have their introduction and body paragraphs complete, I then have them move on to writing the conclusion. At this step, I teach conclusion writing to my students and have them restate the thesis and add a general thought to the end of the paragraph. At this point, I emphasize that students should not be adding in any new information. Also, one way to help students rephrase their thesis statement is to have them rewrite it in two sentences since a thesis statement is typically a one-sentence statement.
Complete peer editing

Provide time for essay revisions
Once students revise their essays and turn them in, I still like to provide students with some time to revise their essays after I grade them. This is where true learning and growth happen. It is when a student thinks they are done but then goes back to try to improve their essay. In this blog post about essay revisions , you can read more about how I conduct them in the classroom.
An entire year of writing instruction
What if I told you that you could have all of your writing instruction for the ENTIRE SCHOOL YEAR planned and ready to go? I’m talking about all the major writing strands and peer editing to grading rubrics. Just imagine how much time and stress you’ll save!
It almost sounds too good to be true, right?
It’s not! My Ultimate Writing Bundle is your one-stop shop for all of your writing instruction needs! Plus, your students will thrive with the built-in scaffolding and consistency throughout the year!
Join the Daring English Teacher community!
Subscribe to receive freebies, teaching ideas, and my latest content by email.
I won’t send you spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
Built with ConvertKit
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

SUBSCRIBE NOW

How to Write an Essay
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Essay Writing Fundamentals
How to prepare to write an essay, how to edit an essay, how to share and publish your essays, how to get essay writing help, how to find essay writing inspiration, resources for teaching essay writing.
Essays, short prose compositions on a particular theme or topic, are the bread and butter of academic life. You write them in class, for homework, and on standardized tests to show what you know. Unlike other kinds of academic writing (like the research paper) and creative writing (like short stories and poems), essays allow you to develop your original thoughts on a prompt or question. Essays come in many varieties: they can be expository (fleshing out an idea or claim), descriptive, (explaining a person, place, or thing), narrative (relating a personal experience), or persuasive (attempting to win over a reader). This guide is a collection of dozens of links about academic essay writing that we have researched, categorized, and annotated in order to help you improve your essay writing.
Essays are different from other forms of writing; in turn, there are different kinds of essays. This section contains general resources for getting to know the essay and its variants. These resources introduce and define the essay as a genre, and will teach you what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab
One of the most trusted academic writing sites, Purdue OWL provides a concise introduction to the four most common types of academic essays.
"The Essay: History and Definition" (ThoughtCo)
This snappy article from ThoughtCo talks about the origins of the essay and different kinds of essays you might be asked to write.
"What Is An Essay?" Video Lecture (Coursera)
The University of California at Irvine's free video lecture, available on Coursera, tells you everything you need to know about the essay.
Wikipedia Article on the "Essay"
Wikipedia's article on the essay is comprehensive, providing both English-language and global perspectives on the essay form. Learn about the essay's history, forms, and styles.
"Understanding College and Academic Writing" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This list of common academic writing assignments (including types of essay prompts) will help you know what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
How to Identify Your Audience
"Audience" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This handout provides questions you can ask yourself to determine the audience for an academic writing assignment. It also suggests strategies for fitting your paper to your intended audience.
"Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
This extensive book chapter from Writing for Success , available online through Minnesota Libraries Publishing, is followed by exercises to try out your new pre-writing skills.
"Determining Audience" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This guide from a community college's writing center shows you how to know your audience, and how to incorporate that knowledge in your thesis statement.
"Know Your Audience" ( Paper Rater Blog)
This short blog post uses examples to show how implied audiences for essays differ. It reminds you to think of your instructor as an observer, who will know only the information you pass along.
How to Choose a Theme or Topic
"Research Tutorial: Developing Your Topic" (YouTube)
Take a look at this short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill to understand the basics of developing a writing topic.
"How to Choose a Paper Topic" (WikiHow)
This simple, step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through choosing a paper topic. It starts with a detailed description of brainstorming and ends with strategies to refine your broad topic.
"How to Read an Assignment: Moving From Assignment to Topic" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Did your teacher give you a prompt or other instructions? This guide helps you understand the relationship between an essay assignment and your essay's topic.
"Guidelines for Choosing a Topic" (CliffsNotes)
This study guide from CliffsNotes both discusses how to choose a topic and makes a useful distinction between "topic" and "thesis."
How to Come Up with an Argument
"Argument" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
Not sure what "argument" means in the context of academic writing? This page from the University of North Carolina is a good place to start.
"The Essay Guide: Finding an Argument" (Study Hub)
This handout explains why it's important to have an argument when beginning your essay, and provides tools to help you choose a viable argument.
"Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument" (University of Iowa)
This page from the University of Iowa's Writing Center contains exercises through which you can develop and refine your argument and thesis statement.
"Developing a Thesis" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page from Harvard's Writing Center collates some helpful dos and don'ts of argumentative writing, from steps in constructing a thesis to avoiding vague and confrontational thesis statements.
"Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
This page offers concrete suggestions for each stage of the essay writing process, from topic selection to drafting and editing.
How to Outline your Essay
"Outlines" (Univ. of North Carolina at Chapel Hill via YouTube)
This short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill shows how to group your ideas into paragraphs or sections to begin the outlining process.
"Essay Outline" (Univ. of Washington Tacoma)
This two-page handout by a university professor simply defines the parts of an essay and then organizes them into an example outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL gives examples of diverse outline strategies on this page, including the alphanumeric, full sentence, and decimal styles.
"Outlining" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Once you have an argument, according to this handout, there are only three steps in the outline process: generalizing, ordering, and putting it all together. Then you're ready to write!
"Writing Essays" (Plymouth Univ.)
This packet, part of Plymouth University's Learning Development series, contains descriptions and diagrams relating to the outlining process.
"How to Write A Good Argumentative Essay: Logical Structure" (Criticalthinkingtutorials.com via YouTube)
This longer video tutorial gives an overview of how to structure your essay in order to support your argument or thesis. It is part of a longer course on academic writing hosted on Udemy.
Now that you've chosen and refined your topic and created an outline, use these resources to complete the writing process. Most essays contain introductions (which articulate your thesis statement), body paragraphs, and conclusions. Transitions facilitate the flow from one paragraph to the next so that support for your thesis builds throughout the essay. Sources and citations show where you got the evidence to support your thesis, which ensures that you avoid plagiarism.
How to Write an Introduction
"Introductions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page identifies the role of the introduction in any successful paper, suggests strategies for writing introductions, and warns against less effective introductions.
"How to Write A Good Introduction" (Michigan State Writing Center)
Beginning with the most common missteps in writing introductions, this guide condenses the essentials of introduction composition into seven points.
"The Introductory Paragraph" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming focuses on ways to grab your reader's attention at the beginning of your essay.
"Introductions and Conclusions" (Univ. of Toronto)
This guide from the University of Toronto gives advice that applies to writing both introductions and conclusions, including dos and don'ts.
"How to Write Better Essays: No One Does Introductions Properly" ( The Guardian )
This news article interviews UK professors on student essay writing; they point to introductions as the area that needs the most improvement.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
"Writing an Effective Thesis Statement" (YouTube)
This short, simple video tutorial from a college composition instructor at Tulsa Community College explains what a thesis statement is and what it does.
"Thesis Statement: Four Steps to a Great Essay" (YouTube)
This fantastic tutorial walks you through drafting a thesis, using an essay prompt on Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter as an example.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through coming up with, writing, and editing a thesis statement. It invites you think of your statement as a "working thesis" that can change.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (Univ. of Indiana Bloomington)
Ask yourself the questions on this page, part of Indiana Bloomington's Writing Tutorial Services, when you're writing and refining your thesis statement.
"Writing Tips: Thesis Statements" (Univ. of Illinois Center for Writing Studies)
This page gives plentiful examples of good to great thesis statements, and offers questions to ask yourself when formulating a thesis statement.
How to Write Body Paragraphs
"Body Paragraph" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course introduces you to the components of a body paragraph. These include the topic sentence, information, evidence, and analysis.
"Strong Body Paragraphs" (Washington Univ.)
This handout from Washington's Writing and Research Center offers in-depth descriptions of the parts of a successful body paragraph.
"Guide to Paragraph Structure" (Deakin Univ.)
This handout is notable for color-coding example body paragraphs to help you identify the functions various sentences perform.
"Writing Body Paragraphs" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
The exercises in this section of Writing for Success will help you practice writing good body paragraphs. It includes guidance on selecting primary support for your thesis.
"The Writing Process—Body Paragraphs" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
The information and exercises on this page will familiarize you with outlining and writing body paragraphs, and includes links to more information on topic sentences and transitions.
"The Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post discusses body paragraphs in the context of one of the most common academic essay types in secondary schools.
How to Use Transitions
"Transitions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill explains what a transition is, and how to know if you need to improve your transitions.
"Using Transitions Effectively" (Washington Univ.)
This handout defines transitions, offers tips for using them, and contains a useful list of common transitional words and phrases grouped by function.
"Transitions" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This page compares paragraphs without transitions to paragraphs with transitions, and in doing so shows how important these connective words and phrases are.
"Transitions in Academic Essays" (Scribbr)
This page lists four techniques that will help you make sure your reader follows your train of thought, including grouping similar information and using transition words.
"Transitions" (El Paso Community College)
This handout shows example transitions within paragraphs for context, and explains how transitions improve your essay's flow and voice.
"Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post, another from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, talks about transitions and other strategies to improve your essay's overall flow.
"Transition Words" (smartwords.org)
This handy word bank will help you find transition words when you're feeling stuck. It's grouped by the transition's function, whether that is to show agreement, opposition, condition, or consequence.
How to Write a Conclusion
"Parts of An Essay: Conclusions" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course explains how to conclude an academic essay. It suggests thinking about the "3Rs": return to hook, restate your thesis, and relate to the reader.
"Essay Conclusions" (Univ. of Maryland University College)
This overview of the academic essay conclusion contains helpful examples and links to further resources for writing good conclusions.
"How to End An Essay" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) by an English Ph.D. walks you through writing a conclusion, from brainstorming to ending with a flourish.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page collates useful strategies for writing an effective conclusion, and reminds you to "close the discussion without closing it off" to further conversation.
How to Include Sources and Citations
"Research and Citation Resources" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL streamlines information about the three most common referencing styles (MLA, Chicago, and APA) and provides examples of how to cite different resources in each system.
EasyBib: Free Bibliography Generator
This online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style. Be sure to select your resource type before clicking the "cite it" button.
CitationMachine
Like EasyBib, this online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style.
Modern Language Association Handbook (MLA)
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of MLA referencing rules. Order through the link above, or check to see if your library has a copy.
Chicago Manual of Style
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of Chicago referencing rules. You can take a look at the table of contents, then choose to subscribe or start a free trial.
How to Avoid Plagiarism
"What is Plagiarism?" (plagiarism.org)
This nonprofit website contains numerous resources for identifying and avoiding plagiarism, and reminds you that even common activities like copying images from another website to your own site may constitute plagiarism.
"Plagiarism" (University of Oxford)
This interactive page from the University of Oxford helps you check for plagiarism in your work, making it clear how to avoid citing another person's work without full acknowledgement.
"Avoiding Plagiarism" (MIT Comparative Media Studies)
This quick guide explains what plagiarism is, what its consequences are, and how to avoid it. It starts by defining three words—quotation, paraphrase, and summary—that all constitute citation.
"Harvard Guide to Using Sources" (Harvard Extension School)
This comprehensive website from Harvard brings together articles, videos, and handouts about referencing, citation, and plagiarism.
Grammarly contains tons of helpful grammar and writing resources, including a free tool to automatically scan your essay to check for close affinities to published work.
Noplag is another popular online tool that automatically scans your essay to check for signs of plagiarism. Simply copy and paste your essay into the box and click "start checking."
Once you've written your essay, you'll want to edit (improve content), proofread (check for spelling and grammar mistakes), and finalize your work until you're ready to hand it in. This section brings together tips and resources for navigating the editing process.
"Writing a First Draft" (Academic Help)
This is an introduction to the drafting process from the site Academic Help, with tips for getting your ideas on paper before editing begins.
"Editing and Proofreading" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page provides general strategies for revising your writing. They've intentionally left seven errors in the handout, to give you practice in spotting them.
"How to Proofread Effectively" (ThoughtCo)
This article from ThoughtCo, along with those linked at the bottom, help describe common mistakes to check for when proofreading.
"7 Simple Edits That Make Your Writing 100% More Powerful" (SmartBlogger)
This blog post emphasizes the importance of powerful, concise language, and reminds you that even your personal writing heroes create clunky first drafts.
"Editing Tips for Effective Writing" (Univ. of Pennsylvania)
On this page from Penn's International Relations department, you'll find tips for effective prose, errors to watch out for, and reminders about formatting.
"Editing the Essay" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This article, the first of two parts, gives you applicable strategies for the editing process. It suggests reading your essay aloud, removing any jargon, and being unafraid to remove even "dazzling" sentences that don't belong.
"Guide to Editing and Proofreading" (Oxford Learning Institute)
This handout from Oxford covers the basics of editing and proofreading, and reminds you that neither task should be rushed.
In addition to plagiarism-checkers, Grammarly has a plug-in for your web browser that checks your writing for common mistakes.
After you've prepared, written, and edited your essay, you might want to share it outside the classroom. This section alerts you to print and web opportunities to share your essays with the wider world, from online writing communities and blogs to published journals geared toward young writers.
Sharing Your Essays Online
Go Teen Writers
Go Teen Writers is an online community for writers aged 13 - 19. It was founded by Stephanie Morrill, an author of contemporary young adult novels.
Tumblr is a blogging website where you can share your writing and interact with other writers online. It's easy to add photos, links, audio, and video components.
Writersky provides an online platform for publishing and reading other youth writers' work. Its current content is mostly devoted to fiction.
Publishing Your Essays Online
This teen literary journal publishes in print, on the web, and (more frequently), on a blog. It is committed to ensuring that "teens see their authentic experience reflected on its pages."
The Matador Review
This youth writing platform celebrates "alternative," unconventional writing. The link above will take you directly to the site's "submissions" page.
Teen Ink has a website, monthly newsprint magazine, and quarterly poetry magazine promoting the work of young writers.
The largest online reading platform, Wattpad enables you to publish your work and read others' work. Its inline commenting feature allows you to share thoughts as you read along.
Publishing Your Essays in Print
Canvas Teen Literary Journal
This quarterly literary magazine is published for young writers by young writers. They accept many kinds of writing, including essays.
The Claremont Review
This biannual international magazine, first published in 1992, publishes poetry, essays, and short stories from writers aged 13 - 19.
Skipping Stones
This young writers magazine, founded in 1988, celebrates themes relating to ecological and cultural diversity. It publishes poems, photos, articles, and stories.
The Telling Room
This nonprofit writing center based in Maine publishes children's work on their website and in book form. The link above directs you to the site's submissions page.
Essay Contests
Scholastic Arts and Writing Awards
This prestigious international writing contest for students in grades 7 - 12 has been committed to "supporting the future of creativity since 1923."
Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest
An annual essay contest on the theme of journalism and media, the Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest awards scholarships up to $1,000.
National YoungArts Foundation
Here, you'll find information on a government-sponsored writing competition for writers aged 15 - 18. The foundation welcomes submissions of creative nonfiction, novels, scripts, poetry, short story and spoken word.
Signet Classics Student Scholarship Essay Contest
With prompts on a different literary work each year, this competition from Signet Classics awards college scholarships up to $1,000.
"The Ultimate Guide to High School Essay Contests" (CollegeVine)
See this handy guide from CollegeVine for a list of more competitions you can enter with your academic essay, from the National Council of Teachers of English Achievement Awards to the National High School Essay Contest by the U.S. Institute of Peace.
Whether you're struggling to write academic essays or you think you're a pro, there are workshops and online tools that can help you become an even better writer. Even the most seasoned writers encounter writer's block, so be proactive and look through our curated list of resources to combat this common frustration.
Online Essay-writing Classes and Workshops
"Getting Started with Essay Writing" (Coursera)
Coursera offers lots of free, high-quality online classes taught by college professors. Here's one example, taught by instructors from the University of California Irvine.
"Writing and English" (Brightstorm)
Brightstorm's free video lectures are easy to navigate by topic. This unit on the parts of an essay features content on the essay hook, thesis, supporting evidence, and more.
"How to Write an Essay" (EdX)
EdX is another open online university course website with several two- to five-week courses on the essay. This one is geared toward English language learners.
Writer's Digest University
This renowned writers' website offers online workshops and interactive tutorials. The courses offered cover everything from how to get started through how to get published.
Writing.com
Signing up for this online writer's community gives you access to helpful resources as well as an international community of writers.
How to Overcome Writer's Block
"Symptoms and Cures for Writer's Block" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue OWL offers a list of signs you might have writer's block, along with ways to overcome it. Consider trying out some "invention strategies" or ways to curb writing anxiety.
"Overcoming Writer's Block: Three Tips" ( The Guardian )
These tips, geared toward academic writing specifically, are practical and effective. The authors advocate setting realistic goals, creating dedicated writing time, and participating in social writing.
"Writing Tips: Strategies for Overcoming Writer's Block" (Univ. of Illinois)
This page from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's Center for Writing Studies acquaints you with strategies that do and do not work to overcome writer's block.
"Writer's Block" (Univ. of Toronto)
Ask yourself the questions on this page; if the answer is "yes," try out some of the article's strategies. Each question is accompanied by at least two possible solutions.
If you have essays to write but are short on ideas, this section's links to prompts, example student essays, and celebrated essays by professional writers might help. You'll find writing prompts from a variety of sources, student essays to inspire you, and a number of essay writing collections.
Essay Writing Prompts
"50 Argumentative Essay Topics" (ThoughtCo)
Take a look at this list and the others ThoughtCo has curated for different kinds of essays. As the author notes, "a number of these topics are controversial and that's the point."
"401 Prompts for Argumentative Writing" ( New York Times )
This list (and the linked lists to persuasive and narrative writing prompts), besides being impressive in length, is put together by actual high school English teachers.
"SAT Sample Essay Prompts" (College Board)
If you're a student in the U.S., your classroom essay prompts are likely modeled on the prompts in U.S. college entrance exams. Take a look at these official examples from the SAT.
"Popular College Application Essay Topics" (Princeton Review)
This page from the Princeton Review dissects recent Common Application essay topics and discusses strategies for answering them.
Example Student Essays
"501 Writing Prompts" (DePaul Univ.)
This nearly 200-page packet, compiled by the LearningExpress Skill Builder in Focus Writing Team, is stuffed with writing prompts, example essays, and commentary.
"Topics in English" (Kibin)
Kibin is a for-pay essay help website, but its example essays (organized by topic) are available for free. You'll find essays on everything from A Christmas Carol to perseverance.
"Student Writing Models" (Thoughtful Learning)
Thoughtful Learning, a website that offers a variety of teaching materials, provides sample student essays on various topics and organizes them by grade level.
"Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
In this blog post by a former professor of English and rhetoric, ThoughtCo brings together examples of five-paragraph essays and commentary on the form.
The Best Essay Writing Collections
The Best American Essays of the Century by Joyce Carol Oates (Amazon)
This collection of American essays spanning the twentieth century was compiled by award winning author and Princeton professor Joyce Carol Oates.
The Best American Essays 2017 by Leslie Jamison (Amazon)
Leslie Jamison, the celebrated author of essay collection The Empathy Exams , collects recent, high-profile essays into a single volume.
The Art of the Personal Essay by Phillip Lopate (Amazon)
Documentary writer Phillip Lopate curates this historical overview of the personal essay's development, from the classical era to the present.
The White Album by Joan Didion (Amazon)
This seminal essay collection was authored by one of the most acclaimed personal essayists of all time, American journalist Joan Didion.
Consider the Lobster by David Foster Wallace (Amazon)
Read this famous essay collection by David Foster Wallace, who is known for his experimentation with the essay form. He pushed the boundaries of personal essay, reportage, and political polemic.
"50 Successful Harvard Application Essays" (Staff of the The Harvard Crimson )
If you're looking for examples of exceptional college application essays, this volume from Harvard's daily student newspaper is one of the best collections on the market.
Are you an instructor looking for the best resources for teaching essay writing? This section contains resources for developing in-class activities and student homework assignments. You'll find content from both well-known university writing centers and online writing labs.
Essay Writing Classroom Activities for Students
"In-class Writing Exercises" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page lists exercises related to brainstorming, organizing, drafting, and revising. It also contains suggestions for how to implement the suggested exercises.
"Teaching with Writing" (Univ. of Minnesota Center for Writing)
Instructions and encouragement for using "freewriting," one-minute papers, logbooks, and other write-to-learn activities in the classroom can be found here.
"Writing Worksheets" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
Berkeley offers this bank of writing worksheets to use in class. They are nested under headings for "Prewriting," "Revision," "Research Papers" and more.
"Using Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism" (DePaul University)
Use these activities and worksheets from DePaul's Teaching Commons when instructing students on proper academic citation practices.
Essay Writing Homework Activities for Students
"Grammar and Punctuation Exercises" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
These five interactive online activities allow students to practice editing and proofreading. They'll hone their skills in correcting comma splices and run-ons, identifying fragments, using correct pronoun agreement, and comma usage.
"Student Interactives" (Read Write Think)
Read Write Think hosts interactive tools, games, and videos for developing writing skills. They can practice organizing and summarizing, writing poetry, and developing lines of inquiry and analysis.
This free website offers writing and grammar activities for all grade levels. The lessons are designed to be used both for large classes and smaller groups.
"Writing Activities and Lessons for Every Grade" (Education World)
Education World's page on writing activities and lessons links you to more free, online resources for learning how to "W.R.I.T.E.": write, revise, inform, think, and edit.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1934 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,812 quotes across 1934 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Headphones for Schools
- Customer cases
- Become a reseller
Language education , Tips for Language Teachers
How to teach essay writing skills.
More about us

Learning any new language is a challenging task. Whether that’s quickly coming up with an answer during a conversation or reading through some text to extract key information, the journey to second language fluency takes time and hard work. This is particularly true when it comes to writing lengthy pieces of text or essays – it’s a massive leap up from translating or writing short sentences.
This skill is particularly important for university students or adult language learners, who are usually trying to develop professional writing skills for international business roles or academic studies. Yet the ability to construct compelling written text is a key, albeit difficult, skill to acquire. This blog post outlines six tips for language teachers to use to help and support their students to write clearer and better structured essays.
6 tips to build your students’ essay writing skills
1. Get the basics right
It is clearly unrealistic to expect students to suddenly be able to write an essay in the target language without support. Build up their confidence over time so that they become familiar with writing increasingly long pieces of text. A key part of this will be to ensure that they understand sentence connectors and know how to write simple, compound and complex sentences – these are the foundations on which more advanced skills can then be developed.
2. Don’t jump straight in
Even in a timed exam situation, it is vital that students take the time to plan their writing and to work out the key points that they wish to communicate. This is also an opportunity for them to identify specific vocabulary or phrases that they might want to include.
Depending on their ability, some of this work can be scaffolded by the teacher to support and encourage progress. Perhaps your students could begin by following an essay structure / word bank you’ve provided or working through a set of questions you’ve prepared? They could then progress to working collaboratively in pairs or groups before tackling a long writing task on their own.
Mind mapping can also be a useful tool to help students organise their ideas and articulate their thoughts before putting pen to paper. It also helps provide a clear reference point for students to revisit whilst writing to ensure that they are still answering the question set!
3. Follow a structure
For most students being asked to write a 1,000 word essay will, at first, feel like a huge ask. So help them to make it feel less of a challenge by breaking it down into manageable chunks. The 5-paragraph essay structure is widely used for second language writers and provides a clear road-map for students to follow.
- Paragraph 1: This is meant to grab the reader’s attention, give them a clear idea of what’s to come and generally sets the tone for the rest of the piece.
- Paragraphs 2 to 4 form the core of the essay’s content. These make specific points that are then backed up by a variety of evidence.
- Paragraph 5 delivers the conclusion, pulling together all of the arguments along with a summary of the key points.
Students may also find the acronym P.E.E useful when writing paragraphs 2 to 4. This stands for Point, Explanation and Evidence. Paragraphs should contain clear points or arguments that support (or reject) the overall theme. This is then followed by a brief explanation and relevant evidence to reinforce the point.
Focusing on these structures can be a big help in building students’ confidence. Their attention can be focused on getting the content and language correct rather than worrying about the essay structure.
4. Share examples of great writing
When writing in their target language it can be very difficult for students to imagine or know what good writing actually looks and sounds like. So share examples with them – from books, the internet or magazines on topics that will engage and interest them.
Whilst it’s important to read them and pick up new words / phrases to include, your students may also find it useful to carefully dissect the examples in detail. Help them to identify what makes a piece of writing entertaining or persuasive and help them build the skills to try it themselves (either individually or as a group)
5. Practice, Practice, Practice
Of course, the very best way to do this is to practice. Writing more often remains the most effective way for students to improve their writing skills. Of course, some of these tasks should be done as homework, but setting small writing tasks in class reduces grade pressure and ensures that educators are on hand to answer any questions and provide constructive feedback.
Pairing students to write practice essays can also be highly effective, particularly when students of mixed ability come together. The weaker student learns from their peers and the stronger student reinforces their understanding by explaining it to their classmate.
It’s also important that educators make the time to review the outputs from writing tasks with students. Highlight the areas where students did well, show them where improvement can be made and get them to look again at grammar / words that they frequently get wrong. This process is vital – it inspires their confidence and encourages students to keep writing and to keep trying to get better.
6. More than words
Every educator will have their own view on the accuracy vs. fluency debate and how they judge the quality of written work students produce will be based on that . Of course, it’s important that students pay attention to using correct grammar, spelling etc, but it’s also vital that the aim of the piece of writing is achieved. More specifically, does it convince? Does it persuade? Does it encourage me to change my behaviour or think again about a topic?
It’s imperative therefore for educators strive to create and deliver writing lessons that cover the core writing skills but which also encourage students to expand their creativity and critical thinking. Helping students to understand the importance of how to plan and structure an argument is also, of course, valuable beyond just language learning. Ultimately these tips aim to help you ensure that students find writing a more fulfilling experience.
How can Sanako help you to teach essay writing skills?
Tools like Sanako Connect can make a big difference in helping students practice and improve their writing skills. It has been specifically designed to help language educators to do this in asynchronous or asynchronous settings. It enables teachers to easily set students tasks that test their writing skills. Connect’s flexibility also allows teachers to upload stimulus material to which students can respond with detailed written answers of any length.
Whatever approach you use to improve your students’ writing skills, Sanako’s market-leading tools include a wealth of unique features that help language educators teach languages more efficiently and more successfully. It’s why the world’s leading educational institutions choose Sanako as their preferred supplier to support online and in-person lesson delivery.
If you are interested in learning more about how Sanako products support language teachers and students and would like to see how they could benefit your institution, book a FREE remote demo now to see them in action.
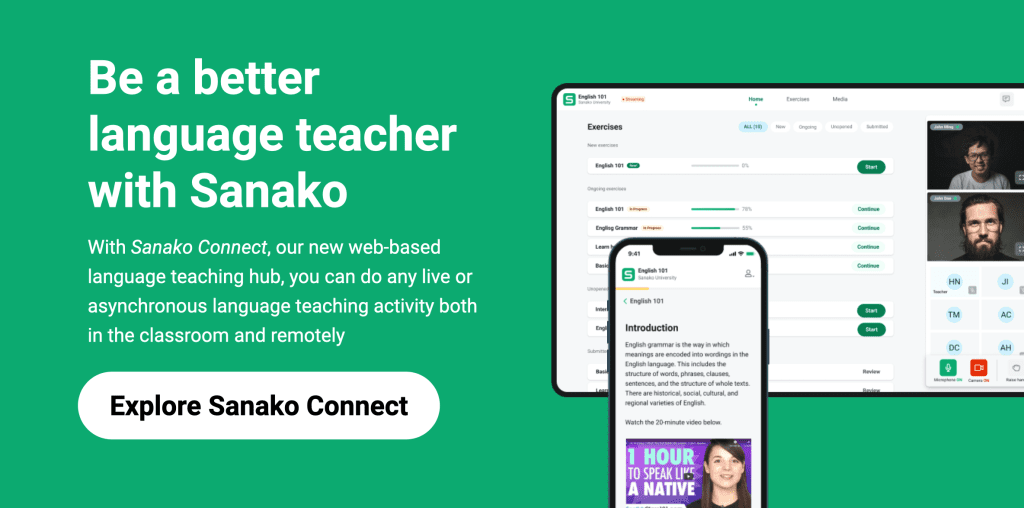
Block "feature-request-pop-up" not found
Become a partner
Brockton Public Schools
How To Teach Essay Writing: Top 5 Tips For Young Teachers
The art of essay writing is an important aspect of the grades and helps your students boost their creativity and express their ideas and notions fluently. Nonetheless, as surprising as it sounds, writing an essay is not a walk in the park and requires proper preparation and effort to establish good writing skills.
The challenge is especially heavier for young teachers seeking to establish rapport with their students while also encouraging them to hone their writing skills. Ideally, even in the finest learning institutions worldwide, it is not uncommon to find students who need to enhance their essay writing skills. But how do you teach essay writing to your students, and ensure they perfect this so important skill?
Luckily, this post has everything every young teacher should know about how to teach essay writing. Here are useful tips you can use to help your students transform into better essay writers!
1. Start By Teaching The Basics Of Good Essay Writing.
The first and most important step to helping your students understand how to write an essay is introducing them to the basics of essay writing. Besides defining essay writing, you must help your students comprehend the proper structure of writing sentences and paragraphs. Once they have this understanding, they can focus on word choice and ideas, among other crucial elements of a good essay. This is often quite similar to reading-you can’t teach your students comprehension before teaching them fluency and decoding, can you?
2. Establish Strong And Regular Writing Routines
As you already know, Practice makes perfect, and this statement is true, especially so with essay writing. Incorporating regular and solid writing routines in your class creates a strong writing culture and promotes creativity.
Ideally, while it is easy for you only to mandate your students to write essays during the normal writing times without offering any extra activities, it
is best to push your students to write through the entire curriculum, especially if you want them to improve their writing skills faster.
It is best to extend writing into every subject area (math included!) by having your students compare, summarize, and contrast journal concepts and ideas. Better yet, incorporating writing into science with multiple activities and research projects allows students to be engaged with current events and even get better at other subjects.
In essence, your students need to see writing-essay writing in virtually everything to allow them to feel comfortable with writing. Oh, and if writing becomes too overwhelming, you can talk about writing in class and get your students engaged in answering questions and floating ideas.
3. Show Your Students Exemplary Essay Samples And Writings To Emulate
For your students to produce better quality essays, they must see a good essay, study how it is established, emulate it, and eventually compare their writings to the necessary standards-rinse and repeat!
You can offer your students two distinct essay writing samples, one weak and the other of superb quality. Initiate an appropriate discussion where the class highlights claims, assess to identify if the topic sentences aptly reinforce the claim and subsequently highlight the key areas of strong argumentation.
Once you grade the samples, your students can then compare their essays to the analyzed samples. The goal you should establish is for your class to make their essays as much as the best sample as possible.
4. Analyze Various Essays Highlighting Both Their Merits And Flaws
On establishing a rapport with your students, you can start offering them various writing pieces regularly for your students to analyze. Depending on their level of understanding, you can twist it, either starting with only a paragraph or offering them a full piece. The best way you can do this is by separating them into various groups ranging from ‘need improvement’ to ‘very good.
Here, you should require your students to justify their reasoning, and when you identify a ‘needs improvement classification,’ ask them to rewrite until it is a good essay.
5. Offer Student-specific And Timely Feedback.
Finally, another crucial aspect you should grasp as a young teacher to help your students create better essays is ensuring you provide them with timely and specific feedback. Once all your students have it, you can spend an entire classroom period analyzing the feedback.
Starting with a mini-lesson is the most effective approach and then divide the classroom into pods, specifically focusing on different essay aspects where your students struggled. What’s more, experts recommend that you pair weak and string writers together to discuss various ways they approach their essay writing process.
With your students having timely feedback regularly, you can spend much of your time planning on re-instruction and better ways to write better essays.
Eventually, with a little desire, effort, and the right guidance from you, every student turns into a better writer. It is upon you to invest both your time and resources in establishing conducive learning and writing culture while offering the necessary guidance to promote their growth and development in the area of essay writing. Using these five easy tips is only a matter of time before your students achieve essay writing success.
Happy Writing!
- How to Teach Essay Writing
Don't just throw your homeschooled-student intoformal essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before movingto more complicated formal essay composition.
Are you a competent essay writer? Even if you know how to write an essay , chances are you are dreading the coming years of teaching homeschool writing just as much as your novice writer could be dreading learning how to write . Writing comes naturally for very few, but most view writing as an insurmountable abstract mountain. The Write Foundation writing curriculum is a divide and conquer method of teaching writing. Focusing on small portions of writing paragraphs and later five-paragraph college level essays, eventually you and your students will be able to use all the necessary writing skills to easily compose wonderfully crafted formal essays .
Start with a good foundation
That is, of course, what The Write Foundation teaches. Don’t just throw your homeschooled-child into the middle of essay crafting. Focus on sentence structure and basic paragraph composition before moving to more complicated formal essay composition . Learn to write essays one bite at a time. This helps students develop writing skills by using writing tools which helps them gain confidence and enables parents who are insecure about their own writing skills learn with their students.
Hold their hand as much as they need you hold their hand.
An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind.
Share the experience with your homeschooler. Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by solidifying the lesson for yourself. As students gain confidence with their new skills they will need your help less and less so they will shoo you away as they learn writing is much easier using the complete writing process.
Use concrete assignments
Creative writing is very subjective, and it is also very abstract for a new writer. You need a writing curriculum which focuses on concrete assignments and provides a variety of writing topics that fit the type of writing being taught in that assignment. Give your students a structure to work into a paragraph using their creative information. Leaving several factors to the unknown, such as type of writing, structure, and so on, leaves more decisions that the novice writer is not ready to determine. An abstract assignment with limited instructions can appear quite daunting to a reluctant, struggling, or just new writer; tiny decisions can become writing blocks in a new writer’s mind. Even experienced writers face writer’s block. Students need to be given tools and taught skills that overcome “But, what do I write about?”
Know your audience
Let your child select from a list of possible writing topics that may be interesting to them. Your child may enjoy the experience more if he is writing about his favorite pastime instead of writing about your favorite pastime. Choosing topics about things that directly influence your child, such as different views about their favorite sport, the influence of network TV or political topics that hit close to home may open the doors for lively discussion and insight into your child’s mind.
Writing is a necessary life skill. When teaching writing remember you are not alone. If you are worried about teaching formal writing to your homeschooler, use the support system of The Write Foundation for any questions you may have through the process, and know that you are not alone. Look into a homeschool writing co-op in your area to lighten the burden and give new perspective on your child’s essay writing development. Use The Write Foundation and use a proven writing system.
Questions or Comments?
Recent articles.
- Correcting Run-on Sentences
- How Does Skipping the Writing Process Affect your Writing?
- Graduating Homeschooling
- Is My Child Ready for Formal Writing?
- Teaching Spelling
- Evaluating Homeschool Writing Curriculums
- Why Most Writing Curriculums Fail (and How to Make Sure your Homeschooler Doesn't!)
- Top Five Reasons Students Hate to Write (and How You can Help!)
- College Preparation for Homeschooled Students
H e is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock. Luke 6:48

View, Print, and Practice the Sample Lessons
(We're here to help you teach!)
Now Available!
Free Reading Lists Get your copy today!
Have a struggling writer? Maybe he hates writing? Does your student just need to learn how to write? Long for teacher-friendly lesson plans you can quickly prepare and teach? Desire a writing curriculum your children will enjoy while learning creatively?
- Complete Lesson Plans
- Free Assessment Tests
- Free Reading Lists
- Organization for Writing
- Checklists & Guidelines
- Brainstorm & Outline Forms
Open doors to writing success!
Contact Rebecca . Rebecca Celsor will answer your questions regarding how to easily teach your child to write.
" At the beginning of this school year I really didn't want to take this class. But it turned out being my favorite class I've taken yet, and I have taken quite a few. I didn't want to take this class because I hated writing papers. Surprisingly I've enjoyed writing my papers, being able to express myself through them and my poetry. You were the most enjoyable and organized teacher I've had yet. "

- Course Selection Assistance
- Suggested Age Levels for Homeschool Writing
- Entry Level I - Prepare to Write
- Entry Level II - Creating Sentences
- Level 1 - Sentence to Paragraph
- Level 2 - Paragraph
- Level 3 - Essay
- Free Curriculum Writing Samples
- Example Teaching Videos
- Online Grading Service
- Writing Skills Reference Folder
- How to Present a Lesson
- Grading Writing
- Key Points for Grading Writing
- MindBenders®
- Order Curriculum Packages
- Order Worksheets Only
- Refund/Return Policy
- Selecting Home School Curriculum
- Writing Preparation
- Writing Development
- High School and Beyond
- Homeschool Co-ops
- Homeschool How To
- The Story Behind TWF
- Why Another Writing Curriculum?
- Copyright Information

He is like a man building a house, who dug deep and laid the foundation on the rock . Luke 6:48
Dedicated to equipping God's children with the ability to communicate His Truth to the world.
- Teaching Tools
- Curriculum Ordering
- homeschool writing curriculum
- home school writing samples
- Mind Benders®
- Online Grading
Copyright © 2021 TheWriteFoundation.org
web site design - evolvethebrand.com
A Quick Guide to Teaching Any Middle School Academic Essay
Using the six traits of writing as common language for teaching any academic essay.
Whenever I met with my middle school English department, sat down with a colleague to collaborate, or simply talked to other others that teach any type of writing, the question would always come up: “So, how do you teach the essay anyway?” The academic essay is often largely subjective in terms of skill sequence and design involved in a unit plan. As I get the opportunity to work with more and more teachers, I find that this type of assignment is largely assigned based on the teacher’s own personal learning experiences, the teacher’s experiences with their mentor teacher, or a commonly known set of skills that everyone thinks is accurate. I am not saying that my way to teach any academic essay is better than anyone else’s method of teaching the essay. This post serves as a starting point for a larger discussion about how the genre of academic essays is implemented throughout the various grade levels. The goal should always be consistent. For the sake of this post, I am going to use the Six Traits of Writing as a common language to talk about how writing is taught in a classroom. I like the six traits of writing because all of the terms used can apply to many different types of writing. Throughout this post, you will find examples and tips on how to approach each part of the academic essay.
What do I mean by academic essay?
An academic essay boils down to an essay that is assigned with a specific prompt and has a particular structure. There is a common expectation for how the assignment will be graded whether that involves teacher feedback, rubrics, or other evaluation tools. This could include many different types of writing including, but not limited to:
Narrative (Personal, descriptive, viewpoint, historical, linear, non-linear)
Expository (Informational, cause & effect, problem & solution, compare & contrast, definition, classification, process)
Argumentative (Persuasive, research, analysis, personal)
Literary Analysis (8th-grade and higher) Note: Literary Analysis is not included in this post.
The expectation is that everyone completes a similar assignment under a number of specified guidelines and a certain set of skills are included in the objectives of the assignment.

Why the Six Traits of Writing?
Use your writing voices.
VOICES is an acronym to remember each part of the Six Traits of Writing. The Six Traits of Writing is a writing framework made largely popular with the books created by Ruth Culham. Often, they are also called Six +1 Traits of Writing when you add the element of Presentation into the equation. Again, this framework applies to all types of writing, so as we move throughout the blog post, you will see how I apply the ideas of the Six Traits of Writing to the academic essay. I also use this framework to help guide my feedback. This is a bonus if you are a newer or pre-service teacher and you are asked, “How are you going to grade this assignment?” Some of these feedback points can be great places to start when it comes to assessing student work.
While it is called VOICES as a way to help you remember what the Six Traits of Writing are called, the order they should be taught is the following:
Organization
Word Choice
Sentence Fluency
Conventions
In middle school, the majority of the time spent on teaching material is on ideas and organization; however, I find many teachers get caught up with teaching and assessing conventions and word choice. While they are important, it is more important to make sure that the awesome ideas that kids have in their minds are getting down on the page. There are some classes that never move on from ideas and organization. As long as you are meeting students where they are, you are able to help move them forward.
The goal is to balance all of the Six Traits of Writing in any given writing piece.
The Six Traits of Writing Explanation and Examples
Voice -the tone and presentation of the piece.
Voice will be determined by the genre of writing. When we start the year with narrative writing, students are introduced to points of view and the first-person, second-person, and third-person. Often, for more informal writing, first-person narration and pronouns are used quite often. In more formal papers like an argument paper or a research paper, a teacher might specify to use third-person narration and pronouns only. This would take the many “I think that…” out of a student’s writing piece and replace them with more direct examples.
Some standards to go by if stuck:
Narrative Writing uses first-person and second-person
Expository Writing uses first-person and third-person depending on the assignment
Argumentative Writing uses third-person depending on the assignment
Example Voice Teacher Feedback Comments:
Third person pronouns only
Too informal of a tone, writing sounds like a casual conversation
Robot writing. Writing does not sound like you.
Remove narration of your own writing. Example: I’m going to show you an example of...
Organization -How the writing is presented to the reader, what goes where
The organization of an academic essay largely depends on who is teaching the setup. All teachers should include examples and give a lesson on how they think an essay should be organized before assigning a paper. Many teachers start with the five-paragraph model as a beginning point on how to show students what a piece of writing should look like. Some people despise the five-paragraph essay. For the sake of this post, I am going to show you the setup that worked for me for over 10+ years of teaching for both a paragraph with evidence and an overall essay. The organization will change depending on genre and assignment, but these are two examples to get you started.
Paragraph Setup:
Topic Sentence
Supporting Detail-Introduces Evidence
Supporting Detail-States and Cites Evidence
Supporting Detail-Explains Evidence (This part may be more than 1 sentence depending on the amount of evidence presented)
Concluding Sentence/Transition

Essay Setup:
Introduction
Hook/Attention Grabber
Summary of Issue/Topic
Claim Statement/Position Statement/Thesis Statement
Body Paragraph (Similar to Paragraph Setup Above)
Topic Sentence (Goes back to claim reason)
**Repeat for each body paragraph**
Restate Claim
Review Reasons
Call-to-Action
Example Organization Teacher Feedback Comments:
Hook missing.
Topic sentences need to go back to reason in the claim
Introduce evidence with a signal phrase
Needs transition words between paragraphs
Needs to restate the claim in the conclusion
The conclusion needs to have a call-to-action
New idea=new paragraph!
Needs a creative title.
Paragraph off-topic
Missing evidence to support reasons
Ideas- The main idea, supporting details, evidence, and explanation
Ideas are the heart of any good paper. This is where you get the argument, the main idea, or the details that really bring the paper to life. Ideas should be the first thing discussed and brainstormed in the writing process. I often recommend using a graphic organizer to help students get their ideas down in a logical way.
Example Ideas Teacher Feedback Comments:
Claim is missing
More background information/summary needed in the introduction
Provide more explanation of evidence in your paragraphs. State why the evidence matters and how it relates to the reason.
Counter-claim is not present/not clear
A repeat of ideas already stated before.
Remove personal opinion
Stating the obvious.
Remove retell of a book or story
Conventions -Editing process involving grammar, punctuation, spelling, and capitalization
Conventions are the typical copy-editing marks that get circled or corrected on a draft. The use of computers has largely made spelling errors an easy conventions mistake to fix before draft turn-in day. Capitalization is also easily corrected. The ideas around grammar and punctuation may require more direct teaching or lessons to help kids learn the rules around these areas.
Example Conventions Comments:
Spelling. Misspelled word.
Comma usage. Insert or delete a comma.
Period usage: Insert or delete a period.
Capitalization error(s)
Missing quotation marks.
Punctuation with quotation marks. Periods and commas always go inside quotation marks.
Cite evidence with quotation marks and page number
Indent paragraphs.
Title formatting. Italicize book titles!
Excellent Word Choice -Vivid word selections to help with meaning, clarity, and interest
This is where the revision and editing process can get more fun! Helping students learn about vivid verbs and swapping out the general “things” and “stuff” for more interesting words is half the fun when working with students on an academic essay. Perhaps, if you have a group of students who use a ton of boring words over and over again, you can have a sort of “word funeral” to outlaw them from some drafts. I did this around Halloween one year, and the kids loved it. You can also have them doing brainstorms on posters for words that are better to use in their papers. Kids love synonyms. Show them how awesome words are on paper and in real life.
Example Word Choice Comments:
Unnecessary words. This section is fluff, filler, or material that just takes up space without saying anything new.
Overused word (s). You seem to use the same word over and over again.
Switch out the word for a more interesting word. Find a synonym.
Needs powerful and active verbs.
Include more adjectives to help your writing with description.
Write out the number. Example 2=two.
Write in present tense. You are talking ABOUT the text now.
Vague pronoun
Sentence Fluency -How the writing SOUNDS, the rhythm and pace
This is one of the more advanced traits to teach, and also the reason why it is second to last on my priority list when I am looking at the Six Traits of Writing. In middle school, you will be focusing on sentence fragments and run-ons. These can also be helped with lessons on punctuation. The goal is to help kids realize that their writing has a particular sound, and the bigger goal is to help them realize that their writing should sound like them-no matter the voice they are using in their writing.
Example Sentence Fluency Comments:
Awkward phrasing/choppy. Avoid choppiness in your writing. You likely have stacked several short sentences together or repeatedly used the same sentence starter. Combine sentences together to connect your ideas and make your writing flow.
Vary how you start sentences. Start sentences with different words.
Vary your sentence length. A lot of your writing sounds the same because the sentences are the same length.
Sentence fragment. A sentence must have a complete thought. Your sentence is missing a piece.
Run-on sentence. Break up your longer sentence into two or three.
Grab an Example Essay Guide in the Digital Downloads Shop!

Want more examples? Want to check out grading best practices for assignments like these?
Read more >>.

Writing Mindset Reflection: How do you teach the academic essay? What is your favorite part of the writing process?

- Professional development
- Planning lessons and courses
Planning a writing lesson
Writing, unlike speaking, is not an ability we acquire naturally, even in our first language - it has to be taught. Unless L2 learners are explicitly taught how to write in the new language, their writing skills are likely to get left behind as their speaking progresses.

But teaching writing is not just about grammar, spelling, or the mechanics of the Roman alphabet. Learners also need to be aware of and use the conventions of the genre in the new language.
What is genre?
Generating ideas
Focusing ideas
Focus on a model text
Organising ideas
- Peer evaluation
A genre can be anything from a menu to a wedding invitation, from a newspaper article to an estate agent's description of a house. Pieces of writing of the same genre share some features, in terms of layout, level of formality, and language. These features are more fixed in formal genre, for example letters of complaint and essays, than in more 'creative' writing, such as poems or descriptions. The more formal genre often feature in exams, and may also be relevant to learners' present or future 'real-world' needs, such as university study or business. However, genre vary considerably between cultures, and even adult learners familiar with a range of genre in their L1 need to learn to use the conventions of those genre in English.
Stages of a writing lesson
I don't necessarily include all these stages in every writing lesson, and the emphasis given to each stage may differ according to the genre of the writing and / or the time available. Learners work in pairs or groups as much as possible, to share ideas and knowledge, and because this provides a good opportunity for practising the speaking, listening and reading skills.
This is often the first stage of a process approach to writing. Even when producing a piece of writing of a highly conventional genre, such as a letter of complaint, using learners' own ideas can make the writing more memorable and meaningful.
- Before writing a letter of complaint, learners think about a situation when they have complained about faulty goods or bad service (or have felt like complaining), and tell a partner.
- As the first stage of preparing to write an essay, I give learners the essay title and pieces of scrap paper. They have 3 minutes to work alone, writing one idea on each piece of paper, before comparing in groups. Each group can then present their 3 best ideas to the class. It doesn't matter if the ideas aren't used in the final piece of writing, the important thing is to break through the barrier of ' I can't think of anything to write.'
This is another stage taken from a process approach, and it involves thinking about which of the many ideas generated are the most important or relevant, and perhaps taking a particular point of view.
- As part of the essay-writing process, students in groups put the ideas generated in the previous stage onto a 'mind map'. The teacher then draws a mind-map on the board, using ideas from the different groups. At this stage he / she can also feed in some useful collocations - this gives the learners the tools to better express their own ideas.
- I tell my students to write individually for about 10 minutes, without stopping and without worrying about grammar or punctuation. If they don't know a particular word, they write it in their L1. This often helps learners to further develop some of the ideas used during the 'Generating ideas' stage. Learners then compare together what they have written, and use a dictionary, the teacher or each other to find in English any words or phrases they wrote in their L1.
Once the students have generated their own ideas, and thought about which are the most important or relevant, I try to give them the tools to express those ideas in the most appropriate way. The examination of model texts is often prominent in product or genre approaches to writing, and will help raise learners' awareness of the conventions of typical texts of different genres in English.
- I give learners in groups several examples of a genre, and they use a genre analysis form to identify the features and language they have in common. This raises their awareness of the features of the genre and gives them some language 'chunks' they can use in their own writing. Genre analysis form 54k
- reason for writing
- how I found out about the job
- relevant experience, skills and abilities
- closing paragraph asking for an interview
- Learners are given an essay with the topic sentences taken out, and put them back in the right place. This raises their awareness of the organisation of the essay and the importance of topic sentences.
Once learners have seen how the ideas are organised in typical examples of the genre, they can go about organising their own ideas in a similar way.
- Students in groups draft a plan of their work, including how many paragraphs and the main points of each paragraph. These can then be pinned up around the room for comment and comparison.
- When preparing to write an essay, students group some of the ideas produced earlier into main and supporting statements.
In a pure process approach, the writer goes through several drafts before producing a final version. In practical terms, and as part of a general English course, this is not always possible. Nevertheless, it may be helpful to let students know beforehand if you are going to ask them to write a second draft. Those with access to a word processor can then use it, to facilitate the redrafting process. The writing itself can be done alone, at home or in class, or collaboratively in pairs or groups. Peer evaluation
Peer evaluation of writing helps learners to become aware of an audience other then the teacher. If students are to write a second draft, I ask other learners to comment on what they liked / didn't like about the piece of work, or what they found unclear, so that these comments can be incorporated into the second draft. The teacher can also respond at this stage by commenting on the content and the organisation of ideas, without yet giving a grade or correcting details of grammar and spelling.
When writing a final draft, students should be encouraged to check the details of grammar and spelling, which may have taken a back seat to ideas and organisation in the previous stages. Instead of correcting writing myself, I use codes to help students correct their own writing and learn from their mistakes. Error correction code 43k
By going through some or all of these stages, learners use their own ideas to produce a piece of writing that uses the conventions of a genre appropriately and in so doing, they are asked to think about the audience's expectations of a piece of writing of a particular genre, and the impact of their writing on the reader.
If you have any ideas that you feel have successfully helped your students to develop their writing why not add them as a comment below and share them.
Further reading
A process genre approach to teaching writing by Badger, Richards and White. ELT Journal Volume 54(2), pp. 153-160 Writing by T Hedge. Oxford University Press. Writing by C Tribble. Oxford University Press Process writing by R White and V Arndt. Longman
Really innovative
- Log in or register to post comments
It was very informative and…
It was very informative and helpful
Interesting article.
Useful information
This is a very nice and…
This is a very nice and informative article.
Thanks for this amazing article
Planning a Writing Lesson Plan
I believe this will make the lesson not only productive but also interesting. Thank you.

Thanks for a very interesting
Thanks for a very interesting and useful article.
Ideas first, then language
Thanks for sharing the plan~
I found in my class that it is always 'Ideas firt, then language follows', similar to L1 writing.
Dear Catherine,
I found your article very useful and I love the advice you give. When I ask my students to write an essay, I tend to correct their mistakes for them and after reading the article I realized that I should be doing it the way you suggested. I learned from my mistakes by finding them out and correcting them not having them corrected for me.
Thank you for a wonderful article.
I am grateful for you for this great article
Research and insight
Browse fascinating case studies, research papers, publications and books by researchers and ELT experts from around the world.
See our publications, research and insight
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Learn English FREE
- Level 3 TEFL Certificate
- Level 5 TEFL Certificate
- Meet Our Trainers
- CPD Workshops
- Safeguarding
- Neo – The AI TEFL Expert
- Teach English Online
- Jobs Search
- My TEFL Resume
- Corporate English Training
- Italian Office
- Employer Dashboard
- Student Sign-up
- Teacher Sign-up
Gallery Teachers
8 easy ways to teach essay writing skills

Teachers play a critical role in teaching various educational skills and developing a young brain. Every genius had modest beginnings and was instructed by a tutor. Teaching is a challenging profession. It often involves dealing with disobedient youngsters who refuse to listen.

Since the pandemic, most high schools, colleges, and universities have moved their lectures online, and students and their tutors must connect using technology.
Due to the global economic downturn, educators have been forced to modify and adjust their instructional methods. They were required to learn new tactics and adapt them to their instruction. Similarly, when a person prepares to become a teacher, they must adjust to the new practices and realities.
However, it involves developing fresh methods to capture the students’ interest, which is not always simple, particularly concerning topics that pupils already deem boring.
Consider academic writing skills as an example. How often have your pupils regarded you with boredom or indifference because you assigned them writing? Writing is an enjoyable and effective means of expression. This post discusses 8 easy ways to teach essay writing skills, which you can share with your students to make essay writing an easy and enjoyable activity.
Nurturing essay writing skills in your pupils
Choose an interesting topic.
The first thing your pupils should consider before writing an essay is the subject. Remember that an essay reveals your students’ research and writing abilities. Therefore, you are responsible for educating them on how to do research. Try to reject the suggested themes if they are too simple for a student, and you will find that writing such an essay will not take much time.
Without research, an essay is not an essay. Explain to your pupils that choosing a subject they understand well and can research is usually preferable. Every student should develop strong research skills. Thus, pay attention to practising various research techniques with them. Describe in detail the methods they may use to gather all the necessary information, how to utilize this knowledge effectively, and how to identify the essential facts.
Focus on the basics of writing
Refreshing your student’s foundational writing abilities should be the first step to teaching essay writing skills. You should pay particular attention to the following: adverbs; adjectives; punctuations; tense; speaking, and so on.
You should not overburden the students. Provide information in logical pieces that pertain to a particular subject. Be sure you are patient since youngsters cannot focus like adults. Always make adjustments and provide straightforward explanations. Give examples so that they may fully comprehend the material.
Start with a thesis statement
You should collaborate with your students to generate a thesis statement. Comprehending this concept is difficult for many people, but it is crucial. To facilitate comprehension, please follow the steps below:
- Give explicit instructions
- Provide simple illustrations
- Help to grasp every detail
- Offer some instructions to get started
Start by elaborating on the significance of a thesis statement in essay writing. It is the essay’s main topic, and your narrative hinges on it. You will know how to convey the narrative if you construct it.
Show students how to write an outline
An outline is one of the most critical components of any essay. It makes a writer disciplined and structured and keeps all the important tasks in front of them. It is particularly crucial for youngsters with limited focus and a tendency to forget key facts. You must demonstrate how to develop an outline and describe its practical significance.
Be careful to demonstrate several outline forms. Teenagers like vivid objects and recall them more quickly. Teach the students first to compose the body, then the introduction, and finally, the conclusion.
Creating an introduction takes time and effort. You’ll need to assemble the fundamental gist of your essay in the beginning, even before you have the complete piece written. Thus, concentrate on the essay’s body first and write the introduction after you have the basic flow jotted down.
How to teach writing skills: What do I use?
Make use of the following items to streamline your tasks.
Use technology
We live in an age of technological advancement that permeates every aspect of human endeavour. Education is not an exception. You can use various intelligent tools with youngsters. Modern students are obsessed with smart applications and devices. It is an ideal opportunity to increase their enthusiasm for essay writing.
Grammar checks and digital organizers are among the most entertaining and helpful applications for high school, college, and university students. When they utilize grammar checkers, they can identify frequent errors that include punctuation, spelling, grammar, selection of words, and stylistics. In addition, there are online essay-writing services that can help students with their essays. In fact, the essay writing service CustomWritings is one of the best sites that allow learners to spend less money on a high-quality custom paper. The website consistently receives high marks in reviews. It has received over 4.7 out of 5 stars on both Trustpilot and Sitejabber, indicating that most customers are satisfied with its services. Most clients who evaluated it were pleased with the guarantees offered, customer service, and work quality. The platform provides assignment assistance, written research papers, affordable essay writing, and various other high-quality, non-plagiarized, and custom-formatted academic services.
Use examples
Without examples, it is difficult to teach. Just provide samples of exceptional essays to help your pupils grasp what constitutes a good piece of writing. It may be an essay written by a former pupil. After seeing an example, the learner will have a concept of what an excellent piece should look like.
Use examples to instruct students on each aspect their essays must have. They will completely understand what constitutes a decent introduction, an instructive body, and a fitting conclusion. In addition, your pupils will be able to examine how sentences are constructed and what grammatical structures are employed.
Insist on having a purpose
Without a purpose, it is hard to compose informative, well-written essays. An essay cannot simply be a piece of writing regarding common knowledge and concepts that everyone fully grasps. Therefore, remind your pupils that they should not rush to write their essays after selecting a subject. Make them choose the essay’s objective. When a student fully comprehends the purpose of their essay, it will be much simpler for them to create an outline and begin writing.
Use clear topic sentences
One of the most important tips to teach writing skills is employing topic sentences. The first sentence of a paragraph establishes its tone. The gist of your content should be communicated in the opening sentence of each paragraph. Ideally, explain your paragraph first, and then expand upon it by providing examples and explanations that support your essential ideas and demonstrate your expertise.
It's Lit Teaching
High School English and TPT Seller Resources
- Creative Writing
- Teachers Pay Teachers Tips
- Shop My Teaching Resources!
- Sell on TPT
3 Hands-on Essay Writing Activities Your Students Will Love

Turning essay writing into an engaging learning experience is definitely a challenge. The content requires a certain amount of lecturing, modeling, reading, and writing. But your essay writing unit doesn’t have to be one long sit-and-get; you can use hands-on essay writing activities to help invigorate your unit!
In this post, I will share three activities that require students to move or use their hands.
You can find more tips for teaching essay writing here.
(Looking for a whole essay writing unit that incorporates these activities? Grab my Five-paragraph Essay Writing Bundle here! )

Hands-on Essay Writing Activities #1: Exemplar Gallery Walk
You’ve probably done a gallery walk in your classroom before, but if not, here’s a quick refresh.
For a gallery walk, you hang up artifacts for students to examine around the room. They are sometimes done in silence (students might use post-its to leave comments on the “gallery”).

As students walk around and look at each artifact, they’ll complete some kind of task.
You can use the gallery walk to show students examples of what an essay should look like. For example, I use a gallery walk activity to teach students what a strong thesis statement looks like.
First, I post a variety of thesis statements around the room. As students read them, they decide if each statement is a “strong” or “weak” example of a thesis statement.
By the end of the activity, students clearly understand what makes a great thesis statement and how to spot problems with weak ones.
(If you’d like this activity for Writing Strong Thesis Statements, you can grab my no-prep resource here!)
You could do this activity with any part of the essay–or whole essays. Regardless of how you use the gallery walk, it’s nice to get your students up and moving while they reflect on writing.
Hands-on Essay Writing Activities #2: Unscramble Activity
Who doesn’t love a good puzzle? Another engaging essay-writing activity is to take an essay and turn it into a puzzle!

I take an example literary essay or research paper and cut it up. Basically, each part of the essay is on its own strip of paper.
Students form groups and each group is given one of the cut-up essays. Together, they must figure out how to unscramble the essay.
( Grab this Unscramble the Five-paragraph Essay Activity here if you don’t want to create your own. )
This not only forces them to remember the organizational structure of an essay, but shows them the importance of clear writing, using transitions, and following a rigid format. Plus, students get to use their hands as they manually move around their strips of paper and collaborate with peers.
You could have students unscramble any kind of essay (save excellent student examples for this!) or even just Works Cited pages if you want them to focus on citation formats.

Hands-on Essay Writing Activities #3: Stations
Stations are just what they sound like–stations set up around your classroom. Each station includes the directions and materials needed to complete a different task. In order for students to complete all of the required tasks, they have to rotate to each station.
While you’ve probably done stations in your classroom before, you may not have considered using them for essay writing. But there are a ton of ways you could set up essay-writing stations.

Each station could guide students through writing a piece or a step of an essay. Stations could each focus on teaching part of the essay writing process. You could even have stations in which students focused on exploring different types of essays or essay topics.
Stations are an engaging activity because they force students to move around the room. They also break up the class period into smaller chunks (a ninety-minute class becomes three thirty-minute stations, for example).
They are especially helpful when you want students to really dive into a specific topic. That’s why they’re also great for essay peer editing.
My peer-editing stations include four tasks: checking essay structure, checking citations, proofreading, and improving diction and fluency. Alternatively, you could set up peer-editing stations that focus on any four common essay issues.
Students trade papers and have to complete each station or task. The stations force students to focus on honing in on each problem area leading to better and more specific feedback for one another.
( Skip creating these stations on your own by grabbing the Five-paragraph Essay Peer-editing Stations here. )
Once you know how many stations you want to use and what topics/tasks will be covered at each, be sure to gather materials students may need. Provide highlighters, markers, and any specialty items students will need.
You’ll also want to create very specific, step-by-step directions for each station. You might also want to provide students with a checklist of the stations, so they can keep track of which ones they’ve completed and which ones they still need to do.

Essay writing might never be your students’ favorite unit, but it certainly doesn’t have to be boring. You include movement and hands-on activities just like you would for any other content topic.
If you’re looking for no-prep essay-writing resources, check out my Five-paragraph Essay Writing Bundle.

How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing

Teaching argumentative essay writing can be a real challenge. In addition to teaching writing, you’re also teaching skills like research and refutation. Luckily, this post includes the tips you need for effectively teaching argumentative essay writing.
I have great news for any of you gearing up to teach argumentative essay writing. Those students of yours love to argue. (Don’t believe me? Just ask their parents!) Students love to stand up for their opinion, proving their view is correct. The challenge, then, is getting them to look at the whole picture, find supporting evidence and understand the opposing viewpoints. Only then can they craft an argument that is both factually strong and persuasive. Overall, it’s about moving them beyond the blinders of their opinions and taking a more sound evidence-based approach.
Teaching argumentative essay writing doesn’t have to be such a painful experience for both you and your students. Follow the steps and strategies below to learn how to approach the dreaded argumentative essay more easily.
The Challenge with Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
Why is teaching argumentative essay writing so difficult, you ask? I’ve been there. The truth is, when teaching argumentative essay writing, you’re teaching more than writing . You’re also teaching research skills and encouraging critical thought and analysis. You also need to explain how to evaluate sources and evidence and the difference between fact and opinion. In many ways, you’re teaching tolerance and perspective. (The list goes on.)
Long story short, it makes sense that it’s a challenge. The key is to not rush into it. Take it step-by-step, building upon what students already know.
Moving Beyond Persuasion
The good news? Many of your students have a foundational knowledge of persuasive writing that you can use as a springboard for teaching argumentative essay writing. However, it’s important to note that, while many use the terms interchangeably, they’re not quite the same. The main difference? Factual evidence. Your students might be used to persuasive writing, meaning writing to convince the reader of a claim rooted in their personal opinion . While it’s likely that students will argue something they are in favor of, argumentative essay writing involves using claims supported by factual evidence. Additionally, a hallmark of the argumentative essay is addressing the opposing viewpoint, a step that many students are unfamiliar with– and find rather challenging.
Consider the following steps as you move from persuasion to argumentative essay writing:
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation
Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don’t even mention the word essay at this point. Keep it fun and casual to break the ice.
There are many ways to approach casual argumentation in class. You can begin with an anticipation guide of controversial yet appropriate statements. After students fill it out, foster a group discussion in which students share their thoughts regarding each statement. Encourage them to move beyond simple opinions by asking why to get them to dig deeper as they support their stance.
To get your students up and moving, consider playing a game like Four Corners to get them to take a stance on a topic. Regardless of which activity you choose, spend time discussing the students’ stances. Small debates are likely to unfold right then and there.
Step 2: Add In Evidence, But Still Keep It Casual
You’ve causally engaged students in basic argumentation. However, before moving into a full-blown argumentative essay, dip students’ toes into the world of supporting evidence. Use the same activity above or write a simple yet controversial topic on the board for them to take a stance on. This time, give students a chance to gather supporting evidence. It might be worth quickly reviewing what makes a sound piece of evidence (research, studies, statistics, expert quotes, etc.). Then, once they pick their stance, allow five to ten minutes to gather the best piece of supportive evidence they can find. After, give them another five to ten minutes to work with the others in their corner/on their side to determine the strongest two or three pieces of evidence to share with the class. Once each team does this, have them take turns sharing their stance and supporting evidence. I like to leave room at the end for “final words” where they can respond to a point made by the other side.
During this simple activity, begin to unpack the importance of solid and relevant supporting evidence.
Step 3: Bring in the Opposing Viewpoints
Don’t stop there. One of the most challenging aspects of argumentative writing for students to grasp is acknowledging and responding to the opposition. They are often blinded by their experiences, perspectives, and opinions that they neglect the opposing side altogether.
Here’s what you can do: Repeat either activity above with a slight twist. Once students pick their side, switch it up. Instead of supporting the side they chose, ask them to research the other side and find the best supporting evidence to bring back to the class. Therefore, students will engage in a casual debate, supporting an opposing viewpoint. (For a simpler, more independent version of this, write a controversial statement on the board, have students take a stance, and then find evidence for the opposing side, putting it all into a written response.) While many students might complain at first, you’d be surprised how quickly they get into the task. Activities like these lay the groundwork for making evidence-based claims. Additionally, students will begin to recognize the role of perspective in argumentation.
Step 4: Introduce the Argumentative Essay
Now it’s time to introduce the argumentative essay. Many students will be tempted to jump right into writing. Therefore, make it clear that argumentative essay writing involves deeply investigating a topic before writing.
Next, explain how argumentative writing aims to take a stance on a topic and back it up with substantial supporting evidence. Additionally, include how argumentative essay writing requires acknowledging the opposing viewpoint. As for persuasion, explain that it must work in coordination with collected evidence rather than being rooted solely in one’s opinion.
When introducing the argumentative essay, it helps to outline the essay structure, showing students where it is both similar and different from the essays they are used to:
- Begin with an introductory paragraph. This is where the students will hook their readers and provide a summary of the issue, any relative background information, and a well-defined claim. (This is a great place to explain that claim is another word for a thesis statement used in argumentative writing.)
- Then comes the logically organized body paragraphs, each unpacking evidential support of the claim. While students are used to using body paragraphs to support their claim, remind them one body paragraph must reference and refute the opposing side.
- Finally comes the conclusion. Students are no strangers to writing conclusions. However, they should be moving beyond simply restating the thesis at the secondary level. Guide them through readdressing it in a way that acknowledges the presented evidence and leaves the author with something to think about.
Students will likely recognize the similarity between this and the traditional five-paragraph essay. Therefore, focus your teaching on the newer elements thrown into the mix that truly make it an argumentative essay.
Teacher Tip.
Incorporate various mentor texts to help students grasp the elements of argumentative essay writing. There are tons you can pull offline written by students and experts alike. ( The New York Times Learning Network has some great mentor text resources!) The more interesting your students find the subject matter, the better. Controversial topics always stir up an engaging conversation as well.
Teaching the Argumentative Essay Writing Process
Remember, students can quickly fall into old habits, neglecting some of the most imperative aspects of argumentative writing. Take it slow, walking students through the following steps – trust me, you’ll be thankful you did when it comes time to read a pile of these essays:
- Choose a topic. I recommend providing a list of argumentative essay writing topics for students to choose from. This prevents students’ classic “I can’t think of anything” roadblock. However, encourage students to choose a topic they are interested in or feel passionate about. With that said, I always give the option of letting students convince me (ha!) to let them use a topic they came up with if not on the list.
- Start the research. This is where students begin gathering evidence and is an opportunity to review what constitutes strong evidence in the first place.
- Understand the opposing side: Students are always confused about why I have them start here. One reason? It’s more challenging for students to see the other side, so this gets it out of the way first. Another? Some students never took the time to understand the other side, and in some cases, they switch their stance before writing their argument. It’s better to do so now than after you’ve done all your research and drafting. Lastly, I explain how understanding the opposing side can help guide your research for your side.
- Make a claim. While students may have an idea of their claim, the strongest claims are driven by evidence . Therefore, remind students that a claim is a statement that can be supported with evidence and reasoning and debated. Playing a quick game of two truths and an opinion (a spin on two truths and a lie) can reinforce the notion of facts vs. opinions.
- Write the body paragraphs. Each body paragraph should focus on supporting the claim with specific evidence. However, don’t forget to rebut the opposition! While they find it challenging, students learn to love this part. (After all, they love being right.) However, their instinct tends to be just to prove the other side wrong without using evidence as to why.
- Round out the intro and the conclusion, put it all together, and voila! An argumentative essay is born.
More Tips for Teaching Argumentative Essay Writing
- Begin with what they know: Build on the well-known five-paragraph essay model. Start with something students know. Many are already familiar with the classic five-paragraph essay, right? Use that as a reference point, noting out where they will add new elements, such as opposing viewpoints and rebuttal.
- Use mentor texts: Mentor texts help give students a frame of reference when learning a new genre of writing. However, don’t stop at reading the texts. Instead, have students analyze them, looking for elements such as the authors’ claims, types of evidence, and mentions of the opposing side. Additionally, encourage students to discuss where the author made the most substantial arguments and why.
- In [ARTICLE NAME/STUDY], the author states…
- According to…,
- This shows/illustrates/explains…
- This means/confirms/suggests…
- Opponents of this idea claim/maintain that… however…
- Those who disagree/are against these ideas may say/ assert that… yet…
- On the other hand…
- This is not to say that…
- Provide clear guidelines: I love using rubrics, graphic organizers, and checklists to help students stay on track throughout the argumentative essay writing process. Use these structured resources to help them stay on track every step of the way– and makes grading much easier for you .
The bottom line? Teaching argumentative essay writing is a skill that transcends the walls of our classrooms. The art of making and supporting a sound, evidence-based argument is a real-life skill. If our goal as teachers is to prepare students to be skilled, active, and engaged citizens of the 21st century, effectively teaching argumentative essay writing is a must. So, what are you waiting for? Teach those kids how to argue the write way.
1 thought on “How To Teach Argumentative Essay Writing”
This is very helpful. I am preparing to teach my student how to write an argumentative essay. This help me know that I am on the right path and to change how I organize some things in a different way. I really like how you recommended they pick out the elements of the writing. This will help them focus on the parts they dislike doing the most. Thanks for the writing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How To Teach Your Students To Write An Essay?
- As a teacher, you may find it difficult to demonstrate to your students the proper way to construct an essay.
- It might not be as hard as you think, though, if you have access to the correct information and tools.
In this piece, we'll go through a few of our prefered strategies for teaching students how to write essays that get results.
Read on for some useful pointers that will be helpful whether you're just starting out or are seeking for new ways to help your pupils improve their writing skills.
Improve your English proficiency and self-assurance with the help of Dr. Study Essential English tutoring services.

Discover The Basic Principles Of An Essay
- Your pupils' initial step before starting to write an essay should be to consider possible topics for the assignment.
- Essays are not just a test of students' writing skills but also of their ability to gather and analyse information from a variety of sources.
So it's up to you to show them the ropes of research methodology. If the subjects picked are too easy for a student, and you know it won't take much time to compose such an essay, you should make an attempt to reject the topics that have been chosen.
An essay that does not require any investigation simply does not exist.
- Tell your students that picking a topic where they have prior knowledge and where they can perform research will give them the highest chance of succeeding.
It is crucial for students to acquire proficient research abilities, therefore, be sure to provide them many opportunities to practise a variety of research methodologies.
For instance, you should clarify how they can find all the required information, how to intelligently utilise this information, and how to discriminate between the key facts and the unnecessary ones.
If you don't have a specific audience in mind as you write, you won't be able to produce a well-organised, informative essay.
A popular essay topic would be regarding material that every reader already knows.
- Therefore, after a topic has been chosen, it is imperative that you stress to your students the need to take their time when writing their essays.
- Instead, have them decide what argument they want to make in the essay.
Once a student has a firm grasp of the reason behind the essay, he or she can more easily sketch out the outline and begin writing.
Learning is impossible if students do not have their own life experiences to draw from. In order for your pupils to better comprehend what makes a good piece of writing, provide them with some examples of exceptional essays.
An essay that one of your previous pupils wrote is one possibility. Once they've viewed a sample, your students will have a much clearer picture of what a good essay looks like.
- Use real-world examples to illustrate to pupils what kinds of information they should include in their essays.
They will fully grasp the elements of an effective opening, the structure of an informative body part, and the suitable conclusion of an essay.
In addition, your pupils will be able to see firsthand the numerous sentence structures and grammatical constructs that are used inside an essay and gain an appreciation for their own use.
It is best to leave outlining until after you've begun writing your essay.
- Pick a topic and brainstorm the information your pupils should include in an essay on the chosen topic.
After applying this strategy, students will have a firmer grasp on what an essay is and how it should be structured.
Please remind your students that using their own personalised essay outlines will greatly facilitate the process of producing this assignment.
Each bullet point on the outline needs to be the topic sentence of a new paragraph, and this needs to be stressed.
Paragraphs should be maintained to a minimum length; this will make the essay more readable. Very long paragraphs can be awkward to read since they make it harder to grasp the author's meaning.
Writing shorter paragraphs of an essay will become second nature to students as they get experience writing essays.
Introduction
Get started on that essay you've been putting off right away! We've now reached the meat of it, the introduction. In most cases, students struggle greatly with this part of their essay since they have no idea how to start a piece of writing in a way that would grab the attention of readers and concisely explain the essay's topic.
It is your job to convey this step to your students because an essay cannot be successful without an appropriate and captivating start.
Warn students that if their writings aren't immediately interesting and easy to follow, no one will bother to read them. In addition, an essay's introduction ought to include some suspense.
- Students have the option, depending on the essay topic, of beginning with a tale from their own experience.
It's a good way to get folks interested in what you have to say.
Involve your pupils in the discussion and pay attention to their feedback as you move forwards.
The conversations will help them retain more information.
How essays are organised; this will help your students immensely as they craft the essay's main body. Now that we've discussed the introduction, we can move on to the conclusion, which is just as crucial as the opening section. In order to create a true work of art, one must ensure that the reader is completely satisfied by the work's conclusion.
Never presume that your students know how to wrap up their papers appropriately. Explain why it's not a good idea, in this case, to cut down on your essay's word count.
Teaching Students to Write Essays
- If this is your first year of teaching, you may be struggling to find the best approach to instructing your pupils in the art of essay writing.
- No matter how long you've been in the classroom, you undoubtedly still have some unanswered questions regarding how to teach students to write effective essays.
It can be difficult to discover ways to express those abilities to students, despite the fact that they are among the most essential building blocks necessary for a student's success.
To teach pupils how to write an essay, how can we sustain their interest?
Is there a way we may help them develop the expertise of expert essay writers? Is there a way to instruct students in the art of essay writing that is distinct from the standard five-paragraph nacho paper or hamburger that most of us were assigned?
Modifying the Task into Smaller Pieces
Teaching your pupils to produce strong essays is not something that can be accomplished in a single class period.
As an alternative, you may commit an entire unit to coaching your pupils as they write their first essays.
Don't worry, though; that doesn't mean the subject matter has to be dull. In its place, you should employ engaging content.
What do burning one's bra, reading Harry Potter, discussing the necessity of pay sharing with employees, and reading comic books have in common? Find out by reading on!
- Each of these methods has been shown to work in keeping students engaged while they are learning the fundamentals of essay writing.
You need to take baby steps, constructing a solid foundation, and building upon it brick by brick, block by block, until your pupils are ready for full release of responsibility and have matured into skilled writers on their own.
Creating a Strong Foundation
- Before beginning anything else, you should make sure that all of your students understand how to write an argumentative paragraph.
They need to be able to write using the PEE format (which stands for "Point, Evidence, and Explanation").
Many schoolchildren have learned how to write essays as a required subject. If you need a review, you can find an assignment related to the short story ALLIGATOR RIVER HERE.
The best way to improve your essay writing abilities is to work through these steps in sequence:
- Ensure that students can write a paragraph that successfully makes a case.
- Teach them how to solve the most typical essay challenges
- Make sure that pupils can successfully outline a five paragraph essay.
- Exhibit right away how to depart from the standard essay format of five paragraphs (Harry Potter)
- Help students see why it's crucial to back up their statements with data. (Bra-Burning)
- Educate students on the proper way to use direct quotes into their papers.
- Show how to organise your thoughts from reading to outlining to writing your article (When it comes to compensation, it's important to be transparent with your coworkers.)
- Using software like Microsoft Word and Google Docs, students learn to make their writing stand out from the rest.
- Give students the assignment to produce a paper using a solid sample as a guide (Comic Books)
- If you follow these stages, your students will not only learn how to write an effective essay, but they will also be able to apply what they learned to expand their own understanding and sense of self. Everyone benefits when learning to read and write is combined with developing other life skills and self-awareness.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Strong Essay Outline, Body Paragraphs, and a Final Draft
Every student should learn how to write essays because it is a vital talent.
Whether you're working on an essay for a timed exam or a certain style of academic essay, such a narrative, persuasive, expository, or descriptive essay, writing regularly is the best method to enhance your writing skills.
In order to help our kids grow as scribes, we should provide them more opportunity to take part in activities that call for longer writing.
Putting in the time required is essential, but it's not enough if you want to write an A+ essay.
The routine really should be working towards something.
- Once students have a general concept of the structure of various types of essays and how they are organised, they are ready to concentrate on the minute details that will help them to fine-tune their work as a lean vehicle of their thoughts and ideas.
In this piece, we'll focus on certain specifics that will assist students strengthen their essay writing abilities and advance to the next level with their writing.
- By using essay writing as the foundation for your lessons, you can cover a wider range of topics and engage your students in more activities.
They are similar to sportsmen in that they can be productive when working alone by focusing on specific physical actions related to their activity.
When you've gotten to the point where doing these things is as easy as breathing, they'll fall into place effortlessly while you play the game (or write the essay).
Do you want to improve your chances of passing the IELTS?
Dr. Study provides students with authentic IELTS activities that foster the development of critical thinking and independent decision making through task-based language instruction and dynamic assessment methodologies.
Break The Question Down: Understand Your Essay Topic
Whether they are working on an in-class assignment given by you or an exam essay prompt given to them, students should always make it a point to reflect on the nature of the task at hand.
To do so, they must first determine what is being asked for. In class, by responding to a variety of essay titles, questions, and prompts, students can receive significant expertise in deconstructing these components.
They can use this as practice for disassembling larger objects.
Then have the students work in small groups to highlight, analyse, and discuss the assigned terms. Is it something you'd like to hear them talk about, describe, debate over, or explain?
- Get a firm handle on the precise nature of the work at hand before proceeding with the planning phase or commencing the writing process.
Make a Mind Map of Your Knowledge and Brainstorm Ideas
- Students should consider what they know and, often, how they feel about the topic after they have gained a knowledge of what is expected of them in the essay job.
When instructing younger children in the art of essay writing, it is common practise to emphasise the significance of allowing the student's personal perspective to shine through.
Some of our younger kids, however, have difficulty articulating their thoughts clearly, even to themselves.
- The process of brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about the issue will allow students to not only discover what they already know about the topic, but also to convey to themselves what they think about the topic.
In addition, it will serve as a template against which they may measure the progress of their own research and, ultimately, the essay they will write. Writing an essay for an exam can be the only "research" a student does before writing a paper, making regular practice of this ability all the more important.
Research Your Essay
Previous work should have made it obvious to the students what direction their research will take generally.
Students no longer need to rely solely on a single, outdated encyclopaedia from the school library as the sole source for their research paper because of the widespread availability of the internet.
In today's society, the greatest difficulty our students confront is, perhaps, narrowing their research down to a manageable amount of sources.
Before going on to the next stage, students should review the material from the previous one. It's crucial at this stage that they do the following:
- Check that the sources you're using are appropriate for the essay you're writing.
- Please have students keep a detailed list of all the sources they found the information they used in their essay.
- Question the information presented and examine their own preconceived notions to gain a deeper understanding.
- Write down the main arguments you plan to make in your essay.
- Consolidate thoughts, counter arguments, and viewpoints.
- Find the main point they want to express in their essay.
After these steps are taken, the learner will be able to organise their thoughts in a logical fashion.

Preparing Your Essay
There are a variety of methods that students can use to get themselves in writing shape.
They can use anything from visual organisers to post-it notes to one of the numerous available writing applications.
They must bear in mind the importance of presenting their arguments in a logical sequence.
Body paragraphs are where you flesh out your thesis, and they will ultimately shape how your student organises their paper.
Paragraph counts in essays can range from three to five or even more, depending on criteria like word count, time allotted, difficulty of question, and other similar considerations.
It is important for students to remember the "Rule of Three," which indicates that every essay they write should have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. This is essential no matter how short the essay is.
Each paragraph in an essay will elaborate on a central thesis statement (the topic sentence) and provide supporting evidence (the body paragraphs). Both the first and last sentences of this paragraph are crucial.
- The reader should get the gist of a paragraph in the first statement, and the paragraph should tie into the essay's larger thesis in the last sentence.
It is crucial to take the time to ensure that students have a clear notion of how each section of the essay functions, that is, of the precise nature of the task that it performs, even though they will likely be familiar with the overarching generic structure of essays.
Having trouble with your VCE exams ?
Exam anxiety can be reduced and academic self-assurance bolstered by working with one of Dr. Study's many skilled teachers.
Teachers may find it difficult to teach students how to construct an essay, but it is possible to do so if they have access to the correct information and tools.
Essays are not just a test of writing skills, but also of their ability to gather and analyse information from a variety of sources.
To help students improve their writing skills, they should discover the basic principles of an essay, consider possible topics, choose a topic where they have prior knowledge and can perform research, and stress the need to take their time when writing their essays.
Additionally, they should provide them with opportunities to practise a variety of research methodologies, such as finding all the required information, intelligently utilising information, and discriminating between the key facts and the unnecessary ones.
Finally, they should decide what argument they want to make in the essay and sketch out the outline and begin writing.
Provide students with examples of exceptional essays to help them understand what makes a good piece of writing, use real-world examples to illustrate the elements of an effective opening, structure of an informative body part, and the suitable conclusion of an essay, and outline their own personalised essay outlines.
Paragraphs should be maintained to a minimum length to make the essay more readable, and students should be warned that if their writings aren't immediately interesting and easy to follow, no one will bother to read them.
Teaching Students to write essays is an important part of teaching, but it can be difficult to find the best approach to instructing them in the art of essay writing. To teach students how to write an essay, it is important to involve them in the discussion and pay attention to their feedback, explain why it is not a good idea to cut down on the essay's word count, and modify the task into smaller pieces.
Additionally, engaging content should be used to create engaging content, such as burning one's bra, reading Harry Potter, discussing the necessity of pay sharing with employees, and reading comic books.
The best way to improve essay writing abilities is to take baby steps, construct a solid foundation, and build upon it brick by brick, block by block.
This includes teaching students how to write an argumentative paragraph, how to solve the most typical essay challenges, how to depart from the standard essay format, how to back up their statements with data, how to use direct quotes, how to organise thoughts from reading to outlining, how to make their writing stand out from the rest, and how to produce a paper using a solid sample as a guide.
Every student should learn how to write essays because it is a vital talent and everyone benefits when learning to read and write is combined with developing other life skills and self-awareness.
In order to help our kids grow as scribes, we should provide them with more opportunities to take part in activities that call for longer writing. This article focuses on certain specifics that will help students strengthen their essay writing abilities and advance to the next level with their writing.
These include understanding the structure of various types of essays and how they are organised, focusing on the minute details that will help them to fine-tune their work, and making a mind map of their knowledge and brainstorming ideas.
Students should consider what they know and how they feel about the topic after they have gained knowledge of what is expected of them in the essay job.
The process of brainstorming and mind-mapping what they know about the issue will allow them to not only discover what they already know about the topic, but also to convey to themselves what they think about the topic.
To prepare their essay, students should research their sources, question the information presented, write down the main arguments, consolidate thoughts, counter arguments, and viewpoints, and find the main point they want to express in their essays.
They should also use visual organisers, post-it notes, and writing applications to get themselves in writing shape. Finally, they should present their arguments in a logical sequence. The "Rule of Three" states that every essay should have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Paragraph counts can range from three to five, and each paragraph should elaborate on a central thesis statement and provide supporting evidence. It is important to ensure that students have a clear notion of how each section of the essay functions.
Content Summary
- In this piece, we'll go through a few of our preferred strategies for teaching students how to write essays that get results.
- Read on for some useful pointers that will be helpful whether you're just starting out or are seeking new ways to help your pupils improve their writing skills.
- So it's up to you to show them the ropes of research methodology.
- In order for your pupils to better comprehend what makes a good piece of writing, provide them with some examples of exceptional essays.
- Get started on that essay you've been putting off right away!
- We've now reached the meat of it, the introduction.
- Is there a way to instruct students in the art of essay writing that is distinct from the standard five-paragraph nacho paper or hamburger that most of us were assigned?
- Many schoolchildren have learned how to write essays as a required subject.
- The best way to improve your essay writing abilities is to work through these steps in sequence:
- Teach them how to solve the most typical essay challenges
- Make sure that pupils can successfully outline a five-paragraph essay.
- If you follow these stages, your students will not only learn how to write an effective essay, but they will also be able to apply what they learned to expand their own understanding and sense of self.
- Everyone benefits when learning to read and write is combined with developing other life skills and self-awareness.
- Whether you're working on an essay for a timed exam or a certain style of academic essay, such as a narrative, persuasive, expository, or descriptive essay, writing regularly is the best method to enhance your writing skills.
- In order to help our kids grow as scribes, we should provide them with more opportunities to take part in activities that call for longer writing.
- In this piece, we'll focus on certain specifics that will assist students to strengthen their essay writing abilities and advance to the next level with their writing.
- When instructing younger children in the art of essay writing, it is common practice to emphasise the significance of allowing the student's personal perspective to shine through.
- In addition, it will serve as a template against which they may measure the progress of their own research and, ultimately, the essay they will write.
- It is important for students to remember the "Rule of Three," which indicates that every essay they write should have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Each paragraph in an essay will elaborate on a central thesis statement (the topic sentence) and provide supporting evidence (the body paragraphs).
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should students not write essays.
There is a disconnection between first-year writing instruction and writing in other college courses. There is even a fundamental disconnection between school and learning. Most essays are unpleasant for students to write and too boring for instructors to read.
What Are The Seven Strategies Of Writing?
To improve students' reading comprehension, teachers should introduce the seven cognitive strategies of effective readers: activating, inferring, monitoring-clarifying, questioning, searching-selecting, summarising, and visualising-organising.
How Can Teachers Be Certain That Students Learn The Skills Needed In Writing While Making Good Use Of Their Time?
Teachers can encourage students to collaborate throughout the writing process by brainstorming ideas about a topic, responding to drafts in a writing group, or helping peers edit or revise their work.
What Makes An Essay A Good Essay?
An essay should have a single clear central idea. Each paragraph should have a clear main point or topic sentence. An essay or paper should be organised logically, flow smoothly, and "stick" together. In other words, everything in writing should make sense to a reader.
What Are Three Writing Strategies?
Let's take a look at three helpful prewriting strategies: freewriting, clustering, and outlining. Often the hardest part of writing is getting started.

Olga has a PhD in Management from Monash University. Her research focused on how personal differences and social networking impact creativity in the tech industry. She has extensive teaching experience at universities and private tutoring centers, praised for her engaging methods and clear insights. Olga also writes for top academic journals and creates innovative programs that enhance skills and consulting methods. She believes in the power of education to inspire ongoing growth in both studies and careers.
View all posts
Essay Writing Unit - Teach Your Students How to Write an Essay PRINT & DIGITAL

- Google Apps™
- Easel Activity
What educators are saying
Products in this bundle (5), also included in.

Description
Teach your students how to write an essay! This comprehensive essay writing bundle includes teaching resources and lessons for every part of an essay.
First, focus on teaching the thesis statement and introductory paragraph.
The first writing unit includes targeted teaching strategies to teach students how to write a thesis statement and an introduction to an essay. This thesis writing teaching unit includes a teaching presentation (PowerPoint and Google Slide) for direct instruction. This teaching presentation includes differentiation and examples to help students become stronger writers. There is also a PDF and a Google Doc for students to practice their work.
Then, teach students about topic sentences and body paragraphs.
The second writing unit helps students learn how to write specific and focused topic sentences and body paragraphs. For the body paragraphs, students will learn how to include and explain examples. This body paragraph and topic sentence teaching unit includes a teaching presentation (PowerPoint and Google Slide) for direct instruction. This teaching presentation includes differentiation and examples to help students become stronger writers. Plus, the examples are color-coded to help students see the various elements of a body paragraph. There is also a PDF and a Google Doc for students to practice their work.
Finally, teach the conclusion.
Teach students how to write a concluding paragraph to their essay. This part of the writing unit also includes direct instruction materials and student practice.
PowerPoint presentations included in this unit are color-coded, engaging, and filled good and bad examples to help your students improve their writing today. The teaching resources and supplementary materials are differentiated and scaffolded to help student writers of all abilities.
The digital version is included - Now optimized for Google Classroom and digital learning!
The PowerPoint/Google Slide:
- 25 slides in three different presentations
- color-coded
- includes writing examples
- includes good and bad examples
Teaching Resources:
- individual and group activities and practice
- introduction, body, and concluding paragraph organizers
- guided introduction, body, and concluding paragraph outlines
- student reference guides
- classroom activities
This BUNDLE includes:
Essay Writing: Mastering the Essay Outline with Guided Instructions
Thesis Statement and Introduction: Essay Writing
Topic Sentence and Body Paragraph: Essay Writing
Essay Writing: Mastering the Conclusion
TEACHERS LIKE YOU SAID…
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Robert R. says, "I'm a writer by trade who is long term subbing and my students LOVED this, especially the 9th graders. It's essay writing, so there's no way to have it not be a little dry, but the powerpoints are excellent, the worksheets are easy for the students to complete, and you have options based on the makeup of your class. My 9th graders had never written a full essay before, and by the end of a week they were able to put out a quality 5 to 6 paragraph essay. I'm stunned!"
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Carley L. says, "Fantastic resource! I used it when preparing for provincial testing with Grade 9 students and it really helped them to organize their ideas. I loved allowing them to choose between having a hard copy or digital copy to work off of as well."
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Tayler S. says, "This was an amazing and well organized resource to help students write their essays. It breaks down the parts of an essay and it chunks all the information in to smaller sections to help the students put together a full essay. I will definitely use this resource again! Thank you!"
⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Ivy V. says, "This was a great resource for my students to use while I was away supervising a band field trip. The students who went away also received a copy to work on when they could. It guided the students through each step for writing an essay and helped boost their confidence!"
Helpful Advice:
* Make sure you click the "follow" button next to my picture so you don’t miss out on sales and new resources
* Please provide feedback on this resource. Doing so will help you earn TPT credits that you can apply toward future purchases! It’s like FREE TPT cash!
© The Daring English Teacher, Inc.
All rights reserved. License good for single-classroom use only.
Questions & Answers
The daring english teacher.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
How to Start a College Essay: 5 Effective Techniques

Access thousands of exclusive scholarships for free

"Be Bold" No-Essay Scholarship
Impressionable Openers
Descriptions and demonstrations, show vulnerability, be authentic, stay personal, fun & quirky, common mistakes to avoid in your college essay.
- Ways to Overcome Writer's Block
Frequently Asked Questions About Starting a College Essay
College essays are a huge part of your college career. If not huge, one of the biggest, and for someone who has been there and done that, I know the amount of pressure the beginning of a college essay, as well as the entire essay, can put on your shoulders.
Not only are you trying to juggle things like word count and grammar errors, but you're also trying to create the perfect college essay introduction that will attract admissions officers to your application or professors to your writing skills. And that, itself, can feel impossible, fill you with dread and self-doubt, but just breathe. I am here to help all present and future students know how to start a college essay.
Today is all about starting a college essay. I have come up with five easy and effective techniques that will help you create essays so good you're going to leave your readers wanting more , starting with your opening sentence! So, this is for all college students and college applicants. Stress no more! This guide was created to help you write a successful college essay. Let's get into it.
Visit our Scholarship Blog to learn how to create your free Bold profile , and start applying for scholarships designed to help you save BIG on your college education.

The beginning of your essay should, first and foremost, always have a strong opening sentence . This sentence sets the tone for not only your readers but for the entire essay. Having a wobbly, almost interesting opener can steer an admissions officer and/or professor away, so you want it to be strong. And it doesn't have to be complicated! Less is more in this situation. Here are a couple of ways you can accomplish this.
- Look within and be relatable
- Use your real life for inspiration
- Think about ways to evoke emotion
Here are some examples of impressionable openers:
- Example 1: When I was 11 years old, my mother told me she had cancer over breakfast.
- Example 2: Maybe yellow isn't my favorite color.
- Example 3: I sat next to this girl in class who made me feel stupid.
DISCLAIMER : your opener should ALWAYS adhere to the essay prompts. These are just a few examples that can capture your reader's attention almost immediately.
In order to keep readers interested, visuals are key . Image-based descriptions will not only add value to your writing, it will give your readers front seats to your essay's journey. These descriptions let actions speak for themselves.
Here is an example of a description and demonstration in an essay:
- Example 1: "I was sitting on a bar stool when the word 'cancer' hit me like the smell of her coffee brewing on the stove. The Rice Krispies were popping in my cereal bowl, and MTV Jams was playing in the background, yet all I could hear was the sound of doom all around me. The lips of my mother were moving, but I was frozen, crumbling on this stool like my mother's health. She was sick, and I didn't know how sick or what that even meant, and that terrified me."
Why This Works:
Here you can clearly feel the writers emotional state: shocked, still, scared. Not only is this moment at breakfast traumatic, you feel frozen in time with the writer. Using descriptions like this will evoke so much emotion and leave your reader wanting more.
Get Matched to Thousands of Scholarships
Create your Bold.org profile to access thousands of exclusive scholarships, available only on Bold.org.
Something one of my teachers told me in high school was any good essay will have personal elements in it, no matter the topic. That always stuck with me and became the way I approached my college essays. Showing vulnerability in your writing will always guarantee interest. It also evokes emotion.
You can show vulnerability by:
- Being honest
- Explaining what's going on inside underneath the exterior
- Describe what's going on around you at the moment
- Letting go of the fear of being seen
- Connecting with the topic
- Being transparent about mistakes/flaws
Examples of showing vulnerability:
- Example 1 : My mother telling me she had cancer over breakfast was not on my bingo card this year.
- Example 2 : I never thought losing someone I love would change me.
- Example 3: I had to lose everything in order to gain everything.
I know being vulnerable can be tough for some , but showing this side of you to college admissions officers and/or professors will not only make you stand out, but it can also help free you of things that might be weighing on your mind. Not to sound corny, but it can be therapeutic and make you a better writer . Just make sure you are staying on track with the essay prompt, and you're set!
Whether it's believed or not, an admissions officer wants to see pieces of you in your personal statement, so starting your essay by showing authenticity is a major major key. Along with being vulnerable, there are a few ways you can achieve this.
- Reflect : Take the time to reflect on your experiences, values, and beliefs that have shaped who you are today. Let your values, passions, and interests shine through in your writing.
- Mind Your Voice : Write in your own voice and avoid trying to sound like someone you're not. Authenticity comes from being genuine and true to yourself.
- Tell Your Story : Share personal anecdotes and insights that show your unique perspective.
- Be True to You : Focus on what matters to YOU (as long as you're on topic!). Write about what is meaningful and important to you rather than what you think admissions officers want to hear.
Above all, be open . Showing introspection and self-awareness in your essay will show any admissions committee who you are beneath the surface, as well as your personal growth.
You can also begin your essay being as random and silly as you'd like . It goes hand-in-hand with other important factors like vulnerability and authenticity. But don't get too crazy . Beginning your essay with something strange will definitely draw readers in. Let me show you what I mean.
- Example 1 : I start my mornings off in silence and solitude to keep people away from me.
- Example 2 : Sometimes, I like to circle big words in complex articles to learn new words. Yeah, but to also keep one in my back pocket for later use.
- Example 3 : Being the youngest child means getting away with everything you want, and that's exactly how I like it.
Do you see how each sentence draws you in? Not only are they light-hearted, but they also make you want to know why you want to keep people away in the morning and what kind of weapon you're forming against others with new words. And every youngest sibling will attest to feeling that exact same way. All of these examples are sure to make your essay fun, show who you are, and leave readers wanting more.

Years of writing college essays have taken me through every high and low of the process possible. And when they're good, they're great! But for some reason, my mistakes stick out more than anything. So, I've compiled a list of common mistakes to avoid when writing your college essay .
- Avoid Being Cliche - While you want to be captivating, you want to avoid overly used syntax and phrases that could potentially lose your reader's curiosity. For example, "in today's day and age," "follow my heart," "don't judge a book by its cover," etc. are all cliches that can be avoided by thinking outside of the box.
- Using Vocabulary to be Impressive - I know you want to impress the admissions committees, but it's important to stick to what you know and not what you can allude to. That is, use verbiage that resonates with your personality. Using extravagant words can work against you, and they can also sound forced. College admissions officers want to see the real you, so show it to them.
- Steer Clear of Controversy - Though it's not said enough, your college essay should tell your personal story and not touch on things that can stir the pot. For instance, talking about politics and religious beliefs may not be the route you want to take UNLESS it's called for in the college essay topic. And if so, stay on track with the essay prompts.
- Procrastinating : Waiting until the last minute to start writing your essay will bite you in the butt. You will feel rushed and end up writing a poorly crafted piece. Give yourself enough time to complete an essay draft, edit the draft, and repeat this two-step cycle until your essay is complete.
- Lack of originality : This goes hand-in-hand with avoiding cliches. Your college essay should exude a lot of your personality, so show admissions officers and teachers who you are! Include your cultural background, test scores that you're proud of, any future aspirations, etc. This all depends on the essay prompts, of course, but in my experience, every essay topic has room to show who you are.
- Ignoring the prompt : This is a major key. STAY ON TRACK. Make sure to carefully read and understand the essay prompt, and write your essay accordingly. The last thing you want to do is write a college essay that has nothing to do with the prompt. Reading is essential here.
- Lack of focus : If you want to know how to start a college essay, that means knowing how to stay focused. Find a quiet space, turn off electronics, hide your phone, and really nestle into how you want to capture your reader's attention. This will help you use your five senses clearly, keep your writing strong and not write an overly wordy essay. Focus is the tool here.
- Poor organization : Make sure your essay has a strong structure with clear transitions between paragraphs. An outline will work best to accomplish this. If you go into starting your college essay without a plan, be prepared to hit all roadblocks.
- Neglecting to Revise and Edit : Like procrastinating, don't fail to revise and edit your work. Always, always, always proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors , as well as clarity and coherence.
- Not Seeking Feedback : Listen, I know that completing an essay is an accomplishment in itself, and you immediately want to submit it, but it's so beneficial to have others read your essay for feedback. You can only spot so many holes in your work when your eyes are constantly reviewing it, so a second, third, or even fourth set of eyes can help point out areas for improvement.
Above all, trust the writing process. Though I do want you to be aware of your jargon, don't get too wrapped up in thinking you're making a mistake. That's what editing is for! Once you complete your college essay, you should always revise and edit accordingly . What you thought sounded good might make you edit it to sound great. Just keep in mind that many colleges are looking for honesty and authenticity vs how well you can sound on paper . So, if you're aware of these factors, you'll be good to go.

Ways to Overcome Writer's Block
Take it from someone who has suffered from chronic writer's block, it's a pain to get through . Imagine being on a writing streak so good that when you stop, the entire essay writing process stops as a whole. It's definitely a challenge, but after 10 years of writing essays and really honing my craft, I learned a few things that have helped me get through even the thickest of writer's blocks, and I want to share them with you. Check them out:
- Take a break : This works every single time. Take a short break and step away from your computer to clear your mind and come back with a fresh perspective. For me, 15 minutes is all I ever need. If you need more time, that's okay. Just try not to make your break a rest.
- Freewriting : Sometimes, I'd start writing without worrying about my structure or grammar to get the ideas flowing, and surprisingly enough, I found my essay taking a pleasant turn.
- Change your environment : Move around. Don't underestimate the effects of a different location or workspace to stimulate creativity. Try coffee shops, bookstores, a park, or a new room in your house. New environment, new energy.
- Set small goals : This one is actually the most important. Some people get overwhelmed with the word "essay" for things like lack of proper writing skills, pressure to write a great essay, etc. But if you try breaking down your writing task into smaller, manageable chunks to make it less overwhelming, it can help. For example, set a goal of three paragraphs one day, take a day to edit those paragraphs, two more the next day, and so forth. Find a formula that works for you.
- Brainstorming : Write down all your ideas--everything. No matter how small you think the idea is, write it down. Even if these ideas seem unrelated, they will help you generate new thoughts and connections.
- Read or listen to music : It took me a while to realize this helps, but engaging in other forms of art can inspire new ideas and break through mental blocks. And new creativity can lead you to impress admissions officers.
- Talk it out : As a writer, it's hard to let people in on the creative process, but discussing my ideas with a friend, family member, or colleague helped me gain new perspectives and insights.
- Relax and Meditate : Hear me out: it works! Practice deep breathing and/or meditation to reduce stress and anxiety that may be contributing to writer's block.
I won't sugarcoat it: the college application process can be intimidating , but it doesn't have to throw you off your game. When it comes to college essays, I see them as opportunities to be fun and expressive. Trust me when I say if you have fun with it, you'll attract the reader's attention , paint vivid details, and write an essay that will leave the admissions officer wanting you at their school. So, take it one step at a time and watch your personal statement come to life.

How can I make my college essay stand out to admissions officers?
Simply put, be yourself. As long as you stay on track with the essay's topic, showing pieces of yourself will allow admissions officers to know more about who you are. Essays are meant to show readers who you are, how you feel, and what you think naturally, not robotically, so be authentic in your writing, and you'll be sure to stand out amongst the rest.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when writing a college essay?
Some common mistakes to avoid in your essay are using cliches and boring wording. You also want to avoid procrastinating, wasting time, not focusing, not editing, etc. When writing your essay, you want to make sure you give your writing the time and attention it deserves, so make sure you're aware of what is pulling you away from your writing. This will help you stay focused. If you have any other doubts, refer to the section about mistakes in this article and let it guide you to success.
How important is the college essay in the admissions process?
Your college essay is key in the admissions process . It's an admissions committee's first impression of you as a writer and potential student, so it should be taken very seriously. Trying to cut corners or rush through the writing process will be obvious, and it will stand out more than things like test scores, academic achievements, extracurricular activities, and any other positive influence you've had in your life. So, don't take the easy way out and really work on your essay.
Feeling confident in your college essay skills and want to explore some other essay content? Explore our blog on the comma splice to enhance your technical writing skills!
Related Posts
The rise of public scholarship, best interior design schools, best colleges in california.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
NEW: Classroom Clean-Up/Set-Up Email Course! 🧽
The Best Student Writing Contests for 2023-2024
Help your students take their writing to the next level.

When students write for teachers, it can feel like an assignment. When they write for a real purpose, they are empowered! Student writing contests are a challenging and inspiring way to try writing for an authentic audience— a real panel of judges —and the possibility of prize money or other incentives. We’ve gathered a list of the best student writing contests, and there’s something for everyone. Prepare highly motivated kids in need of an authentic writing mentor, and watch the words flow.
1. The Scholastic Art & Writing Awards
With a wide range of categories—from critical essays to science fiction and fantasy—The Scholastic Awards are a mainstay of student contests. Each category has its own rules and word counts, so be sure to check out the options before you decide which one is best for your students.
How To Enter
Students in grades 7-12, ages 13 and up, may begin submitting work in September by uploading to an online account at Scholastic and connecting to their local region. There are entry fees, but those can be waived for students in need.
2. YoungArts National Arts Competition
This ends soon, but if you have students who are ready to submit, it’s worth it. YoungArts offers a national competition in the categories of creative nonfiction, novel, play or script, poetry, short story, and spoken word. Student winners may receive awards of up to $10,000 as well as the chance to participate in artistic development with leaders in their fields.
YoungArts accepts submissions in each category through October 13. Students submit their work online and pay a $35 fee (there is a fee waiver option).
3. National Youth Foundation Programs
Each year, awards are given for Student Book Scholars, Amazing Women, and the “I Matter” Poetry & Art competition. This is a great chance for kids to express themselves with joy and strength.
The rules, prizes, and deadlines vary, so check out the website for more info.
4. American Foreign Service National High School Essay Contest
If you’re looking to help students take a deep dive into international relations, history, and writing, look no further than this essay contest. Winners receive a voyage with the Semester at Sea program and a trip to Washington, DC.
Students fill out a registration form online, and a teacher or sponsor is required. The deadline to enter is the first week of April.
5. John F. Kennedy Profile in Courage Essay Contest
This annual contest invites students to write about a political official’s act of political courage that occurred after Kennedy’s birth in 1917. The winner receives $10,000, and 16 runners-up also receive a variety of cash prizes.
Students may submit a 700- to 1,000-word essay through January 12. The essay must feature more than five sources and a full bibliography.
6. Bennington Young Writers Awards
Bennington College offers competitions in three categories: poetry (a group of three poems), fiction (a short story or one-act play), and nonfiction (a personal or academic essay). First-place winners receive $500. Grab a poster for your classroom here .
The contest runs from September 1 to November 1. The website links to a student registration form.
7. The Princeton Ten-Minute Play Contest
Looking for student writing contests for budding playwrights? This exclusive competition, which is open only to high school juniors, is judged by the theater faculty of Princeton University. Students submit short plays in an effort to win recognition and cash prizes of up to $500. ( Note: Only open to 11th graders. )
Students submit one 10-page play script online or by mail. The deadline is the end of March. Contest details will be published in early 2024.
8. Princeton University Poetry Contest for High School Students
The Leonard L. Milberg ’53 High School Poetry Prize recognizes outstanding work by student writers in 11th grade. Prizes range from $100 to $500.
Students in 11th grade can submit their poetry. Contest details will be published this fall.
9. The New York Times Tiny Memoir Contest
This contest is also a wonderful writing challenge, and the New York Times includes lots of resources and models for students to be able to do their best work. They’ve even made a classroom poster !
Submissions need to be made electronically by November 1.
10. Nancy Thorp Poetry Contest
The deadline for this contest is the end of October. Sponsored by Hollins University, the Nancy Thorp Poetry Contest awards prizes for the best poems submitted by young women who are sophomores or juniors in high school or preparatory school. Prizes include cash and scholarships. Winners are chosen by students and faculty members in the creative writing program at Hollins.
Students may submit either one or two poems using the online form.
11. The Patricia Grodd Poetry Prize for Young Writers
The Patricia Grodd Poetry Prize for Young Writers is open to high school sophomores and juniors, and the winner receives a full scholarship to a Kenyon Review Young Writers Workshop .
Submissions for the prize are accepted electronically from November 1 through November 30.
12. Jane Austen Society Essay Contest
High school students can win up to $1,000 and publication by entering an essay on a topic specified by the Jane Austen Society related to a Jane Austen novel.
Details for the 2024 contest will be announced in November. Essay length is from six to eight pages, not including works cited.
13. Rattle Young Poets Anthology
Open to students from 15 to 18 years old who are interested in publication and exposure over monetary awards.
Teachers may choose five students for whom to submit up to four poems each on their behalf. The deadline is November 15.
14. The Black River Chapbook Competition
This is a chance for new and emerging writers to gain publication in their own professionally published chapbook, as well as $500 and free copies of the book.
There is an $18 entry fee, and submissions are made online.
15. YouthPlays New Voices
For students under 18, the YouthPlays one-act competition is designed for young writers to create new works for the stage. Winners receive cash awards and publication.
Scroll all the way down their web page for information on the contest, which accepts non-musical plays between 10 and 40 minutes long, submitted electronically. Entries open each year in January.
16. The Ocean Awareness Contest
The 2024 Ocean Awareness Contest, Tell Your Climate Story , encourages students to write their own unique climate story. They are asking for creative expressions of students’ personal experiences, insights, or perceptions about climate change. Students are eligible for a wide range of monetary prizes up to $1,000.
Students from 11 to 18 years old may submit work in the categories of art, creative writing, poetry and spoken word, film, interactive media and multimedia, or music and dance, accompanied by a reflection. The deadline is June 13.
17. EngineerGirl Annual Essay Contest
Each year, EngineerGirl sponsors an essay contest with topics centered on the impact of engineering on the world, and students can win up to $500 in prize money. This contest is a nice bridge between ELA and STEM and great for teachers interested in incorporating an interdisciplinary project into their curriculum. The new contest asks for pieces describing the life cycle of an everyday object. Check out these tips for integrating the content into your classroom .
Students submit their work electronically by February 1. Check out the full list of rules and requirements here .
18. NCTE Student Writing Awards
The National Council of Teachers of English offers several student writing awards, including Achievement Awards in Writing (for 10th- and 11th-grade students), Promising Young Writers (for 8th-grade students), and an award to recognize Excellence in Art and Literary Magazines.
Deadlines range from October 28 to February 15. Check out NCTE.org for more details.
19. See Us, Support Us Art Contest
Children of incarcerated parents can submit artwork, poetry, photos, videos, and more. Submissions are free and the website has a great collection of past winners.
Students can submit their entries via social media or email by October 25.
20. The Adroit Prizes for Poetry & Prose
The Adroit Journal, an education-minded nonprofit publication, awards annual prizes for poetry and prose to exceptional high school and college students. Adroit charges an entry fee but also provides a form for financial assistance.
Sign up at the website for updates for the next round of submissions.
21. National PTA Reflections Awards
The National PTA offers a variety of awards, including one for literature, in their annual Reflections Contest. Students of all ages can submit entries on the specified topic to their local PTA Reflections program. From there, winners move to the local area, state, and national levels. National-level awards include an $800 prize and a trip to the National PTA Convention.
This program requires submitting to PTAs who participate in the program. Check your school’s PTA for their deadlines.
22. World Historian Student Essay Competition
The World Historian Student Essay Competition is an international contest open to students enrolled in grades K–12 in public, private, and parochial schools, as well as those in home-study programs. The $500 prize is based on an essay that addresses one of this year’s two prompts.
Students can submit entries via email or regular mail before May 1.
23. NSHSS Creative Writing Scholarship
The National Society of High School Scholars awards three $2,000 scholarships for both poetry and fiction. They accept poetry, short stories, and graphic novel writing.
Apply online by October 31.
Whether you let your students blog, start a podcast or video channel, or enter student writing contests, giving them an authentic audience for their work is always a powerful classroom choice.
If you like this list of student writing contests and want more articles like it, subscribe to our newsletters to find out when they’re posted!
Plus, check out our favorite anchor charts for teaching writing..

You Might Also Like

Best 2024 Competitions for Students in Grades K-12
Competitions in STEM, ELA and the arts, and more! Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming education, in both worrisome and beneficial ways. On the positive side of the ledger, new research shows how AI can help improve the way instructors engage with their students, by way of a cutting-edge tool that provides feedback on their interactions in class.

The M-Powering Teachers tool provides feedback with examples of dialogue from the class to illustrate supportive conversational patterns. Click on image to enlarge. (Image credit: Courtesy Dora Demszky)
A new Stanford-led study , published May 8 in the peer-reviewed journal Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, found that an automated feedback tool improved instructors’ use of a practice known as uptake, where teachers acknowledge, reiterate, and build on students’ contributions. The findings also provided evidence that, among students, the tool improved their rate of completing assignments and their overall satisfaction with the course.
For instructors looking to improve their practice, the tool offers a low-cost complement to conventional classroom observation – one that doesn’t require an instructional coach or other expert to watch the teacher in action and compile a set of recommendations.
“We know from past research that timely, specific feedback can improve teaching, but it’s just not scalable or feasible for someone to sit in a teacher’s classroom and give feedback every time,” said Dora Demszky , an assistant professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education (GSE) and lead author of the study. “We wanted to see whether an automated tool could support teachers’ professional development in a scalable and cost-effective way, and this is the first study to show that it does.”
Promoting effective teaching practices
Recognizing that existing methods for providing personalized feedback require significant resources, Demszky and colleagues set out to create a low-cost alternative. They leveraged recent advances in natural language processing (NLP) – a branch of AI that helps computers read and interpret human language – to develop a tool that could analyze transcripts of a class session to identify conversational patterns and deliver consistent, automated feedback.
For this study, they focused on identifying teachers’ uptake of student contributions. “Uptake is key to making students feel heard, and as a practice it’s been linked to greater student achievement,” said Demszky. “But it’s also widely considered difficult for teachers to improve.”

Dora Demszky is an assistant professor at Stanford Graduate School of Education. (Image credit: Courtesy Stanford GSE)
The researchers trained the tool, called M-Powering Teachers (the M stands for machine, as in machine learning), to detect the extent to which a teacher’s response is specific to what a student has said, which would show that the teacher understood and built on the student’s idea. The tool can also provide feedback on teachers’ questioning practices, such as posing questions that elicited a significant response from students, and the ratio of teacher/student talk time.
The research team put the tool to work in the Spring 2021 session of Stanford’s Code in Place , a free online course now in its third year. In the five-week program, based on Stanford’s popular introductory computer science course, hundreds of volunteer instructors teach basic programming to learners worldwide, in small sections with a 1:10 teacher-student ratio.
Code in Place instructors come from all sorts of backgrounds, from undergrads who’ve recently taken the course themselves to professional computer programmers working in the industry. Enthusiastic as they are to introduce beginners to the world of coding, many instructors approach the opportunity with little or no prior teaching experience.
The volunteer instructors received basic training, clear lesson goals, and session outlines to prepare for their role, and many welcomed the chance to receive automated input on their sessions, said study co-author Chris Piech , an assistant professor of computer science education at Stanford and co-founder of Code in Place.
“We make such a big deal in education about the importance of timely feedback for students, but when do teachers get that kind of feedback?” he said. “Maybe the principal will come in and sit in on your class, which seems terrifying. It’s much more comfortable to engage with feedback that’s not coming from your principal, and you can get it not just after years of practice but from your first day on the job.”
Instructors received their feedback from the tool through an app within a few days after each class, so they could reflect on it before the next session. Presented in a colorful, easy-to-read format, the feedback used positive, nonjudgmental language and included specific examples of dialogue from their class to illustrate supportive conversational patterns.
The researchers found that, on average, instructors who reviewed their feedback subsequently increased their use of uptake and questioning, with the most significant changes taking place in the third week of the course. Student learning and satisfaction with the course also increased among those whose instructors received feedback, compared with the control group. Code in Place doesn’t administer an end-of-course exam, so the researchers used the completion rates of optional assignments and course surveys to measure student learning and satisfaction.
Testing in other settings
Subsequent research by Demszky with one of the study’s coauthors, Jing Liu, PhD ’18, studied the use of the tool among instructors who worked one-on-one with high school students in an online mentoring program called Polygence . The researchers, who will present their findings in July at the 2023 Learning at Scale conference, found that on average the tool improved mentors’ uptake of student contributions by 10%, reduced their talk time by 5%, and improved students’ experience with the program as well as their relative optimism about their academic future.
Demszky is currently conducting a study of the tool’s use for in-person, K-12 school classrooms, and she noted the challenge of generating the high-quality transcription she was able to obtain from a virtual setting. “The audio quality from the classroom is not great, and separating voices is not easy,” she said. “Natural language processing can do so much once you have the transcripts – but you need good transcripts.”
She stressed that the tool was not designed for surveillance or evaluation purposes, but to support teachers’ professional development by giving them an opportunity to reflect on their practices. She likened it to a fitness tracker, providing information for its users’ own benefit.
The tool also was not designed to replace human feedback but to complement other professional development resources, she said.
Along with Dora Demszky, Jing Liu, and Chris Piech, the study was co-authored by Dan Jurafsky , a professor of linguistics and of computer science at Stanford, and Heather C. Hill, a professor at the Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Media Contacts
Dora Demszky, Stanford Graduate School of Education: [email protected]
Carrie Spector, Stanford Graduate School of Education: [email protected]

Graduate Teacher Education Students Use and Evaluate ChatGPT as an Essay-Writing Tool
- Anthony G Picciano City University of New York, Hunter College
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been evolving since the mid-20 th Century when luminaries such as Alan Turing, Herbert Simon and Marvin Minsky began developing rudimentary AI applications. For decades, AI programs remained pretty much in the realm of computer science and experimental game playing. This changed radically in the 2020s when commercial vendors such as OpenAI and Google developed generative AI programs (ChatGPT) and (Bard) using large, language modelling (LLM). As a result, generative AI is now being considered for use in all walks of life including education.
In Spring 2023, when ChatGPT burst into the public psyche, twenty-five education students in the author’s graduate seminar were invited to participate in a qualitative study using ChatGPT as a tool for completing an essay assignment. Fifteen (N=15) accepted the offer. The purpose in doing this was to give students in this seminar the opportunity to use ChatGPT in a supportive environment and to collect qualitative data from them on their experiences using ChatGPT.
All of these students have master’s degrees in education and experience as teachers in New York City schools. Their training and experience give them keen insights into pedagogical practice making them ideally suited to evaluate ChatGPT as an instructional tool. This article reports on the results of this study.
Keywords: Artificial Intelligence, AI, ChatGPT, Graduate Teacher Education, Qualitative Research
Author Biography
Anthony g picciano, city university of new york, hunter college.
Copyright (c) 2024 Anthony G Picciano

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
As a condition of publication, the author agrees to apply the Creative Commons – Attribution International 4.0 (CC-BY) License to OLJ articles. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
This licence allows anyone to reproduce OLJ articles at no cost and without further permission as long as they attribute the author and the journal. This permission includes printing, sharing and other forms of distribution.
Author(s) hold copyright in their work, and retain publishing rights without restrictions

The DOAJ Seal is awarded to journals that demonstrate best practice in open access publishing
OLC Membership

OLC Research Center

Information
- For Readers
- For Authors
- For Librarians


COMMENTS
The number of paragraphs contained in an essay will depend on a number of factors such as word limits, time limits, the complexity of the question etc. Regardless of the essay's length, students should ensure their essay follows the Rule of Three in that every essay they write contains an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Outline. The last thing to do before starting to write an essay is to make its outline. Choose some topic and make a list of points your students would need to mention if they wrote an essay on it. Such a technique will give them a better understanding of what and essay is, and how it should be written. Make sure that all students perfectly ...
Teaching students how to write an essay is a big undertaking, but this is a crucial process for any high school or college student to learn. Start by assigning essays to read and then encourage students to choose an essay topic of their own. Spend class time helping students understand what makes a good essay.
The Four Square is a graphic organizer that students can make themselves when given a blank sheet of paper. They fold it into four squares and draw a box in the middle of the page. The genius of ...
Once students have their introduction and body paragraphs complete, I then have them move on to writing the conclusion. At this step, I teach conclusion writing to my students and have them restate the thesis and add a general thought to the end of the paragraph. At this point, I emphasize that students should not be adding in any new information.
Effective writing is a vital component of students' literacy achievement, and writing is a critical communication tool for students to convey thoughts and opinions, describe ideas and events, and analyze information. Indeed, writing is a life-long skill that plays a key role in post-secondary success across academic and vocational disciplines.1
Provide daily time for students to write. Recommendation 2. Teach students to use the writing process for a variety of purposes. Recommendation 2a. Teach students the writing process. 1. Teach students strategies for the various components of the writing process. 2. Gradually release writing responsibility from the teacher to the student. 3.
How to Prepare to Write an Essay. Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages: Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling ...
1. Get the basics right. It is clearly unrealistic to expect students to suddenly be able to write an essay in the target language without support. Build up their confidence over time so that they become familiar with writing increasingly long pieces of text. A key part of this will be to ensure that they understand sentence connectors and know ...
5. Offer Student-specific And Timely Feedback. Finally, another crucial aspect you should grasp as a young teacher to help your students create better essays is ensuring you provide them with timely and specific feedback. Once all your students have it, you can spend an entire classroom period analyzing the feedback.
Discuss writing blocks and ways to overcome them. Discuss the planning process and experience how it helps flesh out an essay. Walk them through each lesson making sure they complete each step successfully before attempting to move on in the writing process. Working side by side with your student also helps you become a better instructor by ...
Ideas- The main idea, supporting details, evidence, and explanation. Ideas are the heart of any good paper. This is where you get the argument, the main idea, or the details that really bring the paper to life. Ideas should be the first thing discussed and brainstormed in the writing process.
Students in groups draft a plan of their work, including how many paragraphs and the main points of each paragraph. These can then be pinned up around the room for comment and comparison. When preparing to write an essay, students group some of the ideas produced earlier into main and supporting statements. Writing.
Students should be encouraged to learn words they frequently misspell, as well as words they wish to include in their writing. Teachers also should help students acquire the skills they need to generate and check plausible spellings for words. 3. Teach students to construct sentences for fluency , meaning and style.
Use clear topic sentences. One of the most important tips to teach writing skills is employing topic sentences. The first sentence of a paragraph establishes its tone. The gist of your content should be communicated in the opening sentence of each paragraph. Ideally, explain your paragraph first, and then expand upon it by providing examples ...
Hands-on Essay Writing Activities #3: Stations. Stations are just what they sound like-stations set up around your classroom. Each station includes the directions and materials needed to complete a different task. In order for students to complete all of the required tasks, they have to rotate to each station.
Step 1: Start with Casual Augmentation. Engage your students in a low-stakes debate before formally teaching argumentative essay writing. This approach will help get students in the right mindset as you begin to lay the foundation for effective argumentation. Don't even mention the word essay at this point.
The best way to improve your essay writing abilities is to work through these steps in sequence: Ensure that students can write a paragraph that successfully makes a case. Teach them how to solve the most typical essay challenges. Make sure that pupils can successfully outline a five paragraph essay.
There are three main stages to writing an essay: preparation, writing and revision. In just 4 minutes, this video will walk you through each stage of an acad...
An essay is a piece of writing where the author proposes an argument, an emotion, or tries to initiate some sort of debate. It's often used to present the author's ideas in a non-fictional manner. It can cover basically any topic in the world - from political discourse through to art criticism and everything in between.
This comprehensive essay writing bundle includes teaching resources and lessons for every part of an essay. First, focus on teaching the thesis statement and introductory paragraph. The first writing unit includes targeted teaching strategies to teach students how to write a thesis statement and an introduction to an essay.
EAP Parts of an Essay Worksheet - Reading and Writing Exercises: True or False, Matching, Labelling, Brainstrorming, Creating an Essay Outline, Writing an Essay - Intermediate (B1-B2) - 90 minutes. In this free parts of an essay worksheet, students learn about the various parts that make up an academic essay and practice writing a structured ...
Ignoring the prompt: This is a major key. STAY ON TRACK. Make sure to carefully read and understand the essay prompt, and write your essay accordingly. The last thing you want to do is write a college essay that has nothing to do with the prompt. Reading is essential here.
Students fill out a registration form online, and a teacher or sponsor is required. The deadline to enter is the first week of April. 5. John F. Kennedy Profile in Courage Essay Contest. This annual contest invites students to write about a political official's act of political courage that occurred after Kennedy's birth in 1917.
Learn from the Experience. Paying for an essay can also be a learning opportunity. Once you receive the completed essay, take the time to review it thoroughly. Analyze the structure, writing style, and how the arguments are presented. This can provide valuable insights and help you improve your own writing skills.
The first study of its kind shows that a tool providing automated feedback improves instructors' communication practices and student satisfaction. Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming ...
In Spring 2023, when ChatGPT burst into the public psyche, twenty-five education students in the author's graduate seminar were invited to participate in a qualitative study using ChatGPT as a tool for completing an essay assignment. Fifteen (N=15) accepted the offer.
Teacher devises an ingenious way to check if students are using ChatGPT to write essays. This video describes a teacher's diabolical method for checking whether work submitted by students was ...