
- Modern History

The four MAIN causes of World War I explained

The First World War was the first conflict that occurred on a staggering scale. World War I (WWI) was unprecedented in its global impact and the extent of its industrialization.
However, the reason why the war originally began is incredibly complex. To try and explain the causes of the war, historians have tried to simplify it down to four main causes.
They create the acronym: MAIN.
Imperialism
Nationalism.
This simplified acronym is a useful way to remember the four MAIN causes of the war.
However, we will explain each of these concepts out of order below.
One of the most commonly discussed causes of WWI was the system of alliances that existed by 1914, the year the war started.
An 'alliance' is an agreement made between two countries, where each side promises to help the other if required.
Most of the time, this involves military or financial assistance. When an alliance is created, the countries involved are known as 'allies'.
By the dawn of the First World War, most European countries had entered into one or more alliances with other countries.
What made this an important cause of WWI, was that many of these alliances were military in nature: that if one country attacked or was attacked, all of their allies had promised to get involved as well.
This meant, that if just one country attacked another, most of Europe would immediately be at war, as each country jumped in to help out their friends.
Imperialism, as a concept, has been around for a very long time in human history. Imperialism is the desire to build an empire for your country.
This usually involves invading and taking land owned by someone else and adding it to your empire.
By the 19th century, many European countries had been involved in imperialism by conquering less advanced nations in Asia, the Americas or Africa.
By 1900, the British Empire was the largest imperial power in the world. It controlled parts of five different continents and owned about a quarter of all land in the world.
France was also a large empire, with control over parts of south-east Asia and Africa.
By 1910, Germany had been trying to build its own empire to rival that of Britain and France and was interested in expanding its colonial holdings.
This meant that when an opportunity for a war of conquest became available, Germany was very keen to take advantage of it.
Militarism is the belief that a country's army and navy (since air forces didn't exist at the start of WWI) were the primary means that nations resolved disagreement between each other.
As a result, countries like to boast about the power of their armed forces.
Some countries spent money improving their land armies, while others spent money on their navies.
Some countries tried to gain the advantage by having the most number of men in their armies, while others focused more on having the most advanced technology in their forces.
Regardless of how they approached it, countries used militarism as a way of gaining an edge on their opponents.
An example of this competition for a military edge can be seen in the race between Britain and Germany to have the most powerful navy.
Britain had recently developed a special ship known as a 'dreadnought’. The Germans were so impressed by this, that they increased their government spending so that they also had some dreadnoughts.
The final of the four causes is 'nationalism'. Nationalism is the idea that people should have a deep love for their country, even to the extent that they are willing to die for it.
Throughout the 19th century, most countries had developed their own form of nationalism, where they encouraged a love of the nation in their citizens through the process of creating national flags and writing national anthems.
Children at schools were taught that their country was the best in the world and that should it ever be threatened, that they should be willing to take up arms to defend it.
The growing nationalist movements created strong animosity between countries that had a history of armed conflict.
A good example of this is the deep anger that existed between Germany and France.
These two countries had a recent history of war and struggling over a small region between the two, called Alsace-Lorraine.
Germany had seized control of it after the Franco-Prussian War in 1871, which the French were deeply upset by.
As a result, France believed that they should be willing to fight and die to take it back.
Conflicts and Crises
In the two decades before WWI started in 1914, there were a number of smaller conflicts and crises that had already threatened to turn into global conflicts.
While these didn't eventually start the global war, it does show the four causes mentioned above and how they interacted in the real world.
The Moroccan Crisis
In 1904, Britain recognized France's sphere of influence over Morocco in North Africa in exchange for France recognizing Britain's sphere of influence in Egypt.
However, the Moroccans had a growing sense of nationalism and wanted their independence.
In 1905, Germany announced that they would support Morocco if they wanted to fight for their freedom.
To avoid war, a conference was held which allowed France to keep Morocco. Then, in 1911, the Germans again argued for Morocco to fight against France.
To again avoid war. Germany received territorial compensation in the French Congo in exchange for recognizing French control over Morocco.
The Bosnian Crisis
In 1908, the nation of Austria-Hungary had been administrating the Turkish regions of Bosnia and Herzegovina since 1878, but they formally annexed it in 1908, which caused the crisis.
The country of Serbia was outraged, because they felt that it should have been given to them. As a result, Serbia threatened to attack Austria-Hungary.
To support them, Russia, who was allied to Serbia, prepared its armed forces. Germany, however, who was allied to Austria-Hungary, also prepared its army and threaten to attack Russia.
Luckily, war was avoided because Russia backed down. However, there was some regional fighting during 1911 and 1912, as Turkey lost control of the region.
Despite this, Serbia and Austria-Hungary were still angry with each other as they both wanted to expand into these newly liberated countries.
Further reading
What do you need help with, download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email

Sign Up Today
Start your 14 day free trial today

The History Hit Miscellany of Facts, Figures and Fascinating Finds
- 20th Century
The 4 M-A-I-N Causes of World War One

Alex Browne
28 sep 2021.
It’s possibly the single most pondered question in history – what caused World War One? It wasn’t, like in World War Two, a case of a single belligerent pushing others to take a military stand. It didn’t have the moral vindication of resisting a tyrant.
Rather, a delicate but toxic balance of structural forces created a dry tinder that was lit by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo . That event precipitated the July Crisis, which saw the major European powers hurtle toward open conflict.
The M-A-I-N acronym – militarism, alliances, imperialism and nationalism – is often used to analyse the war, and each of these reasons are cited to be the 4 main causes of World War One. It’s simplistic but provides a useful framework.
The late nineteenth century was an era of military competition, particularly between the major European powers. The policy of building a stronger military was judged relative to neighbours, creating a culture of paranoia that heightened the search for alliances. It was fed by the cultural belief that war is good for nations.
Germany in particular looked to expand its navy. However, the ‘naval race’ was never a real contest – the British always s maintained naval superiority. But the British obsession with naval dominance was strong. Government rhetoric exaggerated military expansionism. A simple naivety in the potential scale and bloodshed of a European war prevented several governments from checking their aggression.

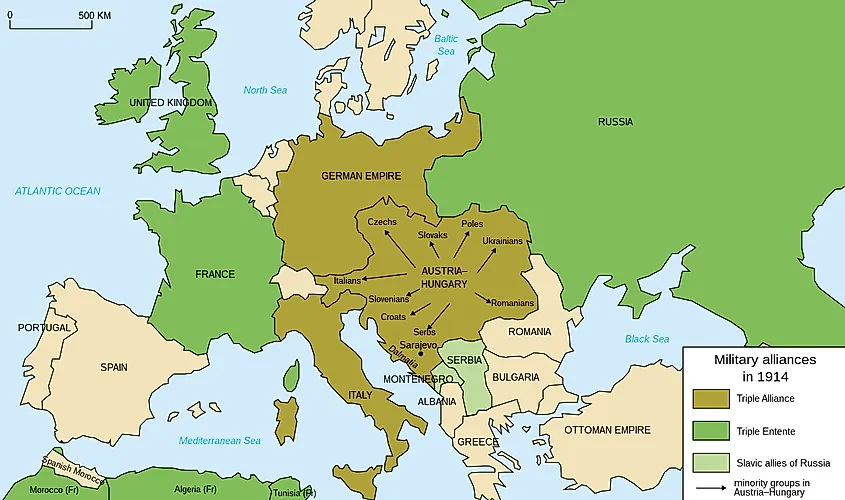
A web of alliances developed in Europe between 1870 and 1914 , effectively creating two camps bound by commitments to maintain sovereignty or intervene militarily – the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance.
- The Triple Alliance of 1882 linked Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy.
- The Triple Entente of 1907 linked France, Britain and Russia.
A historic point of conflict between Austria Hungary and Russia was over their incompatible Balkan interests, and France had a deep suspicion of Germany rooted in their defeat in the 1870 war.
The alliance system primarily came about because after 1870 Germany, under Bismarck, set a precedent by playing its neighbours’ imperial endeavours off one another, in order to maintain a balance of power within Europe
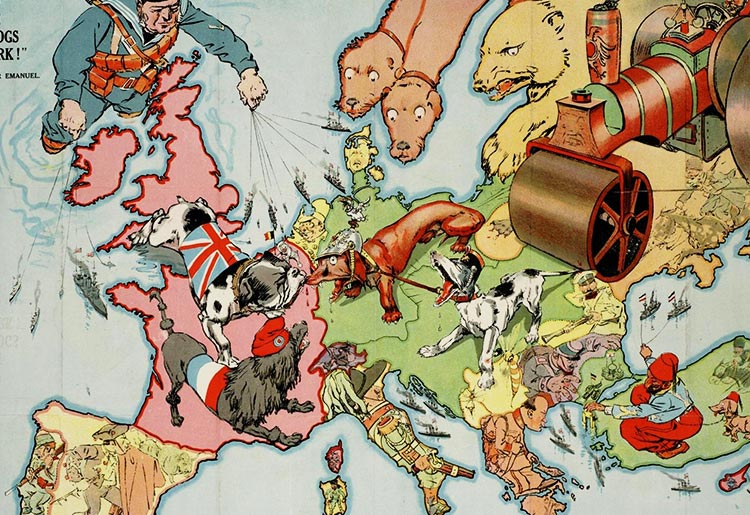
‘Hark! hark! the dogs do bark!’, satirical map of Europe. 1914
Image Credit: Paul K, CC BY 2.0 , via Wikimedia Commons
Imperialism
Imperial competition also pushed the countries towards adopting alliances. Colonies were units of exchange that could be bargained without significantly affecting the metro-pole. They also brought nations who would otherwise not interact into conflict and agreement. For example, the Russo-Japanese War (1905) over aspirations in China, helped bring the Triple Entente into being.
It has been suggested that Germany was motivated by imperial ambitions to invade Belgium and France. Certainly the expansion of the British and French empires, fired by the rise of industrialism and the pursuit of new markets, caused some resentment in Germany, and the pursuit of a short, aborted imperial policy in the late nineteenth century.
However the suggestion that Germany wanted to create a European empire in 1914 is not supported by the pre-war rhetoric and strategy.
Nationalism
Nationalism was also a new and powerful source of tension in Europe. It was tied to militarism, and clashed with the interests of the imperial powers in Europe. Nationalism created new areas of interest over which nations could compete.

For example, The Habsburg empire was tottering agglomeration of 11 different nationalities, with large slavic populations in Galicia and the Balkans whose nationalist aspirations ran counter to imperial cohesion. Nationalism in the Balkan’s also piqued Russia’s historic interest in the region.
Indeed, Serbian nationalism created the trigger cause of the conflict – the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand.
The spark: the assassination
Ferdinand and his wife were murdered in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a member of the Bosnian Serbian nationalist terrorist organization the ‘Black Hand Gang.’ Ferdinand’s death, which was interpreted as a product of official Serbian policy, created the July Crisis – a month of diplomatic and governmental miscalculations that saw a domino effect of war declarations initiated.
The historical dialogue on this issue is vast and distorted by substantial biases. Vague and undefined schemes of reckless expansion were imputed to the German leadership in the immediate aftermath of the war with the ‘war-guilt’ clause. The notion that Germany was bursting with newfound strength, proud of her abilities and eager to showcase them, was overplayed.
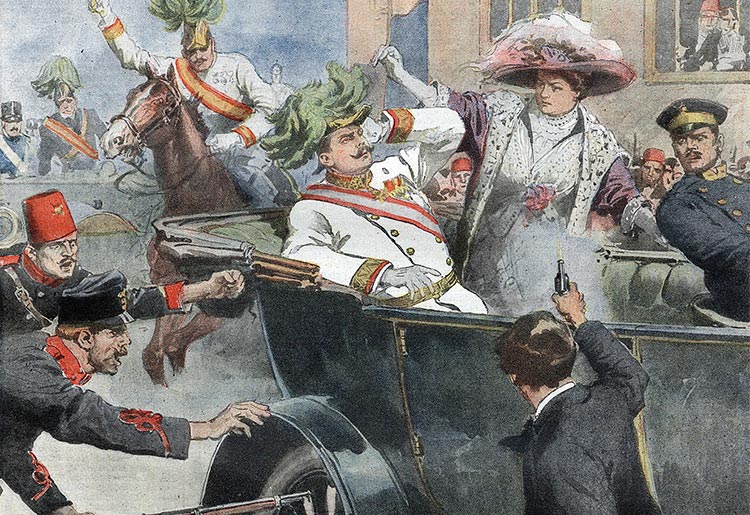
The first page of the edition of the ‘Domenica del Corriere’, an Italian paper, with a drawing by Achille Beltrame depicting Gavrilo Princip killing Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in Sarajevo
Image Credit: Achille Beltrame, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The almost laughable rationalization of British imperial power as ‘necessary’ or ‘civilizing’ didn’t translate to German imperialism, which was ‘aggressive’ and ‘expansionist.’ There is an on-going historical discussion on who if anyone was most culpable.
Blame has been directed at every single combatant at one point or another, and some have said that all the major governments considered a golden opportunity for increasing popularity at home.
The Schlieffen plan could be blamed for bringing Britain into the war, the scale of the war could be blamed on Russia as the first big country to mobilise, inherent rivalries between imperialism and capitalism could be blamed for polarising the combatants. AJP Taylor’s ‘timetable theory’ emphasises the delicate, highly complex plans involved in mobilization which prompted ostensibly aggressive military preparations.
Every point has some merit, but in the end what proved most devastating was the combination of an alliance network with the widespread, misguided belief that war is good for nations, and that the best way to fight a modern war was to attack. That the war was inevitable is questionable, but certainly the notion of glorious war, of war as a good for nation-building, was strong pre-1914. By the end of the war, it was dead.
You May Also Like

Mac and Cheese in 1736? The Stories of Kensington Palace’s Servants

The Peasants’ Revolt: Rise of the Rebels

10 Myths About Winston Churchill

Medusa: What Was a Gorgon?

10 Facts About the Battle of Shrewsbury

5 of Our Top Podcasts About the Norman Conquest of 1066

How Did 3 People Seemingly Escape From Alcatraz?

5 of Our Top Documentaries About the Norman Conquest of 1066

1848: The Year of Revolutions

What Prompted the Boston Tea Party?

15 Quotes by Nelson Mandela

The History of Advent
Home — Essay Samples — History — Imperialism — Main Causes of World War 1: Discussion
Main Causes of World War 1: Discussion
- Categories: Imperialism Nationalism
About this sample

Words: 645 |
Updated: 16 November, 2023
Words: 645 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
The essay explores the causes of World War 1, which took place from 1914 to 1918. It begins with a brief overview of the war's timeline and the major countries involved, including the United Kingdom, France, Russia, Italy, Romania, Japan, the United States of America, Germany, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire. The essay then delves into the four main causes of the war: Militarism, Nationalism, Imperialism, and Alliances.
Militarism is discussed as the policy of maintaining a strong military force and a readiness to use it aggressively for defense. The significant arms buildup and military spending by various countries, including Germany, are highlighted as contributing factors to the outbreak of the war.
Nationalism is described as the strong attachment to one's own nation and culture. It is explained how nationalism led to conflicts, including the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which triggered Austria's desire for revenge.
Imperialism, the expansion of a nation's power by dominating other countries, is presented as a factor due to the competition among European powers over control of African resources and territories.
Lastly, the essay discusses the role of Alliances, where countries formed partnerships to defend each other, often resulting in a domino effect of declarations of war.
Table of contents
- Causes of World War 1
Video Version
Causes o f world war 1, nationalism and imperialism.

A Good Hook Examples for WWI Essay
- A Glimpse into the Trenches: Step back in time and experience the chilling reality of life in the trenches of World War I. In this essay, we’ll immerse ourselves in the harrowing tales of soldiers who faced the horrors of the Great War.
- The War to End All Wars: Explore the monumental impact of World War I on global history. In this essay, we’ll dissect the events that led to the war, the key players, and the lasting consequences that continue to shape our world today.
- The Poetry of Conflict: World War I inspired a generation of poets to capture the raw emotions of battle. Join us as we analyze the powerful verses and poignant imagery that emerged from the trenches.
- Lessons from the Great War: As we commemorate the centennial of World War I, it’s crucial to reflect on the lessons learned from this catastrophic conflict. This essay delves into the war’s impact on diplomacy, technology, and the human spirit.
- Unsung Heroes of WWI: Beyond the famous generals and political leaders, there were countless unsung heroes in the Great War. In this essay, we’ll shine a light on the remarkable stories of bravery and sacrifice from the trenches to the home front.
- Strachan, H. (2014). The First World War: To Arms. Oxford University Press.
- MacMillan, M. (2013). The War That Ended Peace: The Road to 1914. Random House.
- Fay, S. B. (1928). The Origins of the World War (Vol. 1). The Macmillan Company.
- Gildea, R. (2003). Children of the Revolution: The French, 1799-1914. Harvard University Press.
- Kennedy, P. M. (1980). The Rise of the Anglo-German Antagonism, 1860-1914. Allen & Unwin.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: History Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 899 words
4 pages / 1595 words
4 pages / 1650 words
4 pages / 1878 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Imperialism
Imperialism is defined as one country’s domination of the political, economic, and social life of another country. In the late 1800s, Europeans colonized countries, traded slaves, gold, and many other various resources. One of [...]
Imperialism, the policy of extending a nation's authority by territorial acquisition or by the establishment of economic and political dominance over other nations, has long been a topic of interest and debate among historians [...]
Hotel Rwanda is a powerful film that depicts the horrors of the Rwandan genocide in 1994. Directed by Terry George, the movie showcases a true story of how a hotel manager, Paul Rusesabagina, saved countless lives amidst the [...]
American imperialism, the expansion of the United States' influence and territory beyond its continental borders, has been a defining feature of the nation's history. From the late 19th century to the present day, the United [...]
Some claim the domino theory was the key reason for the US intervention in Asia as it halted communist progress, The Domino Theory was the belief that communism was spread from one nation to its neighbours and so on. It was [...]
Imperialism, defined as the policy of extending a country's power and influence through colonization, conquest, or domination of other territories, has had both positive and negative effects throughout history. While imperialism [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault

8 Events that Led to World War I
By: Patrick J. Kiger
Updated: July 13, 2023 | Original: April 6, 2021

World War I , which lasted from 1914 until 1918, introduced the world to the horrors of trench warfare and lethal new technologies such as poison gas and tanks . The result was some of the most horrific carnage the world had ever seen, with more than 16 million military personnel and civilians losing their lives.
It also radically altered the map, leading to the collapse of the sprawling Austro-Hungarian, Ottoman and Russian empires that had existed for centuries, and the formation of new nations to take their place. Long after the last shot had been fired, the political turmoil and social upheaval continued, and ultimately led to another, even bigger and bloodier global conflict two decades later.
The event that sparked the conflagration was the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian Empire, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, in 1914. But historians say that World War I actually was the culmination of a long series of events, stretching back to the late 1800s. The path to war included plenty of miscalculations and actions that turned out to have unforeseen consequences.
“No one can say precisely why it happened,” explains the narration to a film at the National World War I Museum and Memorial in Kansas City. “Which may be, in the end, the best explanation for why it did.”
Here are eight of the events that led to the war.
1. Franco-Russian Alliance (1894)
Both Russia and France, which had been humiliated in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71 , feared the rising power of Germany, which had already formed alliances with Austria-Hungary and Italy. So the two nations decided to join forces for mutual protection as well. It was the start of what would become the Allied side, the Triple Entente, in World War I.
“To my mind, it is the coming together of the Triple Entente in stages—the Franco-Russian Alliance in 1894, the British-French Entente Cordiale of 1904, and the Anglo-Russian Entente of 1907—that really solidified the system of diplomatic agreements that formed the main antagonistic blocs that went to war in 1914,” Richard S. Fogarty , an associate professor of history at University at Albany, explains. “The alliance system was critical to shaping the war, and even in helping bring it on: it created a set of expectations about international rivalry and competition, determining what kind of war Europeans imagined and prepared for.”
2. First German Naval Law, (1898)
This legislation, advocated by Germany’s newly-appointed Secretary of the Imperial Navy, Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, dramatically expanded the size of Germany’s battle fleet. It was the first of five laws dictating a buildup in which the Germans envisioned building a force that was superior to Britain’s Royal Navy.
“Tirpitz aimed at forcing Britain into an alliance with Germany on German terms,” explains Eugene Beiriger , an associate professor of history, peace, justice and conflict studies at DePaul University, and author of the 2018 book World War I: A Historical Exploration of Literature . Instead, the British responded by building even more ships, and by ending their late 1880s policy of “splendid isolation” to form alliances with Japan, France and Russia.
“The German Naval Laws created unintended consequences,” Beiriger says in an email. “They ended up alienating both the government and public of Britain prior to the war.”
3. The Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905)
Russia’s Czar Nicholas II wanted to obtain a port that gave his navy and commercial ships access to the Pacific, and he set his sites on Korea. The Japanese saw Russia’s rising aggressiveness as a menace and launched a surprise attack on Nicholas’ fleet at Port Arthur in China. The resulting war, fought both at sea and on land in China, was won by the Japanese, and as Beiriger notes, it helped shift power the power balance in Europe.
Russia’s allies France and Britain, which were allied with Japan, signed their own agreement in 1904 to avoid being pulled into the war. France later convinced the Russians to enter into an alliance with the British as well, laying the groundwork for their alliance in World War I. In addition, “Russia's expansion in the East had been stopped by Japan,” Beiriger says. “This turned Russian ambitions westward, especially in the Balkans, and influenced hardliners within the government to not back down in future crises.” That Russian combativeness helped trigger World War I less than a decade later.
4. Austria-Hungary’s Annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina (1908)

Under an 1878 treaty, Austria-Hungary was governing Bosnia and Herzegovina, even though technically they were still part of the Ottoman Empire. But after the Austro-Hungarian government annexed their territory , the move backfired. The two provinces’ mostly Slavic population wanted to have their own country, while Slavs in nearby Serbia had the ambition of appropriating the provinces themselves.
“In multi-ethnic empires, nationalistic fervor fueled resistance to distant rulers,” Doran Cart , senior curator of the National World War I Museum and Memorial, says. “Tension was powder-keg high in the Balkans, where Slavic people, aided by the Slavs of Russia, resisted the rule of Austria-Hungary.” Additionally, the move drew Russia, which saw itself as Serbia’s protector, toward a gradual showdown with the Austro-Hungarian regime.
5. The Second Moroccan Crisis (1911)

The French and Germans butted heads for several years over Morocco, where Germany’s Kaiser Wilhelm II meddled in an attempt to pressure the French-British alliance. In the First Moroccan Crisis in 1905, he actually sailed to Tangiers to express his support for the sultan of Morocco against French interests. But instead of backing away from the conflict, the British rose in support of France.
In the Second Moroccan Crisis in 1911, the German foreign secretary, Alfred von Kiderlen- Wächter, sent a naval cruiser to anchor in a harbor on the Moroccan coast, in reaction to a tribal revolt that the Germans thought was being backed by France as a pretext for seizing the country. Again, the British backed the French, and eventually, Germany was forced to agree to recognize a French protectorate in Morocco. The two crises pushed the British and French closer together, and only hastened an eventual confrontation with the Germans.
6. Italy Invades Libya (1911)

The modern Italian state, which didn’t begin until 1861, had been “largely left out of the scramble that built Britain, France, and other powers into worldwide empires,” Fogarty explains. The Italian government set its sights on Libya, a North African country that hadn’t been claimed by another Western European power, and decided to take it from the Ottoman Empire. The Italo-Turkish War ended with a peace treaty, but the Ottoman military left Libya and let the Italians colonize it. It was the first military conflict that featured aerial bombing , but as Fogarty notes, the real significance was that it exposed the shakiness of the Ottoman Empire and its slipping control over peripheral territories. That, in turn, was one of the factors that ultimately led to World War I, which Fogarty describes as “a war of empires, some expanding or seeking to expand, some keen to hold on to what they had, others trying desperately not to lose what they had left,”
7. The Balkan Wars (1912-13)

Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro and Greece, which had broken away from the Ottoman Empire during the 1800s, formed an alliance called the Balkan League . The Russian-backed alliance aimed to take away even more of the Turks’ remaining territory in the Balkans.
In the First Balkan War in 1912, Serbia, Greece and Montenegro defeated Ottoman forces, and forced them to agree to an armistice. But the Balkan League soon disintegrated, and in the Second Balkan War, the Bulgarians fought the Greeks and Serbs over Macedonia, and the Ottoman Empire and Romania jumped into the fray against the Bulgarians as well.
Bulgaria ultimately was defeated. The Balkan Wars made the region even more unstable. In the power void left by the Ottomans, tensions grew between Serbia and Austria-Hungary. That, in turn, led Austria-Hungary and its ally, Germany, to decide that a war with the Serbs would be needed at some point to strengthen Austria-Hungary’s position. “Many historians consider the Balkan Wars as the true beginning of the First World War,” Fogarty says.
8. Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand (1914)
The archduke, who was heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, went to Sarajevo to inspect the imperial troops stationed in Bosnia and Herzegovina. He and his wife Sophie were shot to death in their car by a 19-year-old Serbian revolutionary, Gavrilo Princip.
“The assassination highlighted the nationalism that was pulling the Austro-Hungarian Empire apart at the seams,” Fogarty explains, noting that Serbian extremists actually wanted Franz Ferdinand dead because they feared he was too moderate and would promote a power-sharing arrangement that would keep Slavic peoples in the empire.
“His assassination killed the idea, whether or not it was ever realistic to begin with, and radicalized Serbian defiance and Austrian determination to solve the nationalism problem for good, at least with respect to Serbia,” Fogarty says.
Instead, the tension between European powers increased, as they took different sides in the crisis. As the U.K.’s Imperial War Museum notes , the killing put both Austria-Hungary and Russia, which saw itself as the Serbians’ protector, in a bind. Neither one of them wanted to back down and appear weak. Fearing a fight that would draw in Russia, Austria-Hungary turned for help to Germany, which promised backing if the Austro-Hungarians used force against the Serbians. German support emboldened Austria-Hungary to declare war on Serbia on July 28.
Two days later, Russia’s military mobilized, and the Germans saw that they too were in a bind. They didn’t want to fight both Russia and its ally France on two fronts simultaneously, so it became imperative to knock the French military out of the war before Russia was ready to fight. Germany declared war on Russia on August 1, and two days later declared war against France . German forces gathered on the border of neutral Belgium, which they planned to cross in order to invade France. Belgium called for help, and on August 4, Great Britain declared war on Germany.
World War I had begun.

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us

- The Main Causes of WW1
World War One (also known as the First World War or the Great War) was arguably the most significant event of the 20th century, leading to geopolitical maps being redrawn, new nations emerging, and communism and fascism rising across Europe . However, the causes are as important as the results, as they reveal key details about the conflict and its place in history. Therefore, investigating the contributing factors that led to the First World War is a worthwhile endeavor.
The Assassination Of The Archduke Franz Ferdinand

In 1878, following the end of the Russo-Turkish War, the Austro-Hungarian Empire occupied the previously Ottoman -controlled Bosnia-Herzegovina . The Empire then formally annexed Bosnia in 1908, prompting anger from the numerous different ethnic groups in the region. Serbian nationalists were particularly incensed by this incursion. Thus, with the Archduke of Austria-Hungary Franz Ferdinand scheduled to visit the capital of Sarajevo in June 1914, Young Bosnia, a particularly militant Serbian nationalist group, planned an assassination.
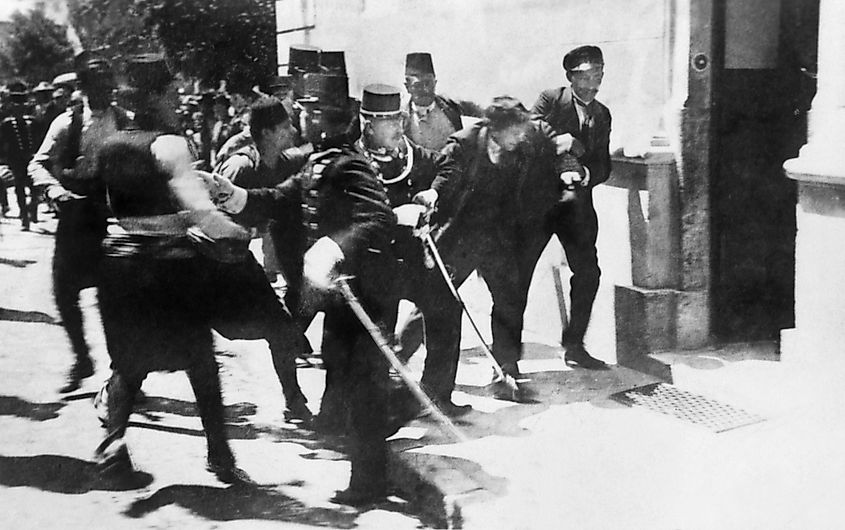

On June 28, at about 10:00 a.m. Nedeljko Čabrinović threw a grenade at the Archduke's motorcade, damaging the vehicles and injuring the politician. About an hour later, Gavrilo Princip, after getting lost and seemingly missing his opportunity to carry out the assassination, stumbled across the motorcade. Princip proceeded to shoot Ferdinand and his wife, killing them both and setting off a chain reaction that resulted in Europe going to war.
Understanding the event that started the Great War is crucial. But, comprehending why it was the spark plug is even more important. In other words, how did a conflict that began in the Balkans escalate into a global affair? Analyzing some longer-term factors explains why this occurred.
In 1882, motivated by anti-Russian and anti-French sentiments, Germany , Austria-Hungary, and Italy formed the Triple Alliance. This alliance was made so that if one of them was attacked, the other two needed to provide military support. The French and Russians followed this with their own agreement in 1894, evolving into the Triple Entente by 1907--a three-way military alliance between the United Kingdom , France , and Russia .
Despite emerging out of a desire for stability, these alliances contributed to the exact opposite. Indeed, following the assassination of the Archduke, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia . Russia, a Serbian ally, then declared war on Austria-Hungary. Being part of the Triple Alliance, Germany was obligated to go to war with Russia, which then brought in the United Kingdom and France. In short, alliances were largely responsible for a regional conflict snowballing into a general European war, as they made military involvement obligatory if one's ally was attacked.
Militarism
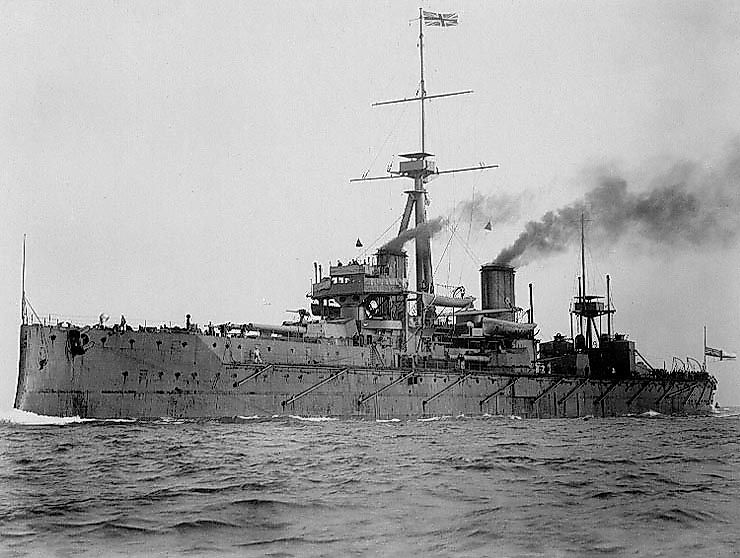

The late 1800s also saw increased militarism. Perhaps the most obvious example of this was the Anglo-German naval arms race. By the 1870s, Britain had the largest navy in Europe. Feeling threatened, Kaiser Wilhelm II began to build up Germany's maritime force. This prompted even more naval investments by the UK, leading to the creation of the Dreadnought--a new ship that far outclassed any others in Europe. It soon became clear that no matter what Germany did, its navy could not match that of the British. Nonetheless, tensions caused by such militarism undeniably contributed to the general fear of a prospective European war. Moreover, these improvements in military technologies ensured that any future conflict would be enormously destructive.
Imperialism/Colonialism

At the 1884 Berlin Conference, Africa was divided between the major European powers, the most notable of which were Britain, France, and Belgium . Despite this diplomacy, difficulties arose. For instance, Germany, not having a particularly strong foothold in Africa, wanted to weaken France's position on the continent. Therefore, on March 31, 1905, Kaiser Wilhelm II visited French-controlled Morocco , touring the city of Tangier and declaring his support for Moroccan independence. Shortly afterward, the Moroccan Sultan rejected a series of French policies. This became known as the First Moroccan Crisis. While Germany did agree to stop interfering in French colonial business following the Algeciras Conference, the crisis resulted in a deepening of alliances, with Austria-Hungary coming to Germany's defense and Britain supporting France. In short, these imperial and colonial affairs increased divisions between the Entente and the Central Powers, contributing to a geopolitical atmosphere that made war possible.
Nationalism

In 1871, Germany and Italy unified, signifying the rise of nationalism across Europe. This change contributed to the perception of politics as a battle between people or races rather than political leaders, posing an existential threat to multiethnic empires like the Austria-Hungary Empire comprising Germans, Hungarians , Czechs , Serbians , Croatians , Poles , Ruthenians, and Romanians . Furthermore, no one group in this Empire made up the majority of the population. All this meant that the Empire was a powder keg, with different nationalities vying for power. As demonstrated by Serbian nationalists assassinating Franz Ferdinand, these often violent sentiments directly led to World War One.
The Great War occurred due to a multitude of factors. The most direct cause was the assassination of Austria-Hungary's Archduke on June 28, 1914. However, the deeper roots can be traced to alliances, militarism, imperialism, and nationalism. These elements thus culminated in one of the deadliest conflicts in world history.
More in History

Russian Civil War
Exploring Ancient Civilizations' Greatest Capital Cities Today

10 Deadliest Bridge Collapses In History

Emu War: Australia's Crusade Against Birds
The War of Alexander's Successors

What Killed Alexander the Great?

Where is Cleopatra's Tomb?

The Destruction Of The 7 Wonders Of The Ancient World
The Causes and Effects of World War I Essay
Introduction.
The effects of World War I can be seen around the world even now, more than one hundred years after its end; however, there is still no consensus as to its cause. In the words of Alfred Korzybski, “the destruction was brought about by nationalism, entangled alliances, narrow ethnic concerns, and desires for political gain – forces that are still with people today.” (cited in Levinson, 2014). Even though the majority of United States citizens did not have the direct experience of the terrific upset that the war caused in Europe, it can be argued that the country’s concern with championing democracy around the globe is one of its products (Levinson, 2014).
Many historians agree that an atmosphere of twentieth-century Europe was conducive to the creation of a complex mixture of economic, social, and political reasons that translated into powerful forces of imperialistic, nationalistic, and militaristic movements leading to the diplomatic crises of 1914 (Donaldson, 2014). Therefore, it can be said that the blame for the war could not be assigned to any individual country or a group of countries.
Nonetheless, the issue of responsibility was the main focus of the world in the years following the Armistice of 1918 (Donaldson, 2014). To this end, the Commission on the Responsibility of the Authors of the War and the Enforcement of Penalties met in Paris in 1919 (Donaldson, 2014). The investigation conducted by the commission showed that Germany and Austria, along with Turkey and Bulgaria as their allies, were responsible for the aggressive foreign policy tactics that led to the precipitation of the war (Donaldson, 2014).
The start of World War I was precipitated by the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, on June 28, 1914 (Mulligan, 2010) The elimination of the high-standing official was carried out by the group of secret society members called Black Hand and directed by Bosnian Serb Danilo Ilić (Storey, 2009). The political objective of the murder was to separate Austria-Hungary’s South Slav provinces to combine them into Yugoslavia (Storey, 2009).
In response to the killing of their official, Austria-Hungary issued an ultimatum to Serbia that commanded its government to prosecute the assassins. The objective of the ultimatum was to make its terms so strict that Serbia would be forced to reject it, thereby giving an excuse for launching a small war against it (Storey, 2009). Taking into consideration that Serbia had diplomatic relationships with Russia strengthened by their shared Slavic ties, the Austro-Hungarian government decided to take precautions against the two countries declaring war on it and allied with Germany. It is agreed that Germany was not opposed to Austro-Hungarian bellicosity, but rather supported and encouraged it, thus providing one more reason for the precipitation of the Great War (Levinson, 2014).
Even though Serbia’s response to the ultimatum was placating, Austria-Hungary decided to take aggressive action and declare war. It is argued that the main reason for World War I was the web of entangling alliances among the countries having an interest in the conflict between Austro-Hungary and Serbia (Storey, 2009). Following the Austro-Hungarian declaration of war, the Russian monarch mobilized his army because of the binding commitment of the treaty signed by the two countries.
As a result, on August 3, 1914, Germany declared war on the Russian Empire (Levinson, 2014). France was bound by treaty to Russia, and, therefore, had to start a war on Austria-Hungary and Germany. Even though a treaty tying France and Britain was loosely worded, the latter country had “a moral obligation” to defend the former (Levinson, 2014). Therefore, Britain and its allies Australia, Canada, India, New Zealand, Japan, and the Union of South Africa also took a bellicose stance against Germany and offered their assistance in the military action against the country (Levinson, 2014). Thus, a gigantic web of entangling alliances pushed numerous countries to the precipice of war over what was intended to be a small-scale conflict between Austria-Hungary and Serbia.
Numerous other reasons led to World War I. The conflicting political interests of Russia and Japan over Manchuria and Korea resulted in a military defeat of Russia (Levinson, 2014). Therefore, the country wanted to restore its dignity by a victorious war. During the same period, a lot of small nations were seething with discontent over the Turkish and Austro-Hungarian rule, thereby providing an opportunity for the Russian Empire further to stir resentment by firing up nationalistic zeal under a pretense of pan-Slavic narrative (Levinson, 2014).
Austria-Hungary, on the other hand, sought an opportunity to establish its influence over a vast territory of mixed nations; the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne provided them with a perfect excuse for the initiation of the war. Political clashes in Germany were a reason for the country’s government to resort to the military conflict as a way of “averting civil unrest” (Levinson, 2014). Another factor that caused World War I was the desire of France to revenge a military defeat in the Franco-Prussian War of 1871 (Levinson, 2014).
It is impossible to name a single reason for the initiation of World War I. However, it is clear that the entangling web of alliances among numerous parties participating in the war, as well as complicated plots of governments and empires, led the small-scale dispute between Austria-Hungary and Serbia escalating into a military conflict that swept the entire world.
Donaldson, P. (2014). Interpreting the origins of the First World War. Teaching History , 155 (4), 32-33.
Levinson, M. (2014). Ten cautionary GS lessons from World War I. Et Cetera, 71 (1), 41-48.
Mulligan, W. (2010). The origins of the First World War . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Storey, W. (2009). The First World War . Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, October 9). The Causes and Effects of World War I. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-causes-and-effects-of-world-war-i/
"The Causes and Effects of World War I." IvyPanda , 9 Oct. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-causes-and-effects-of-world-war-i/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The Causes and Effects of World War I'. 9 October.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The Causes and Effects of World War I." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-causes-and-effects-of-world-war-i/.
1. IvyPanda . "The Causes and Effects of World War I." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-causes-and-effects-of-world-war-i/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The Causes and Effects of World War I." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-causes-and-effects-of-world-war-i/.
- World War I Causes by Ethnic Problems in Austro-Hungary
- First World War Issues and Causes
- World War 1 Origins (How and Why the War Started)
- Events Leading Up to WWI
- Causes of WWI and WWII: Comparing and Contrasting
- The First World War's Long- and Short-Term Causes
- Brusilov Offensive: An Unique Tactics in War
- Eastern Crisis of 1875-1878
- The Late 19th Century and the First World War, 1850-1918
- The Ultimatum Game Research Prospectus
- World War I, Its Origin and Allies
- The Worst Team in History: the Gallipoli Failure
- Principal Causes of the First World War
- "Two Cheers for Versailles" by Mark Mazower
- Germany's Aims in the First World War
5 Key Causes of World War I
Illustration by Hugo Lin. ThoughtCo.
- M.A., History, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
World War I, known as the "war to end all wars," occurred between July 1914 and November 11, 1918. By the end of the war, over 17 million people had been killed, including over 100,000 American troops. While the causes of the war are infinitely more complicated than a simple timeline of events, and are still debated and discussed to this day, the list below provides an overview of the most frequently-cited events that led to war.
Watch Now: 5 Causes of World War I
Mutual defense alliances.
Countries throughout the world have always made mutual defense agreements with their neighbors, treaties that could pull them into battle. These treaties meant that if one country was attacked, the allied countries were bound to defend them. Before World War 1 began, the following alliances existed:
- Russia and Serbia
- Germany and Austria-Hungary
- France and Russia
- Britain and France and Belgium
- Japan and Britain
When Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, Russia got involved to defend Serbia. Germany, seeing that Russia was mobilizing, declared war on Russia. France was then drawn in against Germany and Austria-Hungary. Germany attacked France by marching through Belgium pulling Britain into war. Then Japan entered the war to support its British allies. Later, Italy and the United States would enter on the side of the Allies (Britain, France, Russia, etc.).
Imperialism
Imperialism is when a country increases their power and wealth by bringing additional territories under their control, usually without outright colonizing or resettling them. Before World War I, several European countries had made competing imperialistic claims in Africa and parts of Asia, making them points of contention. Because of the raw materials these areas could provide, tensions around which country had the right to exploit these areas ran high. The increasing competition and desire for greater empires led to an increase in confrontation that helped push the world into World War I.
As the world entered the 20th century, an arms race had begun, primarily over the number of each country's warships, and the increasing size of their armies—countries began training more and more of their young men to be prepared for battle. The warships themselves increased in size, number of guns, speed, method of propulsion, and quality armor, beginning in 1906 with Britain's HMS Dreadnought . Dreadnought was soon out-classed as the Royal Navy and Kaiserliche Marine quickly expanded their ranks with increasingly modern and powerful warships.
By 1914, Germany had nearly 100 warships and two million trained soldiers. Great Britain and Germany both greatly increased their navies in this time period. Further, in Germany and Russia particularly, the military establishment began to have a greater influence on public policy. This increase in militarism helped push the countries involved into war.
Nationalism
Much of the origin of the war was based on the desire of the Slavic peoples in Bosnia and Herzegovina to no longer be part of Austria-Hungary but instead be part of Serbia. This specific essentially nationalistic and ethnic revolt led directly to the assassination of Archduke Ferdinand , which was the event that tipped the scales to war.
But more generally, nationalism in many of the countries throughout Europe contributed not only to the beginning but to the extension of the war across Europe and into Asia. As each country tried to prove their dominance and power, the war became more complicated and prolonged.
Immediate Cause: Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
The immediate cause of World War I that made the aforementioned items come into play (alliances, imperialism, militarism, and nationalism) was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary. In June 1914, a Serbian-nationalist terrorist group called the Black Hand sent groups to assassinate the Archduke. Their first attempt failed when a driver avoided a grenade thrown at their car. However, later that day a Serbian nationalist named Gavrilo Princip shot the Archduke and his wife while they were driving through Sarajevo, Bosnia which was part of Austria-Hungary. They died of their wounds.
The assassination was in protest to Austria-Hungary having control of this region: Serbia wanted to take over Bosnia and Herzegovina. The assassination of Ferdinand led to Austria-Hungary declaring war on Serbia. When Russia began to mobilize to defend its alliance with Serbia, Germany declared war on Russia. Thus began the expansion of the war to include all those involved in the mutual defense alliances.
The War to End All Wars
World War I saw a change in warfare, from the hand-to-hand style of older wars to the inclusion of weapons that used technology and removed the individual from close combat. The war had extremely high casualties over 15 million dead and 20 million injured. The face of warfare would never be the same again.
- Causes of World War I and the Rise of Germany
- The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, 1914
- World War I Timeline From 1914 to 1919
- Biography of Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria
- The Causes and War Aims of World War One
- World War I Timeline: 1914, The War Begins
- World War I Introduction and Overview
- World War 1: A Short Timeline Pre-1914
- The Major Alliances of World War I
- World War I: Opening Campaigns
- The First Battle of the Marne
- The Fourteen Points of Woodrow Wilson's Plan for Peace
- Key Historical Figures of World War I
- The Black Hand: Serbian Terrorists Spark WWI
- The Consequences of World War I
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
World History Project AP®
Course: world history project ap® > unit 7, read: what caused the first world war.
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: How World War I Started – Crash Course World History #209
- WATCH: How World War I Started
- READ: The First World War as a Global War
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: Britain and World War I
- WATCH: Britain and World War I
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: Southeast Asia and World War I
- WATCH: Southeast Asia and World War I
- BEFORE YOU WATCH: The Middle East and World War I
- WATCH: The Middle East and World War I
First read: preview and skimming for gist
Second read: key ideas and understanding content.
- Who killed Franz Ferdinand? Why did they kill him?
- How did the European alliance system help start the war?
- How did imperialism help start the war?
- Why does the author argue that industrialization made the war inevitable once preparations were started?
- How might the First World War have happened on accident?
Third read: evaluating and corroborating
- To what extent does this article explain the causes and consequences of World War I?
- This article gives three broad explanations for the origins of the First World War. Which view, or argument, do you agree with the most, and why? Why not the others?
What Caused the First World War?
World war why, one shot: the assassination of archduke franz ferdinand, deeper trends: help me help you help me, accidental war: missed the memo, hit the target.
- Yes, these terms can get confusing. Nationalism was introduced to you as the idea that a state should govern itself, and not have some empire as its boss. But at some point, that feeling that you should get to govern yourself can turn into the idea that you are better than other nations, and becomes a kind of extreme patriotism. We call that nationalism as well. As we will see, nationalism is a pretty flexible thing, and it can be used for lots of different purposes.
- Top map by Joe Mabel, CC BY-SA 3.0. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Map_of_the_German_Empire_-_1914.PNG
- Bottom map by Andrew0921, CC BY-SA 3.0. https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:British_Empire_in_1914.png
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

COMMENTS
Effects. As many as 8.5 million soldiers and some 13 million civilians died during World War I. Four imperial dynasties collapsed as a result of the war: the Habsburgs of Austria-Hungary, the Hohenzollerns of Germany, the sultanate of the Ottoman Empire, and the Romanovs of Russia. The mass movement of soldiers and refugees helped spread one of ...
9. Tanks are one of the most significant weapons to emerge from World War I. Investigate and discuss the development, early use and effectiveness of tanks in the war. 10. The Hague Convention outlined the 'rules of war' that were in place during World War I. Referring to specific examples, discuss where and how these 'rules of war' were ...
World War I started in 1914, after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, and ended in 1918. During the conflict, the countries of Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria and the Ottoman Empire ...
The First World War was the first conflict that occurred on a staggering scale. World War I (WWI) was unprecedented in its global impact and the extent of its industrialization. However, the reason why the war originally began is incredibly complex. To try and explain the causes of the war, historians have tried to simplify it down to four main causes.
World War I, an international conflict that in 1914-18 embroiled most of the nations of Europe along with Russia, the United States, the Middle East, and other regions. The war pitted the Central Powers —mainly Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Turkey —against the Allies—mainly France, Great Britain, Russia, Italy, Japan, and, from 1917 ...
Killing the archduke then was like killing the crown prince of Britain right now. Also, the assassination was not the only reason for war. the naval arms race and the scramble for africa are also reasons for the world war. basically, everybody wanted war. the killing of the archduke is what instigated it, thats all.
M-A-I-N. The M-A-I-N acronym - militarism, alliances, imperialism and nationalism - is often used to analyse the war, and each of these reasons are cited to be the 4 main causes of World War One. It's simplistic but provides a useful framework.
The identification of the causes of World War I remains a debated issue. World War I began in the Balkans on July 28, 1914, ... However, Schroeder argues that all of that was not the main cause of the war in 1914. Indeed, the search for a single main cause is not a helpful approach to history. Instead, there are multiple causes any one or two ...
Experts continue to fiercely debate this question. Yes, the 1914 assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, heir to the throne of Austria-Hungary, triggered a series of declarations of war. However many scholars argue that several other factors had been creating the conditions for conflict in Europe for decades prior.
Militarism. Militarism emerged as a significant cause of World War 1 due to the escalating arms race and military expenditures among various countries. Germany, in particular, invested heavily in its military, constructing numerous vessels, submarines, U-boats, warships, and conscripting a substantial army.
In the short term, this was indeed one of the spurs for British involvement but the underlying reasons for war stretched back over many years. Wars occur when the aims and ambitions or the ...
Here are eight of the events that led to the war. 1. Franco-Russian Alliance (1894) Both Russia and France, which had been humiliated in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71, feared the rising power ...
The Great War occurred due to a multitude of factors. The most direct cause was the assassination of Austria-Hungary's Archduke on June 28, 1914. However, the deeper roots can be traced to alliances, militarism, imperialism, and nationalism. These elements thus culminated in one of the deadliest conflicts in world history.
Causes. The start of World War I was precipitated by the assassination of the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, on June 28, 1914 (Mulligan, 2010) The elimination of the high-standing official was carried out by the group of secret society members called Black Hand and directed by Bosnian Serb Danilo Ilić (Storey ...
Germany and Austria-Hungary. France and Russia. Britain and France and Belgium. Japan and Britain. When Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, Russia got involved to defend Serbia. Germany, seeing that Russia was mobilizing, declared war on Russia. France was then drawn in against Germany and Austria-Hungary.
A useful way to think about causes in history is to see the difference between immediate and underlying causes. Take, for example, the causes of the American Civil War. Historians generally agree that the immediate cause of the Civil War was the decision by South Carolina soldiers to start firing on federal troops at Fort Sumter. However,
Background Essay Causes of WWi Mini-Q What Was the Underlying Cause of World War I? At the turn of the 20th century Europe was feeling pretty darned good. It controlled empires that circled the globe. Its technology was unsur-passed. Its art and music were the envy of the world. In 1900, Europeans believed the world was their oyster.
As soon as the war began, the major nations issued "color books" containing documents (mostly from July 1914) that helped justify their actions.A color book is a collection of diplomatic correspondence and other official documents published by a government for educational or political reasons, and to promote the government position on current or past events.
Historical Background. World War I, also known as The Great War, was an international conflict lasting from 1914 to 1918. The driving force that led nations to war was imperialism. It was fought between the Central Powers (consisting mainly of Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Turkey) and the Allied Powers (consisting mainly of France, Great ...
Archduke of Austria Hungary-crown prince, heir to Austrian throne from 1896: assassinated on June 28, 1914 during good-will mission in Sarajevo, Bosnia (Aus-Hung) by Serbians, sparking WWI: caused Germany and other Austro Allies to declare war on Serbia and its allies. His murder was one of the causes of World War 1.
It was one of the victims of the First World War, defeated and torn apart by the end of the conflict. But in 1914, the Habsburg family had ruled this empire for almost four centuries. It was a huge, multi-ethnic empire located in the middle of Europe. Franz Ferdinand's uncle, the emperor, ruled over its many ethnic communities with difficulty.
They believed it was a battle of defense after the death of Archduke Ferdinand. He says the cause of the war was "imperialism of all European states." This imperialism led to conflict. When the Russians mobilized, military men took over and diplomacy faded. 2) He stated that Europe had turned to denying and violating the right of man; Europe ...
CAUSES OF WORLD WAR I World War I occurred between July 1914 and November 11, 1918. By the end of the war, over 17 million people would ... World War 1, the following alliances existed: ... (June 28, 1914) was the main catalyst for the start of the Great War (World War I). After the assassination, the following series of events took place:
The origins of the Second World War (1939-45) may be traced back to the harsh peace settlement of the First World War (1914-18) and the economic crisis of the 1930s, while more immediate causes were the aggressive invasions of their neighbours by Germany, Italy, and Japan.A weak and divided Europe, an isolationist USA, and an opportunistic USSR were all intent on peace, but the policy of ...