Citation guides
All you need to know about citations

How to cite a master's thesis in MLA
To cite a master's thesis in a reference entry in MLA style 9th edition include the following elements:
- Author(s) name: Give the last name and name as presented in the source (e. g. Watson, John). For two authors, reverse only the first name, followed by ‘and’ and the second name in normal order (e. g. Watson, John, and John Watson). For three or more authors, list the first name followed by et al. (e. g. Watson, John, et al.)
- Thesis title: Titles are italicized when independent. If part of a larger source add quotation marks and do not italize.
- Year of publication: Give the year of publication as presented in the source.
- University: Give the name of the institution.
- Degree: Type of degree.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of a master's thesis in MLA style 9th edition:
Author(s) name . Thesis title . Year of publication . University , Degree .
Take a look at our works cited examples that demonstrate the MLA style guidelines in action:
A psychology master's thesis with one author
Bauger, Lars . Personality, Passion, Self-esteem and Psychological Well-being among Junior Elite Athletes in Norway . 2011 . U of Tromsø , Master's Thesis .
A master's thesis with one author
Aube, Kyle Eric . A Comparison of Water Main Failure Prediction Models in San Luis Obispo, CA . 2019 . Cal Poly , Master's Thesis .

This citation style guide is based on the MLA Handbook (9 th edition).
More useful guides
- MLA 8th ed. Style Guide: Dissertations, Theses
- MLA, 8th Edition: Master's Thesis or Project
- How do I cite a dissertation in MLA style?
More great BibGuru guides
- APA: how to cite a BrainPOP video
- APA: how to cite a preface
- AMA: how to cite websites
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
ZSR Library
Mla 8th ed. style guide: dissertations, theses.
- Art, Photography, Music
- Business Resources
- Dissertations, Theses
- Emails, Social Media
- Film, Television, Video
- Journal, Newspaper, & Magazine Articles
- Legal Sources
- Parenthetical (in-text) Citations
- Web Sites, Blogs
- Need more help?
Essential Elements
Citations for dissertations/master's theses should include the following:
1. Name of Author
2. Title of dissertation/thesis (italicized)
3. Date of Publication
5. Institution granting the degree (optional)
6. Description of the work (optional)
7. Database and URL if accessed through a database or repository
Sample Citation - Dissertations
Dissertations
The institution granting the degree and description of the work are optional. If you accessed the work online, include that information.

- << Previous: Business Resources
- Next: Emails, Social Media >>
- Last Updated: Sep 1, 2021 12:15 PM
- URL: https://guides.zsr.wfu.edu/mla8

MLA Citation Guide (MLA 9th Edition): Theses & Dissertations
- Advertisements
- Artificial Intelligence
- Audio Materials
- Books, eBooks & Course Packs
- Business Reports from Library Databases
- Case Studies
- Class Materials (including lecture presentation slides & recordings)
- Creative Commons Licensed Works
- Digital Assignments: Citing Your Sources This link opens in a new window
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Games & Objects
- GIS Data This link opens in a new window
- Government & Professional Organization Documents
- Images, Infographics, Maps, Charts, & Tables
- Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers (Oral Communication)
- Journal Articles
- Legal Resources
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communications (including emails and interviews)
- Reference Information from Library Databases
- Religious Works
- Social Media
- Theses & Dissertations
- Translations / Works in Another Language
- Websites (including documents/PDFs posted on websites)
- When Formatting Citation Elements
- When Identifying Citation Elements in Your Source
- When Identifying the Type of Source
- When Information is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source (Indirect Sources)
- Quoting vs. Paraphrasing
- Citation Basics
- MLA Citation FAQs
- Plagiarism This link opens in a new window
- MLA for Faculty This link opens in a new window
- Writing Support This link opens in a new window
Master's Theses & Doctoral Dissertations
Master's theses are research papers that are submitted by those pursuing Master's degrees. Dissertations are extensive research documents typically submitted by doctoral candidates including those pursuing a Ph.D. or other doctoral degrees.
| . Year of Publication. Name of Academic Institution Awarding the Degree if given, Type of source (PhD dissertation or Master's thesis). , URL.
Wiley, Amanda J. . 2021. Columbia University, PhD dissertation. , . PDF download.
Altidor-Brooks, Alison Genevieve. . 2014. University of Toronto, Master's thesis. , . | |
| Author last name, page number (if given)
|
- << Previous: Statistics
- Next: Translations / Works in Another Language >>
- Last Updated: Sep 11, 2024 4:12 PM
- URL: https://library.senecapolytechnic.ca/mla

MLA Citation Style 9th Edition: Theses & Dissertations
- Core Elements
- Audio Materials
- Books & eBooks
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Infographics, Maps, Charts, & Tables
- Indigenous Elders and Knowledge Keepers (Oral Communication)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Personal Communications (including emails and interviews)
- Religious Works
- Social Media
- Theses & Dissertations
- Websites (including documents/PDFs posted on websites)
- Works in Another Language / Translations
- No Author/Date/Etc.
- Sample Paper
- Annotated Bib.
Master's theses are research papers that are submitted by those pursuing Master's degrees. Dissertations are extensive research documents typically submitted by doctoral candidates including those pursuing a Ph.D. or other doctoral degrees.
| Author's Last Name, Author's First Name. . Year of Publication. Name of Academic Institution Awarding the Degree if given, Type of source (PhD dissertation or Master's thesis). , URL.
Wiley, Amanda J. . 2021. Columbia University, PhD dissertation. , . PDF download.
Altidor-Brooks, Alison Genevieve. . 2014. University of Toronto, Master's thesis. , . | |
| (Author's Last Name Page Number if available)
(Wiley 5) |
- << Previous: Statistics
- Next: Videos >>
- Last Updated: Aug 2, 2024 3:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.msubillings.edu/mla9
Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez, Call Box 9000 Mayagüez, PR 00681 (787) 832-4040 ext. 3810, 2151, 2155 [email protected]
MLA 9th Edition Style Guide: Dissertation/Thesis
- Generic Section Labels
- Inclusive Language
- Publisher Abbreviations
- Formatting your Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Social Media
- Audiovisual
- Personal Communication
Dissertation/Thesis
- News Publication
- Classroom Material
- Conference Proceedings and Papers
- Footnotes and Endnotes
- Tables and Figures
- Useful Links
Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting . 2010. Northwestern U,
MA thesis. ProQuest , search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=7432.
Dissertation
PhD dissertation. ProQuest , search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=7432.
- << Previous: Personal Communication
- Next: News Publication >>
- Last Updated: Aug 27, 2024 1:59 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uprm.edu/MLA9/en
Biblioteca General © 2024 - Universidad de Puerto Rico. Todos los derechos reservados.

Citation Help for MLA, 8th Edition: Master's Thesis or Project
- Book Review
- Email and Tweets
- Encyclopedia
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Master's Thesis or Project
- Music Albums & Songs
- Newspaper Article
- Formatting Your Paper
- Parenthetical Documentation
- Ethically Use Sources
Panasuk, Noel. What Variables Appear to Work in Stress Management Programs in the Workplace and How Effective are These Programs? MS Thesis, The College of St. Scholastica, 2008.
Explanation
Author: Panasuk, Noel. Last name first, followed by first and middle names. End with a period.
Title & subtitle of the book: What Variables Appear to Work in Stress Managment Programs in the Workplace and How Effective are These Programs? The title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Capitalize all important and proper words. Place in Italics and end with a period or if it has a question mark in the title, that is sufficient. Status of Publishing: MA Thesis, Use the words MA Thesis followed by a comma. If it is a project, then use the words MA project. If it is a doctoral dissertation, use the word Dissertation. Name of Institution Where Degree was Granted: The College of St. Scholastica, The full name of the college or university followed by a comma. Year of Publication: 2008. List the year of publication, which appears on the title page or the title page verso (back side of title page). End citation with a period.
[Th e above information is based on Purdue OWL .]
- << Previous: Magazine Article
- Next: Music Albums & Songs >>
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 2:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.css.edu/MLA8
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
MLA Formatting and Style Guide

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The following overview should help you better understand how to cite sources using MLA 9 th edition, including how to format the Works Cited page and in-text citations.
Please use the example at the bottom of this page to cite the Purdue OWL in MLA. See also our MLA vidcast series on the Purdue OWL YouTube Channel .
Creating a Works Cited list using the ninth edition
MLA is a style of documentation that may be applied to many different types of writing. Since texts have become increasingly digital, and the same document may often be found in several different sources, following a set of rigid rules no longer suffices.
Thus, the current system is based on a few guiding principles, rather than an extensive list of specific rules. While the handbook still describes how to cite sources, it is organized according to the process of documentation, rather than by the sources themselves. This gives writers a flexible method that is near-universally applicable.
Once you are familiar with the method, you can use it to document any type of source, for any type of paper, in any field.
Here is an overview of the process:
When deciding how to cite your source, start by consulting the list of core elements. These are the general pieces of information that MLA suggests including in each Works Cited entry. In your citation, the elements should be listed in the following order:
- Title of source.
- Title of container,
- Other contributors,
- Publication date,
Each element should be followed by the corresponding punctuation mark shown above. Earlier editions of the handbook included the place of publication and required different punctuation (such as journal editions in parentheses and colons after issue numbers) depending on the type of source. In the current version, punctuation is simpler (only commas and periods separate the elements), and information about the source is kept to the basics.
Begin the entry with the author’s last name, followed by a comma and the rest of the name, as presented in the work. End this element with a period.
Bhabha, Homi K. The Location of Culture. Routledge, 1994.
Title of source
The title of the source should follow the author’s name. Depending upon the type of source, it should be listed in italics or quotation marks.
A book should be in italics:
Henley, Patricia. The Hummingbird House . MacMurray, 1999.
An individual webpage should be in quotation marks. The name of the parent website, which MLA treats as a "container," should follow in italics:
Lundman, Susan. "How to Make Vegetarian Chili." eHow, www.ehow.com/how_10727_make-vegetarian-chili.html.*
A periodical (journal, magazine, newspaper) article should be in quotation marks:
Bagchi, Alaknanda. "Conflicting Nationalisms: The Voice of the Subaltern in Mahasweta Devi's Bashai Tudu." Tulsa Studies in Women's Literature , vol. 15, no. 1, 1996, pp. 41-50.
A song or piece of music on an album should be in quotation marks. The name of the album should then follow in italics:
Beyoncé. "Pray You Catch Me." Lemonade, Parkwood Entertainment, 2016, www.beyonce.com/album/lemonade-visual-album/.
*The MLA handbook recommends including URLs when citing online sources. For more information, see the “Optional Elements” section below.
Title of container
The eighth edition of the MLA handbook introduced what are referred to as "containers," which are the larger wholes in which the source is located. For example, if you want to cite a poem that is listed in a collection of poems, the individual poem is the source, while the larger collection is the container. The title of the container is usually italicized and followed by a comma, since the information that follows next describes the container.
Kincaid, Jamaica. "Girl." The Vintage Book of Contemporary American Short Stories, edited by Tobias Wolff, Vintage, 1994, pp. 306-07.
The container may also be a television series, which is made up of episodes.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation, created by Greg Daniels and Michael Schur, performance by Amy Poehler, season 2, episode 21, Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2010.
The container may also be a website, which contains articles, postings, and other works.
Wise, DeWanda. “Why TV Shows Make Me Feel Less Alone.” NAMI, 31 May 2019, www.nami.org/Blogs/NAMI-Blog/May-2019/How-TV-Shows-Make-Me-Feel-Less-Alone . Accessed 3 June 2019.
In some cases, a container might be within a larger container. You might have read a book of short stories on Google Books , or watched a television series on Netflix . You might have found the electronic version of a journal on JSTOR. It is important to cite these containers within containers so that your readers can find the exact source that you used.
“94 Meetings.” Parks and Recreation , season 2, episode 21, NBC , 29 Apr. 2010. Netflix, www.netflix.com/watch/70152031?trackId=200256157&tctx=0%2C20%2C0974d361-27cd-44de-9c2a-2d9d868b9f64-12120962.
Langhamer, Claire. “Love and Courtship in Mid-Twentieth-Century England.” Historical Journal , vol. 50, no. 1, 2007, pp. 173-96. ProQuest, doi:10.1017/S0018246X06005966. Accessed 27 May 2009.
Other contributors
In addition to the author, there may be other contributors to the source who should be credited, such as editors, illustrators, translators, etc. If their contributions are relevant to your research, or necessary to identify the source, include their names in your documentation.
Foucault, Michel. Madness and Civilization: A History of Insanity in the Age of Reason. Translated by Richard Howard , Vintage-Random House, 1988.
Woolf, Virginia. Jacob’s Room . Annotated and with an introduction by Vara Neverow, Harcourt, Inc., 2008.
If a source is listed as an edition or version of a work, include it in your citation.
The Bible . Authorized King James Version, Oxford UP, 1998.
Crowley, Sharon, and Debra Hawhee. Ancient Rhetorics for Contemporary Students. 3rd ed., Pearson, 2004.
If a source is part of a numbered sequence, such as a multi-volume book or journal with both volume and issue numbers, those numbers must be listed in your citation.
Dolby, Nadine. “Research in Youth Culture and Policy: Current Conditions and Future Directions.” Social Work and Society: The International Online-Only Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, 2008, www.socwork.net/sws/article/view/60/362. Accessed 20 May 2009.
Quintilian. Institutio Oratoria. Translated by H. E. Butler, vol. 2, Loeb-Harvard UP, 1980.
The publisher produces or distributes the source to the public. If there is more than one publisher, and they are all are relevant to your research, list them in your citation, separated by a forward slash (/).
Klee, Paul. Twittering Machine. 1922. Museum of Modern Art, New York. The Artchive, www.artchive.com/artchive/K/klee/twittering_machine.jpg.html. Accessed May 2006.
Women's Health: Problems of the Digestive System . American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 2006.
Daniels, Greg and Michael Schur, creators. Parks and Recreation . Deedle-Dee Productions and Universal Media Studios, 2015.
Note : The publisher’s name need not be included in the following sources: periodicals, works published by their author or editor, websites whose titles are the same name as their publisher, websites that make works available but do not actually publish them (such as YouTube , WordPress , or JSTOR ).
Publication date
The same source may have been published on more than one date, such as an online version of an original source. For example, a television series might have aired on a broadcast network on one date, but released on Netflix on a different date. When the source has more than one date, it is sufficient to use the date that is most relevant to your writing. If you’re unsure about which date to use, go with the date of the source’s original publication.
In the following example, Mutant Enemy is the primary production company, and “Hush” was released in 1999. Below is a general citation for this television episode:
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer , created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, Mutant Enemy, 1999 .
However, if you are discussing, for example, the historical context in which the episode originally aired, you should cite the full date. Because you are specifying the date of airing, you would then use WB Television Network (rather than Mutant Enemy), because it was the network (rather than the production company) that aired the episode on the date you’re citing.
“Hush.” Buffy the Vampire Slayer, created by Joss Whedon, performance by Sarah Michelle Gellar, season 4, episode 10, WB Television Network, 14 Dec. 1999 .
You should be as specific as possible in identifying a work’s location.
An essay in a book or an article in a journal should include page numbers.
Adiche, Chimamanda Ngozi. “On Monday of Last Week.” The Thing around Your Neck, Alfred A. Knopf, 2009, pp. 74-94 .
The location of an online work should include a URL. Remove any "http://" or "https://" tag from the beginning of the URL.
Wheelis, Mark. "Investigating Disease Outbreaks Under a Protocol to the Biological and Toxin Weapons Convention." Emerging Infectious Diseases , vol. 6, no. 6, 2000, pp. 595-600, wwwnc.cdc.gov/eid/article/6/6/00-0607_article. Accessed 8 Feb. 2009.
When citing a physical object that you experienced firsthand, identify the place of location.
Matisse, Henri. The Swimming Pool. 1952, Museum of Modern Art, New York .
Optional elements
The ninth edition is designed to be as streamlined as possible. The author should include any information that helps readers easily identify the source, without including unnecessary information that may be distracting. The following is a list of optional elements that can be included in a documented source at the writer’s discretion.
Date of original publication:
If a source has been published on more than one date, the writer may want to include both dates if it will provide the reader with necessary or helpful information.
Erdrich, Louise. Love Medicine. 1984. Perennial-Harper, 1993.
City of publication:
The seventh edition handbook required the city in which a publisher is located, but the eighth edition states that this is only necessary in particular instances, such as in a work published before 1900. Since pre-1900 works were usually associated with the city in which they were published, your documentation may substitute the city name for the publisher’s name.
Thoreau, Henry David. Excursions . Boston, 1863.
Date of access:
When you cite an online source, the MLA Handbook recommends including a date of access on which you accessed the material, since an online work may change or move at any time.
Bernstein, Mark. "10 Tips on Writing the Living Web." A List Apart: For People Who Make Websites, 16 Aug. 2002, alistapart.com/article/writeliving. Accessed 4 May 2009.
As mentioned above, while the MLA handbook recommends including URLs when you cite online sources, you should always check with your instructor or editor and include URLs at their discretion.
A DOI, or digital object identifier, is a series of digits and letters that leads to the location of an online source. Articles in journals are often assigned DOIs to ensure that the source is locatable, even if the URL changes. If your source is listed with a DOI, use that instead of a URL.
Alonso, Alvaro, and Julio A. Camargo. "Toxicity of Nitrite to Three Species of Freshwater Invertebrates." Environmental Toxicology , vol. 21, no. 1, 3 Feb. 2006, pp. 90-94. Wiley Online Library, doi: 10.1002/tox.20155.
Creating in-text citations using the previous (eighth) edition
Although the MLA handbook is currently in its ninth edition, some information about citing in the text using the older (eighth) edition is being retained. The in-text citation is a brief reference within your text that indicates the source you consulted. It should properly attribute any ideas, paraphrases, or direct quotations to your source, and should direct readers to the entry in the Works Cited list. For the most part, an in-text citation is the author’s name and the page number (or just the page number, if the author is named in the sentence) in parentheses :
When creating in-text citations for media that has a runtime, such as a movie or podcast, include the range of hours, minutes and seconds you plan to reference. For example: (00:02:15-00:02:35).
Again, your goal is to attribute your source and provide a reference without interrupting your text. Your readers should be able to follow the flow of your argument without becoming distracted by extra information.
How to Cite the Purdue OWL in MLA
Entire Website
The Purdue OWL . Purdue U Writing Lab, 2019.
Individual Resources
Contributors' names. "Title of Resource." The Purdue OWL , Purdue U Writing Lab, Last edited date.
The new OWL no longer lists most pages' authors or publication dates. Thus, in most cases, citations will begin with the title of the resource, rather than the developer's name.
"MLA Formatting and Style Guide." The Purdue OWL, Purdue U Writing Lab. Accessed 18 Jun. 2018.

- Collections
- Research Help
- Teaching & Learning
- Library Home
MLA Citation Style Guide: 7th Edition
- Web Sources
- Journal Articles
- Magazine & News Articles
- Encyclopedias, Dictionaries, & Reference Materials
- Audiovisual Media
- Legal & Government Documents
Dissertation and Theses: Unpublished
Dissertation and theses: published, contact kelly.
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited Page
General, Electronic:
Last-name, First-name. “Title of Dissertation.” Diss. Place of Study, Year. Title of Database . Web. Date Month Year of Access.
Forrester, Pearl. “Psychological Distress and Repeated Television Viewing.” Diss. Miskatonic University, 1990. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses . Web. 13 May 2010.
General, Print:
Last-name, First-name. “Title of Dissertation.” Diss. Place of Study, Year. Print.
Forrester, Pearl. “Psychological Distress and Repeated Television Viewing.” Diss. Miskatonic University, 1990. Print.
General Rule:
Author's Last-name, First-name. Title of Disstertaion . Diss. Place of Study, Year. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year of Publication. Format.
Diamond, Oscar. How to Care for Your Diabetic Cat . Diss. West Virginia University, 1999. New York: Knopf, 2000. Print.

- << Previous: Legal & Government Documents
- Next: In-Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Jul 26, 2023 9:04 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wvu.edu/mlaguide7th
- MyExperience
MLA Citation Style, 9th Edition
- Help Guides Home
- In-Text References
- Works Cited
- One Author or Editor
- Multiple Authors or Editors
- Author and Editor
- Author and Translator
- Organization as Author
- Anonymous Work
- Chapter from an Edited Work
- Introduction, Preface, Foreword, or Afterword
- Multivolume Work
- Edition Other than the First
- Dictionary or Encyclopedia
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Book Review
- Basic Webpage
- Video Recording
- Sound Recording
- YouTube Video
- Interview or Personal Communication
- Lecture or Presentation
- Thesis or Dissertation
- Indirect Source
- Government Document
- AI Generated Content
Thesis or Dissertation - Examples
Example 1 – MA Thesis
In-Text:
( Gaudette 47 )
Works Cited:
Example 2 – PhD Dissertation
( Thomson 145-51 )
- Last Updated: Jun 28, 2024 4:05 PM
- URL: https://library.ulethbridge.ca/mlastyle9
Cite a dissertation in MLA style
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
Use the following template or our MLA Citation Generator to cite a dissertation. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator .
Reference list
Place this part in your bibliography or reference list at the end of your assignment.
In-text citation
Place this part right after the quote or reference to the source in your assignment.
Popular MLA Citation Guides
- How to cite a Book in MLA style
- How to cite a Website in MLA style
- How to cite a Journal in MLA style
- How to cite a DVD, video, or film in MLA style
- How to cite a Online image or video in MLA style
Other MLA Citation Guides
- How to cite a Archive material in MLA style
- How to cite a Artwork in MLA style
- How to cite a Blog in MLA style
- How to cite a Broadcast in MLA style
- How to cite a Chapter of an edited book in MLA style
- How to cite a Conference proceedings in MLA style
- How to cite a Court case in MLA style
- How to cite a Dictionary entry in MLA style
- How to cite a Dissertation in MLA style
- How to cite a E-book or PDF in MLA style
- How to cite a Edited book in MLA style
- How to cite a Email in MLA style
- How to cite a Encyclopedia article in MLA style
- How to cite a Government publication in MLA style
- How to cite a Interview in MLA style
- How to cite a Legislation in MLA style
- How to cite a Magazine in MLA style
- How to cite a Music or recording in MLA style
- How to cite a Newspaper in MLA style
- How to cite a Patent in MLA style
- How to cite a Podcast in MLA style
- How to cite a Presentation or lecture in MLA style
- How to cite a Press release in MLA style
- How to cite a Religious text in MLA style
- How to cite a Report in MLA style
- How to cite a Software in MLA style

Plagiarism Checker
Compare your paper to billions of pages and articles with Scribbr’s Turnitin-powered plagiarism checker.
Run a free check

AI Detector
Detect AI-generated content like ChatGPT3.5, GPT4 and Gemini in seconds
Try for free

Paraphraser
Rewrite and paraphrase texts instantly with our AI-powered paraphrasing tool.

Check your Citations
Improve your in-text citations and references for errors and inconsistencies using Scribbr's AI technology or human experts.

Grammar Checker
Eliminate grammar errors and improve your writing with our free AI-powered grammar checker.

AI Proofreader
Correct your document in minutes.
Upload my document

Proofreading & Editing
Have a human editor polish your writing to ensure your arguments are judged on merit, not grammar errors.
Get expert writing help
universalSourceForm.defaults.intro.title
universalSourceForm.overwrites.thesis.intro.text,universalSourceForm.defaults.intro.text
Citation Formats
- Citation Basics
- Chicago/Turabian
MLA 8 and 9
Journal article examples, articles from magazines, newspapers, encyclopedias, and the web, book and anthology examples, dissertations and theses, social media and non-textual sources, additional resources, printable style sheet, mla handbook.
- AI Citation Guide This link opens in a new window
- Science Citation Styles This link opens in a new window
The MLA Handbook, 8th edition, has abandoned the "print" v. "web" designations, and now uses a universal set of guidelines for all sources focusing on "containers" of information. The 9th edition of the handbook continues the same format and provides additional examples.
- A useful practice template for creating source citations is linked in the Additional Resources section below.
- For experienced users of MLA, check out the link to "What's New in the Ninth Edition" for a summary of changes.
Journal article with a DOI (Digital Object Identifier):
Kincaid, Jamaica. "In History." Callaloo, vol. 24, no. 2, Spring 2001, pp. 620-26. Project Muse , doi:10.1353/cal.2001.0097.
Parenthetical citation : (Kincaid 622)
Journal article from a database:
Capperdoni, Alessandra. "Why the Avant-Garde? The Function of the Letter in Canadian Avant-Garde Poetics." Canadian Literature , no. 210/211, Autumn/Winter 2011, pp. 97-114. Academic Search Complete , search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=a9h&AN=73785263&site=ehost-live
Parenthetical Citation : (Capperdoni 100)
Journal article in print (more than 2 authors):
Cooper, Stewart E., et al. "Professional Preparation and Continuing Education for Beginning, Entry, Midlevel, and Senior Consulting Psychologists." Consulting Psychology Journal: Practice and Research , vol. 59, no. 1, 2007, pp. 1-16.
Parenthetical Citation : (Cooper et al. 14)
Journal article reprinted in a book series:
Bergmann, Harrier F. "‘A Piercing Virtue': Emily Dickinson in Margaret Drabble's The Waterfall ." Contemporary Literary Criticism, edited by, Jeffrey W. Hunter, vol. 129, Gale, 2000, pp. 124-29. Originally published in Modern Fiction Studies , vol. 36, no. 2, Summer 1990, pp. 181-93.
Parenthetical Citation : (Bergmann 183)
Journal article from an online repository or other open access site:
Shehan, Constance L., and Amanda B. Moras. “Deconstructing Laundry: Gendered Technologies and the Reluctant Redesign of Household Labor.” Michigan Family Review , vol. 11, no. 1, 2006, pp. 39-54. hdl.handle.net/2027/spo.4919087.0011.104.
Parenthetical Citation : (Shehan and Moras 50)
Print magazine article:
Kates, Robert W. “Population and Consumption: What We Know, What We Need to Know.” Environment , Apr. 2000, pp. 10-19.
Parenthetical Citation : (Kates 12)
Online magazine article:
Deresiewicz, William. “The Death of the Artist—and the Birth of the Creative Entrepreneur.” The Atlantic , 28 Dec.2014, www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2015/01/the-death-of-the-artist-and-the-birth-of-the-creative-entrepreneur/383497/.
Parenthetical Citation : (Deresiewicz)
Print newspaper article:
Ruhe, Pierre. "Pouring it On: Heat Churns in a Vicious Cycle." The Atlanta Journal-Constitution , main edition, 8 Aug. 2008, p. A1.
Parenthetical Citation : (Ruhe)
Online newspaper article (no author):
“The Scientists Speak.” New York Times , 20 Nov. 2007, nyti.ms/25n2Pf9.
Parenthetical Citation : ("The Scientists Speak")
Newspaper article from a library database:
Jeromack, Paul. “This Once, A David of the Art World Does Goliath a Favor.” New York Times, late edition, 13 July 2002, p. B7. LexisNexis Academic , www.lexisnexis.com/lnacui2api/api/version1/getDocCui?lni=468H-Y5C0-01CN-H2CR&csi=270944,270077,11059,8411&hl=t&hv=t&hnsd=f&hns=t&hgn=t&oc=00240&perma=true.
Parenthetical Citation : (Jeromack)
Article in multi-volume encyclopedia:
Schroth, Gwen. "Scheduling." Encyclopedia of Education , edited by James W. Guthrie, 2nd ed., vol. 6, Macmillan Reference USA, 2003, pp. 2095-99.
Parenthetical Citation : (Schroth 2098)
Blog post or web article:
Hollmichel, Stefanie. "The Reading Brain: Differences between Digital and Print." So Many Books , 25 Apr. 2013, somanybooksblog.com/2013/04/25/the-reading-brain-differences-between-digital-and-print/.
Parenthetical Citation : (Hollmichel)
Books in print:
Wieder, Alan. Teacher and Comrade: Richard Dudley and the Fight for Democracy in South Africa . State U of New York P, 2008.
Parenthetical Citation : (Wieder 10-11)
Eggins, Suzanne, and Diana Slade. Analyzing Casual Conversation . Cassell, 1997.
Parenthetical Citation : (Eggins and Slade 32)
Quirk, Randolph, et al. A Comprehensive Grammar of the English Language . Longman,1985.
Parenthetical Citation : (Quirik et al. 11)
Ebook from a library database:
Coutinho, Steve. An Introduction to Daoist Philosophies . Columbia UP, 2014. eBook Collection (EBSCOhost) , search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=nlebk&AN=658170&site=ehost-live.
Parenthetical Citation : (Coutinho 21)
Book chapter in an edited volume:
Bordo, Susan. “The Moral Content of Nabokov’s Lolita .” Aesthetic Subjects , edited by Pamela R. Matthews and David McWhirter, U of Minnesota P, 2003, pp. 125-52.
Parenthetical Citation : (Bordo 132)
Stand-alone work (e.g., a play) in an anthology:
Euripides. The Trojan Women . Ten Plays , translated by Paul Roche, New American Library, 1998, pp. 457-512.
Parenthetical Citation : (Euripides 485)
Dissertation from ProQuest database:
Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting . 2010. Northwestern U, PhD dissertation. ProQuest, search.proquest.com/docview/305212264?accountid=13965.
Parenthetical Citation : (Njus 143)
Print master's thesis:
Remedios, Richard E. Defining My Process: My Journey Through the MFA Acting Program at the University of South Carolina . 2007. U of South Carolina, Master's thesis.
Parenthetical Citation : (Remedios 31-32)
X Post (formally "Tweet")
@USC. "GO GAMECOCKS." X , 13 Mar. 2022, 7:52 p.m., x.com/USC/status/1503157124217675780.
Parenthetical Citation : (@USC)
YouTube video:
"This is How Social Media is Destroying Your Life - The Fake Reality." YouTube , uploaded by MotivationGrid, 16 Jul. 2019, www.youtube.com/watch?v=e2Tq2gvGt80.
Parenthetical Citation : ("This is How Social Media is Destroying Your Life" 02:40-03:25)
Online image with URL and access date:
Van Gogh, Vincent. The Potato Eaters . 1885. Van Gogh Museum, Amsterdam. Van Gogh Museum , artsandculture.google.com/asset/the-potato-eaters-vincent-van-gogh/7gFcKarE9QeaXw. Accessed 20 Mar. 2022.
Parenthetical Citation : (Van Gogh)
Streaming film:
The Untold Story of Emmett Louis Till , directed by Keith Beauchamp, Shout Factory, 2005, Kanopy . sc.kanopy.com/video/untold-story-emmett-louis-till. Accessed 20 Mar. 2022.
Parenthetical Citation : ( The Untold Story of Emmett Louis Till )
- MLA Practice Template
- What's New in the Ninth Edition - MLA
- Using MLA Format Comprehensive help from the MLA Style Center, including quick guides to works cited and in-text citations, help formatting your research paper, and "Ask the MLA" questions and answers about unusual situations.
- MLA 8 Style Sheet
- << Previous: Chicago/Turabian
- Next: AI Citation Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 11, 2024 6:00 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.sc.edu/citation
How do I format a thesis or dissertation in MLA style?
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook . For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
The MLA Handbook does not provide guidelines for formatting a thesis or dissertation—or for preparing the parts of such a project, like a preface, dedication, or acknowledgments page—because most schools maintain their own formatting requirements. Although the MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing , out of print since 2016, summarized some of these requirements, it did so only in a very general way.
Writers of theses and dissertations should follow any guidelines their schools provide. If a school does not provide such guidelines, a successfully defended dissertation in the writer’s department might provide an example to follow.
Fast and free citation generator APA 6th and 7th ed. • MLA 8th ed. • Chicago 16th ed.
- Create Title Page
- Style Guide
- Manage Bibliographies
Mindfullness & COVID-19
MLA Style Guide
Format rules for mla 8th edition.
Please refer to the following guides for more information:
- The MLA Style Center
- Purdue OWL: MLA Formatting and Style Guide
- Citing Sources (Citation Styles): MLA Style, 8th Edition
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Guide on How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in MLA

Students and homework are synonymous in learning institutions today. Any high school or college student is no stranger to the different writing styles used when writing thesis and dissertations . However, you shouldn’t worry if you’re unfamiliar with these writing styles, as you’ll learn about them during your academic career. However, one format stands out among the various writing styles for being relatively easier to follow and implement. This article will discuss this commonly used MLA format and answer the question on how to cite a thesis paper MLA, “where does the thesis go in MLA format?” and, more so, the MLA format for thesis papers. Let’s begin.
What Is the MLA Dissertation Citation Background?
Who uses mla thesis formatting, how do you write a title page in thesis mla format, does a thesis mla format contain a summary, is mla dissertation citation complicated, does mla thesis format simplify your project, why use mla thesis citation, why your examiner wants a good mla citation thesis, advantages of using mla cite dissertation, we can help you cite a thesis mla.
Many students search “how to cite thesis MLA” or ” how to cite dissertation MLA” on the internet but don’t know what those three letters stand for. The letter MLA stands for Modern Language Association , an organization of language or literature scholars. This organization is responsible for publishing various journals in the Ph.D. format.
Perhaps this organization is mainly known for the general writing guidelines that its publication editors came up with. It all started when some literature scholars acknowledged the need of having a standard format for papers. They then came up with this format and asked their students to present their thesis statements in MLA format.
The thesis MLA format, MLA cite thesis, or citing a dissertation MLA may be a common writing style; however, it’s commonly used in the liberal arts and humanities. Here are the disciplines in which writers use the thesis MLA format example in their writing:
- Cultural studies
- Literary criticism
- Foreign languages
- English literature
Another advantage of citing dissertation MLA is the simplicity of making a title page. Unlike in other formats where the requirements for a title page are complicated, you only need your name, course name, instructor’s name, and the date. Remember to use the Times New Roman font with a measurement of 12 and double-space your work when using an MLA dissertation cite.
When using an MLA citation thesis or citing a thesis using this format, a summary is not necessary for other writing styles. Writing a summary is a task that many students find challenging or tedious as it is meant to be a stand-alone paper from your original assignment. However, when citing a dissertation MLA, the summary is not required, thus saving the student time and energy spent working on another paper.
Citing a thesis MLA or an MLA citation dissertation is easy to cite and reference your sources. MLA is simpler than other writing styles, such as the Harvard or Chicago style, where you must use complicated methods of citing and referencing your sources. Additionally, the reader can follow through with your ideas and identify your sources easily without turning pages or following certain numbers.
It’s also simpler to write your bibliography or works cited when using the MLA format as its only requirement is that the sources need to be in Alphabetical order.
This format aims to make students’ work clear and easy to follow by creating a framework for standardized methods of citations. An MLA thesis format example also creates a framework for putting down your bibliography with the help of a cite master at the end of the essay. This format also makes it easier to follow a paper through well-known cues. These cues help with easy referencing outsourced information.
When learning how to cite a master’s thesis MLA or how to cite a thesis in MLA, it’s important to learn why the format is the most common style for students online. Here are some of the reasons why you should use the MLA format thesis in your dissertation:
- To help you get a better grade, follow the required citation format in your MLA works cited thesis.
- To show your knowledge or skill by demonstrating that you are conversant with various methods of citing references.
- To show where you borrowed your ideas from, thus, preventing plagiarism.
The simple MLA rules have morphed into the guidelines used by all students worldwide in their MLA thesis statements. Examiners want you to follow the right MLA format for your thesis paper because:
- It enables them to follow through with your ideas and helps them find specific areas of your paper easily.
- It shows the student’s ability to present a professionally done paper and your knowledge of the writing style.
As previously mentioned, the MLA citation thesis format is students’ most common writing style. There are several benefits of using the MLA thesis style that make students type “how to cite a thesis MLA” or “how to cite a dissertation MLA” on their browsers.
Here are some of the advantages of how to cite a thesis using MLA format:
- Has no operating head: Unlike the headers required when you cite a dissertation APA, the process of putting a header is not applicable in MLA. This makes formatting your assignments much easier than it would use other formats.
- Fewer rules to follow: Unlike its counterparts, such as the Chicago or APA writing style, citing a dissertation, MLA has far fewer rules to remember. This makes it easier for students to cite thesis MLA correctly. Its simplicity makes it the best-suited writing style for those writing lengthy essays.
Do you need help citing a dissertation MLA or any other academic service, including writing a thesis statement in MLA format? If so, look no further, as we have a team full of experts ready to help you out with your thesis or dissertation. You can get in touch with us any day of the week for an MLA thesis example or the answer to “do you include Ph.D. in MLA citation?”
In your quest to learn how to format a thesis, how to cite a thesis, or how to cite a thesis, remember that MLA format is best suited for those who have never used writing styles before. You can always refer to us and we will help you with your Ph.D. formatting using the MLA format for help.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Plagiarism and grammar
- Citation guides
MLA Citation Generator
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper, the complete guide to mla & citations, what you’ll find in this guide.
This page provides an in-depth overview of MLA format. It includes information related to MLA citations, plagiarism, proper formatting for in-text and regular citations, and examples of citations for many different types of sources.
Looking for APA? Check out the Citation Machine’s guide on APA format . We also have resources for Chicago citation style as well.
How to be a responsible researcher or scholar
Putting together a research project involves searching for information, disseminating and analyzing information, collecting information, and repurposing information. Being a responsible researcher requires keeping track of the sources that were used to help develop your research project, sharing the information you borrowed in an ethical way, and giving credit to the authors of the sources you used. Doing all of these things prevents plagiarism.
What is Plagiarism?
Plagiarism is the act of using others’ information without giving credit or acknowledging them. There are many examples of plagiarism. Completely copying another individual’s work without providing credit to the original author is a very blatant example of plagiarism. Plagiarism also occurs when another individual’s idea or concept is passed off as your own. Changing or modifying quotes, text, or any work of another individual is also plagiarism. Believe it or not, you can even plagiarize yourself! Reusing a project or paper from another class or time and saying that it’s new is plagiarism. One way to prevent plagiarism is to add citations in your project where appropriate.
What is a Citation?
A citation shows the reader of your project where you found your information. Citations are included in the body of a project when you add a quote to your project. Citations are also included in the body when you’re paraphrasing another individual’s information. These citations in the body of a research paper are called in-text citations. They are found directly next to the information that was borrowed and are very brief to avoid causing distraction while reading a project. These brief citations include the last name of the author and a page number. Scroll down for an in-depth explanation and examples of MLA in-text citations.
In-text citations provide us with a brief idea as to where you found your information, though they usually don't include the title and other components. Look on the last page of a research project to find complete citations.
Complete citations are found on what MLA calls a works-cited list, which is sometimes called an MLA bibliography. All sources that were used to develop a research project are found on the works-cited list. Complete citations are also created for any quotes or paraphrased information used in the text. Complete citations include the author’s name, the title, publisher, year published, page numbers, URLs, and a few other pieces of information.
Looking to create your citations in just a few clicks? Need an MLA format website or book citation? Visit Citation Machine.net! Our Citation Machine MLA generator, which is an MLA citation website, will create all of your citations in just a few clicks. Click here to see more styles .
Why Does it Matter?
Citing your sources is an extremely important component of your research project. It shows that you’re a responsible researcher and that you located appropriate and reputable sources that support your thesis or claim. In addition, if your work ends up being posted online or in print, there is a chance that others will use your research project in their own work!
Scroll down to find directions on how to create citations.
How the Modern Language Association Helps You Become a Responsible Researcher
What is mla format.
The Modern Language Association is an organization that was created to develop guidelines on everything language and literature related. They have guidelines on proper grammar usage and research paper layouts. In addition, they have English and foreign language committees, numerous books and journal publications, and an annual conference. They are not connected with this guide, but the information here reflects the association’s rules for formatting papers and citations.

What are citations?
The Modern Language Association is responsible for creating standards and guidelines on how to properly cite sources to prevent plagiarism. Their style is most often used when writing papers and citing sources in the liberal arts and humanities fields. “Liberal arts” is a broad term used to describe a range of subjects including the humanities, formal sciences such as mathematics and statistics, natural sciences such as biology and astronomy, and social sciences such as geography, economics, history, and others. The humanities focuses specifically on subjects related to languages, art, philosophy, religion, music, theater, literature, and ethics.
Believe it or not, there are thousands of other types of citation styles. While this citation style is most often used for the liberal arts and humanities fields, many other subjects, professors, and schools prefer citations and papers to be styled in MLA format.
What’s the difference between a bibliography and a works-cited list?
Great question. The two terms cause a lot of confusion and are consistently misused not only by students but educators as well! Let’s start with what the two words mean.
A bibliography displays the sources the writer used to gain background knowledge on the topic and also research it in-depth. Before starting a research project, you might read up on the topic in websites, books, and other sources. You might even dive a bit deeper to find more information elsewhere. All of these sources you used to help you learn about the topic would go in an MLA format bibliography. You might even include other sources that relate to the topic.
A works-cited list displays all of the sources that were mentioned in the writing of the actual paper or project. If a quote was taken from a source and placed into a research paper, then the full citation goes on the works-cited list.
Both the works-cited list and bibliography go at the end of a paper. Most teachers do not expect students to hand in both a bibliography AND a works-cited list. Teachers generally expect to see a works-cited list, but sometimes erroneously call it a bibliography. If you’re not sure what your teacher expects, a page in MLA bibliography format, a works-cited list, or both, ask for guidance.
Why do we use this MLA style?
These specific guidelines and standards for creating citations were developed for numerous reasons. When scholars and researchers in literature, language, and numerous other fields all cite their sources in the same manner, it makes it easier for readers to look at a citation and understand the different components of a source. By looking at an MLA citation, we can see who the author is, the title of the source, when it was published, and other identifiable pieces of information.
Imagine how difficult it would be to understand the various components of a source if we didn’t all follow the same guidelines! Not only would it make it difficult to understand the source that was used, but it would also make it difficult for readers to locate it themselves. This streamlined process aides us in understanding a researcher’s sources.
How is the new version different than previous versions?
This citation style has changed dramatically over the past couple of years. The MLA Handbook is currently in its 9th edition.
The new version expands upon standards previously set in the 8th edition of the MLA Handbook, including the core elements. The structure of citations remains the same, but some formatting guidance and terminology have changed.
- DOI numbers are now formatted as https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx
- Seasons in publishing daters are lowercased: spring 2020
- The term “optional elements” is now “supplemental elements”
- “Narrative in-text citations” are called “citations in prose”
In addition, new information was added on the following:
- Hundreds of works-cited-list entries
- MLA formatting for papers
- Punctuation, spelling, and other mechanics of prose
- Chapter on inclusive language
- Notes (bibliographic and content)
For more information on MLA 9, click here .
A Deeper Look at Citations
What do they look like.
There are two types of citations. The first is a full, or complete, citation. These are found at the end of research projects. These citations are usually listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last names and include all of the information necessary for readers to be able to locate the source themselves.
Full citations are generally placed in this MLA citation format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a DOI, URL, or page range).
There are times when additional information is added into the full citation.
Not sure how to transfer the information from your source into your citation? Confused about the term, “containers”? See below for information and complete explanations of each citation component.
The second type of citation, called an “in-text citation,” is included in the main part, or body, of a project when a researcher uses a quote or paraphrases information from another source. See the next section to find out how to create in-text citations.
What are in-text citations?
As stated above, in-text citations are included in the main part of a project when using a quote or paraphrasing a piece of information from another source. We include these types of citations in the body of a project for readers to quickly gain an idea as to where we found the information.
These in-text citations are found directly next to the quote or paraphrased information. They contain a small tidbit of the information found in the regular MLA citation. The regular, or complete, citation is located at the end of a project, on the works-cited list.
Here’s what a typical in-text citation looks like:
In the book The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements…. Too much fire and you have a bad temper...too little wood and you bent too quickly...too much water and you flowed in too many directions” (Tan 31).
This specific in text citation, (Tan 31), is called an MLA parenthetical citation because the author’s name is in parentheses. It’s included so the reader sees that we are quoting something from page 31 in Tan’s book. The complete, regular citation isn’t included in the main part of the project because it would be too distracting for the reader. We want the reader to focus on our work and research, not get caught up on our sources.
Here’s another way to cite in the text:
In Tan’s novel The Joy Luck Club, the mother uses a vast amount of Chinese wisdom to explain the world and people’s temperaments. She states, “Each person is made of five elements... Too much fire and you have a bad temper... too little wood and you bent too quickly... too much water and you flowed in too many directions" (31).
If the reader would like to see the source’s full information, and possibly locate the source themselves, they can refer to the last part of the project to find the regular citation.
The regular citation, at the end of the project looks like this:
%%Tan, Amy. The Joy Luck Club. Penguin, 1989, p. 31.
Notice that the first word in the full citation (Tan) matches the “Tan” used in the body of the project. It’s important to have the first word of the full citation match the term used in the text. Why? It allows readers to easily find the full citation on the works-cited list.
If your direct quote or paraphrase comes from a source that does not have page numbers, it is acceptable to place a line number (use line or lines), paragraph number (use the abbreviation par. or pars.), sections (sec. or secs.), or chapters (ch. or chs.). Only use these other terms if they are actually labeled on the source. If it specifically says on the source, “Section 1,” for example, then it is acceptable to use “sec. 1” in the in-text citation.
If there are no numbers to help readers locate the exact point in the source, only include the author’s last name.
To determine how to create in-text citations for more than one author, no authors, or corporate authors, refer to the “Authors” section below.
More about quotations and how to cite a quote:
- Use quotes from outside sources to help illustrate and expand on your own points. The majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas.
- Include the quote exactly as you found it. It is okay to use only certain words or phrases from the quote, but keep the words (spelling and capitalization) and punctuation the same.
- It is acceptable to break up a direct quote with your own writing.
Example from a movie:
Dorothy stated, "Toto," then looked up and took in her surroundings, "I’ve a feeling we’re not in Kansas anymore" ( Wizard of Oz ).
- The entire paper should be double-spaced, including quotes.
- If the quote is longer than four lines, it is necessary to make a block quote. Block quotes show the reader that they are about to read a lengthy amount of text from another source.
- Start the quote on the next line, half an inch from the left margin.
- Do not use any indents at the beginning of the block quote.
- Only use quotation marks if there are quotation marks present in the source.
- If there is more than one paragraph in the block quote, indent the beginning of the paragraphs after the first one an additional half an inch from the left margin.
- Add your in-text citation after the final period of the block quote. Do not add an additional period after the parenthetical citation.
While his parents sat there in surprise, Colton went onto say:
“Cause I could see you,” Colon said matter-of-factly. “I went up and out of my body and I was looking down and I could see the doctor working on my body. And I saw you and Mommy. You were in a little room by yourself, praying; and Mommy was in a different room, and she was praying and talking on the phone.” (Burpo xxi)
How to create a paraphrase:
As stated above, the majority of your paper should be your own writing and ideas. It’s acceptable to include quotes, but they shouldn’t crowd your paper. If you’re finding that you’re using too many quotes in your paper, consider adding paraphrases. When you reiterate a piece of information from an outside source in your own words, you create a paraphrase.
Here’s an example:
Readers discover in the very first sentence of Peter Pan that he doesn’t grow up (Barrie 1).
What paraphrases are:
- Recycled information in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.
- They’re still references! Include an in-text citation next to the paraphrased information.
What paraphrases are not:
- A copy and pasted sentence with a few words substituted for synonyms.
Confused about whether footnotes and endnotes should be used?
Footnotes and endnotes are completely acceptable to use in this style. Use a footnote or endnote if:
- Adding additional information will help the reader understand the content. This is called a content note .
- You need to cite numerous sources in one small section of your writing. Instead of clogging up a small paragraph with in-text citations (which could cause confusion for the reader), include a footnote or endnote. This is called a bibliographic note .
Keep in mind that whether you choose to include in-text citations or footnotes/endnotes, you need to also include a full reference on the MLA format works-cited list.
Content note example:
Even Maurice Sendak’s work (the mastermind behind Where the Wild Things Are and numerous other popular children’s picture books) can be found on the banned books list. It seems as though nobody is granted immunity. 1
- In the Night Kitchen ’s main character is nude on numerous pages. Problematic for most is not the nudity of the behind, but the frontal nudity.
Work Cited:
%%Sendak, Maurice. In The Night Kitchen. Harper Collins, 1996.
Bibliographic note example:
Dahl had a difficult childhood. Both his father and sister passed away when he was a toddler. He was then sent away by his mother to boarding school (de Castella). 1
- Numerous books, such as Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG, all feature characters with absent or difficult parents.
MLA Works Cited:
Include 4 full citations for: de Castella’s article, Matilda, James and the Giant Peach, and The BFG .
Don’t forget to create full, or regular citations, and place them at the end of your project.
If you need help with in-text and parenthetical citations, CitationMachine.net can help. Our MLA citation generator is simple and easy to use!
Common Knowledge: What Is It and How Will It Affect My Writing?
Footnotes, endnotes, references, proper structuring. We know it’s a lot. Thankfully, you don’t have to include a reference for EVERY piece of information you add to your paper. You can forget about including a reference when you share a piece of common knowledge.
Common knowledge is information that most people know. For example, these are a few facts that are considered common knowledge:
- The Statue of Liberty is located in New York City
- Tokyo is the capital of Japan
- Romeo and Juliet is a play written by William Shakespeare
- English is the language most people speak in England
- An elephant is an animal
We could go on and on. When you include common knowledge in your paper, omit a reference. One less thing to worry about, right?
Before you start adding tons of common knowledge occurrences to your paper to ease the burden of creating references, we need to stop you right there. Remember, the goal of a research paper is to develop new information or knowledge. You’re expected to seek out information from outside sources and analyze and distribute the information from those sources to form new ideas. Using only common knowledge facts in your writing involves absolutely zero research. It’s okay to include some common knowledge facts here and there, but do not make it the core of your paper.
If you’re unsure if the fact you’re including is common knowledge or not, it doesn’t hurt to include a reference. There is no such thing as being overly responsible when it comes to writing and citing.
Wikipedia - Yay or Nay?
If you’re wondering whether it’s okay to use Wikipedia in your project, the answer is, it depends.
If Wikipedia is your go-to source for quick information on a topic, you’re not alone. Chances are, it’s one of the first websites to appear on your results page. It’s used by tons of people, it’s easily accessible, and it contains millions of concise articles. So, you’re probably wondering, “What’s the problem?”
The issue with Wikipedia is that it’s a user-generated site, meaning information is constantly added and modified by registered users. Who these users are and their expertise is somewhat of a mystery. The truth is anyone can register on the site and make changes to articles.
Knowing this makes some cringe, especially educators and librarians, since the validity of the information is questionable. However, some people argue that because Wikipedia is a user-generated site, the community of registered users serve as “watchdogs,” ensuring that information is valid. In addition, references are included at the bottom of each article and serve as proof of credibility. Furthermore, Wikipedia lets readers know when there’s a problem with an article. Warnings such as “this article needs clarification,” or “this article needs references to prove its validity” are shared with the reader, thus promoting transparency.
If you choose to reference a Wikipedia article in your research project, and your teacher or professor says it’s okay, then you must reference it in your project. You would treat it just as you would with any other web source.
However, you may want to instead consider locating the original source of the information. This should be fairly easy to do thanks to the references at the bottom of each article.
Specific Components of a Citation
This section explains each individual component of the citation, with examples for each section for full citations and in-text citations.
Name of the author
The author’s name is usually the first item listed in the MLA citation. Author names start with the last name, then a comma is added, and then the author’s first name (and middle name if applicable) is at the end. A period closes this information.
Here are two examples of how an author’s name can be listed in a full citation:
Twain, Mark.
Poe, Edgar Allan.
For in-text:
(Author’s Last name page number) or Author’s Last name... (page).
Wondering how to format the author’s name when there are two authors working jointly on a source? When there are two authors that work together on a source, the author names are placed in the order in which they appear on the source. Place their names in this format:
Author 1’s Last Name, First name, and Author 2’s First Name Last Name.
Here are two examples of how to cite two authors:
Clifton, Mark, and Frank Riley.
Paxton, Roberta J., and Michael Jacob Fox.
(Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name page number) or Author 1’s Last name and Author 2’s Last name... (page).
There are many times when three or more authors work together on a source. This often happens with journal articles, edited books, and textbooks.
To cite a source with three or more authors, place the information in this format:
Author 1’s Last name, First name, et al.
As you can see, only include the first author’s name. The other authors are accounted for by using “et al.” In Latin, et al. is translated to “and others.” If using the Citation Machine citation generator, this abbreviation is automatically added for you.
Here’s an example of a citation for three or more authors:
%%Warner, Ralph, et al. How to Buy a House in California. Edited by Alayna Schroeder, 12th ed., Nolo, 2009.
(Author 1’s Last name et al. page number)
Is there no author listed on your source? If so, exclude the author’s information from the citation and begin the citation with the title of the source.
For in-text: Use the title of the source in parentheses. Place the title in italics if the source stands alone. Books and films stand alone. If it’s part of a larger whole, such as a chapter in an edited book or an article on a website, place the title in quotation marks without italics.
( Back to the Future )
(“Citing And Writing”)
Other in-text structures:
Authors with the same last name in your paper? MLA essay format requires the use of first initials in-text in this scenario.
Ex: (J. Silver 45)
Are you citing more than one source by the same author? For example, two books by Ernest Hemingway? Include the title in-text.
Example: (Hemingway, For Whom The Bell Tolls 12).
Are you citing a film or song? Include a timestamp in the format of hours:minutes:seconds. ( Back to the Future 00:23:86)
Was the source found on social media, such as a tweet, Reddit, or Instagram post? If this is the case, in an MLA format paper, you are allowed to start the citation with the author’s handle, username, or screen name.
Here is an example of how to cite a tweet:
%%@CarlaHayden. “I’m so honored to talk about digital access at @UMBCHumanities. We want to share the @libraryofcongress collection.” Twitter , 13 Apr. 2017, 6:04 p.m., twitter.com/LibnOfCongress/status/852643691802091521.
While most citations begin with the name of the author, they do not necessarily have to. Quite often, sources are compiled by editors. Or, your source may be done by a performer or composer. If your project focuses on someone other than the author, it is acceptable to place that person’s name first in the citation. If you’re using the MLA works cited generator at Citation Machine.net, you can choose the individual’s role from a drop-down box.
For example, let’s say that in your research project, you focus on Leonardo DiCaprio’s performances as an actor. You’re quoting a line from the movie Titanic in your project, and you’re creating a complete citation for it in the works-cited list.
It is acceptable to show the reader that you’re focusing on Leonardo DiCaprio’s work by citing it like this in the MLA works-cited list:
%%DiCaprio, Leonardo, performer. Titanic . Directed by James Cameron. Paramount, 1997.
Notice that when citing an individual other than the author, place the individual’s role after their name. In this case, Leonardo DiCaprio is the performer.
This is often done with edited books, too. Place the editor’s name first (in reverse order), add a comma, and then add the word editor.
If you’re still confused about how to place the authors together in a citation, the tools at CitationMachine.net can help! Our website is easy to use and will create your citations in just a few clicks!
Titles and containers
The titles are written as they are found on the source and in title form, meaning the important words start with a capital.
Here’s an example of a properly written title:
Practical Digital Libraries: Books, Bytes, and Bucks.
Wondering whether to place your title in italics or quotation marks? It depends on whether the source sits by itself or not. If the source stands alone, meaning that it is an independent source, place the title in italics. If the title is part of a larger whole, place the title of the source in quotation marks and the source it is from in italics.
When citing full books, movies, websites, or albums in their entirety, these titles are written in italics.
However, when citing part of a source, such as an article on a website, a chapter in a book, a song on an album, or an article in a scholarly journal, the part is written with quotation marks and then the titles of the sources that they are found in are written in italics.
Here are some examples to help you understand how to format titles and their containers.
To cite Pink Floyd’s entire album, The Wall , cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. The Wall. Columbia, 1979.
To cite one of the songs on Pink Floyd’s album in MLA formatting, cite it as:
%%Pink Floyd. “Another Brick in the Wall (Part I).” The Wall, Columbia, 1979, track 3.
To cite a fairy tale book in its entirety, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. The Land of Stories. Little Brown, 2016.
To cite a specific story or chapter in the book, cite it as:
%%Colfer, Chris. “Little Red Riding Hood.” The Land of Stories, Little Brown, 2016, pp. 58-65.
More about containers
From the section above, you can see that titles can stand alone, or they can sit in a container. Many times, sources can sit in more than one container. Wondering how? When citing an article in a scholarly journal, the first container is the journal. The second container? It’s the database that the scholarly journal is found in. It is important to account for all containers, so readers are able to locate the exact source themselves.
When citing a television episode, the first container is the name of the show and the second container is the name of the service that it could be streaming on, such as Netflix .
If your source sits in more than one container, the information about the second container is found at the end of the citation.
Use the following format to cite your source with multiple containers :
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
If the source has more than two containers, add on another full section at the end for each container.
Not all of the fields in the citation format above need to be included in your citation. In fact, many of these fields will most likely be omitted from your citations. Only include the elements that will help your readers locate the source themselves.
Here is an example of a citation for a scholarly journal article found in a database. This source has two containers: the journal itself is one container, and the site it sits on is the other.
%%Zanetti, Francois. “Curing with Machine: Medical Electricity in Eighteenth-Century Paris.” Technology and Culture, vol. 54, no. 3, July 2013, pp. 503-530. Project Muse, muse.jhu.edu/article/520280.
If you’re still confused about containers, the Citation Machine MLA cite generator can help! MLA citing is easier when using the tools at CitationMachine.net.
Other contributors
Many sources have people besides the author who contribute to the source. If your research project focuses on an additional individual besides the author, or you feel as though including other contributors will help the reader locate the source themselves, include their names in the citation.
To include another individual in the citation, after the title, place the role of the individual, the word “by,” and then their name in standard order.
If the name of the contributor comes after a period, capitalize the first letter in the role of the individual. If it comes after a comma, the first letter in the role of the individual is lowercased.
Here’s an example of a citation for a children’s book with the name of the illustrator included:
%%Rubin, Adam. Dragons Love Tacos. Illustrated by Daniel Salmieri, Penguin, 2012.
The names of editors, directors, performers, translators, illustrators, and narrators can often be found in this part of the citation.
If the source that you’re citing states that it is a specific version or edition, this information is placed in the “versions” section of the citation.
When including a numbered edition, do not type out the number, use the numeral. Also, abbreviate the word “edition” to “ed.”
Here is an example of a citation with a specific edition:
%%Koger, Gregory. “Filibustering and Parties in the Modern State.” Congress Reconsidered, edited by Lawrence C. Dodd and Bruce I. Oppenheimer, 10th ed., CQ Press, 2013, pp. 221-236. Google Books, books.google.com/books?id=b7gkLlSEeqwC&lpg=PP1&dq=10th%20edition&pg=PR6#v=onepage&q=10th%20edition&f=false.
Many sources have numbers associated with them. If you see a number different than the date, page numbers, or editions, include this information in the “numbers” section of the citation. For MLA citing, this includes volume and/or issue numbers (use the abbreviations vol. and no.), episode numbers, track numbers, or any other numbers that will help readers identify the specific source that you used. Do not include ISBN (International Standard Book Numbers) in the citation.
It is important to include the name of the publisher (the organization that created or published the source), so that readers can locate the exact source themselves.
Include publishers for all sources except periodicals. Also, for websites, exclude this information when the name of the publisher matches the name of the website. Furthermore, the name of the publisher is often excluded from the citation for second containers, since the publisher of the second container is not necessarily responsible for the creation or production of the source’s content.
Publication dates
Publication dates are extremely important to include in citations. They allow the reader to understand when sources were published. They are also used when readers are attempting to locate the source themselves.
Dates can be written in MLA in one of two ways. Researchers can write dates as:
Day Mo. Year
Mo. Day, Year
Whichever format you decide to use, use the same format for all of your citations. If using the Citation Machine citation generator, the date will be formatted in the same way for each citation.
While it isn’t necessary to include the full date for all source citations, use the amount of information that makes the most sense to help your readers understand and locate the source themselves.
Wondering what to do when your source has more than one date? Use the date that is most applicable to your research.
The location generally refers to the place where the readers can find the source. This includes page ranges, URLs, DOI numbers, track numbers, disc numbers, or even cities and towns.
You can usually leave out http:// or https:// from URLs unless you want to hyperlink them. For DOIs, use http:// or https:// before the DOI: https://doi.org/xx.xxxx/xxx.xxxx.xxxx .
For page numbers, when citing a source found on only one page, use p.
Example: p. 6.
When citing a source that has a page range, use pp. and then add the page numbers.
Example: pp. 24-38.
Since the location is the final piece of the citation, place a period at the end. When it comes to URLs, many students wonder if the links in citations should be live or not. If the paper is being shared electronically with a teacher and other readers, it may be helpful to include live links. If you’re not sure whether to include live links or not, ask your teacher or professor for guidance.
Looking for an online tool to do the work for you? Citation Machine citing tools could help! Our site is simple (and fun!) to use.
Need some more help? There is further good information here .
Common Citation Examples
ALL sources use this format:
%%Last name of the author, First name of the author. “Source’s Title.” Container’s Title, roles and names of any other individuals who helped contribute to the source, the version of the source, any numbers associated with the source, the name of the publisher, the date the source was published, the location where individuals can find the source themselves (usually a URL or page range). *Title of Second Container, roles and names of any other contributors, the version of the second container, any numbers associated with the second container, the name of the second container’s publisher, the date the second container was published, location.
*If the source does not have a second container, omit this last part of the citation.
Remember, the Citation Machine MLA formatter can help you save time and energy when creating your citations. Check out our MLA Citation Machine pages to learn more.
- Journal Articles
How to Format a Paper
When it comes to formatting your paper or essay for academic purposes, there are specific MLA paper format guidelines to follow.
- Use paper that is 8½-by-11 inch in size. This is the standard size for copier and printer paper.
- Use high quality paper.
- Your research paper or essay should have a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the paper.
- While most word processors automatically format your paper to have one-inch margins, you can check or modify the margins of your paper by going to the “Page setup” section of your word processor.
Which font is acceptable to use?
- Use an easily readable font, specifically one that allows readers to see the difference between regular and italicized letters.
- Times New Roman, Arial, and Helvetica are recommended options.
- Use 12-point size font.
Should I double-space the paper, including citations?
- Double-space the entire paper.
- There should be a double space between each piece of information in the heading.
- Place a double space between the heading and the title.
- Place a double space between the title and the beginning of the essay.
- The works-cited list should be double-spaced as well. All citations are double-spaced.
Justification & Punctuation
- Text should be left-justified, meaning that the text is aligned, or flush, against the left margin.
- Indents signal to the reader that a new concept or idea is about to begin.
- Use the “tab” button on your keyboard to create an indent.
- Add one space after all punctuation marks.
Heading & Title
- Include a proper heading and title
- The heading should include the following, on separate lines, starting one inch from the top and left margins:
- Your full name
- Your teacher or professor’s name
- The course number
- Dates in the heading and the body of your essay should be consistent. Use the same format, either Day Month Year or Month Day, Year throughout the entire paper
- Examples: 27 July 2017 or July 27, 2017
- The title should be underneath the heading, centered in the middle of the page, without bold, underlined, italicized, or all capital letters.
Page numbers
- Number all pages, including the very first page and the works-cited list.
- Place page numbers in the top right corner, half an inch from the top margin and one inch from the right margin.
- Include your last name to the left of the page number. Example: Jacobson 4
Here’s an example to provide you with a visual:

If you need help with sentence structure or grammar, check out our paper checker. The paper checker will help to check every noun , verb , and adjective . If there are words that are misspelled or out of place, the paper checker will suggest edits and provide recommendations.
- If a citation flows onto the second line, indent it in half an inch from the left margin (called a “hanging indent”).
- For more information on the works-cited list, refer to “How to Make a Works Cited Page,” which is found below.
How to Create a Title Page
According to the Modern Language Association’s official guidelines for formatting a research paper, it is unnecessary to create or include an individual title page, or MLA cover page, at the beginning of a research project. Instead, follow the directions above, under “Heading & Title,” to create a proper heading. This heading is featured at the top of the first page of the research paper or research assignment.
If your instructor or professor does in fact require or ask for an MLA title page, follow the directions that you are given. They should provide you with the information needed to create a separate, individual title page. If they do not provide you with instructions, and you are left to create it at your own discretion, use the header information above to help you develop your research paper title page. You may want to include other information, such as the name of your school or university.
How to Make a Works Cited Page
The MLA Works Cited page is generally found at the end of a research paper or project. It contains a list of all the citations of sources used for the research project. Follow these directions to format the works-cited list to match the Modern Language Association’s guidelines.
- The “Works Cited” page has its own page at the end of a research project.
- Include the same running head as the rest of the project (Your last name and then the page number). The “Works Cited” page has the final page number for the project.
- Name the page “Works Cited,” unless your list only includes one citation. In that case, title it in MLA “Work Cited.”
- The title of the page (either “Works Cited” or “Work Cited”) is placed one inch from the top of the page, centered in the middle of the document.
- Double space the entire document, even between the title of the page and the first citation.
- Citations are listed in alphabetical order by the first word in the citation (usually the last name of the author or the first word in the title if the citation does not include the author’s name. Ignore “A,” “An,” and “The” if the title begins with these words.)
- If there are multiple citations by the same author, place them in chronological order by the date published.
- Also, instead of writing the author’s name twice in both citations, use three hyphens.
%%Angelou, Maya. I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings. Random House, 2009.
%%---. Gather Together in My Name. Random House, 1974.
- All citations begin flush against the left margin. If the citation is long and rolls onto a second or third line, indent the lines below the first line half an inch from the left margin. This is called a “hanging indent.” The purpose of a hanging indent is to make the citations easier to read. If you’re using our MLA citation machine, we’ll format each of your references with a hanging indent for you.
%%Wai-Chung, Ho. “Political Influences on Curriculum Content and Musical Meaning: Hong Kong Secondary Music Education, 1949-1997.” Journal of Historical Research in Music Education, vol. 22, no. 1, 1 Oct. 2000, pp. 5-25. Periodicals Index Online, search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/pio/docview/1297849364/citation/6B70D633F50C4EA0PQ/78?accountid=35635.
- MLA “Works Cited” pages can be longer than one page. Use as many pages as necessary. If you have only one source to cite, do not place the one citation below the text of your paper. In MLA, a “Work Cited” page is still created for that individual citation.
Here’s a sample paper to give you an idea of what an MLA paper could look like. Included at the end is an MLA “Works Cited” page example.

Looking to add a relevant image, figure, table, or musical score to your paper? Here’s the easy way to do it, while following guidelines set forth by the Modern Language Association:
- Place the image, figure, table, or music close to where it’s mentioned in the text.
- Provide source information and any additional notes directly below the image, figure, table, or music.
For tables:
- Label the table as “Table” followed by an arabic numeral such as “1.” Table 1 is the table closest to the beginning of the paper. The next table mentioned in the text would be Table 2, and so on.
- Create a title for the table and place it below the label. Capitalize all important words.
- The label (Table 1) and the title should be flush against the left margin.
- Double-space everything.
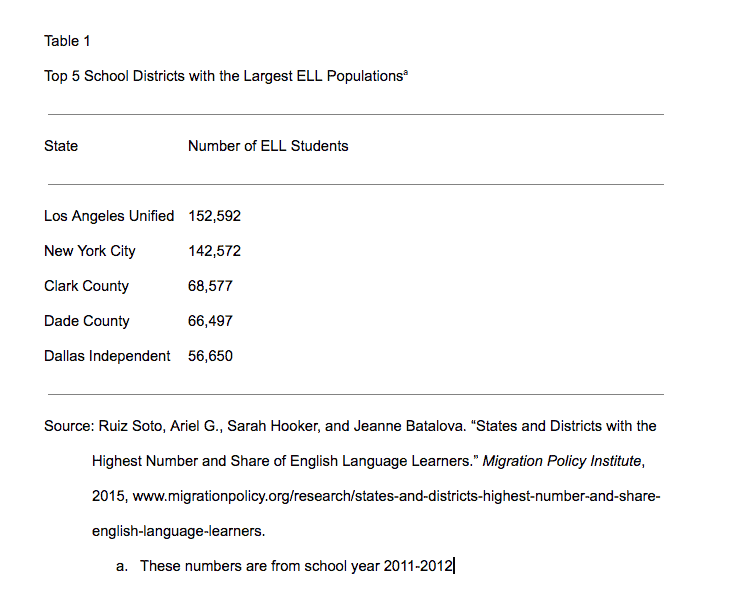
- A figure can be a map, photograph, painting, pie chart, or any other type of image.
- Create a label and place it below the figure. The figure first mentioned in the text of the project is either “Figure 1” or “Fig 1.” Though figures are usually abbreviated to “Fig.” Choose one style and use it consistently. The next mentioned figure is “Figure 2” or “Fig. 2.”, and so on.
- Place a caption next to the label. If all of the source information is included in the caption, there isn’t a need to replicate that information in the works-cited list.
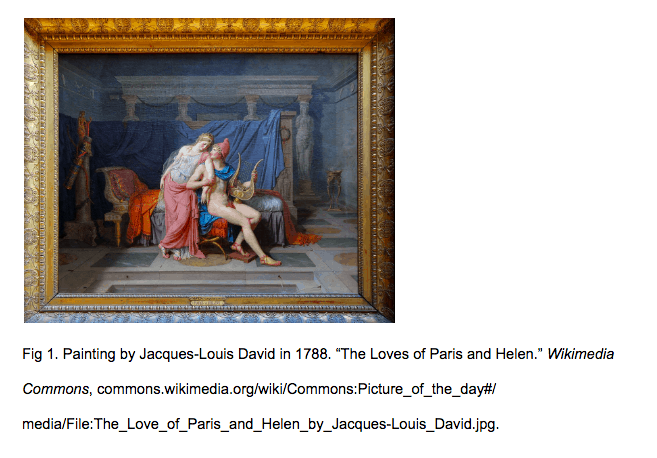
MLA Final Checklist
Think you’re through? We know this guide covered a LOT of information, so before you hand in that assignment, here’s a checklist to help you determine if you have everything you need:
_ Are both in-text and full citations included in the project? Remember, for every piece of outside information included in the text, there should be a corresponding in-text citation next to it. Include the full citation at the end, on the “Works Cited” page.
_ Are all citations, both in-text and full, properly formatted in MLA style? If you’re unsure, try out our citation generator!
_ Is your paper double-spaced in its entirety with one inch margins?
_ Do you have a running header on each page? (Your last name followed by the page number)
_ Did you use a font that is easy to read?
_ Are all citations on the MLA format works-cited list in alphabetical order?
Our plagiarism checker scans for any accidental instances of plagiarism. It scans for grammar and spelling errors, too. If you have an adverb , preposition , or conjunction that needs a slight adjustment, we may be able to suggest an edit.
Common Ways Students Accidentally Plagiarize
We spoke a bit about plagiarism at the beginning of this guide. Since you’re a responsible researcher, we’re sure you didn’t purposely plagiarize any portions of your paper. Did you know students and scholars sometimes accidentally plagiarize? Unfortunately, it happens more often than you probably realize. Luckily, there are ways to prevent accidental plagiarism and even some online tools to help!
Here are some common ways students accidentally plagiarize in their research papers and assignments:
1. Poor Paraphrasing
In the “How to create a paraphrase” section towards the top of this page, we share that paraphrases are “recycled information, in the paper writer’s own words and writing style.” If you attempt to paraphrase a few lines of text and it ends up looking and sounding too close to the original author’s words, it’s a poor paraphrase and considered plagiarism.
2. Incorrect Citations
If you cite something incorrectly, even if it’s done accidentally, it’s plagiarism. Any incorrect information in a reference, such as the wrong author name or the incorrect title, results in plagiarism.
3. Forgetting to include quotation marks
When you include a quote in your paper, you must place quotation marks around it. Failing to do so results in plagiarism.
If you’re worried about accidental plagiarism, try our Citation Machine Plus essay tool. It scans for grammar, but it also checks for any instances of accidental plagiarism. It’s simple and user-friendly, making it a great choice for stress-free paper editing and publishing.
Updated June 15, 2021
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Wendy Ikemoto. Michele Kirschenbaum has been an awesome school librarian since 2006 and is an expert in citing sources. Wendy Ikemoto has a master’s degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
- Citation Machine® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style
- Harvard Referencing
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
- Plagiarism and grammar
- School access
Cite a Thesis in MLA
- powered by chegg.

Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper
Consider your source's credibility. ask these questions:, contributor/author.
- Has the author written several articles on the topic, and do they have the credentials to be an expert in their field?
- Can you contact them? Do they have social media profiles?
- Have other credible individuals referenced this source or author?
- Book: What have reviews said about it?
- What do you know about the publisher/sponsor? Are they well-respected?
- Do they take responsibility for the content? Are they selective about what they publish?
- Take a look at their other content. Do these other articles generally appear credible?
- Does the author or the organization have a bias? Does bias make sense in relation to your argument?
- Is the purpose of the content to inform, entertain, or to spread an agenda? Is there commercial intent?
- Are there ads?
- When was the source published or updated? Is there a date shown?
- Does the publication date make sense in relation to the information presented to your argument?
- Does the source even have a date?
- Was it reproduced? If so, from where?
- If it was reproduced, was it done so with permission? Copyright/disclaimer included?
- EasyBib® Plus
- Citation Guides
- Chicago Style Format
- Terms of Use
- Global Privacy Policy
- Cookie Notice
- DO NOT SELL MY INFO
How to Cite a Dissertation and Master’s Thesis in MLA 9 With Examples
- Icon Calendar 17 May 2024
- Icon Page 2212 words
- Icon Clock 10 min read
Students pursuing a bachelor’s, master’s, or doctoral diploma and writing papers in MLA 9 must prepare to undertake unique academic projects before completing their studies. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the project is writing a thesis, while for doctoral students, it is a dissertation. Basically, this academic project in MLA 9 aims to allow students to demonstrate to themselves, their supervisors, the university, and the public that their knowledge levels have expanded during their time at the university. In this sense, both a thesis and a dissertation in MLA 9 mark the end of a student’s time at the university and entry into another higher learning level or the job market. Hence, students need to learn how to cite a dissertation and Master’s thesis in MLA 9 by reviewing the main rules discussed in this simple guide.
General Aspects of Citing a Dissertation and Master’s Thesis in MLA 9
In higher education, students undertake various activities to advance their academic qualifications. Basically, one of these activities is the writing of a dissertation or Master’s thesis in MLA 9. In particular, it is defined as a single educational project for students in undergraduate or postgraduate studies that accounts for a significant part of their degree. Also, a dissertation is known as a thesis in some contexts, meaning that both are interrelated. While a dissertation is a written project, students sometimes undergo an oral examination to prove their points and defend their work in front of assessors. In turn, it is standard practice in many universities that assessors of students’ oral presentations are professors.

Purpose of a Dissertation and Master’s Thesis
The primary purpose of writing a dissertation and Master’s thesis in MLA 9 is to allow undergraduate and postgraduate students to demonstrate their ability to explore and present scientific findings on a topic. In this case, the academic project provides students a platform upon which they show they have become significantly knowledgeable during their years at the university. Generally, the length of an undergraduate dissertation or Master’s thesis in MLA 9 is a maximum of 12,000 words, while a postgraduate one does not exceed 25,000 words. Hence, writing a dissertation or Master’s thesis in MLA 9 is the most complicated academic project that students undertake during their lifetime at the university.
Contents of a Dissertation in MLA 9
The general characteristic of a dissertation and Master’s thesis in MLA 9 is that it differs from standard essays and other writing projects that students undertake by capturing specific information. Depending on the format of the paper, a student should ensure their dissertation has:
- a title page;
- a copyright page;
- an abstract;
- optional dedication, acknowledgments, and preface pages;
- a table of contents that covers page numbers of headings and subheadings;
- a list of tables, figures, or illustrations;
- a list of abbreviations (if applicable);
- a list of symbols (if applicable);
- chapters throughout the main body;
- an appendix page;
- Works Cited page, References, Bibliography, or List of References.
Types of Dissertations
The three main types of dissertations are an undergraduate thesis, a Master’s thesis, and a doctoral dissertation. Basically, the core difference between a Master’s thesis and a dissertation is that the former marks the completion of an undergraduate or Master’s program, while the latter marks the end of a doctoral program. Consequently, a thesis paper is a student’s compilation of research, denoting an advanced level of knowledge from the day the person joined the undergraduate or master’s program to the day of completion. On the other hand, writing a dissertation in MLA 9 is a doctoral student’s compilation of knowledge that advances knowledge and theories in a specific field. Hence, a dissertation is an academic project that allows students to use what they have learned to develop new concepts in a discipline.
Structural Differences in Citing a Dissertation in MLA 9
Based on the difference in purpose, it stands to reason that citing a Master’s thesis differs from a dissertation in structure by considering the MLA 9 format. In a Master’s thesis, a student researches a topic, analyzes different sources, and comments on the information gathered. Basically, this comment entails discussing how the information researched relates to the particular subject under investigation. Therefore, a Master’s thesis showcases a student’s ability to think critically about a topic and knowledgeably discuss the information and to expand upon a topic relevant to a specialty area they wish to pursue as a profession. In contrast, a dissertation showcases a student’s ability to use others’ research as a guide in developing and proving a new theory or concept. Hence, the bulk of the information in a Master’s thesis is borrowed, while, in a dissertation, the bulk of the information is attributable to the student.
Citing a Dissertation in MLA 9
When writing academic texts, such as essays, students sometimes cite dissertations in MLA 9 as sources of essential, relevant knowledge. Basically, such citations intend to provide student’s arguments with a strong foundation. Therefore, learning to cite a dissertation in MLA 9 is a critical academic exercise. In this case, the core elements that a student should capture in a citation of a dissertation in MLA 9 are the name of the author, the title, and the date of publication. However, other optional components include the name of the institution granting the degree and a description of the work. Hence, a typical citation in the MLA 9 format indicates:
- the author’s name;
- an italicized title;
- the date of publication;
- the university granting the degree;
- a description of the work;
- the database or URL (if available);
- the date of access (if available).
1. Author’s Name
The first element in citing a dissertation in MLA 9 is the name of the author of the dissertation. Basically, the name should start with the last name, a comma, and then the first and middle names (if any). In this case, students should complete this citation with a period. Moreover, a student gets the author’s name from the publication, which can be accessed as a print, on an online database, or on a web page.
2. The Title
The title of the dissertation or Master’s thesis in MLA 9 is the second element in the citation. Basically, students should capture both the title and subtitle, if any, separating both with a colon. Also, they should use a title case, meaning that all the words in the title should be capitalized, and italics when writing the title, ending it with a period or a question mark, whatever applies. Just like the name, a student can access the dissertation title from the publication in its print form, in an online database, or from a web page.
3. Date of Publication
The third element in citing a dissertation in MLA 9 is the date when the dissertation is published. Basically, a student can find this information by looking at the dissertation title, which can be found in the dissertation in its print form, on an online database, or from a web page. Moreover, the date can appear on the backside of the title page in the case of a printed dissertation. In turn, students should end the citation with a period.
4. Name of the Institution
As an academic project in undergraduate and postgraduate studies, a dissertation is affiliated with the university that grants the student a degree. In this case, the university’s name is the fourth element in the citation of a dissertation. Like most of the information about a dissertation, a student can access the name of the institution by accessing the dissertation in its print form, in an online database, or from a webpage. In turn, students should complete the MLA citation with a comma.
5. Status of Publishing
When citing a dissertation in MLA 9, a student should indicate whether it is an undergraduate thesis, a master’s thesis, or a doctoral dissertation. In the case of a Master’s thesis, students should use the word “thesis,” indicating whether it is an undergraduate or a master’s. In the case of a dissertation, students should write it in its short form – Diss. Also, scholars can access this information by accessing the publication in its print form, in an online database, or from a webpage.
6. Dissertation Scenarios
Three scenarios involve a dissertation – unpublished dissertation, database-based dissertation, and online-based dissertation. Basically, the significant difference between these scenarios is based on exposure. Ideally, an unpublished dissertation has limited exposure, as it is only the student, the supervisor, and the university reserve copies. In contrast, both a database- and an online-based dissertation have broad exposure.
Citing an Unpublished Dissertation in MLA 9
When an undergraduate, postgraduate, or doctoral student writes a dissertation in MLA 9, entities that gain access to the work are the student, the dissertation supervisor, and the university library. In some cases, a copy is made for the archive. Also, an unpublished dissertation is rarely widely read. In that case, after serving its purpose of helping a student gain a degree, this type of discourse fades into obscurity.
Published Dissertation
After students gain degrees, it is recommended that they publish their dissertations to protect their work from fading into obscurity. Basically, a published dissertation is often found in peer-reviewed databases, but it can also be found online. In this case, publishing a dissertation in a database ensures it gains the critical title of peer-reviewed academic work, meaning that it is widely read and used as a reference in various works.
Online Publishing
Sometimes, students can publish their dissertations and make them accessible through the online platform and not a database. For example, the Internet has become home to publishers of academic content, especially those who desire to have their work freely accessible to students and other consumers. Basically, such dissertations help to broaden the reach of the publication while expanding the influence of the author. In this case, authors reach a significant number of people and get feedback from influential academics. As a result, such reach and relationships help authors to find access to journal and book publishing.
Scheme of Citing a Dissertation and Master’s Thesis in MLA 9
The scheme of an MLA 9 citation denotes its format, the way it must appear in both in-text and Works Cited citations. As stated above, the MLA 9 format must capture both core elements (author’s name, the title, date of publication) and optional elements (the name of the institution and a description of the work). However, for unpublished dissertations, there is no date of publication. As a result, for the three scenarios described above, the structure of the MLA 9 citation for a dissertation or Master’s thesis would be as follows:
1. Unpublished Dissertation:
Last Name, First and Middle Names. “Title of the Dissertation.” University, Dissertation or Master’s Thesis.
Dong, Yu Ren. “Non-Native Graduate Students’ Thesis/Dissertation Writing in Science: Self-Reports by Students and Their Advisors from Two U.S. Institutions.” 1998. Queens College, Ph.D. Dissertation.
2. Database-Based Published Dissertation:
Last, First and Middle Names. Title of Dissertation. Dissertation or Master’s Thesis, University, Date of Publication. Name of Database. Accessed Date.
Dong, Yu Ren. Non-Native Graduate Students’ Thesis/Dissertation Writing in Science: Self-Reports by Students and Their Advisors from Two U.S. Institutions. Master’s Thesis, Queens College, 1998. Elsevier Dissertations and Theses. Accessed on 31 July 2020.
3. Online-Based Dissertation:
Last, First and Middle Names. Title of Dissertation . Dissertation or Master’s Thesis, University, Date of publication, Link. Date accessed.
Dong, Yu Ren. Non-Native Graduate Students’ Thesis/Dissertation Writing in Science: Self-Reports by Students and Their Advisors from Two U.S. Institutions. Master’s Thesis, Queens College, 1998, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889490697000549. Accessed on 31 July 2020.
Note : these examples are based on a peer-reviewed scholarly article, while such samples serve only for learning purposes.
Summing Up on How to Cite a Dissertation and Master’s Thesis in MLA 9
Students in higher education (undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral studies) undertake a single academic project to mark the end of their studies. Basically, this project is a dissertation, which is also known as a Master’s thesis. Despite the differences in purpose and structure between these two notions, they provide insight into students’ grasp of knowledge during their years at the university. When citing a dissertation and Master’s thesis, a student should determine which scenario best describes the work. In this case, the three primary scenarios are unpublished dissertations, database-based published dissertations, and online-based published dissertations. On differences, the title of an unpublished dissertation is put under quotes, while that of the other two scenarios is italicized. Also, the date noted in an unpublished dissertation denotes the year it is written.
Despite the stated differences, a student should note the following tips when citing a dissertation:
- The author’s full name.
- Which scenario best describes the dissertation.
- The year the dissertation was published.
- The title of the dissertation.
- The type of degree- undergraduate or post-graduate (master’s or doctoral).
- Whether the work is a thesis or a dissertation.
- The name of the institution awarding the degree.
- The name of the database (for a database-based dissertation) or the URL (for an online-based dissertation).
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

Dissertation Defense: Students Guidelines for Successful Presentation
- Icon Calendar 1 August 2020
- Icon Page 4017 words

Autobiography Essay: Student Guidelines & Examples
- Icon Calendar 30 July 2020
- Icon Page 5603 words

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To cite a dissertation, include in the entry the author, title, and date of publication as core elements. As an optional element, list the institution granting the degree and a description of the work. Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting. 2010. Northwestern U, PhD dissertation.
To cite a master's thesis in a reference entry in MLA style 9th edition include the following elements: Author (s) name: Give the last name and name as presented in the source (e. g. Watson, John). For two authors, reverse only the first name, followed by 'and' and the second name in normal order (e. g. Watson, John, and John Watson).
Dissertation - A document submitted to earn an advanced degree, such as a doctorate, at a university. The formatting for thesis and dissertation citations is largely the same. However, you should be sure to include the type of degree after the publication year as supplemental information. For instance, state if the source you are citing is an ...
Citations for dissertations/master's theses should include the following: 1. Name of Author . 2. Title of dissertation/thesis (italicized) 3. Date of Publication. 5. Institution granting the degree (optional) 6. Description of the work (optional) 7. Database and URL if accessed through a database or repository
Master's theses are research papers that are submitted by those pursuing Master's degrees. Dissertations are extensive research documents typically submitted by doctoral candidates including those pursuing a Ph.D. or other doctoral degrees. Works Cited List Citation. Author's Last Name, Author's First Name. Title of Dissertation or Thesis.
Works Cited List Citation: Author's Last Name, Author's First Name. Title of Dissertation or Thesis.Year of Publication. Name of Academic Institution Awarding the Degree if given, Type of source (PhD dissertation or Master's thesis).
This guide will assist you in formatting in-text citations and a Works Cited list in the current MLA style. Skip to Main Content. Recinto Universitario de Mayagüez, Call Box 9000 Mayagüez, PR 00681 (787) 832-4040 ext. 3810, 2151, 2155 [email protected] ... Thesis. Njus, Jesse. Performing the Passion: A Study on the Nature of Medieval Acting ...
Status of Publishing: MA Thesis, Use the words MA Thesis followed by a comma. If it is a project, then use the words MA project. If it is a doctoral dissertation, use the word Dissertation. Name of Institution Where Degree was Granted: The College of St. Scholastica, The full name of the college or university followed by a comma. Year of ...
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is most commonly used to write papers and cite sources within the liberal arts and humanities. This resource, updated to reflect the MLA Handbook (9th ed.), offers examples for the general format of MLA research papers, in-text citations, endnotes/footnotes, and the Works Cited page.
Full Citation Rules. Citing a thesis in MLA on the Works Cited page follows the format for citing a dissertation. Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Dissertation/Thesis. Year. University, Dissertation type. Database.
General, Electronic: Last-name, First-name. "Title of Dissertation." Diss. Place of Study, Year. Title of Database.Web. Date Month Year of Access.
4401 University Drive West. Lethbridge, Alberta. T1K 3M4. Canada. 403-329-2265. [email protected]. Library Directory. The University is located on traditional Blackfoot Confederacy territory. We honour the Blackfoot people and their traditional ways of knowing in caring for this land, as well as all Indigenous Peoples who have helped ...
Search. Use the following template or our MLA Citation Generator to cite a dissertation. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator.
Thesis Paper AI Proofreader Essay Checker PhD dissertation APA editing Academic editing College admissions essay Personal statement English proofreading Spanish, French, or German. ... Improve your in-text citations and references for errors and inconsistencies using Scribbr's AI technology or human experts. Run a free check.
The MLA Handbook, 8th edition, has abandoned the "print" v. "web" designations, and now uses a universal set of guidelines for all sources focusing on "containers" of information. The 9th edition of the handbook continues the same format and provides additional examples. A useful practice template for creating source citations is linked in the ...
Scan your paper for plagiarism mistakes. Get help for 7,000+ citation styles including APA 7. Check for 400+ advanced grammar errors. Create in-text citations and save them. Free 3-day trial. Cancel anytime.*️. Try Citation Machine® Plus! *See Terms and Conditions. Consider your source's credibility.
For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook. The MLA Handbook does not provide guidelines for formatting a thesis or dissertation—or for preparing the parts of such a project, like a preface, dedication, or acknowledgments page—because most schools maintain their own formatting requirements. Although the MLA Style ...
MLA style guide - How to cite dissertation/thesis in your works cited Fast and free citation generator APA 6th and 7th ed. • MLA 8th ed. • Chicago 16th ed.
Another advantage of citing dissertation MLA is the simplicity of making a title page. Unlike in other formats where the requirements for a title page are complicated, you only need your name, course name, instructor's name, and the date. Remember to use the Times New Roman font with a measurement of 12 and double-space your work when using ...
Full Citation Rules. To cite a dissertation in MLA on the Works Cited page, follow this formula: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Dissertation/Thesis. Year. University, Dissertation type. Database.
Generate MLA citations in seconds. Start citing books, websites, journals, and more with the Citation Machine® MLA Citation Generator. ... Thesis. Write/paste citation. Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper. ... Wendy Ikemoto has a master's degree in library and information science and has been working for Citation Machine since 2012.
Don't let plagiarism errors spoil your paper. Scan your paper for plagiarism mistakes. Get help for 7,000+ citation styles including APA 6. Check for 400+ advanced grammar errors. Create in-text citations and save them. Free 3-day trial. Cancel anytime.*. Try Easybib® Plus. *See Terms and Conditions.
1. Author's Name. The first element in citing a dissertation in MLA 9 is the name of the author of the dissertation. Basically, the name should start with the last name, a comma, and then the first and middle names (if any). In this case, students should complete this citation with a period.