
- Join the AMA
- Find learning by topic
- Free learning resources for members
- Credentialed Learning
- Training for teams
- Why learn with the AMA?
Marketing News
- Academic Journals
- Guides & eBooks
- Marketing Job Board
- Academic Job Board
- AMA Foundation
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
- Collegiate Resources
- Awards and Scholarships
- Sponsorship Opportunities
- Strategic Partnerships
We noticed that you are using Internet Explorer 11 or older that is not support any longer. Please consider using an alternative such as Microsoft Edge, Chrome, or Firefox.
AMA Membership rates increase on Oct. 8—renew or join now to secure the current rate! Explore Membership .


Definitions of Marketing

What Is Marketing?

Definition of Marketing
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
The AMA’s definitions of marketing and marketing research are reviewed and reapproved/modified regularly by a panel of five scholars who are active researchers.
Get Started Growing Your Skills

On-Demand Training
An Overview of Marketing
This course introduces marketing, the marketing mix (the Four Ps), the strategic importance of marketing, and customer values and satisfaction.

Brand Strategy 101
With practice and a dash of curiosity, this course will reveal what’s needed to bring a brand to life using this formula: Brand Commitment + Brand Voice + Design + Implementation = Brand Strategy.

Modern Marketing: Strategy and Execution
The course focuses on providing practical, hands-on advice to entrepreneurs and small-business people, including video segments with analysis and commentary from industry-leading practitioners and subject matter experts.
Definition of Marketing Research
Marketing research is the function that links the consumer, customer, and public to the marketer through information—information used to identify and define opportunities and problems; generate, refine, and evaluate actions; monitor performance; and improve understanding of it as a process. It specifies the information required to address these issues, designs the method for collecting information, manages and implements the data collection process, analyzes the results, and communicates the findings and their implications. (Approved 2017)
Definition of Brand
A brand is a name, term, design, symbol, or any other feature that identifies one seller’s goods or service as distinct from those of other sellers.
ISO brand standards add that a brand “is an intangible asset” that is intended to create “distinctive images and associations in the minds of stakeholders, thereby generating economic benefit/values.”
Read More About Brands

The Power of a Brand Name: Why It Matters
An analysis of what makes some brand names more effective than others.

Does the World Really Need More Brands?
Confronting capitalism and brand purpose in the age of anxiety.

The Mythology of Totemic Brands
Radical new principles of engagement to help you see your brand more clearly.
Inbound vs Outbound Marketing

Inbound Marketing
Inbound is when customers initiate contact with the marketer in response to various methods used to gain their attention. These methods include email, events, content and web design.

Outbound Marketing
In this, the marketer initiates contact with the customer through methods such as TV, radio and digital display advertising . It is often used to influence consumer awareness and preference for a brand.
Search and Content

Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of developing a marketing/technical plan to improve visibility within one or more search engines . Typically, this consists of two elements.
On a technical side, SEO refers to ensuring that a website can be indexed properly by the major search engines and includes the use of the proper keywords, content, code, and links.
On the marketing side, SEO refers to the process of targeting specific keywords where the site should “win” in searches . This can be done by modifying a website to score well in the algorithms search engines use to determine rank, or by purchasing placement with individual keywords. Often, SEO programs are a blend of several elements and strategies. [2]
Keyword Marketing
Involves placing a message in front of users based on the specific keywords and phrases they are using to search. [1]
A key advantage of this method is that it gives marketers the ability to reach the right people with the right message at the right time. For many marketers, this method results in the placement of an ad when certain keywords are entered.
Note that in SEO , this term refers to achieving top placement in the search results themselves.
Content Marketing
A technique of creating and distributing valuable , relevant and consistent content to attract and acquire a clearly defined audience —with the objective of driving profitable customer action.
According to the Association of National Advertisers (ANA), it involves various methods to tell the brand story. More and more marketers are evolving their advertising to content marketing/storytelling to create more stickiness and emotional bonding with the consumer.

Areas of Marketing
Relationship marketing.
According to the Association of National Advertisers (ANA), relationship marketing refers to strategies and tactics for segmenting consumers to build loyalty.
Relationship marketing leverages database marketing, behavioral advertising and analytics to target consumers precisely and create loyalty programs.
Influencer Marketing
This focuses on leveraging individuals who have influence over potential buyers and orienting activities around these individuals to drive a brand message to the larger market.
With this, a brand inspires or compensates influencers (which can include celebrities, content creators, customer advocates, and employees) to get the word out on their behalf.
Viral Marketing
A phenomenon that facilitates and encourages people to pass along an advertising message.
Nicknamed “viral” because the number of people exposed to a message mimics the process of passing a virus or disease from one person to another. [1]
Guerilla Marketing
Describes an unconventional and creative strategy intended to get maximum results from minimal resources.
Green Marke t ing
Refers to the development and promotion of products that are presumed to be environmentally safe (i.e., designed to minimize negative effects on the physical environment or to improve its quality).
This term may also be used to describe efforts to produce, promote, package, and reclaim products in a manner that is sensitive or responsive to ecological concerns.
Email Marketing
A common and powerful tool for marketers at all levels. Email marketing has a role in direct, digital, inbound and outbound marketing efforts. It helps marketers with lead generation, brand awareness, relationship building and more.

The 4 Ps of Marketing
A product is defined as a bundle of attributes (features, functions, benefits, and uses) capable of exchange or use, usually a mix of tangible and intangible forms.
A product may be an idea, a physical entity (goods), or a service , or any combination of the three. It exists for the purpose of exchange in the satisfaction of individual and organizational objectives.
Price is the formal ratio that indicates the quantity of money, goods , or services needed to acquire a given quantity of goods or services.
It is the amount a customer must pay to acquire a product .
Place (or Distribution)
Distribution refers to the act of carrying products to consumers . It is also used to describe the extent of market coverage for a given product.
In the 4 Ps , distribution is represented by place or placement.
Promotion includes tactics that encourage short-term purchase, influence trial and quantity of purchase, and are very measurable in volume, share and profit.
Examples include coupons , sweepstakes , rebates, premiums , special packaging, cause-related marketing and licensing .
About Our Definitions
- Bernard Jaworski, Peter F. Drucker Chair in Management and the Liberal Arts, Claremont Graduate University
- Richard Lutz, J.C. Penney Professor of Marketing, University of Florida
- Greg W. Marshall, Charles Harwood Professor of Marketing and Strategy, Rollins College
- Linda Price, Philip H. Knight Chair and Professor of Marketing, University of Oregon
- Rajan Varadarajan, University Distinguished Professor and Distinguished Professor of Marketing and Ford Chair in Marketing & E-Commerce, Texas A&M University
Marketing Dictionary
The AMA helps support the Marketing Dictionary . Head there if you are looking for more definitions of marketing terms.
Keep Reading

What is SEO Marketing? [A Comprehensive Overview]
SEO marketing is a subset of digital marketing that involves the optimization of websites and web pages for major search engines like Google. As these search engines became a predominant way of finding just about anything, various practices have emerged to help organizations improve the visibility of their digital assets. The term “search engine optimization […]

Data and Analytics for Marketers
While being a marketer is often considered a creative field, there is magic in the mashup of data and creativity . Data and analytics take the guesswork out of marketing and allow you to focus on what matters – the success of your marketing campaigns. Plus, they help you get more value from your marketing budget, improve customer efficiency, and understand what is working best in your marketing strategy. Even if you don’t consider yourself a data and analytics expert, it is important to have some knowledge in these areas as a marketer in 2022 and beyond. Additionally, as a marketer, it is important to know how to use data and analytics tools to your advantage to demonstrate your success to your clients or to superiors within your company.

Build Your Digital Marketing Strategy [Step-by-Step Guide]
Most of our consumption of content today exists online. Because of this, companies have had to shift to digital marketing in order to get the word out about their products and services. However, you cannot simply make content for online platforms and hope for the best. You need to build a digital marketing strategy to […]
By continuing to use this site, you accept the use of cookies, pixels and other technology that allows us to understand our users better and offer you tailored content. You can learn more about our privacy policy here
What is Marketing, and What's Its Purpose?
Updated: January 24, 2022
Published: May 31, 2018
Dictionary.com defines marketing as, "the action or business of promoting and selling products or services, including market research and advertising."

If you work in a marketing role like I do, it's probably difficult for you to define marketing even though you see and use it every day -- the term marketing is a bit all-encompassing and variable for a straightforward definition.
![meaning of marketing essay → Click here to download our free guide to digital marketing fundamentals [Download Now].](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/0a42501f-0096-4817-9fbc-923540fe37a6.png)
This definition feels unhelpful.
The selling part, for instance, overlaps a little too snuggly with a "what is sales" definition, and the word advertising makes me think of Mad Men brainstorming sessions.
But upon digging deeper, I began seeing that actually, marketing does overlap heavily with advertising and sales. Marketing is present in all stages of the business, beginning to end.

Digital Marketing For Small Business
Everything you need to know to get started with digital marketing. You'll learn about:
- Content Marketing
- Marketing Analytics
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
What is marketing?
Marketing refers to any actions a company takes to attract an audience to the company's product or services through high-quality messaging. Marketing aims to deliver standalone value for prospects and consumers through content, with the long-term goal of demonstrating product value, strengthening brand loyalty, and ultimately increasing sales.
At first, I wondered why marketing was a necessary component during product development, or a sales pitch, or retail distribution. But it makes sense when you think about it -- marketers have the firmest finger on the pulse of your consumer persona.
The purpose of marketing is to research and analyze your consumers all the time, conduct focus groups, send out surveys, study online shopping habits, and ask one underlying question: "Where, when, and how does our consumer want to communicate with our business?"
Here, let's explore the purposes of marketing, along with types of marketing, the 4 P's of marketing, and the difference between marketing and advertising.
Whether you're a seasoned marketer looking to refresh your definitions, or a beginner looking to understand what marketing is in the first place, we've got you covered. Let's dive in.
Purpose of Marketing
Marketing is the process of getting people interested in your company's product or service. This happens through market research, analysis, and understanding your ideal customer's interests. Marketing pertains to all aspects of a business, including product development, distribution methods, sales, and advertising.
Modern marketing began in the 1950s when people started to use more than just print media to endorse a product. As TV -- and soon, the internet -- entered households, marketers could conduct entire campaigns across multiple platforms. And as you might expect, over the last 70 years, marketers have become increasingly important to fine-tuning how a business sells a product to consumers to optimize success.
In fact, the fundamental purpose of marketing is to attract consumers to your brand through messaging. Ideally, that messaging will helpful and educational to your target audience so you can convert consumers into leads.
Today, there are literally dozens of places one can carry out a marketing campaign -- where does one do it in the 21st century?
Types of Marketing
Where your marketing campaigns live depends entirely on where your customers spend their time. It's up to you to conduct market research that determines which types of marketing -- and which mix of tools within each type -- is best for building your brand. Here are several types of marketing that are relevant today, some of which have stood the test of time:
- Internet marketing: Inspired by an Excedrin product campaign that took place online, the very idea of having a presence on the internet for business reasons is a type of marketing in and of itself.
- Search engine optimization: Abbreviated "SEO," this is the process of optimizing content on a website so that it appears in search engine results. It's used by marketers to attract people who perform searches that imply they're interested in learning about a particular industry.
- Blog marketing: Blogs are no longer exclusive to the individual writer. Brands now publish blogs to write about their industry and nurture the interest of potential customers who browse the internet for information.
- Social media marketing: Businesses can use Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, and similar social networks to create impressions on their audience over time.
- Print marketing: As newspapers and magazines get better at understanding who subscribes to their print material, businesses continue to sponsor articles, photography, and similar content in the publications their customers are reading.
- Search engine marketing: This type of marketing is a bit different than SEO, which is described above. Businesses can now pay a search engine to place links on pages of its index that get high exposure to their audience. (It's a concept called "pay-per-click" -- I'll show you an example of this in the next section).
- Video marketing: While there were once just commercials, marketers now put money into creating and publishing all kinds of videos that entertain and educate their core customers.
Marketing and Advertising
If marketing is a wheel, advertising is one spoke of that wheel.
Marketing entails product development, market research, product distribution, sales strategy, public relations, and customer support. Marketing is necessary in all stages of a business's selling journey, and it can use numerous platforms, social media channels, and teams within their organization to identify their audience, communicate to it, amplify its voice, and build brand loyalty over time.
On the other hand, advertising is just one component of marketing. It's a strategic effort, usually paid for, to spread awareness of a product or service as a part of the more holistic goals outlined above. Put simply, it's not the only method used by marketers to sell a product.
.png)
Free Advertising Planning Kit
Plan and launch an effective and profitable advertising campaign with this guide and set of templates.
- An Overview of Popular Advertising Methods
- The Pros, Cons, and Costs of Advertising Types
- A Planning Template to Outline Timeline, Budget, and Goals
- A Project Pitch Presentation Deck to Share With Stakeholders
Here's an example (keep reading, there's a quiz at the end of it):
Let's say a business is rolling out a brand new product and wants to create a campaign promoting that product to its customer base. This company's channels of choice are Facebook, Instagram, Google, and its company website. It uses all of these spaces to support its various campaigns every quarter and generate leads through those campaigns.
To broadcast its new product launch, it publishes a downloadable product guide to its website, posts a video to Instagram demonstrating its new product, and invests in a series of sponsored search results on Google directing traffic to a new product page on its website.
Now, which of the above decisions were marketing, and which were advertising?
The advertising took place on Instagram and Google . Instagram generally isn't an advertising channel, but when used for branding, you can develop a base of followers that's primed for a gentle product announcement every now and again. Google was definitely used for advertising in this example; the company paid for space on Google -- a program known as pay-per-click (PPC) -- on which to drive traffic to a specific page focused on its product. A classic online ad.
Where did the marketing take place? This was a bit of a trick question, as the marketing was the entire process . By aligning Instagram, Google, and its own website around a customer-focused initiative, the company ran a three-part marketing campaign that identified its audience, created a message for that audience, and delivered it across the industry to maximize its impact.
It’s important to know that this type of marketing campaign requires proper coordination and monitoring of multiple channels. You need to adapt your approach to each specific channel, yet get them to yield the same results -- generate revenue.
This is where a unified marketing software solution can come in handy. It includes the tools necessary to monitor and manage campaigns across multiple channels -- from websites to emails, and online advertisements.
The 4 Ps of Marketing
In the 1960's, E Jerome McCarthy came up with the 4 Ps of marketing: product, price, place, promotion.
Essentially, these 4 Ps explain how marketing interacts with each stage of the business.
Download Now: Free Marketing Mix Templates
.png?width=473&height=355&name=Copy%20of%20chatbot%20(1).png)
Let's say you come up with an idea for a product you want your business to sell. What's next? You probably won't be successful if you just start selling it.
Instead, you need your marketing team to do market research, interpret marketing analytics data into actionable insights, and answer some critical questions: Who's your target audience? Is there market fit for this product? What messaging will increase product sales, and on which platforms? How should your product developers modify the product to increase likelihood of success? What do focus groups think of the product, and what questions or hesitations do they have?
Marketers use the answers to these questions to help businesses understand the demand for the product and increase product quality by mentioning concerns stemming from focus group or survey participants.
Your marketing team will check out competitors' product prices, or use focus groups and surveys, to estimate how much your ideal customer is willing to pay. Price it too high, and you'll lose out on a solid customer base. Price it too low, and you might lose more money than you gain. Fortunately, marketers can use industry research and consumer analysis to gauge a good price range.
It's critical that your marketing department uses their understanding and analysis of your business's consumers to offer suggestions for how and where to sell your product. Perhaps they believe an ecommerce site works better than a retail location, or vice versa. Or, maybe they can offer insights into which locations would be most viable to sell your product, either nationally and internationally.
This P is likely the one you expected from the get-go: promotion entails any online or print advertisement, event, or discount your marketing team creates to increase awareness and interest in your product, and, ultimately, lead to more sales. During this stage, you'll likely see methods like public relations campaigns, advertisements, or social media promotions.
Hopefully, our definition and the four Ps help you understand marketing's purpose and how to define it. Marketing intersects with all areas of a business, so it's important you understand how to use marketing to increase your business's efficiency and success.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in May 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Digital Marketer Jenna Kutcher Thinks You're Overcomplicating It

The Ultimate Guide to Marketing Strategies & How to Improve Your Digital Presence
![meaning of marketing essay 5 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
5 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]
![meaning of marketing essay 4 Clever Olympics Marketing Campaigns [+Top Takeaways]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/best-olympic-marketing-campaigns-1-20240809-9542066.webp)
4 Clever Olympics Marketing Campaigns [+Top Takeaways]
![meaning of marketing essay What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketing-strategy-examples-1-20240801-4880441-1.webp)
What is a Marketing Plan & How to Write One [+ Examples]
![meaning of marketing essay 6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
6 Steps to Create an Outstanding Marketing Plan [Free Templates]

50 Small Business Marketing Ideas for 2024

The 2024 State of Marketing & Trends Report: Data from 1400+ Global Marketers

Mastering Social Media for Nonprofit Promotion: Insights and New Data from Experts

The AIDA Model: A Proven Framework for Converting Strangers Into Customers
An actionable guide on building your digital marketing strategy from the ground up.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

Essay on Marketing
Students are often asked to write an essay on Marketing in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Marketing
The world of marketing.
Marketing is about spreading the word on products and services. It helps companies connect with customers.
Understanding Customers
Effective marketing begins with understanding what customers want and need. Companies study people’s preferences and behaviors.
Creating Products
Using customer insights, businesses develop products that solve problems or bring joy.
Communication is Key
Marketing involves telling people about products through ads, social media, and more. Clear communication is crucial.
Building Brands
Adapting and growing.
Marketing strategies change based on feedback. Companies adapt to stay relevant and successful.
Marketing is like sharing stories that connect what people need with what companies offer. It’s an exciting way to make products part of our lives.
Also check:
250 Words Essay on Marketing
Understanding the power of marketing.
Marketing: a concept that shapes the modern world. It’s more than just ads and promotions; it’s the engine driving business success. Let’s explore its significance.
The Essence of Marketing
At its core, marketing is all about connecting products or services with people’s needs and desires. It’s about creating value, not just selling. Effective marketing answers the question, “Why should customers choose us?”
Segmentation and Targeting
Value creation through branding.
Branding isn’t just a logo; it’s the emotions and perceptions associated with a product. Strong brands build trust and loyalty, allowing companies to command premium prices.
The Digital Revolution
The digital age has revolutionized marketing. Social media, search engines, and online ads allow for precision targeting and personalized communication. It’s not about bombarding, but about engaging.
Content is King
Analyzing and adapting.
Marketing isn’t a one-shot deal. It’s a constant process of analyzing results and adapting strategies. Tools like analytics help track what works and what doesn’t, leading to informed decisions.
Ethics in Marketing
With great power comes great responsibility. Marketing should be ethical, transparent, and respectful. Deceptive practices might bring short-term gains, but they erode trust in the long run.
The Bottom Line
In a nutshell, marketing is the bridge that connects what you offer with those who need it. It’s not just about selling but about creating lasting value. Understanding its principles can propel businesses toward success in the modern world.
500 Words Essay on Marketing
Marketing: connecting the dots for successful business.
Marketing is like a magical thread that weaves businesses and customers together, creating a world where products and services find their perfect match. In this modern age, new-age techniques like Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR), Chatbots and Conversational Marketing, Programmatic SEO , Social Commerce, and Neuromarketing have added exciting dimensions to this field. Let’s delve into the basics of marketing and explore how these techniques have transformed the way businesses reach out to us.
Imagine you’ve baked the most delicious cookies in town. You want everyone to know how tasty they are. That’s where marketing comes into play. Marketing involves all the activities that help you promote and sell your products or services. It’s about understanding what people want, creating something they’ll love, and then letting them know it exists.
Meeting New Friends: Customers and Businesses
In the world of marketing, two important players dance together: customers and businesses. Customers are people like you and me who need things. Businesses are the ones that make those things. Marketing helps these two groups find each other.
Traditional vs. Modern Marketing
Traditional marketing used to be all about newspapers, TV ads, and posters. But today, things have changed a lot. Businesses use new-age techniques to grab our attention in creative ways. Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) let us experience products almost like they’re real. Chatbots talk to us on websites and social media, making shopping feel like chatting with a friend. Social Commerce lets us buy things through platforms like Instagram and Facebook, as if we’re shopping with friends online.
Getting Found: SEO
Think about searching for something online. How often do you go past the first page of search results? That’s why businesses use SEO. It’s like making sure your cookie recipe appears at the top when someone searches for “delicious cookies.” This technique helps businesses get noticed by improving their online visibility.
Understanding Your Brain: Neuromarketing
Ever wondered why some ads just stick in your head? Neuromarketing dives into how our brains respond to ads. Businesses use this technique to create ads that connect with us on a deeper level. It’s like making sure your cookie commercial triggers happy thoughts every time you see it.
Chatting with Businesses: Conversational Marketing
Have you ever had a chat with a robot on a website? That’s Conversational Marketing. Businesses use chatbots to talk to us, answer our questions, and even help us choose the right products. It’s like having a helpful assistant while shopping.
Shopping in Your Pajamas: Social Commerce
Putting it all together.
Marketing is like a puzzle where every piece matters. Businesses create amazing products, use modern techniques like VR/AR, Chatbots, Programmatic SEO, Social Commerce, and Neuromarketing to make us notice them, understand us better, and make shopping a breeze.
In conclusion, marketing is the bridge that connects what we need with what businesses offer. Through traditional and new-age techniques, it has evolved into a captivating journey that is all about understanding, connecting, and engaging with customers. Whether it’s through the immersive experiences of VR/AR, the friendly conversations of chatbots, the smart visibility of SEO, the emotional impact of Neuromarketing, or the convenience of Social Commerce, marketing continues to shape the way we discover, choose, and enjoy the products and services that make our lives better.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Marketing and PR
College Marketing Essays & Papers for Free
- Business and Management
- Finance, Accounting and Banking
- Human Resources (HR)
- Macro & Micro Economics
Business Buyer Behavior
Words: 1264
Saie Competitive Exams - The Best Way to Prepare for Your Exam
Marketing plan of the visiting nurse association of omaha/council bluffs.
Words: 5092
Hire an expert to write you a 100% unique paper aligned to your needs.
10 Nonverbal Status Indicators That You're in Charge
Using information to drive marketing decisions, cross cultural marketing.
Words: 1812
Coronavirus and the Future of Sports League Brands
Words: 2661
Lululemon vs Athleta: Which Brand is Better?
Gantt chart: nevada hike it and spike it, the increasing concerns about climate change.
- Essay of any type
- Scholarship essay
- Admission essay
- College essay
- High School
Fine collection of free essay examples, paper samples and topics
Access a vast arsenal of free writing examples covering any subject or topic. Use these academic essay examples to draw inspiration or deepen your knowledge in various areas. Start exploring now!
- Persuasive essays
- Argumentative essays
- Analytical essays
- Expository essays
- Classification essays
- Cause-and-effect
- Problem-and-solution
- Compare-and-contrast
- Descriptive essays
- Narrative essays
- Definition essays
- Informative essays
- Critical analysis
- Rhetorical analysis
- Admission essays
- Human Resources
- Political Science
- Government Studies
- Linguistics
- Gun control
- Capital punishment
- Domestic violence
- Police brutality
- Marijuana legalization
- Climate change
- Globalization
- Illegal immigration
- Overpopulation
- Gender roles
- American Revolution
- World War 1
- The Great Depression
- World War 2
- Vietnam War
- American Dream
- The Great Gatsby
- Romeo and Juliet
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Catcher in the Rye
- Miscellaneous
What Is a Marketing Essay
The definition of marketing essay describes it as a written piece, exploring product promotion in detail. Such pieces entitle authors to conduct research, study terms, and argumentation. Writing process engages cognitive abilities as well as analytical and critical thinking. While writing, students educate themselves and improve skills in writing and argumentation.
Creating a competent scholarly piece about commerce is always challenging for young authors. College kids should read various data sources and select credible ones. Data must be organized and structured beforehand. Presentation of data, argumentation, as well as reasoning also add many problems for authors. Such papers must be written in compliance with requirements following strict guidelines.
Free Marketing Paper Examples to Download
Website offers countless marketing essay examples of any size and complexity. Browse through a wide selection of topics, opinions, and formats. Each pdf sample is available for free with no registration. All papers were donated by former students. They demonstrate unique approaches to tackling this uneasy task.
Use these text samples as a source of inspiration, guidance, or templates. Extract wording, argumentation techniques, and convincing tactics. Reading sample pieces before writing brings fresh marketing essay ideas. Example articles present perfect language, strong structuring, and smart narration.
Learn new storytelling tricks and perfect personal writing skills by copying selected articles. Look how other students managed to create memorable, well-designed, researched pieces. You may need a human resource management essay; find it in our library. Apply new knowledge in custom papers – boost overall quality and final grades.
Marketing Reflective Essay Examples
A marketing reflective essay challenges authors with critical assessment and taking an analytical look. In reflective pieces, students demonstrate in-depth subject understanding as well as superb writing skills. Such qualities can be achieved either by time-consuming learning or by copying successful papers. Proposed examples demonstrate sublime knowledge of both the article's subject and vocabulary. Here’s how even one reading session of a free marketing essay pdf example can change a student’s style:
- Improved wording, incision
Learn new topic-specific vocables for a big improvement in morphological variability as well as readability.
- Better paper structuring
Check out modern effective methods or text design for more narrative consistency and coherency.
- Thorough informational support
Examine how each statement is backed up by credible information from trustworthy data sources.
Marketing Analysis Paper Examples
Marketing analysis essay takes it further. Similar papers consist mostly of critique and researched material. Students demonstrate extensive academic knowledge and analysis skills. Writing process starts with subject studying and reading competent data sources. A good author must design a clean structure. Create a diverse plan that’ll allow for in-depth coverage. Paper must be kept informative yet captivating. Readers should be entertained and eager to read more.
If you’re short on marketing paper ideas, read proposed paper samples. Articles were donated by students who got the highest scores for these pieces. They present a wide variety of possible topics and analytical approaches. Check out business essays and what made these works great in analysis quality and data presentation. Try indirectly copying smart tricks as well as effectively improving personal writing skills. Make your writing excellent!
Write My Marketing Essay for Me!
To all students out there, here’s a short essay writing marketing online guide. Skim through it, then follow each step to create unique, competent scholarly works.
- Conduct in-depth research. Study all available data regarding the article's subject before essay writing in marketing. Thorough subject exploration is important.
- Arrange arguments. Carefully select only credible, relevant, and important data. Separate it from unchecked or controversial for better academic value.
- Design an outline. Plan narration by creating an article’s structure. Specify which data is mentioned and where. Follow this outline while writing.
- Make drafts. Write two-three versions of your article. Each one will be closer to perfection. After you’re satisfied with the achieved results, do the next step.
- Edit mistakes out. Proofread an article to eliminate spelling errors, grammar faults, and word repetitions. Check for plagiarism to be sure your article is unique.
If you need more help – contact us directly. Our service will be happy to help you tackle this uneasy marketing essay writing assignment.
Great Marketing Essay Topics Ideas
Want more assistance with finding new marketing topics to write about? The chance of creating an interesting scholarly piece significantly improves if the topic is fascinating. Select such a topic in marketing that you’d be eager to share thoughts. With that said, here’s a list of great paper subjects:
- How can consumers protect themselves from viral advertisements?
- Direct sell or a hidden call-to-action? Describe pros/cons of each approach.
- Explore effective methods of selling a bottle of water to a drowning man.
- Online product promotion as a part of modern retail strategies.
- Explain how advertisements can be more effective on social media.
- Business model of TikTok – analyze it in detail.
- How can a company create its image and earn clients’ loyalty?
Hint: Marketing is closely related with communication. So, browse more than one essay on communication in our database.
Topics Related to Marketing
Picking one of marketing related topics instead of purely market-targeted gives additional possibilities. Students get a wider variety of arguments and more abilities to showcase particular knowledge. Subject-related articles develop cognitive skills as well as teach the concept application. We’ve compiled some marketing paper topics that are not entirely about marketing:
- How can kids improve revenues of a lemonade stand?
- Now people are products big companies buy/sell.
- Where to find the best customer for your business? (Consult: essay about business management .)
- Explore first forms of advertisement in Ancient Rome.
- Small entrepreneur struggles of the 21st century.
- How symbols are used in advertising/selling?
- Who was Steve Jobs – market genius or a fraud?
- Instagram and TikTok as the best platforms for selling stuff.
FAQ About Marketing Essays
Numerous free essays on marketing and related subjects are available to any internet user. The website offers countless options for each student to select the right paper sample. Download them as pdf files or examine free samples online. Use these free papers to improve personal grades and perfect writing abilities.
Short papers on marketing focus on densely packing information. Such articles require immense writing skills and experience to complete. Brief papers often are the hardest ones since all the data must be squeezed into a tiny amount. Multiple examples of short scholarly pieces can be downloaded free from this website.
Successful essays on marketing are started with topic statement sentences. Authors supply readers with essential information necessary for text understanding. The first paragraph only hooks attention without providing any concrete facts or arguments. Look at examples for guidance and inspiration. Samples showcase various takes on the article's introduction – choose yours!
All proposed essays about marketing were already submitted by their authors. The papers you see were donated by students. Copy-paste will result in poor originality percentage and grades. Teachers use plagiarism checkers on each submitted work. If you’re aiming at something better than “F”, you better write unique works.
Running out of time ?
Entrust your assignment to proficient writers and receive TOP-quality paper before the deadline is over.

- Business Management
- Career development
- Communication & Skills
- Finance & Accounting
- Marketing & Sales
- Self introduction
- Strategy & Innovation
- Business Tools

What is Marketing? Definition, Concept, Importance & Strategies
Disclaimer : We sometimes use affiliate links in our content. For more information, visit our Disclaimer Page .
Are you curious about what marketing is? Wonder no more! In this post, we’ll define marketing, discuss its concept and importance, and explore some strategies you can use to get started. By the time you’re finished reading, you’ll clearly understand what marketing is and how it can benefit your business. So let’s get started!
What Marketing Is (and What It Isn’t)
There’s a lot of confusion out there about what marketing is. Some people think it’s all about advertising, while others believe it’s the same as sales. Still, others believe that marketing is nothing more than a fancy name for public relations.
The truth is, marketing is none of those things. Yes, advertising, sales, and public relations are all important components of a successful marketing strategy, but they’re not the be-all and end-all of marketing. So, what is marketing? Keep reading to find out.
→ A Definition of Marketing
The American Marketing Association (AMA) defines marketing as “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
In other words, marketing is the process of creating value for your target audience through the creation and distribution of content that is relevant to their needs and wants. Marketing isn’t about selling products or services; it’s about understanding the needs and desires of your target market and then creating content that meets those needs.
→ Components of Marketing
Now that we have a basic understanding of marketing let’s look at some of its key components. As we mentioned earlier, advertising, sales, and public relations are all important parts of any good marketing strategy. But there are other elements you need to consider. Other essential components include market research, branding, customer service, and product development.
Each one of these components plays a vital role in the success of your marketing efforts. For example, market research helps you identify your target market and understand its needs and wants. Branding helps you create an emotional connection with your target market by establishing trust and credibility. And customer service ensures that your target market has a positive experience with your company at every touchpoint.
Marketing: Why It’s Important For Your Business
Many small business owners wear a lot of hats. You’re the CEO, CFO, janitor, bookkeeper, and sales team all rolled into one. And while you may be good at all those things, there’s one area in which you may not be as well-versed: marketing.
Marketing is often seen as an unnecessary expense that can be put on the back burner until the business is booming. But the truth is marketing is essential to the success of any business—no matter its size or industry.
Here’s why:
• Generates Leads & Increases Sales
One of the most important jobs of marketing is to generate leads and increase sales. Without marketing, your business will have a hard time attracting new customers and growing its revenue.
Think about it this way: if you’re not actively working to bring new people into your customer base, your business will eventually stagnate and die. Even if you have a great product or service, without marketing, it will be difficult for people to find out about your business and what you offer.
• Builds Brand Awareness & Recognition
Another critical function of marketing is to build brand awareness and recognition. In today’s competitive marketplace, it’s more important than ever for businesses to establish themselves as leaders in their industry.
One of the best ways to do this is through consistent branding across all your marketing channels. This includes everything from your website design and logo to how you answer your phone and respond to customer inquiries. By presenting a cohesive brand identity to the world, you’ll make it easier for people to remember your business and what it stands for—ultimately leading to more customers and sales down the road.
• Creates Loyal Customers & Brand Advocates
Last but not least, effective marketing can help create loyal customers and brand advocates. People who feel positively about your brand are much more likely to continue doing business with you in the future and recommend your products or services to others.
And while generating new leads is always essential, it’s just as important (if not more) to keep the customers you already have coming back for more. After all, it costs five times more money to attract a new customer than to keep an existing one happy.
The Five Marketing Concepts
As a business owner, it is important to be aware of the different marketing concepts to make the best decisions for your company. The five marketing concepts are production, product, selling, marketing, and societal marketing. Each concept has a different focus and different implications for businesses.
1. Production Concept
The production concept focused on operations and, based on the assumption that customers prioritize availability and affordability, emerged in early 1950s capitalism. This was when companies strove for efficiency in manufacturing to ensure maximum profits and scalability.
2. Product Concept
The product concept focuses on improving its products to offer superior quality, performance, and features. This approach assumes that customers are not as price-sensitive as the production concept suggests and will pay more for a product that offers superior quality, performance, and features. To successfully use this approach, businesses need to have a competitive advantage in product development. This can be achieved through research and development (R&D), which refers to creating or improving new products.
3. Selling Concept
The selling concept is based on the assumption that customers will likely buy a product if it is aggressively marketed and sold to them. This approach focuses on creating demand for the product through aggressive marketing and sales strategies. While this approach can be successful in some cases, it can backfire if customers feel like they are being spammed with marketing messages or pressured into buying a product.
4. Marketing Concept
The marketing concept is a strategic approach that focuses on creating customer value. This concept is based on the belief that customers are essential to a business and that businesses should focus on creating products and services that meet their needs. To successfully use this approach, companies need to deeply understand their target market and what they want or need.
5. The Societal Concept
The societal marketing concept is a more recent marketing approach that considers the well-being of society as a whole. This concept is based on the belief that businesses should focus on creating products and services that meet customers’ needs while also considering the negative impact their business might have on society. Companies must understand the social and environmental issues they face to use this approach successfully.
Related: Societal Marketing Concept
What is Marketing Strategy?

Marketing strategy is the process that organizations use to plan and execute their marketing activities. A well-developed marketing strategy considers the company’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as its opportunities and threats. It also includes a clear statement of the company’s marketing goals and objectives. In short, a marketing strategy is an organization’s game plan for achieving its marketing goals.
There are many different approaches to developing a marketing strategy, but all of them share one common goal: creating a plan to guide the company’s marketing activities. The first step in developing a marketing strategy is to conduct a situation analysis, which assesses the company’s internal and external environment. Then, the situation analysis results are used to identify the company’s target markets and choose the appropriate marketing mix.
The next step is to develop marketing objectives, which are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound goals that will guide the company’s marketing activities. Once the objectives have been developed, the company must create a marketing plan that details how it will achieve its objectives. The final step is implementing and monitoring the marketing plan to ensure it reaches the desired results.
Related: How to Create a Winning Marketing Strategy
5 Types Of Marketing Plans And Strategies
In order to run a successful business, you need to have a solid marketing plan in place. But what kind of marketing plan should you have? There are a few different types of marketing plans and strategies that you can choose from, and the right one for your business will depend on your specific goals and objectives. Let’s take a look at five of the most common types of marketing plans and strategies.
- Marketing mix strategy
- Market Penetration Strategy.
- Market Development Strategy.
- Product Development Strategy.
- Diversification Strategy.
1. Marketing mix strategy
A marketing mix strategy is a plan of action that a company uses to promote its products or services. The marketing mix typically consists of four main elements: product, price, place, and promotion. A company will use a variety of marketing tactics to execute its marketing mix strategy, including advertising, public relations, and personal selling.
Product is the first element of the marketing mix and refers to the good or service that a company offers its customers. A company must carefully select the right product to appeal to its target market. It is crucial to consider the target market’s needs and wants and design a product that meets those needs.
Price is the second element of the marketing mix and refers to how much the company charges for its product or service. The price of a product or service must be reasonable compared to other similar products offered by competitors if the company wants to attract customers.
The place is the third element of the marketing mix and refers to how a company delivers its product to its target market. The place element includes two sub-elements: distribution channels and physical indications. Distribution channels are the paths through which a product or service flows to the market, while physical evidence is anything that impacts where people go. For example, signs pointing to your business location can be considered physical evidence of place.
Promotion is the fourth element of the marketing mix and refers to how a company communicates its product or service benefits to customers. Promotional activities include advertisements, promotional campaigns, public relations efforts, and personal selling.
2. Market Penetration Strategy
The market penetration strategy is focused on increasing the sales of the company’s current products and services in its existing markets. This can be done by increasing the market share of the products or services, increasing the sales volume, or using both measures. The main aim of this strategy is to increase market share as quickly as possible, at the lowest possible cost.
There are several ways to achieve this, including:
- First, lowering prices to increase demand.
- Second, investing in marketing and advertising to create awareness of the product or service.
- Third, offering promotions and discounts to customers.
- Finally, introducing new products or services that complement those already provided.
3. Market Development Strategy
The market development strategy aims to increase the size of an existing market or develop a new market. The main objective here is to open new markets and increase the pool of possible customers by creating demand for products and services that previously did not exist or expanding the market share of existing products and services. This strategy will often focus on complementary product development, such as introducing accessories or new products, or on developing new markets, for example, through diversification.
4. Product Development Strategy
The product development strategy focuses on successfully creating and launching a new product to help expand market share. The main aim here is to create better products than those offered by competitors at higher quality and lower cost, successfully launch them and achieve a high market share as quickly as possible.
The product strategy includes developing new products but can also improve or expand existing lines.
5. Diversification Strategy
A company’s diversification strategy is about making strategic changes to increase profits by exploiting more than one product or market. For example, a diversification strategy might include the development of new products which are radically different from those currently offered by the company or entering into entirely new markets that complement existing lines.
It is important to note that business diversification should not be seen as an alternative for growth in sales and profits but rather as generating new income streams and helping reduce risk.
6 common Marketing theories
Marketing theory means a body of knowledge used to describe, predict and explain marketing phenomena. It attempts to aggregate and generalize the findings from the study.
Here are six common marketing theories you should know about:
→ The Seven Ps of Marketing Mix
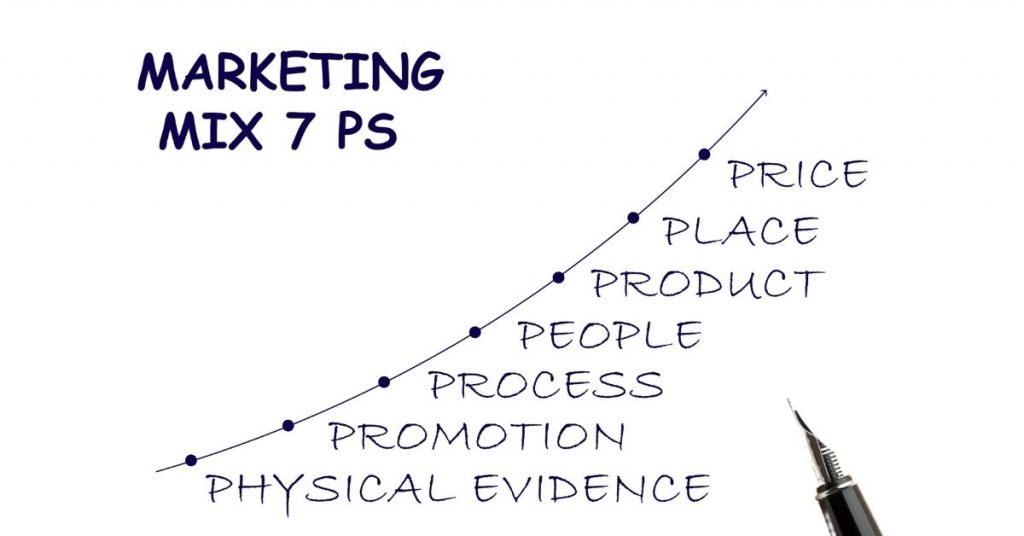
The Seven Ps of Marketing Mix is a marketing theory that describes the different aspects of a company’s marketing plan. It consists of the following seven elements: product, price, place, promotion, process, people, and physical environment. Each part plays an essential role in the success of a marketing campaign.
- Product: The product is at the core of the marketing mix and is what the company offers to its customers. It must be designed with the customer in mind and meet their needs and wants.
- Price: The product’s price must be set correctly to maximize profits while still making it affordable for customers. It is important to find the right balance between price and demand.
- Place: The product is sold, known as the distribution channel. There are four main types of channels: retailers, wholesalers, agents, and distributors.
- Promotion: Promotional activities raise awareness of a company’s products or services with their target market. This will be done through public relations, direct selling, or online advertising campaigns.
- Marketing Process: This element of the marketing mix focuses on making the product or service convenient for customers. It includes factors such as outsourcing, partnerships, and economies of scale.
- People: A company’s employees are its most important resource. Without them, it would be impossible to run a successful business. Therefore, it is essential to ensure they are motivated, trained, and efficient.
- Physical Environment: The physical environment is usually referred to as the retail store environment. It includes lighting, layout, signage, cleanliness, temperature control, storage facilities, etc.
Related: 5 Ps of Marketing
→ SWOT Analysis
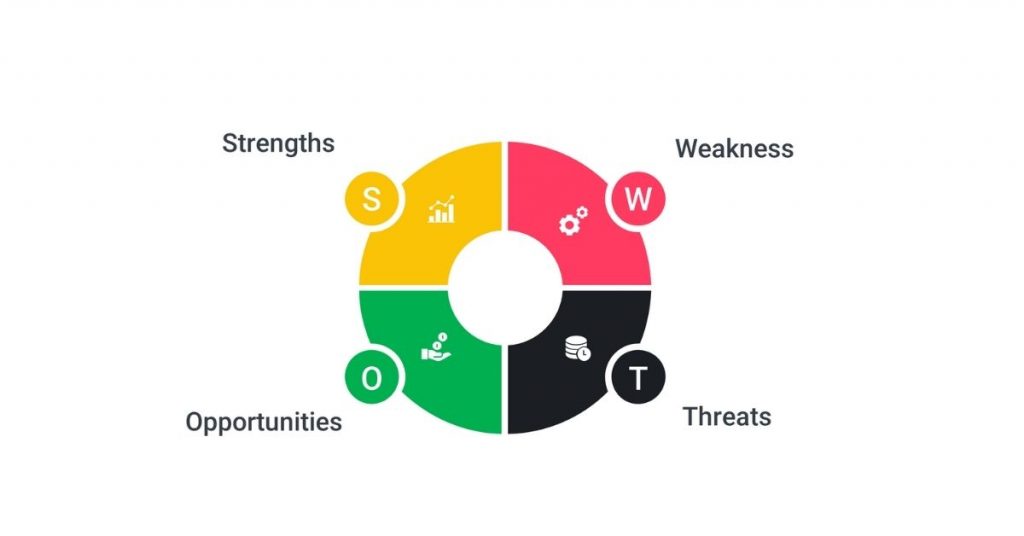
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps businesses assess their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By analyzing these factors, companies can develop a plan to capitalize on their strengths and opportunities while mitigating the effects of their weaknesses and threats.
Related: Nike SWOT Analysis
→ Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
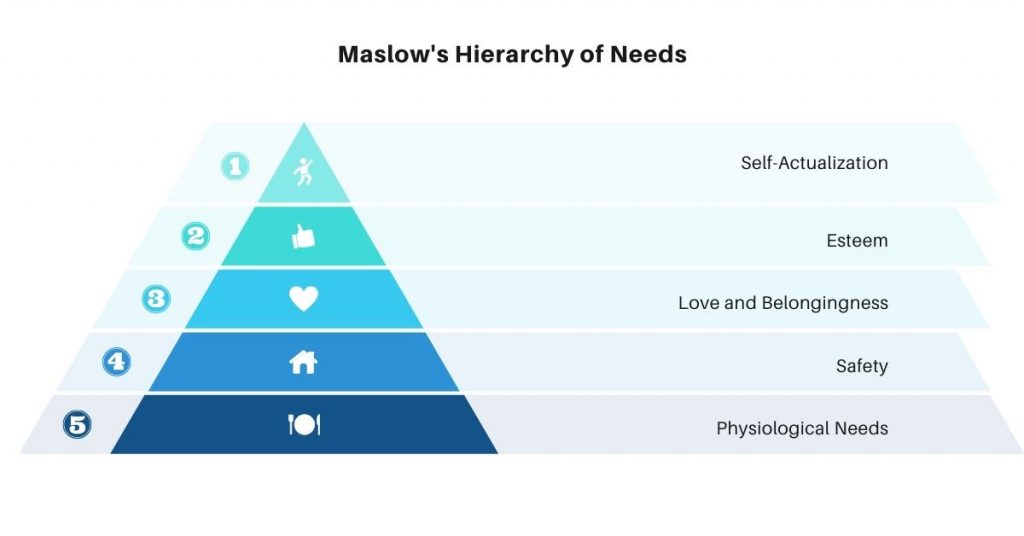
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. There are various elements to the hierarchy, such as physiological (basic requirements for survival such as food and shelter), safety (protection from elements or crime), love/belonging (friendships, romantic relationships), self-esteem (self-confidence and personal worth), and self-actualization (personal growth, realizing personal potential).
→ Market Segmentation Theory
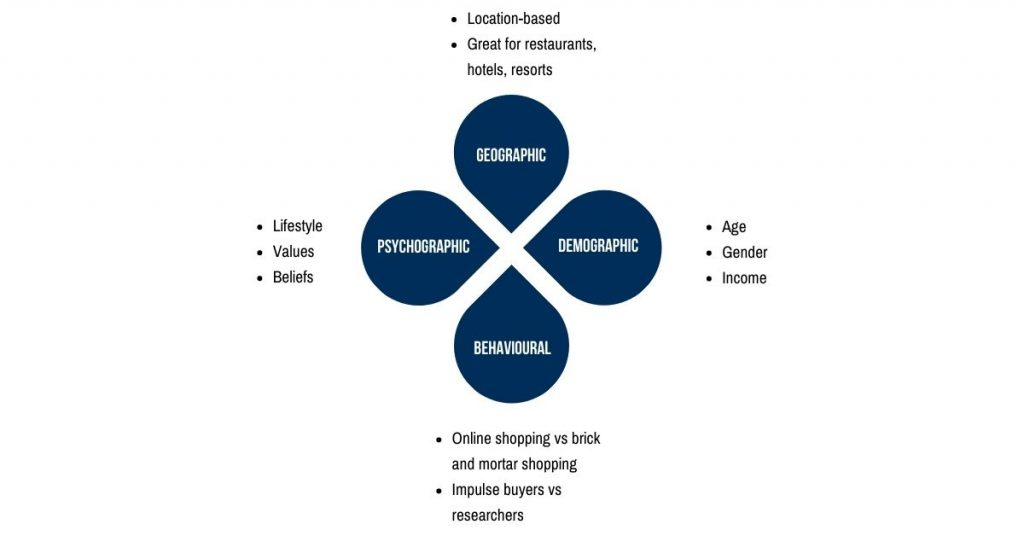
Marketers cannot sell to just anyone. They must identify the different personality types, concerns, and geographical areas they wish to target.
Market segmentation theory is when a marketer divides a market into distinct subsets of consumers. This is done based on specific variables such as age, race, gender, occupation, geographical areas, and income level.
Market segmentation theory is primarily used to determine how marketing resources are distributed across different groups or segments of customers within a given market.
→ Consumer Decision-Making Process
The consumer decision-making process is the steps or stages a consumer goes through when making a purchase. Various factors, such as the customer’s budget, needs, and wants, can influence this process.
There are five main stages of the consumer decision-making process: awareness, interest, evaluation, purchase, and post-purchase. Let’s take a closer look at each one:
- Awareness: The first step is when the customer becomes aware of a problem or need. This can be sparked by advertising or word-of-mouth from friends and family.
- Interest: Once the customer is aware of the need, they will show interest. They begin searching for the product, which can be done online or in-store.
- Evaluation: Now that the customer is interested in the product, they will begin to evaluate possible brands and products that could meet their need/s. They compare different products, brands, prices, and attributes before deciding what to purchase.
- Purchase: The customer has evaluated several options and has decided on a product to purchase. They will then buy the product (most likely online or in-store).
- Post-Purchase: This is when the customer consumes their purchase and evaluates whether or not it was worth the money they spent. If they are satisfied, then the customer goes through the process again. However, if they are dissatisfied, the customer will experience negative emotions, leading to a return of their purchase or complete avoidance of that product or brand in future purchases.
→ Porter’s Five Forces
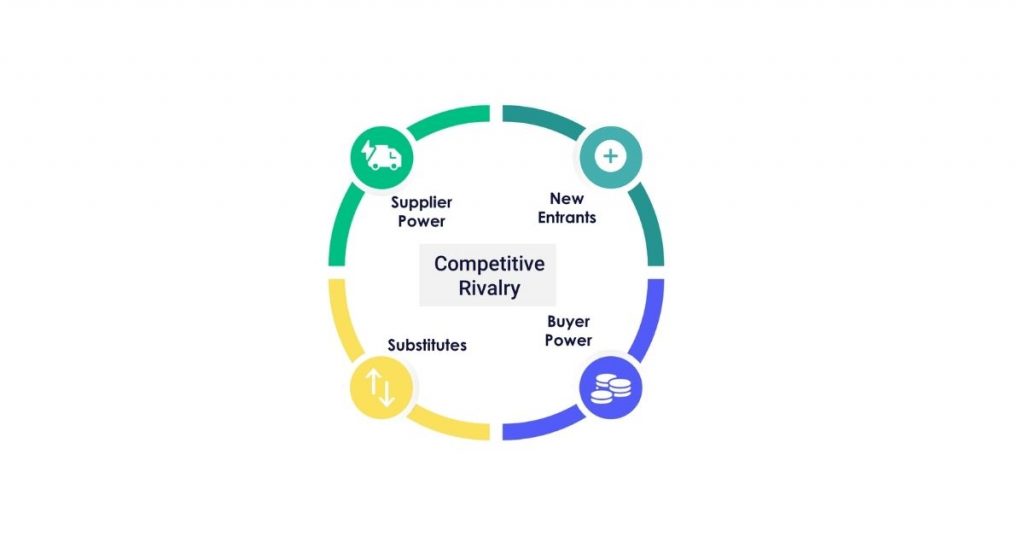
Porter’s Five Forces is another tool for assessing competition within an industry. It helps determine how much rivalry exists between current competitors in the industry and what potential new entrants may do. The implications of Porter’s Five Forces analysis are now briefly considered below:
- Threat of new entrants – this threat narrows if high capital requirements or government licenses are required.
- Threat of substitute products – an example would be petrol car manufacturers from electric cars or the fast-food companies at threat from home-delivered pizza.
- Bargaining power of suppliers – their bargaining power is high when there are many buyers in the industry & few sellers.
- Bargaining power of customers – their bargaining power is high when there are few suppliers in the industry & many customers.
- Competitive rivalry – is intense if current competitors heavily invest to beat each other and barriers to entry (e.g., patents) exist for new competitors.
If the combined effect of Porter’s Five Forces is high, the company may wish to consider strategies for dealing with these forces. For example, understanding how competitive rivalry may impact the industry’s product development and marketing strategy.
Types Of Marketing

→ Traditional Marketing
Traditional marketing is the promotion of a brand using offline channels that were in existence before the internet became popular.
Because knowledge was harder to find and obtain, most traditional marketing relied on outbound strategies such as print advertisements, television advertising, and big boards.
→ Outbound Marketing
Outbound marketing refers to intrusive promotions, such as cold calling, mass emailing to purchased lists, and hard copy advertisements.
Because this type of promotion reaches out to customers regardless of their interest in your goods or services, it is known as “outbound.”
→ Inbound Marketing
On the other hand, inbound marketing is concerned with attracting consumers rather than interrupting them. Digital marketing is the most popular inbound marketing method because customers can research online through their buyer’s journey.
Inbound marketing is based on three principles: Attract, engage, and delight. Your first objective is to produce helpful material that speaks to your target audience and entices them to visit your company.
The third step is interacting with them using conversational technologies such as email marketing , chatbots, and value. Finally, you delight them by acting as an empathetic advisor and specialist.
→ Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is the opposite of traditional marketing; it uses technology like mobile phones, the internet, social media sites, etc., to drive sales and revenue.
Companies use digital marketing to create a presence online. Digital marketing includes social media, search engine optimization (SEO), and pay-per-click ads on Google Adwords or other platforms.
→ Search Engine Marketing
Search Engine Marketing , or SEM, is gaining traffic via search engines. To achieve this, marketers place ads on their rivals’ websites, known as “PPC ads.” They also use optimization techniques to get high placement in organic search results. A keyword is at the heart of SEM.
→ Content Marketing
Inbound and digital marketing relies heavily on content marketing since it is one of the most acceptable ways to attract target audiences.
It is an approach to creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract potential customers.
The success of this marketing technique lies in its ability to establish a relationship with the consumers by providing them with helpful information that they are searching for online.
Content marketing is particularly appealing because it enables you to develop high-value activities at low costs.

→ Social Media Marketing
This form of marketing enables you to reach out to large target audiences anytime and anywhere globally. This approach lets you use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram, etc., to promote your brand or products.
Social media marketing helps you interact and build a relationship with your target audience and present your business as an accessible brand. It is the best way to spread awareness about any product or service, boosting sales in the long run.
→ Email Marketing
Email marketing can be used as an effective tool for online promotion. Like traditional mail, it is a straightforward method to reach out to people.
It allows you to share information about your products or services with potential customers who have subscribed to receive promotional emails from you.
With its high chances of delivering content directly into the inbox, email marketing assists businesses in building a relationship with their audiences.
→ Event Marketing
Event marketing utilizes direct marketing strategies to promote your business by holding live events, fairs, expos, and exhibitions.
This form of promotion is known as one of the most effective ways to attract consumers. It enables marketers to build relationships with their target audiences by hosting events, seminars, conferences, trade fairs, etc.
→ Internet Marketing
Internet Marketing is a subset of digital marketing used to drive traffic to your website or other web assets.
Marketers use different techniques, including SEO, PPC, email marketing, and social media marketing .
→ Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is online marketing in which a business rewards its affiliates for each customer they bring in. This usually takes the form of a commission, but it can also be in the form of coupons, discounts, or even free products. In order to be successful with affiliate marketing, businesses need to find affiliates with an audience that is interested in what they are selling.
Related: 7 Functions of Marketing
Benefits of Marketing to a Business

There are many benefits that a business can enjoy when it comes to marketing. Some of the most notable benefits include:
→ Increased visibility and awareness
Marketing helps get your business in front of more people, increasing awareness and visibility. With more people knowing about your business, you’re likely to see an increase in sales and revenue.
→ Improved customer base
Marketing also helps you to build a better customer base. By targeting the right audience and using the right strategies, you can connect with more customers who are likely to be interested in your offer. This can result in more sales and a more extensive customer base.
→ Greater brand recognition
Marketing also helps to build brand awareness. With more people aware of your company’s name and products, you’re likely to see an increase in revenue and long-term growth for your business.
→ Improved customer loyalty
When people are familiar with your brand, they become more loyal. This leads to happier customers who are more likely to keep coming back and purchasing from you again.
→ Greater sales volume
Marketing is a great way to increase your sales volume without relying on discounts or sales promotions, lowering your profit margin. Some of the ways that you can increase your sales volume include:
- Developing solid relationships with customers.
- Offering a great customer experience.
- Maintaining positive relationships with suppliers.
- Serving as a reliable resource for your customers.
Related: 5 Sales Strategies to Help You Grow
→ Access to new markets
When people are aware of your brand, they’re also more likely to become aware of the markets that you serve. This means that you open up access to more potential customers, resulting in increased sales.
→ Improved employee morale
Doing well usually positively impacts your employees, who will likely feel more motivated to work harder and do their best for your company. This results in greater productivity and improved business performance.
→ Greater revenue diversity
A more significant portion of your revenue comes from long-term buyers than short-term purchasers. This is usually good because you’re more likely to have a steady, reliable monthly income.
→ Brand Loyalty & Trust
Customers will likely trust your company more when familiar with it. They know what you stand for and the products or services you offer. This can lead to greater brand loyalty which means fewer refunds, fewer returns, and higher customer satisfaction scores across the board.
→ Higher profits
Marketing helps to increase your revenue over time, which is beneficial for the growth of your business. It also improves customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and more referrals. Furthermore, it increases the likelihood that you’ll see higher margins on future purchases from existing customers because they’re familiar with your brand.
Related: Marketing Management
10 Basic tips to starting marketing your brand

Hiring an expensive marketing department can be tempting when you’re just starting. Of course, this is a great way to go when you have the budget for it, but if it’s not in your budget right now or shortly, there are still things that you can do to begin marketing your business. Some of the first steps include:
1. Do Market Research
Before you start marketing, you need to know what your customers want and how they talk about your business. If you don’t understand this information, it can be challenging to connect with them. You must do a little marketing research before launching your marketing campaign. First, you need to know your target audience, what’s being said about your company, and how they talk about it.
2. Build an Email List
Email marketing is highly effective because you can reach many potential customers without spending much money on advertising or other promotion methods. The trick to having success with email marketing is getting people to sign up for your list. You can start this process by creating an offer that gets visitors interested in what you’re doing and encourages them to sign up for further information.
3. Write a Great Blog Post
You should create blog posts that educate your target audience about things they care about and fill gaps in their knowledge, helping them solve problems and meet their goals. It’s also important that your blog provides value by offering helpful information not readily available elsewhere.
4. Promote on Social Media
Ensure that you have a social media presence, with prominent links to your website, email list sign-up form, or blog, where people can connect with you and read your content. If you don’t have a social media account set up, you must get on board as soon as possible because this is where many potential customers will spend their time.
5. Start Doing Public Relations
Start reaching out to journalists and bloggers in your niche and find out if they would be interested in reviewing your product or service, interviewing you for an article, or writing about your company. You can contact journalists and bloggers by emailing them a press release that tells them about the exciting things your company is doing.
6. Get Active on Forums & Social Sites
Create LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter profiles, like your customers’ pages, or connect with them on LinkedIn. You can reach out to people in your network, ask current customers for referrals, or sign up for lists of influential people in your industry.
7. Try Local Advertising
Local advertising is a great way to get the word out about your business, connect with prospective customers, and build your brand without spending much money. You can target people living or working nearby by renting an ad on a billboard, posting flyers at local businesses, running newspaper or phone book ads, buying radio advertisements, or sponsoring community events.
8. Invest in PPC Ads
Pay-per-click advertising is one of the most effective ways to get your name in front of people searching for information about the services you offer. One great thing about these ads is that you only pay when someone clicks on your link or ad, which means that it’s easy to track your ROI and figure out which ads and keywords are performing the best.
9. Get Out There and Network
Networking is an integral part of marketing because it’s a way to connect with people who have similar interests, learn about what they’re doing, and find new ways that you can work together or add value to their lives. Networking is an ongoing process that requires regular effort and attention, but when done right, it can help you grow your business into something much more significant than you can do on your own.
10. Measure and Improve Your Results
It’s essential to track the results of your marketing campaigns so you know which ones are working and which aren’t. If you’re paying for ads, it is easy to track how many people click through them and sign up for your services or opt-in to your email list. You should also track your conversions from other marketing efforts, such as social media, press releases, and referrals. Your conversion rate is the percentage of people who take the desired action after seeing or hearing your marketing campaign. For example, if 100 people see your ad and two sign up for your service, you have a 2% conversion rate (2 converts / 100 views).
Now that you know the steps to take to market your small business , all that’s left is for you to implement this plan. Ensure that you constantly measure and improve your results, note which tactics work best, and tweak future campaigns accordingly. Follow these simple steps, and it won’t be long before your small business gets more new customers.
Related: Marketing Goals
Final Thoughts
Marketing is a critical part of any business, but it can be especially challenging for small businesses with limited budgets. Fortunately, there are many low-cost and even free marketing strategies that you can use to reach your target market and grow your business.
By investing time in creating a strong online presence, reaching out to journalists and bloggers, getting active in social media and forums, and networking with other businesses, you can reach a larger audience without spending much money. And by tracking your results and continually improving your campaigns, you can ensure that your marketing efforts are as effective as possible.
What are some of the marketing strategies that you have used to grow your small business? Share your experiences and advice in the comments below.
What is marketing?
What are the advantages of marketing, what are the objectives of marketing, what are the goals of marketing, what are the responsibilities of a marketing department, related posts:.
- What is Traditional Marketing? Explanation, Importance, & Examples
- Mastering Affiliate Marketing: Strategies and Tips for Success
- How to Create a Winning Marketing Strategy for Your Business
- Content Marketing: How to Do It Effectively and Succeed
Nike SWOT Analysis – How Successful is Nike? [In-Depth Analysis]
What is management [the ultimate guide to successful management], related posts.

How To Turn Testimonials Into Powerful Marketing Tools

Revolutionizing Marketing Strategies With Voice API Technology

10 Tips To Brand Your Business
© 2021 interObservers
Navigate Site
- Privacy and Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Welcome Back!
Login to your account below
Remember Me
Retrieve your password
Please enter your username or email address to reset your password.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
103 Digital Marketing Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Digital marketing is a constantly evolving field that requires creativity, strategic thinking, and a deep understanding of consumer behavior. With the rise of social media, online advertising, and search engine optimization, businesses are constantly looking for ways to stand out in the digital landscape.
If you're a student or professional looking for inspiration for your next digital marketing essay, look no further. Here are 103 digital marketing essay topic ideas and examples to help you get started:
- The impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior
- The role of storytelling in digital marketing campaigns
- The rise of video marketing in the digital age
- The importance of personalization in email marketing
- The future of artificial intelligence in digital marketing
- The effectiveness of influencer marketing compared to traditional advertising
- The impact of user-generated content on brand perception
- The role of data analytics in digital marketing strategies
- The benefits of content marketing for small businesses
- The ethics of targeted advertising on social media platforms
- The effectiveness of mobile marketing in reaching younger audiences
- The role of virtual reality in immersive marketing experiences
- The impact of voice search on SEO strategies
- The importance of social listening in digital marketing campaigns
- The benefits of using chatbots for customer service in digital marketing
- The role of gamification in engaging consumers in digital marketing campaigns
- The impact of influencer marketing on brand loyalty
- The effectiveness of email marketing in driving conversions
- The role of social media advertising in reaching new audiences
- The benefits of using data-driven insights to optimize digital marketing campaigns
- The impact of video content on social media engagement
- The effectiveness of using memes in digital marketing campaigns
- The role of virtual events in digital marketing strategies
- The benefits of using interactive content in email marketing campaigns
- The ethics of data collection in digital marketing campaigns
- The impact of social media algorithms on organic reach
- The role of artificial intelligence in personalized marketing experiences
- The effectiveness of using user-generated content in social media campaigns
- The benefits of using influencers for brand collaborations
- The impact of visual storytelling in digital marketing campaigns
- The role of customer reviews in building trust with consumers
- The effectiveness of using social proof in digital marketing strategies
- The benefits of using micro-influencers for niche marketing campaigns
- The impact of social media contests on brand awareness
- The role of brand partnerships in reaching new audiences
- The effectiveness of using retargeting ads in digital marketing campaigns
- The benefits of using interactive quizzes in email marketing
- The impact of personalized recommendations on e-commerce sales
- The role of user-generated content in building community around a brand
- The effectiveness of using augmented reality in digital marketing campaigns
- The benefits of using social media listening tools to track brand sentiment
- The impact of social media influencers on brand perception
- The role of storytelling in building emotional connections with consumers
- The effectiveness of using social media polls to engage audiences
- The benefits of using user-generated content in social media campaigns
- The impact of influencer marketing on brand authenticity
- The role of customer journey mapping in optimizing digital marketing strategies
- The effectiveness of using chatbots for customer service in e-commerce
- The benefits of using social media ads to drive traffic to a website
- The impact of using personalized landing pages in email marketing campaigns
- The role of social media influencers in promoting sustainability initiatives
- The effectiveness of using social media analytics to track campaign performance
- The benefits of using video testimonials in digital marketing campaigns
- The role of data visualization in presenting marketing insights
- The effectiveness of using social media contests to engage audiences
- The benefits of using storytelling to humanize a brand
- The impact of using emojis in social media marketing campaigns
- The role of influencer marketing in promoting diversity and inclusion
- The effectiveness of using social listening tools to track brand sentiment
- The benefits of using user-generated content to build brand advocacy
- The impact of social media influencers on consumer trust
- The role of customer reviews in building credibility for a brand
- The effectiveness of using personalized email campaigns to drive conversions
- The benefits of using interactive content to educate consumers about a product
- The impact of social media influencers on brand loyalty
- The role of data analytics in optimizing digital marketing campaigns
- The effectiveness of using social proof in e-commerce sales
- The benefits of using chatbots for lead generation
- The role of influencer marketing in promoting social causes
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade

Principles of Marketing
(27 reviews)
Copyright Year: 2015
ISBN 13: 9781946135193
Publisher: University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Elaheh Saffari, Marketing Instructor, PhD, Old Dominion University on 6/27/24
This Principles of Marketing textbook has 16 chapters, and most key topic areas are discussed relatively thoroughly. It also offers a nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g., satisfaction metrics, account planning, etc. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
This Principles of Marketing textbook has 16 chapters, and most key topic areas are discussed relatively thoroughly. It also offers a nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g., satisfaction metrics, account planning, etc.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The content is accurate and unbiased. I did not come across any areas that were not accurate. Most contents are explained adequately for concept delivery.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 4
The textbook provides a solid foundation in basic marketing principles. Also, It would benefit from addressing topics such as the growth of virtual retailing, the impact of broken supply chains, challenges in distribution channels, inflation, and advancements in digital marketing. Additionally, incorporating discussions on content streaming, social media, and the innovative uses of VR, AR, and the Metaverse in marketing would make the textbook even more valuable.
Clarity rating: 5
The textbook is easy to read and understand. Definitions & examples are clear.
Consistency rating: 5
Overall, the textbook maintains a consistent framework, with a logical flow and chapter sequence that aligns well with classroom instruction.
Modularity rating: 5
The text consists of 16 chapters, each divided into multiple subsections for flexible reading. It is easy to read, with good spacing and helpful graphics. Video links provide breaks, aiding students in studying for exams.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
The topics are effectively presented and structured. The text begins with broad definitions and concepts before delving into detailed explanations of each subject.
Interface rating: 5
The functionality of the text seemed to be working. Web links, images, and figures allow for easy direction-finding.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors were found.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
The textbook lacks cultural relevance, as it doesn't include many examples or photos that represent diverse races, ethnicities, or backgrounds.
Overall, this is a commendable textbook that effectively covers fundamental marketing principles. However, there are some areas that could benefit from further attention. For instance, the inclusion of topics such as customer interaction with AI, and the impact of technology on customer purchase experiences and business operations would be valuable. Additionally, incorporating discussions on virtual reality, robotics, and augmented reality would enhance the text by addressing contemporary trends in marketing and consumer behavior.
Reviewed by Monisha Gupta, Assistant Professor, Marshall University on 1/2/23
The author of the book has shared that this is an adaptation of a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-SA). The book has 16 clearly defined chapters, each chapter raises a specific aspect of marketing and... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The author of the book has shared that this is an adaptation of a work produced and distributed under a Creative Commons License (CC BY-NC-SA). The book has 16 clearly defined chapters, each chapter raises a specific aspect of marketing and concludes by raising discussion questions and activities. The textbook covers most of the marketing topics that should be included in an introductory course. However, given that the book is dated it is missing some emerging and emergent topics in marketing such as global marketing, data analytics, digital marketing, and the use of social media tools, to name a few. The author has at the outset clarified that the book does not follow the tenets of the 4 Ps of marketing. However, substituting terms such as products or services with terms like “offerings “requires a much deeper understanding of consumer needs, wants, or behavior. This might require a higher level of understanding which might not be in line with the student profile who opts for this course. The author has restructured the traditional 4Ps of the marketing mix and introduces that marketing is composed of four activities centered on customer value: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value. Also, the suggested activities created for each chapter are outside the scope of the chapter’s content. For instance, page 24, after Chapter 1 suggests activities such as “ Explain how the marketing goals, strategies, and markets for the nonprofit differ from a for-profit organization” or “Evaluate personal value equation”. These concepts have not been discussed in chapter 1 and are tackled later in the book by the author. These activities might not need more discussion and clarification before students can actively contribute to the solutions. Overall, the book covers most foundation-level content, but the choice of the author’s distinctive terminology might be a concern for students. Moreso, when they progress from this course to advanced levels of marketing and have trouble aligning the core concepts and keywords.
Not an issue, the content is accurate and provides reference sources.
The OTL textbook is well documented and breaks up the content into smaller and comprehensive blocks of information. If relevance is measured based on the traditional acceptance and present outlook it might fall a little short. The book lacks this by disregarding some key changes in the marketplace such as the pandemic and its impact on consumption cycles, and the emergence of a large service industry. This has reshaped the consumer’s and marketers’ choices of development processes, channel partners, pricing strategies, promotional methodologies, use of social media tools, etc. These aspects need to be addressed in more detail with recent examples for students to appreciate the relevance.
The author has outlined the content in great detail, making it easy to read and understand the textbook. Easy conversational language and links, for example, appeal to students who can find a great deal on the electronic medium.
The chapters in the textbook are organized in the same consistent manner in the entire book. This is helpful for the readers and instructors to follow a format.
Modularity rating: 4
The text is easily and readily divided into smaller reading sections that can be assigned. This lends itself to assigning modules by chapters and units within the chapters.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
I have been teaching this course for the past 4 years and have found that explaining what a marketing plan is and then studying the various stages helps the students appreciate the various phases in this process. This textbook has taken a completely different approach by explaining the marketing plan at the end. While the topics are the same the structure impacts the flow and, in my opinion, the ability to hold the student’s interest. I suggest moving Chapter 16 to Chapter 3 followed by Chapter 5.
Interface rating: 3
The textbook was last updated in 2010, making all images, figures, tables, and video clips mildly outdated. The power of audio-visual aids is very powerful, and the quality is becoming better and better. To keep the students engaged the author might like to consider using technology for simulations, video assignments, etc., these can be useful for the students.
I found no grammatical errors, the content is well-written and easily understandable. The language used is conversational and something the students should find easy to navigate.
Global and international marketing are the mainstays for today, these aspects have not been addressed in the textbook. It warrants at least a chapter on world cultures, the emergence of MNCs, and geo-demographics relevance. It is important to acknowledge that demographic profiling needs to incorporate cultural diversity. The textbook has all US-based industry examples and consumer responses, ignoring the diverse consumer profile even within the US.
Overall, it is a great attempt to provide such detailed material for the students. Given that it was uploaded in 2010 the book needs to be updated to include more current and global marketing aspects. The textbook was created for an entry-level course in marketing. I enjoy the way the author shares the various career options available for marketing majors. However, the student profile who takes this course includes students who major in finance, and journalism. PR, management, etc. It would be relevant for them to see how these skills are transferable and useful in other work fields. The suggested activities need to be more application based and limited to the content of the preceding chapter. More global and culturally applicable examples need to be included.
Reviewed by Rich Metzger, Adjunct Professor, Massachusetts Bay Community College on 11/24/22
The OTL textbook covers the basic principles necessary to form a marketing foundation. The content should be updated to reflex the Pandemic and Post-Pandemic marketing environment. I felt some topics needed more discussion, and explanation, such... read more
The OTL textbook covers the basic principles necessary to form a marketing foundation. The content should be updated to reflex the Pandemic and Post-Pandemic marketing environment. I felt some topics needed more discussion, and explanation, such as a breakdown by age and characteristics of the population.
Content Accuracy rating: 4
The OTL textbook is relevant and is a good guide to basic marketing principles but could be better. I prefer the OTL textbook to include recent marketing techniques and strategies used in today’s difficult business environment. This ranges from the advent of the non-store or virtual retailing, broken supply chains, damaged distribution channels, inflation, digital marketing, content streaming, and social media, just to mention a few new topics.
I found the OTL textbook easy to read and understand. Good comprehension level and in the use of examples, figures, and images to illustrate or compliment the text.
The OTL textbook’s material is laid out in a logical sequence, culminating with the last chapter dedicated to the Marketing Plan.
Chapters progress in a logical manner, allowing the reader to digest the material and prepare for the next chapter.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 3
The organization, structure, and flow of the material are fine, but my concern is the lack of an index and a single depository for key terms and chapter highlights.
Interface rating: 4
The images, figures, tables, and video clips need to be revisited for relevancy. The use of these visual aids helps the reader better understand the topics being discussed.
The content is well written, very limited if any grammatical issues. To make the textbook more relevant, consider using socially accepted pronouns, which in turn would elevate the textbook to today’s sociality expectations.
Cultural Relevance rating: 3
A chapter on world cultures and the different business nuances and practices (ethics) would be beneficial to a student learning about marketing.
As this is my first experience dealing with OER, I wanted to be fair and open to the possibilities presented by this new resource. For comparison purposes, I used my adopted textbook vs the OTL textbook. My goal is to decide if I could adopt the OTL textbook. Similarly, the adopted textbook and the OTL textbook are for a 100-level course. Both textbooks offer entry-level content, relevant material, easy to read and comprehend, more than enough chapters to fill a semester, Contents, Chapter titles, Learning Objectives, topics, images, figures, examples, video clips, Discussion/Review Questions, Activities, and both textbooks offer a test bank. The OTL textbook has Key Takeaways for each topic presented in a chapter, and the adopted textbook has a section in the back of the textbook titled Chapter Review, which contains Learning Objectives and Key Terms. Differences, the adopted textbook has a price point, an OTL textbook lacks an Index, and the adopted textbook offers PowerPoint Slides, Instructor’s manual, Rubrics, and Case Studies. I was unable to find an Instructor’s Resources section for the OTL textbook, but the OTL textbook provides students with financial relief. I believe I could adopt this textbook with a minimal number of self-adjustments.
Reviewed by Victoria Shaw, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Anderson University on 3/11/22
The book does a good job of highlighting basic marketing principles. However, I do find it lacks the basics of e-commerce (just basic industry terms like SEO), global marketing principles (especially B2C), and using tools like PEST analysis for... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 3 see less
The book does a good job of highlighting basic marketing principles. However, I do find it lacks the basics of e-commerce (just basic industry terms like SEO), global marketing principles (especially B2C), and using tools like PEST analysis for external assessment. I think the chapters on B2B behavior and Sales while good, may not be the most value-add for the students in class.
No glaring errors at first glance.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 3
Imagery is very dated. The chapters use the four basic P's, though the latest books tend to introduce up to eight.
Overall, seemed clear and comprehensive. I think the book would have benefitted from multiple, additional visuals to clarify complex topics.
Consistency rating: 4
Seemed consistent across chapters
I liked the way the topics were broken into micro concepts - makes it easy to assign the portions I find most relevant and supplement when needed.
Structure was logical and sequential.
A bit text heavy at times but errors.
No grammatical errors on first read.
I think the author missed the opportunity to bring marketing to a more global context.
This is a great principles textbook overall. My only complaint is because of some omitted or abbreviated topics, an instructor may have to supplement a bit more in order to ensure the curriculum is up to industry standards. But in a larger class where schedules only allow for selected topics to be covered, this would be a very good start.
Reviewed by Amy Strunk, Lecturer, James Madison University on 11/29/21
Basic marketing concepts are covered with sufficient depth, but newer concepts are missing (like digital marketing). read more
Basic marketing concepts are covered with sufficient depth, but newer concepts are missing (like digital marketing).
Some of the information is dated: for example, most would agree that we are not in the relationship era of marketing, but the textbook states that we are in an undefined era (which would have been true 10 years ago).
The book uses “creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value” as elements of the marketing mix/strategy rather than the 4 P’s, and actively argues against the 4 P terminology, which is controversial.
The book also uses "offerings" instead of "product". The authors argue for it effectively, but I don't know anyone in the marketing world who uses that term in the real world.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 2
References are dated: - Foursquare (college-age students in 2021 will have no idea what this is) - Some images are out of date (retrieved in 2008) - Mission statements on p. 27 are outdated and reference links are broken. - References to iPod in the time of iPhones
These references will continue to grow stale.
The content is pretty straight forward. Definitions are clear.
The book is consistent in its own frameworks/terminology (stubbornly so).
Modularity rating: 3
Some of the longer sections could benefit from headings and subheadings.
I would recommend that market research come before the "Creating Offerings" section since that process is so integral to product (or "offering") development.
Interface is sufficient.
Some small issues, for example, using the term “Droid” smartphones on page 6—should be Android.
I did not notice any concerted effort to include diverse backgrounds in this text.
Marketing is changing rapidly thanks to technology, and this book is too outdated to address issues like data privacy and hyper-targeting.
Reviewed by Matthew Lunde, Assistant Professor, Pittsburg State University on 6/4/21
the textbooks is very thorough in covering all the topis needed in a principles of marketing class. It even adds a chapter that is not in many other textbooks: "The Marketing Plan." However, my only criticism is that it does not touch on a huge... read more
the textbooks is very thorough in covering all the topis needed in a principles of marketing class. It even adds a chapter that is not in many other textbooks: "The Marketing Plan." However, my only criticism is that it does not touch on a huge topic area nowadays in marketing: sustainability (sustainable marketing and sustainable competitive advantage).
The content is objective, thorough, and accurate. It uses statistics and example businesses and situations effectively to help teach younger college students the fundamentals of marketing.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The content is up-to-date as best as it can be. Whenever any textbook uses statistics, years, numbers, and other figures, it can date the textbook; however, the content is written in a way that it will last for multiple years to come.
Clarity rating: 4
There is some jargon, but the jargon used is needed to help teach the fundamentals of marketing to new students.
It is great how all the terms in the chapters are easy to find and to read because each term is bold.
Yes, the book is broken down into manageable sections for a younger college student to read and interpret effectively and efficiently.
Yes. This textbook is laid out very well. However, one thing I would add in the chapter titles would be "retailing."
Good! Nothing to add here!
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
The book is written well, free of grammatical errors. However, I see "he or she" is used. Nowadays, for inclusivity, the right pronoun to use would be "they."
However, I see "he or she" is used. Nowadays, for inclusivity, the right pronoun to use would be "they."
Reviewed by Felix Flores, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 4/17/21, updated 5/26/21
The textbook sufficiently covers areas and ideas of subjects and is easy to navigate. I would find it useful to include and discussed an example of an actual marketing plan. read more
The textbook sufficiently covers areas and ideas of subjects and is easy to navigate. I would find it useful to include and discussed an example of an actual marketing plan.
The textbook's content is mostly accurate, error-free, and unbiased.
Some of the links and examples may be dated but contribute to the chapter's main ideas. There are, however, some links that do not work or could be replaced with newer examples. I would recommend reviewing all of the provided links.
The textbook is written in a clear manner.
The textbook is mostly consistent in terms of terminology and framework.
The textbook is easily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned at different points within the course.
The topics are presented in a logical, clear fashion.
The text is free of interface issues or navigation problems.
There may be a small room for improvement in terms of grammar.
I believe the textbook is mostly culturally relevant.
I believe that you can effectively teach a Principles of Marketing class with this textbook, on its own, and especially in combination with other OER textbooks/resources. It will require, however, checking all of the links and updating some examples.
Reviewed by Diane Edmondson, Adjunct Professor, Trine University on 4/16/21
Overall, this textbook covers a majority of the marketing topics that should be covered in a Principles of Marketing class. Since the book is somewhat dated, there is limited coverage on both digital marketing and social media as well as marketing... read more
Overall, this textbook covers a majority of the marketing topics that should be covered in a Principles of Marketing class. Since the book is somewhat dated, there is limited coverage on both digital marketing and social media as well as marketing analytics. These two topic areas have revolutionized the marketing field. However, this marketing textbook contains all of the other key marketing concepts such as the 4 P's of marketing, strategic marketing, target market strategies, consumer and business buying behavior, and how to craft a marketing plan.
Overall, this textbook is accurate and error-free. It does not appear to be biased in any way.
Overall, this textbook is still highly relevant. It is missing some more detailed information related to digital marketing, social media, and marketing analytics as these have drastically changed the marketing field over the past decade; however, the content covered is still relevant to both business-to-business and business-to-consumer markets.
One of the best things about this book is that it is easy to read. The text is written in a way that students should not have a difficult time understanding the concepts being covered. There are multiple examples given for each major topic to help students better understand the material. Terminology is defined to aid understanding.
Overall, a consistent framework is used throughout this textbook. The flow and chapter ordering of the textbook makes natural sense with how it would be taught in the classroom.
The text is made up of 16 chapters; however, each of the chapters is then broken up into multiple subsections. This allows the text to be easily and readily divided into smaller reading sections, based on the desire of the instructor and/or reader.
The chapter layout of this textbook is similar to many other Principles of Marketing textbooks. Topics are presented in a logical and clear manner, which aids readability and understanding.
Overall, the images, charts, tables, and figures were clearly displayed without any distortion. There are a few navigation links that no longer function; however, these are minimal in number.
The Principles of Marketing textbook appears to be free of grammatical errors.
There are a variety of diverse examples throughout the text. None of these should be viewed as culturally insensitive or offensive in any way.
Overall, this textbook is well written and covers most of the major marketing topics. The few topics not covered are primarily because these became dominant marketing elements after this textbook was published originally.
Reviewed by Ricardo McCoy, Adjunct Professor, Trine University on 3/3/21
I have been facilitating marketing, analytics, sales, and consumer behavior classes since 2009 and this textbook does a good job of covering all of the marketing mix. Most important, the content is updated and relevant. The layout is... read more
I have been facilitating marketing, analytics, sales, and consumer behavior classes since 2009 and this textbook does a good job of covering all of the marketing mix. Most important, the content is updated and relevant. The layout is user-friendly and easy to read.
Based on similar marketing text books I have read, this textbook is accurate and contains content that someone who is unfamiliar with marketing concepts will easily understand. The use of examples throughout the textbook is a good way to help a beginner to marketing understand the subject matter.
I like how this book understands how marketing has changed and explains variables in the environment that is effecting this change. This can be seen in Chapter 1 concerning some of these changes:
Ethic and Social Responsibility Sustainability Service-dominant logic Metrics A Global Environment
It is good to see that the textbook is up-to-date and recognizes that marketing must adapt to these changes. Some of the marketing textbooks I read in the past do not recognize these changes.
Overall, the information throughout the chapters was easy to understand. I like how examples were used throughout each chapter. My only recommendation is to add more illustrations consistently throughout the textbook. Based on my experience, most students like to see illustrations (visualize). I think this helps him or her to understand the subject matter.
Overall, the content throughout the textbook is consistent. However, I notice that some of the chapters have more illustrations than other chapters. I think that using more illustrations (and examples) would make the chapters more user-friendly.
P.S. Links to additional resources would also be a good addition.
The sequence throughout the textbook “flows” from section to section. I like the synergy from chapter to chapter. This helps the student to understand how various factors of marketing work together.
I like how Chapter 1 gives a brief description of marketing while summarizing what will be discussed in the preceding chapters. I also like the “key takeaways” at the end of each chapter. The "review questions" are brief, yet add to what was discussed throughout the chapter. This is good to see.
The overall functionality of the textbook is good. The font size and white space makes the content easy to read. I like the use of color throughout the textbook. For example, the use of green for the “Key Takeaway” and blue for the “Review Questions”.
Although it is difficult to check all the content, I did not see any typos or “wordy” sentences. I like how the content “talks to” rather than “talks at” the student.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This is a difficult question to answer because I did not see anything that was insensitive or offensive. Ideally, the content would continue to embrace diversity and inclusion. This is important because we live in a global economy.
I think that Chapter 5 (“Marketing Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning”) should be followed by Chapter 10 (“Gathering and Using Information: Market Research and Market Intelligence”). Both of these chapters are closely related. To properly perform segmentation and targeting, you must understand analytics / gathering information. I was also looking to see slightly more insights on digital analytics in Chapter 10.
Reviewed by Markus Biegel, Adjunct Faculty, California State University, Dominguez Hills on 8/12/20
I compared it to the McGraw Hill book that I have been using for the past 4 years and the topics (Chapters Topics and Sub-Topics) are pretty identical just in a slightly different order. When looking into how in-depth the book goes, it is not... read more
I compared it to the McGraw Hill book that I have been using for the past 4 years and the topics (Chapters Topics and Sub-Topics) are pretty identical just in a slightly different order. When looking into how in-depth the book goes, it is not quite as comprehensive as the McGraw Hill book. However, it is easy to read.
Marketing always is a bit subjective. I think the book does a great job covering all the important topics as unbiased as possible.
This is a basic marketing course focused on teaching students the fundamentals, the book does a good job at that. Given the current COVID situation, a lot of things have changed in business but not the fundamental theories and practices of the profession. Because of that the relevance of the book is current in my opinion.
The text has a logical flow. There is certainly room for improvement from a formatting standpoint. I think it makes it easier for students to learn key terms and key concepts when they are highlighted on the sidebar (similar as in many mainstream textbooks).
Certainly consistent and comprehensive in all the key terms that this book should cover for Principles of Marketing.
The text is very easy to read. There is good spacing in between the paragraphs and graphics/images help further give the mind a reading break. I also think it is great that links are included to videos, this helps students get a "reading break" which is essential when cramming in a few chapters to study for an exam.
Very well organized text. I just wish the key terms and key concepts were featured separately in an almost duplicate fashion on the side of the main text. I think students are used to using these highlighted areas to study for exams.
Didn't notice any problems with the interface. Could have perhaps used better images here and there but overall does the job.
I am not an English professor and this is my second language but I did not notice any grammatical errors. I am sure there are some, including mistyped words but every book I have used had a few of those.
One of the key concepts in Principles of Marketing is target marketing which certainly can be interpreted as offensive to some people. However, I think the book does a great job at explaining the concept. Again, marketing leans into being somewhat controversial based on the subject matter and business practice.
Can't beat a free book. Seems like a great resource to use for students.
Reviewed by Kirti Celly, Professor, California State University, Dominguez Hills on 8/10/20
Principles begins with a question to spark curiosity for the novice student of marketing. Organized into 16 chapters, it takes a traditional strategic planning, consumer and buyer behavior, research and 4Ps approach that addresses all major areas... read more
Principles begins with a question to spark curiosity for the novice student of marketing. Organized into 16 chapters, it takes a traditional strategic planning, consumer and buyer behavior, research and 4Ps approach that addresses all major areas and ideas in a core marketing class. Given the importance of ethical decision making, it needs to add/bolster content on ethics in marketing and add an index/glossary.
Accurate content with image sources and references. I have not tested all these links.
Since the focus is core content, it is written in a nuts and bolts manner and will stay perennial. Consistent with the conditions of use, the text’s simplicity allows for it to be modified easily.
Written professionally and in simple sentences, this makes for accessible, adequate and easy to understand content. Marketing concepts are defined simply and succinctly throughout.
The key take-aways and review questions after each section of a chapter are supplemented by end of chapter discussion questions and activities throughout. This fits nicely with Bloom’s learning taxonomy.
This is a key feature of this book and one most appreciated by my students.
Another key feature of this book, and one appreciated by my students.
Other than a few formatting and pagination issues, nothing to note. Any links I used worked. For the manner in which I use this book as basic material for my classes, not having an excess of photos and images in the body actually works well. Having URLs for case examples also facilitates easy revision and adaptation for various local and regional teaching and learning contexts.
Simple, easy to read, accessible. I did not notice any grammatical errors.
This is less about this book than about the way in which most business textbooks are written. It is in no way offensive; in fact, its style and variety of examples promotes inclusion and it is adaptable to alternate cultural contexts through a shift in frame to include broader contexts.
Our students appreciate having an accessible zero cost course materials course with adds ons from me, the press, and other OER, and low cost or no cost AV materials and marketing math. Thank you.
Reviewed by Sheryl Spann, Marketing Instructor, Oregon State University on 7/28/20
The textbook begins with the question “What is Marketing?” to assist students new to the field of marketing to understand the real definition of marketing versus their perceived ideas of marketing. This is a great place to start as many students... read more
The textbook begins with the question “What is Marketing?” to assist students new to the field of marketing to understand the real definition of marketing versus their perceived ideas of marketing. This is a great place to start as many students either believe that marketing is strictly sales or do not have a full concept of the many aspects of what encompasses marketing. The text covers most of the key areas of marketing such as consumer behavior, market segmentation and target marketing and the principals relating to product, pricing, placement and promotion. Marketing research, new product development and marketing communications is also covered at a basic level. However, based on my experience in the classroom, a few suggestions are in order. I would add three additional chapters on international marketing, market expansion strategies and ethics and social responsibility. The chapter on professional selling could be removed or covered within chapter one as a portion of the explanation on the aspects of marketing. Lastly, I would add more current marketing articles, one-page cases and small group discussion questions to each chapter. For marketing majors, I would add an appendix at the back of the book discussing the various career opportunities in marketing.
The book content is accurate with terminology and marketing concepts accessible for a university level student. The textbook also cites sources for most of the provided information.
In addition to the textbook content for teaching marketing principals, there are many real-world examples offered to improve student understanding. Although most offer longevity, there is a need to augment current examples with more recent examples including company or product examples representing cultural diversity.
The text is easy to read with a combination of informal and professional language for appropriate student learning and understanding.
The text is internally consistent and provides actual examples of the principals covered as well as review questions to ensure student comprehension. This approach is inline with other “Principals of Marketing” textbooks.
The course material is listed in modular fashion to easily transfer to canvas. However, since “Principals of Marketing” is usually the first marketing course for majors and the only course for this topic for non-majors, I would place the chapter on “Strategic Planning” right before the last chapter on “The Marketing Plan”. As indicated in the “comprehensiveness” section of my comments, I also believe that a few topical chapters such as “International Marketing” should be added to the book to improve its overview of the topic.
In general, the topics are presented and organized in an effective format. The text starts with overarching definitions and concepts and then moves toward providing more details on each topic. I believe that the “Strategic Planning” chapter should be moved to the end of the book before “The Marketing Plan” to ensure that students have the foundation needed to better understand this topic plus use its strategic perspective in the development of a marketing plan.
There did not appear to be any interface issues for this book. All video and web page links also worked well.
The text did not have any grammatical errors.
Although cultural examples were included and relevant, additional cultural diversity elements would improve the book. Also, it is important to include examples that are more current to provide better student discussions of this important marketing topic.
Overall, this textbook is a suitable option for an entry level college course on “Marketing Principals”. Adding chapters on “International Marketing”, “Market Expansion Strategies” and “Ethics & Social Responsibility” as well as updating some of the chapter business examples, case studies and discussion questions would be very helpful plus keep this book “current”. Lastly, including a greater overview of the marketing aspects of cultural diversity plus marketing career options would cause this book to stand out among textbook options for this topic.
Reviewed by Zahra Tohidinia, Assistant Professor, Framingham State University on 6/12/20
The text offers a very good review of key marketing principles and provides a comprehensive introduction to the main concept. I would suggest combining the textbook with relevant current marketing articles and cases. read more
The text offers a very good review of key marketing principles and provides a comprehensive introduction to the main concept. I would suggest combining the textbook with relevant current marketing articles and cases.
The content is accurate and the textbook cites sources for most of the provided information.
The content is relevant to marketing. There are a solid number of examples throughout the book. The content related to digital marketing/social media could be expanded, but overall the content is relevant and robust.
The text is easy to read and provides a good balance of informal and professional language.
The structure of the text is consistent and the book gives example-based explanations of the main concepts. There are review questions at the end of each section as well as discussions and activities at the end of each chapter.
The text is easy to navigate. The book is divided into smaller segments. A hyperlinked (clickable) table of contents makes it really easy to move between different chapters and their corresponding sub-segments.
The topics are presented and organized in an effective format. The text starts with overarching definitions and concepts and then moves toward providing more details on each topic.
The links to the videos that I clicked on worked and each opened a new tab. As mentioned before, the hyperlinks make it very easy to navigate between different sections. In some cases, the image headings were separated from the actual image because of page breaks which can be revised in later editions.
The consumer behavior chapter does a good job with embedding cultural variables into the discussion. This could have been integrated more effectively in the other chapters; especially the chapters involving marketing research and intelligence, as well as market segmentation and positioning
This book covers the main concepts of marketing very effectively. This textbook combined with current articles and relevant cases could serve as a comprehensive set of materials for introductory marketing courses at the undergraduate level.
Reviewed by Christian Gilde, Business Faculty, University of Montana - Western on 1/31/20
The textbook has enough depth and addresses all the major parts of the marketing discourse, such as the environment, marketing strategy, consumer behavior and segmentation, and marketing research, as well as the product, place, price, and... read more
The textbook has enough depth and addresses all the major parts of the marketing discourse, such as the environment, marketing strategy, consumer behavior and segmentation, and marketing research, as well as the product, place, price, and promotion variables.
The explanations, terminology, and concepts in the text are accessible and accurate.
The textbook contains applicable examples of marketing that will help the audience learn and appreciate the marketing realm. Most pieces and examples in the book have longevity. A few applications might need to be updated to make the text more timely.
The text is accessible and will help guide the students through the different dimensions of marketing.
The given text follows a certain presentation canon in terms of marketing terminology, concepts, and applications that can be found in textbooks of similar nature.
Many textbooks in marketing follow a certain modular pattern. This same pattern can be found in this text, with each chapter being split into sections for which particular assignments and experiential learning activities are designed.
As far as the organization and structure of this work are concerned, the marketing text is in line with a good number of other principles texts. The structure, flow, and positioning of the different marketing topics within the individual chapters is logical, with the objectives in the beginning and a re-visitation of the key points and review questions at the end.
A few minor grammatical and structural errors can be found in the text.
The cultural illustrations are relevant, to a certain extent. However, it might be useful to update some of these items.
The material in this text is suitable for a basic marketing course. Overall, I would recommend using this text for entry level marketing students.
Reviewed by Kelly Atkins, Associate Professor, East Tennessee State University on 10/21/19
The text contains the expected chapter topics related to Principles of Marketing. In my opinion, there is too much information about Professional Selling (Chapter 13) for the topic of the text. In my opinion, Chapter 11 should include a... read more
The text contains the expected chapter topics related to Principles of Marketing. In my opinion, there is too much information about Professional Selling (Chapter 13) for the topic of the text. In my opinion, Chapter 11 should include a discussion of the basic Communications Model as well as some more modern communications models.
The text content appears to be accurate, error-free and unbiased. In my thorough review, I found nothing to the contrary.
The text contains many relevant, current examples of marketing concepts as well as some images of marketing examples and nice video clips of marketing examples. Some examples in Chapter 2 are from 2006, 2007, 2008 & 2009. These 10+ year old examples are too old to be relevant to students who are only 20 years old. I like the application of marketing concepts to the world of business and to personal branding.
The “voice” of the text is conversational yet professional. The terms used throughout the text seem to be in alignment with other Principles of Marketing textbooks I have used previously.
The text seems to be internally consistent. I saw nothing to indicate otherwise.
The text is organized effectively in most ways, but I have a recommendation. Chapter 3 should be divided into more sections. There are too many learning objectives and key takeaways for section 3.1.
There are significant organization problems in Chapters 4,8 & 13. Each of these chapters is out of order. For example, Chapter 4 is presented in the following sections: 4.4, 4.5, 4.6, 4.7, then 4.1, 4.2, 4.3. The same is true of Chapters 8 & 13.
The way the pages are presented with extra lines on many pages, with figure titles on different pages than the actual figure, or with figure numbers on a different page than the figure itself. See Figures 1.3 and 1.4 in Chapter 1 as examples.
I did not notice any grammar problems in the text (and I typically find lots of grammar problems when I am editing).
In my opinion, he text is culturally sensitive.
• I really like the “key takeaways” and “review questions” at the end of the sections instead of a summary at the end of the chapter. • I would add key terms at the end of each section because the terms and definitions seem to get lost within the chapters. • The “activities” at the end of the chapter are unique and creative. I would use these ideas for my classes.
Reviewed by Donald Chang, Professor, Metropolitan State University of Denver on 4/29/19
The textbook provides basic coverage of main concepts found in most principles of marketing. Overall, the discussion throughout the book tends to be less comprehensive. In some areas, the author glossed over without providing sufficient details.... read more
The textbook provides basic coverage of main concepts found in most principles of marketing. Overall, the discussion throughout the book tends to be less comprehensive. In some areas, the author glossed over without providing sufficient details. To introduce basic concepts, it might be sufficient. For deeper understanding and analysis, it will require additional reading and research by readers. For example, in the very beginning, the author claimed "... about 1950 to 1990, businesses operated in the marketing era" without providing supporting materials to bolster the claim. The discussion also skipped a commonly known period when emphasis on selling was prevalent, skipping from product concept to marketing concepts, while ignoring the discussion on social responsibility in the 80s.
Accuracy is not a major issue for this book. Most contents are explained adequately for concept delivery.
Most basic concepts in marketing, e.g., product life cycle, buying process, pricing strategies, are mostly time free, thus, stay relevant regardless of changes in the marketplace. Examples used are apparently out of date, e.g., iPad. Many of the examples are prior to 2010 so that examples need to be updated to be relevant to today's students. Most basic content is consistent with other textbooks, just on a shallow side.
For marketing, the key strategic decisions are in segmentation, targeting, positioning, and differentiation. It would be probably more appropriate to place strategic planning close to the chapter on segmentation, targeting, and positioning. With so much content in marketing to cover, a standing-alone chapter on professional selling is uncalled for. After all, personal selling is only one of the element of promotion and most companies prefer to train their own sales force, thus very company/product specific, not something could be covered effectively in a principles of marketing textbook. It also incorrectly over-inflates the role of sales in marketing curriculum. Most students, business and non-business, do not see professional selling as their career aspiration either, if they have the choice.
There is an obvious omission in international marketing. The author's claim that global coverage is built in throughout the textbook cannot be observed. Without having a devoted chapter in international marketing, some basic concepts in international management are not presented. The same is for sustainability, ethics, and social responsibility. The author seemed to understand their importance, but not important enough to have their own sections. On the other hand, the author had no issue in having a chapter in professional selling without clear justification for its inclusion. These are obviously the author's own selection bias and personal preferences, not necessarily what students ought to learn from the course.
The writing is good for average college students. It is mostly easy to follow.
The book used "offerings" when referring to products and services consistently throughout the book. Each chapter is presented with discussion questions, activities, key takeaway, review questions with consistent structure and writing style.
The book is organized in a module-like manner, with most materials being free-standing, allowing a section to be borrowed for another marketing course as needed. As the writing is on the succinct side, there is rarely a long writing blocks without division.
While the book is structured well overall, the placement of strategic planning in the very beginning (Chapter 2) is probably off. Students need to know about the subject more before jumping into strategic planning. Other than chapter placement, the overall organization is adequate.
There are no known serious interface issues that are present. Graphs, charts, pictures are clear and easy to see and follow. A few enhancements to market the headings and sub-headings could be added to better break up sections. As examples, "Video Clip" on page 272, 273 could be better presented. The headings are easily overlooked as presented. At times, the reader might not be aware that the topic has shifted to a new one.
The book is grammatical correct overall.
There are no obvious concerns of being culturally insensitive or offensive.
The book is a possible alternative for average high school and college students if the goal is to learn the very fundamental concepts in marketing. For students who look for deeper understanding, this is not the right book for them as much discussion is on the shallow side. The author's own opinions can be found throughout the book without adequate supporting materials. Therefore, it is subject to the author's self selection bias. For marketing major students, I would expect students to learn more than what are presented in this book.
Reviewed by Nicole Lytle, Faculty Lecturer, LaGuardia Community College on 4/24/19
This resources covers all the relevant topics traditionally covered and necessary for an introduction-level course. The material is presented in comprehensive way. read more
This resources covers all the relevant topics traditionally covered and necessary for an introduction-level course. The material is presented in comprehensive way.
I found the text to be accurate, and in line with current marketing practices and pedagogical materials.
The resource is current, but some examples are a bit dated. The instructor using this resource should check all links and examples before assigning.
The resource is clear and easy to understand.
The terminology and framework are consistent with current concepts and expectations of an introductory level course.
The text is well organized; it also lends itself to skipping around and changing the order of the material as the instructor sees fit.
Topics presented are in a logical manner - learning objectives, terms, examples/diagrams, key takeaways, and review questions.
The interface is clear and easy to navigate - clicking images isolates them, which is a good tool for some visual learners.
The resources is not culturally offensive, but it also misses the mark for cultural inclusion.
Reviewed by Duane Bernard, Lecturer, Gettysburg College on 3/12/19
The text book covers all of the typical topics for this level of marketing. If there is any criticism it is that some topics are covered very sparsely. For example, the topic of subliminal messaging is given a few sentences. While it is not... read more
The text book covers all of the typical topics for this level of marketing. If there is any criticism it is that some topics are covered very sparsely. For example, the topic of subliminal messaging is given a few sentences. While it is not necessary to cover this in detail, the explanation provided may not be enough for students to understand what it is. I even had a student that commented on the lack of substance in some areas.
I did not come across any areas that were not accurate. It is written well.
The examples are somewhat dated. While it is perfectly fine to present historical examples, the "new" examples need to be updated. In addition, some of the links are broken.
I have not seen any issues with the understandability of the text. I have also not had any negative comments from students.
The text is consistent with its terminology.
The text is easily separated into subunits. I do not use it as a standalone assignment for reading, as I also have many cases and simulations. I have only directly assigned certain sections for homework. This works well.
The book follows the usual formatting and organization of most of these textbooks.
The only issue I have encountered is some broken links that refer to videos. I have not encountered any other issues.
Grammatical errors have not been found.
I have not detect any offensive content. I have not seen a lot that would be inclusive of other backgrounds.
This book is great as a supplement to other course materials such as cases and lecture. I believe its limitation is that it could go into more depth in many sections.
Reviewed by Lori Rumreich, Assistant Professor of Marketing, Marian University on 3/5/19
This book provides comprehensive coverage of marketing principles equivalent to other textbooks. There is very nice coverage of supply chain and logistics beyond many other principles books. The marketing plan section at the end is very useful.... read more
This book provides comprehensive coverage of marketing principles equivalent to other textbooks. There is very nice coverage of supply chain and logistics beyond many other principles books. The marketing plan section at the end is very useful. Overall there is a lot of content to choose from in this text that makes it easy to select what is needed. A searchable pdf in the downloaded format makes it easy to find content.
The content is accurate and unbiased. Some content may be out of date but with the rapid change happening in much of marketing, especially digital/social, that is to be expected.
The rapid pace of change in marketing, especially digital marketing/social media and media in general make it difficult for textbooks to stay up to date. Updates to these sections should be easy to make. The majority of the text is up-to-date and relevant. The use of review questions and key takeaways for sections are very helpful and reinforce learning of each concept.
This text provides practical and real world examples that are interesting and relevant. Writing style is clear and accessible. The use of pictures and the use of color for highlighting tables, charts, special sections, etc. add to the clarity and readability.
There is a consistent style throughout the text. Clear objectives are at the start of each section, key takeaways and review questions are at the end of each section. This creates a very consistent style that is easy to follow and should help with learning.
It would be nice to provide sub units or groups of chapters within a theme or section of marketing but this is not a requirement. Chapters can be easily divided where needed.
I would prefer that market research to be closer to the front of book. Market research is a first step in understanding customer needs, product features, markets, segments, promotion and ad concepts, etc. It seems out of place near the end of the text. Otherwise, the organization is logical and clear.
The searchable pdf version is very easy to navigate and use. The links to videos and other external content are accessible. All content appears clear and free from distortion. Having multiple formats, pdf, kindle, etc., available is a plus for this text.
The text contains no grammatical errors.
The text appears to be culturally relevant. There is good diversity in the photos shown in the text.
Reviewed by Rosemary Prince, Teaching Faculty III, Florida State University on 12/6/18
The concepts covered in Principles of Marketing - 2015 are appropriate for an introductory level course. The discussion of the 4 Ps as creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging provides an interesting perspective. An index and glossary... read more
The concepts covered in Principles of Marketing - 2015 are appropriate for an introductory level course. The discussion of the 4 Ps as creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging provides an interesting perspective. An index and glossary are not included which would be beneficial.
The concepts, definitions and strategies are accurate and unbiased.
The general principles addressed are relevant. Examples should be updated and some links are no longer available. As noted in the learning objectives Social Media keeps changing and the text needs to be updated. Additionally, e-marketing should be expanded given the changes since 2010. The reference information provided with websites resources and examples and framework of the textbook allows for updating with more recent clips, research, templates, etc.
The text is very clear and terminology is easy to understand.
The framework is consistent with the concepts presented in an introductory level marketing text.
The text is presented in units within each chapter that can be separated and or combined with other units for specific learning assignments or extracted to supplement learning.
The topics in the text are presented in logical order for an introductory marketing text. The layout of the textbook including learning objectives, sequencing, terminology, key takeaways, questions and activities is well organized.
Downloading the text as a PDF, the images and charts were clearly visible. The navigation was straightforward and easy. The links to videos were accessible; however, some were no longer available.
Minor grammar errors were noted.
Updating the video examples would provide a more inclusive text.
Reviewed by Melodi Guilbault, Senior University Lecturer, NJIT on 5/21/18
The book covers all content generally covered in a Principles of or Introduction to Marketing course. The issue is that the content is old. The content is based on a text written in 2010. For example, there are only a few short paragraphs on... read more
The book covers all content generally covered in a Principles of or Introduction to Marketing course. The issue is that the content is old. The content is based on a text written in 2010. For example, there are only a few short paragraphs on social media. There is a clear Table of Contents but I did not see an index or glossary.
The content appears to be accurate. I did not note any errors or any bias. But the content is dated.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 1
The content is dated. The content is adapted from a text written in 2010. There have been significant changes since 2010. Although there are a few more recent links most of the links are from before 2010.
The text is easy to read. Students should find the writing easy to follow. Terminology has been clearly explained.
The way the chapters are organized is consistent throughout the text.
The text is easily and readily divisible into smaller reading sections that can be assigned. This is generally done by chapters and units within the chapters.
The topics are presented in the same order as many Principles of or Introduction to Marketing texts.
I could not get any of the videos to open. Other than that I was able to easily navigate through the chapters. The hyperlinks took me to the appropriate text but it would be helpful to have a return button.
The text did not appear to contain any grammatical errors.
Cultural Relevance rating: 2
I did not note any direct effort to be inclusive in the examples provided.
I like the use of the alternative to the 4Ps. I find the 4Ps to be a dated paradigm and it was refreshing to see a different approach.
Reviewed by David C Taylor, Assistant Pofessor, University of Houston on 3/27/18
A very good comprehensive introduction for marketing. Also would serve as a great refresher text for upper-level marketing courses. read more
A very good comprehensive introduction for marketing. Also would serve as a great refresher text for upper-level marketing courses.
The text is very general, but provides accurate descriptions and overviews of concepts and marketing theory.
We could see more on e-marketing or the evolution of social media over traditional advertising. That said, as a primer on the subject of marketing, this is a great tool in lieu of students having to make a purchase.
Clear, easy to read and understand.
Consistency is strong and consistent across chapters.
I don't think molecularity is practical with an general overview text, unless you wanted to utilize some of the chapters as refreshers in broader topic on marketing.
organized consistently and flow is as with other marketing texts
I did not experience any difficulties
No major grammar issues were identified.
Again, a good primer, or refresh for an upper-level marketing course.
Reviewed by Mary Tripp, Business Faculty, St. Paul College on 2/1/18
The textbook covers the material found in the majority of introductory marketing textbooks. The topics covered are appropriate and the scope meets the basic needs of a principles of marketing course. A searchable index would add to the... read more
The textbook covers the material found in the majority of introductory marketing textbooks. The topics covered are appropriate and the scope meets the basic needs of a principles of marketing course. A searchable index would add to the usefulness of this textbook. A table of content exists but unfortunately no subject index or glossary is provided.
Content Accuracy rating: 3
Overall the accuracy of information, based on the publication date, is acceptable. The textbook is listed as published in 2015 on the Open Textbook Library site. However, the internal publication date is 2010. The internal date seems accurate based on the examples and citations used throughout the textbook. The books examples are all about 10 years old. In the world of marketing, that is a problem. The textbook has some grammatical and spelling errors but nothing that would prevent usage.
The textbook is listed as published in 2015 on the Open Textbook Library site. However, the internal publication date is 2010. The internal date seems accurate based on the examples and citations used throughout the textbook. The books examples are all about 10 years old. In the world of marketing, that is a problem. The subjects of pricing, product, and distribution would be easy to update in the text and/or provide supplements in the classroom. However, the promotion related chapters are very out of date in today's tech driven e-marketing and social media marketing world. If this book had been available in 2009 as an open resource, I would have used it. In 2018, it is unlikely that I would use this resource.
The clarity of the book is great. It is written in a straight forward manner that students would easily understand. The minor grammatical and spelling issues do not hinder the reader.
The consistency of the book meets expectations in regards to terminology and framework.
Each chapter has between 3-8 subsections that allows the material to be easily read by students.
The flow of the chapters is a positive element of the textbook. The organization of the book follows the same structure as many of the principles of marketing textbooks. The table of contents could be restructured to group chapters into subunits for greater student comprehension but it is a small detail.
The interface of the book demonstrated no problems other than the links to videos did not work.
The book contained minor grammatical errors but at a level that the average student would not notice.
Cultural Relevance rating: 1
The cultural relevance of the textbook needs attention. There are not many examples/photos that demonstrate a variety of races, ethnicity, or backgrounds.
1. The cover page and the initial first pages are dull and uninspiring. 2. Overall the textbook is visually dull and students would find the lack of visual interest to be a negative. 3. The examples and references are all at least 10 years old. 4. The text contains only three pages on social media. Not nearly sufficient in today's social media driven environment. 5. The textbook lacks examples of nonprofit organization.
Reviewed by Kristin Hagan, Associate Professor, Northern Virginia Community College on 6/20/17
This text includes all of the major learning objectives covered in an introduction to marketing class. The main topics include the definition of marketing, strategic planning, consumer behavior, the 4 Ps, offerings, marketing channels, selling,... read more
This text includes all of the major learning objectives covered in an introduction to marketing class. The main topics include the definition of marketing, strategic planning, consumer behavior, the 4 Ps, offerings, marketing channels, selling, and overview of a marketing plan. The Table of Contents is easy to access; it serves as a helpful search function. The text is missing a glossary of terms; adding one could be beneficial to readers.
Definitions, principles, and concepts presented in the text are correct. In accordance with marketing principles, the facts presented in the text are true to point. The material was presented in an unbiased way and was primarily free of any grammatical errors.
The examples used in the text are up-to-date and relevant. The large number of real world examples given help the reader understand the learning objectives being presented. Revising these examples and other pertinent information in the text would not be an impossible task.
The layout and formatting of the material is clear and concise. The content of the book uses a lot of extended sentences that could be shortened to help the reader better understand the material. The terms and jargon used is relevant and up-to-date.
The text is extremely consistent in its terminology and framework. Its layout is consistent which makes each new chapter and section easily recognizable. Each chapter has review questions and key summery section which reiterates key points and acts as checkpoint for student.
The layout of the text is very modular. Each chapter is broken down into a minimum of three sections which makes the information very learner-friendly. Each section has a defined learning objective and review material at the end of the section.
The text is organized in a logical way where concepts taught at the beginning of the book are built upon later. The information presented flows well throughout the text. The Table of Contents is extremely beneficial and makes key topics easy to locate in the text.
I did not notice that the text featured any interface issues such as navigational problems, unclear images, or other distortions that would confuse the reader. The images and figures presented in the text are clearly visible to the reader. All images and figures can be enlarged if the viewer clicks on the displayed image.
There were few grammatical errors in the text.
This text presents real life examples relevant to mainstream culture and business in America. Depending on the audience, more culturally diverse examples may be more suiting. The text does a fairly good job of using conational business examples however, some of the images of people could be diversified.
The audio clips located throughout the online text are a nice edition that students reading a traditional textbook can not experience.
Reviewed by Oksana Grybovych, Associate professor, University of Northern Iowa on 12/5/16
The text would greatly benefit from a table of contents, glossary, and an index. Otherwise, most content areas are discussed rather thoroughly - even though, as the previous reviewer mentioned, the text is lacking in its application towards... read more
The text would greatly benefit from a table of contents, glossary, and an index. Otherwise, most content areas are discussed rather thoroughly - even though, as the previous reviewer mentioned, the text is lacking in its application towards services and experiences marketing. Speaking of the latter, there is no discussion of marketing experiences as offerings even though this approach is very common these days.
This text seems to target the North American audience, and readers from elsewhere might not readily relate to the examples provided. The authors could also incorporate more examples from a nonprofit sector.
Most chapters are very relevant to the current marketing practices. However, the authors could consider including or expanding more on the subjects of sustainability (e.g. social corporate sustainability) as well as experience marketing.
Key concepts are well defined, but the structure and formatting of the text are somewhat confusing.
The text is structured around the framework that is outlined by the authors in chapter 1.
There are 16 chapters in the text, each of them is broken up into sections. Such structure makes it very manageable for the instructor to use the text in a typical North American semester.
Some of the chapters could be moved around to allow for a better flow of the contents.
The authors could consider moving all references to the end, as well as including a table of contents that the students could navigate (click on the headings), glossary, and an index.
Very few spelling/grammar errors.
It appears that this text is mainly designed for North American white audience, hence is lacking in its cultural relevance.
Overall this is a very good introductory text, I was happy to see the authors incorporate many important topics that are frequently omitted in other texts. At the same time, a few more important topics could be added, the formatting/ structure of the text revised, and more culturally relevant content added.
Reviewed by Chris Blocker, Assistant Professor, Colorado State University on 1/7/16
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is a very comprehensive text, which addresses the full gamut of topics that an instructor might want to cover. It also offers nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g.,... read more
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is a very comprehensive text, which addresses the full gamut of topics that an instructor might want to cover. It also offers nice integration of some topics that might normally be neglected, e.g., satisfaction metrics, account planning, and other topics.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond articulates the core principles of marketing with accuracy and precision. There is a tight linkage (typically through use of web links) to established definitions (e.g., AMA) and conceptual frameworks (e.g., Product and Market Entry strategies) that have come to reflect the established body of marketing knowledge.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond contains relevant and up-to-date themes based upon emerging paradigms (e.g., Service Dominant Logic) that are synthesized across the chapters.
One of the strengths of Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond, which relates to its comprehensiveness, is the clarity offered for all the concepts presented. Key concepts are well-defined and presented in a plain language that is readily accessible to a wide audience.
Although, no unifying framework is offered to connect the chapters, there is an underlying common conceptual core offered within the Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond
Another key strength of Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is the modularity. Chapters are broken up numerically and into "bite-size" chunks such that instructors would have an easy time assigning aspects of a chapter to modules.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond follows the common flow of the vast majority of Principles texts by beginning with the organization and high-level strategies, then digging into consumer/buyer behavior, and finally, unpacking the marketing mix.
Navigation is easy for Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond; however, some issues with fonts and size of text within images rendered some distractions
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is well written and in an accessible style.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond is not offensive in any way and does offer quite a few diverse examples. However, there is a heavy reliance on North American company examples, such that individuals in other cultures might have difficulty with some.
Principles of Marketing by Tanner & Raymond does a really nice job of offering a comprehensive and relevant marketing text that can easily be modularized by instructors. The authors have effectively integrated up-to-date examples that students will find interesting as well as integrated media (e.g., audio clips) and real life profiles (profiling an analytics manager at BNSF) to produce an engaging text.
Reviewed by Marina Jaffey, Instructor & Program Leader Marketing, Camosun College on 10/9/13
This American Principles of Marketing text covers all the key areas & ideas normally included in a first year College/University Introduction to Marketing course. There are 16 chapters in the text and most key topic areas are discussed... read more
This American Principles of Marketing text covers all the key areas & ideas normally included in a first year College/University Introduction to Marketing course. There are 16 chapters in the text and most key topic areas are discussed relatively thoroughly, with the following exceptions: 1. Pricing 2. Retailing and Distribution as it relates to services Rather than structuring the text around the 4Ps or traditional Marketing Mix, the authors follow the premise that marketing is composed of four activities centered on customer value: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value. The text does not include a Table of Contents, Contents in Brief, or Glossary and/or Index.
Marketing concepts are defined/explained/discussed accurately. All the examples are American, so not as relevant for Canadian students. Similarly, the Environmental Scan and ethical/legal segments are all based on American trends and laws/business practices. In general, the examples tend to focus on large corporations. More examples from medium/small businesses, as well as not-for-profits, would help to provide a broader perspective for students. Based on the scale below: content is accurate, but has a very American bias.
The content is up-to-date, with the exception of: 1. The three chapters on marketing communications. Marketing communications has been and is continuing to change rapidly, and as a result, it is difficult for text books to remain current. Having said this, I believe that it would be relatively easy to make regular updates to the marketing communications chapters. 2. Although the Distribution chapter is up-to-date, it is lacking in its coverage of distribution as it relates to services, as well as retailing. 3. Perhaps most importantly for Canadian students, is the fact that all the examples and all sections that relate to legislation/business practices in the current text are American. It would be more time consuming to up date the text to reflect the Canadian marketing environment.
Clarity rating: 3
Concepts are explained clearly in the body of the text. Ideas to increase retention are: 1. Include more visuals. The current charts/graphs are small and difficult to read. Many of the figures lack sufficient detail. Visuals serve to summarize concepts at-a-glance and help students to understand/recall a concept. 2. Provide a variety of examples to illustrate concepts. 3. Make better use of formatting to ensure students can see quickly key concepts and definitions on a page, for instance, make better use of headings & subheadings and include key concept definitions in the margins of the page. 4. In addition to the summaries at the end of each section within a chapter, include a final end of chapter summary.
Yes, the text is internally consistent in terms of terminology and framework. The text presents the marketing mix in terms of four activities or components of marketing: creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging value.
There are 16 chapters in the text which corresponds nicely with a typically 14 week semester. The order of the chapters in the text is as follows: Ch. 1 - What is Marketing? Ch. 2 - Strategic Planning Ch. 3 - Consumer Behaviour Ch. 4 - Business Buying Behaviour Ch. 5 - Market Segmenting, Targeting, & Positioning Ch. 6 - Creating Offerings Ch. 7 - Developing & Managing Offerings Ch. 8 - Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers Ch. 9 - Using Supply Chains to Create Value for Customers Ch. 10 - Gathering and Using Information: Marketing Research & Market Intelligence Ch. 11 - Advertising, IMC, and the Changing Media Landscape Ch. 12 - Public Relations & Sales Promotions Ch. 13 - Professional Selling Ch. 14 - Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, and Empowerment Ch. 15 - Price Ch. 16 - The Marketing Plan It would be easy and straight forward for an instructor to change the order that these topics are covered in a semester, should he/she wish to do that.
Two changes I recommend are: 1. Put ch. 15 - Price right after ch. 7 - Developing & Managing Offerings. Pricing is a very important marketing concept, and it makes most sense to discuss how to price products/services/offerings right after they are covered in the text. 2. Move ch. 10 - Marketing Research to right after ch. 2 - Strategic Planning. Ch. 2 covers environmental scanning, so it is important for students to learn how to research trends and find information required for planning. Otherwise, the order of the chapters is fine.
Interface rating: 2
I have been working with a print version of the text. A suggestion to make navigation through the print version easier would be to include a Table of Contents, Contents in Brief, and Index/Glossary at the end. Images/charts are small and difficult to read in the print version. Many subheadings sit alone at the bottom of a page. Need to format so that a subheading appears with some or all of the body copy. Also, some chapters begin on the same page that the previous chapter ends. It would be better to start a new chapter on a new page. In several instances, whole pages were simply lists of sources. It is important to cite sources, however it would be better to include these lists of sources at the end of a chapter, rather than in the middle of a chapter.
There are relatively few grammatical or spelling errors. Please see complete list of errors in attached document.
Although the text is not culturally offensive in any way, I believe there could be more examples that reflect a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds. The text mentions that there is a profile of a marketing professional at the beginning of each chapter - this is not the case (no profiles are included). Including profiles of marketing professionals from a variety of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds would be one way of addressing this weaknesses. It would also be appropriate to profile different types of organizations to illustrate marketing concepts/business practices amongst different cultural groups. As mentioned earlier, this is an American text so all examples are American.
Overall this text covers all the key topic areas relevant to a first year college/university overview marketing course. Most topics are covered in an appropriate amount of depth, with a few exceptions including pricing and services marketing. Learning Objectives are included at the start of each segment within a chapter, but not at the start of a chapter. Learning Objectives are all at the lowest two levels of Bloom's Taxonomy - Knowledge (i.e. Describe...) and Comprehension (i.e. Understand...) http://www.coun.uvic.ca/learning/exams/blooms-taxonomy.html The Review Questions and Key Takeaways which appear at the end of each segment within a chapter and the Discussion Questions and Activities at the end of each chapter are generally good and provide students with ways to test understanding and apply relevant concepts. This is an American text, so an instructor would need to provide his/her students with a variety of Canadian examples, as well as Canadian content related to environmental scanning and business practices. All Introduction to Marketing texts offered by publishers provide extensive support materials for instructors and students. I'm not aware of any support materials that come with this text. There are formatting issues which have been mentioned earlier in this review, that would need to be addressed. This review originated in the BC Open Textbook Collection and is licensed under CC BY-ND.
Table of Contents
- Chapter 1: What is Marketing?
- Chapter 2: Strategic Planning
- Chapter 3: Consumer Behavior: How People Make Buying Decisions
- Chapter 4: Business Buying Behavior
- Chapter 5: Market Segmenting, Targeting, and Positioning
- Chapter 6: Creating Offerings
- Chapter 7: Developing and Managing Offerings
- Chapter 8: Using Marketing Channels to Create Value for Customers
- Chapter 9: Using Supply Chains to Create Value for Customers
- Chapter 10: Gathering and Using Information: Marketing Research and Market Intelligence
- Chapter 11: Integrated Marketing Communications and the Changing Media Landscape
- Chapter 12: Public Relations, Social Media, and Sponsorships
- Chapter 13: Professional Selling
- Chapter 14: Customer Satisfaction, Loyalty, and Empowerment
- Chapter 15: Price, the Only Revenue Generator
- Chapter 16: The Marketing Plan
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Principles of Marketing teaches the experience and process of actually doing marketing – not just the vocabulary. It carries five dominant themes throughout in order to expose students to marketing in today's environment:
Service dominant logic — This textbook employs the term "offering" instead of the more traditional First "P" — product. That is because consumers don't sacrifice value when alternating between a product and a service. They are evaluating the entire experience, whether they interact with a product, a service, or a combination. So the fundamental focus is providing value throughout the value chain, whether that value chain encompasses a product, service, or both.
Sustainability — Increasingly, companies are interested in the impact they are having on their local community as well as the overall environment. This is often referred to as the "triple bottom line" of financial, social, and environment performance.
Ethics and social responsibility — Following on the sustainability notion is the broader importance of ethics and social responsibility in creating successful organizations. The authors make consistent references to ethical situations throughout chapter coverage, and end of chapter material in most chapters will encompass ethical situations.
Global coverage — the authors deliberately entitled Chapter 1 "What is Marketing?" Whether it is today's price of gasoline, the current U.S. presidential race, or Midwestern U.S. farming, almost every industry and company needs strong global awareness. And today's marketing professionals must understand the world in which they and their companies operate.
Metrics — Firms today have the potential to gather more information than ever before about their current and potential customers. That information gathering can be costly, but it can also be very revealing. With the potential to capture so much more detail about micro transactions, firms should now be more able to answer "well, what this marketing strategy really worth it?" And "what is the marketing ROI?" And finally, "what is this customer or set of customers worth to us over their lifetime?"
Contribute to this Page
The True Meaning of Marketing Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Despite the fact that marketing might seem a relatively new concept, its origin dates back to the times when the first trade relationships where established; therefore, it can be assumed that marketing existed even in the prehistoric society when the concept of money had not been developed yet.
Defining marketing, however, remains a very complicated task. Incorporating a number of elements and relating to an even greater number of fields, such as advertising, market analysis, etc., marketing is a rather obscure concept. With the help of Glaser’s article Marketing makes the car register ring (Glazer, 2001), defining marketing, however, becomes much easier.
Glaser suggests that marketing should be considered from several viewpoints. The most obvious one concerns the advertizing aspect of marketing. Indeed, one must admit that marketing has a lot to do with promoting specific services or even an entire company; as a result, marketing is often defined from the perspective of its promotion functions. In light of the given facts, it can be assumed that marketing as a tool for enhancing sales.
In a narrow sense, the choice of an advertisement technique often is defined as a marketing practice. According to what Glazer says, “Marketing is everything that is necessary to sell the product or service” (Glazer, 2001).
However, Glazer also stresses that “Although advertising is an important part of marketing, it is just that — only a part of it” (Glazer, 2001). For instance, the recent Google Tour promotion has increased the sales of the product impressively (Chen & Lin, 2012).
Another way to define the marketing is to take a closer look at the word itself. It is obvious that the process has something to do with the market. Indeed, as Glazer explains, marketing also means exploring a specific market, learning about the current demands, the latest innovations, the existing rivals and their performance, the saturation of the market with the specified product, etc.; the list can go on forever.
The thoroughness of the research defines the resulting sales rates. Therefore, marketing can be defined as research within the boundaries of the target market. It is necessary to stress that Glazer offers a rather loose definition of marketing viewed as research. While Glazer does define marketing as a research, he still does not specify every single field that marketing research touches upon.
According to Glazer, marketing research is confined to learning about the target market, i.e., figuring out “if people will buy your good or service, who would buy it, what features they would want and how much they would pay for it” (Glazer, 2001). It would be wrong, however, to narrow marketing research down to these issues. In fact, marketing research embraces the following spheres:
- Target audience;
- Possible rivals;
- Available resources;
- Current demand;
- Probable losses;
- Expected revenues.
The given definition can be applied to the marketing strategy used by General Motors. While the company works on its promotion strategies, its leader clearly gathers the data concerning the new markets for the further expansion (Chevy marketing: Less like apple pie, more like Apple: Q & A agency and marketing executives Jeff Goodby, Goodby, Silverstein & partners, 2011).
While taking every single factor into consideration when doing the marketing research is practically impossible, it is still within the capability of the company’s manager to evaluate the chances of the company to succeed in the specified market.
Finally, Glazer offers the third way of defining marketing. According to the author, marketing can also be interpreted as the means of communicating with the customer. Indeed, marketing presupposes sending specific messages to the target audience and making sure that the latter translates these messages into creating the desired image of a company.
As Glazer explains, “Public opinion is a marketing concern, and a company will spend whatever it takes to maintain positive perception by the public” (Glazer, 2001) It is quite amazing that marketing, like any other method of communication – or even any language, if you will – can take forms of verbal, non-verbal and even subliminal messages.
For instance, a company can promote a product or services with the help of a journal or magazine advertisement or radio commercial, which presupposes that verbal messages are going to be used.
However, when it comes to advertizing specific services or products via internet or TV, it is necessary to use non-verbal messages as well, including the concepts behind the company’s logo, how the actors in the commercial move or gesticulate, etc. Therefore, it can be assumed that marketing is a specific language that creates a link between a company and its potential clients.
Thus, three ways of viewing marketing have been provided. Marketing can be considered a synonym of promotion, research and even a specific language that serves as a link between the company representatives and their target audience.
Even though the aforementioned article provides ample opportunities for finding the right definition for marketing, it is clear that defining the given phenomenon means considering it from a single perspective, which is practically impossible.
The closest one may get to the definition of marketing is introducing it as a series of actions aimed at shaping the customers’ attitude towards the company and/or its product. However, it is important to keep in mind that marketing also involves dealing with a plethora of other issues that are only slightly related to the promotion process.
Reference List
Chen, H.-T. & Lin, T.-W. (2012). How a 3D tour Itinerary promotion affects consumers’ intention to purchase a tour product ? Information technology Journal, 11 (10), 1357–1368.
Chevy marketing: Less like apple pie, more like Apple: Q & A agency and marketing executives Jeff Goodby, Goodby, Silverstein & partners (2011). Automotive News , 34.
Glaser, T. (2001 ). Marketing makes the car register ring. St. Petersburg Times . Web.
- Marketing Strategies Development
- Advertising and Freedom of Speech
- Manchester United - Football and Finance
- SWOT Analyzing a Company's Generally Strategy
- Advertizing and Globalization
- Marketing Plan for FlaBlaster
- Improving Customer Experience in Ritz-Carlton Hotel
- Increasing the Consumption of Healthy Food Products
- Carrefour UAE Marketing Strategy
- Hi-tech Outlets Company Marketing Plan
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, March 15). The True Meaning of Marketing. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-true-meaning-of-marketing/
"The True Meaning of Marketing." IvyPanda , 15 Mar. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/the-true-meaning-of-marketing/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'The True Meaning of Marketing'. 15 March.
IvyPanda . 2020. "The True Meaning of Marketing." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-true-meaning-of-marketing/.
1. IvyPanda . "The True Meaning of Marketing." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-true-meaning-of-marketing/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "The True Meaning of Marketing." March 15, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/the-true-meaning-of-marketing/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
Your Article Library
Essay on marketing: meaning, definition and concept (467 words).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Essay on Marketing: Meaning, Definition and Concept!
Everybody lives by selling some products, services or ideas. Generally, marketing is considered as selling and promotion. However, making a sale, i.e., selling is the old sense of marketing. In its new sense, marketing is satisfying customer needs. Selling is only one aspect of marketing.
It is but one of several marketing functions and that too not the most important one. It means taking certain other steps, such as identifying customer needs, developing good quality product, fixing reasonable prices, distributing and promoting the product effectively. Then his goods will sell very easily.
Some important definitions of marketing are given below:
F, E. Clark, “Marketing consists of those efforts which effect transfer in ownership of goods and core for their physical distribution.”
Stanton and Others, “Marketing is a total system of business activities designed to plan price promotes and distribute wants-satisfying products to target markets to achieve organisational objectives.”
Kotler and Armstrong, “ Marketing is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and values with others.”
American Management Association (1985), “Marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individuals and organisational objectives”. This is a widely accepted definition of Marketing.
Thus marketing is getting the right goods and services to the right people at the right place at the right Lime at the right price with the right communication and promotion. Marketing is the performance of those business activities which are involved in the flow of ideas, goods and services from their point of production to the point of consumption.
The objectives of marketing is to ascertain consumer needs, convert them into ideas, products or services and move such ideas etc. to the final consumer or user, to satisfy certain needs and wants of specific consumer segments with emphasis on profitability, ensuring the optimum use of the resources available to the organisation.
Marketing Concept:
The ‘consumer-oriented’ marketing has led to a new philosophy of doing business known as ‘marketing concept’. Under this concept, marketing is much more than a physical process of distributing goods and services.
It is a distinct philosophy of business under which all business activities are integrated and directed to supply the goods and services which customers want, in the way they want, at the time and place where they want and at a price which they are able and willing to pay for.
Marketing concept is reflected in the following definitions:
“Marketing is the process of discovering and translating consumer wants into products and services and then in turn making it possible for more and more people to enjoy more and more of these products and services.”
Related Articles:
- Marketing: Meaning, Considerations and Essential Elements of Marketing
- Marketing: Approaches, Meaning, Definition and Features
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Marketing Definition
This essay about the definition of marketing in the business context elucidates its comprehensive and strategic nature, beyond the common misconceptions that equate it solely with selling and advertising. It underscores marketing as a vital process of understanding and meeting consumer needs, involving market research, product development, pricing, distribution, and promotion. The essay highlights the scope of marketing as encompassing all aspects of a business, acting as a bridge to the target audience, and adapting to technological and cultural shifts, particularly in the digital realm. It posits that effective marketing is crucial for business growth, brand differentiation, and customer loyalty. By showcasing marketing as a dynamic and integral part of business strategy, the essay affirms its role in driving innovation, competitiveness, and long-term profitability in a constantly evolving marketplace.
How it works
Amidst the vibrant milieu of contemporary commerce, the term ‘marketing’ emerges recurrently, often obscured by misconceptions and oversimplifications. At its essence, marketing transcends mere salesmanship or promotional endeavors; it constitutes a holistic approach aimed at crafting, disseminating, delivering, and exchanging offerings imbued with value for consumers, clientele, associates, and society at large. This discourse endeavors to elucidate the intricate fabric of marketing, delving into its multifaceted nature, breadth, and the pivotal function it assumes in business triumph.
Historically, marketing has been misinterpreted as the culmination of a product’s journey to the consumer, synonymous with promotion and sales.
Nonetheless, this perception is myopic and fails to encapsulate the strategic profundity intrinsic to genuine marketing. Marketing commences with comprehending the needs and aspirations of consumers, long preceding the inception of a product or the conception of a service. It entails scrutinizing and deciphering market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes to inform product formulation, pricing strategies, distribution channels, and promotional endeavors. Fundamentally, marketing is about discerning and gratifying human and societal needs in a sustainable and lucrative manner.
The purview of marketing transcends the confines of conventional advertising. It constitutes an integrative process that permeates every facet of a business, from product conceptualization and pricing to dissemination and customer relations. At its zenith, marketing serves as a conduit between a company’s offerings and its target demographic, ensuring that products not only cater to extant market needs but also anticipate future exigencies. This proactive approach distinguishes successful enterprises from their counterparts, enabling them to innovate incessantly and preserve relevance in an ever-evolving marketplace.
Furthermore, marketing is inherently fluid, adapting to shifts in technology, culture, and consumer predilections. The advent of digital marketing platforms, such as social media, search engines, and email, has revolutionized the modus operandi through which businesses engage with their audiences, presenting unparalleled prospects for interaction, customization, and evaluation. This digital metamorphosis has not only diversified the toolkit accessible to marketers but also elevated consumer expectations, necessitating more genuine, responsive, and tailored interactions with brands.
The import of marketing in business is immeasurable. It constitutes the lifeblood of any organization, propelling expansion, fortifying brand equity, and nurturing patronage. Through effective marketing, enterprises can set themselves apart in saturated markets, furnish value for their clientele, and secure sustainable competitive advantages. It represents a strategic investment that, when executed with perspicacity and ingenuity, can culminate in enduring prosperity and profitability.
In summation, marketing is a labyrinthine, multidimensional discipline that lies at the crux of business stratagem. It encompasses a diverse array of endeavors aimed at comprehending and satiating the needs of consumers and society. By bridging the chasm between enterprises and their clientele, marketing assumes a pivotal role in propelling innovation, expansion, and consumer contentment. As the commercial sphere continues to evolve, the significance of marketing remains undiminished, prompting enterprises to remain at the vanguard of innovation and sustain resonance in the eyes of their patrons.
Cite this page
Marketing Definition. (2024, Apr 14). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/
"Marketing Definition." PapersOwl.com , 14 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Marketing Definition . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/ [Accessed: 27 Sep. 2024]
"Marketing Definition." PapersOwl.com, Apr 14, 2024. Accessed September 27, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/
"Marketing Definition," PapersOwl.com , 14-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/. [Accessed: 27-Sep-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Marketing Definition . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/marketing-definition/ [Accessed: 27-Sep-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Essay on Marketing
List of essays on Marketing. Marketing is a comprehensive term and it includes all resources and a set of activities necessary to direct and facilitate the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer. Businessman regards marketing as a management function to plan, promote and deliver products to the clients or customers. Human efforts, finance and management constitute the primary resources in marketing.
Audience : This essay is written in easy and simple words for school, college and university students.
List of Essays on Marketing for School, College and University Students
Essay on marketing – (1500 words).
Marketing is a comprehensive term and it includes all resources and a set of activities necessary to direct and facilitate the flow of goods and services from producer to consumer. Businessman regards marketing as a management function to plan, promote and deliver products to the clients or customers. Human efforts, finance and management constitute the primary resources in marketing.
Marketing starts with identification of customer’s wants and then satisfying those wants through products and services. The modern concept of marketing is customer-oriented and focuses on earning profit through customer satisfaction.
Prof. Drucker states that the first function of marketing is to create a customer or market. Customer is the most important person in the whole marketing process. He is the cause and purpose of all marketing activities.
According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is a human activity directed at satisfying needs and wants through exchange process.” All marketing activities are basically for meeting the needs of customers and also raising social welfare. We have twin activities which are most significant in marketing- (a) Matching the product with demand, i.e., customer needs and desires or target market, (b) The transfer of ownership and possession at every stage in the flow of goods from the primary producer to the ultimate consumer.
According to William Stanton, “Marketing is a total system of business activities designed to plan, price, promote and distribute want-satisfying products to target markets to achieve organisational objectives.”
The American Marketing Association defines marketing as the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organisational objectives.
Paul Mazur defined marketing as the creation and delivery of a standard of living to society. This definition catches the real spirit of the marketing process. It has consumer- orientation. It duly honours the marketing concept which indicates a shift from product to customer-orientation, i.e., fulfillment of customer needs and desires. It emphasises the major function of marketing, viz., satisfaction of customer and social demand for material goods and services.
Example- In the case of oral care products, currently only 47 per cent of the rural population use toothpaste, 23 per cent use tooth powder and the rest neither. Targeting non-users in rural areas and developing awareness about oral hygiene and converting them to tooth powder/toothpaste users.
Features of Marketing :
1. Marketing activities are aimed at satisfying the needs and desires of consumers and therefore, finding out consumer needs and wants is the starting point for all marketing activities. It starts with consumers and ends with consumers by satisfying their needs.
2. Marketing is a continuous activity and the goods are manufactured and distributed to the consumers as per demand.
3. Marketing deals with exchange of goods and services with money as the medium of exchange.
4. Marketing concept has undergone changes over a period of time i.e., the recent one is the societal marketing concept which focuses on three factors- customer demand satisfaction, public interest and profitability.
5. Marketing creates time, place and possession utilities. The consumer is able to obtain the right product at the right time at the right place as and when he requires.
6. Production and marketing are related and production takes place based on the needs and expectations of the consumer.
7. Marketing facilities large-scale production, employment opportunities and social welfare.
8. Marketing is an integral part of business. The survival and growth of business depend upon the effectiveness of marketing operations in an organisation.
9. Marketing is an integrated process and is based on strategies and plans.
10. The long-term objective of marketing is profit maximization through customer satisfaction.
Modern marketing begins with the customer, not with production, sales, technological landmarks and it ends with the customer satisfaction and social well-being. Under market- driven economy, buyer or customer is the king. The marketer should find out what the consumers wish to purchase and how much they are willing to pay. The company should then decide whether the desired product can be produced and sold at the price consumers will pay and at a profit to the company.
Marketing covers the following:
1. Seeking- The purpose of seeking is to discover the customer and customer needs. The marketing opportunity is revealed through an analysis of the environment.
2. Matching- Marketing is a matching process. Customer demand has to be matched with organisational resources and environmental limitations, such as competition, government regulations, general economic conditions, and so on.
3. Programming- The marketing programme, called the marketing mix, covering Product, Price, Promotion and Place (distribution) strategies (4 P’s) will be formulated and implemented to accomplish the twin objectives of customer satisfaction and profitability.
Marketing is an ongoing process of- (1) Discovering and translating consumer needs and desires into products and services (through planning and producing the planned products), (2) Creating demand for these products and services (through promotion and pricing), (3) Serving the consumer demand (through planned physical distribution) with the help of marketing channels, and then, in turn, (4) Expanding the market even in the face of keen competition.
The modern marketer is called upon to set the marketing objectives, develop the marketing plan, organise the marketing function, implement the marketing plan or programme (marketing mix) and control the marketing programme to assure the accomplishment of the set of marketing objectives. The marketing programme covers product planning or merchandising, price, promotion and physical distribution.
Four basic approaches are commonly used to describe the marketing system:
1. Commodity Approach :
Under the commodity approach, we study the flow of certain commodity and its journey from the original producer right up to the final customer. In such a study, we can locate the centre of production, people engaged in buying and selling of the product, mode of transportation, problem of selling and advertising the product, problems of financing it, problems arising out of its storage and so on.
Through such an approach, we can find out the differences in marketing products, services and problems. Thus, we can have a fuller picture of the field of marketing. Marketing of agricultural products such as cotton, wheat, jute represent the commodity approach.
2. Functional Approach :
Under the functional approach, we concentrate our attention on the specialised service or functions or activities performed by marketers. The study of marketing functions (like, buying, selling, storage, risk-bearing, transport, financing, and providing information) represents the functional approach to the marketing system.
3. Institutional Approach :
Under the institutional approach, our main interest centres round the marketing institutions or agencies such as wholesalers, retailers, transport undertakings, banks and insurance companies etc., who participate in discharging their marketing responsibilities during the movement of distribution of goods. We try to find out how these various business institutions and agencies work together to form a total marketing system.
4. The Systems Approach :
A system is a set of interacting or interdependent components or groups co-ordinated to form a unified whole and organised marketing activities to accomplish a set of objectives.
In the model of systems approach we have:
1. Objective,
3. Processor,
4. Outputs, and
5. Feedback.
The system is designed to achieve objectives or goals according to a plan, which provides for the processing of inputs and the discharge of appropriate outputs. The objectives direct the process control monitors the process. Information feedback gives information from internal and external sources and it is the basis for future change in the system.
An open system has its own environment giving the inputs and accepting the outputs. Inputs are processed, producing outputs to meet the objective. The twin objectives of marketing system are customer satisfaction and profitability.
The systems approach provides the best model for marketing activity. It places emphasis on the inputs to the system and the outputs produced. It helps in the determination of marketing and corporate goals, and the development of marketing programmes and the total marketing mix.
Adoption of a systems approach provides a good basis for the logical and orderly analysis of marketing activities. It stresses marketing linkages inside and outside the firm. It emphasises changing environment. It provides a framework for control. It depends on using the right information. Markets can be understood only through study of information.
The output establishes the purpose or objective of a system. The objective is profits through serving the demand of consumers and community. The output of marketing system is sales of goods. Correct inputs must be available to the processor i.e., marketing administration in order to produce desirable outputs.
These inputs in the marketing system are the elements of marketing-mix and the target market determined through marketing research. The marketing system must operate as per plans and policies and within control which may be internal or external. Of course, feedback must be available for introducing corrections in the future plans and marketing operations.
The flow of information required to check performance is called feedback. Feedback ensures the accomplishment of objectives through continuous marketing managerial process of planning-action-control. Marketing environment can be broken down into a number of layers. The inner layers become the subsystems of the outer layer. Output from one layer becomes the input for the next.
Marketing plan is a system and its parts or components are subsystems. There are four components or subsystems of marketing plan or marketing-mix- (1) The product management system to manage products from introduction to market withdrawal, (2) Channel and physical distribution system to manage distribution channels and the flow of goods to the market, (3) Promotion system to coordinate all means of promotion to stimulate demand, and (4) Price system designing prices for a line of products sold to customers under different selling conditions.
Marketing management revolves around these four areas of marketing- mix or plan. Marketing information system provides data for decision-making in all marketing areas or problems. It is also a part of marketing system.
The systems model (plan-inputs-processing-outputs-feedback-environment) placed emphasis on the inputs of resources as per plan, discharge of outputs and marketing information flow. It enables the determination of goals as well as development of strategies and programmes to achieve those goals through feedback control mechanism.
Essay on Marketing – 2 (1000 Words)
Traditionally, marketing has been defined as follows – “Marketing includes all activities that direct the flow of goods and services from the producers to the consumers or users.” This definition is product oriented as it does not consider the needs of the customers. It emphasises sale of goods produced by the producer and thus considers marketing in a narrow sense of ‘telling and selling’.
Modern definitions of marketing are based on the philosophy that “Satisfaction of customers is the basic purpose of business”. According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is a social process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others”.
This implies matching of products with what is demanded in the market. This requires determining the requirements of potential customers and then developing and supplying those products which meet their requirements. If a business produces the products to satisfy the requirements of customers, it is more likely to be successful in achieving its objectives.
Definitions of Marketing :
Traditional Definition:
Marketing is a social process by which products are matched with markets and through which the consumer is able to use or enjoy the product. It makes goods and services more useful to the society by creating place, time and possession utilities. —Cundiff and Still
Modern Definition:
Marketing is a social process by which individual and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others. —Philip Kotler
The present day marketing is consumer oriented rather than product oriented. Product planning, pricing, promotion and distribution are so organised that the needs of the customers are satisfied fully. In the words of Stanton, “Marketing is a total system of interacting business activities designed to plan, price, promote and distribute wants satisfying products and services to present and potential customers”. Consumer oriented marketing ensures that all business activities revolve around the customer.
The essential elements of marketing are as follows:
(i) Two Parties:
There are at least two parties – buyer or customer on the one hand, and seller or marketer on the other.
(ii) Exchange of Value:
Exchange of goods and services between the seller and the buyer takes place for a valuable consideration. In other words, the parties have something viewed valuable by each other. That means the buyer can offer value and the seller can offer goods which are perceived to be of value by the buyer.
(iii) Freedom:
The parties are free to interact and accept or reject the offer of each other.
(iv) Satisfaction:
Marketing satisfies the needs of both the parties. The consumers gets want satisfying goods and services and the seller gets value in terms of money for his offering.
Marketing as a Process of Managing Profitable Customer Relationships :
According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing is the process by which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return.”
Globalisation and rise of information technology (IT) have increased the expectations of customers. They don’t buy products or brands, but ‘a set of benefits or values’. They expect marketers to be concerned with their total satisfaction. The marketers association with the customer continues even after the sale of the product and this is what is called relationship marketing.
Thus, marketing is a process consisting of the following interrelated elements:
(i) Understand the market and customer needs and wants.
(ii) Design the product to satisfy customer needs and wants.
(iii) Develop an integrated marketing program that delivers superior value to the customer.
(iv) Build profitable relationships with, customers and offer ‘customer delight’.
(v) Capture value from customers to create profits and customer equity.
Marketing enables people to satisfy their needs and wants through exchange relationships. Exchange is the act of obtaining a desired product (or benefit) from a company by offering money value in return. Marketing also involves actions taken by the marketer to build and maintain desirable exchange relationships with target customers.
Marketers try to build strong relationships by consistently delivering superior customer value. Besides attracting new customers, they also try to retain the existing customers. These are the two basic goals of modern marketing.
The key to building lasting customer relationships is to create (i) superior customer value, and (ii) satisfaction. A customer buys from the firm that offers the highest customer perceived value, i.e., the customer’s evaluation of the difference between all the benefits and all the costs of a market offering (i.e., product) relative to those of other firms. Many people prefer to buy sweets from Haldiram’s store as compared to other sweet shops because of higher perceived value.
Market and Related Concepts :
Traditionally, the term ‘market’ refers to the place where buyers and sellers meet for exchange of goods and services. It is in this sense that we refer to Chandni Chowk Market, Kamla Nagar Market, Janpath Market and other markets in Delhi. The buyers go to the market to purchase the goods of their choice.
These days the term ‘market’ has acquired a broader meaning. If refers to actual and potential buyers of a product or service, whom the sellers can approach through various means of communication and transport.
For example, a marketer can approach prospective buyers through web advertising and a customer can purchase goods from his residence or office by placing order on telephone or cell phone or using internet and e-mail. Physical meeting between the parties to buy and sell is not necessary.
Customer Needs, Wants and Demands :
Marketing begins with human needs and wants. Needs are feelings of deprivation of some satisfaction. People need food, air, water, clothing and shelter to survive. These needs exist in the very nature of human biology and marketers do not create them. Wants are desires for satisfaction of needs. Human needs are few but wants are many. Human wants are continually shaped and reshaped by families, social institutions and cultural factors.
Demands are wants for specific products and services. They are backed by the ability and willingness to buy. Wants which are supported by purchasing power become demands. Marketers influence wants and demands by making products attractive, affordable and easily available to the target group of consumers. For example, a marketer might promote the idea that a certain brand of pen (e.g., Parker) would satisfy the need for social status.
Essay on Marketing – 3 (700 Words)
Marketing starts with identifying customer needs and wants and ends with satisfying them through a coordinated set of activities that also allows a firm to achieve its own goals. Awareness of this fact gave rise to the marketing concept. The marketing concept embraces all the activities of a firm. It aims at matching the company’s offering with customer needs, to achieve the desired level of customer satisfaction and generate profits for the company.
The marketing concept is based on the beliefs that are as follows:
(a) The company’s planning and operations are customer-oriented,
(b) The goals of the company should be profitable sales volume and not just volume, and
(c) All marketing activities should be coordinated effectively.
Cundiff and Still, “marketing is the business process by which products are matched with market and through which transfer of ownership affected”.
Tousley, Clark and Clark “marketing consist of those efforts which affect transfer of ownership of goods and services and provide for the physical distribution”.
H.L. Hansen Marketing is the process of discovering and translating consumer needs and wants into products and service specification, creating demand for these products and services and then turns expanding this demand.
According to American Marketing Association, ‘marketing is the process of planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion and distribution of ideas, goods and services to create exchanges that satisfy individual and organizational goals.
Marketing is defined as “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large”.
The term developed from the original meaning which referred literally to going to a market to buy or sell goods or services. Seen from a systems point of view, sales process engineering views marketing as “a set of processes that are interconnected and interdependent with other functions, whose methods can be improved using a variety of relatively new approaches.”
The Chartered Institute of Marketing defines marketing as “the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably”.
Marketing is used to create the customer, to keep the customer and to satisfy the customer. With the customer as the focus of its activities, it can be concluded that marketing management is one of the major components of business management. It is an integrated process through which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return.
Managerial Definition :
As a managerial definition, marketing is described as “the art of selling products”. But Peter Drucker, a leading management theorist, says that “the aim of marketing is to make selling superfluous. The aim of marketing is to know and understand the customer so well that the product or service fits him and sells itself. Ideally, marketing should result in a customer who is ready to buy”.
Traditional and Modern Concepts of Marketing :
Old or traditional concept of marketing was limited up to profit generation by high volume of sales and production of products at a large scale, how to distribute products from producers to customers in an efficient manner. Marketing activities were concentrated toward selling; later on with rise of competition marketers gave more emphasis to promotion activities to increase their market share and profitability. Salesmanship and product promotion were the main part of marketing policy of a business firm.
Modern concept has shifted from selling to customer satisfaction, modern marketing concept aim at how to understand a customer in a better way it is possible by exploring customer’s want and expectations and marketing behaviour. Products manufactured by firms should match with the demand and expectation of customers.
Under marketing concept a customer should be ready to buy the products on his own initiative, how to create demand in market by customer satisfaction is the main essence of modern concept. Now customer is well aware about his rights, quality and customer services, therefore marketing should be customer oriented, a strong communication network is needed to build high brand equity and goodwill in market.
Marketing is an important functional area of business which generates revenues through the sale of satisfying goods and services to the customers. It involves taking decisions in the areas of product, price, place and promotion keeping in view the requirements of the customers business. In this article, the nature of marketing management, implications of modern marketing concept, objectives of marketing, distinction between marketing and selling and also the tools of marketing mix.
Short Essay on Marketing – 4 (400 Words)
Marketing is the process by which companies determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development.
It is an integrated process through which companies create value for customers and build strong customer relationships in order to capture value from customers in return.
Marketing is used to identify the customer, to keep the customer and to satisfy the customer. With the customer as the focus of its activities, it can be concluded that marketing management is one of the major components of business management. The evolution of marketing was caused due to mature markets and overcapacities in the last 2-3 centuries. Companies then shifted the focus from production to the customer in order to stay profitable.
The term marketing concept holds that achieving organizational goals depends on knowing the needs and wants of target markets and delivering the desired satisfactions. It proposes that in order to satisfy its organizational objectives, an organization should anticipate the needs and wants of consumers and satisfy these more effectively than competitors.
Marketing is defined by the American Marketing Association AMA as “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.”
The Chartered Institute of Marketing defines marketing as “the management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably.” A different concept is the value-based marketing which states the role of marketing to contribute to increasing shareholder value.
In this context, marketing is defined as “the management process that seeks to maximise returns to shareholders by developing relationships with valued customers and creating a competitive advantage.”
Marketing practice tended to be seen as a creative industry in the past, which included advertising, distribution and selling. However, because the academic study of marketing makes extensive use of social sciences, psychology, sociology, mathematics, economics, anthropology and neuroscience, the profession is now widely recognized as a science, allowing numerous universities to offer Master-of-Science (MSc) programmes.
The overall process starts with marketing research and goes through market segmentation, business planning and execution, ending with pre and post-sales promotional activities. It is also related to many of the creative arts. The marketing literature is also adept at re-inventing itself and its vocabulary according to the times and the culture.
Essay on Marketing – 5 (1000 Words)
Marketing as a term is widely used in the management of a business and in our day- to-day life. In the era of customer and competition driven business world, marketing is not just the domain for the marketing department in a company. It’s a philosophy; it’s a business orientation now. It is imbibed in the corporate vision and mission of the successful companies.
All the successful companies in India like Tata, Reliance, Mahindra, Bharti Airtel, Maruti, Birla, Bajaj, Dabur, Patanjali etc., are thriving by understanding and delivering value to the Indian consumers to serve them in a better way than their competitors.
“Marketing is a process of exchange through which needs and wants are satisfied”, so can be the definition of markets given by Philip Kotler is paraphrased.
A better explanation can be given-
“Market is not merely spatial in nature; the buyers and sellers constitute the market, even though not face-to-face. Marketing involves not merely selling but reaching out customers to sell things they want. Thus product- mix, price-mix, distribution-mix and promotion-mix are the four corner stones of marketing. Even consumption patterns and the dictates of consumers are a part of the marketing strategy and then we have to include the policies relating to taxes and subsidies and/or regulations as they affect the product, price, distribution and promotion mixes.”
Another famous name in marketing Peter Drucker emphasized that marketing issues permeate all areas of the enterprise.
There are four most important aspects of marketing and they are:
1. Choosing the product mix;
2. Choosing the price mix;
3. Planning the distributional network; and
4. Market promotion.
These are also known as four Ps [product, price, place (distribution) and promotion], “Consumer is the king” (meaning consumer dictates and is always right) has given way to “consumer is the queen”, (meaning thereby that decision are taken by the lady of the house), are the sayings that give guidepost for developing marketing. There are firms, institutions, persons and governments involved in marketing. There are historical stages of marketing.
Rudimentary barter system is exchange of “commodities with commodities” (we should not call “goods” with “goods” from the “secondary/manufacturing” sector.) By the time there is trading in “goods”, barter system gets superseded. Rural marketing in India still has a good-sized component of the barter economy. Vegetables, edible oil, pulses, milk-products and food grains are taken and given in barter in rural areas.
Transitional stage and concurrent stage between barter and monetised exchange exists (as in India even in the 21st Century). As specialisation and industrial activities develop, barter gives way to exchange with money. However, rural areas continue to have barter transactions. (Some kabaadies in India who recycle the wastes of the households as non-functional fans, old newspapers to n number of things sometimes offer double trade e.g., give anything @ Rs. 15/- and make the payment adjusted against the junk that will be taken by them.
All types of modern markets with their spatial ramifications develop in the developing economy as in India.
Fully modern marketing system will have to satisfy two conditions:
1. There is no barter there, and
2. Even plastic money (credit/debit cards) is used.
Micro-management of marketing is not concerned with increasing the purchasing power.
Macro-management of marketing should aim at various things like:
1. Laying down rules and regulations for all types of marketing;
2. Selling “social marketing” of such ideas as of family planning and/or or advising persons how to save themselves from aids; or
3. Improving purchasing power or entitlements of all groups.
Marketing of primary, secondary and tertiary sector (services) follow one basic principle—how to optimise profits, if not maximise.
What is Marketing? – Definitions of Marketing:
The Chartered Institute of Marketing defines marketing as ‘The management process responsible for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably’
Oxford Dictionaries define Marketing ‘as the process of performing market research, selling products and /or services to customers and promoting them via advertising to further enhance sales.’
Kotler Philip, Gary Armstrong, Veronica Wong, and John Saunders are of the view that ‘Marketing as an integrated process through which companies build strong customer relationships and create value for their customers and for themselves.’ It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments.
Paliwoda, Stanley J and John K. Ryans believe in a different concept called the value-based marketing, which states the role of marketing to contribute to increasing shareholder value.
American Marketing Association’s (AMA) has defined as following:
‘Marketing is an organizational function and a set of processes for creating, communicating, and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.’
Above definition was applicable till Sept., 2007. Now with the ever changing business environment, the definition of Marketing also underwent a lot of change from Oct., 2007.
Now, AMA defines Marketing as:
‘Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.’
Marketing is not just an organizational function, but it is an activity and a set of institutions are involved. Now the customers, organisation and its stakeholders have also been rephrased as Customers, Clients, Partners and Society at large. Now Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is as important as Partner Relationship Management (PRM). Societal welfare is as important as the company’s welfare.
Panasonic’s ‘Eco Ideas’, Nokia’s ‘Take Back Campaign’, HP’s ‘Power to Change’ and Toyota’s initiative for Hybrid Green Vehicles are few examples of corporate initiative for the society at large.
Philip Kotler, a well-known authority on marketing has termed marketing as a ‘societal process by which individual and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and freely exchanging products and services of value with others.’ Marketing can also be said as the process of ‘satisfying needs and wants through an exchange process’.
In a simpler way, Kotler has defined Marketing in terms of CCDVTP, which means creating, communicating and delivering value to the target market at a profit.
Thus, Marketing is all about identifying and meeting human and social needs and that too in a profitable way. Ultimately, the objective of any business activity is to make profits.
On the whole, we can say that CCCCC STP PPPP encompasses all the aspects in marketing. Sounds confusing, let me clarify, Marketing is all about 5Cs, STP and 4Ps. 5Cs stands for Customers, Company, Competitors, Collaborators and Context. While STP stands for Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning; whereas 4Ps represent the Marketing Mix i.e. Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
Essay on Business Marketing – 6 (2500 Words)
Marketing plays a critical role in modern business practice, where maximizing shareholder value is an increasingly important goal. The essence of business marketing focuses on how firms attract, retain, grow customers — critical firm assets — by enhancing relationships with them.
Success in delivering customer value leads directly to improving shareholder value and long-run firm prosperity. In Essentials of Managing Marketing, we explore both the strategic aspects of marketing and the tactical implementation decisions marketers make every day. But first, we investigate two quite different but related meanings of marketing.
Marketing as a Philosophy embraces the view that marketing is the guiding force/orientation for the entire corporation. Firms with a marketing philosophy operate with an external orientation. Such firms focus attention, resources outside the corporation — to acquire, retain, grow customers — but take careful account of a range of external environmental forces.
By contrast, internally oriented firms focus on internal issues — products, services, processes. Essentials of Business Marketing embraces the marketing-as-philosophy perspective. The author believes, and has seen in his own career, how powerful and effective a business can be when the entire organization is attuned to the external world. Such agile firms not only sense critical environmental factors, but also adapt to address them.
Marketers must possess the tools/decision-making skills to get the marketing job done. Effective marketers focus on six marketing imperatives. Marketing Imperatives describe the specifics of the marketing job. For executives with marketing/ product-management titles, these imperatives are the must-dos of marketing.
We identify two groups:
1. Strategic Marketing:
Imperative 1-Determine, recommend which markets to address.
Imperative 2- Identify, target market segments.
Imperative 3- Set strategic direction, positioning.
2. Implementing Market Strategy:
Imperative 1- Design the market offer.
Imperative 2- Secure support from other functions.
Imperative 3- Monitor and control execution/ performance.
To broaden this framework, four marketing principles form the basis for marketing decision-making.
These principles act as guidelines for executing the six imperatives:
Principle 1- Selectivity, Concentration
Principle 2- Customer Value
Principle 3- Differential Advantage
Principle 4- Integration
What is Marketing?
Marketing is often confused with advertising and sales. Even many executives are unclear. It seems so intuitive; can’t anybody be a marketer? Marketing is the firm’s fundamental activity. When marketing delivers value to satisfy customer needs, the firm attracts, retains, grows customers, in the face of competitors trying to do the same thing. If costs are in line, profits follow. Profits help the firm survive as an independent entity, secure resources to grow, enhance shareholder value.
Business Marketing’s role includes identifying opportunities; figuring out customer needs; understanding competition; developing appealing products/services; communicating/distributing value to potential customers. When the firm does a good job of completing these tasks, shareholder value increases. Example- Flipkart — successful e-commerce firm — co-founder Sachin Bansal emphasizes that focus on customer satisfaction and owning the entire customer experience has benefited his firm.
The critical weapon in the battle for customers is straightforward in concept, but may be complex/ difficult in execution. The firm must deliver customers greater value than competitors deliver. Customers reward such firms by purchasing their products/services, today and tomorrow. This exchange is the basis of all markets.
The late Peter Drucker, preeminent management theorist, is generally credited with developing the customer orientation and modern marketing perspective. Drucker stated, “If we want to know what a business is, we have to start with its purpose. There is only one valid definition of any business purpose — to create a customer. It is the customer who determines what a business is.
For it is the customer, and he alone, who through being willing to pay for a good or service, converts economic resources into wealth, things into goods…. Because it is [the purpose of a business] to create a customer, [the] business enterprise has two — and only these two — basic functions- marketing and innovation.”‘
Business Marketing and Shareholder Value :
The central focus on shareholder value is deeply rooted in many capitalist countries. The shareholder- value perspective defines managements job as maximizing returns for firm owners — shareholders.
In addition to shareholders, the firm has many other stakeholders — management, labor, public at large. In some capitalist countries, these stakeholders are more favored than shareholders. Indeed, in these countries regulations generally favor managers, and protect them from unwelcome mergers/acquisitions. Regardless, in recent years, developing global capital markets have favored the shareholder-value perspective.
Customers are the sole source of firm revenues; all firm activities are costs of attracting, retaining, growing customers. Unfortunately, managers sometimes forget this fundamental truth. Customers provide revenues/cash flow when they believe firm products/services offer better value than competitive alternatives.
Marketing as a Philosophy- External, Internal Orientations :
The firm enhances shareholder value by attracting, retaining, growing customers. At a philosophical level, each employee has some responsibility; marketing is everybody’s business.
To quote Drucker again, “Marketing is so basic that it cannot be considered a separate function within the business … it is, first, a central dimension of the entire business. It is the whole business … seen from the customers point of view. Concern and responsibility for marketing must, therefore, permeate all areas of the enterprise.”
David Haines, former brand czar at Vodafone, echoed Drucker- “Marketing is too important to be left to the marketers. It’s the obligation of every single individual in the company, whether you’re a phone operator, the CEO, or anyone else in the company.” To put it more crassly- If marketing is unsuccessful, nobody gets a paycheck!
Marketing as a philosophy concerns the firms entire orientation; such firms operate with an external orientation. The externally oriented firm looks outward to the environment; it knows that customers are central to its future. Other firms focusing on internal business drivers have one of several internal orientations-, delivering customer value takes a back seat.
i. External Orientation:
The externally oriented firm knows its current products/services/processes are the reasons for past/ present success. This firm also knows that, as the external environment evolves, its products/services/ processes must also change. The externally oriented does not fear change. This firm goes beyond a customer focus; it works hard to understand competitors markets, other environmental forces. This firm invests in new capabilities/competencies to exploit opportunities for attracting, retaining, growing customers. P&G spends over $400 million annually seeking customer/market insight.
In difficult economic times, when profits are under pressure, many firms cut spending/investment; but the externally oriented firm increases investments — human capital, marketing budgets, mergers, acquisitions. Example- In recent recessions, Amazon, Cisco, Coca-Cola, Intel, Tata Consultancy Services invested heavily; they swept past more internally oriented competitors.
ii. Internal Orientations :
Internally oriented firms place internal business considerations ahead of customer focus.
The orientations are:
1. Operations Orientation:
It overemphasizes improving efficiency, reducing costs. There is nothing inherently wrong with such actions; by contrast, cost reduction should not be a priority when the firm offers new products/services, enters new markets, or otherwise should invest to attract, retain, grow customers.
2. Sales Orientation:
It focuses on short-term sales revenues. The firm is less concerned with profits. Characteristic actions to secure sales- Prices set too low, unsustainable discounts, loose credit terms, excessive product variations. The firm spends little effort on marketing research, planning; targets customers indiscriminately.
3. Finance Orientation:
It focuses too heavily on short-term profits. When a firm manages by the numbers, it tends to avoid expenditures for long- term payoff. The finance-oriented firm mortgages its future by indiscriminately cutting back — advertising, capital investment, R&D, talent.
4. Technology Orientation:
It focuses on R&D, but pays insufficient attention to customer value. First- class products are critical for attracting, retaining, growing customers, but for this firm technology is more important than customers.
The Six Marketing Imperatives :
The job of putting the firms marketing philosophy into practice normally falls to marketing professionals. These people engage in many activities; they must make decisions on how to allocate their time/other resources.
The critical question- Are we doing the right things to attract, retain, grow customers? Put another way- Are we implementing the six marketing imperatives — the firm’s must-dos. Imperatives 1, 2, 3 focus on strategic marketing; imperatives 4, 5, 6 zero in on implementing market strategy.
Imperative 1- Determine, Recommend Which Markets to Address :
The firm must answer critical questions about its business, market portfolios:
i. In which new businesses/markets shall we invest — people, time, dollars?
ii. From which businesses/markets shall we withdraw?
iii. In which current businesses/markets shall we continue to invest?
iv. How much investment shall we make in these various businesses/markets?
Marketing plays two key advisory roles. First, identify opportunities. Marketing is the only function with explicit responsibility to focus attention externally on the market, customers, competitors — outside the firm. Marketing personnel should research the environment to identify potential opportunities, then bring these to top management for go/no-go decisions.
Second, advise on proposed strategic actions. Many parts of the firm develop strategic initiatives. Marketing has the responsibility to insert itself into key decisions — collecting, analyzing relevant data — bearing on market entry/exit. Marketing should fully explore the ramifications of potential firm actions, or disaster may ensue.
Imperative 2- Identify, Target Market Segments :
Marketing must identify market segments — groups of customers with similar needs that value similar benefits with similar priority orders. Once the firm has identified market segments, it must decide which to target for effort. Effective segmentation and targeting are critical for delivering customer value and driving sales, profits.
Imperative 3- Set Strategic Direction, Positioning :
The firm decides how to compete in those market segments it has targeted. For each target segment, marketing must formulate performance objectives, then decide on firm positioning in each segment — target customers, target competitors, value proposition, reasons to believe. Together with Marketing Imperative 2, positioning completes the STP triumvirate — segmentation, targeting, positioning.
Typically, individual market segments are at different developmental stages; hence they require different approaches. Finally, decisions about strategic direction must include questions about branding. The firm must continually assess strategic direction and make necessary course corrections.
Imperative 4- Design the Market Offer :
The market offer is the total benefit package the firm provides customers. Tools for designing offers are the most well-known part of marketing.
The marketing-mix elements — aka 4Ps — comprise the basic building blocks:
i. Product:
Generally, the product embodies major benefits the firm offers to satisfy customer needs — these benefits provide customer value. Product comprises both physical products and intangible services.
ii. Promotion:
Embraces various ways the firm communicates with customers — informing, persuading customers to purchase (or recommend) its products. Core promotional elements include mass communications — advertising, publicity & public relations; digital marketing; personal communications — sales force.
iii. Distribution:
Focuses on how, where customers secure the product (aka place).
The firm establishes its feasible price by the equivalent amount of value it offers customers via product, promotion, distribution.
Imperative 5- Secure Support from Other Functions :
Functional areas must work together to ensure the firm designs and executes the right market offer.
Business marketing requires two very different types of support:
i. Support for design — relates to technical, operational, economic feasibility. This support requires keeping the firm focused on satisfying customer needs and pushing specific functions to encourage evolving their capabilities.
ii. Support for implementation — assumes the firm has agreed upon/fixed the design. Marketers must possess the leadership/interpersonal skills to secure cooperation across multiple functions — internal marketing, getting buy-in.
Imperative 6- Monitor and Control Execution/Performance :
Is the firm achieving desired results? If results are not on track, what changes should the firm make?
Marketing is a key stakeholder in securing answers to three questions; it should act appropriately based on the answers:
i. Are various functions/departments implementing the market offer?
ii. Is market/financial performance reaching planned objectives?
iii. Based on current environmental realities, are objectives, strategies, implementation plans on track? Should the firm make changes?
Four marketing principles serve as guidelines for executing the six imperatives:
Principle 1- Selectivity, Concentration :
Providing advice on market selection — Imperative 1 — and deciding which market segments to target — Imperative 2 — are among marketing’s primary responsibilities.
Underlying these imperatives is the-
i. Selectivity- Carefully choose targets for firm efforts.
ii. Concentration- Concentrate resources against those targets.
This principle is about choosing the firm’s battles. It is dangerous to dissipate limited resources over too many alternatives by trying to do too much. No organization, no matter how large or how successful, has infinite resources.
Some experts re-label this principle Concentration and Concession. Not only must the firm concentrate resources, it should affirmatively decide where it does not want to compete.
Principle 2- Customer Value :
Market success depends on providing value to customers. This principle is central to the marketing job. Customer insight should drive design, implementation of market offers, product/investment decisions, and performance evaluations. The firm develops, produces, delivers products/services, but customers perceive value only in the benefits these products/ services provide.
Customer value is a moving target. As the environment evolves, customers accumulate experience; the needs and benefits they seek evolve also. World-class companies continuously invest in marketing research to probe deeply into customer needs, priorities, expectations, and experiences. They feed these results into the product development process to generate greater value for customers.
Firms that take their eye off the customer ball can get into serious trouble. Shoppers Stop, Aditya Birla Retail, Reliance Retail have closed many unprofitable stores in recent years.
Principle 3- Differential Advantage :
Closely related to the Principle of Customer Value; differential advantage lies at the heart of every successful market strategy —the firm should offer customers something they value, but cannot get elsewhere. Differential advantage is similar to competitive advantage, unique selling proposition, having an edge.
To implement this principle, the firm must develop well-designed market offers, based on the marketing-mix elements, and secure buy-in from other functions.
i. Competition:
Offering customer value is not enough. To avoid competitive parity, the firm must offer greater value than competitors. The firm must create/recreate differential advantage to beat competitors.
ii. Superiority:
Some differential advantages are better than others. Differential advantage based on proprietary intellectual property, unique product design, product availability may be more sustainable than differential advantage based on communications.
A differential advantage based on an organizational process like parts delivery, qualified technicians may be even more sustainable.
iii. Erosion:
Competition will eventually erode even the apparently most sustainable differential advantage. Maintaining differential advantage is marketing’s most fundamental challenge; the search for differential advantage must be continuous.
iv. Cannibalization:
To stay ahead of competition, the firm must be willing to cannibalize its own offers. Many firms will not do so — in part because of strong political constituencies for the status quo; in part because profit margins may be lower. Such unwillingness to act runs the risk of missing opportunities, passing market initiative to a competitor.
v. Differential Advantage and Difference:
A differential advantage is not the same as a difference. Developing a different market offer may not be difficult. Differential advantage must create benefits/values customers recognize, and are willing to pay for.
Principle 4- Integration :
This principle has two dimensions:
i. Customer:
The firm must carefully integrate and coordinate all design and execution elements it offers customers. Poor advertising can ruin an excellent product; delayed promotional materials can doom product launch; improper pricing can cause havoc with sales forecasts.
The firm must carefully integrate/coordinate all internal activities. Different functions/departments must work together; they must avoid squabbles over priorities, turf wars, ambiguous messages by senior managers. Firms with an external orientation are more likely to achieve integration; employees, departments, businesses share a common purpose — serving customers. Sharing responsibility for designing, implementing market offers drives agreement on priorities and close/cooperative working relationships.
Essay on Marketing Topics – 7 (1900 Words)
Marketing refers to a social process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating, offering and exchanging products and services of value freely with others. It is the sum-total of all the activities that facilitate flow of goods and services from producers to the ultimate consumers.
In simple words, marketing involves study and management of exchange relationships. It is used as a tool by business to create the customer, to keep the customer and to satisfy the customer.
Marketing is concerned with all the activities of a company which are associated with buying and selling of a good or a service. It involves activities that aim at making people aware of the company’s goods or services and making sure that these are available to be bought and availed respectively.
Marketers are involved in marketing various types of entities like goods, services, experiences, events, persons, places, properties, organisations, information and ideas. Marketing is an ongoing communication exchange with customers in a way that educates, informs and builds a relationship over time.
It is the process by which a firm profitably translates customers’ needs into revenue. It also involves building a brand and convincing people that a particular brand is the best.
It aims at satisfying the needs and wants of the customers and thereby retaining them for the longest possible period of time. Marketing attracts consumers’ scarce resources, attention and disposable income to derive profitable revenues.
It is the process of getting a product or service from a company to its end-customers from product development through to the final sale and post purchase support.
Essay Topic # 1. Definition of Marketing:
Some Important Definitions of Marketing:
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions and processes for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners and society at large. —American Marketing Association (AMA)
Marketing is the science and art of exploring, creating and delivering value to satisfy the needs of a target market at a profit. Marketing identifies unfulfilled needs and desires. If defines, measures and quantifies the size of the identified market and the profit potential. It pinpoints which segments the company is capable of serving best, and it designs and promotes the appropriate products and services. —Philip Kotler
Marketing is a management activity that identifies, anticipates and satisfies customer requirements efficiently and profitably. —Mark Gwilliam
Marketing is the management process for identifying, anticipating and satisfying customer requirements profitably. —Chartered Institute of Marketing
Marketing is the business process by which products are matched with the markets and through which transfers of ownership are affected. —F.E.Clark
Marketing is that phase of business activity through which the human wants are satisfied by the exchange of goods and services. — J.F.Pyle
Marketing is the social process by which individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creating and exchanging products and value with others. — Philip Kotler
Essay Topic # 2. Nature of Marketing:
(i) Customer Focused – All marketing activities should be customer oriented. They should start with identifying the customer’s needs, followed by developing products, pricing it, promoting it and distributing it as per the customer’s requirements.
(ii) Integrated Process – Being an integrated process, marketing involves coordination of many activities with other business functions like production, personnel, financing, research and development.
(iii) Multi-Disciplinary – Marketing is multi-disciplinary as it has evolved out of commerce and has got its strength from law, psychology, sociology, mathematics and statistics. It is an art as well as a science.
(iv) Interaction with External Environment – It operates within the framework of external environment which comprises of economic, natural, social, legal, political environment etc.
(v) Mutually Beneficial Exchange – It means buyers get want-satisfying goods and sellers get value in exchange of their goods leading to mutual benefit to both the parties.
(vi) Based on System Approach – It is based on system approach as it requires intelligent coordination of four ‘P’s of marketing mix. These are Product, Price, Place and Promotion.
Essay Topic # 3. Importance of Marketing:
(i) It is the beating heart of a business organization – Being the revenue producing department, it is a very important function of management.
(ii) It facilitates creation of place, time and possession utility – As creating these utilities help a marketer to achieve success in the business.
(iii) It helps in improving the standard of living of the people – This is done by offering wide variety of goods and services to the people.
(iv) It generates employment – A large number of people are employed by marketers to carry out various functions of marketing.
(v) It leads to economic development of the nation – It mobilises untapped resources and facilitates full utilisation of production capacity and other assets and hence leads to economic development of the nation.
Essay Topic # 4. Modern Marketing:
The Present Day Marketing is Customer Driven:
Business must find out what the consumers want and then produce goods according to the needs of the consumers. What is offered for sale should be determined by the buyer rather than by the seller. Instead of trying to market (sell) what is easiest for us to make, we must find out much more about what the consumer is willing to buy.
Under consumer-oriented marketing it is highly essential to know what the consumers really want. This is possible only when information is collected from the consumers.
Marketing research and Marketing Information Systems are now-a-days full-fledged functions of marketing. All organisations accept that the marketing activities must start far ahead of production. The company must appreciate and understand the consumers’ strategic position as a determinant of the firm’s survival and growth.
This philosophy of marketing means that the entire marketing is designed to serve consumer needs. The marketing man is introduced at the beginning rather than at the end of the production cycle and marketing is integrated at each phase of the business.
Thus, Marketing, through its studies and research will determine for the engineer, designer and the manufacturing manager, what the consumer wants in a given product, what price he is willing to pay and where and when it will be wanted. The launch of the ‘Nano’, a small car for the common man of India at an affordable price is a glaring example of this statement, i.e., the present day marketing is customer driven.
Marketing Begins before Production and Continues after Sale:
Marketing is an organizational function which includes a set of processes for creating, communicating and delivering value to customers and for managing customer relationships in ways that benefit the organization and its stakeholders.
By stating definition of marketing itself, it becomes clear that marketing also deals with the creation of a product. It is done by means of proactive marketing, i.e., focussing on customers’ latent needs. For this the process of Marketing Research is applied. These days the companies’ strategies have shifted from “make-and-sell” philosophy to “sense-and-respond” philosophy.
In order to identify the needs of customers various surveys are conducted, pilot studies are done. The respondents are not just prospective customers but also front line executives, since they know a lot about the needs of customers.
At each stage of new product development, marketing has a key role to play.
Marketing after sales – Making a new customer is costlier than retaining an old one. Therefore, it is necessary to keep the customers not only satisfied, but rather delighted. This can be done through customer relationship management, where marketers can offer to provide after sales-services, warranties, guarantees, product resale offers, discounts on next purchase etc.
Marketing Creates Value for Customers and Builds Profitable Customer Relationships and Captures Value from Customers in Return:
“Marketing creates value for customers and builds profitable customer relationships and captures value from customers in return.” This statement very aptly describes the essence of marketing in modern scenario. It is a two way process of creating value for customers by offering high quality products in exchange of a price which acts as value from the customers.
It is a mutual beneficial activity where focus is on building and maintaining long-term profitable customer relationships. Today’s successful companies are strongly customer focussed and heavily committed to marketing. They share passion for understanding and satisfying customers’ wants and make a sincere effort to provide solutions by coming out with innovative products.
For example – Procter & Gamble, one of the world’s largest and most respected marketing company creates value for customers by offering innovative products like Tide, Pantene, Gillette, etc. which are widely accepted by customers and in return Procter & Gamble gets rewarded with brand loyal customers.
Similarly, Philips is another company which is always striving to come out with novel solutions for existing problems and produces high quality innovative products like ‘Air Fryer’, ‘Electric Shaver’, etc. They too are rewarded by customers in return with strong loyalty and quick purchases of their products.
Modern Marketing is an Integrated Process of Identification, Assessment and Satisfaction of Human Wants:
The modern marketing concept enunciates that business is essentially a ‘need-satisfying process’ and that any business must be managed keeping the consumer and his needs as the main focus.
All goals of business including profit must be realised through consumer orientation, integrated management action and generation of consumer satisfaction. Matching products with the market implies determining the requirements of potential customers and designing products that satisfy these requirements.
Thus, modern marketing is the integrated process of identification, assessment and satisfaction of human wants. The focus is on the customer and his wants. It is the process of discovering and translating consumer wants into products and services and then in turn making it possible for more and more people to enjoy more and more of these products and services.
Concern for customers’ needs and wants increases the acceptability of the product. When a firm produces the product which meets the requirements of the customers, the need for promotion is reduced. It ensures continuous patronage of customers.
Unification of business activities leads to economy and efficiency in marketing operations. The systems approach to marketing facilitates a rational analysis of all marketing problems along with their effective solutions.
It helps the management to direct organisational effort towards the long-term and wider goals like stability and growth of the firm. Sustained interaction with customers becomes possible.
It is the management orientation that holds that the key task of the organisation is to determine the needs, wants and values of a target market and to adapt the organisation to deliver the desired satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than its competitors.
Thus, modern marketing is an integrated process of identification, assessment and satisfaction of human wants.
Modern Marketing Concept is Applicable to All Business Organisations Irrespective of their Size, Nature or Functionality:
The adoption and use of modern marketing concepts have various benefits for any company irrespective of their size, nature or functionality.
Some of the benefits are listed below:
(i) Concern for customers’ needs and wants rather than itself product increases the acceptability of the product.
(ii) Marketing concept requires an integrated and coordinated approach to marketing. Hence all the business activities are focussed towards a single organisational goal.
(iii) Marketing concept is a system approach to marketing. It facilitates a rational analysis of all marketing problems along with their effective solution.
(iv) A business firm pursuing Marketing concept can respond effectively to the changes occurring in the marketing environment.
(v) Marketing concept has a strategic and philosophical value. It helps the management to direct organisational efforts towards long term and wider goals.
Related Articles:
- Essay on International Marketing
- Essay on Marketing Environment | Company
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Marketing?
Understanding marketing.
- What Are the 4 P's of Marketing?
Types of Marketing Strategies
- Limitations
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Ariel Courage is an experienced editor, researcher, and former fact-checker. She has performed editing and fact-checking work for several leading finance publications, including The Motley Fool and Passport to Wall Street.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ArielCourage-50e270c152b046738d83fb7355117d67.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained CURRENT ARTICLE
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Investopedia / Lara Antal
Marketing refers to the activities a company undertakes to promote the buying or selling of its products or services. Marketing includes advertising and allows businesses to sell products and services to consumers, other businesses, and organizations.
Professionals who work in a corporation's marketing and promotion departments seek to get the attention of key potential audiences through advertising. Promotions are targeted to certain audiences and may involve celebrity endorsements , catchy phrases or slogans, memorable packaging or graphic designs, and overall media exposure.
Key Takeaways
- Marketing refers to all activities a company does to promote and sell products or services to consumers.
- Marketing makes use of the "marketing mix," also known as the four Ps—product, price, place, and promotion.
- Marketing used to be centered around traditional marketing techniques including television, radio, mail, and word-of-mouth strategies.
- Though traditional marketing is still prevalent, digital marketing now allows companies to engage in newsletter, social media, affiliate, and content marketing strategies.
- At its core, marketing seeks to take a product or service, identify its ideal customers, and draw the customers' attention to the product or service available.
Marketing as a discipline involves all the actions a company undertakes to draw in customers and maintain relationships with them. Networking with potential or past clients is part of the work too and may include writing thank you emails, playing golf with prospective clients, returning calls and emails quickly, and meeting with clients for coffee or a meal.
At its most basic level, marketing seeks to match a company's products and services to customers who want access to those products. Matching products to customers ultimately ensures profitability.
Formal Definition:
"Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. " —Official definition from the American Marketing Association, approved 2017.
What Are the 4 P's of Marketing?
Product, price, place, and promotion are the Four Ps of marketing. The Four Ps collectively make up the essential mix a company needs to market a product or service. Neil Borden popularized the idea of the marketing mix and the concept of the Four Ps in the 1950s.
Product refers to an item or items the business plans to offer to customers. The product should seek to fulfill an absence in the market or fulfill consumer demand for a greater amount of a product already available. Before they can prepare an appropriate campaign, marketers need to understand what product is being sold, how it stands out from its competitors, whether the product can also be paired with a secondary product or product line , and whether there are substitute products in the market.
Price refers to how much the company will sell the product for. When establishing a price, companies must consider the unit cost price, marketing costs, and distribution expenses. Companies must also consider the price of competing products in the marketplace and whether their proposed price point is sufficient to represent a reasonable alternative for consumers.
Place refers to the distribution of the product. Key considerations include whether the company will sell the product through a physical storefront, online, or through both distribution channels. When it's sold in a storefront, what kind of physical product placement does it get? When it's sold online, what kind of digital product placement does it get?
Promotion, the fourth P, is the integrated marketing communications campaign. Promotion includes a variety of activities such as advertising , selling, sales promotions, public relations, direct marketing, sponsorship, and guerrilla marketing .
Promotions vary depending on what stage of the product life cycle the product is in. Marketers understand that consumers associate a product’s price and distribution with its quality, and they take this into account when devising the overall marketing strategy.
Marketing refers to any activities undertaken by a company to promote the buying or selling of a service. If there is a limited quantity of a product, a company may market itself in an attempt to be better positioned as one of the few who get to buy something.
Marketing is comprised of an incredibly broad and diverse set of strategies. The industry continues to evolve, and the strategies below may be better suited for some companies over others.
Traditional Marketing Strategies
Before technology and the Internet, traditional marketing was the primary way companies would market their goods to customers. The main types of traditional marketing strategies include:
- Outdoor Marketing: This entails public displays of advertising external to a consumer's house. This includes billboards, printed advertisements on benches, sticker wraps on vehicles, or advertisements on public transit.
- Print Marketing: This entails small, easily printed content that is easy to replicate. Traditionally, companies often mass-produced printed materials, as the printed content was the same for all customers. Today, more flexibility in printing processes means that materials can be differentiated.
- Direct Marketing : This entails specific content delivered to potential customers. Some print marketing content could be mailed. Otherwise, direct marketing mediums could include coupons, vouchers for free goods, or pamphlets.
- Electronic Marketing: This entails the use of TV and radio for advertising. Through short bursts of digital content, a company can convey information to a customer through visual or auditory media that may grab a viewer's attention better than a printed form.
- Event Marketing: This entails attempting to gather potential customers at a specific location for the opportunity to speak with them about products or demonstrate products. This includes conferences, trade shows, seminars, roadshows , or private events.
Digital Marketing
The marketing industry has been forever changed with the introduction of digital marketing. From the early days of pop-up ads to targeted placements based on viewing history, there are now innovative ways companies can reach customers through digital marketing.
- Search Engine Marketing: This entails companies attempting to increase search traffic through two ways. First, companies can pay search engines for placement on result pages. Second, companies can emphasize search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to organically place high on search results.
- E-mail Marketing: This entails companies obtaining customer or potential customer e-mail addresses and distributing messages or newsletters. These messages can include coupons, discount opportunities, or advance notice of upcoming sales.
- Social Media Marketing: This entails building an online presence on specific social media platforms. Like search engine marketing, companies can place paid advertisements to bypass algorithms and obtain a higher chance of being seen by viewers. Otherwise, a company can attempt to organically grow by posting content, interacting with followers, or uploading media like photos and videos.
- Affiliate Marketing: This entails using third-party advertising to drive customer interest. Often, an affiliate that will get a commission from a sale will do affiliate marketing as the third party is incentivized to drive a sale for a good that is not their own original product.
- Content Marketing: This entails creating content, whether eBooks, infographics, video seminars, or other downloadable content. The goal is to create a product (often free) to share information about a product, obtain customer information, and encourage customers to continue with the company beyond the content.
In 1978, Gary Thuerk sent a message to roughly 400 people using ARPANET, the first public packet-switched computer network. With that message, the first ever recorded spam e-mail message had been sent.
What Are the Benefits of Marketing?
Well-defined marketing strategies can benefit a company in several ways. It may be challenging to develop the right strategy or execute the plan; when done well, marketing can yield the following results:
- Audience Generation. Marketing allows a company to target specific people it believes will benefit from its product or service. Sometimes, people know they have the need. Other times, they don't realize it. Marketing enables a company to connect with a cohort of people that fit the demographic of whom the company aims to serve.
- Inward Education. Marketing is useful for collecting information to be processed internally to drive success. For example, consider market research that finds a certain product is primarily purchased by women aged 18 to 34 years old. By collecting this information, a company can better understand how to cater to this demographic, drive sales, and be more efficient with resources.
- Outward Education. Marketing can also be used to communicate with the world what your company does, what products you sell, and how your company can enrich the lives of others. Campaigns can be educational, informing those outside of your company why they need your product. In addition, marketing campaigns let a company introduce itself, its history, its owners, and its motivation for being the company it is.
- Brand Creation. Marketing allows for a company to take an offensive approach to creating a brand. Instead of a customer shaping their opinion of a company based on their interactions, a company can preemptively engage a customer with specific content or media to drive certain emotions or reactions. This allows a company to shape its image before the customer has ever interacted with its products.
- Long-lasting. Marketing campaigns done right can have a long-lasting impact on customers. Consider Poppin' Fresh, also known as the Pillsbury Doughboy. First appearing in 1965, the mascot has helped create a long-lasting, warm, friendly brand for Pillsbury.
- Financial Performance. The ultimate goal and benefit of marketing are to drive sales. When relationships with customers are stronger, well-defined, and positive, customers are more likely to engage in sales. When marketing is done right, customers turn to your company, and you gain a competitive advantage over your competitors. Even if both products are exactly the same, marketing can create that competitive advantage for why a client picks you over someone else.
According to MarTech, a digital marketing provider, the world will spend $4.7 trillion on marketing by 2025. This estimate includes an increase of $1.1 trillion from 2021 to 2025.
What Are the Limitations of Marketing?
Though there are many reasons a company embarks on marketing campaigns, there are several limitations to the industry.
- Oversaturation. Every company wants customers to buy its product and not its competitors. Therefore, marketing channels can be competitive as companies strive to garner more positive attention and recognition. If too many companies are competing, a customer's attention may be strongly diluted, resulting in any form of advertising not being effective.
- Devaluation. When a company promotes a price discount or sale, the public may psychologically eventually see that product as worth less in the future. If a campaign is so strong, customers may even wait to purchase a good knowing or remembering what the sale price was from before. For example, some may intentionally hold off buying goods if Black Friday is approaching.
- No Guaranteed Success. Marketing campaigns may incur upfront expenses that hold no promise of future success. This is also true of market research studies, where time, effort, and resources are poured into a study that may yield no usable or helpful results.
- Customer Bias. Loyal, long-time customers need no enticing to buy a company's brand or product. However, newer, uninitiated customers may. Marketing naturally is biased towards non-loyal patrons as those who already support the company would be better served by further investment in product improvement.
- Cost. Marketing campaigns may be expensive. Digital marketing campaigns may be labor-intensive to set up and costly to maintain the scheduling, implementation, and execution of the plan. Don't forget about the headlines that promote Super Bowl commercial expenses in the millions.
- Economy-Dependent. Marketing is most successful when people have capital to spend. Though marketing can create non-financial benefits such as brand loyalty and product recognition, the ultimate goal is to drive sales. During unfavorable macroeconomic conditions when unemployment is high or recession concerns are elevated, consumers may be less likely to spend no matter how great a marketing campaign may be.
Marketing is a division of a company, product line, individual, or entity that promotes its service. Marketing attempts to encourage market participants to buy their product and commit loyalty to a specific company .
Why Is Marketing So Important?
Marketing is important for a few reasons. First, marketing campaigns may be the first time a customer interacts or is exposed to a company's product. A company has the opportunity to educate, promote, and encourage potential buyers.
Marketing also helps shape the brand image a company wants to convey. For example, an outdoor camping gear company that wants to be known for its rugged, tough goods can embark on specific campaigns that embody these traits and make these emotions memorable to prospective customers.
What Is the Purpose of Marketing?
An important goal of marketing is propelling a company’s growth. This can be seen through attracting and retaining new customers.
Companies may apply many different marketing strategies to achieve these goals. For instance, matching products with customers' needs could involve personalization, prediction, and essentially knowing the right problem to solve.
Another strategy is creating value through the customer experience. This is demonstrated through efforts to elevate customer satisfaction and remove any difficulties with the product or service.
What Are the 4 Ps of Marketing?
A commonly used concept in the marketing field, the Four Ps of marketing looks at four key elements of a marketing strategy. The Four Ps consist of product, price, place, and promotion.
What Are the Types of Marketing?
There are dozens of types of marketing, and the types have proliferated with the introduction and rise of social media, mobile platforms, and technological advancements. Before technology, marketing might have been geared towards mail campaigns, word-of-mouth campaigns, billboards, delivery of sample products, TV commercials, or telemarketing. Now, marketing encompasses social media, targeted ads, e-mail marketing, inbound marketing to attract web traffic, and more.
Marketing is an essential part of any business. It allows for a business's products or services to be known to consumers and it helps entice consumers to buy its product over a competitor's. Though marketing costs a significant amount of money, companies create marketing budgets as a part of expenses in the hope that sales and profits will outweigh the marketing costs.
American Marketing Association. " What Is Marketing? "
World Economic Forum. " 40 Years On From the First Spam E-mail, What Have We Learned? "
Pillsbury. " How Well Do You Know the Pillsbury Doughboy? "
MarTech. " Worldwide Spend on Marketing to Hit $4.7 Trillion By 2025 ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/clickbank-5bfc37da46e0fb0051c11e27.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
1.1 Marketing and the Marketing Process
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- 1 Define and describe marketing.
- 2 Describe the benefits of marketing to the organization, its interested parties, and society.
- 3 Explain the marketing process.
Marketing Defined
When you ask a group of people, “What’s marketing?” most people will answer “advertising” or “selling.” It’s true that both of these functions are part of marketing, but marketing is also so much more. The American Marketing Association (AMA) defines marketing as “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.” 6 That’s kind of a mouthful, so let’s see if we can simplify it a bit.
At its most basic level, marketing is made up of every process involved in moving a product or service from the organization to the consumer. It includes discerning the needs of customers, developing products or services to meet those needs, identifying who is likely to purchase the products or services, promoting them, and moving them through the appropriate distribution channels to reach those customers. Marketing, quite simply, is about understanding what your customers want and using that understanding to drive the business.
Marketing can also be defined as the set of activities involved in identifying and anticipating customer needs and then attempting to satisfy those needs profitably. 7 But what does that really mean? Let’s break down that definition:
- Identifying customer needs . This is typically where marketing research comes in. Methods of marketing research will be covered in a later chapter, but market research helps a company develop a detailed picture of its customers, including a clear understanding of their wants and needs.
- Anticipating customer needs . After analyzing the data collected, marketers can predict how products might be changed, adapted, or updated.
- Satisfying customer needs . If marketers have done their homework correctly and clearly understand their customers’ needs, consumers will be pleased with their product purchase and will be more likely to make additional purchases.
- Profitably . Profitability is a relatively simple term; it’s when a company’s revenue is greater than its expenses. In terms of marketing, the road to profitability means adding value to a product so that the price customers pay is greater than the cost of making the product. 8
Marketing in Practice
Reconciling segmentation and diversity.
We live in a multicultural world where diversity, equity, inclusion, and belonging (DEIB) is no longer the “right” thing to do; rather, it’s imperative. This is particularly true in marketing, because as the consumer population diversifies, brands have to authentically reflect a wide range of backgrounds and life experiences in order to effectively connect with consumers. Therefore, marketers must increasingly respect individual preferences, celebrate differences, and promote customization of products and services to meet customers’ needs, wants, and preferences.
At the same time, to profitably produce and sell a viable product or service, marketers must identify potential customer groups and types with certain characteristics in common—i.e., market segmentation. Segmentation requires assigning individuals to predefined categories with predictable behaviors, based on standardized assumptions.
How does segmentation differ from stereotyping? How can segmentation support diversity?
Read the following articles to further explore these nuances:
- Chron: “ Difference Between Stereotyping & Market Segmentation ”
- Retail Dive: “ Segmentation is dead !”
- Spectrem Group Blog: “ Why Segmentation Is OK in Market Research Not Life ”
Keep these questions in mind as you explore Unit 2 of this book, where you will learn more about Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning before exploring the considerations of Marketing in a Diverse Marketplace .
How Marketing Benefits the Organization, Its Interested Parties, and Society
Before we go on, let’s consider all the people and groups that an organization needs to consider and serve. Interested parties are those persons or entities that have an interest in the success or failure of a company. These parties can be categorized into two types: internal and external, as shown in Figure 1.2 . You may see these people and groups referred to as “stakeholders” in business writing and other media.
Internal interested parties are entities that reside within the organization and that affect—or are affected by—the actions of the company. These entities include employees, owners, managers, and investors (shareholders). When we think about marketing, marketers often tend to look outward. They build strategies to engage customers and show them what the company has to offer.
You might think that marketing would be primarily directed toward those outside the company, like customers, but marketing is also directed toward internal groups. Internal marketing involves promoting the objectives, products, and services of a company to its internal constituents—particularly employees. 9
Think about a recent interaction you have had with a business employee. It could be the server who took your order at lunch or the sales associate at a big box store who showed you the features of the new laptop you were looking to purchase. Which interactions left you with a positive experience? Chances are that your evaluation of the experience is based on the interaction you had with the server or sales associate. That’s a function and benefit of good internal marketing, employees who are motivated and empowered to deliver a satisfying customer experience.
External interested parties include those outside the company, such as customers, creditors, suppliers, distributors, and even society at large. External groups don’t have a direct say in the company’s decision-making process. However they are vital to the success of the company because companies can only succeed with the support of others.
How does marketing benefit external parties? First, consider what marketing does for consumers. It draws out their needs, creates new demand, locates untapped opportunities, and determines the possibilities of selling new products. Second, marketing creates form, time, place, and possession utilities for the company’s goods and services. Utility refers to a product’s usefulness to customers so that they are convinced enough to make a purchase. In other words, when you hear “utility” in marketing, think “usefulness to customers.”
Marketing creates several different types of utility:
- Form utility . Form utility refers to how well an organization can increase the value of its product in the customer’s eyes by making changes and altering its physical appearance. 10 For example, when you want a donut or a pastry, you don’t want to buy the ingredients to make it; you want a donut in its final form so you can eat it. That’s where the bakery and form utility come into play. The bakery combines flour, sugar, eggs, and other ingredients to make the cakes, donuts, and pastries that you purchase.
- Time utility . Marketing creates time utility when it makes products and services available to customers so that they can buy it when it is most convenient for them. Consider how many stores are open evenings, weekends, or even 24/7 to make it convenient for customers to shop there!
- Place utility . Marketing creates place utility when it makes goods or services physically available, convenient, and accessible to customers. Consider the ease a company like Uber Eats adds to your life when you’re craving tacos in the middle of the night and you don’t feel like getting dressed and driving to go get them. You can have your food delivered to you!
- Possession utility . Marketers facilitate possession utility by ensuring that a product is relatively easy to acquire. For example, many automobile manufacturers offer low (or sometimes no) interest rates on car loans to make it easy for you to walk out the door with a new set of car keys. Possession utility also encompasses the pride or satisfaction you get from owning a new product, such as a great-fitting pair of running shoes or a smartphone with all of the features you’ve been wanting.
Marketing’s primary benefit to society is that it drives the consumer economy. Marketing leads to increased sales and revenue for a business which enables them to expand operations, create more internal jobs and external jobs for partners like suppliers. Marketing also contributes tax revenue to local, state, and federal governments, ultimately leading to overall economic growth.
The Marketing Process Defined
The marketing process refers to the series of steps that assist businesses in planning, analyzing, implementing, and adjusting their marketing strategy. Do an internet search for “steps in the marketing process,” and you’ll immediately see that some websites outline a 10-step process, whereas others propose a 4-step or 6-step process. For our purposes, we’re going to use a 5-step process.
Steps in the Marketing Process
The 5-step process (see Figure 1.3 ) involves understanding the marketplace and customers, developing a marketing strategy, delivering value, growing customer relations, and capturing value from customers. 11
Step 1: Understand Both the Marketplace and Customers
Before you can start the marketing process, you need to have a good idea of what your marketplace looks like. This means answering some basic questions about your customers, like who they are, their income and purchasing power, and how much they’re likely to spend (particularly on your products or services). If you decide to sell at lower prices in order to attain higher unit sales volume, your marketing strategy would look very different than if you decided to sell fewer products at a higher price.
Another way to approach this is to create separate brands and compete in both arenas. Consider Volkswagen . You might immediately think of the VW Beetle or the Jetta, but the company’s brand portfolio extends beyond VW passenger cars and SUVs. It’s also the parent company for Audi, Bentley, Lamborghini, Porsche, and others, and these vehicles sell at very different price points than VW passenger cars. 12
Step 2: Develop a Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy
Marketing strategy refers to a business’s overall “game plan” to focus its limited resources in order to reach prospective customers and turn them into paying customers, hopefully for the long run.
It’s said that there are two basic types of marketing strategy: a product-driven, “build-it-and-they-will-come” strategy and a customer-driven strategy, in which you analyze prospective consumers and then—and only then—create something that they want or need. We’re going to focus on the latter strategy. What happens in a customer-driven marketing strategy is that the company shifts the focus from the product or service itself to its users. Customers’ needs are the central focus and the point of beginning, not an afterthought. Your primary goal in a customer-driven marketing strategy is to determine what users want and/or need and then satisfy those users. Instead of being product-centric, it’s about being customer-centric and developing a mutually beneficial relationship with customers. 13
In a nutshell, it’s about establishing a connection and a relationship. It’s about understanding who your customers are, what their needs and wants are, and how you can best meet those needs and wants. It’s about knowing your target market better than your competitors do and creating a strong value proposition for those users—a promise of value that communicates the benefits of your company’s products or services. In short, it’s what makes your product or service desirable to potential customers, helps them understand why they should buy it, how your company’s product or service differs from those of its competitors, and how your offerings are superior to similar offerings from your competitors. 14
Step 3: Deliver High Customer Value
Customers have myriad buying options and alternatives today. Given that, how can a company attract and—even more importantly—retain its customers? The answer is relatively simple: you give them value for their money. By definition, customer value is the ratio between the perceived benefits and costs incurred by the customer in acquiring your products or services.
The mathematical formula is simple:
But “value” from the customer’s perspective is a complex term, because we’re really considering four different values types:
- Functional value: what the product “does” for the customer in terms of solving a particular want or need
- Monetary value: what the product actually costs relative to its perceived worth
- Social value: how much owning the product allows the customer to connect with others
- Psychological value: how much that product allows the customer to “feel better” 15
Value is increased by boosting the benefits (in the form of product, place, or promotion) or minimizing the price.
Step 4: Grow Profitable Customer Relations
The bottom line is that profitable customer relationships are the “secret sauce” of any business. This step in the marketing process is where marketers acquire, keep, and grow customer relationships. Successful marketers know that acquiring customers is one of the hardest (not to mention one of the most expensive) elements of marketing. However, when you know clearly who those potential customers are, you can more effectively determine how to reach them, thus maximizing your marketing dollars.
It isn’t enough to have a one-and-done sale. You want repeat buyers, so marketers need to remind customers about the company’s products and/or services and how those products and services have met their needs and improved their lives so they make repeat purchases. Marketers need to consider how to reach customers about their offerings and make it easy and convenient for those customers to make continued purchases.
When customers have a positive relationship with a company or its products or services, they’re more likely to become repeat buyers. Satisfied customers are also more likely to be interested in buying additional products or services from your company, and they tend to recommend products to others, further reducing the company’s costs of getting new customers. 16
Step 5: Capture Customer Value in the Form of Profits
The goal of successful customer relationship management (CRM) is creating high customer equity —the potential profits a company earns from its current and potential customers. It’s a relatively simple concept: increasing customer loyalty results in higher customer equity.
Increasing customer equity is the goal of marketers because it’s a bellwether for financial success. Think about it in simple terms: the higher a company’s customer equity, the more profit the company generates, and the more valuable that company (and its products or services) becomes on the market. 17
Careers In Marketing
Marketing jobs.
In every chapter of this book, you’ll find this Careers in Marketing section. It’s meant to outline various jobs so you can be well informed of all the things marketers do. These sections will outline various job roles, what you do day-to-day, qualifications needed, and sometimes even salary information.
If you’ve decided you want a job in marketing, it’s important to know what kinds of jobs exist and what’s expected in each role. Google and YouTube searches will bring you all kinds of information. It’s recommended that you check out the insights from people in these roles and maybe even connect with them to ask them questions. Please do your homework, and determine what you like to do with your day, what you’re good at, and how to build a network to find the right job for you.
Here are a handful of resources to get your thinking started:
- HubSpot: “ How to Start Your Marketing Career When You Know Nothing About Marketing ”
- Setup: “ The Marketing Career Path: From Entry-Level to Chief Marketing Officer ”
- Coursera: “ Your Guide to Landing an Entry-Level Marketing Job ”
- Skillshare: “ 12 Entry-Level Marketing Jobs You Can Pursue Right Now ”
- Indeed: “ Entry Level Marketing Salary in the United States ”
Whatever job role you choose, marketing is a creative, interesting, and at times exciting role where you can make a real impact on people’s lives. Enjoy!
Knowledge Check
It’s time to check your knowledge on the concepts presented in this section. Refer to the Answer Key at the end of the book for feedback.
- Form utility
- Time utility
- Place utility
- Possession utility
- Marketing creates value.
- Marketing is made up of every process involved in moving a product or service from your organization to the consumer.
- Marketing includes distribution decisions.
- Marketing is about building relationships.
- customer equity
- the value proposition
- customer value
- the marketing process
- Developing a customer-driven marketing strategy
- Delivering high customer value
- Growing profitable customer relations
- Capturing value from customers
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Dr. Maria Gomez Albrecht, Dr. Mark Green, Linda Hoffman
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Marketing
- Publication date: Jan 25, 2023
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-marketing/pages/1-1-marketing-and-the-marketing-process
© Jan 9, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Digital Marketing
Digital marketing typically refers to online marketing campaigns that appear on a computer, phone, tablet, or other device. It can take many forms, including online video, display ads, search engine marketing, paid social ads and social media posts.
Digital marketing is often compared to “traditional marketing” such as magazine ads, billboards, and direct mail. Oddly, television is usually lumped in with traditional marketing.
Did you know nine-in-ten U.S. adults go online on a daily basis? Not only that, 41% are online “ almost constantly .” As a marketer, it’s important to take advantage of the digital world with an online advertising presence, by building a brand, providing a great customer experience that also brings more potential customers and more, with a digital strategy.
A digital marketing strategy allows you to leverage different digital channels–such as social media, pay-per-click, search engine optimization, and email marketing–to connect with existing customers and individuals interested in your products or services. As a result, you can build a brand, provide a great customer experience, bring in potential customers, and more.

Maximize your digital marketing
Use Mailchimp to promote your brand, reach your target audience, and grow your business.
What is digital marketing?
Digital marketing, also called online marketing, is the promotion of brands to connect with potential customers using the internet and other forms of digital communication. This includes not only email , social media , and web-based advertising, but also text and multimedia messages as a marketing channel .
Essentially, if a marketing campaign involves digital communication, it's digital marketing.
Inbound marketing versus digital marketing
Digital marketing and inbound marketing are easily confused, and for good reason. Digital marketing uses many of the same tools as inbound marketing—email and online content, to name a few. Both exist to capture the attention of prospects through the buyer’s journey and turn them into customers. But the two approaches take different views of the relationship between the tool and the goal .
Digital marketing considers how individual tools or digital channels can convert prospects. A brand's digital marketing strategy may use multiple platforms or focus all of its efforts on one platform. For example, a company may primarily create content for social media platforms and email marketing campaigns while ignoring other digital marketing avenues.
On the other hand, inbound marketing is a holistic concept. It considers the goal first, then looks at the available tools to determine which will effectively reach target customers, and then at which stage of the sales funnel that should happen. As an example, say you want to increase website traffic to generate more prospects and leads. You can focus on search engine optimization when developing your content marketing strategy, resulting in more optimized content, including blogs , landing pages, and more.
The most important thing to remember about digital marketing and inbound marketing is that as a marketing professional, you don’t have to choose between the two. In fact, they work best together. Inbound marketing provides structure and purpose for effective digital marketing to digital marketing efforts, making sure that each digital marketing channel works toward a goal.
Why is digital marketing important?
Any type of marketing can help your business thrive. However, digital marketing has become increasingly important because of how accessible digital channels are. In fact, there were 5.45 billion internet users globally as of July 2024 .
From social media to text messages, there are many ways to use digital marketing tactics in order to communicate with your target audience. Additionally, digital marketing has minimal upfront costs, making it a cost-effective marketing technique for small businesses.
B2B versus B2C digital marketing
Digital marketing strategies work for B2B (business to business) as well as B2C (business to consumer) companies, but best practices differ significantly between the two. Here's a closer look at how digital marketing is used in B2B and B2C marketing strategies:
- B2B clients tend to have longer decision-making processes, and thus longer sales funnels . Relationship-building strategies work better for these clients, whereas B2C customers tend to respond better to short-term offers and messages.
- B2B transactions are usually based on logic and evidence , which is what skilled B2B digital marketers present. B2C content is more likely to be emotionally-based, focusing on making the customer feel good about a purchase.
- B2B decisions tend to need more than 1 person's input . The marketing materials that best drive these decisions tend to be shareable and downloadable. B2C customers, on the other hand, favor one-on-one connections with a brand.
Of course, there are exceptions to every rule. A B2C company with a high-ticket product, such as a car or computer, might offer more informative and serious content. As a result, your digital marketing strategy always needs to be geared toward your own customer base, whether you're B2B or B2C.
Take a look at your current audience to create well-informed and targeted online marketing campaigns. Doing so ensures your marketing efforts are effective and you can capture the attention of potential customers.
Types of digital marketing
There are as many specializations within digital marketing as there are ways of interacting using digital media. Here are a few key examples of types of digital marketing tactics.
Search engine optimization
Search engine optimization, or SEO , is technically a marketing tool rather than a form of marketing in itself. It is often called "an art and a science."
The "science" part of SEO is what’s most important. SEO is a science because it requires you to research and weigh different contributing factors to achieve the highest possible ranking on a search engine results page (SERP) .
Today, the most important elements to consider when optimizing a web page for search engines include:
- Quality and uniqueness of content
- Optimization of key elements for the targeted keyword (URL, title tag, H1, sub headlines)
- Level of user engagement (time on page, bounce rate)
- Number and quality of backlinks
- Internal linking
In addition to the elements above, you need to prioritize technical SEO , which is all the back-end components of your site. This includes mobile-friendliness and loading times. Improving your technical SEO can help search engines better navigate and crawl your site.
The strategic use of these factors makes search engine optimization a science, but the unpredictability involved makes it an "art" that often requires experienced SEO professionals.
Ultimately, the goal is to rank at or near the top of the first page of a search engine’s result page or in Google's AI Overviews . This ensures that those searching for a specific query related to your brand can easily find your products or services. While there are many search engines, digital marketers often focus on Google since it's a global leader in the search engine market.
Google and other search engines change their algorithm almost constantly , so SEO is a never-ending progress. And your competitors most likely also invest in SEO. What you can do is closely monitor your page's performance and make adjustments as needed.
Content marketing
As mentioned, the quality of your content is a key component of an optimized page. As a result, SEO is a major factor in content marketing , a strategy based on the distribution of relevant and valuable content to a target audience .
As in any marketing strategy, the goal of content marketing is to attract leads that ultimately convert into customers. But it does so differently than traditional advertising. Instead of enticing prospects with potential value from a product or service, it offers value for free in the form of written material, such as:
- Newsletters
- Video or audio transcripts
- Whitepapers
- Infographics
Content marketing matters , and there are plenty of stats to prove it:
- 84% of consumers expect companies to produce entertaining and helpful content experiences
- 62% of companies that have at least 5,000 employees produce content daily
- 92% of marketers believe that their company values content as an important asset
As effective as content marketing is, it can be tricky. Content marketing writers need to be able to rank highly in search engine results while also engaging people who will read the material, share it, and interact further with the brand. When the content is relevant, it can establish strong relationships throughout the pipeline.
To create effective content that’s highly relevant and engaging, it’s important to identify your audience. Who are you ultimately trying to reach with your content marketing efforts? Once you have a better grasp of your audience, you can determine the type of content you'll create. You can use many formats of content in your content marketing, including videos, blog posts, printable worksheets, and more.
Regardless of which content you create, it’s a good idea to follow content marketing best practices. This means making content that’s grammatically correct, free of errors, easy to understand, relevant, and interesting. Your content should also funnel readers to the next stage in the pipeline, whether that’s a free consultation with a sales representative or a signup page.
Social media marketing
Social media marketing means driving traffic and brand awareness by engaging people in discussion online. You can use social media marketing to highlight your brand, products, services, culture, and more. With billions of people spending their time engaging on social media platforms, focusing on social media marketing can be worthwhile.
The most popular digital platforms for social media marketing are Facebook , X, and Instagram , with LinkedIn and YouTube not far behind. Ultimately, which social media platforms you use for your business depends on your goals and audience. For example, if you want to find new leads for your FinTech startup, targeting your audience on LinkedIn is a good idea since industry professionals are active on the platform. On the other hand, running social media ads on Instagram may be better for your brand if you run a B2C focused on younger consumers.
Because social media marketing involves active audience participation, it has become a popular way of getting attention. Social media marketing offers built-in engagement metrics , which are extremely useful in helping you to understand how well you're reaching your audience . You get to decide which types of interactions mean the most to you, whether that means the number of shares, comments, or total clicks to your website .
Direct purchase may not even be a goal of your social media marketing strategy . Many brands use social media marketing to start dialogues with audiences rather than encourage them to spend money right away. This is especially common in brands that target older audiences or offer products and services not appropriate for impulse buys . It all depends on your company's social media marketing goals.
To create an effective social media marketing strategy, it’s crucial to follow best practices. Here are a few of the most important social media marketing best practices:
- Craft high-quality and engaging content
- Reply to comments and questions in a professional manner
- Create a social media posting schedule
- Post at the right time
- Hire social media managers to support your marketing efforts
- Know your audience and which social media channels they’re most active on
To learn more about how Mailchimp can help with your social media strategy, check out the comparison of our free social media management tools versus others.
Pay-per-click marketing
Pay-per-click, or PPC, is a form of digital marketing in which you pay a fee every time someone clicks on your digital ads. So, instead of paying a set amount to constantly run targeted ads on online marketing channels, you only pay for the ads individuals interact with. How and when people see your ad is a bit more complicated.
One of the most common types of PPC is search engine advertising, and because Google is the most popular search engine, many businesses use Google Ads for this purpose. When a spot is available on a search engine results page , also known as a SERP, the engine fills the spot with what is essentially an instant auction. An algorithm prioritizes each available ad based on a number of factors, including:
- Keyword relevance
- Landing page quality
PPC ads are then placed at the top of search engine result pages based on the factors above whenever a person searches for a specific query.
Each PPC campaign has 1 or more target actions that viewers are meant to complete after clicking an ad. These actions are known as conversions, and they can be transactional or non-transactional. Making a purchase is a conversion, but so is a newsletter signup or a call made to your home office.
Whatever you choose as your target conversions, you can track them via your chosen digital marketing channels to see how your campaign is doing.
Affiliate marketing
Affiliate marketing is a digital marketing tactic that lets someone make money by promoting another person's business. You could be either the promoter or the business who works with the promoter, but the process is the same in either case.
It works using a revenue sharing model. If you're the affiliate, you get a commission every time someone purchases the item that you promote. If you're the merchant, you pay the affiliate for every sale they help you make.
Some affiliate marketers choose to review the products of just 1 company, perhaps on a blog or other third-party site. Others have relationships with multiple merchants.
Whether you want to be an affiliate or find one, the first step is to make a connection with the other party. You can use digital channels designed to connect affiliates with retailers, or you can start or join a single-retailer program.
If you're a retailer and you choose to work directly with affiliates, there are many things you can do to make your program appealing to potential promoters. You'll need to provide those affiliates with the tools that they need to succeed. That includes incentives for great results as well as marketing tools and pre-made materials.
Native advertising
Native advertising is digital marketing in disguise. Its goal is to blend in with its surrounding content so that it’s less blatantly obvious as advertising.
Native advertising was created in reaction to the cynicism of today's consumers toward ads. Knowing that the creator of an ad pays to run it, many consumers will conclude that the ad is biased and consequently ignore it.
A native ad gets around this bias by offering information or entertainment before it gets to anything promotional, downplaying the "ad" aspect.
It’s important to always label your native ads clearly. Use words like “promoted” or “sponsored.” If those indicators are concealed, readers might end up spending significant time engaging with the content before they realize that it's advertising.
When your consumers know exactly what they're getting, they'll feel better about your content and your brand. Native ads are meant to be less obtrusive than traditional ads, but they’re not meant to be deceptive.
Influencer marketing
Like affiliate marketing, influencer marketing relies on working with an influencer–an individual with a large following, such as a celebrity, industry expert, or content creator–in exchange for exposure. In many cases, these influencers will endorse your products or services to their followers on several social media channels.
Influencer marketing works well for B2B and B2C companies who want to reach new audiences. However, it’s important to partner with reputable influencers since they’re essentially representing your brand. The wrong influencer can tarnish the trust consumers have with your business.
Marketing automation
Marketing automation uses software to power digital marketing campaigns, improving the efficiency and relevance of advertising. As a result, you can focus on creating the strategy behind your digital marketing efforts instead of cumbersome and time-consuming processes.
While marketing automation may seem like a luxury tool your business can do without, it can significantly improve the engagement between you and your audience.
According to statistics:
- 90% of US consumers find personalization either “very” or “somewhat” appealing
- 81% of consumers would like the brands they engage with to understand them better
Marketing automation lets companies keep up with the expectation of personalization. It allows brands to:
- Collect and analyze consumer information
- Design targeted marketing campaigns
- Send and post digital marketing messages at the right times to the right audiences
Many marketing automation tools use prospect engagement (or lack thereof) with a particular message to determine when and how to reach out next. This level of real-time customization means that you can effectively create an individualized marketing strategy for each customer without any additional time investment.
Mailchimp's marketing automation tools ensure you can interact with your audience via behavior-based automations, transactional emails, date-based automations, and more.
Email marketing
The concept of email marketing is simple—you send a promotional message and hope that your prospect clicks on it. However, the execution is much more complex. First of all, you have to make sure that your emails are wanted. This means having an email marketing provider that offers the following is crucial:
- Individualizes the content, both in the body and in the subject line
- An email signature that offers a clear unsubscribe option
- Both, transactional and promotional emails
You want your prospects to see your campaign as a valued service, not just as a promotional tool.
Email marketing is a proven, effective technique all on its own, but it can be even better if you incorporate other digital marketing techniques such as marketing automation, which lets you segment and schedule your emails so that they meet your customer's needs more effectively.
If you’re considering email marketing, here are a few tips that can help you craft great email marketing campaigns:
- Segment your audience to send relevant campaigns to the right people
- Ensure emails look good on mobile devices
- Create a campaign schedule
- Run A/B tests
Mobile marketing
Mobile marketing is a digital marketing strategy that allows you to engage with your target audience on their mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. This can be via SMS and MMS messages, social media notifications, mobile app alerts, and more.
It’s crucial to ensure that all content is optimized for mobile devices. According to the Pew Research Center, Nine-in-ten Americans own a smartphone , so your marketing efforts can go a long way when you create content for computer and mobile screens.
The benefits of digital marketing
Digital marketing has become prominent largely because it reaches such a wide audience of people. However, it also offers a number of other advantages that can boost your marketing efforts. These are a few of the benefits of digital marketing.
A broad geographic reach
When you post an ad online, people can see it no matter where they are (provided you haven’t limited your ad geographically). This makes it easy to grow your business's market reach and connect with a larger audience across different digital channels.
Cost efficiency
Digital marketing not only reaches a broader audience than traditional marketing but also carries a lower cost. Overhead costs for newspaper ads, television spots, and other traditional marketing opportunities can be high. They also give you less control over whether your target audiences will see those messages in the first place.
With digital marketing, you can create just one content piece that draws visitors to your blog as long as it's active. You can create an email marketing campaign that delivers messages to targeted customer lists on a schedule, and it's easy to change that schedule or the content if you need to do so.
When you add it all up, digital marketing gives you much more flexibility and customer contact for your ad spend.
Quantifiable results
To know whether your marketing strategy works, you have to find out how many customers it attracts and how much revenue it ultimately drives. But how do you do that with a non-digital marketing strategy?
There's always the traditional option of asking each customer, “How did you find us?"
Unfortunately, that doesn't work in all industries. Many companies don't get to have one-on-one conversations with their customers, and surveys don't always get complete results.
With digital marketing, results monitoring is simple. Digital marketing software and platforms automatically track the number of desired conversions that you get, whether that means email open rates, visits to your home page, or direct purchases.
Easier personalization
Digital marketing allows you to gather customer data in a way that offline marketing can't. Data collected digitally tends to be much more precise and specific.
Imagine you offer financial services and want to send out special offers to internet users people who have looked at your products. You know you'll get better results if you target the offer to the person's interest, so you decide to prepare 2 campaigns. One is for young families who have looked at your life insurance products, and the other is for millennial entrepreneurs who have considered your retirement plans.
How do you gather all of that data without automated tracking? How many phone records would you have to go through? How many customer profiles? And how do you know who has or hasn't read the brochure you sent out?
With digital marketing, all of this information is already at your fingertips.
More connection with customers
Digital marketing lets you communicate with your customers in real-time. More importantly, it lets them communicate with you.
Think about your social media strategy. It's great when your target audience sees your latest post, but it's even better when they comment on it or share it. It means more buzz surrounding your product or service , as well as increased visibility every time someone joins the conversation.
Interactivity benefits your customers as well. Their level of engagement increases as they become active participants in your brand's story. That sense of ownership can create a strong sense of brand loyalty .
Easy and convenient conversions
Digital marketing lets your customers take action immediately after viewing your ad or content. With traditional advertisements, the most immediate result you can hope for is a phone call shortly after someone views your ad. But how often does someone have the time to reach out to a company while they're doing the dishes, driving down the highway, or updating records at work?
With digital marketing, they can click a link or save a blog post and move along the sales funnel right away. They might not make a purchase immediately, but they’ll stay connected with you and give you a chance to interact with them further.
How to create a digital marketing strategy
For many small businesses and beginner digital marketers, getting started with digital marketing can be difficult. However, you can create an effective digital marketing strategy to increase brand awareness, engagement, and sales by using the following steps as your starting point.
Set SMART goals
Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timely (SMART) goals is crucial for any marketing strategy. While there are many goals you may want to achieve, try to focus on the ones that will propel your strategy forward instead of causing it to remain stagnant.
Identify your audience
Before starting any marketing campaign, it’s best to identify your target audience. Your target audience is the group of people you want your campaign to reach based on similar attributes, such as age, gender, demographic, or purchasing behavior. Having a good understanding of your target audience can help you determine which digital marketing channels to use and the information to include in your campaigns.
Create a budget
A budget ensures you’re spending your money effectively towards your goals instead of overspending on digital marketing channels that may not provide the desired results. Consider your SMART goals and the digital channel you’re planning to use to create a budget.
Select your digital marketing channels
From content marketing to PPC campaigns and more, there are many digital marketing channels you can use to your advantage. Which digital marketing channels you use often depends on your goals, audience, and budget.
Refine your marketing efforts
Make sure to analyze your campaign's data to identify what was done well and areas for improvement once the campaign is over. This allows you to create even better campaigns in the future. With the help of digital technologies and software, you can obtain this data in an easy-to-view dashboard. Mailchimp’s digital marketing analytics reports will help you keep track of all your marketing campaigns in one centralized location.
Digital marketing creates growth
Digital marketing should be one of the primary focuses of almost any business’s overall marketing strategy. Never before has there been a way to stay in such consistent contact with your customers, and nothing else offers the level of personalization that digital data can provide. The more you embrace the possibilities of digital marketing, the more you'll be able to realize your company's growth potential.
In our Marketing Library , you can find numerous articles on all aspects of digital marketing.
Take your business to the next level
More From Forbes
What are the ‘when gen-z writes the marketing script’ memes about.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
TikTok, where the 'when Gen-Z write the marketing script' memes came from.
There’s a new trend in town: the “when Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes. Normally posted on an organization’s TikTok account, they feature an older member of staff reading a marketing script written by a younger person that’s filled with Gen-Z slang.
The most popular of these so far has been from the Royal Armouries Museum, which has over 1.3 million likes at the time of writing. In it, an older British man walks around historical artefacts using anachronistic words like “slay” (which means doing exceptionally well):
While these memes are undoubtedly funny, acting against type also shines a light on generational differences—but in a wholly positive way.
On top of that, the success of these videos is proof once again of the power of meme marketing.
Truly, this trend is, as Gen-Z say, giving me life.
Hurricane Helene Makes Landfall In Florida As Category 4 Storm—Here’s What To Know
Today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for friday, september 27, election 2024 swing state polls: harris leads in 6 of 7 battlegrounds in latest survey, the birth and success of the ‘when gen-z write the marketing script’ tiktok trend.
While the origin of these memes is hard to pinpoint precisely, one of the posts that rocketed it mainstream started in the U.K. where a video by Currys—an electronics retailer—racked up millions of views. You can watch it here:
After the Currys video, a gamut of other brands and organizations created their own versions of the meme—and many captured the public’s imagination.
Another example is a post from Beamish, a living open air museum in the North West of England, which also received millions of views. Again, the combination of old-timey situations and hyper-modern lingo is as cute as it is amusing:
And it didn’t stop there. Many , many other brands and institutions got involved, filming their own versions of the “when Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes. At this point in time, there have been hundreds of millions of combined views of this TikTok trend.
It ate, as young people might say. Which, for the older amongst us, means it did very well.
Why Are These Memes So Popular? And What Do They Say About Society?
One reason why the “when Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes have garnered so many views is because of their purity.
On a fundamental level, it’s an old-fashioned joke where two seemingly contradictory elements collide. Hearing older generations stumble through phrases like “live rent free” or “fire af” is heartwarming in a very earnest, inclusive way. There’s no mockery when one might expect it; it’s two different worldviews coming together.
The world baby boomers grew up in. (Jim Heimann Collection/Getty Images)
There is something deeper going on, though.
We’re living in a world with increasing divisions between the older and younger generations— especially in the workplace . This can arise from millennials and Gen-X’ers feeling aged out or, according to a Fast Company-Harris poll , a significant percentage of Gen-Z workers feeling overly criticized or questioned.
Research shows that , broadly speaking, people from older generations such as baby boomers trend toward being work-centric and conservative. Gen-Z, the newest generation to enter the workforce, value openness, communication and diversity of thought. Their jobs are lower down on that list.
This divide gets even deeper when you consider Gen-Z are the first generation to grow up in an entirely digital world, while baby boomers were fully grown adults by the time the first personal computers appeared.
Even the communication systems between the generations are different. Older people value face-to-face discussion, while younger individuals much prefer digital chatting.
The result? A working world culture clash that finds older generations negatively baffled by the younger ones.
“When Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes turn this narrative on its head.
With these, we can clearly see a positive connection between the generations. The TikTok trend shows older and younger generations working together, forming a metaphorical bridge.
Even more so, Dr. Alexis Abramson , an expert on "generational cohorts" who's been studying the science of aging for over two decades, believes that the key to overcoming differences is acknowledging that “the younger folks can teach the older folks something and the older folks can teach the younger folks something,” as reported by the BBC .
Rather than baby boomers and Gen-Z raging at each other and struggling to communicate , the meme format brings them together. It shows that the internet and humor can actually bond people in the workforce, creating something that’s totally new, but can be enjoyed by people of all ages.
This coming together of generations is also effective marketing. The hundreds of millions of combined views brands has achieved is because they’ve made an emotional connection to watchers across demographics, producing something that feels unique and authentic. Research published in the Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services shows that, in large part due to emotional resonance, meme marketing can net as much as 30 times more engagement on social media than traditional methods like Google AdWords.
Of course, you can make the argument that the humor in the meme is masking the real challenges that generations are facing, issues like the lack of job security and inequality, or that it’s just a Band-Aid on a missing leg, but I think that’s missing the point.
While politics has a large generational divide that splits us apart, the “when Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes shows that we still can all get along. More than that, it shows that dialogue between generations is possible, and can be embraced by all sides.
Just look at the comments in the Royal Armouries Museum’s video and you can see Gen-Z’ers saying things like: “we must protect this man at all costs” or “I love this guy” to understand there’s real affection here.
The “when Gen-Z writes the marketing script” memes could’ve easily been ridiculed and the reaction negative, but that hasn’t happened. People love this type of intergenerational connection. For once, the internet is a positive force bringing us together. It’s giving us all life.

- Editorial Standards
- Forbes Accolades
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

COMMENTS
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large. The AMA's definitions of marketing and marketing research are reviewed and reapproved/modified regularly by a panel of five scholars who are ...
Purpose of Marketing. Marketing is the process of getting people interested in your company's product or service. This happens through market research, analysis, and understanding your ideal customer's interests. Marketing pertains to all aspects of a business, including product development, distribution methods, sales, and advertising.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Marketing; 250 Words Essay on Marketing Understanding the Power of Marketing. Marketing: a concept that shapes the modern world. It's more than just ads and promotions; it's the engine driving business success. Let's explore its significance.
The importance of marketing can be summed up in the words of the world famous economist Peter Drucker. He has said that "Because the purpose of business is to create a customer, the business enterprise has two-and only two-basic functions: marketing and innovation. Marketing and innovation produce results; all the rest are costs ...
The role of marketing. The main purpose of marketing is to identify the consumer of a product or service, to retain the client, and to gratify him or her. With the customer as the spotlight of any business, it is therefore appropriate to conclude that marketing is a key element of the running of such establishments.
Marketing Definition. ... Content marketing is the process of creating blogs, white papers, videos, infographics and other forms of media to attract customers.
Kotler and Armstrong (2008) defined marketing as an exchange system which fulfill the needs and wants of individuals. While ( Lancaster and Withey, 2007) also stated that marketing is a management which foresees and satisfies the consumer needs timely. Nowadays, people tend to define marketing as the development along with the industrial ...
The definition of marketing essay describes it as a written piece, exploring product promotion in detail. Such pieces entitle authors to conduct research, study terms, and argumentation. Writing process engages cognitive abilities as well as analytical and critical thinking. While writing, students educate themselves and improve skills in ...
Marketing strategy is the process that organizations use to plan and execute their marketing activities. A well-developed marketing strategy considers the company's strengths and weaknesses, as well as its opportunities and threats. It also includes a clear statement of the company's marketing goals and objectives.
Here are 103 digital marketing essay topic ideas and examples to help you get started: The impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior. The role of storytelling in digital marketing campaigns. The rise of video marketing in the digital age. The importance of personalization in email marketing. The future of artificial intelligence ...
The concern with this definition is that it is incomplete; marketing management is important, but it is not all of marketing. The essay discusses six limitations that arise from the narrow conception that has been adopted and then presents the broadened conception of an "aggregate marketing system" that should adjoin marketing management as ...
The main topics include the definition of marketing, strategic planning, consumer behavior, the 4 Ps, offerings, marketing channels, selling, and overview of a marketing plan. The Table of Contents is easy to access; it serves as a helpful search function. The text is missing a glossary of terms; adding one could be beneficial to readers.
The given definition can be applied to the marketing strategy used by General Motors. While the company works on its promotion strategies, its leader clearly gathers the data concerning the new markets for the further expansion (Chevy marketing: Less like apple pie, more like Apple: Q & A agency and marketing executives Jeff Goodby, Goodby ...
Essay on Marketing: Meaning, Definition and Concept! Everybody lives by selling some products, services or ideas. Generally, marketing is considered as selling and promotion. However, making a sale, i.e., selling is the old sense of marketing. In its new sense, marketing is satisfying customer needs. Selling is only one aspect of marketing.
This essay about the definition of marketing in the business context elucidates its comprehensive and strategic nature, beyond the common misconceptions that equate it solely with selling and advertising. It underscores marketing as a vital process of understanding and meeting consumer needs, involving market research, product development ...
Essay Topic # 1. Definition of Marketing: Some Important Definitions of Marketing: Marketing is the activity, set of institutions and processes for creating, communicating, delivering and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners and society at large. —American Marketing Association (AMA)
Marketing is currently defined by the American Marketing Association (AMA) as "the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large". [14] However, the definition of marketing has evolved over the years. The AMA reviews this definition and its definition for ...
Another definition of marketing is the "selling of products or services: the business activity of presenting products or services in such a way as to …show more content…. This entire process is known as marketing management " the art and science of choosing target markets and getting, keeping, and growing customers through creating ...
Marketing is the process of creating and delivering value to customers. Learn about different types and strategies of marketing with Investopedia.
definition of marketing across time, this essay identifies the 2004 effort as actually a definition of "marketing management," not of the larger field of marketing itself. The concern with this definition is that it is incomplete; marketing management is important, but it is not all of marketing. The essay
Let's break down that definition: Identifying customer needs. This is typically where marketing research comes in. Methods of marketing research will be covered in a later chapter, but market research helps a company develop a detailed picture of its customers, including a clear understanding of their wants and needs. Anticipating customer ...
Digital marketing typically refers to online marketing campaigns that appear on a computer, phone, tablet, or other device. It can take many forms, including online video, display ads, search engine marketing, paid social ads and social media posts. Digital marketing is often compared to "traditional marketing" such as magazine ads ...
TikTok, where the 'when Gen-Z write the marketing script' memes came from. Getty Images. There's a new trend in town: the "when Gen-Z writes the marketing script" memes.