Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 6 with Answers CBSE
Direct and indirect speech exercises for class 6 with answers cbse pdf.
Rules For Changing Direct Speech To Reported Speech
1. Changes in reporting verb
- Affirmative sentences: said, told (object), asserted, replied, assured, informed, responded, whispered, alleged, believed, assumed, thought
- Interrogative sentences: asked, inquired, wanted to know, enquired
- Imperative sentences: ordered, begged, pleaded, implored, advised, demanded
2. Change of pronouns
| Meeta said, ‘I live in Himachal’.’ | Meeta said that he lived in Himachal. |
- The conjunction that is used to connect the reporting verb with what is said.
- A first-person and second-person generally change to third person (depending upon object to reporting verb)
- In case the reporting verb is in present, the tense of verb in reported speech continues to remain in the present tense.
3. Change of tenses When we report something after a certain period of time, and what we are talking about has already happened, we change the tense of the sentence being reported into a corresponding past tense. Read the following table carefully.
| Kalpana said, ‘I teach in a school.’ | Kalpana said that she taught in a school. |
| Kalpana said, ‘I am teaching in a school.’ | Kalpana said that she was teaching in a school. |
| Kalpana said, ‘I have taught in a school.’ | Kalpana said that she had taught in a school. |
| Kalpana said, ‘I have been teaching in a school for the past one year. ’ | Kalpana said that she had been teaching in a school for the past one year. |
| Kalpana said, ‘I taught in a school for two years.’ | Kalpana said that she had taught in a school for two years. |
| Kalpana said, ‘I was working at a call centre before I started teaching.’ | Kalpana said that she had been working at a call centre before she started teaching. |
In general, present tense becomes past tense:
- Past tense becomes past perfect tense.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous tense.
- Past perfect and past perfect continuous remain unchanged.
4. Change of situations When we report sentences in indirect speech, the words denoting places or time are changed.
| Puja said, ‘I went to Rohtak last week.’ | Puja said that she had gone to Rohtak the previous week. |
| this | that |
| last week | the previous week |
| here | there |
| now | then |
| today | that day |
| yesterday | the day before/the previous day |
| tomorrow | the next/coming day |
| last week | the week before/the previous week |
| next month | the next month/the coming month |
5. Universal truths When universal truths are being reported we may choose either to retain the original tense of the sentence or to change it.
| The teacher said, ‘The earth is round.’ | The teacher said that the earth is round. |
6. Questions and answers
| Rahul asked his sister, ‘Have you taken your purse?’ (Yes/No question) | Rahul asked his sister if/whether she had taken her purse. |
| Rahul asked his sister, “Where are the keys?’ (Wh- question) | Rahul asked his sister where the keys were. |
7. Commands, orders and requests
| The teacher said, “You must be honest.” | The teacher advised the students to be honest. |
| The policeman said to the driver, “Drive cautiously.” | The policeman ordered the driver to drive cautiously. |
| The Inspector said to the crowd, “Tell me the details.” | The Inspector asked the crowd to tell him the details. |
| “Why don’t you take up acting?” I suggested to my sister. | I suggested to my sister to take up acting. |
8. Modals verbs
| Kunal said, ‘I can drive.’ | Kunal said that he could drive. |
Changes in modals
- can – could
- will – would
- shall – should
- may – might
Would, should, could, might, ought to and must are unchanged.
1. What does Ditya want to buy and why? 2. Why Ditya’s clothes are not suitable for the occasion? 3. What does father reply in the end of the story above?
B. Change the following sentences into indirect speech from the story above.
1. Ditya says to her father, “I want to buy new clothes for my graduation ceremony.” ___________________________________________________ 2. “These dresses are not suitable for the occasion,” says Ditya. ___________________________________________________ 3. “You have just borrowed three dresses a few days ago,” replies father. ___________________________________________________

Direct And Indirect Speech Practice Exercises for Class 6 CBSE
A. Complete the sentences into indirect speech.
1. Mohan (to Seema): I like your hairstyle. Mohan tells Seema : ____________
2. Parrot: I can speak English. The parrot says ____________
3. The fairy (to boy): I will grant you a wish if you won’t tell a lie. The fairy tells the boy ____________
4. The doctor (to a patient): I prescribed you a medicine but I did not charge you for it. The doctor tells ____________
5. The guide (to tourists): We are going to visit the Mahendra caves and there we will get to see bats. The guide says ____________
B. Change the following Direct speech into Indirect.
1. She says, “I will do this work.” ___________________________________
2. Sunita says, “He can come and stay in my flat.” ___________________________________
3. Amrita says to Hari, “I am taking my lunch now.” ___________________________________
4. Nancy says, “I am going to Paris next month.” ___________________________________
5. Vikas says, “I work hard on this project.” ___________________________________
6. She says, “This book is mine.” ___________________________________
7. Aunt Kajol says to me, “You will send these books to my place the day after tomorrow.” ___________________________________
8. Chetan says to mother, “I will tell you the truth.” ___________________________________
9. I have told him, “My father is a doctor.” ___________________________________
10. Meeta says, “I am sure everything will be alright after the operation.” ___________________________________
C. Write the correct pronouns in the following sentences in Reported speech.
1. Ankit: “I work in an office.” Ankit told me (that) ____________ worked in an office.
2. La lit and Puneet: “We play football.” Lalit and Puneet told me (that) ____________ played football.
3. Anjali: “I like my cat.” Anjali told me (that) ____________ liked ____________ cat.
4. Sanju: “Can you see me?” Sanju asked me ¡f ____________ could see ____________.
5. Kanika : “I will have to borrow your pencil.” Kanika told me (that) ____________ would have to borrow ____________ pencil.
6. Meera: “My father is American.” Meera told me (that) ____________ father is American.
7. Pooja and Rajni: “Can we use your camera?” Pooja and Rajni asked me if could use ____________ camera.
8. Raja: “How is your journey?” Raja asked me how ____________ journey was.
9. Priya and Ritu: “We love our pets.” Priya and Ritu told me (that) ____________ loved ____________ Pets.
10. Grandmother: “Piease bring me a cup of my tea.” Grandmother told me to bring ____________ a cup of tea.
Direct And Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 6 – Part II
Fundamentals: If the Reported Verb is in Past tense (Said, told instead of say, tell) then the tense in the reporting speech changes accordingly.
1. Why does Rita argue with her mother? 2. Why does Rita’s mother never give her a pizza or a burger to eat? Give two reasons. 3. What does Rita’s mother advice her in the end of the story?
B. Read the conversation between mother and daughter in the story above and complete the paragraph that follows.
Mother told Rita 1. ____________. Rita replied that 2. ____________ and told her mother that she never gave her a pizza or burger. Mother said that they are not good for her health and reminded her 3. ____________. Rita then asked her mother to give her french fries and a shake. Mother warned her that if she lived on junk food, she would spoil her health.
Direct And Indirect Speech Worksheets With Answers Pdf
A. Change the following into reported speech.
1. Nikhil said, “I will come tomorrow.” ____________________________________
2. Paras said, “I have passed the examination.” ____________________________________
3. He said, “We are going for a picnic today.” ____________________________________
4. She said, “Aayush is working hard.” ____________________________________
5. She said, “I have been writing for an hour.” ____________________________________
6. Rita said, “The girls were singing in the music period.” ____________________________________
7. The teacher says, “Sehaj does not work hard.” ____________________________________
8. I said to her, “I can solve the sum.” ____________________________________
9. Aman said, “Vinay may not come to school today.” ____________________________________
10. The teacher said, “The earth is round.” ____________________________________
11. He said to his friend, “My sister has written a letter.” ____________________________________
12. The priest said, “God is great.” ____________________________________
13. Arjun said, “I can play sitar.” ____________________________________
14. Mohan said, “My sister has been studying since morning.” ____________________________________
16. They said to me, “We cannot help you now.” ____________________________________
17. Sambhav said, “My father is writing a letter.” ____________________________________
18. She said to me, “I will go to the library tomorrow.” ____________________________________
B. Finish the sentences using Reported speech.
Question 1. Niru: Will you please give me your notebook? Indu: Yes. Which one do you need? Niru asked Indu if ……………………………….. Indu said, ……………………………….. She asked ……………………………….. Answer: Niru asked Indu if she would give Niru her notebook . Indu said yes . She asked Niru which one she needed .
Question 2. Mohini said, “Where can I find the post office?” The policeman said, “It is on the road behind the clock tower.” Mohini said, “Thank you. I have been looking for it for a while.” Mohini asked the policeman ………………………………. . The policeman said ………………………………. . Mohini ……………………………….. him and added that she had ……………………………….. Answer: Mohini asked the policeman where he could find the post office . The policeman said that it was on the road behind the clock tower . Mohini thanked him and added that she had been looking for it for w while .
Question 3. Teacher: Rohan, what are you thinking? Hurry up and finish your work. Rohan: Ma’am, I have almost finished. I was trying to recall my last week’s lessons.
The teacher ……………………………….. Rohan ……………………………….. She told him to ……………………………….. Rohan replied ……………………………….. He said that he ……………………………….. Answer: The teacher asked Rohan what he was thinking . She told him to hurry up and finish his work . Rohan replied that he had almost finished . He said that he was trying to recall his previous week lessons .
Question 4. Father: You look worried. What’s the matter? Son: It’s about my admission to an engineering college. Father: When are your results expected? Son: Within a week, Father.
The father noticed that his son ……………………………….. He asked him ………………………………. . The son replied ………………………………. . The father asked ………………………………. . The son replied ……………………………….. Answer: The father noticed that his son looked worried . He asked him what the matter was . The son replied that it was about his admission to an engineering college . The father asked his son when were his reults expected . The son replied that they were expected within a week .
Question 5. Jenny: Let’s go for a walk. Susan: Yes. Give me ten minutes. Jenny: Let’s go now. Susan: I will just take a few more minutes. Jenny: Why must you delay? Susan: What makes you so impatient?
Jenny asked Susan ……………………………….. Susan replied politely ……………………………….. Jenny was, however, impatient and said ……………………………….. Susan ……………………………….. Answer: Jenny asked Susan to go for a walk . Susan replied politely in the affirmative and asked to be given ten minutes . Jenny was, however, impatient and said that she wanted to go then . Susan said that she would take a few more minutes. Jenny asked her why she must delay. To this, Susan asked Jenny what made her so impatient .
- English Grammar
- Grammar Exercises
- Direct And Indirect Speech Exercises
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
Direct and indirect speech is one topic in English grammar that confuses most language learners. It need not necessarily be so; if you understand how it works, you can easily use it in your writing.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises with Answers
When converting direct speech to indirect speech or vice-versa, you will have to take care to convert the verb , pronoun and the adverb appropriately. Go through the following exercises and try them out. Answers are given below each exercise; refer to them to see if your answers are right.

Exercise 1: Change into indirect speech
Read the following sentences and convert them into indirect speech.
- Rahul told to me, “When are you leaving?”
- “Where do you live?” the stranger asked Aladdin.
- The teacher said to Shelly, “Why are you laughing?”
- Dhronacharya said to Arjun, “Shoot the bird’s eye.”
- “Call the first convict,” said the jury.
- “Call the ambulance,” said the man.
- Bruce said to me, “I shall do the work.”
- My mother said to me, “You were wrong.”
- Mr Richard said to me, “Please wait here till I return.”
- The captain said to me, “Bravo! You have played well.”
- Raj said, “Alas! My pet died.”
- Ruchi said, “I may go there.”
- Bucky said to Steve, “Do you hear me?”
- The boy said, “Let me come in.”
- Granny said to me, “May God bless you.”
Answers –
- Rahul asked me when I was leaving.
- The stranger asked Aladdin where he lived.
- The teacher asked Shelly why he was laughing.
- Dhronacharya ordered Arjun to shoot the fish’s eye.
- The jury ordered to call the first convict.
- The man urged to call the ambulance.
- Bruce said to me he would do the work.
- My mother told me that I was wrong.
- Mr Richard requested me to wait there till he returned.
- The captain applauded me, saying that I had played well.
- Raj exclaimed sadly that his pet died.
- Ruchi said that she might go there.
- Bucky asked Steve if he heard him.
- The boy asked to let him come in.
- Granny prayed that God might bless me.
Convert the following into Direct Speech
Read the following passage and convert it into direct speech.
One of them told Issac that the latter had forgotten one thing that belonged to a mill. Issac enquired what that was. The friend asked where the miller was. Issac replied that (absence of the miller) was true – and he must look for one.
“But Issac,” said one of them, “you have forgotten one thing that belongs to a mill.”
“What is that?” asked Issac.
“Why, where is the miller?” said his friend.
“That is true – I must look for one,” said Issac.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is direct narration.
When the actual words/sentences as spoken by the speaker are quoted in a speech, it’s called direct speech/narration.
What is indirect speech?
When the quoted speech is reported in the form of a narrative without changing the meaning of the actual quotation/words by the speaker, it’s called indirect speech/narration.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 24 Direct and Indirect Speech
Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 24 Direct and Indirect Speech. The word—speech—means whatever we speak or write. Speaking or writing the words of an another person can be done in two ways, 1. by repeating the words of the other person as they were, 2. by stating the meaning of the words of the other person in your own words. Suppose Aman speaks the words: “I am ill today.” Any person other than Aman can express his words in the following two ways: (a) Either he says: Aman said, “I am ill today.” (b) Or he can say: Aman said that he was ill that day.
- Class 6 English Grammar Direct and Indirect Speech
- Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 24 Revision Book
- Class 6 English Grammar Next Chapter
- Class 6 English Grammar Main Page
- Class 6 English NCERT Solutions
| Class: 6 | English Grammar |
| Chapter: 24 | Direct and Indirect Speech |
| Content Type: | Textbook and Revision Notes |
| Session: | 2024-25 |
Direct Speech
Aman said, “I am ill today.” In this sentence, the very words of the speaker, i.e., “I am ill today” are quoted within inverted commas (” “). This is called the Direct Speech. The sentence within ” ” is called reported speech. The verb that introduces the reporting speech is called reporting verb.
INDIRECT SPEECH Aman said that he was ill that day. In the above sentence, we have reported what the speaker said, i.e. he was ill that day without quoting the exact words. This is called Indirect Speech. Carefully Read the following points: In Direct Speech: 1. The Reported Speech is put within Inverted Commas (” “). 2. The first word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital letter. In Indirect Speech: 1. Inverted commas are not used for the Reported Speech It is generally introduced by the conjunction that, if, etc. 2. The comma separating the Reporting Verb from the Reported Speech is removed. 3. The tense of the Reporting Verb is never changed.
RULES FOR THE CHANGE OF TENSES
Conversion of Assertive Sentences into Indirect Speech Rule: If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech is not changed at all as,
| Direct | Indirect |
|---|---|
| I say, “Reena is a student.” | I say that Reena is a student. |
| He says, “She is a nurse.” | He says that she is a nurse. |
| I shall say, Ayush is a doctor.” | I shall say that Ayush is a doctor. |
CHANGE IN TENSES
Rule: If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the tense of the R.S. will change as under: Simple Present changes into Simple Past: Direct: He said, “Sandhya sings a nice song.” Indirect: He said that Sandhya sang a nice song. Present Continuous changes into Past Continuous: Direct: He said, “The girls are picking flowers.” Indirect: He said that the girls were picking flowers. Present Perfect changes into Past Perfect: Direct: Father said to me, “It has been raining since morning.” Indirect: Father told me that it had been raining since morning. Simple Past changes into Past Perfect: Direct: I said to him, “They enjoyed the magic show.” Indirect: I told him that they had enjoyed the magic show. Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous are not changed: Direct: She said, “He had not seen the Taj before.” Indirect: She said that he had not seen the Taj before. Shall and will of future tense become should/would: Direct: I said to her, “I shall help Sagun”. Indirect: I told her that I should/would help Sagun. All Present Tenses change into their corresponding Past forms: is, am become was can becomes could are becomes were may becomes might has, have become had was/were become had been The forms of could, should, would, might, had are not changed: Direct: I said to him, “I am a poor man.” Indirect: I told him that I was a poor man.
CHANGE OF PRONOUN
Pronouns of the first person change according to the person of the Subject of the Reporting Verb: Direct: I said, “I have done my duty.” Indirect: I said that I had done my duty. Rule: Pronouns of the third person remain unchanged. Direct: I said, “He has done his duty.” Indirect: I said that he had done his duty. CHANGE OF WORDS DENOTING TIME AND POSITION here becomes there this becomes that ago becomes before today becomes that day thus becomes so now becomes then CONVERSION OF QUESTIONS INTO INDIRECT SPEECH 1. The Reporting Verb is changed to asked, enquired, demanded etc. 2. Whether or if is used if the R.S. begins with a Helping Verb or a Modal Auxiliary like do, does, did, is, am, are and can, could, should, would etc. in place of comma and inverted commas. 3. All questions beginning with interrogative words like how, what etc. remain unchanged. 4. The Interrogative form is changed into assertive form. The Question Mark is dropped. 5. Tenses, Pronouns and Words denoting nearness are changed according to the rules already stated. Direct: 1. He said to me, “Do you take tea?” Indirect: He asked me if I took tea.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education


200+Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers (2025)

Direct and indirect speech exercises and answers (2025) help learners understand the transformation between direct statements and reported speech, enhancing their comprehension and expression abilities.
We frequently employ direct and indirect speech in our everyday interactions to accurately convey what was said and summarize information efficiently.
Enhance your understanding of Direct and Indirect Speech with our extensive collection of over 200 exercises and corresponding answers.
Through practice in transforming quotations into reported speech, grasp the principles and methods involved, and refine your differentiation between direct and indirect speech.
Elevate your language proficiency and deepen your comprehension of English with our comprehensive set of over 200 Direct and Indirect Speech exercises and answers.
Understanding Direct Speech
Direct speech is when the exact words spoken by a person are quoted within quotation marks. It provides a direct representation of what was said, maintaining the original wording and tone. Direct speech adds authenticity and immediacy to the narrative.
For example,
- Direct Speech: My aunt said, ‘Every mother loves her child.’
- Direct Speech: Mon said to me, ‘I shall go, but you will stay.’
Explore Indirect Speech
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, conveys someone else’s words without quoting them directly. Indirect speech offers a concise summary, enabling effective communication and storytelling.
- Indirect Speech: My aunt said that every mother loves her child.
- Indirect Speech: Mon told me that she would go but I should stay.
Before delving into the direct and indirect speech exercises, consider how Tense , Pronouns , Time , and Place change when transitioning from direct to indirect speech and vice versa.
Exercises and Answers for Direct and Indirect Speech (2025)
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and answers, along with examples are given in the following for practice. It’s important for students as well as for competitive Exams. For practice and easy comprehension, Direct and indirect speech Exercises and answers have been arranged according to different rules in the following.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers with Tense Transformations
Exercises and answers with tense alterations facilitate practice and comprehension of verb tense transformations.
Exercise 1:
Change the mode of narration from direct Speech to indirect speech .
(1) He said , ‘I need some money.’ Ans: He said that he needed some money.
(2) She said, ‘I am waiting for him.’ Ans: She said that she was waiting for him.
(3) The boy said , ‘I have done my homework.’ Ans: The boy said that he had done his homework.
(4) You said, ‘The baby has been sleeping .” Ans: You said that the baby had been sleeping .
(5) You say, ‘I am always busy.’ Ans: You say that you are always busy.
(6) The child will say , ‘Mum knows everything.’ Ans: The child will say that Mum knows everything.
(7) He said , ‘I did it.’ Ans: He said that he had done it.
(8) She said, ‘He was talking .’ Ans: She said that he had been talking .
(9) The monk said , ‘Man will die .’ Ans: The monk said that man will die.
(10) He said , ‘The sun gives us light.’ Ans: He said that the sun gives us light.
Exercise 2:
Switch the narrative style from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) He said to me, “I can’t recall your name.” Ans: He told me that he could not recall my name.
(2) Poulami says , “I am fine.” Ans: Poulomi says that she is fine.
(3) He said, “I did it.” Ans: He said that he had done it.
(4) “I know her address,” said Gopi. Ans: Gopi said that he knew her address.
(5) Ram said, “The earth is round.” Ans: Ram said that the Earth is round.
(6) “We planted it ourselves,” said the grandfather. Ans: The Gran Father said that they had planted it themselves.
(7) Debu said, “I have been playing rugby.” Ans: Debu said that he had been playing rugby.
(8) Purbasha said to me,” I am afraid of ghosts.” Ans: Purbasha told me that she was afraid of ghosts.
People Also Ask
| to Change Direct to Indirect Speech | |
Exercise 3:
Turn the following sentences from direct Speech to indirect speech .
(1) The boys said , “It has been raining since morning. We cannot play today.” Ans: The boys said that it had been raining since morning so they could not play that day.
(2) Anjan’s mother said, “Your father has left for Mumbai.” Ans: Anjan’s mother said that my father had left for Mumbai.
(3) My teacher said , “Practice makes a man perfect.” Ans: My teacher said that practice makes a man perfect.
(4) He says, “I go to the temple every morning.” Ans: He says that he goes to the temple every morning.
(5) He said to me, “I will not get down from the bus.” Ans: He told me that he would not get off the bus.
(6) Rita says to Mita, “I will go with you.” Ans: Rita tells Mita that she w ill go with her.
(7) The boy said to his friend, “I went to school yesterday.” Ans: The boy told his friend that he had gone to school the previous day.
(8) You said, “I was right.” Ans: You said that you had been right.
(9) “I ‘ll go to the top,” said the young lady. Ans: The young lady said that she would go to the top.
(10) I ‘ ve got my rules,” the conductor said to me. Ans: The conductor told me that he had got his rules.
Pronouns in Direct and Indirect Speech: Exercises and Answers
Exercises and answers incorporating pronouns in direct and indirect speech facilitate learners’ understanding and application of pronoun changes in reported speech structures.
Exercise 4:
(1) You said, ‘ I never smoked.” Ans: You said that you never smoked.
(2) I said, ‘ I am always busy.” Ans: I said that I was alway busy
(3) I said to you , ‘ You look tired.” Ans: I said to you that you looked tired.
(4) You said to me , ‘ You are dependable.” Ans: You said to me that I was dependable.
(5) You said, “ He is right.” Ans: You said that he was right.
(6) I said, “ They will be late. Ans: I said that they w ould be late.
(7) He said to (Deep) , ‘ You told it so.” Ans: He said to Deep that he (Deep) had told it so.
(8) Mon said to Moon , “ You are naughty.” Ans: Mon said to Moon that she (Moon) was naughty.
Exercise 5:
Alter the narrative style from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) He said to me, “ I have done the job.” Ans: He told me that he had done the job.
(2) Rohit said, “ I was absent yesterday.” Ans: Rohit said that he (Rohit) had been absent the previous day.
(3) The boy said, “ My father died two years ago.” Ans: The boy said that his father had died two years before.
(4) He said, “ My goal is to climb Mt Everest. “ Ans: He said that his goal was to climb Mount Everest.
(5) “ I shall certainly do nothing of this kind”, the woman. Ans: The woman said that she would certainly do nothing of that kind.
(6) The man said, “ I am exhausted.” Ans: The man said that he was exhausted.
(7) He said, “ I am washing my hands.” Ans: He said that he was washing his hands.
(8) Mother bird said to her little ones, “Today I will teach you how to fly.” Ans: Mother bird told her little ones that that day, she would teach them how to fly.
(9) Rita’s father says. “ I have done this for you. Ans: Rita’s father says that he had done that for her.
(10) Sumana said to her sister, “ I want to play with you.” Ans: Sumana told her sister that she wanted to play with her.
Time and Place Expressions in Direct and Indirect Speech: Exercises and Answers
Exercises and answers on time and place expressions in direct and indirect speech aid learners in accurately conveying temporal and spatial information while mastering reported speech conventions.
Exercise 6:
Turn the following direct speech into indirect speech
(1) I said to you, “I wish to start business next year. “ Ans: I said to you that I wished to start business the following years.
(2) You said to them, “ Now I shall tell you a nice story.” Ans: You told them that then you would tell them a nice story.
(3) She said to him, “I bought the book yesterday. “ Ans: She told him that she had bought the book the previous day .
(4) He said to me, “I saw your sister two years ago . Ans: He told me that he had seen my sister two years before.
(5) He said to his son, “You may come with me tomorrow. Ans: He told his son that he (his son) might go with him the next day.
(6) He said to her, I’m talking to you now for your good.” Ans: He told her that he was talking to her then for her good.
(7) The girl said to me, My father died two years ago. “ Ans: The girl told me that her father died two years before.
Exception: But if ‘ now ‘, ‘ here ‘, ‘ this ‘ refer to things present before the speaker at the time of reporting, no change is needed.
(8) He said to me, ‘I have no friend here. ‘ Ans: He told me that he had no friend here.
(9) I said, ‘We cannot be happy in this world.’ Ans: I said that we cannot be happy in this world.
(10) She said, “ This is the house where I was born.” Ans: She said that this was the house where she was born.
Exercise 7:
Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
(1) The boy said to his father, “I had my tiffin in school yesterday. “ Ans: The boy told his father that he had had his tiffin in school the previous day .
(2) The captain informed, “The tournament was postponed last year. “ Ans: The captain informed us that the tournament was postponed the previous year .
(3) She said, “We have been living here for two years.” Ans: She said that they had been living there for two years.
(4) Arnab said to Ajit,” I am happy today .” Ans: Arna told Ajit that he was happy that day.
(5) My friend said to me, “We went to the zoo yesterday. “ Ans: My friend told me that they had gone to the zoo the previous day.
(6) The clerk said, “I’ll do the work now. “ Ans: Clark said that he would do the work then.
(7) Hiten said to Mihir, “I received this letter yesterday. “ Ans: Hiten told me that he had received that letter the previous day.
(8) Rajib said to me. “I shall go to the picture today. “ Ans: Rajiv told me that he would go to the picture that day.
(9) He said, “We are very happy here. “ Ans: He said that they were very happy there.
(10) The farmer said, “I’ll sow the seeds now. “ Ans: The farmer said that he will show the seats then.
(12) The man said to me, “I received your gift yesterday. “ Ans: The man told me that he had received my gift the previous day.
(15) I said to my friend, “You were present in the class yesterday. “ Ans: I told my friend that he had been present in the class the previous day.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers of Assertive Sentences
Direct and indirect speech exercises and answers focusing on assertive sentences enable learners to grasp the nuances of reporting statements confidently and accurately.
Exercise 8:
Transform the following direct speech into indirect speech
(1) My aunt said, ‘Every mother loves her child.’ Ans: My aunt said that every mother loves her child.
(2) Mon said to me, ‘I shall go, but you will stay.’ Ans: Mon told me that she would go but I should stay.
(3) He said to his father, ‘I shall always carry out your order.’ Ans: He told his father that he would always carry out his order.
(4) She said, ‘I sang a song at today’s function.’ Ans: She said that she had sung a song at today’s function.
(5) He said to me, ‘You are wicked, so I shall not mix with you.’ Ans: He told me that I was wicked, so he would not mix with me.
Exercise 9:
Change the following sentences converting the direct speeches into indirect speeches.
(1) The teacher said to the boy, “You have forgotten the lesson.” Ans: The teacher told the boy that he had forgotten the lesson.
(2) The boy said, “I shall go out and play.” Ans: The boy said that he would go out and play.
(3) He said, “I am happy to be here today.” Ans: He said that he was happy to be there that day.
(4) They said, “We shall play the game again tomorrow.” Ans: They said that they would play the game again the next day.
(5) The boy said, “Two and two make four.” Ans: The boy said that two and two make four.
Exercise 10:
Change the form of narration from indirect speech into direct speech.
(1) She told them that she had lost her books and theirs too. Ans : “I have lost my books and yours too”, she told them.
(2) The princess says that she has lost her way. Ans: The princess says, “I have lost my way.”
(3) They say that they must keep their locality clean. Ans: They say, “We must keep our locality clean.”
(4) The girl says that those books are theirs, but that one is hers. Ans: The girl says, “These books are theirs, but this one is mine.”
(5) The Happy prince said that he had led the dance in the Great Hall. Ans: The Happy Prince said, “I led the dance in the great hall.”
Interrogative Sentences Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers
Engage with interrogative sentences through direct and indirect speech exercises and answers to sharpen your ability to convey questions effectively within different narrative frameworks.
Exercise 11:
(1) Mother said to her, ‘Are you feeling feverish?’ Ans: Mother inquired of her if she was feeling feverish.
(2) ‘Was it not a piece of luck?’ said Slavator. Ans: Salvtor wanted to know if that was not a piece of luck.
(3) The host said to me, ‘Have all the guests arrived?’ Ans: The host asked me whether all the guests had arrived.
(4) I said, ‘Do you know who will preside over the meeting?’ Ans: I asked whether he knew who would be presiding over the meeting.
(5) I said to the boy, ‘Did you pass the examination?’ Ans: I asked the boy if had passed the examination.
(6) She said to him, ‘Which of the books do you want to buy? Ans: She asked him which of the books he wanted to buy.
(7) The king said, ‘Who is not ready to due for his land, my countryman?’ Ans: The king asked his countrymen who was not ready to due for his land.
(8) He said to her, ‘Whose type writer are you using? Ans: He inquired of her whose type- writer she was using.
(9) The girl said to the strang ‘Whom do you want to see? Ans: The girl asked the stranger whom he wanted to see.
(10) The teacher said to the student, ‘Why are you late regularly? Ans: The teacher asked the student why he was late regularly.
Exercise 12:
Turn the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) Bulbuli said to her friend, “Will you come tomorrow?” Ans: Bulbuli asked her friend if she would on the next day.
(2) The policeman said to the stranger, “What are you looking for?” Ans: The police asked the stranger what he was looking for.
(3) Nikhil said to me, “Why do you look sad? Ans: Nikhil asked me why I looked sad.
(4) I said to her, “Did you take tea ?” Ans: I asked her if she had taken tea.
(5) The girl said to her mother, “Will you give me your bangles ?” Ans: The girl asked her mother if she would give her her bangles.
(6) Father said to me, “Why are you so upset?” Ans: Father asked me why I was so upset.
Exercise 13:
Change the following indirect speech into Direct speech.
(1) She asked me if I had called her. Ans: She said to me, “Did you call me ?”
(2) He asked me if I was writing a letter. Ans: He asked me, “Are you writing a letter ?”
(3) The man asked the child how he had got there. Ans: “How did you get here, child ?”, the man said.
(4) The police asked me if I could show my identity card. Ans: The police said to me, “Can you show your identity card ?”
(5) He asked us if we were attending the meeting that day. Ans: He said to us, “Are you attending the meeting today?”
(6) I asked her if she had taken medicine. Ans: I said to her, “Did you take medicine ?”
(7) Raja asked Dipu if he would go to school that day. Ans: Raja said to Dipu, “Will you go to school today?
Imperative Sentences Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers
Master imperative sentences through direct and indirect speech exercises and answers, refining your skill in conveying commands and requests within diverse linguistic contexts.
Exercise 14:
Change the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech.
(1) The teacher said, ‘Boys, go to your classes.’ Ans: The teacher ordered the boys to go to their classes.
(2) She said to him, ‘Please lend me your pen.’ Ans: She requested him to lend her his pen.
(3) The mother said to her son, ‘Wait here for me.’ Ans: The mother told her son to wait there for her.
(4) He said to me, ‘Go home at once.’ Ans: He advised me to go home at once.
(5) I said to my teacher, ‘Please explain the passage. Ans: I requested my teacher to explain the passage.
(6) The student said to the teacher, “Excuse me, sir.’ Ans: The student begged the teacher to excuse him.
(7) He said, ‘Friends, lend me your ears. Ans: Addressing them as friends, he requested them to lend him their ears.
Exercise 15:
(1) The teacher said to the students, “Keep quiet.” Ans: The teachers ordered the students to keep quiet.
(2) My teacher said to me. “Do not neglect your studies.” Ans: My teacher advised me not to neglect my studies.
(3) The man said to his son, “Always try to be honest.” Ans: The man advised it’s on to always try to be honest.
(4) Mother said to Raju, “Do not run in the sun.” Ans: Mother ordered Raju not to run in the sun.
(5) The man said to me, “Brother, please help me.” Ans: Addressing as a brother, the man requested me to help him.
(6) The students said, “Please allow us to play in the field.” Ans: The students requested to allow them to play on the field.
(7) He said to me, “Please give me some money.” Ans: He requested me to give him some money.
Exercise 16:
Change the following sentences from Indirect speech to Direct Speech of narration.
(1) He advised me not to waste my valuable time. Ans: He said to me, “Don’t waste your valuable time.”
(2) The grandson advised the children not to pluck flowers. Ans: The gardener said to the children, “Do not pluck flowers.”
(3) Tom forbade Sid to shake him. Ans: Tom said to Sid, “Don’t shake me.”
(4) The master ordered the servant to sort the door. Ans: The master said to the servant, “Shut the door.”
(5) The commander ordered the soldiers to stand at ease. Ans: The commander said to the soldiers, “Stand at ease.”
(6) Addressing as sethji, the vendor told him not to rob the poor. Ans: “Sethji, don’t rob the poor”, said the vendor.
(7) The doctor advised the patient to take proper vitamins to stay healthy. Ans: The doctor said to the patient, “Take proper vitamins to stay healthy.”
(8) The teacher ordered the students to do it then. Ans: The teacher said to the students, “Do it now.”
Direct and indirect speech Exercises and Answers with “Let”
Enhance your understanding of direct and indirect speech through exercises and answers featuring the usage of “let,” allowing you to effectively report permissions, suggestions, or proposals in various contexts
Exercise 17:
Change the following sentences from direct speech to indirect speech mode of narration.
(1) He said to her, ‘Let us go out for a walk,’ Ans: He proposed to her that they should go out for a walk.
(2) Mon said to Mohan, ‘Let us dis- cuss the matter,’ Ans: Mon suggested to Mohan that they should discuss the matter.
(3) The chairman said, ‘Let us put the motion to vote. Ans: The chairman proposed that they should put the motion to vote.
(4) I said to her, ‘Let us have some music,’ Ans: I proposed to her that we should have some music.
(5) ‘Let us hurry or we may miss the bus,’ said he, Ans: He urged all to hurry or they might miss the bus.
(6) She said, ‘Let me come in.’ Ans: She requested that she might be allowed to come in.
(7) He said, ‘Let her say whatever she likes.’ Ans: He said that she might say whatever she liked.
(8) He said, ‘Let me have a cup of coffee.’ Ans: He wished that he might have a cup of coffee.
(9) The player said to the captain, ‘Let me have a chance, please.’ Ans: The player requested the captain to let him have a chance.
(10) I said, ‘Let him work ever so hard, he cannot win the prize.’ Ans: He said that the visitor might be allowed to wait outside.
Exercise 18:
(1) Rahim said, “Let us decide the matter together.” Ans: Rahim suggested that they should decide the matter together.
(2) The boy said to me, “Let us play cricket.” Ans: The boy proposed that they should play cricket.
(3) He said, “Let me go home.” Ans: He wished that he might go home.
(4) He said to me, “Let him say whatever he likes.” Ans: He wished me that he might say whatever he liked.
(5) He shouted, “Let me go out. Ans: He shouted at me to go out.
Exercise 19:
Change the following sentences from indirect speech to direct speech mode of narration.
(1) She proposed that they should go to the cinema. Ans: She said, “Let us go to the cinema.”
(2) He suggested that they should drop the matter. Ans: He said, “Let us drop the matter”
(3) They suggested that they should make him give them their fears back. Ans: “Let’s make him give us our fares back,” they said.
(4) Shabnam proposed Chandni that they should go for a walk. Ans: “Let us go for a walk.” said Shabnam to Chandni.
(5) The leader suggested that they should hold a meeting the next day. Ans: The leader said, “Let’s hold a meeting tomorrow.”
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers of Optative Sentences
Practice direct and indirect speech with exercises and answers focusing on optative sentences, enabling you to accurately report wishes, prayers, or blessings while honing your linguistic proficiency.
Exercise 20:
Change the following from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech.
(1) Mother said, ‘May you be happy.’ Ans: Mother wished that I might be happy.
(2) He said to you, ‘May God bless you.’ Ans: He prayed that God might bless you.
(3) She said, ‘Had I been there!’ Ans: She wished that she had been there.
(4) He said to me, ‘May you succeed.’ Ans: He wished that I might succeed.
(5) They said, ‘Long live the leader.’ Ans: They prayed that the leader might live long.
(6) He said to me, ‘May your mother recover soon. Ans: He wished that my mother might recover soon.
(7) The monk said, ‘May peace prevail.’ Ans: The monk hoped that peace would prevail.
(8) The boy siad, ‘Had I the wings of a bird.’ Ans: The boy wished that he could have the wings of a bird.
Exercise 21:
(1) I said to him, “May you be happy.” Ans: I wished that he might be happy.
(2) Mother said to me, “May God bless you.” Ans: Mother prayed that God might bless me.
(3) He said, “May his soul rest in peace.” Ans: He prayed that his soul might rest in peace.
(4) The girl said, “Oh, had I the wings of a dove.” Ans: The girl wished that she could have the wings of a dove.
(5) I said to him, “May you live long.” Ans: I wished him that he might live long.
Exercise 22:
Change the following from Indirect Speech to Direct Speech.
(1) Nilima wished me that I might recover soon. Ans: Nilima said to me, “May you recover soon.”
(2) Mother wished him that God might grant him a long life. Ans : Mother said to him, “May God grant you a long life.”
(3) The holy man wished that peace might prevail. Ans: The holy man said, “May peace prevail.”
(4) She wished that Mother Teresa might recover from illness soon. Ans: She said, “May Mother Teresa recover from illness soon.”
(5) He wished that he could bring his departed friend back to life. Ans: He said, “Oh, if I could bring my departed friend back to life.”
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises of Exclamatory Sentences
Engage in direct and indirect speech exercises focusing on exclamatory sentences to refine your ability in reporting strong emotions or exclamations accurately within different narrative frameworks.
Exercise 23:
(1) The supporters said, ‘Hurrah! we have won?’ Ans: The supporter exclaimed in joy that they had won.
(2) The girl said, ‘How wonderful love is!’ Ans: The girl exclaimed in joy that love is wonderful.
(3) The teacher said, ‘Bravo! Well done!’ Ans: The teacher applauded his students by saying that they had done well.
(4) ‘Alas! I am undone’, said the women. Ans: They women cried out in sorrow that she was undone.
(5) He said, ‘Good bye, my friends !’ Ans: He bade his friends good bye.
(6) The old man said to the youth, ‘Fie! You are such a coward.’ Ans: The old man exclaimed that it was shameful for the youth to be such a coward.
(7) ‘How dirty the house is!’ he observed. Ans: He exclaimed in irritation that the house was very dirty.
(8) ‘Good God! I am saved’, said he. Ans: He exclaimed in the name of merciful God that he was saved.
Exercise 24:
(1) The boys triumphantly said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” Ans: The boys exclaimed in joy that they had won the match.
(2) The old man said to the girl, “May you be happy !” Ans: The old man wished the girl that she might be happy.
(3) He said, “What good news!” Ans: He exclaimed in joy that it was very good news.
(4) The children said, “How happy we were there!” Ans: The children gloomily said that they had been very happy there.
(5) He said to you. “May God bless you.” Ans: He wished you that God might bless you.
(6) My friend said to me. “What a fool you are!” Ans: My friend exclaimed in despair that she was a big fool.
Exercise 25:
(1) Piyali exclaimed in sorrow that she had lost her phone. Ans: “Alas! I have lost my phone”, said Piyali.
(2) Mother wished Roy that his dreams might come true. Ans: Mother said to Roy, “May your dreams come true.”
(3) The girl exclaimed that she had been very sensible. Ans: How insensible I have been!”, said the girl.
(4) The girl exclaimed in sorrow that she had torn her frock. Ans: The girl said, “Oh dear! I have torn my frock.”
(5) She exclaimed in sorrow that she was undone. Ans: She said, “Alas! I am undone.”
(6) They wished me happy birthday. Ans: They said to me. “Happy birthday!”
(7) The students bade their teacher good morning. Ans: “Good morning, Madam!”, said the students to the teacher.
Practice Worksheet for Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises
A . Change the following into reported speech .
1. Rita says, “Kishore sang a song”.
2. The saint said, “Man is mortal”
3. You said, “we are learning our lesson’.
4. He said to me, “My father went to Mumbai last week.
5. I said to her, “Are you leaving tonight?”
6. He said to her, “Can you lend me your umbrella?”
7. She said, “I saw a tiger here’.
8. The principal said, “well done! my boys”.
9. She said, “Let them play.”
10. I said to Harsh, “Please help me.”
B. Change the direct speech into Indirect Speech
1. He asked me, “Where has he gone?”
2. The Prime Minister said, “National Integrity will be preserved at all costs.
3. She said, “My uncle came yesterday.”
4. Sheela said to us, “You must work hard.”
5. They said, “We trust in God.”
6. The officer said to him. “You will be dismissed if you do not attend the office in time.'”
7. He said to me “I am reading a book.”
8. He said, “Thanks for reminding me.’
9. She said,” Keep this room open.’
10. I said to him, “I went there on Tuesday.”
C. Choose the correct option .
1. I advised him ____________ it.
(a) to not do
(b) not to do
2. She told me ____________ careful.
(c) that be
3. She asked me if I ____________ my lunch.
(b) have eaten
(c) had eaten
4. She asked me ____________ going to the movies
(a) that I was
(b) if was I
(c) if I was
5. The dentist suggested ____________ get a new toothbrush.
(b) that I should
(c) me that I should
6. She said that no one ____________ me
(c) had called
7. He asked me ____________ to deserve such a cruel punishment.
(a) what had he done
(b) what he had done
(c) that he had done
8. He promised he ____________ do it by the end of the week.
9. She said that ____________ me before.
(a) she hadn’t met
(b) she did not meet
(c) she will not meet
10. I requested her____________ me.
(b) to help
(c) that help
D. Complete the sentences in the reported speech.
1. The girl said that it ___________ to be there that evening.
(a) gave her great pleasure
(b) gives her great pleasure
(c) gives her great pleasure
2. The man said that he ___________ as soon as possible.
(a) must go
(b) had gone
(c) should be gone
3. She said that she ___________ to se any of them.
(a) does not want
(b) did not want
(c) had not wanted
4. The teacher says that if you work hard you ___________
(a) would pass
(b) will pass
5. He said that he ___________
(b) has won
(c) had won
6. He proposed that they ___________ for her return.
(a) shall wait
(b) will wait
(c) should wait
7. Alice exclaimed how clever ___________
(a) she was
(b) was she
(c) she has been
8. The young man asked which way she ___________
(a) has gone
(c) would go.
9. He asked me where ___________ going.
10. She requested them to wait there till she ___________
(a) returns
(b) returned
(c) will return

E. Complete the sentence in the reported speech.
1. Ravi said, “I love this place”.
Ravi said _______________
2. “Do you like football?” He asked me.
He asked me_______________
3. “I can’t drive a lorry”, he said.
He said _______________
4. “Be nice to your brother”, he said
He asked me _______________
5. “Don’t be nasty, “he said
He urged me _______________
6. “Don’t waste your money “she said,
She told the boys _______________
7. “What have you decided to do? “she asked
him. She asked him _______________
8. “I always wake up early”. he said,
He said_______________
9. “You should revise your lessons’, he said,
He advised the students _______________
10. “Where have you been? “he asked me
He wanted to know _______________
F. Complete the sentence in the reported speech.
1. She said, “I went to cinema yesterday,”
She said _______________
2. You said, “I will do this for him.”
You said _______________
3. He said, “I am writing a test tomorrow,
4. She said, “I am not hungry now”,
5. They said, “We have never been here before.”
They said _______________
6. They said, “We were in London last week.”
7. He said, “They won’t sleep.”
8. “Have you been shopping?” he asked us.
9. She said, “It is very quiet here.
10. “I don’t speak Italian”, she said.
She said_______________
G. Read the dialogue and complete the following passage.
Susan: Why have you not brought my party dress? Jenny: I haven’t brought it because I had gone to my uncle’s house with my parents, so I forgot to keep it. Susan: Don’t give me silly excuses. I want to know the truth. Jenny: I am sorry Susan. I was chatting with my friends till late. I forgot that you needed it urgently today.
Susan asked Jenny (a) …………… Jenny said that she (b) …………… . Susan (c) …………… . Jenny said that she was sorry and further added that she was chatting with her friends till late and she had forgotten that Jenny needed it urgently that day.
H. Read the following conversation and complete the passage that follows.
Dilip: I’ve been watching the sea and there hasn’t been any trace of a ship. Ralph: I told you yesterday too that we’ll be rescued, so have patience. Dilip: Why do you ask me to keep quiet whenever I say something? Ralph: Have you ever said anything sensible?
Dilip said (a) ………… . Ralph replied (b) ………… and so asked him to have patience. Dilip angrily asked Ralph (c) ………… to which Ralph wanted to know (d) …………
Direct and Indirect Speech Answers Key
1. Rita says that Kishore sang a song.
2. The saint said that the man is mortal.
3. You said that you were learning your lesson.
4. He hold me that his father had gone to Mumbai the previous week.
5. I asked her if she was leaving that night.
6. He asked her if she could lend him her umbrella.
7. She said that she had seen a tiger there.
8. The principal exclaimed with applause that the boys had done well.
9. She suggested that they should be allowed to play.
10. I requested Harsh to help me.
1. He asked me where he had gone.
2. The Prime Minister declared that the National Integrity would be preserved at all costs.
3. She said that her uncle had come the previous day.
4. Sheela told us that we must work hard.
5. They said that they trusted in God.
6. The officer warned him that he would be dismissed
if he did not attend the office in time.
7. He told me that he was reading a book.
8. He thanked me for reminding him.
9. She ordered to keep that room open.
10. I told him that I had gone there on Tuesday.
1. (b) not to do
2. (b) to be
3. (c) had eaten
4. (c) if I was
5. (b) that I should
6. (c) had called
7. (b) what he had done
8. (b) would
9. (a) she hadn’t met
10. (b) to help
D. Complete the sentences in reported speech.
1. (a) gave her great pleasure.
2. (a) must go
3. (b) did not want
4. (b) will pass
5. (c) had won
6. (c) should wait
7. (a) she was
8. (b) had gone
9. (a) I was
10. (b) returned
E. Complete the sentence in reported speech.
1. that he loved that place
2. whether I liked football
3. that he couldn’t drive a lorry
4. to be nice to my brother
5. not to be nasty
6. not to waste their money
7. what he had decided to do
8. that he always wake up early
9. to revise their lessons
10. where I had been
F. Complete the sentence in reported speech.
1. that she had gone to cinema the previous day.
2. that you would do that for him.
3. that he will be writing a test the next day.
4. that she was not hungry then.
5. that they had never been there before.
6. that they had been in London the previous week.
7. that they wouldn’t sleep.
8. whether we had been shopping.
9. that it was very quiet there.
10. that she didn’t speak Italian.
G. Read the dialogue and complete the following passage
(a) why she had not brought her party dress
(b) hadn’t brought it as she had gone to her uncle’s house with her parents; so she had forgotten to keep it
(c) told her not to give silly excuses and further said that she wanted to know the truth.
(a) that he had been watching the sea and that there had not been any trace of a ship
(b) that he had told him the day before that they would be rescued
(c) why he asked him to keep quiet whenever he said something
(d) if he had ever said anything sensible
FAQs on Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises and Answers
Q: what’s the purpose of the indirect speech.
A: Indirect speech allows us to convey someone else’s words without quoting them verbatim. It’s useful for summarizing and paraphrasing.
Q: Are tense changes mandatory in indirect speech?
A: Yes, tense changes are often necessary to accurately reflect the timing of the original statement.
Q: Can reporting verbs be used interchangeably?
A: While reporting verbs can be interchangeable to some extent, their nuances can impact the meaning of the reported speech.
Q: Is it possible to transform any direct speech into indirect speech?
A: Yes, most direct speech can be converted into indirect speech, although some cases may require adjustments.
Q: How can I identify indirect speech in a sentence?
A: Look for keywords like “said,” “asked,” or other reporting verbs, as well as changes in pronouns, tenses, and time expressions.
Q: Why is mastering direct and indirect speech important?
A: Mastering these skills enhances communication clarity, adds variety to language use, and fosters effective expression.
Conclusion:
Direct and indirect speech exercises and answers are invaluable tools for effective communication. By honing this skill, you’ll not only convey information accurately but also showcase your language expertise. Remember that practice makes perfect, and the more you engage in these exercises, the more naturally you’ll incorporate them into your everyday language use.
Related Posts:

Simple English Grammar

- Direct Indirect Speech
Direct and Indirect Speech Online Exercise for Class 6
Exercise 1 :
Change the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech sentences. This work out will make you understand the concept of the language more efficiently:
- I said, “I am waiting for my friend”.
- The villager said, “It becomes difficult for us to survive without electricity here specially at nights”.
- Mother told us, “You will return home before 6 o’ clock in the evening”.
- I said to the servant, “Please get a glass of water for me”.
- Pamela said to me, “I have received the gift yesterday”.
- Rajiv said to me, “I am leaving for America tomorrow”.
- Manish said to us, “We will win the tournament”.
- I said to Kiran, “I have not taken the pen from here”.
- The boss said to the employees, “Stop the work and come to my cabin now”.
- We told to the class teacher, “Give us more time till next week.”
- I said that I was waiting for my friend.
- The villager said that it became difficult for them to survive without electricity there specially at nights.
- Mother ordered us to return home before 6 o’ clock in the evening.
- I requested the servant to get a glass of water for me.
- Pamela said to me that she had received the gift the previous day.
- Rajiv said to me that he was leaving for America the next day.
- Manish said to us that we would win the tournament.
- I said to Kiran that I had not taken the pen from there.
- The boss ordered the employees to stop the work and go to his cabin then.
- We requested the class teacher to give us more time till next week.
Exercise 2:
Change the following indirect speech sentences into direct speech sentences. This work out will make you understand the concept of the language more efficiently:
- Paltu asked his sister why she was standing there.
- Manju asked to us where we should go for the party.
- Lily asked Peter what he was doing the previous night.
- The patient asked the nurse if she would let him drink cold-drink.
- The stranger asked the local man which the way to the bakery shop was.
- Mrs. Singh told to her husband that their baby had been playing the whole day.
- Papa asked me if I needed anything from the store that day.
- Alka requested us to drink mango shake before leaving for our home.
- Juhi asked me why I was not on speaking terms with Roohi.
- The policeman asked the guard why he was not at the gate, when the thieves entered into.
- Paltu said to his sister, “Why are you standing here?”
- Manju said to us, “Where shall we go for the party?”
- Lily said to Peter, “What were you doing last night?”
- The patient said to the nurse, “Will you let me drink cold-drink?”
- The stranger said to the local man, “Which is the way to the bakery shop?”
- Mrs. Singh said to her husband, “Our baby was playing the whole day.”
- Papa said to me, “Do you need anything from the store today?”
- Alka said to us, “Please drink mango shake before leaving for your home.”
- Juhi asked me, “Why are you not on speaking terms with Roohi?”
- The policeman said to the guard, “Why were you not at the gate, when the thieves entered into?”
Adjective Exercise for Standard 6
Conjunction online exercise for standard 6.
Related posts
Imperative sentence example (आज्ञासूचक वाक्य), direct and indirect speech, direct and indirect speech online exercise for class 4, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Question and Answer forum for K12 Students

Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 6 CBSE With Answers
When we use the exact words of the speaker, it is called direct speech. Indirect or Reported Speech refers to a sentence reporting what someone has said.
Basic English Grammar rules can be tricky. In this article, we’ll get you started with the basics of sentence structure, punctuation, parts of speech, and more.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 6 CBSE With Answers PDF
When we do not quote the exact words of a speaker while we report what he/she said – it is known as reported speech.
There are two parts of speech – Reported Verb (R.V.) and Reported Speech (R. S)
She says, “I like gold fish.” (R.V.) (R. S.)
The sentence in the question tag is called Direct speech. The sentence without the question tag is called Indirect speech.
When the Reporting verb is in present tense or future tense then there will be no change in reporting speech except in the change of pronouns, place and time of expression. Example:
- He says, “I write poems.”
- He says that he writes poems.
While converting ‘Direct’ into ‘Indirect’ Speech pronouns, tenses, place and time of expression are to be considered.
To convert direct speech into indirect speech ‘that’ conjunction is used to join the reported verb to reported speech.
The pronouns of the direct speech are changed to indicate the relations with the reporter and the hearer. The formula for converting pronouns of Direct speech
Remember this equation = RV/RS = Son/123 = S = Subject, O = Object, N = No change
- If the RS is in first-person, it shall be changed according to the ‘Subject’ of the RV.
- If RS is in second-person it shall be changed according to the ‘Object’ of the RV.
- if RS is in third-person then there will be no change.
Indirect:-She says that her dad likes roasted chicken.
Place, demonstratives and time expressions:-Place, demonstratives and time expressions change if the context of the reported statement (i.e. the location and/ or the period of time) is different from that of the direct speech.
In the following table, you will find the different changes in place; demonstratives and time expressions.
| today | that day |
| now | then |
| yesterday | the day before |
| … days ago | … days before |
| last week | the week before |
| next year | the following year |
| tomorrow | the next day / the following day |
| here | there |
| this | that |
| these | those |
“These dresses are not suitable for the at the occasion,” says Ditya. “We need to wear some traditional clothes like salwar – kameez on this occasion,” says Ditya.
The modal verbs could, should, would, might, needn’t, ought to, used to do not normally change.
- He said, “She might be right.”
- He said that she might be right.
Other modal verbs may change:
| Can | “I can do it.” | He said he could do it. |
| May | “May I go out?” | He wanted to know if he might go out. |
| Must | “She must apply for the job.” | He said that she must/had to apply for the job. |
| Will | “They will call you.” | He told her that they would call her. |
Universal truths remain unchanged in reported speech. Example:
- The guru said, “The sun rises in the east.”
- The guru said that the sun rises in the east.
Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheets for Class 6 CBSE
A. Read the dialogues given below and change it to indirect speech.
1. Harish: “Poonam is at home.” Harish said (that) _____________
2. Karan: “Learners often read a book.” Karan told me (that) _____________
3. Suman: “I’m watching TV.” Suman said to me (that) _____________
4. Simran: “Kanu was ill.” Simran said (that) _____________
5. Palak: “The girls helped in the house.” Palak told me (that) _____________
6. Roma: “I am going to ride a skateboard.” Roma said to me (that) _____________
7. Ronnit and Kajal: “We have cleaned the windows.” Ronnit and Kajal told me (that) _____________
8. Harshit: “I didn’t have time to do my homework.” Harshit remarked (that) _____________

Direct and Indirect Speech English Grammar For Class 6
- No Comments
Direct and Indirect Speech
There are two different ways speaker in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration: It contains the actual Example: Sarla said, “My father has a roaring business in Delhi.” In this sentence, the actual words of the speaker are given within inverted commas without any change. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration: It reports the speaker’s speech without quoting the actual words. Example: Sarla said that her father had a roaring business in Delhi. Direct Speech or Direct Narration has two parts: (i) Reporting Verb and (ii) Reported Speech.
Reporting Verb: The verb which introduces the reported speech is called the reporting verb. Reported Speech: The actual words of the speaker given in inverted commas are called the reported speech. In the above sentence, “said” is the Reporting Verb and “My father has a roaring business in Delhi” is the Reported Speech. Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and the Indirect Speech. (a) In Direct Speech 1. The reported speech is put within inverted commas. 2. The reporting verb is separated from the reporting speech by a comma. 3. The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter. 4. In the reported speech, we may use any tense required by the sense and any kind of sentence.
(b) In Indirect Speech 1. Inverted commas are not used. 2. The comma separating the reporting verb from the reported speech is removed. 3. The reported speech is introduced by some Conjunction (that, if, what, why, etc.). 4. The tense of the reported speech changes according to the reporting verb. 5. The tense of the reporting verb is never changed. 6. All kinds of sentences change into assertive ones. RULES FOR CHANGE OF TENSES Rule 1: If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the Tense of the Verb in the reported speech remains unchanged. 1. Direct : Sonia says, “Monica will meet me on Monday.” (Simple Present) Indirect : Sonia says that Monica will meet her on Monday. (Unchanged) 2. Direct : Rajesh says, “She has brought a fair name to her family.” (Simple Present) Indirect: Rajesh says that she has brought a fair name to her family. (Unchanged) 3. Direct : The servant will say, “Dinner is ready.” (Simple Future) Indirect: The servant will say that dinner is ready. (Unchanged) Rule 2: If the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the Tenses in the Reported Speech are changed according to the Past Tense. The Simple Present is changed into the Simple Past Tense (play-played; do-did, etc.). 1. Direct : Anil said, “I write a letter.” (Past) (Simple Present) Indirect: Anil said that he wrote a letter. 2. Direct : Sohan said, “Rama works efficiently.” (Past) (Simple Present) Indirect : Sohan said that Rama worked efficiently. The Present Continuous is changed into Past Continuous is/am/are playing-was/were playing). 1. Direct : He said, “Rohan is singing a sweet song.” (Past) (Present Continuous) Indirect: He said that Rohan was singing a s weet song. 2. Direct : The students said, “The teachers are teaching a lesson.” (Past) (Present Continuous) Indirect: The students said that the teachers were teaching a lesson.
The Present Perfect is changed into the Past Perfect (has/have played-had played). 1. Direct : She said, “The bus has arrived at the bus stand.” (Past)(Present Perfect) Indirect : She said that the bus had arrived at the bus stand. 2. Direct : The teacher said, “All the boys have gone to their homes.” (Past) (Present Perfect) Indirect: The teacher said that all the boys had gone to their homes. The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is changed into the Past Perfect Continuous Tense. (has been/have been playing-had been playing) 1. Direct : Mohit said, “Malini has been waiting for a long time.” (Past) (Present Perfect Continuous) Indirect : Mohit said that Malini had been waiting for a long time. 2. Direct : Ramesh said, “Dinesh has been playing since morning.” (Past) (Present Perfect Continuous) Indirect : Ramesh said that Dinesh had been playing since morning. The Simple Past is changed into the Past Perfect. (played had played; did not play-had not played) 1. Direct : Mohit said, “Rakesh wrote a letter.” (Simple Past) (Past) Indirect : Mohit said that Rakesh had written a letter. 2. Direct : The mother said, “Shanti waited for her sister.” (Past) (Simple Past) Indirect: The mother said that Shanti had waited for her sister.
The Past Continuous Tense is changed into the Past Perfect Continuous Tense. (was/were playing had been playing) 1. Direct : Rama said, “She was solving the sums.” (Past) (Past Continuous) Indirect : Rama said that she had been solving the sums. 2. Direct : She said, “Sarita was collecting information.” (Past) (Past Continuous) Indirect : She said that Sarita had been collecting information. The Past Perfect Tense remains unchanged. Direct : Ashish said, “Rohan had already finished his work.” (Past) (Past Perfect) Indirect : Ashish said that Rohan had already finished his work.
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense also remains unchanged. Direct : The father said, “He had been working for an hour.” (Past) (Past Perfect Continuous) Indirect: The father said that he had been working for an hour. Note the changes given below in case the reporting verb is in Past Tense
| play, plays | played | |
| do not play/does not play | did not play | |
| is, are, am | was, were | |
| has, have | had | |
| played | had played | |
| did not play | had not played | |
| was, were | had been | |
| had | had | |
| will | would | |
| shall | should/would | |
| can | could | |
| may | might |
Some examples are given below: 1. Direct: Rajesh said, “I am in the room.” Indirect: Rajesh said that he was in the room. 2. Direct : Pritam said, “He will tell the truth.” Indirect : Pritam said that he would tell the truth. 3. Direct : Priyanka said, “Priya will help her.” Indirect Priyanka said that Priya would help her. 4. Direct : He said, “It may rain in the evening.” Indirect : He said that it might rain in the evening. 5. Direct : :Shalini said, “She can swim in the river.” Indirect: Shalini said that she could swim in the river. 6. Direct : Raja said, “There is no sugar in the tea.” Indirect : Raja said that there was no sugar in the tea. 7. Direct : The boys said, “They have no homework to do.” Indirect: The boys said that they had no homework to do. 8. Direct: Mother said, “There are no apples in the basket.” Indirect: Mother said that there were no apples in the basket. Rule 3 (Exception to Rule 2): If the reported speech expresses a universal truth or a habitual fact, its tense is not changed. Examples: 1. Direct: The teacher said, “The Earth moves around the Sun.” (The reported speech is a Universal Truth). Indirect: The teacher (Unchanged) said that the Earth moves around the Sun. 2. Direct : She said, “She is an early riser.” (A habitual fact) Indirect : She said that she is an early riser. (Unchanged) 3. Direct : The science master said, “Heat expands gases.” (A Universal Truth) Indirect: The science master said that heat expands gases. (Unchanged) Exercise 1 Change the following sentences into Indirect Form of Speech: 1. The teacher said, “He is the best student.” 2. She said, “Mother is cooking food.” 3. The doctor said, “The patient will be all right soon.” 4. The father said, “Radha is working hard.” 5. The principal said, “The students will remain in discipline in the school.” 6. The farmer said, “It may rain.” 7. Shakuntala said, “Father will not attend the meeting.” 8. She said, “Manu was living in Japan.” 9. The inspector said, “The police were trying to arrest the culprit.” 10. Surjit Singh said, “They have planted a tree in the school compound.” 11. The postman said, “He will deliver all the letters in time.” 12. The doctors said, “Swine flu is not a serious disease.” 13. Our teachers said, “Honesty is the best policy.” 14. She said, “My mother does not eat meat at all.” 15. He said, “He daily goes out for a walk.” RULES FOR CHANGE OF PRONOUNS Rule 1: The First person pronouns of the reported speech are changed according to the subjects of the reporting verbs. Examples: 1. Direct : I said, “I have taken my dinner.” Indirect : I said that I had taken my dinner. 2. Direct : You said, “I have taken my dinner.” Indirect: You said that you had taken your dinner. 3. Direct : She said, “I have taken my dinner.” Indirect : She said that she had taken her dinner. 4. Direct : The teacher said, “I have taken my dinner.” Indirect : The teacher said that he (the teacher) had taken the dinner.
Rule 2: The Second person pronouns of the reported speech are changed according to the objects of the reporting verbs. Note: Change ‘said to’ of the reporting verb into ‘told’. Also, told is not followed by preposition ‘to’. Examples: 1. Direct : Mihir said to me, “You have taken your dinner.” Indirect Mihir told me that I had taken my dinner. 2. Direct : Mihir said to you, “You have taken your dinner.” Indirect: Mihir told you that you had taken your dinner. 3. Direct: Mihir said to him, “You have taken your dinner.” Indirect: Mihir told him that he had taken his dinner.
Rule 3: The Pronouns of the third person remain unchanged. Examples: 1. Direct : I said to my sister, “She has taken her dinner.” Indirect: I told my sister that she had taken her dinner. 2. Direct : She said to me, “She is doing her homework.” Indirect: She told me that she was doing her homework. Exercise 2 Change the following into Indirect Form of Speech: 1. Ram said, “I am punctual.” 2. His brother said, “My purse has been stolen.” 3. Radha said to Sharmila, “I can help you solve the problem.” 4. The officer said to the peon, “You should reach the office in time.” 5. My brother said, “I have been very tired.” 6. She said, “I am quite well.” 7. You said to her, “You are in the wrong.” 8. The passenger said, “I shall go to Delhi.” 9. You said to her, “She is quite lazy.” 10. You said to him, “I have warned my servant many times.” 11. He said to her, “I have found your purse.” 12. He said to me, “You are an intelligent boy.” 13. Smith said to the peon, “You have not obeyed my orders.” 14. The saint said, “God is everywhere.” 15. Sheela said to her mother, “I want to go on a tour.” 16. The teacher said, “A friend in need is a friend indeed.” 17. Lalit said to me, “I have lost my pen.” 18. Ramesh said to Suresh, “You waited for him.” 19. The boys said to the teacher, “We are going to see the match in the ground.”
Change of words denoting nearness words are changed if the reporting verb is in the Past Tense: Direct Speech/Indirect Speech
| This | becomes | That |
| These | becomes | Those |
| Here | becomes | There |
| Thus | becomes | So |
| Now | becomes | Then |
| Ago | becomes | Before |
| Today | becomes | That day |
| Tonight | becomes | That night |
| Yesterday | becomes | The previous day/the day before |
| Tomorrow | becomes | The next day/the following day |
| Last night | becomes | The previous night |
| Next year/week | becomes | The following year/week |
Examples: 1. Direct : He said, “I am feeling out of sorts today.” Indirect He said that he was feeling out of sorts that day. 2. Direct : She said, “Father will have reached home by now.” Indirect She said that father would have reached home by then. 3. Direct : Sonam said, “I may go to Chandigarh tomorrow.” Indirect: Sonam said that she might go to Chandigarh the next day. 4. Direct : They said, “We saw the movie three days ago.” Indirect They said that they had seen that movie three days before.
Exercise 3 Change the following sentences into Indirect Form of Speech and rewrite: 1. He said, “I went to the zoo yesterday.” 2. Shankar said, “I shall go to Bhopal tomorrow.” 3. He said to me, “I am not going to school today.” 4. My father said, “He will construct a house here.” 5. He said, “I saw Mr. Sharma this morning.” 6. The teacher said, “Tomorrow will be a holiday.” 7. Dinesh said, “I cannot waste my time now.” 8. She said, “I had a peaceful sleep last night.” 9. The visitor said, “I came here three days ago.” 10. Hari said, “Rice does not grow here.” CONVERSION OF INTERROGATIVE SENTENCES (QUESTIONS) INTO INDIRECT SPEECH While changing direct speech into indirect speech, the following changes are made: (i) ‘said’ or ‘said to’ is changed into ‘asked, enquired or demanded’, etc. (ii) After removing inverted commas, use ‘if’ or ‘whether’, when the question begins with ‘Do, Does, Is, Are, Am, Has, Have, Did, Was, Were, Had, Will, Shall, Can, May (helping words), etc.’ (iii) The interrogative sentence is changed into an assertive sentence. (iv) The sign of interrogation mark is removed. (v) If relative pronouns like Who, Whose, Whom, When, Where, Why, What, How, Which, make the sentences Interrogative, these words are retained after removing inverted commas. (vi) Tenses, Pronouns are changed according to the rules already stated. Examples: 1. Direct : He said to me, “Do you play any game?” Indirect He asked me if (whether) I played any game. 2. Direct : I said to my friend, “Are you going to join some academy?” Indirect I asked my friend if he was going to join some academy. 3. Direct : The teacher said to the boys, “Why are you making a noise?” Indirect: The teacher asked the boys why they were making a noise. 4. Direct : My friend said to him, “Did you attend the meeting yesterday?” Indirect My friend asked him if he had attended the meeting the previous day. 5. Direct : The clerk said to me, “What do you want?” Indirect: The clerk asked me what I wanted. Exercise 4 Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: 1. My mother said to me, “Where do you come from?” 2. The teacher said, “Boys, have you understood the sum?” 3. He said, “Who is waiting for me?” 4. My mother said to me, “Shall I write a letter to him tomorrow?” 5. I said to the bookseller, “Can you show me some good books?” 6. His teacher said to him, “Where have you come from?” 7. “Have you taken the breakfast?” said Mohan to his brother. 8. They said to us, “Did you learn your lesson?” 9. Our teacher said to him, “Why are you disturbing the class?” 10. The stranger said to me, “Does he know the way to the market?” 11. You said to him, “Can you cross this river?” 12. “Do you respect your elders?” said I to Roma. CONVERSION OF IMPERATIVE SENTENCES INTO INDIRECT SPEECH Rules: Change the Reporting Verb according to its sense. 1. Request: request, beg, entreat, ask, etc. 2. Advice: advise, forbid, urge, etc. 3. Order: order, command, etc. 4. The imperative word is changed into infinitive one. 5. No conjunction is used to introduce the reported speech. 6. If the conjunction that is used, ‘should’ is placed before the infinitive. 7. Observe the rules for the change of pronouns and words showing nearness.
Examples: 1. Direct : Father said to me, “Put the book on the table.” Indirect Father told me to put the book on the table. 2. Direct : The teacher said to the boys, “Work hard and be regular in your studies.” Indirect: The teacher advised the boys to work hard and be regular in their studies. 3. Direct : The officer said to the peon, “Bring me a glass of water.” Indirect: The officer ordered the peon to bring him a glass of water. 4. Direct: The Principal said to the boys, “Do not pluck the flowers.” Indirect : The Principal forbade the boys to pluck the flowers. or Indirect : The Principal ordered the boys not to pluck the flowers. 5. Direct : Ramesh said to Leela, “Please help me in this matter.” Indirect: Ramesh requested Leela to help him in that matter. 6. Direct : Sonu said to his father, “Let us go to Shimla in summer holidays.” Indirect: Sonu suggested to his father that they should go to Shimla in summer holidays. Exercise 5 Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: 1. The student said, “Let me go home now, Sir.” 2. The master said to the servant, “Send the visitors inside.” 3. The teacher said, “Open your books, boys.” 4. The commander said, “Attack the enemy.” 5. The teacher said, “Do not disturb the class.” 6. The beggar said, “Give me alms.” 7. “Please do me a favour,” said he to you. 8. The boys said to their teacher, “Allow us to go on a tour to Agra.” 9. The teacher said to the boys, “Stand up on the benches.” 10. Father said to me, “Go and wash your hands.” 11. He said to me, “Have a cup of tea with me, please.” 12. The old man said to his child, “My son, don’t make a noise.” 13. Mother said, “Son, always help the needy.” 14. The boys said to the teacher, “Repeat this lesson, please.” 15. “Do not spit on the floor, boys,” said the teacher. CONVERSION OF EXCLAMATORY AND OPTATIVE SENTENCES TO INDIRECT SPEECH In reporting a wish or exclamation in Indirect Speech: 1. The Reporting Verb is changed into wish, bless, cry, exclaim, curse, etc. with phrases such as ‘with regret’, ‘with delight or joy’, ‘with sorrow’, etc., wherever necessary. 2. The interjections and exclamatory words, such as ‘Oh, well, hurrah, , pray, alas, bravo’, are omitted and their sense is expressed by means of phrases. 3. The exclamatory sentences are changed into statements before they are converted into indirect speech. 4. The mark of exclamation is omitted. 5. Other rules are followed as explained earlier. Examples: 1. I said, “How sad he is!” I exclaimed that he was very sad. 2. He said, “Hurrah! We have won the match.” He exclaimed with joy that they had won the match. 3. The poor man said to him, “May you live long!” The poor man wished that he might live long. Exercise 6 Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: 1. She said, “May you live long!” 2. The father said to his son, “May God bless you with a good fortune!” 3. The merchant said, “Alas! I am undone.” 4. The visitor said, “What a beautiful sunset!” 5. The player said, “Hurrah! India has won the cricket match.” 6. She said, “Alas! I have lost my gold ring.” 7. The spectators said, “Bravo! Well played, Ram.” 8. She said, “How lovely the child is!” 9. “Oh! I am hurt!” said the captain. 10. She said to me, “Wish that I were rich!”
Exercise 7 Change the following sentences into Indirect Speech: 1. He says, “I daily go out for a walk.” 2. You will say to them, “We cannot cross the lake.” 3. He said to me, “I am solving the sums of Arithmetic.” 4. The teacher said, “Girls, do not make a noise.” 5. I said to him, “May I help you?” 6. The teacher said to me, “Can you tell me how you solved the sum?” 7. She said to me, “Who taught you English?” 8. The General said to the soldiers, “March forward.” 9. The king said to the executioner, “Put the prisoner to death.” 10. The gardener said, “Do not pluck the flowers.”
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Ncert books.
- NCERT BOOKS 12
- NCERT BOOKS 11
- NCERT BOOKS 10
- NCERT BOOKS 9
- NCERT BOOKS 8
- NCERT BOOKS 7
- NCERT BOOKS 6
- NCERT BOOKS 5
- NCERT BOOKS 4
- NCERT BOOKS 3
- NCERT BOOKS 2
- NCERT BOOKS 1
NCERT SOLUTIONS
- Solutions Class 12
- Solutions Class 11
- Solutions Class 10
- Solutions Class 9
- Solutions Class 8
- Solutions Class 7
- Solutions Class 6
- Solutions Class 5
- Solutions Class 4
- Solutions Class 3
- Solutions Class 2
- Solutions Class 1
CBSE SYLLABUS
- CBSE Syllabus Class 12
- CBSE Syllabus Class 11
- CBSE Syllabus Class 10
- CBSE Syllabus Class 9
- CBSE Syllabus Class 8
- CBSE Syllabus Class 7
- CBSE Syllabus Class 6
- CBSE Syllabus Class 5
- CBSE Syllabus Class 4
- CBSE Syllabus Class 3
- CBSE Syllabus Class 2
- CBSE Syllabus Class 1
SAMPLE PAPERS
- Sample Paper Class 12
- Sample Paper Class 11
- Sample Paper Class 10
- Sample Paper Class 9
- Sample Paper Class 8
- Sample Paper Class 7
- Sample Paper Class 6
- Sample Paper Class 5
- Sample Paper Class 4
- Sample Paper Class 3
- Sample Paper Class 2
- Sample Paper Class 1
ROCOMMENDED BOOKS
- RD Sharma Class 6 to 12
- RS Aggarwal Class 6 to 12
- NCERT Urdu Class 1 to 12
© 2020 Edugross. All rights reserved
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
CBSE Class 6 English Grammar Reported Speech
August 28, 2019 by Sastry CBSE
1. There are two different ways in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration.
2. (a) Direct Speech contains the actual words of the speaker ; as— Sarla said, “My father has a roaring business in Mumbai” He said to me, “I am feeling unwell today.” In these sentences, actual words of the speaker are given within inverted commas without any change. (b) Indirect Speech gives the substance of the speaker’s actual words and not the exact words spoken by him or her ; as— Sarla said that her father had a roaring business in Mumbai He told me that he was feeling unwell that day.
3. The actual words of the speaker, given within ‘ inverted commas’ are called the Reported Speech. In the same way, the Verb which introduces the Reported Speech is called the Reporting Verb. In the sentence above ‘said’ is the Reporting Verb and ‘My father has a roaring business in Mumbai’ is the Reported Speech.
Reporting Verb and Reported Speech. Look at the following sentences : Radha says, “I shall’ finish my home-work today.” Sushma said to Pushpa, “Show me your dolls.”
The verbs ‘says and said’ in the above sentences are ‘Reporting Verbs’. The exact words of the speaker given within the inverted commas are ‘Reported Speech’.
4. Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and Indirect Speech :
In the Direct Speech
- The Reported Speech is put within Reported (Inverted) Commas.
- The Reported Speech and the Reporting Verb are separated by a Comma.
- The first word of the Reported Speech begins with a capital letter.
Transformation of Direct Speech into Indirect Speech I. Rules for the Change of Tense
| If the Reporting Verb is in the Present or Future Tense, the Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change. |
Examples 1. Direct: Rajesh says, “She has brought fame to her family.” Indirect: Rajesh says that she has brought fame to her family. 2. Direct: Rohit has said, “I cannot displease my friend.” Indirect: Rohit has said that he cannot displease his friend. 3. Direct: I shall say, “I went to Agra on Monday.” Indirect: I shall say that I went to Agra on Monday. 4. Direct: She will say, “I have sent him a present.” Indirect:She will say that she has sent him a present.
| if the Reporting Verb is in the Past Tense, the tense of the verb in the Reported Speech must be changed into the corresponding Past Tense. |
Examples 1. Direct: I said, “I am speaking the truth.” Indirect: I said that I was speaking the truth. 2. Direct: The teacher said, “Boys fail because they do not study regularly.” Indirect: The teacher said that boys Jailed because they did not study regularly.
Exception to Rule II (i) If there is a Universal Truth or Habitualfact in the Reported Speech, the Tense of the verb is never changed ; as— 1. Direct : He said, “Face is the index of mind.” (Proverbial truth) Indirect: He said that face is the index of mind. 2. Direct: The teacher said, “The earth rotates round its axis.” (Geographical truth) Indirect: The teacher said that the earth rotates round its axis. 3. Direct: Horatius said, “Death comes sooner or later.” (Universal truth) Indirect : Horatius said that death comes sooner or later.
(ii) The Tense of the Verb in the Reported Speech does not change if the reported speech states a past historical fact; as— 1. Direct : He said, “India became free on 15th August, 1947.” Indirect : He said that India became free on 15th August, 1947. 2. Direct : She said, “Her father lived at Lahore for ten years.” Indirect : She said that her father lived at Lahore for ten years.
(iii) If two such actions are given in the Reported Speech which take place at the same time, the Past Indefinite or Continuous Tense does not change. Direct: He said, “Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute.” Indirect: He said that Mohan was singing a song while Gopal was playing on a flute. Examples 1. Direct: She said, “I am a top-class singer.” Indirect: She said that she was a top-class singer. 2. Direct: We said, “He is writing a poem.” Indirect: We said that, he was writing a poem. 3. Direct: He said, “It may rain tonight.” Indirect: He said that it might rain that night. 4. Direct: He said, “A devil ever remains a devil.” Indirect: He said that a devil ever remains a devil.
The future tense of the reported speech Is changed as under : Future Indefinite—would / should Future Continuous—would/should be Future Perfect—would/should have Future Perfect Continuous—would/should have been Examples 1. Direct: You said, “He is a very good athlete.” Indirect: You said that he was a very good athlete. 2. Direct: I said, “I have finished my work.” Indirect: I said that I had finished my work. 3. Direct: He said, “Her parents will pay a visit to Delhi.” Indirect: He said that her parents would pay a visit to Delhi.
B. Interrogative Sentences
Conversion Of Interrogative Sentences A From Direct Into Indirect
| 1. The Reporting Verb is changed, into ‘ask. enquire, inquire or demand’ 2. No conjunction is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the question begins with (an interrogative) word ; such as—what, who, whose, which, when, where, why, how. whom etc. 3. If or whether is used to introduce the Reported Speech if the reported speech has no question word. 4. Change the questions into statements. Put Jail stop in place of mark of interrogation (?). |
Examples (a) Questions beginning with a Helping Verb 1. Direct: He said to her, “Shall I accompany you to Agra ?” Indirect: He asked her if he would (should) accompany her to Agra. 2. Direct: She said to him, “Had I been absenting myself from school for a month ?” Indirect: She asked him if she had been absenting herself from school for a month. 3. Direct: He said to us, “Has she been spinning since yesterday ?” Indirect: He asked us if she had been spinning since the previous day. 4. Direct: They said to you, “Shall we be going on picnic tomorrow ?” Indirect: They asked you if they would be going on picnic the next day. 5. Direct: I said to her, “Will you have ironed your clothes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she would have ironed her clothes.
(b) Sentences having ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ 1. Direct: “Are there any more files ?” He asked. “Yes, sir,” said the peon. Indirect: He asked the peon if there were any more files. The peon replied respectfully in affirmative. 2. Direct: The teacher said to Lila, “Did you break the window pane ?” “No, sir,” said Lila, “I did not.” Indirect: The teacher asked Lila if she had broken the window pane. Lila replied respectfully and refused it (to have done it). 3. Direct: “If you find my answers satisfactory, will you give me five rupees ?” said the astrologer. “No, ’ replied the customer. Indirect: The astrologer asked the customer whether he would give him five rupees if he found his answers satisfactory. The customer replied in negative. 4. Direct: I said to him, “Do you want to go to Chandigarh ?” He said, “No, sir.” Indirect: I asked him if he wanted to go to Chandigarh and respectfully he replied in negative. 5. Direct: He said to me, “Does Mohan still play ?” I. said, “Yes, sir.” Indirect: He asked me if Mohan still played and I replied in positive.
(c) Questions beginning with Interrogative Words 1. Direct: He said to me, “Whom does she want to contact ?” Indirect: He asked me whom she wanted to contact. 2. Direct: They said to her, “Whose house are you purchasing ?” Indirect: They asked her whose house she was purchasing. 3. Direct: You said to him “Why are you making mischief ?” Indirect: You asked him why he was making mischief. 4. Direct: They said to us, “How have you solved this sum ?” Indirect: They asked us how we had solved that sum. 5. Direct : We said to them, “Who has misguided you ?” Indirect: We asked them who had misguided them.
(d) Questions beginning with modal auxiliaries 1. Direct: I said to him, “May Sunita come in to discuss with you something ?” Indirect: I asked him if Sunita might come in to discuss with him something. 2. Direct: The traveller said to me, “Can you tell me the way to the nearest inn ? Indirect: The traveller asked me if I could tell him the way to the nearest inn. 3. Direct: He said to me, “Must I leave for Mumbai tomorrow ?” Indirect: He asked me if he had to leave for Mumbai the next day. 4. Direct: I said to her, “Could you give me your notes ?” Indirect: I asked her if she could give me her notes. 5. Direct: I said to him, “Need I go to him ?” Indirect: I asked him if I had to go to him.
Multiple Choice Questions
Read the statements given below and tick the correct option : I. Identify the Reporting Verbs as directed : Question 1. Present (i) Radha will say ……… (ii) Radha said …… (iii) Radha had said ……….. (iv) Radha says ………..
Question 2. Past (i) The commander orders (ii) the commander order (iii) The commander said (iv) The commander will order
Question 3. Future (i) She requests (ii) She will say (iii) She informed (iv) She will enquire.
Question 4. Direct Speech (i) He said that the sun rises in the east (ii) Sun rises in the east (iii) She enquired about the holiday (iv) He enquired to be given a holiday
Question 5. Indirect speech (i) ‘I want to go for a walk’. (ii) He suggested going out for a walk (iii) ‘Get me a book’. (iv) ‘GO out’.
II. Fill in the blanks : Question 6. I said ……….. (i) why are you going (ii) him to go (iii) that he was going (iv) to go out of the room
Question 7. He asked …….. (i) whether was he fine (ii) was he fine (iii) if he is fine (iv) if he was fine
III. Tick the correct option : Question 8. The teacher said to them, (i) ‘Who had been teaching them English ?’ (ii) ‘Who teaches you English ?’ (iii) ‘Who taught your English ?’ (iv) ‘Whom you teach English ?’
Question 9. The teacher asked the students (i) whom were they taught English (ii) who taught them English. (iii) by whom were they taught English (iv) were they taught English
Question 10. He said, “The earth revolves around its axis” (i) He said that the earth revolved around its axis (ii) He said that the earth will revolve around its axis (iii) He said that the earth would revolve around its axis (iv) He said that the earth revolves around its axis. Answers 1. (iv) 2. (iii) 3. (ii) 4. (ii) 5. (ii) 6. (iii) 7. (iv) 8. (ii) 9. (ii) 10. (iv)
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
Direct and Indirect Speech – Exercises for Class 6
Fresh Reads
Direct speech refers to the exact words used by a speaker. These words are placed with quotation marks. Example: Ria said, “I am going to school.”
Indirect speech is used to communicate what someone else has said, without using the exact words. Example: Ria said she was going to school.
Q. Change the following sentences into indirect speech.
- Anil said, “I have done my homework.”
- Ramesh said, “She has been sleeping since 11 pm.”
- Neha said, “I am baking a cake for my family.”
- Beena said, “The sun rises in the east.”
- He said, “I have lived in Jaipur for twenty years.”
- Anil said that he has done his homework.
- Ramesh said that she has been sleeping since 11pm
- Neha said that She is baking a cake for his family.
- Beena said that the sun rises in the east.
- He said that he lived in Jaipur for twenty years.
Related posts:
- In Equal Sacrifice by Robert Frost
- The Lesson for Today by Robert Frost
- Summary of John Keats’ Ode to a Nightingale
- Question Mark (?) or Full Stop (.) for Class 1
Why I Write by George Orwell
What is fascism by george orwell, the shoemaker and the devil by anton chekhov.
Try aiPDF , our new AI assistant for students and researchers
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercise
Turn the following sentences into indirect speech.
1. John said, ‘I am very busy now.’ 2. He said, ‘The horse has been fed.’ 3. ‘I know her name and address,’ said John. 4. ‘German is easy to learn,’ she said. 5. He said, ‘I am writing letters.’ 6. ‘It is too late to go out,’ Alice said. 7. He said to me, ‘I don’t believe you.’ 8. He says, ‘I am glad to be here this evening.’ 9. He said to me, ‘What are you doing?’ 10. ‘Where is the post office?’ asked the stranger. 11. He said, ‘Will you listen to me?’ 12. John said to Peter, ‘Go away.’ 13. She said to me, ‘Please wait here till I return.’ 14. ‘Call the witness,’ said the judge. 15. The speaker said, ‘Be quiet and listen to my words.’
1. John said that he was very busy then. 2. He said that the horse had been fed. 3. John said that he knew/knows her name and address. (Note that the tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth.) 4. She said that German is/was easy to learn. 5. He said that he was writing letters. 6. Alice said that it was too late to go out. 7. He told me that he didn’t believe me. OR He said he didn’t believe me. 8. He says that he is glad to be here this evening. (When the reporting verb is in the present tense, adverbs of time and place do not normally change in indirect speech.) 9. He asked me what I was doing. 10. The stranger asked where the post office is/was. 11. He asked me if I would listen to him. 12. John ordered Peter to go away. 13. She asked me to wait there till she returned. 14. The judge commanded them to call the first witness. 15. He urged them to be quiet and listen to them.

Search Articles
Recent articles.
- Prepositions Quiz
- General Grammar Exercise
- Pronouns Exercise
- Proper Nouns Exercise
- General Vocabulary Exercise
- Identify the Adverbs Exercise
- Grammar Exercise (Intermediate Level)
- Intermediate Level Grammar Exercise
- General Grammar Worksheet
- Vocabulary Exercise
- Gap Filling Tenses Exercise
- Gap Filling Grammar Exercise
- More resources
EnglishPractice.com © 2024 - All rights Reserved.
- Grade Levels
- Search Site
- Grade 6 >>
Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheets
Related ela standard: l.6-7.1.
Direct speech is basically a quote or the literal words that were spoken by a subject. When you use this in your writing it must be surrounded by quotation marks (" "). Using direct quotes helps your audience understand the frame of mind of the subject. Indirect speech is reporting what was said by a subject. Since all indirect speech has already happened it is reported in the past tense. To display indirect speech we surround it with inverted commas (' '). These worksheets will have students using this technique in the own writing and help them with syntax and mechanics of their work.
Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheets To Print:
What's Your Approach - Determine whether each sentence below contains this form of expression. Write direct or indirect on the line.
Sentence Smasher - Rewrite each sentence using indirect speech.
Peter and Dan - Read the passage. Underline the speaker's words. Then, rewrite the passage, incorporating this in there.
Too Much? - If the sentence is uses the direct form, write a D on the line. If it uses the indirect form, write an I on the line.
Be The Director - The comic strip below uses speech bubbles to show the direct form. Rewrite the comic strip on the lines below, using the indirect form.
Revising the Direct Form - Read the script. On the lines, rewrite the script as a paragraph, using indirect speech.
Speaker's Words - Indirect speech is when a speaker's words are reported by someone else, and the words are not quoted.
A Walk in the Park - Read the script. Rewrite it in paragraph form using both formats. Follow the directions in parentheses.
Play Re-writes - John said his train would arrive at noon and maybe it did.
Using Roundabouts - Read the cartoon. Then describe what is happening. Use the indirect technique in your paragraph to tell the reader what Abe and Lauren say.
Who Said That? - Underline what the speaker says in each sentence. Then rewrite each sentence using the proper form.
About the Car... - You want to know if Dad will let you take the car.
What Did They Say? - Rewrite the sentences using all the techniques that you have learned so far. Make sure the syntax is spot on.
Tell Me About the Party - Will told us all about the party. He said there were about ten people there. I asked him about Robert, and confirmed that Robert was in attendance.
Writing The Other Way - Most students find this harder to do then its counterpart.
What Is the Difference Between Direct and Indirect Speech
Here are the basic differences between direct and indirect speech.
Difference In Meaning
There are two ways to describe the speech. These two ways are known as indirectly and directly. These two methods are widely used in the English language to imply what others have said. Both have different rules when writing.
The direct form occurs when the exact same words of the speech are repeated without any interruptions or additions. Direct speech implies exactly what has been said in the same tone. The actual words that were used by the speaker are written in indirect speech. Nothing new is added. Expressions are also mentioned in the exact same way by maintaining the tone of the actual speaker. The direct form is used when you do want to keep things simple and accurate.
The indirect form occurs when the actual words of the speaker are not quoted. Indirect speech changes certain elements from the actual words. It occurs when someone else tries to speak the original words.
Difference In Alternative Name
Both direct and indirect speech have their own alternative names. Direct format is commonly known as quoted speech. Whereas, indirect form is commonly known as reported speech.
Difference In Point Of View
The indirect and direct speech also differ in point of views. The point of view of the direct speech is that of the speaker. Whereas, the point of view of indirect form is that of the listener.
Difference In Usage
The use of this technique in written has a difference in purpose and usage as well. The direct form is used when we want the reader to know what exactly was said by the speaker. No change in the message really ever occurs. Whereas, the indirect technique is used when we use our own words to report the words of someone else.
Difference In Quotation Marks
Direct technique uses quotation marks whereas, the indirect form does not use quotation marks.
Direct: She said, "I am going to the market". Indirect: She said that she was going to the market.
Teachers: Upgrade Now
- Print all 25,000+ worksheets
- All grade levels and topics
- Save endless hours of your time...
- Answers to everything too!
Get FREE English Worksheets In Your Email
- How We Are Aligned To The Common Core
- Educator Resources
- Privacy Policy
- Newsletters
© English Worksheets Land . All rights reserved.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Learn Insta
RD Sharma Solutions , RS Aggarwal Solutions and NCERT Solutions
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 6 CBSE With Answers
July 29, 2021 by Prasanna

You have learned that we can report the words of a speaker in two ways. We may quote the speaker’s actual words. This is called direct speech. My friends said, “We enjoyed our holiday in London.” Kavish said, “I was working on my project.” “I shall come to your party,” Navya promised.
This grammar section explains English Grammar in a clear and simple way. There are example sentences to show how the language is used. You can also visit the most accurate and elaborate NCERT Solutions for Class 6 English . Every question of the textbook has been answered here.
Reported Speech Exercises for Class 6 CBSE With Answers Pdf
Note that indirect speech
- inverted commas are used to indicate the exact words of the speaker. (You may use either single or double inverted commas.)
- a comma is placed immediately after the reporting verb. (In the third example the sentence ends with the reporting verb and is, therefore, followed by a full stop.)
- the punctuation at the end of the sentence in direct speech is placed before the closed inverted comma(s).
We can also report what the speaker said without quoting his / her exact words. This is called indirect speech or reported speech.
My friends said that they had enjoyed their holiday in London. Kavish said that he was/had been working on his project. Navya promised that she would come to my party.
In indirect speech, we:
- use the conjunction that immediately before the reported words.
- change the person of the first and second-person pronouns.
- change the tense of the verb.
- do not use inverted commas.
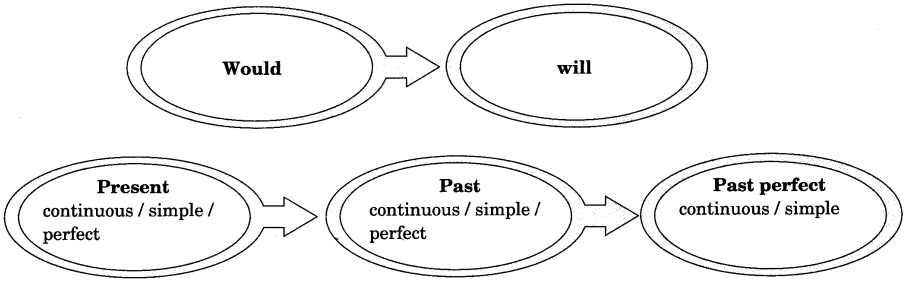
Tense Change
| is/am | was |
| are | were |
| have | had |
| do | did |
| was/ were | had been |
| will | would |
| can | could |
Modal Change
| will | would |
| can | could |
| must/ have to | must or had to |
| may/might | might |
| should | should |
| ought to | ought to |
Place and Time
| today | that day |
| now | then/at the moment |
| yesterday | the day before |
| days ago | days before |
| last week | the week before |
| next year | the following years |
| tomorrow | the next day, the following day |
| here | there |
| this | that |
| these | those |
| ago | previously/before |
| tonight | that night |
Direct Speech
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 6 CBSE
Question 1. Change into reported speech. (i) Rahul said, “I like fiction. (ii) The girl said, ‘I am writing a letter’. (iii) The boy said to the girl, ‘I am waiting for you.’ (iv) The masons said, ‘We have finished the job. (v) The boy said, ‘I have been selected.’ (vi) The teacher said to the girl, ‘Have you done your homework?’ (vii) The teacher said to the boy, ‘Work hard.’ (viii) The man said, ‘I have lost my bag.’ (ix) The traveller said, ‘Where is the nearest inn?’ (x) I said to him, “Will you help me?’ Answer: (i) Rahul said that he like fiction. (ii) The girl said that she was writing a letter. (iii) The boy said that he was waiting for you. (iv) The masons said that they had finished the job. (v) The boy said that he had been selected. (vi) The teacher asked the girl if she had done your homework. (vii) The teacher encouraged the boy to work hard. (viii) The man said that he had lost his bag. (ix) The traveller asked where the nearest inn was. (x) I asked him if he would help me.
Question 2. Change this direct speech into reported speech. (i) ‘He works in a bank’ She said ________________________ (ii) We went out last night She told me ________________________ (iii) ‘I’m coming! She said ________________________ (iv) ‘I was waiting for the bus when he arrived She told me ________________________ (v) ‘I’d never been there before’ She said ________________________ (vi) ‘I didn’t go to the party She told me ________________________ (vii) ‘Lucy’ll come later She said ________________________ (viii) ‘He hasn’t eaten breakfast She told me ________________________ (v) ‘I can help you tomorrow’ She said ________________________ (vi) You should go to bed early She told me ________________________ Answer: (i) She said (that) he worked in a bank. (ii) She told me (that) they went (had gone) out last night (the night before). (iii) She said (that) she was coming. (iv) She told me (that) she was waiting for the bus when he arrived. (v) She said (that) she had never been there before. (vi) She told me (that) she didn’t go (hadn’t gone) to the party. (vii) She said (that) Lucy would come later. (viii) She told me (that) he hadn’t eaten breakfast. (v) She said (that) she could help me tomorrow. (vi) She told me (that) I should go to bed early.
Reported Speech Practice Examples Exercises for Class 7 CBSE
Question 1. Below you can read a conversation between Reena and her husband SorrttL Complete the following sentence reporting what they discussed.
Reena: Our new servant has a tendency to steal things. Somu: Is anything missing? Reena: Yes, he has stolen one of our watches. Somu: Which one? Reena: It’s the one we bought from Pacific Mall.
Reena told her husband that (a) ______________ a tendency to steal things. Somu asked her (b) ______________ She told him that (c) ______________ When Somu asked her which one it was, she replied that it was the one they had bought from Pacific Mall.
Question 2. Read the conversation given below and complete the paragraph.
Mother: When is the fancy dress competition going to be held in your school? Rani: After two weeks. Mother: Are you taking part in it? Rani: Yes! I am going to be a fairy. Mother: Why have you chosen that part? Rani: So that I can show my magical powers.
Mother asked Rani when the fancy dress competition in her school was going to be held. Rani replied that (a) ______________. Mother enquired whether (b) ______________. Rani (c) ______________. Mother asked why she had chosen that part. She replied that she had chosen that part so that she could show her magical powers.
Have an account?

GRADE 6 - DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH
20 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
“Please help me carry this”She_______________
She asked me help her carry this.
She asked me to help her carry that.
“Please come early”She_______________
She asked me to come early.
She asked come early.
“Please buy some milk”She_______________
She asked me to buy some milk.
She asked to buy some milk.
“Could you please open the window?”She_______________
She asked me to the window.
She asked me to open the window.
“Could you bring the book tonight?”She_______________
. She to bring the book tonight (that night).
. She asked me to bring the book tonight (that night).
“Go to bed!”She_______________
She told me to go to bed.
She told me go to bed.
“Don’t be late!”She_______________
She told me not to be late.
She told me to be late.
“Tidy your room!”She_______________
She told to tidy my room.
She told me to tidy my room.
“Would you bring me a cup of coffee, please?”She_______________
She asked me to her a cup of coffee.
She asked me to bring her a cup of coffee.
“Do the washing-up!”She_______________
She me to do the washing-up.
She told me to do the washing-up.
“Don’t do this!” She ______________
She told me not to do that.
She told me not to do this.
“Don’t smoke!”
She told me not to smoke.
She told me do not to smoke.
“Don’t make a mess!” She ________________________
She told me not to make a mess.
She not to make a mess.
“Eat your dinner!” She ____________
She told me to eat her dinner.
She told me to eat my dinner.
“Wait here!”She_______________
She told me to wait here
She told me to wait here (there).
“Do your homework!”She_____________
She told me to do my homework.
She told do my homework.
“I was wondering if you could possibly tell me the time?”She_______________
She asked me to tell her the time.
She asked me to tell me the time.
“Would you mind lending me a pencil?”She______________
. She asked to lend her a pencil.
. She asked me to lend her a pencil.
“Would you mind passing the salt?”She_______________
She asked me pass the salt.
She asked me to pass the salt.
. “Can you help me with my homework, please?”She_______________
She asked me to help her with her homework
She asked me to help her with my homework
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
Grade 6 direct and indirect worksheet
Brandyverheem
language direct and indirect worksheet
Loading ad...
- Google Classroom
- Microsoft Teams
- Download PDF


Direct and Indirect Speech for Class 6
1. what are types of speech, 2. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. she says, “my father works in the air force”., 3. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. shyam said, “i will come tomorrow evening to take my bicycle”., 4. convert the following sentence into direct speech. he ordered to them to shut the door., 5. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. rohan said, “i called raman for tonight dinner”., 6. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. riya said, “i played this game last month”., 7. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. i said, “i don’t trust you”., 8. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. arjun said, “i visited here long time ago”., 9. convert the following sentence into indirect speech. radhika said, “i want to see a movie”., 10. ram said, “i will help”., leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
English grammar PDF Free Download

Join Our Newsletter Today On The Writers Cookbook

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Direct And Indirect Speech Exercises for Class 6 - Part II. Fundamentals: If the Reported Verb is in Past tense (Said, told instead of say, tell) then the tense in the reporting speech changes accordingly. Examples of the main changes in tense: Presentation: Read the picture story. A. Answer the following questions as per the story. 1.
Direct and Indirect Speech Exercises with Answers. When converting direct speech to indirect speech or vice-versa, you will have to take care to convert the verb, pronoun and the adverb appropriately. Go through the following exercises and try them out. Answers are given below each exercise; refer to them to see if your answers are right.
on June 15, 2023, 7:09 AM. Class 6 English Grammar Chapter 24 Direct and Indirect Speech. The word—speech—means whatever we speak or write. Speaking or writing the words of an another person can be done in two ways, 1. by repeating the words of the other person as they were, 2. by stating the meaning of the words of the other person in your ...
Practice direct and indirect speech with exercises and answers focusing on optative sentences, enabling you to accurately report wishes, prayers, or blessings while honing your linguistic proficiency. Exercise 20: Change the following from Direct Speech to Indirect Speech. (1) Mother said, 'May you be happy.'.
Direct and Indirect Speech Online Exercise for Class 6. Exercise 1: Change the following direct speech sentences into indirect speech sentences. This work out will make you understand the concept of the language more efficiently: I said, "I am waiting for my friend". The villager said, "It becomes difficult for us to survive without ...
Miscellaneous Exercise on Direct & Indirect Speech for class 6. Convert the sentences from direct speech to indirect speech given below. The teacher said, "Nobody can answer the questions". The traffic police asked the man, "Do not park your vehicle here". The guide said, "You shall go to see the fort".
Universal truths remain unchanged in reported speech. Example: The guru said, "The sun rises in the east." The guru said that the sun rises in the east. Direct and Indirect Speech Worksheets for Class 6 CBSE. A. Read the dialogues given below and change it to indirect speech. 1. Harish: "Poonam is at home." Harish said (that) _____ 2.
Here are some distinctive points regarding the Direct Speech and the Indirect Speech. (a) In Direct Speech. 1. The reported speech is put within inverted commas. 2. The reporting verb is separated from the reporting speech by a comma. 3. The first word of the reported speech begins with a capital letter. 4.
CBSE Class 6 English Grammar Reported Speech. 1. There are two different ways in which we can report the words of a speaker : (a) Direct Speech or Direct Narration. (b) Indirect Speech or Indirect Narration. 2. (a) Direct Speech contains the actual words of the speaker ; as—. Sarla said, "My father has a roaring business in Mumbai". He ...
Direct and Indirect Speech - Exercises for Class 6. Direct speech refers to the exact words used by a speaker. These words are placed with quotation marks. Example: Ria said, "I am going to school.". Indirect speech is used to communicate what someone else has said, without using the exact words. Example: Ria said she was going to school.
The speaker said, 'Be quiet and listen to my words.'. Answers. 1. John said that he was very busy then. 2. He said that the horse had been fed. 3. John said that he knew/knows her name and address. (Note that the tenses may not change if the statement is still relevant or if it is a universal truth.)
The indirect and direct speech also differ in point of views. The point of view of the direct speech is that of the speaker. Whereas, the point of view of indirect form is that of the listener. Difference In Usage. The use of this technique in written has a difference in purpose and usage as well. The direct form is used when we want the reader ...
🔴Click on this link to Enroll English Spoken Course - https://www.magnetbrains.com/course/spoken-english-full-video-course/' previous Video : https://www.yo...
Reported Speech Solved Examples Exercises for Class 6 CBSE. Question 1. Change into reported speech. (i) Rahul said, "I like fiction. (ii) The girl said, 'I am writing a letter'. (iii) The boy said to the girl, 'I am waiting for you.'. (iv) The masons said, 'We have finished the job.
Exercise no. A 00:05Exercise no. B 02:51Exercise no. C 05:39Exercise no. D 07:11Exercise no. E 09:00Exercise no. F 11:06Exercise no. G 13:06Exercise no. H 15:12
GRADE 6 - DIRECT AND INDIRECT SPEECH quiz for 6th grade students. Find other quizzes for English and more on Quizizz for free!
The document discusses direct and indirect speech for class 6 students. It provides definitions and examples of direct and indirect speech. Direct speech repeats the exact words spoken, while indirect speech reports the general idea without using the exact words. The document also outlines rules for changing direct speech into indirect speech, such as changing present tenses to past tenses. An ...
Definition: In Indirect narration, the sentences are designed in such a type, the words that are used by the person are not exactly the same as the speaker said or conveyed. Indirect speech is also known as reported speech. It generally talks about the past. Examples of Indirect speech For Class 6. 1.
Liveworksheets transforms your traditional printable worksheets into self-correcting interactive exercises that the students can do online and send to the teacher. ... Grade 6 direct and indirect worksheet ... Country: South Africa. School subject: English language (1061957) Main content: Direct and indirect speech (2057325) From worksheet ...
A) He ordered to them, "Shut the door". B) He orders, "Shut the door". C) He ordered, "Shut the door". D) None of the above. 5. Convert the following sentence into indirect speech. Rohan said, "I called Raman for tonight dinner". A) Rohan said that he has called Raman for that day night dinner. B) Rohan said that he had called ...
Class- 6 ACE english grammar and composition. Solved exercises of Direct and Indirect speech.#Class6solvedACEenglishgrammarexercises#solvedexercisesofdirecta...
This document discusses direct and indirect speech for class 6 students. It defines direct speech as repeating the exact words spoken, using quotation marks, while indirect speech reports the general meaning without quotations. The document provides examples of each. It then outlines rules for changing direct speech into the past tense indirect ...