- Privacy Policy

Home » 300+ Social Media Research Topics

300+ Social Media Research Topics

Social media has become an integral part of our lives, and it has transformed the way we communicate, share information, and interact with each other. As social media platforms continue to evolve and gain popularity, they have also become a rich source of data for researchers. Social media research is a rapidly growing field that encompasses a wide range of topics , from understanding the psychological and social effects of social media to analyzing patterns of user behavior and identifying trends in online conversations. In this era of data-driven decision-making, social media research is more important than ever, as it provides insights into how we use and are influenced by social media. In this post, we will explore some of the most fascinating and relevant social media research topics that are shaping our understanding of this powerful medium.
Social Media Research Topics
Social Media Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on mental health
- The role of social media in political polarization
- The impact of social media on relationships
- The use of social media by businesses for marketing
- The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The influence of social media on consumer behavior
- The use of social media for education
- The effects of social media on language use and grammar
- The impact of social media on news consumption
- The role of social media in activism and social change
- The use of social media for job seeking and career development
- The effects of social media on sleep patterns
- The influence of social media on adolescent behavior
- The impact of social media on the spread of misinformation
- The use of social media for personal branding
- The effects of social media on political participation
- The influence of social media on fashion trends
- The impact of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for mental health support
- The effects of social media on creativity
- The role of social media in cultural exchange
- The impact of social media on language learning
- The use of social media for crisis communication
- The effects of social media on privacy and security
- The influence of social media on diet and exercise behavior
- The impact of social media on travel behavior
- The use of social media for citizen journalism
- The effects of social media on political accountability
- The role of social media in peer pressure
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships
- The use of social media for community building
- The effects of social media on gender identity
- The influence of social media on music consumption
- The impact of social media on academic performance
- The use of social media for social support
- The effects of social media on social skills
- The role of social media in disaster response
- The impact of social media on nostalgia and memory
- The use of social media for charity and philanthropy
- The effects of social media on political polarization in developing countries
- The influence of social media on literary consumption
- The impact of social media on family relationships
- The use of social media for citizen science
- The effects of social media on cultural identity
- The role of social media in promoting healthy behaviors
- The impact of social media on language diversity
- The use of social media for environmental activism
- The effects of social media on attention span
- The influence of social media on art consumption
- The impact of social media on cultural values and norms.
- The impact of social media on mental health
- The impact of social media on mental health.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem.
- The use of social media for political activism and social justice movements.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusivity.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships and dating.
- The use of social media for customer service and support.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being among young adults.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and partisanship.
- The use of social media for health communication and behavior change.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards vaccination.
- The impact of social media on political participation and civic engagement.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and echo chambers.
- The use of social media for political campaigning and the manipulation of public opinion.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards vaccination and public health.
- The impact of social media on news consumption and trust in journalism.
- The use of social media for promoting sustainable fashion practices and ethical consumption.
- The role of social media in influencing beauty standards and body image.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and the role of social media influencers.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among healthcare professionals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gun violence and gun control policies.
- The impact of social media on social activism and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting cross-cultural communication and intercultural understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards climate change and environmental policies.
- The impact of social media on public health during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and access to financial services for low-income individuals.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards immigration policies and refugee crises.
- The impact of social media on political activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology education in developing countries.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards gender and sexual orientation.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior in the food and beverage industry.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among first responders.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards racial justice and police brutality.
- The impact of social media on privacy concerns and data security.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and religious tolerance.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards income inequality and economic justice.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military personnel.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The impact of social media on the hospitality industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intergenerational communication and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards animal welfare and animal rights.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills among seniors.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards renewable energy and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on the advertising industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among children and adolescents.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The impact of social media on the beauty industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural preservation and heritage tourism.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized communities.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards sustainable development goals.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural communication in the workplace.
- The role of social media in shaping public attitudes towards mental health policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and sustainable tourism practices.
- The use of social media for health information seeking and patient empowerment.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and sustainable practices.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- The use of social media for promoting education and lifelong learning.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards mental health issues.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and fast fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting social entrepreneurship and social innovation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun control.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of adolescents.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural exchange and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change.
- The impact of social media on political advertising and campaign strategies.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy relationships and communication skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police brutality and racial justice.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and personal finance management.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards LGBTQ+ rights.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and fan engagement.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among marginalized populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration and border policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of journalists.
- The use of social media for promoting community building and social cohesion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards healthcare policies.
- The impact of social media on the food industry and consumer behavior.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gender equality.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and athlete-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and access to banking services.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards animal welfare.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards privacy and data security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality and poverty.
- The use of social media for promoting digital literacy and technology skills.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards renewable energy.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among elderly populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards online privacy and security.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards criminal justice reform.
- The impact of social media on online activism and social movements.
- The use of social media for business-to-business communication and networking.
- The role of social media in promoting civic education and engagement.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry and sustainable fashion practices.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards police reform.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of frontline healthcare workers.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and investment education.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental sustainability and conservation.
- The impact of social media on body image and self-esteem among adolescent girls.
- The use of social media for promoting intercultural dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies and refugees.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of healthcare professionals.
- The use of social media for promoting community resilience and disaster preparedness.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards the Black Lives Matter movement.
- The impact of social media on the music industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy eating habits and nutrition education.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among college students.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting workplace diversity and inclusion.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards climate change policies.
- The impact of social media on the travel industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among military veterans.
- The role of social media in promoting intergenerational dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of educators.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and advocacy.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards reproductive rights.
- The impact of social media on the sports industry and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting financial inclusion and literacy among underprivileged populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among LGBTQ+ populations.
- The impact of social media on the food and beverage industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun ownership.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among caregivers.
- The role of social media in promoting sustainable tourism practices.
- The impact of social media on the gaming industry and gamer culture.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage tourism and preservation.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards public transportation policies.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among homeless populations.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among immigrants and refugees.
- The use of social media for promoting financial literacy and entrepreneurship among youth.
- The use of social media for political mobilization and participation in authoritarian regimes.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards immigration policies.
- The impact of social media on the professional development of teachers and educators.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during public health crises.
- The role of social media in promoting LGBTQ+ rights and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on body positivity and self-acceptance among women.
- The use of social media for public diplomacy and international relations.
- The impact of social media on the mental health and well-being of marginalized communities.
- The use of social media for crisis management and disaster response in the corporate sector.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental activism and conservation.
- The impact of social media on the professional development and networking of entrepreneurs.
- The use of social media for medical education and healthcare communication.
- The role of social media in promoting cultural exchange and understanding.
- The impact of social media on social capital and civic engagement among young adults.
- The use of social media for disaster preparedness and community resilience.
- The role of social media in promoting religious pluralism and tolerance.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy in the non-profit sector.
- The role of social media in promoting interfaith dialogue and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the travel and tourism industry and consumer behavior.
- The use of social media for customer engagement and brand loyalty in the retail sector.
- The impact of social media on the political attitudes and behaviors of young adults.
- The use of social media for promoting gender equality and women’s empowerment.
- The use of social media for promoting animal welfare and adoption.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and well-being among the elderly.
- The impact of social media on the art industry and artist-fan interactions.
- The use of social media for promoting healthy food choices and nutrition.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards income inequality.
- The use of social media for promoting political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability rights and advocacy.
- The use of social media for promoting voter registration and participation.
- The role of social media in promoting entrepreneurship and small business development.
- The use of social media for promoting mental health and well-being among incarcerated populations.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and attitudes towards gun violence prevention.
- The use of social media for promoting cultural heritage and preservation.
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being.
- The relationship between social media use and academic performance.
- The use of social media for emergency communication during natural disasters.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media and journalism.
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion and discourse.
- The use of social media for online learning and education.
- The impact of social media on the fashion and beauty industry.
- The use of social media for brand awareness and marketing.
- The impact of social media on privacy and security.
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment.
- The impact of social media on political polarization and extremism.
- The use of social media for online harassment and cyberbullying.
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness and sustainability.
- The impact of social media on youth culture and identity formation.
- The use of social media for travel and tourism marketing.
- The impact of social media on consumer behavior and decision-making.
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards and body positivity.
- The use of social media for crisis communication and disaster response.
- The impact of social media on the music industry.
- The use of social media for fundraising and philanthropy.
- The role of social media in promoting healthy lifestyles and wellness.
- The impact of social media on sports fandom and fan behavior.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the entertainment industry.
- The use of social media for healthcare communication and patient engagement.
- The role of social media in promoting gender equality and feminism.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant and food industry.
- The use of social media for volunteerism and community service.
- The role of social media in promoting religious tolerance and interfaith dialogue.
- The impact of social media on the art industry.
- The use of social media for political satire and humor.
- The role of social media in promoting disability awareness and advocacy.
- The impact of social media on the real estate industry.
- The use of social media for legal advocacy and justice reform.
- The role of social media in promoting intercultural communication and understanding.
- The impact of social media on the automotive industry.
- The use of social media for pet adoption and animal welfare advocacy.
- The role of social media in promoting mental health and wellness for marginalized communities.
- The impact of social media on the retail industry.
- The use of social media for promoting civic engagement and voter participation.
- The impact of social media on the film and television industry.
- The use of social media for fashion and style inspiration.
- The role of social media in promoting activism for human rights and social issues.
- The effectiveness of social media for political campaigns.
- The role of social media in promoting fake news and misinformation.
- The impact of social media on self-esteem and body image.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships.
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice movements.
- The impact of social media on traditional news media.
- The impact of social media on interpersonal communication skills.
- The impact of social media on the fashion industry.
- The use of social media for social support and mental health awareness.
- The use of social media for political lobbying and activism.
- The impact of social media on travel and tourism behavior.
- The use of social media for customer feedback and market research.
- The impact of social media on the restaurant industry.
- The role of social media in political activism
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication
- The relationship between social media use and body image concerns
- The impact of social media on self-esteem
- The role of social media in shaping cultural norms and values
- The use of social media by celebrities and its impact on their image
- The role of social media in building and maintaining personal relationships
- The use of social media for job searching and recruitment
- The impact of social media on children and adolescents
- The use of social media by political candidates during election campaigns
- The role of social media in education
- The impact of social media on political polarization
- The use of social media for news consumption
- The effect of social media on sleep habits
- The use of social media by non-profit organizations for fundraising
- The role of social media in shaping public opinion
- The influence of social media on language and communication patterns
- The use of social media in crisis communication and emergency management
- The role of social media in promoting environmental awareness
- The influence of social media on music preferences
- The impact of social media on body positivity movements
- The role of social media in shaping beauty standards
- The influence of social media on sports fandom
- The use of social media for health promotion and education
- The impact of social media on political participation
- The role of social media in shaping parenting practices
- The influence of social media on food preferences and eating habits
- The use of social media for peer support and mental health advocacy
- The role of social media in shaping religious beliefs and practices
- The influence of social media on humor and comedy
- The use of social media for online activism and social justice advocacy
- The impact of social media on public health awareness campaigns
- The role of social media in promoting cultural diversity and inclusion
- The influence of social media on travel behavior and decision-making
- The use of social media for international diplomacy and relations
- The impact of social media on job satisfaction and employee engagement
- The role of social media in shaping romantic preferences and dating behavior
- The influence of social media on language learning and language use
- The use of social media for political satire and humor
- The impact of social media on social capital and community building
- The role of social media in shaping gender identity and expression
- The influence of social media on fashion and beauty advertising.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

300+ Communication Research Topics

300+ Science Research Topics

500+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics

350+ Biology Research Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Computer Science Research Topics
13 social media research topics to explore in 2024
Last updated
15 January 2024
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
To help you choose a specific area to examine, here are some of the top social media research topics that are relevant in 2024.
- What makes a strong social media research topic?
Consider the factors below to ensure your topic is strong and compelling:
Clarity: regardless of the topic you investigate, clarity is essential. It ensures readers will be able to understand your work and any wider learnings. Your argument should be clear and your language unambiguous.
Trend relevancy: you need to know what’s currently happening in social media to draw relevant conclusions. Before choosing a topic, consider current popular platforms, trending content, and current use cases to ensure you understand social media as it is today.
New insights: if your research is to be new, innovative, and helpful for the wider population, it should cover areas that haven’t been studied before. Look into what’s already been thoroughly researched to help you uncover knowledge gaps that could be good focus areas.
- Tips for choosing social media research topics
When considering social media research questions, it’s also important to consider whether you’re the right person to conduct that area of study. Your skills, interests, and time allocated will all impact your suitability.
Consider your skillset: your specific expertise is highly valuable when conducting research. Choosing a topic that aligns with your skills will help ensure you can add a thorough analysis and your own learnings.
Align with your interests: if you’re deeply interested in a topic, you’re much more likely to enjoy the process and dedicate the time it needs for a thorough analysis.
Consider your resources: the time you have available to complete the research, your allocated funds, and access to resources should all impact the research topic you choose.
- 13 social media research paper topics
To help you choose the right area of research, we’ve rounded up some of the most compelling topics within the sector. These ideas may also help you come up with your own.
1. The influence of social media on mental health
It’s well-documented that social media can impact mental health. For example, a significant amount of research has highlighted the link between social media and conditions like anxiety, depression, and stress—but there’s still more to uncover in this area.
There are high rates of mental illness worldwide, so there’s continual interest in ways to understand and mitigate it. Studies could focus on the following areas:
The reasons why social media can impact mental health
How social media can impact specific mental health conditions (you might also look at different age groups here)
How to reduce social media’s impact on mental health
2. The effects of social media exposure on child development
There are many unknowns with social media. More research is needed to understand how it impacts children. As such, this is a very valuable research area.
You might explore the following topics:
How social media impacts children at different ages
The long-term effects of childhood social media use
The benefits of social media use in children
How social media use impacts childhood socialization, communication, and learning
3. The role of social media in political campaigning
Social media’s role in political campaigning is nothing new. The Cambridge Analytica Scandal, for example, involved data from millions of Facebook profiles being sold to a third party for political advertising. Many believe this could have impacted the 2016 US election results. Ultimately, Facebook had to pay a private class-action lawsuit of $725 million.
The role of social media in political campaigns is of global significance. Concerns are still high that social media can play a negative role in elections due to the spread of misinformation, disinformation, and the bandwagon effect.
Research in this area could look into the following topics:
How people are influenced by social media when it comes to voting
Ways to mitigate misinformation
Election interference and how this can be prevented
4. The role of social media in misinformation and disinformation
Misinformation and disinformation mean slightly different things. Misinformation is unintentionally sharing false or inaccurate information, while disinformation is sharing false information with the deliberate intent to mislead people.
Both can play a role not just in elections but throughout social media. This became particularly problematic during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Research into this area is important given the widespread risk that comes with spreading false information about health and safety-related topics.
Here are some potential research areas:
How misinformation and disinformation are spread via social media
The impact of false information (you could focus on how it impacts health, for example)
Strategies for mitigating the impact of false information and encouraging critical thinking
The avenues through which to hold technology companies accountable for spreading misinformation
5. The impact of AI and deepfakes on social media
AI technology is expected to continue expanding in 2024. Some are concerned that this could impact social media. One concern is the potential for the widespread use of deepfake technology—a form of AI that uses deep learning to create fake images.
Fake images can be used to discredit, shame, and control others, so researchers need to deeply understand this area of technology. You might look into the following areas:
The potential impacts of deepfakes on businesses and their reputations
Deepfake identities on social media: privacy concerns and other risks
How deepfake images can be identified, controlled, and prevented
6. How social media can benefit communities
While there’s much research into the potential negative impacts of social media, it can also provide many benefits.
Social media can establish connections for those who might otherwise be isolated in the community. It can facilitate in-person gatherings and connect people who are physically separated, such as relatives who live in different countries. Social media can also provide critical information to communities quickly in the case of emergencies.
Research into the ways social media can provide these key benefits can make interesting topics. You could consider the following:
Which social media platforms offer the most benefits
How to better use social media to lean into these benefits
How new social platforms could connect us in more helpful ways
7. The psychology of social media
Social media psychology explores human behavior in relation to social media. There are a range of topics within social media psychology, including the following:
The influence of social media on social comparison
Addiction and psychological dependence on social media
How social media increases the risk of cyberbullying
How social media use impacts people’s attention spans
Social interactions and the impact on socialization
Persuasion and influence on social media
8. How communication has evolved through social media
Social media has provided endless ways for humans to connect and interact, so the ways we do this have evolved.
Most obviously, social media has provided ways to connect instantaneously via real-time messaging and communicate using multimedia formats, including text, images, emojis, video content, and audio.
This has made communication more accessible and seamless, especially given many people now own smartphones that can connect to social media apps from anywhere.
You might consider researching the following topics:
How social media has changed the way people communicate
The impacts of being continuously connected, both positive and negative
How communication may evolve in the future due to social media
9. Social media platforms as primary news sources
As social media use has become more widespread, many are accessing news information primarily from their newsfeeds. This can be particularly problematic, given that newsfeeds are personalized providing content to people based on their data.
This can cause people to live in echo chambers, where they are constantly targeted with content that aligns with their beliefs. This can cause people to become more entrenched in their way of thinking and more unable or unwilling to see other people’s opinions and points of view.
Research in this area could consider the following:
The challenges that arise from using social media platforms as a primary news source
The pros and cons of social media: does it encourage “soloization” or diverse perspectives?
How to prevent social media echo chambers from occurring
The impact of social media echo chambers on journalistic integrity
10. How social media is impacting modern journalism
News platforms typically rely on an advertising model where more clicks and views increase revenue. Since sensationalist stories can attract more clicks and shares on social media, modern journalism is evolving.
Journalists are often rewarded for writing clickbait headlines and content that’s more emotionally triggering (and therefore shareable).
Your research could cover the following areas:
How journalism is evolving due to social media
How to mitigate social media’s impact on neutral reporting
The importance of journalistic standards in the age of social media
11. The impact of social media on traditional advertising
Digital advertising is growing in popularity. Worldwide, ad spending on social media was expected to reach $207.1 billion in 2023 . Experts estimate that ad spending on mobile alone will reach $255.8 billion by 2028 . This move continues to impact traditional advertising, which takes place via channels like print, TV, and radio.
Most organizations consider their social strategy a critical aspect of their advertising program. Many exclusively advertise on social media—especially those with limited budgets.
Here are some interesting research topics in this area
The impact of different advertising methods
Which social media advertising channels provide the highest return on investment (ROI)
The societal impacts of social media advertising
12. Impacts of social media presence on corporate image
Social media presence can provide companies with an opportunity to be visible and increase brand awareness . Social media also provides a key way to interact with customers.
More and more customers now expect businesses to be online. Research shows that 63% of customers expect companies to offer customer service via their social media channels, while a whopping 90% have connected with a brand or business through social media.
Research in this area could focus on the following topics:
The advantages and disadvantages of social media marketing for businesses
How social media can impact a business’s corporate image
How social media can boost customer experience and loyalty
13. How social media impacts data privacy
Using social media platforms is free for the most part, but users have to provide their personal data for the privilege. This means data collection , tracking, the potential for third parties to access that data, psychological profiling, geolocation, and tracking are all potential risks for users.
Data security and privacy are of increasing interest globally. Research within this area will likely be in high demand in 2024.
Here are some of the research topics you might want to consider in this area:
Common privacy concerns with social media use
Why is social media privacy important?
What can individuals do to protect their data when using social media?
- The importance of social media research
As social media use continues to expand in the US and around the world, there’s continual interest in research on the topic. The research you conduct could positively impact many groups of people.
Topics can cover a broad range of areas. You might look at how social media can harm or benefit people, how social media can impact journalism, how platforms can impact young people, or the data privacy risks involved with social media use. The options are endless, and new research topics will present themselves as technology evolves.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
234 Social Media Research Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 2646 words
- Icon Clock 12 min read
Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation, self-presentation, the psychology of virtual interactions, and others. Additionally, studies examine the influence of social media on politics, activism, and public opinion, uncovering patterns of information dissemination and polarization. Privacy concerns, cyberbullying, and online safety are also explored in-depth, seeking strategies to mitigate the associated risks. In this article, people can find many social media research topics, ideas, and examples.
Hot Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Social Media and Internet Algorithms on User Experience
- The Rise of TikTok: A Socio-Cultural Analysis
- Dealing With Cyberbullying: Strategies and Solutions
- Understanding the Phenomenon of Social Media ‘Cancel Culture’
- NFTs and Social Media: The Future of Digital Art?
- Ethical Concerns in the Era of Influencer Marketing
- Social Media’s Role in Accelerating E-Commerce Growth
- Impacts of Internet and Social Media on Journalism and News Reporting
- Understanding the Psychology of Viral Challenges on Social Platforms
- Cryptocurrency and Social Media: The Intersection
- Mitigating Misinformation and ‘Fake News’ on Social Media
- Augmented Reality (AR) in Social Media: A Game Changer?
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Political Campaigns
- Social Media’s Influence on Fashion and Beauty Trends
- Privacy, Safety, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Networking
- Roles of Free Access and Social Media in Promoting Sustainable Practices
- Implications of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health
- Examining Social Media’s Role in Crisis Communication
- The Power of User-Generated Content in Branding
- Influence of Social Media on Food Culture and Dining Trends
Easy Social Media Research Topics
- Impacts of Online Videos and Social Media on Mental Health
- Influencer Marketing: Efficacy and Ethical Concerns
- Evolution of Privacy Policies Across Social Platforms
- Understanding Virality: What Makes Content Shareable?
- Cyberbullying: Prevalence and Prevention Strategies
- Social Media and Political Polarization: An In-Depth Study
- Role of Social Media in Modern Business Strategies
- Effect of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships
- Social Platforms as Tools for Social Change
- Navigating Online Hate Speech: A Legal Perspective
- Emerging Trends in Social Media Advertising
- Online Identity Construction and Self-Presentation
- The Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management and Communication
- Sentiment Analysis in Social Media and Its Implications
- Social Media Algorithms: Bias and Implications
- The Phenomenon of Cancel Culture on Social Platforms
- Cybersecurity Threats in the Era of Social Media
- Analyzing Adverse Impacts of Social Media on Consumer Behavior

Interesting Social Media Research Topics
- Evaluating the Effects of Social Media on Language and Communication
- Roles of Social Media in Fostering Political Engagement
- Misinformation and Propaganda Spread Through Social Platforms
- Analyzing the Shift From Traditional Media to Social Media
- Dark Patterns in Social Media: Hidden Manipulative Tactics
- Social Media and Digital Activism: Revolutionizing Advocacy
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Its Impact on Social Networking
- Exploring Cybersecurity Issues in Social Media Platforms
- Roles and Effects of Social Media and News in Mental Health Promotion
- Strategies for Effective Social Media Crisis Management
- The Power of Live Streaming for Brands and Influencers
- Using Social Media to Enhance Classroom Learning
- Analyzing the Influence of Memes on Internet Culture
- Impacts of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior
- Assessing the Correlation Between Social Media and Loneliness
- Geotagging and Its Implications for Personal Privacy
- Social Media and E-commerce: A Cross-Industry Study
- The Ethics of Digital Advertising on Social Platforms
- Understanding the Psychology of Social Media Trolls
- The Cultural Shift Caused by Social Media Localization
Social Media Research Paper Topics for High School
- The Phenomenon of Cyberbullying: Prevention and Strategies
- How Does Social Media Influence Teen Body Image?
- Evaluating the Educational Potential of Social Media Platforms
- Impacts of Social Media on Adolescents’ Self-Esteem
- Roles of Free Connection and Social Media in Modern Political Activism
- Exploring the Concept of ‘Digital Citizenship’ Among Teenagers
- The Ethics of Social Media Privacy: User Rights and Responsibilities
- Social Media Addiction: Understanding Its Causes and Effects
- Influence of Social Media on Modern Communication Styles
- Analyzing Positive Roles of Social Media in Promoting Reading Culture
- Social Media and Mental Health: Correlation or Causation?
- The Role of Social Media in Global Environmental Awareness
- Examining Social Media’s Impact on Real-Life Social Skills
- Social Media Platforms: Tools for Personal Branding or Narcissism?
- Influence of Social Media Trends on Youth Fashion Choices
- Impacts of Social Media on Teenagers’ Sleep Patterns
- Online Safety: The Role of Parents and Schools in Social Media Usage
- How Does Social Media Influence Teenagers’ Views on Relationships?
- Social Media and Empathy: Does Online Interaction Decrease Compassion?
Social Media Research Paper Topics for College Students
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- The Influence of Social Media on Voting Patterns Among Young Adults
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Social Change: A Case Study Approach
- Unveiling the Psychology of Social Media Addiction
- Social Media’s Role in Modern Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Privacy Implications of Data Collection on Social Media Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Age of Social Media: Scope and Solutions
- The Ethical Aspects of Social Media Influencer Marketing
- Roles and Effects of Social Media in Crisis Communication and Management
- Social Media and Its Effects on Interpersonal Communication Skills
- Analyzing Social Media Strategies of Successful Businesses
- Impacts of Internet Use and Social Media on Mental Health Among College Students
- The Roles That Social Media Has in Modern Political Campaigns
- Understanding the Social Media Algorithm: Bias and Implications
- Social Media and Consumer Behavior: The Power of Influencer Marketing
- Fake News, Authors, and Disinformation Spread Through Social Media Platforms
- Exploring Direct Links Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Social Media’s Role in Promoting Sustainable Lifestyle Choices
- Regulation of Hate Speech and Offensive Content on Social Media
- The Power and Peril of Virality in the Age of Social Media
Social Media Research Paper Topics for University
- The Effect That Social Media Has on Global Politics
- The Ethics of Data Mining in Social Media
- Roles of Social Media in Business Marketing Strategies
- Social Media, Internet Use, and Their Impacts on Mental Health: A Systematic Review
- Algorithmic Bias in Social Media Platforms: Causes and Consequences
- The Influence of Colors and Social Media on Consumer Behavior
- Exploring Possible Relationships Between Social Media Use and Academic Performance
- Privacy, Morality, and Security Concerns in the Age of Social Media
- Social Media as a Platform for Digital Activism
- Impacts of Social Media on Interpersonal Communication and Relationships
- Cyberbullying on Social Media: Scope, Impact, and Preventive Measures
- The Role of Social Media in Spreading Health-Related Misinformation
- Analyzing the Effect of Social Media on Journalism Practices
- Understanding the Influence of Social Media on Body Image Perceptions
- Social Media’s Role in Crisis Management: Case Studies
- The Power and Effectiveness of Influencer Marketing on Social Media
- Fake News and Disinformation in the Social Media Age
- Regulatory Approaches to Hate Speech on Social Media Platforms
- The Economic Implications of Social Media: From Startups to Giants
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Masters
- Advanced Algorithms and Their Role in Shaping Social Media Interactions
- Evaluating the Impact of Social Media on Democratic Processes Globally
- The Intersection of Privacy, Data Mining, and Ethics in Social Media
- Quantitative Analysis of Social Media’s Impact on Consumer Buying Behavior
- Cybersecurity Threats in Social Media: Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
- Analyzing the Psychological Implications of Social Media Addiction
- Using Social Media Data to Predict Market Trends: An Econometric Approach
- Role of Social Media in Crisis Management: A Comparative Study
- The Sociolinguistic Impact of Social Media on Communication
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: An Examination of Emerging Trends
- Social Media as a Valid Tool for Public Health: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media’s Influence on Modern Journalism: A Critical Analysis
- Mapping Social Networks: A Graph Theory Approach
- Evaluating the Efficacy of Social Media Campaigns in Social Change Movements
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Corporate Reputation Management
- Data Privacy Laws and Social Media: A Comparative Study
- The Use of Small and Big Data Analytics in Social Media Marketing
- Social Media and Its Role in Strengthening Democracy: A Deep Dive
- The Impact of Social Media on Cultural Assimilation and Identity
- Ethics of Artificial Intelligence in Social Media Content Moderation
Social Media Research Paper Topics for Ph.D.
- Analyzing the Impact of Social Media Algorithms on User Behavior and Perceptions
- Deciphering the Influence of Social Media on Political Campaign Strategies
- Examining the Role of Social Media in Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives
- Social Media and Mental Health: A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Studies
- Effects of Social Media and Internet Use on Consumer Buying Behavior: An Econometric Approach
- Social Media and Digital Diplomacy: A Critical Analysis
- Ethical Implications of Data Mining Techniques in Social Media Platforms
- Unpacking the Psychological Mechanisms of Social Media Addiction
- Role of Social Media in Contemporary Journalism: Opportunities and Challenges
- Social Media and Privacy: A Comparative Study of Data Protection Laws
- Machine Learning and AI in Social Media: Identifying Future Trends
- Social Media’s Possible Influence on People, Body Image, and Self-Esteem: A Meta-Analysis
- Analyzing the Role of Social Media in Crisis Management and Communication
- Impacts of Social Media on Different Language and Communication Styles
- Cybersecurity in Social Media: An Analysis of Current Threats and Mitigation Strategies
- Social Media as a Good Tool for Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
- Effects of Social Media on Children and Their Parents: Social Skills and Interpersonal Relationships
- Roles of Social Media in Promoting Gender Equality and Women’s Rights
- Social Media and its Influence on Cultural Assimilation and Identity Formation
Social Media Research Topics for Argumentative Papers
- Impacts of Social Media on Social and Political Discourses: Enhancing or Hindering Democratic Engagement?
- Social Media and Mental Health: Exploring the Association Between Excessive Usage and Psychological Well-Being
- Fostering Online Activism and Social Movements: The Role of Social Media
- Balancing Personal Information Sharing and Data Protection: Social Media and Privacy
- Exploring the Effects of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Reinforcing Echo Chambers or Encouraging Diverse Perspectives?
- Youth Culture and Identity Formation: The Influence of Social Media
- Fake News and Misinformation: Combating Inaccurate Information in the Era of Social Media
- Social Media and Cyberbullying: Examining the Impact on Mental Health and Well-Being
- The Ethics of Social Media Research: Privacy, Informed Consent, and Ethical Considerations
- Relationships in the Digital Age: Exploring the Influence of Social Media Use
- The Influence of Internet, Technology, and Social Media on Consumer Behavior and Buying Decisions
- Analyzing the Role of Online Platforms in Elections: Social Media and Political Campaigns
- Social Media in Education: Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Integration in the Classroom
- Impacts of Social Media and Interface on News Consumption and Journalism Practices
- Body Politics in the Digital Space: Examining Representations of Gender, Race, and Body Image on Social Media
- Addressing Ethical and Security Concerns in the Digital Age: Social Media and Cybersecurity
- Shaping Consumer Behavior and Brand Perception: The Role of Social Media Influencers
- Civic Engagement in the Digital Era: Assessing the Role of Social Media Platforms
- The Influence of Social Media Algorithms on Information Consumption and Personalization
Social Media Research Topics for Persuasive Papers
- The Power of Social Media in Driving Social and Political Change
- Promoting Digital Literacy: Empowering Users to Navigate the Complexities of Social Media
- Social Media as a Catalyst for Social Justice Movements: Amplifying Marginalized Voices
- Countering Fake News and Misinformation on Social Media: Strategies for Critical Thinking
- Harnessing the Influence of Social Media for Environmental Activism and Sustainability
- The Dark Side of Social Media: Addressing Online Harassment and Cyberbullying
- Influencer Marketing: Ethical Considerations and Consumer Protection in the Digital Age
- Leveraging Social Media for Public Health Campaigns: Increasing Awareness and Behavioral Change
- Social Media and Mental Health: Promoting Well-Being in a Hyperconnected World
- Navigating the Privacy Paradox: Balancing Convenience and Personal Data Protection on Social Media
- Roles of Social Media and Internet in Fostering Civic Engagement and Democratic Participation
- Promoting Positive Body Image on Social Media: Redefining Beauty Standards and Empowering Individuals
- Enhancing Online Safety: Developing Policies and Regulations for Social Media Platforms
- Social Media and the Spread of Disinformation: Combating the Infodemic
- Roles of Social Media and Technology in Building and Sustaining Relationships: Connecting in a Digital Era
- Influencer Culture and Materialism: Examining the Impact on Consumer Behavior
- Social Media and Education: Maximizing Learning Opportunities and Bridging the Digital Divide
- The Power of Viral Hashtags: Exploring Social Movements and Online Activism
- Social Media and Political Polarization: Bridging Divides and Encouraging Constructive Dialogue
Social Media Topics for Pros and Cons Research Papers
- Examining the Social Effects of Digital Connectivity: Pros and Cons of Using Social Media
- Balancing Privacy Concerns in the Digital Age: Evaluating the Cons and Risks of Social Media Use
- Information Sharing in the Digital Era: Uncovering the Advantages of Social Media Platforms
- Building Online Communities: Analyzing the Strengths and Weaknesses of Social Media Interaction
- Navigating Political Discourse in the Digital Age: The Disadvantages of Social Media Engagement
- Mental Health in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Benefits and Drawbacks of Social Media
- Combating Cyberbullying: Addressing the Negative Side of Online Social Interactions
- Personal Branding in the Digital Landscape: Empowerment vs. Self-Objectification on Social Media
- Establishing Meaningful Connections: Exploring the Pros and Cons of Social Media Relationships
- Leveraging the Educational Potential of Digital Platforms: Examining the Benefits of Social Media in Learning
- Body Image and Self-Esteem in the Age of Social Media: Weighing the Positives and Negatives
- From Digital Activism to Political Change: Assessing the Opportunities and Limitations of Social Media
- Unraveling the Influence: Social Media and Consumer Behavior in the Digital Marketplace
- Misinformation in the Digital Landscape: The Pros and Cons of Social Media in the Spread of Disinformation
- Crisis Communication in the Digital Age: Navigating the Benefits and Challenges of Social Media
- Tackling Fake News: Navigating Misinformation in the Era of Social Media
- Maximizing Business Opportunities: Evaluating the Advantages and Disadvantages of Social Media Marketing
- The Psychology of Social Media: Analyzing the Upsides and Downsides of Digital Engagement
- Exploring the Impact of Social Media on Socialization: Benefits, Drawbacks, and Implications
- Online Activism: The Power and Limitations of Social Media Movements
Social Media Topics for Cause and Effect Research Papers
- Enhancing Political Activism: Exploring the Relationship Between Social Media and Civic Engagement
- The Psychological Effects of Digital Connectivity: Investigating the Relationship Between Mental Health of People and Social Media Use
- Political Polarization in the Online Sphere: Understanding the Impact of Digital Networks
- Disrupted Sleep Patterns in the Digital Era: Exploring the Role of Online Platforms
- Digital Distractions and Academic Performance: Analyzing the Effects of Online Engagement
- Navigating Online Relationships: Understanding the Impacts of Digital Interactions
- The Digital Marketplace: Exploring Consumer Behavior in the Age of Online Platforms
- The Loneliness Epidemic: Investigating the Relationship Between Social Media Use and Social Isolation
- Redefining Political Participation: The Influence of Digital Networks on Democracy
- Unmasking Digital Identities: The Psychological Effects of Social Media Use
- News Consumption in the Digital Era: Exploring the Impacts of Online Platforms
- Cyberbullying in the Virtual World: Analyzing the Effects of Online Interactions
- The Digital Campaign Trail: Investigating the Influence of Online Platforms on Voter Behavior
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) in the Digital Age: Exploring the Psychological Consequences
- Body Dissatisfaction in the Digital Sphere: Understanding the Impacts of Online Presence
- Information Overload: Coping With the Digital Deluge in the Information Age
- Privacy Concerns in the Online Landscape: Analyzing the Implications of Digital Footprints
- Unveiling the Dark Side: Exploring the Relationship Between Online Activities and Substance Abuse
- Bridging the Political Divide: The Impact of Digital Networks on Sociopolitical Polarization
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

431 Music Essay Topics & Ideas
- Icon Calendar 24 May 2023
- Icon Page 4272 words

Essay on My Escape From North Korea
- Icon Calendar 25 April 2023
- Icon Page 713 words
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
74 Best Social Media Research Paper Topics

Whether in college or high school, you will come across research writing as a student. In most cases, the topic of research is assigned by your teacher/professor. Other times, students have to come up with their topic. Research writing in school is inescapable. It’s a task you are bound to undertake to fulfill your academic requirements. If you are in college, there are several topics for research depending on your discipline. For high school students, the topic is usually given. In this article, we focus on social media and topics about social media.
A social media paper is a research paper about social media that studies social media generally or an aspect of it. To write research papers on social media, you’ll need to conduct thorough research for materials and scholarly materials that’ll assist you. For social media, most of the scholarly works will be media-focused.
Sometimes, Professors or teachers ask students to write an essay or research a topic without narrowing it down. In that case, students will have to develop specific research topics. If you’re writing a paper on social media, we’ve provided you with helpful topics to consider for research.
How to Start a Social Media Research Paper
Social media topics to write about, social media research topics for college students, interesting topics to research for fun, research questions about social media, social media essay topics for high school students, narrow research topic ideas students can consider, research paper on social media marketing, good social topics for research papers, easy social issues to write about, social science research topics for college students, interesting research topics for high school students, comprehensive social networking research papers, final words about social media topics.
Before giving a research writing, Professors and teachers believe students already know how to write one. Not every student knows how to write a research paper in most cases.
Research writing follows a systematic pattern, which applies to research on social media. Below is the pattern of a research paper to use;
- Paper title
- Introduction
- Statement of problem
- Research methodology
- Research objective
- Critical analysis
- Results and discussion
Every research follows this basic pattern, and it also applies to your research paper on social media.
Social media has become a powerful tool for engagement of various kinds. Before now, social media was merely apps used for interpersonal affairs. Today, with the modification of digital technology, social media encompasses a lot more. Below are some social media topics to write about.
- The impact of social media in promoting interpersonal relationships
- A study on how social media is a vital tool for social change
- Social media censorship: A new form of restriction on freedom of speech
- The constantly growing oversharing nature of social media
- Social media is a vital tool for political campaign
- The proliferation of social media platforms into a buying space
- The juxtaposition of personal engagement and business on social media platforms
There is a wide range of topics to coin from social media for college students because social media is a platform with diverse issues that can form into topics. Here are some research topics about social media to consider.
- Breach of Privacy: A study on the ability of the government to monitor personal affairs on social media
- A study of the toxicity brewing within social media
- The increased cyberbullying perpetrated on social media platforms
- The evolution of Twitter into a space for diverse conversations
- A study of the emergence and growth of social media over the years
- Effects of social media: How social media is breeding laziness amongst children
- Social media as a distraction tool for students
If you are searching for interesting topics, there are many interesting research topics on social media. Examples of research paper topics that sound fun to choose from include;
- A study on how the emergence of social media and social media advertising has infiltrated its primary purpose
- An evaluation of how social media has created employment opportunities for people
- Social media influence and its negative impact on society
- Advertising on social media: Will influencer businesses take over advertising agencies?
- A study on ways to improve advertisement for social media engagement
- A look into how social media creates a distorted view of real life
- Social media and real-life: Does social media obscure reality?
Research questions are helpful when carrying out research in a particular field. To know more about your thesis on social media, you will need to create research questions on social media to help inform your writing. Some social media research questions to ask are;
- Are social media platforms designed to be addictive?
- What is a social media Algorithm, and how to navigate it?
- To what extent are personal data stored on social app databases protected?
- Can social media owners avoid government monitoring?
- Should parents allow their children to navigate social media before they are 15?
- Have social media jobs come to stay, or are they temporary?
- Is social media influencer culture overtaking celebrity culture?
- To what extent can social media help to curb racism and homophobia?
- Does social media exacerbate or curb discriminatory practices?
- Is social media an effective tool for learning?
Everyone has access to social media apps until they’ve reached a certain age. There are several social media essay topics for high school students to write about. Some social media titles for essays include;
- How social media affects the academic performance of students
- Why the use of social media is prohibited during school hours
- Why students are obsessed with Tiktok
- Running a profitable social media business while in high school and the challenges
- The dangers of overusing editing apps
- A critical essay on how editing apps and filters promote an unrealistic idea of beauty
- The death of TV: how social media has stolen student’s interest
The challenge students have with their topic ideas for research papers is that they’re broad. A good social media thesis topic should be narrowed down. Narrowing a topic down helps you during research to focus on an issue.
Some narrow social media topics for the research paper include;
- A study of how social media is overtaking Television in entertainment
- A study of how social media has overtaken traditional journalism
- An evaluation of the rise of influencer culture on Instagram
- YouTube and how it has created sustainable income for black content creators
- A comparative study of social media managers and content creators
- A study of the decline of Instagram since the emergence of Tiktok
- How Twitter breeds transphobic conversations
There are several areas of social media to focus your research on. If you are looking for some social media marketing topics, below are some social media research paper topics to consider;
- Influencer culture and a modified model of mouth-to-mouth marketing
- The growth of video marketing on Instagram
- Social media managers as an essential part of online marketing
- A study on how social media stories are optimized for marketing
- An analysis of social media marketing and its impact on customer behavior
- An evaluation of target marketing on social media
There are so many topics to choose from in this aspect. Some social issues research paper topics to explore are;
- The growth of cyberattacks and cyberstalking in social media
- Social media and how it promotes an unrealistic idea of life
- Social media and the many impacts it has on users and businesses
- Social media detox: Importance of taking scheduled social media breaks
- How social media enable conversation on social challenges
Writing a research paper on social issues touches on various areas. Some are challenging, while others are easier to navigate.
Below are some of the easy social issues topics to choose from.
- The growing issue of women’s and trans people’s rights
- Religious bigotry and how it affects social progress
- Sustainable living and why it’s important to the society
- The social impact of climate change and global warming
Social science is a broad discipline. If you are looking for social science essay topics, below are some social science topics for research papers to look into;
- Consumerism and how it’s perpetrated on social media
- How religious beliefs impact social relationships
- Inflation and how it affects the economy of a nation
- A study of the limited availability of work opportunities for minority groups
- A look into the concept of “low wage” jobs
Research writing is not always technical or challenging. Sometimes, it can be fun to write. It all depends on your choice of topic. Below are some topics on social media that are fun to work on;
- The importance of social media branding for small businesses
- A look into the monetization of Instagram
- User engagement and how it can be converted into business leads
- The study of emojis and their role in social media engagement
- From Instagram to Tiktok: the poaching nature of social media apps
Research writing on social media networking studies social networking and its design and promotion on social media platforms. Some research papers on social media networking are;
- The impact of social media networking on business owners
- Social media networking and how it impacts influencer culture
- Social media and how it’s used to build and develop social relationships
- How social media made social networking services easier
Social media research writing is one of the most interesting research to conduct. It cuts across several interesting areas. The writer can handle almost every aspect of the dissertation or thesis statement about social media . But, students who find it challenging should seek professional help. You can reach out to our expert team of writers to help you handle every element of your writing. We have the best on our team who are always ready to give you their best.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Explore your training options in 10 minutes Get Started
- Graduate Stories
- Partner Spotlights
- Bootcamp Prep
- Bootcamp Admissions
- University Bootcamps
- Coding Tools
- Software Engineering
- Web Development
- Data Science
- Tech Guides
- Tech Resources
- Career Advice
- Online Learning
- Internships
- Apprenticeships
- Tech Salaries
- Associate Degree
- Bachelor's Degree
- Master's Degree
- University Admissions
- Best Schools
- Certifications
- Bootcamp Financing
- Higher Ed Financing
- Scholarships
- Financial Aid
- Best Coding Bootcamps
- Best Online Bootcamps
- Best Web Design Bootcamps
- Best Data Science Bootcamps
- Best Technology Sales Bootcamps
- Best Data Analytics Bootcamps
- Best Cybersecurity Bootcamps
- Best Digital Marketing Bootcamps
- Los Angeles
- San Francisco
- Browse All Locations
- Digital Marketing
- Machine Learning
- See All Subjects
- Bootcamps 101
- Full-Stack Development
- Career Changes
- View all Career Discussions
- Mobile App Development
- Cybersecurity
- Product Management
- UX/UI Design
- What is a Coding Bootcamp?
- Are Coding Bootcamps Worth It?
- How to Choose a Coding Bootcamp
- Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses
- Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Community College
- Coding Bootcamp vs. Self-Learning
- Bootcamps vs. Certifications: Compared
- What Is a Coding Bootcamp Job Guarantee?
- How to Pay for Coding Bootcamp
- Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans
- Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants
- Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps
- Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your Employer
- GI Bill and Coding Bootcamps
- Tech Intevriews
- Our Enterprise Solution
- Connect With Us
- Publication
- Reskill America
- Partner With Us
- Resource Center
- Bachelor’s Degree
- Master’s Degree
The Top 10 Most Interesting Social Media Research Topics
Finding social media research topics you’re interested in is tricky. Social media is a fairly new field, and the constant arrival of new technology means that it’s always evolving. So, students have a lot to think about in their search for topics.
In this article, we’re going to walk you through social media research paper topics that are timely and relevant. We’ll also show you examples of social media research topics you can get inspiration from. Lastly, we’re going to lay out some social media research questions you can ponder while formulating your topic.
Find your bootcamp match
What makes a strong social media research topic.
A strong social media research topic requires clarity of focus. This means that your topic must be timely, relevant, and coherent. This allows your research topic to be compelling and easily understandable to others.
Tips for Choosing a Social Media Research Topic
- Know the trends. Learning what social media topics are trending allows you to know the relevant issues and emergent themes in the field of social media. This also lets you know what topics are well-researched and which ones are still emerging.
- Explore knowledge gaps. Knowing what previous researchers have written prevents you from repeating knowledge that has already been explored and shared. Nobody wants to reinvent the wheel when doing research. Exploring knowledge gaps lets you increase the impact of your work and identify opportunities for further research.
- Choose something that you’re interested in. Diving deep into a topic that you’re interested in motivates you to learn more about it. The research process becomes more engaging when you know you care about your topic.
- Be specific. Knowing what you want to research and what you don’t want to research are keys to the research process. This entails narrowing down your topic to a specific area, subject, theme, or relationship. You want to know the scope and the limitations of your study.
- Check your timeframe. Limiting your topic to a specific timeframe helps in narrowing down what you need to study. For example, you can decide to study a phenomenon that has emerged in just the last three years. By doing this, you’re making sure that your research is both specific and relevant.
What’s the Difference Between a Research Topic and a Research Question?
The difference between a research topic and a research question is in the scope. Research topics tend to be broader than research questions. Research topics focus on a specific area of study within a larger field, while a research question further narrows down what you are researching. A good research question allows you to write on your topic with greater precision.
How to Create Strong Social Media Research Questions
The key to creating strong social media research questions is learning enough about your topic to know where the gaps are. This means that you have to conduct a thorough social media literature review, reading previous studies until you have a handle on what’s been said and what questions are still unanswered. Your question will emerge from this preliminary research.
Top 10 Social Media Research Paper Topics
1. a comparative review of facebook, instagram, and tiktok as primary marketing platforms for small businesses.
A lot of small businesses have flocked to various social media sites to market their products and services. Social networking sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Tiktok are platforms that deliver constant online content to their users. Comparing the marketing and advertising strategies of these online platforms will shed light on how social media helps businesses .
2. The Influence of Social Media on Mental Health
Mental health has been an important topic in social media research these past few years. Social media use and its connection to mental health has even been the subject of systematic reviews. This means that there’s a huge body of previous studies that you can look to when developing your research question.
Exploring both the positive effects and negative impacts of social media sites on mental health helps people and firms establish guidelines that help user communities. This research topic might also cover strategies for helping social media users improve their mental health.
3. The Role of Social Media in Political Campaigning
Social media is a new tool for political campaigning. Exploring what social media strategies have been conducted by politicians running for office helps in determining how social media aids in political campaigning. Studying new strategies like user-generated content for political campaigning allows you to know how voters interact with political candidates.
4. The Role of Social Media in Disinformation
The rise of fake news has coincided with the rise of social networking websites. This topic involves dissecting how social media technologies allow certain types of online content to thrive and make it easier for bad actors to spread disinformation.
5. How Social Media Can Benefit Communities
More and more social issues have been popularized through online content. Diving deep into how social media can facilitate organizational networking lets you compare the traditional and new organizing strategies being created in digital spaces. It also lets you understand how social media activity influences trends in virtual communities.
6. The Effects of Social Media Exposure on Child Development
Children also use social media sites. Some children use social networking sites under the supervision of their parents, and some do not. Social interaction, online or not, affects how children develop. Studying the psychological effects of social media exposure lets you know how social media may improve or derail the growth of children.
7. How Communication Has Evolved Through Social Media
Body language, tone of voice, and other non-verbal cues are absent in online forms of communication. In their place, emojis and other new ways to express thoughts and emotions have appeared. Learning how social media changes the way we talk to one another allows you to develop a theory of communication that takes into account the role of digital communities.
8. Social Media Platforms as Primary News Sources
A lot of people now are getting their daily dose of news and current events through social media. News networks have also established their social media presence on platforms that they can use to deliver news and current events to their audiences. Researching this topic lets you investigate the changes and innovations in information dissemination.
9. How Social Media Paves Way for Non-Traditional Advertising
Regular social media posts, advertisements, and other forms of online content aren’t the only ways businesses market to their audiences. Social media has paved the way for user-generated content and other non-traditional types of online marketing. With this topic, you can learn social media marketing strategies that have been capitalized on the social connection fostered by social networking websites.
10. Impacts of Social Media Presence on Corporate Image
More businesses increasingly build and curate their digital presence through various social networks. Knowing how a business can improve its corporate image through social media influence clarifies the role of technology in modern economics and online marketing.
Other Examples of Social Media Research Topics & Questions
Social media research topics.
- Social Media Addiction and Adolescent Mental Health
- The Rise of Social Media Influencers
- The Role of Social Media Sites as Political Organizing Tools Under Repressive Governments
- Social Media Influencers and Adolescent Mental Health
- How Social Media Is Used in Natural Disasters and Critical Events
Social Media Research Questions
- How was Facebook used as a political campaigning tool in the 2020 United States presidential election?
- What social platforms are the most effective in influencing consumer behavior?
- How does user-generated content boost the credibility of a business?
- How do different types of online content disseminated through popular networks affect the attention span of people?
- What are the most effective forms of online content and social media strategies for increasing sales conversions for small businesses?
Choosing the Right Social Media Research Topic
Choosing the right social media research topic helps you create meaningful contributions to the discipline of social media studies. Knowing the most popular topics in the field can make you an expert on social media. By reading up on previous studies, you will not only be more informed but you will also be in a position to make a positive impact on future studies.
Studying the relationship between social media and different fields produces valuable knowledge. Even if you’re only interested in exploring one social platform or a single social media event or phenomenon, your research can help people better understand how social media engagement changes the face of social relationships in the world at large.

Social Media Research Topics FAQ
Social media is a computer-based technology that allows digital communities to exchange information through user networks. Various social media networks specialize in text, photo, or video transfer. All of these are ways for people on the Internet to share information and ideas with each other.
Social media research is important because it helps you contribute to the growing body of knowledge about digital social settings. In 2021, according to DataReportal, at least 4.88 billion people around the world use the Internet . The more that people connect with each other through the social media domain, the more their quality of life changes, for better or worse.
According to Statista, the most popular social media platforms right now are Facebook, YouTube, and WhatsApp , each of which has at least two billion users. These social networks allow users to share text, picture, and video content with one another.
People use social media to connect with each other, share information, and entertain themselves. Social media sites can broadly serve all of these purposes or be focused on just one of these functions.
About us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers. Learn about the CK publication .
What's Next?
Get matched with top bootcamps
Ask a question to our community, take our careers quiz.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *


Social Media Research: A Comprehensive Guide
Guv Callahan
May 20, 2024
8 min. read
Social media research helps you unlock the potential of social content for business. We’re living in a world where tweets hold power and likes shape perceptions. When you know what to publish and who you’re posting it for, you can construct a stronger strategy that helps you meet key goals.
Data isn’t just about numbers; it’s about uncovering narratives and following the breadcrumbs of likes, shares, and comments to gain deeper understandings. There’s a method to the madness of selfies and status updates. The right approach to social media research helps you learn more about the collective consciousness of society — and use it to your advantage.
Let’s explore the language of social media likes and shares and dig beneath the surface of our digital interactions.
What is Social Media Research?
Tools and techniques for social media research, understanding the difference: social media research vs. traditional research, harnessing the power of social media research for your business, ethics and privacy in social media research, success stories: real world examples of social media research.

Social media research is the process of using social media data to learn about trending topics, audiences, and content performance. Reviewing social data gives you quantitative insights (e.g., engagement rates , best posting times ), but it can also lead to qualitative learnings like human behaviors, preferences, and opinions.
When conducting social media research, companies can look for patterns and sentiments to drive their social media marketing strategy. They can decide what content to create, which channels to post on, how to reach their audience, when to post content, and a myriad of other decisions that will lead to faster results.

There’s no single best way to do social media research. You can manually review engagement on your posts or look at your competitors’ content. Or you can use third-party social listening tools to aggregate social data for you.
Social media research can be formal (like a traditional research project) or informal. You might have a certain goal in mind, or you might not know what you’re looking for and just want to see what pops up.
Let’s review some options.
Social media analytics
No matter what channels you choose, you can gain a wealth of insights from built-in social analytics. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter give you instant intel about your content performance and audiences.
Even better, you don’t always need to know what you’re looking for. You can start combing through your analytics, then jot down questions or ideas you want to explore further.
Tip: Learn more in our blog The Complete Guide to Social Media Analytics .
Google Alerts
Google Alerts is a free and underrated tool that gives you unique angles and insights on a given topic. You can set up a Google Alert related to a keyword or topic of your choice, then receive a daily digest of articles published on that topic.
From there, you can learn more about what other brands and businesses are publishing. Repurpose your findings into your social media content to get ahead of trends and topics. You can lead conversations instead of joining them after they blow up on social.
Social listening tools
Social listening tools like Meltwater let you be the fly on the wall in the social world. You can “listen” to what your audience is saying and truly be everywhere all at once.
These tools monitor billions of publicly available data points across multiple social channels, like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. They help brands track mentions of their products or brand names in real time so you can become part of important conversations.
You can also track topics related to your niche or learn more about what your audience is talking about beyond your brand. This gives you direct insight into their lifestyles so you can meet them where they are authentically.
Want to learn more about how Meltwater could help your social media research? Fill out the form below and an expert will be in touch!
Media intelligence tools
Taking social listening a step further, you can add media intelligence tools to the mix to learn what’s being talked about beyond social media. Meltwater’s media intelligence suite lets you monitor TV and radio channels, blogs, print media, and other new sources around the world.
This gives you more comprehensive insights into hot topics and trends that you can repurpose for social media. News-worthy events make their way to social media, giving you an easy “in” to your audience’s attention.

Aside from the social-specific aspect, social media research holds a few advantages over traditional research.
For starters, social research gives you real-time data that’s constantly changing. You can also get the most specific insights according to your audience and social channels, not just general info. This means you can shorten the research curve and get faster insights about topics that matter to you.
By comparison, traditional research is often a more structured approach with specific goals in mind. It typically requires lots of sources and manual effort. It takes time to find and vet sources, cross-reference data, and ensure a high level of accuracy.
Combining both types of research can give you the most comprehensive view of your audience.
Now that you know what social media research is, let’s explore some ways you can apply it to your business.
Identify your target audience
Analyzing social media data can help you pinpoint who your target audience is (because it’s not always who you think). You might have your audience defined on the surface with basics like age, gender, and geographic location, but social research can dig several layers deeper to uncover new audience segments you haven’t considered.
Audiences evolve all the time. Their preferences, needs, and interests change. This means that who you want to reach today might not be the same person you want to connect with in the future. Constantly finding new things about your audience will help you continue generating content that captures their interests.
Improve brand reputation
Monitoring online conversations and feedback gives companies a direct path to reputation management . You can more easily spot when trouble might be brewing so you can act fast and defend against hits to your brand image.
Proactively engaging with customers on social platforms shows that the company values their opinions and is committed to providing excellent customer service. This not only builds trust and loyalty but also strengthens the brand's reputation as a customer-centric organization.
Optimize social media marketing campaigns
When you know more about your audience and past content performance, you’re in a better position to create better posts that resonate. Learn what type of content your audience prefers based on engagement metrics. Tailor your content and messaging to reflect their interests and needs.
You’ll also have insights about what’s hot in the social media world. You can use these trends as the foundation for your own content, taking the guesswork out of what you should talk about.
Tip: Learn more about tailoring your content and messaging in our Personalization at Scale Guide !

Collecting social media research from outside data sources brings ethics and privacy into question. Marketers should be proactive in asking where their data is coming from and how it was obtained.
Ideally, you’ll choose tools that are in compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Know how they obtain data and whether they safeguard individual users’ information. Getting ahead of your competitors shouldn't be at the expense of your customers’ privacy or potential legal challenges.
Companies around the world use social media research to drive engagement, create better content, and grow their brand presence.
Take Shiseido , for instance. This Meltwater customer uses our Explore solution to learn what makes their brand special across 120 markets. The company uses social listening to monitor competitors, unify social mentions in a single dashboard, and understand the brand’s presence on a global stage.
Another Meltwater customer, Fifty Acres , uses the platform to learn about relevant narratives happening on social media. Learning what others are talking about allows them to shape their own stories, pitch new ideas for business growth, and connect with people in the right places at the right times.
W Hotels in Singapore is another great example of social media research at work. The company uses Meltwater to learn more about what customers like when traveling, allowing them to create custom experiences in their hotels.
Last but not least, Mailchimp uses Meltwater to inform its content strategy. The company looks for trends and themes on social media that resonate with creators, allowing them to easily scale their content by making their audience go bananas over every post.
Learn more when you request a demo by filling out the form below.
Continue Reading

Personalization at Scale: Removing Guesswork from Consumer Research
Top Secondary Market Research Companies | Desk Research Companies

Customer Segmentation Models: Types, Benefits & Uses

The Ultimate Social Listening Guide - Never Miss a Social Mention

Insight-Driven Marketing, Your New Strategic Advantage
147 Best Social Media Research Topics To Beat The Trend In 2023

With the advancement of technology, social media has become an essential part of our lives. It provides a platform for people to express themselves and share their thoughts with others. It also allows people to connect on a global scale. Social media has helped to make the world smaller and more connected.
Social Media is essential in many industries today – from marketing, advertising, and public relations to education, healthcare, and even entertainment. Social Media is now so widespread that it has become a necessity for businesses.
As writers who have a lot of knowledge regarding custom writing services would share what we know about social media research topics that can make your day.
Table of Contents
Social Media Research: Related To Trends, Privacy, Psychology and more
We are rooting for you to leave your competition behind in your research. That is why we have 147 of the most engaging social media research topics that work as a muse and introduce you to an uncanny inspiration. Let’s go ahead and discover together!
Trendy Social Media Research Topics

Have you been following the trends lately? If the answer is no, you don’t need to panic. We’ve extracted all of the trendy social media topics for you.
- What is quality management for social media?
- Branding and Social Media? How does it work? What are the best strategies?
- Use of the Internet networks, social networks, and mobile in 2021
- Facebook as a source of distribution of content and remote communication
- Training of professionals toward their audiences for social media platforms
- Facebook: A place of digital socialization among top social media sites
- The place of social networks in journalistic information
- The positive aspects of the Internet and social networks
- Increasing impact and importance of social media networks
- The future of social media: Would Facebook remain a monopoly?
- The negative aspects of social media sites and the internet
- Instagram vs. Facebook: A complete research on features. Which is better?
- The rise in popularity of TikTok
- Role of social media politics in the society
Read More: Accounting Research Topics
Social Media Platforms Research Topics Related Journalism

Social media and journalism go side by side. How can it be? Well, these research topics for social media research papers will give you an idea:
- News and citizenship in the digital age
- Mutations in journalism in the digital age
- What is multimedia journalism? How can social media be a part of it?
- Rise of influence of journalists with social media sites
- Do we still need journalists in the time of social media sites?
- What role can social media sites play in overcoming the impact of toxic journalism?
- How to deal with the swarming misinformation on social media?
Read More: Research Paper Topics
Social Media Research Topics For Psychology

Social media research can be written for many psychological research topics as well.
- Temptations of Social Media and its effects on marriages
- Is social media leading spouses to infidelity?
- The Internet is a free universe without any control. How to make your mental health a priority in the social media dilemma?
- Social media addiction and its impact on mental health
- Has social media increased the cases of mental health problems? Prove write or wrong with analytics and data.
- How Social Media is isolating children from parents and teachers
- The psychology behind social media addiction
- The positive aspects of the Internet and social networks on mental health
- Do you think that the Internet, in general, and social networks pose Psychological risks for an individual?
- How social media is affecting family mental health
- Mental health problems in adolescents caused by Social Media
- Symptoms of anxiety, depression, and loneliness in people who spend 3-6 hours a day on Social Media
- Best and safest social media websites
- The dangers of social media addiction to mental health
- Isolation and radicalization are rising because of Social Media
- How social media is different than mass media?
- Nazi and fascist presence on social media: Campaigns against minority
- The psychology behind online hate speech and bullying
- Can social media lead to lower self-esteem?
Read More: Business Research Topics
Social Behavior And Social Media Research Topics
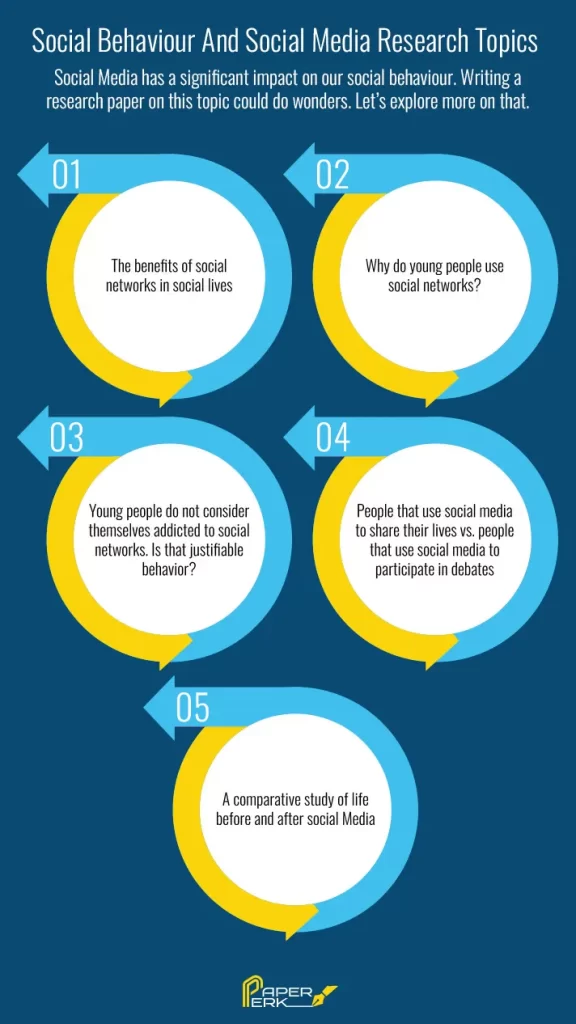
Social media has been a significant impact on our social behavior. Writing a research paper on this topic could do wonders. Let’s explore more on that.
- The benefits of social networks in social lives
- Why do young people use social networks?
- How people’s behavior differs on multiple social media websites
- Behavior of people who have been victims of cyberbullying on social networks
- The social response to cyberbullying and online harassment through social networks
- An examination of the mental health implications of social networks
- What is the impact of Social Media on our happiness?
- As a result of social media, we need more time to concentrate.
- As a result of the extensive use of social media, we experience a decline in the quality of our sleep.
- The adverse effects of Instagram and Snapchat on our self-esteem and self-confidence
- As a result of social media, people are more likely to experience depression, loneliness, and isolation.
- Virtual worlds pose a threat to our brains because of the overload of information they provide
- What are the chances of social networks improving for us in the future?
- Which social networks are trustworthy, and which are untrustworthy?
- How much time do we spend on social media, and is it bad for us?
Read More: Nursing Research Topics
Social Media Research Topics Related To Activism

- Be it social work topics or activism themes, you can see that social media papers has helped us in more than one way.
- Respect for freedom of expression
- The wave of publications of feminist works powered and empowered by social Media.
- Social Media is the origin of vast protest movements.
- Role of social media in Arab Spring
- How Wael Ghonim changed the fate of Egypt with the help of Social media?
- Conduct relevant campaigns based on an analysis of digital news
- A campaign that conveys solid values and convictions is an activist marketing campaign.
- Activists can use social platforms as practical tools.
- Increasingly engaged social media users can spread moral messages more widely.
- As fake news becomes more prevalent, activism becomes more critical.
- Youth of Generation Z: more aggressive than ever? In what ways does online aggression originate?
- How social media creates more opportunities for marginalized societies
- Managing a positive social media political campaign
- The most effective way to be a better ally for people of color
- What role does body diversity play outside of fashion?
- Even though sexual racism affects everyone, it is a phenomenon that must be addressed
Read More: Qualitative Research Topics
Social Media Research Topics On Cyber Security and Privacy

Security and privacy are now a fundamental human rights in the virtual world. You can contribute by writing a thesis for your research paper to promote online security awareness.
- Security regulation of social networks
- The essential protection of Internet users and social cohesion
- Security risks involved in using social networks like Facebook
- Can terrorists use social media to provoke violence? How can we deal with it?
- The morality of social networks, sensitivity, and responsibility
- Bullying and Harassment in social mass media
- How to get over the social media addiction
- How to promote cyber security?
- Professional and private life: How to maintain family safety on Social Media
- How social media poses a threat to family privacy and security
- Barriers between professional and private life diminishing with social networks
- How secure privacy settings on social media are?
- Is social media impenetrable for hackers? The hanging sword of data leaks
- GBWhatsApp Data Leaks: A study on insecure methods leading to harmful privacy dangers
- Cybercrimes on social media: Identity theft
Read More: US History Research Topics
Social Media Criminology Research Papers Topics
Cybercrime is one of the most talked about issues among criminal justice research topics . Here are some of the most critical topics for social media criminology:
- How to report and prosecute cyberbullying in Social Media
- Using social networks to process information
- Advertising on YouTube is a popular method of cybercrime
- Using automatic publication functions on certain sites and forums for malicious purposes
- In the age of cybercrime, Twitter has become the preferred platform for advertising
- Cybercrime can be dealt with by acquiring both human and technical skills
- Definition, characteristics, and types of Social Media
- The Characteristics, Motivations, and Strategies of Cybercrime from a Criminological Perspective
- What are the forms of cyberbullying on social media and what can be done to prevent it?
- Defamation, the most common cybercrime handled by law enforcement
- Facebook and social media users should be aware of cybercrime and hoax information
- Cases of child prostitution on social media during the lead-up to elections
- Using Social media is dangerous because of hoaxes and low trust
- The use of information technology facilities as a means of committing crime
- Using social media to commit cybercrime is common
- Fraud Committed Through Social Media in Online Shops
- Child pornography and pedophilia: The Darkside of Social Media
- How can we control and put a stop to the rise of cyberbullying against children on social media ?
Read More: High School Research Paper Topics
University Social Media Research Paper Topics

Whether you’re writing for a university or researching for high school research topics, you can always talk about social media. Won’t you love to write something about one of the favorite parts of your life, that is social media?
- The uses of digital social networks in the context of socio-educational support
- The contributions of social network analysis to the management of communities
- Social Media is a useful tool for evaluating and improving the functioning of piloted communities
- How can students deal with social media addiction?
- Innovation and social networks: new sociabilities for another sociality
- Creating a Science of the network through social media: A Case Study
- The social network as a space of hodological individuation
- Learning through social networks. How has social media presence helped adapt to changes after COVID?
- Role of Social Media in the time of the Coronavirus Pandemic
Read More: Political Science Research Topics
Social Media Marketing Research Paper Topics

Next to business research topics , most of the orders we receive are for social media marketing research. You would like some of the following examples for sure when writing for a social media research topic:
- The different types of advertisements used on social networks
- The presence of companies on social networks in the era of digitalization
- How to counter competition on social networks?
- How to deal with negative social media effect on your business
- Why is it essential to be able to stand out from others, and how to achieve this?
- How can such a social media marketing strategy have a lasting impact on a company’s reputation on the Internet?
- How does influencer marketing add value to brands?
- How the influencers have formed and transformed the modern market for gen-z entrepreneurs?
- Social media vs. mass media: Pros and cons for each of them
- Building your audience based on tweets, occupation, interests, and location
- How to define and manage audiences when working on social media marketing?
- How can social media insights keep you updated with modern trends?
- How to establish your analytical milestones while working with social media?
- How has Google Trends helped a business into a global transformation? A Case study
- Beating the boundaries with social media platforms. The global business boost on Facebook marketing
- Competition and social networks: how do companies stand out?
- How do companies choose the advertising method that suits them best?
- How has digitization made the use of the internet essential for the success of a company?
Social Media transformed our lives into something amazing. However, everything comes at a price. Regardless, of whatever aspects of social Media you are looking for, we are sure that you will find them in our social media research topics. If you need any further help, you can talk to us through Paper Perk contact page. We can help you with finding your research topics , or any research help that you need.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
Advances in Social Media Research: Past, Present and Future
- Open access
- Published: 06 November 2017
- Volume 20 , pages 531–558, ( 2018 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Kawaljeet Kaur Kapoor 1 ,
- Kuttimani Tamilmani 2 ,
- Nripendra P. Rana 2 ,
- Pushp Patil 2 ,
- Yogesh K. Dwivedi 2 &
- Sridhar Nerur 3
441k Accesses
643 Citations
21 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Social media comprises communication websites that facilitate relationship forming between users from diverse backgrounds, resulting in a rich social structure. User generated content encourages inquiry and decision-making. Given the relevance of social media to various stakeholders, it has received significant attention from researchers of various fields, including information systems. There exists no comprehensive review that integrates and synthesises the findings of literature on social media. This study discusses the findings of 132 papers (in selected IS journals) on social media and social networking published between 1997 and 2017. Most papers reviewed here examine the behavioural side of social media, investigate the aspect of reviews and recommendations, and study its integration for organizational purposes. Furthermore, many studies have investigated the viability of online communities/social media as a marketing medium, while others have explored various aspects of social media, including the risks associated with its use, the value that it creates, and the negative stigma attached to it within workplaces. The use of social media for information sharing during critical events as well as for seeking and/or rendering help has also been investigated in prior research. Other contexts include political and public administration, and the comparison between traditional and social media. Overall, our study identifies multiple emergent themes in the existing corpus, thereby furthering our understanding of advances in social media research. The integrated view of the extant literature that our study presents can help avoid duplication by future researchers, whilst offering fruitful lines of enquiry to help shape research for this emerging field.
Similar content being viewed by others

Social Media as Online Information Grounds: A Preliminary Conceptual Framework

Bright ICT: Social Media Analytics for Society and Crisis Management

A Literature Review on Application Areas of Social Media Analytics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Social media allows relationship forming between users from distinct backgrounds, resulting in a tenacious social structure. A prominent output of this structure is the generation of massive amounts of information, offering users exceptional service value proposition. However, a drawback of such information overload is sometimes evident in users’ inability to find credible information of use to them at the time of need. Social media sites are already so deeply embedded in our daily lives that people rely on them for every need, ranging from daily news and updates on critical events to entertainment, connecting with family and friends, reviews and recommendations on products/services and places, fulfilment of emotional needs, workplace management, and keeping up with the latest in hashion, to name but a few.
When we refer to social media, applications such as Facebook, WhatsApp, Twitter, YouTube, LinkedIn, Pinterest, and Instagram often come to mind. These applications are driven by user-generated content, and are highly influential in a myriad of settings, from purchasing/selling behaviours, entrepreneurship, political issues, to venture capitalism (Greenwood and Gopal 2015 ). As of April 2017, Facebook enjoys the exalted position of being the market leader of the social media world, with 1.97 billion monthly users (Statista 2017 ). In addition to posts, social media sites are bombarded with photo and video uploads, and according to the recent numbers, about 400 million snaps a day have been recorded on Snapchat, with around 9000 photos being shared every second (Lister 2017 ). While 50 million businesses are active on Facebook business pages, two million businesses are using Facebook advertising. Apparently, 88% businesses use Twitter for marketing purposes (Lister 2017 ).
Academics and practitioners have explored and examined the many sides of social media over the past years. Organizations engage in social media mostly with the aim of obtaining feedback from stakeholders (Phang et al. 2015 ). Consumer reviews are another big part of social media, bringing issues of information quality, credibility, and authenticity to the forefront. To a large extent, online communities have been successful in bringing together people with similar interests and goals, making the concept of micro blogging very popular. While most messages exchanged on social media sites are personal statuses or updates on current affairs, some posts are support seeking, where people are looking for assistance and help. Interestingly, these have been recognized as socially exhausting posts that engender social overload, causing other members to experience negative behavioural and psychological consequences, because they feel compelled to respond (Maier et al. 2015a ).
Given the relevance of social media to various stakeholders, and the numerous consequences associated with its use, social media has attracted the attention of researchers from various fields, including information systems. This is evidenced by the large number of scholarly articles that have appeared in various outlets. Researchers have to expend an enormous amount of time and effort in collating, analysing, and synthesising findings from existing works before they embark on a new research project. Given the significant number of studies that have already been published, a comprehensive and systematic review can offer valuable assistance to researchers intending to engage in social medi research. Our literature search suggests that there are reviews on social media in the marketing context (see for example, AlAlwan et al. 2017 ; Dwivedi et al. 2017a ; Dwivedi et al. 2015 ; Ismagilova et al. 2017 ; Kapoor et al. 2016 ; Plume et al. 2016 ). However, there exists no comprehensive review that integrates and synthesises the findings from the articles published in Information Systems journals. Such an endeavour will not only provide a holistic view of the extant research on social media, but will also provide researchers a comprehensive intellectual platform that can be used to pursue fruitful lines of enquiry to help advance research in this rapidly expanding area. To fulfill this goal, this study reviewed relevant articles to elucidate the key thematic areas of research on social media, including its benefits and spill-over effects. The resulting review is expected to serve as a one-stop source, offering insight into what has been accomplished so far in terms of research on social media, what is currently being done, and what challenges and opportunities lie ahead. By doing so, this study explores the following aspects of existing research on social media:
How is social media defined in the IS literature?
How has social media literature evolved from a multidisciplinary perspective?
How have social media technologies, applications, practices, and research evolved over the past 20 years?
Which social media issues and themes have already been examined in IS research?
What are the major limitations of extant literature on social media?
The next section of this paper gives a brief overview of the method employed for carrying out the literature search. The succeeding section discusses citation and text analyses of social media publications. Subsequently, we outline the various ways in which scholars have defined social media. This is followed by a section that focuses on the evolution of social media research from an IS perspective. Next, we articulate the major themes emerging from prior research and use them as a backdrop for our review of the literature on social media. The ensuing section discusses our findings, followed by key conclusions and limitations of the study.
2 Literature Search Method
The literature search for this analysis was conducted in the following two phases: (1) keyword-based search and analysis to explore the overall evolution of social media literature; and (2) manual search across specific IS journals to understand the emerging IS perspectives on this topic.
2.1 Keywords Based Search and Analysis
In order to gain a deeper understanding of social media, we analyzed relevant abstracts that were downloaded from the Web of Science (WOS) database. Our search terms Footnote 1 yielded a total of 13,177 records, out of which 12,597 unique abstracts were obtained. The analysis of these records was undertaken in two steps. First, we used VOSviewer (Van Eck and Waltman 2011 ) to perform a co-citation analysis of first authors in the downloaded corpus. VOSviewer allows visualization of similarities in publications and authors through an examination of bibliometric networks. Furthermore, we used VOSviewer to analyze words derived from titles and abstracts. Second, we used Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) (see Blei 2012 ) to extract key thematic areas latent in the literature on social media. Further details about these analyses and results are presented in section 3 .
2.2 Manual Search and Analysis
Given the inconsistencies in the use of keywords in social media research, a manual search, rather than a keyword-based one, was deemed to be more appropriate for identifying the existing literature on social media. Furthermore, since keywords in the social media literature tend to overlap with topics and/or theories in other related research areas, a keyword search may yield irrelevant articles. For instance, a keyword search for “Social network” returns articles related to social network theories, which are not necessarily part of social media. The articles reviewed in this study are from the following eight Senior Scholars’ Basket of Information Systems journals: European Journal of Information Systems (EJIS); Information Systems Journal (ISJ); Information Systems Research (ISR); Journal of the Association for Information Systems (JAIS); Journal of Information Technology (JIT); Journal of Management Information Systems (JMIS); Journal of Strategic Information Systems (JSIS) and Management Information Systems Quarterly (MISQ)). Along with these eight journals, we have also analysed relevant articles from Information Systems Frontier (ISF) journal. This is because it focuses on examining “new research and development at the interface of information systems (IS) and information technology (IT) from analytical, behavioural, and technological perspectives. It provides a common forum for both frontline industrial developments as well as pioneering academic research”. Footnote 2 ISF enjoys the reputation of a high quality journal across continents. For example, a journal quality ranking by Chartered Association of Business Schools, UK, has given it a three star (high ranking) quality rating, while journal ranking by the Australian Business Deans Council (ABDC) has rated it as an ‘A’ class journal (the second highest quality journal category after A*, which is reserved for premier publications). In light of these observations, it was deemed appropriate to consider articles from ISF along with the aforementioned eight journals.
Relevant articles were then identified and downloaded from each of the target journals by going through their archives. Specifically, all volumes and issues published in these journals between 1997 and 2017 were considered in our analysis. Articles, research notes, introductions, research commentaries, and editorial overviews relevant to social media were downloaded and numbered to prepare an APA style reference list. The first literature search resulted in 181 articles that had some relevance to the social media domain. A closer examination of individual abstracts and full articles led to the elimination of 49 irrelevant articles, thus giving us a total of 132 articles pertinent to the domain of interest (i.e., social media).
3 Citation and Text Analyses of Social Media Publications
3.1 author co-citation analysis (aca).
Author Co-Citation Analysis (ACA) is a bibliometric technique that has been widely used to explicate the conceptual structure of disciplines (for example, see White and Griffith 1981 ; McCain 1984 ; Culnan 1986 ; Nerur et al. 2008 ). The underlying assumption in ACA is that authors who are frequently cited together tend to work on similar concepts. Thus, frequently co-cited authors are likely to cluster together when an ACA is performed. VOSviewer considers only first authors when it performs ACA. Only authors who had 50 or more citations were included in the analysis. Figure 1 shows the results of ACA.
Author clusters from ACA
VOSviewer identified seven distinct clusters:
Cluster 1: Authors in this cluster have contributed to research on Twitter (e.g., Sakaki), social network analysis (e.g., Wasserman), topic modeling (e.g., Blei), sociality and cognition (e.g., Dunbar), sentiment analysis of tweets (e.g., Thelwall), and other related topics.
Cluster 2: Authors in this cluster are well known for their work on technology adoption (e.g., Venkatesh), diffusion of technology (Rogers), culture (Hofstede), theory of planned behavior (Ajzen), marketing/consumer behavior (e.g., Hennig-Thurau), and statistical methods (e.g., Bagozzi, Fornell, Hair).
Cluster 3: This cluster comprises of authors who deal with a variety of issues related to social media (Facebook and Twitter) use. For example, Steinfied and Ellison examined social capital across Facebook; Kuss studied online/social networking addiction (e.g., gaming addiction), and Lenhart focused on teens and technology (e.g., mobile internet use), particularly in the use of social media. Other topics include Bandura’s self-efficacy, use and benefits of Twitter by scholars, and personality and social characteristics of Facebook users (e.g., Ross).
Cluster 4: Prominent social theorists/sociologists who have contributed to social capital theory, structuration theory and modern sociological theory are distinguished members of this cluster. These include Bourdieu, Coleman, Giddens, and Habermas. Papacharissi has written about a variety of topics including the exploration of factors that predict Internet use as well as users’ behaviors, identity, sense of community and culture on social media. Tufekci has studied privacy and disclosure on social media, as well as other topics, including how social networking sites such as Facebook might influence one’s decision to participate in protests.
Cluster 5: In this cluster, there is evidence of the influence of Vygotsky’s socio cultural learning theory as well as Lave and Wenger’s work on communities of practice. In addition to his work on collaborative learning, Kirschner has examined the relationship between Facebook and academic performance. Likewise, Selwyn has explored pedagogical and learning engendered by the use of information and computer technologies (ICT).
Cluster 6: This cluster appears to reflect two broad themes. The first is a range of topics related to medical Internet research, broadly referred to as e-health (Eysenbach) or online health (Duggan). Themes in this category include electronic support groups and health in virtual communities (Eysenbach), and policies and healthcare associated with social media, and professionals among medical students and physicians in the use of social media (Chretien, Greysen). The second main thematic area in this cluster deals with scholarship on social media, scholarly communication, and metrics for evaluating impact of articles on the web (e.g., Weller, Bormann, Priem).
Cluster 7: The dominant theme here is the nature and content of communication. In particular, scholars in this cluster have focused on communication and response in the face of crises (Coombs), including image restoration after a controversy (Benoit), analysis and reliability of content (Krippendorff), and the use of social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter by government agencies and non-profit organizations to engage stakeholders (Waters).
3.2 Text Analysis of Words in Titles and Abstracts
VOSviewer was used to analyze terms (i.e., words) in the titles and abstracts of our corpus to obtain a two-dimensional map showing proximities of words that are likely to be related based on their co-occurrences. Specifically, VOSviewer relies on the Apache OpenNLP Toolkit to identify noun phrases, and then compares their overall co-occurrence distribution with their distribution across other noun phrases to compute a relevance score (Van Eck and Waltman 2011 ). The intuition is that frequently co-occurring noun phrases with high relevance are likely to unravel a topic or theme that is latent in the corpus. The term map from VOSviewer is shown in Fig. 2 . Only terms that occurred 50 times or more were included. Furthermore, relevance scores computed by VOSviewer for every term were used to select the top 80% that met the threshold.
Term map showing clusters of related words/noun phrases
VOSviewer identified five clusters here. It is evident from the clusters that research on social media has dealt with a broad range of topics, including but not restricted to diffusion of information and opinions, spread of diseases (e.g., influenza), identification of social and emotional health concerns and attendant interventions to deal with them, social media as an influence, the use of social media for marketing purposes, and the implications of social media as a tool for pedagogy (i.e., teaching and learning) and medical practice. These have been summarized in Table 1 .
It must be noted that the topics are broad and don’t reveal the nuances of research areas embodied in the abstracts examined in this study. The next sub-section presents the results of topic modeling, which has the potential to unravel more focused themes embodied in the large corpus that we analyzed.
3.3 Topic Modeling
The fact that our search terms yielded over 12,000 abstracts suggests that scholars are investing increased interest on research issues related to social media. While an informed researcher may have a general idea of the nature of research undertaken so far, it is humanly impossible to discern the thematic structure of all scholarly documents available on social media. Recent advances in topic modeling have made this task relatively easy. Topic modeling relies on algorithms and statistical methods to elicit the topics latent in a large corpus (Blei 2012 ). The term topic refers to a specific and often recognizable theme defined by a cohesive set of words that have a high probability of belonging to that topic. There are several options available for topic modeling: non-negative matrix factorization (NNMF), Latent Semantic Analysis/Indexing (LSA/LSI), and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). In this study, we use LDA, arguably the most widely used topic modeling algorithm. In order to perform topic modeling on a corpus, the researcher has to specify the number of topics to be extracted. In this study, we extracted the top 100 topics reflected in the scholarship on social media. LDA starts with the assumption that each abstract in our study reflects each of these topics to varying degrees (Blei 2012 ). Thus, each abstract has a distribution of the desired 100 topics. The 100 topics that were extracted from our abstracts are shown in Table 2 . The machine learning for language toolkit (MALLET) (McCallum 2002 ) was used for this purpose.
4 Analysis of Social Media Research from an IS Perspective
4.1 how is social media defined in the is literature.
In studying the existing literature on social media, it becomes apparent that the authors in this field have not focussed on defining social media. Of all the studies included in this review, only a handful of studies have come close to defining, or clarifying the concept of social media. For instance, Lundmark et al. ( 2016 , p3) suggest, “social media, as a unique form of communication, integrates multiple sources of legitimacy, and as a result, presents a unique and important context through which to study the topic. Indeed, social media are a means for the dissemination of both internally and externally generated information pertaining to firms, industries, and society in general.” According to Schlagwein and Hu ( 2016 ), social media constitutes internet-based communication and collaboration channels, widely in use since 2005, and, from an IS perspective, social media tools and their surrounding organizational and managerial structures constitute social information systems. Wakefield and Wakefield ( 2016 , p140) describe “social media technologies as an ensemble IS artefact composed of technical, informational, and relational subsystems that interact distinctly according to the context of use.” In their study, they also identify a “recent definition of social media and social networks referring to social media networks as specific types of social media platforms and Internet sites with common attributes such as (1) user profile (2) user access to digital content (3) a user list of relational ties, and (4) user ability to view and traverse relational ties” (Wakefield and Wakefield 2016 ; p144).
In a more relatable and simple definition, Miranda et al. ( 2016 ; p304) explain social media being “mainly conceived of as a medium wherein ordinary people in ordinary social networks (as opposed to professional journalists) can create user-generated news.” A few other authors like Spagnoletti et al. ( 2015 ) and Xu and Zhang ( 2013 ) commonly refer to social media as a set of interned-based technologies/applications, which are aimed at promoting the creation, modification, update and exchange of user-generated content, whilst establishing new links between the content creators themselves. Bharati et al. ( 2014 ; p258) refer to social media as a technology “not focussed on transactions but on collaboration and communication across groups both inside and outside the firm.” Lastly, Tang et al. ( 2012 ; p44) also identify social media as user-generated media, which is a source of “online information created, initiated, circulated, and used by consumers intent on educating each other about products, brands, services, personalities, and issues.”
All of the aforementioned descriptions clearly regard social media as communication tools supported by internet-based technologies for dissemination of information. Most of them acknowledge the high concentration of user generated content across such platforms. Based on our understanding of social media and the aforementioned definitions, we propose the following definition: Social media is made up of various user-driven platforms that facilitate diffusion of compelling content, dialogue creation, and communication to a broader audience. It is essentially a digital space created by the people and for the people, and provides an environment that is conducive for interactions and networking to occur at different levels (for instance, personal, professional, business, marketing, political,and societal) .
4.2 Evolution of Social Media Research in the IS Literature
In the past two decades, various issues related to social media have been examined in line with the rapid evolution of underlying technologies/applications and their appropriation to enable different types of social media usage. An analysis of 132 articles from selected IS journals suggests that publications until 2011 were still examining user-generated content as a new type of online content (Burgess et al. 2011 ). However, in the last six years, research in this field has made tremendous progress, not just in terms of its scope, but also in explicating the highs and lows associated with the use of social media. While it is difficult to pinpoint evolution on a yearly basis, it has been possible to identify the major aspects of social media research that have emerged over time. Publications between 1997 and 2017 have been reviewed here. Interestingly, only one publication of interest to this study (Griffiths and Light 2008 ) was identified between the period 1997 and 2009.
Out of the 132 studies individually reviewed here, about 21 studies examined the behavioural side of social media use. While most of the initial studies (for instance, Massari 2010 ; Garg et al. 2011 ) restricted interest to peer influence and information disclosure willingness (2010–2012), the latter studies (for instance, Gu et al. 2014 ; Krasnova et al. 2015 ) were seen to be more exploratory in examining the positive, dysfunctional, cognitive and affective, heterophily and homophily tendencies of social media users (2012–2016). There were 18 studies investigating the very popular aspect of reviews and recommendations on social networks, with 2013 being a popular year for such studies. Most of these studies (for instance, Hildebrand et al. 2013 ; Zhang and Piramuthu 2016 ) were interested in improving their understanding of the information quality of these reviews and the associated consequences (2010–2016). There were 17 studies (2011–2016) evaluating the integration of social media for varied organizational purposes . While some studies investigated the employee side (e.g., innovativeness, retention, and motivation) of social media use (for instance, Aggarwal et al. 2012 ; Miller and Tucker 2013 ), the others discussed the relationship between social enterprise systems and organizational networking (for instance, Trier and Richter 2015 ; Van Osch and Steinfield 2016 ).
Around 13 publications studied the use of social media as a marketing tool . The early studies here (2010–2013) explored consumer purchase behaviour and firm tactics, such as involving consumers in marketing strategies (for instance, García-Crespo et al. 2010 ; Goh et al. 2013 ). The later studies (2015–2016), however, became more focussed on studying social commerce across networking sites such as Facebook, MySpace, and YouTube (e.g., Chen et al. 2015 ; Sung et al. 2016 ). Ten studies were interested in online communities and blogging (see Singh et al. 2014 ; Dennis et al. 2016 ). These were mostly interested in blogger behaviours, reader retention, online content, contributing capacity, and blog visibility (2011–2016). Nine publications revealed the risks associated with the use of social media. These are either very early studies (2008–2010; for instance, Tow et al. 2010 ) or fairly recent (2014–2016) learning about scamming and farcing issues faced by users. They focus on combating issues of privacy and security, whilst trying to differentiate between fake and authentic online content (for instance, Zhang et al. 2016 ).
Up until 2015, about eight studies analysed the negative stigma attached to using social media at the workplace (for instance, Koch et al. 2013 ). While a couple of studies also revealed the positive side of social media (for instance, Lu et al. 2015 ), most were seen discussing its ill-effects on work outputs, routine performance, and clash of notions in the personal and professional space (for instance, Ali-Hassan et al. 2015 ). About seven studies were interested in exploring the relationship between social media use and value creation (for instance, Luo et al. 2013 ; Barrett et al. 2016 ) in terms of firm equity, customer retention, social position, and firm value (2010–2016). Another seven studies investigated the use of media sites to share and exchange information during natural disasters and critical events (2011–2015). Interestingly, most of the studies documenting this aspect of social media used Twitter data for their analyses (for instance, Oh et al. 2013 ; Lee et al. 2015a ). A very small percentage of studies (five studies) in 2014 and 2015 focussed on analysing the effects of social media posts that were seeking help/support from other social media users (for instance, Spagnoletti et al. 2015 ; Yan et al. 2015a ). Only a handful of studies (five studies), particularly in 2010 and 2016, were examined the use of social media in public administration and political contexts, such as open governance and transparency (for instance, Baur 2017 ; Rosenberger et al. 2017 ). Also, just about three studies (Wattal et al. 2010 ; Dewan and Ramaprasad 2014 ; Miranda et al. 2016 ) dedicated their efforts to comparing traditional media with social media . The last set of studies (2013–2016), around nine in total (for instance, Bharati et al. 2014 ; Chung et al. 2017 ), were identified as those limiting themselves to developing and testing social media constructs in relation to previously established theories and models (technology acceptance model, theory of planned behaviour, and others).
4.3 Literature Synthesis
As outlined in the previous section, social media research is evolving at a fast pace. In reviewing the shortlisted articles, various themes were identified based on the similarities observed across the issues addressed in social media research.
4.3.1 Social Media Use Behaviours and Consequences
Many scholars explore the behavioural side of social media, and interestingly, some find factors that prevent users from continuing its use. Turel and Serenko ( 2012 ) warn against excessive use of social media sites, which can result in strong pathological and maladaptive psychological dependency on social media. In a subsequent study, Turel ( 2015 ) used cognitive theory to reveal that guilt feelings associated with the use of a website can increase discontinuance intentions. Matook et al. ( 2015b ) show that online social networks can be linked with perceived loneliness, which depends on user’s active/passive engagement with social media. Krasnova et al. ( 2015 ) suggest that in response to social information consumption, envy plays a significant role in reducing cognitive and affective wellbeing of a user. However, Maier et al. ( 2015b ) disclose that, while social networking stress creators can increase discontinuance intentions, switching stress-creators and exhaustion (i.e. switching to alternatives) can reduce such intentions. Chang et al. ( 2014 ) find that dissatisfaction and regret, alternative attractiveness, and switching costs affect switching intentions. Xu et al. ( 2014 ) find that dissatisfaction from support and entertainment values, continuity cost and peer influence encourage switching between social networks.
Wakefield and Wakefield ( 2016 ) focus on Facebook and Twitter to show that excitement combined with passion acts as a favourable factor for increased social media engagement. Chiu and Huang ( 2015 ) use media communication theories to show that user gratification from social networking sites positively affects their social media usage intention. In studying virtual investment communities, Gu et al. ( 2014 ) reveal that despite benefits of heterophily, investors are allured by homophily in their interactions. Zeng and Wei ( 2013 ) analyse Flickr data and find that at the time of forming a social tie, members exhibit similar behaviour, which evolves differently later. Shi et al. ( 2014 ) examine retweet relationships and find that those with weak ties have a higher probability of engaging in content sharing. Kreps ( 2010 ) introduces poststructuralist critique to explore how closely an individual’s personality is reflected in their social media profile, such as Facebook.
Chen et al. ( 2014 ) find affective and continuance types of commitments to be good predictors of user behaviours on social media sites. Stieglitz and Dang-Xuan ( 2013 ) examine the relationship between user behaviour and sentiment to conclude that emotional Twitter messages have a higher retweet tendency. Khan and Jarvenpaa ( 2010 ) analyse event creation pages on Facebook to find that the social groups demonstrate differential interactive behaviour prior and post the midpoint of event creation. Chen and Sharma ( 2015 ) disclose that the extent of self-disclosure on social media sites depends on member attitude. Massari ( 2010 ) finds that MySpace users tend to disclose substantial personal details that put them at the risk of security and privacy breach. Xu et al. ( 2016 ) find that one’s image and moral beliefs combined with community policies and peer pressure act as deterrents to aggression on social media. Garg et al. ( 2011 ) measure peer influence in an online music community and find that peers can significantly increase music discovery. Susarla et al. ( 2012 ) examine video and user information dataset from YouTube, and find that the success of a video hugely depends on social interactions, which also determines its impact magnitude.
The review of studies related to this theme suggests that since 2010, IS researchers have focussed on examining the dysfunctional consequences of social media adoption, such as - addiction, stress, information overload, and others. Use behaviour was examined across a variety of platforms like Facebook, Twitter, MySpace, and Flickr. Media content, such as picture, video, and tweets have also been explored by the studies in this category.
4.3.2 Reviews and Recommendations on Social Media Sites
A predominant characteristic of social media networks is product/service reviews and recommendations. People are beginning to rely on others’ experiences, for instance, before making a purchase, visiting a place, or searching for accommodation.. Such online reviews complement product/service information. An early study on online travel information found that consumers invest higher trust in reviews published on government/tourism websites in comparison to those on a social media site (Burgess et al. 2011 ). Hwang et al. ( 2011 ) analysed the social bookmarking sites for impact of positive and negative reviews on collective wisdom and found that negative reviews are capable of stabilizing system performance. Dellarocas et al. ( 2010 ) suggest that online forums looking to increase reviews of lesser-known products should make information on previously posted reviews a less prominent feature. Cheung et al. ( 2012 ) empirically tested a consumer review website to conclude that argument quality, review consistency, and source are critical for assessing review credibility.
Chen et al. ( 2011 ) investigate the effect of moderation and reveal that the commentators generate high quality content to build a stronger reputation. Wei et al. ( 2013 ) developed a multi-collaborative filtering trust network algorithm for Web 2.0 with improved accuracy for filtering information based on user preferences and trusted peer users. Luo and Zhang ( 2013 ) refer to user-generated reviews and recommendations as consumer buzz to find that advocacy and consumer attitude can impact firm value. Hildebrand et al. ( 2013 ) use data from a European car manufacturer allowing self-designed products to reveal that feedback from other community members lessens uniqueness whilst increasing dissatisfaction. Centeno et al. ( 2015 ) address the skewed reputation rankings problem in movie ratings by suggesting the use of comparative user opinions. Ma et al. ( 2013 ) analyse data from Yelp to test bias in online reviews and find that frequent and longer reviews successfully combat such biases. Lukyanenko et al. ( 2014 ) demonstrate that participants tend to provide accurate information in classifying a phenomenon at a general level, and higher accuracy where they are allowed free form data. Shi and Whinston ( 2013 ) explore the possible impact of friend check-ins on social media, and find it has no positive effect in generating new user visits.
Goes et al. ( 2014 ) disclose that user popularity results in increased and objective reviews, while numeric ratings turn more varied and negative with it. Matook et al. ( 2015a ) use relationship theories to show that past recommendation experience, closeness, and excessive posting behaviour positively affect trust and person’s intention to act on the made recommendation. Yan et al. ( 2015b ) evaluate revisit intentions for restaurants, and find that food and service quality, price and value, and the atmosphere govern such intentions. Kuan et al. ( 2015 ) analysed Amazon reviews and observed that certain characteristics such as length, readability, valence, extremity, and reviewer credibility are more likely to be recognized. In a different study, Zhang and Piramuthu ( 2016 ) suggest that product/service information on seller’s websites are often limited, and propose a Latent Dirichlet Allocation model to reveal the useful complementary hidden information in customer reviews. In a parallel conversation, Wu and Gaytán 2013 suggest that buyers integrate product price with seller reviews in configuring their willingness to pay.
The review under this theme suggests that studies as early as 2010 focussed on evaluating the authenticity of product and service reviews/recommendations published online. Overall, these studies reveal that the effect of review volume is often moderated by a buyer’s risk attitude. Most studies identify that the combination of consumer’s interest and available reviews helps users choose products/services that offer best value to them.
4.3.3 Social Media and Associated Organizational Impact
Publications have also shown interest in investigating the effects of user-generated content on entrepreneurial behaviour. For instance, Greenwood and Gopal ( 2015 ) find that discourse in both traditional and user-generated media has a notable influence on IT firm founding rates. Lundmark et al. ( 2016 ) reveal that higher usage of Twitter, alongside follower numbers and retweets result in higher levels of under pricing for initial public offerings (IPO). Trier and Richter ( 2015 ) find that online organizational networking has many unbalanced multiplex relationships, mostly comprising of weak ties and temporal change. They attribute the uneven user contribution in social networking sites to discourse drivers and information retrievers. Schlagwein and Hu ( 2016 ) identify collaboration, broadcast, dialogue, sociability, and knowledge management as the social media types that serve varied organizational purposes. Claussen et al. ( 2013 ) study Facebook to conclude that social media networks can exercise management not only by excluding participants, but also by driving softer changes in incentive/reward systems.
Subramaniam and Nandhakumar ( 2013 ) study enterprise system users and find that integrating social media facilitates user interaction that helps embed relationship ties between virtual actors. Another study concerning social features in enterprise systems reveals that business interactions are less social, and highly context specific (Mettler and Winter 2016 ). Van Osch and Steinfield ( 2016 ) showed that the enterprise system user involved in social network posting will show differences in team boundary spanning activities based on their hierarchical position (leadership, team member, etc.). Benthaus et al. ( 2016 ) analyse Twitter data to find that social media management tools have a catalysing effect on employee output as they enrich the user engagement process. Gray et al. ( 2011 ) study the social bookmarking system to find that social diversity of information sources is a good predictor of employee innovativeness. Kuegler et al. ( 2015 ) show that using enterprise social networking within teams strongly influences task performance and employee innovativeness. Leonardi ( 2014 ) reveals that communication visibility increases meta-knowledge between organizations, which results in innovative products and services minus knowledge duplication. Aggarwal et al. ( 2012 ) interestingly reveal positive effects of negative employee posts on an organization’s reputation, given that such posts attract larger audience.
Miranda et al. ( 2015 ) suggest that diffusion of social media is based on an organization’s vision that offers a well-defined range of moves to choose from, with the freedom to improvise. Xu and Zhang ( 2013 ) regard Wikipedia as a social media platform and conclude that it improves information environment in the financial market and the value of information aggregation. Qiu et al. ( 2014 ) study prediction markets to find that users with increased social connections are less likely to invest in information acquisition from external sources. Miller and Tucker ( 2013 ) study the extent of social media managed by firms to report that most firm postings are centred on firm’s achievement and are not necessarily in clients’ interest. In summary, studies reviewed under this theme are focussed on analysing the impact of integrating social media within work roles in organizations. Effective management and utilization of social media is agreed to provoke employee activity, which helps in employee innovativeness, retention, and motivation. Studies also hint against ignoring social media engagement, which can reportedly have a negative impact on a company’s image.
4.3.4 Social Media for Marketing
Social media sites are now a huge part of marketing tactics, and the documented studies are a good showcase of the extent to which social media is being integrated in marketing strategies. García-Crespo et al. ( 2010 ) study the continuous interaction between customers and organizations, as it impacts the social web environment with implications for marketing and new product development. Goh et al. ( 2013 ) study the user and market generated content for engagement in social media brand community to find that it has a positive impact on purchase expenditures. Rishika et al. ( 2013 ) demonstrate how higher social media activity directly correlates with higher participation and customer patronage. Aggarwal and Singh ( 2013 ) find that blogs help managers with their products in the screening stage, and also offer leverage in negotiating better contract terms. Dou et al. ( 2013 ) research optimizing the strength of a network by adjusting the embedded social media features with the right market seeding and pricing strategies.
Oestreicher-Singer and Zalmanson ( 2013 ) reveal that the firms are more viable when they integrate social media in purchase and consumption experience, rather than using it as a substitute for soft online marketing. Lee et al. ( 2015b ) study the importance of social commerce in marketplace to find that Facebook likes increase sales, drive traffic, and introduce socialization in the shopping experience. Xie and Lee ( 2015 ) scan purchase records on Facebook to find that exposure to owned and earned social media activities positively impacts consumers’ likeliness to purchase brands. Chen et al. ( 2015 ) study music sales on MySpace to find that broadcasting, timing and content of the personal message has significant effect on sales. Qiu et al. ( 2015 ) study YouTube data to find that learning and network mechanisms statistically and economically impact video views. Sung et al. ( 2016 ) use Facebook data of universities and colleges across the US to show that people in the same class year or same major tend to form denser groups/networks. In a slightly different study, Oh et al. ( 2016 ) investigate the pricing models for an online newspaper, and find that charging for previously free online content has a disproportionate impact on word of mouth for niche and popular topics/articles. Susarla et al. ( 2016 ) find that social media initiatives succeed when a sustained conversation with likely adopters is maintained.
Studies within this theme focus on the role of community structure and structural patterns in using social media for marketing purposes. For successful social media implementation, it is important to effectively incorporate social computing with content delivery in the digital content industry with growing user population. Most studies identify meaningful conversations with customers as an important attribute of social media marketing. Also, identifying specific customer segments across social media site, for instance, members of a forum/group or organization, helps e-marketers to target specific customers based on demographic patterns and similar interests.
4.3.5 Social Media and Participation in Online Communities
There are many facets to developing and maintaining an online community, and user participation plays an integral role in it. Ray et al. ( 2014 ) identify that user engagement increases user intention to revisit an online community. Singh et al. ( 2014 ) analyse employee blog reading behaviour and show how reader attraction and retention are influenced by textual characteristics that appeal to reader sentiments. Butler and Wang ( 2012 ) find that changing content in an online discussion community affects member dynamics and community responsiveness, both positively and negatively. An early study on participation in online communities finds that different community commitments impact behaviours differently (Bateman et al. 2011 ). Chau and Xu ( 2012 ) develop a framework capable of gathering, extracting, and analyzing blog information that can be applied to any organization, topic, or product/service.
Goes et al. ( 2016 ) study goal setting and status hierarchy theories to find that glory-based incentives motivate users to contribute more user-generated content only before/until the goal is reached, with the contribution dropping significantly later. Khansa et al. ( 2015 ) examine Yahoo! Answers, and find that artefacts like incentives, membership tenure, and habit or past behaviour hugely influence active online participation. Tang et al. ( 2012 ) examine the concept of incentives on social media, particularly YouTube, for content contribution and find that a user is driven to contribute on social media based on their desire for revenue sharing, exposure, and reputation. Zhang and Wang ( 2012 ) use economic and social role theories in a Wikipedia context to show that in a collaborative network, the editor determines the total contribution towards collaborative work. Dennis et al. ( 2016 ) create a theoretical framework for corporate blogs and analyse Fortune 500 companies to find that a blog’s target audience and the alignment of blog content and its management significantly impact the visibility of that blog. Most of the studies under this theme focus on analyzing data on blogs. They highlight the importance of word of mouth, which is closely associated with user satisfaction. It also emerges from these studies that user engagement and consequent satisfaction play parallel and mediating roles within such online communities.
4.3.6 Risks and Concerns with the Use of Social Media
Social media and its associated risks have captured the attention of many authors. A very early study by Griffiths and Light ( 2008 ) focuses on the problem of media convergence, whereby a gaming website includes social media features, putting vulnerable young audience at the risk of scamming. An Australian study suggests that many users are unaware of the potential risks of disclosing personal information on social media site, or consider themselves as low risk targets (Tow et al. 2010 ). Krasnova et al. ( 2010 ) find that the ease of forming and maintaining relationships on an enjoyable social platform motivates users to disclose personal information. Their study shows that user trust in a service/network provider, and privacy control options on a networking site greatly dismiss user perceptions of associated risk. Vishwanath ( 2015 ) finds that farcing attacks on Facebook occur at two levels – victim to phishers with phony profiles and victim to phishers soliciting personal information directly from them.
To combat the privacy problem of photos, videos, and other content posted online, Fogués et al. ( 2014 ) developed a Best Friend Forever tool that automatically distinguishes friends on a user’s profile by assigning individual values based on relationship ties. Zhang et al. ( 2016 ) find that incorporating non-verbal features of reviewers can massively improve the performance of online fake review detection models. Gerlach et al. ( 2015 ) find that user perception of privacy risks has a mediating effect on the relationship between policy monetization and user willingness to share information. Burtch et al. ( 2016 ) analyse a large online crowd funding platform and report that when campaign contributors control/conceal visibility from public display, there is a negative impact on subsequent visitor’s conversion likelihood and average contributions. In a different study, Choi et al. ( 2015 ) find that information dissemination and network commonality has a high impact on individual’s perception of privacy invasion and relationship bonding that impedes transactional and interpersonal avoidances.
Studies reviewed here discuss a social contagion effect of risks associated with social media use. Recent studies (2014–2016) suggest educating audiences about the threats associated with the extent of personal information being disclosed on social media sites. They recommend government agencies to keep the users informed, and the social media sites to control some of their security features. It is necessary to define and control privacy settings across these many existing social networks.
4.3.7 Negative Stigma Attached to Social Media Use
Some studies suggest that there is a negative stigma associated with the use of social media in the workplace. In a typical case study, Koch et al. ( 2012 ) analyze three employee layers in an organization to find that new hires (users of social media sites) showed improved morale and employee engagement, some middle managers (non users) were frustrated and experienced isolation, while the senior execs were wary of social media use. In a contrasting case, Cao et al. ( 2015 ) suggest that social media has the potential to build employees’ social capital to positively influence their knowledge integration. In discussing the impact of social media on organizational life, Koch et al. ( 2013 ) find that conflicts can stem between workplace values and the values these employees ascribe to social media.
In a gender-based study on social network facilitated team collaboration, Shen et al. ( 2010 ) found that the collective intention in men was influenced by positive emotions, attitude and group norms, while the collective participation intention in women was affected by negative emotions and social identity. Huang et al. ( 2015 ) debate the concept of communicational ambidexterity to understand the conflicting demands of managing internal organization communication in contrast to open and distributed social media communication. Wu ( 2013 ) suggests information-rich networks enabled by social media tend to drive job security and employee performance. Lu et al. ( 2015 ) use the social network theory to conclude that structural and cognitive dimensions of social relationships positively impact job performance. Ali-Hassan et al. ( 2015 ) show social and cognitive use of social media has a positive influence on employee performance, while hedonic use of social media leaves a negative impact on routine performance.
These reviewed studies showcase that social networking encourages shared language and trust between employees in a workspace. Another emerging suggestion highlights that organizations should exercise policy, and use socialization and leadership-based mechanisms to counter any problems resulting from differing workplace values. Some of these studies show interest in the cognitive side of social ties that positively nurture social relationships and innovation performance.
4.3.8 Social Media and Value Creation
Studies in the extant literature have particularly focussed on the aspect of value creation within online communities. As Ridings and Wasko ( 2010 ) have observed, an online discussion group/community is a direct product of its social and structural dynamics. Porter et al. ( 2013 ) investigate firm value and find that a sponsor’s efforts are stronger with positive and direct effect on trust building. Luo et al. ( 2013 ) suggest that social media has faster predictive value than conventional online media, and that the embedded metrics like consumer ratings are leading indicators of a firm’s equity. Hu et al. ( 2015 ) develop a formative model with an aggregate online social value construct and identify factors to increase user benefits and satisfaction, ensuring customer retention via continued usage of online services. In a public organization study focussing on social networking system, Karoui et al. ( 2015 ) suggest that differing perceptions of social capital can result in actors adopting differing strategies for holding their social position within an organization. Barrett et al. ( 2016 ) find that value creation in online communities expands beyond the dyadic relationship between a firm and the community to include a more intricate relationship involving stakeholders of a wider ecosystem. Dong and Wu ( 2015 ) use data from Dell and Starbucks and find substantial evidence for online user innovation-enabled implementation increasing firm value. Overall, the studies on social media and value creation emphasize on influence of social and structural interplay on sustainability, which is visible over longitudinal examination of their relationship to one another.
4.3.9 Role of Social Media During Critical/Extreme Events
Certain authors are more interested in micro-blogging used at the time of critical/extreme events. In an attempt to filter real time news/updates from irrelevant personal messages and spam, Cheng et al. ( 2011 ) propose analysis of information diffusion patterns for a large set of micro-blogs that update emergency news. They claim that their approach (using Twitter data) outperforms other benchmark solutions to offer diverse user preferences and customized results during critical events. Cheong and Lee ( 2011 ) use Twitter data to propose a framework that is useful for Homeland Securities and Law enforcement agencies to record and respond to terror situations. Oh et al. ( 2013 ) also study Twitter data from three extreme events to find that information without any clear source is at the top, personal involvement comes second, with anxiety at third place in the list of rumour causing factors during social crisis events. Wang et al. ( 2014 ) affirm that news spreads widely through online portals. They find that news first posted even on a small news portal can be picked and reposted by a major news portal, forming a hotspot event for the news to rapidly spread over the Internet.
Lee et al. ( 2015a ) performed negative binomial analysis of the 2013 Boston marathon tragedy Tweets to find that follower numbers, reaction time, and hash tagging significantly affected the diffusion of Tweets. Oh et al. ( 2015 ) analysed Twitter data from the 2011 Egypt revolution and found that hash tags played a critical role in gathering information and maintaining situational awareness during such politically unstable phases. Ling et al. ( 2015 ) undertake a qualitative study of 2011 Thailand flooding data to conclude that social media can offer a community: structural, resource, and psychological empowerment to achieve collaborative control and collective participation. In summary, studies since 2011 have been particularly examining Twitter data, and have derived significant insights on their positive effect during critical/extreme events.
4.3.10 Social Media for Help/Support
Some users post updates on social media with an aim to seek help/support from online communities. Maier et al. ( 2015a ) find that such posts cause social overload for other users, and the psychological consequences include feelings of exhaustion, low user satisfaction, and high intentions of reducing/stopping the use of social media sites. Yan et al. ( 2015a ) find that healthcare traits of patients help them establish social connections online, which is influenced by their cognitive abilities. Spagnoletti et al. ( 2015 ) develop a user utility model for integrating social media in personalized elderly healthcare that is capable of challenging traditional organizational boundaries to transform the internal and external stakeholder engagement. Yan and Tan ( 2014 ) propose a partially observed Markov decision process model to find sufficient evidence suggesting emotional support is most significant in improving patient health. Kallinikos and Tempini ( 2014 ) study the ups and downs of having a large unsupervised social network based on patient self-reporting for gathering and examining data on patients’ health.
Limited number of studies has been recorded for this theme. These studies are fairly recent suggesting a new emerging trend, where health/support based communities are being formed. The expanse of such communities seems to be largely dependent on the information processing capacity and the range of social ties that the members of such networks can handle. Using social media to bring together people with similar health conditions suggests that informational and social support can have varying influence on patient health.
4.3.11 Public Bodies and Social Media Interaction
User-generated content from social media is becoming one of the important information channels across public administrative bodies and political contexts. Baur ( 2017 ) has developed a MarketMiner framework that massively improves the utilization of multi-source, multi-language social media content, which can be applied to areas such as open government. Rosenberger et al. ( 2017 ) use abstraction-based modelling to conceptualize the data structure, and conclude that wrapping social network application programming interfaces allow mutual integration of most user activities. Gonzalez-Bailon et al. ( 2010 ) show that political discussions in online networks are larger and deeper compared to other networks. Ameripour et al. ( 2010 ) analyse the restricted Iranian social networks, subject to surveillance and censorship to find that Internet conviviality is not an independent variable with deterministic outcomes, but is a technology shaped by economic and political forces. Although, not published in the list of journals included in this review, Kapoor and Dwivedi ( 2015 ) provided a detailed discussion on how social media was used intensively to transform electoral campaigns during India’s last general election. Similar use has also been reported in other contexts (for example, US presidential elections) by other studies.
Except one study (that is, Ameripour et al. 2010 ), the remaining reviewed under this category are very recent (2015–2016). These studies suggest the use of social media for increasing public engagement and transparency. Most of these studies used technical frameworks and modelling techniques to identify communication clusters and structures to derive insights relevant to open government and political campaigns.
4.3.12 Traditional v/s Social Media
Another set of studies investigate the differences between traditional and social media. A very early study by Wattal et al. ( 2010 ) compares the big money tactics for political campaigning with social media campaigning to reveal that Internet and the blogosphere can majorly influence campaigning and election results. Dewan and Ramaprasad ( 2014 ) examine the importance of new and old media within the music industry; they find radio positively and consistently affecting sales of songs and albums, and sales displacement from free online sampling overpowering positive word of mouth on sales. Miranda et al. ( 2016 ) compare traditional and social media to suggest that there are evils associated with the societal benefits of social media, and mass media has a detrimental effect on public discourse.
4.3.13 Testing Pre-Established Models
Some studies in literature restrict focus to pre-established models and relationships for evaluating varied aspects of social media. Fang et al. ( 2013 ) apply social network theories to suggest positive social influence on adoption probabilities. Levina and Arriaga ( 2014 ) use Bourdieu’s theory to explain the role of status markers and external sources in shaping social dynamics. Bharati et al. ( 2014 ) combine institutional theory and organizational innovation, whereby institutional pressures significantly predict absorptive capacity. Kekolahti et al. ( 2015 ) use Bayesian networks to indicate the decrease in perceived importance of communication with increase in age. Chang et al. ( 2015 ) integrate social distance with clustering methods to show shorter social distance results in satisfactory trust. Chung et al. ( 2017 ) employ the Technology Acceptance Model, and find positive effects between traveller readiness and ease of using geo-tagging. Zhao et al. ( 2016 ) use theory of planned behaviour and attribution theory to find that virtual rewards for sharing knowledge online undermine enjoyment. Yu et al. ( 2015 ) use the causation and heuristic theories to find that affect influences self disclosure indirectly by adjusting perceived benefits. Stanko ( 2016 ) employs Innovation Diffusion Theory, and finds that community interaction influences innovations that are used to aid a further innovation.
5 Discussion
In reviewing the publications gathered for this paper, commonalities have been observed in the myriad aspects of social media chosen for investigation. While many studies focussed their attention on understanding the behaviours of social media users, the others examined entrepreneurial participation and firm behaviour. A number of studies have focussed on the content being posted in online communities, several of which report on the repercussions of some of this content being used as an awareness medium during critical events and tragedies. Interesting revelations were made by authors studying the use of social media as a platform to render and/or receive help or support, and its incorporation in the field of healthcare and public administration. Value creation and the ill-effects associated with the use of social media at the workplace were also discussed. Several studies chose to test previously established hypotheses and models, while others compared traditional media with social media. Prior research has also provided insights into how firms have been using social media to market their products and services. These strategies run in parallel with the reviews and recommendations posted by users on social media sites, which have also received considerable attention in the literature. In summary, given that different types of social media platforms are emerging, and different consequences are associated with their use, research in this field will continue to evolve. This is also evidenced by the increased number of publications related to usage and impact over the past five years.
Social media platforms have essentially redefined the ways in which people choose to communicate and collaborate. An online community is a socio-technological space where a sense of communal identity drives engagement, which, in turn, enhances satisfaction (Ray et al. 2014 ). Intriguingly, social media are facilitating the emergence of virtual knowledge communities and self help networks. These web-based arrangements allow medical practice and research to access patient experience on a daily basis, which was not possible earlier. However, since research in this area is still in its early stages, it is difficult to assess the social complexity involved (e.g., stability of a networking platform that brings together patients with medical experts) in the process (Kallinikos and Tempini 2014 ).
Firms are recognizing social media as a prominent indicator of equity value that not only improves short-term performance, but also brings about long-term productivity benefits (Luo et al. 2013 ). The reviewed studies suggest that incorporatin social media in firms increases meta-knowledge (who’s who in an organization and who does what), which helps avoid knowledge duplication and promotes new ways of managing work (Leonardi 2014 ). Active management of social media has been observed to be more effective when those inside rather than outside a firm are engaged (Miller and Tucker 2013 ).
A specific line of research focuses on consumers, who substantially rely on online reviews before making any purchase decision. The research papers reviewed in this study exhibit diversity in studying authenticity of reviews for travel sites, social bookmarking and review sites, movie ratings, car manufacturing, and social media check-ins. Studies concur that there has been an exponential increase in the number of fake reviews, which is severely damaging the credibility of online reviews and putting business values at risk (Zhang et al. 2016 ). Some studies have also empirically identified consumers’ social media participation as a key metric contributing to the profitability of a business (Rishika et al. 2013 ). There evidently exists a direct correlation between consumer engagement on social media sites and their shopping intentions, which makes the issue of legitimate reviews all the more important for businesses and consumers. Although some studies have proposed models and algorithms that claim to filter authentic reviews from the rest, there is no single and straightforward solution reported yet that can fully combat this problem.
The issue of negative posts has received considerable attention in the literature. Prior research suggests that, overall, the impact of negative posts or electronic word of mouth is much higher than the positive ones that increase readership (Aggarwal et al. 2012 ). This problem is also prevalent in organizations. According to the studies reviewed here, organizations either prohibit employees from posting controversial content online, or employees themselves refrain from doing so, fearing negative repercussions. The same employees also share positive posts, and the adverse effect of the few negative posts is offset by positive ones. It is in a firm’s interests to encourage free will enterprise blogging to break down knowledge silos and yield higher employee productivity (Singh et al. 2014 ).
Businesses looking to monetize online content and social search rely heavily on substantial understanding of consumer behaviour in terms of their interaction and participation in social settings (Susarla et al. 2012 ). As consumers gain access to social platforms that offer free content consumption without an obligatory payment, the relationship between sampling and sales becomes all the more important (Dewan and Ramaprasad 2014 ). There is much research supporting the belief that online word of mouth has a critical role to play in a firm’s overall performance, and introducing a pay-wall (for previously free content) can significantly reduce the volume of word of mouth for popular content in comparison to niche content (Oh et al. 2016 ). Determining consumers’ social influence in an online community is of critical interest to managers, who seek to gain some leverage from the potential of social media (Shi et al. 2014 ). Some researchers find it difficult to distinguish social influence from users’ self selection preferences. From an analysis point of view, it then becomes necessary to separate factors affecting user membership in a social network from various types of social influence (Susarla et al. 2012 ).
The findings on the use of social media in emergencies suggests that a general user response in an online community is very different from that during a crisis, as those responses then become more reflexive. It has been observed that in times of crisis, lack of information sources coupled with too many situation reports being shared by the users of a social media platform can precipitate a rumour mill. It thus becomes incumbent on emergency responders to release reliable information, whilst trying to control collective anxiety in the community, to suppress the rumour threads (Oh et al. 2013 ). Furthermore, security concerns are increasingly common with involuntary online exposure on social media, and research on this subject suggests that information dissemination with network commonality affects privacy invasion and user bonding (Choi et al. 2015 ). It has been learnt that an individual’s or firm’s decision to withhold information in the interest of privacy can have both positive and negative effects on their utility (Burtch et al. 2016 ).
In reviewing the 132 publications on social media and social networking, it was observed that many studies relied primarily on social exchange theory, network theory and organization theory. Table 3 , shown below, lists other theories that have been used by at least two publications. There were several other theories that were used by at least once, including social role theory, game theory, structural holes theory, management and commitment theories, institutional theory, deterrence and mitigation theories, and self determination and self categorization theories. It is noteworthy that dominant IS adoption theories such as Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (Dwivedi et al. 2017b , c ; Rana et al. 2017 ; Venkatesh et al. 2003 ), Technology Acceptance Model (Davis 1989 ) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (Kapoor et al. 2015 ) are less widely utilised.
In addition, our review of the literature on social media identified dominant research methods employed by scholars. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods were used by most of these studies. Closer scrutiny of the 132 publications reviewed in this study revealed the multitude of techniques applied for gathering data. Quantitative methods employed in these studies mostly adopted analytical techniques and surveys (Table 4 ). On the other hand, publications using qualitative methods mainly used case studies and interviews to gather the required data (Table 4 ). As expected, studies employing mixed methods used a combination of analytical and conceptual techniques, alongside surveys and content analysis (Table 4 ). Table 4 summarizes the various research approaches used by publications in our corpus.
The reviewed publications were also analyzed to determine the nature of the social network that were studied. Precisely 46 websites emerged, with Facebook, online communities, Twitter, Blogs and YouTube being most frequently targeted. Networks analysed by at least two or more studies have been identified in Table 5 . The other networks that received attention from the reviewed publications include Ebay, Flickr, Flixster, Gtalk, microsoft, MSN Space, Patientslikeme, New York Times, TripAdvisor.com , and Boxofficemojo.com . Studies also focussed on websites related to online news, Q&A websites, discussion groups and forums, online radio and television, and medical sites such as Webmd.com .
5.1 Limitations and Future Research Directions
Studies, such as the one by Cheung et al. ( 2012 ), that examine aspects of popular websites, warn against consumer perceptions being under the influence of brand equity of those websites. They recommend exercising caution while generalizing such findings in the context of other websites (Cheung et al. 2012 ). Rosenberger et al. ( 2017 ) identify a similar problem with relying on publicly available data, in that the underlying abstraction makes findings valid only for the specific social media site that was analyzed, whilst significantly restricting its generalizability to other sites. In a similar vein, other studies (Krasnova et al. 2015 ; Khan and Jarvenpaa 2010 ; Tow et al. 2010 ) have acknowledged the limitation of restricting their research to a single social media site, and recommend future researchers to adopt a cross-platform perspective for drawing significant inferences.
Mettler and Winter ( 2016 ) suggest that there is a paucity of studies on Enterprise Social Systems because of its novelty, and urge researchers to fill this void. Turel and Serenko ( 2012 ) identify the lack of conceptualization in the notion of technology addiction; they recognize that the process of defining it is still in the early stages, and is being debated across communities. For researchers interested in examining aspects of Twitter, Cheng et al. ( 2011 ) recommend incorporating the location metric focused on Twitter’s geo location feature allowing users to trace the latitude and longitude of Tweets. Another recommendation for Twitter related studies comes from Benthaus et al. ( 2016 ), where they suggest researchers should study user involvement differently, based on how often users choose to ‘like’ the content of a company. As for use of social media for marketing in firms, the literature has restricted focus to the resulting marketing benefits, with limited evidence supporting the effectiveness of social platforms for enhancing employee communications (Miller and Tucker 2013 ).
For behavioural studies, researchers need to be wary of the fact that motivation for users to adopt social media is different, often contingent on their culture (Chiu and Huang 2015 ; Shen et al. 2010 . It is also important to note that behavioural reactions are susceptible to change over time, and changing habits have a role to play (Chiu and Huang 2015 ). Longitudinal research is thus always expected to offer a better understanding of the research problem when the intended behavioural reactions transfer into behaviour with time (Maier et al. 2015a ). In studying online reviews and recommendations, researchers can assume that these reviews are independent of one another and remain static over time; however, Zhang and Piramuthu ( 2016 ) suggest that this may not be true and future researchers should now concentrate on how this has evolved, and if herding behaviour exists on such online platforms. In studying behaviours, it has also emerged that users develop discontinuance intentions after continuance intentions, with the latter never being completely replaced by the former. Turel ( 2015 ) thus recommends studying the initiation of discontinuance intentions, whilst identifying the factors leading to its dominance and actual discontinuance attempts.
Matook et al. ( 2015a ) identify that there is a need to study the aspect of trust formation between individuals on social media, where no personal relationships exist (unlike sites such as Facebook). Chung et al. ( 2017 ) identify that researchers often associate the use of certain social media with young users (for instance, Maier et al. 2015b ), and fail to study the usage perceptions across various ages (Vishwanath 2015 ). Van Osch and Steinfield ( 2016 ) suggest that future researchers should explore the potential of Enterprise Social Media to gain insights into the tools that support disentanglement of team boundary spanning. Finally, researchers have established that the lifecycle of information and communication technologies tend to be emancipatory in their infancy but eventually evolve into hegemonic tools. They warn social media policymakers to be wary of reproducing this pattern with digital media; the recommendation is to involve more citizens in the development of Internet governance framework, rather than resting decisions with the members of political or economic power (Miranda et al. 2016 ).
6 Conclusions
This paper discusses the findings of 132 publications contributing to the literature on social media. Multiple emergent themes in this body of literature have been identified to enhance understanding of the advances in social media research. By building on empirical findings of previous social media research, many new studies have been successful in theorizing the nature of most social media platforms. User-generated content allows collective understanding, which is a massive machine-human knowledge processing function capable of managing chaotic volumes of information. Some key conclusions relevant to stakeholders, including researchers, have been identified here.
Social media technologies are no longer perceived just as platforms for socialization and congregation, but are being acknowledged for their ability to encourage aggregation.
In reviewing the 132 publications on social media and social networking, it was observed that most studies used social exchange theory, network theory and organization theory to support their studies.
Facebook, online communities, and twitter are the three most popular networks targeted by publications in the field of social media research.
Publications in 2011 were still reporting user-generated content as a new type of online content. However, the last six years have seen tremendous scholarly progression in discussing the many applications of social networking, highlighting the highs and lows associated with its use.
Majority of the publications reviewed in this study are focussed on behavioural side of social media, reviews, and integration of social media for marketing and organizational purposes.
Many publications in the year 2013 concentrated their efforts in investigating the very popular aspect of reviews and recommendations on social networks.
Publications have become more focussed on studying social commerce across networking sites, particularly, Facebook, MySpace, YouTube and so on between 2015 and 2016.
Publications have not shown much interest in support-seeking posts and negative stigma attached to social media use after the year 2015.
Most studies unanimously acknowledge social media for its information sharing and information exchange capabilities, with a focussed group of studies recognizing its effectiveness during natural disasters and critical events.
Almost all publications studying information sharing during natural disasters and critical events focus on Twitter data.
Publications on administration and political contexts were particularly found in 2010 and 2016, with no interest expressed in these contexts between 2011 and 2015.
With information systems now expanding beyond organizational peripheries to become a part of the larger societal context, it is important for strategic information systems research to delve into the competitive setting of dynamic social systems. Online communities are introducing extrinsic rewards that do not limit users’ intrinsic motivations. Research on such communities should expand to study the interplay between extrinisic and intrinsic rewards, particularly in terms of their ability to cultivate and sustain users’ intrinsic motivations. From an organizational perspective, research on social media should move past the conventional dyadic view of the relationship between an online community and a firm, and focus on reconceptualising online users as an ecosystem of stakeholders. Social media has re-established the dynamics between organizations, employees, and consumers. Given the rise in number of publications focussing on workplace setting since 2014, future researchers should aim to analyze stakeholders’ potential in adopting social media tools to successfully accomplish their work goals. As for the limitations of this collective review, publications reviewed here were limited to only nine journals. This potentially means studies with significant contributions to social media literature published in other journals have been overlooked. Future researchers can look to overcome such exclusions and focus on the overall review of literature on social media platforms. Future reviews may focus on reviewing articles published in a larger number of IS journals related to a specific type of social media (i.e. social networking sites, blogs), or specific issues related to social media use, such as information load, stress, and impact on productivity. Despite these limitations, our study provides a comprehensive and robust intellectual framework for social media research that would be of value to adacemics and practitioners alike.
TITLE: (“Social Media” or “social networking” or “facebook” or “linkedin” or “instagram” or “twitter”)
Refined by: DOCUMENT TYPES: (ARTICLE OR PROCEEDINGS PAPER)
Timespan: All years. Indexes: SCI-EXPANDED, SSCI, A&HCI, CPCI-S, CPCI-SSH, ESCI.
http://www.springer.com/business+%26+management/business+information+systems/journal/10796
Aggarwal, R., & Singh, H. (2013). Differential influence of blogs across different stages of decision making: The case of venture capitalists. MIS Quarterly, 37 (4), 1093–1112.
Article Google Scholar
Aggarwal, R., Gopal, R., Sankaranarayanan, R., & Singh, P. V. (2012). Blog, blogger, and the firm: Can negative employee posts lead to positive outcomes? Information Systems Research, 23 (2), 306–322.
AlAlwan, A., Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Algharabat, R. (2017). Social Media in Marketing: A review and analysis of the existing literature. Telematics and Informatics Available at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0736585317301077 .
Ali-Hassan, H., Nevo, D., & Wade, M. (2015). Linking dimensions of social media use to job performance: The role of social capital. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (2), 65–89.
Ameripour, A., Nicholson, B., & Newman, M. (2010). Conviviality of internet social networks: An exploratory study of internet campaigns in Iran. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 244–257.
Baek, H., Ahn, J., & Choi, Y. (2012). Helpfulness of online consumer reviews: Readers' objectives and review cues. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 17(2), 99-126.
Barrett, M., Oborn, E., & Orlikowski, W. (2016). Creating value in online communities: The sociomaterial configuring of strategy, platform, and stakeholder engagement. Information Systems Research, 27 (4), 704–723.
Bateman, P. J., Gray, P. H., & Butler, B. S. (2011). Research note-the impact of community commitment on participation in online communities. Information Systems Research, 22 (4), 841–854.
Baur, A. W. (2017). Harnessing the social web to enhance insights into people’s opinions in business, government and public administration. Information Systems Frontiers, 19 (2), 231–251.
Benthaus, J., Risius, M., & Beck, R. (2016). Social media management strategies for organizational impression management and their effect on public perception. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 25 (2), 127–139.
Bharati, P., Zhang, C., & Chaudhury, A. (2014). Social media assimilation in firms: Investigating the roles of absorptive capacity and institutional pressures. Information Systems Frontiers, 16 (2), 257–272.
Blei, D. M. (2012). Probabilistic topic models. Communications of the ACM, 55 (4), 77–84.
Burgess, S., Sellitto, C., Cox, C., & Buultjens, J. (2011). Trust perceptions of online travel information by different content creators: Some social and legal implications. Information Systems Frontiers, 13 (2), 221–235.
Burtch, G., Ghose, A., & Wattal, S. (2016). Secret admirers: An empirical examination of information hiding and contribution dynamics in online Crowdfunding. Information Systems Research, 27 (3), 478–496.
Butler, B. S., & Wang, X. (2012). The cross-purposes of cross-posting: Boundary reshaping behavior in online discussion communities. Information Systems Research, 23 (3-part-2), 993–1010.
Cao, X., Guo, X., Liu, H., & Gu, J. (2015). The role of social media in supporting knowledge integration: A social capital analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (2), 351–362.
Centeno, R., Hermoso, R., & Fasli, M. (2015). On the inaccuracy of numerical ratings: Dealing with biased opinions in social networks. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (4), 809–825.
Chang, I., Liu, C. C., & Chen, K. (2014). The push, pull and mooring effects in virtual migration for social networking sites. Information Systems Journal, 24 (4), 323–346.
Chang, W. L., Diaz, A. N., & Hung, P. C. (2015). Estimating trust value: A social network perspective. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (6), 1381–1400.
Chau, M., & Xu, J. (2012). Business intelligence in blogs: Understanding consumer interactions and communities. MIS Quarterly, 36 (4), 1189–1216.
Google Scholar
Chen, R., & Sharma, S. K. (2015). Learning and self-disclosure behavior on social networking sites: The case of Facebook users. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (1), 93–106.
Chen, J., Xu, H., & Whinston, A. B. (2011). Moderated online communities and quality of user-generated content. Journal of Management Information Systems, 28 (2), 237–268.
Chen, A., Lu, Y., Chau, P. Y., & Gupta, S. (2014). Classifying, measuring, and predicting users’ overall active behavior on social networking sites. Journal of Management Information Systems, 31 (3), 213–253.
Chen, H., De, P., & Hu, Y. J. (2015). IT-enabled broadcasting in social media: An empirical study of artists’ activities and music sales. Information Systems Research, 26 (3), 513–531.
Cheng, J., Sun, A., Hu, D., & Zeng, D. (2011). An information diffusion-based recommendation framework for micro-blogging. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 12 (7), 463–486.
Cheong, M., & Lee, V. C. (2011). A microblogging-based approach to terrorism informatics: Exploration and chronicling civilian sentiment and response to terrorism events via twitter. Information Systems Frontiers, 13 (1), 45–59.
Cheung, C. M. Y., Sia, C. L., & Kuan, K. K. (2012). Is this review believable? A study of factors affecting the credibility of online consumer reviews from an ELM perspective. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 13 (8), 618.
Chiu, C. M., & Huang, H. Y. (2015). Examining the antecedents of user gratification and its effects on individuals’ social network services usage: The moderating role of habit. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (4), 411–430.
Choi, B. C., Jiang, Z., Xiao, B., & Kim, S. S. (2015). Embarrassing exposures in online social networks: An integrated perspective of privacy invasion and relationship bonding. Information Systems Research, 26 (4), 675–694.
Chung, N., Tyan, I., & Han, H. (2017). Enhancing the smart tourism experience through geotag. Information Systems Frontiers, 19 (4), 731–742.
Claussen, J., Kretschmer, T., & Mayrhofer, P. (2013). The effects of rewarding user engagement: The case of facebook apps. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 186–200.
Culnan, M. J. (1986). The intellectual development of management information systems, 1972-1982: A co-citation analysis. Management Science, 32 (2), 156.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13 (3), 318–339.
Dellarocas, C., Gao, G., & Narayan, R. (2010). Are consumers more likely to contribute online reviews for hit or niche products? Journal of Management Information Systems, 27 (2), 127–158.
Dennis, A. R., Minas, R. K., & Lockwood, N. S. (2016). Mapping the corporate blogosphere: Linking audience, content, and management to blog visibility. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 17 (3), 162.
Dewan, S., & Ramaprasad, J. (2014). Social media, traditional media, and music sales. MIS Quarterly, 38 (1), 101–121.
Dong, J. Q., & Wu, W. (2015). Business value of social media technologies: Evidence from online user innovation communities. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (2), 113–127.
Dou, Y., Niculescu, M. F., & Wu, D. J. (2013). Engineering optimal network effects via social media features and seeding in markets for digital goods and services. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 164–185.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Kapoor, K. K., & Chen, H. (2015). Social media marketing and advertising. The Marketing Review, 15 (3), 289–309.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., & Alryalat, M. (2017a). Affiliate marketing: An overview and analysis of emerging literature. The Marketing Review, 17 (1), 33–50.
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., Jeyaraj, A., Clement, M., & Williams, M. D. (2017b). Re-examining the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT): Towards a revised theoretical model. Information Systems Frontiers , 1–16. Available at. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9774-y .
Dwivedi, Y. K., Rana, N. P., Janssen, M., Lal, B., Williams, M. D., & Clement, M. (2017c). An empirical validation of a unified model of electronic government adoption (UMEGA). Government Information Quarterly, 34 (2), 211–230.
Fang, X., Hu, P. J. H., Li, Z., & Tsai, W. (2013). Predicting adoption probabilities in social networks. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 128–145.
Fogués, R. L., Such, J. M., Espinosa, A., & Garcia-Fornes, A. (2014). BFF: A tool for eliciting tie strength and user communities in social networking services. Information Systems Frontiers, 16 (2), 225–237.
García-Crespo, Á., Colomo-Palacios, R., Gómez-Berbís, J. M., & Ruiz-Mezcua, B. (2010). SEMO: A framework for customer social networks analysis based on semantics. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 178–188.
Garg, R., Smith, M. D., & Telang, R. (2011). Measuring information diffusion in an online community. Journal of Management Information Systems, 28 (2), 11–38.
Gerlach, J., Widjaja, T., & Buxmann, P. (2015). Handle with care: How online social network providers’ privacy policies impact users’ information sharing behavior. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (1), 33–43.
Goes, P. B., Lin, M., & Au Yeung, C. M. (2014). “Popularity effect” in user-generated content: Evidence from online product reviews. Information Systems Research, 25 (2), 222–238.
Goes, P. B., Guo, C., & Lin, M. (2016). Do incentive hierarchies induce user effort? Evidence from an online knowledge exchange. Information Systems Research, 27 (3), 497–516.
Goh, K. Y., Heng, C. S., & Lin, Z. (2013). Social media brand community and consumer behavior: Quantifying the relative impact of user-and marketer-generated content. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 88–107.
Gonzalez-Bailon, S., Kaltenbrunner, A., & Banchs, R. E. (2010). The structure of political discussion networks: A model for the analysis of online deliberation. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 230–243.
Gray, P. H., Parise, S., & Iyer, B. (2011). Innovation impacts of using social bookmarking systems. MIS Quarterly, 35 (3), 629–643.
Greenwood, B. N., & Gopal, A. (2015). Research note—Tigerblood: Newspapers, blogs, and the founding of information technology firms. Information Systems Research, 26 (4), 812–828.
Griffiths, M., & Light, B. (2008). Social networking and digital gaming media convergence: Classification and its consequences for appropriation. Information Systems Frontiers, 10 (4), 447–459.
Gu, B., Konana, P., Raghunathan, R., & Chen, H. M. (2014). Research note—The allure of Homophily in social media: Evidence from investor responses on virtual communities. Information Systems Research, 25 (3), 604–617.
Hildebrand, C., Häubl, G., Herrmann, A., & Landwehr, J. R. (2013). When social media can be bad for you: Community feedback stifles consumer creativity and reduces satisfaction with self-designed products. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 14–29.
Hu, T., Kettinger, W. J., & Poston, R. S. (2015). The effect of online social value on satisfaction and continued use of social media. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (4), 391–410.
Huang, J., Baptista, J., & Newell, S. (2015). Communicational ambidexterity as a new capability to manage social media communication within organizations. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (2), 49–64.
Hwang, Y. C., Yuan, S. T., & Weng, J. H. (2011). A study of the impacts of positive/negative feedback on collective wisdom—Case study on social bookmarking sites. Information Systems Frontiers, 13 (2), 265–279.
Ismagilova, E., Dwivedi, Y. K., Slade, E. L., & Williams, M. D. (2017). Electronic word of mouth (eWOM) in the marketing context: A state of the art analysis and future directions . Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
Kallinikos, J., & Tempini, N. (2014). Patient data as medical facts: Social media practices as a foundation for medical knowledge creation. Information Systems Research, 25 (4), 817–833.
Kapoor, K. K., & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2015). Metamorphosis of Indian electoral campaigns: Modi’s social media experiment. International Journal of Indian Culture & Business Management, 11 (4), 496–516.
Kapoor, K. K., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Williams, M. D. (2015). Examining the role of three sets of innovation attributes for determining adoption of the interbank mobile payment service. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (5), 1039–1056.
Kapoor, K. K., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Piercy, N. (2016). Pay-per-click advertising: A review of literature. The Marketing Review, 16 (2), 183–202.
Karoui, M., Dudezert, A., & Leidner, D. E. (2015). Strategies and symbolism in the adoption of organizational social networking systems. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (1), 15–32.
Kekolahti, P., Karikoski, J., & Riikonen, A. (2015). The effect of an individual’s age on the perceived importance and usage intensity of communications services—A Bayesian network analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (6), 1313–1333.
Khan, Z., & Jarvenpaa, S. L. (2010). Exploring temporal coordination of events with Facebook. Com. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 137–151.
Khansa, L., Ma, X., Liginlal, D., & Kim, S. S. (2015). Understanding members’ active participation in online question-and-answer communities: A theory and empirical analysis. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (2), 162–203.
Koch, H., Gonzalez, E., & Leidner, D. (2012). Bridging the work/social divide: The emotional response to organizational social networking sites. European Journal of Information Systems, 21 (6), 699–717.
Koch, H., Leidner, D. E., & Gonzalez, E. S. (2013). Digitally enabling social networks: Resolving IT–culture conflict. Information Systems Journal, 23 (6), 501–523.
Krasnova, H., Spiekermann, S., Koroleva, K., & Hildebrand, T. (2010). Online social networks: Why we disclose. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 109–125.
Krasnova, H., Widjaja, T., Buxmann, P., Wenninger, H., & Benbasat, I. (2015). Research note—Why following friends can hurt you: An exploratory investigation of the effects of envy on social networking sites among college-age users. Information Systems Research, 26 (3), 585–605.
Kreps, D. (2010). My social networking profile: Copy, resemblance, or simulacrum? A poststructuralist interpretation of social information systems. European Journal of Information Systems, 19 (1), 104–115.
Kuan, K. K., Hui, K. L., Prasarnphanich, P., & Lai, H. Y. (2015). What makes a review voted? An empirical investigation of review voting in online review systems. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 16 (1), 48.
Kuegler, M., Smolnik, S., & Kane, G. (2015). What’s in IT for employees? Understanding the relationship between use and performance in enterprise social software. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (2), 90–112.
Lee, J., Agrawal, M., & Rao, H. R. (2015a). Message diffusion through social network service: The case of rumor and non-rumor related tweets during Boston bombing 2013. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (5), 997–1005.
Lee, K., Lee, B., & Oh, W. (2015b). Thumbs up, sales up? The contingent effect of Facebook likes on sales performance in social commerce. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (4), 109–143.
Leonardi, P. M. (2014). Social media, knowledge sharing, and innovation: Toward a theory of communication visibility. Information Systems Research, 25 (4), 796–816.
Levina, N., & Arriaga, M. (2014). Distinction and status production on user-generated content platforms: Using Bourdieu’s theory of cultural production to understand social dynamics in online fields. Information Systems Research, 25 (3), 468–488.
Ling, C. L. M., Pan, S. L., Ractham, P., & Kaewkitipong, L. (2015). ICT-enabled community empowerment in crisis response: Social media in Thailand flooding 2011. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 16 (3), 174.
Lister, M. (2017). 40 essential social media marketing statistics for 2017. Available at: http://www.wordstream.com/blog/ws/2017/01/05/social-media-marketing-statistics . Accessed 22 June 2017.
Lu, B., Guo, X., Luo, N., & Chen, G. (2015). Corporate blogging and job performance: Effects of work-related and nonwork-related participation. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (4), 285–314.
Lukyanenko, R., Parsons, J., & Wiersma, Y. F. (2014). The IQ of the crowd: Understanding and improving information quality in structured user-generated content. Information Systems Research, 25 (4), 669–689.
Lundmark, L. W., Oh, C., & Verhaal, J. C. (2016). A little Birdie told me: Social media, organizational legitimacy, and underpricing in initial public offerings. Information Systems Frontiers , 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9654-x .
Luo, X., & Zhang, J. (2013). How do consumer buzz and traffic in social media marketing predict the value of the firm? Journal of Management Information Systems, 30 (2), 213–238.
Luo, X., Zhang, J., & Duan, W. (2013). Social media and firm equity value. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 146–163.
Ma, X., Khansa, L., Deng, Y., & Kim, S. S. (2013). Impact of prior reviews on the subsequent review process in reputation systems. Journal of Management Information Systems, 30 (3), 279–310.
Maier, C., Laumer, S., Eckhardt, A., & Weitzel, T. (2015a). Giving too much social support: Social overload on social networking sites. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (5), 447–464.
Maier, C., Laumer, S., Weinert, C., & Weitzel, T. (2015b). The effects of technostress and switching stress on discontinued use of social networking services: A study of Facebook use. Information Systems Journal, 25 (3), 275–308.
Massari, L. (2010). Analysis of MySpace user profiles. Information Systems Frontiers, 12 (4), 361–367.
Matook, S., Brown, S. A., & Rolf, J. (2015a). Forming an intention to act on recommendations given via online social networks. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (1), 76–92.
Matook, S., Cummings, J., & Bala, H. (2015b). Are you feeling lonely? The impact of relationship characteristics and online social network features on loneliness. Journal of Management Information Systems, 31 (4), 278–310.
McCain, K. W. (1984). Longitudinal author Cocitation mapping: The changing structure of macroeconomics. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 35 (6), 351–359.
McCallum, A. K. (2002). Mallet: A machine learning for language toolkit. From http://mallet.cs.umass.edu
Mettler, T., & Winter, R. (2016). Are business users social? A design experiment exploring information sharing in enterprise social systems. Journal of Information Technology, 31 (2), 101–114.
Miller, A. R., & Tucker, C. (2013). Active social media management: The case of health care. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 52–70.
Miranda, S. M., Kim, I., & Summers, J. D. (2015). Jamming with social media: How cognitive structuring of organizing vision facets affects it innovation diffusion. MIS Quarterly, 39 (3), 591–614.
Miranda, S. M., Young, A., & Yetgin, E. (2016). Are social media emancipatory or hegemonic? Societal effects of mass media digitization. MIS Quarterly, 40 (2), 303–329.
Nerur, S. P., Rasheed, A. A., & Natarajan, V. (2008). The intellectual structure of the strategic management field: An author co-citation analysis. Strategic Management Journal, 29 (3), 319–336.
Oestreicher-Singer, G., & Zalmanson, L. (2013). Content or community? A digital business strategy for content providers in the social age. MIS Quarterly, 37 (2), 591–616.
Oh, O., Agrawal, M., & Rao, H. R. (2013). Community intelligence and social media services: A rumor theoretic analysis of tweets during social crises. MIS Quarterly, 37 (2), 407–426.
Oh, O., Eom, C., & Rao, H. R. (2015). Research note—Role of social Media in Social Change: An analysis of collective sense making during the 2011 Egypt revolution. Information Systems Research, 26 (1), 210–223.
Oh, W., Moon, J. Y., Hahn, J., & Kim, T. (2016). Research note—Leader influence on sustained participation in online collaborative work communities: A simulation-based approach. Information Systems Research, 27 (2), 383–402.
Phang, C. W., Kankanhalli, A., & Tan, B. C. (2015). What Motivates Contributors vs. Lurkers? An Investigation of Online Feedback Forums. Information Systems Research, 26(4), 773–792
Plume, C. J., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Slade, E. L. (2016). Social Media in the Marketing Context: A state of the art analysis and future directions (1st ed.). Oxford: Chandos Publishing Ltd.
Porter, C. E., Devaraj, S., & Sun, D. (2013). A test of two models of value creation in virtual communities. Journal of Management Information Systems, 30 (1), 261–292.
Qiu, L., Rui, H., & Whinston, A. B. (2014). Effects of social networks on prediction markets: Examination in a controlled experiment. Journal of Management Information Systems, 30 (4), 235–268.
Qiu, L., Tang, Q., & Whinston, A. B. (2015). Two formulas for success in social media: Learning and network effects. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (4), 78–108.
Rana, N. P., Dwivedi, Y. K., Lal, B., Williams, M. D., & Clement, M. (2017). Citizens’ adoption of an electronic government system: Towards a unified view. Information Systems Frontiers, 19 (3), 549–568.
Ray, S., Kim, S. S., & Morris, J. G. (2014). The central role of engagement in online communities. Information Systems Research, 25 (3), 528–546.
Ridings, C., & Wasko, M. (2010). Online discussion group sustainability: Investigating the interplay between structural dynamics and social dynamics over time. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 11 (2), 95.
Rishika, R., Kumar, A., Janakiraman, R., & Bezawada, R. (2013). The effect of customers' social media participation on customer visit frequency and profitability: An empirical investigation. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 108–127.
Rosenberger, M., Lehrer, C., & Jung, R. (2017). Integrating data from user activities of social networks into public administrations. Information Systems Frontiers, 19 (2), 253–266.
Schlagwein, D., & Hu, M. (2016). How and why organisations use social media: Five use types and their relation to absorptive capacity. Journal of Information Technology, 32 (2), 194–209.
Shen, A. X., Lee, M. K., Cheung, C. M., & Chen, H. (2010). Gender differences in intentional social action: We-intention to engage in social network-facilitated team collaboration. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 152–169.
Shi, Z., & Whinston, A. B. (2013). Network structure and observational learning: Evidence from a location-based social network. Journal of Management Information Systems, 30 (2), 185–212.
Shi, Z., Rui, H., & Whinston, A. B. (2014). Content sharing in a social broadcasting environment: Evidence from twitter. MIS Quarterly, 38 (1), 123–142.
Singh, P. V., Sahoo, N., & Mukhopadhyay, T. (2014). How to attract and retain readers in Enterprise blogging? Information Systems Research, 25 (1), 35–52.
Spagnoletti, P., Resca, A., & Sæbø, Ø. (2015). Design for Social Media Engagement: Insights from elderly care assistance. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 24 (2), 128–145.
Stanko, M. A. (2016). Toward a theory of remixing in online innovation communities. Information Systems Research, 27 (4), 773–791.
Statista. (2017). Most famous social network sites worldwide as of April 2017, Ranked by number of active users (in millions). Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/272014/global-social-networks-ranked-by-number-of-users/ . Accessed 22 June 2017.
Stieglitz, S., & Dang-Xuan, L. (2013). Emotions and information diffusion in social media—Sentiment of microblogs and sharing behavior. Journal of Management Information Systems, 29 (4), 217–248.
Subramaniam, N., & Nandhakumar, J. (2013). Exploring social network interactions in enterprise systems: The role of virtual co-presence. Information Systems Journal, 23 (6), 475–499.
Sung, Y. S., Wang, D., & Kumara, S. (2016). Uncovering the effect of dominant attributes on community topology: A case of facebook networks. Information Systems Frontiers , 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9696-0 .
Susarla, A., Oh, J. H., & Tan, Y. (2012). Social networks and the diffusion of user-generated content: Evidence from YouTube. Information Systems Research, 23 (1), 23–41.
Susarla, A., Oh, J. H., & Tan, Y. (2016). Influentials, Imitables, or Susceptibles? Virality and word-of-mouth conversations in online social networks. Journal of Management Information Systems, 33 (1), 139–170.
Tang, Q., Gu, B., & Whinston, A. B. (2012). Content contribution for revenue sharing and reputation in social media: A dynamic structural model. Journal of Management Information Systems, 29 (2), 41–76.
Tow, W. N. F. H., Dell, P., & Venable, J. (2010). Understanding information disclosure behaviour in Australian Facebook users. Journal of Information Technology, 25 (2), 126–136.
Trier, M., & Richter, A. (2015). The deep structure of organizational online networking–an actor-oriented case study. Information Systems Journal, 25 (5), 465–488.
Turel, O. (2015). Quitting the use of a habituated hedonic information system: A theoretical model and empirical examination of Facebook users. European Journal of Information Systems, 24 (4), 431–446.
Turel, O., & Serenko, A. (2012). The benefits and dangers of enjoyment with social networking websites. European Journal of Information Systems, 21 (5), 512–528.
Van Eck, N. J., & Waltman, L. (2011). Text mining and visualization using VOSviewer, ISSI . Newsletter, 7 (3), 50–54.
Van Osch, W., & Steinfield, C. W. (2016). Team boundary spanning: Strategic implications for the implementation and use of enterprise social media. Journal of Information Technology, 31 (2), 207–225.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27 (3), 425–478.
Vishwanath, A. (2015). Diffusion of deception in social media: Social contagion effects and its antecedents. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (6), 1353–1367.
Wakefield, R., & Wakefield, K. (2016). Social media network behavior: A study of user passion and affect. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 25 (2), 140–156.
Wang, Y., Zeng, D., Zhu, B., Zheng, X., & Wang, F. (2014). Patterns of news dissemination through online news media: A case study in China. Information Systems Frontiers, 16 (4), 557–570.
Wattal, S., Schuff, D., Mandviwalla, M., & Williams, C. B. (2010). Web 2.0 and politics: The 2008 US presidential election and an e-politics research agenda. MIS Quarterly, 34 (4), 669–688.
Wei, C., Khoury, R., & Fong, S. (2013). Web 2.0 recommendation service by multi-collaborative filtering trust network algorithm. Information Systems Frontiers, 15 (4), 533–551.
White, H. D., & Griffith, B. C. (1981). Author Cocitation: A literature measure of intellectual structure. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 32 (3), 163–171.
Wu, L. (2013). Social network effects on productivity and job security: Evidence from the adoption of a social networking tool. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 30–51.
Wu, J., & Gaytán, E. A. A. (2013). The role of online seller reviews and product price on buyers' willingness-to-pay: A risk perspective. European Journal of Information Systems, 22 (4), 416–433.
Xie, K., & Lee, Y. J. (2015). Social media and brand purchase: Quantifying the effects of exposures to earned and owned social media activities in a two-stage decision making model. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (2), 204–238.
Xu, S. X., & Zhang, X. M. (2013). Impact of Wikipedia on market information environment: Evidence on management disclosure and investor reaction. MIS Quarterly, 37 (4), 1043–1068.
Xu, Y. C., Yang, Y., Cheng, Z., & Lim, J. (2014). Retaining and attracting users in social networking services: An empirical investigation of cyber migration. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 23 (3), 239–253.
Xu, B., Xu, Z., & Li, D. (2016). Internet aggression in online communities: A contemporary deterrence perspective. Information Systems Journal, 26 (6), 641–667.
Yan, L., & Tan, Y. (2014). Feeling blue? Go online: An empirical study of social support among patients. Information Systems Research, 25 (4), 690–709.
Yan, L., Peng, J., & Tan, Y. (2015a). Network dynamics: How can we find patients like us? Information Systems Research, 26 (3), 496–512.
Yan, X., Wang, J., & Chau, M. (2015b). Customer revisit intention to restaurants: Evidence from online reviews. Information Systems Frontiers, 17 (3), 645–657.
Yu, J., Hu, P. J. H., & Cheng, T. H. (2015). Role of affect in self-disclosure on social network websites: A test of two competing models. Journal of Management Information Systems, 32 (2), 239–277.
Zeng, X., & Wei, L. (2013). Social ties and user content generation: Evidence from Flickr. Information Systems Research, 24 (1), 71–87.
Zhang, J., & Piramuthu, S. (2016). Product recommendation with latent review topics. Information Systems Frontiers , 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9697-z .
Zhang, X., & Wang, C. (2012). Network positions and contributions to online public goods: The case of Chinese Wikipedia. Journal of Management Information Systems, 29 (2), 11–40.
Zhang, D., Zhou, L., Kehoe, J. L., & Kilic, I. Y. (2016). What online reviewer behaviors really matter? Effects of verbal and nonverbal behaviors on detection of fake online reviews. Journal of Management Information Systems, 33 (2), 456–481.
Zhao, L., Detlor, B., & Connelly, C. E. (2016). Sharing knowledge in Social Q&a Sites: The unintended consequences of extrinsic motivation. Journal of Management Information Systems, 33 (1), 70–100.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Eastern Gateway Building, Brunel University London, Uxbridge, UB8 3PH, UK
Kawaljeet Kaur Kapoor
Emerging Markets Research Centre (EMaRC), School of Management, Swansea University Bay Campus, Swansea, SA1 8EN, UK
Kuttimani Tamilmani, Nripendra P. Rana, Pushp Patil & Yogesh K. Dwivedi
Information Systems & Operations Management, University of Texas at Arlington, Arlington, TX, 76019, USA
Sridhar Nerur
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nripendra P. Rana .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kapoor, K.K., Tamilmani, K., Rana, N.P. et al. Advances in Social Media Research: Past, Present and Future. Inf Syst Front 20 , 531–558 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9810-y
Download citation
Published : 06 November 2017
Issue Date : June 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-017-9810-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Information systems
- Social networks
- Social media research
- Systematic review
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Social media research is a rapidly growing field that encompasses a wide range of topics, from understanding the psychological and social effects of social media to analyzing patterns of user behavior and identifying trends in online conversations.
Exploring social media research questions helps people understand the impacts, effects, and intricacies of social media on individuals and the wider community. To help you choose a specific area to examine, here are some of the top social media research topics that are relevant in 2024.
Social media research encompasses a broad range of different topics that delve into the ever-evolving digital landscape. People investigate the impact of social platforms on society, exploring subjects, such as online identity formation, self-presentation, the psychology of virtual interactions, and others.
Sometimes, Professors or teachers ask students to write an essay or research a topic without narrowing it down. In that case, students will have to develop specific research topics. If you’re writing a paper on social media, we’ve provided you with helpful topics to consider for research.
Learn how to choose solid social media research paper topics and what it takes to write a strong research proposal.
Tools and Techniques for Social Media Research. Understanding the Difference: Social Media Research vs. Traditional Research. Harnessing the Power of Social Media Research for Your Business. Ethics and Privacy in Social Media Research. Success Stories: Real World Examples of Social Media Research.
How does it work? What are the best strategies? Use of the Internet networks, social networks, and mobile in 2021. Facebook as a source of distribution of content and remote communication. Training of professionals toward their audiences for social media platforms. Facebook: A place of digital socialization among top social media sites.
It is evident from the clusters that research on social media has dealt with a broad range of topics, including but not restricted to diffusion of information and opinions, spread of diseases (e.g., influenza), identification of social and emotional health concerns and attendant interventions to deal with them, social media as an influence, the ...
Specifically, we have four major goals to accomplish: (a) to propose a theoretically-anchored framework to organize the social media marketing literature along key research streams; (b) to assess each of these streams along theoretical, methodological, and thematic grounds, and monitor their evolution over time; (c) to propose valuable direction...
This article presents a descriptive methodological analysis of qualitative and mixed methods approaches for social media research. It is based on a systematic review of 229 qualitative or mixed methods research articles published from 2007 through 2013 where social media played a central role.