Are you seeking one-on-one college counseling and/or essay support? Limited spots are now available. Click here to learn more.

How to Write a Body Paragraph for a College Essay
January 29, 2024
No matter the discipline, college success requires mastering several academic basics, including the body paragraph. This article will provide tips on drafting and editing a strong body paragraph before examining several body paragraph examples. Before we look at how to start a body paragraph and how to write a body paragraph for a college essay (or other writing assignment), let’s define what exactly a body paragraph is.
What is a Body Paragraph?
Simply put, a body paragraph consists of everything in an academic essay that does not constitute the introduction and conclusion. It makes up everything in between. In a five-paragraph, thesis-style essay (which most high schoolers encounter before heading off to college), there are three body paragraphs. Longer essays with more complex arguments will include many more body paragraphs.
We might correlate body paragraphs with bodily appendages—say, a leg. Both operate in a somewhat isolated way to perform specific operations, yet are integral to creating a cohesive, functioning whole. A leg helps the body sit, walk, and run. Like legs, body paragraphs work to move an essay along, by leading the reader through several convincing ideas. Together, these ideas, sometimes called topics, or points, work to prove an overall argument, called the essay’s thesis.
If you compared an essay on Kant’s theory of beauty to an essay on migratory birds, you’d notice that the body paragraphs differ drastically. However, on closer inspection, you’d probably find that they included many of the same key components. Most body paragraphs will include specific, detailed evidence, an analysis of the evidence, a conclusion drawn by the author, and several tie-ins to the larger ideas at play. They’ll also include transitions and citations leading the reader to source material. We’ll go into more detail on these components soon. First, let’s see if you’ve organized your essay so that you’ll know how to start a body paragraph.
How to Start a Body Paragraph
It can be tempting to start writing your college essay as soon as you sit down at your desk. The sooner begun, the sooner done, right? I’d recommend resisting that itch. Instead, pull up a blank document on your screen and make an outline. There are numerous reasons to make an outline, and most involve helping you stay on track. This is especially true of longer college papers, like the 60+ page dissertation some seniors are required to write. Even with regular writing assignments with a page count between 4-10, an outline will help you visualize your argumentation strategy. Moreover, it will help you order your key points and their relevant evidence from most to least convincing. This in turn will determine the order of your body paragraphs.
The most convincing sequence of body paragraphs will depend entirely on your paper’s subject. Let’s say you’re writing about Penelope’s success in outwitting male counterparts in The Odyssey . You may want to begin with Penelope’s weaving, the most obvious way in which Penelope dupes her suitors. You can end with Penelope’s ingenious way of outsmarting her own husband. Because this evidence is more ambiguous it will require a more nuanced analysis. Thus, it’ll work best as your final body paragraph, after readers have already been convinced of more digestible evidence. If in doubt, keep your body paragraph order chronological.
It can be worthwhile to consider your topic from multiple perspectives. You may decide to include a body paragraph that sets out to consider and refute an opposing point to your thesis. This type of body paragraph will often appear near the end of the essay. It works to erase any lingering doubts readers may have had, and requires strong rhetorical techniques.
How to Start a Body Paragraph, Continued
Once you’ve determined which key points will best support your argument and in what order, draft an introduction. This is a crucial step towards writing a body paragraph. First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly. You should be looking at your thesis throughout the drafting of your body paragraphs.
Finally, make sure that your introduction indicates which key points you’ll be covering in your body paragraphs, and in what order. While this level of organization might seem like overkill, it will indicate to the reader that your entire paper is minutely thought-out. It will boost your reader’s confidence going in. They’ll feel reassured and open to your thought process if they can see that it follows a clear path.
Now that you have an essay outline and introduction, you’re ready to draft your body paragraphs.
How to Draft a Body Paragraph
At this point, you know your body paragraph topic, the key point you’re trying to make, and you’ve gathered your evidence. The next thing to do is write! The words highlighted in bold below comprise the main components that will make up your body paragraph. (You’ll notice in the body paragraph examples below that the order of these components is flexible.)
Start with a topic sentence . This will indicate the main point you plan to make that will work to support your overall thesis. Your topic sentence also alerts the reader to the change in topic from the last paragraph to the current one. In making this new topic known, you’ll want to create a transition from the last topic to this one.
Transitions appear in nearly every paragraph of a college essay, apart from the introduction. They create a link between disparate ideas. (For example, if your transition comes at the end of paragraph 4, you won’t need a second transition at the beginning of paragraph 5.) The University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center has a page devoted to Developing Strategic Transitions . Likewise, the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center offers help on paragraph transitions .
How to Draft a Body Paragraph for a College Essay ( Continued)
With the topic sentence written, you’ll need to prove your point through tangible evidence. This requires several sentences with various components. You’ll want to provide more context , going into greater detail to situate the reader within the topic. Next, you’ll provide evidence , often in the form of a quote, facts, or data, and supply a source citation . Citing your source is paramount. Sources indicate that your evidence is empirical and objective. It implies that your evidence is knowledge shared by others in the academic community. Sometimes you’ll want to provide multiple pieces of evidence, if the evidence is similar and can be grouped together.
After providing evidence, you must provide an interpretation and analysis of this evidence. In other words, use rhetorical techniques to paraphrase what your evidence seems to suggest. Break down the evidence further and explain and summarize it in new words. Don’t simply skip to your conclusion. Your evidence should never stand for itself. Why? Because your interpretation and analysis allow you to exhibit original, analytical, and critical thinking skills.
Depending on what evidence you’re using, you may repeat some of these components in the same body paragraph. This might look like: more context + further evidence + increased interpretation and analysis . All this will add up to proving and reaffirming your body paragraph’s main point . To do so, conclude your body paragraph by reformulating your thesis statement in light of the information you’ve given. I recommend comparing your original thesis statement to your paragraph’s concluding statement. Do they align? Does your body paragraph create a sound connection to the overall academic argument? If not, you’ll need to fix this issue when you edit your body paragraph.
How to Edit a Body Paragraph
As you go over each body paragraph of your college essay, keep this short checklist in mind.
- Consistency in your argument: If your key points don’t add up to a cogent argument, you’ll need to identify where the inconsistency lies. Often it lies in interpretation and analysis. You may need to improve the way you articulate this component. Try to think like a lawyer: how can you use this evidence to your advantage? If that doesn’t work, you may need to find new evidence. As a last resort, amend your thesis statement.
- Language-level persuasion. Use a broad vocabulary. Vary your sentence structure. Don’t repeat the same words too often, which can induce mental fatigue in the reader. I suggest keeping an online dictionary open on your browser. I find Merriam-Webster user-friendly, since it allows you to toggle between definitions and synonyms. It also includes up-to-date example sentences. Also, don’t forget the power of rhetorical devices .
- Does your writing flow naturally from one idea to the next, or are there jarring breaks? The editing stage is a great place to polish transitions and reinforce the structure as a whole.
Our first body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Argument Essay .” Here’s the prompt: Write an essay that argues your position on the value of striving for perfection.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Striving for perfection can only lead us to shortchange ourselves. Instead, we should value learning, growth, and creativity and not worry whether we are first or fifth best.” Now let’s see how this writer builds an argument against perfection through one main point across two body paragraphs. (While this writer has split this idea into two paragraphs, one to address a problem and one to provide an alternative resolution, it could easily be combined into one paragraph.)
“Students often feel the need to be perfect in their classes, and this can cause students to struggle or stop making an effort in class. In elementary and middle school, for example, I was very nervous about public speaking. When I had to give a speech, my voice would shake, and I would turn very red. My teachers always told me “relax!” and I got Bs on Cs on my speeches. As a result, I put more pressure on myself to do well, spending extra time making my speeches perfect and rehearsing late at night at home. But this pressure only made me more nervous, and I started getting stomach aches before speaking in public.
“Once I got to high school, however, I started doing YouTube make-up tutorials with a friend. We made videos just for fun, and laughed when we made mistakes or said something silly. Only then, when I wasn’t striving to be perfect, did I get more comfortable with public speaking.”
Body Paragraph Example 1 Dissected
In this body paragraph example, the writer uses their personal experience as evidence against the value of striving for perfection. The writer sets up this example with a topic sentence that acts as a transition from the introduction. They also situate the reader in the classroom. The evidence takes the form of emotion and physical reactions to the pressure of public speaking (nervousness, shaking voice, blushing). Evidence also takes the form of poor results (mediocre grades). Rather than interpret the evidence from an analytical perspective, the writer produces more evidence to underline their point. (This method works fine for a narrative-style essay.) It’s clear that working harder to be perfect further increased the student’s nausea.
The writer proves their point in the second paragraph, through a counter-example. The main point is that improvement comes more naturally when the pressure is lifted; when amusement is possible and mistakes aren’t something to fear. This point ties back in with the thesis, that “we should value learning, growth, and creativity” over perfection.
This second body paragraph example comes from the College Transitions article “ How to Write the AP Lang Rhetorical Analysis Essay .” Here’s an abridged version of the prompt: Rosa Parks was an African American civil rights activist who was arrested in 1955 for refusing to give up her seat on a segregated bus in Montgomery, Alabama. Read the passage carefully. Write an essay that analyzes the rhetorical choices Obama makes to convey his message.
Here’s the example thesis statement, taken from the introduction paragraph: “Through the use of diction that portrays Parks as quiet and demure, long lists that emphasize the extent of her impacts, and Biblical references, Obama suggests that all of us are capable of achieving greater good, just as Parks did.” Now read the body paragraph example, below.
“To further illustrate Parks’ impact, Obama incorporates Biblical references that emphasize the importance of “that single moment on the bus” (lines 57-58). In lines 33-35, Obama explains that Parks and the other protestors are “driven by a solemn determination to affirm their God-given dignity” and he also compares their victory to the fall the “ancient walls of Jericho” (line 43). By including these Biblical references, Obama suggests that Parks’ action on the bus did more than correct personal or political wrongs; it also corrected moral and spiritual wrongs. Although Parks had no political power or fortune, she was able to restore a moral balance in our world.”
Body Paragraph Example 2 Dissected
The first sentence in this body paragraph example indicates that the topic is transitioning into biblical references as a means of motivating ordinary citizens. The evidence comes as quotes taken from Obama’s speech. One is a reference to God, and the other an allusion to a story from the bible. The subsequent interpretation and analysis demonstrate that Obama’s biblical references imply a deeper, moral and spiritual significance. The concluding sentence draws together the morality inherent in equal rights with Rosa Parks’ power to spark change. Through the words “no political power or fortune,” and “moral balance,” the writer ties the point proven in this body paragraph back to the thesis statement. Obama promises that “All of us” (no matter how small our influence) “are capable of achieving greater good”—a greater moral good.
What’s Next?
Before you body paragraphs come the start and, after your body paragraphs, the conclusion, of course! If you’ve found this article helpful, be sure to read up on how to start a college essay and how to end a college essay .
You may also find the following blogs to be of interest:
- 6 Best Common App Essay Examples
- How to Write the Overcoming Challenges Essay
- UC Essay Examples
- How to Write the Community Essay
- How to Write the Why this Major? Essay
- College Essay
Kaylen Baker
With a BA in Literary Studies from Middlebury College, an MFA in Fiction from Columbia University, and a Master’s in Translation from Université Paris 8 Vincennes-Saint-Denis, Kaylen has been working with students on their writing for over five years. Previously, Kaylen taught a fiction course for high school students as part of Columbia Artists/Teachers, and served as an English Language Assistant for the French National Department of Education. Kaylen is an experienced writer/translator whose work has been featured in Los Angeles Review, Hybrid, San Francisco Bay Guardian, France Today, and Honolulu Weekly, among others.
- 2-Year Colleges
- ADHD/LD/Autism/Executive Functioning
- Application Strategies
- Best Colleges by Major
- Best Colleges by State
- Big Picture
- Career & Personality Assessment
- College Search/Knowledge
- College Success
- Costs & Financial Aid
- Data Visualizations
- Dental School Admissions
- Extracurricular Activities
- General Knowledge
- Graduate School Admissions
- High School Success
- High Schools
- Homeschool Resources
- Law School Admissions
- Medical School Admissions
- Navigating the Admissions Process
- Online Learning
- Outdoor Adventure
- Private High School Spotlight
- Research Programs
- Summer Program Spotlight
- Summer Programs
- Teacher Tools
- Test Prep Provider Spotlight
“Innovative and invaluable…use this book as your college lifeline.”
— Lynn O'Shaughnessy
Nationally Recognized College Expert
College Planning in Your Inbox
Join our information-packed monthly newsletter.
Body Paragraph: Craft the Heart of Your Essay
Table of contents
- 1 Purpose of a Body Paragraph
- 2 Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraph Structure
- 4 Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
- 5 How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
- 6.1 Using Different Types of Evidence.
- 6.2 Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
- 6.3 Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
- 6.4 Maintaining Consistency.
- 6.5 Supporting the Overall Thesis.
- 6.6 Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
- 6.7 Avoiding Transitions at the End.
- 7 Essay Body Paragraph Example
- 8 Conclusion
Completing an essay is more than just combining words – creating effective body paragraphs. They are like the building blocks of your text, giving it substance and strengthening your main point.
In this article, we’ll explore how to write a body paragraph for an essay and what methods to use to make it impactful.
- We’ll walk you through the body paragraph format, purpose, and principal elements,
- Cover using evidence wisely and make sure your sentences connect well,
- Deliver step-by-step guidelines and tips to create paragraphs that grab attention,
- Provide a body essay example.
Let’s start this journey into the writing world and learn how to make your essay interesting and well-structured.
Purpose of a Body Paragraph
This section is the backbone of any essay. A well-organized structure of the body paragraph helps your writing be readable. That’s why organizing the information to achieve this goal is essential. When writing body paragraphs in an essay, you focus on presenting and developing one point that supports the main argument.
Whether you write the text for yourself or go for essay papers for sale , each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect of the topic. It provides evidence, examples, analysis, or elaboration to strengthen and clarify the main point. The body of a paper helps guide the reader by making the ideas flow smoothly. This section aims to make a strong case for the essay’s thesis. It should keep the reader interested with well-developed and organized content.
Key Elements in the Structure of a Body Paragraph
Knowledge is the basis for any writing. Thus, any text you deliver should reflect your level of knowledge. For this, posing strategic and insightful questions to refine your thoughts and reinforce your argument is essential. A well-written body section is a compulsory component of any impactful document.
There are several key parts of a body paragraph in an essay.
- The first element is a transition, linking the preceding and current paragraphs. It should be clear, helping the reader in tracking the conversation. Using starting words for body paragraphs signals a change in focus or introduces a fresh idea.
- The second body paragraph element is the main idea, which is crucial for any text. You must state your argument in the topic sentence, which should be precise and brief. The main statements should relate to the thesis and support the idea.
- The third component is analysis, where the writer elaborates on the perspective. Providing proof and explaining how it supports the thesis statement is necessary. The examination should also be relevant and focused on the introduced topic. This way, you will make the essay structure coherent and easy to follow.
- The final element is the warrant, which explains how the evidence supports the main view. The warrant must be clear and connect the data to the principal argument. It should also focus on the topic and strengthen the argument.
Body Paragraph Structure
Well-thought-out body paragraphs are critical in an essay outline and the writer’s arguments. To effectively structure the body paragraph, you must understand its overall organization. A well-formatted academic essay helps writers communicate their reasoning and convince their audience. However, it’s better not to consider this a fixed and immovable object. Depending on the treated argument, its goal, length, and structure can be adapted to your needs.
You can imagine the skeleton of this part of the text in the following way:
- Topic sentence
- Supporting sentences
- Concluding sentence
The topic sentence is one of the ways to start a body paragraph. It should be a precise and focused statement that encapsulates the main argument of the passage. It connects the introduction paragraph in the essay with a thesis and provides a roadmap for the rest of the section. It will help the reader understand the point and how it relates to the writing. In some cases, it can even be formulated as a question.
Following the topic sentence for the body paragraph, you must provide supporting sentences. They present evidence and analysis to underpin the central idea. They should connect to the topic sentence and be clear and concise. Use language that is easy for the reader to understand.
To create a persuasive assertion, provide information that supports the main argument. The evidence can take many forms, including facts, statistics, or examples. Data should be reliable and relevant to the topic discussed. Research-based proof helps the writer convince the reader that their position is credible.
The concluding sentence is the ultimate statement and a kind of short conclusion you should use when you base your essay on body paragraphs. Its purpose is to summarize the idea and provide a transition to the later passage. This sentence helps the reader comprehend the main claim and its implications. Think of it as the answer to a question or the core information.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Transition Sentences of a Body Paragraph
To make your writing flow smoothly and be more engaging, use transition words that help connect ideas. You can utilize three types of linking words and phrases:
- Bridging the introductory paragraph to subsequent sections (e.g., a transition from introduction to body): To begin with; In the first place; Initially; As an introduction; Turning to; As we delve into; Now that we have established.
- Connecting body paragraphs: Furthermore; Moreover; In addition; Additionally; Similarly; Likewise; Not only…but also; Besides that; In the same vein; Another key point.
- Linking the final body sentence to the conclusion: In conclusion; To sum up; Finally; In summary; Ultimately; Concluding; To conclude; To wrap things up; As a final point; All in all.
These words and phrases contribute to a coherent and logical essay, guiding the reader through the content. Use transitions to introduce a body paragraph and make your ideas clear and captivating to the audience.
How Do You Write a Body Paragraph of an Essay?
Completing this section requires consideration and attention to detail. It can be challenging to organize your thoughts and reasoning. However, it might be daunting, and professional assistance may be necessary. And this is where PapersOwl can be of great help. Our seasoned paper writing website offers expert homework help to achieve your academic goals.
How long should a body paragraph be? A general recommendation is to aim for 5-7 sentences. It allows you to explore one idea without giving too much information. The most important thing is to keep in mind the following guidelines:
- Introducing a concise topic sentence will be a good way to start a first body paragraph. Topic sentences should be specific and concise. Using them, you provide the reader with a clear understanding of the point you will discuss further. It should also relate to the thesis and connect to the perspective.
- After the topic sentence, use supporting sentences to provide additional information and analysis. This way, you will bolster the main argument. These parts of a body paragraph can include examples, facts, statistics, or expert opinions. Ensure that the information used is reliable and relevant to your idea.
- Employ transition sentences to link your ideas to the preceding and subsequent paragraphs. They make it easier for the reader to follow the main argument.
- Use brief and clear language to present your ideas and rationale. Avoid using complicated vocabulary or technical jargon that may confuse the reader. Instead, be straightforward when writing a body paragraph.
- Finally, end this section with a conclusion sentence. It acts as a summary of the main statement and offers a transition to the next section. The concluding sentence should bring closure to the point in one paragraph. It should also prepare the reader for the next parts of the writing.
When you write a body paragraph in an essay, follow these steps to ensure clarity, conciseness, and persuasiveness in your essay. Adhere to these guidelines to make your ideas concise and transparent and your arguments strong and persuasive. If you follow these steps, your essay will be concise and compelling. Implementing these measures ensures that your text is clear, persuasive, and effective.
Essential Tips to Write Flawless Body Paragraphs
Discover the following comprehensive strategies for crafting effective body paragraphs for your research.
Using Different Types of Evidence.
Incorporate a variety of quotes, statistics, and anecdotes to provide evidence and enhance the appeal and credibility of your writing. This multifaceted approach captivates the reader and reinforces your argument with diverse supporting elements.
Varying Sentence Length and Structure.
Mitigate monotony in the body of an essay by diversifying sentence length and structure. Integrate a mix of simple, compound, and complex sentences to enhance the overall readability of your composition. This nuanced use of syntax contributes to a more engaging and dynamic writing style.
Avoiding Irrelevant Information.
Don’t introduce irrelevant information that might distract or dilute the focus of your paragraph. Each sentence should serve a purpose, aligning seamlessly with the central theme and your essay’s purpose.
Maintaining Consistency.
Stay consistent with the tone and style throughout your text. The body paragraphs should harmonize with the established voice of your writing, creating a cohesive and unified reading experience for your audience.
Supporting the Overall Thesis.
When you start a body paragraph, ensure that each sentence significantly reinforces your overall thesis. Every argument, example, or piece of evidence should advance the central claim of your essay, reinforcing its coherence and persuasiveness.
Using Clear and Concise Sentences.
Break down complex topic sentences into clear and concise points. It facilitates a better understanding of your ideas and prevents the reader from feeling overwhelmed by overly intricate or convoluted language.
Avoiding Transitions at the End.
Refrain from using transition words and phrases at the end of paragraphs, as this can disrupt the natural flow of your writing. Instead, strive for seamless transitions within the paragraph’s content, allowing ideas to connect organically without explicitly signaling the conclusion.
Follow these tips to create a strong body paragraph layout for your document. If you need support or lack time and energy to craft your academic papers, do not hesitate to contact our writing experts. When you pay for a paper at PapersOwl, be sure your essay will adhere to all these instructions and requirements with zero flaws. Our team of writers has expertise in various fields and crafts quality papers for you. We deliver plagiarism-free essays and guarantee timely delivery. Whether you need an essay for school, college, or university, PapersOwl is the right choice.
Essay Body Paragraph Example
What is a body paragraph, and how to complete it correctly? Here is a good example to clarify these questions:
[Start with a topic sentence] J K Rowling, in her first book – Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone, claims that the appearance of a person can sometimes be misleading, [followed by supporting details] showing one of the kindest and most favorite characters – Hagrid as a scary person. His eyes are ‘glinting like black beetles,’ and his face is ‘almost completely hidden by a long, shaggy mane of hair and a wild, tangled beard,’ says the author (Rowling 46). [Then goes an explanation] The author declares that the main character of the book – Harry Potter, is frightened by this intimidating figure, which misleads the reader, making Hagrid appear as a villain. [Explains the significance] However, this image is wrong. Later the reader gets to know Hagrid’s true character, which is the opposite. [Ends with a conclusion and transition to the following part] This example proves how misleading an appearance of someone can be, which is easily proved by many other examples from literature and real life.”
Crafting effective body paragraphs in an essay is an indispensable skill for anyone seeking to elevate their writing. This article gives suggestions to help you write a good body paragraph. Our recommendations allow you to transform your essays into compelling and persuasive texts. These strategies can help both experienced writers and beginners with essay construction. They serve as a valuable toolkit for enhancing the impact and coherence of your text. When you write, remember that a well-organized essay body helps express thoughts clearly, engage readers, and convince them.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Is MasterClass right for me?
Take this quiz to find out.
How to Write a Strong Body Paragraph for an Essay
Written by MasterClass
Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read
From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project.


TOPIC SENTENCE/ In his numerous writings, Marx critiques capitalism by identifying its flaws. ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ By critiquing the political economy and capitalism, Marx implores his reader to think critically about their position in society and restores awareness in the proletariat class. EVIDENCE/ To Marx, capitalism is a system characterized by the “exploitation of the many by the few,” in which workers accept the exploitation of their labor and receive only harm of “alienation,” rather than true benefits ( MER 487). He writes that “labour produces for the rich wonderful things – but for the worker it produces privation. It produces palaces—but for the worker, hovels. It produces beauty—but for the worker, deformity” (MER 73). Marx argues capitalism is a system in which the laborer is repeatedly harmed and estranged from himself, his labor, and other people, while the owner of his labor – the capitalist – receives the benefits ( MER 74). And while industry progresses, the worker “sinks deeper and deeper below the conditions of existence of his own class” ( MER 483). ANALYSIS OF EVIDENCE/ But while Marx critiques the political economy, he does not explicitly say “capitalism is wrong.” Rather, his close examination of the system makes its flaws obvious. Only once the working class realizes the flaws of the system, Marx believes, will they - must they - rise up against their bourgeois masters and achieve the necessary and inevitable communist revolution.
Not every paragraph will be structured exactly like this one, of course. But as you draft your own paragraphs, look for all three of these elements: topic sentence, evidence, and analysis.
- picture_as_pdf Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning objectives.
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary support can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments. Judgments are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony. Testimony consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentence that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:
Author J.D. Salinger relied primarily on his personal life and belief system as the foundation for the themes in the majority of his works.
The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced themes in many of his works.
In Note 9.19 “Exercise 2” , you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:
Thesis statement: Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
Supporting point 1: Dogs can scare cyclists and pedestrians.
Supporting details:
- Cyclists are forced to zigzag on the road.
- School children panic and turn wildly on their bikes.
- People who are walking at night freeze in fear.
Supporting point 2:
Loose dogs are traffic hazards.
- Dogs in the street make people swerve their cars.
- To avoid dogs, drivers run into other cars or pedestrians.
- Children coaxing dogs across busy streets create danger.
Supporting point 3: Unleashed dogs damage gardens.
- They step on flowers and vegetables.
- They destroy hedges by urinating on them.
- They mess up lawns by digging holes.
The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.
Salinger, a World War II veteran, suffered from posttraumatic stress disorder, a disorder that influenced the themes in many of his works. He did not hide his mental anguish over the horrors of war and once told his daughter, “You never really get the smell of burning flesh out of your nose, no matter how long you live.” His short story “A Perfect Day for a Bananafish” details a day in the life of a WWII veteran who was recently released from an army hospital for psychiatric problems. The man acts questionably with a little girl he meets on the beach before he returns to his hotel room and commits suicide. Another short story, “For Esmé – with Love and Squalor,” is narrated by a traumatized soldier who sparks an unusual relationship with a young girl he meets before he departs to partake in D-Day. Finally, in Salinger’s only novel, The Catcher in the Rye , he continues with the theme of posttraumatic stress, though not directly related to war. From a rest home for the mentally ill, sixteen-year-old Holden Caulfield narrates the story of his nervous breakdown following the death of his younger brother.
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 9.18 “Exercise 1” , draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

4c. Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs present the reasoning and evidence to demonstrate your thesis. In academic essays, body paragraphs are typically a bit more substantial than in news reporting so a writer can share their own ideas, develop their reasoning, cite evidence, and engage in conversation with other writers and scholars. A typical body paragraph in a college essay contains the following elements, which can be remembered through the useful acronym TREAT.
The TREAT Method
- T opic Sentence – an assertion that supports the thesis and presents the main idea of the paragraph
- R easoning – critical thinking and rhetorical appeals: ethos, logos, and pathos
- E vidence – facts, examples, and other evidence integrated into the paragraph using summaries, paraphrases, and quotations
- A nalysis – examination and contextualization of the evidence and reasoning
- T ransition – the flow of ideas from one paragraph to the next
Effective body paragraphs are:
- Specific and narrow . Topic sentences provide your audience a point of transition and flow from paragraph to paragraph. Topic sentences help you expand and develop your thesis and set up the organization of each paragraph. Developing specific reasoning and specific, concrete examples and evidence in each paragraph will build your credibility with readers. If used properly, well-developed reasoning and evidence are more compelling than general facts and observations.
- Relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Body paragraphs should show, explain, and prove your thesis without delving into irrelevant details. With practice and the understanding that there is always another essay, effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Keeping your audience and purpose in mind when choosing examples will help you make sure to stay focused on your thesis.
- Detailed . Academic paragraphs are typically longer than newspaper and magazine paragraphs because scholars need space to develop their reasoning and provide sufficiently detailed evidence to support their claims. Using multiple examples and precise details shows readers that you have considered the facts carefully and enhances the impact of your ideas.
- Organized . If your paragraph starts to include information or ideas that stray from your topic sentence, either the paragraph or the topic sentence might need to change.
Reasoning and Evidence
In written and oral communication, we demonstrate our critical thinking skills through the various types of rhetorical appeals we make to our audience. The purpose and audience for a writing task shape the way writers develop reasoning and select evidence to support their ideas. Writers develop reasoning in body paragraphs through three primary methods: ethos, logos, and pathos. Writers can deploy many forms of evidence to support their reasoning, including: facts, examples, judgments, testimony, and personal experience.
The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle developed a simple method for categorizing forms of reasoning by identifying three primary modes of argumentative reasoning: ethos, logos, and pathos.
- Ethos is reasoning that establishes a writer’s credibility. By showing yourself to be a critical and sympathetic reader, who considers multiple perspectives and demonstrates ethical thinking, you can establish ethos in your body paragraphs.
- Logos is reasoning that develops logical arguments and demonstrates a writer’s command of the facts. Demonstrating your knowledge of the facts and showing that you can distinguish between competing claims at truth will ground your writing in common sense and objectivity.
- Pathos is reasoning that appeals to human emotions and psychological motivations. Humans are subjective animals, and our ability to develop an emotional connection with an audience can have a powerful or subtle impact on whether they will agree with a writer’s reasoning.
A fourth form of reasoning, kairos , can occasionally be used to make an appeal to an audience that the perfect moment or right opportunity has arisen for action. Arguments for changing policies, ending wars, starting revolutions, or engaging in radical social change typically deploy kairos in addition to ethos, logos, and pathos in order to motivate people to take action a critical times in history.
Evidence includes anything that can help you support your reasoning and develop your thesis. As you develop body paragraphs, you reveal evidence to your readers and then provide analysis to help the reader understand how the evidence supports the reasoning and assertions you are making in each body paragraph. Be sure to check with each instructor to confirm what types of evidence are appropriate for each writing task you are assigned. The following kinds of evidence are commonly used in academic essays:
- Facts . Facts are the best kind of evidence to use for academic essays because they often cannot be disputed or distorted. Facts can support your stance by providing background information or a solid evidence-based foundation for your point of view. Remember that facts need explanations. Be sure to use signal phrases like “according to” and “as demonstrated by” to introduce facts and use analysis to explain the relevance of facts to your readers.
- Examples show readers that your ideas are grounded in real situations and contexts. Examples help you highlight general trends and ground your facts in the real world. Be careful not to take examples out of context or overgeneralize based on individual cases.
- Judgments . Judgments are the conclusions of experts drawn from a set of examples or evidence. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and a thorough examination of a topic. Citing a credible expert to support your opinion can be a powerful way to build ethos in your writing.
- Testimony . Testimony consists of direct quotations from eyewitnesses or expert witnesses. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; they add authenticity and credibility to an argument or perspective based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive expertise or experience with a topic. This person provides commentary based on their interpretation of the facts or extensive knowledge on a topic or event.
- Personal Experience . Personal observation is similar to eyewitness or expert testimony but consists of your own experiences and/or expertise. Personal experience can be effective in academic essays if directly relevant to the topic and suited to the purpose of a writing task.
Key Takeaways
- Always be aware of your purpose for writing and the needs of your audience. Cater to those needs in every sensible way.
- Write paragraphs of an appropriate length for your writing assignment. Paragraphs in college-level writing can be up to a page long, as long as they cover the main topics in your outline.
- Use your prewriting and outline to guide the development of your paragraphs and the elaboration of your ideas.
Addressing Counterarguments and Different Perspectives
“Few things are more difficult than to see outside the bounds of your own perspective—to be able to identify assumptions that you take as universal truths but which, instead, have been crafted by your own unique identity and experiences in the world.”
~David Takacs
Why acknowledge and respond to other points of view?
- Address potential weaknesses in your argument before others can point them out to you.
- Acknowledge the complexity of an issue by considering different perspectives and aspects of an issue. No issue has a simple solution or is just Side A versus Side B.
- Establish your writing ethos (can your reader trust you?): your reader is more likely to trust you if you thoughtfully analyze an issue from multiple angles.
- Add to your essay’s word count!
Four steps to acknowledging and responding to other points of view
Step one: know your standpoint, what is my standpoint and why should i know it.
- Standpoint is the unique perspective from which you view the world. It includes: your background and experiences, your political and religious beliefs, your identity (gender, ethnicity, class, sexuality, and ability), your relationship to others, and your social privilege. These are things that will affect how you view and understand an issue.
- It’s important to acknowledge your standpoint because it affects what and how you argue.
Good writers are good readers! And good readers. . .

- Who are you?
- Make a list of what you’ll bring to a conversation about the issue on which you’re writing. What are your assumptions, your background and experience, your knowledge and expertise? Be honest!
Consider writing your standpoint into your essay
- Writing your standpoint into your essay builds trust with your readers. Even if they have a different standpoint, they will respect your honesty and hopefully listen respectfully to what you have to say.
- Writing from your standpoint can make your writing feel more authentic , to you and your reader. “This is me!”
Even if you don’t explicitly reveal your standpoint to your reader, you’ll want to know your standpoint so that you are aware of your own implicit bias as you write.
How do I write in my standpoint? Can I use “I”?
Try one of these templates:
- “What concerns me as a business major . . .”
- “I write this essay during a time when . . .”
- “I am concerned about. . .”
See how other writers we’ve read have done it:
- “Now, as a professor at the Harvard Graduate School of Education , I. . .” [From Anthony Abraham Jack, “I Was a Low-Income College Student. Classes Weren’t the Hard Part.” The New York Times Magazine ]
- “From my first day as a sociology professor at a university with a Division I football and men’s basketball team , education and athletics struck me as being inherently at odds. . .” [From Jasmine Harris, “It’s Naive to Think College Athletes Have Time for School,” The Conversation ]
- “In this society, that norm is usually defined as white, thin, male, young, heterosexual, Christian, and financially secure. It is within this mythical norm that the trappings of power reside. Those of us who stand outside that power , for any reason, often identify one way in which we are different, and we assume that quality to be the primary reason for all oppression. . .” [From Audre Lorde, “The Transformation of Silence into Language and Action”]
- “I might not carry with me the feeling of my audience in stating my own belief. . .” [From Ralph Waldo Emerson, “The American Scholar”]
Step Two: C onsider potential weaknesses in your argument and different points of view on the issue
What potential weaknesses in your argument might you address.
- Logic : would a reader question any of your assumptions?
- between your reasoning and your claim: your main unstated assumption
- or between your evidence and your reasoning: is there evidence or types of evidence a reader might be skeptical of?
- Does the reader hold false assumptions about the issue?
- Could a reader give a different explanation of the issue ?
- Could a reader draw a different conclusion from the evidence ?
- Is there a specific reader who would disagree?
What alternative points of view on the issue might you consider?
- How might someone think differently about the issue?
- How might someone approach the issue from a different standpoint?
- What might keep someone from trusting or believing a claim or point you make?
- What might make someone tentative about taking action?
- What might keep a person from having an open mind?
Which one should I choose to address?
It depends on the essay’s length. You might consider 1-2 counterarguments that are most important for you to address in a paper (depending on the length).
- this could be a view your audience/community is likely to hold themselves
- or a common-knowledge one you think everyone will think of while reading
- and of course the one that is most specific to your argument
- if you can get one that fits more than one of these criteria, that’s even better!
What NOT to do when considering a counterargument

Build a straw man counterargument
- A straw man argument is a logical fallacy where the writer misrepresents or oversimplifies someone else’s argument in order to make it easier to refute.
- Writers also create straw man arguments when they make up a potential counterargument that is easy to refute, but isn’t something most people would reasonably believe.
Step Three: It’s time to write your counterargument into your essay
An exemplary counterargument:.
- exists as its own paragraph
- you fully acknowledge and respond to it
- Note: You don’t have to refute a counterargument for your argument to work. Our world is big enough to hold multiple points of view. The paragraph should ultimately support your thesis, but you may amend, qualify, complicate, or open up your claim, which is often why, organizationally, discussion of counterarguments or different points of view work best in the introduction of your essay to set up your claim or as the last body paragraph to lead into your conclusion.
- relates to your audience/community’s likely concerns and interests
- seems like a realistic thing someone might think (is not a straw man or caricature)
- ideally, is specific to your argument, not your topic in general
- considers both sides respectfully
- may be more than one counterargument or different perspective, but you’d need a separate paragraph for each in order to give them full consideration
Addressing a counterargument versus a different perspective
A true counterargument is the opposing claim on an issue:
- Claim: Academic probation does not help students progress.
- Counterargument: Academic probation does help students progress.
Different perspectives might offer different reasoning, consider different factors or conditions, or ask about different groups of people or situations.
A counterargument needs to be rebutted. Different perspectives can help you amend, qualify, complicate, or open up your claim.
You might use a counterargument to qualify your thesis
An example:
Reasoned thesis : Hook-up culture is now at the center of the institution of higher education because it is thick, palpable, the air students breathe, and we find it on almost every residential campus in America. [From Lisa Wade, “Sociology and the New Culture of Hooking Up on College Campuses“]
A counterargument : Research findings suggest that the sexual practices of college students haven’t changed much since the 1980s. [From David Ludden, “Is Hook-Up Culture Dominating College Campuses?”]
Qualified claim : Although sexual practices of college students haven’t changed much in the last few decades , hook-up culture is now at the center of the institution of higher education because it is thick, palpable. . .
Counterargument paragraph : “The topic of my book, then, isn’t just hooking up; it’s hook-up culture . . .” (Wade).
A template for a counterargument paragraph
I recognize that others may have a different perspective than [state your claim*]. They might believe that [state their claim]. They believe this because [provide several sentences of support]. However, [restate your claim and explain in several sentences why you believe the way you do].
*You can also consider counterpoints to your reasoning, evidence, or standpoint.
Step Four: Decide where to organize your counterargument paragraph
|
| |
|---|---|
| An effective counterargument does not just say “someone might disagree,” but attempts to be specific: who (ideally someone like your reader) might disagree and why? What can you say that acknowledges their concerns but shows that your idea is still convincing? Some essays naturally acknowledge the counterargument all the way through because they’re proposing a change, which means the current situation is already a counterargument. In this case, it makes sense to address the counterargument early on: Why are things this way now? What’s wrong with it? Then consider if someone might agree that things should change but disagree about your course of action. | Example 1: The current method of ranking college basketball teams came into existence because. . . (This paragraph would likely be in the beginning.) Example 2: Some college basketball fans might think that while the rankings aren’t completely correct in predicting winnings, they’re more complicated than I’m allowing for in this discussion; this idea merits consideration but does not ultimately derail my argument. (This counterargument might come near the beginning, too, because it discusses a potential flaw in the basic idea: someone might disagree that the problem is as bad as I’m saying. In this case, it’s likely good to talk about that early on, because if a reader thinks this they will probably not read all the way to page four to see you address their concern. Also note how this topic sentence ends by saying how the paragraph will end: with my idea still being better.) |
|
|
|
|---|---|
| If your topic doesn’t seem very controversial on its face. . . | consider putting the counterargument in the beginning, to establish the controversy. |
| If your counterargument is similar to one of your best points in the body of the essay. . . | maybe put the counterargument paragraph before that body paragraph so your response logically leads into the next paragraph about a similar point. |
| If you have several counterarguments paragraphs you want to include. . . | you could put them throughout the body. |
| If you have one solid counterargument paragraph but a couple of other opposed points you want to mention. . . | you can address those points in other paragraphs where they fit most closely, including in a context paragraph and the regular evidentiary body paragraphs. |
| If none of those seems true—it’s just another paragraph that could come anywhere—. . . | reconsider your overall structure and find the place where this information needs to come. What do readers need to know first? Why? What needs to come later? |
Being aware of different perspectives can also help you develop your conclusion paragraph. In your conclusion, you can reaffirm your claim and then:
- amend part of your claim
- qualify your claim
- complicate your claim
- open up your claim
Writing as collaboration
Think of adding in counterarguments or different perspectives as collaborating with others on addressing an issue. . .

Brazuca illustrations by Cezar Berje, CC0
Opening up our minds and our hearts to different perspectives makes us stronger.
Writing as Inquiry Copyright © 2021 by Kara Clevinger and Stephen Rust is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay: Steps & Example

Critical thinking is a powerful skill that helps you analyze information and form well-reasoned arguments. As a matter of fact, the human brain uses more energy when critically thinking than when relaxing. This article will guide you through the steps of writing a successful critical thinking essay.
In this article, you will learn:
- How to craft a strong essay
- The importance of these essays
- The structure with an example
- Valuable bonus tips to strengthen your writing
By following these steps and incorporating the provided information, you'll be well on your way to writing impressive essays. If you need further guidance, always count on our fast essay writing service .
What is Critical Thinking Essay
A critical thinking essay is a type of writing where you analyze a topic thoroughly. You'll consider different viewpoints, evaluate evidence from studies or expert opinions, and form your own well-reasoned conclusion. Here, you need to look at an issue from all angles before deciding where you stand. This type of essay goes beyond memorizing facts. It actively engages with information, questions assumptions, and develops your own thoughtful perspective.
Is Your Essay Giving You a Headache?
Don't call an ambulance; call EssayPro! Let our experts conquer any of your assignments!
Importance of Critical Thinking and Its Use in Writing
Critical thinking is a skill that benefits all types of writing, not just essays. It helps you become a more informed and effective communicator. Here's why it's important:
- Stronger Arguments: Critical thinking helps you build solid arguments. You won't just state your opinion but back it up with evidence and consider opposing viewpoints. This makes your writing more persuasive and convincing.
- Deeper Understanding: When writing a critical thinking essay, you'll analyze information, identify biases, and think about the bigger picture. This leads to a richer understanding of the topic and a more insightful essay.
- Clearer Communication: By organizing your thoughts critically, your writing becomes clearer and more focused. You'll present your ideas in a logical order, making it easier for readers to follow your argument.
- Spotting Fake News: Critical thinking skills help you evaluate the information you encounter online and in the world around you. You'll be better equipped to identify unreliable sources and biased information, making you a more discerning reader and writer.
- Improved Problem-Solving: Critical thinking helps you approach challenges thoughtfully. As you write, you'll learn to analyze complex issues, consider different solutions, and ultimately develop well-reasoned conclusions. This skill extends beyond writing and can be applied to all areas of your life.
For more detailed information on the importance of critical thinking , visit our dedicated article.
Critical Thinking Essay Format
In a critical thinking essay outline, each piece has its place and contributes to the overall picture. Here's a breakdown of the key components:
| Element 🔍 | Content 📝 |
|---|---|
| 1. Title | Should be concise and reflective of your essay's content. |
| 2. Introduction | Introduce the topic's importance. Clearly state your main argument. |
| 3. Body Paragraphs | Each paragraph supports your thesis. Use credible sources for support. Connect evidence and analyze. Address opposing views. |
| 4. Conclusion | Briefly recap the key points. Restate your thesis, highlighting its significance. Leave a final thought or call to action. |
| 5. References/Bibliography | This section lists all your cited sources. Format them in a citation style like APA, MLA, or Chicago to credit original authors. |
Check out our critical analysis example to see how this format comes to life.
Critical Thinking Essay Questions
Now that you understand the structure of this essay, let's get your brain working! Here are some questions to help you generate strong critical thinking essay topics:
- How can you tell if a source of information is reliable?
- What are the potential biases that might influence research or news articles?
- How can you identify logical fallacies in arguments?
- How can you weigh the pros and cons of a complex issue?
- How can your own experiences or background influence your perspective on a topic?
Sample Essay Topics:
- History: Should historical monuments that celebrate controversial figures be removed or repurposed?
- Science: With advancements in gene editing, should we allow parents to choose their children's traits?
- Art & Culture: Does artificial intelligence pose a threat to the creativity and value of human art?
- Space Exploration: Should we prioritize colonizing Mars or focus on solving problems on Earth?
- Business Ethics: Is it ethical for companies to automate jobs and potentially displace workers?
- Education: In a world with readily available information online, is traditional classroom learning still necessary?
- Global Issues: Is focusing solely on national interests hindering efforts to address global challenges like climate change?
Remember, these are just a few ideas to get you started. Choose a topic that interests you and allows you to explore different perspectives critically.
How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay
We've covered the foundation – the structure and key elements of a critical thinking essay. Now, let's dive into the writing process itself! Remember, the steps on how to start a critical thinking essay, such as defining your topic, crafting a thesis, gathering evidence, etc., are all interconnected. As you write, you'll move back and forth between them to refine your argument and build a strong essay.
If you're looking for a hassle-free solution, simply buy cheap argumentative essay from our experts.
.webp)
Understand the Assignment Requirements
Taking some time to understand the assignment from the beginning will save you time and frustration later. Grasping your critical thinking paper instructions ensures you're on the right track and meeting your teacher's expectations. Here's what to focus on:
- The Prompt: This is the core of the assignment, outlining the topic and what you're expected to do. For example, if it asks what critical thinking skills are, Look for keywords like "define," "describe," or "explain." These indicate the type of essay you need to write and the approach you should take.
- Specific Requirements: Pay attention to details like the essay length, formatting style (e.g., MLA, APA), and any specific sources you need to use. Missing these guidelines can lead to point deductions.
- Grading Rubric (if provided): This is a goldmine! The rubric often outlines the criteria your essay will be graded on, like clarity of argument, use of evidence, and proper citation style. Knowing these expectations can help you tailor your writing to excel.
Select a Critical Thinking Topic
Think about the prompt or theme provided by your teacher. Are there any aspects that pique your interest? Perhaps a specific angle you haven't explored much? The best topics are those that spark your curiosity and allow you to engage with the material in a meaningful way.
Here are some tips for selecting a strong critical thinking essay topic:
- Relevance to the Assignment: Make sure your chosen topic directly relates to the prompt and allows you to address the key points. Don't stray too far off course!
- Interest and Engagement: Choose a topic that you find genuinely interesting. Your enthusiasm will show in your writing and make the research and writing process more enjoyable.
- Complexity and Scope: Aim for a topic that's complex enough to provide depth for analysis but not so broad that it becomes overwhelming. You want to be able to explore it thoroughly within the essay's length limitations.
- Availability of Sources: Ensure you have access to credible sources like academic journals, news articles from reputable sources, or books by experts to support your argument.
Remember: Don't be afraid to get creative! While some prompts may seem broad, there's often room to explore a specific angle or sub-topic within the larger theme.
Conduct In-Depth Research
This is where you'll gather the information and evidence when writing a critical thinking essay. However, don't just copy information passively. Critically analyze the sources you find.
- Start with Reliable Sources: Steer clear of unreliable websites or questionable information. Focus on credible sources like academic journals, scholarly articles, reputable news outlets, and books by established experts in the field.
- Use Library Resources: Librarians can guide you towards relevant databases, academic journals, and credible online resources.
- Search Engines Can Be Your Friend: While you shouldn't rely solely on search engines, they can be helpful starting points. Use keywords related to your topic, and be critical of the websites you visit. Look for sites with a clear "About Us" section and reputable affiliations.
- Vary Your Sources: Don't just rely on one type of source. Seek out a variety of perspectives, including research studies, data, historical documents, and even opposing viewpoints. This will give your essay well-roundedness and depth.
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement encapsulates your main argument or perspective on the topic. A strong thesis statement tells your readers exactly what your essay will be about and prepares them for the evidence you'll present.
During your critical thinking process, make sure you include these key characteristics:
- Specificity: It goes beyond simply stating the topic and clearly outlines your position on it.
- Focus: It focuses on a single main point that you'll develop throughout the essay.
- Argumentative: It indicates your stance on the issue, not just a neutral observation.
- Clarity: It's clear, concise, and easy for the reader to understand.
For example, here's a weak thesis statement:
Deepfakes are a new technology with both positive and negative implications.
This is too vague and doesn't tell us anything specific about ethics. Here's a stronger version:
While deep lakes have the potential to revolutionize entertainment and education, their ability to create highly convincing misinformation poses a significant threat to democracy and social trust.
This thesis is specific, focused, and clearly states the argument that will be explored in the essay.
Outline the Structure of Your Essay
With a strong thesis statement guiding your way, it's time to create a roadmap for your essay. This outline will serve as a blueprint, ensuring your arguments flow logically and your essay has a clear structure. Here's what a basic outline for a critical thinking essay might look like:
| Section 📚 | Content 📝 |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Briefly introduce the topic and its significance. Clearly state your thesis statement. |
| Body Paragraphs (one for each main point) | Introduce paragraph's point and link to thesis. Use credible sources to support. Explain and analyze evidence. Address opposing views' weaknesses. |
| Conclusion | Briefly summarize the key points of your essay. Restate your thesis in a new way, emphasizing its importance. Leave your reader with a final thought or call to action (optional). |
This is a flexible structure, and you may need to adapt it based on your specific topic and the length of your essay. However, having a clear outline will help you stay organized and ensure your essay flows smoothly from point to point.
Write an Engaging Introduction
The introduction should be captivating and give your reader a taste of what's to come. Here are some tips for crafting a strong introduction:
- Start with a Hook: Use an interesting fact, a thought-provoking question, or a relevant anecdote to grab your reader's attention right from the start. This will pique their curiosity and make them want to read more.
- Introduce the Topic: Briefly introduce the topic you'll be exploring and explain its significance. Why is this topic important to discuss?
- Present Your Thesis: Clearly and concisely state your thesis statement. This tells your reader exactly what your essay will argue and prepares them for the evidence you'll present.
For example, Let's say your essay is about the growing popularity of online learning platforms. Here's an introduction that uses a hook, introduces the topic, and presents a thesis statement:
With millions of students enrolled in online courses worldwide, the way we learn is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Traditionally associated with brick-and-mortar classrooms, education is now readily available through virtual platforms, offering flexibility and accessibility. This essay will examine the advantages and challenges of online learning, ultimately arguing that while it offers valuable opportunities, it cannot entirely replace the benefits of a traditional classroom setting.
Construct Analytical Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs are the heart of your essay, where you develop your argument and convince your reader of your perspective.
- Focus on One Point Per Paragraph: Each paragraph should address a single point that directly relates to your thesis statement. Don't try to cram too much information into one paragraph.
- Start with a Topic Sentence: This sentence introduces the main point of the paragraph and explains how it connects to your thesis.
- Support with Evidence: Back up your claims with credible evidence from your research. This could include facts, statistics, quotes from experts, or relevant examples.
- Analyze and Explain: Don't just list the evidence! Use critical thinking in writing - explain how it supports your argument and analyze its significance. What does this evidence tell you about the issue?
- Consider Counterarguments (Optional): In some cases, it can be effective to acknowledge opposing viewpoints and briefly explain why they're not as strong as your argument. This demonstrates your awareness of the complexity of the issue and strengthens your own position.
For example: Let's revisit the online learning example. Imagine one of your body paragraphs focuses on the flexibility of online learning platforms. Here's a breakdown of how you might structure it:
- Topic Sentence: Online learning platforms offer students unparalleled flexibility in terms of scheduling and pace of learning.
- Evidence: A recent study by the Online Learning Consortium found that 74% of online students reported being able to manage their coursework around their work and personal commitments.
- Analysis: This flexibility allows students who may have work or family obligations to pursue their education without sacrificing other responsibilities. It also empowers students to learn at their own pace, revisiting challenging concepts or accelerating through familiar material.
Craft a Thoughtful Conclusion
The conclusion is your final opportunity to wrap up the story in a satisfying way and leave the audience with something to ponder. Here's how to write a strong conclusion for your critical thinking essay:
- Summarize Key Points: Briefly remind your reader of the main points you've discussed throughout the essay.
- Restate Your Thesis: Restate your thesis statement in a new way, emphasizing its significance.
- Final Thought or Call to Action (Optional): Leave your reader with a final thought that provokes reflection, or consider including a call to action that encourages them to take a particular stance on the issue.
Here's an example conclusion for the online learning essay:
In conclusion, while online learning platforms offer valuable flexibility and accessibility, they cannot entirely replace the benefits of a traditional classroom setting. The social interaction, real-time feedback, and personalized attention offered by in-person learning remain crucial components of a well-rounded educational experience. As technology continues to evolve, future advancements may bridge this gap, but for now, a blended approach that leverages the strengths of both online and traditional learning may be the optimal solution.
Critical Thinking Essay Example
Let's now take a look at a complete critical thinking essay to see how these steps come together. This example will show you how to structure your essay and build a strong argument.
5 Tips on How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinking helps you form well-reasoned arguments and make sound decisions. Here are 5 tips to sharpen your critical thinking skills:
.webp)
- Question Everything (Respectfully): Don't just accept information at face value. Ask questions like "Why is this important?" "What evidence supports this claim?" or "Are there other perspectives to consider?". Develop a healthy skepticism (doubt) but be respectful of others' viewpoints.
- Dig Deeper than Headlines: In today's fast-paced world, headlines can be misleading. Go beyond the surface and seek out credible sources that provide in-depth analysis and evidence. Look for articles from reputable news organizations, academic journals, or books by established experts.
- Embrace Different Viewpoints: Exposing yourself to various perspectives strengthens your critical thinking. Read articles that present opposing viewpoints, watch documentaries that explore different sides of an issue, or engage in respectful discussions with people who hold contrasting opinions.
- Spot Logical Fallacies: Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning that can lead to flawed conclusions. Learn to identify common fallacies like bandwagon appeals (appealing to popularity), ad hominem attacks (attacking the person instead of the argument), or slippery slope arguments (suggesting a small step will lead to a disastrous outcome).
- Practice Makes Progress: Critical thinking is a skill that improves with practice. Engage in activities that encourage analysis and debate. Write persuasive essays, participate in class discussions, or join a debate club. The more you exercise your critical thinking muscles, the stronger they become.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you'll be well on your way to becoming a more critical thinker. Remember, keep questioning things, explore different ideas, and practice your writing!
Drowning in Research and Thesis Statements that Just Don't Click?
Don't waste another minute battling writer's block. EssayPro's expert writers are here to be your research partner!
What is an Example of Critical Thinking?
How do you start writing a critical thinking essay, how to structure a critical thinking essay.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Critical thinking and writing . (n.d.). https://studenthub.city.ac.uk/__data/assets/pdf_file/0011/372818/2.-Critical-thinking-guide_FINAL.pdf
- Lane, J. (2023, September 6). Critical thinking for critical writing | SFU Library . Www.lib.sfu.ca . https://www.lib.sfu.ca/about/branches-depts/slc/writing/argumentation/critical-thinking-writing
.webp)
How to Write a Critical Essay
Hill Street Studios / Getty Images
- An Introduction to Punctuation
Olivia Valdes was the Associate Editorial Director for ThoughtCo. She worked with Dotdash Meredith from 2017 to 2021.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Olivia-Valdes_WEB1-1e405fc799d9474e9212215c4f21b141.jpg)
- B.A., American Studies, Yale University
A critical essay is a form of academic writing that analyzes, interprets, and/or evaluates a text. In a critical essay, an author makes a claim about how particular ideas or themes are conveyed in a text, then supports that claim with evidence from primary and/or secondary sources.
In casual conversation, we often associate the word "critical" with a negative perspective. However, in the context of a critical essay, the word "critical" simply means discerning and analytical. Critical essays analyze and evaluate the meaning and significance of a text, rather than making a judgment about its content or quality.
What Makes an Essay "Critical"?
Imagine you've just watched the movie "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory." If you were chatting with friends in the movie theater lobby, you might say something like, "Charlie was so lucky to find a Golden Ticket. That ticket changed his life." A friend might reply, "Yeah, but Willy Wonka shouldn't have let those raucous kids into his chocolate factory in the first place. They caused a big mess."
These comments make for an enjoyable conversation, but they do not belong in a critical essay. Why? Because they respond to (and pass judgment on) the raw content of the movie, rather than analyzing its themes or how the director conveyed those themes.
On the other hand, a critical essay about "Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory" might take the following topic as its thesis: "In 'Willy Wonka and the Chocolate Factory,' director Mel Stuart intertwines money and morality through his depiction of children: the angelic appearance of Charlie Bucket, a good-hearted boy of modest means, is sharply contrasted against the physically grotesque portrayal of the wealthy, and thus immoral, children."
This thesis includes a claim about the themes of the film, what the director seems to be saying about those themes, and what techniques the director employs in order to communicate his message. In addition, this thesis is both supportable and disputable using evidence from the film itself, which means it's a strong central argument for a critical essay .
Characteristics of a Critical Essay
Critical essays are written across many academic disciplines and can have wide-ranging textual subjects: films, novels, poetry, video games, visual art, and more. However, despite their diverse subject matter, all critical essays share the following characteristics.
- Central claim . All critical essays contain a central claim about the text. This argument is typically expressed at the beginning of the essay in a thesis statement , then supported with evidence in each body paragraph. Some critical essays bolster their argument even further by including potential counterarguments, then using evidence to dispute them.
- Evidence . The central claim of a critical essay must be supported by evidence. In many critical essays, most of the evidence comes in the form of textual support: particular details from the text (dialogue, descriptions, word choice, structure, imagery, et cetera) that bolster the argument. Critical essays may also include evidence from secondary sources, often scholarly works that support or strengthen the main argument.
- Conclusion . After making a claim and supporting it with evidence, critical essays offer a succinct conclusion. The conclusion summarizes the trajectory of the essay's argument and emphasizes the essays' most important insights.
Tips for Writing a Critical Essay
Writing a critical essay requires rigorous analysis and a meticulous argument-building process. If you're struggling with a critical essay assignment, these tips will help you get started.
- Practice active reading strategies . These strategies for staying focused and retaining information will help you identify specific details in the text that will serve as evidence for your main argument. Active reading is an essential skill, especially if you're writing a critical essay for a literature class.
- Read example essays . If you're unfamiliar with critical essays as a form, writing one is going to be extremely challenging. Before you dive into the writing process, read a variety of published critical essays, paying careful attention to their structure and writing style. (As always, remember that paraphrasing an author's ideas without proper attribution is a form of plagiarism .)
- Resist the urge to summarize . Critical essays should consist of your own analysis and interpretation of a text, not a summary of the text in general. If you find yourself writing lengthy plot or character descriptions, pause and consider whether these summaries are in the service of your main argument or whether they are simply taking up space.
- Critical Analysis in Composition
- Writing About Literature: Ten Sample Topics for Comparison & Contrast Essays
- What Is a Critique in Composition?
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- A Critical Analysis of George Orwell's 'A Hanging'
- What Are the Different Types and Characteristics of Essays?
- literary present (verbs)
- Book Report: Definition, Guidelines, and Advice
- personal statement (essay)
- Definition Examples of Collage Essays
- Definition and Examples of Evaluation Essays
- Composition Type: Problem-Solution Essays
- What Is Plagiarism?
- The Power and Pleasure of Metaphor
- Quotes About Close Reading
- What Is a Compelling Introduction?
How To Write A Critical Analysis Essay With Examples
Declan Gessel
May 4, 2024

A Critical Analysis Essay is a form of academic writing that requires students to extract information and critically analyze a specific topic. The task may seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can become an exciting task.
Critical Analysis Essays help students improve their analytical skills and foster principles of logic. In this article, we are going to discuss how to write an essay and break it down for you. So sit back, relax, and enjoy the ride!
Table Of Content
What is a critical analysis essay, why the subject of your critical analysis essay is important, 5 reading strategies for critical analysis essay, building the body of your analysis, 5 things to avoid when writing your critical analysis essay, write smarter critical analysis essay with jotbot — start writing for free today.

When you write a critical analysis essay, you move beyond recounting the subject's main points and delve into examining it with a discerning eye. The goal? To form your own insights about the subject, based on the evidence you gather.
This involves dissecting and contemplating the author's arguments , techniques, and themes while also developing your own critical response. While forming your own conclusions may sound intimidating, it's a key aspect of fine-tuning your critical thinking skills and organizing your thoughts into a cohesive, argumentative response.
Key Skills in the Craft
This process consists of two key elements: understanding the core components of the subject and forming your own critical response, both supported by evidence. The first part involves grasping the subject's main arguments, techniques, and themes. The second part entails taking that knowledge and constructing your analytical and evaluative response.
Deconstructing the Subject
In other words, roll up your sleeves and get deep into the subject matter. Start by identifying the author's main point, deconstructing their arguments, examining the structure and techniques they use, and exploring the underlying themes and messages. By engaging with the subject on this level, you'll have a thorough understanding of it and be better prepared to develop your own response.
The Power of Evidence
Remember that evidence is your secret weapon for crafting a convincing analysis. This means going beyond summarizing the content and instead using specific examples from the subject to support your own arguments and interpretations. Evidence isn't just about facts, either; it can also be used to address the effectiveness of the subject, highlighting both its strengths and weaknesses.
The Art of Evaluation
Lastly, put your evaluation skills to work. Critically assess the subject's effectiveness, pinpointing its strengths and potential shortcomings. From there, you can offer your own interpretation, supported by evidence from the subject itself. This is where you put everything you've learned about the subject to the test, showcasing your analytical skills and proving your point.
Related Reading
• Argumentative Essay • Essay Format • Expository Essay • Essay Outline • How To Write A Conclusion For An Essay • Transition Sentences • Narrative Essay • Rhetorical Analysis Essay • Persuasive Essay

Let’s delve on the importance of understanding the Work you'll be analyzing:
Main Argument
When diving into a work, one must unravel the central point or message the author is conveying. All other analyses stem from this fundamental point. By identifying and comprehending the main argument, one can dissect the various elements that support it, revealing the author's stance or point of view.
Themes are the underlying concepts and messages explored in the subject matter. By venturing into the depths of themes, one can unravel the layers of meaning within the work. Understanding these underlying ideas not only enriches the analysis but also sheds light on the author's intentions and insights.
Structure & Techniques
Understanding how the work is built - be it a chronological story, persuasive arguments, or the use of figurative language - provides insight into the author's craft. Structure and techniques can influence the way the work is perceived, and by dissecting them, one can appreciate the intricacies of the author's style and the impact it has on the audience.
In critical analysis, understanding the context can add an extra layer of depth to the analysis. Considering the historical, social, or cultural context in which the work was created can provide valuable insights into the author's influences, intentions, and the reception of the work. While not always necessary, contextual analysis can elucidate aspects of the work that might otherwise go unnoticed.
To conduct a comprehensive critical analysis , understanding the work you'll be analyzing is the foundation on which all other interpretations rely. By identifying the main argument, themes, structure, techniques, and context, a nuanced and insightful analysis can be crafted. This step sets the stage for a thorough examination of the work, bringing to light the nuances and complexities that make critical analysis a valuable tool in literary and artistic exploration.

1. Close Reading: Go Deeper Than Skimming
Close reading is a focused approach to reading where you don't just skim the text. Instead, you pay close attention to every word, sentence, and detail. By doing this, you can uncover hidden meanings, themes, and literary devices that you might miss if you were reading too quickly. I recommend underlining or annotating key passages, literary devices, or recurring ideas. This helps you remember these important details later on when you're writing your critical analysis essay.

2. Active Note-Taking to Capture Important Points
When reading a text for a critical analysis essay, it's important to take active notes that go beyond summarizing the plot or main points. Instead, try jotting down the author's arguments, interesting details, confusing sections, and potential evidence for your analysis. These notes will give you a solid foundation to build your essay upon and will help you keep track of all the important elements of the text.
3. Identify Recurring Ideas: Look for Patterns
In a critical analysis essay, it's crucial to recognize recurring ideas, themes, motifs, or symbols that might hold deeper meaning. By looking for patterns in the text, you can uncover hidden messages or themes that the author might be trying to convey. Ask yourself why these elements are used repeatedly and how they contribute to the overall message of the text. By identifying these patterns, you can craft a more nuanced analysis of the text.
4. Consider the Author's Purpose
Authorial intent is an essential concept to consider when writing a critical analysis essay. Think about the author's goals: are they trying to inform, persuade, entertain, or something else entirely? Understanding the author's purpose can help you interpret the text more accurately and can give you insight into the author's motivations for writing the text in the first place.
5. Question and Analyze your Arguments
In a critical analysis essay, it's important to take a critical approach to the text. Question the author's ideas, analyze the effectiveness of their arguments, and consider different interpretations. By approaching the text with a critical eye, you can craft a more thorough and nuanced analysis that goes beyond a surface-level reading of the text.
Jotbot is your personal document assistant. Jotbot does AI note taking, AI video summarizing, AI citation/source finder, it writes AI outlines for essays, and even writes entire essays with Jotbot’s AI essay writer. Join 500,000+ writers, students, teams, and researchers around the world to write more, write better, and write faster with Jotbot. Write smarter, not harder with Jotbot. Start writing for free with Jotbot today — sign in with Google and get started in seconds.

Let’s delve on the essentials of building the body of your analysis:
Topic Sentence Breakdown: The Purpose of a Strong Topic Sentence
A powerful topic sentence in each paragraph of your critical analysis essay serves as a roadmap for your reader. It tells them the focus of the paragraph, introducing the main point you will explore and tying it back to your thesis. For instance, in an essay about the role of symbolism in "The Great Gatsby," a topic sentence might read, "Fitzgerald's use of the green light symbolizes Gatsby's unattainable dreams, highlighting the theme of the American Dream's illusion."
Evidence Integration: The Significance of Evidence from the Subject
To bolster your arguments, you need to use evidence from the subject you are analyzing. For example, in "To Kill a Mockingbird," when explaining Atticus Finch's moral compass, using a quote like, "You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view - until you climb into his skin and walk around in it," can back up your analysis. It proves that the character values empathy and understanding.
Textual Evidence: Integrating Quotes, Paraphrases, or Specific Details
When you quote or paraphrase text, ensure it directly relates to your analysis. For example, when discussing Sylvia Plath's use of imagery in "The Bell Jar," quote, "I saw my life branching out before me like the green fig tree in the story." This paints a vivid picture for readers and helps solidify your point about the protagonist's feelings of entrapment.
Visual Evidence: Analyzing Specific Elements in the Artwork
If you are analyzing a painting, you can use visual details like color, lines, or symbolism as evidence. For instance, if exploring Van Gogh's "Starry Night," you could delve into the calming effect of the swirls in the sky or the stark contrast between the bright stars and the dark village below. This visual evidence helps explain the painting's emotional impact on viewers.
Analysis & Explanation: The Importance of Going Beyond Evidence Presentation
When examining evidence, don't stop at merely presenting it. Analyze how it supports your thesis. For instance, when exploring the role of the conch in "Lord of the Flies," after showing how it represents order, explain how its loss signals the boys' descent into savagery. By unpacking the evidence's meaning, you help readers understand why it matters and how it connects to your overall argument.
• Words To Start A Paragraph • Essay Structure • Types Of Essays • How To Write A Narrative Essay • Synthesis Essay • Descriptive Essay • How To Start Off An Essay • How To Write An Analytical Essay • Write Me A Paragraph • How To Write A Synthesis Essay

1. Avoiding Summary vs. Analysis Pitfalls
When crafting a critical analysis essay, it's crucial not to fall into the trap of merely summarizing the subject without offering your own critical analysis. A summary merely recaps the content, while an analysis breaks down and interprets the subject. If you overlook this vital distinction, your essay will lack the depth and insight that characterize a strong critical analysis. Ensure your critical analysis essay doesn't read like an extended book report.
2. Steering Clear of Weak Thesis Statements
A critical analysis essay lives and dies on the strength of its thesis statement, the central argument that guides your analysis. A weak or vague thesis statement will result in an unfocused essay devoid of direction, leaving readers unclear about your point of view. It's essential to craft a thesis statement that is specific, arguable, and concise, setting the tone for a thoughtful and illuminating analysis.
3. Using Evidence is Key
The use of evidence from the subject matter under analysis is instrumental in substantiating your critical claims. Without evidence to back up your assertions, your analysis will appear unsubstantiated and unconvincing. Be sure to provide detailed examples, quotes, or data from the text under scrutiny to support your analysis. Evidence adds credibility, depth, and weight to your critical analysis essay.
4. The Importance of Clear and Supported Analysis
A successful critical analysis essay goes beyond simply presenting evidence to analyzing its significance and connecting it to your central argument. If your essay lacks clear analysis, readers won't understand the relevance of the evidence you present. Go beyond description to interpret the evidence, explaining its implications and how it supports your thesis. Without this analysis, your essay will lack depth and will not persuade your audience.
5. Addressing Counter Arguments
In a critical analysis essay, it's vital to acknowledge and engage with potential counterarguments. Ignoring opposing viewpoints undermines the credibility of your essay, presenting a one-sided argument that lacks nuance. Addressing counter arguments demonstrates that you understand the complexity of the issue and can anticipate and respond to objections.
By incorporating counterarguments, you strengthen your analysis and enhance the overall persuasiveness of your critical essay.

Jotbot is an AI-powered writing tool that offers a wide range of features to assist writers in producing high-quality written content efficiently. These features include AI note-taking, video summarization, citation and source finding, generating essay outlines, and even writing complete essays. Jotbot is designed to streamline the writing process, enabling writers to create content more effectively and quickly than traditional methods.
AI Note-Taking
Jotbot's AI note-taking feature helps writers collect and organize information in a structured manner. By enabling writers to jot down key points and ideas during research or brainstorming sessions, Jotbot ensures that important details are not missed and can be easily accessed during the writing process.
AI Video Summarization
The AI video summarization feature of Jotbot allows writers to input videos for summarization and analysis. Jotbot’s AI engine processes the content of the video and provides a concise summary. This feature is particularly useful for writers who need to reference video content in their work but may not have the time to watch the entire video.
AI Citation/Source Finder
Jotbot's AI citation and source finding feature helps writers accurately reference and cite sources in their work. By analyzing the text and identifying key information, Jotbot streamlines the citation process, reducing the time and effort involved in finding and citing sources manually.
AI Outlines for Essays
Jotbot generates AI outlines for essays based on the writer's input. These outlines provide a structured framework that writers can use to organize their thoughts and ideas before beginning the writing process. By creating a roadmap for the essay, Jotbot helps writers maintain focus and coherence throughout their work.
AI Essay Writer
Jotbot's AI essay writer feature can generate complete essays based on the writer's input and preferences. By analyzing the given information, Jotbot constructs an essay that meets the writer's criteria, enabling users to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently. With its advanced AI capabilities, Jotbot helps writers write more, write better, and write faster.
• How To Write A Personal Essay • Chat Gpt Essay Writer • How To Write An Outline For An Essay • What Makes A Good Thesis Statement • Essay Writing Tools • How To Write A 5 Paragraph Essay • How To Write A Rhetorical Analysis Essay • First Person Essay • How To Write A Header For An Essay • Memoir Essay • Formula For A Thesis Statement
Trusted by top universities and businesses

Loved by 1,000,000+
Write more, better, faster..
Your personal AI document assistant
Start writing — it's free
Your personal document assistant.
Start for free
Press enquiries
Influencer Program
Terms & Conditions
Privacy policy
AI Source Finder
AI Outline Generator
How to Use JotBot AI
© 2024 JotBot AI by SLAM Ventures, LLC all rights reserved
© 2024 SLAM Ventures, LLC
- Monash Online
Student Academic Success
- 1:1 Consultation 1:1 Consultation
- Study better Study better
- Build digital capabilities Build digital capabilities
- Understand assessments Understand assessments
- Excel at writing Excel at writing
- Enhance your thinking Enhance your thinking
- Present confidently Present confidently
- Collaborate with others Collaborate with others
- Improve your academic English Improve your academic English
- Maintain academic integrity Maintain academic integrity
- Advance your graduate studies Advance your graduate studies
- O-week workshops O-week workshops
- Let's Talk Assessments Let's Talk Assessments
- Set up for academic success Set up for academic success
- Writing classes Writing classes
- End of semester End of semester
- PhD writing workshops and courses PhD writing workshops and courses
- First Year Undergraduate Success First Year Undergraduate Success
- Graduate coursework success Graduate coursework success
- Academic Language Skills Analysis Academic Language Skills Analysis
- Mathematics skills analysis Mathematics skills analysis
- Orientation Orientation
- SAS cafe SAS cafe
- SAS pop up SAS pop up
- Written Feedback Written Feedback
- About us About us
- Skip to content
- Skip to navigation
How to build an essay
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
Preparing an outline
You are ready to write an essay after you have done these steps:
- Identified all the components that you must cover so that you address the essay question or prompt
- Conducted your initial research and decided on your tentative position and line of argument
- Created a preliminary outline for your essay that presents the information logically.
Most essays follow a similar structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, as shown in the diagram below.
Click on the plus icons for more information.
| Note There is no set requirement for the number of paragraphs in an essay. The important point is that the argument is logically developed through a series of well-structured paragraphs. |
Writing an introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to give your reader a clear idea of what your essay will cover. It should provide some background information on the specific problem or issue you are addressing, and should clearly outline your answer. Depending on your faculty or school, ‘your answer’ may be referred to as your position, contention, thesis or main argument . Whatever term is used, this is essentially your response to the essay question, which is based on the research that you have undertaken or the readings you have analysed.
An essay is not like a mystery novel which keeps the reader in suspense; it should not slowly reveal the argument to the reader. Instead, the contention and supporting arguments are usually stated in the introduction.
When writing an introduction, you should typically use a general to specific structure. This means that you introduce the particular problem or topic the essay will address in a general sense to provide the context before you narrow down to your particular position and line of argument.

Key elements of an introduction
Click on each of the elements to reveal more.
Content Container
Provide some background information and context.
The introduction usually starts by providing some background information about your particular topic, so the reader understands the key problem being addressed and why it is an issue worth writing about. However, it is important that this is brief and that you only include information that is directly relevant to the topic.
This might also be an appropriate place to introduce the reader to key terms and provide definitions, if required.
Don’t be tempted to start your essay with a grand generalisation, for instance: ‘War has always been a problem for humanity….’, or ‘Since the beginning of time…’. Instead, make sure that your initial sentence relates directly to the problem, question or issue highlighted by the essay topic.
Limit the scope of your discussion
Setting the parameters of the essay is important. You can’t possibly cover everything on a topic - and you are not expected to - so you need to tell your reader how you have chosen to narrow the focus of your essay.
State your position / contention
State your position on the topic (also referred to as your main argument , or contention , or thesis statement ). Make sure that you are directly answering the question (and the whole essay question if there is more than one part to it).
"Stating your position" can be a single sentence answer to the essay question but will often include 2-3 sentences explaining the answer in more detail.
Outline the structure or main supporting points of your essay
This usually involves providing details of the most important points you are going to make which support your argument.
Sample introduction
[1] Business leadership has been described as the ‘ability to influence, motivate and enable others to contribute to the effectiveness and success of the organisations of which they are members’ (House, Hanges, Javidan, Dorfman & Gupta, 2004, p. 63). Whether this ability is something a person is born with, or whether it is something that a person can learn, has been the subject of considerable debate. Kambil (2010) has outlined two categories of leadership attributes that help to frame the discussion: 'traits' (mostly innate) and 'skills' which can be developed through experience or training. [2] This essay will draw on the trait theory of leadership to argue that that leaders are first born, but then must be made. [3] While good business leaders share certain traits that are essential to success, including ‘curiosity, courage, perseverance, personal ethics and confidence’ (Kambil, 2010, p.43), they also need learnable skills, such as communication, negotiation and conflict resolution, that are only developed through practice. A potential leader should develop their natural traits as well as learn and practise skills which will help them to persuade, equip and inspire others to realise their vision.
Legend: [1] Background / Context ; [2] Position / Contention ; [3] Structure or main point of essay
Check your understanding View
Key features of an introduction.
Read the paragraph in the accordion below and see if you can identify the key features of an introduction. This is an introduction written in response to the essay question: 'Can Rome's actions towards Carthage be described as defensive imperialism?'
Writing a body paragraph
The body of the essay is where you fully develop your argument. Each body paragraph should contain one key idea or claim, which is supported by relevant examples and evidence from the body of scholarly work on your topic (i.e. academic books and journal articles).
Together, the body paragraphs form the building blocks of your argument.
How do I structure paragraphs?
The TEECL structure provides an effective way of organising a paragraph. TEECL stands for Topic sentence, Explanation, Evidence, Comment, and Link. You may find it helpful to add C for Comment before Link. A paragraph structured this way would contain the following:
- Topic sentence – the first sentence in a body paragraph that tells the reader what the main idea or claim of the paragraph will be.
- Explanation – Explain what you mean in greater detail.
- Evidence – Provide evidence to support your idea or claim. To do this, refer to your research. This may include: case studies, statistics, documentary evidence, academic books or journal articles. Remember that all evidence will require appropriate citation.
- Comment – Consider the strengths and limitations of the evidence and examples that you have presented. Explain how your evidence supports your claim (i.e. how does it ‘prove’ your topic sentence?).
- Link – Summarise the main idea of the paragraph, and make clear how this paragraph supports your overall argument.
Sample paragraph
[1] One of the main obstacles to reaching international consensus on climate change action is the ongoing debate over which countries should shoulder the burden. [2] Because the developed world has historically been responsible for the majority of greenhouse gas emissions, it has been argued that they should reduce emissions and allow developed nations to prioritise development over environmental concerns (Vinuales, 2011). [3] The notion of ‘common but differentiated responsibility’ (CBDR) was formalised in the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 (UNFCCC, 1992). Article 3.1 explicitly states 'Accordingly, the developed country Parties should take the lead in combating climate change and the adverse effects thereof' (p. 4). [4] However, because CBDR outlines a principle and not an actionable plan it has remained problematic. For example, it does not stipulate the extent to which, under the principle of CBDR, developing nations should be exempt from specific emissions targets. This has continued to be a point of contention in global negotiations on climate change, with developed countries such as the USA arguing that developed nations should do more to reduce emissions (Klein et. al., 2017). [5] Fairness and equity need to be pursued in reaching a global agreement on climate change, but transforming this into an actionable strategy is problematic.
Legend : [1] Topic sentence [2] Explanation [3] Evidence / Example [4] Comment [5] Link
What is missing?
The paragraph below was written in response to the essay question: '"Leaders are made rather than born." Do you agree or disagree? Provide reasons for your opinion.'
Read the paragraph then answer the question that follows.
The function of a conclusion is to draw together the main ideas discussed in the body of the essay. However, a good conclusion does more than that.
You may choose to also:
- reflect on the broader significance of the topic
- discuss why it is difficult to arrive at a definitive answer to the question posed
- raise other questions that could be considered in a subsequent essay
- make a prediction or a caution or a recommendation about what will happen to the phenomenon under investigation
When writing a conclusion, a specific to general structure is usually recommended. Yes, this is opposite to the introduction! Begin by re-stating or re-emphasising your position on the topic, then summarise your line of argument and key points. Finish off by commenting on the significance of the issue, making a prediction about the future of the issue, or a recommendation to deal with the problem at hand.

Sample conclusion
[1] No single theory can adequately explain the relationship between age and crime, and the debate over their correlation is ongoing. Instead, each theory provides valuable insight into a particular dimension of age and crime. [2] The emergence of the criminal propensity versus criminal career debate in the 1980s demonstrated the importance of both arguments. It is now believed that the age-crime curve created by Gottfredson and Hirschi is a good basic indicator for the age-crime relationship. However, the criminal career position has stood up to stringent empirical testing, and has formed an integral part of developmental theories such as Thornberry’s interactional theory. [3] These theories provide important insight into the complex relationship between age and crime, but, more than this, are useful for developing strategies for delinquency and crime prevention.
Legend : [1] Specific contention ; [2] Specific summary of main points ; [3] Broader and general significance
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Learning Objectives
- Identify characteristics of a good topic sentence
- Identify the three parts of a developed paragraph
- Apply knowledge of topic sentences and parts of a developed paragraph in an assignment
This section addresses paragraph composition. In the next chapter, we will look at identifying common assignment purposes and how to select appropriate content for a particular audience, but here we will look at what actually makes up a paragraph. Composing an effective paragraph requires a method similar to building a house. You may have the finest content, or materials, but if you do not arrange them in the correct order, then the final product will not hold together very well.
Imagine reading one long block of text, with each idea blurring into the next. Even if you are reading a thrilling novel or an interesting news article, you will likely very quickly lose interest in what the author. During the writing process, it is helpful to position yourself as a reader. Ask yourself whether you can focus easily on each point you make. One technique that effective writers use is to begin a fresh paragraph for each new idea they introduce.
Paragraphs separate ideas into logical, manageable chunks. One paragraph focuses on only one main idea and presents coherent sentences to support that one point. Because all the sentences in one paragraph support the same point, a paragraph may stand on its own. To create longer assignments and to discuss more than one point, writers group together paragraphs.
A strong paragraph contains three distinct components:
- Topic sentence . The topic sentence is the main idea of the paragraph.
- Body . The body is composed of the supporting sentences that develop the main point.
- Conclusion . The conclusion is the final sentence that summarizes the main point.
The foundation of a good paragraph is the topic sentence, which expresses the main idea of the paragraph. The topic sentence relates to the thesis, or main point, of the essay and guides the reader by signposting what the paragraph is about. All the sentences in the rest of the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
This section covers the major components of a paragraph and examines how to develop an effective topic sentence.
- Paragraph Length
- How long should a paragraph be?
One answer to this important question may be “long enough”—long enough for you to address your points and explain your main idea. To grab attention or to present succinct supporting ideas, a paragraph can be fairly short and consist of two to three sentences. A paragraph in a complex essay about some abstract point in philosophy or archaeology can be two-thirds of a page or more in length. As long as the writer maintains close focus on the topic and does not ramble, a long paragraph is acceptable. In general, try to keep the paragraphs longer than one sentence but shorter than two-thirds of a page of double spaced text, or roughly 75 to 200 words in length.
You may find that a particular paragraph you write may be longer than one that will hold your audience’s interest. In such cases, you should divide the paragraph into two or more shorter paragraphs, adding a topic statement or some kind of transitional word or phrase at the start of the new paragraph. Transition words or phrases show the connection between the two ideas.
In all cases, however, be guided by what your instructor wants and expects to find in your draft. Many instructors will expect you to develop a mature style as you progress through the semester’s assignments.
Developing a Topic Sentence
Pick up any newspaper or magazine and read the first sentence of an article. Are you fairly confident that you know what the rest of the article is about? If so, you have likely read the topic sentence. An effective topic sentence combines a main idea with the writer’s personal attitude or opinion. It serves to orient the reader and provides an indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph. Read the following example.
Creating a national set of standards for math and English education will improve student learning in many provinces.
This topic sentence declares a favourable position for standardizing math and English education. After reading this sentence, a reader might reasonably expect the writer to provide supporting details and facts as to why standardizing math and English education might improve student learning in many provinces. If the purpose of the essay is actually to evaluate education in only one particular province or to discuss math or English education specifically, then the topic sentence is misleading.
Main Idea versus Controlling Idea
Topic sentences contain both a main idea (the subject, or topic that the writer is discussing) and a controlling idea (the writer’s specific stance on that subject). Just as a thesis statement includes an idea that controls a document’s focus, a topic sentence must also contain a controlling idea to direct the paragraph. Different writers may use the same main idea but can steer their paragraph in a number of different directions according to their stance on the subject. Read the following examples.
Marijuana is a destructive influence on teens and causes long-term brain damage.
The anti-nausea properties in marijuana are a lifeline for many cancer patients.
Legalizing marijuana would create a higher demand for Class A and Class B drugs.
Although the main idea—marijuana—is the same in all three topic sentences, the controlling idea differs depending on the writer’s viewpoint.
Self-Practice Exercise 3.9
H5P: Self-Practice 3.9
Exercising three times a week is the only way to maintain good physical health.
Sexism and racism are still rampant in today’s workplace.
Raising the legal driving age to 21 would decrease road traffic accidents.
Owning a business is the only way to achieve financial success.
Dog owners should be prohibited from taking their pets on public beaches.
Characteristics of a Good Topic Sentence
Five characteristics define a good topic sentence:
- Weak example. People rarely give firefighters the credit they deserve for such a physically and emotionally demanding job. (The paragraph is about a specific incident that involved firefighters; therefore, this topic sentence is too general.)
- Stronger example. During the October riots, Unit 3B went beyond the call of duty. (This topic sentence is more specific and indicates that the paragraph will contain information about a particular incident involving Unit 3B.)
- Weak example. In this paper, I am going to discuss the rising suicide rate among young professionals. (This topic sentence provides a main idea, but it does not present a controlling idea or thesis.)
- Stronger example. The rising suicide rate among young professionals is a cause for immediate concern. (This topic sentence presents the writer’s opinion on the subject of rising suicide rates among young professionals.)
- Weak example. In general, writing an essay, thesis, or other academic or nonacademic document is considerably easier and of much higher quality if you first construct an outline, of which there are many different types. (This topic sentence includes a main idea and a controlling thesis, but both are buried beneath the confusing sentence structure and unnecessary vocabulary. These obstacles make it difficult for the reader to follow.)
- Stronger example. Most forms of writing can be improved by first creating an outline. (This topic sentence cuts out unnecessary verbiage and simplifies the previous statement, making it easier for the reader to follow.)
- Weak example. Salaries should be capped in baseball for many reasons, most importantly so we don’t allow the same team to win year after year. (This topic sentence includes a supporting detail that should be included later in the paragraph to back up the main point.)
- Stronger example. Introducing a salary cap would improve the game of baseball for many reasons. (This topic sentence omits the additional supporting detail so that it can be expanded upon later in the paragraph.)
- Weak example. The military deserves better equipment. (This topic sentence includes a main idea and a controlling thesis, but the language is bland and unexciting.)
- Stronger example. The appalling lack of resources provided to the military is outrageous and requires our immediate attention. (This topic sentence reiterates the same idea and controlling thesis, but adjectives such as appalling and immediate better engage the reader. These words also indicate the writer’s tone.)
Self-Practice Exercise 3.10
H5P: Choose the most effective topic sentence from the following sentence pairs.
- This paper will discuss the likelihood of the Liberals winning the next election.
- To boost their chances of winning the next election, the Liberals need to listen to public opinion.
- Union workers are crippling the economy because companies are unable to remain competitive as a result of added financial pressure.
- The unrealistic demands of union workers are crippling the economy for three main reasons.
- The introduction of new technology will devastate the literary world.
- Authors are losing money as a result of technological advances.
- This essay will consider whether talent is required in the rap music industry.
- Rap music is produced by untalented individuals with oversized egos.
Self-Practice Exercise 3.11
H5P: Prompts
Create your own topic sentences using the following subjects. Remember to include a controlling idea (opinion) in addition to the topic.
- Create a topic sentence that expresses an opinion.
- A controversial film or novel.
Writing at Work
When creating a workplace document, use the “top down” approach—keep the topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph so that readers immediately understand the gist of the message. This method saves busy colleagues precious time and effort trying to figure out the main points and relevant details.
Headings are another helpful tool. In a text-heavy document, break up each paragraph with individual headings. These serve as useful navigation aids, enabling colleagues to skim through the document and locate paragraphs that are relevant to them.
Developing Paragraphs That Use Topic Sentences, Supporting Ideas, and Transitions Effectively
Learning how to develop a good topic sentence is the first step toward writing a solid paragraph. Once you have composed your topic sentence, you have a guideline for the rest of the paragraph. To complete the paragraph, a writer must support the topic sentence with additional information and summarize the main point with a concluding sentence.
This section identifies the three major structural parts of a paragraph and covers how to develop a paragraph using transitional words and phrases.
Identifying Parts of a Paragraph
An effective paragraph contains three main parts: a topic sentence, the body, and the concluding sentence. A topic sentence is often the first sentence of a paragraph. The body of the paragraph usually follows, containing supporting details. Supporting sentences help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence. The concluding sentence is the last sentence in the paragraph. It reminds the reader of the main point by restating it in different words. Figure 3.4 provides a template you can use for organizing your paragraphs.

Read the following paragraph. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
After reading the new TV guide this week , I had just one thought—why are we still being bombarded with reality shows? This season, the plague of reality television continues to darken our airwaves. Along with the return of viewer favourites, we are to be cursed with yet another mindless creation. Prisoner follows the daily lives of eight suburban housewives who have chosen to be put in jail for the purposes of this fake psychological experiment. A preview for the first episode shows the usual tears and tantrums associated with reality television. I dread to think what producers will come up with next season, but if any of them are reading this blog—stop it! We’ve had enough reality television to last us a lifetime!
The first sentence of this paragraph is the topic sentence. It tells the reader that the paragraph will be about reality television shows, and it expresses the writer’s distaste for these shows through the use of the word bombarded .
Each of the following sentences in the paragraph supports the topic sentence by providing further information about a specific reality television show. The final sentence is the concluding sentence. It reiterates the main point that viewers are bored with reality television shows by using different words from the topic sentence.
Paragraphs that begin with the topic sentence move from the general to the specific. They open with a general statement about a subject (reality shows) and then discuss specific examples (the reality show Prisoner ). Most academic essays contain the topic sentence at the beginning of the first paragraph.
Now take a look at another paragraph. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
Last year, a cat travelled 200 kilometres to reach its family, who had moved to another city and had left their pet behind. Even though the cat had never been to the new home, it cat was able to track down its former owners. A dog in my neighbourhood can predict when its master is about to have a seizure. It makes sure that he does not hurt himself during an epileptic fit. Compared to many animals, our own senses are almost dull.
The last sentence of this paragraph is the topic sentence. It draws on specific examples (a cat that tracked down its owners and a dog that can predict seizures) and then makes a general statement that draws a conclusion from these examples (animals’ senses are better than humans’). In this case, the supporting sentences are placed before the topic sentence and the concluding sentence is the same as the topic sentence.
This technique is frequently used in persuasive writing. The writer produces detailed examples as evidence to back up his or her point, preparing the reader to accept the concluding topic sentence as the truth.
Sometimes, the topic sentence appears in the middle of a paragraph. Read the following example. The topic sentence is underlined for you.
For many years, I suffered from severe anxiety every time I took an exam. Hours before the exam, my heart would begin pounding, my legs would shake, and sometimes I would become physically unable to move. Last year, I was referred to a specialist and finally found a way to control my anxiety—breathing exercises. It seems so simple, but by doing just a few breathing exercises a couple of hours before an exam, I gradually got my anxiety under control. The exercises help slow my heart rate and make me feel less anxious. Better yet, they require no pills, no equipment, and very little time. It is amazing how just breathing correctly has helped me learn to manage my anxiety symptoms.
In this paragraph, the underlined sentence is the topic sentence. It expresses the main idea—that breathing exercises can help control anxiety. The preceding sentences enable the writer to build up to his main point (breathing exercises can help control anxiety) by using a personal anecdote (how the writer used to suffer from anxiety). The supporting sentences then expand on how breathing exercises help the writer by providing additional information. The last sentence is the concluding sentence and restates how breathing can help manage anxiety.
Placing a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph is often used in creative writing. If you notice that you have used a topic sentence in the middle of a paragraph in an academic essay, read through the paragraph carefully to make sure that it contains only one major topic.
Implied Topic Sentences
Some well-organized paragraphs do not contain a topic sentence at all. Instead of being directly stated, the main idea is implied in the content of the paragraph. Read the following example:
Heaving herself up the stairs, Luella had to pause for breath several times. She let out a wheeze as she sat down heavily in the wooden rocking chair. Tao approached her cautiously, as if she might crumble at the slightest touch. He studied her face, like parchment; stretched across the bones so finely he could almost see right through the skin to the decaying muscle underneath. Luella smiled a toothless grin.
Although no single sentence in this paragraph states the main idea, the entire paragraph focuses on one concept—that Luella is extremely old. The topic sentence is thus implied rather than stated. This technique is often used in descriptive or narrative writing. Implied topic sentences work well if the writer has a firm idea of what he or she intends to say in the paragraph and sticks to it. However, a paragraph loses its effectiveness if an implied topic sentence is too subtle or the writer loses focus.
Self-Practice Exercise 3.12
H5P: Identify the topic sentence, one example of a supporting sentence, and the concluding sentences.
The desert provides a harsh environment in which few mammals are able to adapt. Of these hardy creatures, the kangaroo rat is possibly the most fascinating. Able to live in some of the most arid parts of the southwest, the kangaroo rat neither sweats nor pants to keep cool. Its specialized kidneys enable it to survive on a minuscule amount of water. Unlike other desert creatures, the kangaroo rat does not store water in its body but instead is able to convert the dry seeds it eats into moisture. Its ability to adapt to such a hostile environment makes the kangaroo rat a truly amazing creature.
Supporting Sentences
If you think of a paragraph as a hamburger, the supporting sentences are the meat inside the bun. They make up the body of the paragraph by explaining, proving, or enhancing the controlling idea in the topic sentence. Most paragraphs contain three to six supporting sentences depending on the audience and purpose for writing. A supporting sentence usually offers one of the following:
- Sentence: The refusal of the baby boom generation to retire is contributing to the current lack of available jobs.
- Sentence: Many families now rely on older relatives to support them financially.
- Sentence: Nearly 10 percent of adults are currently unemployed in the United States.
- Sentence: “We will not allow this situation to continue,” stated Senator Johns.
- Sentence: Last year, Bill was asked to retire at the age of 55.
The type of supporting sentence you choose will depend on what you are writing and why you are writing. For example, if you are attempting to persuade your audience to take a particular position, you should rely on facts, statistics, and concrete examples, rather than personal opinions. Read the following example:
There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car. (Topic sentence)
First, they get 20 percent to 35 percent more kilometres to the litre than a fuel-efficient gas-powered vehicle. (Supporting sentence 1: statistic)
Second, they produce very few emissions during low-speed city driving. (Supporting sentence 2: fact)
Because they do not require as much gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump. (Supporting sentence 3: reason)
Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance. (Supporting sentence 4: example)
“It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas-powered vehicles I’ve owned.” (Supporting sentence 5: quotation)
Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future. (Concluding sentence)
To find information for your supporting sentences, you might consider using one of the following sources:
- Reference book
- Academic journal/article
- Newspaper/magazine
- Encyclopedia
- Biography/autobiography
- Previous experience
- Personal research
Concluding Sentences
An effective concluding sentence draws together all the ideas you have raised in your paragraph. It reminds readers of the main point—the topic sentence—without restating it in exactly the same words. Using the hamburger example, the top bun (the topic sentence) and the bottom bun (the concluding sentence) are very similar. They frame the “meat” or body of the paragraph. Compare the topic sentence and concluding sentence from the previous example:
Topic sentence: There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car.
Concluding sentence: Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Notice the use of the synonyms advantages and benefits . The concluding sentence reiterates the idea that owning a hybrid is advantageous without using the exact same words. It also summarizes two examples of the advantages covered in the supporting sentences: low running costs and environmental benefits.
You should avoid introducing any new ideas into your concluding sentence. A conclusion is intended to provide the reader with a sense of completion. Introducing a subject that is not covered in the paragraph will confuse the reader and weaken your writing.
A concluding sentence may do any of the following:
- Example: Childhood obesity is a growing problem in North America.
- Example: A lack of healthy choices, poor parenting, and an addiction to video games are among the many factors contributing to childhood obesity.
- Example: These statistics indicate that unless we take action, childhood obesity rates will continue to rise.
- Example: Based on this research, more than 60 percent of children in North American will be morbidly obese by the year 2030 unless we take evasive action.
- Example: Childhood obesity is an entirely preventable tragedy.
Self-Practice Exercise 3.13
H5P: Self-Practice Exercise 3.13
- If a paragraph is a hamburger, the topic sentence is the ____ bun and the concluding sentence is the ____bun. This makes the body of the paragraph the ____(unless you prefer a veggie burger).
- These examples from recent research show how criminalizing drugs has not protected communities or served individual drug users.
- The war on drugs has not resulted in a reduction in suffering.
- Given all we know about outcome of failed drug policy, the next step is to consider decriminalization.
- The war on drugs has damaged society because it has resulted in a more dangerous drug supply and a criminalized population.
- The traumas and violence inflicted by the war on drugs could have been prevented.
- Make a prediction, suggestion, or recommendation about the information in the paragraph.
- Draw a conclusion based on the information in the paragraph.
- Offer an additional observation about the controlling idea.
- Restate the main idea.
- Summarize the key points in the paragraph.
- top, bottom, meat/patty
Transitions
A strong paragraph moves seamlessly from the topic sentence into the supporting sentences and on to the concluding sentence. To help organize a paragraph and ensure that ideas logically connect to one another, writers use transitional words and phrases. A transition is a connecting word that describes a relationship between ideas. Take another look at the earlier example:
There are numerous advantages to owning a hybrid car. First , they get 20 percent to 35 percent more kilometres to the litre than a fuel-efficient gas-powered vehicle. Second , they produce very few emissions during low speed city driving. Because they require less gas, hybrid cars reduce dependency on fossil fuels, which helps lower prices at the pump. Alex bought a hybrid car two years ago and has been extremely impressed with its performance. “It’s the cheapest car I’ve ever had,” she said. “The running costs are far lower than previous gas-powered vehicles I’ve owned.” Given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Each of the underlined words is a transition word. Words such as first and second are transition words that show sequence or clarify order. They help organize the writer’s ideas by showing that he or she has another point to make in support of the topic sentence. Other transition words that show order include third , also , and furthermore .
The transition word because is a transition word of consequence that continues a line of thought. It indicates that the writer will provide an explanation of a result. In this sentence, the writer explains why hybrid cars will reduce dependency on fossil fuels (because they require less gas). Other transition words of consequence include as a result , so that , since , or for this reason .
To include a summarizing transition in her concluding sentence, the writer could rewrite the final sentence as follows:
In conclusion, given the low running costs and environmental benefits of owning a hybrid car, it is likely that many more people will follow Alex’s example in the near future.
Table 3.1: Transitional Words and Phrases to Connect Sentences provides some useful transition words to connect supporting sentences and concluding sentences. (In other chapters of this book, you will be exposed to more transitional words and phrases for other purposes.)
| For Supporting Sentences | For Concluding Sentences |
|---|---|
Self-Practice Exercise 3.14
H5P: Practice what you’ve learned about paragraphs!
Exercise Explanation
For this exercise, you will draft a paragraph after spending some time reflecting on the criteria for good paragraphs that you learned about in this chapter. You can choose any topic you like for your paragraph — maybe there’s something you’re thinking about for this or another class that would benefit from some time to do some writing about — but if you need help with a prompt, consider writing about one of the issues in this chapter or answer one of these questions:
- Can online friendships be as meaningful as offline ones?
- Is college or university always the right decision for people leaving high school?
- What can people do to manage their stress levels?
You don’t need to do research to approach this exercise (though you are welcome to, if you wish!). Instead, your own personal experience will be sufficient here.
Key Paragraph Details
Here you will reflect on what makes a good paragraph before you take a run at it yourself. Remember, a good paragraph has the following criteria:
- A topic sentence (that makes a claim/states an opinion!).
- A concluding sentence.
- Appropriate supporting details.
- Use of transitional words/phrases.
In the exercise below, click on the “criteria” button and make notes for yourself about how you can address the key criteria for paragraphs. Try make four points: one for each key element your paragraph needs to have.
Paragraph Composition
Based on the criteria you outlined on the previous page, draft a paragraph.
Review Criteria and Goals
Rate how well you’ve achieved each of the criteria, and reflect on how you can strengthen the thesis statement.
- Doesn’t meet criteria.
- Meets criteria partially.
- Strongly meets criteria.
Transitional words and phrases are useful tools to incorporate into workplace documents. They guide the reader through the document, clarifying relationships between sentences and paragraphs so that the reader understands why they have been written in that particular order.
For example, when writing an instructional memo, it may be helpful to consider the following transitional words and phrases: before you begin , first , next , then , finally , after you have completed . Using these transitions as a template to write your memo will provide readers with clear, logical instructions about a particular process and the order in which steps are supposed to be completed.
Key Takeaways
- A good paragraph contains three distinct components: a topic sentence, body, and concluding sentence.
- The topic sentence expresses the main idea of the paragraph combined with the writer’s attitude or opinion about the topic.
- Good topic sentences contain both a main idea and a controlling idea, are clear and easy to follow, use engaging vocabulary, and provide an accurate indication of what will follow in the rest of the paragraph.
- Topic sentences may be placed at the beginning, middle, or end of a paragraph. In most academic essays, the topic sentence is placed at the beginning of a paragraph.
- Supporting sentences help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence by offering facts, reasons, statistics, quotations, or examples.
- Concluding sentences summarize the key points in a paragraph and reiterate the main idea without repeating it word for word.
- Transitional words and phrases help organize ideas in a paragraph and show how these ideas relate to one another.
Supplemental Exercises
Select one of the following topics or choose a topic of your choice:
- Drilling for oil in Alberta
- Health care reform
- Introducing a four day work week
- Bringing pets to work
- Create a topic sentence based on the topic you chose, remembering to include both a main idea and a controlling idea. Next, write an alternative topic sentence using the same main idea but a different controlling idea.
Collaboration: Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Group activity. Working in a group of four or five, assign each group member the task of collecting one document each. These documents might include magazine or newspaper articles, workplace documents, academic essays, chapters from a reference book, film or book reviews, or any other type of writing. As a group, read through each document and discuss the author’s purpose for writing. Use the information you have learned in this chapter to decide whether the main purpose is to summarize, analyze, synthesize, or evaluate. Write a brief report on the purpose of each document, using supporting evidence from the text.
Group activity. Working in a small group, select a workplace document or academic essay that has a clear thesis. Examine each paragraph and identify the topic sentence, supporting sentences, and concluding sentence. Then, choose one particular paragraph and discuss the following questions:
- Is the topic sentence clearly identifiable or is it implied?
- Do all the supporting sentences relate to the topic sentence?
- Does the writer use effective transitions to link his or her ideas?
- Does the concluding sentence accurately summarize the main point of the paragraph?
As a group, identify the weakest areas of the paragraph and rewrite them. Focus on the relationship between the topic sentence, supporting sentences, and concluding sentence. Use transitions to illustrate the connection between each sentence in the paragraph.
Peer activity. Using the information you have learned in this chapter, write a paragraph about a current event. Underline the topic sentence in your paragraph. Now, rewrite the paragraph, placing the topic sentence in a different part of the paragraph. Read the two paragraphs aloud to a peer and have him or her identify the topic sentence. Discuss which paragraph is more effective and why. Collaboration: Please share with a classmate, compare your answers, and discuss the contrasting results.
Journal Entry 2
H5P: Question Prompts
- Reflecting on what you read about sentence structure in this chapter, think about your writing tendencies. Which of the common sentences errors apply to your writing? How do you plan to address these?
- What challenges did you face when summarizing and paraphrasing? What will you try to focus on doing or not doing in the future when writing summaries?
- Reflect on the goals you set previously. Is there anything you would like to add or already feel more confident with doing?
ENGL Resources Copyright © by Tara Horkoff. All Rights Reserved.
Share This Book
How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay: Examples & Guide
A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases.
Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you have the right approach. In this guide by our custom writing team, you will find:
- Different types of critical analysis;
- Best ways to structure your essay;
- Two excellent critical analysis essay examples.
- 📝 Critical Analysis Definition
- ✍️ Writing Guide
- ✅ Critical Analysis Types
- 📑 Examples & Tips
📝 What Is a Critical Analysis?
Criticism is the process of appraising things such as works of art and literature. It comes from the word meaning “able to make judgments”. A critical analysis essay is often referred to as a critical thinking essay, critical response paper, critical evaluation essay, and summary and response essay.
When we hear the word “criticism,” we often associate it with negative judgments. However, to criticize doesn’t necessarily mean to find faults. Even though criticism involves active disagreement, it strives to understand the meaning further and evaluate its efficiency. We call it constructive criticism .
In other words, critical analysis is an evaluation of a piece of work that promotes its better understanding . Have a look at this comparison and see what critical analysis is and what it isn’t:
| Critical analysis is: | Critical analysis is not: |
|---|---|
Aside from art and literature, critical analysis is often used in theoretical research, nursing, and social work. In any of these areas, you have an opportunity to exercise your critical faculties.
Analysis in Writing: Definition & Examples
Analysis is a step you take before writing any paper. It’s aimed at evaluating and interpreting the sources. To do it, you break them down and study them in detail. You can learn more from this article on critical analysis by Southeastern Louisiana University .
In the following table, we’ve compiled several forms of analysis in writing and illustrated each type with a topic example:
| Type of Analysis | Explanation | Topic example |
|---|---|---|
| Rhetorical Analysis | The purpose of this analysis type is to discover how a text persuades its readers. It can help you develop an ability to detect manipulations. | Techniques that Sir Ken Robinson to emotionally appeal to the viewer in his TED talk |
| Process Analysis | This form of analysis divides a business, social, or political process into several steps. There are two distinct types of process analysis: | How to purify water using carbon filtering. |
| Causal Analysis | This type of analysis focuses on the events that already happened and may try to predict what will happen in the future. Counter-arguments are a crucial part of the causal analysis. | Causes and effects of internet addiction among younger generations. |
| Critical analysis | This type of analysis aims to evaluate a work and to promote its better understanding. | The role of Zen Buddhism in JD Salinger’s . |
What Is the Difference between Summary and Analysis?
Students often confuse analysis with summary and get a lower grade as a result. Here is how two notions differ. A summary is a brief restatement of the text’s main points that involves paraphrasing. An analysis is a detailed examination of the evidence that uncovers something new.
Check out this comparison to understand the difference better:
| Summary | Analysis |
|---|---|
✍️ How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay
Now, we will show you the steps to writing a critical analysis with examples to guide you through this process. Keep in mind that the purpose of your critical analysis paper is to help readers understand a subject to a full extent.

Critical analysis consists of two stages: critical reading and critical writing. Read on to learn more about them.
Critical Reading Examples & Definition
Critical reading a technique that involves discovering and evaluating the text’s meaning and incorporating it into what you already know. It’s the first stage of critical analysis.
According to Cleveland State University, critical reading occurs after you’ve skimmed the research material and decided where to focus your efforts. While you are reading, use the following techniques to stay on track:
- Determine the central claim and identify how it is argued;
- Look for the large patterns that give purpose, order, and meaning to arguments;
- Contextualize the text within an original historical, political, or religious context;
- Distinguish the kinds of reasoning and methodology the text employs;
- Examine the evidence;
- Recognize manipulations.
When it comes to recognizing manipulations, authors use three persuasive appeals to convince their readers of something: ethos , pathos , and logos .
| Ethos, or the appeal to ethics, refers to the author’s effort to convince you of their credibility through appropriate language. It refers to the author’s reputation and the reader’s trust. | |
| Pathos, or the appeal to feelings, refers to the effort to persuade a reader by making them feel a particular emotion. It is achieved through language, tone of voice, use of anecdotes, and metaphors. | |
| Logos, or the appeal to rationality, is persuasion through logic and reason. Storytelling, historical facts, recorded evidence, and exceptional arguments are the authors’ tools to convince you. |
Now, let’s apply the critical reading techniques to an actual text:
The death estimates during the US invasions of Tokyo were exaggerated by a factor of ten to twenty. The wartime casualty estimates were based on inaccurate assumptions. The data was not updated to exclude the civilians’ deaths and justify the strategic decision to drop off an atomic bomb.
- What is the text saying? US bombs killed up to two million people.
- What is the text doing? The death estimates were exaggerated to downplay the casualties and emphasize the importance of dropping the atomic bomb.
When you are able to recognize these persuasive modes in your reading, you can master them in writing.
What Is Critical Writing: Definition & Techniques
Critical writing is a process of commenting on another piece of work using several writing strategies. It is the second stage of critical analysis.
Want to know how to write critically? Have a look at the following tips:
- Take a critical stance: recognize that every text comes from a perspective and is subject to interpretation.
- Pay close attention: look not only for the facts but also for explanations.
- Think big picture : put your sources in context with the time it was written.
- Bring yourself in: consider the connections between several texts and add your own perspective.
When it comes to the critical writing, certain strategies can be beneficial. Yet, others are better to avoid. We’ve compiled the most important dos and don’ts in the table below:
| ✔️ Dos | ❌ Don’ts |
|---|---|
| . The more thorough you are with your primary and additional sources, the stronger your argument will be. . Credible sources and strong arguments will help you to prove your point. . The way you communicate your point and structure your paper will determine how confident your writing sounds. . Present the reader not only with facts and quotes but also with in-depth research and thorough analysis. | . The only essay part where you can take advantage of descriptive writing is the summary. . Question your sources and always back up your arguments. . Instead of drawing attention to yourself, focus on the strengths or weaknesses of the piece you are analyzing. . Always use proper citation style and have works cited page at the end of your paper. . Instead, re-read it out loud. Look for mistakes and missing information. |
Want to learn more? Check out our article on critical writing .
Critical Analysis Essay Topics: How to Choose
Now that you’ve learned about critical analysis, there is a big question to answer: how do you choose the topic for your essay? It might require using a specific strategy to make the right choice.
Many students find it helpful to have a list of critical thinking questions to answer while brainstorming. We’ve prepared them for you:
- Theme : How well does the author approach the central theme? Are the arguments strong enough?
- Organization : Is this piece of work well-structured and easy to follow?
- Audience : Who is the audience? Are there any manipulations the author is using to persuade the reader?
- Tone : Is there a specific tone used by the author throughout their work? How does it affect the reader?
- Bias and informational gaps : Does the author look at their work from several angles? Are there any contradicting arguments or missing information?
- Word choice : Does the author invent new words? Is the vocabulary serious or silly, casual or technical? How does it affect the overall writing?
- Logos : Does the author use logic to prove their point?
- Ethos : Does the author have any proof of their credibility? Do they claim to be an expert? In what ways is the reader’s trust gained?
- Pathos : Does the author use emotion to connect with the reader? Does the writing appeal to common beliefs and values?
Answering these questions will help you with deciding on critical thinking essay topics. If you want some additional inspiration, feel free to use our topic generator .
Critical Analysis Template
After carefully analyzing all of your sources, you can start writing your first draft using our critical analysis template. Use this outline to structure your essay and to ensure your arguments are related to your thesis.
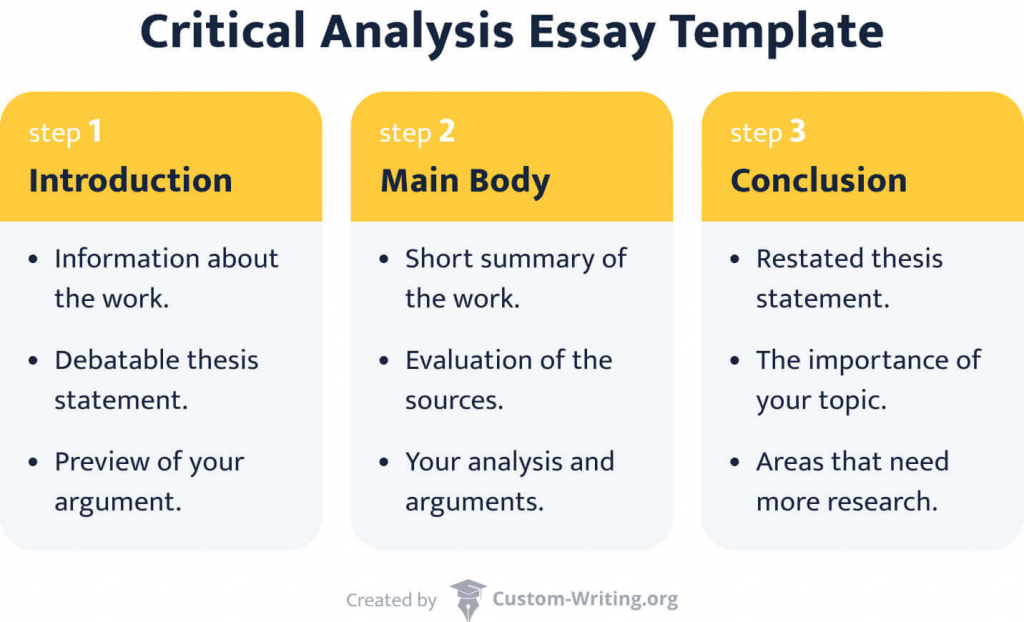
How to Start a Critical Analysis Essay
To create an outstanding opening paragraph, you may want to start it with a hook. It can be a quote from your source or a rhetorical question. Be sure to make it catchy so that it will grab your reader’s attention.
After you’re done with the hook, write the following:
- the work’s title and some background information,
- an outline of the main ideas from your sources,
- your thesis statement.
Here are two introduction examples for your inspiration:
What happens when there is a considerable wage gap between the upper and middle classes? The unsurprising reality forces poor people to use credit cards to pay off their debt. Credit card industries collect interest from those who can’t pay off their debt right away.
A romantic novel Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen is about overcoming social stereotypes in the name of love. Its main character, Elizabeth Bennet, has to fight against her discrimination against wealthy men like Mr. Darcy to find love and be happy.
Critical Analysis Essay: Thesis
A thesis statement is what you are aiming to prove. Ideally, it should be the first thing you write because every other part of your critical analysis paper will be connected to it.
To create a strong thesis statement, you want to start with a broader idea of what you would like to critique. Then, you narrow it down. Choose a debatable thesis so you can back it up with evidence from your sources and anchor your entire paper around it.
The examples below will help you write your essay’s thesis:
People in positions of power are less likely to recognize the social injustice than marginalized groups of the civilian population.
In a 1989 American superhero film Batman, Tim Burton subverts the concept of heroism by refraining Batman from murder and making him morally ambiguous.
Critical Analysis Essays: Summary and Response
The body paragraphs of a critical essay consist of your source’s summary and a response with arguments.

A summary should present specific facts from your source to help your reader understand your arguments better. You can use these sentence starters to structure a summary:
- The book is about…
- The theme of the article is…
- The author argues that…
- The author concludes…
- The main character is…
- The main points are…
The main plot of Elizabeth Bennet’s plan to save her family from poverty intersects with stereotypes that romantic love and marriage don’t go together. She does not accept a marriage proposal from Mr. Darcy because she does not want to be walking proof that women marry for money. The rejected proposal leads Darcy to open up and change Elizabeth’s perception of him.
A response should present your main arguments that support your thesis statement. Each argument is a sub-thesis that connects to your central thesis. It’s crucial to discuss each point in detail and prove it with strong evidence.
Your arguments should be:
- clear, informative, and persuasive;
- well-researched and backed up with solid evidence;
- connected to your thesis.
At first, Elizabeth Bennet sees Mr. Darcy only as a powerful man with wealth and high social status. For her, he represents a marriage of convenience that she is so desperately trying to fight against. After Mr. Darcy attempts to separate Jane and Bingley, Elizabeth gets proof for her ideas about powerful men who do everything in their power to destroy a loving relationship for a better financial suit.
Critical Essay Outline: Conclusion
The final stage of essay writing is to ensure you have proven your arguments. The goal of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your thesis and the essay’s main points. You may also want to leave them with some final statements for consideration.
Keep in mind that the concluding paragraph is not a place to introduce new evidence. Instead, you can do the following:
- Restate your thesis;
- Summarize your main ideas;
- Talk about the work’s overall performance or outcome;
- Identify potential opportunities for further research or investigation.
Elizabeth Bennet struggles with the societal association of marriage with financial stability. Eventually, she marries a rich man, Mr. Darcy, but she marries him for love rather than his money and social status. Her pride and prejudice towards him were destroyed by his acts of kindness and true love. Their relationship had a rough start, but both of them could get their happy ending by breaking out of old beliefs and habits.
✅ Types of Critical Analysis
Choosing the correct type of analysis will help you stay on track with your research objectives. It will give you the anchor to develop your essay around in a systematic manner.
Critical analysis can be categorized into 4 main types:
- Literary analysis gives a critical evaluation of a literary text.
- Article analysis reflects upon arguments presented in an article.
- Media analysis essay interprets messages conveyed through visual media, music, or radio.
- Cultural analysis interprets cultural phenomena and practices.
Literary Analysis: Definition & Characteristics
Literary analysis is an argument that expresses one’s critical evaluation of a poem, novel, short story, or play. A critique of literature has the same characteristics as other types of critical essays. The difference is the kind of information you can include in this type of essay.
Here’s how to analyze literature:
You will find more interesting info in our article on literary analysis essays .
How to Write an Analysis of an Article
Critical analysis of an article aims to analyze the writing strategies and techniques an author uses to develop their argument. The process is a little different than persuading the reader to accept a particular point of view. Here is a sample outline:
Critical Film Analysis: Types & How to Write
Film analysis goes beyond the plot structure and includes composition elements such as camera work, lighting, costume choices, etc. After watching the film at least twice, you can select what type of film analysis you will be performing. Check out the types and see what they’re about:
- Semiotic analysis involves interpretation of signs and symbols within a film.
- Narrative analysis examines the story the film seeks to tell.
- Historical analysis is an examination of a film’s relationship to a cultural or historical context.
- Mise-en-scène analysis is an analysis of compositional elements used in a scene or a single shot.
Once you’ve chosen a topic, use this outline to guide you through the writing process:
You can learn more from our article on film analysis .
How to Write a Cultural Analysis Essay
Critical analysis essay refers to your comment upon one specific cultural aspect that works or doesn’t work in a society. After you’ve chosen a topic for your cultural analysis paper, you can start drafting your outline. Here is how the structure of this kind of paper differs from others:
Critical Analysis Essay Topics
- Critical analysis of qualitative research article.
- Rhetorical analysis of articles on qualitative studies in healthcare.
- American Exodus by James N. Gregory: Rhetorical Analysis.
- Critical analysis of religion and faith .
- Analyze the sonnet My Mistress’ Eyes by W. Shakespeare .
- Critical essay on issues of cognitive neuroscience.
- A Doll House as an example of feminist literature: rhetorical analysis.
- Conduct a comparative critical analysis of Judaism and Christianity.
- Rhetorical analysis of an Anglo-Saxon poem Beowulf .
- Semantic meaning of The Bell Jar by Sylvia Plath .
- Critical evaluation of Seligman articles.
- Analyze psychological literature based on A Clean, Well-Lighted Place by E. Hemingway.
- Rhetorical analysis of literary devices and expressive means in A Good Man Is Hard to Find .
- Analyze the characteristic features of drama using the example of Death of a Salesman .
- Critical analysis of the most popular business strategies .
- Discuss the problem of childhood obesity in Active Living by Van Kann.
- Analyze IT strategies and planning.
- Critical analysis of a controversial art using the example of Home by Yann Arthus-Bertrand.
- Emotional impact of comedy films.
- Rhetorical analysis of Sophocles’ Antigone as an example of Greek drama.
- Influence of Socrate’s philosophy on the ancient Greek playwrights.
- Critical analysis of Sophocles’ plays.
- Different sets of values in Everyday Use by A. Walker .
- Analysis of corporate crimes using the example of Lehman Brothers’ scandal.
- Critical analysis of a scientific article based on Nursing Pain Management .
- Different interpretations of A Good Man Is Hard to Find by Flannery O’Connor.
- Critical analysis of Longinus’ idea of sublime .
- The importance of a teacher’s role in Freedom Writers .
- Critical analysis of the efficiency of CBT.
- Rhetorical analysis of an article on a proactive care program.
- The concept of emotional intelligence: critical analysis.
- Evaluate implementation of Windsome’s risk management strategy to enhance the company’s response to stress.
- The importance of symbolism in Truman Capote’s Breakfast at Tiffany’s .
- Critical analysis of Thomas Paine’s pamphlets.
- Rhetorical techniques used in Hamlet by W. Shakespeare .
- In-depth analysis of the modern world’s social issues in The Handmaid’s Tale .
- Social messages in Robinson’s and Kincaid’s stories.
- Analysis of rhetorical strategies used in Dwellings by Linda Hogan.
- Critical analysis of issues elucidated in A Loss for Words by J. Thurman.
- Discuss the problems of alienation and perception in The Things They Carried .
📑 Critical Analysis Essay Examples & Bonus Tips
The following writing tips will help you understand how to apply your critical thinking skills in practice and write an excellent critical essay on your own.
Critical Essay Format & Free Samples
Looking for some tips on how to format your paper? This section reflects the latest guidelines for citing your sources with the latest APA 7th and MLA 9th publication manuals.
| APA format | MLA format | |
|---|---|---|
| Not required. | ||
| Sources in alphabetical order. | Sources in alphabetical order. |
Before you dive into writing your critical analysis paper, get inspired with some compelling essay examples. The first is a film analysis example. You can download the PDF file below:
The Birds by Alfred Hitchcock is a thriller that derives its suspense from the violence which stands on the borderline with divine retribution. The birds of the film are the symbol of the said violence and primary actors that contribute to the semiotic revelations of the film.
The following critical analysis essay is concerned with a literary work. You can download it below:
Feminism has been influential in various aspects of society for many decades. With the beginning of women’s emancipation, humanity has progressed not only in political and social life but also in science, culture, and literary studies. A feminist standpoint in literature research points to the limited portrayal of the characters in literary works, which showed the world mainly from a patriarchal perspective.
Here’s the list of critical analysis essay examples. You can check them out to get a better understanding of critical analysis and to gain some inspiration.
- Managing Business Risks: A Critical Analysis
- Nursing Skills for Palliative Care: A Critical Analysis
- Critical Analysis of Quantitative vs. Qualitative Research
- Nighthawks by Edward Hopper: Critical Analysis
- Roosevelt and Obama: Critical Analysis of Two Speeches
- “The Love of My Life” by T. C. Boyle Critical Analysis
- Nursing Education-Practice Gap: Critical Analysis
- Affordable Care Act: A Critical Analysis
- Mother Tongue by Amy Tan: Critical Analysis
Bonus Tips: Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the process of conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and evaluating information. It is about careful reasoning directed to a goal. The main components of this process include observing, wondering, imagining, experimenting, judging, and deciding.
This type of thinking is instrumental in conducting a critical analysis. To succeed at it, you need to be attentive, confident, and open-minded. Below are some questions that you can ask yourself while thinking critically:
- Why are you being told this?
- What are you not being told?
- Who is telling you this?
- How reliable is this information?
- Are there any manipulations involved?
- How else can you analyze the same material?
Critical thinking is a skill that develops with time and effort. However, you may encounter barriers that can prevent you from making accurate judgments. The following tips will help you overcome them:
- Step back from your personal feelings and biases
- Look for different ways to examine the data
- Check your sources for reliability
- Do your best to detect manipulations in arguments
- Always conceptualize what you are reading
- Challenge your worldview
Want to learn more? Feel free to check out our article on critical thinking essays .
Now you know everything necessary to write a perfect critical analysis essay. Feel free to share this article or leave a comment!
Further reading
- How to Write a Critique Paper: Tips + Critique Essay Examples
- How to Write an Art Critique: Examples & Strategies
- How to Write an Analysis Essay: Examples + Writing Guide
- How to Write a Book Review: Format, Outline, & Example
- How to Write a Rhetorical Analysis Essay: Outline, Steps, & Examples
❓ Critical Analysis Essay FAQs
When analyzing any literary text, it is essential to evaluate the work and use the theme to support your opinion. The response’s goal is to show the reader what the selection of the source and the theme means to you personally.
The purpose of a response to a literature essay is to inform your reader about something interesting and insightful you found in a literary work. It may focus on the characters, plot, or theme of the story.
In a critical essay, choose the formal language and avoid using “I” statements. Focus on the piece you are analyzing, its strengths, and weaknesses. Using the first-person singular will take away the reader’s attention from your argument to you.
A critical source is a source that interprets, analyzes, critiques, and adds to the discussion of the primary source. It is then integrated into critical writing. The best critical sources can be found through library catalogs and scholarly databases.
🔍 References
- Critical Analysis: University of Wollongong
- Some Suggestions on Critically Evaluating Your Reading in History: Carleton College
- Criticism and Critical Analysis: Kansas State University
- Resources for Writers: Analytical Writing: Drew University
- Critical Thinking and Writing: University of Kent
- Writing Critical Essays about Literature: Gallaudet University
- Film Analysis: University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Cultural Critique: Southern Illinois University Edwardsville
- Writing a Critical or Rhetorical Analysis: Bellevue College
- Writing Critical Analysis Papers: University of Washington
- Critical Analysis Template: Thompson Rivers University
- Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays: Colorado State University
- Rhetorical/Critical Analysis: Houston Community College
- Writing Critical Reviews: Queen’s University
- General APA Guidelines: Purdue University
- Using MLA Format: MLA.org
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: So, let’s start digging deeper into this topic! ♻️ What Is Process Analysis? A process analysis describes and explains the succession of...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

You don’t need to be a nerd to understand the general idea behind cause and effect essays. Let’s see! If you skip a meal, you get hungry. And if you write an essay about it, your goal is achieved! However, following multiple rules of academic writing can be a tough...
![how to write a body paragraph for a critical essay How to Write an Argumentative Essay: 101 Guide [+ Examples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/young-writer-taking-notes-284x153.jpg)
An argumentative essay is a genre of academic writing that investigates different sides of a particular issue. Its central purpose is to inform the readers rather than expressively persuade them. Thus, it is crucial to differentiate between argumentative and persuasive essays. While composing an argumentative essay, the students have to...
![how to write a body paragraph for a critical essay How to Title an Essay: Guide with Creative Examples [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-woman-making-greeting-card-new-year-christmas-2021-friends-family-scrap-booking-diy-writing-letter-with-best-wishes-design-her-homemade-card-holidays-celebration-284x153.jpg)
It’s not a secret that the reader notices an essay title first. No catchy hook or colorful examples attract more attention from a quick glance. Composing a creative title for your essay is essential if you strive to succeed, as it: Thus, how you name your paper is of the...

The conclusion is the last paragraph in your paper that draws the ideas and reasoning together. However, its purpose does not end there. A definite essay conclusion accomplishes several goals: Therefore, a conclusion usually consists of: Our experts prepared this guide, where you will find great tips on how to...
![how to write a body paragraph for a critical essay How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/closeup-shot-woman-working-studying-from-home-with-red-coffee-cup-nearby-284x153.jpg)
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present...

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved September 20, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, what is your plagiarism score.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A body paragraph is any paragraph in the middle of an essay, paper, or article that comes after the introduction but before the conclusion.Generally, body paragraphs support the work's thesis and shed new light on the main topic, whether through empirical data, logical deduction, deliberate persuasion, or anecdotal evidence.
This is a crucial step towards writing a body paragraph. First, it will set the tone for the rest of your paper. Second, it will require you to articulate your thesis statement in specific, concise wording. Highlight or bold your thesis statement, so you can refer back to it quickly.
Writing an essay body paragraph is not an easy task, but here you find helpful information about structure and an example of a body paragraph for an essay. ... Well-thought-out body paragraphs are critical in an essay outline and the writer's arguments. To effectively structure the body paragraph, you must understand its overall organization ...
Written by MasterClass. Last updated: Jun 7, 2021 • 2 min read. From magazines to academic essays, you can find body paragraphs across many forms of writing. Learn more about how to write engaging body paragraphs that support the central idea of your writing project.
A strong paragraph in an academic essay will usually include these three elements: A topic sentence. The topic sentence does double duty for a paragraph. First, a strong topic sentence makes a claim or states a main idea that is then developed in the rest of the paragraph. Second, the topic sentence signals to readers how the paragraph is ...
Start wherever you want. Many writers do not begin writing at the introduction, or even the early body paragraphs.Start writing your essay where it seems most natural for you to do so. Some writers might prefer to start with the easiest section to write, while others prefer to get the most difficult section out of the way first.
Step 1: Write a Topic Sentence. Consider the first sentence in a body paragraph a mini-thesis statement for that paragraph. The topic sentence should establish the main point of the paragraph and bear some relationship to the essay's overarching thesis statement. In theory, by reading only the topic sentence of every paragraph, a reader should ...
Key Takeaways. Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement. Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis. Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis. Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
To write an effective body paragraph, follow these steps: begin with a clear topic sentence that logically supports the thesis statement. support the argument by providing facts, examples, quotations, or statistics that develop or support the central claim of the paragraph. explain the significance of each fact, example, quote, or statistic ...
I. Topic Sentence-- the first sentence of the paragraph (tells the reader what the paragraph will be about and relates back to the essay's thesis statement) II. Examples from the text—quotes from or paraphrases of the reading/research These examples should be specific to support the topic sentence. Add a lead-in before a quote.
In the body section of your essay, you make arguments, explain ideas, and give evidence. This video will show you how to write a strong paragraph in just 3 s...
Body Paragraphs - Writing as Inquiry. 4c. Body Paragraphs. Body paragraphs present the reasoning and evidence to demonstrate your thesis. In academic essays, body paragraphs are typically a bit more substantial than in news reporting so a writer can share their own ideas, develop their reasoning, cite evidence, and engage in conversation with ...
Construct Analytical Body Paragraphs. The body paragraphs are the heart of your essay, where you develop your argument and convince your reader of your perspective. Focus on One Point Per Paragraph: Each paragraph should address a single point that directly relates to your thesis statement. Don't try to cram too much information into one paragraph.
Central claim.All critical essays contain a central claim about the text. This argument is typically expressed at the beginning of the essay in a thesis statement, then supported with evidence in each body paragraph.Some critical essays bolster their argument even further by including potential counterarguments, then using evidence to dispute them.
Write a draft of a whole paper to see how you express ideas on paper. Outline your essay to structure the ideas you have. Set a timer and write a draft within a set amount of time. Analyze your draft at the sentence level and see if your paper makes sense. Highlight the main point of your paper.
In a critical analysis essay, it's important to take a critical approach to the text. Question the author's ideas, analyze the effectiveness of their arguments, and consider different interpretations. By approaching the text with a critical eye, you can craft a more thorough and nuanced analysis that goes beyond a surface-level reading of the text.
Writing a body paragraph. The body of the essay is where you fully develop your argument. Each body paragraph should contain one key idea or claim, which is supported by relevant examples and evidence from the body of scholarly work on your topic (i.e. academic books and journal articles). Together, the body paragraphs form the building blocks ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
An effective paragraph contains three main parts: a topic sentence, the body, and the concluding sentence. A topic sentence is often the first sentence of a paragraph. The body of the paragraph usually follows, containing supporting details. Supporting sentences help explain, prove, or enhance the topic sentence.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
Critical analysis of an article aims to analyze the writing strategies and techniques an author uses to develop their argument. The process is a little different than persuading the reader to accept a particular point of view. Here is a sample outline: Introduction. Introduce the author and the work under analysis.
Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them. Paragraph structure. A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs: the three paragraphs of the body, plus the ...