- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
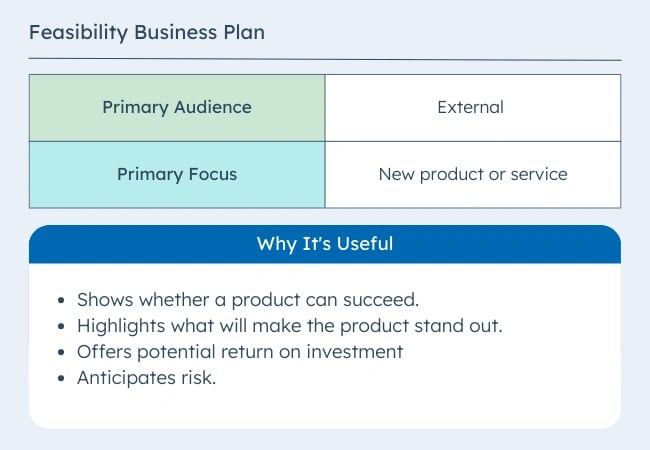
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![the definition of the business plan How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
![the definition of the business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![the definition of the business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

How To Start A Print On Demand Business In 2024
HR For Small Businesses: The Ultimate Guide
How One Company Is Using AI To Transform Manufacturing
Not-For-Profit Vs. Nonprofit: What’s The Difference?
How To Develop an SEO Strategy in 2024
How To Make Money On Social Media in 2024
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. Before joining the team, she was a Content Producer at Fit Small Business where she served as an editor and strategist covering small business marketing content. She is a former Google Tech Entrepreneur and she holds an MSc in International Marketing from Edinburgh Napier University. Additionally, she is a Columnist at Inc. Magazine.
How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples

Noah Parsons
24 min. read
Updated May 7, 2024
Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated.
In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
- The basics of business planning
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan .
You understand that planning helps you:
- Raise money
- Grow strategically
- Keep your business on the right track
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is .
At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow.
A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals.
After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business.
We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article.
There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create.
It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business.
Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What to include in your business plan
Executive summary
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan.
Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts .
Your executive summary should include:
- A summary of the problem you are solving
- A description of your product or service
- An overview of your target market
- A brief description of your team
- A summary of your financials
- Your funding requirements (if you are raising money)
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary
Products and services description
This is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service.
This is usually called a problem and solution statement .
To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers.
This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success.
Market analysis
Your target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business.
A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry .
Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market.
Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.”
Related: Target market examples
Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them.
Next, provide any additional information you have about your market.
What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis
Competitive analysis
Part of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers.
Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service.
For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone.
A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage.
Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan
Marketing and sales plan
The marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics.
The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement .
This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning.
For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products.
Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy .
This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services.
While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer.
If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process.
A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal.
Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers.
Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan
Business operations
The operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like.
Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
- Supply chain management
- Manufacturing processes
- Equipment and technology
- Distribution
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains.
These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome.
If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building.
For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services.
Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan
Key milestones and metrics
Although it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success.
Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
- A description of each task
- The proposed due date
- Who is responsible for each task
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap.
Possible milestones might be:
- Website launch date
- Store or office opening date
- First significant sales
- Break even date
- Business licenses and approvals
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
- Conversion rates
- Customer acquisition costs
- Profit per customer
- Repeat purchases
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking.
Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan
Organization and management team
Investors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running.
Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality.
Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before?
If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section.
Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
- Sole proprietor
- Partnership
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided?
Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment.
Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team
Financial plan
Last, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter.
Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast.
A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
- Sales forecast : An estimate of the sales expected over a given period. You’ll break down your forecast into the key revenue streams that you expect to have.
- Expense budget : Your planned spending such as personnel costs , marketing expenses, and taxes.
- Profit & Loss : Brings together your sales and expenses and helps you calculate planned profits.
- Cash Flow : Shows how cash moves into and out of your business. It can predict how much cash you’ll have on hand at any given point in the future.
- Balance Sheet : A list of the assets, liabilities, and equity in your company. In short, it provides an overview of the financial health of your business.
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment.
Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets
This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan.
Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data.
Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section.
Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix
Optional: Business plan cover page
Adding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference.
Your cover page should be simple and include:
- Company logo
- Business name
- Value proposition (optional)
- Business plan title
- Completion and/or update date
- Address and contact information
- Confidentiality statement
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together.
Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page
How to use AI to help write your business plan
Generative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan.
The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity.
AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers.
There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI.
Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
- Writing tips and strategies
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes .
Determine why you are writing a business plan
Knowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project.
For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure.
If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them.
Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin.
Keep things concise
Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it.
So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible.
Have someone review your business plan
Writing a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand.
Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor.
If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it.
Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get started
Knowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template.
There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search).
But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses.
Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples .
We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type.
Common pitfalls and how to avoid them
It’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started.
Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them:
Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
- Overly optimistic sales and profit forecasts: By nature, entrepreneurs are optimistic about the future. But it’s good to temper that optimism a little when you’re planning, and make sure your forecasts are grounded in reality.
- Spending too much time planning: Yes, planning is crucial. But you also need to get out and talk to customers, build prototypes of your product and figure out if there’s a market for your idea. Make sure to balance planning with building.
- Not revising the plan: Planning is useful, but nothing ever goes exactly as planned. As you learn more about what’s working and what’s not—revise your plan, your budgets, and your revenue forecast. Doing so will provide a more realistic picture of where your business is going, and what your financial needs will be moving forward.
- Not using the plan to manage your business: A good business plan is a management tool. Don’t just write it and put it on the shelf to collect dust – use it to track your progress and help you reach your goals.
- Presenting your business plan
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise.
With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas.
A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members.
Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck
Use your business plan to manage your business
One of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed.
And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business.
That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results.
Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
- Did you meet your sales goals?
- Is spending following your budget?
- Has anything gone differently than what you expected?
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets.
Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees.
Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs.
A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success.
Learn More: How to run a regular plan review
Free business plan templates and examples
Kickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.

Free business plan template
Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups.
Download Template

One-page plan template
Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.

Sample business plan library
Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries.
View Sample Plans
How to write a business plan FAQ
What is a business plan?
A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are.
What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth.
Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time.
What are the 7 steps of a business plan?
The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
- Write a brief executive summary
- Describe your products and services.
- Conduct market research and compile data into a cohesive market analysis.
- Describe your marketing and sales strategy.
- Outline your organizational structure and management team.
- Develop financial projections for sales, revenue, and cash flow.
- Add any additional documents to your appendix.
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes?
There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
- 1. Not taking the planning process seriously.
- Having unrealistic financial projections or incomplete financial information.
- Inconsistent information or simple mistakes.
- Failing to establish a sound business model.
- Not having a defined purpose for your business plan.
What questions should be answered in a business plan?
Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan.
However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
- How will your business make money?
- Is there a need for your product or service?
- Who are your customers?
- How are you different from the competition?
- How will you reach your customers?
- How will you measure success?
How long should a business plan be?
The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place.
If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place.
What are the different types of business plans?
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix.
Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan?
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision.
However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- Use AI to help write your plan
- Common planning mistakes
- Manage with your business plan
- Templates and examples
Related Articles

3 Min. Read
What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

5 Min. Read
How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.

How to make a business plan
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
Business Plan Example and Template
Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance templates and cheat sheets. Start Free
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
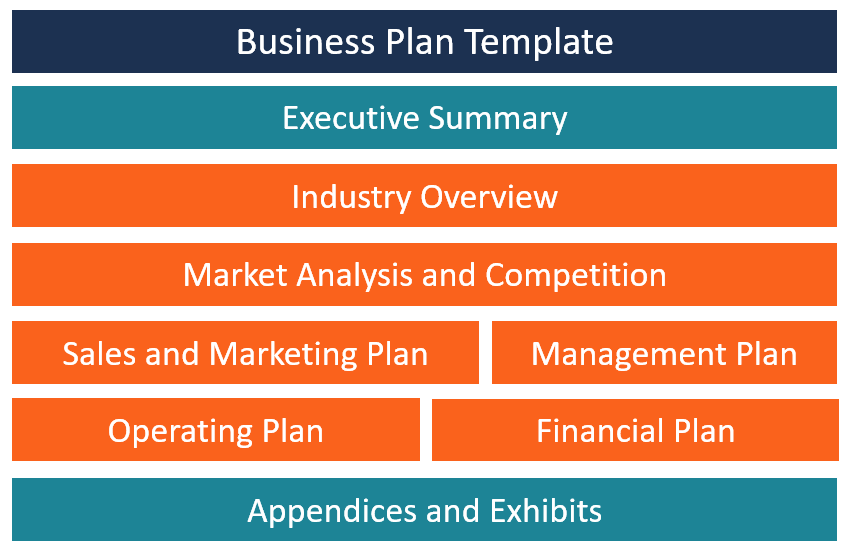
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Business Plan
By Entrepreneur Staff
Business Plan Definition:
A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
A business plan is also a road map that provides directions so a business can plan its future and helps it avoid bumps in the road. The time you spend making your business plan thorough and accurate, and keeping it up-to-date, is an investment that pays big dividends in the long term.
Your business plan should conform to generally accepted guidelines regarding form and content. Each section should include specific elements and address relevant questions that the people who read your plan will most likely ask. Generally, a business plan has the following components:
Title Page and Contents A business plan should be presented in a binder with a cover listing the name of the business, the name(s) of the principal(s), address, phone number, e-mail and website addresses, and the date. You don't have to spend a lot of money on a fancy binder or cover. Your readers want a plan that looks professional, is easy to read and is well-put-together.
Include the same information on the title page. If you have a logo, you can use it, too. A table of contents follows the executive summary or statement of purpose, so that readers can quickly find the information or financial data they need.
Executive Summary The executive summary, or statement of purpose, succinctly encapsulates your reason for writing the business plan. It tells the reader what you want and why, right up front. Are you looking for a $10,000 loan to remodel and refurbish your factory? A loan of $25,000 to expand your product line or buy new equipment? How will you repay your loan, and over what term? Would you like to find a partner to whom you'd sell 25 percent of the business? What's in it for him or her? The questions that pertain to your situation should be addressed here clearly and succinctly.
The summary or statement should be no more than half a page in length and should touch on the following key elements:
- Business concept describes the business, its product, the market it serves and the business' competitive advantage.
- Financial features include financial highlights, such as sales and profits.
- Financial requirements state how much capital is needed for startup or expansion, how it will be used and what collateral is available.
- Current business position furnishes relevant information about the company, its legal form of operation, when it was founded, the principal owners and key personnel.
- Major achievements points out anything noteworthy, such as patents, prototypes, important contracts regarding product development, or results from test marketing that have been conducted.
Description of the Business The business description usually begins with a short explanation of the industry. When describing the industry, discuss what's going on now as well as the outlook for the future. Do the necessary research so you can provide information on all the various markets within the industry, including references to new products or developments that could benefit or hinder your business. Base your observations on reliable data and be sure to footnote and cite your sources of information when necessary. Remember that bankers and investors want to know hard facts--they won't risk money on assumptions or conjecture.
When describing your business, say which sector it falls into (wholesale, retail, food service, manufacturing, hospitality and so on), and whether the business is new or established. Then say whether the business is a sole proprietorship, partnership, C or Sub chapter S corporation. Next, list the business' principals and state what they bring to the business. Continue with information on who the business' customers are, how big the market is, and how the product or service is distributed and marketed.
Description of the Product or Service The business description can be a few paragraphs to a few pages in length, depending on the complexity of your plan. If your plan isn't too complicated, keep your business description short, describing the industry in one paragraph, the product in another, and the business and its success factors in two or three more paragraphs.
When you describe your product or service, make sure your reader has a clear idea of what you're talking about. Explain how people use your product or service and talk about what makes your product or service different from others available in the market. Be specific about what sets your business apart from those of your competitors.
Then explain how your business will gain a competitive edge and why your business will be profitable. Describe the factors you think will make it successful. If your business plan will be used as a financing proposal, explain why the additional equity or debt will make your business more profitable. Give hard facts, such as "new equipment will create an income stream of $10,000 per year" and briefly describe how.
Other information to address here is a description of the experience of the other key people in the business. Whoever reads your business plan will want to know what suppliers or experts you've spoken to about your business and their response to your idea. They may even ask you to clarify your choice of location or reasons for selling this particular product.
Market Analysis A thorough market analysis will help you define your prospects as well as help you establish pricing, distribution, and promotional strategies that will allow your company to be successful vis-à-vis your competition, both in the short and long term.
Begin your market analysis by defining the market in terms of size, demographics, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. Next, determine how often your product or service will be purchased by your target market. Then figure out the potential annual purchase. Then figure out what percentage of this annual sum you either have or can attain. Keep in mind that no one gets 100 percent market share, and that a something as small as 25 percent is considered a dominant share. Your market share will be a benchmark that tells you how well you're doing in light of your market-planning projections.
You'll also have to describe your positioning strategy. How you differentiate your product or service from that of your competitors and then determine which market niche to fill is called "positioning." Positioning helps establish your product or service's identity within the eyes of the purchaser. A positioning statement for a business plan doesn't have to be long or elaborate, but it does need to point out who your target market is, how you'll reach them, what they're really buying from you, who your competitors are, and what your USP (unique selling proposition) is.
How you price your product or service is perhaps your most important marketing decision. It's also one of the most difficult to make for most small business owners, because there are no instant formulas. Many methods of establishing prices are available to you, but these are among the most common.
- Cost-plus pricing is used mainly by manufacturers to assure that all costs, both fixed and variable, are covered and the desired profit percentage is attained.
- Demand pricing is used by companies that sell their products through a variety of sources at differing prices based on demand.
- Competitive pricing is used by companies that are entering a market where there's already an established price and it's difficult to differentiate one product from another.
- Markup pricing is used mainly by retailers and is calculated by adding your desired profit to the cost of the product.
You'll also have to determine distribution, which includes the entire process of moving the product from the factory to the end user. Make sure to analyze your competitors' distribution channels before deciding whether to use the same type of channel or an alternative that may provide you with a strategic advantage.
Finally, your promotion strategy should include all the ways you communicate with your markets to make them aware of your products or services. To be successful, your promotion strategy should address advertising, packaging, public relations, sales promotions and personal sales.
Competitive Analysis The purpose of the competitive analysis is to determine:
- the strengths and weaknesses of the competitors within your market.
- strategies that will provide you with a distinct advantage.
- barriers that can be developed to prevent competition from entering your market.
- any weaknesses that can be exploited in the product development cycle.
The first step in a competitor analysis is to identify both direct and indirect competition for your business, both now and in the future. Once you've grouped your competitors, start analyzing their marketing strategies and identifying their vulnerable areas by examining their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you determine your distinct competitive advantage.
Whoever reads your business plan should be very clear on who your target market is, what your market niche is, exactly how you'll stand apart from your competitors, and why you'll be successful doing so.
Operations and Management The operations and management component of your plan is designed to describe how the business functions on a continuing basis. The operations plan highlights the logistics of the organization, such as the responsibilities of the management team, the tasks assigned to each division within the company, and capital and expense requirements related to the operations of the business.
Financial Components of Your Business Plan After defining the product, market and operations, the next area to turn your attention to are the three financial statements that form the backbone of your business plan: the income statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet.
The income statement is a simple and straightforward report on the business' cash-generating ability. It is a scorecard on the financial performance of your business that reflects when sales are made and when expenses are incurred. It draws information from the various financial models developed earlier such as revenue, expenses, capital (in the form of depreciation), and cost of goods. By combining these elements, the income statement illustrates just how much your company makes or loses during the year by subtracting cost of goods and expenses from revenue to arrive at a net result, which is either a profit or loss. In addition to the income statements, include a note analyzing the results. The analysis should be very short, emphasizing the key points of the income statement. Your CPA can help you craft this.
The cash flow statement is one of the most critical information tools for your business, since it shows how much cash you'll need to meet obligations, when you'll require it and where it will come from. The result is the profit or loss at the end of each month and year. The cash flow statement carries both profits and losses over to the next month to also show the cumulative amount. Running a loss on your cash flow statement is a major red flag that indicates not having enough cash to meet expenses-something that demands immediate attention and action.
The cash flow statement should be prepared on a monthly basis during the first year, on a quarterly basis for the second year, and annually for the third year. The following 17 items are listed in the order they need to appear on your cash flow statement. As with the income statement, you'll need to analyze the cash flow statement in a short summary in the business plan. Once again, the analysis doesn't have to be long and should cover highlights only. Ask your CPA for help.
The last financial statement you'll need is a balance sheet. Unlike the previous financial statements, the balance sheet is generated annually for the business plan and is, more or less, a summary of all the preceding financial information broken down into three areas: assets, liabilities and equity.
Balance sheets are used to calculate the net worth of a business or individual by measuring assets against liabilities. If your business plan is for an existing business, the balance sheet from your last reporting period should be included. If the business plan is for a new business, try to project what your assets and liabilities will be over the course of the business plan to determine what equity you may accumulate in the business. To obtain financing for a new business, you'll need to include a personal financial statement or balance sheet.
In the business plan, you'll need to create an analysis for the balance sheet just as you need to do for the income and cash flow statements. The analysis of the balance sheet should be kept short and cover key points.
Supporting Documents In this section, include any other documents that are of interest to your reader, such as your resume; contracts with suppliers, customers, or clients, letters of reference, letters of intent, copy of your lease and any other legal documents, tax returns for the previous three years, and anything else relevant to your business plan.
Some people think you don't need a business plan unless you're trying to borrow money. Of course, it's true that you do need a good plan if you intend to approach a lender--whether a banker, a venture capitalist or any number of other sources--for startup capital. But a business plan is more than a pitch for financing; it's a guide to help you define and meet your business goals.
Just as you wouldn't start off on a cross-country drive without a road map, you should not embark on your new business without a business plan to guide you. A business plan won't automatically make you a success, but it will help you avoid some common causes of business failure, such as under-capitalization or lack of an adequate market.
As you research and prepare your business plan, you'll find weak spots in your business idea that you'll be able to repair. You'll also discover areas with potential you may not have thought about before--and ways to profit from them. Only by putting together a business plan can you decide whether your great idea is really worth your time and investment.
More from Business Plans
Financial projections.
Estimates of the future financial performance of a business
Financial Statement
A written report of the financial condition of a firm. Financial statements include the balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in net worth and statement of cash flow.
Executive Summary
A nontechnical summary statement at the beginning of a business plan that's designed to encapsulate your reason for writing the plan
Latest Articles
These are the highest paying jobs in every u.s. state, according to a new report.
Certain states pay higher salaries for the same job.
T-Mobile Acquires USCellular in $4.4 Billion Deal: 'Even More Consumers Will Benefit'
The deal was announced on Tuesday.
Canva Is Going Viral For a Questionable Musical Performance at a Company Conference: 'Peak Cringe'
Canva Create took place in Los Angeles on May 23.
Home > Business > Business Startup
How To Write a Business Plan

We are committed to sharing unbiased reviews. Some of the links on our site are from our partners who compensate us. Read our editorial guidelines and advertising disclosure .

Starting a business is a wild ride, and a solid business plan can be the key to keeping you on track. A business plan is essentially a roadmap for your business — outlining your goals, strategies, market analysis and financial projections. Not only will it guide your decision-making, a business plan can help you secure funding with a loan or from investors .
Writing a business plan can seem like a huge task, but taking it one step at a time can break the plan down into manageable milestones. Here is our step-by-step guide on how to write a business plan.
Table of contents
- Write your executive summary
- Do your market research homework
- Set your business goals and objectives
- Plan your business strategy
- Describe your product or service
- Crunch the numbers
- Finalize your business plan

By signing up I agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Step 1: Write your executive summary
Though this will be the first page of your business plan , we recommend you actually write the executive summary last. That’s because an executive summary highlights what’s to come in the business plan but in a more condensed fashion.
An executive summary gives stakeholders who are reading your business plan the key points quickly without having to comb through pages and pages. Be sure to cover each successive point in a concise manner, and include as much data as necessary to support your claims.
You’ll cover other things too, but answer these basic questions in your executive summary:
- Idea: What’s your business concept? What problem does your business solve? What are your business goals?
- Product: What’s your product/service and how is it different?
- Market: Who’s your audience? How will you reach customers?
- Finance: How much will your idea cost? And if you’re seeking funding, how much money do you need? How much do you expect to earn? If you’ve already started, where is your revenue at now?
Step 2: Do your market research homework
The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research . This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to gather this information. Your method may be formal or more casual, just make sure that you’re getting good data back.
This research will help you to understand the needs of your target market and the potential demand for your product or service—essential aspects of starting and growing a successful business.
Step 3: Set your business goals and objectives
Once you’ve completed your market research, you can begin to define your business goals and objectives. What is the problem you want to solve? What’s your vision for the future? Where do you want to be in a year from now?
Use this step to decide what you want to achieve with your business, both in the short and long term. Try to set SMART goals—specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound benchmarks—that will help you to stay focused and motivated as you build your business.
Step 4: Plan your business strategy
Your business strategy is how you plan to reach your goals and objectives. This includes details on positioning your product or service, marketing and sales strategies, operational plans, and the organizational structure of your small business.
Make sure to include key roles and responsibilities for each team member if you’re in a business entity with multiple people.
Step 5: Describe your product or service
In this section, get into the nitty-gritty of your product or service. Go into depth regarding the features, benefits, target market, and any patents or proprietary tech you have. Make sure to paint a clear picture of what sets your product apart from the competition—and don’t forget to highlight any customer benefits.
Step 6: Crunch the numbers
Financial analysis is an essential part of your business plan. If you’re already in business that includes your profit and loss statement , cash flow statement and balance sheet .
These financial projections will give investors and lenders an understanding of the financial health of your business and the potential return on investment.
You may want to work with a financial professional to ensure your financial projections are realistic and accurate.

Step 7: Finalize your business plan
Once you’ve completed everything, it's time to finalize your business plan. This involves reviewing and editing your plan to ensure that it is clear, concise, and easy to understand.
You should also have someone else review your plan to get a fresh perspective and identify any areas that may need improvement. You could even work with a free SCORE mentor on your business plan or use a SCORE business plan template for more detailed guidance.
Compare the Top Small-Business Banks
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$0.00 | ||||||
$10.00 (waivable) | ||||||
$0.00 |
Data effective 1/10/23. At publishing time, rates, fees, and requirements are current but are subject to change. Offers may not be available in all areas.
The takeaway
Writing a business plan is an essential process for any forward-thinking entrepreneur or business owner. A business plan requires a lot of up-front research, planning, and attention to detail, but it’s worthwhile. Creating a comprehensive business plan can help you achieve your business goals and secure the funding you need.
Related content
- 5 Best Business Plan Software and Tools in 2023 for Your Small Business
- How to Get a Business License: What You Need to Know
- What Is a Cash Flow Statement?
Best Small Business Loans

5202 W Douglas Corrigan Way Salt Lake City, UT 84116
Accounting & Payroll
Point of Sale
Payment Processing
Inventory Management
Human Resources
Other Services
Best Inventory Management Software
Best Small Business Accounting Software
Best Payroll Software
Best Mobile Credit Card Readers
Best POS Systems
Best Tax Software
Stay updated on the latest products and services anytime anywhere.
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Disclaimer: The information featured in this article is based on our best estimates of pricing, package details, contract stipulations, and service available at the time of writing. All information is subject to change. Pricing will vary based on various factors, including, but not limited to, the customer’s location, package chosen, added features and equipment, the purchaser’s credit score, etc. For the most accurate information, please ask your customer service representative. Clarify all fees and contract details before signing a contract or finalizing your purchase.
Our mission is to help consumers make informed purchase decisions. While we strive to keep our reviews as unbiased as possible, we do receive affiliate compensation through some of our links. This can affect which services appear on our site and where we rank them. Our affiliate compensation allows us to maintain an ad-free website and provide a free service to our readers. For more information, please see our Privacy Policy Page . |
© Business.org 2024 All Rights Reserved.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
What Is a Business Plan?
Definition and Examples of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Morsa Images / Getty Images
A business plan is a document that summarizes the operational and financial objectives of a business. It is a business's road map to success with detailed plans and budgets that show how the objectives will be realized.
Keep reading to learn the basic components of a business plan, why they're useful , and how they differ from an investment plan.
A business plan is a guide for how a company will achieve its goals. For anyone starting a business , crafting a business plan is a vital first step. Having these concrete milestones will help track the business's success (or lack thereof). There are different business plans for different purposes, and the best business plans are living documents that respond to real-world factors as quickly as possible.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a practice in due diligence. When it's done well, it will prevent entrepreneurs from wasting time and money on a venture that won't work.
How Does a Business Plan Work?
If you have an idea for starting a new venture, a business plan can help you determine if your business idea is viable. There's no point in starting a business if there is little or no chance that the business will be profitable, and a business plan helps to figure out your chances of success.
In many cases, people starting new businesses don't have the money they need to start the business they want to start. If start-up financing is required, you must have an investor-ready business plan to show potential investors that demonstrates how the proposed business will be profitable.
Since the business plan contains detailed financial projections, forecasts about your business's performance, and a marketing plan, it's an incredibly useful tool for everyday business planning. To be as effective as possible, it should be reviewed regularly and updated as required.
Business owners have leeway when crafting their business plan outline. They can be short or long, and they can include whatever detail you think will be useful. There are basic templates you can work from, and you'll likely notice some common elements if you look up examples of business plans.
Market Analysis
The market analysis will reveal whether there is sufficient demand for your product or service in your target market . If the market is already saturated, your business model will need to be changed (or scrapped).
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis will examine the strengths and weaknesses of the competition and help direct your strategy for garnering a share of the market in your marketing plan . If the existing market is dominated by established competitors, for instance, you will have to come up with a marketing plan to lure customers from the competition (lower prices, better service, etc.).
Management Plan
The management plan outlines your business structure, management, and staffing requirements. If your business requires specific employee and management expertise, you will need a strategy for finding and hiring qualified staff and retaining them.
Operating Plan
The operating plan describes your facilities, equipment, inventory, and supply requirements. Business location and accessibility are critical for many businesses. If this is the case for your business, you will need to scout potential sites. If your proposed business requires parts or raw materials to produce goods to be sold to customers, you will need to investigate potential supply chains.
Financial Plan
The financial plan is the determining factor as to whether your proposed business idea is likely to be a success. If financing is required, your financial plan will determine how likely you are to obtain start-up funding in the form of equity or debt financing from banks, angel investors , or venture capitalists . You can have a great idea for a business, along with excellent marketing, management, and operational plans, but if the financial plan shows that the business will not be profitable enough, then the business model is not viable and there's no point in starting that venture.
Business Plan vs. Investment Proposal
| Business Plan vs. Investment Proposal | |
|---|---|
| Internal document | External document |
| Guides decision-making within the business | Attempts to convince those outside the company to invest in the business |
A business plan is similar to an investment proposal. In fact, investment proposals are sometimes called investor-ready business plans . Generally speaking, they both have the same contents. You can think of an investment proposal as a business plan with a different audience.
The business plan is largely an internal document, intended to guide the decisions of executives, managers, and employees. The investment proposal, on the other hand, is designed to be presented to external agencies.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a detailed road map that explains what the company's goals are and how it will achieve them.
- The exact details of a business plan will depend on the intended audience and the nature of the business.
- It's a good idea to regularly revisit your business plan so you know it's as accurate, realistic, and detailed as possible.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

Try for free
Business Plan
Who should write a business plan, pros and cons of a business plan, the anatomy of a business plan, .css-uphcpb{position:absolute;left:0;top:-87px;} what is a business plan, definition of a business plan.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them.
In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and which tactics you plan to use to reach commercial success.
Whilst every enterprise should have a plan of some sort, a business plan is of particular importance during the investment process. Banks, venture capitalists, and angel investors alike will need to see a detailed plan in order to make sound investment decisions — think of your plan as a way of convincing them your idea is worth their resources.
Roadmapping From A to Z

Business plans can also be useful as a guide to keeping a new business on track, especially in the first few months or years when the road ahead isn’t too clear.
Starting a business isn’t an exact science. Some companies organically develop out of trial and error, while others are plotted out from start to finish.
So if you’re asking whether your company needs a lengthy business plan, the answer would be ‘no’. That said, there are definitely a few situations in which writing a plan makes sense and can help increase the chances of a business becoming successful:
In situations when the market is new and untested — or simply volatile — it can be very helpful to have a business plan to refer back to when the road ahead isn’t clear.
For those who have an exciting business idea but haven’t necessarily distilled it down into black-and-white. Writing a business plan is a great way to look at a concept from all angles and spot any potential pitfalls.
How to write a business plan?
The most important step in writing a business plan is to identify its purpose.
Who are you trying to attract with it, and why?
Here are a few key pointers for writing a business plan:
Are you looking to secure a bank loan, get funding from private investors, or to lure skilled professionals to join you?
Include a brief history of your business, the concept, and the products or services. Keep it professional and transparent.
Don’t exaggerate your experience or skills, and definitely don’t leave out information investors need to know. They’ll find out at some point, and if they discover you lied, they could break off their involvement. Trust is crucial.
Explain what the product or service your business offers in simplistic terms.
Watch out for complex language and do whatever you can to prevent readers from becoming confused.
Focus on the benefits the business offers, how it solves the core audience’s problem(s), and what evidence you have to prove that there is a space in the market for your idea. It’s important to touch on the market your business will operate in, and who your main competitors are.
Another essential aspect of writing an effective business plan is to keep it short and sweet. Just focus on delivering the crucial information the reader has to know in order to make a decision. They can always ask you to elaborate on certain points later.
Still, deciding whether or not a business plan will benefit you at this stage of your venture?
Let’s look at a few reasons why you might (or might not) want to write a business plan.
A business plan will help you to secure funding even when you have no trading history. At the seed stage, funding is all-important — especially for tech and SaaS companies. It’s here that a business plan can become an absolute lifesaver.
Your business plan will maintain a strategic focus as time goes on. If you’ve ever heard of “mission creep”, you’ll know how important an agreed can be — and your business plan serves exactly that purpose.
Having a plan down in black and white will help you get other people on board . Again, with no trading history, it can be hard to convince new partners that you know what you’re doing. A business plan elegantly solves this problem.
Your business plan can cause you to stop looking outward. Sometimes, especially in business, you need to be reactive to market conditions. If you focus too much on your original business plan, you might make mistakes that can be costly or miss golden opportunities because they weren’t in the plan.
A lot of time can be wasted analyzing performance. It’s easy to become too focused on the goals and objectives in your business plan — especially when you’re not achieving them. By spending too much time analyzing past performance and looking back, you may miss out on other ways to push the business forward.
A business plan is out of date as soon as it’s written. We all know how quickly market conditions change. And, unfortunately, certain elements in your business plan may have lost relevance by the time you’re ready to launch. But there is another way ��— by transferring your strategic plan into an actionable roadmap , you can get the best of both worlds. The business plan contains important detail that is less likely to change, such as your mission statement and target audience, and the roadmap clarifies a flexible, adaptable, route forward.
So, you’ve decided to write a business plan — a great choice!
But now comes the tricky task of actually writing it.
This part can be a little frustrating because there is no one-size-fits-all template appropriate for all business plans. The best approach, in fact, is to look at common ingredients of a business plan and pick out the ones that make sense for your venture.
The key elements of a great business plan include:
An overview of the business concept . This is sometimes referred to as an executive summary and it’s essentially the elevator pitch for your business.
A detailed description of the product or service. It’s here that you’ll describe exactly what your core offering will be — what’s your USP , and what value do you deliver?
An explanation of the target audience. You need a good understanding of who you’ll be selling your product or service to, backed up by recent market research.
Your sales and marketing strategy. Now that you know who you’re targeting, how do you plan to reach them? Here you can list primary tactics for finding and maintaining an engaged client base.
Your core team . This section is all about people: do you have a team behind you already? If not, how will you build this team and what will the timeline be? Why are you the right group of people to bring this idea to the market? This section is incredibly important when seeking external investment — in most cases, passion can get you much further than professional experience.
Financial forecasts . Some investors will skim the executive summary and skip straight to the finances — so expect your forecasts to be scrutinized in a lot of detail. Writing a business plan for your eyes only? That’s fine, but you should still take time to map out your financial requirements: how much money do you need to start? How do you plan to keep money coming in? How long will it take to break even ? Remember, cash is king. So you need a cash flow forecast that is realistic, achievable and keeps your business afloat, especially in the tricky first few years.

General FAQ
Glossary categories.

Feedback Management

Prioritization

Product Management

Product Strategy

Roadmapping
Build great roadmaps
Book a demo
Experience the new way of doing product management

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Business plans
- Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurial business strategy
- Entrepreneurial exit strategy
- Entrepreneurial finance
- Entrepreneurial financing

Creating a Post-Covid Business Plan
- Dev Patnaik
- Michelle Loret de Mola
- Brady Bates
- January 08, 2021
Making Your Ideas Credible
- Prashant Pundrik
- March 07, 2011
Spinning Out a Star
- Michael D. Lord
- Stanley W. Mandel
- Jeffrey D. Wager
- From the June 2002 Issue
Keeping Your Business Plan Flexible
- September 02, 2010

When It's Time to Pivot, What's Your Story?
- Rory McDonald
- Robert Bremner
- From the September–October 2020 Issue
Great Businesses Don't Start With a Plan
- Anthony K. Tjan
- May 16, 2012
Is "Google Will Buy Us" a Solid Business Plan?
- David S. Evans
- April 18, 2007
Business Plans and Other Works of Fiction
- Scott D. Anthony
- November 06, 2013

When Your Business Needs a Second Growth Engine
- James Allen
- From the May–June 2022 Issue

Forget Business Plans; Here’s How to Really Size Up a Startup
- Jim Dougherty
- October 17, 2013
Value Captor's Process: Getting the Most Out of Your New Business Ventures
- Rita Gunther McGrath
- Thomas Keil
- From the May 2007 Issue
Gearing Up at REI
- Dennis Madsen
- Gardiner Morse
- From the May 2003 Issue
Crossing the River
- Lynda M. Applegate
Secure Your Plan with the Right Team
- Heide Abelli
- June 22, 2015
To Succeed in the Long Term, Focus on the Middle Term
- Geoffrey A. Moore
- From the July–August 2007 Issue
How to Write a Winning Business Plan
- Stanley R. Rich
- David E. Gumpert
- From the May 1985 Issue

Why the Best CEOs Are Already Thinking About Their Exits
- Stanislav Shekshnia
- October 31, 2019

How to Figure Out What Your Side Hustle Should Be
- Dorie Clark
- January 05, 2018
Fix Their Problem, Win the Deal
- Bill Taylor

The Explainer: How to Write a Great Business Plan
- William A. Sahlman
- April 17, 2017

Martin Blair
- Howard H. Stevenson
- Michael J. Roberts
- December 10, 2013
Extend Fertility
- Myra M. Hart
- Sylvia Sensiper
- December 16, 2004
Golden Baseball League (A): From Idea to "Play Ball"
- George Foster
- Mike Harkey
- January 23, 2006

Entrepreneurship Reading: Leading High-Growth Ventures
- June 12, 2015
Science Technology Co.--1985
- Thomas R. Piper
- February 02, 1989
Golden Baseball League (B): Final Standings, Season One
- July 21, 2006
Hip to be Square: Disruption in the U.S. Mobile Payment Market
- Sarit Markovich
- Anirudh Parasher Malkani
- Andrew Tseng
- Evan Meagher
- February 19, 2014
Rudi Gassner and the Executive Committee of BMG International (A)
- Linda A. Hill
- Katherine S. Weber
- November 29, 1993
Analyzing New Venture Opportunities
- June 23, 2009
Note on Shared Ownership
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Nick Rekenthaler
- August 20, 2019
Galen: Co-Creating the Future of Medical Technology
- Filip Ziolek
- May 21, 2020
J. Perez Foods (A)
- John A. Davis
- Kacie Lachapelle
- November 01, 2000
Zipcar: Refining the Business Model
- Julia D. Stevens
- January 13, 2003
Farm to School of Park County: A Journey from Program to Nonprofit (C)
- Karen L Cates
- Liz Livingston Howard
- January 10, 2019
Ripe 'n Ready
- Ray A. Goldberg
- Laura Winig
- October 26, 2005
Digital Equipment Corp.: The Endpoint Model (A)
- David A. Garvin
- Janet Simpson
- January 21, 1988
Mandic BBS: An Entrepreneurial Harvesting Decision
- Walter Kuemmerle
- March 18, 1999
Profits, Politics, and Pipelines: Europe, Russia, and the Challenge of Nord Stream 2 (A)
- Rawi Abdelal
- Galit Goldstein
- Cressida Arkwright
- Khilola Zakhidova
- March 13, 2019
Quincy Apparel (A)
- Thomas R. Eisenmann
- Lisa Mazzanti
- February 11, 2015
Blue Haven Initiative: The PEGAfrica Investment
- Vikram Gandhi
- Caitlin Lindsay Reimers Brumme
- Amram Migdal
- February 01, 2018

Rethinking the First-Mover Advantage
- Kirsten D. Sandberg
- May 01, 2001
5% Termination Policy
- Shlomo Ben-Hur
- November 24, 2015
Strategy is Destiny: A Perspective on Strategic Leadership
- Robert A. Burgelman
- March 08, 2004
Popular Topics
Partner center.
- Build your business
Business Tools
- Profit Margin Calculator
- Business Name Generator
- Slogan Generator
- Traffic Calculator
- Ecommerce Statistics
- Ecommerce Wiki
Free business tools
Start a business and design the life you want – all in one place.
- © 2015-2024 Oberlo

The 7 Best Business Plan Examples (2024)
As an aspiring entrepreneur gearing up to start your own business , you likely know the importance of drafting a business plan. However, you might not be entirely sure where to begin or what specific details to include. That’s where examining business plan examples can be beneficial. Sample business plans serve as real-world templates to help you craft your own plan with confidence. They also provide insight into the key sections that make up a business plan, as well as demonstrate how to structure and present your ideas effectively.
Example business plan
To understand how to write a business plan, let’s study an example structured using a seven-part template. Here’s a quick overview of those parts:
- Executive summary: A quick overview of your business and the contents of your business plan.
- Company description: More info about your company, its goals and mission, and why you started it in the first place.
- Market analysis: Research about the market and industry your business will operate in, including a competitive analysis about the companies you’ll be up against.
- Products and services: A detailed description of what you’ll be selling to your customers.
- Marketing plan: A strategic outline of how you plan to market and promote your business before, during, and after your company launches into the market.
- Logistics and operations plan: An explanation of the systems, processes, and tools that are needed to run your business in the background.
- Financial plan: A map of your short-term (and even long-term) financial goals and the costs to run the business. If you’re looking for funding, this is the place to discuss your request and needs.
7 business plan examples (section by section)
In this section, you’ll find hypothetical and real-world examples of each aspect of a business plan to show you how the whole thing comes together.
- Executive summary
Your executive summary offers a high-level overview of the rest of your business plan. You’ll want to include a brief description of your company, market research, competitor analysis, and financial information.
In this free business plan template, the executive summary is three paragraphs and occupies nearly half the page:
- Company description
You might go more in-depth with your company description and include the following sections:
- Nature of the business. Mention the general category of business you fall under. Are you a manufacturer, wholesaler, or retailer of your products?
- Background information. Talk about your past experiences and skills, and how you’ve combined them to fill in the market.
- Business structure. This section outlines how you registered your company —as a corporation, sole proprietorship, LLC, or other business type.
- Industry. Which business sector do you operate in? The answer might be technology, merchandising, or another industry.
- Team. Whether you’re the sole full-time employee of your business or you have contractors to support your daily workflow, this is your chance to put them under the spotlight.
You can also repurpose your company description elsewhere, like on your About page, Instagram page, or other properties that ask for a boilerplate description of your business. Hair extensions brand Luxy Hair has a blurb on it’s About page that could easily be repurposed as a company description for its business plan.
- Market analysis
Market analysis comprises research on product supply and demand, your target market, the competitive landscape, and industry trends. You might do a SWOT analysis to learn where you stand and identify market gaps that you could exploit to establish your footing. Here’s an example of a SWOT analysis for a hypothetical ecommerce business:
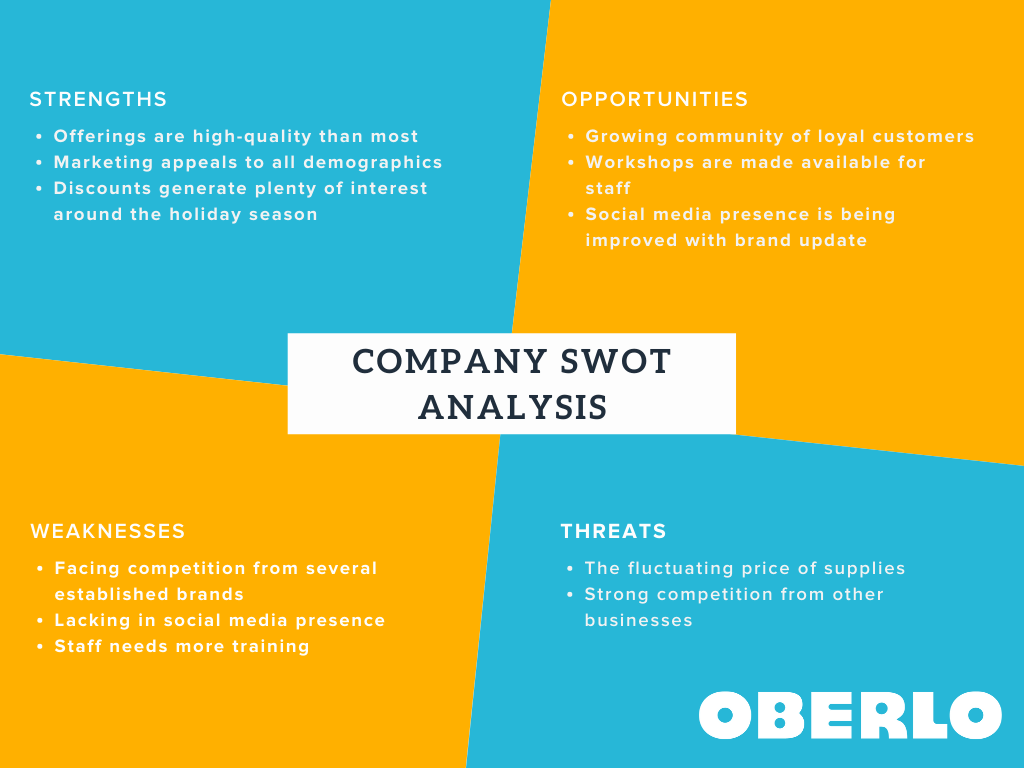
You’ll also want to run a competitive analysis as part of the market analysis component of your business plan. This will show you who you’re up against and give you ideas on how to gain an edge over the competition.
- Products and services
This part of your business plan describes your product or service, how it will be priced, and the ways it will compete against similar offerings in the market. Don’t go into too much detail here—a few lines are enough to introduce your item to the reader.
- Marketing plan
Potential investors will want to know how you’ll get the word out about your business. So it’s essential to build a marketing plan that highlights the promotion and customer acquisition strategies you’re planning to adopt.
Most marketing plans focus on the four Ps: product, price, place, and promotion. However, it’s easier when you break it down by the different marketing channels . Mention how you intend to promote your business using blogs, email, social media, and word-of-mouth marketing.
Here’s an example of a hypothetical marketing plan for a real estate website:

Logistics and operations
This section of your business plan provides information about your production, facilities, equipment, shipping and fulfillment, and inventory.
Financial plan
The financial plan (a.k.a. financial statement) offers a breakdown of your sales, revenue, expenses, profit, and other financial metrics. You’ll want to include all the numbers and concrete data to project your current and projected financial state.
In this business plan example, the financial statement for ecommerce brand Nature’s Candy includes forecasted revenue, expenses, and net profit in graphs.
It then goes deeper into the financials, citing:
- Funding needs
- Project cash-flow statement
- Project profit-and-loss statement
- Projected balance sheet
You can use Shopify’s financial plan template to create your own income statement, cash-flow statement, and balance sheet.
Types of business plans (and what to write for each)
A one-page business plan is a pared down version of a standard business plan that’s easy for potential investors and partners to understand. You’ll want to include all of these sections, but make sure they’re abbreviated and summarized:
- Logistics and operations plan
- Financials
A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there’s a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example. Shopify has a great business plan template for startups that include all the below points:
- Market research: in depth
- Financials: in depth
Your internal business plan acts as the enforcer of your company’s vision. It reminds your team of the long-term objective and keeps them strategically aligned toward the same goal. Be sure to include:
- Market research
Feasibility
A feasibility business plan is essentially a feasibility study that helps you evaluate whether your product or idea is worthy of a full business plan. Include the following sections:
A strategic (or growth) business plan lays out your long-term vision and goals. This means your predictions stretch further into the future, and you aim for greater growth and revenue. While crafting this document, you use all the parts of a usual business plan but add more to each one:
- Products and services: for launch and expansion
- Market analysis: detailed analysis
- Marketing plan: detailed strategy
- Logistics and operations plan: detailed plan
- Financials: detailed projections
Free business plan templates
Now that you’re familiar with what’s included and how to format a business plan, let’s go over a few templates you can fill out or draw inspiration from.
Bplans’ free business plan template

Bplans’ free business plan template focuses a lot on the financial side of running a business. It has many pages just for your financial plan and statements. Once you fill it out, you’ll see exactly where your business stands financially and what you need to do to keep it on track or make it better.
PandaDoc’s free business plan template

PandaDoc’s free business plan template is detailed and guides you through every section, so you don’t have to figure everything out on your own. Filling it out, you’ll grasp the ins and outs of your business and how each part fits together. It’s also handy because it connects to PandaDoc’s e-signature for easy signing, ideal for businesses with partners or a board.
Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template

Miro’s Business Model Canvas Template helps you map out the essentials of your business, like partnerships, core activities, and what makes you different. It’s a collaborative tool for you and your team to learn how everything in your business is linked.
Better business planning equals better business outcomes
Building a business plan is key to establishing a clear direction and strategy for your venture. With a solid plan in hand, you’ll know what steps to take for achieving each of your business goals. Kickstart your business planning and set yourself up for success with a defined roadmap—utilizing the sample business plans above to inform your approach.
Business plan FAQ
What are the 3 main points of a business plan.
- Concept. Explain what your business does and the main idea behind it. This is where you tell people what you plan to achieve with your business.
- Contents. Explain what you’re selling or offering. Point out who you’re selling to and who else is selling something similar. This part concerns your products or services, who will buy them, and who you’re up against.
- Cash flow. Explain how money will move in and out of your business. Discuss the money you need to start and keep the business going, the costs of running your business, and how much money you expect to make.
How do I write a simple business plan?
To create a simple business plan, start with an executive summary that details your business vision and objectives. Follow this with a concise description of your company’s structure, your market analysis, and information about your products or services. Conclude your plan with financial projections that outline your expected revenue, expenses, and profitability.
What is the best format to write a business plan?
The optimal format for a business plan arranges your plan in a clear and structured way, helping potential investors get a quick grasp of what your business is about and what you aim to achieve. Always start with a summary of your plan and finish with the financial details or any extra information at the end.
Want to learn more?
- Question: Are You a Business Owner or an Entrepreneur?
- Bootstrapping a Business: 10 Tips to Help You Succeed
- Entrepreneurial Mindset: 20 Ways to Think Like an Entrepreneur
- 101+ Best Small Business Software Programs
- Disaster recovery planning and management

Downtime can do serious damage to an organization's bottom line and reputation. Business continuity and disaster recovery -- two closely related practices -- help keep an organization running even in the wake of disaster. This guide explains how BCDR works, why you need it and how to build a BCDR plan for your organization to protect it today and into the future.
Disaster recovery (dr).
- Kinza Yasar, Technical Writer
- Erin Sullivan, Senior Site Editor
- Paul Crocetti, Executive Editor
What is disaster recovery (DR)?
Disaster recovery (DR) is an organization's ability to respond to and recover from an event that negatively affects business operations.
The goal of DR is to reduce downtime, data loss and operational disruptions while maintaining business continuity by restoring critical applications and infrastructure ideally within minutes after an outage. To prepare for this, organizations often perform an in-depth analysis of their systems and IT infrastructure and create a formal document to follow in times of crisis. This document is known as a disaster recovery plan .
What is a disaster?
The practice of DR revolves around serious events. These events are often thought of in terms of natural disasters, but they can also be caused by systems or technical failures, human errors or intentional attacks. These events are significant enough to disrupt or completely stop critical systems and business operations for a period of time. Types of disasters include the following:
- Cyberattacks, such as malware, distributed denial-of-service and ransomware .
- Power outages.
- Hardware failures.
- Equipment failures.
- Epidemics or pandemics, such as COVID-19.
- Terrorist attacks or biochemical threats.
- Industrial accidents.
- Hurricanes.
- Earthquakes.
Why is disaster recovery important?
Disasters can inflict damage with varying levels of severity, depending on the scenario. A brief network outage could result in frustrated customers and some loss of business to an e-commerce system. A hurricane or tornado could destroy an entire manufacturing facility, data center or office.
Also, the shift to public, private, hybrid and multi-cloud systems and the rise of remote workforces are making IT infrastructures more complex and potentially risky. An effective disaster recovery plan lets organizations respond promptly to disruptive events, offering the following benefits in return:
This article is part of
What is BCDR? Business continuity and disaster recovery guide
- Which also includes:
- 7 top business continuity certifications to consider in 2024
- ITGC audit checklist: 6 controls you need to address
- 12 key points a disaster recovery plan checklist must include
- Business continuity. Disasters can significantly harm business operations, incurring costs and disrupting productivity. A DR plan enables automation and the swift restart of backup systems and data, ensuring a prompt resumption of scheduled operations.
- Data loss reduction. A well-designed disaster recovery plan aims to reduce the amount of data lost by using methods such as frequent backups, quick recovery and redundancy checks. The probability of data loss increases with the length of time an organization experiences a system outage, but effective DR planning reduces this risk.
- Cost reduction. The monetary costs of disasters and outages can be significant. According to results from Uptime Institute's "Annual outage analysis 2023" survey , 25% of respondents reported in 2022 that their latest outage incurred more than $1 million in direct and indirect costs, indicating a consistent upward trend in expenses. In addition, 45% reported that the cost of their most recent outage ranged between $100,000 and $1 million. With disaster recovery procedures in place, companies can get back on their feet quickly after outages, reducing recovery and operational costs.
- Help with compliance regulations. Many businesses are required to create and follow plans for disaster recovery, business continuity and data protection to meet compliance regulations. This is particularly important for organizations operating in the financial, healthcare, manufacturing and government sectors. Failure to have DR procedures in place can result in legal or regulatory penalties, so understanding how to comply with resilience standards is important.
- System security. A business can reduce the detrimental effects of ransomware, malware and other security threats by incorporating data protection, backup and restoration procedures into a disaster recovery plan. For instance, several built-in security mechanisms in cloud data backups can minimize questionable activity before it affects the company.
- Improved customer retention. When a disaster strikes, customer confidence in an organization's security and services can be questioned and easily lost. A solid disaster recovery plan, including employee training for handling inquiries, can boost customer assurance by demonstrating that the company is prepared for any disaster.
- Emergency preparedness. Thinking about disasters before they happen and creating a response plan can provide many benefits. It raises awareness about potential disruptions and helps an organization prioritize its mission-critical functions. It also provides a forum for discussing these topics and making careful decisions about how to best respond in a low-pressure setting. While preparing for every potential disaster might seem extreme, the COVID-19 pandemic illustrated that even scenarios that seem farfetched can happen. For example, businesses with emergency measures to support remote work had a clear advantage over unprepared companies when stay-at-home orders were enacted during the pandemic.
DR initiatives are more attainable by businesses of all sizes today due to widespread cloud adoption and the high availability of virtualization technologies that make backup and replication easier. However, much of the terminology and best practices developed for DR were based on enterprise efforts to re-create large-scale physical data centers. This involved plans to transfer, or failover , workloads from a primary data center to a secondary location or DR site to restore data and operations.
What is the difference between disaster recovery and business continuity?
On a practical level, DR and business continuity are often combined into a single corporate initiative and even abbreviated together as BCDR , but they aren't the same thing. While the two disciplines have similar goals relating to an organization's resilience, they differ greatly in scope.
Key points of DR and business continuity include the following:
- BC is a proactive discipline intended to minimize risk and help ensure the business can continue to deliver its products and services no matter the circumstances. It focuses especially on how employees continue to work and how the business continues operations while a disaster is occurring.
- DR is a subset of business continuity that focuses on the IT systems that enable business functions. It addresses the specific steps an organization must take to recover and resume technology operations following an event.
- BC is also closely related to business resilience , crisis management and risk management, but each of these disciplines has different goals and parameters.
- DR measures could typically include developing extra safety precautions for employees, such as buying emergency supplies or holding fire drills.
- A business continuity plan helps guarantee that communication channels, including phones and network servers, stay operational during a disaster.
- DR is also a reactive process by nature. While planning for it must be done in advance, DR activity isn't kicked off until a disaster actually occurs.
- Business continuity ensures the overall functioning and resilience of an organization throughout the entirety of an event, rather than solely focusing on the immediate aftermath.
- The disaster recovery process is complete once systems fail over to backup systems and are finally restored. With business continuity, plans stay in place for the entirety of the event and even after the systems are back up following the disaster.
- Top of Form
Elements of a disaster recovery strategy
Organizations should consider several factors while developing a disaster recovery strategy. Common elements of a DR strategy include the following:
Risk analysis
Risk analysis, or risk assessment , is an evaluation of all the potential risks the business could face, as well as their outcomes. Risks can vary greatly depending on the industry the organization is in and its geographic location. The assessment should identify potential hazards, determine whom or what these hazards would harm, and use the findings to create procedures that take these risks into account.
Business impact analysis
A business impact analysis ( BIA ) evaluates the effects of the identified risks on business operations. A BIA can help predict and quantify costs, both financial and nonfinancial. It also examines the effects of different disasters on an organization's safety, finances, marketing, business reputation, legal compliance and quality assurance.
Understanding the difference between risk analysis and BIA and conducting the assessments can also help an organization define its goals when it comes to data protection and the need for backup. Organizations generally quantify these using measurements called recovery point objective ( RPO ) and recovery time objective ( RTO ).
- RPO. RPO is the maximum age of files that an organization must recover from backup storage for normal operations to resume after a disaster. The RPO determines the minimum frequency of backups. For example, if an organization has an RPO of four hours, the system must back up at least every four hours.
- RTO. RTO refers to the amount of time an organization estimates its systems can be down without causing significant or irreparable damage to the business. In some cases, applications can be down for several days without severe consequences. In others, seconds can do substantial harm to the business.
RPO and RTO are both important elements in disaster recovery, but the metrics have different uses. RPO is acted on before a disruptive event takes place to ensure data is backed up, while RTO comes into play after an event occurs.
Incident response
This encompasses detecting, containing, analyzing and resolving a disruptive event. Incident response includes activating the disaster recovery plan, evaluating the incident's scope and effect, executing the recovery strategy, restoring normal operations and deactivating the plan. To maintain accountability and promote ongoing improvement, it's also essential to record and report incident response actions and results.
The components of a DR strategy can vary depending on the size, industry and particular demands of an organization. Therefore, these plans should be customized to meet the unique requirements of each business.
What's in a disaster recovery plan?
Once an organization has thoroughly reviewed its risk factors , recovery goals and technology environment, it can write a disaster recovery plan. The DR plan is the formal document that specifies these elements and outlines how the organization will respond when disruption or disaster occurs. The plan details recovery goals including RTO and RPO, as well as the steps the organization will take to minimize the effects of the disaster.
A DR plan should include the following components:
- A DR policy statement, plan overview and main goals of the plan.
- Key personnel and DR team contact information.
- A risk assessment and BIA to identify potential threats, vulnerabilities and negative effects on business.
- An updated IT inventory that includes details on hardware, software assets and essential cloud computing services, specifying their business-critical status and ownership, such as owned, leased or utilized as a service.
- A plan outlining how backups will be carried out along with an RPO that states the frequency of backups and an RTO that defines the maximum downtime that's acceptable after a disaster.
- A step-by-step description of disaster response actions immediately following an incident.
- A diagram of the entire network and recovery site.
- Directions for how to get to the recovery site.
- A list of software and systems that staff will use in the recovery.
- Sample templates for a variety of technology recoveries, including technical documentation from vendors.
- A communication that includes internal and external contacts, as well as a boilerplate for dealing with the media.
- A summary of insurance coverage.
- Proposed actions for dealing with financial and legal issues.
An organization should consider its DR plan a living document. It should schedule regular disaster recovery testing to ensure the plan is accurate and will work when a recovery is required. The plan should also be evaluated against consistent criteria whenever there are changes in the business or IT systems that could affect disaster recovery.
How to build a disaster recovery team
A DR team is entrusted with creating, documenting and carrying out processes and procedures for an organization's data recovery and business continuity in the event of a disaster or failure.
The key steps and considerations for building a disaster recovery team include the following:
- Identify the key stakeholders. Determine who within the organization should be involved in the disaster recovery planning process. A DR team typically includes cross-departmental employees and executives, such as the chief information officer , IT personnel, department heads, business continuity experts, impact assessment and recovery advisors and crisis management coordinators.
- Define roles and responsibilities. Once the members of the DR team are determined, the next step is to assign them specific roles and responsibilities to ensure effective management of the recovery process. Common roles include team leaders, IT experts, business continuity experts, disaster recovery coordinators and department liaisons.
- Assess expertise. If the organization lacks internal expertise, it can outsource or engage a service provider. These providers can offer external expertise to aid the team, deliver disaster recovery as a service ( DRaaS ), or provide consulting services to bolster the capabilities of the internal team.
- Develop a recovery plan. The team should outline a detailed disaster recovery plan that outlines procedures for responding to various types of disasters. This plan should include steps for data backup and recovery, system restoration, communication protocols and employee safety procedures.
- Train team members. It's important to teach and train team members on their responsibilities within the disaster recovery strategy. This could entail doing frequent drills and simulations to evaluate the plan's efficacy and pinpointing areas in need of development. For example, this could include testing all apps and finding ways to access the critical ones in the event of a disaster.
- Regularly revise the DR plan. The disaster recovery plan needs to be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect organizational changes and how they affect the recovery process.
- Document the procedures. All procedures and protocols within the DR plan should be documented in a clear and accessible format. This ensures that team members can easily reference and follow the necessary steps during a crisis.
Disaster recovery sites
An organization uses a DR site to recover and restore its data, technology infrastructure and operations when its primary data center is unavailable. DR sites can be internal, external or cloud-based.
An organization sets up and maintains an internal DR site. Organizations with large information requirements and aggressive RTOs are more likely to use an internal DR site, which is typically a second data center. When building an internal site, the business must consider hardware configuration, supporting equipment, power maintenance, heating and cooling of the site, layout design, location and staff.
An external disaster recovery site is owned and operated by a third-party provider. External sites can be hot, warm or cold.
- Hot site. A hot site is a fully functional data center with hardware and software, personnel and customer data, which is typically staffed 24/7 and operationally ready in the event of a disaster.
- Warm site. A warm site is an equipped data center that doesn't have customer data. An organization can install additional equipment and introduce customer data following a disaster.
- Cold site. This type of site has infrastructure to support IT systems and data, but no technology until an organization activates DR plans and installs equipment. These sites are sometimes used to supplement hot and warm sites during a long-term disaster.
A cloud-based disaster recovery site is another option, which is also scalable. An organization should consider site proximity, internal and external resources, operational risks, service-level agreements (SLAs) and cost when contracting with cloud providers to host their DR assets or outsourcing additional services .
Disaster recovery tiers
In addition to choosing the most appropriate DR site, it can be helpful for organizations to consult the tiers of disaster recovery identified by the Share Technical Steering Committee and IBM in the 1980s. The tiers feature a variety of recovery options organizations can use as a blueprint to help determine the best DR approach depending on their business needs.
The recognized disaster recovery tiers include the following:
- Tier 7. Tier 7 is a highly advanced level of disaster recovery capability. At this level, artificial intelligence and automation are likely to play a key part in the recovery process.
- Tier 6. Tier 6 disaster recovery capabilities are comparable to Tier 5's, but they often include even more sophisticated technology and techniques for rapid recovery and minimal data loss.
- Tier 5. Tier 5 often implies advanced disaster recovery capabilities beyond a hot site. This can include capabilities such as real-time data replication , automated failover and enhanced monitoring and administration tools.
- Tier 4. This tier includes a hot site, which is a DR site that's fully functioning and ready to use. Hot sites replicate the primary data center's systems and operations in real time, enabling quick failover and minimal downtime. They provide the maximum availability and recovery speed, but they're also the most expensive alternative.
- Tier 3. By electronically vaulting mission-critical data, Tier 3 options improve upon the capabilities of Tier 2. Electronic vaulting of data involves electronically transferring data to a backup site, in contrast to the traditional method of physically shipping backup tapes or disks. After a disaster, there's less chance of data loss or re-creation because the electronically vaulted data is usually more recent than data sent through conventional means.
- Tier 2. This tier improves upon Tier 1 with the addition of a hot site, which are disaster recovery locations that have hardware and network infrastructure already set up to facilitate faster recovery times. There might still be a need for additional setup and configuration.
- Tier 1. This level consists of cold sites that provide basic infrastructure but lack preinstalled systems. Businesses in this category have data backups, but recovery involves manual intervention and hardware configuration, which lengthens recovery times.
- Tier 0. This tier denotes the lowest preparedness level and is usually associated with organizations that don't have disaster recovery or off-site data backups . Because recovery in this tier is entirely dependent on on-site technologies, recovery times can be unpredictable.

Another type of DR tiering involves assigning levels of importance to different types of data and applications and treating each tier differently based on the tolerance for data loss. This approach recognizes that some mission-critical functions might not be able to tolerate any data loss or downtime, while others can be offline for longer or have smaller sets of data restored.
Types of disaster recovery
In addition to choosing a DR site and considering DR tiers, IT and business leaders must evaluate the best way to put their DR plan into action. This will depend on the IT environment and the technology the business chooses to support its DR strategy.
Types of disaster recovery can vary, based on the IT infrastructure and assets that need protection, as well as the method of backup and recovery the organization decides to use. Depending on the size and scope of the organization, it might have separate DR plans and response and resilience teams specific to different departments.
Major types of DR include the following:
- Data center disaster recovery. Organizations that house their own data centers must have a DR strategy that considers all the IT infrastructure within the data center as well as the physical facility. Backup to a failover site at a secondary data center or a colocation facility is often a large part of the plan. IT and business leaders should also document and make alternative arrangements for a wide range of facilities-related components, including power systems, heating and cooling, fire safety, and physical security.
- Network disaster recovery. Network connectivity is essential for internal and external communication, data sharing, and application access during a disaster. A network DR strategy must provide a plan for restoring network services, especially in terms of access to backup sites and data.
- Virtualized disaster recovery. Virtualization provides disaster recovery by letting organizations replicate workloads in an alternate location or the cloud. The benefits of virtual DR include flexibility, ease of deployment, efficiency and speed. Since virtualized workloads have a small IT footprint, replication can be done frequently, and failover can be initiated quickly.
- Cloud disaster recovery. The widespread acceptance of cloud services lets organizations, typically reliant on alternate or on-premises DR locations, host their disaster recovery in the cloud. Cloud DR goes beyond simple backup to the cloud. It requires an IT team to set up automatic failover of workloads to a public cloud platform in the event of a disruption.
- DRaaS. DRaaS is the commercially available version of cloud DR. In DRaaS, a third party provides replication and hosting of an organization's physical and virtual machines. The provider assumes responsibility for deploying the DR plan when a crisis arises, based on an SLA. In the event of a disaster, the DRaaS provider shifts an organization's computer processing to its cloud infrastructure. This enables uninterrupted business operations to be carried out seamlessly from the provider's location, even if the organization's servers are offline.
- Point-in-time snapshots. Point-in-time snapshots or copies generate a precise replica of the database at a specific time. Data recovery from these backups is possible, provided they're stored offsite or on an external machine unaffected by the catastrophe.
Disaster recovery services and vendors
Disaster recovery providers can take many forms, as DR is more than just an IT issue, and business continuity affects the entire organization. DR vendors include those selling backup and recovery software, as well as those offering hosted or managed services. Because disaster recovery is also an element of organizational risk management, some vendors couple it with other aspects of security planning, such as incident response and emergency planning.
Examples of options for DR services and vendors include the following:
- Backup and data protection platforms.
- DRaaS providers.
- Add-on services from data center and colocation providers.
- Infrastructure-as-a-service providers.
Choosing the best option for an organization ultimately depends on top-level business continuity plans and data protection goals, as well as which option best meets those needs and budgetary goals.
Examples of DR software and DRaaS providers include the following:
- Acronis Cyber Protect Cloud.
- Carbonite Disaster Recovery.
- Dell EMC RecoverPoint.
- Druva Data Resiliency Cloud.
- IBM Storage Protect Plus.
- Microsoft Azure Site Recovery.
- Unitrends Backup and Recovery.
- Veeam Backup & Replication.
- VMware Live Cyber Recovery (formerly known as VMware Cloud DR).
Emergency communication vendors are also a key part of the disaster recovery process, as they help keep employees informed during a crisis by sending them notifications and communications. Examples of vendors and their systems include AlertMedia, BlackBerry AtHoc, Cisco Emergency Responder, Everbridge Crisis Management and Rave Alert.
Download a free SLA template for use with disaster recovery products and services .
While some organizations might find it challenging to invest in comprehensive disaster recovery planning, none can afford to ignore the concept when planning for long-term growth and sustainability. In addition, if the worst were to happen, organizations that have prioritized DR would experience less downtime and be able to resume normal operations faster.
Businesses often prepare for minor disruptions, but it's easy to overlook larger and more intricate disasters. Examine the top scenarios for IT disasters that disaster recovery teams should test vigorously.
Continue Reading About disaster recovery (DR)
- SME disaster recovery: Key points to consider
- Game-changing disaster recovery trends
- Maximize the benefits of virtual disaster recovery
- Real-life business continuity failures: Examples to study
- Disaster recovery plan best practices for any business
Related Terms
Dig deeper on disaster recovery planning and management.

Get the most out of Azure Site Recovery DRaaS

Define RPO and RTO tiers for storage and data protection strategy

IT resilience management, planning top of mind for DR pros

The tiers of disaster recovery, explained

The capacity of LTO tape breaks records yet again in annual shipments, but it might be the increase in density more than new ...
Veeam products and services in the spotlight at the VeeamON 2024 user conference included secure backups in the cloud, a ...
After going public in April, Rubrik is returning to its roots, saying additions to its Rubrik Security Cloud platform are all in ...
As the focus for enterprise AI spreads beyond compute, Western Digital introduces a new SSD and HDD. It also released an AI ...
This HPE Discover 2024 conference guide will cover event news from June 17 to 20. There will be three new programs: edge and ...
Explore this updating guide on Dell Technologies World 2024. The show will shine a major spotlight on AI, but also cover topics ...
APIs are essential, but hackers find them attractive targets. A comprehensive API risk assessment strategy helps you identify ...
Threat actors are targeting vulnerable Progress Telerik Report Server systems just days after a proof of concept was published ...
The public sector took the brunt of ransomware in May, while another damaging attack against a healthcare company disrupted ...
As U.S. states like Colorado pass their own AI laws, businesses will need to prepare compliance measures if they do business in ...
Digital transformation success requires cross-organizational alignment, actionable goals and top-notch project management. Here's...
President Joe Biden throws his support behind Microsoft to build an AI data center in Racine, Wis., as big tech companies invest ...
Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How to Create the Best One for 2024
It is more important than ever to create and maintain a powerful marketing strategy. Here are the 10 main steps to help you create the ultimate marketing strategy.
Omer is the COO and Co-Founder at Mayple. Started the platform over 5 years ago. 1000+ experts and 600+ happy customers later he is leading the marketing + customer service teams. Avid surfer and remote work enthusiast.
Learn about our
Natalie is a content writer and manager who is passionate about using her craft to empower others. She thrives on team dynamic, great coffee, and excellent content. One of these days, she might even get to her own content ideas.
Updated May 1, 2024.

Marketing is a dynamic and ever-changing field. The top digital marketing strategies change with the consumer and technology trends of the day. This is why every company needs a good marketing strategy that's well-planned and has well-defined milestones and objectives. Once you have the right map, the chances you’ll reach the goals you’ve set for your business are much higher.
That means, that while most of us are eager to start launching our marketing efforts the minute after we decide to start a business, we actually need to invest in planning so we won’t waste our limited budget and energies on the wrong things.
If you're a company/startup owner or marketer you need a good digital marketing strategy to hit your goals.
In this guide, we've put together the 10 main steps that you need to follow to build the ultimate marketing strategy for your business. We will take you step-by-step through the process, so you won’t miss a thing and get your digital marketing strategy all figured out.
We have some very useful tips and examples that will make it easier to understand.
If you want to read up on marketing strategy check out our list of the best marketing strategy books.
Now, let's define some of the basic terms.
What is marketing strategy?
Marketing strategy is a long-term, forward-looking approach and an overall game plan of any organization or any business with the fundamental goal of achieving a sustainable competitive advantage by understanding the needs and wants of customers.
A marketing strategy is a broad strategy that encompasses everything from how a company positions itself, to the creative, the strategic partners, the media relations, the marketing mix , and the channels and tactics.
A marketing strategy refers to a firm's overall game plan for reaching prospective consumers and turning them into customers of their products or services. It also contains the company's value proposition, key brand messaging, data on target audience and customer demographics, and other high-level elements.
The broad marketing strategy is what used to fall under the term "branding" back in the more ambiguous days of marketing. It's a practical summary of the key details of the strategy and some of the broad goals and methods used to achieve them.
What is the difference between a marketing strategy and a tactic?
Marketing strategies are broader than specific tactics. For example, a business could have a content strategy for their social media channels or for search engine optimization, and then they could have specific tactics they execute for each channel.
Here's the correct order to follow:
Overall marketing strategy -> Digital marketing strategy -> Specific tactics
For example, here's a great video that introduces specific marketing tactics. These aren't strategies, these are very specific ways you could grow your sales, which would all be included as part of a larger set of marketing strategies inside of your marketing plan.
» Looking for specific tactics? Head over to our Ultimate Guide on Digital Marketing.
What is the importance of marketing strategy?
Sometimes marketers and eCommerce owners get lost in the weeds, in the bits and bytes. They lose track of the overall vision of the business and the large goals. They lose track of the target audience and the main pain points that their product solves for the customer. When that happens, the specific tactics that the business employs can lose their effectiveness.
So, a marketing strategy is not some dusty old document that you put on the top shelf and forget about it. It's a vital process of discovering your company's top goals and objectives and ways to achieve them. That becomes a blueprint or a sample marketing plan for everything you do to better market your product or service.
Let's jump into it.
1. Define your brand value and offering
Your brand strategy is about defining the core values of your brand to make sure that they align with what your prospect and existing customer find important, that they align to your industry trends and competitive environment, and to what you actually offer ie your product.
That’s not an easy task, but without it, all the other marketing tasks become much more difficult.
Here are some good marketing strategy examples from data-driven brands that succeeded in doing it right:
AllBirds - Sustainable, transparent, comfortable
AllBirds began as a darling brand in Silicon Valley in 2014 and quickly grew to a $1.4B valuation in 2018. The shoe company set out to create the world's most comfortable, and they overshot their goal.
Their products are fully sustainable and made out of wool and bamboo, and their branding is impeccable. Their mission statement reads - "Allbirds is on a mission to prove that comfort, good design, and sustainability don't have to be mutually exclusive".
In just four years they became the market pioneers of sustainable footwear. It all started with a launch on Kickstarter, in fact, here's their Kickstarter video:
The brand has a really quirky brand voice, and its values are transparency, sustainability, and comfort.
Here's an email with an order confirmation:

You can see the same quirky humorous brand voice in their social media posts.

Besides the humor and the spunky brand personality, the brand has really taken advantage of this concept of transparency. They display the materials they use in a creative way and get down to the fine details.
And that ties really nicely with their overall mission and their third brand value - sustainability.

Ultimately, the quirky brand voice and the incredible brand values of sustainability and transparency led Allbirds to build a super-engaged audience online that has contributed the most to the brand's growth.
Yes, it is a really comfortable product (the NY Times called it "the most comfortable shoe in the world"), but without a strong brand and a focus on the user experience, Allbirds would not have been the giant that it is today.
Casper - "here to awaken the potential of a well-rested world"
Casper is a mattress company that has completely revolutionized the industry. They were the first direct-to-consumer mattress company and quickly grew to a $1.1B valuation in 2019.
Casper's brand values are all about dreaming big, innovation, and bringing joy to a tired industry.
Look how they merge the "dreaming big" brand value with a pun about sleeping in their purchase receipt email.
And here's another great email asking for a review.
Casper's strong brand helped it launch other successful products, like the Casper Glow, which is an innovative bedtime light that changes its light temperature and brightness automatically and can be remotely controlled through an app.

There are a lot of big and abstract words thrown around when talking about brand value creation, so here's a simple way to think about it.
A simple formula to find the right values that define your brand is this:
- Think about the main pain points/needs/frictions your brand is solving
- Translate it into a value-based language
- Make sure it fits your beliefs and motivations
2. Identify customer pain points and expectations
"People don't want to buy a quarter-inch drill. They want a quarter-inch hole!" - Theodore Levitt, Harvard Business School Professor
One of the top reasons why products or services fail is when their makers fail to identify the customers' pain points. In other words, they don't meet the customer's needs or they don't solve a vital problem in their lives. Also, those needs may change over time so it's important to continue examining the customer journey and solve your current customer challenges.
One of the classic examples is the Segway. It was a device that was said to eliminate walking. It could go up to 12.5 miles per hour, had a lithium battery, and made you look like a dork. It was hailed as the device that would make walking obsolete, and it failed miserably.
It's a sad story but the creator of the device actually drove it off a cliff and died. The problem with the Segway is that no one wanted to stop walking, people love walking, people loved running, so it failed to meet the customer's need and to identify a pain point.

What are the different types of customer pain points?
the most basic pain point is financial. Does your product help your customers save money? Is it more cost-effective than the alternatives? Are the savings short-term or long-term? And if your product is cheaper than the alternatives, does that price difference create enough value for the customer?
These are some of the important questions you should ask yourself. An example of this is Target's launch of the brand Smartly with hygiene/cleaning products all under $2 (approximately 70% less than similar products by other brands).

Convenience
Another really important pain point is convenience. Does your product make your peoples' life more convenient? The classic example of this is Netflix, a brand that became a household name because it was incredibly more convenient than it competitor Blockbuster.
Instead of having to shlep to Blockbuster, for example, and pay all of those late fees customers could now get DVD's straight to their doorstep. Fast forward to 2020, Netflix is worth $203 billion and Blockbuster is is out of business. The company that made me more convenient for people won.
Service is another major factor in solving a customer's pain point. Service refers to the entire customer experience and includes things like - warranty, maintenance, replacements, customer service , and ease of use. A really good example of this is the solar company SolarCity, which was acquired by Tesla in 2016.
SolarCity's solar panels weren't cheaper than the competitors they simply had a better warranty and maintenance on them and that's why customers preferred them. This is one of the major drivers that helped SolarCity become the nation's largest residential solar provider.

Easy steps to identify your customer's pain point
Ok, so we've talked about the type of customer pain points that there are, but how do you identify them for your own company and product? Here are some helpful suggestions that will get you on the right path.
Create a customer journey map
Identify what makes your customers buy your product and how they arrived at your physical or online store. This should include the channels that they visited - a search result, a Facebook ad, a social media post, an email, and other online and physical media. At each stage identify possible pain points and uncover the customer's motivation for using your product.
This will also help you evaluate your marketing mix and see if there are any channels that you need to add.
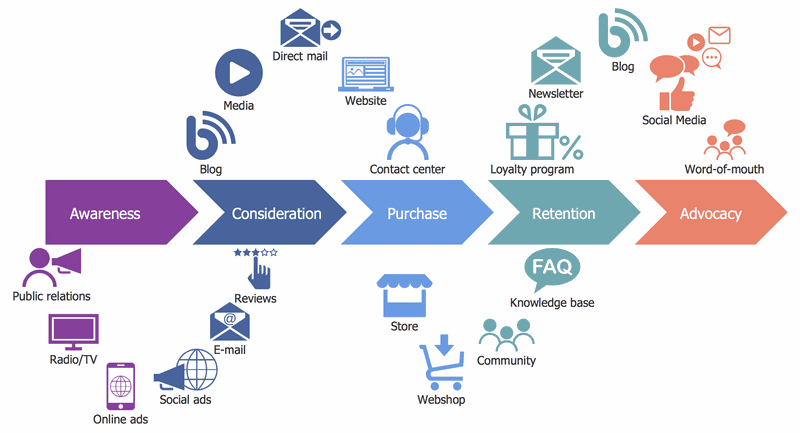
Survey your customers
Another good way to find the customer pain point is by surveying your customers. Ask your customers what they like and don't like about your product and what are some of the factors that led to their choice. There are a ton of survey tools you could use like Typeform or SurveyMonkey .
Look at customer reviews
If you are thinking of launching a new product you should look at the customer reviews of your existing products. These will tell you a lot about your customers' preferences, expectations, and pain points. What's particularly powerful for eCommerce sites are visual reviews - photos or videos that customers post alongside the text of their reviews. You can use tools like Pixlee, Yotpo, or Loox to collect and display visual reviews.
Ask your sales team
Another good way to find your customer's pain points is to ask your sales team. After all, your salespeople are the ones that hear and have to respond to the objections of your prospects and customers, hence they are the most aware of what people are looking for in your products or services.
Sit down and have a discussion with your sales team. Try to find out what your customers like/dislike about your product, what are the issues that they bring up the most, and what makes them turn down the product. If your marketing team interfaces directly with your customers you could also ask them for feedback.

Study your competitors
It's super important to conduct a competitor analysis to analyze the competitor landscape, in any industry. That's how Netflix and Apple began when they strove to make a product that's better and more innovative than the status quo. Identify where you are, and what your market position is .
Look at all your competitor products, their marketing mix, the type of promotion and media they publish, and their strategies. Identify the pain points that they are solving and ones that are still unresolved. One strategy is to try to solve the same pain points, just better. Another strategy is to go after pain points that remain unresolved, to create something that people haven't seen before.
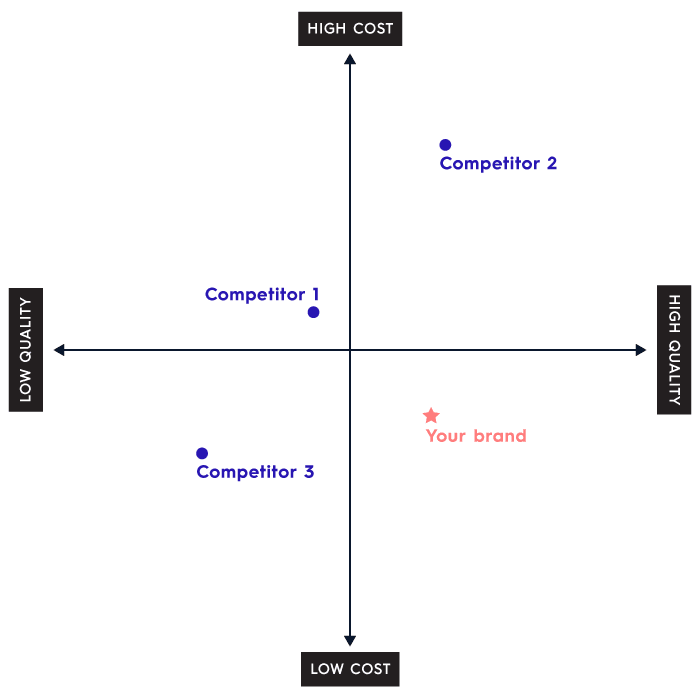
Use the STP framework
Another effective marketing technique is to use the STP framework. STP stands for segmenting, targeting, and positioning.
- Segmenting - is where you divide the market into distinct groups (or target market segments).
- Targeting - is where you determine which customer segment you want to focus your marketing efforts on. And
- Positioning - is the creation of the brand position, the marketing mix, and other various marketing strategies in order to appeal to your potential customers in your target market and try to influence them to make a purchase decision.
The STP framework helps brands identify the types of marketing strategies and channels that will be required to successfully market their product or service to their customers.
3. Identify market trends and competition
That brings us to our next topic - creating a competitive analysis. This is a crucial step in the marketing strategy plan creation because this is where you will identify what differentiates your product or service from the competition.
You can do this through a simple SWOT analysis to determine your brand's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Without this step, it's going to be very difficult to create a product that provides unique value to the consumer and stays competitive with the market trends of the day. So this analysis is crucial and this is how you go about it:
Identify your competitors
The first step of any competitive analysis is to find out who your competitors are. Find out all the different companies that have similar products and services. Look at their social media content, search in related or niche online communities, news mentions, and product reviews.
Categorize your competitors
Now that you have a detailed list of all of your competitors it's time to categorize them. Put them into different groups - primary, secondary, and tertiary competitors. This will help you get clarity on which of your competitors are directly competing with you and which ones you should focus on in your analysis.
Take a look at their social media and branding
The next step of the competitive analysis is to find out all you can about each competitor. Look at all the various social media pages, the content, and the branding that they use on their site and their email marketing campaigns. This will give you a visual understanding of their brand positioning and how your product or service differs from theirs.
Be sure to check out their influencer marketing campaigns to see the kind of branded image that they try to portray online. Look at their display ads (owned media) and UGC(earned media).
Conduct a site audit to look at traffic sources and positioning
This part is the more technical side of the branding audit. Use a tool like Ahrefs , SimilarWeb , or Alexa to check the keywords that each competitor ranks for and their various traffic channels. This will give you the precise search terms that the user searches for and the specific needs that your competitors meet.
For example, you might discover that a competitor is using a type of content that you're not using yet or a traffic channel that you haven't expanded into. This is super valuable information to have for your online marketing strategy.
Look at their pricing
Use a tool to track competitor prices and see how you compare on various products, categories, and by season. Your cometitors may be using different pricing strategies on holidays, weekends, or busy seasons (depending on your niche) and you can get ahaed just by using a few dynamic pricing rules and tweaking your strategy a bit. So this part of the research is critical.
4. Create your value proposition
Now that you have your story right, it’s time to build the right strategy for your marketing. That means making business decisions about what you are delivering and to whom.
Your product or service tells the most about your brand.
This is the actual hands-on experience prospects and customers have with your brand, and it can affect their perception of it the most.
Use your values to make sure you walk the talk and implement what you said about yourself in your offering.
Here are some examples to help you get the hang of it:
Walmart - translating brand values to service language

IKEA - Brand values & design

Most people will know right away this is IKEA’s products - humble, simple and functional.

5. Identify your target audience
Deciding on your target audience could change the way you present your brand and even the language you use to do it.
We love to use simple models for complex decisions.
We found it is much more effective and fun.
Use this model to map the different target audience groups that you have, and prioritize them accordingly in your audience analysis.
(This is actually one of the models we used to determine our target audiences)
You would want your first-tier target audience to have good market potential for business growth, and it wouldn’t be a Via Delarosa to convince them to buy what you have to offer.
This is not the only tool you need to characterize the people you are going to invest most of your marketing spend to reach out to.
The second tool we recommend for you to use is defining your personas - or, in other words, asking who your ideal customer is, your target customer, to the smallest details.
To define your main persona you can use this question list:
- Who is my persona? Is he a male or is she a female? What age is he or she? Name your persona and attach a photo so it will be easier for you to plan your messaging accurately.
- What is my persona's initial state of mind? - his or her emotions and thoughts before starting the decision-making process?
- What are the different stages of his or her decision-making process until purchase?
If you’re about to launch a new service or product that prospects or customers are not used to using or buying, you might consider applying this psychology of change model. After all, you’re trying to change people's perception here.
Each stage represents a psychological state of mind of people until they reach a decision to take action. You can use the needs that are listed below to create your marketing creative tools that will effectively move your persona to take action.
Identify the following for each stage of the buyer's journey:
- What are your persona’s expectations? What are his goals?
- What process does she go through in this stage? Where does she look for information? Who do they speak with?
- How would you describe the customer's experience at each point of the customer journey?
- What is your objective for each of their decision-making stages?
- What actions can help you achieve these objectives?
Now that you've identified your ideal customers, how are you going to reach them?
That brings us to the next step.
6. Identify partners and potential collaborators
Identifying your potential partners or collaborations is a critical step of reaching your ideal customer. It may be that there are online communities that already exist where your customers hang out. It could be that you need to work with a distributor or get a marketing partner to help you reach them.
This is a critical point to consider before you execute your inbound marketing strategy. Sometimes finding and working with the right partner could give you access and help you achieve 10X the results. This could be through revenue sharing or an affiliate program . It could also be done by social networking at industry events or online conferences.
We’re on the digital marketing portion of our guide and it contains 3 parts - deciding on your creative & messaging, selecting the marketing channels that you’ll be using, and deciding on a strategy and a marketing budget for each channel.
Let’s dive in.
7. Decide on the messaging and creative of your brand
Most businesses (and especially startups) can’t afford to hire a digital marketing specialist in-house so they use the services of freelancers or digital agencies .
From now on, you have a critical job of guarding your brand’s values and strategy in the messaging and creative you’ll create and the different tactics you’ll use.
That’s what storytelling is about .
Make sure that the service provider you hired is aligned with your brand and the various marketing strategies that you want to employ, so they can apply your strategy to the actual marketing communication you’ll have with your potential customers.
Here are two brilliant brands that keep to their authentic brand strategy throughout their messaging:
National Geographic - how to create the “wow” and “wonder” visually
National Geographic knows how to present stunning photography and help us discover the wonders of our world. They constantly keep the language they use on their ads (paid and earned media) to be aligned with these brand values.

8. Define your marketing channels
Now that you have defined your value proposition, your partners, and your creative assets and messaging it's time to select the right marketing channels for your marketing mix.
This is one of the most crucial steps in the process of creating your marketing strategy. Each digital marketing campaign will vary greatly based on the marketing channels that you'll pick. You need to select those marketing channels that fit your brand and your product.
Let's cover a few of the main marketing channels and their best practices.
Social media
Social media marketing is a vital part of any digital inbound marketing strategy and there are certainly a lot of things that you could do. Also, keep in mind that successful social media campaigns can help you get more traffic from search.
Organic social media is used for the awareness stage, or the lead generation stage, of the marketing funnel while a Facebook ad is used for the last stage, or the conversion stage. There are a lot of various platforms and strategies you could use and it's important to pick the right channel for your product.
Here’s a breakdown of some of the best and most effective social media channels to use for different types of companies:
- For visual eCommerce products - use Instagram and Pinterest, TikTok, Facebook, Snapchat and Twitter
- For B2B companies - use LinkedIn, Instagram, ProductHunt, and Angellist
- For B2C companies - use Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest
- For written content-heavy companies - use Medium, Quora, and Reddit
- For GenZ-focused companies - focus on Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok
Red Bull is a great example of a brand that has a brilliant social media marketing strategy. Early on they realized that if they wanted to connect to their target consumer they couldn’t just use the traditional marketing and sales campaigns that all the other beverage companies were using.
They decided to create videos of athletes breaking world records and doing unthinkable things like jumping off airplanes and falling 23 miles and skiing down the Himalayas. To date, the Red Bull YouTube channel has garnered more than 10 million subscribers and more than 2.5 trillion views.
This is obviously a very expensive strategy and won’t make sense for most brand marketing budgets, but it’s a good example of a brand sharing success stories and targeting their consumers the right way on social media.
Social advertising
Ads are becoming more and more popular on social media platforms because the recent algorithm changes continue to favor them and decrease organic reach. After all, that’s how social platforms make their money so you have to use paid media to get anywhere these days.
Pinterest, Facebook, and Instagram are the most popular platforms for advertising. For B2B you can use Quora, Reddit, or LinkedIn.
Top Advertising Tips:
- Create a lookalike audience on each platform and for each type of campaign that you're running
- Organize your campaigns based on the marketing funnel (top, middle, and bottom)
- Match your copy and designs to your target audience
- Retarget your audience and site visitors on Facebook, Pinterest, and Google.
Paid Advertising
Social media advertising is just a subset of online advertising. Other digital advertising can include native advertising, Google ads, Google shopping, banner ads, and much more. Each ad requires thorough strategic planning to make sure that the messaging and creatives match your market segments to help attract new leads and retain current customers.
Influencer marketing
Working with influencers is one of the most lucrative marketing channels you could go into. Studies show that businesses make $5.20 for every $1 that they spend on influencer marketing. And 49% of consumers depend on influencer recommendations for their purchase decisions. That’s huge.
That means that on average about half of your customers are going to be searching for influencer posts so it is essential that these people are recommending you and your product online. Now, influencer marketing is different than when your users post images of your product. Influencer shots are called paid media (just like ad campaigns) while user-generated content (UGC) is called earned media.
Top Influencer Marketing Tips:
- Pick influencers based on the type of audience they have, and their level of engagement (not the size of their following)
- Run giveaway campaigns with groups of influencers
- Run stories on Instagram because they are clickable
- Conduct competitor research to see which influencers they are using on all the relevant platforms
- Use YouTube influencers to create videos about your product or service
- Use real data to determine which influencers are your best performers
Pro tip: Looking to find the right influencers for your next campaign? Check out our list of the top influencer marketing tools .
Email marketing
This is going to surprise you but the ROI of emails still remains among the highest in all of the different digital marketing channels and platforms. Studies show that email marketing provides a $42 return on every $1 you spend , which is terrific.
Top Email Marketing Tips:
- Use UGC or earned media in your campaigns
- Set up email campaigns and email flows (cart abandonment flow, welcome flow, sunset flow)
- Create campaigns with educational content, don't just send constant product promotion
- A/B test different types of content, copy and formats based your data to better match your campaigns with your audience
- Continue to grow your email list with popups, subscription forms, contests, giveaways, and promotions
- Create segments based on customer engagement or average order value and create personalized campaigns
That is not to say that the other channels don’t help or assist the sale, it’s like the functions of the various team members in a soccer match. There could have been 5-6 players that touched the ball before it reached the goal post. The same thing happens in marketing.
A user can interact with a brand on numerous channels before they buy their products or services. Which is why it’s really important to have an effective “omnichannel” strategy, a strategy that includes many marketing channels.
Here are a few examples of channels that work really well when combined with email marketing:
Push notifications
Push notifications are those messages you get on your browser on a desktop device or on your mobile screen. They work really well when combined with emails. You could send off the email in the morning for example, and then follow it with a push notification 30-60 minutes later, to remind the user to check out your deal of the day.
Push notifications have a click through rate that’s 7 times higher than emails , so when sent after the email they increase your chances of getting a sale that much more.
Chatbots and messaging
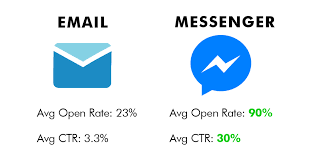
One of the quickest and most effective ways to communicate with customers is through text messages and this has become its own marketing channel. You can set up automated messages and flows that gets sent to a customer or even a chatbot that is able to bring them from product discovery all the way to purchase, without any human involvement.
You can also use this channel to send people a product promotion, a cart abandonment flow, or a content promotion.
Text messages are much more personal and that’s what makes them so powerful for brands. According to Social Media Today , chatbot messages get open rates of over 80% and click-through rates of over 50% so these messages provide an additional and very effective way to augment and boost your email marketing performance.
Search Engine Optimization
One of the most overlooked strategies is Search Engine Optimization, especially for eCommerce. It involves optimizing a site's content to make it easier for search engines to find it and display it.
There are numerous new ways to get displayed on search engines than ever before - in the images section, as videos, quotes, products, how-to's, Q&A, and much more. SEO is a super effective marketing channel and can bring a lot of targeted and high-quality traffic to any site.
Top SEO tips:
- Use Google Search Console data to find the keywords and searches that you get the most traffic from
- Optimize your on-page content with a tool like Ahrefs or Moz
- Build a comprehensive backlink strategy based on competitor data and best practices
Now remember, not all SEO best practices will fit your needs or make sense. It's a delicate balance between SEO and the user experience (UX) and that requires some tough decisions sometimes. So always learn from your data and keep your audience as first priority and you will win.
Content Marketing
Last but not least, let's talk about your content marketing strategy. Content provides a way for users to find your product or service online. Use content to target your ideal buyer persona, acquire new customers, and delight and retain your existing customer base.
To use content marketing successfully, brands have to create different content for each part of their marketing or sales funnel. For example, a company might put educational content at the top of the funnel for first-time visitors and more promotional content for those shoppers who are ready to buy.
Top Content Marketing Tips:
- Write long-form blog posts for organic search traffic
- Publish comparison and shopping guides for the middle-of-the-funnel visitors
- For B2B: create lead magnets, white papers, and gated marketing research
- Use UGC, video content, and longer descriptions on your social media posts to tell your story
Public Relations (PR)
Last but not least, there's PR. Public relations is one of the most effective growth strategies that can help solidify your brand image and expand your digital presence.
Now that we’ve covered the various marketing channels that you should consider to grow your business, let’s talk strategy.
9. Select a strategy and budget for each channel
It’s now time to select a specific strategy and a budget for each of the marketing channels that you’ve chosen for your brand. Here are a few helpful steps:
Identify your business goals
What are your goals? Pick a few strategic business goals or KPIs (key performance indicators) to focus on in the short term. A really helpful rubric for this is what’s called SMART goals . Smart stands for:
- S pecific - describe clearly what you want to accomplish
- M easurable - set goals that you could measure
- A chievable - these goals have to be achievable and not way out of reach
- R elevant - set goals that improve the specific aspects of your marketing, so no vanity metrics.
- T ime-bound - pick marketing objectives that you can achieve within a certain time frame.
Now that you’ve set up your goals it’s time to look at your market.
Here's a fantastic video from Hubspot to watch about setting the right marketing goals for your business:
Conduct market research
Gather information about your market - the size, growth, social trends, search trends, and demographics of your target market. Find out what is possible and feasible to accomplish and which channels, content types, and media, are used to reach your target customer, and which you should add to your marketing mix. You can use a PEST analysis or a SWOT analysis to help you with your market research .
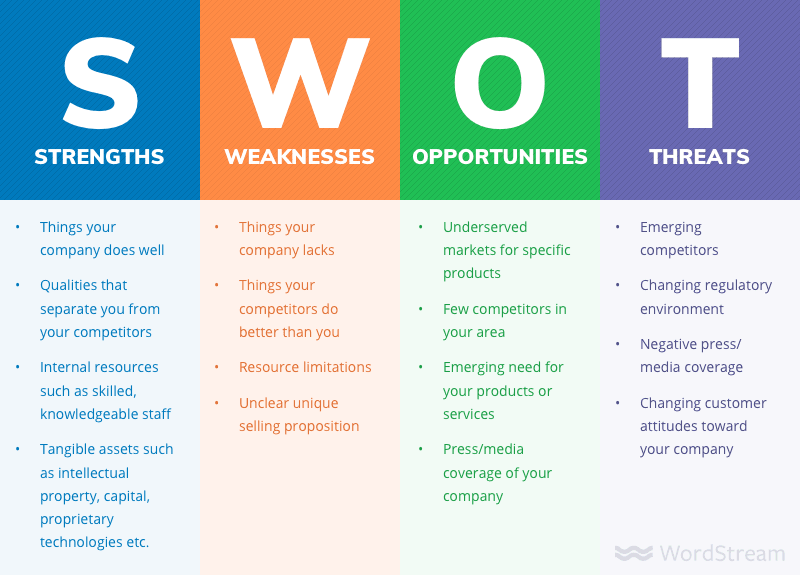
A PESTEL analysis is a marketing framework or management method that helps businesses assess major external factors that influence its operation, in order to become more competitive in the market.
PESTEL stands for political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal. For example, legal factors could include a new regulation that significantly limits a brand's ability to sell their product in a particular region. Political factors could include new trade restrictions, tariffs, or a new tax policy. Environmental factors could include weather conditions, seasonality, and even natural disasters.
Align your strategy with your ideal customer
Go back to the customer personas that you’ve created at the beginning of this process and make sure that your strategy aligns with your personas. Look at the trends, at the type of customers that you are going to be able to reach, and tweak accordingly.
It’s performance time!
At this point, you have your brand story and values, your go-to market strategy, and a professional to run your marketing efforts.
From this point forward, you should focus on much more tactical management. That means iterative testing of your content and creatives, of your target audience segments and even of the words you use on your ads CTAs (call-to-action buttons).
Which brings us to the last step of the process:
10. Analyze your results
This is one of the most crucial steps in anything you do in marketing. Once you test something you have to analyze the results and continue testing. Data is crucial in every aspect of marketing and the omnichannel data you get from testing marketing strategies is the best kind of data to have. Smart marketing managers use data to continue iterating and optimizing their growth strategies.
Once you have the results of your strategy you can then make the changes you need to make and A/B test various aspects to get even better results.
BONUS: Examples of Marketing Strategy Templates
There’s no one-size-fits-all marketing strategy, and if you’ve read this entire guide to this point - you’re probably eager to implement some of the various strategies we talked about. And you’ve probably discovered a lot of topics that you should learn more about to really perfect your marketing strategy.
Here are some of our favorite resources + marketing strategy examples + templates. These are really effective and comprehensive. They cover a really broad range of channels and use cases so you can find some value regardless of which business you’re in. Choosing the right marketing strategy template is the secret behind creating an effective marketing strategy.
How to Plan Your Marketing Strategies in 12 Steps ( CoSchedule )
This beautiful strategy guide has everything you need to know to create the perfect strategy. The best part is that it shows everything visually in each section, and has a really simple marketing strategy template to follow to create your own strategy.
Plus, CoSchedule started off as a content marketing tool for inbound marketing teams (they are now much more than that), so they go into a brief history of content marketing, inbound marketing, and how it all started.
The best part about CoSchedule is that they have a feature where that allows you to divide the tasks among your team members. For example, if you're a content team manager you can use this to visually display who writes each piece of content, who edits it, and who publishes that piece of content on the team.
This is a crucial and super effective step that gets missed pretty often. Once a brand makes their strategy, it’s important to delegate the work and get started on the execution.

10 Marketing Strategies to Fuel Your Business Growth ( Entrepreneur )
This is an old one but when we read it we thought it has the perfect sequence of some of the most successful marketing strategies for an eCommerce business. It has literally everything you need to market successfully.
We’re talking influencers, email marketing automation, content marketing, video content, Facebook retargeting and search engine optimization. This post is an excellent broad overview of eCommerce marketing at its finest.
The Essential Guide to Marketing Strategies ( Hurree )
Hurree is one of the best marketing blogs ever. This post in particular gives a really good detailed overview of each step of creating a marketing strategy. It also has a variety of videos sprinkled throughout the post that explain concepts deeper, and the best part - they have a whole section of marketing automation. Hurree is a marketing automation platform so you know to expect some talk of automation in every single one of their posts. This is a segway from traditional marketing principles to present-day automation and beyond.
The 11 Best Marketing Strategies We Tried This Year ( WordStream )
This post is for the more advanced marketer who wants to really hone in on the top strategies that work in 2022. It’s written by Sujan Patel, the one and only, and he goes over things like webinars, reaching out to other tools in the industry, brand partnerships, search marketing, evergreen content, SMS, and non-traditional social media channels. Check out this post, even though it was written in 2018, it remains one of the best lists of marketing strategies on the web.
The Ultimate Digital Marketing Strategies Guide ( HubSpot )
This is a classic resource from HubSpot and we like about it is how clearly they define every term, every type of content and marketing tactics that you should develop. They also include 5 examples of marketing ads and dissect each one. It’s a great read and you will get a lot of value out of it.
That’s it, folks.
Now that you have a better idea of how to craft the ultimate marketing strategy for your business or startup it’s time to go out there and absolutely smash it.
What are the 5 marketing strategies?
The 5 P's of Marketing are - Product, Price, Promotion, Place, and People. These are key marketing strategies that are used to position any business strategically.
What are the 5 C's of marketing?
The 5 C's is a technique used to help marketers better position their business and make more informed business decisions. The "5 C's" stand for Company, Customers, Competitors, Collaborators, and Climate. It's a type of analysis that helps marketers look at the whole picture as an ecosystem in which the business lives in.
Related Articles

Ben Kazinik
Ecommerce Marketing in 2024: Channels & Growth Hacks

How True Classic Grew to Over $150M
Octavia Drexler
20 Mailchimp A/B Test Ideas to Drive Better Email Marketing Results

The Ultimate Guide to Ecommerce Chatbots

The Beginner’s Guide to SMS Marketing: The Benefits, Strategies & Tools
- Agile project management
Program management vs. project management
How program and project management work together to improve organizational performance

Browse topics
Programs and projects are at the heart of many business endeavors. To use a metaphor, projects are like trains operated by project managers, who help pull the work of a team to achieve goals and ultimately arrive with a finished good or service.
To continue with the metaphor, a program is like a collection of trains running on different tracks, yet headed to the same station, or goal. The program manager is the station conductor, directing the various project trains.
What is program management?
Program management is the process of managing programs mapped to business objectives that improve organizational performance. Program managers oversee and coordinate the various projects and other strategic initiatives throughout an organization.
Program managers also help to drive organizational change by helping with agile transformations, including helping to implement DevOps practices and principles. Program managers may align program management practices and processes with agile values such as collaboration, team autonomy and empowerment, delivering value to customers, and adapting to change in the moment. A program manager can bring agile and DevOps to life for teams across large programs or individual projects by tailoring programs to the specific requirements and opportunities of the business.
A program manager can bring agile and DevOps to life for teams across large programs or individual projects by tailoring programs to the specific requirements and opportunities of the business.
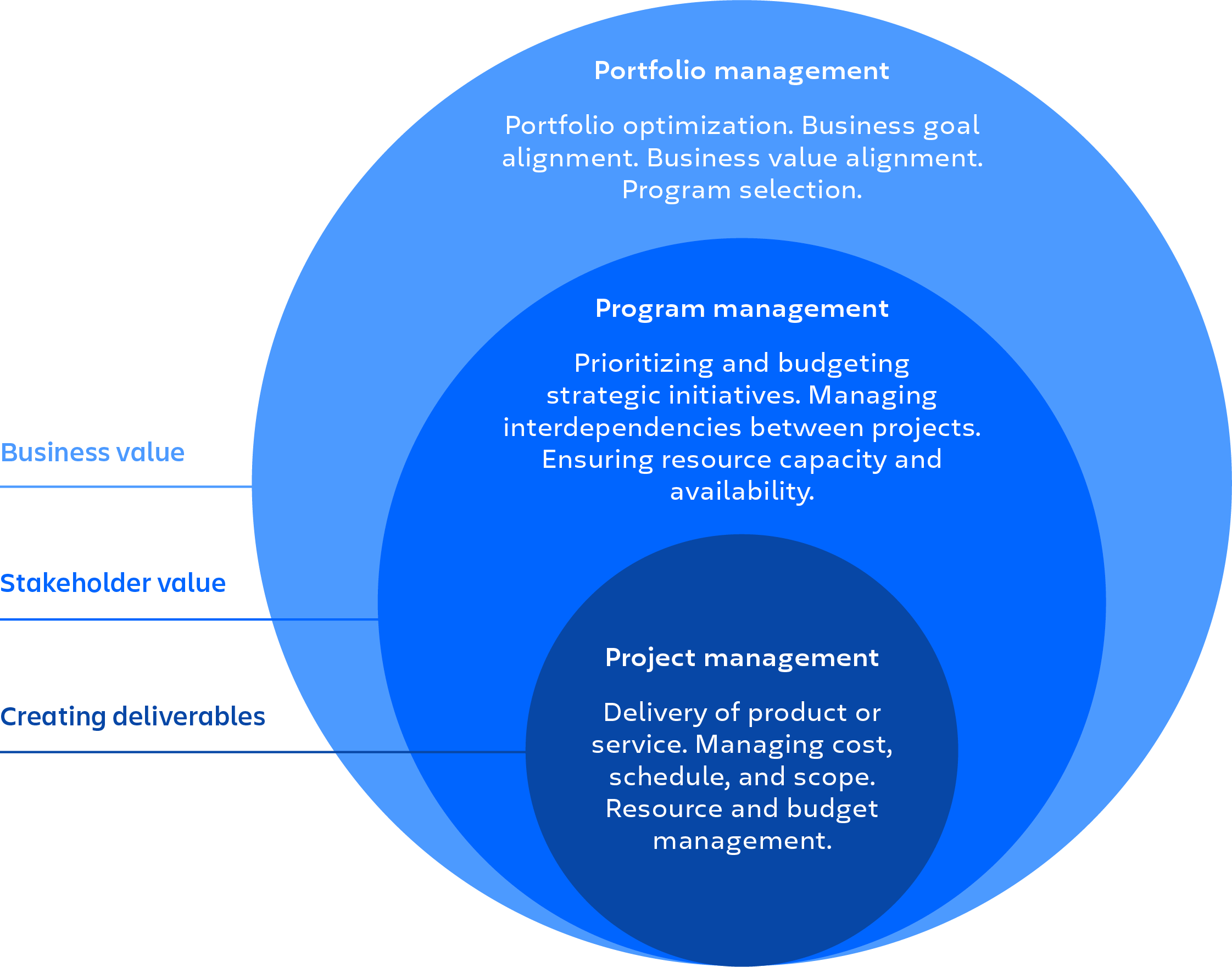
Program management is sometimes confused with project management. Project management is the process of leading a project performed by a team to achieve certain goals, such as building a new product.
A project represents a single, focused piece of work with a specific scope and defined output. Projects can run for several years, but their main focus remains the same. A project’s success can be measured by the delivery of artifacts and deliverables that roll up to a program’s larger goals.
Project management is the process of delivering value that incrementally moves a program forward. Despite the emphasis on artifacts and deliverables, project management still involves strategy and planning, since a project manager must determine how to meet the goals laid out at the beginning of the project. Once a project is underway, a project manager tracks progress, allocates resources, manages risks, communicates, and more.
Program management entails managing a program with multiple, related projects. Since programs are linked to strategic initiatives, they are often long-running and possibly permanent. Programs continue through organizational change, contribute to multiple goals, and contain many projects that deliver specific components of the larger strategic initiative.
At the highest level, a project generally focuses on outputs, while a program focuses on outcomes.
Projects have:
- A set of tasks with a clear deliverable and a deadline for completion
- Relates to creating, updating, or reviewing a particular document, process, outcome, or another single unit of work
- A predefined scope that is limited to a specific output
- Improves quality, efficiency, cost management, or customer satisfaction in a specific and predetermined way
Programs have:
- Unknown or fluid deadlines due to the large scope and impact of the work that must be done continuously over a long period of time
- Multiple deliverables with inter-related dependencies that may continue to evolve based on changing business needs
- A series of deliverables completed together to increase efficiency, accuracy, reliability, or other business needs
- The work enables the company to achieve a long-term business goal or initiative that will run in perpetuity
- Success delivers long-term benefits or unlocks new capabilities for the organization
What does a program manager do?
Program managers need to balance delivering artifacts, engaging with strategic decisions, managing stakeholders, and mitigating risks across the program. In a fully empowered organizational program, program managers should be able to solve — or connect to people who can solve — and plan to mitigate any problem that impacts the strategic initiative they seek to achieve.
Because of the breadth of their responsibilities, program managers play a key enabling role in companies. The role is flexible by design to meet the different challenges that teams encounter while going to production.
On any given day a program manager may do any of the following tasks:
Evaluate the state of the portfolio
A program manager reviews and evaluates a portfolio by connecting with teams to identify any risk mitigation or improvement opportunities. These connections can be coffee chats or team meetings. The program manager’s goal is to stay connected and engaged enough to work in lockstep towards shared goals. This includes connecting with project teams to ensure the project managers are supported and unblocked.
Manage risks
Risk management is a key element of portfolio management. Risks include a project timeline slipping, changing requirements, or the discovery of additional stakeholders. A program manager should be aware of anything that could impact the progress or outcome of the program and related projects. Ideally, a program manager can take corrective actions to reduce or manage risks in the portfolio.
Run the program
Program managers are responsible for running the program, which includes:
- Managing budgets and resources in cooperation with project managers
- Defining the operating parameters and controls
- Maintaining the core elements of the program that set the foundation from team charters and other establishing documents
Engage with stakeholders
A program manager connects with stakeholders to get a sense of the wider context that surrounds goals. These conversations provide key insights into the overall landscape. By partnering with stakeholders, a program manager can help guide project teams.
Refine the operating model
The operating model shapes how teams progress toward their goals. This can include establishing communication channels and reporting methods, identifying goals, establishing priorities across the entire program. During the course of a program, a program manager optimizes the operating model to increase the likelihood of success and reduce the impact of risks.
Support decisions
Decision-making takes many forms, from running a meeting with decision-makers, to compiling background information on what decisions are needed, or doing a comparative analysis of multiple options. Specific program managers may lean into different areas, depending on their strengths. The program manager reviews outcomes to identify opportunities for improvement in systems, processes, or results.
The focus and scope of each program manager shape the specifics of how they engage with these practices.
What does a project manager do?
A typical day for a project manager can include:
- Checking on the status of a deliverable to determine whether it will be delivered on time and within budget
- Reviewing a queue to identify new work, monitor existing tasks, and unblock specific elements for the project team
- Create a plan for how to reach a specific milestone that describes the stakeholder management and communications opportunities
- Ensure that project work meets the quality and reliability requirements established at the beginning of the project
As you can see, program and project managers work on highly related tasks. The primary difference between these two roles is scope and ambiguity:
- Projects are scoped tightly and controlled from the beginning, while programs have a larger scope that may change over the course of the program.
- Projects have limited ambiguity because success has been clearly defined at the start, while programs need to work through ambiguity to define what needs to be done and how to conceptualize “success” for the overall program.
| Plans projects | Tracks progress of projects | Allocates resources | Manage risks | Communicate |
In conclusion...
The Program Management Institute notes that “organizations with mature program management are far more successful than those without it.” That’s because program management allows organizations to achieve better alignment with strategic goals, management of project interdependencies, better resource management, and more.
Jira Align provides program management features that connect business strategy to technical execution. Its program management features include visual program boards, forecasting and simulation, program tracking, multi-tiered roadmaps, dependency management, and more.
Learn more about Jira Align’s program management features . Also be sure to check out Jira’s advanced planning for strategic planning.
Laureli Mallek is a builder at heart who supports organizational effectiveness by removing blockers to fulfilling work. As a program manager and coach, she empowers teams to be more resilient, scalable, and human-centric by crafting tailored solutions that span process improvement, team practices, and leadership development. Laureli has spent much of her career in tech, where she focused on security and privacy at large and small companies.
Iron Triangle Project Management
Learn how to use iron triangle project management and agile together to manage different variables and make the best decisions to reach business goals.
Agile Quarterly Planning - 8 Steps to Start
Agile quarterly planning helps you build great software while keeping the big picture in mind. Start here with 8 steps as your quarterly planning template.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections.Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over ...
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business. Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research, analyze their competitors, validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition.
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Definition. A business plan is a detailed written document that describes your business's activities, goals, and strategy. A strong plan outlines everything from the products a company sells to the executive summary to the overall management. In essence, a business plan should guide a founder's actions through each stage of growth.
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing. A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all ...
Business Plan Definition: A written document describing the nature of the business, the sales and marketing strategy, and the financial background, and containing a projected profit and loss statement
Step 2: Do your market research homework. The next step in writing a business plan is to conduct market research. This involves gathering information about your target market (or customer persona), your competition, and the industry as a whole. You can use a variety of research methods such as surveys, focus groups, and online research to ...
Startups is the world's largest startup platform, helping over 1 million startup companies find customers, funding, mentors, and world-class education. An introductory guide to explain what a business plan is, why you need it (and how it helps), key components, how long it should be, how to write it, who needs to see it, and much more.
Creating a business plan is an indispensable part of any business. The main purpose of creating such a document is to attract prospective investors to provide capital to the enterprise. Therefore, the plan should cover all the important perspectives of a business - financial, operational, personnel, competition, etc.
A business plan is a detailed road map that explains what the company's goals are and how it will achieve them. The exact details of a business plan will depend on the intended audience and the nature of the business. It's a good idea to regularly revisit your business plan so you know it's as accurate, realistic, and detailed as possible.
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy, including its capital and people. Business plans can help decision-makers see how specific projects relate to the organization's strategic plan.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
A business plan is a strategic document which details the strategic objectives for a growing business or startup, and how it plans to achieve them. In a nutshell, a business plan is a written expression of a business idea and will describe your business model, your product or service, how it will be priced, who will be your target market, and ...
business plan: A business plan is a document demonstrating the feasibility of a prospective new business and providing a roadmap for its first several years of operation.
The business plan admits the entrepreneur to the investment process. Without a plan furnished in advance, many investor groups won't even grant an interview. And the plan must be outstanding if ...
Logistics and operations plan. Financials. Startup. A startup business plan is meant to secure outside funding for a new business. Typically, there's a big focus on the financials, as well as other sections that help determine the viability of your business idea—market analysis, for example.
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries and its allies — a group of leading oil producers known as OPEC+ — agreed Sunday to extend production cuts announced last year into 2025.
backup and recovery testing: A backup and recovery test is the process of assessing the effectiveness of an organization's software and methods of replicating data for security and its ability to reliably retrieve that data should the need arise.
Written by Coursera Staff • Updated on Apr 19, 2024. Data analysis is the practice of working with data to glean useful information, which can then be used to make informed decisions. "It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts," Sherlock ...
10. Analyze your results. This is one of the most crucial steps in anything you do in marketing. Once you test something you have to analyze the results and continue testing. Data is crucial in every aspect of marketing and the omnichannel data you get from testing marketing strategies is the best kind of data to have.
Program management is sometimes confused with project management. Project management is the process of leading a project performed by a team to achieve certain goals, such as building a new product. A project represents a single, focused piece of work with a specific scope and defined output. Projects can run for several years, but their main ...
Get Registered. The first thing you'll need to do is handle your registrations, which include the following: Business registration: Small tax preparation businesses typically file a "doing business as" (DBA) with their state or form a Limited Liability Company (LLC). EIN: If your business needs an EIN, apply for one.