

Creating an Outline for Your Master’s Thesis
1. introduction.
Your master’s thesis serves to explain the research that you have done during your time as a masters student. For many students, the master’s thesis is the longest document that they’ve ever written, and the length of the document can feel intimidating. The purpose of this CommKit is to cover a key element of writing your thesis: the outline.
2. Criteria for Success
The most important criterion for success is that you’ve shown an outline with your chapter breakdown to your advisor. Your advisor is the one that formally signs off on your thesis as completed, so their feedback is the most important.
Every master’s thesis will have the following elements.
- Introduction – Familiarize the reader with the topic and what gap exists in the field.
- Literature Review – Provide a detailed analysis of similar work in the field and how your work is unique. Master’s thesis literature reviews typically have at least 60 citations throughout the entire document
- Methods – Explain how you produced your results
- Results – Show your results and comment on their significance and implications.
- Conclusion – Summarize the methodology you used to generate results, your key findings, and any future areas of work.
Having an outline for your master’s thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master’s thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks.
4. Analyze Your Audience
The most important audience member for your master’s thesis is your advisor, as they are ultimately the person that signs off on whether or not your thesis is sufficient enough to graduate. The needs of any other audience members are secondary.
Ideally, a good master’s thesis is accessible to people that work in your field. In some cases, master’s theses are passed on to newer students so that that research can continue. In these cases, the thesis is used as a guide to introduce newer students to the research area. If you intend for your thesis to be used as a guide for new students, you may spend more time explaining the state of the field in your introduction and literature review. Additionally, your thesis will be posted publicly on DSpace , MIT’s digital repository for all theses.
5. Best Practices
5.1. identify your claims.
A key element to figuring out the unique structure to your master’s thesis is identifying the claims of your work. A claim is an answer to a research question or gap. Your thesis can have both a higher level claim and also lower level claims that motivate the research projects that you worked on. Identifying your claims will help you spot the key objectives which you want to highlight in the thesis. This will keep your writing on topic.
Some examples are shown below:
Gap/Question : There are no field-portable microplastic sensing technologies to measure their distribution in the environment.
→ Claim : Impedance spectroscopy can be used in a microfluidic device to rapidly distinguish organic matter from polymers.
Gap/Question: How effective are convolutional neural networks for pose estimation during in-space assembly?
→ Claim : Convolutional neural networks can be used to estimate the pose of satellites, but struggle with oversaturated images and images with multiple satellites.
5.2. Support Your Claims
Once you have identified your claim, the next step is to identify evidence that will support it. The structure of your paper will be very dependent on the claim that you make. Figure 1 and 2 demonstrate two different structures to support a claim. In one outline, the claim is best supported by a linear structure that describes the building, testing, and validation of a model. In another outline, the claim is best supported by a trifold structure, where three independent methods are discussed. Depending on the extent of the evidence, you could break this trifold structure into 3 separate chapters, or they could all be discussed in a singular chapter. The value of identifying claims and evidence is that it helps you organize your paper coherently at a high level. The number of chapters that are output as a result of your claim identification is up to you and what you think would be sufficient discussion for a chapter within your thesis.
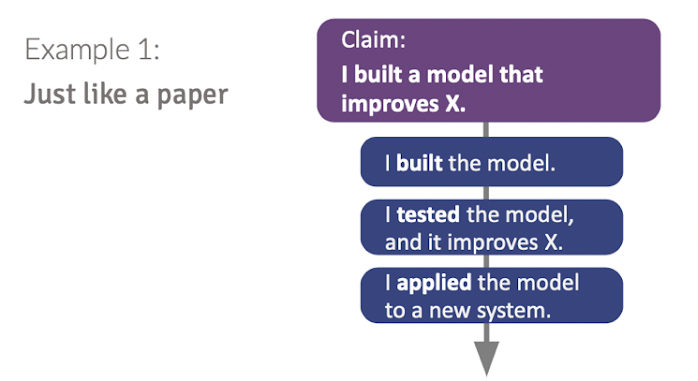
5.3. Connect the Evidence to Your Claims with Reasoning
One common mistake that students make when writing their thesis is treating each chapter as an isolated piece of writing. While it is helpful to break down the actual task of thesis writing into chapter-size pieces, these chapters should have some connection to one another. For your outline, it is ideal to identify what these connections were. Perhaps what made you start on one project was that you realized the weaknesses in your prior work and you wanted to make improvements. For readers who were not doing the research with you, describing the connections between your work in different chapters can help them understand the motivation and value of why you pursued each component.
5.4. Combine Your Claims, Evidence, and Reasoning to Produce Your Outline
Once you have identified your claims, the evidence you have surrounding each claim, and the reasoning that connects each piece of your work, you can now create your full outline, putting the pieces together like a jigsaw puzzle. An example outline is provided as an annotated example.
There are no requirements for minimum or maximum number of chapters that your master’s thesis can have. Therefore, when translating your outline to a literal chapter breakdown, you should feel free to use as many chapters as needed. If your methods section for a claim is extremely long, it may make more sense to have it be a standalone chapter, as shown in the attached annotated pdf.
6. Additional Resources
Every IAP, the Comm Lab hosts a workshop on how to write your master’s thesis. This workshop provides tips for writing each of these sections, and steps you through the process of creating an outline.
Resources and Annotated Examples
Example 1. structure diagram and table of contents, example 2. table of contents.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis Outline – Example, Template and Writing Guide
Thesis Outline – Example, Template and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Thesis Outline
Thesis outline is a document that outlines the structure and content of a thesis , which is a long-form academic paper that presents an original argument or research on a particular topic. The outline serves as a roadmap for the thesis, providing an overview of the major sections, sub-sections, and the general flow of the argument.
Thesis outline typically follows a standard format and includes the following sections:
- Title page: This page includes the thesis title, author’s name, department, university, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This section is a brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the main points and conclusions. It usually contains around 150-300 words.
- Table of contents: This page lists all the chapters, sections, and subsections of the thesis, along with their page numbers.
- Introduction: This section introduces the topic of the thesis, presents the research question or hypothesis, and provides an overview of the methodology and the scope of the study.
- Literature review: This chapter provides a critical analysis of the existing literature on the topic, highlighting the gaps, inconsistencies, and controversies.
- Methodology : This section explains the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques used in the study.
- Results : This chapter presents the findings of the study, using tables, charts, and graphs to illustrate the data.
- Discussion : This section interprets the results and relates them to the research question or hypothesis. It also discusses the implications, limitations, and future directions of the study.
- Conclusion : This section summarizes the main points of the thesis, restates the research question or hypothesis, and provides a final conclusion.
- References : This page lists all the sources cited in the thesis, following a specific citation style (APA, MLA, etc.).
- Appendices : This section includes any additional materials, such as questionnaires, interview transcripts, or raw data, that are relevant to the study but not included in the main text.
Thesis Outline Example
Thesis Outline Example and Template Sample is as follows:
I. Introduction
- Background and Context
- Problem Statement
- Research Questions
- Objectives and Scope
- Significance of the Study
- Chapter Overview
II. Literature Review
- Introduction to Literature Review
- Theoretical Framework
- Previous Research on the Topic
- Critical Analysis of the Literature
- Summary and Conclusion
III. Methodology
- Introduction to Methodology
- Research Design and Approach
- Sampling Strategy
- Data Collection Methods
- Data Analysis Techniques
- Ethical Considerations
- Limitations and Delimitations
IV. Results
- Introduction to Results
- Presentation of Data
- Analysis of Findings
- Discussion of Results
V. Discussion
- Introduction to Discussion
- Interpretation of Results
- Comparison with Previous Research
- Implications and Applications of the Findings
- Limitations and Future Directions
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of Findings
- Conclusions and Recommendations
- Contribution to the Field
- Implications for Future Research
VII. References
VIII. Appendices
- Survey Instrument
- Data Tables and Figures
- Institutional Review Board Approval
- Informed Consent Form
How to Write Thesis Outline
Here are some steps to follow when writing a thesis outline:
- Identify the purpose and scope of your thesis: Before you start writing, you should have a clear understanding of the research questions , objectives, and hypotheses of your thesis, as well as the specific requirements and guidelines of your institution.
- Organize your ideas into sections: Divide your thesis into logical sections, such as introduction, literature review , methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Think about the main points you want to make in each section and how they relate to the overall theme of your thesis.
- Write a brief summary for each section: Write a few sentences summarizing the main ideas and objectives of each section. This will help you stay focused and avoid including irrelevant or redundant information.
- Create a table of contents: List the main sections and subsections of your thesis, along with their page numbers, to create a clear and organized outline.
- Review and revise your outline: Make sure your outline follows a logical and coherent structure, and that each section flows smoothly into the next. Revise your outline as necessary to ensure that it accurately reflects the content and structure of your thesis.
- Seek feedback from your advisor or committee: Share your outline with your thesis advisor or committee members to get their feedback and suggestions for improvement.
Purpose of Thesis Outline
The purpose of a thesis outline is to provide a clear and organized structure for your thesis, which will help you to:
- Stay organized : An outline helps you to break down your thesis into manageable sections, making it easier to plan your research and writing process.
- Ensure logical flow: A well-structured outline ensures that your thesis has a logical and coherent flow, with each section building on the previous one.
- Avoid duplication and irrelevant information: An outline helps you to avoid including duplicate or irrelevant information, ensuring that your thesis is focused and to-the-point.
- Meet institutional requirements: Many institutions have specific guidelines for the structure and format of a thesis, and an outline can help you to ensure that your thesis meets these requirements.
- Get feedback and guidance: An outline can be shared with your thesis advisor or committee members for feedback and guidance, helping you to refine your research and writing approach.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Context of the Study – Writing Guide and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Step-By-Step Guide To Write Your Thesis Outline
Navigating the intricate maze of thesis writing can be daunting for many students. Unearthing the secrets of creating a coherent structure that communicates complex ideas with clarity is no small task.
Yet, every academic journey hinges on the effective presentation of one’s research, findings, and conclusions. Dive into this comprehensive guide, brimming with insider knowledge, to unravel the mysteries of crafting the perfect thesis outline.
| – Set a logical roadmap with the introduction. – State specific claims to prove – Use flexible, evolving thesis statements. – Use online or traditional thesis templates. | |
| – Start with a clear research question and thesis. – Stay adaptable with the literature review. – Cite past works for claim support. – Align ideas with research methods. – Use supervisor or AI feedback for improvement. | |
| – Clearly describe research methods for replication. – Define the approach and data type. – Explain data collection and tools used. – Describe analysis methods and their justification. | |
| – Present research results objectively. – Use statistics for quantitative findings. – For qualitative, focus on themes and examples. – Keep conclusions for later; present in past tense. | |
| – Revisit and summarise the main research question. – Conclude by tying all findings together. – Suggest future research or applications. |
What Is A Thesis Outline?
Thesis Outline is a step-by-step guide that helps you list all the major topics and subtopics in a logical order. For example:
- Introduction : Overview of your research.
- Literature Review : Summary of existing research on the topic.
- Methodology : Research methods employed.
- Chapters : Organise your main ideas, claims, and supporting ideas in sections.
- Conclusion : Conclude your findings, limitations, and future implications.

Chapter 1: Introduction & Thesis Statement
Crafting an impactful introduction and thesis statement is a critical step in the writing process. Having a well-organised introduction and thesis statement can be the roadmap that ensures your research paper flows logically.
Thesis Statement : Often at the end of introduction, it is a specific sentence that states your claims, which you intend to prove with evidence. For instance, “An effective way to prevent youth gang involvement is through community engagement and education.”
Research Question : This guides your thesis or dissertation outline and dictates the scope of your investigation. For instance, “What strategies can communities employ to prevent youth gang involvement?”
Butte College, a reputable academic institution, suggests that thesis statements should remain flexible. As you draft and revise, you might discover new information that could lead to adjustments.
AI tools, like Google Docs, can simplify this iterative process, with features enabling researchers to copy, paste, and reorganise content.
For those unsure where to start, numerous thesis outline templates are available online. Some may even prefer the traditional method of using Roman numerals and capital letters for the organisational structure.
Always remember, your thesis statement and outline are preliminary; as your research unfolds, they should evolve. So, embrace the dynamic nature of the writing process and adapt as necessary.
Chapter 2: Review of Related Literature and Research
To begin, formulate a specific research question and a thesis statement that states your claims. This is the backbone of your literature review, ensuring your content remains focused.
Once you have a draft, critically analyze the content for repetitive elements. Engage in critical thinking: does each sentence and paragraph add value?
As you delve deeper into academic writing, the scope of your literature review might shift. It’s essential to keep your thesis statement flexible and revise it as needed. You may find new information or methodologies that can influence your overview.
Your literature review should also cite previous works effectively. Proper citation:
- Supports your claims
- Gives an overview of the existing research methods.
Every citation and summary should help prove your thesis with evidence. Don’t just copy and paste, understand and integrate.
As you organize your ideas and subtopics, ensure they align with your research methods, offering a clear pathway from introduction to conclusion. For those using the APA format, there are specific guidelines and thesis outline templates available.
Always remember to consult with your supervisor or use AI tools to enhance your literature review’s quality. By maintaining a logical order and clarity, your literature review will form a foundational chapter in your academic thesis or dissertation.
Chapter 3: Methodology
The methodology chapter allows a researcher to outline their specific methods, offering a clear guide for replicating the study if needed. When drafting this chapter:
- You must be precise, presenting content in a logical order to ensure clarity.
- Explain your methodological approach. Did you opt for a quantitative or qualitative method?
- Elaborate on the research question your thesis aims to answer and specify if you collected primary or secondary data.
This forms the foundation of your methodology and provides a framework for your readers.
Next, delve into your methods of data collection. Whether it’s surveys or interviews, detail the research methods, offering a sample paragraph, perhaps.
Organize your ideas and describe the tools and procedures used. In a research paper or thesis document, it’s essential to ensure that another researcher can replicate your methods. Therefore, being specific about:
- Instruments
- Softwares, and
- Sampling method
These information can be invaluable to your future readers.
The subsequent step involves explaining your methods of analysis. For instance, if dealing with numbers, mention any statistical software like SPSS and the specific tests employed. For qualitative data, elucidate how you categorised responses.
Lastly, don’t forget to justify your methodological choices. If certain popular methods weren’t used, provide reasons. An effective way to bolster this section is by referencing similar existing research or citing academic guidelines that support your approach.
Chapter 4: Findings
This chapter should objectively report the results of your research, ensuring the content remains separate from any personal interpretation.
Quantitative Research: Structure this section around your research questions or hypotheses. Include both descriptive (e.g., means, standard deviations) and inferential statistics (like t-scores and p-values).
Consider to incorporate visual aids like graphs and tables only when they genuinely add value for the reader.
Qualitative Research: Findings might revolve around key themes that emerged during data analysis. Here, present general observations and cite specific quotations that resonate with the research question.
You may find it helpful to create an outline, ensuring each theme is explored in a logical order. If you have extensive data, like full interview transcripts, consider adding them to an appendix.
Always draft and revise this chapter in the past tense. And remember, while the findings section provides a summary of your research, refrain from speculative conclusions—these belong in the discussion and conclusion chapters.
Using these guidelines, you’ll ensure your findings are presented in a clear and academic manner.
Chapter 5: Summary, Conclusions, Discussion, and Recommendations
In your thesis, this chapter offers an opportunity to concisely encapsulate your research. It is essential to maintain a logical order while constructing this section. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Summary & Discussion : Synthesise the main findings from your research paper into a summary, addressing how the results provide answers. Consider the implications of your findings and any unexpected insights that arose during the research process.
- Conclusions : It’s the point where you cement the importance of your research. Discuss how your findings either confirm or challenge existing literature review insights. Your conclusion should tie all the chapters together, providing an overview of key points that support your main claims without introducing new data.
- Recommendations : Elaborate on future research implications, ensuring they don’t undermine your work but rather enrich your conclusions. If your research has practical applications, like in policy, frame your suggestions in a way that’s not imperative.
- Final Touches : Once the chapter is drafted, revise it as needed. Utilise thesis outline templates or tools like Google Docs to ensure organisational structure. Always cite sources accurately and check the format.
Remember, this chapter is a reflection of your critical thinking and academic writing abilities. It’s more than a summary; it’s an assertion of your contribution to your field. And if you ever need assistance, consider using AI tools or consult Butte College resources for additional insights.
Wrapping Up: Creating Thesis Outline Is Not Rocket Science
Crafting a thesis outline need not be an overwhelming challenge. This guide simplifies the process, providing clear steps to shape your academic work.
From the foundation of introductions and thesis statements to utilising AI tools for drafts, the path to a coherent and impactful thesis outline is demystified. Hopefully you are now well-equipped to navigate the world of academic writing with confidence.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Your Outline
As I stated earlier, I love reading books in the productivity/self-help sort of space. When I was starting to realize that things were going south in the first incarnation of my thesis, I turned to these types of resources. I knew that I needed to bring some clarity to the task at hand if I was going to succeed on this project. I went to every library system in the central Ohio area, CML , Grandview , Upper Arlington , OSU … and got every book I could that seemed related to writing in any variation of long-form writing or thesis writing. I read a lot of stuff, in books and online, and a pattern started to emerge. I cross-referenced this pattern with several theses that had been written recently in the department and it seem to hold true. This works in your favor quite a bit.
This is the pattern, or maybe more accurately, the observation made by myself and countless authors on the subject.
The Overall Thesis Structure
A thesis is an extremely formulaic type of writing.Every thesis follows pretty much the same organizational structure.
There are four primary parts of every single thesis. They may vary a little as to how many chapters each part has, but every thesis has at least one chapter covering thesis four parts.
- Introduction: Don’t mess around with it! The only purpose is to introduce the research. You will outline the problem you intend to investigate, state the aim of the research, limit the scope of the investigation, and provide an overview of what lies ahead. 3-5 pages is usually sufficient.
- Background: The purpose is to position your research into the context of what has gone on before, what is currently taking place, and prove you know how research is generally conducted in this area. This is generally where your literature review goes. You might have chapters that cover the brief history of the topic area, current theory or practice, and/or results of any preliminary studies you may have carried out to help define your problem.
- Your Own Work: This part is really comprised of two parts nearly always: Your methodology and your Data and Analysis . Your methodology is the design of research developed to test hypotheses or answer questions developed from the background section. Your Data & Analysis is just that, the data and results of your methodology.
- Synthesis: This is your new contribution to the body of knowledge and is usually handled in two parts. This first part is a discussion that examines your work (part 3) in light of the background you presented (part 2). This may lead to the development of a new model or theory. The second part is a set of conclusions that should arise directly out of the discussion and and respond directly to the aim of the work stated in the Introduction (part 1)
How Many Chapters?
Largely this will develop out of your content and will be a bit different for everyone, but for planning and visualizing the end goal, I found the following useful.
In “How to write a better thesis” by David Evans and Paul Gruba , it states these general guidelines for thinking about the overall structure.
- Each of your four parts, Intro, Background, Your Own Work, and Synthesis should have between 1-3 chapters. I can tell you now… your introduction will only be one chapter, and a short one.
- If you have more than 10 chapters total, you should suspect that some are actually only subsections of other chapters and start consolidating. You might be framing your chapters in a less than logical way or attempting to cover more than you need.
- We should expect no more than 8-10 chapters. Many theses are accomplished in 5-7 chapters.
For right now though, do not worry too much about this. Now just seemed like the most logical place to include this. For now, we are going to operate under the assumption that you are going to have exactly five “chapters”.
I know what you are thinking, five chapters? But Gabe, you said there were Four primary parts. You are right, and kudos to you for reading so attentively. I also said that the “Your Own Work” part (part 3) is nearly always accomplished in two parts: Your methodology and your Data and Analysis. This gives us five parts.
How to begin structuring a chapter
I do not want to get too into the specifics of chapter construction just yet, as this will be covered a bit more in the “Managing Writing” section, but chapters are also extremely formulaic. This should really be a refresher from your high school composition, but here is the big insight for now.
With the exception of the Introduction Chapter, which is its own sort of beast, every chapter will follow this basic structure:
- Introduction: Every chapter should have an introduction of some kind. People who read theses will scan these to decide if they want to read the chapter. This will link back to previous chapters, state the aim/purpose/function of the the chapter, and outline how you intend to achieve this aim/purpose/function.
- Content: The stuff of your chapter.
- Conclusion: Every Chapter should have a Conclusion. This should cover what has been achieved or established in the chapter that previously had not.
That is it. With this information your very first outline is already complete. It is very generic, but the basic structure is there ready for you to start capturing ideas and making the outline about YOUR thesis.
Your FIRST Outline
Just to make this easy on you, here is your first outline. You should be able to essentially copy and paste this into your text editor of choice and get to work organizing your ideas.
Your outline will expand from here, but this is the bare minimum to achieve something resembling a thesis document. In case you are wondering, my outline started exactly this way, and this is what it grew into.

So now that we have your basic outline as a way to start wrangling the content of your thesis, time to address the materials that are related to this process.
- Enroll & Pay
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Degree Programs
Example MS Thesis Outline
- describe what you trying to do
- clearly state the question being addressed
- when appropriate formulate a testable hypothesis
- Describe the motivation; who is interested in the solution.
- Summarize the results and their significance.
- Describe current understanding of the problem, existing solutions, and the barriers to these solutions.
- Review of the pertinent literature.
- Methodology: Describe the approach to addressing the problem
- Presentation of Work (Could be more than one chapter)
- Summary of results
- Recommendations: generalize conclusions to appropriate design decisions, practices and/or procedures
- Implications to existing knowledge/theory
- Implications for further study
- Future Work
How to Write a Master's Thesis: A Guide to Planning Your Thesis, Pursuing It, and Avoiding Pitfalls
#scribendiinc
Part 1: Initial Considerations
Who needs to write a master’s thesis.
Thesis writing is one of the more daunting challenges of higher education. That being said, not all master's students have to write a thesis. For example, fields that place a stronger emphasis on applied knowledge, such as nursing, business, and education, tend to have projects and exams to test students on the skills and abilities associated with those fields. Conversely, in disciplines that require in-depth research or highly polished creative abilities, students are usually expected to prove their understanding and independence with a thesis.
What's Your Goal?
Do you want to write a thesis? The process is a long one, often spanning years. It's best to know exactly what you want before you begin. Many people are motivated by career goals. For example, hiring managers may see a master's degree as proof that the candidate is an expert within their field and can lead, motivate, and demonstrate initiative for themselves and others. Others dream of earning their doctorate, and they see a master's degree as a stepping stone toward their Ph.D .

No matter what your desired goal is, you should have one before you start your thesis. With your goal in mind, your work will have a purpose, which will allow you to measure your progress more easily.
Major Types of Theses
Once you've carefully researched or even enrolled in a master's program—a feat that involves its own planning and resources —you should know if you are expected to produce a quantitative (which occurs in many math and science programs), qualitative (which occurs in many humanities programs), or creative (which occurs in many creative writing, music, or fine arts programs) thesis.
Time and Energy Considerations
Advanced degrees are notoriously time and energy consuming. If you have a job, thesis writing will become your second job. If you have a family, they will need to know that your thesis will take a great deal of your attention, energy, and focus.

Your studies should not consume you, but they also should not take a back seat to everything else. You will be expected to attend classes, conduct research, source relevant literature, and schedule meetings with various people as you pursue your master's, so it's important to let those you care about know what's going on.
As a general note, most master's programs expect students to finish within a two-year period but are willing to grant extra time if requested, especially if that time is needed to deal with unexpected life events (more on those later).
Part 2: Form an Initial Thesis Question, and Find a Supervisor
When to begin forming your initial thesis question.
Some fields, such as history, may require you to have already formed your thesis question and to have used it to create a statement of intent (outlining the nature of your research) prior to applying to a master’s program. Others may require this information only after you've been accepted. Most of the time, you will be expected to come up with your topic yourself. However, in some disciplines, your supervisor may assign a general research topic to you.
Overall, requirements vary immensely from program to program, so it's best to confirm the exact requirements of your specific program.
What to Say to Your Supervisor
You will have a supervisor during your master's studies. Have you identified who that person will be? If yes, have you introduced yourself via email or phone and obtained information on the processes and procedures that are in place for your master's program? Once you've established contact, request an in-person meeting with him or her, and take a page of questions along with you. Your questions might include:
- Is there a research subject you can recommend in my field?
- I would like to pursue [target research subject] for my thesis. Can you help me narrow my focus?
- Can you give me an example of a properly formatted thesis proposal for my program?
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help (to a Degree)
Procedures and expectations vary from program to program, and your supervisor is there to help remove doubt and provide encouragement so you can follow the right path when you embark on writing your thesis. Since your supervisor has almost certainly worked with other graduate students (and was one at some point), take advantage of their experience, and ask questions to put your mind at ease about how to write a master’s thesis.
That being said, do not rely too heavily on your supervisor. As a graduate student, you are also expected to be able to work independently. Proving your independent initiative and capacity is part of what will earn you your master's degree.
Part 3: Revise Your Thesis
Read everything you can get your hands on.
Whether you have a question or need to create one, your next step is simple and applies to all kinds of theses: read.

Seek Out Knowledge or Research Gaps
Read everything you can that relates to the question or the field you are studying. The only way you will be able to determine where you can go is to see where everyone else has been. After you have read some published material, you will start to spot gaps in current research or notice things that could be developed further with an alternative approach. Things that are known but not understood or understood but not explained clearly or consistently are great potential thesis subjects. Addressing something already known from a new perspective or with a different style could also be a potentially valuable project. Whichever way you choose to do it, keep in mind that your project should make a valuable contribution to your field.

Talk with Experts in Your Field (and Don't Be Afraid to Revise Your Thesis)
To help narrow down your thesis topic, talk to your supervisor. Your supervisor will have an idea of what is current in your field and what can be left alone because others are already working on it. Additionally, the school you are attending will have programs and faculty with particular areas of interest within your chosen field.
On a similar note, don't be surprised if your thesis question changes as you study. Other students and researchers are out there, and as they publish, what you are working on can change. You might also discover that your question is too vague, not substantial enough, or even no longer relevant. Do not lose heart! Take what you know and adjust the question to address these concerns as they arise. The freedom to adapt is part of the power you hold as a graduate student.
Part 4: Select a Proposal Committee
What proposal committees are and why they're useful.
When you have a solid question or set of questions, draft a proposal.

You'll need an original stance and a clear justification for asking, and answering, your thesis question. To ensure this, a committee will review your thesis proposal. Thankfully, that committee will consist of people assigned by your supervisor or department head or handpicked by you. These people will be experts who understand your field of study and will do everything in their power to ensure that you are pursuing something worthwhile. And yes, it is okay to put your supervisor on your committee. Some programs even require that your supervisor be on your committee.
Just remember that the committee will expect you to schedule meetings with them, present your proposal, respond to any questions they might have for you, and ultimately present your findings and thesis when all the work is done. Choose those who are willing to support you, give constructive feedback, and help address issues with your proposal. And don't forget to give your proposal a good, thorough edit and proofread before you present it.
How to Prepare for Committee Meetings
Be ready for committee meetings with synopses of your material for committee members, answers for expected questions, and a calm attitude. To prepare for those meetings, sit in on proposal and thesis defenses so you can watch how other graduate students handle them and see what your committee might ask of you. You can even hold rehearsals with friends and fellow students acting as your committee to help you build confidence for your presentation.

Part 5: Write Your Thesis
What to do once your proposal is approved.
After you have written your thesis proposal and received feedback from your committee, the fun part starts: doing the work. This is where you will take your proposal and carry it out. If you drafted a qualitative or quantitative proposal, your experimentation or will begin here. If you wrote a creative proposal, you will now start working on your material. Your proposal should be strong enough to give you direction when you perform your experiments, conduct interviews, or craft your work. Take note that you will have to check in with your supervisor from time to time to give progress updates.

Thesis Writing: It's Important to Pace Yourself and Take Breaks
Do not expect the work to go quickly. You will need to pace yourself and make sure you record your progress meticulously. You can always discard information you don't need, but you cannot go back and grab a crucial fact that you can't quite remember. When in doubt, write it down. When drawing from a source, always create a citation for the information to save your future self time and stress. In the same sense, you may also find journaling to be a helpful process.
Additionally, take breaks and allow yourself to step away from your thesis, even if you're having fun (and especially if you're not). Ideally, your proposal should have milestones in it— points where you can stop and assess what you've already completed and what's left to do. When you reach a milestone, celebrate. Take a day off and relax. Better yet, give yourself a week's vacation! The rest will help you regain your focus and ensure that you function at your best.
How to Become More Comfortable with Presenting Your Work
Once you start reaching your milestones, you should be able to start sharing what you have. Just about everyone in a graduate program has experience giving a presentation at the front of the class, attending a seminar, or watching an interview. If you haven't (or even if you have), look for conferences and clubs that will give you the opportunity to learn about presenting your work and become comfortable with the idea of public speaking. The more you practice talking about what you are studying, the more comfortable you'll be with the information, which will make your committee defenses and other official meetings easier.
Published authors can be called upon to present at conferences, and if your thesis is strong, you may receive an email or a phone call asking if you would share your findings onstage.
Presenting at conferences is also a great way to boost your CV and network within your field. Make presenting part of your education, and it will become something you look forward to instead of fear.
What to Do If Your Relationship with Your Supervisor Sours
A small aside: If it isn't already obvious, you will be communicating extensively with others as you pursue your thesis. That also means that others will need to communicate with you, and if you've been noticing things getting quiet, you will need to be the one to speak up. Your supervisor should speak to you at least once a term and preferably once a week in the more active parts of your research and writing. If you give written work to your supervisor, you should have feedback within three weeks.
If your supervisor does not provide feedback, frequently misses appointments, or is consistently discouraging of your work, contact your graduate program advisor and ask for a new supervisor. The relationship with your supervisor is crucial to your success, especially if she or he is on your committee, and while your supervisor does not have to be friendly, there should at least be professional respect between you.
What to Do If a Crisis Strikes
If something happens in your life that disrupts everything (e.g., emotional strain, the birth of a child, or the death of a family member), ask for help. You are a human being, and personal lives can and do change without warning. Do not wait until you are falling apart before asking for help, either. Learn what resources exist for crises before you have one, so you can head off trauma before it hits. That being said, if you get blindsided, don't refuse help. Seek it out, and take the time you need to recover. Your degree is supposed to help you become a stronger and smarter person, not break you.
Part 6: Polish and Defend Your Master's Thesis
How to write a master’s thesis: the final stages.
After your work is done and everything is written down, you will have to give your thesis a good, thorough polishing. This is where you will have to organize the information, draft it into a paper format with an abstract, and abbreviate things to help meet your word-count limit. This is also where your final editing and proofreading passes will occur, after which you will face your final hurdle: presenting your thesis defense to your committee. If they approve your thesis, then congratulations! You are now a master of your chosen field.
Conclusion and Parting Thoughts
Remember that you do not (and should not) have to learn how to write a master’s thesis on your own. Thesis writing is collaborative, as is practically any kind of research.

While you will be expected to develop your thesis using your own initiative, pursue it with your own ambition, and complete it with your own abilities, you will also be expected to use all available resources to do so. The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names. If you already have the skills necessary to motivate yourself, lead others, and drive change, you may only need your master's as an acknowledgement of your abilities. If you do not, but you apply yourself carefully and thoroughly to the pursuit of your thesis, you should come away from your studies with those skills in place.
A final thought regarding collaboration: all theses have a section for acknowledgements. Be sure to say thank you to those who helped you become a master. One day, someone might be doing the same for you.
Image source: Falkenpost/Pixabay.com
We’re Masters at Master’s Theses! Make Yours Shine.
Let our expert academic editors perfect your writing, or get a free sample, about the author.

A Scribendi in-house editor, Anthony is happily putting his BA in English from Western University to good use with thoughtful feedback and incisive editing. An avid reader and gamer, he can be found during his off hours enjoying narrative-driven games and obscure and amusing texts, as well as cooking for his family.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation

Selecting a Thesis Committee

Thesis/Dissertation Writing Series: How to Write a Literature Review
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Writing a Top Thesis Outline – Your Comprehensive Guide

A thesis paper outline is a simple way of ensuring that each of your paragraphs serves a specific purpose in your paper. All students need to master this writing tool as it helps you organize your work.
What is a Thesis Outline?
A thesis outline is an organizational tool that writers use in their academic and professional thesis papers. Like a blueprint for your essay, it forms the foundation of the entire writing process. It is used to structure the main ideas into a list of easy and quick to follow contents.
Creating a thesis outline is vital in the following ways:
It gives a precise organization of the ideas Identifies parts of the paper that need special attention It singles out sections that need to be reduced or omitted Helps create connections and transitions where necessary It enables a student to fit the ideas systematically
Having a clearly defined thesis statement is better than a thousand thesis writers being dispatched at your disposal.
Thesis Outline Template
Now, what will make or break your master’s thesis outline or senior thesis outline is understanding its structure. It is not enough to have what to write but how to register it as well. That is why you need this template when writing a thesis outline.
Thesis Outline Format
A conventional thesis paper will have the following sections:
- Introduction (contains the background and thesis statement)
- The body paragraphs
- The conclusion
To attain this thesis structure’s best, you have to understand each part’s significance and how it contributes to the overall thesis paper. Let us look at how to write a thesis outline while delving deep into every section.
Thesis topic outline
A topic is described as the trigger button of your paper. It will determine whether your reader will have the interest to read your thesis or not. Therefore, when you are thinking about your thesis topic, consider the following:
- It should be brief and to the point (Do not explain or illustrate, just state)
- Use the keywords provided in the assignment for your topic
- AVOID using punctuations at the end
- It should be an eye-catcher and act as a bait
For you to have a good thesis topic, it should offer a solution. Nobody wants to spend his precious time on a paper that does not address a prevailing societal problem.
- How to do a thesis statement outline
The thesis statement is written in the introductory paragraph. Since this is the main idea for your paper, there is no room for error. Start with an attention-grabber that will lead the reader to your thesis statement.
Example of an attention grabber : Did you know that the average person who stays at home every day consumes over 10 tons of calories in a week?
Sample thesis statement : Excess calorie is a contributing factor to the high obesity rates patients witnessed in hospitals.
When creating a thesis statement outline, ensure that it relates to your introductory paragraph’s first two or three statements. Let it come out clearly so that the reader is prepared for what is coming next in the paper’s body.
They are made up of arguments in support of the thesis statement. This section carries a lot of weight as it either persuades or turns off the reader. Here is an outline for thesis paper body paragraphs:
Identify the main points Look for supporting ideas or evidence Have a list of transitional words from one section to another
The body of a thesis consists of the Literature Review, Research Methods, Results, and Discussion. It is recommended to begin with the literature review first before proceeding to the other two sections.
Since the Discussion is the longest part of the thesis, ensure that you gather all the necessary information needed to furnish it. In this part, you will need to identify the following aspects of your research process:
- Limitations of your study,
- Explanations for unexpected results, and
- Identify any questions that remain unanswered.
Every argument should be crystal clear to prevent any doubt or object on the part of the reader.
- The Conclusion
Though it appears last, it is one of the most critical sections of your thesis. It is the chapter that shows whether you achieved your research objectives or not. In this part, you can point out the following:
Point out the challenges you encountered in your study Your lessons from the research Make recommendations for future research
The conclusion should be a point where you identify whether every hypothesis was met or objective was achieved. It is vital to note that this chapter should short and clear to the end. Now that you have argued your case make this as your final nail to the coffin.
How To Make a Thesis Outline – Step By Step Guide
A superb outline can ease your research process and make your thesis writing process quick and easy. When you are thinking of creating a thesis paper outline, consider the following steps:
Read and understand the question first. If your tutor has given you a topic or question for your thesis, ensure that you digest it well to understand what is required of you. It will help to align your thesis outline correctly. Check for similar thesis outlines on the same topic. You can Google for any reliable thesis outline example that is similar to your topic of research. By doing this, you will get a rough idea of what is expected of you. Consult with your professor on the thesis outline format for your institution. Different institutions have varying structures, and thus, you need to use one that matches your institution’s house style. Do not rush into creating the outline. Before you draft your strategy, ensure that you have all the essentials at your fingertips first. Since this will be your guiding principle, it should be devoid of any errors or bogus steps.
After setting your house in order, writing your thesis paper is now time for the real task.
If you did not know how to create a thesis outline, we hope that this writing guide has served that purpose for you. Nevertheless, we also have a thesis writing service that offers students with online assistance.
Get help with thesis outline at affordable rates today. You can also find a master thesis outline example from gurus who have been in this business for decades. What is holding you now?

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="master's thesis outline"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Guide to writing your thesis/dissertation, definition of dissertation and thesis.
The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master’s degrees. The dissertation is a requirement of the Ph.D. degree.
Formatting Requirement and Standards
The Graduate School sets the minimum format for your thesis or dissertation, while you, your special committee, and your advisor/chair decide upon the content and length. Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical issues are your sole responsibility. Generally, the thesis and dissertation should conform to the standards of leading academic journals in your field. The Graduate School does not monitor the thesis or dissertation for mechanics, content, or style.
“Papers Option” Dissertation or Thesis
A “papers option” is available only to students in certain fields, which are listed on the Fields Permitting the Use of Papers Option page , or by approved petition. If you choose the papers option, your dissertation or thesis is organized as a series of relatively independent chapters or papers that you have submitted or will be submitting to journals in the field. You must be the only author or the first author of the papers to be used in the dissertation. The papers-option dissertation or thesis must meet all format and submission requirements, and a singular referencing convention must be used throughout.
ProQuest Electronic Submissions
The dissertation and thesis become permanent records of your original research, and in the case of doctoral research, the Graduate School requires publication of the dissertation and abstract in its original form. All Cornell master’s theses and doctoral dissertations require an electronic submission through ProQuest, which fills orders for paper or digital copies of the thesis and dissertation and makes a digital version available online via their subscription database, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses . For master’s theses, only the abstract is available. ProQuest provides worldwide distribution of your work from the master copy. You retain control over your dissertation and are free to grant publishing rights as you see fit. The formatting requirements contained in this guide meet all ProQuest specifications.
Copies of Dissertation and Thesis
Copies of Ph.D. dissertations and master’s theses are also uploaded in PDF format to the Cornell Library Repository, eCommons . A print copy of each master’s thesis and doctoral dissertation is submitted to Cornell University Library by ProQuest.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
University Thesis and Dissertation Templates

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Theses and dissertations are already intensive, long-term projects that require a lot of effort and time from their authors. Formatting for submission to the university is often the last thing that graduate students do, and may delay earning the relevant degree if done incorrectly.
Below are some strategies graduate students can use to deal with institutional formatting requirements to earn their degrees on time.
Disciplinary conventions are still paramount.
Scholars in your own discipline are the most common readers of your dissertation; your committee, too, will expect your work to match with their expectations as members of your field. The style guide your field uses most commonly is always the one you should follow, and if your field uses conventions such as including all figures and illustrations at the end of the document, you should do so. After these considerations are met, move on to university formatting. Almost always, university formatting only deals with things like margins, font, numbering of chapters and sections, and illustrations; disciplinary style conventions in content such as APA's directive to use only last names of authors in-text are not interfered with by university formatting at all.
Use your university's formatting guidelines and templates to your advantage.
If your institution has a template for formatting your thesis or dissertation that you can use, do so. Don't look at another student's document and try to replicate it yourself. These templates typically have the necessary section breaks and styles already in the document, and you can copy in your work from your existing draft using the style pane in MS Word to ensure you're using the correct formatting (similarly with software such as Overleaf when writing in LaTeX, templates do a lot of the work for you). It's also often easier for workers in the offices that deal with theses and dissertations to help you with your work if you're using their template — they are familiar with these templates and can often navigate them more proficiently.
These templates also include placeholders for all front matter you will need to include in your thesis or dissertation, and may include guidelines for how to write these. Front matter includes your table of contents, acknowledgements, abstract, abbreviation list, figure list, committee page, and (sometimes) academic history or CV; everything before your introduction is front matter. Since front matter pages such as the author's academic history and dissertation committee are usually for the graduate school and not for your department, your advisor might not remember to have you include them. Knowing about them well before your deposit date means you won't be scrambling to fill in placeholders at the last minute or getting your work returned for revision from the graduate school.
Consider institutional formatting early and often.
Many graduate students leave this aspect of submitting their projects until it's almost too late to work on it, causing delays in obtaining their degree. Simply being aware that this is a task you'll have to complete and making sure you know where templates are, who you can ask for help in your graduate office or your department, and what your institution's guidelines are can help alleviate this issue. Once you know what you'll be expected to do to convert to university formatting, you can set regular check-in times for yourself to do this work in pieces rather than all at once (for instance, when you've completed a chapter and had it approved by your chair).
Consider fair use for images and other third-party content.
Most theses and dissertations are published through ProQuest or another publisher (Harvard, for instance, uses their own open publishing service). For this reason, it may be the case that your institution requires all images or other content obtained from other sources to fall under fair use rules or, if an image is not considered under fair use, you'll have to obtain permission to print it in your dissertation. Your institution should have more guidance on their specific expectations for fair use content; knowing what these guidelines are well in advance of your deposit date means you won't have to make last-minute changes or removals to deposit your work.


Writing your thesis
Follow these steps, thesis proposal arrow_drop_down.
Most doctoral programs and some master’s programs require students to submit a formal thesis proposal. The thesis proposal is an excellent planning tool. It helps bring the thesis topic into sharper focus. A thesis proposal may start out being vague, but as the student works on the proposal and discusses it with his or her supervisor, the proposal should outline:
- the topic or the central research question
- the resources from which the topic or research question is drawn, and
- where relevant, the strategies and instruments used for data collection and analysis.
The research conducted for the proposal will be a useful foundation in preparing the thesis. With this in mind, during this proposal writing stage, the student should start “building” what will eventually become footnotes or endnotes, and a full bibliography or list of references. This means taking meticulous notes and keeping track of the author, title, place and date of publication, and any relevant page numbers in works consulted.
Where appropriate, it is helpful to outline in the proposal the actual papers that will be submitted should the work proceed as planned, including authorships in the case of collaborative projects. This will give the student and the supervisor a clear idea of responsibilities and expectations.
The student may have to present the proposal formally as part of the approval process. This is an opportunity to sharpen the student's focus and to set out exactly how he or she intends to proceed.
Some research projects require other approvals such as ethical clearances. The thesis supervisor should know what approvals are required and how they can be obtained, but the student is ultimately responsible for obtaining these approvals.
Topic registration arrow_drop_down
The topic of the thesis is to be determined in consultation with the student's research supervisor.
From the uoZone Application tab, click Service Requests to create a service request and register your thesis topic.
Work plan arrow_drop_down
The work plan should include realistic target dates for all the major milestones. Students should show their thesis supervisor a work plan as soon as possible. This will help ensure that the student has not forgotten anything, and give the student a sense of whether his or her expectations about turnaround time and feedback are feasible for the supervisor. Once the student and supervisor have discussed and agreed on the work plan, the student should give the supervisor a copy. Information supplements are at the student's disposal to help them prepare their work plan.
Components of a work plan
The work plan, at a minimum should include at least ballpark dates for these:
- narrowing down the thesis topic
- beginning the research
- completing the field work, the mining of sources, or the experimental part or the data collection
- coming up with at least a rough thesis outline at a point appropriate to the topic and discipline
- completing most of your research
- where relevant, drafting and submitting each chapter to the thesis supervisor
- where relevant, receiving feedback on each chapter submitted
- submitting a completed first draft to the supervisor
- hearing back from the supervisor after the student submits the completed first draft
- doing changes that the student and supervisor have agreed on
- providing the last version of the thesis to the supervisor for approval before submission of the thesis
- submitting articles to journals
- presenting research at conferences
- submitting the completed thesis
- defending the thesis (some master's programs do not require an oral defence)
Research arrow_drop_down
By the time the candidate becomes a graduate student, he or she should know quite a bit about writing papers even though the sheer size of the thesis project makes a difference. The supervisor will help, but any student embarking on a thesis should also read up independently on how to research and write a thesis. The style guide appropriate to the student's discipline will include tips on research, the mechanics of writing, and citing sources properly.
Improving skills
The students will need to use their research, writing and oral presentation skills to complete their thesis. They will improve in all these areas with practice. If a candidate lacks confidence in any of the skills necessary for success, he or she should speak to the thesis supervisor about training courses that may be offered at the University to address what they perceive as shortcomings in the required abilities. Avail of the Academic Writing Help Centre’s (AWHC) resources about the mechanics of writing.
Literature review
The purpose of a literature review is to demonstrate the student’s knowledge of, and ability to synthesize, major aspects of the scholarly literature of the field in which the student’s thesis is situated. The review also helps the reader to place the student’s work in its context. As a finished product, the literature review shows that the student is familiar with the literature pertinent to his topic; shows the importance of his decision to conduct research and write on the topic with the approach chosen; explores what has been written on the topic and by whom; and, explores what the literature tells, what it does not tell, and why both of these are important for his topic.
The scope of the literature review must be broader than the topic of the student’s thesis. It must cover the major scholarly contributions to the field of study in which the student’s thesis is situated.
Narrow down your topic
The students should discuss potential topics with the supervisor and colleagues, and think carefully about the feasibility of the topic in relation to the number and complexity of the experiments required, the lab equipment required, their knowledge of the different related fields, the extent of the reading required, and the accessibility of the books or items to be studied.
Get approvals
As already discussed, the students have to obtain all the necessary approvals for your thesis topic. In addition to ethics and other approvals, a student who plans to travel abroad to do research must investigate possible international travel restrictions. Depending on the country in which the research will be conducted, students should check with the Office of Risk Management and uOInternational before making plans to do research abroad.
Research: collect and analyze data
When researching the topic, or collecting and analyzing data, the student should read as widely as possible and take meticulous notes identifying each source. They should also sharpen their focus as they go, if necessary, and keep developing and refining their thesis outlines.
Hints on note-taking and proper referencing
Writing arrow_drop_down
Depending on the discipline and topic, the student may finish all their research and then begin writing, or they may move back and forth between research and writing.
It is important to know when it is time to stop researching and start writing. The students should give themselves time to develop ideas, but recognize real procrastination and try to avoid it.
When the students start writing, they shouldn't get stuck on the introduction. The thesis will have a linear structure in the end, but that doesn’t mean it starts out that way. The student should get as much written as they can. Then they can really start to work with it. Since writing is a way of thinking, in some disciplines the students may have to write all the way to the end of a section before they arrive at what they really want to say—at that point they may move the end to the beginning and start again.
A cademic Writing Help Centre (AWHC)
Revision arrow_drop_down
The students should expect to have to make revisions to what they have already written, either as a result of their own analyses of the ideas, structure and organization of the paper or as a result of feedback from others. Revision as a result of feedback is an important part of writing a thesis and good practice—in many workplaces, revision as a result of feedback is part of the job.
Editing arrow_drop_down
There are many kinds of editing the student might have to do to their thesis. These range from relatively superficial proofreading and copy editing for spelling and typographical errors to more substantive edits that get at the heart of the paper and border on revision—reorganizing sections, for example.
It is possible to seek professional proofreading assistance by hiring an editor. Students should always consult their thesis supervisor before seeking services of professional proofreaders /editors. In such cases, the student is entirely responsible for the cost of services rendered by the editor. It is the student’s responsibility to accept, decline or challenge the advice and corrections suggested by a proofreader. Students must formally acknowledge the use of a proofreader in the final submitted version of the thesis.
Beyond the basic steps outlined above, how the student proceeds with the research and writing will depend a lot on the chosen discipline, the topic and the student's personal style.
Academic Writing Help Center (AWHC)
Thesis seminar arrow_drop_down
Some academic units require a student to lead a seminar on the thesis topic towards the end of the thesis preparation period usually a couple of months before the thesis defence. Fellow students, supervisors, members of the thesis committee and other members of the academic unit often attend.
In some cases, students present their research within a seminar course, usually referred to as a research seminar. This seminar provides an ideal forum for a student to discuss the thesis and to practice for the upcoming defence.
The student should check with his or her thesis supervisor and academic unit to see whether this is possible or required in the chosen program.
Also, the students should attend seminars given by other students in the chosen program or in other programs. This way, they can get a realistic idea of what will be expected. They should also attend or present at the annual interdisciplinary conference organized by the Graduate Student’s Association (GSAÉD) at the University of Ottawa.
Learn about thesis types
Master thesis arrow_drop_down.
A master’s thesis must show that the student is able to work in a scholarly manner and is acquainted with the principal works published on the subject of the thesis. As much as possible, it should be an original contribution. Some disciplines require that the thesis be of publishable quality. There is an oral examination for a master’s thesis, in the presence of examiners, if that is a program requirement. Some master’s programs do not require an oral examination for the thesis.
Doctoral thesis arrow_drop_down
A doctoral thesis must make a significant contribution to knowledge in a field of study, embody the results of original investigation and analysis, and be of such quality as to merit publication.
A doctoral thesis may build upon and continue the work done by a student in his or her master’s thesis, but must go significantly beyond the master’s thesis and be substantially different from that thesis. There is an oral examination for a doctoral thesis, in presence of examiners.
Thesis formats
Monograph thesis arrow_drop_down.
The monograph thesis is the most usual form in the humanities and social sciences and it resembles a non-fiction book in that it deals in depth with a particular topic.
Monograph components
Thesis as a series of articles arrow_drop_down
A significant number of thesis, especially in the sciences, engineering and medicine, consist of a series of articles or, very rarely, a single article. Each individual academic unit decides which format is suitable for its discipline, so before the student embarks on the thesis, he or she should check with the academic unit to see what format is accepted.
Components of a thesis in a series of articles (see C-7.3)
Non-traditional thesis arrow_drop_down
It is the responsibility of each program to determine what non-traditional thesis forms are acceptable.
Components of a non-traditional thesis (see C-7.3)
Additional information
Ethics and collaboration arrow_drop_down.
If the research embodied in the article or articles required approval of an ethics board or was part of a collaboration, this must be spelled out in a preface. In this preface or statement, the student must indicate what ethics approvals were secured and give a detailed account of the contributions of collaborators and/or co-authors which clearly distinguishes the contributions of this student from those of all other collaborators or co-authors, and identifies in detail all other contributions.
Copyright arrow_drop_down
The student must get permission to use copyrighted material from any co-authors as well as from publishers.

Thesis toolbox
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Published on September 21, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic .
The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development of your research. It helps you choose a type of research to pursue, as well as whether to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
You can download our templates in the format of your choice below.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What should your proposal contain, dissertation question examples, what should your proposal look like, dissertation prospectus examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about proposals.
Prior to jumping into the research for your thesis or dissertation, you first need to develop your research proposal and have it approved by your supervisor. It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives .
Depending on your department’s requirements, there may be a defense component involved, where you present your research plan in prospectus format to your committee for their approval.
Your proposal should answer the following questions:
- Why is your research necessary?
- What is already known about your topic?
- Where and when will your research be conducted?
- Who should be studied?
- How can the research best be done?
Ultimately, your proposal should persuade your supervisor or committee that your proposed project is worth pursuing.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Strong research kicks off with a solid research question , and dissertations are no exception to this.
Dissertation research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
- What are the main factors enticing people under 30 in suburban areas to engage in the gig economy?
- Which techniques prove most effective for 1st-grade teachers at local elementary schools in engaging students with special needs?
- Which communication streams are the most effective for getting those aged 18-30 to the polls on Election Day?
An easy rule of thumb is that your proposal will usually resemble a (much) shorter version of your thesis or dissertation. While of course it won’t include the results section , discussion section , or conclusion , it serves as a “mini” version or roadmap for what you eventually seek to write.
Be sure to include:
- A succinct introduction to your topic and problem statement
- A brief literature review situating your topic within existing research
- A basic outline of the research methods you think will best answer your research question
- The perceived implications for future research
- A reference list in the citation style of your choice
The length of your proposal varies quite a bit depending on your discipline and type of work you’re conducting. While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we’ve compiled some examples for you to get your started.
- Example #1: “Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907” by Maria Lane
- Example #2: “Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society” by Dimitri Nakassis
- Example #3: “Manhood Up in the Air: A Study of Male Flight Attendants, Queerness, and Corporate Capitalism during the Cold War Era” by Phil Tiemeyer
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal. Scribbr. Retrieved August 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis-dissertation-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, a step-by-step guide to the writing process, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, what is your plagiarism score.
18 Thesis Outline Templates and Examples (Word | PDF)
Most people have come across thesis in college or high school. However, you might be needed to write a thesis several times or once in your entire lifetime. Therefore, a thesis is an essential document that significantly impacts your high school or college success. Furthermore, it can promote you to your next academic level or acquire a referral.
Therefore, you need to exercise sufficient care and diligence when writing your thesis. To ensure that you are always at the top of the game when developing a thesis, you must incorporate a thesis outline template to help you focus on your thesis. Suppose you are not familiar with the thesis outline template, worry less because this article has you covered.
What is a Thesis Outline?
A thesis outline is a list of critical points of your essay. It is made to make sure that the plans for your thesis are gathered together so that the entire variables necessary to your study scope are considered correctly. In addition, a thesis outline is an excellent way of creating a perfect research paper because it enables you to organize your data appropriately.
What Is a Thesis Outline Template?
A thesis outline template is a fillable or editable document that guides the researchers through the entire process, which they require to complete the whole research planning, gathering of data, assessment of results, and finally implementation.
Thesis Outline Examples & Templates

How to Write a Thesis Outline?
Below are a few steps that will guide you on writing a thesis outline:
- Put your thesis statement at the start
- State the primary points that support your thesis and label them using Roman numerals
- List arguments and ideas that support every central point and label them using capital letters
- If possible, continue sub-dividing every supporting idea until you confirm that your entire outline is fully created and label them in numbers or small letters.
Types of Thesis Outline
There are four types of thesis outline. They include:
- Clustering- It is a random outline form
- Index card outlining- This outline allows continuous reorganization of ideas
- A summary outlining- Here, the researcher estimates the sum chapters in their manuscript
- Classical outlining- It entails numbers, letters, and roman numerical for subheadings and headings
Sample Thesis Outline

Thesis Outline Template

Thesis Outline Template (PDF)
An thesis essay outline template is a template containing how an essay ought to be drafted, stored in a PDF version. As expected, such templates are stored in such a portal so as to enable ease of sharing among the interested parties [could be students, researchers, tutors etc].

Thesis Outline Template (Word)

Masters Thesis Proposal Outline Template
A master’s thesis outline is a document that contains a guideline on how to write a thesis for those students undertaking a master’s degree program. The document resembles any thesis outline in its general outlook, only that the expected level of research is a bit more technical. The basic components of this outline include an Introduction, Review, Research Questions, Methodology and a Conclusion.

Senior Thesis Outline

Thesis Statement & Outline Template
Thesis statement outline examples are examples that project the rough idea of what a researcher’s viewpoints are. Such examples usually contain the declarations officially made by the researcher just before they conduct their research. The examples show what the researcher is confident about fulfilling out of the research.

Thesis Proposal Outline Template

Honors Thesis Outline Template

Thesis Essay Outline Template

Academic Thesis Outline Template

Thesis Paper Outline (Word)
A thesis paper outline example is a draft that details all the key points that would normally go in a thesis paper. Such an example has an introduction, the content body and a conclusion in rough draft. These would later be used by the writer in composing the actual thesis paper.

What is a good thesis outline?
A good thesis outline is a specific strong thesis statement that showcases what your research is all about. Furthermore, it helps you keep your paper to a topic you can easily handle without any problem.
What are the different parts of a thesis?
Here are different parts of a thesis:
Introduction and problem statement
The introduction of your thesis usually sets out the context and locates a particular problem that you as the researcher address. In addition, it includes relevant technical, geographical, and historical information, which is relevant to your specific problem and wide field. On the other hand, it clearly articulates the issue you seek to address. Therefore, ensure you state your primary problem in your introduction.
Literature review
This section of your thesis shows you have accomplished relevant research, reading, and coming up with sensible external research. Literature review needs you to include some tips, such as putting together related research and organizing your scholarship in chronological order.
Methodology section
The methodology section gives you a chance to talk about the kind of field you work in. It would help if you mentioned how researchers in your field accomplish their work. It can either be historical, theoretical, close reading, or data-intensive.
The analysis depends on the needed length of your thesis and field. It makes an essential part of your research. On the other hand, your analysis has to make sense, whether scientific evaluation findings or theoretical analysis. A doctoral-level project, this portion features multiple chapters. Additionally, this section gives you a chance to showcase why your research is crucial.
Here you need to summarize the essential elements of your entire findings as you demonstrate how your entire research can be advanced further.
How do you write a strong thesis statement?
Below are several steps you need to follow to write a strong thesis statement:
- State the topic
- State your primary idea concerning the topic
- Offer a reason, which supports your major idea
- Provide another reason which supports your primary idea and add more reasons
- Involve an opposing viewpoint to your primary idea, where applicable
How many chapters should a thesis have?
A thesis should feature 4 to 6 chapters in a commonly used structure.
Final Thoughts
You now clearly understand the thesis outline based on the comprehensive post above. The outline usually helps you to organize your information in a logical order and hierarchical manner. For example, suppose you are working on research papers; a formal outline will assist you in recording sufficient information. Use this post for guidance, and you will come up with a perfect thesis outline.
How did our templates helped you today?
Opps what went wrong, related posts.

24 FREE Story Outline Templates and Examples (Novel, Book, Plot)

Basic Speech Outline

Biography Outline Templates & Examples

Outline Template for Essay – Word, PDF

Literature Review Outline Templates (in Word & PDF)

12+ Body Outline Templates

Research Paper Outline Template

Novel Outline Template
Thank you for your feedback.
Limited Business Hours
Due to the Chilled Water System Outage, the Office of Graduate Education will be closed until further notice. For more information and updates regarding the outage, please visit: facilities.gatech.edu/chilled-water-outage
Graduate Education
Office of graduate and postdoctoral education, thesis templates.
The following thesis format templates should help you get started with formatting your thesis or dissertation. Georgia Tech provides free Overleaf Professional accounts for all students, faculty, and staff who would like to use the collaborative, online LaTeX editor for their projects.
- LaTeX Template (.zip) - updated May 2020
- Featured LaTeX templates on Overleaf
- Word Thesis Template (.docx) - updated August 2016
- Georgia Tech Engineering Reference Management System (GTERMS)
LaTeX Resources
- LaTeX Project
- Set the Quick Build command configuration to: “PdfLaTeX + Bib(la)tex) + PdfLaTeX (x2) + View Pdf”.
- Use the Quick Build command to compile and view your .pdf file.
- If you decide to use a “build” subdirectory for output files, you must point BibTeX to the proper subdirectory.
LaTeX is a powerful text processing and formatting tool that produces clean, consistent results. This high-quality typesetting system is a free service provided by Georgia Tech. It is available on many platforms and can be used with the editor of your choice. LaTeX is the de facto standard for the communication and publication of scientific documents.
Although Graduate Education does not offer direct technical support, Tech does provide help via campus partners such as the Library and Overleaf (online LaTeX editor). Please check the Library events page for courses on LaTex, or contact Overleaf directly.
Many students have also found useful tips for dealing with specific problems by entering keywords such as "LaTeX formatting table captions" in their favorite search engines.
Most Common LaTeX to PDF Problem
The most common problem we see with Electronic Theses & Dissertations (ETDs) created in LaTeX is the altering of the page size, particularly an increase of the bottom margin to more than one inch, and sometimes an accompanying decrease in the top and/or right margins to less than the requisite one inch. Less frequently, there will also be problems with figures disappearing or changing appearance. The sizing error may be introduced inadvertently during the conversion from .dvi to .pdf or .ps when the program doing the converting defaults to the A4 European page size. Always check your PDF file after conversion, even if your source file looked perfect.
The following fixes have been found by your fellow Tech graduate students and passed along to the Graduate Thesis Office. We hope they help you:
- First, before converting the .tex file to .dvi, make sure the class header file in your .tex file says something like "\documentclass[12pt, letter]{article}".
- If you are converting the resulting .dvi file to a .ps file, be sure the dvips options specify "-P pdf -t letter".
- When you are converting to .pdf from either the .dvi file directly or from a .ps file, locate the C:\texmf\dvipdfm\config\config\ or analogous folder for PDFs in your system. Replace the line "p a4" with "p letter".
Check our frequently asked questions (FAQ) to see if your question has already been answered. Else, contact [email protected] .
Accessibility Information
Download Microsoft Products > Download Adobe Reader >
- Faculty/Staff
- MyMichiganTech
- Safety Data Sheets
- Website Settings
- Graduate School
- Policies and Procedures
- Theses and Dissertations
Formatting and Preparing
Formatting requirements.
Students will follow the requirements in the guide . To assist with the requirements, the following resources are available:
- A review checklist - see a sample review form.
- A dissertation template
- A thesis template
New dissertations and theses available in the Library are listed at the bottom of this page; they may serve as examples for students. Keep in mind that formatting changes over time, and some volumes may have been embargoed for a year or longer before being available in the Library.
Preparing Assistance
In addition to the requirements above, there are some suggested formatting guidelines and tools to help as students prepare their documents. See the links below for formatting suggestions and aids.
- Sample Documents —Digital Commons contains all recent documents published by the Library. Note that some volumes may have been embargoed and may not reflect current formatting requirements.
- EndNote —Manage references and bibliographies
- Editing Services —Copy editing is available for a fee through the Center for Teaching and Learning.
- Acrobat Tips —Check and fix documents (popular tips listed below)
- How to determine if fonts are embedded in a PDF file
- How to check PDF conversion settings for images and embedding fonts
- How to check your paper size and page number location —learn how to check those pesky margins and the location of your page numbers so the formatting is right the first time
- How to change color pages to black and white
- How to use a preflight profile —check the image quality or number of color pages in your document
- How to rotate landscape pages in a PDF file
- How to use the TouchUp text tool —fix simple errors in your PDF file
- MS Office Tips —popular tips listed below
- How to check PDF conversion settings for images and embedding fonts —learn how to select the proper settings to embed all fonts and maintain image quality
- How to apply a style to a paragraph
- How to create a new style
- How to edit a style
- How to create bookmarks using Word and Adobe Acrobat
- How to create a hyperlinked table of contents— also describes how to create a table of contents without typing each line in by hand!
- How to turn off image compression in Word
- How to use tabs to align text
- How to view hidden formatting characters
- Tutorial for rotated page numbers on landscape pages
- Digital Tools —Learn about your Degree Progress Checklist, Canvas, ProQuest, and Google Calendar
- Check if your dissertation, thesis, or report is complete
- How to use your Degree Progress Checklist
- How to schedule a meeting using the Google calendar
- How to submit an assignment to Canvas
- How to submit a document to ProQuest/UMI
- Online Seminars —Topics include Microsoft Word, Adobe Acrobat, LaTeX, Great Images, EndNote, and more!
- Turnitin.com —Students can submit documents for plagiarism review. The web site is in the Graduate School Canvas course. Only graduate students will have access to the information needed to access the site. Contact the Graduate School for assistance with accessing the Canvas course or turnitin.com site.
- Turnitin Draft Coach is available for grammar, citation, and similarity checks in Google Docs.
| MS/PhD Template | (.zip) | |
| Presentation Template | (.zip) |
New Dissertations and Theses in Library
Rocket Lab's Growth Could Be Ready For Orbit
- Rocket Lab reported record revenue of $106 million, up 71% year-over-year, with an order backlog of $1.07 billion.
- Launch Services segment revenue slightly exceeded guidance, while space system segment revenue met expectations.
- The company has a strong balance sheet to manage its operating timeline and has a project scheduled for 2025 that can compete with the market leader.

Rocket Lab ( NASDAQ: RKLB ) reported a record revenue this week and the stock could be ready for its growth to take off. I'll outline why the stock is currently my best growth idea.
Rocket Lab records best-ever quarter
Record Lab reported second-quarter earnings this week, with the highlight being the company's first quarter of revenue of more than $100 million. The company reported a 15% quarterly increase to $106 million, up 71% year-over-year. The company also noted an order backlog of $1.07 billion.
The company's Launch Services segment produced revenue of $29.4M, slightly above management's guidance, while the space system segment produced $77M in the quarter, which met guidance.
"Our current backlog continues to support our current year target average revenue per launch of $7.5M," management said.
Management expects Q3 revenue to be similar, within a range of $100-$105 million.
Rocket Lab's Profit (Seeking Alpha)
Annual revenue is also growing steadily as the company builds its capabilities.
Rocket Lab's Expenses (Seeking Alpha)
Operating losses are remaining steady on a quarterly basis in a range of -$38.9 million to -$47.9 million.
Innovation is key to the company's growth story
With a strengthening financial picture, Rocket Lab is creating space to innovate for future growth.
In the latest earnings presentation, the company announced 17 new contracts with a total value of $141 million. The company's backlog, new contract wins, and time-based revenue will mean the company can continue to grow toward profitability.
Rocket Lab's Billing (Rocket Lab)
Alongside the latest earnings, the company also announced a key technical milestone for its Archimedes engine, which will fire its Neutron rockets.
Rocket Lab founder and CEO, Sir Peter Beck, said: "Hot firing Archimedes is a major development milestone for Neutron and our team has done it on an accelerated timeline. Taking a new staged combustion liquid rocket engine from cleansheet design to hot fire in just a couple of years is industry-leading stuff."
The press release also noted that many of the critical components for the new engine are 3D printed, reducing the cost footprint.
The Neutron rocket is critical to the company's stated goal to become an end-to-end space company.
“If you look at where we ultimately want to go, in a lot of ways we want to emulate what SpaceX has successfully done, which is work their way towards the applications market,” Rocket Lab CFO Adam Spice said .
The earnings presentation also said that the Neutron rocket is "well-positioned to capitalize" on a $10 billion launch Total Addressable Market.
Space Systems segment also growing
Rocket Lab's Space Systems segment is also growing fast, with $720 million in satellites in development or production.
Analysts at McKinsey have estimated that the global space economy will be worth $1.8 trillion by 2035, up from $630 billion in 2023. That figure will be driven by demand for “backbone” applications such as satellites, television and GPS. Alongside "reach" applications, where analysts used the example of Uber combining satellite signals and smartphone chips for city navigation.
The Space Foundation said that 2023 was a record year for commercial launches, up 50% on the previous year.
Rocket Lab has an agreement on preliminary terms for $49.4m in federal and state local incentives. The company already makes solar cells and panels in a New Mexico and will use the funds for expansion.
The company is also nearing completion of its initial work with Varda Space Industries . The company builds products such as fiber optic cables in zero gravity situations, which are of higher performance. Other sectors could turn to space manufacturing tests, such as pharmaceuticals.
"Traditionally, almost all in-space manufacturing research has been carried out on the International Space Station. This research has demonstrated that innovative materials and products can be created in the consistent microgravity environment of low-Earth orbit, an environment that can’t be replicated on Earth," a statement said.
Other considerations
The company said that Research & Development expenses had "ramped up" due to the Neutron and Archimedes testing. That will ease ahead of the proposed mid-2025 launch and free up working capital.
Rocket Lab had $546.8 million in cash and cash equivalents at the end of the most recent quarter. That allows for around 13 quarters at the current operating loss level of around -$40 million.
The company's CEO highlighted the future potential of a Neutron-driven constellation this week, saying :
“We can build and launch our own spacecraft at cost, and we don't have to wait in line for limited launch capacity. We completely avoid the pain point that most constellation operators face: being at the mercy of suppliers on cost and schedule, often causing deeply disruptive delays and bringing capability online at scale.”
Beck was also hopeful that his company can break the "monopoly" of the SpaceX Falcon, which is the dominant rocket due to its high payload. Rocket Lab is also showing an ability to manufacture and fly at a similar speed to SpaceX.
The company's Electron beat the Falcon as the fastest-commercial rocket to 50 launches. Neutron's proposed 4.3 year announcement to launch schedule would also beat the 4.8 years of SpaceX.
In June of this year, Bloomberg reported that insider share sales of the privately-owned SpaceX were set to create a valuation of around $210 billion. By mid-2025, Rocket Lab could have a viable alternative to take market share from the company. That followed tender offers valued at $137 billion and $180 billion.
The current market capitalization of Rocket Lab is $2.35 billion, and it therefore has the funding to comfortably get to its mid-2025 Neutron launch and begin tapping into new contract opportunities.
As the company gets closer to that date, positive contract wins and development news on its key project could fire up the stock price beyond the current price/sales ratio of around 8x.
Downside risks to the thesis
The key risk to the thesis is a problem with development of the Neutron rocket. The company is on a steady path to tap into a growing market for satellites, but Neutron can be a gamechanger for the company to rival SpaceX with its own constellation and a stronger reputation for large projects.
Another downside is obviously in safety, if the company suffered any negative effects in its manufacturing, and/or launches.
Rocket Lab has logged its best ever quarter with revenue of over $100 million. The company is making a loss each month, but the current operating loss is around the cost of R&D and other expenses are remaining steady. The company has more than $500 million in cash, which can see it continue operations for 13 months comfortable, but there is also an operating backlog of more than $1 billion, while the company is starting to see growth in its Space Systems segment with its largest contract win earlier this year for satellites. That could see the company move closer to profitability by year-end. The real moonshot for Rocket Lab is the development of its Neutron rocket. The Archimedes engine for this engine just reached a major milestone and is scheduled to launch by mid-2025. The rocket will have a payload to compete with the dominant SpaceX and can tap into a Total Addressable Market of $10 billion.
Editor's Note: This article was submitted as part of Seeking Alpha's Best Growth Idea investment competition , which runs through August 9. With cash prizes, this competition -- open to all analysts -- is one you don't want to miss. If you are interested in becoming an analyst and taking part in the competition, click here to find out more and submit your article today!
This article was written by
Analyst’s Disclosure: I/we have a beneficial long position in the shares of RKLB either through stock ownership, options, or other derivatives. I wrote this article myself, and it expresses my own opinions. I am not receiving compensation for it (other than from Seeking Alpha). I have no business relationship with any company whose stock is mentioned in this article.
Seeking Alpha's Disclosure: Past performance is no guarantee of future results. No recommendation or advice is being given as to whether any investment is suitable for a particular investor. Any views or opinions expressed above may not reflect those of Seeking Alpha as a whole. Seeking Alpha is not a licensed securities dealer, broker or US investment adviser or investment bank. Our analysts are third party authors that include both professional investors and individual investors who may not be licensed or certified by any institute or regulatory body.
Recommended For You
About rklb stock.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|
More on RKLB
Related stocks.
| Symbol | Last Price | % Chg |
|---|---|---|
| RKLB | - | - |
Trending Analysis
Trending news.

COMMENTS
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline ... Tegan is an American based in Amsterdam, with master's degrees in political science and education administration. While she is definitely a political scientist at heart, her ...
Having an outline for your master's thesis will help you explain the motivation behind your work, and also connect the different experiments or results that you completed. Furthermore, an outline for your master's thesis can help break down the larger task of writing the entire thesis into smaller, more manageable chapter-sized subtasks. 4.
Thesis outline typically follows a standard format and includes the following sections: Title page: This page includes the thesis title, author's name, department, university, and the date of submission. Abstract: This section is a brief summary of the thesis, highlighting the main points and conclusions. It usually contains around 150-300 words.
1. Introduction. 1.1. Objectives. The purpose of a master degree thesis is to demonstrate your understanding. and mastery of a particular subject area and your ability to develop new. scientific knowledge independently. For these reasons, writing a thesis is. different from studying for exams.
Introduction &. Thesis Statement. - Set a logical roadmap with the introduction. - State specific claims to prove. - Use flexible, evolving thesis statements. - Use online or traditional thesis templates. Literature Review. - Start with a clear research question and thesis. - Stay adaptable with the literature review.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on 8 June 2022 by Tegan George. ... Tegan is an American based in Amsterdam, with master's degrees in political science and education administration. While she is definitely a political scientist at heart, her experience working at universities led to a passion for making ...
Introduction: Don't mess around with it! The only purpose is to introduce the research. You will outline the problem you intend to investigate, state the aim of the research, limit the scope of the investigation, and provide an overview of what lies ahead. 3-5 pages is usually sufficient.
Example MS Thesis Outline. Introduction. Problem definition. describe what you trying to do. clearly state the question being addressed. when appropriate formulate a testable hypothesis. Describe the motivation; who is interested in the solution. Summarize the results and their significance. Background.
The purpose of a master's thesis is to help you develop your own independent abilities, ensuring that you can drive your own career forward without constantly looking to others to provide direction. Leaders get master's degrees. That's why many business professionals in leadership roles have graduate degree initials after their last names.
Now, what will make or break your master's thesis outline or senior thesis outline is understanding its structure. It is not enough to have what to write but how to register it as well. That is why you need this template when writing a thesis outline. Thesis Outline Format. A conventional thesis paper will have the following sections: Title
Definition of Dissertation and Thesis. The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master's ...
Writing. 9. Each thesis or dissertation is unique but all share several common elements. The following is not an exact guide but rather a general outline. Chapter 1: Purpose and Significance of the Study. In the first chapter, clearly state what the purpose of the study is and explain the study's significance.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
University Thesis and Dissertation Templates. Theses and dissertations are already intensive, long-term projects that require a lot of effort and time from their authors. Formatting for submission to the university is often the last thing that graduate students do, and may delay earning the relevant degree if done incorrectly.
Correct spelling, punctuation, and grammar. Correct formatting of margins, headings, and citations according to the style manual specified by the student (APA, Turabian, MLA). Make suggestions on writing style, such as shortening long sentences, without changing the meaning of the text.
A thesis could consist of an average of 70 to 100 pages, including a bibliography, citations, and various sections. It is written under the guidance of a faculty advisor and should be publishable as an article. Your master's thesis reflects the literature in your field, challenges, evidence, and arguments around your writing topics.
The thesis proposal is an excellent planning tool. It helps bring the thesis topic into sharper focus. A thesis proposal may start out being vague, but as the student works on the proposal and discusses it with his or her supervisor, the proposal should outline: the topic or the central research question
A Thesis Proposal is a document that sets forth what is to be studied as a thesis project, why and in what way. It contains a number of important sections. The purpose of the proposal is to communicate the plan for the work to the faculty of the Division of Emerging Media Studies via the First Reader (principal thesis advisor) and a Second Reader.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
A master's thesis outline is a document that contains a guideline on how to write a thesis for those students undertaking a master's degree program. The document resembles any thesis outline in its general outlook, only that the expected level of research is a bit more technical. The basic components of this outline include an Introduction ...
Current Students. Theses & Dissertations. Thesis Templates. The following thesis format templates should help you get started with formatting your thesis or dissertation. Georgia Tech provides free Overleaf Professional accounts for all students, faculty, and staff who would like to use the collaborative, online LaTeX editor for their projects.
An outline of the entire process to complete your thesis or dissertation from selecting your advisory committee to graduating as a published author can be found on the Thesis and Dissertation Guidelines page on the College of Graduate Studies' website at
Foreword. This guidebook summarizes the procedures followed by the Office of Graduate Studies and Research for students who are planning to write theses for their master's degree. This manual also is intended to guide students in the elements and structure generally contained in a thesis as well as to provide a reference to the appropriate ...
Formatting Requirements. Students will follow the requirements in the guide.To assist with the requirements, the following resources are available: A review checklist- see a sample review form.; A dissertation template; A thesis template; New dissertations and theses available in the Library are listed at the bottom of this page; they may serve as examples for students.
Rocket Lab reported record revenue of $106 million, up 71% year-over-year, with an order backlog of $1.07 billion. Launch Services segment revenue slightly exceeded guidance, while space system ...