

Should university education be free?
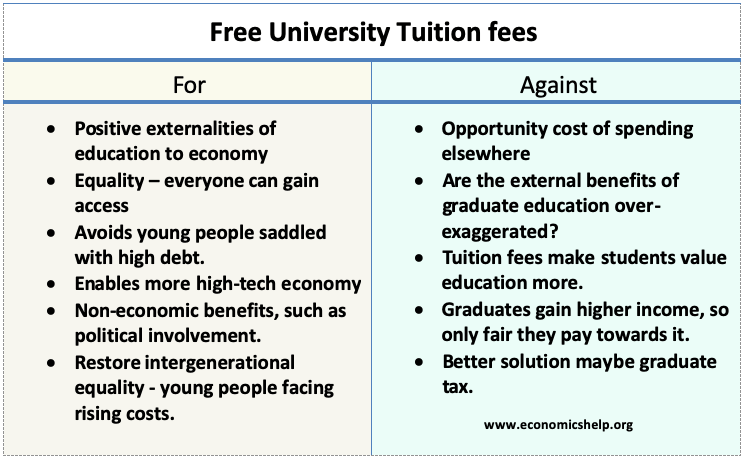
Education has positive benefits for the rest of society. If university education is left to market forces, there may be under-provision, and the economy may suffer from a lack of skilled graduates. Furthermore, in a free market, higher education would become the preserve of wealthy families who can afford to send their children to university. Therefore there is a strong case for the government providing higher education free at the point of use.

However, others argue the positive externalities of higher education are limited, and the prime beneficiaries of a university degree are the graduates who can command a higher paying job. If the external benefits of many degrees are limited, government spending may be misallocated in offering relatively expensive university education. Rather than fund 3-4 year university degrees, governments may be able to get a better return from spending money on primary education and vocational training – training which is more relevant to the needs of the economy.
More details
In recent years, the UK government has sought to increase the amount students pay for studying at university. In the UK, the government have phased out grants and introduced top-up fees. With tuition fees and rising living costs, students could end up paying £50,000 for a three-year degree, and leave university with significant debts.
Some argue this is a mistake. Charging for university education will deter students and leave the UK with a shortfall of skilled labour – and arguably this will damage the long-term prospects of the UK economy. Furthermore, charging to study at university will increase inequality of opportunity as students with low-income parents will be more likely to be deterred from going to university.
Arguments for free university education
- Positive externalities of higher education . Generally, university education does offer some external benefits to society. Higher education leads to a more educated and productive workforce. Countries with high rates of university education generally have higher levels of innovation and productivity growth. Therefore, there is a justification for the government subsidising higher education.
- Equality . There is also a powerful argument that university education should be free to ensure equality of opportunity. If students have to pay for university education, this may dissuade them. In theory, students could take out loans or work part-time, but this may be sufficient to discourage students from studying and instead may enter the job market earlier.
- Increased specialisation of work . The global economy has forced countries, such as the UK to specialise in higher-tech and higher value-added products and services. The UK’s biggest export industries include pharmaceuticals, organic chemicals, optical and surgical instruments, and nuclear technology (see: what does the UK produce? ). Therefore, there is a greater need for skilled graduates who can contribute to these high-tech industries.
- Education is a merit good . One characteristic of a merit good is that people may underestimate the benefits of studying and undervalue higher education. Government provision can encourage people to study.
- Young people facing rising costs . In recent years, we have seen a rise in the cost of living. House prices and rents have risen faster than inflation. This means young people are struggling to meet living costs – even in work. The thought of student debt on top of high living costs, may dissuade people from studying. Free tuition fees is a way to restore the income inequality across generations.
- Non-economic benefits of education . It is tempting to think of university education in purely monetary terms. But graduates can also gain skills and awareness of civic institutions which offer intangible benefits to society.
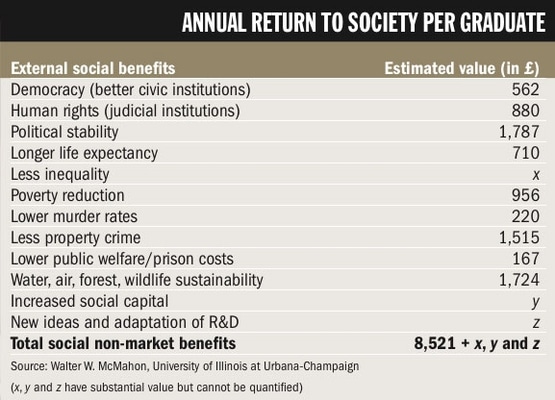
Source: Times Higher Education
Higher Learning, Greater Good: The Private and Social Benefits of Higher Education (2009) Professor McMahon examined the “private non-market benefits” for individuals of having degrees.
This includes better personal health and improved cognitive development in their children, alongside the “social non-market benefits”, such as lower spending on prisons and greater political stability.
- If you wished to evaluate this point, we could ask – is it university education which causes these civic virtues or is it because university education is dominated by middle classes who are more likely to have better health e.t.c. already?
Arguments against free university education
- Opportunity cost . If we spend billions on free university education, there is an opportunity cost of higher taxes or less spending elsewhere. Arguably, there is a greater social benefit from providing vocational training – e.g. so people could become plumbers, electricians e.t.c. There is often a real shortage of these skills in an economy. The UK Commission for skills and education report significant skills shortages in the basic ‘core generic skills’ such as literacy, numeracy and communication skills. These skill shortages are prominent in industries like building, health care, plumbing, social care and construction. The problem is not a shortage of graduates with art degrees, but a shortage of lower-level vocational skills. (See: BBC – skills shortage in the UK ) Therefore, there is a case for charging students to study at university – allowing higher public spending to tackle more basic skill shortages.
- Do we have too many graduates? In recent decades there has been a rapid rise in the number of graduates. But many graduates are now leaving university to take jobs which don’t require a degree. A study by the ONS found that nearly 50% of workers who left university in the past five years are doing jobs which don’t require a degree. ( Telegraph link ) Therefore, it is a mistake to continue to fund the public expansion of university education because the economy doesn’t need more graduates as much as other vocational skills.
- Higher quality of education . The rapid rise in university numbers means that greater pressure is being put on university resources. Since the government is struggling to increase real spending, there is a danger that university education and research may suffer, causing UK education to lag behind other countries. If universities can charge students, it will help maintain standards, quality of teaching and the reputation of UK universities.
- Makes people value education more . If people have to pay to go to university, you could argue that they would value education more. If higher education is free, it may encourage students to take an easy three years of relaxation.
- Signalling function of higher education . Arguably, higher education acts as a signal to employers that graduates have greater capacity. As a consequence, people who gain a degree, end up with a relatively higher salary. Therefore, if they financially gain from studying at university, it is perhaps fair they pay part of the cost. This is especially important for middle-class families, who send a higher proportion of people to higher education.
Another issue is whether we need 50% of 18-year-olds to go to university . The increase in student numbers is a significant contributory factor to the increased financial pressures on universities. Rather than encouraging students to automatically go to university (as some schools do), it may be better to encourage more students to take vocational training and avoid three years of academic study. If less went to university, it would mean the cost per student would be relatively lower.
Another issue is how do you charge students for going to university? If students leave university with large debts, this has negative consequences. But, if we finance university education through a graduate tax paid when graduates get a decent income then it may be less of a disincentive.
Abolition of Tuition Fees
In the 2017 and 2019 election, the Labour party proposed to abolition tuition fees. This is estimated to cost £16 billion.
- How should university education be funded ?
- Arguments for Free Education
- Arguments against Free education
48 thoughts on “Should university education be free?”
In my perceptive the government must allow free education system for two category only. One is the children comes merited and secondly for lower class people
Aka free collage to welfare state
Dear Tejvan Pettinger,
You misspelled Subsidizing*
The E-Time Guy
Subsidizing is American-English spelling. But I use British-English ‘subsidising’
I don’t think you realised/realized that EconomicsHelp is a British-founded website.
Lmao! He must have felt well chuffed with himself…until you pointed that out!
Wouldn’t it be hard to manage that sort of, uh, selection?
Just give everyone a free college degree. No debts, no tax dollars to send Timmy off for free 4 years of living. Free college = tax payer pays to get more competition for his job. Free college = college degree is pointless cause everyone has one
- Pingback: Should Higher Education be Available for Everyone? – /lacher-prisee/
The best way is to offer relatively large number of places free of charge, for instance, 80% of overall demand in the economy to be free/state paid places.
The entrance competition must be held to get the place. The rest will be private places.
Erm..we just that read that…but I guess thanks for repeating it…
I agree that education improves how productive people are in the workforce. A friend of mine is majoring in computer science and they are much more adept because of what they are learning. If governments cannot offer compensation for education then I hope that companies will.
Education has positive benefits for the rest of society. If university education is left to market forces, there may be under-provision, and the economy may suffer from a lack of skilled graduates. Furthermore, in a free market, higher education would become the preserve of wealthy families who can afford to send their children to university. Therefore there is a strong case for the government providing higher education free at the point of use. However, others argue the positive externalities of higher education are limited, and the prime beneficiaries of a university degree are the graduates who can command a higher paying job. If the external benefits of many degrees are limited, government spending may be misallocation in offering relatively expensive university education. Rather than fund 3-4 year university degrees, governments may be able to get better return from spending money on primary education and vocational training – training which is more relevant to the needs of the economy.
plagiarized from another article but great response (next time cite)
Great post and interesting argument here. I have to say that with everything there is going to be advantages and disadvantages. If you offer free university education, it will devalue those who already have a university education. I think if there is a plan to offer free university education, then there needs to be guidelines around it – such as certain state schools, specific courses, etc.
Sorry, I’m not so sure I understand what you mean by “devalue” here. I think university is an opportunity and surely the value in an opportunity is in what you gain out of it, not its availability?
“devalue” as towards the degree itself, not the user. The more of anything (“degrees”) lowers the value, supply and demand. I’m a pretty lefty guy (51. Male, UK) but this one I’m not for, students seem to think degree courses were free before the fees were started under Tony Blair, they wernt, I applied and was refused due to my grade not being good enough. Only a set number of people were given grants. Now after working my way up the slippy pole, I would feel cheated if I have to pay extra tax for someone else to go to Uni. However it this was fully funded from a wealth tax (which I would not pay as I dont have much wealth), then yer go on do it.
I think the university fees should not be free. Maybe exceptions can be made for students from more poor backgrounds and they pay lesser fees but it should not be free because then there is no point. No one would take it seriously anymore & if u paid for something you value it more and work harder You should work hard for something you want and not expect everything to be handed on a silver plater
It’s not being handed on a silver plate – you still have to work to be accepted and work to graduate. Making uni free doesn’t devalue its certification.
I totally agree when you said that it would be hard for low-income parents to send their children to universities. This is the actual problem of my cousin which is why he is lucky that his dad is a military because there might be assistance for them. I will suggest this to them since they might not be aware, and he will be going to college in two years time.
all the Arguments against free university education written here are silly and nothing to do with how things work in real life, you can see it in all quality countries that have free tertiary education, like in northern europe. or in any other europe country, you can check it out.
I don’t get the argument about too many people going to university and getting a degree? Or am I the thick one here?
We’re not handing out free degrees, we’re giving everyone an equal OPPORTUNITY to get a degree, and a higher education for their future. So many people would’ve made very useful citizens had they have had a chance to fully develop their skills, and we forget that making uni free doesn’t make it any easier to get into and to graduate from.
Making uni free doesn’t devalue its certification btw
Very interesting, good job and thanks for sharing such a good blog.
Everyone grows up going to school and unless it is a private school, the government funds it once we enroll and all we need to do is show up. Once we graduate high school or get a GED, suddenly the price for a good quality education sky rockets and everyone starts scrambling to find a job, or get as many grants, scholarships, and loans as they possibly can to cover the ever growing debt most people will have once they graduate college. The debate on whether or not to make college free or at least more affordable has grown, and more and more people including politicians are looking for ways to make this happen. With every good idea there will be problems that are solved, but new ones will arise. Some reasons people want college level education to be free is it will give everyone a chance for education past high school, it avoids student debt, and it was free when they first made colleges, but the downfalls might include raised taxes, a sacrifice of standards, and financial irresponsibility from the students. Most of the people that attend college are from wealthier families because they are able to pay the bill. When colleges were first made, they were all actually free due to the lack of students and establishments under the Morrill Act of 1862 (Beelineweb.com et al.). This act allowed colleges to be created by the state on federal lands to make a higher education system available to all who desired it regardless of class or income. Now the sum that these schools require is absolutely outrageous. Even the wealthy are not able to afford quality education without taking out a loan. With all the loans, people are acquiring more and more debt, but without the cost of tuition, that debt would decrease dramatically (Pettinger). Many people that need loans currently, would be able to attend and get a quality education without worrying about the debt that will follow them for a long time. Along with that, more people that are not able to go to college now will be able to attend just because they want to instead of forgetting about college as even an option because it costs an arm and a leg (Ayres). Free college education would open many doors that have been shut due to financial struggles. With all the good that would come from free college level education, there are quite a bit of issues that might arise with it. Although free college-level education might seem great, there quite a few things that would be sacrificed with the elimination of tuition costs. With the sacrificed costs, some of the quality of education might be sacrificed as well (Ayres). Without the constant funds coming in from the enrolled students, the facilities might go a while without very necessary updates and repairs. There is always going to be a need for money to pay for all the things colleges provide and if students are not paying for it, the costs would shift from being a personal expense to a societal expense (Beelineweb.com et al.). The reality for everyone would be the increase of taxes to cover the necessary costs. Students would have their tuition covered by the government issued taxes. Without the need for loans, students might lose their financial responsibility because they will not have needed to manage their money to pay for their classes and take their education for granted (Amit Kumar). Some might actually devalue their diploma because they did not pay for the classes. The diploma would have the same value as a high school diploma. Although these things are factors that need to be considered, having education that is at least partially free would be good to allow more people to get the opportunity for getting a better education. Hopefully we will be able to find a way where we are able to go back to when colleges were first made, give everyone an equal opportunity for their education, and avoid debt, but also avoid some of the downfalls from taxes, sacrificed standards, and financial irresponsibility.
Comments are closed.
University Education and Its Purpose Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
University education refers to a level of education that is offered at universities. This type education normally follows upon a successful completion of education at secondary school or other mid-level colleges and tertiary institutions, students are normally awarded academic degrees after going through an undergraduate or a postgraduate education by the respective universities. University education takes high school, tertiary and college education to a higher level and students are required to major in a major field of study that will form their career once they graduate. It is for this purpose that university education must lead to the development of the learner in all aspects and not just on career development.
When the university education was set up almost a century ago, academicians clearly set the basic function of these institutions to be that of imparting wisdom and enlightenment to the learners and they were meant for the few elite and well-endowed people. Unfortunately, this has not been adhered to in many universities, most of which have now shifted their focus and are now commercialized with many people trooping in to attain a degree in various fields. Though mass university education is a turn of good events, this has diluted its basic function of developing a learner into an all rounded individual, rather, most universities now focus on enabling a leaner achieve an ‘A’ grade. It is no wonder universities base their success is based on the number of graduates who obtain good grades, rather than on the ability of these students to come up with solutions to problems affecting the society.
One of the most important functions of university education is developing the learner’s character and training them on real-life expectations. One might argue that these should be already developed before entering the university, they should, unfortunately, the education systems at pre-university levels do not give the learner an opportunity to discover himself and have an uninterrupted character growth. This is due to congestion in the syllabi as education at this level is more generalized and as a result, learners spend most of their time grasping new ideas given in class. A student gets to have a complete character evolution once he enters the university and it is common for a person who was troublesome in his teenage years get out of university mature and well behaved.
This character modeling, however, must be accompanied by working hard in class to make one more productive in future. Students should not just grasp ideas taught in class for passing exams, classroom sessions should be used to further one’s knowledge in a particular field in a manner that they can apply such skills in real life situations. The classroom knowledge gives one the qualifications to acquire a job, but character is needed to maintain such a job. For example, a person may land a well-paying job but may find himself jobless after a few months due to poor relationship with co-workers or poor work attitude. Character must develop in tandem with one’s academic qualification.
In summary, the main purpose of university education is to impart knowledge to the learners and help them undergo character development. A lack of either of these would lead to a shaky future in the social arena. Universities should also restructure to enable the students undergo both learning processes and not just the classroom knowledge.
- Tertiary Hospital's Employee Behavior by Maslow
- The Future of the Tertiary Sectors of Economy in Canada
- The Plight of Pharmacists at Tertiary Hospital
- The Education in The Early National Period
- The Concept of a Bachelor’s Degree in Education
- Decision-Making. College or Break After High School
- Reflection of Personal Learning Style in Psychology
- Who Should Go to College
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, December 30). University Education and Its Purpose. https://ivypanda.com/essays/university-education-and-its-purpose/
"University Education and Its Purpose." IvyPanda , 30 Dec. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/university-education-and-its-purpose/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'University Education and Its Purpose'. 30 December.
IvyPanda . 2021. "University Education and Its Purpose." December 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/university-education-and-its-purpose/.
1. IvyPanda . "University Education and Its Purpose." December 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/university-education-and-its-purpose/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "University Education and Its Purpose." December 30, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/university-education-and-its-purpose/.
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

Creative samples from the experts
↑ Return to Essay Samples
Argumentative Essay: Getting a Good Education
Getting an education is compulsory in the developed world, but so many of us don’t appreciate it enough. We should value our education a lot more and work harder, because it is compulsory for so many different reasons and adds so much value to our lives. There are so many positive outcomes of education, but most of them come under the two banners of allowing us to develop personally, and improving our life chances.
Learning gives us so much that we otherwise wouldn’t have. Besides the obvious skills and facts that we learn, we learn self-discipline and self-motivation, timekeeping skills, social and communication skills and so much more. We also gain confidence and self-esteem through completing tasks and being praised for good work, as well as learning right and wrong as we are punished for any wrongdoing from a young age. Being educated is shown to increase people’s sense of self-worth, life satisfaction and overall happiness, so ultimately being a well-rounded person with lots of potential of happiness is a major outcome of education.
This development in itself increases our chances in life and our potential to do the things we want to do, as social skills gained allow us to form good relationships, and all of the other skills will help when it comes to getting a job. There is, unsurprisingly, a positive correlation between the level of education that people receive and the amount of money they earn. People that are educated are less likely to be unemployed or be on low wages with which they can barely feed their families. They are more likely to afford a nice house in a good area, a nice car, and regular family vacations. Educated people are also less likely to go to prison, because they will be able to provide for their families without crime and are less likely to be violent as they can communicate better with language.
Getting a good high school education also improves our chances of being able to go to college . This further study adds so many different skills to your arsenal that employment prospects and earning potential become better again. Whatever level someone has studied to though, a good education will get them further than someone with little or no education.
This is because of the marketable skills that they have gained. Literacy and basic math skills are at the foundation of independent living and being able to work. Good communication skills and ability to work both with a team and independently are often a basic requirement for any job, and these are developed in the education system through group and individual projects. All in all, education gives us so many skills that it is necessary for both happiness and success in life.

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
Not Every Student Should Go to College. And That’s OK

- Share article
Forty years ago 32 percent of counselors and teachers advised all students to go to college. Just 10 years later, in 1990, that percentage had doubled with roughly two-thirds of educators recommending college for all. Despite a recent surge in popularity for career and technical education, signs indicate that the college recommendation trend has increased over the last generation.
All that college-going advice may do harm in ways most adults in the lives of teenagers hadn’t realized. Research we conducted over the past several years suggests that a “college for all” message causes far too many students from all demographics to make choices that result in failure.
Instead of forcing college on students, educators would do better to encourage them to consider more than one pathway into a good life. Some pathways will include college now or later and some not. Educators also have a responsibility to help create those pathways, and students’ choices rather than their backgrounds should determine which they take.
Students who attend college for extrinsic reasons suffer poor outcomes.
In our research, we collected and analyzed more than 200 stories from students about their postsecondary education choices and surveyed over 1,000 more students to understand what caused them to enroll in college, both two- and four-year institutions, as well as some coding bootcamps and shorter graduate programs. Our participants were roughly representative of the population of students that attend college in the United States across gender, racial, and ethnic lines. Forty-six percent were first-generation college students, meaning neither of their parents had completed a bachelor’s degree. Eighteen percent had at least one child, and 60 percent lived in households with incomes that placed them in the bottom three socio-economic quintiles.
We learned that a significant number of students from all backgrounds enroll in college to do what’s expected of them or to help them get away from a bad circumstance in their lives. These students go to college not because they want the college experience or because of what college will help them obtain. In other words, they are motivated by external factors not internal goals. They choose college because it is a socially acceptable answer to what they are doing next.
Students who attend college for extrinsic reasons suffer poor outcomes. According to our research, 74 percent of those who attended college to “do what was expected of them” dropped out or transferred. Of those who went to college “to get away,” over half had left the school they were attending without a degree at the time we talked to them.
One student we talked to, who was the first in her family to attend college, chose college to get away from a bad relationship with her stepdad. She enrolled in a college three hours away from home—even though it didn’t have the courses of study in which she was interested. Once there, she took a heavier-than-usual course load first semester, partied hard, and found herself on academic probation.
Things improved a little second semester, but the improvement was not enough to justify the money she was spending on tuition, she thought. She still struggled with time management and a nagging sense that she didn’t know why she was enrolled. So with $40,000 in federal and private student loans outstanding, she dropped out, returned home, mended things with her family, and started to find jobs to help pay off the debt.
Too many students go to college not knowing what they want to get out of it or how to make it work for them. Committing to a four-year school and taking on lots of debt when they lack passion and focus for the endeavor is risky, particularly given the grim college completion and student debt statistics.
Over 40 percent of first-time, full-time students who started college in the fall of 2012 failed to graduate from four-year programs within six years, according to the National Student Clearinghouse Research Center. Non-completers not only lose out on the benefits of a college degree, but also face increased debt without increased earnings. Non-completers have a three-fold higher risk of default than completers, according to the Center for American Progress.
Instead of adding to the pressure around college, which parents often fuel, high school educators should be the first line of defense for students who might benefit more from another path. Yes, educators must avoid the low expectations that direct students away from college because of their family’s income, their race, or their ethnicity. Instead, they should encourage all students to reflect on their goals and explore more than one pathway to purpose and success.
One way to help is through courses that are now emerging to give students structured opportunities to discover what drives them. But high schools should go further. They must counter the narrowing of the curriculum over the last couple decades caused by an overemphasis on test results and the decrease in career and technical education pathways in many schools. Extracurricular activities, experiential learning, and opportunities to build relationships with adults outside of school through real-world projects can help students discover their strengths and interests. Rather than marginalize these opportunities, schools should integrate them into every student’s program.
Our research in no way implies that college is a one-time decision. Just because college isn’t the right step now
for a student doesn’t mean it will never be the right step. College and, more to the point, education can help bring a lifetime of happiness, as studies have documented . But that education has to be at the right time and in the right circumstance.
If students aren’t yet ready, then taking a gap year can be a smart move. The stereotype of rich kids gallivanting around Europe is outmoded. An increasing number of programs offer gap-year experiences with financial aid so that all students can partake of them. Counselors and teachers should help students explore these opportunities, which are filled with immersive activities that help students learn about themselves and, in many cases, earn money through holding a series of jobs. This can make a gap year considerably more affordable than college.
Far better than a monolithic college-for-all vision is for individuals to know where they are in their lives, what they want, and how to articulate it. Only then can we ensure that education delivers on its promise of helping people build their passions, fulfill their human potential, and live a lifetime of productive struggle and happiness.
A version of this article appeared in the March 11, 2020 edition of Education Week as The Danger of ‘College for All’
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an a+ argumentative essay.
Miscellaneous

You'll no doubt have to write a number of argumentative essays in both high school and college, but what, exactly, is an argumentative essay and how do you write the best one possible? Let's take a look.
A great argumentative essay always combines the same basic elements: approaching an argument from a rational perspective, researching sources, supporting your claims using facts rather than opinion, and articulating your reasoning into the most cogent and reasoned points. Argumentative essays are great building blocks for all sorts of research and rhetoric, so your teachers will expect you to master the technique before long.
But if this sounds daunting, never fear! We'll show how an argumentative essay differs from other kinds of papers, how to research and write them, how to pick an argumentative essay topic, and where to find example essays. So let's get started.
What Is an Argumentative Essay? How Is it Different from Other Kinds of Essays?
There are two basic requirements for any and all essays: to state a claim (a thesis statement) and to support that claim with evidence.
Though every essay is founded on these two ideas, there are several different types of essays, differentiated by the style of the writing, how the writer presents the thesis, and the types of evidence used to support the thesis statement.
Essays can be roughly divided into four different types:
#1: Argumentative #2: Persuasive #3: Expository #4: Analytical
So let's look at each type and what the differences are between them before we focus the rest of our time to argumentative essays.
Argumentative Essay
Argumentative essays are what this article is all about, so let's talk about them first.
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance.
An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the factually and logically correct one. This means that an argumentative essay must use only evidence-based support to back up a claim , rather than emotional or philosophical reasoning (which is often allowed in other types of essays). Thus, an argumentative essay has a burden of substantiated proof and sources , whereas some other types of essays (namely persuasive essays) do not.
You can write an argumentative essay on any topic, so long as there's room for argument. Generally, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one, so long as you support the argumentative essay with hard evidence.
Example topics of an argumentative essay:
- "Should farmers be allowed to shoot wolves if those wolves injure or kill farm animals?"
- "Should the drinking age be lowered in the United States?"
- "Are alternatives to democracy effective and/or feasible to implement?"
The next three types of essays are not argumentative essays, but you may have written them in school. We're going to cover them so you know what not to do for your argumentative essay.
Persuasive Essay
Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays, so it can be easy to get them confused. But knowing what makes an argumentative essay different than a persuasive essay can often mean the difference between an excellent grade and an average one.
Persuasive essays seek to persuade a reader to agree with the point of view of the writer, whether that point of view is based on factual evidence or not. The writer has much more flexibility in the evidence they can use, with the ability to use moral, cultural, or opinion-based reasoning as well as factual reasoning to persuade the reader to agree the writer's side of a given issue.
Instead of being forced to use "pure" reason as one would in an argumentative essay, the writer of a persuasive essay can manipulate or appeal to the reader's emotions. So long as the writer attempts to steer the readers into agreeing with the thesis statement, the writer doesn't necessarily need hard evidence in favor of the argument.
Often, you can use the same topics for both a persuasive essay or an argumentative one—the difference is all in the approach and the evidence you present.
Example topics of a persuasive essay:
- "Should children be responsible for their parents' debts?"
- "Should cheating on a test be automatic grounds for expulsion?"
- "How much should sports leagues be held accountable for player injuries and the long-term consequences of those injuries?"
Expository Essay
An expository essay is typically a short essay in which the writer explains an idea, issue, or theme , or discusses the history of a person, place, or idea.
This is typically a fact-forward essay with little argument or opinion one way or the other.
Example topics of an expository essay:
- "The History of the Philadelphia Liberty Bell"
- "The Reasons I Always Wanted to be a Doctor"
- "The Meaning Behind the Colloquialism ‘People in Glass Houses Shouldn't Throw Stones'"
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay seeks to delve into the deeper meaning of a text or work of art, or unpack a complicated idea . These kinds of essays closely interpret a source and look into its meaning by analyzing it at both a macro and micro level.
This type of analysis can be augmented by historical context or other expert or widely-regarded opinions on the subject, but is mainly supported directly through the original source (the piece or art or text being analyzed) .
Example topics of an analytical essay:
- "Victory Gin in Place of Water: The Symbolism Behind Gin as the Only Potable Substance in George Orwell's 1984"
- "Amarna Period Art: The Meaning Behind the Shift from Rigid to Fluid Poses"
- "Adultery During WWII, as Told Through a Series of Letters to and from Soldiers"

There are many different types of essay and, over time, you'll be able to master them all.
A Typical Argumentative Essay Assignment
The average argumentative essay is between three to five pages, and will require at least three or four separate sources with which to back your claims . As for the essay topic , you'll most often be asked to write an argumentative essay in an English class on a "general" topic of your choice, ranging the gamut from science, to history, to literature.
But while the topics of an argumentative essay can span several different fields, the structure of an argumentative essay is always the same: you must support a claim—a claim that can reasonably have multiple sides—using multiple sources and using a standard essay format (which we'll talk about later on).
This is why many argumentative essay topics begin with the word "should," as in:
- "Should all students be required to learn chemistry in high school?"
- "Should children be required to learn a second language?"
- "Should schools or governments be allowed to ban books?"
These topics all have at least two sides of the argument: Yes or no. And you must support the side you choose with evidence as to why your side is the correct one.
But there are also plenty of other ways to frame an argumentative essay as well:
- "Does using social media do more to benefit or harm people?"
- "Does the legal status of artwork or its creators—graffiti and vandalism, pirated media, a creator who's in jail—have an impact on the art itself?"
- "Is or should anyone ever be ‘above the law?'"
Though these are worded differently than the first three, you're still essentially forced to pick between two sides of an issue: yes or no, for or against, benefit or detriment. Though your argument might not fall entirely into one side of the divide or another—for instance, you could claim that social media has positively impacted some aspects of modern life while being a detriment to others—your essay should still support one side of the argument above all. Your final stance would be that overall , social media is beneficial or overall , social media is harmful.
If your argument is one that is mostly text-based or backed by a single source (e.g., "How does Salinger show that Holden Caulfield is an unreliable narrator?" or "Does Gatsby personify the American Dream?"), then it's an analytical essay, rather than an argumentative essay. An argumentative essay will always be focused on more general topics so that you can use multiple sources to back up your claims.
Good Argumentative Essay Topics
So you know the basic idea behind an argumentative essay, but what topic should you write about?
Again, almost always, you'll be asked to write an argumentative essay on a free topic of your choice, or you'll be asked to select between a few given topics . If you're given complete free reign of topics, then it'll be up to you to find an essay topic that no only appeals to you, but that you can turn into an A+ argumentative essay.
What makes a "good" argumentative essay topic depends on both the subject matter and your personal interest —it can be hard to give your best effort on something that bores you to tears! But it can also be near impossible to write an argumentative essay on a topic that has no room for debate.
As we said earlier, a good argumentative essay topic will be one that has the potential to reasonably go in at least two directions—for or against, yes or no, and why . For example, it's pretty hard to write an argumentative essay on whether or not people should be allowed to murder one another—not a whole lot of debate there for most people!—but writing an essay for or against the death penalty has a lot more wiggle room for evidence and argument.
A good topic is also one that can be substantiated through hard evidence and relevant sources . So be sure to pick a topic that other people have studied (or at least studied elements of) so that you can use their data in your argument. For example, if you're arguing that it should be mandatory for all middle school children to play a sport, you might have to apply smaller scientific data points to the larger picture you're trying to justify. There are probably several studies you could cite on the benefits of physical activity and the positive effect structure and teamwork has on young minds, but there's probably no study you could use where a group of scientists put all middle-schoolers in one jurisdiction into a mandatory sports program (since that's probably never happened). So long as your evidence is relevant to your point and you can extrapolate from it to form a larger whole, you can use it as a part of your resource material.
And if you need ideas on where to get started, or just want to see sample argumentative essay topics, then check out these links for hundreds of potential argumentative essay topics.
101 Persuasive (or Argumentative) Essay and Speech Topics
301 Prompts for Argumentative Writing
Top 50 Ideas for Argumentative/Persuasive Essay Writing
[Note: some of these say "persuasive essay topics," but just remember that the same topic can often be used for both a persuasive essay and an argumentative essay; the difference is in your writing style and the evidence you use to support your claims.]

KO! Find that one argumentative essay topic you can absolutely conquer.
Argumentative Essay Format
Argumentative Essays are composed of four main elements:
- A position (your argument)
- Your reasons
- Supporting evidence for those reasons (from reliable sources)
- Counterargument(s) (possible opposing arguments and reasons why those arguments are incorrect)
If you're familiar with essay writing in general, then you're also probably familiar with the five paragraph essay structure . This structure is a simple tool to show how one outlines an essay and breaks it down into its component parts, although it can be expanded into as many paragraphs as you want beyond the core five.
The standard argumentative essay is often 3-5 pages, which will usually mean a lot more than five paragraphs, but your overall structure will look the same as a much shorter essay.
An argumentative essay at its simplest structure will look like:
Paragraph 1: Intro
- Set up the story/problem/issue
- Thesis/claim
Paragraph 2: Support
- Reason #1 claim is correct
- Supporting evidence with sources
Paragraph 3: Support
- Reason #2 claim is correct
Paragraph 4: Counterargument
- Explanation of argument for the other side
- Refutation of opposing argument with supporting evidence
Paragraph 5: Conclusion
- Re-state claim
- Sum up reasons and support of claim from the essay to prove claim is correct
Now let's unpack each of these paragraph types to see how they work (with examples!), what goes into them, and why.
Paragraph 1—Set Up and Claim
Your first task is to introduce the reader to the topic at hand so they'll be prepared for your claim. Give a little background information, set the scene, and give the reader some stakes so that they care about the issue you're going to discuss.
Next, you absolutely must have a position on an argument and make that position clear to the readers. It's not an argumentative essay unless you're arguing for a specific claim, and this claim will be your thesis statement.
Your thesis CANNOT be a mere statement of fact (e.g., "Washington DC is the capital of the United States"). Your thesis must instead be an opinion which can be backed up with evidence and has the potential to be argued against (e.g., "New York should be the capital of the United States").
Paragraphs 2 and 3—Your Evidence
These are your body paragraphs in which you give the reasons why your argument is the best one and back up this reasoning with concrete evidence .
The argument supporting the thesis of an argumentative essay should be one that can be supported by facts and evidence, rather than personal opinion or cultural or religious mores.
For example, if you're arguing that New York should be the new capital of the US, you would have to back up that fact by discussing the factual contrasts between New York and DC in terms of location, population, revenue, and laws. You would then have to talk about the precedents for what makes for a good capital city and why New York fits the bill more than DC does.
Your argument can't simply be that a lot of people think New York is the best city ever and that you agree.
In addition to using concrete evidence, you always want to keep the tone of your essay passionate, but impersonal . Even though you're writing your argument from a single opinion, don't use first person language—"I think," "I feel," "I believe,"—to present your claims. Doing so is repetitive, since by writing the essay you're already telling the audience what you feel, and using first person language weakens your writing voice.
For example,
"I think that Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
"Washington DC is no longer suited to be the capital city of the United States."
The second statement sounds far stronger and more analytical.
Paragraph 4—Argument for the Other Side and Refutation
Even without a counter argument, you can make a pretty persuasive claim, but a counterargument will round out your essay into one that is much more persuasive and substantial.
By anticipating an argument against your claim and taking the initiative to counter it, you're allowing yourself to get ahead of the game. This way, you show that you've given great thought to all sides of the issue before choosing your position, and you demonstrate in multiple ways how yours is the more reasoned and supported side.
Paragraph 5—Conclusion
This paragraph is where you re-state your argument and summarize why it's the best claim.
Briefly touch on your supporting evidence and voila! A finished argumentative essay.
Your essay should have just as awesome a skeleton as this plesiosaur does. (In other words: a ridiculously awesome skeleton)
Argumentative Essay Example: 5-Paragraph Style
It always helps to have an example to learn from. I've written a full 5-paragraph argumentative essay here. Look at how I state my thesis in paragraph 1, give supporting evidence in paragraphs 2 and 3, address a counterargument in paragraph 4, and conclude in paragraph 5.
Topic: Is it possible to maintain conflicting loyalties?
Paragraph 1
It is almost impossible to go through life without encountering a situation where your loyalties to different people or causes come into conflict with each other. Maybe you have a loving relationship with your sister, but she disagrees with your decision to join the army, or you find yourself torn between your cultural beliefs and your scientific ones. These conflicting loyalties can often be maintained for a time, but as examples from both history and psychological theory illustrate, sooner or later, people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever.
The first two sentences set the scene and give some hypothetical examples and stakes for the reader to care about.
The third sentence finishes off the intro with the thesis statement, making very clear how the author stands on the issue ("people have to make a choice between competing loyalties, as no one can maintain a conflicting loyalty or belief system forever." )
Paragraphs 2 and 3
Psychological theory states that human beings are not equipped to maintain conflicting loyalties indefinitely and that attempting to do so leads to a state called "cognitive dissonance." Cognitive dissonance theory is the psychological idea that people undergo tremendous mental stress or anxiety when holding contradictory beliefs, values, or loyalties (Festinger, 1957). Even if human beings initially hold a conflicting loyalty, they will do their best to find a mental equilibrium by making a choice between those loyalties—stay stalwart to a belief system or change their beliefs. One of the earliest formal examples of cognitive dissonance theory comes from Leon Festinger's When Prophesy Fails . Members of an apocalyptic cult are told that the end of the world will occur on a specific date and that they alone will be spared the Earth's destruction. When that day comes and goes with no apocalypse, the cult members face a cognitive dissonance between what they see and what they've been led to believe (Festinger, 1956). Some choose to believe that the cult's beliefs are still correct, but that the Earth was simply spared from destruction by mercy, while others choose to believe that they were lied to and that the cult was fraudulent all along. Both beliefs cannot be correct at the same time, and so the cult members are forced to make their choice.
But even when conflicting loyalties can lead to potentially physical, rather than just mental, consequences, people will always make a choice to fall on one side or other of a dividing line. Take, for instance, Nicolaus Copernicus, a man born and raised in Catholic Poland (and educated in Catholic Italy). Though the Catholic church dictated specific scientific teachings, Copernicus' loyalty to his own observations and scientific evidence won out over his loyalty to his country's government and belief system. When he published his heliocentric model of the solar system--in opposition to the geocentric model that had been widely accepted for hundreds of years (Hannam, 2011)-- Copernicus was making a choice between his loyalties. In an attempt t o maintain his fealty both to the established system and to what he believed, h e sat on his findings for a number of years (Fantoli, 1994). But, ultimately, Copernicus made the choice to side with his beliefs and observations above all and published his work for the world to see (even though, in doing so, he risked both his reputation and personal freedoms).
These two paragraphs provide the reasons why the author supports the main argument and uses substantiated sources to back those reasons.
The paragraph on cognitive dissonance theory gives both broad supporting evidence and more narrow, detailed supporting evidence to show why the thesis statement is correct not just anecdotally but also scientifically and psychologically. First, we see why people in general have a difficult time accepting conflicting loyalties and desires and then how this applies to individuals through the example of the cult members from the Dr. Festinger's research.
The next paragraph continues to use more detailed examples from history to provide further evidence of why the thesis that people cannot indefinitely maintain conflicting loyalties is true.
Paragraph 4
Some will claim that it is possible to maintain conflicting beliefs or loyalties permanently, but this is often more a matter of people deluding themselves and still making a choice for one side or the other, rather than truly maintaining loyalty to both sides equally. For example, Lancelot du Lac typifies a person who claims to maintain a balanced loyalty between to two parties, but his attempt to do so fails (as all attempts to permanently maintain conflicting loyalties must). Lancelot tells himself and others that he is equally devoted to both King Arthur and his court and to being Queen Guinevere's knight (Malory, 2008). But he can neither be in two places at once to protect both the king and queen, nor can he help but let his romantic feelings for the queen to interfere with his duties to the king and the kingdom. Ultimately, he and Queen Guinevere give into their feelings for one another and Lancelot—though he denies it—chooses his loyalty to her over his loyalty to Arthur. This decision plunges the kingdom into a civil war, ages Lancelot prematurely, and ultimately leads to Camelot's ruin (Raabe, 1987). Though Lancelot claimed to have been loyal to both the king and the queen, this loyalty was ultimately in conflict, and he could not maintain it.
Here we have the acknowledgement of a potential counter-argument and the evidence as to why it isn't true.
The argument is that some people (or literary characters) have asserted that they give equal weight to their conflicting loyalties. The refutation is that, though some may claim to be able to maintain conflicting loyalties, they're either lying to others or deceiving themselves. The paragraph shows why this is true by providing an example of this in action.
Paragraph 5
Whether it be through literature or history, time and time again, people demonstrate the challenges of trying to manage conflicting loyalties and the inevitable consequences of doing so. Though belief systems are malleable and will often change over time, it is not possible to maintain two mutually exclusive loyalties or beliefs at once. In the end, people always make a choice, and loyalty for one party or one side of an issue will always trump loyalty to the other.
The concluding paragraph summarizes the essay, touches on the evidence presented, and re-states the thesis statement.
How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 8 Steps
Writing the best argumentative essay is all about the preparation, so let's talk steps:
#1: Preliminary Research
If you have the option to pick your own argumentative essay topic (which you most likely will), then choose one or two topics you find the most intriguing or that you have a vested interest in and do some preliminary research on both sides of the debate.
Do an open internet search just to see what the general chatter is on the topic and what the research trends are.
Did your preliminary reading influence you to pick a side or change your side? Without diving into all the scholarly articles at length, do you believe there's enough evidence to support your claim? Have there been scientific studies? Experiments? Does a noted scholar in the field agree with you? If not, you may need to pick another topic or side of the argument to support.
#2: Pick Your Side and Form Your Thesis
Now's the time to pick the side of the argument you feel you can support the best and summarize your main point into your thesis statement.
Your thesis will be the basis of your entire essay, so make sure you know which side you're on, that you've stated it clearly, and that you stick by your argument throughout the entire essay .
#3: Heavy-Duty Research Time
You've taken a gander at what the internet at large has to say on your argument, but now's the time to actually read those sources and take notes.
Check scholarly journals online at Google Scholar , the Directory of Open Access Journals , or JStor . You can also search individual university or school libraries and websites to see what kinds of academic articles you can access for free. Keep track of your important quotes and page numbers and put them somewhere that's easy to find later.
And don't forget to check your school or local libraries as well!
#4: Outline
Follow the five-paragraph outline structure from the previous section.
Fill in your topic, your reasons, and your supporting evidence into each of the categories.
Before you begin to flesh out the essay, take a look at what you've got. Is your thesis statement in the first paragraph? Is it clear? Is your argument logical? Does your supporting evidence support your reasoning?
By outlining your essay, you streamline your process and take care of any logic gaps before you dive headfirst into the writing. This will save you a lot of grief later on if you need to change your sources or your structure, so don't get too trigger-happy and skip this step.
Now that you've laid out exactly what you'll need for your essay and where, it's time to fill in all the gaps by writing it out.
Take it one step at a time and expand your ideas into complete sentences and substantiated claims. It may feel daunting to turn an outline into a complete draft, but just remember that you've already laid out all the groundwork; now you're just filling in the gaps.
If you have the time before deadline, give yourself a day or two (or even just an hour!) away from your essay . Looking it over with fresh eyes will allow you to see errors, both minor and major, that you likely would have missed had you tried to edit when it was still raw.
Take a first pass over the entire essay and try your best to ignore any minor spelling or grammar mistakes—you're just looking at the big picture right now. Does it make sense as a whole? Did the essay succeed in making an argument and backing that argument up logically? (Do you feel persuaded?)
If not, go back and make notes so that you can fix it for your final draft.
Once you've made your revisions to the overall structure, mark all your small errors and grammar problems so you can fix them in the next draft.
#7: Final Draft
Use the notes you made on the rough draft and go in and hack and smooth away until you're satisfied with the final result.
A checklist for your final draft:
- Formatting is correct according to your teacher's standards
- No errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation
- Essay is the right length and size for the assignment
- The argument is present, consistent, and concise
- Each reason is supported by relevant evidence
- The essay makes sense overall
#8: Celebrate!
Once you've brought that final draft to a perfect polish and turned in your assignment, you're done! Go you!

Be prepared and ♪ you'll never go hungry again ♪, *cough*, or struggle with your argumentative essay-writing again. (Walt Disney Studios)
Good Examples of Argumentative Essays Online
Theory is all well and good, but examples are key. Just to get you started on what a fully-fleshed out argumentative essay looks like, let's see some examples in action.
Check out these two argumentative essay examples on the use of landmines and freons (and note the excellent use of concrete sources to back up their arguments!).
The Use of Landmines
A Shattered Sky
The Take-Aways: Keys to Writing an Argumentative Essay
At first, writing an argumentative essay may seem like a monstrous hurdle to overcome, but with the proper preparation and understanding, you'll be able to knock yours out of the park.
Remember the differences between a persuasive essay and an argumentative one, make sure your thesis is clear, and double-check that your supporting evidence is both relevant to your point and well-sourced . Pick your topic, do your research, make your outline, and fill in the gaps. Before you know it, you'll have yourself an A+ argumentative essay there, my friend.
What's Next?
Now you know the ins and outs of an argumentative essay, but how comfortable are you writing in other styles? Learn more about the four writing styles and when it makes sense to use each .
Understand how to make an argument, but still having trouble organizing your thoughts? Check out our guide to three popular essay formats and choose which one is right for you.
Ready to make your case, but not sure what to write about? We've created a list of 50 potential argumentative essay topics to spark your imagination.
Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

8 Effective Strategies to Write Argumentative Essays
In a bustling university town, there lived a student named Alex. Popular for creativity and wit, one challenge seemed insurmountable for Alex– the dreaded argumentative essay!
One gloomy afternoon, as the rain tapped against the window pane, Alex sat at his cluttered desk, staring at a blank document on the computer screen. The assignment loomed large: a 350-600-word argumentative essay on a topic of their choice . With a sigh, he decided to seek help of mentor, Professor Mitchell, who was known for his passion for writing.
Entering Professor Mitchell’s office was like stepping into a treasure of knowledge. Bookshelves lined every wall, faint aroma of old manuscripts in the air and sticky notes over the wall. Alex took a deep breath and knocked on his door.
“Ah, Alex,” Professor Mitchell greeted with a warm smile. “What brings you here today?”
Alex confessed his struggles with the argumentative essay. After hearing his concerns, Professor Mitchell said, “Ah, the argumentative essay! Don’t worry, Let’s take a look at it together.” As he guided Alex to the corner shelf, Alex asked,
Table of Contents
“What is an Argumentative Essay?”
The professor replied, “An argumentative essay is a type of academic writing that presents a clear argument or a firm position on a contentious issue. Unlike other forms of essays, such as descriptive or narrative essays, these essays require you to take a stance, present evidence, and convince your audience of the validity of your viewpoint with supporting evidence. A well-crafted argumentative essay relies on concrete facts and supporting evidence rather than merely expressing the author’s personal opinions . Furthermore, these essays demand comprehensive research on the chosen topic and typically follows a structured format consisting of three primary sections: an introductory paragraph, three body paragraphs, and a concluding paragraph.”
He continued, “Argumentative essays are written in a wide range of subject areas, reflecting their applicability across disciplines. They are written in different subject areas like literature and philosophy, history, science and technology, political science, psychology, economics and so on.
Alex asked,
“When is an Argumentative Essay Written?”
The professor answered, “Argumentative essays are often assigned in academic settings, but they can also be written for various other purposes, such as editorials, opinion pieces, or blog posts. Some situations to write argumentative essays include:
1. Academic assignments
In school or college, teachers may assign argumentative essays as part of coursework. It help students to develop critical thinking and persuasive writing skills .
2. Debates and discussions
Argumentative essays can serve as the basis for debates or discussions in academic or competitive settings. Moreover, they provide a structured way to present and defend your viewpoint.
3. Opinion pieces
Newspapers, magazines, and online publications often feature opinion pieces that present an argument on a current issue or topic to influence public opinion.
4. Policy proposals
In government and policy-related fields, argumentative essays are used to propose and defend specific policy changes or solutions to societal problems.
5. Persuasive speeches
Before delivering a persuasive speech, it’s common to prepare an argumentative essay as a foundation for your presentation.
Regardless of the context, an argumentative essay should present a clear thesis statement , provide evidence and reasoning to support your position, address counterarguments, and conclude with a compelling summary of your main points. The goal is to persuade readers or listeners to accept your viewpoint or at least consider it seriously.”
Handing over a book, the professor continued, “Take a look on the elements or structure of an argumentative essay.”
Elements of an Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components:
Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
2. Evidence
Evidence must consist of factual information, data, examples, or expert opinions that support the claim. Also, it lends credibility by strengthening the writer’s position.
3. Counterarguments
Presenting a counterclaim demonstrates fairness and awareness of alternative perspectives.
4. Rebuttal
After presenting the counterclaim, the writer refutes it by offering counterarguments or providing evidence that weakens the opposing viewpoint. It shows that the writer has considered multiple perspectives and is prepared to defend their position.
The format of an argumentative essay typically follows the structure to ensure clarity and effectiveness in presenting an argument.
How to Write An Argumentative Essay
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an argumentative essay:
1. Introduction
- Begin with a compelling sentence or question to grab the reader’s attention.
- Provide context for the issue, including relevant facts, statistics, or historical background.
- Provide a concise thesis statement to present your position on the topic.
2. Body Paragraphs (usually three or more)
- Start each paragraph with a clear and focused topic sentence that relates to your thesis statement.
- Furthermore, provide evidence and explain the facts, statistics, examples, expert opinions, and quotations from credible sources that supports your thesis.
- Use transition sentences to smoothly move from one point to the next.
3. Counterargument and Rebuttal
- Acknowledge opposing viewpoints or potential objections to your argument.
- Also, address these counterarguments with evidence and explain why they do not weaken your position.
4. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement and summarize the key points you’ve made in the body of the essay.
- Leave the reader with a final thought, call to action, or broader implication related to the topic.
5. Citations and References
- Properly cite all the sources you use in your essay using a consistent citation style.
- Also, include a bibliography or works cited at the end of your essay.
6. Formatting and Style
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- Use a professional and academic tone in your writing and edit your essay to avoid content, spelling and grammar mistakes .
Remember that the specific requirements for formatting an argumentative essay may vary depending on your instructor’s guidelines or the citation style you’re using (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Always check the assignment instructions or style guide for any additional requirements or variations in formatting.
Did you understand what Prof. Mitchell explained Alex? Check it now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Prof. Mitchell continued, “An argumentative essay can adopt various approaches when dealing with opposing perspectives. It may offer a balanced presentation of both sides, providing equal weight to each, or it may advocate more strongly for one side while still acknowledging the existence of opposing views.” As Alex listened carefully to the Professor’s thoughts, his eyes fell on a page with examples of argumentative essay.
Example of an Argumentative Essay
Alex picked the book and read the example. It helped him to understand the concept. Furthermore, he could now connect better to the elements and steps of the essay which Prof. Mitchell had mentioned earlier. Aren’t you keen to know how an argumentative essay should be like? Here is an example of a well-crafted argumentative essay , which was read by Alex. After Alex finished reading the example, the professor turned the page and continued, “Check this page to know the importance of writing an argumentative essay in developing skills of an individual.”
Importance of an Argumentative Essay
After understanding the benefits, Alex was convinced by the ability of the argumentative essays in advocating one’s beliefs and favor the author’s position. Alex asked,

“How are argumentative essays different from the other types?”
Prof. Mitchell answered, “Argumentative essays differ from other types of essays primarily in their purpose, structure, and approach in presenting information. Unlike expository essays, argumentative essays persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action on a controversial issue. Furthermore, they differ from descriptive essays by not focusing vividly on describing a topic. Also, they are less engaging through storytelling as compared to the narrative essays.
Alex said, “Given the direct and persuasive nature of argumentative essays, can you suggest some strategies to write an effective argumentative essay?
Turning the pages of the book, Prof. Mitchell replied, “Sure! You can check this infographic to get some tips for writing an argumentative essay.”
Effective Strategies to Write an Argumentative Essay

As days turned into weeks, Alex diligently worked on his essay. He researched, gathered evidence, and refined his thesis. It was a long and challenging journey, filled with countless drafts and revisions.
Finally, the day arrived when Alex submitted their essay. As he clicked the “Submit” button, a sense of accomplishment washed over him. He realized that the argumentative essay, while challenging, had improved his critical thinking and transformed him into a more confident writer. Furthermore, Alex received feedback from his professor, a mix of praise and constructive criticism. It was a humbling experience, a reminder that every journey has its obstacles and opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
An argumentative essay can be written as follows- 1. Choose a Topic 2. Research and Collect Evidences 3. Develop a Clear Thesis Statement 4. Outline Your Essay- Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion 5. Revise and Edit 6. Format and Cite Sources 7. Final Review
One must choose a clear, concise and specific statement as a claim. It must be debatable and establish your position. Avoid using ambiguous or unclear while making a claim. To strengthen your claim, address potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints. Additionally, use persuasive language and rhetoric to make your claim more compelling
Starting an argument essay effectively is crucial to engage your readers and establish the context for your argument. Here’s how you can start an argument essay are: 1. Begin With an Engaging Hook 2. Provide Background Information 3. Present Your Thesis Statement 4. Briefly Outline Your Main 5. Establish Your Credibility
The key features of an argumentative essay are: 1. Clear and Specific Thesis Statement 2. Credible Evidence 3. Counterarguments 4. Structured Body Paragraph 5. Logical Flow 6. Use of Persuasive Techniques 7. Formal Language
An argumentative essay typically consists of the following main parts or sections: 1. Introduction 2. Body Paragraphs 3. Counterargument and Rebuttal 4. Conclusion 5. References (if applicable)
The main purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the reader to accept or agree with a particular viewpoint or position on a controversial or debatable topic. In other words, the primary goal of an argumentative essay is to convince the audience that the author's argument or thesis statement is valid, logical, and well-supported by evidence and reasoning.
Great article! The topic is simplified well! Keep up the good work
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Industry News
6 Reasons Why There is a Decline in Higher Education Enrollment: Action plan to overcome this crisis
Over the past decade, colleges and universities across the globe have witnessed a concerning trend…

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![argumentative essay on university education should be made compulsory What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
How to Improve Lab Report Writing: Best practices to follow with and without…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.3: The Argumentative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 58378
- Lumen Learning
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Examine types of argumentative essays
Argumentative Essays
You may have heard it said that all writing is an argument of some kind. Even if you’re writing an informative essay, you still have the job of trying to convince your audience that the information is important. However, there are times you’ll be asked to write an essay that is specifically an argumentative piece.
An argumentative essay is one that makes a clear assertion or argument about some topic or issue. When you’re writing an argumentative essay, it’s important to remember that an academic argument is quite different from a regular, emotional argument. Note that sometimes students forget the academic aspect of an argumentative essay and write essays that are much too emotional for an academic audience. It’s important for you to choose a topic you feel passionately about (if you’re allowed to pick your topic), but you have to be sure you aren’t too emotionally attached to a topic. In an academic argument, you’ll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you’ll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions.

Argumentative essays are quite common in academic writing and are often an important part of writing in all disciplines. You may be asked to take a stand on a social issue in your introduction to writing course, but you could also be asked to take a stand on an issue related to health care in your nursing courses or make a case for solving a local environmental problem in your biology class. And, since argument is such a common essay assignment, it’s important to be aware of some basic elements of a good argumentative essay.
When your professor asks you to write an argumentative essay, you’ll often be given something specific to write about. For example, you may be asked to take a stand on an issue you have been discussing in class. Perhaps, in your education class, you would be asked to write about standardized testing in public schools. Or, in your literature class, you might be asked to argue the effects of protest literature on public policy in the United States.
However, there are times when you’ll be given a choice of topics. You might even be asked to write an argumentative essay on any topic related to your field of study or a topic you feel that is important personally.
Whatever the case, having some knowledge of some basic argumentative techniques or strategies will be helpful as you write. Below are some common types of arguments.
Causal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you argue that something has caused something else. For example, you might explore the causes of the decline of large mammals in the world’s ocean and make a case for your cause.
Evaluation Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make an argumentative evaluation of something as “good” or “bad,” but you need to establish the criteria for “good” or “bad.” For example, you might evaluate a children’s book for your education class, but you would need to establish clear criteria for your evaluation for your audience.
Proposal Arguments
- In this type of argument, you must propose a solution to a problem. First, you must establish a clear problem and then propose a specific solution to that problem. For example, you might argue for a proposal that would increase retention rates at your college.
Narrative Arguments
- In this type of argument, you make your case by telling a story with a clear point related to your argument. For example, you might write a narrative about your experiences with standardized testing in order to make a case for reform.
Rebuttal Arguments
- In a rebuttal argument, you build your case around refuting an idea or ideas that have come before. In other words, your starting point is to challenge the ideas of the past.
Definition Arguments
- In this type of argument, you use a definition as the starting point for making your case. For example, in a definition argument, you might argue that NCAA basketball players should be defined as professional players and, therefore, should be paid.
https://assessments.lumenlearning.co...essments/20277
Essay Examples
- Click here to read an argumentative essay on the consequences of fast fashion . Read it and look at the comments to recognize strategies and techniques the author uses to convey her ideas.
- In this example, you’ll see a sample argumentative paper from a psychology class submitted in APA format. Key parts of the argumentative structure have been noted for you in the sample.
Link to Learning
For more examples of types of argumentative essays, visit the Argumentative Purposes section of the Excelsior OWL .
Contributors and Attributions
- Argumentative Essay. Provided by : Excelsior OWL. Located at : https://owl.excelsior.edu/rhetorical-styles/argumentative-essay/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of a man with a heart and a brain. Authored by : Mohamed Hassan. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : pixabay.com/illustrations/decision-brain-heart-mind-4083469/. License : Other . License Terms : pixabay.com/service/terms/#license
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Student Loans
- Paying for College
Should College Be Free? The Pros and Cons
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KellyDilworthheadshot-c65b9cbc3b284f138ca937b8969079e6.jpg)
Types of Publicly Funded College Tuition Programs
Pros: why college should be free, cons: why college should not be free, what the free college debate means for students, how to cut your college costs now, frequently asked questions (faqs).
damircudic / Getty Images
Americans have been debating the wisdom of free college for decades, and more than 30 states now offer some type of free college program. But it wasn't until 2021 that a nationwide free college program came close to becoming reality, re-energizing a longstanding debate over whether or not free college is a good idea.
And despite a setback for the free-college advocates, the idea is still in play. The Biden administration's free community college proposal was scrapped from the American Families Plan . But close observers say that similar proposals promoting free community college have drawn solid bipartisan support in the past. "Community colleges are one of the relatively few areas where there's support from both Republicans and Democrats," said Tulane economics professor Douglas N. Harris, who has previously consulted with the Biden administration on free college, in an interview with The Balance.
To get a sense of the various arguments for and against free college, as well as the potential impacts on U.S. students and taxpayers, The Balance combed through studies investigating the design and implementation of publicly funded free tuition programs and spoke with several higher education policy experts. Here's what we learned about the current debate over free college in the U.S.—and more about how you can cut your college costs or even get free tuition through existing programs.
Key Takeaways
- Research shows free tuition programs encourage more students to attend college and increase graduation rates, which creates a better-educated workforce and higher-earning consumers who can help boost the economy.
- Some programs are criticized for not paying students’ non-tuition expenses, not benefiting students who need assistance most, or steering students toward community college instead of four-year programs.
- If you want to find out about free programs in your area, the University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education has a searchable database. You’ll find the link further down in this article.
Before diving into the weeds of the free college debate, it's important to note that not all free college programs are alike. Most publicly funded tuition assistance programs are restricted to the first two years of study, typically at community colleges. Free college programs also vary widely in the ways they’re designed, funded, and structured:
- Last-dollar tuition-free programs : These programs cover any remaining tuition after a student has used up other financial aid , such as Pell Grants. Most state-run free college programs fall into this category. However, these programs don’t typically help with room and board or other expenses.
- First-dollar tuition-free programs : These programs pay for students' tuition upfront, although they’re much rarer than last-dollar programs. Any remaining financial aid that a student receives can then be applied to other expenses, such as books and fees. The California College Promise Grant is a first-dollar program because it waives enrollment fees for eligible students.
- Debt-free programs : These programs pay for all of a student's college expenses , including room and board, guaranteeing that they can graduate debt-free. But they’re also much less common, likely due to their expense.
Proponents often argue that publicly funded college tuition programs eventually pay for themselves, in part by giving students the tools they need to find better jobs and earn higher incomes than they would with a high school education. The anticipated economic impact, they suggest, should help ease concerns about the costs of public financing education. Here’s a closer look at the arguments for free college programs.
A More Educated Workforce Benefits the Economy
Morley Winograd, President of the Campaign for Free College Tuition, points to the economic and tax benefits that result from the higher wages of college grads. "For government, it means more revenue," said Winograd in an interview with The Balance—the more a person earns, the more they will likely pay in taxes . In addition, "the country's economy gets better because the more skilled the workforce this country has, the better [it’s] able to compete globally." Similarly, local economies benefit from a more highly educated, better-paid workforce because higher earners have more to spend. "That's how the economy grows," Winograd explained, “by increasing disposable income."
According to Harris, the return on a government’s investment in free college can be substantial. "The additional finding of our analysis was that these things seem to consistently pass a cost-benefit analysis," he said. "The benefits seem to be at least double the cost in the long run when we look at the increased college attainment and the earnings that go along with that, relative to the cost and the additional funding and resources that go into them."
Free College Programs Encourage More Students to Attend
Convincing students from underprivileged backgrounds to take a chance on college can be a challenge, particularly when students are worried about overextending themselves financially. But free college programs tend to have more success in persuading students to consider going, said Winograd, in part because they address students' fears that they can't afford higher education . "People who wouldn't otherwise think that they could go to college, or who think the reason they can't is [that] it's too expensive, [will] stop, pay attention, listen, decide it's an opportunity they want to take advantage of, and enroll," he said.
According to Harris, students also appear to like the certainty and simplicity of the free college message. "They didn't want to have to worry that next year they were not going to have enough money to pay their tuition bill," he said. "They don't know what their finances are going to look like a few months down the road, let alone next year, and it takes a while to get a degree. So that matters."
Free college programs can also help send "a clear and tangible message" to students and their families that a college education is attainable for them, said Michelle Dimino, an Education Director with Third Way. This kind of messaging is especially important to first-generation and low-income students, she said.
Free College Increases Graduation Rates and Financial Security
Free tuition programs appear to improve students’ chances of completing college. For example, Harris noted that his research found a meaningful link between free college tuition and higher graduation rates. "What we found is that it did increase college graduation at the two-year college level, so more students graduated than otherwise would have."
Free college tuition programs also give people a better shot at living a richer, more comfortable life, say advocates. "It's almost an economic necessity to have some college education," noted Winograd. Similar to the way a high school diploma was viewed as crucial in the 20th century, employees are now learning that they need at least two years of college to compete in a global, information-driven economy. "Free community college is a way of making that happen quickly, effectively, and essentially," he explained.
Free community college isn’t a universally popular idea. While many critics point to the potential costs of funding such programs, others identify issues with the effectiveness and fairness of current attempts to cover students’ college tuition. Here’s a closer look at the concerns about free college programs.
It Would Be Too Expensive
The idea of free community college has come under particular fire from critics who worry about the cost of social spending. Since community colleges aren't nearly as expensive as four-year colleges—often costing thousands of dollars a year—critics argue that individuals can often cover their costs using other forms of financial aid . But, they point out, community college costs would quickly add up when paid for in bulk through a free college program: Biden’s proposed free college plan would have cost $49.6 billion in its first year, according to an analysis from Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce. Some opponents argue that the funds could be put to better use in other ways, particularly by helping students complete their degrees.
Free College Isn't Really Free
One of the most consistent concerns that people have voiced about free college programs is that they don’t go far enough. Even if a program offers free tuition, students will need to find a way to pay for other college-related expenses , such as books, room and board, transportation, high-speed internet, and, potentially, child care. "Messaging is such a key part of this," said Dimino. Students "may apply or enroll in college, understanding it's going to be free, but then face other unexpected charges along the way."
It's important for policymakers to consider these factors when designing future free college programs. Otherwise, Dimino and other observers fear that students could potentially wind up worse off if they enroll and invest in attending college and then are forced to drop out due to financial pressures.
Free College Programs Don’t Help the Students Who Need Them Most
Critics point out that many free college programs are limited by a variety of quirks and restrictions, which can unintentionally shut out deserving students or reward wealthier ones. Most state-funded free college programs are last-dollar programs, which don’t kick in until students have applied financial aid to their tuition. That means these programs offer less support to low-income students who qualify for need-based aid—and more support for higher-income students who don’t.
Community College May Not Be the Best Path for All Students
Some critics also worry that all students will be encouraged to attend community college when some would have been better off at a four-year institution. Four-year colleges tend to have more resources than community colleges and can therefore offer more support to high-need students.
In addition, some research has shown that students at community colleges are less likely to be academically successful than students at four-year colleges, said Dimino. "Statistically, the data show that there are poorer outcomes for students at community colleges […] such as lower graduation rates and sometimes low transfer rates from two- to four-year schools."
With Congress focused on other priorities, a nationwide free college program is unlikely to happen anytime soon. However, some states and municipalities offer free tuition programs, so students may be able to access some form of free college, depending on where they live. A good resource is the University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education’s searchable database of Promise Programs , which lists more than 100 free community college programs, though the majority are limited to California residents.
In the meantime, school leaders and policymakers may shift their focus to other access and equity interventions for low-income students. For example, higher education experts Eileen Strempel and Stephen Handel published a book in 2021 titled "Beyond Free College: Making Higher Education Work for 21st Century Students." The book argues that policymakers should focus more strongly on college completion, not just college access. "There hasn't been enough laser-focus on how we actually get people to complete their degrees," noted Strempel in an interview with The Balance.
Rather than just improving access for low-income college students, Strempel and Handel argue that decision-makers should instead look more closely at the social and economic issues that affect students , such as food and housing insecurity, child care, transportation, and personal technology. For example, "If you don't have a computer, you don't have access to your education anymore," said Strempel. "It's like today's pencil."
Saving money on college costs can be challenging, but you can take steps to reduce your cost of living. For example, if you're interested in a college but haven't yet enrolled, pay close attention to where it's located and how much residents typically pay for major expenses, such as housing, utilities, and food. If the college is located in a high-cost area, it could be tough to justify the living expenses you'll incur. Similarly, if you plan to commute, take the time to check gas or public transportation prices and calculate how much you'll likely have to spend per month to go to and from campus several times a week.
Now that more colleges offer classes online, it may also be worth looking at lower-cost programs in areas that are farther from where you live, particularly if they allow you to graduate without setting foot on campus. Also, check out state and federal financial aid programs that can help you slim down your expenses, or, in some cases, pay for them completely. Finally, look into need-based and merit-based grants and scholarships that can help you cover even more of your expenses. Also, consider applying to no-loan colleges , which promise to help students graduate without going into debt.
Should community college be free?
It’s a big question with varying viewpoints. Supporters of free community college cite the economic contributions of a more educated workforce and the individual benefit of financial security, while critics caution against the potential expense and the inefficiency of last-dollar free college programs.
What states offer free college?
More than 30 states offer some type of tuition-free college program, including Arkansas, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Michigan, Nevada, New York, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Virginia, and Washington State. The University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education lists over 100 last-dollar community college programs and 16 first-dollar community college programs, though the majority are limited to California residents.
Is there a free college?
There is no such thing as a truly free college education. But some colleges offer free tuition programs for students, and more than 30 states offer some type of tuition-free college program. In addition, students may also want to check out employer-based programs. A number of big employers now offer to pay for their employees' college tuition . Finally, some students may qualify for enough financial aid or scholarships to cover most of their college costs.
Scholarships360. " Which States Offer Tuition-Free Community College? "
The White House. “ Build Back Better Framework ,” see “Bringing Down Costs, Reducing Inflationary Pressures, and Strengthening the Middle Class.”
The White House. “ Fact Sheet: How the Build Back Better Plan Will Create a Better Future for Young Americans ,” see “Education and Workforce Opportunities.”
Coast Community College District. “ California College Promise Grant .”
Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce. “ The Dollars and Cents of Free College ,” see “Biden’s Free College Plan Would Pay for Itself Within 10 Years.”
Third Way. “ Why Free College Could Increase Inequality .”
Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce. “ The Dollars and Cents of Free College ,” see “Free-College Programs Have Different Effects on Race and Class Equity.”
University of Pennsylvania Graduate School of Education. “ College Promise Programs: A Comprehensive Catalog of College Promise Programs in the United States .”
Should University Education Be Made Compulsory? Essay
- Category: Education
- Published: 12.27.19
- Views: 2226

Tournaments exist in every single modern metropolis. It is of no doubt that you will have a better working environment if you have a university level. Those, who have are only graduated from high-schools, are more likely to be used as commercial workers as well as to be using manual jobs. That is the way the real world works.
If the govt forces all high-school graduates to go to university or college, inequality can now be caused towards the ones who may have the real capacity to enter school. Therefore , university or college education really should not be compulsory for all students. Its not all student is usually eager to head to university as being a students lack the learning incentive and are more interested in earning money by going to job. Extra burden is put on their shoulder blades because they cannot have the interests and ability in learning.
Besides, the government needs to access enormous assets to supply financial financial assistance to all poor students who also cannot afford the expensive college or university tuition charges in Hk. Of course , many people want to study for university. Producing university education compulsory seems to be a good idea. However , that is not accurate. If all people get a college or university degree and work in your workplace, then that will work for the industries or restaurants?
The society might be messed up. The only solution is always to raise the task requirement because everyone keeps a school degree. Because of this, only the ones who happen to be graduated coming from overseas universities, have a master level, or even have got a doctor degree can work within an office. Nonetheless it does not seem sensible at all.
Really does that mean that those who have the talent and potential and they are graduated by local universities do not ought to have to get a better job. Actually making school education compulsory is a waste of time and money. As we know, not every students are able to enter university. The educational institutions may have to adjust the entry requirement to cater for the needs coming from all students in Hong Kong. After that, a college or university degree no more represents a high standard of education.
It seems like to be a daily news near the feet that everyone can easily get it. It really is useless. In summary, making school education required is certainly not fair to all students as different pupils are good at different fields. Going to university or college is not really the only choice. More importantly, each of our society requires a balanced amount of blue-tie workers and while-tie employees.
Although it is definitely cruel to many students, that may be how the globe works.

Related Documents:
Top two issues facing community college essay.
- Paper: #6091
This kind of topic came up repeatedly as I was researching crucial issues intended for higher education in the community college environment, the vo-tech training universities, and the four-year postsecondary universities. Grace Chen (2011) publishes articles Community college or university leaders have not yet created a opinion on what it means for students to become […]
Grading vs Marking Essay
- Paper: #5697
Which is better, grades or marks? A chicken and egg problem did you say? Not really related, yet definitely because difficult to response. They say getting rid of marks eliminates the stress, eliminates the the academic pressure students encounter. So now, the infamous 9-to-5 world has hopeless chances of survival. The common issue, “He got […]
Benjamin Collins Quarshie Kwesi Essay
- Paper: #5525
Honorable Headmaster, Members of Staff, Co-aspirant, Out-going Prefect, Fellow Student, Ladies and Gentlemen. I greet you all. I actually am extremely grateful if you are given to be able to read my own manifesto for you, as an aspirant to get the position of boy college prefect. My spouse and i am Dernier-ne Quarshie, another […]
Formative assessment Essay
- Paper: #6307
“We utilize the general term assessment to relate to all individuals activities carried out by instructors — and by their pupils in assessing themselves — that provide information to be used as responses to modify educating and learning activities. Such assessment turns into formative examination when the data is actually accustomed to adapt the teaching […]
The position of any civil professional
- Paper: #17842
Civil Architectural, Engineering This kind of career episode is based on my personal starting working experience in the Detrimental construction discipline as a Detrimental Engineer. I actually finished my own four years bachelor’s in civil architectural in 2013 from Khwopa Engineering School (Purbanchal University). Then I joined up with Creative Designer and Planner, one of […]
High school Essay
- Paper: #6877
In ancient India, schools were in the form of Gurukuls. Gurukuls had been traditional Indio residential schools of learning; typically the teacher’s house or possibly a monastery. During the Mughal secret, Madrasahs had been introduced in India to educate the children of Muslim parents. British documents show that indigenous education was widespread in the eighteenth […]
Clarify strategies employed in health and cultural
- Paper: #17484
P4 “Explain strategies used in health insurance and social attention environments to overcome barriers to effective communication Powerful communication is usually part of the key skills required by all health and social care practitioners to ensure that they may be effective at getting together with the requires of the people that use the providers. In […]
Dalit Discourse in Indian Education Dhanaraju Vulli Essay
- Paper: #6849
The 2nd part covers the concept of mother tongue and its importance in the contextualizing of educational discourse in India. Inside the third portion I would emphasize the current controversy on vocabulary policy and its importance in the Indian educational system. Everyone these days in the knowledge of politics of medium of language in our […]
Conceptual construction for studying hiv in the
- Paper: #17499
Grand Theory, Epistemological, Aids, Canada Excerpt via Research Conventional paper: GRAND THEORY: HIV IN GROUP POPULATION Introduction of the Structure The conceptual framework found in the article may be the Grand theory framework. The idea of using grand theory on this page is based on the aspect of the set of subjective ideas that together […]
Role of a college education over the term paper
- Paper: #17751
Complacency, Adapted Physical Education, College Entrance, College Application Excerpt via Term Daily news: Position of a School Education During the last several years, the importance of a university education continues to be continually debated. This is because there are plenty of examples of individuals who never visited or fallen out of school that are good. […]
How do I learn best Essay
- Paper: #10965
How do I study best? Induration state School The more various ways a person discovers something, a lot more truly the face understands that principle, (Lazear, 2008) gains a deeper understanding of the subject and retains the info longer. In utilizing the multimodal structure of education, the instructor can accommodate use of several tools like […]
History of education Essay
- Paper: #11171
Jim Henson when said, “Kids don’t keep in mind what you make an effort to teach these people. They keep in mind what you are. ” Instructing doesn’t necessarily mean that you have to always be smart, you have to be a instructor or mentor. Being a great and mental person does make you fit […]
- Business and professional
- Death essays
- Literary arts essays
- Religion and spirituality
- Alcohol essays
- David essays
- Personality
- Automobile and automobiles
- Commentary essays
- Carrying out
- Catcher in the rye essays
- American dream essays
- Media artistry essays
- Personal issues
- College essays
- Sports activities
- Real estate
- Fictional arts documents
- Globe studies
- Bravery essays
- Dissertation examples
- Family and child rearing
- Essay illustrations
- World studies
- Christianity essays
- Zoroastrian faravahar logo design
- Worship wayne white s manuscript protestant
- Zipcar essay
- Wwi once world conflict i term paper
- Zoonotic encephalitides caused by arboviruses
- Maine s industrial lobster sector essay
- Zinn and johnson article
- Testing make up on pets or animals research daily
- Workplace the information are sobering research
- Why we should stop dog testing essay
- Zero tolerance policy to avoid plagiarism
- Zara promoting research article
- Youth information essay
- Zappos project composition
- Youtube as the perfect platform to get budding
- Youth a portrait in the artist because term
- Zora neale hurston essay
- Zimbabwe a cultural examination the work of term
- Your wine industry canada essay
Need writing help?
We can write an essay on your own custom topics!
Your Name (required)
Your Email (required)
Your Message
Please leave this field empty.
Home — Essay Samples — Education — Importance of Education — The Arguments Why Education Should Be Free For Everyone
The Arguments Why Education Should Be Free for Everyone
- Categories: College Tuition Importance of Education
About this sample

Words: 854 |
Published: Mar 18, 2021
Words: 854 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Works Cited:
- Alpha History. (n.d.). Nationalism as a cause of World War I.
- Bernhardi, F. von. (1914). Germany and the Next War. London: Edward Arnold.
- Cawley, J. (n.d.). Nationalism as the cause of European competitiveness that led to World War I.
- History Home. (n.d.). The causes of World War One. Retrieved from https://www.historyhome.co.uk/europe/causeww1.htm
- Rosenthal, L. (2016). The great war, nationalism and the decline of the West. Retrieved from https://lawrencerosenthal.net/2016/05/16/the-great-war-nationalism-and-the-decline-of-the-west/
- Bloy, M. (n.d.). Nationalism in the 19th century. Retrieved from https://www.historyhome.co.uk/europe/natquest.htm

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1317 words
1 pages / 493 words
2 pages / 1082 words
1 pages / 545 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Importance of Education
Civic education is integral to the development of responsible and engaged citizens in modern society. It is the process through which individuals learn about their rights, responsibilities, and duties towards their communities [...]
Academic success is not merely a measure of one's knowledge but a path to personal and professional growth. In this essay, we will explore the profound importance of academic success and how it contributes to an individual's [...]
Education, a term that spans cultures and epochs, finds itself defined in various ways by different individuals and societies. In this comprehensive essay, we shall delve into the multifaceted concept of the purpose of [...]
In recent years, there has been a growing debate over whether or not cursive handwriting should continue to be taught in schools. With the rise of technology and the increasing use of digital communication, some argue that [...]
When I was in high school I remember waking up every morning for school with the smell of freshly brewed coffee in the air. I could not start the day off without a cup and I’m pretty sure I get it from my mom. Through out all of [...]
Social mobility, the ability of individuals to move up or down the socioeconomic ladder within a society, has long been a topic of interest and debate. Education stands as a cornerstone in discussions surrounding social [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Higher Education Needs More Socrates and Plato

By Ezekiel J. Emanuel and Harun Küçük
Dr. Emanuel and Dr. Küçük are on the faculty of the University of Pennsylvania, where Dr. Emanuel is a professor and the vice provost for global initiatives and Dr. Küçük is an associate professor of the history and sociology of science.
The right attacks colleges and universities as leftist and woke. Progressives castigate them as perpetuating patriarchy and white privilege. The burdens of these culture war assaults are compounded by parents worried that the exorbitant costs of higher education aren’t worth it.
No wonder Americans’ faith in universities is at a low. Only 36 percent of Americans have confidence in higher education, according to a survey by Gallup last year, a significant drop from eight years ago. And this was before colleges and universities across the country were swept up in a wave of protests and counter-protests over the war in Gaza.
But the problems facing American higher education are not just the protests and culture war attacks on diversity, course content, speech and speakers. The problem is that higher education is fundamentally misunderstood. In response, colleges and universities must reassert the liberal arts ideals that have made them great but that have been slipping away.
By liberal arts, we mean a broad-based education that aspires to send out into society an educated citizenry prepared to make its way responsibly in an ever-more complex and divided world. We worry that at many schools, students can fulfill all or most of their general education requirements and take any number of electives without having had a single meaningful discussion that is relevant to one’s political life as a citizen.
Over the past century, what made American higher education the best in the world is not its superiority in career training, but educating students for democratic citizenship, cultivating critical thinking and contributing to the personal growth of its students through self-creation. To revive American higher education, we need to reinvigorate these roots.
In Europe and many countries elsewhere, colleges and universities have undergraduates specialize from Day 1, focusing on developing area-specific skills and knowledge. College students are trained to become doctors, lawyers or experts in international relations, English literature or computer science.
In the United States, European-style specialization for medical, legal, business or public policy careers is the purpose of post-collegiate professional schools. Traditionally, the American college has been about imparting a liberal arts education, emphasizing reasoning and problem solving. Those enduring skills are the critical ingredients for flourishing companies and countries.
Historically, students arriving on American college campuses spent a majority of their first two years taking classes outside their projected majors. This exposed them to a common curriculum that had them engage with thoughtful writings of the past to develop the skills and capacity to form sound, independent judgments.
Over the past half century, American colleges and universities have moved away from this ideal , becoming less confident in their ability to educate students for democratic citizenship. This has led to a decline in their commitment to the liberal arts, a trend underscored in the results last year of a survey of chief academic officers at American colleges and universities by Inside Higher Ed. Nearly two-thirds agreed that liberal arts education was in decline, and well over half felt that politicians, college presidents and university boards were increasingly unsympathetic to the liberal arts.
Today, there is almost no emphasis on shared courses among majors that explore and debate big questions about the meaning of equality, justice, patriotism, personal obligations, civic responsibility and the purpose of a human life. Majors that once required only eight or 10 courses now require 14 or more, and students are increasingly double majoring — all of which crowds out a liberal arts education. Ambitious students eager to land a prestigious consulting, finance or tech job will find it too easy to brush aside courses in the arts, humanities and social and natural sciences — the core of a liberal education.
The devaluing of the first two years of a shared liberal arts education has shortchanged our students and our nation. Educating young adults to be citizens is why the first two years of college still matter.
To that end, the so-called Great Books have long been the preferred way to foster citizenship. This approach is not, contrary to critics on the left and right, about sanctifying specific texts for veneration or a mechanism for heritage transmission.
Books by Plato, Aristotle, Hobbes, Locke, Kant, Emerson, Thoreau, Whitman as well as Wollstonecraft, Austen, Woolf, Baldwin, Hurston and Orwell are worthy of introductory collegiate courses for students of all majors. These writers address the fundamental questions of human life. They explore the ideas of self-determination, friendship, virtue, equality, democracy and religious toleration and race that we have all been shaped by.
As students address those big questions, the Great Books authors provide a road map as they challenge and criticize one another and the conventional wisdom of the past. The Socrates of Plato’s dialogues is the exemplar — asking about beliefs and then subjecting them to respectful but critical analysis and skepticism.
These books are best studied in small seminar discussions, which model and inculcate in students democratic behavior. This discourse is an antidote to the grandstanding in today’s media and social media.
The teacher is less an expert in specific writers and more a role model for intellectual curiosity, asking probing questions, offering critical analyses and seeking deeper understanding. In an idealized Socratic fashion, these discussions require listening at length and speaking briefly and, most important, being willing to go where the argument leads.
Parents who are paying for college might question the value of spending $80,000 a year so that their son or daughter can read Plato, Hobbes and Thoreau instead of studying molecular biology or machine learning. But discussing life’s big value questions in seminars gives students personal engagement with professors that can never be reproduced in large lecture halls. Discussions among students on their deepest thoughts cultivates curiosity and empathy, and forges bonds of friendship important for citizenship and fulfilling lives.
Although we like to set ourselves apart from the past by appeals to modernity, the fundamental questions that we find ourselves asking are not always modern, and the latest answer is not always right. But how would you know how to think beyond the readily presented check boxes if you haven’t done the work of laying things out and putting them back together for yourself?
War was no less a concern for Thucydides, Tacitus and Thoreau than it is today. Discussing Great Books allows students to gain distance from the daily noise and allows their reason to roam free among principles and foundations rather than becoming absorbed in contemporary events. Our biggest problems are often best addressed not by leaning in but by stepping away to reflect on enduring perspectives.
Liberal arts education is not value neutral. That is why it is indispensable today. Freedom of thought, critical reasoning, empathy for others and respectful disagreement are paramount for a flourishing democratic society. Without them, we get the unreasoned condemnations so pervasive in today’s malignant public discourse. With them, we have a hope of furthering the shared governance that is vital to America’s pluralistic society.
Ezekiel Emanuel and Harun Küçük are on the faculty of the University of Pennsylvania, where Dr. Emanuel is a professor and the vice provost for global initiatives and Dr. Küçük is an associate professor of the history and sociology of science.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
- Use Messenger
- Send us an email
Why Do We Need to Make Education Compulsory
“We don’t need no education…”,- everyone knows that Pink Floyd song. Basically it tells us about how education system ruins you personality . However, let’s not be so radical first and think about good sides of education .
First of all, it actually educates us . It gives us basic knowledge of important subjects and teaches us how to do usual things. Due to the fact that normally children are taught in groups, educational system helps them to learn how to interact with each other and to understand basics of the art of communication. To my mind, these two functions can not be underestimated when we talk about children as full-fledged members of society .
Now let us not forget that people come from different backgrounds. Some of them are far from what is considered regular. So, children, raised in specific circumstances only, have no other choice but become inconsequent. There are different displays of that – starting from extremely religious community and ending with what we all know as Ghetto. Of course, we can say that we are open minded enough to accept all kinds of people . But let’s be honest with ourselves: the further one go from standards, the harder it is for him to adjust in society.
If a child wants to stand out in an extravagant way, it should be his own choice, but not the one of the community that raised him. And the task of education system is to show him the regular way.
As to me, the main reason educational system should be made compulsory all around the world is because it can even everybody and give them relatively same chances to reach their goals.
Main Disadvantages of Wearing School Uniform
Imagine that you wake up every single day early in the morning, get up and put on the same clothes you had on yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last month and so on. And you’re not the only one who does the same routine every morning. School uniforms become more and more popular….
Essay on “Poem”
The poem begins with a declaration where the persona declares a stand of being voiceless in the public domain. The tone of the poem at the start portrays some who has relented in poetry and especially in the eyes of many. On the same stanza, the persona proceeds to seek solace where he asks, ‘who…
How to Write Logical Appeal (Logos)
When the question is about writing logical appeals (logos), it is usually meant that the writer has to describe some relationship’s rational presentation. The point is that they need to be built up in a manner that your readers could hardly refute. In the majority of situations, the writer has to bring together individual pieces…
Our Services
- Academic ghostwriting
- Admission essay help
- Article writing
- Assignment writing
- College paper writing
- Coursework writing
- Dissertation writing
- Homework writing
- Online classes
- Personal statement writing
- Report writing
- Research paper writing
- Speech writing
- Term paper writing
- Writing tips
- Write my paper
Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: should they be Mandatory?
This essay about the necessity of school uniforms presents a nuanced exploration of both sides of the debate. Advocates highlight uniforms as tools for unity and focus, while opponents emphasize the importance of individual expression and addressing deeper social issues. It argues for a balanced approach that values inclusivity and community while acknowledging the complexities of identity and diversity in education.
How it works
In the grand arena of educational discourse, the debate over the compulsion of school uniforms unfolds like a captivating drama, with each argument and counterargument adding layers of complexity to the narrative. Should the school uniform be an emblem of cohesion and order, or should the cloak of individuality drape freely over students’ shoulders? Let us embark on an intellectual odyssey, navigating through the turbulent seas of opinion to uncover the hidden treasures of wisdom buried within the folds of this contentious issue.
Advocates of mandatory school uniforms march forward with banners unfurled, extolling the virtues of uniformity and solidarity. They argue that uniforms serve as great unifiers, erasing the visible disparities in socio-economic status and fostering a sense of belonging within the school community. In a world where labels and logos often dictate social hierarchies, uniforms stand as equalizers, stripping away the superficial layers of attire to reveal the inherent worth of each student beneath.
Furthermore, proponents argue that school uniforms are bulwarks against the tempest of distractions that often buffet the shores of education. By standardizing attire, uniforms alleviate the burden of choice, liberating students from the daily quandary of what to wear and allowing them to focus their energies on more consequential matters. In the crucible of academia, where every ounce of mental acuity is precious, uniforms act as catalysts for concentration, forging an environment conducive to learning and intellectual growth.
However, amidst the chorus of uniform proponents, dissenting voices rise like solitary lighthouses against the backdrop of conformity. Opponents of mandatory school uniforms decry them as stiflers of individuality and creativity, lamenting the loss of personal expression in a sea of uniformity. They argue that adolescence is a time of self-discovery and exploration, and clothing serves as a canvas upon which students paint the vibrant tapestries of their identities. To deny them this form of expression, they assert, is to rob them of a fundamental aspect of their humanity.
Moreover, detractors argue that the imposition of school uniforms does little to address the root causes of social inequality and bullying. While uniforms may obscure the outward manifestations of economic disparity, they do nothing to dismantle the systemic barriers that perpetuate injustice. In fact, some argue that uniforms may exacerbate these tensions by promoting a culture of conformity over diversity, further marginalizing those who dare to deviate from the norm.
As the pendulum of debate swings back and forth, it becomes clear that the issue of school uniforms is not merely a matter of fabric and stitching, but a reflection of deeper societal values and beliefs. It is a tug-of-war between conformity and individuality, tradition and progress, unity and diversity. And perhaps therein lies the solution – not in the rigid enforcement of one extreme or the other, but in the delicate balance between the two.
Perhaps the true essence of the school uniform lies not in its fabric or design, but in the values it represents – values of inclusivity, respect, and community. In a world that is increasingly fragmented and polarized, perhaps what we need most is not uniformity, but unity – a unity that celebrates our differences while recognizing our shared humanity. And in this quest for unity, perhaps the school uniform can serve not as a barrier, but as a bridge – a bridge that connects us all in the pursuit of knowledge, understanding, and mutual respect.
Cite this page
Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory?. (2024, Jun 01). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/
"Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory?." PapersOwl.com , 1 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory? . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/ [Accessed: 3 Jun. 2024]
"Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory?." PapersOwl.com, Jun 01, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/
"Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory?," PapersOwl.com , 01-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/. [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Debating the Necessity of School Uniforms: Should They Be Mandatory? . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/debating-the-necessity-of-school-uniforms-should-they-be-mandatory/ [Accessed: 3-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
Should Vaccination Be Compulsory?
While science is clear that vaccines are safe and effective, it is silent on whether or not mandating compulsory vaccination is the right thing to do.
![argumentative essay on university education should be made compulsory By DFID - UK Department for International Development (Flickr: Bracing for a short, sharp jab) [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://daily.jstor.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/1024px-Bracing_for_a_short_sharp_jab.jpg)
President Obama and Republican hopeful Chris Christie joined the measles debate this week . Though both urged parents to vaccinate their children against measles, Christie argued that parents should have a “measure of choice.”

Let’s get one thing straight. There is no debate over the efficacy or safety of the measles vaccine.
It works and it is safe . Asking whether the Measles Mumps and Rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe is like asking whether ambulances are safe. Sure, very occasionally things go wrong. Vaccines cause 1 serious allergic reaction per million . But, with these odds, refusing a vaccine is like a seriously injured patient refusing to travel in an ambulance because they occasionally crash .
So everyone agrees that– with a few very limited exceptions –all children should be vaccinated against measles. The only debate is how to achieve this goal: via educational campaigns that encourage parents to vaccinate their children, or laws that compel them to do so. Some of the arguments arguments for and against each side are summarized in Peter Bradley’s interesting review article in the Journal of Medical Ethics .
One argument against compulsory vaccination is that it is unnecessary: Herd immunity does not demand a 100% vaccination rate, and many European countries achieve rates of well over 90% through education alone . (US readers might be surprised to learn that in most European countries, including the UK, vaccination is completely voluntary, even for children attending public schools). However, as epidemiologist John Fox argues , the concept of herd immunity applies straightforwardly only to populations in which individuals mix randomly. Thus an overall rate of 90% immunization can hide pockets of vulnerable groups (e.g., very young children, or those who refuse immunization for religious reasons).
This brings us to the second argument against compulsory vaccination; that any such law would not dramatically increase immunization rates, as it would be subject to a raft of exemptions. For example, although all US states mandate vaccinations for all children attending public schools, all but two allow religious exemptions, and almost half (19 states) allow exemptions due to personal or philosophical objections . An obvious counterargument is that one could simply disallow exemptions, or at least restrict them to religious groups will well-documented long-standing objections.
The final argument—and, for many, the knockdown argument—against compulsory vaccination is that it is a violation of parental choice (a point discussed extensively in Bradley’s review ). In one way or another, the three major arguments in favor of compulsory vaccination are all attempts to refute this point.
The first is that the rights of parents not to vaccinate their children must be balanced against the rights of parents who do not want their children—particularly those too young to be vaccinated—to catch measles from other, unvaccinated children.
The second—an argument that does not seem to be heard as much as one might expect—is that children themselves have the right to be vaccinated, regardless of what their parents think.
Bradley argues that when the rights of parents and children collide in this way, it is far from clear how to decide whose rights should be overridden. This brings us to the third argument for compulsory vaccination; that—to put it bluntly— the views of anti-vaccination parents should be disregarded, because they have been swayed by misleading information in the media. For example, huge studies of entire national cohorts of children have shown conclusively that, contra an always-speculative and now-retracted 1998 paper, there is absolutely no link between the MMR vaccine and autism (see also this BMJ opinion piece ). Yet many still suspect a cover up, or refuse more generally to believe that vaccines are safe .
Once a Week
Get your fix of JSTOR Daily’s best stories in your inbox each Thursday.
Privacy Policy Contact Us You may unsubscribe at any time by clicking on the provided link on any marketing message.
While the science is clear that vaccines are safe and effective, it is of course silent on whether or not mandating compulsory vaccination is the right thing to do.
For what it’s worth, my own personal view is that we in the UK should, at the very least, adopt the US model of insisting on vaccinations for children who attend public schools or use public (i.e., NHS) surgeries or hospitals. After all, we are not so squeamish when it comes to forcing parents to take other active steps to ensure the health of their children, such as providing them with food, clothing and shelter. Why should vaccines be any different?
Read more about the recent measles outbreak here .

JSTOR is a digital library for scholars, researchers, and students. JSTOR Daily readers can access the original research behind our articles for free on JSTOR.
Get Our Newsletter
More stories.

Wild Saints and Holy Fools

Building Classroom Discussions around JSTOR Daily Syllabi

Scaffolding a Research Project with JSTOR

Making Implicit Racism
Recent posts.
- The Joy of Burglary
- Saving Art from the Revolution, for the Revolution
- Reading for LGBTQ+ Pride Month
- Creating Communities for Disability Activism
- Sui Sin Far, the Chinese Canadian-American Sentimentalist
Support JSTOR Daily
Sign up for our weekly newsletter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Views. 12599. Competitions are ubiquitous in modern cities, and the significance of university education in shaping the working environment is undeniable. This essay critically examines the proposition of making university education compulsory for all students, exploring the potential repercussions on individual aspirations, societal dynamics ...
Equality. There is also a powerful argument that university education should be free to ensure equality of opportunity. If students have to pay for university education, this may dissuade them. In theory, students could take out loans or work part-time, but this may be sufficient to discourage students from studying and instead may enter the ...
In summary, the main purpose of university education is to impart knowledge to the learners and help them undergo character development. A lack of either of these would lead to a shaky future in the social arena. Universities should also restructure to enable the students undergo both learning processes and not just the classroom knowledge.
After high school graduation, the first student can access more than $10,000 annually in public funds to support his college experience. Federal funding for higher education has grown by 133 ...
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Argumentative Essay: Getting a Good Education. Getting an education is compulsory in the developed world, but so many of us don't appreciate it enough. We should value our education a lot more and work harder, because it is compulsory for so many different reasons and adds so much value to our lives. There are so many positive outcomes of ...
1 "Article 28 . 1. States Parties recognize the right of the child to education, and with a view to achieving this right progressively and on the basis of equal opportunity, they shall, in particular: (a) Make primary education compulsory and available free to all; (…) (UN General Assembly, 1989 ).".
Forty years ago 32 percent of counselors and teachers advised all students to go to college. Just 10 years later, in 1990, that percentage had doubled with roughly two-thirds of educators ...
An argumentative essay attempts to convince a reader to agree with a particular argument (the writer's thesis statement). The writer takes a firm stand one way or another on a topic and then uses hard evidence to support that stance. An argumentative essay seeks to prove to the reader that one argument —the writer's argument— is the ...
An argumentative essay comprises five essential components: 1. Claim. Claim in argumentative writing is the central argument or viewpoint that the writer aims to establish and defend throughout the essay. A claim must assert your position on an issue and must be arguable. It can guide the entire argument.
In an academic argument, you'll have a lot more constraints you have to consider, and you'll focus much more on logic and reasoning than emotions. Figure 1. When writing an argumentative essay, students must be able to separate emotion based arguments from logic based arguments in order to appeal to an academic audience.
Developing an argument requires a significant understanding of the subject matter from all angles. Let's take a look at the steps to writing an argumentative essay: 1. Choose appropriate argumentative essay topics. Although topics for an argumentative essay are highly diverse, they are based on a controversial stance.
A FUNDAMENTAL TENSION WITHIN A FUNDAMENTAL RIGHT. by JOSÉ-LUIS GAVIRIA , Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid. ABSTRACT: This paper is on the paradox of a right, the right to education that is almost universally declared as compulsory. The reason for the compulsion seems to be in its nature as a right. Within a Hohfeldian framework, any ...
Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce. "The Dollars and Cents of Free College," see "Biden's Free College Plan Would Pay for Itself Within 10 Years." Third Way. "Why Free College Could Increase Inequality." Georgetown University Center on Education and the Workforce.
1. Many today would argue that higher education is a basic right that should extend to all, regardless of socioeconomic background. 2. In my opinion, I largely disagree since there is more value in improving the relationships between social classes. Paraphrase the overall essay topic. Write a clear opinion.
Actually making school education compulsory is a waste of time and money. As we know, not every students are able to enter university. The educational institutions may have to adjust the entry requirement to cater for the needs coming from all students in Hong Kong.
The Arguments Why Education Should Be Free for Everyone. Education is the lighting guide in our successful route. Education can be described as the process of gaining understanding, beliefs, values, abilities, and practices that teach us to be a real human being. Whatever we learned whether imposed or willingly comes under the domain of education.
This has led to a decline in their commitment to the liberal arts, a trend underscored in the results last year of a survey of chief academic officers at American colleges and universities by ...
Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
the knowledge of how to write an argumentative essay, the format of which they are unfamiliar with. Most importantly; as Díaz (2002) claims, an argumentative essay must be written on controversial topics. Additionally, a typical argumentative essay should have a beginning, a middle or 'body', and an ending (Batteiger, 1994).
This essay argues that compulsory vaccination by the state is justified only when herd ... The scope of the argument must also be clarified; the application of this argument is towards ... 3 McCombs School of Business -The University of Texas. n.d. Utilitarianism. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://ethicsunwrapped.utexas.edu/glossary ...
Type of paper: Essays Subject: Education, Personal Words: 281. "We don't need no education…",- everyone knows that Pink Floyd song. Basically it tells us about how education system ruins you personality. However, let's not be so radical first and think about good sides of education. First of all, it actually educates us.
Essay Example: In the grand arena of educational discourse, the debate over the compulsion of school uniforms unfolds like a captivating drama, with each argument and counterargument adding layers of complexity to the narrative. Should the school uniform be an emblem of cohesion and order, or
One argument against compulsory vaccination is that it is unnecessary: Herd immunity does not demand a 100% vaccination rate, and many European countries achieve rates of well over 90% through education alone. (US readers might be surprised to learn that in most European countries, including the UK, vaccination is completely voluntary, even for ...