- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support

Overview of the Problem-Solving Mental Process
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Rachel Goldman, PhD FTOS, is a licensed psychologist, clinical assistant professor, speaker, wellness expert specializing in eating behaviors, stress management, and health behavior change.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Rachel-Goldman-1000-a42451caacb6423abecbe6b74e628042.jpg)
- Identify the Problem
- Define the Problem
- Form a Strategy
- Organize Information
- Allocate Resources
- Monitor Progress
- Evaluate the Results
Frequently Asked Questions
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue.
The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything they can about the issue and then using factual knowledge to come up with a solution. In other instances, creativity and insight are the best options.
It is not necessary to follow problem-solving steps sequentially, It is common to skip steps or even go back through steps multiple times until the desired solution is reached.
In order to correctly solve a problem, it is often important to follow a series of steps. Researchers sometimes refer to this as the problem-solving cycle. While this cycle is portrayed sequentially, people rarely follow a rigid series of steps to find a solution.
The following steps include developing strategies and organizing knowledge.
1. Identifying the Problem
While it may seem like an obvious step, identifying the problem is not always as simple as it sounds. In some cases, people might mistakenly identify the wrong source of a problem, which will make attempts to solve it inefficient or even useless.
Some strategies that you might use to figure out the source of a problem include :
- Asking questions about the problem
- Breaking the problem down into smaller pieces
- Looking at the problem from different perspectives
- Conducting research to figure out what relationships exist between different variables
2. Defining the Problem
After the problem has been identified, it is important to fully define the problem so that it can be solved. You can define a problem by operationally defining each aspect of the problem and setting goals for what aspects of the problem you will address
At this point, you should focus on figuring out which aspects of the problems are facts and which are opinions. State the problem clearly and identify the scope of the solution.
3. Forming a Strategy
After the problem has been identified, it is time to start brainstorming potential solutions. This step usually involves generating as many ideas as possible without judging their quality. Once several possibilities have been generated, they can be evaluated and narrowed down.
The next step is to develop a strategy to solve the problem. The approach used will vary depending upon the situation and the individual's unique preferences. Common problem-solving strategies include heuristics and algorithms.
- Heuristics are mental shortcuts that are often based on solutions that have worked in the past. They can work well if the problem is similar to something you have encountered before and are often the best choice if you need a fast solution.
- Algorithms are step-by-step strategies that are guaranteed to produce a correct result. While this approach is great for accuracy, it can also consume time and resources.
Heuristics are often best used when time is of the essence, while algorithms are a better choice when a decision needs to be as accurate as possible.
4. Organizing Information
Before coming up with a solution, you need to first organize the available information. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? The more information that is available the better prepared you will be to come up with an accurate solution.
When approaching a problem, it is important to make sure that you have all the data you need. Making a decision without adequate information can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
5. Allocating Resources
Of course, we don't always have unlimited money, time, and other resources to solve a problem. Before you begin to solve a problem, you need to determine how high priority it is.
If it is an important problem, it is probably worth allocating more resources to solving it. If, however, it is a fairly unimportant problem, then you do not want to spend too much of your available resources on coming up with a solution.
At this stage, it is important to consider all of the factors that might affect the problem at hand. This includes looking at the available resources, deadlines that need to be met, and any possible risks involved in each solution. After careful evaluation, a decision can be made about which solution to pursue.
6. Monitoring Progress
After selecting a problem-solving strategy, it is time to put the plan into action and see if it works. This step might involve trying out different solutions to see which one is the most effective.
It is also important to monitor the situation after implementing a solution to ensure that the problem has been solved and that no new problems have arisen as a result of the proposed solution.
Effective problem-solvers tend to monitor their progress as they work towards a solution. If they are not making good progress toward reaching their goal, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies .
7. Evaluating the Results
After a solution has been reached, it is important to evaluate the results to determine if it is the best possible solution to the problem. This evaluation might be immediate, such as checking the results of a math problem to ensure the answer is correct, or it can be delayed, such as evaluating the success of a therapy program after several months of treatment.
Once a problem has been solved, it is important to take some time to reflect on the process that was used and evaluate the results. This will help you to improve your problem-solving skills and become more efficient at solving future problems.
A Word From Verywell
It is important to remember that there are many different problem-solving processes with different steps, and this is just one example. Problem-solving in real-world situations requires a great deal of resourcefulness, flexibility, resilience, and continuous interaction with the environment.
Get Advice From The Verywell Mind Podcast
Hosted by therapist Amy Morin, LCSW, this episode of The Verywell Mind Podcast shares how you can stop dwelling in a negative mindset.
Follow Now : Apple Podcasts / Spotify / Google Podcasts
You can become a better problem solving by:
- Practicing brainstorming and coming up with multiple potential solutions to problems
- Being open-minded and considering all possible options before making a decision
- Breaking down problems into smaller, more manageable pieces
- Asking for help when needed
- Researching different problem-solving techniques and trying out new ones
- Learning from mistakes and using them as opportunities to grow
It's important to communicate openly and honestly with your partner about what's going on. Try to see things from their perspective as well as your own. Work together to find a resolution that works for both of you. Be willing to compromise and accept that there may not be a perfect solution.
Take breaks if things are getting too heated, and come back to the problem when you feel calm and collected. Don't try to fix every problem on your own—consider asking a therapist or counselor for help and insight.
If you've tried everything and there doesn't seem to be a way to fix the problem, you may have to learn to accept it. This can be difficult, but try to focus on the positive aspects of your life and remember that every situation is temporary. Don't dwell on what's going wrong—instead, think about what's going right. Find support by talking to friends or family. Seek professional help if you're having trouble coping.
Davidson JE, Sternberg RJ, editors. The Psychology of Problem Solving . Cambridge University Press; 2003. doi:10.1017/CBO9780511615771
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. Published 2018 Jun 26. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
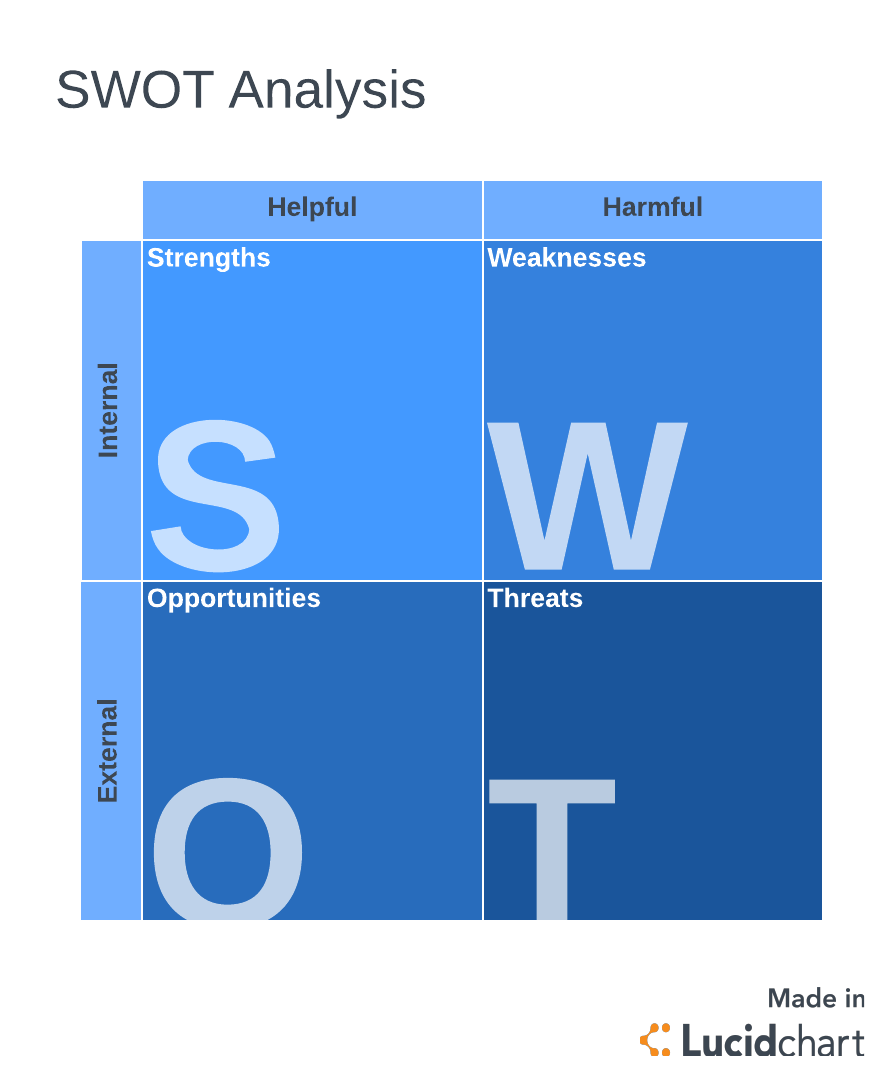
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Problem Solving? A Comprehensive Guide
In this blog, we will explore "What is Problem Solving?" In detail. From defining the nature of Problem Solving to understanding the key process in resolving issues, this blog covers it all. So, wait no more; let’s go deeper into this fundamental concept.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Introduction to Management
- Personal & Organisational Development
- Workforce Resource Planning Training
- Supervisor Training
- Introduction to Managing Budgets

Table of contents
1) What is Problem Solving definition?
2) The process of Problem Solving
3) Key skills for effective Problem Solving
4) Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
5) Problem Solving tools and techniques
6) Conclusion
What is Problem Solving definition?

The process of Problem Solving
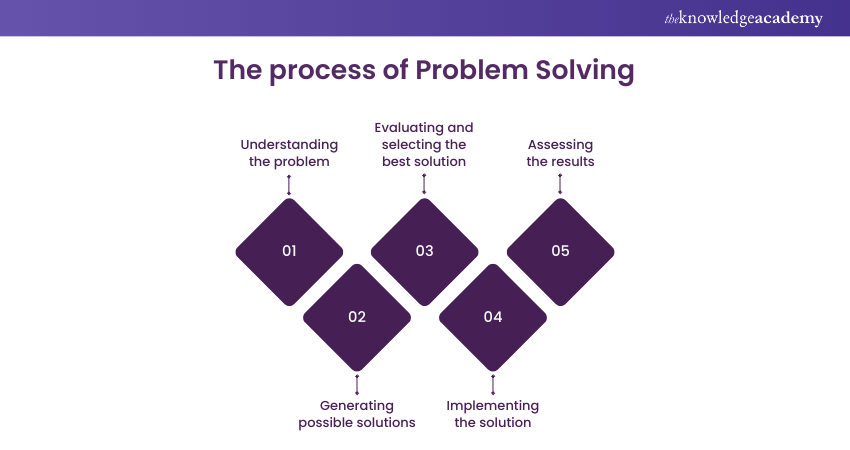
Understanding the problem
The first step in Problem Solving is gaining a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Take the time to thoroughly analyse the problem and gather relevant information. Ask yourself questions like:
1) What is the nature of the problem?
2) What are the factors contributing to the problem?
3) What are the desired outcomes?
4) Are there any constraints or limitations to consider?
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the problem, you lay a solid foundation for finding an effective solution.
Generating possible solutions
Once you have a clear grasp of the problem, it's time to brainstorm potential solutions. Encourage creativity and think outside the box. Consider all possible options without judgment or criticism. The goal at this stage is to generate a variety of ideas and alternatives.
Evaluating and selecting the best solution
After generating a list of possible solutions, it's important to evaluate each option based on its feasibility, effectiveness, and alignment with the desired outcome. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each and every solution. Assess its practicality and the resources required for implementation.
Additionally, take into account the potential risks and benefits associated with each solution. Consider any potential consequences or impacts on other aspects. Based on this evaluation, select the solution that appears most viable and promising.
Implementing the solution
Once you have chosen the best solution, it's time to put it into action. Develop a detailed plan outlining the necessary steps and allocate the required resources. Determine responsibilities and deadlines to ensure a smooth implementation process.
During implementation, monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments or adaptations. Stay proactive and address any challenges or obstacles that may arise along the way. Effective communication and collaboration with others involved in the process can greatly contribute to successful implementation.
Assessing the results
After implementing the solution, it's essential to assess the results. Evaluate whether the problem has been properly resolved or if further adjustments are required. Analyse the outcomes and compare them against the desired goals and expectations.
Consider whether the chosen solution has brought about the intended benefits and if any unexpected consequences have emerged. Reflect on the overall effectiveness of the Problem Solving process and identify any lessons learned for future reference.
Remember, Problem Solving is an iterative process, and it's not uncommon to revisit and refine solutions based on ongoing evaluation and feedback. Embrace a continuous improvement mindset and be open to seeking alternative approaches if necessary.
By following this Problem Solving process, you can approach challenges systematically and increase your chances of finding effective solutions. Remember that practice and experience play a vital role in honing your skills.
Master the art of solving problems and become a catalyst for innovation and success with our Problem Solving Training – sign up now!
Key skills for effective Problem Solving
What one must do to become an effective problem solver is to develop key skills that enhance your Problem Solving abilities. The skills give you the ability to tackle challenges with a strategic mind and find the needed solutions. Below is a dive into the most important of them:
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that includes the objective analysis of information, considering different viewpoints, and being able to arrive at a sensible judgment. This helps you to assess problems with the right accuracy in judgment and also find suitable solutions.
It means that creativity is the ability of a person to think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions. It includes pressing the mind toward new possibilities and viewing the problem in different ways.
Analytical skills
In this ability, there is the aspect of breaking down a problem into subunits that helps in identifying the patterns, relationships, and causes within the problem.
Decision-making
Sound skills in decision making call for the assessment of the pros and cons of all solutions provided and thus choosing the best alternative. Risks must always be considered with the benefits any alternative might bring.
Strategies for enhancing Problem Solving abilities
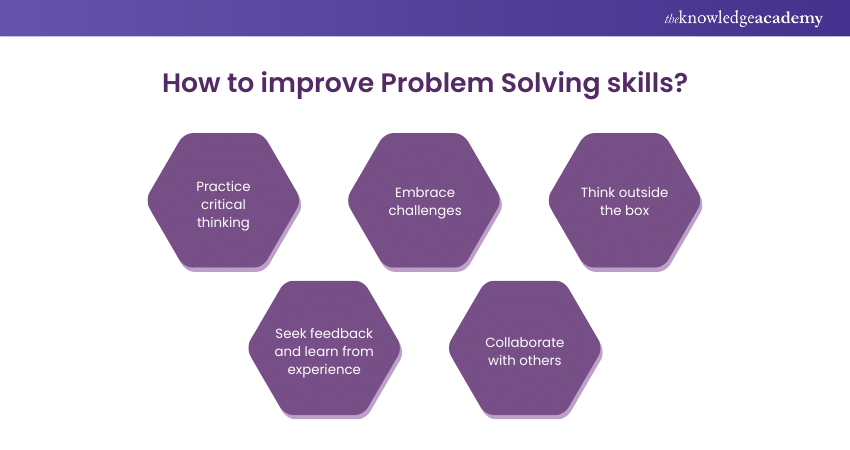
Practice critical thinking
Engage yourself in activities which require critical thinking, including solving puzzles, complex discussion, challenging all assumptions. This will increase your ability to enhance sharpening of your analytical skills and let you think critically at a time when problems are in your way.
Seek feedback and learn from experience
Seek responses from your mentors, course peers, and Problem Solving experts. From the successes and failures, reflect on the reasons for the occurrences over previous experiences and point out what could be improved. Treat the opportunity of Problem Solving as one of the chances that shall be given to you to grow and develop each time you make it through a problem.
Embrace challenges
You can redesign your problematic issues and take every challenge coming across as an opportunity for growth. Hence, it paves the way for the ability of resilience and strengthens your Problem Solving abilities.
Collaborate with others
In Problem Solving, collaboration is embraced by pooling different perspectives and ideas. Work with others in activities that involve groups to discuss issues and seek input from others, listening actively to various viewpoints. Working collaboratively with others helps expand your knowledge of various ways of Problem Solving and encourages innovation.
Think outside the box
Encourage creative thinking by exploring unconventional ideas and solutions. Challenge every assumption and all its related alternatives. Shift to this kind of mindset, and it can drive innovative Problem Solving strategies, letting you uncover newer ways to solve age-old complex problems.
Problem Solving tools and techniques
When faced with complex problems, utilising specific tools and techniques can help facilitate the solving process and lead to more effective solutions. Here are some commonly used Problem Solving tools and techniques:
Root cause analysis
Root cause analysis is a methodology used to detect the underlying causes of a problem. It involves investigating the problem's symptoms and tracing them back to their fundamental causes. By addressing the root causes, Problem Solvers can prevent the issue from recurring.
Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats (SWOT) analysis
SWOT analysis is a planning tool that strategically helps measure the weaknesses and internal strengths of a situation. Moreover, it can find external opportunities and threats. By assessing these factors, Problem Solvers can gain insights into the current state and make informed decisions about potential solutions.
Fishbone diagrams
Fishbone diagrams, also known as cause-and-effect diagrams or Ishikawa Diagrams, visually represent the possible causes contributing to a problem. By organising causes into categories (such as people, process, equipment, and environment), Problem Solvers can systematically analyse the problem's potential sources.
Decision matrices
Decision matrices are used to evaluate and compare different options based on multiple criteria. This tool helps Problem Solvers weigh the importance of various factors and objectively assess each alternative, leading to an informed decision.
Six Thinking Hats
Six Thinking Hats is a technique initially developed by Edward de Bono that encourages parallel thinking by exploring different perspectives. Each "hat" represents a different thinking approach (e.g., logical, creative, emotional), allowing Problem Solvers to consider diverse viewpoints and generate innovative solutions.
These are just a few examples of Problem Solving tools and techniques. Depending on the nature of the problem, other methods, such as brainstorming, mind mapping, flowcharts, or Pareto analysis, can also be applied. Choosing the appropriate tool or technique depends on the specific problem and the desired outcome.
Navigate conflicts with finesse and foster collaboration with our transformative Conflict Management Training – sign up today!
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about What is Problem Solving? Developing effective skills is crucial for overcoming challenges, making informed decisions, and achieving success. By embracing problems as opportunities and applying strategic approaches, individuals can become proficient Problem Solvers in various domains of life.
Unlock your management potential and elevate your skills to new heights with our cutting-edge Management Training Courses – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
There are two major types of Problem Solving: Reflective and Creative. Regardless of the type, it focuses on understanding the issues, considering all factors and finding a solution.
Problem Solving in the workplace refers to an individual’s ability to manage difficult situations and find solutions to complex business issues.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses including Business Process Improvement Training, Performance Management Training and Introduction to Managing People. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Resource Planning Template .
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to musical instruments, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills as a Music Producer, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 23rd Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Search form

- Table of Contents
- Troubleshooting Guide
- A Model for Getting Started
- Justice Action Toolkit
- Best Change Processes
- Databases of Best Practices
- Online Courses
- Ask an Advisor
- Subscribe to eNewsletter
- Community Stories
- YouTube Channel
- About the Tool Box
- How to Use the Tool Box
- Privacy Statement
- Workstation/Check Box Sign-In
- Online Training Courses
- Capacity Building Training
- Training Curriculum - Order Now
- Community Check Box Evaluation System
- Build Your Toolbox
- Facilitation of Community Processes
- Community Health Assessment and Planning
- Section 1. An Introduction to the Problem-Solving Process
Chapter 17 Sections
- Section 2. Thinking Critically
- Section 3. Defining and Analyzing the Problem
- Section 4. Analyzing Root Causes of Problems: The "But Why?" Technique
- Section 5. Addressing Social Determinants of Health and Development
- Section 6. Generating and Choosing Solutions
- Section 7. Putting Your Solution into Practice
- Main Section
What is a problem?
Why is a group process particularly important, what is the problem-solving process.
"We must try to trust one another. Stay and cooperate." - Jomo Kenyatta, (1891 - 1978), former president of the Republic of Kenya
Imagine for a moment that your coalition's mission is to encourage development in a traditionally poor downtown neighborhood. Your first goal is to recruit members, but you find a lack of interest among area residents. So you work for months to convince people to join, and meet with some modest success. Then, at your first all-coalition meeting, you find that members don't want to work together. The students you have recruited don't trust the police officers who have shown up; the police officers, in turn, pay no attention to the students; and an argument has broken out in one corner of the room between a few fundamentalist Christians and gay rights activists. Your head is in your hands. You are halfway through your grant, and it seems that you haven't made any headway whatsoever towards your stated goal. What are you going to do now?
Problems are a fact of life at home, at play, and at work. Unfortunately, problems aren't always isolated cases. They tend to be like onions - you peel away one problem only to find another, and then another, and you can't solve the problem you were first interested in until you solve a variety of related problems. For example, you can't increase safety at a crosswalk until you hire more crossing guards. And nobody will apply for the job until you can increase the salary.
In short, we will always be confronted with problems, so the importance of problem solving can't be overstated. That's why this chapter of the Tool Box is focused wholly on the subject. Because most of us labor in groups or coalitions that are working together on an issue, we will focus primarily on the group problem-solving process.
So, what's a problem? How would you define one? We usually define a problem fairly negatively: a problem is a hassle, it's a pain in the neck. This is often true, but more generally, a problem can be considered the difference between what is , and what might or should be. And believe it or not, problems have their advantages, too. What are some of the good things about problems?
- Most problems are solvable (or partially solvable, or at least improvable). We can do something about them. The task may seem overwhelming (it surely did when David fought Goliath, or when suffragettes worked to give women the right to vote), but it's not hopeless. Our optimistic assumption is that we can change the world.
- Problems are opportunities to make some good things happen. If it weren't for problems, what would be our motivation to create change?
- Problems are also challenges . They call upon the best of our abilities, and ask us to go beyond what we thought we could do. They make life interesting, and, at least sometimes, fun. Without problems, life could be pretty boring.
You don't agree? Think of all of the games based on problem solving. Chess is thousands of years old and is still as popular as ever, based on the number of books you might find on it at your local bookstore. The Rubik's Cube was a national rage some years back. True, the stakes may be very different between a chess game and finding a way to connect with local young people. But both can present a challenge that stretches us in the same ways.
With all this in mind, what is "problem solving?" A good definition can be found in Lead on! The complete handbook for group leaders. The authors define problem solving as "an individual or collaborative process composed of two different skills: (1) to analyze a situation accurately, and (2) to make a good decision based on that analysis."
Why are we focusing on a collaborative process in this chapter? Well, for several reasons. You probably already do a lot of individual problem solving , and there's a good deal of merit in that. But many of the problems and challenges we face as members of our organizations affect everyone in the group. It makes sense then, that everyone is part of the solution. And, as the saying goes, two heads are better than one - so just imagine what can be accomplished with a room full of dedicated people!
Now, let's change the emphasis for a moment. Why are we focusing on a collaborative process in this chapter? Maybe your group is used to doing things haphazardly on an as-absolutely-necessary basis. Why should you take more time (already a precious commodity among most groups) to go through a lengthy process?
- Effective group processes enhance a group's ability to solve problems and make decisions. When working with more than just a couple of people, solving a problem with a set process becomes more manageable.
- It increases the group's efficiency and productivity.
- It increases the group's participation - more people tend to be involved, and, as a result,
- It increases group satisfaction. This means, among other things, that the group is more likely to want to take on other problems. And when they do so, they'll be better placed to solve them.
Like any other process, there are many different tasks that need to be done to properly solve problems. And again, like any other process, skipping some of the steps will make the job more difficult in the long run. Here is a brief explanation of each of the steps, to be discussed in more detail in the following sections:
- Running effective meetings - Since your work will be in a group, the first thing you need to understand is how to hold a good meeting. You may have the problem-solving process down pat, but that won't make any difference if nobody shows up at your meeting, or if no one pays attention to what goes on.
- Developing facilitation skills - Strong facilitation skills go hand in hand with running an effective meeting. A good facilitator helps diffuse explosive emotions, makes sure everyone's voice is heard, and steers the group towards the best decisions.
- Developing recorder skills - Again, these skills are part of running an effective meeting. A good recorder works hand in hand with the facilitator, and together, they make sure that not only are everyone's opinions heard, they are also seen, remembered, and followed up on. Having a good recorder is one of the most important parts of setting up an effective meeting.
- Defining and analyzing the problem - This is the core of the problem solving process. Sometimes, the real problem isn't originally apparent.
- Generating and choosing solutions
- Putting your solution into practice - If you have followed the process carefully, you'll be surprised at how easy implementing it actually is!
In Summary:
As we said before, the world is full of problems, and some of them look pretty challenging, to say the least. But the rewards are great. Solutions that are well thought out and carefully implemented can work. How much can you do?
Print Resources
Avery, M., Auvine, B., Streibel, B., & Weiss, L. (1981). A handbook for consensus decision making: Building united judgement . Madison, WI: Center for Conflict Resolution.
Dale, D., & Mitiguy, N. Planning, for a change: A citizen's guide to creative planning and program development .
Dashiell, K.A. (1990). Managing meetings for collaboration and consensus Honolulu, HI: Neighborhood Justice Center of Honolulu, Inc.
Interaction Associates, Inc. (1987). Facilitator institute handbook . San Francisco, CA: Author.
Lawson, L., Donant, F., & Lawson, J. (1982). Lead on! The complete handbook for group leaders . San Luis Obispo, CA: Impact Publishers.
Meacham, W. (1980). Human development training manual . Austin, TX: Human Development Training.
Morrison, E.(1994). Leadership skills: Developing volunteers for organizational success . Tucson, AZ: Fisher Books.

Problem Solving Skills for the Digital Age
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 6 min
Let’s face it: Things don’t always go according to plan. Systems fail, wires get crossed, projects fall apart.
Problems are an inevitable part of life and work. They’re also an opportunity to think critically and find solutions. But knowing how to get to the root of unexpected situations or challenges can mean the difference between moving forward and spinning your wheels.
Here, we’ll break down the key elements of problem solving, some effective problem solving approaches, and a few effective tools to help you arrive at solutions more quickly.
So, what is problem solving?
Broadly defined, problem solving is the process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. But you already knew that. Understanding problem solving frameworks, however, requires a deeper dive.
Think about a recent problem you faced. Maybe it was an interpersonal issue. Or it could have been a major creative challenge you needed to solve for a client at work. How did you feel as you approached the issue? Stressed? Confused? Optimistic? Most importantly, which problem solving techniques did you use to tackle the situation head-on? How did you organize thoughts to arrive at the best possible solution?
Solve your problem-solving problem
Here’s the good news: Good problem solving skills can be learned. By its nature, problem solving doesn’t adhere to a clear set of do’s and don’ts—it requires flexibility, communication, and adaptation. However, most problems you face, at work or in life, can be tackled using four basic steps.
First, you must define the problem . This step sounds obvious, but often, you can notice that something is amiss in a project or process without really knowing where the core problem lies. The most challenging part of the problem solving process is uncovering where the problem originated.
Second, you work to generate alternatives to address the problem directly. This should be a collaborative process to ensure you’re considering every angle of the issue.
Third, you evaluate and test potential solutions to your problem. This step helps you fully understand the complexity of the issue and arrive at the best possible solution.
Finally, fourth, you select and implement the solution that best addresses the problem.
Following this basic four-step process will help you approach every problem you encounter with the same rigorous critical and strategic thinking process, recognize commonalities in new problems, and avoid repeating past mistakes.
In addition to these basic problem solving skills, there are several best practices that you should incorporate. These problem solving approaches can help you think more critically and creatively about any problem:
You may not feel like you have the right expertise to resolve a specific problem. Don’t let that stop you from tackling it. The best problem solvers become students of the problem at hand. Even if you don’t have particular expertise on a topic, your unique experience and perspective can lend itself to creative solutions.
Challenge the status quo
Standard problem solving methodologies and problem solving frameworks are a good starting point. But don’t be afraid to challenge assumptions and push boundaries. Good problem solvers find ways to apply existing best practices into innovative problem solving approaches.
Think broadly about and visualize the issue
Sometimes it’s hard to see a problem, even if it’s right in front of you. Clear answers could be buried in rows of spreadsheet data or lost in miscommunication. Use visualization as a problem solving tool to break down problems to their core elements. Visuals can help you see bottlenecks in the context of the whole process and more clearly organize your thoughts as you define the problem.
Hypothesize, test, and try again
It might be cliche, but there’s truth in the old adage that 99% of inspiration is perspiration. The best problem solvers ask why, test, fail, and ask why again. Whether it takes one or 1,000 iterations to solve a problem, the important part—and the part that everyone remembers—is the solution.
Consider other viewpoints
Today’s problems are more complex, more difficult to solve, and they often involve multiple disciplines. They require group expertise and knowledge. Being open to others’ expertise increases your ability to be a great problem solver. Great solutions come from integrating your ideas with those of others to find a better solution. Excellent problem solvers build networks and know how to collaborate with other people and teams. They are skilled in bringing people together and sharing knowledge and information.
4 effective problem solving tools
As you work through the problem solving steps, try these tools to better define the issue and find the appropriate solution.
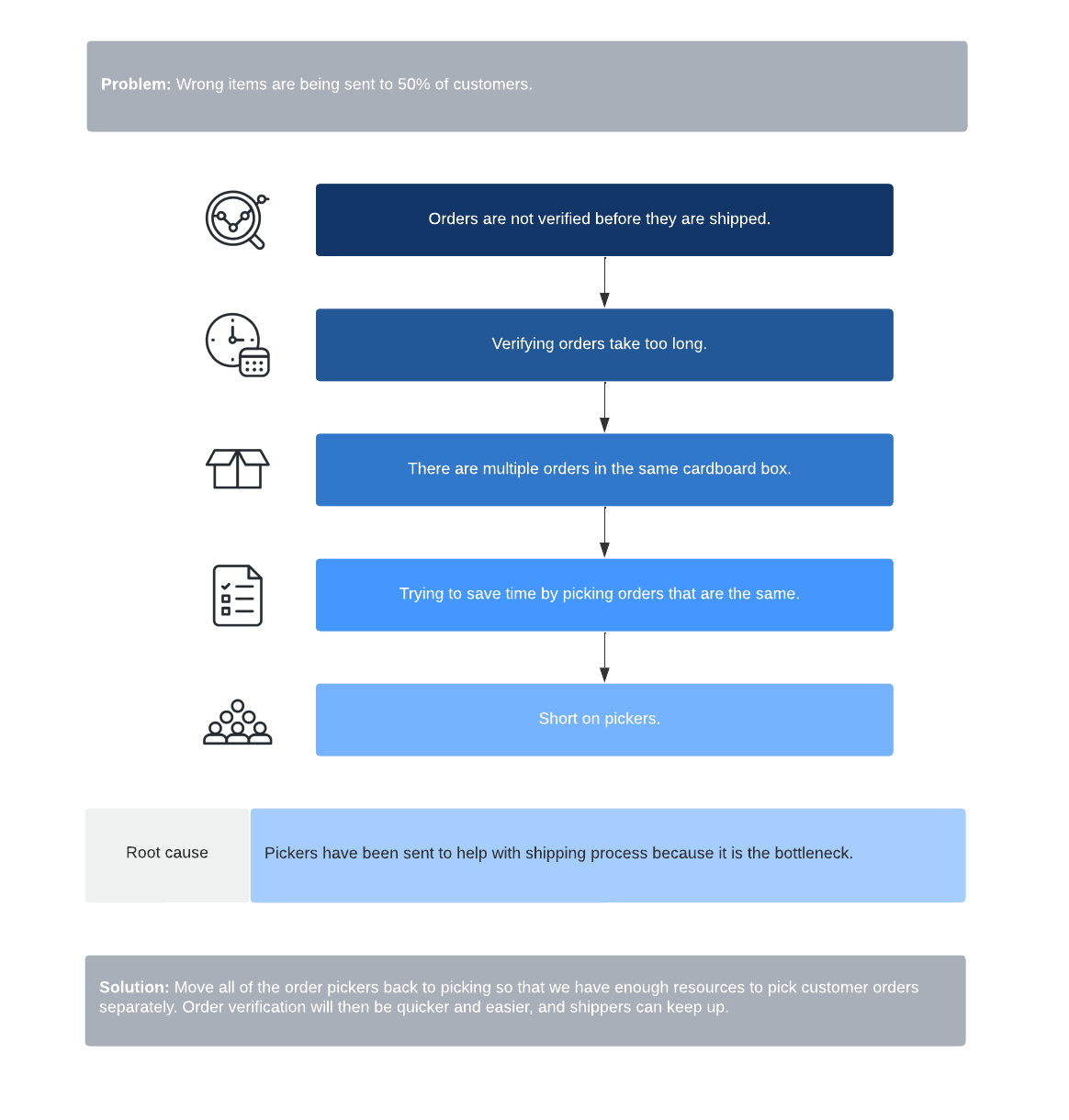
Root cause analysis
Similar to pulling weeds from your garden, if you don’t get to the root of the problem, it’s bound to come back. A root cause analysis helps you figure out the root cause behind any disruption or problem, so you can take steps to correct the problem from recurring. The root cause analysis process involves defining the problem, collecting data, and identifying causal factors to pinpoint root causes and arrive at a solution.
Less structured than other more traditional problem solving methods, the 5 Whys is simply what it sounds like: asking why over and over to get to the root of an obstacle or setback. This technique encourages an open dialogue that can trigger new ideas about a problem, whether done individually or with a group. Each why piggybacks off the answer to the previous why. Get started with the template below—both flowcharts and fishbone diagrams can also help you track your answers to the 5 Whys.
Brainstorming
A meeting of the minds, a brain dump, a mind meld, a jam session. Whatever you call it, collaborative brainstorming can help surface previously unseen issues, root causes, and alternative solutions. Create and share a mind map with your team members to fuel your brainstorming session.
Gap analysis
Sometimes you don’t know where the problem is until you determine where it isn’t. Gap filling helps you analyze inadequacies that are preventing you from reaching an optimized state or end goal. For example, a content gap analysis can help a content marketer determine where holes exist in messaging or the customer experience. Gap analysis is especially helpful when it comes to problem solving because it requires you to find workable solutions. A SWOT analysis chart that looks at a problem through the lens of strengths, opportunities, opportunities, and threats can be a helpful problem solving framework as you start your analysis.
A better way to problem solve
Beyond these practical tips and tools, there are myriad methodical and creative approaches to move a project forward or resolve a conflict. The right approach will depend on the scope of the issue and your desired outcome.
Depending on the problem, Lucidchart offers several templates and diagrams that could help you identify the cause of the issue and map out a plan to resolve it. Learn more about how Lucidchart can help you take control of your problem solving process .
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
How you can use creative problem solving at work.
Sometimes you're faced with challenges that traditional problem solving can't fix. Creative problem solving encourages you to find new, creative ways of thinking that can help you overcome the issue at hand more quickly.
Solve issues faster with the root cause analysis process
Root cause analysis refers to any problem-solving method used to trace an issue back to its origin. Learn how to complete a root cause analysis—we've even included templates to get you started.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .

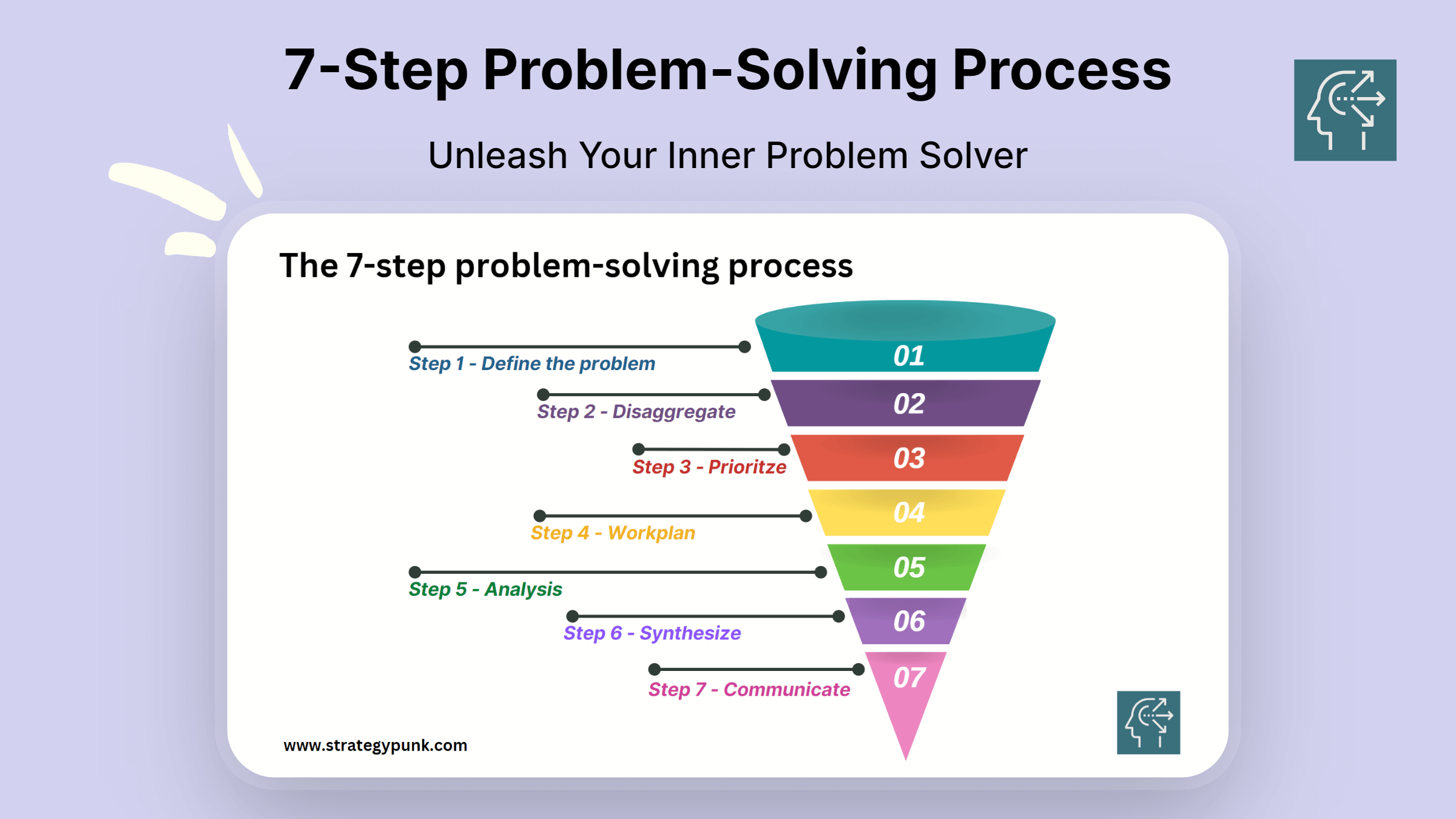
Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
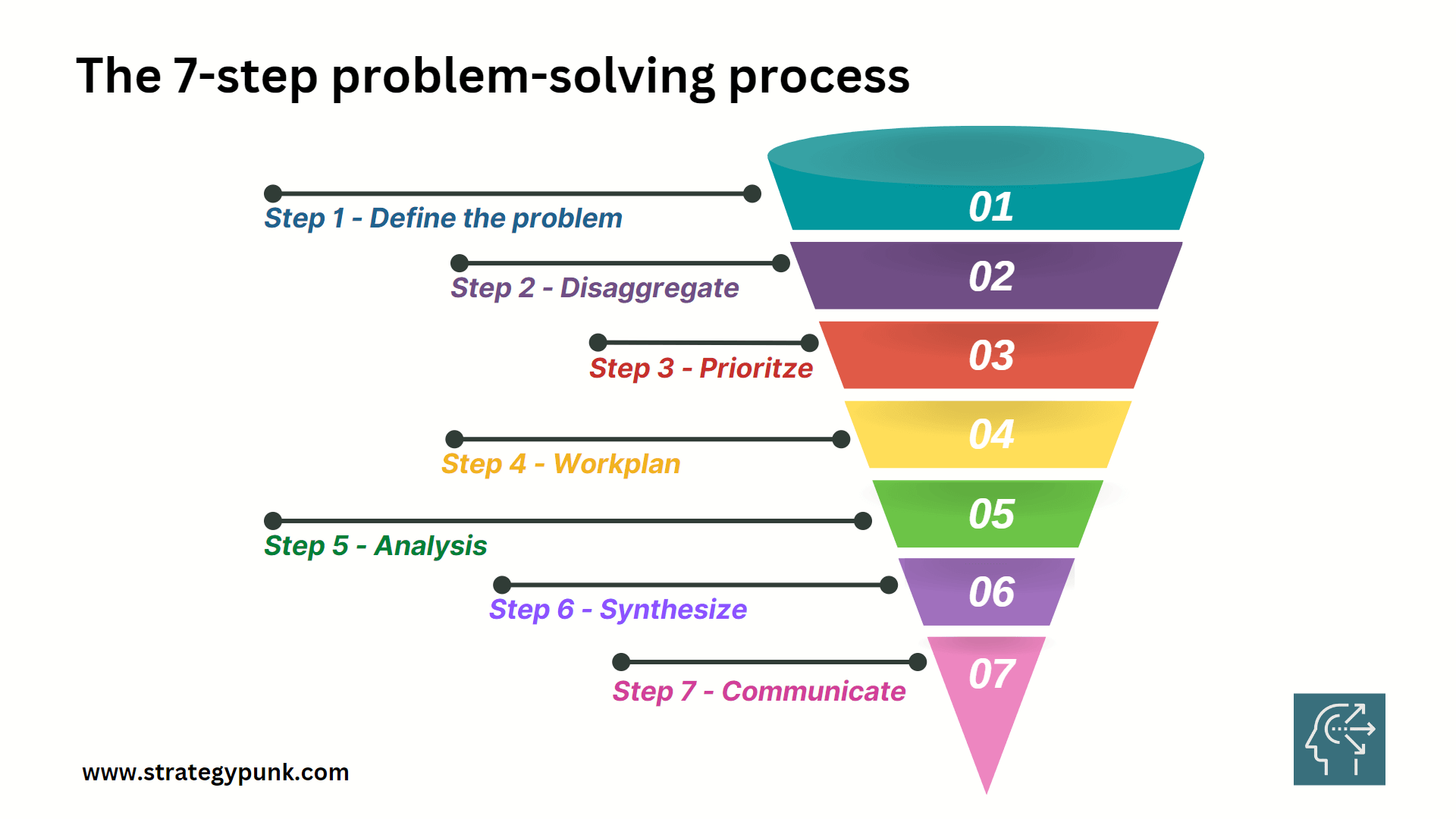
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate the definition to all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
It is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process, considering their concerns and needs. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. By using a combination of methods, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the decision-making process is successful. Stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal by communicating the findings clearly and concisely.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
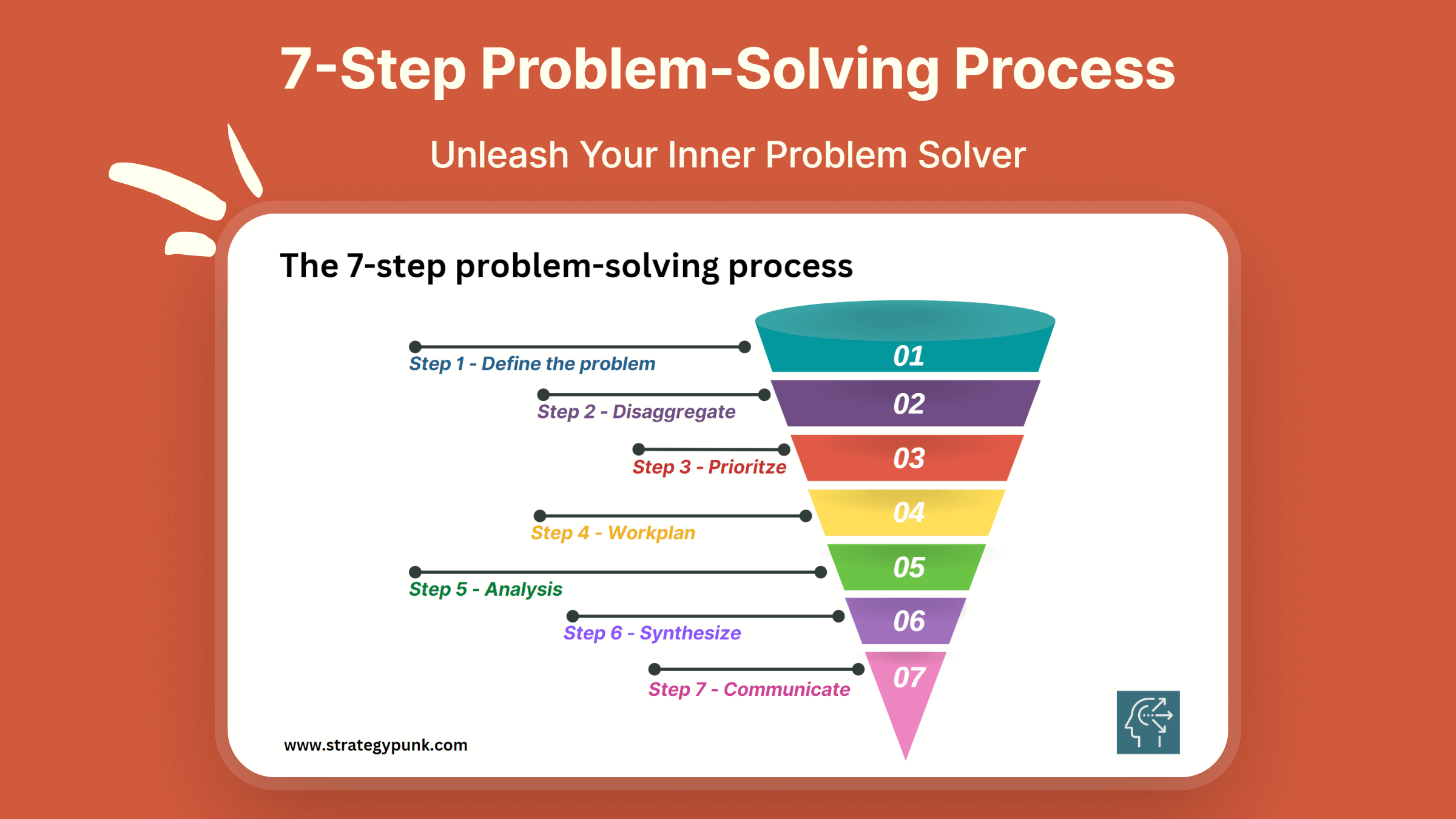
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.

7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

Lidl SWOT Analysis: Free PPT Template and In-Depth Insights
Discover Lidl's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with our free PowerPoint template. This in-depth SWOT analysis provides valuable insights to help you understand Lidl's market position and strategic direction.

Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Download our free PPT template for in-depth PESTLE insights into Nestlé's global strategy. Learn more today!

PESTLE Analysis: Decoding Reddit's Landscape (Free PPT)
Decode Reddit's global influence with our free PowerPoint PESTLE Analysis. Explore the hub of vibrant discussions and ideas.

Navigating the Terrain: A PESTLE Analysis of Lululemon (Free PowerPoint)
Explore Lululemon's business terrain with our free PESTLE analysis PowerPoint. Instant access!

Join our FREE training and learn the 5 things you can do to become a top 1% facilitator
What is problem-solving and how to do it right steps, processes, exercises.
The better your problem-solving skills are, the better (and easier!) your life will be. Organized problem-solving is a killer career skill - learn all about it here.
Whether we’re trying to solve a technical problem at work, or trying to navigate around a roadblock that Google Maps doesn’t see – most people are problem-solving every single day .
But how effective are you at tackling the challenges in your life? Do you have a bullet-proof process you follow that ensures solid outcomes, or... Do you act on a whim of inspiration (or lack thereof) to resolve your pressing problems?
Here’s the thing: the better your problem-solving skills are - the better (and easier!) your life will be (both professionally and personally). Organized problem-solving is a killer career (and life!) skill, so if you want to learn how to do it in the most efficient way possible, you’ve come to the right place.
Read along to learn more about the steps, techniques and exercises of the problem-solving process.
- 1. Do you want a Career in UX?
- Learn the Principles of UX Design
- Master a UX Design Tool
What is Problem-Solving?
We’re faced with the reality of having to solve problems every day, both in our private and professional lives. So why do we even need to learn about problem-solving? Aren’t we versed in it well enough already?
Well, what separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions. Or in other words, problem-solving allows you to knock out those problems with less effort.
Just like with any other skill, there’s an efficient way to solve problems, and a non-efficient one. While it might be tempting to go for the quickest fix for your challenge without giving it much thought, it will only end up costing you more time down the road. Quick fixes are rarely (if ever!) effective and end up being massive time wasters.
What separates problem-solving from dealing with the usual day-to-day issues is that it’s a distinct process that allows you to go beyond the standard approaches to solving a problem and allows you to come up with more effective and efficient solutions.
On the other hand, following a systemized clear process for problem-solving allows you to shortcut inefficiencies and time-wasters, turn your challenges into opportunities, and tackle problems of any scope without the usual stress and hassle.
What is the process that you need to follow, then? We’re glad you asked...
The Five Stages of Problem-Solving
So what’s the best way to move through the problem-solving process? There’s a 5-step process that you can follow that will allow you to solve your challenges more efficiently and effectively. In short, you need to move through these 5 steps:
- Defining a problem
- Ideating on a solution
- Committing to a course of action
- Implementing your solution
- And finally – analyzing the results.

Let’s look at each of those stages in detail.
Step 1: Defining The Problem
The first step might sound obvious, but trust us, you don’t want to skip it! Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, instead of being distracted by a myriad of other options, problems and issues that come up.
For once, you have to make sure you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it. For instance, if you keep losing users during your app onboarding process, you might jump to the conclusion that you need to tweak the process itself: change the copy, the screens, or the sequence of steps.
But unless you have clear evidence that confirms your hypothesis, your challenge might have an entirely different root cause, e.g. in confusing marketing communication prior to the app download.
Clearly defining and framing your challenge will help you guide your efforts and make sure you’re focussing on the things that matter, all the while ensuring that you’re trying to solve the root cause, and not trying to mend the symptoms of it
That’s why it’s essential you take a close look at the entire problem, not just at a fraction of it.
There are several exercises that can help you get a broader, more holistic view of the problem, some of our all-time favorites include Expert Interviews, How Might We, or The Map. Check out the step-by-step instructions on how to run them (along with 5 more exercises for framing your challenge!) here.
When in doubt, map out your challenge, and always try to tackle the bottlenecks that are more upstream - it’s likely that solving them will solve a couple of other challenges down the flow.
You also have to be mindful of how you frame the challenge: resist the urge to include a pre-defined solution into your problem statement. Priming your solutions to a predestined outcome destroys the purpose of following a step-by-step process in the first place!
Steer clear of formulations like:
We need to change the onboarding process... or We need to improve ad copy to increase conversions.
Instead, opt for more neutral, problem-oriented statements that don’t include a solution suggestion in them:
The drop off rate during the onboarding process is too high or Our ad conversion rates are below the norm.
Pro tip: Reframing your challenge as a ‘How Might We’ statement is a great way to spark up new ideas, opening your problem to a broader set of solutions, and is just a great way to reframe your problem into a more positive statement (without implying the possible solution!)
For example, following the onboarding drop-off rate problem we mentioned earlier, instead of framing it as a problem, you could opt for:
How Might We decrease the drop-off rate during the onboarding process?
Find out more about the best exercises for problem framing here!
Now that you have a clear idea of what you’re trying to solve, it’s move on to the next phase of the problem-solving process.
Learn more about facilitation and workshopping in our FREE FACILITATION COMMUNITY
Step 2: ideating a solution.
Get ready to roll up your sleeves and challenge the status quo! This step of the problem-solving process is all about thinking outside of the box, challenging old assumptions, and thinking laterally.
This stage is the one that tends to cause the most overwhelm in teams because it requires just the right balance of creativity and critical thinking, which tends to cause a lot of friction.
Our best advice?
Let go of the pressure to produce a polished, thought-through solution at this stage. You can hash out the details at a later point. Our goal right now is to come up with a direction, a prototype if you may, of where we want to move towards.
Embrace the “quantity over quality” motto, and let your creative juices flow! Now, we’re not saying you should roll with sub-par ideas. But you shouldn’t get too fixated on feasibility and viability just yet .
Your main goal during this step is to spark ideas, kick off your thinking process in the right direction, venture out of the familiar territories and think outside the box.
For the ideation to be the most effective your team will have to feel safe to challenge the norm and wide-spread assumptions. So lay judgment by side, there is no space for “that’s the way it’s always been done” in this step.
For your ideation sessions to be as efficient as possible, we highly recommend to run them in a workshop setting: this helps reduce the usual drawbacks of open discussions in teams (i.e. groupthink & team politics!)
Our favorite exercises to run during this phase include Lightning Demos, Sketching, and variations of Brainstorming. We crafted an entire article on how to run and facilitate these exercises in a separate article, so check it out of you’re going to be running an ideation session anytime soon!
Step 3: Choosing the Best Strategy & Committing
It’s time to decide which of the ideas that you generated in the last step will be the one you’ll implement.
This step is arguably the hardest one to complete smoothly: groupthink, team politics, differences in opinions and communication styles all make it very hard to align a team on a common course of action.
If you want to avoid the usual pitfalls of team decision-making, we recommend you steer clear of open unstructured discussion. While it’s useful in some scenarios, it’s a poor choice for when you need to make a decision, because it tends to reward the loudest people in the room, rather than give way to the best ideas.
It’s crucial you not only commit to a course of action but get full buy-in from the team. If your team members don’t understand the reasons for a decision, or are not fully onboard, the implementation of your decision will be half-hearted, and that’s definitely not what you want!
To achieve that, opt for anonymized, multi-layered voting, and include guided exercises like Storyboarding to prioritize your ideas.
We’ve gathered the list of our top-rated decision-making exercises, along with step-by-step instructions on how to run them in this article!
As a bonus tip, we recommend you involve a facilitator throughout the entire process. They will help align the team, and guide them through prioritizing and de-prioritizing solutions, as well as defining the next steps.
Pro tip : If you’re not the ultimate decision maker on the issue you’re trying to solve, make sure they’re in the room when the call is being made! Having a Decider in the room ensures that the decisions you come to will actually get executed on after, instead of getting shut down by your superiors after.
Join our FREE community and connect with other Facilitators and Workshoppers
Step 4: implementing your solution.
Here’s a truth that might be hard to swallow: it doesn’t matter how innovative, creative, or original your idea is, if your execution is weak.
One of our favourite illustrations of how this works in practice comes from the book “ Anything you want ” by Derek Sivers. He reveals that ideas should be treated as multipliers of execution. What this means is that a mediocre, “so-so” idea could be worth millions if executed well, while a “brilliant” idea can completely flop with bad execution.
That’s why this step is crucial if you want to really master the problem-solving process.
What do we mean by execution? Everything that happens after the whiteboards are wiped clean and your team starts to action the outcomes of your sessions, be it prototyping, development, or promotion.
But don’t just take our word for it, look at the example of how execution affected Nintendo’s sales:
In the past few years, Nintendo has come up with 3 products: the Wii, the Wii U and the Switch. Check out their sales figures on the graph below - Wii is the clear-cut leader, followed by Switch, and finally Wii U lagging behind.

The Wii was unbelievably successful - it was a genuinely unique, “brilliant”-level idea and it had a “brilliant” execution (20x $10 million = $200 million). It is one of the fastest selling game consoles of all time and it completely took over the market.
The next product was called Wii U and it was a “great” concept but the execution was absolutely terrible. So even though this product was very interesting and innovative, the end result was 15x $1,000 = $15,000.
Finally, Nintendo took the Wii U concept and tried it again with the Switch. The idea was “so so” as it was already done before, but the execution was “brilliant”. So, 5x $10 million = $50 million! Much better.

Bottom line?
The same idea can either make no dent in the market and damage your share price OR become a market hit and increase your share price dramatically. The only difference between the two scenarios – execution.
So shift your focus from coming up with crazy, innovative, outlandish ideas that will disrupt the market, and concentrate on really nailing down your execution instead.
This is likely the least “workshoppy” step out of the entire problem-solving process because it requires less alignment and decision-making and more..well.. Execution!
But hey, we wouldn’t be called “Workshopper” if we didn't offer you at least one way to optimize and workshopify (yup, we’re making it a thing) your execution process.
Cue in….prototyping.
We’re huge fans of prototyping all big solutions (and testing them!) The main reason?
This saves us time AND money! Prototyping and testing your solutions (especially if they’re time and investment-demanding) is a great way to make sure you’re creating something that is actually needed.
The key with prototyping the right way is to keep it simple. Don’t invest too much time, or resources into it. The goal is to gather data for your future decisions, not to create a near-to-perfect mockup of your solution.
There are LOADS of prototyping forms and techniques, and if you’d like to learn more on the subject you should definitely check out our extensive prototyping guide.
Step 5: Analyzing the Results
You’re nearly done, woo! Now that you have defined the right problem to tackle, brainstormed the solutions, aligned your team on the course of action, and put your plan into action it’s time to take stock of your efforts.
Seek feedback from all involved parties, analyze the data you’ve gathered, look at the bottom line of your efforts, and take a hard look at your problem: did it get solved? And even more than that, did the process feel smoother, easier, and more efficient than it normally is?
Running a retrospective is a great way to highlight things that went well and that you should keep for your next round of problem.solving, as well as pinpoint inefficiencies that you can eliminate.
But which kind of retrospective should you run? There are loads of options, and it’s easy to feel overwhelmed by them all, so we gathered our favorite retrospective variations in this article.
And there you have it, you just completed the cycle of problem-solving. We highly recommend you follow through with all the steps, without leaving any out. They all complement and build on each other, and it’s the combination of all 5 of them that makes the process effective.
Now that you have the problem solving process down, you might be wondering…
Do I need any special skills in order to be able to move through that process?
And the answer is… sort of! More in this in the next section.
Problem-Solving Skills
While your skill set will need to adapt and change based on the challenges you’ll be working on, most efficient problem-solvers have a solid foundation of these key skills:
- Active listening. While you might be the expert in the area of your challenge, there’s not a single person on Earth that knows it all! Being open to others’ perspectives and practicing active listening will come in very handy during step 1 of the process, as you’re trying to define the scope and the exact angle of the problem you’re working on.
- Analytical approach. Your analytical skills will help you understand problems and effectively develop solutions. You will also need analytical skills during research to help distinguish between effective and ineffective solutions.
- Communication. Is there a single area of expertise that DOESN’T require strong communication skills? We honestly don’t think so! Just like with any other life area, clear communication can make or break your problem-solving process. Being able to clearly communicate why you need to solve this challenge to your team, as well as align your team on the course of action are crucial for the success of the process.
- Decision-making. Ultimately, you will need to make a decision about how to solve problems that arise. A process without outcomes–regardless of how well thought-out and elaborate–is useless! If you want your problem-solving huddles to be effective, you have to come to grips with prioritization techniques and decision-making frameworks.
- Facilitation. Problem-solving revolves around being able to guide a group or a team to a common decision, and facilitation skills are essential in making that happen. Knowing how to facilitate will make it easy to keep the group focussed on the challenge, shortcut circular discussions, and make sure you’re moving along to solving the problem instead of just treading waters with fruitless discussions.
Not checking every single skill of your list just yet? Not to worry, the next section will give you practical tools on how to level up and improve your problem-solving skills.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
Just like with any other skill, problem-solving is not an innate talent that you either have or you don’t. There are concrete steps you can take to improve your skills.
Here are some things that will get you closer to mastering the problem-solving process:
- Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice makes perfect, and problem-solving skills are no exception! Seek opportunities to utilize and develop these skills any time you can.
If you don’t know where or how to start just yet, here’s a suggestion that will get you up and running in no time: run a quick problem-solving session on a challenge that has been bothering your team for a while now.
It doesn’t need to be the big strategic decision or the issue defining the future of the company. Something easy and manageable (like optimizing office space or improving team communication) will do.
As you start feeling more comfortable with the problem-solving techniques, you can start tackling bigger challenges. Before you know it, you’ll master the art of creative problem-solving!
- Use a tried and tested problem-solving workshop
Facilitation is one of the essential skills for problem-solving. But here’s the thing… Facilitation skills on their own won’t lead you to a solved challenge.
While being able to shortcut aimless discussions is a great skill, you have to make sure your problem-solving session has tangible outcomes. Using a tried and tested method, a workshop, is one of the easiest ways to do that.
Our best advice is to get started with a tried and tested problem-solving workshop like the Lightning Decision Jam . The LDJ has all the right ingredients for quick, effective problem solving that leads to tangible outcomes. Give it a go!
- Learn from your peers
You may have colleagues who are skilled problem solvers. Observing how those colleagues solve problems can help you improve your own skills.
If possible, ask one of your more experienced colleagues if you can observe their techniques. Ask them relevant questions and try to apply as many of the new found skills i your career as possible.
- Learn & Practice the best problem-solving exercises
Having a toolbox of problem-solving exercises to pull from that can fit any type of challenge will make you a more versatile problem-solver and will make solving challenges that much easier for you!
Once you get used to the groove of learning how to combine them into effective sessions or workshops, there’ll be no stopping you. What are some of the most effective problem-solving exercises? Glad you asked! We’ve gathered our favorite ones here, check it out!
And there you have it, you’re now fully equipped for running creative problem-sessions with confidence and ease! Whichever method or exercise you choose, remember to keep track of your wins, and learn as much as you can from your losses!
Anastasia Ushakova
Brand Strategist, Digital Marketer, and a Workshopper.


When Do You Need a Facilitator?
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Suspendisse varius enim in eros elementum tristique. Duis cursus.

The Ultimate Facilitation Glossary: 50 Facilitation Terms You Should Know (From A-Z)

How To Improve Team Collaboration

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 4 min read
The Problem-Solving Process
Looking at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself.
We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious complaint, require a significant amount of time, thought and investigation. Others, such as a printer running out of paper, are so quickly resolved they barely register as a problem at all.

Despite the everyday occurrence of problems, many people lack confidence when it comes to solving them, and as a result may chose to stay with the status quo rather than tackle the issue. Broken down into steps, however, the problem-solving process is very simple. While there are many tools and techniques available to help us solve problems, the outline process remains the same.
The main stages of problem-solving are outlined below, though not all are required for every problem that needs to be solved.
1. Define the Problem
Clarify the problem before trying to solve it. A common mistake with problem-solving is to react to what the problem appears to be, rather than what it actually is. Write down a simple statement of the problem, and then underline the key words. Be certain there are no hidden assumptions in the key words you have underlined. One way of doing this is to use a synonym to replace the key words. For example, ‘We need to encourage higher productivity ’ might become ‘We need to promote superior output ’ which has a different meaning.
2. Analyze the Problem
Ask yourself, and others, the following questions.
- Where is the problem occurring?
- When is it occurring?
- Why is it happening?
Be careful not to jump to ‘who is causing the problem?’. When stressed and faced with a problem it is all too easy to assign blame. This, however, can cause negative feeling and does not help to solve the problem. As an example, if an employee is underperforming, the root of the problem might lie in a number of areas, such as lack of training, workplace bullying or management style. To assign immediate blame to the employee would not therefore resolve the underlying issue.
Once the answers to the where, when and why have been determined, the following questions should also be asked:
- Where can further information be found?
- Is this information correct, up-to-date and unbiased?
- What does this information mean in terms of the available options?
3. Generate Potential Solutions
When generating potential solutions it can be a good idea to have a mixture of ‘right brain’ and ‘left brain’ thinkers. In other words, some people who think laterally and some who think logically. This provides a balance in terms of generating the widest possible variety of solutions while also being realistic about what can be achieved. There are many tools and techniques which can help produce solutions, including thinking about the problem from a number of different perspectives, and brainstorming, where a team or individual write as many possibilities as they can think of to encourage lateral thinking and generate a broad range of potential solutions.
4. Select Best Solution
When selecting the best solution, consider:
- Is this a long-term solution, or a ‘quick fix’?
- Is the solution achievable in terms of available resources and time?
- Are there any risks associated with the chosen solution?
- Could the solution, in itself, lead to other problems?
This stage in particular demonstrates why problem-solving and decision-making are so closely related.
5. Take Action
In order to implement the chosen solution effectively, consider the following:
- What will the situation look like when the problem is resolved?
- What needs to be done to implement the solution? Are there systems or processes that need to be adjusted?
- What will be the success indicators?
- What are the timescales for the implementation? Does the scale of the problem/implementation require a project plan?
- Who is responsible?
Once the answers to all the above questions are written down, they can form the basis of an action plan.
6. Monitor and Review
One of the most important factors in successful problem-solving is continual observation and feedback. Use the success indicators in the action plan to monitor progress on a regular basis. Is everything as expected? Is everything on schedule? Keep an eye on priorities and timelines to prevent them from slipping.
If the indicators are not being met, or if timescales are slipping, consider what can be done. Was the plan realistic? If so, are sufficient resources being made available? Are these resources targeting the correct part of the plan? Or does the plan need to be amended? Regular review and discussion of the action plan is important so small adjustments can be made on a regular basis to help keep everything on track.
Once all the indicators have been met and the problem has been resolved, consider what steps can now be taken to prevent this type of problem recurring? It may be that the chosen solution already prevents a recurrence, however if an interim or partial solution has been chosen it is important not to lose momentum.
Problems, by their very nature, will not always fit neatly into a structured problem-solving process. This process, therefore, is designed as a framework which can be adapted to individual needs and nature.
Join Mind Tools and get access to exclusive content.
This resource is only available to Mind Tools members.
Already a member? Please Login here
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Pain Points Podcast - Presentations Pt 2

NEW! Pain Points - How Do I Decide?
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Finding the Best Mix in Training Methods
Using Mediation To Resolve Conflict
Resolving conflicts peacefully with mediation
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Talent management overview.
This Document Provides an Overview of Talent Management
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
6.2 Creative Problem-Solving Process
Portions of the material in this section are based on original work by Geoffrey Graybeal and produced with support from the Rebus Community. The original is freely available under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license at https://press.rebus.community/media-innovation-and-entrepreneurship/.
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the five steps in the creative problem-solving process
- Identify and describe common creative problem-solving tools
Creativity can be an important trait of an entrepreneur, as the chapter on Creativity, Innovation, and Invention discussed. In that discussion, we learned about creativity’s role in innovation . Here, we will look in more depth at creativity’s role in problem solving . Let’s first formally define creativity as the development of original ideas to solve an issue. The intent of being an entrepreneur is to break away from practical norms and use imagination to embrace quick and effective solutions to an existing problem, usually outside the corporate environment.
The Steps of the Creative Problem-Solving Process
Training oneself to think like an entrepreneur means learning the steps to evaluating a challenge: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate ( Figure 6.9 ).
Step 1: Clarify
To clarify is the critical step of recognizing the existence of a gap between the current state and a desired state. This can also be thought of as having need awareness , which occurs when the entrepreneur notes a gap between societal or customer needs and actual circumstances. Clarifying the problem by speaking with clients and developing a detailed description of the problem brings the specifics of a problem to light. Failure to identify the specifics of a problem leaves the entrepreneur with the impossible task of solving a ghost problem, a problem that is fully unknown or unseen. To establish and maintain credibility, an entrepreneur must clarify the problem by focusing on solving the problem itself, rather than solving a symptom of the problem.
For example, a farm could have polluted water, but it would not be enough to solve the problem only on that farm. Clarifying would involve identifying the source of the pollution to adequately tackle the problem. After gaining an understanding of a problem, the entrepreneur should begin to formulate plans for eliminating the gap. A fishbone diagram , as shown in Figure 6.10 , is a tool that can be used to identify the causes of such a problem.
In the case of our water pollution example, a fishbone diagram exploring the issue might reveal the items shown in Figure 6.11 .
Step 2: Ideate
To ideate is the step of the creative problem-solving process that involves generating and detailing ideas by the entrepreneur. After collecting all information relevant to the problem, the entrepreneur lists as many causes of the problem as possible. This is the step in which the largest variety of ideas are put forth. Each idea must be evaluated for feasibility and cost as a solution to the problem. If a farm does not have clean water, for example, the entrepreneur must list causes of toxic water and eliminate as many of those causes as possible. The entrepreneur must then move forward investigating solutions to bring the water back to a safe state. If, say, nearby livestock are polluting the water, the livestock should be isolated from the water source.
Step 3: Develop
To develop is the step in which the entrepreneur takes the list of ideas generated and tests each solution for feasibility. The entrepreneur must consider the cost of each idea and the obstacles to implementation. In the preceding example, adding a chemical to the water may not be a feasible solution to the farmer. Not every farmer wants additional chloride or fluoride added to the water due to the effect on both humans and livestock. These tradeoffs should be addressed in the feasibility assessment. The farmer might prefer a filtration system, but the cost of that solution might not be practicable. The entrepreneur should identify and assess alternative solutions to find one that is most cost-effective and feasible to the customer.
Step 4: Implement
To implement is the step in which the solution to the problem is tested and evaluated. The entrepreneur walks through the planned implementation with the client and tests each part of the solution, if a service, or thoroughly tests a developed good. The entrepreneur implements the solution and goes through a structured system of follow-up to ensure the solution remains effective and viable. In the water example, the solution would be reducing runoff from toxic insecticides by adding prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams.
Step 5: Evaluate
To evaluate is the step in which the final solution is assessed. This is a very important step that entrepreneurs often overlook. Any fallacy in the implementation of the product or service is reassessed, and new solutions are implemented. A continual testing process may be needed to find the final solution. The prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams chosen in the farming water example should then be analyzed and tested to ensure the chosen solution changed the content of the water.
Are You Ready?
Implementing creative problem solving.
Removing waste is a problem, and it can also present an entrepreneurial opportunity. Try to examine ways in which waste products that you usually pay to have hauled away can now generate revenue. Whether it’s recycling aluminum cans or cardboard, or garbage that could be used to feed animals, your task is to come up with solutions to this entrepreneurial-oriented problem.
- Try following the first step of the creative problem-solving process and clearly identify the problem.
- Next, gather data and formulate the challenge.
- Then, explore ideas and come up with solutions.
- Develop a plan of action.
- Finally, note how you would evaluate the effectiveness of your solution.
Using Creativity to Solve Problems
Entrepreneurs are faced with solving many problems as they develop their ideas for filling gaps, whether those opportunities involve establishing a new company or starting a new enterprise within an existing company. Some of these problems include staffing, hiring and managing employees, handling legal compliance, funding, marketing, and paying taxes. Beyond the mundane activities listed, the entrepreneur, or the team that the entrepreneur puts in place, is indispensable in maintaining the ongoing creativity behind the product line or service offered. Innovation and creativity in the business are necessary to expand the product line or develop a groundbreaking service.
It is not necessary for the entrepreneur to feel isolated when it comes to finding creative solutions to a problem. There are societies, tools, and new methods available to spur the creativity of the entrepreneur that will further support the success and expansion of a new enterprise. 14 Learning and using entrepreneurial methods to solve problems alleviates the stress many startup owners feel. The entrepreneur’s creativity will increase using collaborative methodologies . Some entrepreneurial collaborative methodologies include crowdsourcing, brainstorming, storyboarding, conducting quick online surveys to test ideas and concepts, and team creativity activities.
Crowdsourcing
Professor Daren Brabham at the University of Southern California has written books on crowdsourcing and touts its potential in for-profit and not-for-profit business sectors. He defines it simply as “an online, distributed problem-solving and production model.” 15 Crowdsourcing involves teams of amateurs and nonexperts working together to form a solution to a problem. 16 The idea, as cbsnews.com’s Jennifer Alsever has put it, is to “tap into the collective intelligence of the public at large to complete business-related tasks that a company would normally either perform itself or outsource to a third-party provider. Yet free labor is only a narrow part of crowdsourcing's appeal. More importantly, it enables managers to expand the size of their talent pool while also gaining deeper insight into what customers really want. The challenge is to take a cautionary approach to the ‘wisdom of the crowd,’ which can lead to a ‘herd’ mentality.” 17
Link to Learning
Read this article that discusses what crowdsourcing is, how to use it, and its benefits for more information.
This new business prototype, similar to outsourcing, features an enterprise posting a problem online and asking for volunteers to consider the problem and propose solutions. Volunteers earn a reward, such as prize money, promotional materials like a T-shirt, royalties on creative outlets like photos or designs, and in some cases, compensation for their labor. Before proposing the solution, volunteers learn that the solutions become the intellectual property of the startup posting the problem. The solution is then mass produced for profit by the startup that posted the problem. 18 The process evolves into the crowdsourcing process after the enterprise mass produces and profits from the labor of the volunteers and the team. Entrepreneurs should consider that untapped masses have solutions for many issues for which agendas do not yet exist. Crowdsourcing can exploit those agendas and add to the tools used to stimulate personal creativity. This type of innovation is planned and strategically implemented for profit.
For example, Bombardier held a crowdsourced innovation contest to solicit input on the future of train interiors, including seat design and coach class interior. A corporate jury judged the submissions, with the top ten receiving computers or cash prizes. Companies are often constrained, however, by internal rules limiting open source or external idea sourcing, as they could be accused of “stealing” an idea. While crowdsourcing outside of software can be problematic, some products such as MakerBot ’s 3D printers, 3DR’ s drones, and Jibo ’s Social Robot have used developer kits and “makers” to help build a community and stimulate innovation from the outside.
Work It Out
A crowdsourced potato chip.
In an effort to increase sales among millennials, PepsiCo turned to crowdsourcing to get new flavor ideas for their Lay’s potato chips (called Walker’s in the UK). Their 2012 campaign, “Do Us a Flavor,” was so successful that they received over 14 million submissions. The winner was Cheesy Garlic Bread, which increased their potato chip sales by 8 percent during the first three months after the launch.
- What are some other products that would work well for a crowdsourced campaign contest?
- What items wouldn’t work well?
Amazon ’s Mechanical Turk is an online crowdsourcing platform that allows individuals to post tasks for workers to complete. In many instances, these tasks are compensated, but the payment can be less than one dollar per item completed. Mechanical Turk is one of the largest and most well-known crowdsourcing platforms, but there are a number of other more niche ones as well that would apply to smaller markets. In the case of innovation contests and outsourced tasks from corporations, those tasks may be hosted internally by the corporation.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is the generation of ideas in an environment free of judgment or dissension with the goal of creating solutions. See Creativity, Innovation, and Invention to refresh yourself on this technique. Brainstorming is meant to stimulate participants into thinking about problem solving in a new way. Using a multifunctional group, meaning participants come from different departments and with different skill sets, gives entrepreneurs and support teams a genuine chance to suggest and actualize ideas. The group works together to refine and prototype potential solutions to a problem.
Brainstorming is a highly researched and often practiced technique for the development of innovative solutions. One of the more successful proponents of brainstorming is the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) . UNICEF faces unique problems of solving resource problems for mothers and children in underdeveloped nations. See how UNICEF practices brainstorming to solve problems including child survival, gender inclusion, refugee crises, education, and others.
The setting for a brainstorming session should remain as informal and relaxed as possible. The group needs to avoid standard solutions. All ideas are welcome and listed and considered with no censorship and with no regard to administrative restrictions. All team members have an equal voice. The focus of brainstorming is on quantity of ideas rather than on the ideal solution provided in every suggestion. A classic entrepreneurial brainstorming activity, as popularized by business software developer Strategyzer , is known as the “silly cow” exercise. Teams come up with ideas for new business models pertaining to a cow, with the results often outrageous, ranging from sponsored cows to stroking cows for therapeutic release. Participants are asked to identify some aspect of a cow and develop three business models around that concept in a short time period, typically two minutes or fewer. The activity is designed to get creative juices flowing.
Watch this video from ABC’s Nightline that shows how IDEO designed a new shopping cart for an example of a design process that involves brainstorming.
Storyboarding
Storyboarding is the process of presenting an idea in a step-by-step graphic format, as Figure 6.12 shows. This tool is useful when the entrepreneur is attempting to visualize a solution to a problem. The steps to the solution of a problem are sketched and hung in graphic format. Once the original graphic is placed, images of steps working toward a solution are added, subtracted, and rearranged on a continual basis, until the ultimate solution emerges in the ultimate graphic format. For many years, entrepreneurs have used this process to create a pre-visual for various media sequences.
Team Creativity
Team creativity is the process whereby an entrepreneur works with a team to create an unexpected solution for an issue or challenge. Teams progress through the same creative problem-solving process described already: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate. The main advantage of team creativity is the collaboration and support members receive from one another. Great teams trust in other team members, have diverse members with diverse points of view, are cohesive, and have chemistry.
Team members should work in a stress-free and relaxing environment. Reinforcement and expansion of ideas in the team environment motivates the team to continually expand horizons toward problem solution. A small idea in a team may spark the imagination of a team member to an original idea. Mark Zuckerberg , cofounder of Facebook , once said, “The most important thing for you as an entrepreneur trying to build something is, you need to build a really good team. And that’s what I spend all my time on.” 19
Entrepreneur In Action
Taaluma totes 20.
Young entrepreneurs Jack DuFour and Alley Heffern began to notice the beautiful fabrics that came from the different countries they visited. The entrepreneurs thought about what could be done with the fabrics to create employment opportunities both in the country from which the fabric originated and in their home base of Virginia. They decided to test producing totes from the fabrics they found and formed Taaluma Totes ( Figure 6.13 ). DuFour and Heffern also wanted to promote the production of these fabrics and help underserved populations in countries where the fabric originated maintain a living or follow a dream.
The team continued to test the process and gathered original fabrics, which they sent to Virginia to create totes. They trained individuals with disabilities in Virginia to manufacture the totes, thus serving populations in the United States. The entrepreneurs then decided to take 20 percent of their profits and make microloans to farmers and small business owners in the countries where the fabric originated to create jobs there. Microloans are small loans, below $50,000, which certain lenders offer to enterprising startups. These startups, for various reasons (they are in poor nations, at poverty level), can’t afford a traditional loan from a major bank. The lenders offer business support to the borrower, which in turn helps the borrower repay the microloan. The microloans from Taaluma are repaid when the borrower is able. Repayments are used to buy more fabric, completing Taaluma’s desire to serve dual populations. If the process proved unsuccessful, the co-owners would revise the process to meet the plan’s requirements.
DuFour and Heffern now have fabrics from dozens of countries from Thailand to Ecuador. The totes are specialized with features to meet individual needs. The product line is innovated regularly and Taaluma Totes serves a dual purpose of employing persons with disabilities in Virginia and creating employment for underserved populations in other countries.
- 14 “Creating a World of Opportunities.” The Collegiate Entrepreneurs’ Organization . n.d. https://www.c-e-o.org/
- 15 Daren C. Brabham. “Crowdsourcing as a Model for Problem Solving: An Introduction and Cases.” Convergence: The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies 14, no. 1 (2008): 75–90.
- 16 Michael Houlihan and Bonnie Harvey. “How Crowdsourcing Is Shaping the Future of Everything.” Entrepreneur. January 13, 2018. https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/307438
- 17 Jennifer Alsever. “What Is Crowdsourcing?” CBS News . May 1, 2008. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/what-is-crowdsourcing
- 18 Daren C. Brabham. “Crowdsourcing as a Model for Problem Solving: An Introduction and Cases.” Convergence: The International Journal of Research into New Media Technologies 14, no. 1 (2008): 75–90.
- 19 “Three Tips for Entrepreneurs Creating the Perfect Team.” Virgin . n.d. https://www.virgin.com/entrepreneur/three-tips-entrepreneurs-creating-perfect-team
- 20 “Backpacks That Carry a Country.” Taaluma Totes. n.d. https://www.carryacountry.com/pages/about
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/6-2-creative-problem-solving-process
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- Miles Anthony Smith
- Sep 12, 2022
- 12 min read
The Ultimate Problem-Solving Process Guide: 31 Steps and Resources
Updated: Jan 24, 2023
GOT CHALLENGES WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS? ARE YOU FRUSTRATED?
prob·lem-solv·ing noun -the process of finding solutions to difficult or complex issues. It sounds so simple, doesn’t it? But in reality problem-solving is hard. It's almost always more complex than it seems. That's why problem-solving can be so frustrating sometimes. You can feel like you’re spinning your wheels, arguing in circles, or just failing to find answers that actually work. And when you've got a group working on a problem, it can get even muddier …differences of opinions, viewpoints colored by different backgrounds, history, life experiences, you name it. We’re all looking at life and work from different angles, and that often means disagreement. Sometimes sharp disagreement. That human element, figuring out how to take ourselves out of the equation and make solid, fact-based decisions , is precisely why there’s been so much written on problem-solving. Which creates its own set of problems. Whose method is best? How can you possibly sift through them all? Are we to have one person complete the entire problem-solving process by themselves or rely on a larger team to find answers to our most vexing challenges in the workplace ? Today, we’re going to make sense of it all. We’ll take a close look at nine top problem-solving methods. Then we’ll grab the best elements of all of them to give you a process that will have your team solving problems faster, with better results , and maybe with less sharp disagreement. Ready to dive in? Let’s go!
9 PROFITABLE PROBLEM-SOLVING TECHNIQUES AND METHODS
While there are loads of methods to choose from, we are going to focus on nine of the more common ones. You can use some of these problem-solving techniques reactively to solve a known issue or proactively to find more efficient or effective ways of performing tasks. If you want to explore other methods, check out this resource here . A helpful bit of advice here is to reassure people that you aren’t here to identify the person that caused the problem . You’re working to surface the issue, solve it and make sure it doesn’t happen again, regardless of the person working on the process. It can’t be understated how important it is to continually reassure people of this so that you get unfiltered access to information. Without this, people will often hide things to protect themselves . After all, nobody wants to look bad, do they? With that said, let’s get started...
1. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING (CPS)
Alex Osborn coined the term “Creative Problem Solving” in the 1940s with this simple four-step process:
Clarify : Explore the vision, gather data, and formulate questions.
Ideate : This stage should use brainstorming to generate divergent thinking and ideas rather than the random ideas normally associated with brainstorming.
Develop : Formulate solutions as part of an overall plan.
Implement : Put the plan into practice and communicate it to all parties.
2. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY

Source: http://www.davidcooperrider.com/ai-process/ This method seeks, first and foremost, to identify the strengths in people and organizations and play to that “positive core” rather than focus our energies on improving weaknesses . It starts with an “affirmative topic,” followed by the “positive core (strengths).” Then this method delves into the following stages:
Discovery (fact-finding)
Dream (visioning the future)
Design (strategic purpose)
Destiny (continuous improvement)
3. “FIVE WHYS” METHOD
This method simply suggests that we ask “Why” at least five times during our review of the problem and in search of a fix. This helps us dig deeper to find the the true reason for the problem, or the root cause. Now, this doesn’t mean we just keeping asking the same question five times. Once we get an answer to our first “why”, we ask why to that answer until we get to five “whys”.
Using the “five whys” is part of the “Analyze” phase of Six Sigma but can be used with or without the full Six Sigma process.
Review this simple Wikipedia example of the 5 Whys in action:
The vehicle will not start. (the problem)
Why? - The battery is dead. (First why)
Why? - The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
Why? - The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
Why? - The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
Why? - The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
4. LEAN SIX SIGMA (DMAIC METHOD)

While many people have at least heard of Lean or Six Sigma, do we know what it is? Like many problem-solving processes, it has five main steps to follow.
Define : Clearly laying out the problem and soliciting feedback from those who are customers of the process is necessary to starting off on the right foot.
Measure : Quantifying the current state of the problem is a key to measuring how well the fix performed once it was implemented.
Analyze : Finding out the root cause of the problem (see number 5 “Root Cause Analysis” below) is one of the hardest and least explored steps of Six Sigma.
Improve : Crafting, executing, and testing the solution for measureable improvement is key. What doesn’t get implemented and measured really won’t make a difference.
Control : Sustaining the fix through a monitoring plan will ensure things continue to stay on track rather than being a short-lived solution.
5. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS
Compared to other methods, you’ll more often find this technique in a reactive problem-solving mode, but it is helpful nonetheless. Put simply, it requires a persistent approach to finding the highest-level cause, since most reasons you’ll uncover for a problem don’t tell the whole story.
Most of the time, there are many factors that contributed to an issue. The main reason is often shrouded in either intentional or unintentional secrecy. Taking the time to drill down to the root of the issue is key to truly solving the problem.
6. DEMING-SHEWHART CYCLE: PLAN-DO-CHECK-ACT (PDCA)
Named for W. Edwards Deming and Walter A. Shewhart, this model follows a four-step process:
Plan: Establish goals and objectives at the outset to gain agreement. It’s best to start on a small scale in order to test results and get a quick win.
Do: This step is all about the implementation and execution of the solution.
Check: Study and compare actual to expected results. Chart this data to identify trends.
Act/Adjust: If the check phase showed different results, then adjust accordingly. If worse than expected, then try another fix. If the same or better than expected, then use that as the new baseline for future improvements.
7. 8D PROBLEM-SOLVING

While this is named “8D” for eight disciplines, there are actually nine , because the first is listed as step zero. Each of the disciplines represents a phase of this process. Its aim is to implement a quick fix in the short term while working on a more permanent solution with no recurring issues.
Prepare and Plan : Collecting initial information from the team and preparing your approach to the process is a necessary first step.
Form a Team : Select a cross-functional team of people, one leader to run meetings and the process, and one champion/sponsor who will be the final decision-maker.
Describe the Problem : Using inductive and deductive reasoning approaches, lay out the precise issue to be corrected.
Interim Containment Action : Determine if an interim solution needs to be implemented or if it can wait until the final fix is firmed up. If necessary, the interim action is usually removed once the permanent solution is ready for implementation.
Root Cause Analysis and Escape Point : Finding the root of the issue and where in the process it could’ve been found but was not will help identify where and why the issue happened.
Permanent Corrective Action : Incorporating key criteria into the solution, including requirements and wants, will help ensure buy-in from the team and your champion.
Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action : Measuring results from the fix implemented validates it or sends the team back to the drawing board to identity a more robust solution.
Prevent Recurrence : Updating work procedure documents and regular communication about the changes are important to keep old habits in check.
Closure and Team Celebration : Taking time to praise the team for their efforts in resolving the problem acknowledges the part each person played and offers a way to move forward.
8. ARMY PROBLEM SOLVING PROCESS
The US Army has been solving problems for more than a couple of centuries , so why not take a look at the problem-solving process they’ve refined over many years? They recommend this five step process:
Identify the Problem : Take time to understand the situation and define a scope and limitations before moving forward.
Gather Information : Uncover facts, assumptions, and opinions about the problem, and challenge them to get to the truth.
Develop Screening and Evaluation Criteria :
Five screening items should be questioned. Is it feasible, acceptable, distinguishable, and complete?
Evaluation criteria should have these 5 elements: short title, definition, unit of measure, benchmark, and formula.
Generate, Analyze, and Compare Possible Solutions : Most fixes are analyzed, but do you compare yours to one another as a final vetting method?
Choose a Solution and Implement : Put the fix into practice and follow up to ensure it is being followed consistently and having the desired effect.
9. HURSON'S PRODUCTIVE THINKING MODEL

Tim Hurson introduced this model in 2007 with his book, Think Better. It consists of the following six actions.
Ask "What is going on?" : Define the impact of the problem and the aim of its solution.
Ask "What is success?" : Spell out the expected outcome, what should not be in fix, values to be considered, and how things will be evaluated.
Ask "What is the question?" : Tailor questions to the problem type. Valuable resources can be wasted asking questions that aren’t truly relevant to the issue.
Generate answers : Prioritize answers that are the most relevant to solutions, without excluding any suggestion to present to the decision-makers.
Forge the solution : Refine the raw list of prioritized fixes, looking for ways to combine them for a more powerful solution or eliminate fixes that don’t fit the evaluation criteria.
Align resources: Identify resources, team, and stakeholders needed to implement and maintain the solution.
STEAL THIS THOROUGH 8-STEP PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS

Now that we’ve reviewed a number of problem-solving methods, we’ve compiled the various steps into a straightforward, yet in-depth, s tep-by-step process to use the best of all methods.
1. DIG DEEP: IDENTIFY, DEFINE, AND CLARIFY THE ISSUE
“Elementary, my dear Watson,” you might say.
This is true, but we often forget the fundamentals before trying to solve a problem. So take some time to gain understanding of critical stakeholder’s viewpoints to clarify the problem and cement consensus behind what the issue really is.
Sometimes it feels like you’re on the same page, but minor misunderstandings mean you’re not really in full agreement.. It’s better to take the time to drill down on an issue before you get too far into solving a problem that may not be the exact problem . Which leads us to…
2. DIG DEEPER: ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS

This part of the process involves identifying these three items :
What happened?
Why did it happen?
What process do we need to employ to significantly reduce the chances of it happening again ?
You’ll usually need to sort through a series of situations to find the primary cause. So be careful not to stop at the first cause you uncover . Dig further into the situation to expose the root of the issue. We don’t want to install a solution that only fixes a surface-level issue and not the root. T here are typically three types of causes :
Physical: Perhaps a part failed due to poor design or manufacturing.
Human error: A person either did something wrong or didn’t do what needed to be done.
Organizational: This one is mostly about a system, process, or policy that contributed to the error .
When searching for the root cause, it is important to ensure people that you aren’t there to assign blame to a person but rather identify the problem so a fix can prevent future issues.
3. PRODUCE A VARIETY OF SOLUTION OPTIONS
So far, you’ve approached the problem as a data scientist, searching for clues to the real issue. Now, it’s important to keep your eyes and ears open, in case you run across a fix suggested by one of those involved in the process failure. Because they are closest to the problem, they will often have an idea of how to fix things. In other cases, they may be too close, and unable to see how the process could change.
The bottom line is to solicit solution ideas from a variety of sources , both close to and far away from the process you’re trying to improve.
You just never know where the top fix might come from!
4. FULLY EVALUATE AND SELECT PLANNED FIX(ES)

Evaluating solutions to a defined problem can be tricky since each one will have cost, political, or other factors associated with it. Running each fix through a filter of cost and impact is a vital step toward identifying a solid solution and hopefully settling on the one with the highest impact and low or acceptable cost.
Categorizing each solution in one of these four categoriescan help teams sift through them:
High Cost/Low Impact: Implement these last, if at all, since t hey are expensive and won’t move the needle much .
Low Cost/Low Impact: These are cheap, but you won’t get much impact.
High Cost/High Impact: These can be used but should be second to the next category.
Low Cost/High Impact: Getting a solid “bang for your buck” is what these fixes are all about. Start with these first .
5. DOCUMENT THE FINAL SOLUTION AND WHAT SUCCESS LOOKS LIKE
Formalize a document that all interested parties (front-line staff, supervisors, leadership, etc.) agree to follow. This will go a long way towards making sure everyone fully understands what the new process looks like, as well as what success will look like .
While it might seem tedious, try to be overly descriptive in the explanation of the solution and how success will be achieved. This is usually necessary to gain full buy-in and commitment to continually following the solution. We often assume certain things that others may not know unless we are more explicit with our communications.
6. SUCCESSFULLY SELL AND EXECUTE THE FIX

Arriving at this stage in the process only to forget to consistently apply the solution would be a waste of time, yet many organizations fall down in the execution phase . Part of making sure that doesn’t happen is to communicate the fix and ask for questions multiple times until all parties have a solid grasp on what is now required of them.
One often-overlooked element of this is the politics involved in gaining approval for your solution. Knowing and anticipating objections of those in senior or key leadership positions is central to gaining buy-in before fix implementation.
7. RINSE AND REPEAT: EVALUATE, MONITOR, AND FOLLOW UP
Next, doing check-ins with the new process will ensure that the solution is working (or identity if further reforms are necessary) . You’ll also see if the measure of predefined success has been attained (or is making progress in that regard).
Without regularly monitoring the fix, you can only gauge the success or failure of the solution by speculation and hearsay. And without hard data to review, most people will tell their own version of the story.
8. COLLABORATIVE CONTINGENCIES, ITERATION, AND COURSE CORRECTION

Going into any problem-solving process, we should take note that we will not be done once the solution is implemented (or even if it seems to be working better at the moment). Any part of any process will always be subject to the need for future iterations and course corrections . To think otherwise would be either foolish or naive.
There might need to be slight, moderate, or wholesale changes to the solution previously implemented as new information is gained, new technologies are discovered, etc.
14 FRUITFUL RESOURCES AND EXERCISES FOR YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING JOURNEY

Want to test your problem-solving skills?
Take a look at these twenty case study scenario exercises to see how well you can come up with solutions to these problems.
Still have a desire to discover more about solving problems?
Check out these 14 articles and books...
1. THE LEAN SIX SIGMA POCKET TOOLBOOK: A QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE TO NEARLY 100 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QUALITY AND SPEED
This book is like a Bible for Lean Six Sigma , all in a pocket-sized package.
2. SOME SAGE PROBLEM SOLVING ADVICE

The American Society for Quality has a short article on how it’s important to focus on the problem before searching for a solution.
3. THE SECRET TO BETTER PROBLEM SOLVING: HARVARD BUSINESS REVIEW
Wondering if you are solving the right problems? Check out this Harvard Business Review article.
4. PROBLEM SOLVING 101 : A SIMPLE BOOK FOR SMART PEOPLE
Looking for a fun and easy problem-solving book that was written by a McKinsey consultant? Take a look!
5. THE BASICS OF CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING – CPS

If you want a deeper dive into the seven steps of Creative Problem Solving , see this article.
6. APPRECIATIVE INQUIRY : A POSITIVE REVOLUTION IN CHANGE
Appreciative Inquiry has been proven effective in organizations ranging from Roadway Express and British Airways to the United Nations and the United States Navy. Review this book to join the positive revolution.
7. PROBLEM SOLVING: NINE CASE STUDIES AND LESSONS LEARNED
The Seattle Police Department has put together nine case studies that you can practice solving . While they are about police work, they have practical application in the sleuthing of work-related problems.
8. ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS : THE CORE OF PROBLEM SOLVING AND CORRECTIVE ACTION
Need a resource to delve further into Root Cause Analysis? Look no further than this book for answers to your most vexing questions .
9. SOLVING BUSINESS PROBLEMS : THE CASE OF POOR FRANK

This solid case study illustrates the complexities of solving problems in business.
10. THE 8-DISCIPLINES PROBLEM SOLVING METHODOLOGY
Learn all about the “8Ds” with this concise primer.
11. THE PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS THAT PREVENTS GROUPTHINK HBR
Need to reduce groupthink in your organization’s problem-solving process ? Check out this article from the Harvard Business Review.
12. THINK BETTER : AN INNOVATOR'S GUIDE TO PRODUCTIVE THINKING

Tim Hurson details his own Productive Thinking Model at great length in this book from the author.
13. 5 STEPS TO SOLVING THE PROBLEMS WITH YOUR PROBLEM SOLVING INC MAGAZINE
This simple five-step process will help you break down the problem, analyze it, prioritize solutions, and sell them internally.
14. CRITICAL THINKING : A BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO CRITICAL THINKING, BETTER DECISION MAKING, AND PROBLEM SOLVING!
LOOKING FOR ASSISTANCE WITH YOUR PROBLEM-SOLVING PROCESS?
There's a lot to take in here, but following some of these methods are sure to improve your problem-solving process. However, if you really want to take problem-solving to the next level, InitiativeOne can come alongside your team to help you solve problems much faster than you ever have before.
There are several parts to this leadership transformation process provided by InitiativeOne, including a personal profile assessment, cognitive learning, group sessions with real-world challenges, personal discovery, and a toolkit to empower leaders to perform at their best.
There are really only two things stopping good teams from being great. One is how they make decisions and two is how they solve problems. Contact us today to grow your team’s leadership performance by making decisions and solving problems more swiftly than ever before!
- Featured Post
Recent Posts
Does Your Leadership Deserve Two Thumbs Up?
3 Ways to Harness the Power of Inspiration
Leadership Self-Check
Comentarios

- Guide: Problem Solving
Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is an experienced continuous improvement manager with a Lean Six Sigma Black Belt and a Bachelor's degree in Business Management. With more than ten years of experience applying his skills across various industries, Daniel specializes in optimizing processes and improving efficiency. His approach combines practical experience with a deep understanding of business fundamentals to drive meaningful change.
- Last Updated: January 7, 2024
- Learn Lean Sigma
Problem-solving stands as a fundamental skill, crucial in navigating the complexities of both everyday life and professional environments. Far from merely providing quick fixes, it entails a comprehensive process involving the identification, analysis, and resolution of issues.
This multifaceted approach requires an understanding of the problem’s nature, the exploration of its various components, and the development of effective solutions. At its core, problem-solving serves as a bridge from the current situation to a desired outcome, requiring not only the recognition of an existing gap but also the precise definition and thorough analysis of the problem to find viable solutions.
Table of Contents
What is problem solving.

At its core, problem-solving is about bridging the gap between the current situation and the desired outcome. It starts with recognizing that a discrepancy exists, which requires intervention to correct or improve. The ability to identify a problem is the first step, but it’s equally crucial to define it accurately. A well-defined problem is half-solved, as the saying goes.
Analyzing the problem is the next critical step. This analysis involves breaking down the problem into smaller parts to understand its intricacies. It requires looking at the problem from various angles and considering all relevant factors – be they environmental, social, technical, or economic. This comprehensive analysis aids in developing a deeper understanding of the problem’s root causes, rather than just its symptoms.

Finally, effective problem-solving involves the implementation of the chosen solution and its subsequent evaluation. This stage tests the practicality of the solution and its effectiveness in the real world. It’s a critical phase where theoretical solutions meet practical application.
The Nature of Problems
The nature of the problem significantly influences the approach to solving it. Problems vary greatly in their complexity and structure, and understanding this is crucial for effective problem-solving.
Simple vs. Complex Problems : Simple problems are straightforward, often with clear solutions. They usually have a limited number of variables and predictable outcomes. On the other hand, complex problems are multi-faceted. They involve multiple variables, stakeholders, and potential outcomes, often requiring a more sophisticated analysis and a multi-pronged approach to solving.
Structured vs. Unstructured Problems : Structured problems are well-defined. They follow a specific pattern or set of rules, making their outcomes more predictable. These problems often have established methodologies for solving. For example, mathematical problems usually fall into this category. Unstructured problems, in contrast, are more ambiguous. They lack a clear pattern or set of rules, making their outcomes uncertain. These problems require a more exploratory approach, often involving trial and error, to identify potential solutions.
Understanding the type of problem at hand is essential, as it dictates the approach. For instance, a simple problem might require a straightforward solution, while a complex problem might need a more comprehensive, step-by-step approach. Similarly, structured problems might benefit from established methodologies, whereas unstructured problems might need more innovative and creative problem-solving techniques.
The Problem-Solving Process
The process of problem-solving is a methodical approach that involves several distinct stages. Each stage plays a crucial role in navigating from the initial recognition of a problem to its final resolution. Let’s explore each of these stages in detail.
Step 1: Identifying the Problem

Step 2: Defining the Problem
Once the problem is identified, the next step is to define it clearly and precisely. This is a critical phase because a well-defined problem often suggests its solution. Defining the problem involves breaking it down into smaller, more manageable parts. It also includes understanding the scope and impact of the problem. A clear definition helps in focusing efforts and resources efficiently and serves as a guide to stay on track during the problem-solving process.
Step 3: Analyzing the Problem

Step 4: Generating Solutions

Step 5: Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
After generating a list of possible solutions, the next step is to evaluate each one critically. This evaluation includes considering the feasibility, costs, benefits, and potential impact of each solution. Techniques like cost-benefit analysis, risk assessment, and scenario planning can be useful here. The aim is to select the solution that best addresses the problem in the most efficient and effective way, considering the available resources and constraints.
Step 6: Implementing the Solution

Step 7: Reviewing and Reflecting
The final stage in the problem-solving process is to review the implemented solution and reflect on its effectiveness and the process as a whole. This involves assessing whether the solution met its intended goals and what could have been done differently. Reflection is a critical part of learning and improvement. It helps in understanding what worked well and what didn’t, providing valuable insights for future problem-solving efforts.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Problem Solving
Problem-solving is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a variety of tools and techniques to navigate effectively. Different stages of the problem-solving process can benefit from specific strategies, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of the solutions developed. Here’s a detailed look at some key tools and techniques:
Brainstorming

SWOT Analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)

Root Cause Analysis
This is a method used to identify the underlying causes of a problem, rather than just addressing its symptoms. One popular technique within root cause analysis is the “ 5 Whys ” method. This involves asking “why” multiple times (traditionally five) until the fundamental cause of the problem is uncovered. This technique encourages deeper thinking and can reveal connections that aren’t immediately obvious. By addressing the root cause, solutions are more likely to be effective and long-lasting.

Mind Mapping

Each of these tools and techniques can be adapted to different types of problems and situations. Effective problem solvers often use a combination of these methods, depending on the nature of the problem and the context in which it exists. By leveraging these tools, one can enhance their ability to dissect complex problems, generate creative solutions, and implement effective strategies to address challenges.
Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Developing problem-solving skills is a dynamic process that hinges on both practice and introspection. Engaging with a diverse array of problems enhances one’s ability to adapt and apply different strategies. This exposure is crucial as it allows individuals to encounter various scenarios, ranging from straightforward to complex, each requiring a unique approach. Collaborating with others in teams is especially beneficial. It broadens one’s perspective, offering insights into different ways of thinking and approaching problems. Such collaboration fosters a deeper understanding of how diverse viewpoints can contribute to more robust solutions.
Reflection is equally important in the development of problem-solving skills. Reflecting on both successes and failures provides valuable lessons. Successes reinforce effective strategies and boost confidence, while failures are rich learning opportunities that highlight areas for improvement. This reflective practice enables one to understand what worked, what didn’t, and why.
Critical thinking is a foundational skill in problem-solving. It involves analyzing information, evaluating different perspectives, and making reasoned judgments. Creativity is another vital component. It pushes the boundaries of conventional thinking and leads to innovative solutions. Effective communication also plays a crucial role, as it ensures that ideas are clearly understood and collaboratively refined.
In conclusion, problem-solving is an indispensable skill set that blends analytical thinking, creativity, and practical implementation. It’s a journey from understanding the problem to applying a solution and learning from the outcome.
Whether dealing with simple or complex issues, or structured or unstructured challenges, the essence of problem-solving lies in a methodical approach and the effective use of various tools and techniques. It’s a skill that is honed over time, through experience, reflection, and the continuous development of critical thinking, creativity, and communication abilities. In mastering problem-solving, one not only addresses immediate issues but also builds a foundation for future challenges, leading to more innovative and effective outcomes.
- Mourtos, N.J., Okamoto, N.D. and Rhee, J., 2004, February. Defining, teaching, and assessing problem solving skills . In 7th UICEE Annual Conference on Engineering Education (pp. 1-5).
- Foshay, R. and Kirkley, J., 2003. Principles for teaching problem solving. Technical paper , 4 (1), pp.1-16.
Q: What are the key steps in the problem-solving process?
A : The problem-solving process involves several key steps: identifying the problem, defining it clearly, analyzing it to understand its root causes, generating a range of potential solutions, evaluating and selecting the most viable solution, implementing the chosen solution, and finally, reviewing and reflecting on the effectiveness of the solution and the process used to arrive at it.
Q: How can brainstorming be effectively used in problem-solving?
A: Brainstorming is effective in the solution generation phase of problem-solving. It involves gathering a group and encouraging the free flow of ideas without immediate criticism. The goal is to produce a large quantity of ideas, fostering creative thinking. This technique helps in uncovering unique and innovative solutions that might not surface in a more structured setting.
Q: What is SWOT Analysis and how does it aid in problem-solving?
A : SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats involved in a situation. In problem-solving, it aids by providing a clear understanding of the internal and external factors that could impact the problem and potential solutions. This analysis helps in formulating strategies that leverage strengths and opportunities while mitigating weaknesses and threats.
Q: Why is it important to understand the nature of a problem before solving it?
A : Understanding the nature of a problem is crucial as it dictates the approach for solving it. Problems can be simple or complex, structured or unstructured, and each type requires a different strategy. A clear understanding of the problem’s nature helps in applying the appropriate methods and tools for effective resolution.
Q: How does reflection contribute to developing problem-solving skills?
A : Reflection is a critical component in developing problem-solving skills. It involves looking back at the problem-solving process and the implemented solution to assess what worked well and what didn’t. Reflecting on both successes and failures provides valuable insights and lessons, helping to refine and improve problem-solving strategies for future challenges. This reflective practice enhances one’s ability to approach problems more effectively over time.

Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.
Free Lean Six Sigma Templates
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

Other Guides
Was this helpful.

Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
By Dr. Josh Axe Leaders Staff
Dr. Josh Axe
CEO/Founder
Dr. Josh Axe is the co-founder of Ancient Nutrition and the founder and CEO of Leaders.com. He earned his doctorate...
Learn about our editorial policy
Updated May 17, 2023
Reviewed by Colin Baker
Colin Baker
Leadership and Business Writer
Colin Baker is a business writer for Leaders Media. He has a background in as a television journalism, working as...
What Is Problem-Solving? How to Use Problem-Solving Skills to Resolve Issues
What is problem-solving, what is the general process of problem-solving, the best problem-solving strategies and tools, what to do when a problem feels too big to solve.
Great businesses don’t exist to simply grow and make money. Instead, they solve the world’s problems , from tiny issues to giant dilemmas. Problem-solving is essentially the main function of organizations. An effective organization will have systems and processes in place to reach their goals and solve problems. If a company has team members and leaders who have poor problem-solving skills, that means they’re ineffective at one of the core functions of a business.
You need to be good at both external problem-solving (solving problems for others) and internal problem-solving (solving problems before or when they arise within the business). An organization that can solve problems will see its teams come closer together as they bond over providing solutions to serious issues. Companies that solve problems well will also be able to carry out their purpose more efficiently.
Learn the steps you can follow to solve problems both great and small. Additionally, discover some real-world methods and problem-solving skills successful business leaders use to solve problems of their own.
Problem-solving involves the search for solutions that follow an effective process of discovery, identification, ideation, and execution. Problem-solving usually requires overcoming numerous obstacles that stand in the way of reaching your goal. Often, the act of problem-solving includes coming up with solutions to many smaller problems before eventually solving the main issue that prompted the process in the first place.
The key to cultivating excellent problem-solving skills is having a distinct process designed to produce solutions. While it may seem like problem-solving involves a complex strategy, it features several steps that are easy to follow. The following steps represent a general problem-solving process you can use when you need to find a solution.
1. Define the Problem
The first step to take as part of the problem-solving process involves defining what that problem is. While this may seem like a simple idea to follow, the key is to get to the root of the problem . Only once you’re able to identify the root issue you’re tackling through a root cause analysis can you be sure you’re on the right path. Sometimes the surface issue isn’t what you need to address. Just like an earthquake, organizational issues have an epicenter—complete with shockwaves that negatively impact the business. If you don’t resolve the core problem, it can expand , and the damage becomes detrimental. All problem-solving jobs begin with this important first step.
If your organization has a problem with employee retention , you may think you’ll solve it by increasing pay or perks. However, that might not address the root of the issue. If you were to investigate further, you may discover that a manager is creating a toxic work environment, causing good employees to find work elsewhere.
2. Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Once you have a solid idea of what the real problem is, you can proceed to create possible solutions you can pursue. Take the time to brainstorm different solutions. No two problems are the same, and each one will require a creative approach. Make sure you write down the alternative solutions so you can research them in depth. During the course of your brainstorming, you may stumble upon a solution you wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
As you follow this step, you may need to find the best way to inspire your critical thinking skills. Think about when and where you generate ideas and get the creative juices flowing. Then, try to put yourself in that environment as often as possible.
Sara Blakely , the founder of SPANX®, says her most productive creative thinking happens when she’s driving in her car . Even though she doesn’t have a real commute, she gets in the car and makes one up. “I live really close to Spanx,” she said on the “Masters of Scale” podcast, “so I’ve created what my friends call my ‘fake commute,’ and I get up an hour early before I’m supposed to go to Spanx, and I drive around aimlessly in Atlanta with my commute so that I can have my thoughts come to me.” As a result, she sets time aside for developing her best problem-solving strategies every single day.
3. Research Several Options
After you’ve come up with several possible alternative solutions, pick two or three that seem the most promising using your analytical skills. Then you’ll need to buckle down and do some research to see which one to pursue. Conduct your research using primary and secondary resources.
Conduct primary research by:
- Having a discussion with a mentor
- Interviewing a person who’s successfully solved this problem before
- Strategizing with team members closest to the issue
Great secondary sources include:
- Trustworthy online articles and news sources from credible websites
- Leadership books from experts who have written about the problem
- Business podcast interviews on the issue
- YouTube videos featuring established leaders
4. Select a Solution
At the conclusion of your research, you’ll be better equipped to select the right solution. Evaluate the data you have gathered. To ensure you make a good pick, you’ll need to keep several considerations in mind.
Here are some good questions to ask when picking a solution:
- Is this solution in line with the company’s core values?
- Is it a realistic option?
- Could it lead to additional problems?
- Will everyone involved accept the solution?
- Does it truly solve the problem, or does it only delay negative effects?
As you employ your creative thinking skills in answering these questions, you’ll eventually need to settle on a single solution. Adhering to a decision-making process helps you objectively choose the best solution out of many options. Don’t make a quick decision you may later regret. Be deliberate in your analysis, and try to remain as objective as possible.
In order to make the most objective decision:
- Get into a humble mindset and make sure you’re willing to listen and learn.
- Don’t let emotions influence the choice.
- Reverse-engineer the possible outcome of any given solution.
- Weigh the pros and cons of each choice.
- Seek wise counsel from trusted mentors, leaders, and team members.
5. Develop an Action Plan
Once you’ve settled on a solution, you’ll be ready to pursue it. Before moving too quickly, revisit step one and make sure your choice aligns with the main objective . If it doesn’t, although it may be a valid choice, it’s most likely not the best for your team. If this is the case, don’t get discouraged. Creative problem-solving takes time.
When the right choice is made, and the solution is placed into the overall strategy, start developing an action plan . Lay out the “who,” “what,” “when,” “why,” and “how.” Visualize exactly what success looks like with this new plan. When working through the problem-solving process, write all the details down. This helps leaders construct action items and delegate them accordingly. Never leave this part of the process empty-handed. Your team needs a clear picture of expectations so they can properly implement the solution. And if everything works, you can use this problem-solving model in the future.
You will undoubtedly encounter many problems that need to be solved in your life. There are a variety of ways to solve those problems. With all the problem-solving techniques out there, it can be helpful to learn some of them so you can employ the best one at the right moment. The following are just a few examples of what these strategies and problem-solving tools look like in the real world.
One of the best ways to discover the root cause of a problem is by utilizing the 5 Whys method. This strategy was developed by Sakichi Toyoda, founder of Toyota Industries. It’s as simple as it sounds. When a problem occurs, ask why it happened five times. In theory, the last answer should get to the heart of the issue.
Here’s an example of how the 5 Whys work in action:

When business leaders use the 5 Whys method , problems are given more context. Uncovering how, when, and why they happen helps company owners and executives identify the organization’s core issues.
First Principles Thinking
When one engages in first principles thinking , they end up questioning what everyone just assumes to be true. It effectively removes those assumptions , breaking things down into their most basic elements that are probably true. It’s all about getting to that core foundation of truth and building out from there. Problem-solving skills should always include first principles thinking.
Elon Musk most famously pursued this strategy when it comes to space travel. Instead of accepting that building a rocket was too expensive, he got to the fundamental truths of construction, all the way down to pricing each component. Musk once explained that he follows first principles thinking by following three simple steps .
- Identify the assumptions
- Break down the issue into its core, fundamental components
- Innovate by creating new solutions
Other business leaders have engaged in similar strategies, such as Jeff Bezos when he advised the need for finding out key truths for yourself. First principles thinking is an important part of innovating beyond what we assume can’t be changed. It’s a way to use analytical skills to discover potential solutions through constant learning and acquiring new information.
Steve Jobs’ Problem-Solving Method
Steve Jobs gained a reputation for solving problems through Apple. He was always on the lookout for simple solutions to complex problems. He followed his own three-step method that helped him tackle difficult issues.
- Zoom Out: When facing a problem, zoom out to get a larger view of the bigger picture. This is another way to help you define the problem and pinpoint the root cause.
- Focus In: After defining the problem, focus all your attention on solving it. Concentrate your efforts, and don’t stop until the problem is fixed. Give yourself a period of intense focus and dedication as you bring the solution to life.
- Disconnect: If things aren’t proceeding the way you thought they would, it may be time to disconnect. That means walking away and giving yourself a break so you can clear your mind. Sometimes, a break is all you need to approach the problem once more, this time from a fresh angle with your mind fully reenergized.
From increasing sales to engaging in conflict resolution , business leaders have a lot of problems to solve. However, some people may still feel overwhelmed, especially if the problem is large in scope and could even threaten to close the company. Fortunately, there are steps you can take to get in the right mindset as outlined by James Clear, author of Atomic Habits :
- Break the bigger problem down into a lot of smaller problems
- Focus on one small problem and solve it
- Use what you learned from solving that problem to increase your knowledge about the bigger problem
- Repeat these steps until the larger problem is solved
Tackling a problem that feels too big to solve requires a can-do, positive mindset. In order to improve your problem-solving, you’ll need to take remember these steps. Imagine what is possible instead of focusing on what seems impossible. As you do so, you’ll become skilled in solving all sorts of problems while also improving your decision-making.
For more help in growing your skillset, check out the following article:
Growth Mindset: Creating an Environment for Innovation
Leaders Media has established sourcing guidelines and relies on relevant, and credible sources for the data, facts, and expert insights and analysis we reference. You can learn more about our mission, ethics, and how we cite sources in our editorial policy .
- Abadi, Mark. “The CEO of Spanx Wakes up an Hour Early to Drive around ‘Aimlessly’ on a ‘Fake Commute’ Because She Does Her Best Thinking in the Car.” Insider , 15 Nov. 2018, https://www.businessinsider.com/spanx-ceo-sara-blakely-fake-commute-2018-11.
- Oshin, Mayo. “Elon Musks’ ‘3-Step’ First Principles Thinking: How to Think and Solve Difficult Problems Like A….” Mission.Org , 2 Nov. 2020, https://medium.com/the-mission/elon-musks-3-step-first-principles-thinking-how-to-think-and-solve-difficult-problems-like-a-ba1e73a9f6c0.
- Clear, James. “How to Solve Big Problems.” James Clear , 25 July 2014, https://jamesclear.com/narrow-focus.
- Nast, C. (n.d.). WIRED. https://www.wired.com/2012/10/ff-elon-musk-qa/all/
- Just a moment. . . (n.d.). https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/5-whys-example
- inc.com . (n.d.). https://www.inc.com/kelly-main/apple-steve-jobs-problem-solving.html
- How to find your big idea . (2022, October 6). Masters of Scale. https://mastersofscale.com/sara-blakely-how-to-find-your-big-idea/
- EX-99.1 . (n.d.). https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1018724/000119312517120198/d373368dex991.htm
Search Leaders.com


The Five-Step Problem-Solving Process
Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from…

Sometimes when you’re faced with a complex problem, it’s best to pause and take a step back. A break from routine will help you think creatively and objectively. Doing too much at the same time increases the chances of burnout.
Solving problems is easier when you align your thoughts with your actions. If you’re in multiple places at once mentally, you’re more likely to get overwhelmed under pressure. So, a problem-solving process follows specific steps to make it approachable and straightforward. This includes breaking down complex problems, understanding what you want to achieve, and allocating responsibilities to different people to ease some of the pressure.
The problem-solving process will help you measure your progress against factors like budget, timelines and deliverables. The point is to get the key stakeholders on the same page about the ‘what’, ‘why’ and ‘how’ of the process. ( Xanax ) Let’s discuss the five-step problem-solving process that you can adopt.
Problems at a workplace need not necessarily be situations that have a negative impact, such as a product failure or a change in government policy. Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also “problems” that need to be “solved”.
Here are the steps of a problem-solving process:
1. Defining the Problem
The first step in the process is often overlooked. To define the problem is to understand what it is that you’re solving for. This is also where you outline and write down your purpose—what you want to achieve and why. Making sure you know what the problem is can make it easier to follow up with the remaining steps. This will also help you identify which part of the problem needs more attention than others.
2. Analyzing the Problem
Analyze why the problem occurred and go deeper to understand the existing situation. If it’s a product that has malfunctioned, assess factors like raw material, assembly line, and people involved to identify the problem areas. This will help you figure out if the problem will persist or recur. You can measure the solution against existing factors to assess its future viability.
3. Weighing the Options
Once you’ve figured out what the problem is and why it occurred, you can move on to generating multiple options as solutions. You can combine your existing knowledge with research and data to come up with viable and effective solutions. Thinking objectively and getting inputs from those involved in the process will broaden your perspective of the problem. You’ll be able to come up with better options if you’re open to ideas other than your own.
4. Implementing The Best Solution
Implementation will depend on the type of data at hand and other variables. Consider the big picture when you’re selecting the best option. Look at factors like how the solution will impact your budget, how soon you can implement it, and whether it can withstand setbacks or failures. If you need to make any tweaks or upgrades, make them happen in this stage.
5. Monitoring Progress
The problem-solving process doesn’t end at implementation. It requires constant monitoring to watch out for recurrences and relapses. It’s possible that something doesn’t work out as expected on implementation. To ensure the process functions smoothly, you can make changes as soon as you catch a miscalculation. Always stay on top of things by monitoring how far you’ve come and how much farther you have to go.
You can learn to solve any problem—big or small—with experience and patience. Adopt an impartial and analytical approach that has room for multiple perspectives. In the workplace, you’re often faced with situations like an unexpected system failure or a key employee quitting in the middle of a crucial project.
Problem-solving skills will help you face these situations head-on. Harappa Education’s Structuring Problems course will show you how to classify and categorize problems to discover effective solutions. Equipping yourself with the right knowledge will help you navigate work-related problems in a calm and competent manner.
Explore topics such as Problem Solving , the PICK Chart , How to Solve Problems & the Barriers to Problem Solving from our Harappa Diaries blog section and develop your skills.


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

3.3: Creative Problem-Solving Process
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 62756
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the five steps in the creative problem-solving process
- Identify and describe common creative problem-solving tools
Creativity can be an important trait of an entrepreneur. In that discussion, we learned about creativity’s role in innovation . Here, we will look in more depth at creativity’s role in problem-solving . Let’s first formally define creativity as the development of original ideas to solve an issue. The intent of being an entrepreneur is to break away from practical norms and use imagination to embrace quick and effective solutions to an existing problem, usually outside the corporate environment.
The Steps of the Creative Problem-Solving Process
Training oneself to think like an entrepreneur means learning the steps to evaluating a challenge: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate (Figure 3.3.1).

Step 1: Clarify
To clarify is the critical step of recognizing the existence of a gap between the current state and a desired state. This can also be thought of as having need awareness , which occurs when the entrepreneur notes a gap between societal or customer needs and actual circumstances. Clarifying the problem by speaking with clients and developing a detailed description of the problem brings the specifics of a problem to light. Failure to identify the specifics of a problem leaves the entrepreneur with the impossible task of solving a ghost problem, a problem that is fully unknown or unseen. To establish and maintain credibility, an entrepreneur must clarify the problem by focusing on solving the problem itself, rather than solving a symptom of the problem.
For example, a farm could have polluted water, but it would not be enough to solve the problem only on that farm. Clarifying would involve identifying the source of the pollution to adequately tackle the problem. After gaining an understanding of a problem, the entrepreneur should begin to formulate plans for eliminating the gap. A fishbone diagram, as shown in Figure 3.3.2, is a tool that can be used to identify the causes of such a problem.

In the case of our water pollution example, a fishbone diagram exploring the issue might reveal the items shown in Figure 3.3.3.

Step 2: Ideate
To ideate is the step of the creative problem-solving process that involves generating and detailing ideas by the entrepreneur. After collecting all information relevant to the problem, the entrepreneur lists as many causes of the problem as possible. This is the step in which the largest variety of ideas are put forth. Each idea must be evaluated for feasibility and cost as a solution to the problem. If a farm does not have clean water, for example, the entrepreneur must list causes of toxic water and eliminate as many of those causes as possible. The entrepreneur must then move forward investigating solutions to bring the water back to a safe state. If, say, nearby livestock are polluting the water, the livestock should be isolated from the water source.
Step 3: Develop
To develop is the step in which the entrepreneur takes the list of ideas generated and tests each solution for feasibility. The entrepreneur must consider the cost of each idea and the obstacles to implementation. In the preceding example, adding a chemical to the water may not be a feasible solution to the farmer. Not every farmer wants additional chloride or fluoride added to the water due to the effect on both humans and livestock. These tradeoffs should be addressed in the feasibility assessment. The farmer might prefer a filtration system, but the cost of that solution might not be practicable. The entrepreneur should identify and assess alternative solutions to find one that is most cost-effective and feasible to the customer.
Step 4: Implement
To implement is the step in which the solution to the problem is tested and evaluated. The entrepreneur walks through the planned implementation with the client and tests each part of the solution, if a service, or thoroughly tests a developed good. The entrepreneur implements the solution and goes through a structured system of follow-up to ensure the solution remains effective and viable. In the water example, the solution would be reducing runoff from toxic insecticides by adding prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams.
Step 5: Evaluate
To evaluate is the step in which the final solution is assessed. This is a very important step that entrepreneurs often overlook. Any fallacy in the implementation of the product or service is reassessed, and new solutions are implemented. A continual testing process may be needed to find the final solution. The prairie strips, buffers of grass, and vegetation along banks of streams chosen in the farming water example should then be analyzed and tested to ensure the chosen solution changed the content of the water.
ARE YOU READY?
Implementing Creative Problem Solving
Removing waste is a problem, and it can also present an entrepreneurial opportunity. Try to examine ways in which waste products that you usually pay to have hauled away can now generate revenue. Whether it’s recycling aluminum cans or cardboard, or garbage that could be used to feed animals, your task is to come up with solutions to this entrepreneurial-oriented problem.
- Try following the first step of the creative problem-solving process and clearly identify the problem.
- Next, gather data and formulate the challenge.
- Then, explore ideas and come up with solutions.
- Develop a plan of action.
- Finally, note how you would evaluate the effectiveness of your solution.
Using Creativity to Solve Problems
Entrepreneurs are faced with solving many problems as they develop their ideas for filling gaps, whether those opportunities involve establishing a new company or starting a new enterprise within an existing company. Some of these problems include staffing, hiring and managing employees, handling legal compliance, funding, marketing, and paying taxes. Beyond the mundane activities listed, the entrepreneur, or the team that the entrepreneur puts in place, is indispensable in maintaining the ongoing creativity behind the product line or service offered. Innovation and creativity in the business are necessary to expand the product line or develop a groundbreaking service.
It is not necessary for the entrepreneur to feel isolated when it comes to finding creative solutions to a problem. There are societies, tools, and new methods available to spur the creativity of the entrepreneur that will further support the success and expansion of a new enterprise. 14 Learning and using entrepreneurial methods to solve problems alleviates the stress many startup owners feel. The entrepreneur’s creativity will increase using collaborative methodologies. Some entrepreneurial collaborative methodologies include crowdsourcing, brainstorming, storyboarding, conducting quick online surveys to test ideas and concepts, and team creativity activities.
Crowdsourcing
Professor Daren Brabham at the University of Southern California has written books on crowdsourcing and touts its potential in for-profit and not-for-profit business sectors. He defines it simply as “an online, distributed problem-solving and production model.” 15 Crowdsourcing involves teams of amateurs and nonexperts working together to form a solution to a problem. 16 The idea, as cbsnews.com’s Jennifer Alsever has put it, is to “tap into the collective intelligence of the public at large to complete business-related tasks that a company would normally either perform itself or outsource to a third-party provider. Yet free labor is only a narrow part of crowdsourcing's appeal. More importantly, it enables managers to expand the size of their talent pool while also gaining deeper insight into what customers really want. The challenge is to take a cautionary approach to the ‘wisdom of the crowd,’ which can lead to a ‘herd’ mentality.” 17
LINK TO LEARNING
Read this article that discusses what crowdsourcing is, how to use it, and its benefits for more information.
This new business prototype, similar to outsourcing, features an enterprise posting a problem online and asking for volunteers to consider the problem and propose solutions. Volunteers earn a reward, such as prize money, promotional materials like a T-shirt, royalties on creative outlets like photos or designs, and in some cases, compensation for their labor. Before proposing the solution, volunteers learn that the solutions become the intellectual property of the startup posting the problem. The solution is then mass-produced for profit by the startup that posted the problem. 18 The process evolves into the crowdsourcing process after the enterprise mass produces and profits from the labor of the volunteers and the team. Entrepreneurs should consider that untapped masses have solutions for many issues for which agendas do not yet exist. Crowdsourcing can exploit those agendas and add to the tools used to stimulate personal creativity. This type of innovation is planned and strategically implemented for profit.
For example, Bombardier held a crowdsourced innovation contest to solicit input on the future of train interiors, including seat design and coach class interior. A corporate jury judged the submissions, with the top ten receiving computers or cash prizes. Companies are often constrained, however, by internal rules limiting open source or external idea sourcing, as they could be accused of “stealing” an idea. While crowdsourcing outside of software can be problematic, some products such as MakerBot’s 3D printers, 3DR’s drones, and Jibo’s Social Robot have used developer kits and “makers” to help build a community and stimulate innovation from the outside.
WORK IT OUT
A Crowdsourced Potato Chip
In an effort to increase sales among millennials, PepsiCo turned to crowdsourcing to get new flavor ideas for their Lay’s potato chips (called Walker’s in the UK). Their 2012 campaign, “Do Us a Flavor,” was so successful that they received over 14 million submissions. The winner was Cheesy Garlic Bread, which increased their potato chip sales by 8 percent during the first three months after the launch.
- What are some other products that would work well for a crowdsourced campaign contest?
- What items wouldn’t work well?
Amazon’s Mechanical Turk is an online crowdsourcing platform that allows individuals to post tasks for workers to complete. In many instances, these tasks are compensated, but the payment can be less than one dollar per item completed. Mechanical Turk is one of the largest and most well-known crowdsourcing platforms, but there are a number of other more niche ones as well that would apply to smaller markets. In the case of innovation contests and outsourced tasks from corporations, those tasks may be hosted internally by the corporation.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is the generation of ideas in an environment free of judgment or dissension with the goal of creating solutions. Brainstorming is meant to stimulate participants into thinking about problem-solving in a new way. Using a multifunctional group, meaning participants come from different departments and with different skill sets, gives entrepreneurs and support teams a genuine chance to suggest and actualize ideas. The group works together to refine and prototype potential solutions to a problem.
Brainstorming is a highly researched and often practiced technique for the development of innovative solutions. One of the more successful proponents of brainstorming is the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF). UNICEF faces unique problems of solving resource problems for mothers and children in underdeveloped nations. See how UNICEF practices brainstorming to solve problems including child survival, gender inclusion, refugee crises, education, and others.
The setting for a brainstorming session should remain as informal and relaxed as possible. The group needs to avoid standard solutions. All ideas are welcome and listed and considered with no censorship and with no regard to administrative restrictions. All team members have an equal voice. The focus of brainstorming is on quantity of ideas rather than on the ideal solution provided in every suggestion. A classic entrepreneurial brainstorming activity, as popularized by business software developer Strategyzer, is known as the “silly cow” exercise. Teams come up with ideas for new business models pertaining to a cow, with the results often outrageous, ranging from sponsored cows to stroking cows for therapeutic release. Participants are asked to identify some aspect of a cow and develop three business models around that concept in a short time period, typically two minutes or fewer. The activity is designed to get creative juices flowing.
Watch this video from ABC’s Nightline that shows how IDEO designed a new shopping cart for an example of a design process that involves brainstorming.
Storyboarding
Storyboarding is the process of presenting an idea in a step-by-step graphic format, as Figure 3.3.4 shows. This tool is useful when the entrepreneur is attempting to visualize a solution to a problem. The steps to the solution of a problem are sketched and hung in graphic format. Once the original graphic is placed, images of steps working toward a solution are added, subtracted, and rearranged on a continual basis, until the ultimate solution emerges in the ultimate graphic format. For many years, entrepreneurs have used this process to create a pre-visual for various media sequences.

Team Creativity
Team creativity is the process whereby an entrepreneur works with a team to create an unexpected solution for an issue or challenge. Teams progress through the same creative problem-solving process described already: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate. The main advantage of team creativity is the collaboration and support members receive from one another. Great teams trust in other team members, have diverse members with diverse points of view, are cohesive, and have chemistry.
Team members should work in a stress-free and relaxing environment. Reinforcement and expansion of ideas in the team environment motivates the team to continually expand horizons toward problem solution. A small idea in a team may spark the imagination of a team member to an original idea. Mark Zuckerberg, co-founder of Facebook, once said, “The most important thing for you as an entrepreneur trying to build something is, you need to build a really good team. And that’s what I spend all my time on.” 19
ENTREPRENEUR IN ACTION
Taaluma Totes 20
Young entrepreneurs Jack DuFour and Alley Heffern began to notice the beautiful fabrics that came from the different countries they visited. The entrepreneurs thought about what could be done with the fabrics to create employment opportunities both in the country from which the fabric originated and in their home base of Virginia. They decided to test producing totes from the fabrics they found and formed Taaluma Totes (Figure 3.3.5). DuFour and Heffern also wanted to promote the production of these fabrics and help underserved populations in countries where the fabric originated maintain a living or follow a dream.

The team continued to test the process and gathered original fabrics, which they sent to Virginia to create totes. They trained individuals with disabilities in Virginia to manufacture the totes, thus serving populations in the United States. The entrepreneurs then decided to take 20 percent of their profits and make microloans to farmers and small business owners in the countries where the fabric originated to create jobs there. Microloans are small loans, below $50,000, which certain lenders offer to enterprising startups. These startups, for various reasons (they are in poor nations, at the poverty level), can’t afford a traditional loan from a major bank. The lenders offer business support to the borrower, which in turn helps the borrower repay the microloan. The microloans from Taaluma are repaid when the borrower is able. Repayments are used to buy more fabric, completing Taaluma’s desire to serve dual populations. If the process proved unsuccessful, the co-owners would revise the process to meet the plan’s requirements.
DuFour and Heffern now have fabrics from dozens of countries from Thailand to Ecuador. The totes are specialized with features to meet individual needs. The product line is innovated regularly and Taaluma Totes serves a dual purpose of employing persons with disabilities in Virginia and creating employment for underserved populations in other countries.

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Define the Problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically. Identify what standard or expectation is violated. Determine in which process the problem lies. Avoid trying to solve the problem without data.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
In general, effective problem-solving strategies include the following steps: Define the problem. Come up with alternative solutions. Decide on a solution. Implement the solution. Problem-solving ...
At this stage, the group may return to step one to revise the definition of the problem. Step Three: Develop Alternative Solutions . Analytical, creative problem solving is about creating a variety of solutions, not just one. Often the most obvious answer is not the most effective solution to the problem. The PS group focuses on: •
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Step 1 - Define the Problem. The definition of the problem is the first step in effective problem solving. This may appear to be a simple task, but it is actually quite difficult. This is because problems are frequently complex and multi-layered, making it easy to confuse symptoms with the underlying cause.
Problem Solving refers to the cognitive process of identifying, analysing, and resolving a challenge or obstacle. It involves using logical reasoning, critical thinking, and creativity to find effective solutions. It requires an in-depth analysis to solve problems in many situations, whether simple everyday problems or complex issues.
Defining and analyzing the problem - This is the core of the problem solving process. Sometimes, the real problem isn't originally apparent. Generating and choosing solutions; Putting your solution into practice - If you have followed the process carefully, you'll be surprised at how easy implementing it actually is! In Summary:
Here's the good news: Good problem solving skills can be learned. By its nature, problem solving doesn't adhere to a clear set of do's and don'ts—it requires flexibility, communication, and adaptation. However, most problems you face, at work or in life, can be tackled using four basic steps. First, you must define the problem. This ...
Step 1: Define the Problem. The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable. One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions.
Justify the need. Understand the problem and its wider context. Write a problem statement. The Problem-Definition Process encourages you to define and understand the problem that you're trying to solve, in detail. It also helps you confirm that solving the problem contributes towards your organization's objectives.
There's a 5-step process that you can follow that will allow you to solve your challenges more efficiently and effectively. In short, you need to move through these 5 steps: Defining a problem. Ideating on a solution. Committing to a course of action. Implementing your solution. And finally - analyzing the results.
Here are the basic steps involved in problem-solving: 1. Define the problem. The first step is to analyze the situation carefully to learn more about the problem. A single situation may solve multiple problems. Identify each problem and determine its cause. Try to anticipate the behavior and response of those affected by the problem.
1. Define the Problem: The first step in problem-solving is to clearly define the problem at hand. Take the time to understand the root cause, identify the desired outcome, and gather relevant ...
Join today and save on an annual membership! Although problem-solving is something everyone does on a daily basis, many people lack confidence in their ability. Here we look at the basic problem-solving process to help keep you on the right track.
Try following the first step of the creative problem-solving process and clearly identify the problem. Next, gather data and formulate the challenge. Then, explore ideas and come up with solutions. Develop a plan of action. Finally, note how you would evaluate the effectiveness of your solution.
Discovery (fact-finding) Dream (visioning the future) Design (strategic purpose) Destiny (continuous improvement) 3. "FIVE WHYS" METHOD. The 5 Whys of Problem-Solving Method. This method simply suggests that we ask "Why" at least five times during our review of the problem and in search of a fix.
A: The problem-solving process involves several key steps: identifying the problem, defining it clearly, analyzing it to understand its root causes, generating a range of potential solutions, evaluating and selecting the most viable solution, implementing the chosen solution, and finally, reviewing and reflecting on the effectiveness of the ...
Key Activities in Step 1. · Identify the current state and desired state. · Gather information from multiple sources. · Conduct research and analysis. · Involve key stakeholders in the problem ...
The key to cultivating excellent problem-solving skills is having a distinct process designed to produce solutions. While it may seem like problem-solving involves a complex strategy, it features several steps that are easy to follow. The following steps represent a general problem-solving process you can use when you need to find a solution. 1.
Making a decision to alter the way your team works may also be a problem. Launching new products, technological upgrades, customer feedback collection exercises—all of these are also "problems" that need to be "solved". Here are the steps of a problem-solving process: 1. Defining the Problem. The first step in the process is often ...
The Steps of the Creative Problem-Solving Process. Training oneself to think like an entrepreneur means learning the steps to evaluating a challenge: clarify, ideate, develop, implement, and evaluate (Figure 3.3.1). Figure 3.3.1 3.3. 1: The process of creativity is not random; it is a specific and logical process that includes evaluation.
Solution selling was developed in 1975 by a man named Frank Watts, who introduced his methodology to the corporate world in the 1980s. In the years since, solution selling has become a mainstay of sales professionals, offering a customer-centric alternative to the previously standard approach of "box pushing," which focused on selling product features and specs in, more or less, the same ...