- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
- Indian Society

Indian Society - Syllabus, Strategy Overview [UPSC Exam]
Indian Society is one of the important subjects in the UPSC syllabus. The subject finds its mention in Prelims, Mains and Optional papers of the IAS Exam . This article will help you get an overview of the Indian Society syllabus, the right strategy to prepare for it and also relevant notes’ articles for UPSC preparation.
Indian Society Syllabus – What is asked in the IAS paper?
Indian Society & UPSC Prelims
In prelims examination, candidates know that UPSC has not mentioned an elaborative syllabus but has mentioned major topics from which questions are asked. The table below mentions all those topics that are related to the Indian Society subject so that candidates know which segment to focus on for its UPSC Syllabus completion. Though the topics that can be related to Indian Society are also relevant to Economy & Social Development, hence, aspirants should take a wider view while covering these.
#Indian Society & UPSC Mains
After prelims, there are nine subjective papers in UPSC Mains . Indian Society is covered under its syllabus of General Studies Paper 1 and certain facets are also covered in Mains General Studies Paper 2. The table below will mention what topics related to Indian Society are mentioned by the commission in GS 1 and 2 syllabi:
Indian Society & UPSC Optionals
Candidates should know that there is no such subject called ‘Indian Society,’ but there is a Sociology subject that covers important fragments of Indian Society. Under paper-II of the Sociology subject, topics related to structure and changes of Indian Society are mentioned. You can get the full Sociology Optional Syllabus from the linked article. Some of the Indian Society topics that are covered in UPSC Sociology optional syllabus are mentioned in the table below:
Indian Society Questions Trend Analysis – Prelims & Mains
In Prelims, questions are majorly asked from social sector schemes, or welfare schemes that the central government or state government flag off for the attainment of development goals.
Check the kind of questions asked in UPSC Prelims on topics related to Indian Society:
Points to note for Indian Society Questions asked in UPSC Prelims:
Referring to the above-mentioned questions that have been asked in Prelims 2019, 2018, 2017 respectively, candidates can take note of the points mentioned below:
- Questions are majorly targeted at the social sector schemes that are for the welfare of people.
- Questions on basic concepts like social capital, equality in the society have also found a place in UPSC Prelims.
- Unlike in the Mains exam where questions on Indian Society are general in nature, in Prelims Indian Society questions will need good factual understanding so as to opt for the correct option while answering.
Indian Society Questions – UPSC Mains
The graph below explains the trend in a number of questions that are asked from the Indian Society topic in UPSC Mains:
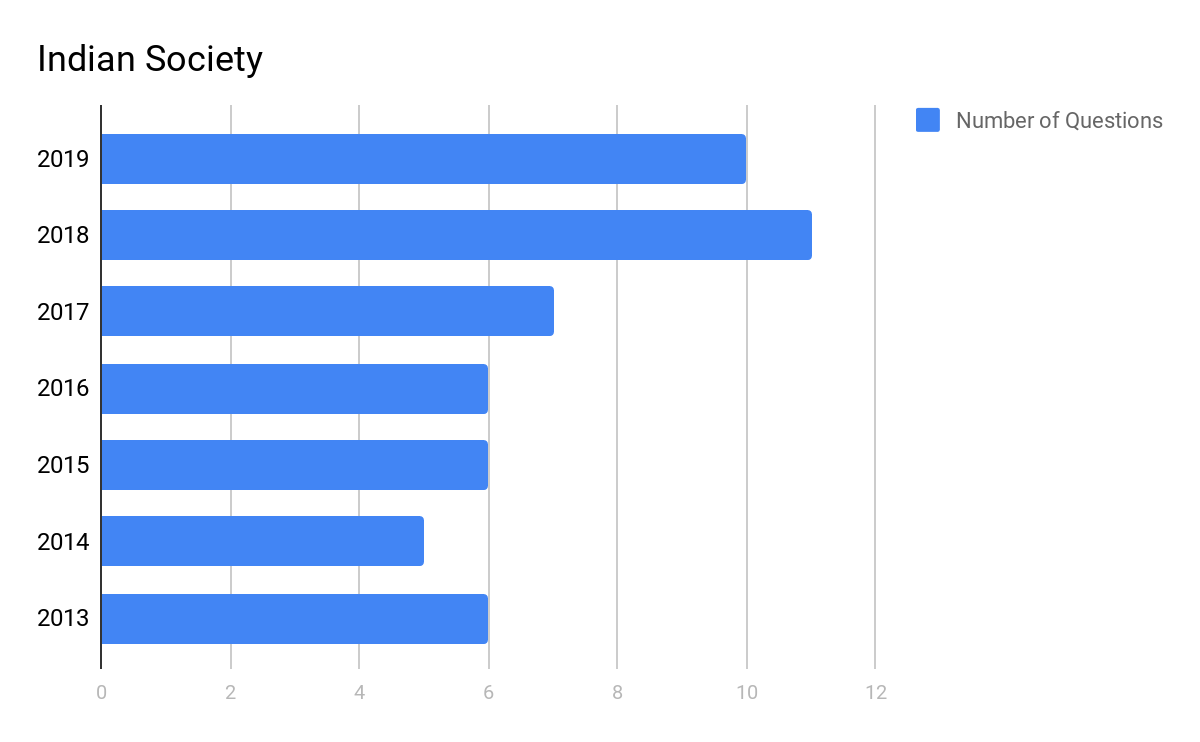
As the graph suggests, UPSC Mains GS 1 has seen an increase in questions related to Indian Society or Social Issues. For reference and practice of the Indian Society questions related to different topics, one can get all the previous years’ Indian Society Questions of UPSC Mains GS 1 , in the linked article.
For complete preparation of UPSC Mains GS 1, candidates can refer to the links below:
How to Prepare Indian Society Topic for UPSC?
Prelims Strategy:
The IAS candidates can take help of the points mentioned below before they start their preparation of GS 1 topic – Indian Society:
- What is the topic?
- Why is it important?
- Has the topic been in the news?
- Cramming the figures for the topics related to social issues is not very important from the exam perspective, rather aspirants should try to focus on the root causes of social issues. For issues like women’s safety, social empowerment, poverty, urbanization, health; an aspirant should know the background of such topics with the current initiatives taken up by the government (central or state) for the improvement of the same.
Mains Strategy:
While practicing Mains answer writing, aspirants should know what will make it easier for them when they write answers on questions related to Indian Society and its issues:
- Focus on the crux of social issues like casteism, communalism, poverty, gender inequality, hunger issues and other similar Indian Society issues. An aspirant should be aligned with the development initiatives relating to these issues.
- A general view on social issues is important rather than an extreme view. An aspirant should try to find answers to these issues by analysing the problems recurring in the Indian Society.
- A holistic view of the social issue is desired in the UPSC exam by an aspirant. A candidate who knows what, where, why, which, who and how of a social issue, becomes a desirable candidate.
- An aspirant should always keep in mind that his/her aim will be to crack the exam and not change the world that day; hence he/she should shy away from writing unfeasible and unrealistic solutions to the social issues in the Indian society.
- A desirable candidate is who knows how to connect culture, society, polity, geography, and economics with the issues of the Indian Society. Hence, one should always try to read from different perspectives and try to form a balanced opinion.
To get the best books for the Indian Society , you can check the linked article. Here, you will get a list of books that are useful for both prelims and mains.
UPSC Questions related to Indian Society
What should one read for indian society in upsc.
NCERT Class 11 – Understanding Society.
NCERT Class 12 – Indian Society.
NCERT Class 12 – Social Change & Development in India.
What is the social problems in India?
What is indian society and its types.

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation, register with byju's & download free pdfs, register with byju's & watch live videos.
General Studies
All Programmes
Study Material
UPSC Essay Topics - Important Essay Topics for UPSC Mains 2023
By vajiram & ravi.
Essay Course for UPSC
UPSC CSE Mains 2023 Essay Question Paper
UPSC Mains Optional Test Series
Mentorship Program for UPSC 2024
Understanding UPSC Essay Topics holds significant importance as it evaluates the candidate's ability to analyse, present arguments, and communicate effectively. In this article, we will explore the diverse range of UPSC essay topics, their significance, and essential tips to excel in this section. Get ready to enhance your writing and analytical skills and make a strong impression on the evaluators with well-crafted essays.
UPSC Essay Paper
The Essay paper in the UPSC Mains examination requires candidates to write multiple essays , each on a different topic, chosen from a given list of options. The essay topics for UPSC cover a wide range of issues, including social, economic, political, cultural, and philosophical aspects, both national and international.
The essay paper holds significant weightage in the UPSC Mains examination, contributing 250 marks out of the total 1750 marks . Scoring well in this section can have a considerable impact on the overall ranking and selection for the coveted civil services.
Weekly UPSC Essay Topics By Vajiram & Ravi
The UPSC Essay Paper is an opportunity for candidates to demonstrate their proficiency in expressing ideas and analysing complex issues. Vajiram & Ravi Pensive-Weekly Essay Writing Programme provides you with two Essay Topics every Saturday based on the previous year's question papers and the changing trends analysis. You can submit your Essay for peer evaluation on vajiramandravi.com. This will help you nourish your writing skills, give you clarity of thought, and build the capacity to express opinions in a logical and coherent manner.
Important Essay Topics for UPSC 2023
The purpose of the essay paper is to assess the candidate's ability to critically analyse a topic, present well-structured arguments, and communicate their ideas effectively. It also evaluates their knowledge of various issues, their clarity of thought, and their capacity to express opinions in a logical and coherent manner.
Some of the Important Essay Topics to prepare for the UPSC Mains Examination 2023 are:
- Gender Equality
- Environment/Urbanization
- Economic Growth
- Federalism/Decentralization
- Agriculture
- Economics
UPSC Essay Topics on Philosophy
Every year, UPSC typically provides you with two or more essay topics centred around philosophical thoughts, Indian philosophical schools, or quotes from notable personalities. To effectively address these philosophical topics, you should refer to Philosophy Books to gain a foundational understanding. Here is a list of UPSC Essay Topics on Philosophy :
- Everything comes to him, who hustles while he waits.
- We are always blind as we want to be.
- You cannot step twice in the same river.
- A disciplined mind brings happiness.
- The price of Greatness is Responsibility.
- People would rather Believe than Know.
- Mind - A beautiful Servant? Or a dangerous Master?
UPSC Essay Topics on Art and Culture
The UPSC Essay Topics related to Indian society, art, and culture cover a wide range of subjects, offering great diversity. To gain knowledge about the static content on these topics, you should rely on fundamental books on society, as recommended for the exam. Here is a list of UPSC Essay Topics on Indian Art and Culture :
- Culture changes with economic development.
- Culture is what we are, Civilization is what we have.
- Social reform is a myth if places of worship are open only to all castes and not to all genders.
- Impact of Globalization on Indian Art and Culture.
- Caste System - India’s Enduring Curse.
- Godmen - A Threat to Indian Art and Culture?
UPSC Essay Topics on Science and Technology
UPSC essay topics on Science and Technology can largely be addressed through current affairs. You may also benefit from consulting a Science and Technology Book for UPSC to compose a comprehensive and well-rounded essay. Here are some UPSC Essay Topics on Science and Technology:
- Deglobalisation is good for the world.
- Science is organised Knowledge. Wisdom is Organised life.
- Technology is a Weapon against Poverty.
- Prioritising Education Technology for Global Growth.
- Technology is the silent factor in International Relations.
- Scientific and Technological Progress cannot be equated with Human Progress.
UPSC Essay Topics on Education
Education stands as one of the preferred UPSC Essay Topics, with an essay related to this subject often appearing in the paper each year. To tackle this topic effectively, you should stay abreast of Current Affairs , incorporating significant changes and advancements in the field. Let's explore some of the Essay topics for UPSC centred around education:
- Self Education is a lifelong curiosity.
- Education Breeds Peace.
- Education is a progressive discovery of our own ignorance.
- Education must also train one for quick, resolute and effective thinking.
- Schooling is not Education.
UPSC Essay Topics on Polity and Governance
To comprehensively address Polity and Governance topics, you should acquire fundamental knowledge from Polity Books for UPSC and Current Affairs. These resources offer static information about relevant issues and their historical context, which proves valuable while writing UPSC Essay Topics on Polity. Here are some Essay Topics on Polity and Governance:
- The Role of Politics in Development.
- Should Youth in India Consider Politics as a Career?
- Art, Freedom and Creativity will change society faster than politics.
- The politics of Identity is the Politics of the Weak.
- People should not be afraid of their Government. The Government should be afraid of its people.
- Government Surveillance - Good or Bad?
UPSC Essay Topics on Economy
Essays concerning economic growth are frequently included in the Essay Paper. To tackle these topics effectively, you should refer to Economy Notes for UPSC to gain a comprehensive understanding. Once the fundamentals are grasped, you can enhance their essays by incorporating examples, data, and statistics to create a multidimensional perspective. Here is a list of UPSC Essay Topics on Economy:
- We don't have to sacrifice a Strong Economy for a Healthy Environment.
- India, a $5 trillion Economy - Dream or Reality?
- Digital Economy: A leveller or a source of Economic Inequality?
- Innovation is the key determinant of social welfare and economic growth.
- Labour Reforms in India and its Role in Economic Growth.
UPSC Essay Topics on Social Issues
Social issues are a significant aspect of the UPSC essay paper, reflecting the candidates' understanding of societal challenges and their ability to propose viable solutions. These essays provide a platform for candidates to analyse, critique, and suggest measures for pressing social concerns. Topics related to social issues in the UPSC Essay paper may include:
- Inclusivity and Plurality are the hallmarks of a Peaceful Society.
- A Gender-sensitive Indian Society is a prerequisite for Women and Child Empowerment.
- The weaker sections of Indian Society - are their Rights and Access to Justice getting Better?
Previous Year UPSC Essay Topics
Practising previous year's essay topics will help you become familiar with the UPSC exam pattern , word limit, and the types of essay questions frequently asked in the Mains Examination. Analysing past essay topics will also allow you to identify recurring themes and trends, enabling you to prioritise their preparation accordingly. Regular practice with past essay topics will instil confidence in you, helping you feel more comfortable and prepared for the actual exam.
- Forests are the best case studies for economic excellence.
- Poets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world.
- History is a series of victories won by the scientific man over the romantic man.
- A ship in the harbour is safe, but that is not what a ship is for.
- The time to repair the roof is when the sun is shining.
- A smile is the chosen vehicle for all ambiguities.
- Just because you have a choice, it does not mean that any of them has to be right.
Tips to Excel in UPSC Essay Paper
- Understand the Topics: Thoroughly comprehend the essay topics, including the keywords and instructions. Choose a topic that aligns with your strengths and interests.
- Plan and Structure: Devote some time to plan your essay. Create an outline and organise your thoughts in a structured manner, with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Be Objective: Present balanced arguments and avoid a biased or one-sided approach. Consider multiple perspectives and present a holistic view.
- Provide Examples and Evidence: Support your arguments with relevant examples, data, quotes and evidence to strengthen your essay.
- Maintain Clarity: Write in a clear and concise manner. Use simple language and avoid jargon or overly complex vocabulary.
- Practice Regularly: Regular practice is essential to improve Essay writing skills. Write essays on diverse topics to enhance your versatility.
- Time Management: Allocate appropriate time for planning, writing, and revising each essay to manage time effectively during the examination.
- Revise and Edit: Review your essays for coherence, grammar, and structure. Make necessary edits to refine your work.
FAQs on UPSC Essay Topics
What are the important UPSC Essay Topics?
Here is a list of UPSC Essay Topics asked in Mains Examination previously:
- Culture is what we are, civilization is what we have.
- Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication.
- What is research but a blind date with knowledge?
- Best for an individual is not necessarily best for society.
- Wisdom finds truth.
- Ships don’t sink because of water around them, ships sink because of water that gets into them.
- Patriarchy is the least noticed yet the most significant structure of social inequality.
- Technology as the silent factor in international relations.
How do I Prepare for the UPSC Essay?
To prepare for the UPSC essay, focus on understanding the essay syllabus and past topics to identify recurring themes. Regularly practise writing essays on various topics to improve your writing skills and time management. Structure your essays with a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion.
Which is the best source to practise UPSC Essay Topics?
The best sources to prepare Essay for UPSC include official UPSC materials, newspapers, and magazines like The Hindu, Yojana , and Kurukshetra for current affairs, standard books on diverse subjects, government reports and publications, online platforms like PIB and PRS India, UPSC previous year papers for understanding the exam pattern, and regular practice of essay writing on various topics.
© 2024 Vajiram & Ravi. All rights reserved
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Indian Culture Essay in English for Students
August 10, 2021 by Sandeep
Essay on Indian Culture: Indian culture is one of the oldest and unique cultures worldwide. It has influenced many foreign countries due to its richness in heritage and diverse paths. Indian culture is splendid in its traditions, customs, art forms, food and cuisines, music and dance forms, etc. The joint family system, elaborate weddings, multicultural festivals, languages, and extensions of the Indian cultural diaspora.
Essay on Indian Culture
Below we have provided an Indian Culture Essay in English, suitable for classes 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 & 10. This short essay on Indian culture is helpful for school students who are participating in the essay writing competition.
Our Indian culture is diverse and vibrant and considered to be the oldest and supreme one. India’s identity all over the world is due to its tradition and mixed religions. It consists of vital components like linguistic differences, etiquette, customs, rituals, beliefs, values, etc. Even though India has adopted modernisation in its lifestyle, but they haven’t changed their traditional methods. Hence this sets it apart from other nations making it unique and dynamic. Every one respects different culture and peacefully follow their religion.
Components of Indian Culture
Despite having religious, language, and state differences, Indian culture teaches us to co-exist harmoniously. Indians accept this vast diversification with a broad outlook and look forward to work and stay together happily. People celebrate all festivals irrespective of their different caste with great pomp and reverence.
Indian culture instils positivity to a great extent by motivating to keep hope alive. Through the Epic stories of Ramayana and Mahabharata, it infuses the values of strong will and determination. Ramayana teaches to respect elders and be duty-bound towards parents. Be committed to your duty and be loyal to your spouse.
It stresses to remain grounded no matter how successful a person becomes. Mahabharata depicts an eternal bond of friendship. Stand by what you believe and never giving up attitude are the crux of its teachings. Jainism gave us five vows or principles: Non-Violence, Truth, Non-stealing, Celibacy, and Non-attachment. These were the cornerstone of Jainism given by Vardhaman Mahavir the 24th Tirthankara.
The most important highlight of his teachings was freedom to women and belief in soul and karma. Despite being a king, Gautama Buddha gave up worldly things and went on the journey to find enlightenment. After attaining enlightenment, he had given the four noble truths that one must adhere to. It states that everyone suffers, and the cause of such suffering is greed, desires, and ignorance.
One can live without such pains if they follow a correct path and eightfold path, including right knowledge, attitude, speech, action, means of livelihood, efforts, awareness, and meditation. Despite being a king gave up worldly things and went on the journey to find enlightenment. Bhagwat Gita (The holy book of Hindus) inspires one to follow the right conduct and virtue and has three main themes-knowledge, action, and love. It guides us to follow the path of devotion and compassion.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
Effects of Globalization on Indian Society
Last updated on April 9, 2022 by ClearIAS Team

Globalization has virtually diminished the distances and connected the whole world. Read here to know the effect of globalization on Indian society.
Globalization is a term used to describe how trade and technology have made the world a more connected and interdependent place. Globalization also captures in its scope the economic and social changes that have come about as a result.
In today’s world, consumers have a wide choice of goods and services before them. The latest models of digital cameras, mobile phones, and televisions made by the leading manufacturers of the world are within the reach. Every season, new models of automobiles can be seen on Indian roads. Gone are the days when Ambassador and Fiat were the only cars on Indian roads.
Today, Indians are buying cars produced by nearly all the top companies in the world. A similar explosion of brands can be seen for many other goods: from shirts to televisions to processed fruit juices. Such a wide-ranging choice of goods in our markets is a relatively recent phenomenon.
One wouldn’t have found such a wide variety of goods in Indian markets two decades back. In a matter of years, our markets have been transformed! How do we understand these rapid transformations? What are the factors that brought about these changes? And, how did these changes affect the lives of the people? The answer to all these questions starts with ‘globalization’.
Table of Contents
Effect of globalization on Indian society
Globalization has several aspects and can be political, cultural, social, and economic, out of which financial integration is the most common aspect. India is one of the fastest-growing economies in the world and is predicted to reach the top three in the next decade.

India’s massive economic growth is largely due to globalization which was a transformational change that didn’t occur until the 1990s. Since then, the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) has grown at an exponential rate.
The many effects of globalization on Indian society and multiple aspects of it have been discussed here.
Impact of globalization on the Indian economy
Overall, globalization has improved various aspects of India, like:
- International trade relations
- Technology and communication
- Corporate world
- Social and cultural expansion
The reduction of export subsidies and import barriers enabled free trade that made the Indian market attractive to the international community. The untapped potential of the nascent Indian market was opened to the global market and the significant changes were made to its industrial, financial, and agricultural sectors:
Industrial sector: It saw a massive influx of both foreign capital investments ’ India became a favorite offshore market for pharmaceutical manufacturing, chemical, and petroleum industries. This brought advanced technologies and processes that helped in the modernization of the Indian industrial sector.
Financial sector: Prior to globalization and privatization, India’s financial sector had been mismanaged by a combination of corrupt and inept government officials. The privatization of the financial space created a much more dynamic financial services sector.
Agricultural sector: India still has a largely agrarian society , with a significant majority of the country’s population depending on this sector either directly or indirectly for their livelihood. The new technological capabilities of farmers have increased helping drive global exports of Indian products such as tea, coffee, and sugar.

The betterment of these sectors has brought about an increase in national income, employment, exports, and GDP growth.
Advantages of globalization for India
- The increasing globalization of India has access to markets of the country to foreign companies seeking to invest and operate within the massive Indian market.
- Increase in employment opportunities.
- Initially, globalization gave foreigners access to an inexpensive, robust labor force. But as the country has progressed, the labor force has grown more skilled and educated over time. Now India has the largest diaspora living abroad.
- For foreign investors considering the economy as a whole, India offers a well-diversified export basket. This has been highlighted in the Economic Survey of India as well.
The cultural impact of globalization on Indian society
The process of globalization increased access to television and other entertainment sources over the years. Even in the rural areas satellite television has an established market. In the cities, Internet facility is everywhere and it is being extended to rural areas also through schemes like Smart Cities Mission .
There is an increase in the global food chain and restaurants in the urban areas of India. Multiple movie halls, big shopping malls, and high-rise residential are seen in every city.
The entertainment sector in India has now obtained a global market. After economic liberalization, Bollywood expanded its area and showed a major presence on the global scale. Bollywood movies are quite famous in Middle Eastern and many African countries as well.
Western styles began to be incorporated into Bollywood films to expand the outreach.
As these new cultural ideologies began to permeate the Indian population, the Indian urban population was pushed to re-evaluate their traditional Indian cultural ideology.
Bollywood movies are also distributed and accepted at the international level. Big international companies like Walt Disney, 20th Century Fox, and Columbia Pictures are investing in this sector.
Similarly, famous International brands such as Armani, Gucci, Nike, and Omega are also making investments in the Indian market with the changing of fashion statement of Indians.
Women are getting the equal opportunities they very well deserve now in more numbers due to the globalization of the market. Their empowerment has given considerable opportunities and possibilities for improving employment conditions through global solidarity and coordination. It is found that the growth of computers and other technologies enabled women with better waged, flex timings, and capacity to negotiate their role and status in-home and at the corporate level.
Effects of Globalization on Indian Education:
There is a profound effect observed in the educational sector due to globalization such as the literacy rate becoming high.
Foreign Universities are collaborating with different Indian Universities now, expanding the reach for Indian students.
The Indian educational system embraced globalization through Information technology and it offers opportunities to evolve new paradigms shifts in developmental education.
The shift from largely uneducated to an industrial society to an information society has gradually taken shape.
Globalization promotes new tools and techniques such as E-learning, Flexible learning, Distance Education Programs, and Overseas training.
Many government schemes like the ‘ New Education Policy ’ are pushing for a more global education system to make Indian students from every walk of life at par with the global community.
Challenges of globalization in Indian society
- Economically, for a large market like India is harder to maintain a free, convertible, and open access enabled transnational market.
- Globalization also means growing interdependence in other nations- this can issues like misdistribution of resources. The parity between underdeveloped, developing, and developed remains status quo in many cases.
- The universalization of information technology has boons but also banes, in terms of cybercrimes and other darknet activities . The increase in the number of cyberattacks in India is proof of this.
- Globalization does have a great effect on the ecologies and environments of nations that need safeguards that lessen the negative effects rather than exploiting them without regard to such concerns.
- The negative effects of globalization on the Indian Industry are that with the coming of technology the number of labor required is decreased and this resulted in increasing unemployment, especially in the arena of the pharmaceutical, chemical, manufacturing, and cement industries.
- There are a few challenges for companies due to globalization such as Migration, relocation, labor shortages, competition, and changes in skills and technology.
The effects of globalization on Indian society are manifold and have been discussed in detail. The process of globalization has changed the industrial pattern and social life of people. This has had an immense impact on Indian trade, finance, and cultural system.
The globalization of the economic, social, and cultural structures happened in simultaneously. Previously, the pace of the process was slow but now the change is happening in every arena at lightning-fast speed with the use of information technology.
Globalization has resulted in an increase in the production of a range of goods and services. MNCs have established manufacturing plants all over the world. It has positive effects on India and the administration is trying its best to overcome many obstacles and adopt global policies to expand business an international scale.
India is surely gaining international recognition which leads to the strengthening of economic and political areas.
Truly, globalization has made the world a small place, a whole lot of different people interconnected in diverse ways.

Aim IAS, IPS, or IFS?

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
Take ClearIAS Mock Exams: Analyse Your Progress
Analyse Your Performance and Track Your All-India Ranking
Ias/ips/ifs online coaching: target cse 2025.

Are you struggling to finish the UPSC CSE syllabus without proper guidance?

Table of Contents
Indian Society (UPSC Mains) – Previous Year Questions
- Do you think marriage as a sacrament is loosing its value in Modern India?
- Explain why suicide among young women is increasing in Indian society.
- Child cuddling is now being replaced by mobile phones. Discuss its impact on the socialization of children.
- Why did human development fail to keep pace with economic development in India?
- Does urbanization lead to more segregation and/or marginalization of the poor in Indian metropolises?
- Why is caste identity in India both fluid and static?
- Discuss the impact of post-liberal economy on ethnic identity and communalism.
- Explore and evaluate the impact of ‘Work From Home’ on family relationships.
- How is the growth of Tier 2 cities related to the rise of a new middle class with an emphasis on the culture of consumption?
- Given the diversities among tribal communities in India, in which specific contexts should they be considered as a single category?
- Analyse the salience of ‘sect’ in Indian society vis-a-vis caste, region and religion.
- Are tolerance, assimilation and pluralism the key elements in the making of an Indian form of secularism? Justify your answer.
- Examine the uniqueness of tribal knowledge system when compared with mainstream knowledge and cultural systems.
- Examine the role of ‘Gig Economy’ in the process of empowerment of women in India.
- What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India?
- Discuss the main objectives of Population Education and point out the measures to achieve them in India in detail.
- What is Cryptocurrency? How does it affect global society? Has it been affecting Indian society also?
- How does Indian society maintain continuity in traditional social values? Enumerate the changes taking place in it.
- Has caste lost its relevance in understanding the multi-cultural Indian Society? Elaborate your answer with illustrations.
- COVID-19 pandemic accelerated class inequalities and poverty in India. Comment.
- Do you agree that regionalism in India appears to be a consequence of rising cultural assertiveness? Argue.
- Is diversity and pluralism in India under threat due to globalisation? Justify your answer.
- Customs and traditions suppress reason leading to obscurantism. Do you agree?
- How have digital initiatives in India contributed to the functioning of the education system in the country? Elaborate your answer.
- What makes the Indian society unique in sustaining its culture? Discuss.
- “Empowering women is the key to control population growth.” Discuss.
- What are the challenges to our cultural practices in the name of secularism?
- Do we have cultural pockets of small India all over the nation? Elaborate with examples.
- What are the continued challenges for women in India against time and space?
- Are we losing our local identity for the global identity? Discuss.
- “Caste system is assuming new identities and associational forms. Hence, the caste system cannot be eradicated in India.” Comment.
- ‘Despite the implementation of various programmes for the eradication of poverty by the government in India, poverty is still existing’. Explain by giving reasons.
- How the Indian concept of secularism different from the western model of secularism? Discuss.
- ‘Women’s movement in India has not addresses the issues of women of lower social strata.’ Substantiate your view.
- ‘Globalisation is generally said to promote cultural homogenisation but due to this cultural specificities appear to be strengthened in the Indian society.’ Elucidate.
- ‘Communalism arises either due to power struggle or relative deprivation.’ Argue by giving suitable illustrations.
- In the context of the diversity of India, can it be said that the regions form cultural units rather than the States? Give reasons with examples for your view point.
- What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)?
- The spirit of tolerance and love is not only an interesting feature of Indian society from very early times, but it is also playing an important part at the present. Elaborate.
- Distinguish between religiousness/religiosity and communalism giving one example of how the former has got transformed into the latter in independent India.
- “The growth of cities as I.T. hubs has opened up new avenues of employment, but has also created new problems”. Substantiate this statement with examples.
- Has the formation of linguistic states strengthened the cause of Indian unity?
- To what extent globalisation has influenced the core of cultural diversity in India? Explain.
- “An essential condition to eradicate poverty is to liberate the poor from the process of deprivation.” Substantiate this statement with suitable examples.
- Why are the tribals in India referred to as ‘the Scheduled Tribes’? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment.
- With a brief background of quality of urban life in India, introduce the objectives and strategy of the ‘Smart City Programme.”
- What is the basis of regionalism? Is it that unequal distribution of benefits of development on regional basis eventually promotes regionalism? Substantiate your answer.
- Describe any four cultural elements of diversity in India and rate their relative significance in building a national identity.
- Critically examine whether growing population is the cause of poverty OR poverty is the main cause of population increase in India.
- How do you explain the statistics that show that the sex ratio in Tribes in India is more favourable to women than the sex ratio among Scheduled Castes?
- Discuss the changes in the trends of labour migration within and outside India in the last four decades.
- Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India.
- Debate the issue of whether and how contemporary movements for assertion of Dalit identity work towards annihilation of caste.
- Smart cities in India cannot sustain without smart villages. Discuss this statement in the backdrop of rural urban integration.
- How does patriarchy impact the position of a middle class working woman in India?
- Why do some of the most prosperous regions of India have an adverse sex ratio for women? Give your arguments.
- The life cycle of a joint family depends on economic factors rather than social values. Discuss.
- Discuss the various economic and socio-cultural forces that are driving increasing feminization of agriculture in India.
- How do the Indian debates on secularism differ from the debates in the West?
- Discussion the various social problems which originated out of the speedy process of urbanization in India.
- Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment.
- Critically examine the effects of globalization on the aged population in India.
- Growing feeling of regionalism is an important factor in the generation of demand for a separate state. Discuss.

- UPSC IAS Exam Pattern
- UPSC IAS Prelims
- UPSC IAS Mains
- UPSC IAS Interview
- UPSC IAS Optionals
- UPSC Notification
- UPSC Eligibility Criteria
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Admit Card
- UPSC Results
- UPSC Cut-Off
- UPSC Calendar
- Documents Required for UPSC IAS Exam
- UPSC IAS Prelims Syllabus
- General Studies 1
- General Studies 2
- General Studies 3
- General Studies 4
- UPSC IAS Interview Syllabus
- UPSC IAS Optional Syllabus
Westernization – Features and Impact on Indian Society – UPSC Modern History Notes
- Westernization is a process whereby societies come under or adopt Western culture in areas such as industry, technology, law, politics, economics, lifestyle, diet, clothing, language, alphabet, religion, philosophy, and values. Westernization has been an accelerating influence across the world in the last few centuries, with some thinkers assuming Westernization to be the equivalent of modernization, a way of thought that is often debated. The overall process of Westernization is often two-sided in that Western influences and interests themselves are joined with parts of the affected society, at minimum, to change towards a more Westernized society, in the hope of attaining a Western life or some aspects of it, while Western societies are themselves affected by this process and interaction with non-Western groups.
- The concept was also constructed by M.N. Srinivas to describe the process of social and cultural mobility in the traditional social structure of India. It has also emerged, in Srinivas’ study of the Coorgs of south India. The author has defined westernization as “the change brought about in Indian society and culture as a result of over 150 years of British rule, the term subsuming changes occurring at different levels in technology, institutions, ideology, and values”. M.N. Srinivas refers Westernisation to as ‘the changes brought about in Indian society and culture as a result of over 150 years of British rule and the term subsumes changes occurring at different levels – technology, institutions, ideology, values.’
- He traces westernization from the period of the British Raj. Surely, colonial rule brought with it the exploitation and suppression of the masses of people both at the rural and urban levels. At the same time, it also brought certain radical changes in Indian society and culture. The land was surveyed, revenue was settled, a new bureaucracy emerged, and an army, police, and law courts were established. The British rule also developed communications, railways, and post and telegraph and also started schools and colleges.
- Yet another force released by British rule was the working of Christian missionaries. The Christian missionaries worked in different parts of the country, particularly in those that were backward and inhabited by tribals and untouchables. This brought the weaker sections closer to Westernisation.
- In contemporary India, when we talk about westernization, a tremendous change has come in rural India. The impact of the five-year plans has brought the village people into the wider network of communication and modernization. The democratic institutions such as the Panchayati Raj and the massive spread of education have brought the villagers closer to Westernization.
Table of Contents
Impact of Westernization on Indian Society:
- The encounter between the Indian tradition and Western culture was of immense sociological significance. The Western tradition had a meaningful impact on the cultural, political, and social systems of India to such an enormous extent that it has been told that such contact initiated a new era of change in the Indian cultural tradition. The mode of the Western cultural impact on the Indian tradition had distinctive features. Historically, various Western traditions came to India with differing political and cultural orientations and exerted variegated influences upon Indian society and culture. The following are some of the areas in which the Western impact was visibly noticed.
Growth of a Universalistic Legal System:
- The process of Westernization brought in its wake new legal norms which contributed to the growth of a universalistic positive form of law in India. Formerly the legal system was founded on the principles of hierarchy and holism. Accordingly, justice was meted out based on the status of various castes and classes in the local hierarchy. Thus, following the prescription of Manu, a Brahmin slandering a Kshatriya had to pay a fine of fifty Panas, but for slandering a Vaishya or Shudra he had to pay twenty-five and twelve Panas respectively. If the lower castes slandered the high castes, the penalties were more severe. The principle of hierarchy was strictly followed in matters of dispensing justice.
- Our traditional legal system continued to be group-oriented and non-equalitarian. With the establishment of the British power in India, there came a new turning point in the legal system of the country. Various forms of legal innovation based on the principles of universalism, rationalism, and individualism were introduced thereby making the new judicial system individual-oriented and universalistic. It enacted legislation introducing social reforms in many sensitive areas such as marriage customs the age of marriage, and the age of consent for marriage. It established the principle of equality and generated a consciousness of positive rights among the downtrodden castes.
Impact of Westernization on Education:
- Contemporary education is of Western origin. Traditionally, the content of education was metaphysical. It was confined to the upper classes or the twice-born castes. Its structure was hereditary and closed. The roles of both the teachers and the teachers were qualitative-ascriptive. But Modern education has a fundamentally different orientation and organization. Its content is liberal and it preaches a scientific worldview. Freedom equality, humanism, and denial of faith in dogmatism are the major themes of modern education. Its professional structure is not ascriptive. It can be achieved by merit by anyone in the society.
Impact on the Communication network:
- The media of communication have been introduced in India through Western contact. Printed newspapers came into existence only after India’s contact with the West. The Britishers introduced the telegraph, railways, and modern postal system in India. Similar improvements have also been made in the other media of communication and transport. The expansion in transport by the railways, roadways, airways, and waterways has contributed to the intensification of the volume of interaction and contact between one region with another. The concept of purity and pollution has been given a discount since people of all castes are traveling in the same railway coach or bus.
Growth of Nationalism:
- Both Nationalism and democracy in the contemporary form are the gifts of Westernization. Nationalism implies consciousness of one’s nationhood. Its sociological manifestation is the idea of the nation-state. Democracy is a special form of political organization and system of values on which a nation-state can be founded. The feeling of nationality and respect for democratic norms is a consequence of Westernization.
- It was the fervent patriotic zeal of the Western people that made our leaders think of developing India as a united country. Most of the nationalist leaders of the freedom struggle in India got inspiration from Western literature and thought. Indian nationalism, however, was not modeled completely on the Western pattern.
Impact on Food Habits and Mode of Eating:
- Westernization has reached the level of food habits and ways of eating. Traditionally, Indians ate their meals sitting on the floor. Food was served either on the leaves or on brass, bronze or silver plates. Among the upper castes, and especially among Brahmin, eating was a religious act. The food had to be cooled while the women in charge of cooking and serving it must be in a ritually purer state. Food was being served to children and adults in order of seniority. At the end of the meal, the dining leaves became impure and were thrown out and the places where the leaves rested were purified with a solution of cow dung.
- But now the Westernized groups increasingly prefer to eat at tables with stainless steel utensils, spoons etc. Thus the new mode of eating has contributed to an increase in secularization as the table is not likely to be purified with cow dung after meals and the ritual acts traditionally performed before and after meals almost dropped. Changing food habits has brought people nearer to modern food technologies. The use of ghee has increasingly been replaced by vegetable oil both in rural and urban areas. Tea shops are now common in most roadside villages and persons of all castes take tea in china cups, glasses or earthen cups, even if tea might be drawn by a lower caste person. Eating meat and eggs by higher caste members is on the increase. Poultry farms which were previously considered polluting are opened in large numbers.
Impact on the Dress Pattern:
- Under the influence of westernization even people living in villages have opted for factory-made clothes like nylon, Terylene, tricot etc. in place of home-spun clothes, readymade garments have become popular. The mode of dress has also undergone a drastic change. The old style of shirt has been replaced by the modern style shirts. It marked a gradual weakening of ideas of ritual purity. Western clothes became more popular even Brahmins sat at dinner with their shirts on.
Change in Language:
- Many terms from the English language have entered the dialects of the rural folk. The expansion of civil administration popularized terms like court, collector, judge, barristers, etc. Similarly, the expansion of transport facilities has rendered terms like rail, station, signals, etc. matter in daily usage. The politicization of villages since Independence has introduced villages to terms like party, socialism, communism, ministry, etc. and similarly, the spread of medical facilities now makes expressions like injections, mixture, penicillin, etc also household words.
Weakening of Traditional Culture:
- Modern education and increased utilitarian and rational values of the Indian elite led them to make sharp criticisms of their own culture. They began casting aspersion on the evils of our traditional culture which used to make us submissive. The loathing of and longing for a new culture, and the rising aspirations of the population for a better future made them sort out what was desirable and vice versa. Indians today are more individualistic, and free-thinking and lead a relatively more free life. Modernization of the tradition is taking place in India today under the impact of the process of Westernization.
Impact on Marriage:
- Westernization has also brought about noticeable changes in matrimonial relationships. Marriage today is no longer seen as a relationship between two families rather it has transformed into the relationship of two individuals i.e. husband and wife. Husband and wife do not treat each other as superior or inferior but as friends and companions. Love and marriage have sidelined religion. Even the marriage ceremony itself has changed.
Impact on Family:
- Western culture preaches the individualistic ideology of family which is opposed to the collective ethos on which the joint family system is founded, imbibing the individualistic philosophy people give importance to the individual over the group thereby encouraging self-men. This has cut the joint family from its very root for which it has started crippling down. Members of a family today prefer freedom to enjoy marital life. Today’s brides do not like to remain under the control of laws. New democratic conventions find their place in household affairs too.
Impact on the Status of Women:
- The strong influence of the West is tangible in the status of women today. The medieval period in Indian history is witness to the status of women sinking to the nadir and if we find today women getting their due in almost all fields, a major part of the credit goes to Westernization. Education on the one hand generated and encouraged liberal ideas among men while on the other hand, it prepared women to strive for the natural status of equality.
Impact on Religion:
- The impact of science and Western education did bring about a significant change in our perception of religion. Uncritical acceptance of religious ideas is being replaced by logical interpretation and acceptance. The social value of religion has gone down. From a collective activity religion has become an individualistic activity. The activity pace of religion is gradually decreasing. There was a time when social, economic, and political scenes were all dominated by religion but now it is evolving more or less as an independent institution.
Impact on Customs:
- Indian masses which were a bit reluctant initially to accept the ways of the West are now jumping to their ways. From clothes to houses we live in, all bear the stamp of Western style and it has become a status symbol. Cosmetics, decoration of pieces, crockery, and even the methods of greetings have all become Westernized. In fact, in every activity of life, the impact of the West is easily seen as far as customs are concerned.
Impact on Art and Literature:
- The literal sub-culture of India was too influenced by the English literary tradition. ‘Romanticism’ and ‘Psychiatrist’ of the West can be found in almost every kind of literary expression of today. Experimentalism, Hedonism, and Romanticism have found a place in Indian poetry. Equality, environment, freedom, social movement, and other related topics have also got a place in Indian art and literature. Modern art is a by-product of Westernization which could not be easily adopted because of its radically different concepts.
Eradication of Social Evils:
- Social evils that had plagued the society and in a way were responsible for making Indian society so vulnerable to foreign annexation, could only be given a determined fight after the process of westernization took its root. No doubt, a few social workers had raised their fingers against these social evils before but it was the process of Westernization that prepared a broad base through which efforts against these evils could bear fruit.
- The practice of widow burning, infanticides, stealing of children for slavery, child marriage, ban on widow marriage, and untouchability are some of those social evils which are still being fought. Science and technology from the West have had some demystifying effects on these types of practices.
Features of Westernization:
- The process of Westernization subsumes changes occurring at different levels of technology, institutions, ideology and values. Broadly, it includes all changes that any non-western country like India or any other colonial country undergoes as a result of prolonged contact with Western culture.
The most important area of change was the value preferences of the non-western societies:
- A most important value which in turn subsumes several other values is what may broadly be characterized as humanitarianism which means active concern for the welfare of all human beings irrespective of social inequalities based on caste, economic position, religion, age or sex. Equalitarianism and secularization also form part of the value of humanitarianism. Humanitarianism refers to many of the reforms introduced by the British in the first half of the 19th century such as civil, penal, and procedural laws which put an end to certain inequalities that were part of the Hindu and Islamic jurisprudence.
- The principle of equality found expression in the abolition of slavery, and in the opening of new schools and colleges- which were, in theory at least, opened to all irrespective of religion, race, and caste. The new economic opportunities were also open to all, although in practice caste and other elite groups who traditionally lived in the big towns, enjoyed considerable advantages over others.
The introduction of reforms and new laws by the British led to several changes in the Indian customs which were earlier enforced as part of one’s religious duty:
- A religious custom had to satisfy the test of reason and humanitarianism if it was to be allowed to survive. As British rule gained roots in India, the values of rationality and humanitarianism also became firmly entrenched in the caste-ridden society. The formal system of education introduced by the British played an effective role in perpetuating these values.
Westernization is an all-inclusive term:
- It covers a wide range of changes from Western technology at one end to the experimental method of modern science and modern historiography at the other. In the field of technology, it has revolutionized the process of mass communication, transportation, industrialization, and improved health care facilities and has made available new comfortable gadgets for better living conditions. These changes are intimately linked with the life of the common man and have proved consequential.
The process of Westernization in India was uneven :
- Only a tiny fraction of the Indian population came into direct, face-to-face contact with the British. And those who came in contact with the British officers did not always become a force for change. Indian servants of the British, for instance, probably wielded some influence among their kin groups and local caste groups but not among others. They often came from the low castes as well. Their westernization was of a superficial kind as the upper castes made fun of them.
The process of Westernization has neatly intensified in many ways since 1947:
- The first and most critical step in Westernization was the establishment of Pax Britannica and the revolutions in communications that followed. Extension of the administrative and trading frontiers broke the centuries-old isolation of the different groups inhabiting the remote parts of the country. Similarly, the means of transportation and communication opened up avenues for new contacts.
- Thus, the development of communications and the removal of internal customs barriers integrated the economics of various regions in the country. In a word the political and administrative integration of India as well as the development of communication and the beginning of industrialization and agricultural development, increased spatial and social mobility of both the elite and the rural poor which laid the foundation of subsequent nationwide westernization.
The form and pace of Westernization of India varied from region to region and from one section of the population to another:
- For instance, one group of people became Westernized in their dress, diet, manners, speech, sports and in the gadgets they used while another absorbed Western science, knowledge and literature, remaining free from external attributes of Westernization. For example, Brahmins accepted the Western style of dressing and appearance and sent their children to Westernized schools using gadgets like the radio, cars, etc. but they did not accept the British diet, dancing, hunting, and the casual attitude of the British about population.
Another feature of Westernization is that it creates many intercontradictory forces that, instead of consolidating, contradict each other:
- In the political and cultural fields, westernization has given birth not only to nationalism but also to revivalism, communalism, casteism, linguism, regionalism, etc.

Q1. How has Western culture impacted Indian society, particularly in terms of lifestyle, values, and traditions?
The impact of Western culture on Indian society has resulted in a complex interplay of cultural exchange, leading to changes in lifestyle, values, and traditions. This influence is evident in various aspects, including clothing, cuisine, language, education, and entertainment. Westernization has also contributed to the evolution of social norms, family structures, and gender roles within the Indian context.
Q2. What does ‘Westernization’ signify in the field of sociology?
In sociology, ‘Westernization’ refers to the process by which societies adopt Western cultural, social, political, and economic practices. This often involves the adoption of Western values, ideologies, institutions, and technologies, which can lead to significant shifts in the cultural and social fabric of the adopting society. Westernization is a multidimensional concept that can impact various aspects of a society’s structure and functioning.
Q3. Where can I find reliable information about Westernization in sociology, particularly in a PDF format?
There are several reputable academic sources and research papers available online that delve into the topic of Westernization in sociology. To find PDFs specifically, consider searching academic databases, online repositories, or university websites that provide access to scholarly articles, journals, and research papers related to the sociological aspects of Westernization.
Q4. How does the concept of Westernization relate to the syllabus of the UPSC (Union Public Service Commission) examination in India?
In the context of the UPSC examination in India, the concept of Westernization is often relevant in understanding the sociocultural dynamics of modern Indian society and its historical development. Candidates must grasp the sociological dimensions of Westernization, including its impact on Indian society, culture, and governance. Aspiring candidates can refer to relevant books, journals, and scholarly articles that provide insights into the dynamics of Westernization in India for their preparation.
In case you still have your doubts, contact us on 9811333901.
For UPSC Prelims Resources, Click here
For Daily Updates and Study Material:
Join our Telegram Channel – Edukemy for IAS
- 1. Learn through Videos – here
- 2. Be Exam Ready by Practicing Daily MCQs – here
- 3. Daily Newsletter – Get all your Current Affairs Covered – here
- 4. Mains Answer Writing Practice – here
Visit our YouTube Channel – here
- Ahmedabad Mill Strike (1918) – UPSC Modern History Notes
- Evaluation of Khilafat and Non-Cooperation Movements – UPSC Modern History Notes
- Revolutionary Activities Abroad – UPSC Modern History Notes
- The INA Rebellion – Modern History Notes
Edukemy Team
Changes and impact of british policies in india – modern..., western thoughts and education – modern history notes, rise of regional states – upsc modern history notes, rise of british supremacy in india – modern history notes, socio-religious reform movement – modern history notes, reasons for the emergence of revolutionary activities – upsc modern..., the government of india act 1935 – upsc modern history..., the revolt of 1857 – overview and causes – upsc..., women’s movement in india – upsc modern history notes, indian national movement – upsc modern history notes, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Our website uses cookies to improve your experience. By using our services, you agree to our use of cookies Got it
Keep me signed in until I sign out
Forgot your password?
A new password will be emailed to you.
Have received a new password? Login here

- Our Centers Delhi Bhubaneswar Lucknow
- My Schedule
- Payment History
- Help/Support
- Profile Settings
UPSC SYLLABUS
Indian society (indian society (mains)), upsc syllabus.
- Indian Society
- Indian Society (Mains)
- Ancient History
- Medieval India
- Modern History
- Modern India (Mains)
- Indian Culture (Prelims)
- Indian Culture (Mains)
- Post Independence Consolidation (Mains)
- World History (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: PIC (Mains)
- Geography (Prelims)
- Physical Geography: World & India (Mains)
- Economic & Human Geography (Mains)
- Indian Polity And Governance (Prelims)
- Features Of Indian Polity & Constitution (Mains)
- Executive, Judiciary, Legislature (Mains)
- Governance (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Features of Indian Polity & Constitution (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: (Executive, Judiciary, Legislature) (Mains)
- Constitutional/Non-Constitutional Bodies
- Contemporary Issues: Governance (Mains)
- International Relations (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: International Relations (Mains)
- Economy (Prelims)
- Sectors Of Indian Economy (Mains)
- Policy & Reforms In Indian Economy (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Sectors Of Indian Economy (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Policy & Reforms In Indian Economy (Mains)
- Science And Technology (Prelims)
- General Science (Prelims)
- Science And Technology (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Science & Technology (Mains)
- Environment (Prelims)
- Environment (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Environment (Mains)
- Internal Security Challenges In India (Mains)
- Contemporary Issues: Internal Security Challenges In India (Mains)
- Ethics (Mains)
- Applied Ethics
- Salient features of Indian Society
- Diversity of India
- Effects of globalization on Indian society
- National Integration, communalism, regionalism & secularism
- Role of women and women’s organization
- Social empowerment, poverty and developmental issues
- Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable section
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources
- Issues relating to poverty and hunger
- Inclusive growth and issues arising from it.
Unity in Diversity
- Concepts of Unity and Diversity
- Forms of Diversity in India
- Reasons for so much Diversity
- Bonds of Unity In India
- Geo-political Unity
- The Institution of Pilgrimage
- Tradition of Accommodation
- Tradition of Interdependence
- Role of Sensitive Leaders
- Constitutional Safeguards – Role of Constitution Framers
Challenges of Diversity to Unity (Challenges to National Integration)
- Diversity of Constituents
- Regionalism and Cultural Identities
- Communalism
- Social Inequalities
- Regional Disparities
- Ethno-Nationality and Ethnic Conflicts
- Tribal Identity
- Basic Sociological Concepts
- The Family and Kinship
- Concept of Patriarchy In India
- Secularism And Secularization
- Western and Indian Concept
- Process of Secularization
- Secularism and Forced Conversion in India
Regionalism, Communalism, Fundamentalism and communal Violence
- Regionalism
- Regionalism in India
- Types of Regionalism
- Effects of Regionalism
- Regionalism: Demand for Smaller States
- Strategies to tackle Regionalism
- Sons of Soil Concept
- Communilism Concept, Orgin, Impact
- Fundamentalism-religious, Cultural
- Communal Violence
Social Empowerment
- Constitutional Provisions Relevant to Social Justice & Empowerment of Scheduled Caste & Scheduled Tribes
- Status of Minorities In India
The Scheduled Castes: From Untouchable to Dalit
- Population of the Scheduled Castes
- Types of Disabilities of the SCs
- From Untouchables to the Dalits: The Process of Identity Formation
- Combating Mechanism against Caste Atrocities and Violence
- The State Efforts for Dalit Emancipation
- Identify Political Implications on Dalits
Tribals in India
- Chronic Indebtedness
- Forest Related Problems
- Destruction of the Forest Environment and the Tribal People
- Development and Displacement
- Analysis of Forest Rights Act
Women Movements
- 19th Century Women Movements – Under Social Reform Movements
- Women’s Issues During Gandhian Era
- Issues in Post Independence Era
- Violence Against Women
- Developmental Movement
- Uniform Civil Code
- Feminism and Post Feminism
Social Justice
- Concept of Casteism in India
- Caste and Politics
- The Reservation Policy Debate
- Social Justice and Social Development
Social Security In India
- Social Security System in India
- Organized Sector and Social Security
- Unorganised Sector and Social Security
- Centrally Funded Social Assistance Programmes
- Public Initiatives
- Review of the implementation of Social Security Laws in the Country
- Suggestions for Improving the Social Security Matrix
- Social security code for all
Understanding Poverty
- Dimensions of Poverty
- Linkage between Poverty and Development
- Recommendations of Rangarajan Committee Report
- Poverty Alleviation Strategy Since Independence
- Programmes for Poverty Alleviation
- Concept of Inequality
Globalization
- Meaning of Globalization
- Reasons for Globalization
- Dimensions/Impact
- Cultural and Social
- Anti-Globalization Movement
- New Localism
- NPM (New public management)
Urbanization & Census 2011
- Urbanization
- Trend and pattern of Urbanization
- Issues Related to Urbanization in India
- Status of Service Delivery and Governance
- Urban Development Projects
- Critical Analysis of Smart City Mission
- SDG’s and urbanization
Census 2011
- Highlights of 2011 Census
- Analysis of Sex Ratio Data
- Impact of Skewed Ratio
- Laws related to Prevent Female Infanticide
- Recent initiatives
- Trend and Current Scenario of Literacy in India
- Literacy Challenges in India as Whole
- Efforts to Improve the Literacy in Country
- Child Health Indicators and Maternal Health
- Initiatives taken by the Government
- Why the Health schemes fail to bring change?
- Family Planning and Population Policy of India
- Analysis on Status of Old Age Population: Issues & Policy Initiative
- Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011
Contemporary Issues
- Secularism and Anti Conversion
- Regionalism: Demand for Smaller States
- Socio-Economic Caste Census, 2011
- Gender Discrimination in the Corporate Sector
Issues Related to Women
- Gender Discrimination in Corporate Sector
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Bill on Banning Triple Talaq
- Issues of women entry to place of worship
- Adultery No Longer a Crime : SC
- Unwanted Girls in India
- Altruistic Surrogacy in India
- Women in Panchayats
- Women Participation in Economy
- # Me Too Movement
- Draft National Policy for Women, 2016
- Laws Related to Stalking in India
- Debate on the Issue of Marital Rape
- India’s Maternity Laws need Serious Tweaking
- Women in Judiciary Matters
- SC’s Judgment on Dowry
- Gender Budgeting: Critical Analysis
Issues Related to Children
- Issues Faced by Children in War Zone
- High Dropout Rate of Girls in India
- Child Trafficking
- Safety of Children in Schools
- Issue of Malnutrition in India
- Amendments Proposed in Child Labour Act
- Plight of Street Children
- Juvenile Justice System
- Child Marriages in India
- Death for child Rape
- Draft National Child Protection Policy
- National Action Plan for Children, 2016
Other Issues
- India’s Family Planning Programme: Critical Analysis
- Demography and Policy Planning
- India’s Ageing Report
- Legalising Same Sex Marriage
- Domestic Workers: Issues and Laws
- Development Leading to Displacement
- Moral Policing
- Euthanasia and Living Will
- Inadequacies in existing Human Trafficking laws in India
- Transgender Bill passed in Lok Sabha with Amendments
- Mental Health Care Bill
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act
- Manual Scavenging
- Mob lynching and Rule of Law
- Issue Related to Under trials
- Income Inequality in India
- Indigenous People in India : An Analysis
- Debate Over Death Penalty
- Global Slavery Index Report
- Right to Privacy Judgement
- SC Verdict on SC/ST Atrocities Bill
- Social Stigma Attached with HIV
Health & Education
- Status Health sector
- Status of Education sector
- Allied Health Care Professions Bill, 2018
- Ahead on Malaria: On reduction in cases in India
- India and Neglected Disease Treatment
- TB Status in India and Bedaquiline Patent Challenge
- Status of E-Pharmacies in India
- Changes Proposed in No Detention Policy
- National Policy on Education
- Capacity Building for Primary Health Care
- NITI Aayog on Privatisation of Urban Health Care
- National Health Policy, 2017
- Regulating Private Healthcare
- India’s Nutrition Challenge
- Food Fortification
- Sanitation and Nutrition Linkage
- Ayushman Bharat
Miscellaneous
- Is social media polarizing society?
- Online political adverstising and challenge for democracy and society
- Draft Social Security Code
- Critical Analysis of Stand Up India Scheme
- SC Suggests for Prison Reforms
- Statue of Unity

Verifying, please be patient.
Our Centers
DELHI (Karol Bagh)
GS SCORE, 1B, Second Floor, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Get directions on Google Maps
BHUBANESWAR (Jaydev Vihar)
GS SCORE, Plot No.2298, Jaydev Vihar Square, Near HCG Day Care, BBSR - 751013
LUCKNOW (Aliganj)
GS SCORE, 2nd Floor, B-33, Sangam Chauraha, Sector H, Aliganj, Lucknow, UP - 226024
Delhi (Karol Bagh) Centre
GS SCORE, Second Floor, Metro Tower, 1B, Pusa Road, Karol Bagh, New Delhi - 110005 (Beside Karol Bagh Metro Station Gate No. 8)
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +91 8448496262
Classroom / online / Live programs
- Mains Classes
- Mains Advance Classes
- Ethics & Essay Classes
- IAS Foundation
- Aadhar:NCERT Foundation
- Target PT:Prelims Classes
- Current Affairs Mentorship Program
TEST SERIES/ MENTORSHIP
- ITS:Integrated Test Series
- GS Mains Q&A (Mentorship & Test Series)
- GS TEST SERIES
- Ethics & Essay Test Series
- Samarth - Mains Answer Writing
STUDY MATERIAL
- PRELIMS STUDY MATERIAL
- MAINS STUDY MATERIAL
- MAINS ANSWER WRITING WORKBOOK
OTHER COURSES
- OPTIONAL FOUNDATION COURSES
- OPTIONAL Q&A (TEST SERIES)
- Mains Previous Year Questions
- © 2024 - IAS SCORE
All Rights Reserved.
Welcome to our secure login portal. Access your account with ease.

- Using Password
Not registered yet? register here!
Welcome to our secure register portal. For a brighter future, register now and unlock endless learning opportunities.
User Register
Already have an account? Login
Oops, forgot your password? Don't worry, we've got you covered. Reset it here
Lost your login details? No problem! forgot your password in just a few clicks
Forgot Password
Verify your mobile number, you have successfully logged in.
Join Us on WhatsApp

Impact of globalization on Indian culture | Sociology Optional for UPSC Civil Services Examination | Triumph IAS

Table of Contents
IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN CULTURE
Relevant for ups-cse general studies paper 1 (impact of globalization of indian society).
GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN CULTURE
Globalization is a process of increasing interdependence, interconnectedness and integration of economies and societies to such an extent that an event in one part of the globe affects people in other parts of world.
The effect of globalization is far reaching. It affects us all but affects us differently. Thus, while for some it may mean new opportunities, for others the loss of livelihood. Women silk spinners and twisters of Bihar lost their jobs once the Chinese and Korean silk yarn entered the market. Weavers and consumers prefer this yarn as it is somewhat cheaper and has a shine.
Similar displacements have come with the entry of large fishing vessels into Indian waters. These vessels take away the fish that used to be earlier collected by Indian fishing vessels. The livelihood of women fish sorters, dryers, vendors and net makers thereby get affected. In Gujarat, women gum collectors, who were picking from the ‘julifera’ (Baval trees), lost their employment due to the import of cheaper gum from Sudan. In almost all cities of India, the rag pickers lost some of their employment due to import of waste paper from developed countries.
It is obvious that globalization is of great social significance. But its impact on different sections of society is very different. There are, therefore, sharply divided views about the impact of globalization regarding its effect. Some believe that it is necessary to herald a better world.
Impact of Globalization on Indian Culture
- There are many ways that globalization affects culture. Over the ages India has had an open approach to cultural influences and has been enriched because of this. The last few decades have seen major cultural changes leading to fears that our local cultures would be overtaken. Thus there are heated debates in our society not just about political and economic issues but also about changes in clothes, styles, music, films, languages, body language. The debate is not new and 19th century reformers and early nationalists also debated on culture and tradition. The issues today are in some ways the same, in some ways different. What is perhaps different is the scale and intensity of change.
- A central contention is that all cultures will become similar, that is homogeneous. Others argue that there is an increasing tendency towards globalization of culture. Globalization refers to the mixing of the global with the local. It is not entirely spontaneous. Nor is it entirely delinked from the commercial interests of globalization. It is a strategy often adopted by foreign firms while dealing with local traditions in order to enhance their marketability. In India, we find that all the foreign television channels like Star, MTV, Channel V and Cartoon Network use Indian languages. Even McDonald sells only vegetarian and chicken products in India and not its beef products, which are popular abroad. McDonald’s goes vegetarian during the Navaratri festival . In the field of music, one can see the growth of popularity of ‘ Bhangra pop ’, ‘Indi pop’, fusion music and even remixes.
- Joint family has been adversely affected due to globalization. There has been an increase in nuclear families. This can be clearly manifested in the increasing number of old age homes that are present now. The diversity in family forms has given way to a dominance of nuclear family in the globalized India
- Due to opening up of food joints like McDonalds, KFC across the country, there has been a homogenization of food available across the country, but there has also been heterogenization in food. Old restaurants are now replaced by Mc. Donalds . Fast food and Chinese dishes have replaced juice corners and Parathas.
- Borrowing of money has become more acceptable now as compared to the past. Taking loans is very common due to increasing access to financial institutions
- In place of old cinema halls, multiplex theatres are coming up.
- Use of English has increased manifold in urban areas, this has led to a homogenization in language across the country, but the rural areas have been less affected by it.
Globalization of Culture
- India has its unique cuisine, but the cuisines of foreign countries have become more easily available, they are modified to suit the taste buds of Indians (like Paneer Tikka Burger in McDonalds) . This has led to a wide variety of food being available, leading to heterogenization French, German and Spanish are taught to students right from school level along with indigenous languages, this is an exemplification of hybridization of culture
- Popularity of foreign movies has increased, Hollywood, Chinese, French and Korean movies are quite popular among the urban youth. Along with this, dubbing of these foreign movies in local languages is testimony of increased glocalization. Festivals: celebrations of Valentines’ day, Friendship day are examples of change in cultural values related to festival. However, along with these new days, traditional festivals are celebrated with equal enthusiasm.
- Importance of marriage is decreasing, there has been an increase in divorce, increase in live-in relationships, and single parenting is increasing. Marriage used to be considered as bonding of the souls; but today marriage is becoming professional and contractual. However, despite change in forms of marriage, it has not declined as an institution.
Revival of Culture
- Revival of Yoga in the country as well as in the international level. This can be seen in the popularity of the ‘Art of Living’ course by Ravi Shankar, or the celebration of International Yoga day across the world
- There has been a revival of ayurvedic medicines in the country as well as outside it.
- Due to increasing uncertainty by inter-linkage with the outside world, there has been religious revivalism. This can be manifested in the use of religion to attract voters, or mobilizing people on the basis of religion.
- Increasing demand for local handicraft products in global market, such as Chikenkari or bandhani.
- Due to increasing global tourism, locals are making efforts to preserve their diversity and revive their traditions.
All these changes have led to drastic changes to Indian culture, though most of these changes are confined to the urban areas, but the rural areas are fast catching up. We can see that the western culture is influencing the Indian culture, but it is not replacing it, rather there is a mixture of both cultures. It is to be noted that culture cannot be seen as an unchanging fixed entity that can either collapse or remain the same when faced with social change. What is more likely even today is that globalization will lead to the creation of not just new local traditions but global ones too.

To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and participation in the Best Sociology Optional Coaching. These avenues provide comprehensive assistance, ensuring a solid understanding of sociology’s diverse methodologies and techniques.
Impact of Globalization, Indian Culture, Social Significance, Globalization of Culture, Revival of Culture, Nuclear Families, Revival, Social Structures, Chikenkari or bandhani
Why Vikash Ranjan’s Classes for Sociology?
Proper guidance and assistance are required to learn the skill of interlinking current happenings with the conventional topics. VIKASH RANJAN SIR at TRIUMPH IAS guides students according to the Recent Trends of UPSC, making him the Best Sociology Teacher for Sociology Optional UPSC.
At Triumph IAS, the Best Sociology Optional Coaching platform, we not only provide the best study material and applied classes for Sociology for IAS but also conduct regular assignments and class tests to assess candidates’ writing skills and understanding of the subject.
Choose T he Best Sociology Optional Teacher for IAS Preparation?
At the beginning of the journey for Civil Services Examination preparation, many students face a pivotal decision – selecting their optional subject. Questions such as “ which optional subject is the best? ” and “ which optional subject is the most scoring? ” frequently come to mind. Choosing the right optional subject, like choosing the best sociology optional teacher , is a subjective yet vital step that requires a thoughtful decision based on facts. A misstep in this crucial decision can indeed prove disastrous.
Ever since the exam pattern was revamped in 2013, the UPSC has eliminated the need for a second optional subject. Now, candidates have to choose only one optional subject for the UPSC Mains , which has two papers of 250 marks each. One of the compelling choices for many has been the sociology optional. However, it’s strongly advised to decide on your optional subject for mains well ahead of time to get sufficient time to complete the syllabus. After all, most students score similarly in General Studies Papers; it’s the score in the optional subject & essay that contributes significantly to the final selection.
“A sound strategy does not rely solely on the popular Opinion of toppers or famous YouTubers cum teachers.”
It requires understanding one’s ability, interest, and the relevance of the subject, not just for the exam but also for life in general. Hence, when selecting the best sociology teacher, one must consider the usefulness of sociology optional coaching in General Studies, Essay, and Personality Test.
The choice of the optional subject should be based on objective criteria, such as the nature, scope, and size of the syllabus, uniformity and stability in the question pattern, relevance of the syllabic content in daily life in society, and the availability of study material and guidance. For example, choosing the best sociology optional coaching can ensure access to top-quality study materials and experienced teachers. Always remember, the approach of the UPSC optional subject differs from your academic studies of subjects. Therefore, before settling for sociology optional , you need to analyze the syllabus, previous years’ pattern, subject requirements (be it ideal, visionary, numerical, conceptual theoretical), and your comfort level with the subject.
This decision marks a critical point in your UPSC – CSE journey , potentially determining your success in a career in IAS/Civil Services. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose wisely, whether it’s the optional subject or the best sociology optional teacher . Always base your decision on accurate facts, and never let your emotional biases guide your choices. After all, the search for the best sociology optional coaching is about finding the perfect fit for your unique academic needs and aspirations.
Follow us :
🔎 https://www.instagram.com/triumphias
🔎 www.triumphias.com
🔎https://www.youtube.com/c/TriumphIAS
🔎 https://t.me/VikashRanjanSociology
Find More Blogs
One comment.
Hey there! Your essay was rather eye-opening, but I couldn’t help but notice that you, in your admirable attempt to convey the widespread effects of globalisation in our country, may have conveyed what can be best described as unsubstantiated hearsay and anecdotal evidence as proof of your claims. I would love to see some data regarding the various points you’ve gone over in your essay. Cheers.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Civilsdaily
No. 1 UPSC IAS Platform for preparation
UPSC Mains Topic-Wise PYQs – Indian Culture

We will be going through the UPSC Mains Topic-Wise PYQs – Indian Culture. The official UPSC Syllabus reads – Indian Culture – Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
Before starting by yourself for Mains, understand the process. Connect 1:1 with Arvind Sir
Read More – Complete UPSC Mains Topic-Wise PYQs (2013-2023)
Don’t know how to make notes for UPSC Mains? Learn 1:1 from Arvind Sir
Join the community, join us across social media platforms..

Your better version awaits you!

Essay on Cultural Diversity in India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Cultural Diversity in India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Cultural Diversity in India
Introduction to cultural diversity.
India is famously known for its rich cultural diversity. It is a land where people of different religions, castes, and ethnic groups live together, each contributing to the country’s unique cultural fabric.
Religious Diversity
India is home to many religions, including Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, and Jainism. Each religion has its own set of rituals, festivals, and traditions, which adds to the cultural richness.
Language Diversity
India is a linguistically diverse country with over 1600 spoken languages. Every state has its own language, and people take pride in their linguistic heritage.
Art and Cuisine
Indian art and cuisine vary greatly from region to region. The music, dance, and food of each area are influenced by its history, geography, and local traditions. This diversity in art and cuisine is a testament to India’s cultural richness.
In conclusion, cultural diversity is one of India’s greatest strengths. It fosters a sense of unity in diversity, making India a vibrant and inclusive nation.
250 Words Essay on Cultural Diversity in India
Introduction.
India, often referred to as a ‘melting pot’ of cultures, stands as a testament to the confluence of diverse traditions, religions, and languages. Its cultural diversity is a rich tapestry woven with threads of myriad hues, each representing a unique cultural facet.
India is the birthplace of religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism, which coexist with Islam, Christianity, Zoroastism, Judaism, and others. Each religion has contributed to the cultural mosaic of India, leaving indelible imprints on its art, architecture, literature, music, and dance.
Linguistic Diversity
The linguistic diversity in India is astonishing, with the constitution officially recognizing 22 languages. Each language has its literature, folklore, and scripts, contributing to the cultural richness of the nation.
Social and Cultural Practices
The social and cultural practices in India vary significantly across its length and breadth. Festivals like Diwali, Eid, Christmas, Pongal, Baisakhi, and many others are celebrated with great fervor, each having its unique customs and traditions.
Indian art, ranging from classical dance forms to folk arts like Madhubani and Warli, showcases the cultural diversity. Indian cuisine, with its wide range of regional dishes, reflects the diversity in its culinary practices.
The cultural diversity of India is a testament to its pluralistic society, which embraces differences and promotes unity in diversity. It is this cultural diversity that makes India a vibrant and dynamic nation, offering a rich cultural experience.
500 Words Essay on Cultural Diversity in India
Introduction to cultural diversity in india.
India, often hailed as the epitome of cultural diversity, is a country where myriad cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexist in harmony. This cultural diversity is the cornerstone of India’s pluralistic society and has shaped its history, politics, and social fabric.
Cultural Mosaic: Languages and Religions
India is home to over 2,000 distinct ethnic groups and more than 1,600 spoken languages. This linguistic diversity is a testament to the country’s cultural richness. Each language carries its unique folklore, literature, and art forms, contributing to the cultural mosaic of the nation.
Similarly, India’s religious diversity is unparalleled. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism originated here, and the country also houses substantial populations of Muslims, Christians, and other religious communities. These religions, with their unique rituals, festivals, and philosophies, add to the cultural kaleidoscope of India.
Art, Music, and Dance
Indian art, music, and dance forms are as diverse as its languages and religions. Each region boasts its distinct classical and folk music and dance styles. For instance, Kathakali from Kerala, Bharatanatyam from Tamil Nadu, and Kathak from North India are renowned dance forms, each with its unique storytelling method.
Similarly, Indian music ranges from the classical Carnatic and Hindustani styles to various folk traditions. Indian art, too, displays a wide range from Madhubani paintings of Bihar to Warli art of Maharashtra, each narrating a tale of its people and history.
Cuisine and Clothing
Indian cuisine, known for its flavors and spices, also mirrors the country’s cultural diversity. Each region has its culinary specialities, influenced by local produce, climate, and historical interactions. For example, coastal regions like Kerala and Goa have seafood-based cuisine, while Rajasthan’s arid climate has led to the development of a cuisine rich in dairy products and grains.
Clothing in India also varies regionally, reflecting local climatic conditions, traditions, and influences. From the ‘sarees’ and ‘dhotis’ of the south to the ‘pherans’ and ‘pathanis’ of the north, Indian attire is a vibrant display of its cultural diversity.
Challenges and Opportunities
While cultural diversity is India’s strength, it also poses challenges. Communal tensions, regional disparities, and language conflicts are some issues that stem from this diversity. However, these challenges also provide opportunities for dialogue, mutual understanding, and unity in diversity.
Cultural diversity in India is an enriching and complex tapestry of traditions, beliefs, and practices. It is a testament to the country’s historical openness to different cultures, its adaptability, and its inherent pluralism. This diversity, while posing challenges, also provides a framework for mutual respect and coexistence, making India a fascinating study in cultural diversity.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Cashless India
- Essay on National Flag of India
- Essay on Fit India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
One Comment
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


SIMPLIFYING UPSC IAS EXAM PREPARATION
- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

[Mission 2024] STATIC QUIZ, 1 June 2024 – History

Quiz-summary
0 of 5 questions completed
Information
We will post 5 questions daily on static topics mentioned in the UPSC civil services preliminary examination syllabus. Each week will focus on a specific topic from the syllabus, such as History of India and Indian National Movement, Indian and World Geography, and more.
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You have to finish following quiz, to start this quiz:
0 of 5 questions answered correctly
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 points, ( 0 )
- Not categorized 0%
1 . Question
With respect to Indian freedom struggle, how is the word “Swadeshi” different from “boycott”?
- While Swadeshi attracted the lower strata of Indian society, Boycott attracted the higher strata.
- Swadeshi was essentially economic movement, boycott was not.
Select the correct answer code:
- c) Both 1 and 2
- d) Neither 1 nor 2
Solution: d)
The people had adopted the twin programme of ‘Boycott’ and ‘Swadeshi ‘ as parts of one and the same movement. These two words are two sides of the same coin and both were used as economic as well as political tools. Boycott referred to the boycott of British goods in order to register protest with the British public against the grave injustice inflicted upon Bengal. Boycott was a seemingly negative programme and Swadeshi as its positive corollary was accepted along with. Swadeshi meant use of, and encouragement to, native products as against foreign goods. Thus, the Boycott and Swadeshi movement brought all classes of Indian society, particularly in Bengal to a common platform for a national cause.
2 . Question
Consider the following statements regarding Home Rule League Movement.
- Home Rule League Movement was the Indian response to the First World War.
- Jawaharlal Nehru, Mohammad Ali Jinnah and Madan Mohan Malaviya supported the Home Rule agitation.
- The Russian Revolution of 1917 led to the decline of the Home Rule League Movement.
How many of the above statements is/are correct?
- (a) Only one
- (b) Only two
- (c) All three
Solution: b)
Statement 3 is incorrect.
The Home Rule Movement was the Indian response to the First World War.
The Indian Home Rule Leagues were organized on the lines of the Irish Home Rule Leagues and they represented the emergence of a new trend of aggressive politics. Annie Besant and Tilak were the pioneers of this new trend.
The Home Rule agitation was later joined by Motilal Nehru, Jawaharlal Nehru , Bhulabhai Desai, Chittaranjan Das, Madan Mohan Malaviya , Mohammad Ali jinnah , Tej Bahadur Sapru and Lala Lajpat Rai. Some of these leaders became heads of local branches.
The League campaign aimed to convey to the common man the message of Home Rule as self-government. The Russian Revolution of 1917 proved to be an added advantage for the Home Rule campaign.
3 . Question
Consider the following statements.
- A Khilafat Committee was formed in 1915 to defend the Khalifa’s temporal powers.
- Muhammad Ali and Shaukat Ali, two prominent leaders, decided to boycott the Khilafat Committee.
Which of the above statements is/are incorrect?
Solution: c)
The Khilafat committee was formed in the aftermath of the First World War (ending in 1919).
Post-war, there were rumours that a harsh peace treaty was going to be imposed on the Ottoman emperor – the spiritual head of the Islamic world (the Khalifa).
To defend the Khalifa’s temporal powers, a Khilafat Committee was formed in Bombay in March 1919.
A young generation of Muslim leaders like the brothers Muhammad Ali and Shaukat Ali, began discussing with Mahatma Gandhi about the possibility of a united mass action on the issue.
Gandhiji saw this as an opportunity to bring Muslims under the umbrella of a unified national movement.
At the Calcutta session of the Congress in September 1920, he convinced other leaders of the need to start a non-cooperation movement in support of Khilafat as well as for swaraj.
4 . Question
The Ghadar party was
- A revolutionary organization
- Founded in Punjab
- Aiming at securing India’s independence from British rule
- a) Only one
- b) Only two
- c) All three
Statement 2 is incorrect.
The Ghadr Party was a revolutionary group organized around a weekly newspaper The Ghadr with its headquarters at San Francisco and branches along the US coast and in the Far East with the aim of securing India’s independence from British rule.
Key members included Lala Har Dayal, Sohan Singh Bhakna, Abdul Hafiz Mohamed Barakatullah, Kartar Singh Sarabha, and Rashbehari Bose.
5 . Question
Consider the following statements regarding Morley-Minto Reforms
- It retained official majority in the Central Legislative Council but allowed the provincial legislative councils to have non-official majority.
- It introduced a system of communal representation for Muslims by accepting the concept of ‘separate electorate’.
- It granted franchise to a limited number of people on the basis of property, tax or education.
Features of Act of 1909:
- It retained official majority in the Central Legislative Council but allowed the provinciallegislative councils to have non-official majority.
- It introduced a system of communal representation for Muslims by accepting the concept of‘separate electorate’. Under this, the Muslim members were to be elected only by Muslim
Government of India Act of 1919 granted franchise to a limited number of people on the basis of property, tax or education.
Join our Official Telegram Channel HERE for Motivation and Fast Updates
Subscribe to our YouTube Channel HERE to watch Motivational and New
Join our Twitter Channel HERE
Follow our Instagram Channel HERE
Follow us on LinkedIn : HERE

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

COMMENTS
Indian society is represented by a set of local cultural traits like local languages, different food choices, dressing styles, classical music, family structure, cultural values, etc. There has been a growing sense of insecurity among the Indian masses regarding the gradual degradation or loss of our local identity.
Best IAS UPSC coaching in India India's narrative tradition is a testament to its rich cultural heritage, offering timeless wisdom and universal themes that resonate across different eras and societies.
The previously mentioned salient features of Indian society very well define how the factors have influenced the diverse yet united culture of Indian society. There have been instances in history wherein the unity of the country was tested like during the partition, communal riots in Gujarat and Karnataka are a few dark chapters. But each time ...
In times of global divisiveness, India's composite culture stands tall as a testament to the strength and beauty of unity in diversity. Why Sociology for Success in CSE. To master these intricacies and fare well in the Sociology Optional Syllabus, aspiring sociologists might benefit from guidance by the Best Sociology Optional Teacher and ...
Thus, diversity means variety of races, of religions, of languages, of castes and of cultures. Unity means integration. It is a social psychological condition. It connotes a sense of one- ness, a sense of we-ness. It stands for the bonds, which hold the members of a society together. Unity in diversity essentially means "unity without ...
Insights IAS: Simplifying UPSC IAS Exam Preparation. InsightsIAS has redefined, revolutionized and simplified the way aspirants prepare for UPSC IAS Civil Services Exam. Today, it's India's top website and institution when it comes to imparting quality content, guidance and teaching for the IAS Exam.
Institutions Responsible: The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) under the Ministry of Culture, is the premier organization for the archaeological research and protection of the cultural heritage of the nation. It administers more than 3650 ancient monuments, archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
Indian Society - Syllabus, Strategy Overview [UPSC Exam] Indian Society is one of the important subjects in the UPSC syllabus. The subject finds its mention in Prelims, Mains and Optional papers of the IAS Exam. This article will help you get an overview of the Indian Society syllabus, the right strategy to prepare for it and also relevant ...
Indian Culture based questions can be asked in Civil Services Exam - prelims and mains. As per the latest UPSC syllabus for IAS mains exam, Indian Culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature, and Architecture from ancient to modern times. The topic comes under UPSC Civil Services Mains General Studies Paper 1.
2. Impact of Globalization on Indian Culture Student Notes: There are many ways that globalization affects culture. Over the ages India has had an open approach to cultural influences and has been enriched because of this. The last few decades have seen major cultural changes leading to fears that our local cultures would be overtaken.
UPSC Essay Topics on Art and Culture. The UPSC Essay Topics related to Indian society, art, and culture cover a wide range of subjects, offering great diversity. To gain knowledge about the static content on these topics, you should rely on fundamental books on society, as recommended for the exam. Here is a list of UPSC Essay Topics on Indian ...
Essay on Indian Culture: Indian culture is one of the oldest and unique cultures worldwide. It has influenced many foreign countries due to its richness in heritage and diverse paths. Indian culture is splendid in its traditions, customs, art forms, food and cuisines, music and dance forms, etc. The joint family system, elaborate weddings ...
Summary. The effects of globalization on Indian society are manifold and have been discussed in detail. The process of globalization has changed the industrial pattern and social life of people. This has had an immense impact on Indian trade, finance, and cultural system. The globalization of the economic, social, and cultural structures ...
Critically examine the effects of globalization on the aged population in India. Growing feeling of regionalism is an important factor in the generation of demand for a separate state. Discuss. History of Modern India (UPSC Mains) - Previous Year Questions. 2023 Do you think marriage as a sacrament is loosing its value in Modern India?
Westernization - Features and Impact on Indian Society - UPSC Modern History Notes. by Edukemy Team October 12, 2023. Westernization is a process whereby societies come under or adopt Western culture in areas such as industry, technology, law, politics, economics, lifestyle, diet, clothing, language, alphabet, religion, philosophy, and values.
UPSC Syllabus. Salient features of Indian Society. Diversity of India. Effects of globalization on Indian society. National Integration, communalism, regionalism & secularism. Role of women and women's organization. Social empowerment, poverty and developmental issues. Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre ...
Bridging the gender gap: There is a desperate need to bridge the gender gap in Indian social structure. Focus should be on increasing literacy and economic opportunity for women. Modernity will usher in the Indian society when its women possess a modern rational view of culture and are not bound by rudimentary practices like Patriarchy.
Explore the effects of Globalisation on Indian society—benefits like economic growth and challenges such as threats to local industries and agriculture. ... Political History of South India | UPSC Ancient History Notes; MAURYAN EMPIRE (322-185 BCE): Reign, Ruler & Historical Significance ... Danes in India: Colonial Legacy. Cultural Exchange ...
IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN CULTURE RELEVANT FOR UPS-CSE GENERAL STUDIES PAPER 1 (IMPACT OF GLOBALIZATION OF INDIAN SOCIETY). GLOBALIZATION ON INDIAN CULTURE. Globalization is a process of increasing interdependence, interconnectedness and integration of economies and societies to such an extent that an event in one part of the globe affects people in other parts of world.
We will be going through the UPSC Mains Topic-Wise PYQs - Indian Culture. The official UPSC Syllabus reads - Indian Culture - Salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times. Before starting by yourself for Mains, understand the process. Connect 1:1 with Arvind Sir. Talk to our Mentor.
Effects of globalization on Indian society. Turn your IAS dreams into reality with Best IAS Coaching in Bangalore. Expert guidance, comprehensive IAS coaching, and proven success. Best IAS|UPSC coaching in India.
500 Words Essay on Cultural Diversity in India Introduction to Cultural Diversity in India. India, often hailed as the epitome of cultural diversity, is a country where myriad cultures, religions, languages, and traditions coexist in harmony. This cultural diversity is the cornerstone of India's pluralistic society and has shaped its history ...
We will post 5 questions daily on static topics mentioned in the UPSC civil services preliminary examination syllabus. Each week will focus on a specific topic from the syllabus, such as History of India and Indian National Movement, Indian and World Geography, and more.