Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.

How to Write a Body Paragraph for a College Essay
January 29, 2024
No matter the discipline, college success requires mastering several academic basics, including the body paragraph. This article will provide tips on drafting and editing a strong body paragraph before examining several body paragraph examples. Before we look at how to start a body paragraph and how to write a body paragraph for a college essay (or other writing assignment), let’s define what exactly a body paragraph is.
What is a Body Paragraph?
Simply put, a body paragraph consists of everything in an academic essay that does not constitute the introduction and conclusion. It makes up everything in between. In a five-paragraph, thesis-style essay (which most high schoolers encounter before heading off to college), there are three body paragraphs. Longer essays with more complex arguments will include many more body paragraphs.
We might correlate body paragraphs with bodily appendages—say, a leg. Both operate in a somewhat isolated way to perform specific operations, yet are integral to creating a cohesive, functioning whole. A leg helps the body sit, walk, and run. Like legs, body paragraphs work to move an essay along, by leading the reader through several convincing ideas. Together, these ideas, sometimes called topics, or points, work to prove an overall argument, called the essay’s thesis.
If you compared an essay on Kant’s theory of beauty to an essay on migratory birds, you’d notice that the body paragraphs differ drastically. However, on closer inspection, you’d probably find that they included many of the same key components. Most body paragraphs will include specific, detailed evidence, an analysis of the evidence, a conclusion drawn by the author, and several tie-ins to the larger ideas at play. They’ll also include transitions and citations leading the reader to source material. We’ll go into more detail on these components soon. First, let’s see if you’ve organized your essay so that you’ll know how to start a body paragraph.
How to Start a Body Paragraph
It can be tempting to start writing your college essay as soon as you sit down at your desk. The sooner begun, the sooner done, right? I’d recommend resisting that itch. Instead, pull up a blank document on your screen and make an outline. There are numerous reasons to make an outline, and most involve helping you stay on track. This is especially true of longer college papers, like the 60+ page dissertation some seniors are required to write. Even with regular writing assignments with a page count between 4-10, an outline will help you visualize your argumentation strategy. Moreover, it will help you order your key points and their relevant evidence from most to least convincing. This in turn will determine the order of your body paragraphs.
The most convincing sequence of body paragraphs will depend entirely on your paper’s subject. Let’s say you’re writing about Penelope’s success in outwitting male counterparts in The Odyssey . You may want to begin with Penelope’s weaving, the most obvious way in which Penelope dupes her suitors. You can end with Penelope’s ingenious way of outsmarting her own husband. Because this evidence is more ambiguous it will require a more nuanced analysis. Thus, it’ll work best as your final body paragraph, after readers have already been convinced of more digestible evidence. If in doubt, keep your body paragraph order chronological.
It can be worthwhile to consider your topic from multiple perspectives. You may decide to include a body paragraph that sets out to consider and refute an opposing point to your thesis. This type of body paragraph will often appear near the end of the essay. It works to erase any lingering doubts readers may have had, and requires strong rhetorical techniques.
How to Start a Body Paragraph, Continued
Once you’ve determined which key points will best support your argument and in what order, draft an introduction. This is a crucial step towards writing a body paragraph. First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly. You should be looking at your thesis throughout the drafting of your body paragraphs.
Finally, make sure that your introduction indicates which key points you’ll be covering in your body paragraphs, and in what order. While this level of organization might seem like overkill, it will indicate to the reader that your entire paper is minutely thought-out. It will boost your reader’s confidence going in. They’ll feel reassured and open to your thought process if they can see that it follows a clear path.
Now that you have an essay outline and introduction, you’re ready to draft your body paragraphs.
How to Draft a Body Paragraph
At this point, you know your body paragraph topic, the key point you’re trying to make, and you’ve gathered your evidence. The next thing to do is write! The words highlighted in bold below comprise the main components that will make up your body paragraph. (You’ll notice in the body paragraph examples below that the order of these components is flexible.)
Start with a topic sentence . This will indicate the main point you plan to make that will work to support your overall thesis. Your topic sentence also alerts the reader to the change in topic from the last paragraph to the current one. In making this new topic known, you’ll want to create a transition from the last topic to this one.
Transitions appear in nearly every paragraph of a college essay, apart from the introduction. They create a link between disparate ideas. (For example, if your transition comes at the end of paragraph 4, you won’t need a second transition at the beginning of paragraph 5.) The University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center has a page devoted to Developing Strategic Transitions . Likewise, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center offers help on paragraph transitions .
How to Draft a Body Paragraph for a College Essay ( Continued)
With the topic sentence written, you’ll need to prove your point through tangible evidence. This requires several sentences with various components. You’ll want to provide more context , going into greater detail to situate the reader within the topic. Next, you’ll provide evidence , often in the form of a quote, facts, or data, and supply a source citation . Citing your source is paramount. Sources indicate that your evidence is empirical and objective. It implies that your evidence is knowledge shared by others in the academic community. Sometimes you’ll want to provide multiple pieces of evidence, if the evidence is similar and can be grouped together.
After providing evidence, you must provide an interpretation and analysis of this evidence. In other words, use rhetorical techniques to paraphrase what your evidence seems to suggest. Break down the evidence further and explain and summarize it in new words. Don’t simply skip to your conclusion. Your evidence should never stand for itself. Why? Because your interpretation and analysis allow you to exhibit original, analytical, and critical thinking skills.
Depending on what evidence you’re using, you may repeat some of these components in the same body paragraph. This might look like: more context + further evidence + increased interpretation and analysis . All this will add up to proving and reaffirming your body paragraph’s main point . To do so, conclude your body paragraph by reformulating your thesis statement in light of the information you’ve given. I recommend comparing your original thesis statement to your paragraph’s concluding statement. Do they align? Does your body paragraph create a sound connection to the overall academic argument? If not, you’ll need to fix this issue when you edit your body paragraph.
How to Edit a Body Paragraph
As you go over each body paragraph of your college essay, keep this short checklist in mind.
- Consistency in your argument: If your key points don’t add up to a cogent argument, you’ll need to identify where the inconsistency lies. Often it lies in interpretation and analysis. You may need to improve the way you articulate this component. Try to think like a lawyer: how can you use this evidence to your advantage? If that doesn’t work, you may need to find new evidence. As a last resort, amend your thesis statement.
- Language-level persuasion. Use a broad vocabulary. Vary your sentence structure. Don’t repeat the same words too often, which can induce mental fatigue in the reader. I suggest keeping an online dictionary open on your browser. I find Merriam-Webster user-friendly, since it allows you to toggle between definitions and synonyms. It also includes up-to-date example sentences. Also, don’t forget the power of rhetorical devices .
- Does your writing flow naturally from one idea to the next, or are there jarring breaks? The editing stage is a great place to polish transitions and reinforce the structure as a whole.
Our first body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay .” Here’s the prompt: Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.” Now let’s see how this writer builds an argument against perfection through one main point across two body paragraphs. (While this writer has split this idea into two paragraphs, one to address a problem and one to provide an alternative resolution, it could easily be combined into one paragraph.)
“Students often feel the need to be perfect in their classes, and this can cause students to struggle or stop making an effort in class. In elementary and middle school, for example, I was very nervous about public speaking. When I had to give a speech, my voice would shake, and I would turn very red. My teachers always told me “relax!” and I got Bs on Cs on my speeches. As a result, I put more pressure on myself to do well, spending extra time making my speeches perfect and rehearsing late at night at home. But this pressure only made me more nervous, and I started getting stomach aches before speaking in public.
“Once I got to high school, however, I started doing YouTube make-up tutorials with a friend. We made videos just for fun, and laughed when we made mistakes or said something silly. Only then, when I wasn’t striving to be perfect, did I get more comfortable with public speaking.”
Body Paragraph Example 1 Dissected
In this body paragraph example, the writer uses their personal experience as evidence against the value of striving for perfection. The writer sets up this example with a topic sentence that acts as a transition from the introduction. They also situate the reader in the classroom. The evidence takes the form of emotion and physical reactions to the pressure of public speaking (nervousness, shaking voice, blushing). Evidence also takes the form of poor results (mediocre grades). Rather than interpret the evidence from an analytical perspective, the writer produces more evidence to underline their point. (This method works fine for a narrative-style essay.) It’s clear that working harder to be perfect further increased the student’s nausea.
The writer proves their point in the second paragraph, through a counter-example. The main point is that improvement comes more naturally when the pressure is lifted; when amusement is possible and mistakes aren’t something to fear. This point ties back in with the thesis, that “we should value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfection.
This second body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay .” Here’s an abridged version of the prompt: Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.” Now read the body paragraph example, below.
“To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.”
Body Paragraph Example 2 Dissected
The first sentence in this body paragraph example indicates that the topic is transitioning into biblical references as a means of motivating ordinary citizens. The evidence comes as quotes taken from Obama’s speech. One is a reference to God, and the other an allusion to a story from the bible. The subsequent interpretation and analysis demonstrate that Obama’s biblical references imply a deeper, moral and spiritual significance. The concluding sentence draws together the morality inherent in equal rights with Rosa Parks’ power to spark change. Through the words “no political power or fortune,” and “moral balance,” the writer ties the point proven in this body paragraph back to the thesis statement. Obama promises that “All of us” (no matter how small our influence) “are capable of achieving greater good”—a greater moral good.
What’s Next?
Before you body paragraphs come the start and, after your body paragraphs, the conclusion, of course! If you’ve found this article helpful, be sure to read up on how to start a college essay and how to end a college essay .
You may also find the following blogs to be of interest:
- 6 Best Common App Essay Examples
- How to Write the Overcoming Challenges Essay
- UC Essay Examples
- How to Write the Community Essay
- How to Write the Why this Major? Essay
- College Essay
Kaylen Baker
With a BA in Literary Studies from Middlebury College, an MFA in Fiction from Columbia University, and a Master’s in Translation from Université Paris 8 Vincennes-Saint-Denis, Kaylen has been working with students on their writing for over five years. Previously, Kaylen taught a fiction course for high school students as part of Columbia Artists/Teachers, and served as an English Language Assistant for the French National Department of Education. Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How To Write Essay Body Paragraphs

- 3-minute read
- 4th October 2022
Writing essays is an unavoidable part of student life . And even if you’re not pursuing a career that involves much writing, if you can boost the quality of your essays , you’ll improve your grades and have a better chance of reaching your goals.
One effective way to improve your writing is to strengthen your essay body paragraphs. Those are the paragraphs between the introduction and the conclusion. In our guide below, we’ll consider four components of body paragraphs:
● Purpose
● Evidence
● Analysis
● Connection
For each paragraph you write , ask yourself: Why are you writing this paragraph? What point are you trying to make? This can be turned into a topic sentence, which is a brief sentence at the beginning of the paragraph clearly stating its focus.
Let’s say our essay is arguing that Fall is the best season, and, in this paragraph, we’re promoting the enjoyableness of Fall activities. Our topic sentence could be something like:
Fall activities, like apple picking, visiting a pumpkin patch, and playing in the leaves, are more enjoyable than activities in other seasons.
Now that you have a clear idea of the point you’d like to make, you must support it with facts. You can do this by citing scientific and/or academic sources; sharing data from case studies; and providing information that you’ve discovered yourself, such as by conducting your own study or describing a real-life experience.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
We sent a survey to 100 participants. One question asked: “Which activity do you prefer: apple picking, building a snowman, planting flowers, or kayaking?” Sixty percent of respondents chose apple picking.
Now that you’ve provided evidence, critically analyzing it is key to strengthening your essay. This involves explaining how the presented facts support your argument, what counterarguments exist, and if there are any alternative points of view.
Although the response to one question indicated that 55% of respondents prefer swimming to jumping in piles of leaves, the responses to the rest of the questions in the survey showed that most participants chose Fall activities as their favorites. These findings indicate that Fall activities are more enjoyable than other types of activities.
Each paragraph must be connected to the paragraphs around it and the main point. You can achieve this by using transitional words and sentences at the end of the paragraph to summarize the current paragraph’s findings and introduce the next one. Transition words include likewise , however , furthermore , accordingly , and in summary .
Therefore, Fall is the best season when it comes to activities. Furthermore, the clothing worn during this season is also superior.
Proofreading and Editing
This step should not be overlooked. Even the best writers will miss errors in their own writing, so it’s crucial to have an outside pair of eyes check your work for spelling, grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and readability.
Our expert editors can also ensure your referencing style is followed correctly, offer suggestions for areas where your meaning isn’t clear, and even format your document for you! Try our service for free today by uploading a 500-word sample .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template (2024)
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway
Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
| {{item.snippet}} |
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback

How to write an essay: Body
- What's in this guide
- Introduction
- Essay structure
- Additional resources
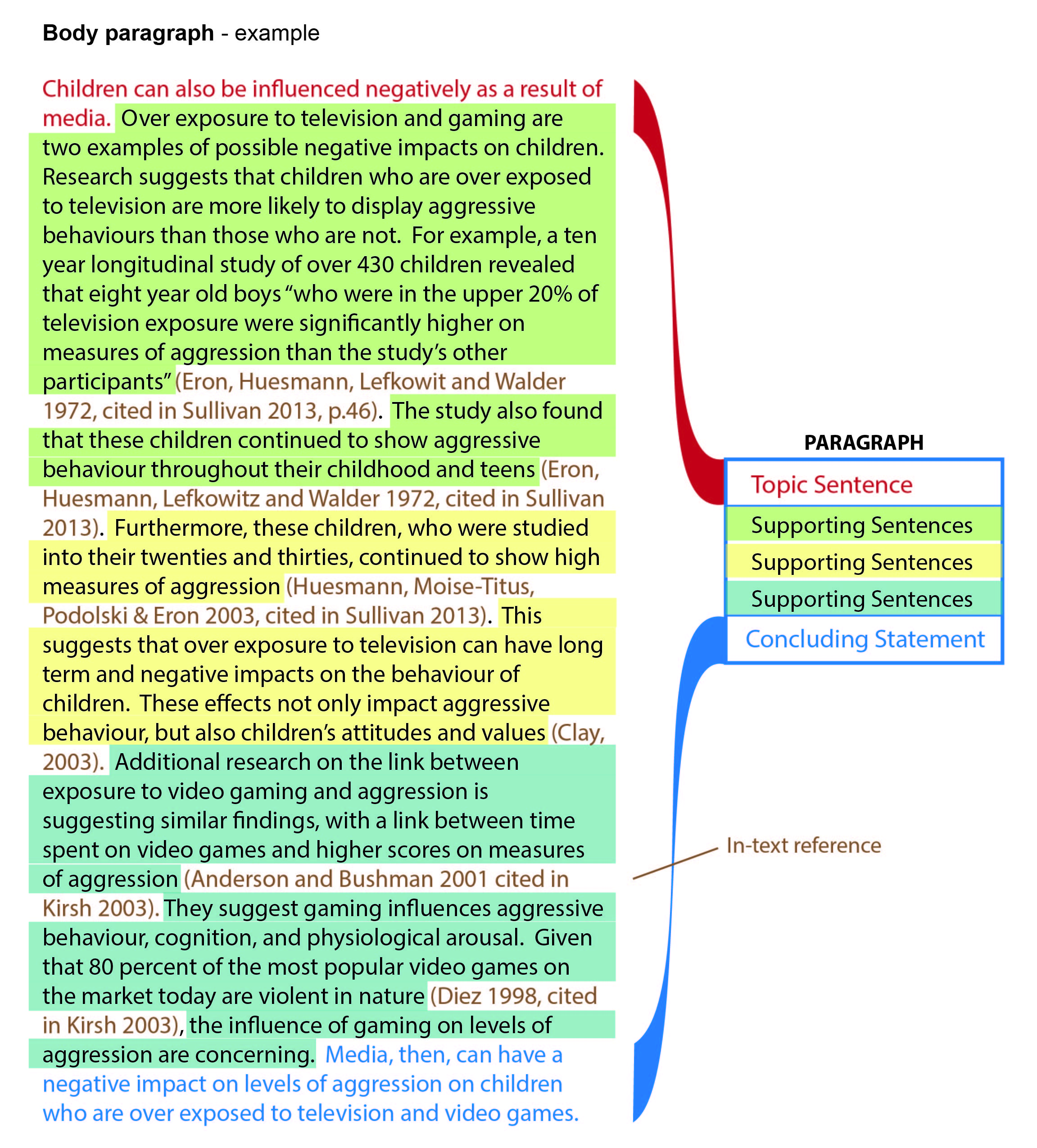
Body paragraphs
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly.
Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence . This lets the reader know what the paragraph is going to be about and the main point it will make. It gives the paragraph’s point straight away. Next – and largest – is the supporting sentences . These expand on the central idea, explaining it in more detail, exploring what it means, and of course giving the evidence and argument that back it up. This is where you use your research to support your argument. Then there is a concluding sentence . This restates the idea in the topic sentence, to remind the reader of your main point. It also shows how that point helps answer the question.
Pathways and Academic Learning Support

- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Nov 29, 2023 1:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay
Home ➔ Essay Structure ➔ Body Paragraphs
Guide to Writing a Body Paragraph
Body paragraphs are the parts where you present your evidence and make arguments, which one may argue makes them the most important part of any essay. In this guide, you will learn how to write clear, effective, and convincing body paragraphs in an academic essay.
To learn more about general ways of organizing an essay, you can read our full guide here: Essay Structure Guide .
3 Major Characteristics of a Good Body Paragraph
There are three main elements of a good body paragraph. In short, unity means that the body paragraphs speak only about one concept. Coherence refers to the logical progression of sentences and ideas. And finally, a paragraph that has a good flow uses transition phrases so that each sentence leads on to the next logically. Now, let’s take a closer look at each of these.
Each main paragraph should focus only on one main point, subtopic, or piece of evidence and relay information only about that concept. If a body paragraph contains many different ideas, it can be complicated to understand and less convincing. On the other hand, a paragraph with unity fully explains a concept and ties it to the thesis statement without adding extra information that feels misplaced and may dilute the message.
- The topic sentence of a body paragraph should clearly state the main idea being explored in that paragraph. Each such sentence should have its own paragraph.
- Discuss the connection between the topic sentence and the paper’s thesis.
- All the supporting evidence in the paragraph should connect to the topic sentence.
- Move important information not connected to the topic sentence to another paragraph or revise the topic sentence of that body paragraph.
2. Coherence
Coherence means that there is a logical progression to the sentences and ideas in the paragraph. In other words, paragraphs should be structured in such a way so that they have maximum impact on the audience and make sense. There are several ways to increase coherence within a body paragraph (these are explained later on in this guide):
- Chronological order
- Spatial order
- Emphatic order
Flow refers to the overall readability of a paragraph. Sentences that flow into each other naturally engage the reader and make them more likely to absorb information. One of the simplest ways of improving the flow in a paragraph is by using transitional words and phrases like “specifically,” “on the other hand,” “which leads to the conclusion,” “therefore,” etc. These transition words connect one sentence to another and help the audience keep track of what is happening. Other ways to improve your paragraph flow are:
- Using similar sentence structure throughout the paragraph
- Using pronouns instead of proper nouns
- Repeating important words
Body Paragraph Structure
There is a standard basic structure of a body paragraph that helps bring together unity, coherence, and flow. This structure works well for the standard five-paragraph format of academic writing, but more creative pieces of writing (like a narrative essay ) may deviate from this structure and have more than the standard three body paragraphs.
Topic Sentence
The first sentence of a body paragraph should be the topic sentence . Topic sentences clearly state the central idea of the paragraph. You can think of it as one of the main pieces of information or arguments you want to present to back your thesis.
Supporting Evidence
The next few sentences are where you present evidence and research that back up the topic sentence. These supporting sentences logically present research in such a way that strengthens the main claim of the paragraph. Make sure you know the correct citation style for facts and figures and that you cite every piece of information. A well-written body paragraph can still get a bad grade because of low-quality sources or improper citation.
Want to learn more about citing sources? Check related questions here: Citation Guide .
Analysis (Commentary)
After presenting the supporting sentences, you should analyze how the evidence connects to the topic sentence and what it means for the paper overall. Do not assume that the reader will automatically make connections, it is important to make it clear in this writer’s analysis section so that the overall links and ideas are fully explained.
Commentary in an Essay – learn more about analysis in essays and see some examples of commentaries.
Concluding Sentence
The conclusion is usually one or two sentences that clearly show how the supporting facts connect to the topic sentence and why it is important. A concluding sentence is the main takeaway and should present deeper insight into the supporting details and claims made in the paragraph.
Transition Link
This last sentence of a body paragraph is useful to improve the flow of the essay overall. It is not always required but essentially hints at the content of the next paragraph and leads into its first sentence.
Alternative Body Paragraph Structures
There are two other ways of structuring a body paragraph that you should be aware of. They are very similar to the format above, but you may find them useful for writing different kinds of essays.
P.I.E Format
P.I.E stands for points, information, and explanation. The first thing you should talk about in any paragraph is the answer to, “What is the main point of this paragraph?” This is essentially the same as a topic sentence, which explains what the paragraph will be about or what argument you are going to put forth.
“I” stands for information, which means that you present factual information as supporting sentences that back up your claim. And “E” stands for explanation, which is where you explain why the information you presented is important and how it connects to the overall purpose of the essay.
T.T.E.B Format
T.T.E.B stands for Transition, Topic sentences, Evidence and analysis, and a Brief wrap-up sentence. In this structure, the first thing you do is write a short transition sentence leading on from the previous paragraph to improve flow. After that, it is pretty much the same as we described before. Follow this up with a topic sentence, then present your supporting details and some analysis, and finally end with concluding sentences.
Body Paragraph Examples
Each body paragraph example below is color-coded to show every element it contains.

Body Paragraph Order
In this case, paragraph order can refer to two different things: either the position of the paragraph itself or how the information within a paragraph is ordered. This is closely tied to the concept of coherence and is important to improve the logical build-up of an essay.
Emphatic (Rank)
Emphatic order means presenting evidence in order of importance. This works both for paragraph positions as well as information within a paragraph. The first challenge is ranking your information in terms of strength. This can be determined by the quality of evidence and sources or the logical connection to the thesis statement. The most common way of using this structure is presenting weaker evidence first and building up to the strongest evidence. This leaves the reader with the strongest convincing argument, but in some cases, starting with the strongest evidence and moving to the weakest evidence is useful, for example, when writing for a skeptical audience.

Chronological (Time)
Chronological order is one of the simplest ways of structuring a paragraph because it presents information based on when something happened. It is mostly used to structure paragraph order in narrative essays and process essays but can be used within paragraphs to structure information as well.

Spatial (Place)
Organizing the information in a paragraph spatially makes the most sense when describing something. This type of ordering uses cues like top to bottom, far to near, and outside to inside to describe things logically in terms of their spatial relations.

Deduction (General to Specific)
This method of organizing a paragraph starts with general information and works its way to specific information. You can start with a general claim and then pick on specific parts of it to bring attention to a unique aspect of it. This is useful in showing cause and effect and drawing conclusions from overarching concepts.

Induction (Specific to General)
This method of organizing paragraphs starts with specific information and works its way to general information. This is useful to show how specific things are connected to larger concepts and how concepts should be compared and contrasted.
Induction vs. Deduction – Comparison between the two methods with examples.
How to Write a Body Paragraph (6 Steps)
Now that you know all the important elements of a body paragraph, as well as the general structures and ordering methods, let’s see what steps you would need to take to actually write one.
1. Decide on your order
The first thing you should do is arrange your outline in an order that makes sense for each body paragraph, as well as the order of information within the paragraphs. Keep in mind that just because you have structured your paragraphs in a certain way does not mean that individual paragraphs must follow the same format. Use whichever ordering method makes the most sense to present the information within each separate body paragraph.
2. Write a topic sentence
A topic sentence determines the information included in the paragraph, so it should be the first thing you write. In other words, think about what the overall purpose of the paragraph is and condense it into one sentence. Imagine having a conversation with a friend and presenting three things that support the main topic. What would those three things be? This is a good mental exercise to pinpoint important arguments.
Often, a thesis statement would contain three main ideas, and each could be extended into a topic sentence.
3. Provide evidence
Logically present your research and evidence in supporting sentences, ensuring unity, coherence, and flow. Think about how this evidence will leave the biggest impact and make sure to cite every source correctly.
4. Analyze the evidence
Explain how the evidence connects to the topic sentence and why the evidence is important. Draw conclusions to strengthen the main claim made in the paragraph.
5. Conclude and transition
Write a conclusion sentence that wraps up the paragraph and reiterates the main idea. A conclusion can be a good transition, or you can add a transition sentence that briefly explains the purpose of the next paragraph.
6. Revise the paragraph
After writing each paragraph, go over it to make sure that it has unity, coherence, and flow. Don’t be afraid to move information around or remove certain pieces of information. You will have another chance to edit the entire paper after your first draft, so only look for the large-scale problems.

- Rochester Institute of Technology – Paragraph Body
- American University – Paragraph Unity and Coherence
- Purdue University – Body Paragraphs
Was this article helpful?
What is a Body Paragraph? (Definition, Examples, How to Start)

What is a body paragraph? How do I start a body paragraph? A body paragraph is the most important part of the sentence subject . It delivers the most impactful information and helps to transition in and out of paragraphs more effectively.

What is a body paragraph?
Any essay, article, or academic writing starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion. The text between the introduction and conclusion is the body paragraph.
A body paragraph supports the idea that was mentioned in the introduction by shedding light on new details using facts, statistics, arguments, or other information.
What role does a body paragraph play in an article or an essay?
A body paragraph acts as a connection between the introduction and the conclusion. The body paragraph’s role is to justify the thesis stated in the introduction of an essay or article. As mentioned previously it comes between the introduction and the conclusion which is where most of the writing is done. This signifies its importance.
There can be multiple body paragraphs in an article or an essay. That said, each of the body paragraphs should logically connect with one another. In addition to this, all the body paragraphs should focus on the main idea stated in the introduction. Also, the sentences should not be long, so that readers can easily consume the information.
Here is a brief breakdown of the structure of a body paragraph:
How to structure a body paragraph
Every body paragraph has four main parts. They are:
- Topic Sentence
- Evidence Or Supporting Sentences
- Ending Or Conclusion
Here is a detailed breakdown of each one of them.
Topic sentence
The topic sentence is the first sentence in a body paragraph. This sentence discusses the main idea of the topic and indicates what information to expect in the rest of the paragraph. It sets the stage for the rest of the paragraph.
Evidence or supporting sentences
After the topic sentence comes the supporting sentences. These sentences are used to justify the claim that was stated in the topic sentence. Text citations, evidence, statistics, and examples are used to justify the claim. For example, if the topic sentence discusses “Switzerland is a must visit place”, then the supporting sentences should discuss the beautiful parts of Switzerland with examples to justify the claim.
One sentence to another sentence should flow seamlessly and this is possible by using transition words . Transition words like “however”, “although”, “in addition to”, “next”, and “in contrast” helps in doing exactly the same.
Ending or concluding sentence
Every body paragraph should end with a conclusion which comes after the supporting sentences. It summarizes the main idea of the body paragraph and emphasizes the supporting details. The conclusion gives way to the next line of the next paragraph.
Transitions are a few words that help in the smooth flow of the previous paragraph to the next paragraph. These words can be at the beginning of topic sentences or at the end of the body paragraph. They connect one idea of a paragraph to the next idea of another paragraph.
How to write an effective body paragraph
Keep the body paragraph’s focus on the topic.
All the body paragraphs should support the claim made in the introduction of an essay or an article. It should be consistent with the main idea of the topic. It is recommended to avoid adding unnecessary information in the body paragraph that doesn’t relate to the main idea of the topic.
Break complicated topic sentences into smaller parts
If the topic sentence has many parts to it, the topic sentence should be divided into smaller ideas and each idea should be expressed in a different body paragraph. Having too many parts in a topic sentence will lead to many support sentences in the body paragraph which will be too lengthy for readers to grasp.
Add counterarguments
If it is an academic essay or an opinion article, counterarguments should be included in the piece. Adding counterarguments in such pieces will give a broader perspective of the piece. Such inclusions will strengthen the essay or article.
Use signals when more than one paragraph deals with the same evidence
If multiple body paragraphs deal with the same evidence, there are a few signal phrases that will help the reader connect with evidence used earlier in other paragraphs. The signal phrases like “As mentioned previously” and “As already mentioned” can be used.

Include paragraph breaks
It is a single-line space that divides one paragraph from another. This is necessary because too long paragraphs make it difficult for readers to grasp the information. A space between paragraphs will help the readers to easily wade through the text. A paragraph break also signals the transition of one idea of one body paragraph to an idea of another body paragraph.
The body paragraph should be short
The body paragraph should be short and concise . The paragraphs should not exceed one page. Paragraphs exceeding a page will make the article or essay complicated to comprehend the information.
Body paragraphs should be proofread
After writing the body paragraph, proofreading is done. This will help in finding and fixing mistakes. It will also help in removing unnecessary sentences in the body paragraph. The ideal way to proofread is by reading the body paragraph loudly. Doing so will help in identifying awkward word placements in the sentence.
In addition to this, asking questions like “is the body paragraph sticking to the main idea of the topic?” should be exercised. It will give a sense that if the paragraph is heading in the right direction or not.
How to start a body paragraph
The first sentence in a body paragraph is the topic sentence and it is the hardest sentence to write. The topic sentence sets the stage for the rest of the sentences in the paragraph.
Once the reader reads the topic sentence, the reader should get a sense that what the rest of the paragraph will be.
So, it should be concise and to the point, revealing enough information that will help the reader to know what the paragraph will be all about.
How to conclude a body paragraph
At the end of the body paragraph, the sentence should summarize the claim stated in the topic sentence and should also include a brief explanation of the supporting sentences. It should be written in such a way that the sentence is concise and at the same time reveals the main points.
This sentence will help the reader to get a gist of what the paragraph is all about.
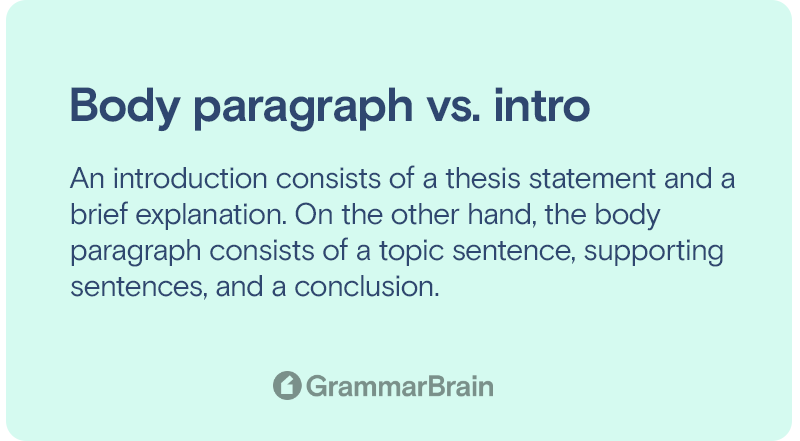
Difference between body paragraph and introduction
Though both of them are paragraphs, they are very different. Firstly, the structure of an introduction is constructed differently than the body paragraph. An introduction consists of a thesis statement and a brief explanation. On the other hand, the body paragraph consists of a topic sentence, supporting sentences, and a conclusion.
Secondly, the introduction comes first in an essay or an article. In comparison, the body paragraph comes after the introduction. It comes after the introduction and before the conclusion of an essay or article.
A typical body paragraph should contain at least six sentences.
To develop a well-structured paragraph:
- Construct a topic sentence.
- Include evidence to support the claim expressed in the topic sentence.
- Add analysis to the paragraph.
- End it with a conclusion summarizing the key points of the paragraph.
- Finally, proofread the paragraph to identify and fix mistakes.
An introduction is the first paragraph of an essay or article. It gets the reader’s attention regarding the topic and provides the thesis statement of the topic. To write a good introduction:
- Keep the introduction paragraph short.
- In one to two sentences explain the thesis statement of the article or essay.
There is no fixed number of words that a body paragraph should have. That said, typically a paragraph contains about a hundred to two hundred words which are six to seven sentences.
Yes, an essay or article can have more than one body paragraph. Some essays have three to four body paragraphs. That said, having two of these is enough to cover important points of the essay.
A conclusion comes after the body paragraph at the end of the essay. A long essay can have two or three paragraphs to conclude. It summarizes the main idea of the topic.
- Body Paragraphs: How to Write Perfect Ones | Grammarly blog
- Body Paragraph Example & Structure
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph
- How to Write a Body Paragraph | BestColleges
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjunction
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Interjection
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons

Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

Body Paragraphs

In a typical academic paper, the basic structure includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. See our handouts on introductions and conclusions for more information on the particulars related to them, but for this handout, we will be covering body paragraphs and what to include when you write them.
Body paragraphs are situated between the introduction and the conclusion and reveal the support for your argument. You can organize these body paragraphs in a variety of ways (see our handout on Organizational Strategies ), but whichever way you choose, make sure you are consistent, so your reader always knows what is coming next in your paper.
Basic Parts of a Body Paragraph
- Topic sentence
- Evidence cycle (Assertion, evidence, commentary)
- Concluding statement
As you can tell, there are several “moving parts” to a successful body paragraph. However, with a clear understanding of your paper’s purpose and guidelines, you should be able to tackle your content, no problem.
Now the handout will go over each of these aspects of a body paragraph in detail, with examples, so you can see how easy it is for a body paragraph to take shape!
Transition Placement
Transitions can be placed either at the end of a body paragraph to preview the next or at the beginning of the next body paragraph to connect it to the previous. If you’re unsure which you should use, check with your instructor to see if they have any particular preference.
The transition also does not have to be a separate sentence—sometimes the topic sentence and concluding statements can also do the work of the transition sentence.
Sample Paragraph
Since “Tick Tock” is played in reverse, we are not able to physically hear or make out what the characters are saying. As an alternative, Ien Chi uses subtitles to ensure the audience knows what the characters are conflicting about and to understand the plot at a higher level. With the use of the subtitles, the audience is able to see and relate to Emit’s mindset. Also, we are given a taste of the pain Emit is going through as he thinks he is about to die. Emit confesses his love for Rena in a way where one can tell he screwed up somewhere in the past. Then, we see him telling off his professor saying his teaching sucks and his lectures are stupid. With this, one can tell that Emit has a lot of anger built up inside of him. Then, we see him donating his whole wallet to a donation station. Emit calls his parents and apologizes for being a horrible son and for treating them so badly, but he loved them. He wanted to clear some things up and leave this earth on a good note, and the subtitles help us realize that. What better time to let it all out than when you are about to die? We are soon exposed to the whole reason why Emit is racing around asking for forgiveness. He has taken some pills that his buddy claims will kill him within minutes. This is a prank but quite a life changing one. Without the use of subtitles, we would not be exposed to the plot correctly. We would just see this guy running around frantically. This may have caused people to see this story as comedic rather than serious like it is supposed to be. Through the use of subtitles as an alternative dialogue, we are able to understand what is truly important to Emit when he is put at the face of death and how he got in this position in the first place.
This body paragraph contains all of the necessary parts to make it successful. Let’s dissect it to see each of these parts in more detail.
As we mentioned above in the tip box, transitions can go either at the end of a body paragraph to preview the next, or at the beginning of a body paragraph to sum up the previous. In this paragraph, the transition comes first:
“Since ‘Tick Tock’ is played in reverse, we are not able to physically hear or make out what the characters are saying.”
We know that the previous body paragraph dealt with the way the film plays in reverse, and can see that the direction for this new paragraph is how that affects the sound, or lack of sound, in the film.
Topic Sentence
The topic sentence follows the transition to give a more detailed introduction to the main idea of this paragraph. The topic sentence from the example paragraph above is:
“As an alternative, Ien Chi uses subtitles to ensure the audience knows what the characters are conflicting about and to understand the plot at a higher level.”
While it is still a little vague (the argument could be specified here and connected more clearly to the thesis of the paper), it allows the reader a preview so they’re prepared for the evidence to come.
Evidence Cycle
Next comes the support, which is the main bulk of the paragraph. This three-prong system repeats again and again until the paragraph is complete. In this paragraph, we have identified two different evidence cycles for you.
Assertation
The assertion introduces or provides context for the evidence you are about to give your reader. From the paragraph above there are two assertions.
First assertion: “Also, we are given a taste of the pain Emit is going through as he thinks he is about to die.”
Second assertion: “We are soon exposed to the whole reason why Emit is racing around asking for forgiveness.”
In these two examples from the above paragraph, we get a preview about this more specific point.
The evidence is the actual example or detail you will use, usually from a source of some kind. The first piece of evidence from the sample paragraph above is:
“Emit confesses his love for Rena in a way where one can tell he screwed up somewhere in the past. Then, we see him telling off his professor saying his teaching sucks and his lectures are stupid.”
The second piece of evidence is:
“He has taken some pills that his buddy claims will kill him within minutes.”
These two examples are specific moments from the short film that the author is using to prove the point posed in the topic sentence, and which builds on the argument made in the thesis statement.
The commentary follows through on the evidence presented with the author’s own ideas or analysis. The first example of commentary from the above sample paragraph is:
“With this, one can tell that Emit has a lot of anger built up inside of him.”
The second example of commentary from the above sample paragraph is:
“This is a prank but quite a life changing one. Without the use of subtitles, we would not be exposed to the plot correctly. We would just see this guy running around frantically. This may have caused people to see this story as comedic rather than serious like it is supposed to be.”
These examples of commentary provide further information to tie the details more fully and exactly to the argument of the paragraph and, thus, the paper as a whole.
Concluding Statement
Before moving on to the next paragraph, a body paragraph should end with some sort of concluding statement that provides closure to the main idea of that paragraph. The concluding statement from the above sample paragraph is:
“Through the use of subtitles as an alternative dialogue, we are able to understand what is truly important to Emit when he is put at the face of death and how he got in this position in the first place.”
With this sentence, the reader fully understands the point of the body paragraph and is ready to learn more and become more convinced by the information in the next body paragraph.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
What is your plagiarism score?
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.
- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub
How to Write a Body Paragraph
Last Updated: June 4, 2023
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Christopher M. Osborne, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been viewed 27,416 times.
Writing a paragraph might seem simple on the surface—it just needs a starting point, an ending point, and some related sentences in between to fill it out. However, a quality paragraph states a clear main idea, supports and analyzes this main idea based on strong evidence, and ties it all into the overall focus of your essay. This is especially true of body paragraphs, which make up the heart of your essay between the introduction and conclusion.
Planning Before Writing

- As a mini essay, each paragraph needs to have a main point (or thesis), supporting evidence, analysis of that evidence, commentary, and a recap of the main point based on the evidence and analysis. Your topic sentence acts as the thesis for the paragraph, providing a road map of what you'll discuss.
- Each paragraph should feel complete if you read it on its own, but also logically connect to the other paragraphs in the essay.
- For instance, a topic sentence might look like this: "As the length of playoff games expand, baseball fans lose interest in the game."
- Supporting evidence for this topic sentence could include statistics of how many fans watched the games, results of fan polls, and quotes from reliable sports articles.

- Like that freight train, your paragraph should move in only one direction—forward toward your end point. Each sentence needs to build on the last.
- So, before you start writing, jot down the concept for the paragraph’s main idea and start thinking how the paragraph will advance it forward.

- A body paragraph is only as good as its evidence. Your main idea will fall flat if you have flimsy evidence—or no evidence—to advance it forward.
- If you don’t have adequate evidence to support your proposed main idea for the paragraph, you’ll either have to do additional research or adjust your claim to suit your evidence.
- Great sources of evidence include books, journal articles, reliable websites, and newspaper articles.
Writing the Paragraph

- For instance, if your previous paragraph focused on revealing how exciting baseball’s World Series has been in recent years, you might start by writing, “While there’s no doubt the World Series has provided numerous exciting moments recently,...”
- Repeating a key phrase can also make a good transition. To keep with the baseball theme, you might repeat the phrase “big hit” in the last sentence of the previous paragraph and the first sentence of the current one.

- The main idea should be a claim that you can make a convincing argument to support, not a statement of fact.
- For instance: “While there’s no doubt the World Series has provided numerous exciting moments recently, the increasing amount of time it takes to complete each game likely decreases overall interest.”

- For example: “The average Major League Baseball playoff game (as of 2017) takes over three-and-a-half hours to complete, an increase in more than thirty minutes from the average length of World Series games in 1988.” [5] X Research source
- Also: “Since World Series games start after 8 pm in the Eastern Time Zone, they often don’t end until midnight or later for many viewers in the U.S.”

- While including longer quotes can sometimes be helpful, it’s usually best to incorporate smaller snippets from quotations into your own sentence.
- Introduce the quote with “asserts,” “claims,” “proposes,” or similar: “As 12-year old Boston Red Sox fan Tim Green bemoans, ‘I haven’t been able to watch the end of a single game of the World Series,’ due to the length of the games.”
- Make sure to provide a citation with the source of the quotation, according to the citation style you’re using.

- Your analysis might include anticipating counter-perspectives to your evidence: “While many baseball fans embrace the notion that it’s one of few sports without a game clock, it’s hard to imagine that anyone finds it easy to stay engaged and enthused—if tuned in at all—to a four-plus hour game.”

- Imagine that you're answering the question, "So what?" What should people take from your paragraph? How should they feel about your topic?
- For instance: “The long games and late conclusions during baseball’s showcase time of year threaten to alienate fans, especially the younger ones who are essential to the sport’s future.”
- Closing the current paragraph with an enhancement of your main idea provides a solid transition into the next paragraph, without having to write an actual transition (as you did at the start of the paragraph).
Revising Your Work

- Try having a friend or family member read the paragraph, then ask them, “What’s it about?” They should answer with some version of your main idea.

- Try cutting sentences or sections you’re not sure about and see if they are missed—if not, get rid of them permanently.

- Make sure each sentence builds logically from the one before it, and leads logically into the one after it. Try rearranging content if necessary.
- Verbal bridges can be transitions (“Also,” “However,” “So,” etc.), or you can use strategies like repetition or synonyms to link each sentence to the next.

- It’s very easy to miss mistakes in your own writing, so have a fresh set of eyes look over your work whenever possible.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://slc.berkeley.edu/some-tips-writing-efficient-effective-body-paragraphs
- ↑ https://ctl.yale.edu/sites/default/files/basic-page-supplementary-materials-files/body_paragraph_analysis_0.pdf
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://www.usatoday.com/story/sports/mlb/2017/10/23/pace-of-play-playoffs/791927001/
About this article

Reader Success Stories
Sep 29, 2023
Did this article help you?

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
How to Write the Body Paragraphs of Argumentative Essay in 2022
by Antony W
November 5, 2021

We’ve covered quite a lot on argumentative essay writing at Help for Assessment.
As of this far, you know how to come up with arguable claims and write a killer introduction for the essay.
You even know how to include a hook in space as small as the introduction paragraph.
But writing an argument goes beyond your ability to hook a reader with your introduction. You also have to work on your body paragraphs to make sure they’re up to the standard.
If this is the first time you’re working on an argumentative essay, it can be a challenge to get the body paragraphs written well.
So in this guide, we’ll show you how to work on the body paragraphs and get the section done right the first time.
Do you need help with your Argumentative Essay?
Get in touch with your professional team of writers.
How to Write The Body Paragraphs Of An Argumentative Essay
The following are the seven steps to help you build up the body paragraphs of your argumentative essay.
1. Start with a Topic Sentence
While we can argue that a topic sentence can appear anywhere in the body paragraph of your essay, it’s best to include at the very beginning.
Think about why the sentence is important based on the context of the thesis statement of your argument. While not necessarily mandatory, you can highlight an argument from the thesis statements to establish a good connection.
Keep in mind that the role of a topic sentence goes beyond showing a connection between your body paragraphs and the statement that summarizes the essay.
Your audience should look at the sentence and see that you’ve moved your argument a level higher. So you have to make your writing as unique as possible.
To be clear, some paragraphs in the body section of your argumentative essay won’t need a topic sentence.
There are instances when it would make a lot of sense to omit it, especially if you’re explaining a series of events where the next paragraph develops a concept that you already introduced.
2. Explain Your Topics Sentence – if Necessary
More often than not, your topic sentence will be self-explanatory and require no further information.
However, if you feel like there’s a need to add more information to make your ideas clear, don’t hesitate to do so. However, don’t go head on adding a big wall of text.
Another one to two sentence should be enough to explain your point.
3. Introduce Your Argument’s Evidence
When writing an argumentative essay , you must include reasonable and objective evidence to support your arguable claims.
Including your evidence to support your position can move your audience to believe that you invested your time to investigate the topic in-depth.
The evidence can be anything, from an anecdote, real life experiences, statistics, as well as quoted materials.
Integrate evidence into your essay in a way that moves your readers from just reading your words to buying into your argument without feeling a logical jolt.
4. Insert and Unpack Your Evidence
Now that you’ve introduced your evidence, it’s time to insert and then unpack it. Quotes make a good option for inserting evidence into the text, although you shouldn’t hesitate to do so using personal examples.
The next thing you need to do is unpack the evidence, and you do so by giving a thorough explanation, which naturally brings out a clear picture about why the evidence is significant to your argument.
Unpacking your evidence increases the credibility of the essay as it shows your audience that you know what you’re talking about even if they won’t agree with you.
Keep in mind that you don’t have a lot of room to unpack your evidence. Mostly, you should keep it as short as 1 to 2 sentences give or take, although you might expand it just a little if the evidence is so complicated that it requires further explanation.
5. Explain Your Evidence
Unpacking your evidence is not good enough. You have to go as far as to explain why it’s important in the first place. In other words, is the evidence that you’ve provided good enough to prove that you have a point?
Your explanation should be objective and debatable, and it’s okay to include your own opinion provided what you write makes sense.
Again, you need to keep your explanation as short as possible. You have a writing space of 1 to 3 sentences.
So pack it only with the most useful information that can convince your audience that you know what you’re talking about.
6. Write a Closing Link
A closing link is the conclusion for each paragraph. This section is a no brainer, so you don’t exactly have to think too much outside the box.
You want the concluding paragraph to assure your audience that your paragraph does indeed add up to the development of your argument. Consider using a strong transition in the closing link.
This helps to maintain the flow of your ideas in a logical order. Not to mention it makes it easy for the reader to move on to the next consequent paragraph without feeling lost.
One of the very important rules when it comes to writing a closing link is to avoid ending with a transition. Start with it instead.
Get Argumentative Essay Writing Help
Now that you know how to write the body section of your argumentative essay, it should be easy for you to complete the project on your own.
However, if you don’t have enough to complete the project and you have a tight deadline to beat, you should consider outsourcing your essay writing work to Help for Assessment.
We have a great team of writers who work hard around the clock to help people like you write great essays in just a short amount of time.
Whether you’ve run of deadlines or you have a topic have no idea how to start, our writers will work with you from start to finish. You can click here to place your order with us.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Free Al Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
- Articles of Word
How to Start An Essay- Steps with Examples
Once you have a single idea to anchor your essay, build the entire piece around it. Starting an essay can be challenging; it's like revving up the engine and keeping your ideas flowing throughout. But I've got a foolproof plan for you. In this article I will show you how to start an essay and write a powerful, impactful piece for your class.
What is the Process of Writing an Essay?
Just like any task that requires organization, writing an essay follows a structured process. If you want to ensure that your essay is well-organized and not just a free flow of ideas, consider the following process:
Read and Understand the Prompt: Begin by carefully reading the essay prompt to fully grasp what is being asked of you. Break it down into manageable parts to ensure you cover every aspect in your essay.
Plan Your Essay: Take time to brainstorm and organize your ideas. Creating an outline or a web of your ideas and supporting details will make the writing process much smoother. This will help you structure your essay logically and ensure all your points are well thought out.
Use and Cite Sources: Conduct thorough research to gather information and evidence to support your arguments. Use quotes and paraphrases from credible sources, but always avoid plagiarism by properly citing your sources.
Write a Draft: Start by writing a rough draft. As Ernest Hemingway said, “The first draft of anything is always crap.” This stage allows you to get all your ideas down without worrying about perfection. Drafts are essential for organizing your thoughts and refining your arguments.
Develop a Strong Thesis: Your thesis statement is the main argument of your essay and the most important sentence you'll write. Make it clear and compelling, setting the stage for your entire essay.
Respond to the Prompt: Once you've refined your draft, ensure that you are directly addressing every part of the prompt. Your final draft should be a polished version of your ideas, with a clear and logical flow.
Proofread: Review your essay carefully to catch any grammatical errors, typos, or awkward sentences. Proofreading is crucial because even small mistakes can undermine the professionalism and clarity of your essay.
What is the Structure of an Essay?
Although more advanced academic papers have their own unique structures, the basic high school or college essay typically follows a standardized five-paragraph format:
1.Introduction
Writing a well-structured essay is crucial for clearly conveying your ideas and arguments. While advanced academic papers may have complex structures, the basic high school or college essay typically follows a standardized five-paragraph format. This format includes an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion, each serving a specific purpose to guide the reader through your argument.
The introduction paragraph is where you start by grabbing the reader’s attention with an engaging "hook," such as a relevant quote or a surprising fact. Following this, you introduce your thesis statement, which is the central argument or point of your essay. To set the stage for the rest of the essay, you provide a brief preview of the three main points that will be covered in the body paragraphs.
The first body paragraph begins with a topic sentence that introduces the first subtopic related to your thesis. This paragraph includes supporting details or examples that illustrate your point, followed by an explanation of how these details or examples support your thesis. This structured approach ensures clarity and coherence, making your argument more persuasive.
The second body paragraph follows a similar format. It starts with a topic sentence that introduces the second subtopic. Again, you provide supporting details or examples and explain their relevance to your thesis. This repetition of structure helps reinforce your argument and makes it easier for the reader to follow your reasoning.
The third body paragraph introduces the third subtopic with a topic sentence. Just like the previous paragraphs, it includes supporting details or examples and explains how they support your thesis. This consistent format throughout the body paragraphs ensures that each point is clearly presented and thoroughly examined.
3.Conclusion
The conclusion paragraph begins with a concluding transition, such as "in conclusion," signaling that you are wrapping up your essay. You restate your thesis in a new way to reinforce your main argument. Then, you summarize the key points discussed in the body paragraphs, tying them back to your thesis.
Finally, you end with a "global statement" or call to action, leaving the reader with a final thought or suggestion related to your topic. This structured approach to essay writing helps ensure that your arguments are clear, cohesive, and compelling from start to finish.
How to Start an Essay [3 Steps with examples]
Starting an essay can bring a mix of thoughts: how to begin, how to end, what supporting points to use. This confusion often leads students to produce subpar essays. Writing an essay is a process that requires structure, which is why learning how to start an essay is crucial.
From my experience, the first tip is to analyze the question and begin brainstorming. This is followed by a series of steps I'll discuss to help you craft an essay that communicates your message effectively. Let's explore how to start an essay, including examples, samples, and techniques like opening with a thought-provoking question. Whether you're looking for "how to start an essay with examples" or a "how to start an essay sample," these tips will guide you towards a strong introduction that sets the tone for your entire piece.
1.Writing the Introduction
Your introduction sets the tone for your entire essay. It's your opportunity to grab the reader's attention and provide a roadmap for what's to come. Let's break down the key components following up with how to start an essay examples:
The hook is your opening statement that captivates your audience. It should be intriguing, thought-provoking, and relevant to your topic. A strong hook can take various forms, such as a startling statistic, a provocative question, or a vivid anecdote. The key is to pique your reader's curiosity and make them eager to read more.
a) "Imagine a world where your morning coffee could power your entire house for a day. While this might sound like science fiction, recent advancements in bioenergy are bringing us closer to this reality."
b) "In the time it takes you to read this sentence, over 200 species will have gone extinct. The alarming rate of biodiversity loss is not just a statistic—it's a call to action that we can no longer ignore."
Context / Background
After hooking your reader, provide context that helps them understand the significance of your topic. This background information should bridge the gap between your hook and your thesis statement. Explain why your topic matters, touch on recent developments or historical context, and set the stage for your main argument.
"The concept of artificial intelligence (AI) has evolved from the realm of science fiction to a cornerstone of modern technology. Over the past decade, AI has permeated various aspects of our lives, from voice assistants in our homes to complex algorithms driving social media platforms. As AI continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, it raises profound questions about the future of work, privacy, and even what it means to be human. Understanding the implications of this technological revolution is crucial as we navigate an increasingly AI-driven world."
Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the cornerstone of your essay. It clearly articulates your main argument or purpose, providing a preview of what you'll discuss in the body of your essay. A strong thesis should be specific, arguable, and concise. It sets expectations for your readers and guides the structure of your essay.
"This essay will examine the ethical implications of AI development, arguing that while artificial intelligence offers tremendous benefits in fields such as healthcare and environmental protection, it also poses significant risks to privacy, job security, and social equality. By analyzing these challenges and proposing a framework for responsible AI development, I aim to demonstrate that proactive ethical considerations are essential to harnessing AI's potential while mitigating its dangers."
Overview Ending (Optional)
To round off your introduction, you might choose to provide a brief overview of your essay's structure. This can help orient your readers and give them a clear idea of what to expect. However, be careful not to give away too much—you want to maintain some element of anticipation.
"In exploring the ethical landscape of AI, we will first delve into its transformative potential across various sectors. Then, we'll critically examine the challenges and risks associated with widespread AI adoption. Finally, we'll propose a set of ethical guidelines and policy recommendations aimed at fostering responsible AI development. Through this analysis, we'll uncover how balancing innovation with ethical considerations is crucial for creating an AI-enhanced future that benefits all of humanity."
Once we have written our overview ending, our introduction paragraph is complete. Here is an example of an introduction paragraph:
This might initially appear daunting due to its size, but leveraging WPS AI can streamline and condense the content effectively. Here's how you can simplify and refine it:
Step 1: Select your entire introduction paragraph, and then click on the "WPS AI" icon in the hover menu.
Step 2: From the list of WPS AI options, click on "Make shorter" to help reduce the length of your content.
Step 3: WPS AI will display a shorter version of your introduction in a small window; click on "Replace".
Step 4: The introduction paragraph will now be replaced with a shorter version for your essay.
2.Writing the Body
The body of your essay is where you develop your arguments and provide evidence to support your thesis. It's the meat of your essay, where you dive deep into your topic and showcase your knowledge and critical thinking skills.
Present and develop the main arguments that support your thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea or argument that contributes to your overall thesis. This structure helps your reader follow your logic and understand your points clearly.
Let's say your thesis is about the impact of renewable energy on climate change mitigation. One argument could be:
"The widespread adoption of solar power technology has significantly reduced carbon emissions in countries that have invested heavily in this renewable energy source."
Support each argument with solid evidence that reinforces your point. Evidence can include facts, statistics, research findings, expert opinions, or examples from real-life situations. The stronger and more varied your evidence, the more convincing your argument will be.
"According to a 2023 report by the International Energy Agency, countries with high solar power adoption have seen an average reduction in carbon emissions of 15% over the past five years. For instance, Germany, a leader in solar energy, has cut its carbon emissions by 28% since 2010, with solar power contributing to more than half of this reduction."
Ideas (Paragraphs)
Organize your ideas into coherent paragraphs. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Follow this with your evidence and analysis, explaining how this information supports your argument and relates to your thesis.
Topic sentence: "Beyond reducing carbon emissions, solar power adoption also stimulates economic growth and job creation in the renewable energy sector."
Evidence and analysis: "A study by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects that solar panel installer will be the fastest-growing job in the United States over the next decade, with an expected growth rate of 52%. This surge in employment opportunities not only helps to offset job losses in traditional energy sectors but also contributes to overall economic resilience. For example, in California, the solar industry has created over 86,000 jobs, boosting the state's economy while simultaneously reducing its carbon footprint."
This structure is followed for each body paragraph added. So, if you think you have 3 sub-topics, you will have 3 body paragraphs, stating the sub-topic followed by evidence to back your argument.
Transitions
Use transitions to link your paragraphs and ideas together smoothly. These can be words or phrases that show how one idea leads to another or how different viewpoints contrast. Good transitions help your essay flow logically and coherently.
"While solar power demonstrates significant benefits for both the environment and economy, it's essential to consider other renewable energy sources that complement its strengths and address its limitations."
Here is how a body paragraph would look like:
3.Writing the Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final opportunity to leave a lasting impression on your reader. It should tie together all the threads of your essay and reinforce your main points.
Summary / Synthesis
Summarize the main points you have discussed throughout the essay. This reminder helps solidify your arguments in the reader's mind.
"Throughout this essay, we've explored the multifaceted impact of renewable energy, particularly solar power, on our fight against climate change. We've seen how solar technology significantly reduces carbon emissions, stimulates economic growth through job creation, and complements other renewable energy sources. Moreover, we've examined the challenges of energy storage and distribution that come with increased reliance on solar power."
Importance of Your Topic
Explain why your topic is important or relevant. Connect the discussion back to the broader context or implications of your thesis statement.
"The transition to renewable energy sources like solar power is not just an environmental imperative; it's a pivotal moment in human history. As we face the growing threats of climate change, including rising sea levels, extreme weather events, and biodiversity loss, our energy choices today will shape the world for generations to come. The widespread adoption of solar and other renewable energy sources offers a path to a more sustainable, resilient, and equitable future."
Strong Closing Statement
End your conclusion with a strong closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a prediction, or a thought-provoking question.
"As we stand at this critical juncture, the choice is clear: embrace the power of the sun and other renewable sources, or continue down a path of environmental degradation. By investing in solar technology, supporting policies that encourage renewable energy adoption, and making conscious energy choices in our daily lives, we can harness the immense potential of renewable energy. The future of our planet is bright - if we choose to make it so. Will you be part of this solar revolution?"
The final conclusion, including all the main functions, would look something like this:
Bonus Tips: How to Polish your Essay with WPS AI
The great thing about WPS Office isn't just that it comes equipped with everything a student in any field needs and has all the tools for you to write the perfect essay, but also that WPS AI helps you improve the quality of what you have at hand.
Grammar and Spelling Check:
WPS Office includes advanced grammar and spelling check tools that automatically identify and correct errors. This feature ensures that your writing is free of typos and grammatical mistakes, enhancing the overall readability and professionalism of your essays.
Let's say you have your completed essay open in WPS Office. With the help of WPS AI spell check, proofreading and spell-checking would become much easier. Simply click on "Accept All" to make all the necessary changes.
Style and Clarity Enhancement:
Beyond just fixing errors, WPS AI offers suggestions to improve your writing style and clarity. It helps you refine your sentence structure, choose more precise words, and eliminate unnecessary jargon. This ensures that your arguments are presented clearly and effectively, making your essays more compelling and easier to understand.
Writing Assistance:
WPS AI acts as a writing assistant, providing guidance on how to continue developing your ideas. Whether you’re stuck on how to transition between paragraphs or need help expanding on a particular point, the AI offers suggestions and tips to keep your writing process smooth and efficient. This can be especially helpful in maintaining a logical flow and ensuring that all your points are well-supported and clearly articulated.
FAQs About Starting an Essay
1. what is the purpose of the introduction in an essay.
The purpose of the introduction in an essay is to familiarize the reader with the topic, highlighting its significance and relevance. It captures the reader's interest while providing essential background information. Additionally, the introduction outlines the main points of the essay and presents the thesis statement, which acts as the core argument that forms the foundation of the entire essay. By laying out these components, the introduction clarifies the importance of the topic and prepares the reader for what lies ahead in the essay.
2. What is a topic sentence?
A topic sentence is a statement that conveys the primary idea of a paragraph. It conveys the main point and establishes the paragraph's focus, ensuring that all subsequent sentences are connected to this key idea. Every paragraph in your paper should include a topic sentence to clarify its purpose.
3. Why do I need a thesis statement?
A thesis statement is crucial because it defines the main argument of an essay, guiding the writer's direction and helping the reader understand the central focus. It serves as a roadmap for the content that follows, ensuring that all points are relevant to the main idea.
4. How can I make my essay introduction stand out?
To create a memorable essay introduction, begin with an engaging hook, such as an intriguing fact, a thought-provoking quote, or a vivid illustration. Additionally, ensure that your introduction is concise, focused, and directly related to the main topic of the essay. This approach will draw the reader in and establish a solid foundation for your argument.
Create Compelling Essays With WPS Office
Learning how to start an essay will ultimately help you transform your ideas into a compelling narrative. All you need is a prompt and a topic to craft the best essay possible. Remember to infuse your work with a bit of heart to give it a personalized touch, making your writing truly unique and engaging. WPS Office is an excellent tool to help you achieve a well-crafted essay. It assists in forming proper sentences and generating new ideas, ensuring your essay is both coherent and creative.
With features like grammar and spelling checks, style and clarity enhancement, and writing assistance, WPS Office supports you every step of the way in your writing process. Download WPS Office now and experience its capabilities for yourself. It’s designed to make essay writing easier and more efficient, allowing you to focus on expressing your ideas and arguments effectively.
- 1. How to Use Transitions to Start a Paragraph [Tips with Examples]
- 2. Amazing AI Essay Generator - Make Your Essay Writing Easier
- 3. How to Start an Email (in Company and College)
- 4. 10 Must-have software for college students to start school
- 5. How to Craft the Perfect Academic Essay Steps & Examples
- 6. How to Write an Argumentative Essay- Steps with Examples

15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A body paragraph is any paragraph in the middle of an essay, paper, or article that comes after the introduction but before the conclusion. Generally, body paragraphs support the work's thesis and shed new light on the main topic, whether through empirical data, logical deduction, deliberate persuasion, or anecdotal evidence.
From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project.
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together. This article gives you some practical tips ...
How to Write a Body Paragraph - we explain the best way to start a body paragraph in a college essay or other school writing assignment.
Anatomy of a Body Paragraph. When you write strong, clear paragraphs, you are guiding your readers through your argument by showing them how your points fit together to support your thesis. The number of paragraphs in your essay should be determined by the number of steps you need to take to build your argument.
This post breaks down the four components of strong essay body paragraphs: purpose, evidence, analysis, and connection.
In the body section of your essay, you make arguments, explain ideas, and give evidence. This video will show you how to write a strong paragraph in just 3 steps: identify the paragraph's ...
The Sweetland Center for Writing exists to support student writing at all levels and in all forms and modes. This guide will walk you through crafting an intro, conclusion, and body paragraph of a traditional academic essay.
The essay body itself is organised into paragraphs, according to your plan. Remember that each paragraph focuses on one idea, or aspect of your topic, and should contain at least 4-5 sentences so you can deal with that idea properly. Each body paragraph has three sections. First is the topic sentence. This lets the reader know what the ...
Part of doing well in college is learning how to write a body paragraph, which should support your essay's thesis claim through evidence and cogent analysis.
Learn everything you need to know about body paragraphs: their core features, general structure, and ways of ordering within your essay.
Writing Body Paragraphs. Follow these steps below to write good body paragraphs. Step 1: Develop a Topic Sentence. Step 2: Provide Evidence to Support your Topic Sentence and Overall Argument. Step 3: Add your Own Analysis and Interpretation. Step 4: Conclude. Step 5: Revise and Proofread. A P.I.E. Paragraph. For Example.
This video explains how to write essay body paragraphs from the topic sentence to the conclusion sentence for each body paragraph in an essay. (There is also a shorter video on this topic shown in ...
Any essay, article, or academic writing starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion. The text between the introduction and conclusion is the body paragraph. A body paragraph supports the idea that was mentioned in the introduction by shedding light on new details using facts, statistics, arguments, or other information.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Read this post, and learn how to write Band 6 body paragraphs. Strong paragraph structure is crucial for a sustained argument.
Body Paragraphs. In a typical academic paper, the basic structure includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. See our handouts on introductions and conclusions for more information on the particulars related to them, but for this handout, we will be covering body paragraphs and what to include when you write them.
To write a strong essay, you need an introduction, a main body organized into paragraphs, and a conclusion. See how it's done with examples.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific ...
Writing a paragraph might seem simple on the surface—it just needs a starting point, an ending point, and some related sentences in between to fill it out. However, a quality paragraph states a clear main idea, supports and analyzes this main idea based on strong evidence, and ties it all into the overall focus of your essay. This is especially true of body paragraphs, which make up the ...
How to Write The Body Paragraphs Of An Argumentative Essay. The following are the seven steps to help you build up the body paragraphs of your argumentative essay. 1. Start with a Topic Sentence. While we can argue that a topic sentence can appear anywhere in the body paragraph of your essay, it's best to include at the very beginning.
A body paragraph topic sentence introduces the main idea of the paragraph and tells the reader what to expect. For example, if an essay is laying out an argument, the topic sentence of the body ...
Learn how to start an essay in 2024 with these steps and examples. Master introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions to create impactful essays.
The Anatomy of a Body Paragraph When you write strong, clear paragraphs, you are guiding your readers through your argument by showing them how your points fit together to support your thesis. The number of paragraphs in your essay should be determined by the number of steps you need to take to build your argument. To write strong paragraphs, try to focus each paragraph on one main point—and ...
This post outlines how to create references for large language model AI tools like ChatGPT and how to present AI-generated text in a paper.