- How it works

"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

How To Write Recommendations In A Research Study
Published by Alvin Nicolas at July 12th, 2024 , Revised On July 12, 2024
The ultimate goal of any research process is not just to gather knowledge, but to use that knowledge to make a positive impact. This is where recommendations come in. A well-written recommendations section in your research study translates your findings into actionable steps and guides future research on the topic.
This blog is your ultimate guide to understanding how to write recommendations in a research study. But before that, let’s see what is recommendation in research.
What Is Recommendation In Research
In a research study, the recommendation section refers to a suggested course of action based on the findings of your research . It acts as a bridge between the knowledge you gained and its practical implications.
Recommendations take your research results and propose concrete steps on how to use them to address a problem or improve a situation. Moreover, you can suggest new avenues and guide future research in building upon your work. This will improve the credibility of your research. For studies that include real-world implications, recommendations are a great way to provide evidence-based suggestions for policymakers or practitioners to consider.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Research recommendations and implications often confuse researchers. They cannot easily differentiate between the two. Here is how they are different.
Where To Add Recommendations
Recommendations are mostly part of your conclusion and discussion sections. If you are writing a practical dissertation , you can include a separate section for your recommendations.
Types of Research Recommendations
There are different forms of recommendations in research. Some of them include the following.
How To Construct The Recommendations Section
There are different ways in which different scholars write the recommendations section. A general observation is a research question → conclusion → recommendation.
The following example will help you understand this better.
Research Question
How can the education of mothers impact the social skills of kindergarten children?
The role of mothers is a significant contributor towards the social skills of children. From an early age, kids tend to observe how their mother interacts with others and follow in her footsteps initially. Therefore, mothers should be educated and interact with good demeanour if they want their children to have excellent social skills.
Recommendation
The study revealed that a mother’s education plays an important role in building the social skills of children on kindergarten level. Future research could explore how the same continues in junior school level children.
How To Write Recommendations In Research
Now that you are familiar with the definition and types, here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a recommendation in research.
Step 1: Revisit Your Research Goals
Before doing anything else, you have to remind yourself of the objectives that you set out to achieve in your research. It allows you to match your recommendations directly to your research questions and see if you made any contribution to your goals.
Step 2: Analyse Your Findings
You have to examine your data and identify your key results. This analysis forms the foundation for your recommendations. Look for patterns and unexpected findings that might suggest new areas for other researchers to explore.
Step 3: Consider The Research Methods
Ask these questions from yourself: were the research methods effective? Is there any other way that would have been better to perform this research, or were there any limitations associated with the research methods?
Step 4: Prioritise Recommendations
You might have a lot of recommendations in mind, but all are not equal. You have to consider the impact and feasibility of each suggestion. Prioritise these recommendations, while remaining realistic about implementation.
Step 5: Write Actionable Statements
Do not be vague when crafting statements. Instead, you have to use clear and concise language that outlines specific actions. For example, if you want to say “improve education practices,” you could write “implement a teacher training program” for better clarity.
Step 6: Provide Evidence
You cannot just make suggestions out of thin air, and have to ground them in the evidence you have gathered through your research. Moreover, cite relevant data or findings from your study or previous literature to support your recommendations.
Step 7: Address Challenges
There are always some limitations related to the research at hand. As a researcher, it is your duty to highlight and address any challenges faced or what might occur in the future.
Tips For Writing The Perfect Recommendation In Research
Use these tips to write the perfect recommendation in your research.
- Be Concise – Write recommendations in a clear and concise language. Use one sentence statements to look more professional.
- Be Logical & Coherent – You can use lists and headings according to the requirements of your university.
- Tailor According To Your Readers – You have to aim your recommendations to a specific audience and colleagues in the field of study.
- Provide Specific Suggestions – Offer specific measures and solutions to the issues, and focus on actionable suggestions.
- Match Recommendations To Your Conclusion – You have to align your recommendations with your conclusion.
- Consider Limitations – Use critical thinking to see how limitations may impact the feasibility of your solutions.
- End With A Summary – You have to add a small conclusion to highlight suggestions and their impact.
Example Of Recommendation In Research
Context of the study:
This research studies how effective e-learning platforms are for adult language learners compared to traditional classroom instruction. The findings suggest that e-learning platforms can be just as effective as traditional classrooms in improving language proficiency.
Research Recommendation Sample
Language educators can incorporate e-learning tools into existing curriculums to provide learners with more flexibility. Additionally, they can develop training programs for educators on how to integrate e-learning platforms into their teaching practices.
E-learning platform developers should focus on e-learning platforms that are interactive and cater to different learning styles. They can also invest in features that promote learner autonomy and self-directed learning.
Future researchers can further explore the long-term effects of e-learning on language acquisition to provide insights into whether e-learning can support sustained language development.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write recommendations in a research paper.
- Revisit your research goals
- Analyse your findings
- Consider the research methods
- Prioritise recommendations
- Write actionable statements
- Provide evidence
- Address challenges
How to present recommendations in research?
- Be concise
- Write logical and coherent
- Match recommendations to conclusion
- Ensure your recommendations are achievable
What to write in recommendation in research?
Your recommendation has to be concrete and specific and support the research with a clear rationale. Moreover, it should be connected directly to your research. Your recommendations, however, should not undermine your own work or use self-criticism.
You May Also Like
Dissertation discussion is where you explore the relevance and significance of results. Here are guidelines to help you write the perfect discussion chapter.
Want to dedicate your dissertation to someone? Learn what a dedication dissertation is, how to write it, and dedication dissertation examples.
Appendices or Appendixes are used to provide additional date related to your dissertation research project. Here we explain what is appendix in dissertation
As Featured On

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing Guide
Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Recommendations
Definition:
Research recommendations refer to suggestions or advice given to someone who is looking to conduct research on a specific topic or area. These recommendations may include suggestions for research methods, data collection techniques, sources of information, and other factors that can help to ensure that the research is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner. Research recommendations may be provided by experts in the field, such as professors, researchers, or consultants, and are intended to help guide the researcher towards the most appropriate and effective approach to their research project.
Parts of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations can vary depending on the specific project or area of research, but typically they will include some or all of the following parts:
- Research question or objective : This is the overarching goal or purpose of the research project.
- Research methods : This includes the specific techniques and strategies that will be used to collect and analyze data. The methods will depend on the research question and the type of data being collected.
- Data collection: This refers to the process of gathering information or data that will be used to answer the research question. This can involve a range of different methods, including surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments.
- Data analysis : This involves the process of examining and interpreting the data that has been collected. This can involve statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a combination of both.
- Results and conclusions: This section summarizes the findings of the research and presents any conclusions or recommendations based on those findings.
- Limitations and future research: This section discusses any limitations of the study and suggests areas for future research that could build on the findings of the current project.
How to Write Research Recommendations
Writing research recommendations involves providing specific suggestions or advice to a researcher on how to conduct their study. Here are some steps to consider when writing research recommendations:
- Understand the research question: Before writing research recommendations, it is important to have a clear understanding of the research question and the objectives of the study. This will help to ensure that the recommendations are relevant and appropriate.
- Consider the research methods: Consider the most appropriate research methods that could be used to collect and analyze data that will address the research question. Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the different methods and how they might apply to the specific research question.
- Provide specific recommendations: Provide specific and actionable recommendations that the researcher can implement in their study. This can include recommendations related to sample size, data collection techniques, research instruments, data analysis methods, or other relevant factors.
- Justify recommendations : Justify why each recommendation is being made and how it will help to address the research question or objective. It is important to provide a clear rationale for each recommendation to help the researcher understand why it is important.
- Consider limitations and ethical considerations : Consider any limitations or potential ethical considerations that may arise in conducting the research. Provide recommendations for addressing these issues or mitigating their impact.
- Summarize recommendations: Provide a summary of the recommendations at the end of the report or document, highlighting the most important points and emphasizing how the recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
Example of Research Recommendations
Example of Research Recommendations sample for students:
- Further investigate the effects of X on Y by conducting a larger-scale randomized controlled trial with a diverse population.
- Explore the relationship between A and B by conducting qualitative interviews with individuals who have experience with both.
- Investigate the long-term effects of intervention C by conducting a follow-up study with participants one year after completion.
- Examine the effectiveness of intervention D in a real-world setting by conducting a field study in a naturalistic environment.
- Compare and contrast the results of this study with those of previous research on the same topic to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies in the findings.
- Expand upon the limitations of this study by addressing potential confounding variables and conducting further analyses to control for them.
- Investigate the relationship between E and F by conducting a meta-analysis of existing literature on the topic.
- Explore the potential moderating effects of variable G on the relationship between H and I by conducting subgroup analyses.
- Identify potential areas for future research based on the gaps in current literature and the findings of this study.
- Conduct a replication study to validate the results of this study and further establish the generalizability of the findings.
Applications of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations are important as they provide guidance on how to improve or solve a problem. The applications of research recommendations are numerous and can be used in various fields. Some of the applications of research recommendations include:
- Policy-making: Research recommendations can be used to develop policies that address specific issues. For example, recommendations from research on climate change can be used to develop policies that reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
- Program development: Research recommendations can guide the development of programs that address specific issues. For example, recommendations from research on education can be used to develop programs that improve student achievement.
- Product development : Research recommendations can guide the development of products that meet specific needs. For example, recommendations from research on consumer behavior can be used to develop products that appeal to consumers.
- Marketing strategies: Research recommendations can be used to develop effective marketing strategies. For example, recommendations from research on target audiences can be used to develop marketing strategies that effectively reach specific demographic groups.
- Medical practice : Research recommendations can guide medical practitioners in providing the best possible care to patients. For example, recommendations from research on treatments for specific conditions can be used to improve patient outcomes.
- Scientific research: Research recommendations can guide future research in a specific field. For example, recommendations from research on a specific disease can be used to guide future research on treatments and cures for that disease.
Purpose of Research Recommendations
The purpose of research recommendations is to provide guidance on how to improve or solve a problem based on the findings of research. Research recommendations are typically made at the end of a research study and are based on the conclusions drawn from the research data. The purpose of research recommendations is to provide actionable advice to individuals or organizations that can help them make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, or implement changes that address the issues identified in the research.
The main purpose of research recommendations is to facilitate the transfer of knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or other stakeholders who can benefit from the research findings. Recommendations can help bridge the gap between research and practice by providing specific actions that can be taken based on the research results. By providing clear and actionable recommendations, researchers can help ensure that their findings are put into practice, leading to improvements in various fields, such as healthcare, education, business, and public policy.
Characteristics of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations are a key component of research studies and are intended to provide practical guidance on how to apply research findings to real-world problems. The following are some of the key characteristics of research recommendations:
- Actionable : Research recommendations should be specific and actionable, providing clear guidance on what actions should be taken to address the problem identified in the research.
- Evidence-based: Research recommendations should be based on the findings of the research study, supported by the data collected and analyzed.
- Contextual: Research recommendations should be tailored to the specific context in which they will be implemented, taking into account the unique circumstances and constraints of the situation.
- Feasible : Research recommendations should be realistic and feasible, taking into account the available resources, time constraints, and other factors that may impact their implementation.
- Prioritized: Research recommendations should be prioritized based on their potential impact and feasibility, with the most important recommendations given the highest priority.
- Communicated effectively: Research recommendations should be communicated clearly and effectively, using language that is understandable to the target audience.
- Evaluated : Research recommendations should be evaluated to determine their effectiveness in addressing the problem identified in the research, and to identify opportunities for improvement.
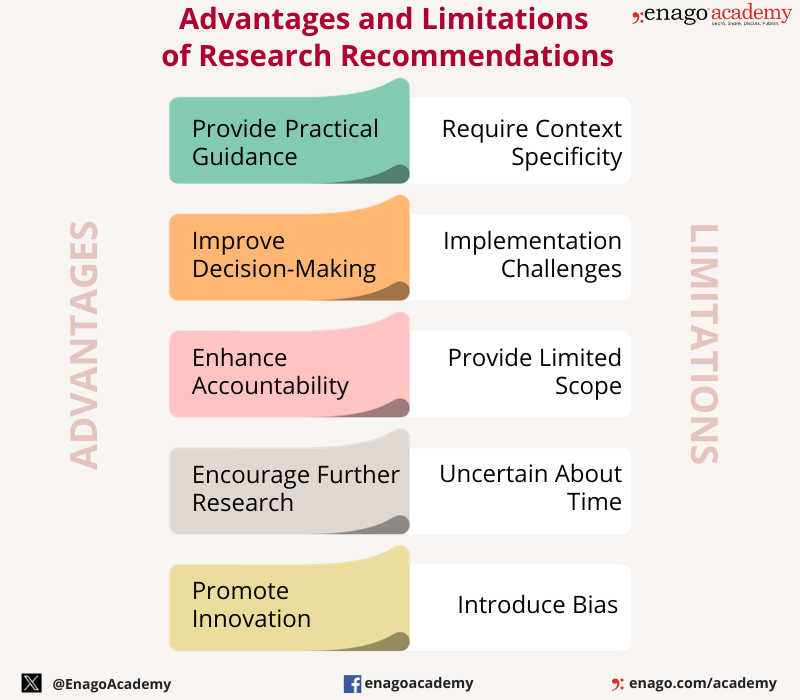
Advantages of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations have several advantages, including:
- Providing practical guidance: Research recommendations provide practical guidance on how to apply research findings to real-world problems, helping to bridge the gap between research and practice.
- Improving decision-making: Research recommendations help decision-makers make informed decisions based on the findings of research, leading to better outcomes and improved performance.
- Enhancing accountability : Research recommendations can help enhance accountability by providing clear guidance on what actions should be taken, and by providing a basis for evaluating progress and outcomes.
- Informing policy development : Research recommendations can inform the development of policies that are evidence-based and tailored to the specific needs of a given situation.
- Enhancing knowledge transfer: Research recommendations help facilitate the transfer of knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or other stakeholders who can benefit from the research findings.
- Encouraging further research : Research recommendations can help identify gaps in knowledge and areas for further research, encouraging continued exploration and discovery.
- Promoting innovation: Research recommendations can help identify innovative solutions to complex problems, leading to new ideas and approaches.
Limitations of Research Recommendations
While research recommendations have several advantages, there are also some limitations to consider. These limitations include:
- Context-specific: Research recommendations may be context-specific and may not be applicable in all situations. Recommendations developed in one context may not be suitable for another context, requiring adaptation or modification.
- I mplementation challenges: Implementation of research recommendations may face challenges, such as lack of resources, resistance to change, or lack of buy-in from stakeholders.
- Limited scope: Research recommendations may be limited in scope, focusing only on a specific issue or aspect of a problem, while other important factors may be overlooked.
- Uncertainty : Research recommendations may be uncertain, particularly when the research findings are inconclusive or when the recommendations are based on limited data.
- Bias : Research recommendations may be influenced by researcher bias or conflicts of interest, leading to recommendations that are not in the best interests of stakeholders.
- Timing : Research recommendations may be time-sensitive, requiring timely action to be effective. Delayed action may result in missed opportunities or reduced effectiveness.
- Lack of evaluation: Research recommendations may not be evaluated to determine their effectiveness or impact, making it difficult to assess whether they are successful or not.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of exploration. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and an ever-expanding knowledge base, refining the process of generating research recommendations becomes imperative.
But, what is a research recommendation?
Research recommendations are suggestions or advice provided to researchers to guide their study on a specific topic . They are typically given by experts in the field. Research recommendations are more action-oriented and provide specific guidance for decision-makers, unlike implications that are broader and focus on the broader significance and consequences of the research findings. However, both are crucial components of a research study.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Although research recommendations and implications are distinct components of a research study, they are closely related. The differences between them are as follows:
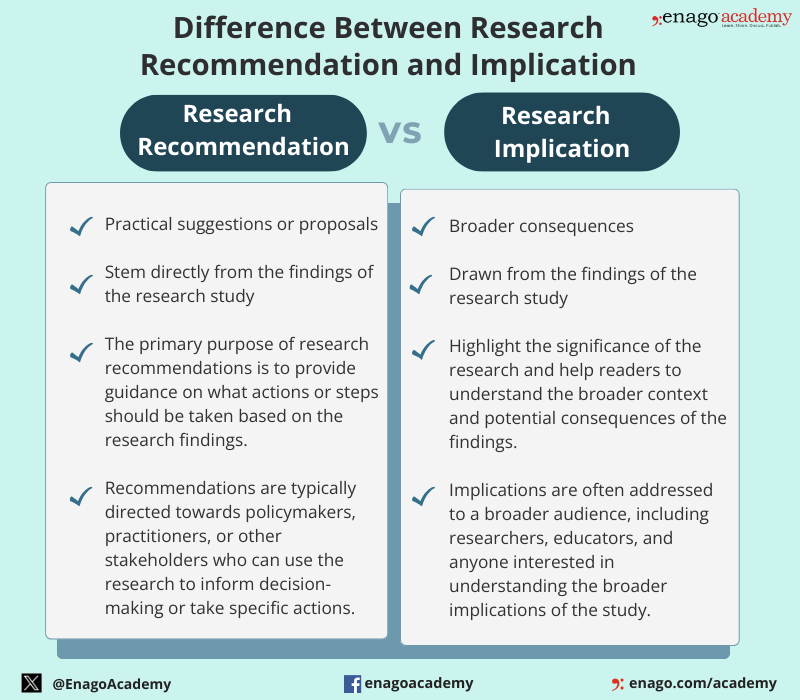
Types of Research Recommendations
Recommendations in research can take various forms, which are as follows:
These recommendations aim to assist researchers in navigating the vast landscape of academic knowledge.
Let us dive deeper to know about its key components and the steps to write an impactful research recommendation.
Key Components of Research Recommendations
The key components of research recommendations include defining the research question or objective, specifying research methods, outlining data collection and analysis processes, presenting results and conclusions, addressing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. Here are some characteristics of research recommendations:
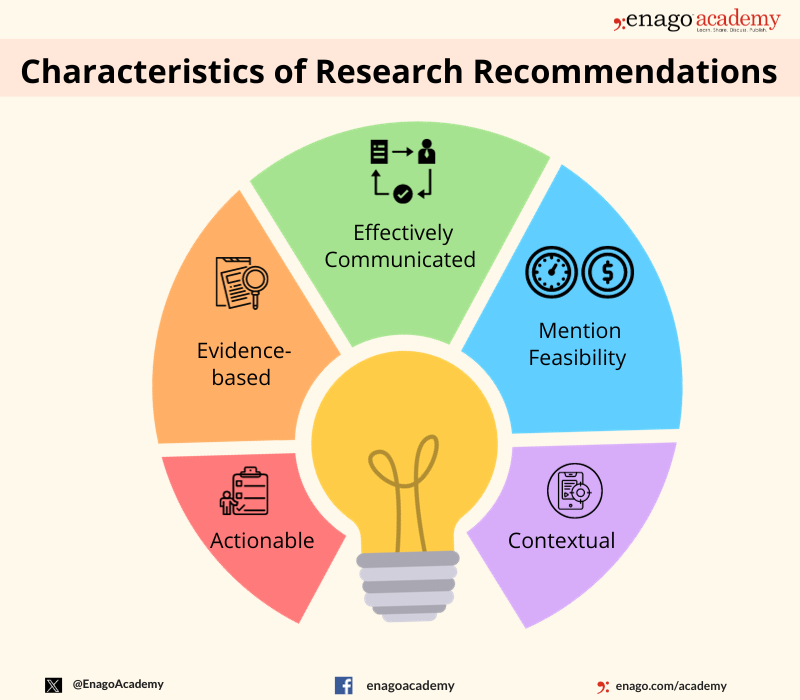
Research recommendations offer various advantages and play a crucial role in ensuring that research findings contribute to positive outcomes in various fields. However, they also have few limitations which highlights the significance of a well-crafted research recommendation in offering the promised advantages.
The importance of research recommendations ranges in various fields, influencing policy-making, program development, product development, marketing strategies, medical practice, and scientific research. Their purpose is to transfer knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving outcomes in different domains.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Research recommendations can be generated through various means, including algorithmic approaches, expert opinions, or collaborative filtering techniques. Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations.
1. Understand the Research Question:
Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study.
2. Review Existing Literature:
Familiarize yourself with relevant existing literature to help you identify gaps , and offer informed recommendations that contribute to the existing body of research.
3. Consider Research Methods:
Evaluate the appropriateness of different research methods in addressing the research question. Also, consider the nature of the data, the study design, and the specific objectives.
4. Identify Data Collection Techniques:
Gather dataset from diverse authentic sources. Include information such as keywords, abstracts, authors, publication dates, and citation metrics to provide a rich foundation for analysis.
5. Propose Data Analysis Methods:
Suggest appropriate data analysis methods based on the type of data collected. Consider whether statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a mixed-methods approach is most suitable.
6. Consider Limitations and Ethical Considerations:
Acknowledge any limitations and potential ethical considerations of the study. Furthermore, address these limitations or mitigate ethical concerns to ensure responsible research.
7. Justify Recommendations:
Explain how your recommendation contributes to addressing the research question or objective. Provide a strong rationale to help researchers understand the importance of following your suggestions.
8. Summarize Recommendations:
Provide a concise summary at the end of the report to emphasize how following these recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
By following these steps, you can create research recommendations that are actionable and contribute meaningfully to the success of the research project.
Download now to unlock some tips to improve your journey of writing research recommendations.
Example of a Research Recommendation
Here is an example of a research recommendation based on a hypothetical research to improve your understanding.
Research Recommendation: Enhancing Student Learning through Integrated Learning Platforms
Background:
The research study investigated the impact of an integrated learning platform on student learning outcomes in high school mathematics classes. The findings revealed a statistically significant improvement in student performance and engagement when compared to traditional teaching methods.
Recommendation:
In light of the research findings, it is recommended that educational institutions consider adopting and integrating the identified learning platform into their mathematics curriculum. The following specific recommendations are provided:
- Implementation of the Integrated Learning Platform:
Schools are encouraged to adopt the integrated learning platform in mathematics classrooms, ensuring proper training for teachers on its effective utilization.
- Professional Development for Educators:
Develop and implement professional programs to train educators in the effective use of the integrated learning platform to address any challenges teachers may face during the transition.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
Establish a monitoring and evaluation system to track the impact of the integrated learning platform on student performance over time.
- Resource Allocation:
Allocate sufficient resources, both financial and technical, to support the widespread implementation of the integrated learning platform.
By implementing these recommendations, educational institutions can harness the potential of the integrated learning platform and enhance student learning experiences and academic achievements in mathematics.
This example covers the components of a research recommendation, providing specific actions based on the research findings, identifying the target audience, and outlining practical steps for implementation.
Using AI in Research Recommendation Writing
Enhancing research recommendations is an ongoing endeavor that requires the integration of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. By embracing data-driven approaches and leveraging advanced technologies, the research community can create more effective and personalized recommendation systems. However, it is accompanied by several limitations. Therefore, it is essential to approach the use of AI in research with a critical mindset, and complement its capabilities with human expertise and judgment.
Here are some limitations of integrating AI in writing research recommendation and some ways on how to counter them.
1. Data Bias
AI systems rely heavily on data for training. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the AI model may produce biased results or recommendations.
How to tackle: Audit regularly the model’s performance to identify any discrepancies and adjust the training data and algorithms accordingly.
2. Lack of Understanding of Context:
AI models may struggle to understand the nuanced context of a particular research problem. They may misinterpret information, leading to inaccurate recommendations.
How to tackle: Use AI to characterize research articles and topics. Employ them to extract features like keywords, authorship patterns and content-based details.
3. Ethical Considerations:
AI models might stereotype certain concepts or generate recommendations that could have negative consequences for certain individuals or groups.
How to tackle: Incorporate user feedback mechanisms to reduce redundancies. Establish an ethics review process for AI models in research recommendation writing.
4. Lack of Creativity and Intuition:
AI may struggle with tasks that require a deep understanding of the underlying principles or the ability to think outside the box.
How to tackle: Hybrid approaches can be employed by integrating AI in data analysis and identifying patterns for accelerating the data interpretation process.
5. Interpretability:
Many AI models, especially complex deep learning models, lack transparency on how the model arrived at a particular recommendation.
How to tackle: Implement models like decision trees or linear models. Provide clear explanation of the model architecture, training process, and decision-making criteria.
6. Dynamic Nature of Research:
Research fields are dynamic, and new information is constantly emerging. AI models may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing landscape and may not be able to adapt to new developments.
How to tackle: Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Regularly update the recommendation system based on user feedback and emerging research trends.
The integration of AI in research recommendation writing holds great promise for advancing knowledge and streamlining the research process. However, navigating these concerns is pivotal in ensuring the responsible deployment of these technologies. Researchers need to understand the use of responsible use of AI in research and must be aware of the ethical considerations.
Exploring research recommendations plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry. It serves as a compass, guiding researchers toward more robust methodologies, collaborative endeavors, and innovative approaches. Embracing these suggestions not only enhances the quality of individual studies but also contributes to the collective advancement of human understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of recommendations in research is to provide practical and actionable suggestions based on the study's findings, guiding future actions, policies, or interventions in a specific field or context. Recommendations bridges the gap between research outcomes and their real-world application.
To make a research recommendation, analyze your findings, identify key insights, and propose specific, evidence-based actions. Include the relevance of the recommendations to the study's objectives and provide practical steps for implementation.
Begin a recommendation by succinctly summarizing the key findings of the research. Clearly state the purpose of the recommendation and its intended impact. Use a direct and actionable language to convey the suggested course of action.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
Graphical Abstracts Vs. Infographics: Best practices for using visual illustrations for increased research impact
Dr. Sarah Chen stared at her computer screen, her eyes staring at her recently published…

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…

- Career Corner
- Reporting Research
How to Create a Poster That Stands Out: Tips for a smooth poster presentation
It was the conference season. Judy was excited to present her first poster! She had…

- Diversity and Inclusion
6 Reasons Why There is a Decline in Higher Education Enrollment: Action plan to overcome this crisis
Over the past decade, colleges and universities across the globe have witnessed a concerning trend…
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?
The Ultimate Guide to Crafting Impactful Recommendations in Research

Are you ready to take your research to the next level? Crafting impactful recommendations is the key to unlocking the full potential of your study. By providing clear, actionable suggestions based on your findings, you can bridge the gap between research and real-world application.
In this ultimate guide, we'll show you how to write recommendations that make a difference in your research report or paper.
You'll learn how to craft specific, actionable recommendations that connect seamlessly with your research findings. Whether you're a student, writer, teacher, or journalist, this guide will help you master the art of writing recommendations in research. Let's get started and make your research count!
Understanding the Purpose of Recommendations
Recommendations in research serve as a vital bridge between your findings and their real-world applications. They provide specific, action-oriented suggestions to guide future studies and decision-making processes. Let's dive into the key purposes of crafting effective recommendations:
Guiding Future Research
Research recommendations play a crucial role in steering scholars and researchers towards promising avenues of exploration. By highlighting gaps in current knowledge and proposing new research questions, recommendations help advance the field and drive innovation.
Influencing Decision-Making
Well-crafted recommendations have the power to shape policies, programs, and strategies across various domains, such as:
- Policy-making
- Product development
- Marketing strategies
- Medical practice
By providing clear, evidence-based suggestions, recommendations facilitate informed decision-making and improve outcomes.
Connecting Research to Practice
Recommendations act as a conduit for transferring knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, and stakeholders. They bridge the gap between academic findings and their practical applications, ensuring that research insights are effectively translated into real-world solutions.
Enhancing Research Impact
By crafting impactful recommendations, you can amplify the reach and influence of your research, attracting attention from peers, funding agencies, and decision-makers.
Addressing Limitations
Recommendations provide an opportunity to acknowledge and address the limitations of your study. By suggesting concrete and actionable possibilities for future research, you demonstrate a thorough understanding of your work's scope and potential areas for improvement.
Identifying Areas for Future Research
Discovering research gaps is a crucial step in crafting impactful recommendations. It involves reviewing existing studies and identifying unanswered questions or problems that warrant further investigation. Here are some strategies to help you identify areas for future research:
Explore Research Limitations
Take a close look at the limitations section of relevant studies. These limitations often provide valuable insights into potential areas for future research. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance our understanding of the topic at hand.
Critically Analyze Discussion and Future Research Sections
When reading articles, pay special attention to the discussion and future research sections. These sections often highlight gaps in the current knowledge base and propose avenues for further exploration. Take note of any recurring themes or unanswered questions that emerge across multiple studies.
Utilize Targeted Search Terms
To streamline your search for research gaps, use targeted search terms such as "literature gap" or "future research" in combination with your subject keywords. This approach can help you quickly identify articles that explicitly discuss areas for future investigation.
Seek Guidance from Experts
Don't hesitate to reach out to your research advisor or other experts in your field. Their wealth of knowledge and experience can provide valuable insights into potential research gaps and emerging trends.
By employing these strategies, you'll be well-equipped to identify research gaps and craft recommendations that push the boundaries of current knowledge. Remember, the goal is to refine your research questions and focus your efforts on areas where more understanding is needed.
Structuring Your Recommendations
When it comes to structuring your recommendations, it's essential to keep them concise, organized, and tailored to your audience. Here are some key tips to help you craft impactful recommendations:
Prioritize and Organize
- Limit your recommendations to the most relevant and targeted suggestions for your peers or colleagues in the field.
- Place your recommendations at the end of the report, as they are often top of mind for readers.
- Write your recommendations in order of priority, with the most important ones for decision-makers coming first.
Use a Clear and Actionable Format
- Write recommendations in a clear, concise manner using actionable words derived from the data analyzed in your research.
- Use bullet points instead of long paragraphs for clarity and readability.
- Ensure that your recommendations are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely (SMART).
Connect Recommendations to Research
By following this simple formula, you can ensure that your recommendations are directly connected to your research and supported by a clear rationale.
Tailor to Your Audience
- Consider the needs and interests of your target audience when crafting your recommendations.
- Explain how your recommendations can solve the issues explored in your research.
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints of your study that may impact the implementation of your recommendations.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
- Don't undermine your own work by suggesting incomplete or unnecessary recommendations.
- Avoid using recommendations as a place for self-criticism or introducing new information not covered in your research.
- Ensure that your recommendations are achievable and comprehensive, offering practical solutions for the issues considered in your paper.
By structuring your recommendations effectively, you can enhance the reliability and validity of your research findings, provide valuable strategies and suggestions for future research, and deliver impactful solutions to real-world problems.
Crafting Actionable and Specific Recommendations
Crafting actionable and specific recommendations is the key to ensuring your research findings have a real-world impact. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
Embrace Flexibility and Feasibility
Your recommendations should be open to discussion and new information, rather than being set in stone. Consider the following:
- Be realistic and considerate of your team's capabilities when making recommendations.
- Prioritize recommendations based on impact and reach, but be prepared to adjust based on team effort levels.
- Focus on solutions that require the fewest changes first, adopting an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach.
Provide Detailed and Justified Recommendations
To avoid vagueness and misinterpretation, ensure your recommendations are:
- Detailed, including photos, videos, or screenshots whenever possible.
- Justified based on research findings, providing alternatives when findings don't align with expectations or business goals.
Use this formula when writing recommendations:
Observed problem/pain point/unmet need + consequence + potential solution

Adopt a Solution-Oriented Approach
Foster collaboration and participation.
- Promote staff education on current research and create strategies to encourage adoption of promising clinical protocols.
- Include representatives from the treatment community in the development of the research initiative and the review of proposals.
- Require active, early, and permanent participation of treatment staff in the development, implementation, and interpretation of the study.
Tailor Recommendations to the Opportunity
When writing recommendations for a specific opportunity or program:
- Highlight the strengths and qualifications of the researcher.
- Provide specific examples of their work and accomplishments.
- Explain how their research has contributed to the field.
- Emphasize the researcher's potential for future success and their unique contributions.
By following these guidelines, you'll craft actionable and specific recommendations that drive meaningful change and showcase the value of your research.
Connecting Recommendations with Research Findings
Connecting your recommendations with research findings is crucial for ensuring the credibility and impact of your suggestions. Here's how you can seamlessly link your recommendations to the evidence uncovered in your study:
Grounding Recommendations in Research
Your recommendations should be firmly rooted in the data and insights gathered during your research process. Avoid including measures or suggestions that were not discussed or supported by your study findings. This approach ensures that your recommendations are evidence-based and directly relevant to the research at hand.
Highlighting the Significance of Collaboration
Research collaborations offer a wealth of benefits that can enhance an agency's competitive position. Consider the following factors when discussing the importance of collaboration in your recommendations:
- Organizational Development: Participation in research collaborations depends on an agency's stage of development, compatibility with its mission and culture, and financial stability.
- Trust-Building: Long-term collaboration success often hinges on a history of increasing involvement and trust between partners.
- Infrastructure: A permanent infrastructure that facilitates long-term development is key to successful collaborative programs.
Emphasizing Commitment and Participation
Fostering quality improvement and organizational learning.
In your recommendations, highlight the importance of enhancing quality improvement strategies and fostering organizational learning. Show sensitivity to the needs and constraints of community-based programs, as this understanding is crucial for effective collaboration and implementation.
Addressing Limitations and Implications
If not already addressed in the discussion section, your recommendations should mention the limitations of the study and their implications. Examples of limitations include:
- Sample size or composition
- Participant attrition
- Study duration
By acknowledging these limitations, you demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of your research and its potential impact.
By connecting your recommendations with research findings, you provide a solid foundation for your suggestions, emphasize the significance of collaboration, and showcase the potential for future research and practical applications.
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the full potential of your study. Remember to prioritize actionable, specific, and evidence-based recommendations that foster collaboration and drive meaningful change.
As you embark on your research journey, embrace the power of well-crafted recommendations to amplify the impact of your work. By following the guidelines outlined in this ultimate guide, you'll be well-equipped to write recommendations that resonate with your audience, inspire further investigation, and contribute to the advancement of your field. So go forth, make your research count, and let your recommendations be the catalyst for positive change.
Q: What are the steps to formulating recommendations in research? A: To formulate recommendations in research, you should first gain a thorough understanding of the research question. Review the existing literature to inform your recommendations and consider the research methods that were used. Identify which data collection techniques were employed and propose suitable data analysis methods. It's also essential to consider any limitations and ethical considerations of your research. Justify your recommendations clearly and finally, provide a summary of your recommendations.
Q: Why are recommendations significant in research studies? A: Recommendations play a crucial role in research as they form a key part of the analysis phase. They provide specific suggestions for interventions or strategies that address the problems and limitations discovered during the study. Recommendations are a direct response to the main findings derived from data collection and analysis, and they can guide future actions or research.
Q: Can you outline the seven steps involved in writing a research paper? A: Certainly. The seven steps to writing an excellent research paper include:
- Allowing yourself sufficient time to complete the paper.
- Defining the scope of your essay and crafting a clear thesis statement.
- Conducting a thorough yet focused search for relevant research materials.
- Reading the research materials carefully and taking detailed notes.
- Writing your paper based on the information you've gathered and analyzed.
- Editing your paper to ensure clarity, coherence, and correctness.
- Submitting your paper following the guidelines provided.
Q: What tips can help make a research paper more effective? A: To enhance the effectiveness of a research paper, plan for the extensive process ahead and understand your audience. Decide on the structure your research writing will take and describe your methodology clearly. Write in a straightforward and clear manner, avoiding the use of clichés or overly complex language.
Sign up for more like this.

How to write a research conclusion and recommendations?
28 June 2024
Magda Wojcik
Conclusion and recommendations are the final part of the research paper, which synthesises the research, highlights its significance and provides a roadmap for future studies and practical applications. A well-crafted conclusion not only summarises the key points of the research but also emphasises its broader implications and suggests potential areas for further exploration. Similarly, research recommendations offer specific, actionable insights that can guide future research, inform policy decisions and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of how to effectively write conclusions and recommendations, detailing their purposes, components and examples across various disciplines. Additionally, it offers resources and tools to assist researchers in crafting clear, impactful final sections of their papers, ensuring they are well-prepared for publication.
What is a research conclusion?
What are research recommendations, example 1: conclusion and recommendations in business, example 2: conclusion and recommendations in literary history, example 3: conclusion and recommendations in environmental science, resources for writing research conclusions and recommendations, how to prepare research papers for publication.
A research conclusion is the final section of a research paper where the author wraps up the study and presents the key findings. It synthesises the main points discussed in the paper, highlights the significance of the research and suggests potential implications or applications. The conclusion leaves a lasting impression on the reader. It often includes recommendations for future research or practical applications of the study’s findings.
Purpose of a research conclusion
- Summarisation : To provide a concise summary of the main findings and arguments presented in the paper.
- Synthesis : To synthesise the information, showing how it contributes to the overall understanding of the topic.
- Implications : To highlight the significance of the research findings and their broader implications.
- Future research : To suggest areas for further investigation or unanswered questions.
- Closure : To provide a sense of closure to the reader, ensuring the research paper feels complete and comprehensive.
Components of a research conclusion
- Restatement of the thesis : Begin by restating the thesis or main research question, reflecting the insights gained from the study.
- Summary of main points : Summarise the key findings and arguments made in the paper. This should be concise and focused, highlighting the most critical aspects.
- Implications of the findings : Discuss the broader implications of the research findings. This might include their significance for the field, practical applications, policy implications or theoretical advancements.
- Limitations of the study : Acknowledge any limitations encountered during the research. This demonstrates a critical and reflective approach to the research process.
- Recommendations for future research : Suggest areas where further research is needed. This could involve new questions that arose from the study or unexplored aspects of the topic.
- Final thoughts : End with a strong closing statement. This could be a thought-provoking quote, a call to action or a reflection on the importance of the topic.
Research recommendations are a section of a research paper where the author suggests specific actions, areas for further study or changes in practice based on the findings of the research. These recommendations are intended to guide future research, inform policymakers, practitioners or other stakeholders and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
Purpose of research recommendations
- Guidance for future research : To provide a roadmap for future studies that can build on the current research or explore new aspects of the topic.
- Practical applications : To suggest practical changes or actions that can be implemented based on the research findings.
- Policy implications : To inform policy decisions or suggest policy changes.
- Contribution to knowledge : To highlight potential areas where further investigation can contribute to the broader understanding of the subject matter.
Components of research recommendations
- Specificity : Clearly state specific actions or studies that should be undertaken.
- Justification : Provide a rationale for why these recommendations are important and how they are supported by the research findings.
- Feasibility : Discuss the feasibility of the recommendations, considering available resources, time and potential challenges.
- Impact : Highlight the potential impact of implementing these recommendations on the field, practice or policy.
- Prioritisation : If multiple recommendations are provided, prioritise them based on their importance or urgency.
In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of the impact of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on consumer loyalty in the retail sector. The data collected from a sample of 500 consumers across various demographics indicates a significant positive correlation between CSR initiatives and consumer loyalty. Specifically, companies that actively engage in environmental sustainability and community support programs tend to enjoy higher customer retention rates and increased brand loyalty (Smith, 2021; Johnson & Lee, 2020). These findings are consistent with previous research suggesting that modern consumers are increasingly valuing ethical business practices (Brown et al., 2019).
Recommendation
Based on these findings, it is recommended that retail companies enhance their CSR strategies to foster greater consumer loyalty. Specifically, businesses should invest in sustainable practices, such as reducing carbon footprints and supporting local communities, as these actions have been shown to positively influence consumer perceptions and loyalty (Green & White, 2022). Furthermore, future research should explore the long-term impacts of CSR on brand loyalty across different retail sectors, considering the potential differences in consumer behaviour and expectations. Implementing these recommendations could lead to a more sustainable and loyal customer base, ultimately driving long-term business success.
In conclusion, this analysis of Gothic literature in the nineteenth century reveals a profound connection between socio-political anxieties and the thematic elements of Gothic fiction. By examining key works such as Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein (1818) and Bram Stoker’s Dracula (1897), the study demonstrates how these novels reflect contemporary fears related to scientific advancements, immigration, and the destabilisation of traditional social structures (Jones, 2021; Parker, 2019). The recurrence of monstrous figures and dark settings in these texts underscores the period’s cultural anxieties and the writers’ responses to the changing societal landscape (Wilson, 2020).
To further understand the complex relationship between Gothic literature and socio-political contexts, it is recommended that future research should focus on lesser-known Gothic works and their portrayal of contemporary issues. Additionally, interdisciplinary studies that incorporate historical, sociological, and literary analysis could provide deeper insights into how Gothic fiction both shaped and was shaped by the anxieties of its time (Miller & Thompson, 2022). By expanding the scope of research to include a wider range of texts and perspectives, scholars can gain a more nuanced understanding of the Gothic genre’s role in reflecting and influencing nineteenth-century society.
In conclusion, this study provides a detailed examination of the effects of urban green spaces on local air quality in metropolitan areas. The data collected from 20 cities worldwide indicates that urban green spaces significantly reduce levels of airborne pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter (PM10). Specifically, areas with dense vegetation and large parklands showed an average reduction in NO2 and PM10 levels by 20% compared to areas with minimal green cover (Garcia et al., 2021; Zhang & Li, 2020). These findings are in line with previous research demonstrating the role of vegetation in air purification and the mitigation of urban heat islands (Wang et al., 2019).
Based on these findings, it is recommended that urban planners and policymakers prioritise the expansion and maintenance of green spaces in urban areas to improve air quality and public health. This can be achieved through initiatives such as the creation of new parks, green roofs, and green walls, as well as the preservation of existing natural habitats (Smith & Johnson, 2022). Future research should focus on the long-term impacts of different types of vegetation on air quality and the optimal spatial distribution of green spaces for maximum environmental benefits. Implementing these recommendations could lead to healthier urban environments and enhanced quality of life for city residents.
Academic writers and researchers can benefit greatly from a variety of resources and tools when crafting conclusions and recommendations .
- How to Write a Lot: A Practical Guide to Productive Academic Writing by Paul J. Silvia offers strategies for making writing a regular part of your academic life, including tips for writing conclusions and recommendations.
- The Craft of Research by Wayne C. Booth, Gregory G. Colomb and Joseph M. Williams offers practical advice on every aspect of the research process, including how to effectively write conclusions and recommendations.
- Writing Science: How to Write Papers That Get Cited and Proposals That Get Funded by Joshua Schimel provides insights into writing clear and concise scientific papers, with specific chapters dedicated to crafting conclusions and recommendations.
Online resources
- The Harvard College Writing Center offers resources and advice on writing effective conclusions. Their guides cover how to restate the thesis, summarise key points and articulate the significance of the research.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab provides detailed guides on writing various parts of a research paper, including conclusions and recommendations. It also offers examples and exercises to help improve writing skills.
- University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Writing Center provides tips and strategies for writing conclusions, including how to create a sense of closure and address the broader implications of your research.
Software and tools
- EndNote is a reference management tool that helps organise research and references, making it easier to cite sources accurately.
- Hemingway is a writing assistant that helps improve clarity, readability and style by highlighting complex sentences and common errors. It ensures that conclusions and recommendations are clear and concise.
- Mendeley is another reference management tool that helps manage and share research papers, discover research data and collaborate online. It is useful for organising references used in writing conclusions and recommendations.
Editing services play a crucial role in preparing research papers for publication by ensuring that the content is clear, coherent and professionally presented. Here is how different types of editing services can help specifically with conclusions and recommendations, as well as the overall quality of a research paper:
Developmental editing
Developmental editing focuses on the structure and content of the paper, ensuring logical flow and clarity. In particular, developmental editing can help with conclusions and recommendations. For instance, it improves the structure and clarity of conclusions and recommendations by ensuring they are logically organised and clearly articulated. Moreover, it provides feedback on the content, suggesting improvements or additions to make the conclusions and recommendations more impactful and comprehensive. Finally, developmental editing improves consistency by ensuring that the conclusions and recommendations are consistent with the findings and arguments presented in the body of the paper.
The overall impact of developmental editing enhances the coherence and structure of the entire research paper. In addition, it ensures that all sections of the paper, including the conclusions and recommendations, align well with the research objectives and findings.
Line editing
Line editing focuses on improving the writing style, clarity and readability at the sentence and paragraph level. It improves the clarity and precision of the language used in the conclusions and recommendations, making them more understandable and impactful. Furthermore, it enhances the flow and readability, ensuring that the sections are engaging and easy to follow. Last, line editing adjusts the tone and style to ensure they are appropriate for the intended audience and purpose of the paper.
The impact of line editing lies in enhancing the overall readability and engagement of the research paper and ensuring that the writing is clear, concise and professional.
Copyediting
Copyediting focuses on correcting grammar, punctuation, spelling and syntax errors. It ensures that the conclusions and recommendations are free from grammatical, punctuation and spelling errors, enhancing professionalism. In addition, copyediting ensures consistency in terminology, formatting and style throughout the sections.
Overall, it provides a polished and professional final draft and ensures that the paper adheres to the style guide or publication standards.
Translation editing
Translation editing ensures that translated texts are accurate, culturally appropriate and retain the original meaning. First, translation editing ensures that the conclusions and recommendations in translated research papers accurately reflect the original content. Next, this service ensures that the language used is culturally appropriate and understandable to the target audience. Last, translation editing maintains consistency with the original paper’s tone, style and terminology.
All in all, translation editing facilitates the dissemination of research findings to a broader, multilingual audience. Furthermore, it ensures that translated research papers meet the same high standards as the original texts.
Proofreading
Proofreading provides a final check for minor errors in grammar, punctuation, spelling and formatting. For instance, proofreading catches any remaining errors in the conclusions and recommendations, ensuring they are polished and professional. Moreover, it ensures consistency in formatting and presentation, aligning with publication standards.
In sum, proofreading ensures that the research paper is error-free and ready for submission or publication.
Key takeaways
A research conclusion synthesises the study’s main points, highlights its significance and suggests potential implications or applications. It summarises the findings, underscores the broader implications, acknowledges limitations and recommends future research. Essential components include restating the thesis, summarising key points, discussing implications and limitations and providing a strong closing statement.
Research recommendations propose specific actions, areas for further study or changes in practice based on the findings. They guide future research, suggest practical applications, inform policy decisions and advance knowledge. Effective recommendations are specific, justified, feasible, impactful and prioritised.
I am an editor and indexer working with academic writers, journals and presses. If your academic manuscript needs a second pair of eyes, contact me for a free sample edit (and remember to use my early bird discount ).
I'm a freelance editor and indexer with a PhD in literary history. I work with non-fiction, academic and business texts.
Memberships

Incorporated in England and Wales. Company number: 10809565. Registered office: 124 City Road, London, England, EC1V 2NX
© MWEditing 2023
Writing the parts of scientific reports
22 Writing the conclusion & recommendations
There are probably some overlaps between the Conclusion and the Discussion section. Nevertheless, this section gives you the opportunity to highlight the most important points in your report, and is sometimes the only section read. Think about what your research/ study has achieved, and the most important findings and ideas you want the reader to know. As all studies have limitations also think about what you were not able to cover (this shows that you are able to evaluate your own work objectively).
Possible structure of this section:
Use present perfect to sum up/ evaluate:
This study has explored/ has attempted …
Use past tense to state what your aim was and to refer to actions you carried out:
- This study was intended to analyse …
- The aim of this study was to …
Use present tense to evaluate your study and to state the generalizations and implications that you draw from your findings.
- The results add to the knowledge of …
- These findings s uggest that …
You can either use present tense or past tense to summarize your results.
- The findings reveal …
- It was found that …
Achievements of this study (positive)
- This study provides evidence that …
- This work has contributed to a number of key issues in the field such as …
Limitations of the study (negative)
- Several limitations should be noted. First …
Combine positive and negative remarks to give a balanced assessment:
- Although this research is somewhat limited in scope, its findings can provide a basis for future studies.
- Despite the limitations, findings from the present study can help us understand …
Use more cautious language (modal verbs may, can, could)
- There are a number of possible extensions of this research …
- The findings suggest the possibility for future research on …
- These results may be important for future studies on …
- Examining a wider context could/ would lead …
Or indicate that future research is needed
- There is still a need for future research to determine …
- Further studies should be undertaken to discover…
- It would be worthwhile to investigate …
Academic Writing in a Swiss University Context Copyright © 2018 by Irene Dietrichs. All Rights Reserved.

How to write recommendations in a research paper
Many students put in a lot of effort and write a good report however they are not able to give proper recommendations. Recommendations in the research paper should be included in your research. As a researcher, you display a deep understanding of the topic of research. Therefore you should be able to give recommendations. Here are a few tips that will help you to give appropriate recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should be the objective of the research. Therefore at least one of your objectives of the paper is to provide recommendations to the parties associated or the parties that will benefit from your research. For example, to encourage higher employee engagement HR department should make strategies that invest in the well-being of employees. Additionally, the HR department should also collect regular feedback through online surveys.
Recommendations in the research paper should come from your review and analysis For example It was observed that coaches interviewed were associated with the club were working with the club from the past 2-3 years only. This shows that the attrition rate of coaches is high and therefore clubs should work on reducing the turnover of coaches.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from the data you have analysed. For example, the research found that people over 65 years of age are at greater risk of social isolation. Therefore, it is recommended that policies that are made for combating social isolation should target this specific group.
Recommendations in the research paper should also come from observation. For example, it is observed that Lenovo’s income is stable and gross revenue has displayed a negative turn. Therefore the company should analyse its marketing and branding strategy.
Recommendations in the research paper should be written in the order of priority. The most important recommendations for decision-makers should come first. However, if the recommendations are of equal importance then it should come in the sequence in which the topic is approached in the research.
Recommendations in a research paper if associated with different categories then you should categorize them. For example, you have separate recommendations for policymakers, educators, and administrators then you can categorize the recommendations.
Recommendations in the research paper should come purely from your research. For example, you have written research on the impact on HR strategies on motivation. However, nowhere you have discussed Reward and recognition. Then you should not give recommendations for using rewards and recognition measures to boost employee motivation.
The use of bullet points offers better clarity rather than using long paragraphs. For example this paragraph “ It is recommended that Britannia Biscuit should launch and promote sugar-free options apart from the existing product range. Promotion efforts should be directed at creating a fresh and healthy image. A campaign that conveys a sense of health and vitality to the consumer while enjoying biscuit is recommended” can be written as:
- The company should launch and promote sugar-free options
- The company should work towards creating s fresh and healthy image
- The company should run a campaign to convey its healthy image
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
- About WordPress
- Get Involved
- WordPress.org
- Documentation
- Learn WordPress
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write an “Implications of Research” Section

4-minute read
- 24th October 2022
When writing research papers , theses, journal articles, or dissertations, one cannot ignore the importance of research. You’re not only the writer of your paper but also the researcher ! Moreover, it’s not just about researching your topic, filling your paper with abundant citations, and topping it off with a reference list. You need to dig deep into your research and provide related literature on your topic. You must also discuss the implications of your research.
Interested in learning more about implications of research? Read on! This post will define these implications, why they’re essential, and most importantly, how to write them. If you’re a visual learner, you might enjoy this video .
What Are Implications of Research?
Implications are potential questions from your research that justify further exploration. They state how your research findings could affect policies, theories, and/or practices.
Implications can either be practical or theoretical. The former is the direct impact of your findings on related practices, whereas the latter is the impact on the theories you have chosen in your study.
Example of a practical implication: If you’re researching a teaching method, the implication would be how teachers can use that method based on your findings.
Example of a theoretical implication: You added a new variable to Theory A so that it could cover a broader perspective.
Finally, implications aren’t the same as recommendations, and it’s important to know the difference between them .
Questions you should consider when developing the implications section:
● What is the significance of your findings?
● How do the findings of your study fit with or contradict existing research on this topic?
● Do your results support or challenge existing theories? If they support them, what new information do they contribute? If they challenge them, why do you think that is?
Why Are Implications Important?
You need implications for the following reasons:
● To reflect on what you set out to accomplish in the first place
● To see if there’s a change to the initial perspective, now that you’ve collected the data
● To inform your audience, who might be curious about the impact of your research
How to Write an Implications Section
Usually, you write your research implications in the discussion section of your paper. This is the section before the conclusion when you discuss all the hard work you did. Additionally, you’ll write the implications section before making recommendations for future research.
Implications should begin with what you discovered in your study, which differs from what previous studies found, and then you can discuss the implications of your findings.
Your implications need to be specific, meaning you should show the exact contributions of your research and why they’re essential. They should also begin with a specific sentence structure.
Examples of starting implication sentences:
● These results build on existing evidence of…
● These findings suggest that…
● These results should be considered when…
● While previous research has focused on x , these results show that y …
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
You should write your implications after you’ve stated the results of your research. In other words, summarize your findings and put them into context.
The result : One study found that young learners enjoy short activities when learning a foreign language.
The implications : This result suggests that foreign language teachers use short activities when teaching young learners, as they positively affect learning.
Example 2
The result : One study found that people who listen to calming music just before going to bed sleep better than those who watch TV.
The implications : These findings suggest that listening to calming music aids sleep quality, whereas watching TV does not.
To summarize, remember these key pointers:
● Implications are the impact of your findings on the field of study.
● They serve as a reflection of the research you’ve conducted.
● They show the specific contributions of your findings and why the audience should care.
● They can be practical or theoretical.
● They aren’t the same as recommendations.
● You write them in the discussion section of the paper.
● State the results first, and then state their implications.
Are you currently working on a thesis or dissertation? Once you’ve finished your paper (implications included), our proofreading team can help ensure that your spelling, punctuation, and grammar are perfect. Consider submitting a 500-word document for free.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript
- 4 minute read
- 38.2K views
Table of Contents
The discussion section in scientific manuscripts might be the last few paragraphs, but its role goes far beyond wrapping up. It’s the part of an article where scientists talk about what they found and what it means, where raw data turns into meaningful insights. Therefore, discussion is a vital component of the article.
An excellent discussion is well-organized. We bring to you authors a classic 6-step method for writing discussion sections, with examples to illustrate the functions and specific writing logic of each step. Take a look at how you can impress journal reviewers with a concise and focused discussion section!
Discussion frame structure
Conventionally, a discussion section has three parts: an introductory paragraph, a few intermediate paragraphs, and a conclusion¹. Please follow the steps below:

1.Introduction—mention gaps in previous research¹⁻ ²
Here, you orient the reader to your study. In the first paragraph, it is advisable to mention the research gap your paper addresses.
Example: This study investigated the cognitive effects of a meat-only diet on adults. While earlier studies have explored the impact of a carnivorous diet on physical attributes and agility, they have not explicitly addressed its influence on cognitively intense tasks involving memory and reasoning.
2. Summarizing key findings—let your data speak ¹⁻ ²
After you have laid out the context for your study, recapitulate some of its key findings. Also, highlight key data and evidence supporting these findings.
Example: We found that risk-taking behavior among teenagers correlates with their tendency to invest in cryptocurrencies. Risk takers in this study, as measured by the Cambridge Gambling Task, tended to have an inordinately higher proportion of their savings invested as crypto coins.
3. Interpreting results—compare with other papers¹⁻²
Here, you must analyze and interpret any results concerning the research question or hypothesis. How do the key findings of your study help verify or disprove the hypothesis? What practical relevance does your discovery have?
Example: Our study suggests that higher daily caffeine intake is not associated with poor performance in major sporting events. Athletes may benefit from the cardiovascular benefits of daily caffeine intake without adversely impacting performance.
Remember, unlike the results section, the discussion ideally focuses on locating your findings in the larger body of existing research. Hence, compare your results with those of other peer-reviewed papers.
Example: Although Miller et al. (2020) found evidence of such political bias in a multicultural population, our findings suggest that the bias is weak or virtually non-existent among politically active citizens.
4. Addressing limitations—their potential impact on the results¹⁻²
Discuss the potential impact of limitations on the results. Most studies have limitations, and it is crucial to acknowledge them in the intermediary paragraphs of the discussion section. Limitations may include low sample size, suspected interference or noise in data, low effect size, etc.
Example: This study explored a comprehensive list of adverse effects associated with the novel drug ‘X’. However, long-term studies may be needed to confirm its safety, especially regarding major cardiac events.
5. Implications for future research—how to explore further¹⁻²
Locate areas of your research where more investigation is needed. Concluding paragraphs of the discussion can explain what research will likely confirm your results or identify knowledge gaps your study left unaddressed.
Example: Our study demonstrates that roads paved with the plastic-infused compound ‘Y’ are more resilient than asphalt. Future studies may explore economically feasible ways of producing compound Y in bulk.
6. Conclusion—summarize content¹⁻²
A good way to wind up the discussion section is by revisiting the research question mentioned in your introduction. Sign off by expressing the main findings of your study.
Example: Recent observations suggest that the fish ‘Z’ is moving upriver in many parts of the Amazon basin. Our findings provide conclusive evidence that this phenomenon is associated with rising sea levels and climate change, not due to elevated numbers of invasive predators.
A rigorous and concise discussion section is one of the keys to achieving an excellent paper. It serves as a critical platform for researchers to interpret and connect their findings with the broader scientific context. By detailing the results, carefully comparing them with existing research, and explaining the limitations of this study, you can effectively help reviewers and readers understand the entire research article more comprehensively and deeply¹⁻² , thereby helping your manuscript to be successfully published and gain wider dissemination.
In addition to keeping this writing guide, you can also use Elsevier Language Services to improve the quality of your paper more deeply and comprehensively. We have a professional editing team covering multiple disciplines. With our profound disciplinary background and rich polishing experience, we can significantly optimize all paper modules including the discussion, effectively improve the fluency and rigor of your articles, and make your scientific research results consistent, with its value reflected more clearly. We are always committed to ensuring the quality of papers according to the standards of top journals, improving the publishing efficiency of scientific researchers, and helping you on the road to academic success. Check us out here !
Type in wordcount for Standard Total: USD EUR JPY Follow this link if your manuscript is longer than 12,000 words. Upload
References:
- Masic, I. (2018). How to write an efficient discussion? Medical Archives , 72(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2018.72.306-307
- Şanlı, Ö., Erdem, S., & Tefik, T. (2014). How to write a discussion section? Urology Research & Practice , 39(1), 20–24. https://doi.org/10.5152/tud.2013.049

Navigating “Chinglish” Errors in Academic English Writing

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing
You may also like.

Submission 101: What format should be used for academic papers?

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Stylistic devices
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Dissertation Recommendations — How To Write Them
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recommendations are crucial to your paper because they suggest solutions to your research problems. You can include recommendations in the discussion sections of your writing and briefly in the conclusions of your dissertation , thesis, or research paper . This article discusses dissertation recommendations, their purpose, and how to write one.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Dissertation recommendations
- 3 How to write dissertation recommendations
- 4 Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
- 5 Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Dissertation Recommendations — In a Nutshell
- Dissertation recommendations are an important aspect of your research paper.
- They should be specific, measurable, and have the potential of future possibilities.
- Additionally, these recommendations should offer practical insights and suggestions for solving real-life problems.
When making your recommendations, please ensure the following:
- Your recommendations are an extension of your work instead of a basis for self-criticism
- Your research stands independently instead of suggesting recommendations that will complete it
- Your dissertation recommendations offer insights into how future research can build upon it instead of undermining your research
Definition: Dissertation recommendations
Dissertation recommendations are the actionable insights and suggestions presented after you get your research findings. These suggestions are usually based on what you find and help to guide future studies or practical applications. It’s best to place your dissertation recommendations at the conclusion.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
How to write dissertation recommendations
When writing your academic paper, you can frame dissertation recommendations using one of the following methods:
Use the problem: In this approach, you should address the issues highlighted in your research.
Offer solutions: You can offer some practical solutions to the problems revealed in your research.
Use a theory: Here, you can base your recommendations on your study’s theoretical approach.
Here are some helpful tips for writing dissertation recommendations that you should incorporate when drafting a research paper:
- Avoid general or vague recommendations
- Be specific and concrete
- Offer measurable insights Ensure your suggestions are practical and implementable
- Avoid focusing on theoretical concepts or new findings but on future possibilities
“Based on the study’s outcomes, it’s recommended that businesses and organizations develop mental health well-being frameworks to reduce workplace stress. This training should be mandatory for all employees and conducted on a monthly basis.”
Dissertation recommendations based on your findings
After analysing your findings, you can divide your dissertation recommendations into two subheadings as discussed below:
What can be done?
This section highlights the steps you can use when conducting the research. You may also include any steps needed to address the issues highlighted in your research question. For instance, if the study reveals a lack of emotional connection between employees, implementing dynamic awareness training or sit-downs could be recommended.
Is further research needed?
This section highlights the benefits of further studies that will help build on your research findings. For instance, if your research found less data on employee mental well-being, your dissertation recommendations could suggest future studies.
Purpose of dissertation recommendations
Note: Dissertation recommendations have the following purposes:
- Provide guidance and improve the quality of further studies based on your research findings
- Offer insights, call to action, or suggest other studies
- Highlight specific, clear, and realistic suggestions for future studies
When writing your dissertation recommendations, always remember to keep them specific, measurable, and clear. You should also ensure that a comprehensible rationale supports these recommendations. Additionally, your requests should always be directly linked to your research and offer suggestions from that angle.
Note that your suggestions should always focus on future possibilities and not on present new findings or theoretical concepts. This is because future researchers may use your results to draw further conclusions and gather new insights from your work.
Can I include new arguments in the conclusion of a dissertation
Dissertations follow a more formal structure; hence, you can only present new arguments in the conclusion. Use your dissertation’s concluding part as a summary of your points or to provide recommendations.
How is the conclusion different from the discussion sections?
The discussion section describes a detailed account of your findings, while the conclusion answers the research question and highlights some recommendations.
What shouldn't I include in the dissertation recommendations?
Avoid concluding with weak statements like “there are good insights from both ends…”, generic phrases like “in conclusion…” or evidence that you failed to mention in the discussion or results section.
BachelorPrint was phenomenal! I ordered two copies of my Ph.D. dissertation on...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, how to write a case study in research..., online ai writing tools: cost-efficient help for dissertation..., how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

COMMENTS
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Step 1: Revisit Your Research Goals. Before doing anything else, you have to remind yourself of the objectives that you set out to achieve in your research. It allows you to match your recommendations directly to your research questions and see if you made any contribution to your goals.
For example, recommendations from research on climate change can be used to develop policies that reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability. Program development: Research recommendations can guide the development of programs that address specific issues. For example, recommendations from research on education can be used to develop ...
Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations. 1. Understand the Research Question: Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study. 2.
Recommendations should be clear and include actionable words. While completing this section, the writer should show a solution-oriented approach by highlighting the scope for future investigation. Using bullet points is a better way to ensure clarity instead of writing long paragraphs. Look at the following recommendation in a research paper ...
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the ...
Components of a research conclusion. Restatement of the thesis: Begin by restating the thesis or main research question, reflecting the insights gained from the study. Summary of main points: Summarise the key findings and arguments made in the paper. This should be concise and focused, highlighting the most critical aspects.
Here you can include a personal assessment of what you have learnt (if you are asked to provide it) Suggestions for future research: Suggest how your work reported in this paper opens new research possibilities. Implications of the study: Place the study in a wider context of research in the discipline and/ or a situation in the real world.
In a more empirical paper, you can close by either making recommendations for practice (for example, in clinical or policy papers), or suggesting directions for future research. Whatever the scope of your own research, there will always be room for further investigation of related topics, and you'll often discover new questions and problems ...
The inclusion of an action plan along with recommendation adds more weightage to your recommendation. Recommendations should be clear and conscience and written using actionable words. Recommendations should display a solution-oriented approach and in some cases should highlight the scope for further research.
To summarize, remember these key pointers: Implications are the impact of your findings on the field of study. They serve as a reflection of the research you've conducted. They show the specific contributions of your findings and why the audience should care. They can be practical or theoretical. They aren't the same as recommendations.
1.Introduction—mention gaps in previous research¹⁻². 2. Summarizing key findings—let your data speak¹⁻². 3. Interpreting results—compare with other papers¹⁻². 4. Addressing limitations—their potential impact on the results¹⁻². 5. Implications for future research—how to explore further¹⁻².
Here are some helpful tips for writing dissertation recommendations that you should incorporate when drafting a research paper: Avoid general or vague recommendations. Be specific and concrete. Offer measurable insights Ensure your suggestions are practical and implementable. Avoid focusing on theoretical concepts or new findings but on future ...
Summarization: The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research's main contributions. 3. Relevance: Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper's main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4.
If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you're writing to meet their expectations. Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader.
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
Here are a few best practices: Your results should always be written in the past tense. While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible. Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions.