
7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
In this ultimate guide, I will explain to you exactly how to write an evaluation essay.
1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
An evaluation essay should provide a critical analysis of something.
You’re literally ‘evaluating’ the thing you’re looking up.
Here’s a couple of quick definitions of what we mean by ‘evaluate’:
- Merriam-Webster defines evaluation as: “to determine the significance, worth, or condition of usually by careful appraisal and study”
- Collins Dictionary says: “If you evaluate something or someone, you consider them in order to make a judgment about them, for example about how good or bad they are.”
Here’s some synonyms for ‘evaluate’:
So, we could say that an evaluation essay should carefully examine the ‘thing’ and provide an overall judgement of it.
Here’s some common things you may be asked to write an evaluation essay on:
This is by no means an exhaustive list. Really, you can evaluate just about anything!
Get a Pdf of this article for class
Enjoy subscriber-only access to this article’s pdf
2. How to write an Evaluation Essay
There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria.
Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument
Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
The evaluation argument will show your reader what you have decided is the final value of the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating.
But in order to convince your reader that your evaluative argument is sound, you need to do some leg work.
The aim will be to show that you have provided a balanced and fair assessment before coming to your conclusion.
In order to appear balanced you should:
- Discuss both the pros and cons of the thing
- Discuss both the strengths and weaknesses of the thing
- Look at the thing from multiple different perspectives
- Be both positive and critical. Don’t make it look like you’re biased towards one perspective.
In other words, give every perspective a fair hearing.
You don’t want to sound like a propagandist. You want to be seen as a fair and balanced adjudicator.
Use an Evaluation Criteria
One way to appear balanced is to use an evaluation criteria.
An evaluation criteria helps to show that you have assessed the ‘thing’ based on an objective measure.
Here’s some examples of evaluation criteria:
- Strength under pressure
- Longevity (ability to survive for a long time)
- Ease of use
- Ability to get the job done
- Friendliness
- Punctuality
- Ability to predict my needs
- Calmness under pressure
- Attentiveness
A Bed and Breakfast
- Breakfast options
- Taste of food
- Comfort of bed
- Local attractions
- Service from owner
- Cleanliness
We can use evaluation criteria to frame out ability to conduct the analysis fairly.
This is especially true for if you have to evaluate multiple different ‘things’. For example, if you’re evaluating three novels, you want to be able to show that you applied the same ‘test’ on all three books!
This will show that you gave each ‘thing’ a fair chance and looked at the same elements for each.
3. How to come up with an Evaluation Argument
After you have:
- Looked at both good and bad elements of the ‘thing’, and
- Used an evaluation criteria
You’ll then need to develop an evaluative argument. This argument shows your own overall perspective on the ‘thing’.
Remember, you will need to show your final evaluative argument is backed by objective analysis. You need to do it in order!
Analyze first. Evaluate second.
Here’s an example.
Let’s say you’re evaluating the quality of a meal.
You might say:
- A strength of the meal was its presentation. It was well presented and looked enticing to eat.
- A weakness of the meal was that it was overcooked. This decreased its flavor.
- The meal was given a low rating on ‘cost’ because it was more expensive than the other comparative meals on the menu.
- The meal was given a high rating on ‘creativity’. It was a meal that involved a thoughtful and inventive mix of ingredients.
Now that you’ve looked at some pros and cons and measured the meal based on a few criteria points (like cost and creativity), you’ll be able to come up with a final argument:
- Overall, the meal was good enough for a middle-tier restaurant but would not be considered a high-class meal. There is a lot of room for improvement if the chef wants to win any local cooking awards.
Evaluative terms that you might want to use for this final evaluation argument might include:
- All things considered
- With all key points in mind
4. Evaluation Essay Outline (with Examples)
Okay, so now you know what to do, let’s have a go at creating an outline for your evaluation essay!
Here’s what I recommend:
4.1 How to Write your Introduction
In the introduction, feel free to use my 5-Step INTRO method . It’ll be an introduction just like any other essay introduction .
And yes, feel free to explain what the final evaluation will be.
So, here it is laid out nice and simple.
Write one sentence for each point to make a 5-sentence introduction:
- Interest: Make a statement about the ‘thing’ you’re evaluating that you think will be of interest to the reader. Make it a catchy, engaging point that draws the reader in!
- Notify: Notify the reader of any background info on the thing you’re evaluating. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge. What is a historical fact about the ‘thing’?
- Translate: Re-state the essay question. For an evaluative essay, you can re-state it something like: “This essay evaluates the book/ product/ article/ etc. by looking at its strengths and weaknesses and compares it against a marking criteria”.
- Report: Say what your final evaluation will be. For example you can say “While there are some weaknesses in this book, overall this evaluative essay will show that it helps progress knowledge about Dinosaurs.”
- Outline: Simply give a clear overview of what will be discussed. For example, you can say: “Firstly, the essay will evaluate the product based on an objective criteria. This criteria will include its value for money, fit for purpose and ease of use. Next, the essay will show the main strengths and weaknesses of the product. Lastly, the essay will provide a final evaluative statement about the product’s overall value and worth.”
If you want more depth on how to use the INTRO method, you’ll need to go and check out our blog post on writing quality introductions.
4.2 Example Introduction
This example introduction is for the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society.
“Facebook is the third most visited website in the world. It was founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg in his college dorm. This essay evaluates the impact of Facebook on society and makes an objective judgement on its value. The essay will argue that Facebook has changed the world both for the better and worse. Firstly, it will give an overview of what Facebook is and its history. Then, it will examine Facebook on the criteria of: impact on social interactions, impact on the media landscape, and impact on politics.”
You’ll notice that each sentence in this introduction follows my 5-Step INTRO formula to create a clear, coherent 5-Step introduction.
4.3 How to Write your Body Paragraphs
The first body paragraph should give an overview of the ‘thing’ being evaluated.
Then, you should evaluate the pros and cons of the ‘thing’ being evaluated based upon the criteria you have developed for evaluating it.
Let’s take a look below.
4.4 First Body Paragraph: Overview of your Subject
This first paragraph should provide objective overview of your subject’s properties and history. You should not be doing any evaluating just yet.
The goal for this first paragraph is to ensure your reader knows what it is you’re evaluating. Secondarily, it should show your marker that you have developed some good knowledge about it.
If you need to use more than one paragraph to give an overview of the subject, that’s fine.
Similarly, if your essay word length needs to be quite long, feel free to spend several paragraphs exploring the subject’s background and objective details to show off your depth of knowledge for the marker.
4.5 First Body Paragraph Example
Sticking with the essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society , this might be your paragraph:
“Facebook has been one of the most successful websites of all time. It is the website that dominated the ‘Web 2.0’ revolution, which was characterized by user two-way interaction with the web. Facebook allowed users to create their own personal profiles and invite their friends to follow along. Since 2004, Facebook has attracted more than one billion people to create profiles in order to share their opinions and keep in touch with their friends.”
Notice here that I haven’t yet made any evaluations of Facebook’s merits?
This first paragraph (or, if need be, several of them) should be all about showing the reader exactly what your subject is – no more, no less.
4.6 Evaluation Paragraphs: Second, Third, Forth and Fifth Body Paragraphs
Once you’re confident your reader will know what the subject that you’re evaluating is, you’ll need to move on to the actual evaluation.
For this step, you’ll need to dig up that evaluation criteria we talked about in Point 2.
For example, let’s say you’re evaluating a President of the United States.
Your evaluation criteria might be:
- Impact on world history
- Ability to pass legislation
- Popularity with voters
- Morals and ethics
- Ability to change lives for the better
Really, you could make up any evaluation criteria you want!
Once you’ve made up the evaluation criteria, you’ve got your evaluation paragraph ideas!
Simply turn each point in your evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
How do you do this?
Well, start with a topic sentence.
For the criteria point ‘Impact on world history’ you can say something like: “Barack Obama’s impact on world history is mixed.”
This topic sentence will show that you’ll evaluate both pros and cons of Obama’s impact on world history in the paragraph.
Then, follow it up with explanations.
“While Obama campaigned to withdraw troops from Iraq and Afghanistan, he was unable to completely achieve this objective. This is an obvious negative for his impact on the world. However, as the first black man to lead the most powerful nation on earth, he will forever be remembered as a living milestone for civil rights and progress.”
Keep going, turning each evaluation criteria into a full paragraph.
4.7 Evaluation Paragraph Example
Let’s go back to our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
I’ve decided to use the evaluation criteria below:
- impact on social interactions;
- impact on the media landscape;
- impact on politics
Naturally, I’m going to write one paragraph for each point.
If you’re expected to write a longer piece, you could write two paragraphs on each point (one for pros and one for cons).
Here’s what my first evaluation paragraph might look like:
“Facebook has had a profound impact on social interactions. It has helped people to stay in touch with one another from long distances and after they have left school and college. This is obviously a great positive. However, it can also be seen as having a negative impact. For example, people may be less likely to interact face-to-face because they are ‘hanging out’ online instead. This can have negative impact on genuine one-to-one relationships.”
You might notice that this paragraph has a topic sentence, explanations and examples. It follows my perfect paragraph formula which you’re more than welcome to check out!
4.8 How to write your Conclusion
To conclude, you’ll need to come up with one final evaluative argument.
This evaluation argument provides an overall assessment. You can start with “Overall, Facebook has been…” and continue by saying that (all things considered) he was a good or bad president!
Remember, you can only come up with an overall evaluation after you’ve looked at the subject’s pros and cons based upon your evaluation criteria.
In the example below, I’m going to use my 5 C’s conclusion paragraph method . This will make sure my conclusion covers all the things a good conclusion should cover!
Like the INTRO method, the 5 C’s conclusion method should have one sentence for each point to create a 5 sentence conclusion paragraph.
The 5 C’s conclusion method is:
- Close the loop: Return to a statement you made in the introduction.
- Conclude: Show what your final position is.
- Clarify: Clarify how your final position is relevant to the Essay Question.
- Concern: Explain who should be concerned by your findings.
- Consequences: End by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance. The ‘concern’ and ‘consequences’ sentences can be combined
4.9 Concluding Argument Example Paragraph
Here’s a possible concluding argument for our essay question: Write an Evaluation Essay on Facebook’s Impact on Society .
“The introduction of this essay highlighted that Facebook has had a profound impact on society. This evaluation essay has shown that this impact has been both positive and negative. Thus, it is too soon to say whether Facebook has been an overall positive or negative for society. However, people should pay close attention to this issue because it is possible that Facebook is contributing to the undermining of truth in media and positive interpersonal relationships.”
Note here that I’ve followed the 5 C’s conclusion method for my concluding evaluative argument paragraph.
5. Evaluation Essay Example Template
Below is a template you can use for your evaluation essay , based upon the advice I gave in Section 4:
| Introduction | Use the to write an introduction. This introduction should clearly state what you are evaluating, the criteria that you will be using to evaluate it, and what will be. |
| Body Paragraph 1: Outline of the Subject | Before evaluating the subject or ‘thing’, make sure you use a paragraph or two to clearly explain what it is to the reader. This is your chance to show your depth of knowledge about the topic. |
Body Paragraphs 2 – 5: Evaluate the Subject | Use the evaluation criteria you have decided upon to evaluate the subject. For each element of the criteria, write one paragraph looking at the pros and cons of the subject. You might want to use my to write your paragraphs. |
Conclusion | Use my to write a 5-sentence conclusion. Make sure you show your final evaluative argument in the conclusion so your reader knows your final position on the issue. |
6. 23+ Good Evaluation Essay Topics
Okay now that you know how to write an evaluation essay, let’s look at a few examples.
For each example I’m going to give you an evaluation essay title idea, plus a list of criteria you might want to use in your evaluation essay.
6.1 Evaluation of Impact
- Evaluate the impact of global warming on the great barrier reef. Recommended evaluation criteria: Level of bleaching; Impact on tourism; Economic impact; Impact on lifestyles; Impact on sealife
- Evaluate the impact of the Global Financial Crisis on poverty. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on jobs; Impact on childhood poverty; Impact on mental health rates; Impact on economic growth; Impact on the wealthy; Global impact
- Evaluate the impact of having children on your lifestyle. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on spare time; Impact on finances; Impact on happiness; Impact on sense of wellbeing
- Evaluate the impact of the internet on the world. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on connectedness; Impact on dating; Impact on business integration; Impact on globalization; Impact on media
- Evaluate the impact of public transportation on cities. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on cost of living; Impact on congestion; Impact on quality of life; Impact on health; Impact on economy
- Evaluate the impact of universal healthcare on quality of life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on reducing disease rates; Impact on the poorest in society; Impact on life expectancy; Impact on happiness
- Evaluate the impact of getting a college degree on a person’s life. Recommended evaluation criteria: Impact on debt levels; Impact on career prospects; Impact on life perspectives; Impact on relationships
6.2 Evaluation of a Scholarly Text or Theory
- Evaluate a Textbook. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of explanations; relevance to a course; value for money; practical advice; depth and detail; breadth of information
- Evaluate a Lecture Series, Podcast or Guest Lecture. Recommended evaluation criteria: clarity of speaker; engagement of attendees; appropriateness of content; value for monet
- Evaluate a journal article. Recommended evaluation criteria: length; clarity; quality of methodology; quality of literature review ; relevance of findings for real life
- Evaluate a Famous Scientists. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to scientific knowledge; impact on health and prosperity of humankind; controversies and disagreements with other scientists.
- Evaluate a Theory. Recommended evaluation criteria: contribution to knowledge; reliability or accuracy; impact on the lives of ordinary people; controversies and contradictions with other theories.
6.3 Evaluation of Art and Literature
- Evaluate a Novel. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Play. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate a Film. Recommended evaluation criteria: plot complexity; quality of acting; moral or social value of the message; character development; relevance to modern life
- Evaluate an Artwork. Recommended evaluation criteria: impact on art theory; moral or social message; complexity or quality of composition
6.4 Evaluation of a Product or Service
- Evaluate a Hotel or Bed and Breakfast. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; flexibility of check-in and check-out times; cleanliness; location; value for money; wi-fi strength; noise levels at night; quality of meals; value for money
- Evaluate a Restaurant. Recommended evaluation criteria: quality of service; menu choices; cleanliness; atmosphere; taste; value for money.
- Evaluate a Car. Recommended evaluation criteria: fuel efficiency; value for money; build quality; likelihood to break down; comfort.
- Evaluate a House. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; build quality; roominess; location; access to public transport; quality of neighbourhood
- Evaluate a Doctor. Recommended evaluation criteria: Quality of service; knowledge; quality of equipment; reputation; value for money.
- Evaluate a Course. Recommended evaluation criteria: value for money; practical advice; quality of teaching; quality of resources provided.
7. Concluding Advice

Evaluation essays are common in high school, college and university.
The trick for getting good marks in an evaluation essay is to show you have looked at both the pros and cons before making a final evaluation analysis statement.
You don’t want to look biased.
That’s why it’s a good idea to use an objective evaluation criteria, and to be generous in looking at both positives and negatives of your subject.
Read Also: 39 Better Ways to Write ‘In Conclusion’ in an Essay
I recommend you use the evaluation template provided in this post to write your evaluation essay. However, if your teacher has given you a template, of course use theirs instead! You always want to follow your teacher’s advice because they’re the person who will be marking your work.
Good luck with your evaluation essay!

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Green Flags in a Relationship
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Signs you're Burnt Out, Not Lazy
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Toxic Things Parents Say to their Children
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Red Flags Early in a Relationship
2 thoughts on “7 Steps for How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Example & Template)”
What an amazing article. I am returning to studying after several years and was struggling with how to present an evaluative essay. This article has simplified the process and provided me with the confidence to tackle my subject (theoretical approaches to development and management of teams).
I just wanted to ask whether the evaluation criteria has to be supported by evidence or can it just be a list of criteria that you think of yourself to objectively measure?
Many many thanks for writing this!

Usually we would want to see evidence, but ask your teacher for what they’re looking for as they may allow you, depending on the situation.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.4 Evaluation
This section discusses the purpose and structure of evaluation, as many students prepare to write their own evaluative essays.
The Purpose of Evaluative Writing
Writers evaluate arguments in order to present an informed and well-reasoned judgment about a subject. While the evaluation will be based on their opinion, it should not seem opinionated. Instead, it should aim to be reasonable and unbiased. This is achieved through developing a solid judgment, selecting appropriate criteria to evaluate the subject, and providing clear evidence to support the criteria.
Evaluation is a type of writing that has many real-world applications. Anything can be evaluated. For example, evaluations of movies, restaurants, books, and technology ourselves are all real-world evaluations.
The Structure of an Evaluation Essay
Evaluation essays are structured as follows.
First, the essay will present the subject . What is being evaluated? Why? The essay begins with the writer giving any details needed about the subject.
Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria.
The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for evaluating the subject under consideration. Appropriate criteria will help to keep the essay from seeming biased or unreasonable. If authors evaluated the quality of a movie based on the snacks sold at the snack bar, that would make them seem unreasonable, and their evaluation may be disregarded because of it.
The evidence of an evaluation essay consists of the supporting details authors provide based on their judgment of the criteria.
For example, if the subject of an evaluation is a restaurant, a judgment could be “Kay’s Bistro provides an unrivaled experience in fine dining.” Some authors evaluate fine dining restaurants by identifying appropriate criteria in order to rate the establishment’s food quality, service, and atmosphere. The examples are the evidence.
Another example of evaluation is literary analysis; judgments may be made about a character in the story based on the character’s actions, characteristics, and past history within the story. The scenes in the story are evidence for why readers have a certain opinion of the character.
Job applications and interviews are more examples of evaluations. Based on certain criteria, management and hiring committees determine which applicants will be considered for an interview and which applicant will be hired.
- Evaluate a restaurant. What do you expect in a good restaurant? What criteria determines whether a restaurant is good?
- List three criteria that you will use to evaluate a restaurant. Then dine there. Afterwards, explain whether or not the restaurant meets each criteria, and include evidence (qualities from the restaurant) that backs your evaluation.
- Give the restaurant a star rating. (5 Stars: Excellent, 4 Stars: Very Good, 3 Stars: Good, 2 Stars: Fair, 1 Star: Poor). Explain why the restaurant earned this star rating.
Further Resources
Parts of this section are adapted from OER material from Susan Wood, “Evaluation Essay,” Leeward CC ENG 100 OER, licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. Original content contributed by Susan Wood .
English Composition Copyright © 2019 by Contributing Authors is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Academic Evaluations
In our daily lives, we are continually evaluating objects, people, and ideas in our immediate environments. We pass judgments in conversation, while reading, while shopping, while eating, and while watching television or movies, often being unaware that we are doing so. Evaluation is an equally fundamental writing process, and writing assignments frequently ask us to make and defend value judgments.
Evaluation is an important step in almost any writing process, since we are constantly making value judgments as we write. When we write an "academic evaluation," however, this type of value judgment is the focus of our writing.
A Definition of Evaluation
Kate Kiefer, English Professor Like most specific assignments that teachers give, writing evaluations mirrors what happens so often in our day-to-day lives. Every day we decide whether the temperature is cold enough to need a light or heavy jacket; whether we're willing to spend money on a good book or a good movie; whether the prices at the grocery store tell us to keep shopping at the same place or somewhere else for a better value. Academic tasks rely on evaluation just as often. Is a source reliable? Does an argument convince? Is the article worth reading? So writing evaluation helps students make this often unconscious daily task more overt and prepares them to examine ideas, facts, arguments, and so on more critically.
To evaluate is to assess or appraise. Evaluation is the process of examining a subject and rating it based on its important features. We determine how much or how little we value something, arriving at our judgment on the basis of criteria that we can define.
We evaluate when we write primarily because it is almost impossible to avoid doing so. If right now you were asked to write for five minutes on any subject and were asked to keep your writing completely value-free, you would probably find such an assignment difficult. Readers come to evaluative writing in part because they seek the opinions of other people for one reason or another.
Uses for Evaluation
Consider a time recently when you decided to watch a movie. There were at least two kinds of evaluation available to you through the media: the rating system and critical reviews.
Newspapers and magazines, radio and TV programs all provide critical evaluations for their readers and viewers. Many movie-goers consult more than one media reviewer to adjust for bias. Most movie-goers also consider the rating system, especially if they are deciding to take children to a movie. In addition, most people will also ask for recommendations from friends who have already seen the movie.
Whether professional or personal, judgments like these are based on the process of evaluation. The terminology associated with the elements of this process--criteria, evidence, and judgment--might seem alien to you, but you have undoubtedly used these elements almost every time you have expressed an opinion on something.
Types of Written Evaluation
Quite a few of the assignments writers are given at the university and in the workplace involve the process of evaluation.
One type of written evaluation that most people are familiar with is the review. Reviewers will attend performances, events, or places (like restaurants, movies, or concerts), basing their evaluations on their observations. Reviewers typically use a particular set of criteria they establish for themselves, and their reviews most often appear in newspapers and magazines.
Critical Writing
Reviews are a type of critical writing, but there are other types of critical writing which focus on objects (like works of art or literature) rather than on events and performances. Literary criticism, for instance, is a way of establishing the worth or literary merit of a text on the basis of certain established criteria. When we write about literary texts, we do so using one of many critical "lenses," viewing the text as it addresses matters like form, culture, historical context, gender, and class (to name a few). Deciding whether a text is "good" or "bad" is a matter of establishing which "lens" you are viewing that text through, and using the appropriate set of criteria to do so. For example, we might say that a poem by an obscure Nineteenth Century African American poet is not "good" or "useful" in terms of formal characteristics like rhyme, meter, or diction, but we might judge that same text as "good" or "useful" in terms of the way it addresses cultural and political issues historically.
Response Essays
One very common type of academic writing is the response essay. In many different disciplines, we are asked to respond to something that we read or observe. Some types of response, like the interpretive response, simply ask us to explain a text. However, there are other types of response (like agree/disagree and analytical response) which demand that we make some sort of judgment based on careful consideration of the text, object, or event in question.
Problem Solving Essays
In writing assignments which focus on issues, policies, or phenomena, we are often asked to propose possible solutions for identifiable problems. This type of essay requires evaluation on two levels. First of all, it demands that we use evaluation in order to determine that there is a legitimate problem. And secondly, it demands that we take more than one policy or solution into consideration to determine which will be the most feasible, viable, or effective one, given that problem.
Arguing Essays
Written argument is a type of evaluative writing, particularly when it focuses on a claim of value (like "The death penalty is cruel and ineffective") or policy claim (like "Oakland's Ebonics program is an effective way of addressing standard English deficiencies among African American students in public schools"). In written argument, we advance a claim like one of the above, then support this claim with solid reasons and evidence.
Process Analysis
In scientific or investigative writing, in which experiments are conducted and processes or phenomena are observed or studied, evaluation plays a part in the writer's discussion of findings. Often, these findings need to be both interpreted and analyzed by way of criteria established by the writer.
Source Evaluation
Although not a form of written evaluation in and of itself, source evaluation is a process that is involved in many other types of academic writing, like argument, investigative and scientific writing, and research papers. When we conduct research, we quickly learn that not every source is a good source and that we need to be selective about the quality of the evidence we transplant into our own writing.
Relevance to the Topic
When you conduct research, you naturally look for sources that are relevant to your topic. However, writers also often fall prey to the tendency to accept sources that are just relevant enough . For example, if you were writing an essay on Internet censorship, you might find that your research yielded quite a few sources on music censorship, art censorship, or censorship in general. Though these sources could possibly be marginally useful in an essay on Internet censorship, you will probably want to find more directly relevant sources to serve a more central role in your essay.
Perspective on the Topic
Another point to consider is that even though you want sources relevant to your topic, you might not necessarily want an exclusive collection of sources which agree with your own perspective on that topic. For example, if you are writing an essay on Internet censorship from an anti-censorship perspective, you will want to include in your research sources which also address the pro-censorship side. In this way, your essay will be able to fully address perspectives other than (and sometimes in opposition to) your own.
Credibility
One of the questions you want to ask yourself when you consider using a source is "How credible will my audience consider this source to be?" You will want to ask this question not only of the source itself (the book, journal, magazine, newspaper, home page, etc.) but also of the author. To use an extreme example, for most academic writing assignments you would probably want to steer clear of using a source like the National Enquirer or like your eight year old brother, even though we could imagine certain writing situations in which such sources would be entirely appropriate. The key to determining the credibility of a source/author is to decide not only whether you think the source is reliable, but also whether your audience will find it so, given the purpose of your writing.
Currency of Publication
Unless you are doing research with an historical emphasis, you will generally want to choose sources which have been published recently. Sometimes research and statistics maintain their authority for a very long time, but the more common trend in most fields is that the more recent a study is, the more comprehensive and accurate it is.
Accessibility
When sorting through research, it is best to select sources that are readable and accessible both for you and for your intended audience. If a piece of writing is laden with incomprehensible jargon and incoherent structure or style, you will want to think twice about directing it toward an audience unfamiliar with that type of jargon, structure, or style. In short, it is a good rule of thumb to avoid using any source which you yourself do not understand and are not able to interpret for your audience.
Quality of Writing
When choosing sources, consider the quality of writing in the texts themselves. It is possible to paraphrase from sources that are sloppily written, but quoting from such a source would serve only to diminish your own credibility in the eyes of your audience.
Understanding of Biases
Few are sources are truly objective or unbiased . Trying to eliminate bias from your sources will be nearly impossible, but all writers can try to understand and recognize the biases of their sources. For instance, if you were doing a comparative study of 1/2-ton pickup trucks on the market, you might consult the Ford home page. However, you would also need to be aware that this source would have some very definite biases. Likewise, it would not be unreasonable to use an article from Catholic World in an anti-abortion argument, but you would want to understand how your audience would be likely to view that source. Although there is no fail-proof way to determine the bias of a particular journal or newspaper, you can normally sleuth this out by looking at the language in the article itself or in the surrounding articles.
Use of Research
In evaluating a source, you will need to examine the sources that it in turn uses. Looking at the research used by the author of your source, what biases can you recognize? What are the quantity and quality of evidence and statistics included? How reliable and readable do the excerpts cited seem to be?
Considering Purpose and Audience
We typically think of "values" as being personal matters. But in our writing, as in other areas of our lives, values often become matters of public and political concern. Therefore, it is important when we evaluate to consider why we are making judgments on a subject (purpose) and who we hope to affect with our judgments (audience).
Purposes of Evaluation
Your purpose in written evaluation is not only to express your opinion or judgment about a subject, but also to convince, persuade, or otherwise influence an audience by way of that judgment. In this way, evaluation is a type of argument, in which you as a writer are attempting consciously to have an effect on your readers' ways of thinking or acting. If, for example, you are writing an evaluation in which you make a judgment that Mountain Bike A is a better buy than Mountain Bike B, you are doing more than expressing your approval of the merits of Bike A; you are attempting to convince your audience that Bike A is the better buy and, ultimately, to persuade them to buy Bike A rather than Bike B.
Effects of Audience
Kate Kiefer, English Professor When we evaluate for ourselves, we don't usually take the time to articulate criteria and detail evidence. Our thought processes work fast enough that we often seem to make split-second decisions. Even when we spend time thinking over a decision--like which expensive toy (car, stereo, skis) to buy--we don't often lay out the criteria explicitly. We can't take that shortcut when we write to other folks, though. If we want readers to accept our judgment, then we need to be clear about the criteria we use and the evidence that helps us determine value for each criterion. After all, why should I agree with you to eat at the Outback Steak House if you care only about cost but I care about taste and safe food handling? To write an effective evaluation, you need to figure out what your readers care about and then match your criteria to their concerns. Similarly, you can overwhelm readers with too much detail when they don't have the background knowledge to care about that level of detail. Or you can ignore the expertise of your readers (at your peril) and not give enough detail. Then, as a writer, you come across as condescending, or worse. So targeting an audience is really key to successful evaluation.
In written evaluation, it is important to keep in mind not only your own system of value, but also that of your audience. Writers do not evaluate in a vacuum. Giving some thought to the audience you are attempting to influence will help you to determine what criteria are important to them and what evidence they will require in order to be convinced or persuaded by your evaluative argument. In order to evaluate effectively, it is important that you consider what motivates and concerns your audience.
Criteria and Audience Considerations
The first step in deciding which criteria will be effective in your evaluation is determining which criteria your audience considers important. For example, if you are writing a review of a Mexican restaurant to an audience comprised mainly of senior citizens from the midwest, it is unlikely that "large portions" and "fiery green chile" will be the criteria most important to them. They might be more concerned, rather, with "quality of service" or "availability of heart smart menu items." Trying to anticipate and address your audience's values is an indispensable step in writing a persuasive evaluative argument. Your next step in suiting your criteria to your audience is to determine how you will explain and/or defend not only your judgments, but the criteria supporting them as well. For example, if you are arguing that a Mexican restaurant is excellent because, among other reasons, the texture of the food is appealing, you might need to explain to your audience why texture is a significant criterion in evaluating Mexican food.
Evidence and Audience Considerations
The amount and type of evidence you use to support your judgments will depend largely on the demands of your audience. Common sense tells us that the more oppositional an audience is, the more evidence will be needed to convince them of the validity a judgment. For instance, if you were writing a favorable review of La Cocina on the basis of their fiery green chile, you might not need to use a great deal of evidence for an audience of people who like spicy food but have not tried any of the Mexican restaurants in town. However, if you are addressing an audience who is deeply devoted to the green chile at Manuel's, you will need to provide a fair amount of solid evidence in order to persuade them to try another restaurant.
Parts of an Evaluation
When we evaluate, we make an overall value claim about a subject, using criteria to make judgments based on evidence. Often, we also make use of comparison and contrast as strategies for determining the relative worth of the subject we are considering. This section examines these parts of an evaluation and shows how each functions in a successful evaluation.
Overall Claim
An overall claim or judgment is an evaluator's final decision about worth. When we evaluate, we make a general statement about the worth of objects, goods, services, or solutions to problems.
An overall claim or judgment in an evaluation can be as simple as "See this movie!" or "Brand X is a better buy than the name brand." It can also be complex, particularly when the evaluator recognizes certain conditions that affect the judgment: If citizens of our community want to improve air and water quality and are willing to forego 300 additional jobs, then we should not approve the new plant Acme is hoping to build here.
Qualifications
An overall claim or judgment usually requires qualification so that it seems balanced. If judgments are weighted too much to one side, they will sometimes mar the credibility of your argument. If your overall judgment is wholly positive, your evaluation will wind up sounding like propaganda or advertisement. If it is wholly negative, you might present yourself as overly critical, unfair, or undiplomatic. An example of a qualified claim or judgment might be the following: Although La Cocina is not without its faults, it is the best Mexican restaurant in town. Qualifications are almost always positive additions to evaluative arguments, but writers must learn not to overuse them. If you make too many qualifications, your audience will be unable to determine your final position on your subject, and you will appear to be "waffling."
Example Text
Creating more parking lots is a possible solution to the horrendous traffic congestion in Taiwan's major cities. When a new building permit is issued, each building must include a certain number of spaces for parking. However, new construction takes time, and results will be seen only as new buildings are erected. This solution alone is inadequate for most of Taiwan's problem areas, which need a solution whose results will be noticed immediately.
Comment Notice how this sentence at the end of the paragraph seems to be a formal "thesis" or "claim" which might drive the rest of the essay. Based on this claim, we would assume that the remainder of the essay will deal with the reasons why the proposed policy along is "inadequate," and will address other possible solutions.
Supporting Judgments
In academic evaluations, the overall claim or judgment is backed up by smaller, more detailed judgments about aspects of a subject being evaluated. Supporting judgments function in the same way that "reasons" function in most arguments. They provide structure and justification for a more general claim. For example, if your overall claim or judgment in your evaluation is
"Although La Cocina is not without its faults, it is the best Mexican restaurant in town,"
one supporting judgment might be
"La Cocina's green chile is superb."
This judgment would be based on criteria you have established, and it would be supported by evidence.
Providing more parking spaces near buildings is not the only act necessary to solve Taiwan's parking problems. A combination of more parking spaces, increased fines, and lowered traffic volume may be necessary to eliminate the nightmare of driving in the cities. In fact, until laws are enforced and fines increased, no number of new parking spaces will impact the congestion seen in downtown areas.
Comment There are arguably three supporting judgments being made here, as three possible solutions are being suggested to rectify this problem of parking in Taiwan. If we were reading these supporting judgments at the beginning of an essay, we would expect the essay to discuss them in depth, pointing out evidence that these proposed solutions would be effective.
When we write evaluations, we consciously adopt certain standards of measurement, or criteria .
Criteria can be concrete standards, like size or speed, or can be abstract, like practicality. When we write evaluations in an academic context, we typically avoid using criteria that are wholly personal, and rely instead on those that are less "subjective" and more likely to be shared by the majority of the audience we are addressing. Choosing appropriate criteria often involves careful consideration of audience demands, values, and concerns.
As an evaluator, you will sometimes discover that you will need to explain and/or defend not only your judgments, but also the criteria informing those judgments. For example, if you are arguing that a Mexican restaurant is excellent because (among other reasons) the texture of the food is appealing, you might need to explain to your audience why texture is a significant criterion in evaluating Mexican food.
Types of Criteria
If you are evaluating a concrete canoe for an engineering class, you will use concrete criteria such as float time, cost of materials, hydrodynamic design, and so on. If you are evaluating the suitability of a textbook for a history class, you will probably rely on more abstract criteria such as readability, length, and controversial vs. mainstream interpretation of history.
In evaluation, we often rely on concrete , measurable standards according to which subjects (usually objects) may be evaluated. For example, cars may be evaluated according to the criteria of size, speed, or cost.
Many academic evaluations, however, don't focus on objects that we can measure in terms of size, speed, or cost. Rather, they look at somewhat more abstract concepts (problems and solutions often), which we might measure in terms of "effectiveness," "feasibility," or other abstract criteria. When writing this kind of evaluation, it is vital to be as clear as possible when articulating, defining, and using your criteria, since not all readers are likely to understand and agree with these criteria as readily as they would understand and agree with concrete criteria.
Related Information: Abstract Criteria
Abstract criteria are not easily measurable, and they are usually less self-evident, more in need of definition, than concrete criteria. Even though criteria may be abstract, they should not be imprecise. Always state your criteria as clearly and precisely as possible. "Feasibility" is one example of an abstract criterion that a writer might use to evaluate a solution to a problem. Feasibility is the degree of likelihood of success of something like a plan of action or a solution to a problem. "Capability of being implemented" is a way to look at feasibility in terms of solutions to problems. The relative ease with which a solution would be adopted is sometimes a way to look at feasibility. The following example mentions directly the criteria it is using (the words in italics). Fire prevention should be the major consideration of a family building a home. By using concrete, the risk of fire is significantly decreased. But that is not all that concrete provides. It is affordable , suitable for all climates , and helps reduce deforestation . Since all of these factors are important, concrete should be demanded more than it is, and it should certainly be used more than wood for homebuilding.
Related Information: Concrete Criteria
Concrete criteria are measurable standards which most people are likely to understand and (usually) to agree with. For example, a person might make use of criteria like "size," "speed," and "cost" when buying a car.
If size is your main criterion, and something with a larger size will receive a more favorable evaluation.
Perhaps the only quality that you desire in a car is low initial cost. You don't need to take into account anything else. In this case, you can put judgments on these three cars in the local used car lot:
Nissan | $1,000 |
Toyota | $1,200 |
Saab | $3,000 |
Because the Nissan has the lowest initial price, it receives the most favorable judgment. The evidence is found on the price tag. Each car is compared by way of a single criterion: cost.
Using Clear and Well-defined Criteria
When we evaluate informally (passing judgments during the course of conversation, for instance), we typically assume that our criteria are self-evident and require no explanation. However, in written evaluation, it is often necessary that we clarify and define our criteria in order to make a persuasive evaluative argument.
Criteria That Are Too Vague or Personal
Although we frequently find ourselves needing to use abstract criteria like "feasibility" or "effectiveness," we also must avoid using criteria that are overly vague or personal and difficult to support with evidence. As evaluators, we must steer clear of criteria that are matters of taste, belief, or personal preference. For example, the "best" lamp might simply be the one that you think looks prettiest in your home. If you depend on a criterion like "pretty in my home," and neglect to use more common, shared criteria like "brightness," "cost," and "weight," you are probably relying on a criterion that is too specific to your own personal preferences. To make "pretty in my home" an effective criterion, you would need to explain what "pretty in my home" means and how it might relate to other people's value systems. (For example: "Lamp A is attractive because it is an unoffensive style and color that would be appropriate for many people's decorating tastes.")
Using Criteria Based on the Appropriate "Class" of Subjects
When you make judgments, it is important that you use criteria that are appropriate to the type of object, person, policy, etc. that you are examining. If you are evaluating Steven Spielburg's film, Schindler's List , for instance, it is unfair to criticize it because it isn't a knee-slapper. Because "Schindler's List" is a drama and not a comedy, using the criterion of "humor" is inappropriate.
Weighing Criteria
Once you have established criteria for your evaluation of a subject, it is necessary to decide which of these criteria are most important. For example, if you are evaluating a Mexican restaurant and you have arrived at several criteria (variety of items on the menu, spiciness of the food, size of the portions, decor, and service), you need to decide which of these criteria are most critical to your evaluation. If the size of the portions is good, but the service is bad, can you give the restaurant a good rating? What about if the decor is attractive, but the food is bland? Once you have placed your criteria in a hierarchy of importance, it is much easier to make decisions like these.
When we evaluate, we must consider the audience we hope to influence with our judgments. This is particularly true when we decide which criteria are informing (and should inform) these judgments.
After establishing some criteria for your evaluation, it is important to ask yourself whether or not your audience is likely to accept those criteria. It is crucial that they do accept the criteria if, in turn, you expect them to accept the supporting judgments and overall claim or judgment built on them.
Related Information: Explaining and Defending Criteria
In deciding which criteria will be effective in your evaluation is determining which criteria your audience considers important. For example, if you are writing a review of a Mexican restaurant to an audience comprised mainly of senior citizens from the midwest, it is unlikely that "large portions" and "fiery green chile" will be the criteria most important to them. They might be more concerned, rather, with "quality of service" or "availability of heart smart menu items." Trying to anticipate and address your audience's values is an indispensable step in writing a persuasive evaluative argument.
Related Information: Understanding Audience Criteria
How Background Experience Influences Criteria
Laura Thomas - Composition Lecturer Your background experience influences the criteria that you use in evaluation. If you know a lot about something, you will have a good idea of what criteria should govern your judgments. On the other hand, it's hard if you don't know enough about what you're judging. Sometimes you have to research first in order to come up with useful criteria. For example, I recently went shopping for a new pair of skis for the first time in fifteen years. When I began shopping, I realized that I didn't even know what questions to ask anymore. The last time I had bought skis, you judged them according to whether they had a foam core or a wood core. But I had no idea what the important considerations were anymore.
Evidence consists of the specifics you use to reach your conclusion or judgment. For example, if you judge that "La Cocina's green chile is superb" on the basis of the criterion, "Good green chile is so fiery that you can barely eat it," you might offer evidence like the following:
"I drank an entire pitcher of water on my own during the course of the meal."
"Though my friend wouldn't admit that the chile was challenging for him, I saw beads of sweat form on his brow."
Related Information: Example Text
In the following paragraph, evidence appears in italics. Note that the reference to the New York Times backs up the evidence offered in the previous sentence:
Since killer whales have small lymphatic systems, they catch infections more easily when held captive ( Obee 23 ). The orca from the movie "Free Willy," Keiko, developed a skin disorder because the water he was living in was not cold enough. This infection was a result of the combination of tank conditions and the animal's immune system, according to a New York Times article .
Types of Evidence
Evidence for academic evaluations is usually of two types: concrete detail and analytic detail. Analytic detail comes from critical thinking about abstract elements of the thing being evaluated. It will also include quotations from experts. Concrete detail comes from sense perceptions and measurements--facts about color, speed, size, texture, smell, taste, and so on. Concrete details are more likely to support concrete criteria (as opposed to abstract criteria) used in judging objects. Analytic detail will more often support abstract criteria (as opposed to concrete criteria), like the criterion "feasibility," discussed in the section on criteria. Analytic detail also appears most often in academic evaluations of solutions to problems, although such solutions can also sometimes be evaluated according to concrete criteria.
What Kinds of Evidence Work
Good evidence ranges from personal experience to interviews with experts to published sources. The kind of evidence that works best for you will depend on your audience and often on the writing assignment you have been given.
Evidence and the Writing Assignment
When you choose evidence to support the judgments you are making in an evaluation, it will be important to consider what type of evaluation you are being asked to do. If, for instance, you are being asked to review a play you have attended, your evidence will most likely consist primarily of your own observations. However, if your assignment asks you to compare and contrast two potential national health care policies (toward deciding which is the better one), your evidence will need to be more statistical, more dependent on reputable sources, and more directed toward possible effects or outcomes of your judgment.
Comparison and Contrast
Comparison and contrast is the process of positioning an item or concept being evaluated among other like items or concepts. We are all familiar with this technique as it's used in the marketing of products: soft drink "taste tests," comparisons of laundry detergent effectiveness, and the like. It is a way of determining the value of something in relation to comparable things. For example, if you have made the judgment that "La Cocina's green chile is superb" and you have offered evidence of the spiciness and the flavor of the chile, you might also use comparison by giving your audience a scale on which to base judgment: "La Cocina's chile is even more fiery and flavorful than Manuel's, which is by no means a walk in the park."
In this case, the writer compares limestone with wood to show that limestone is a better building material. Although this comparison could be developed much more, it still begins to point out the relative merits of limestone. Concrete is a feasible substitute for wood as a building material. Concrete comes from a rock called limestone. Limestone is found all over the United States. By using limestone instead of wood, the dependence on dwindling forest reserves would decrease. There are more sedimentary rocks than there are forests left in this country, and they are more evenly distributed. For this reason, it is quite possible to switch from wood to concrete as the primary building material for residential construction.
Determining Relative Worth
Comparing and contrasting rarely means placing the item or concept being evaluated in relation to another item or concept that is obviously grossly inferior. For instance, if you are attempting to demonstrate the value of a Cannondale mountain bike, it would be foolish to compare it with a Huffy. However, it would be useful to compare it with a Klein, arguably a similar bicycle. In this type of maneuver, you are not comparing good with bad; rather, you are deciding which bike is better and which bike is worse. In order to determine relative worth in this way, you will need to be very careful in defining the criteria you are using to make the comparison.
Using Comparison and Contrast Effectively
In order to make comparison and contrast function well in evaluation, it is necessary to be attentive to: 1) focusing on the item or concept under consideration and 2) the use of evidence in comparison and contrast. When using comparison and contrast, writers must remember that they are using comparable items or concepts only as a way of demonstrating the worth of the main item or concept under consideration. It is easy to lose focus when using this technique, because of the temptation to evaluate two (or more) items or concepts rather than just the one under consideration. It is important to remember that judgments made on the basis of comparison and contrast need to be supported with evidence. It is not enough to assert that "La Cocina's chile is even more fiery and flavorful than Manuel's." It will be necessary to support this judgment with evidence, showing in what ways La Cocina's chile is more flavorful: "Manuel's chile relies heavily on a tomato base, giving it an Italian flavor. La Cocina follows a more traditional recipe which uses little tomato and instead flavors the chile with shredded pork, a dash of vinegar, and a bit of red chile to give it a piquant taste."
The Process of Writing an Evaluation
A variety of writing assignments call for evaluation. Bearing in mind the various approaches that might be demanded by those particular assignments, this section offers some general strategies for formulating a written evaluation.
Choosing a Topic for Evaluation
Sometimes your topic for evaluation will be dictated by the writing assignment you have been given. Other times, though, you will be required to choose your own topic. Common sense tells you that it is best to choose something about which you already have a base knowledge. For instance, if you are a skier, you might want to evaluate a particular model of skis. In addition, it is best to choose something that is tangible, observable, and/or researchable. For example, if you chose a topic like "methods of sustainable management of forests," you would know that there would be research to support your evaluation. Likewise, if you chose to evaluate a film like Pulp Fiction , you could rent the video and watch it several times in order to get the evidence you needed. However, you would have fewer options if you were to choose an abstract concept like "loyalty" or "faith." When evaluating, it is usually best to steer clear of abstractions like these as much as possible.
Brainstorming Possible Judgments
Once you have chosen a topic, you might begin your evaluation by thinking about what you already know about the topic. In doing this, you will be coming up with possible judgments to include in your evaluation. Begin with a tentative overall judgment or claim. Then decide what supporting judgments you might make to back that claim. Keep in mind that your judgments will likely change as you collect evidence for your evaluation.
Determining a Tentative Overall Judgment
Start by making an overall judgment on the topic in question, based on what you already know. For instance, if you were writing an evaluation of sustainable management practices in forestry, your tentative overall judgment might be: "Sustainable management is a viable way of dealing with deforestation in old growth forests."
Brainstorming Possible Supporting Judgments
With a tentative overall judgment in mind, you can begin to brainstorm judgments (or reasons) that could support your overall judgment by asking the question, "Why?" For example, asking "Why?" of the tentative overall judgment "Sustainable management is a viable way of dealing with deforestation in old growth forests" might yield the following supporting judgments:
- Sustainable management allows for continued support of the logging industry.
- It eliminates much unnecessary waste.
- It is much better for the environment than unrestricted, traditional forestry methods.
- It is less expensive than these traditional methods.
Anticipating Changes to Your Judgments After Collecting Evidence
When brainstorming possible judgments this early in the writing process, it is necessary to keep an open mind as you enter into the stage in which you collect evidence. Once you have done observations, analysis, or research, you might find that you are unable to advance your tentative overall judgment. Or you might find that some of the supporting judgments you came up with are not true or are not supportable. Your findings might also point you toward other judgments you can make in addition to the ones you are already making.
Defining Criteria
To prepare to organize and write your evaluation, it is important to clearly define the criteria you are using to make your judgments. These criteria govern the direction of the evaluation and provide structure and justification for the judgments you make.
Looking at the Criteria Informing Your Judgments (Working Backwards)
We often work backwards from the judgments we make, discovering what criteria we are using on the basis of what our judgments look like. For instance, our tentative judgments about sustainable management practices are as follows:
If we were to analyze these judgments, asking ourselves why we made them, we would see that we used the following criteria: wellbeing of the logging industry, conservation of resources, wellbeing of the environment, and cost.
Thinking of Additional Criteria
Once you have identified the criteria informing your initial judgments, you will want to determine what other criteria should be included in your evaluation. For example, in addition to the criteria you've already come up with (wellbeing of the logging industry, conservation of resources, wellbeing of the environment, and cost), you might include the criterion of preservation of the old growth forests.
Comparing Your Criteria with Those of Your Audience
In deciding which criteria are most important to include in your evaluation, it is necessary to consider the criteria your audience is likely to find important. Let's say we are directing our evaluation of sustainable management methods toward an audience of loggers. If we look at our list of criteria--wellbeing of the logging industry, conservation of resources, wellbeing of the environment, cost, and preservation of the old growth forests--we might decide that wellbeing of the logging industry and cost are the criteria most important to loggers. At this point, we would also want to identify additional criteria the audience might expect us to address: perhaps feasibility, labor requirements, and efficiency.
Deciding Which Criteria Are Most Important
Once you have developed a long list of possible criteria for judging your subject (in this case, sustainable management methods), you will need to narrow the list, since it is impractical and ineffective to use of all possible criteria in your essay. To decide which criteria to address, determine which are least dispensable, both to you and to your audience. Your own criteria were: wellbeing of the logging industry, conservation of resources, wellbeing of the environment, cost, and preservation of the old growth forests. Those you anticipated for your audience were: feasibility, labor requirements, and efficiency. In the written evaluation, you might choose to address those criteria most important to your audience, with a couple of your own included. For example, your list of indispensable criteria might look like this: wellbeing of the logging industry, cost, labor requirements, efficiency, conservation of resources, and preservation of the old growth forests.
Criteria and Assumptions
Stephen Reid, English Professor Warrants (to use a term from argumentation) come on the scene when we ask why a given criterion should be used or should be acceptable in evaluating the particular text, product, or performance in question. When we ask WHY a particular criterion should be important (let's say, strong performance in an automobile engine, quickly moving plot in a murder mystery, outgoing personality in a teacher), we are getting at the assumptions (i.e., the warrant) behind why the data is relevant to the claim of value we are about to make. Strong performance in an automobile engine might be a positive criterion in an urban, industrialized environment, where traveling at highway speeds on American interstates is important. But we might disagree about whether strong performance (accompanied by lower mileage) might be important in a rural European environment where gas costs are several dollars a litre. Similarly, an outgoing personality for a teacher might be an important standard of judgment or criterion in a teacher-centered classroom, but we could imagine another kind of decentered class where interpersonal skills are more important than teacher personality. By QUESTIONING the validity and appropriateness of a given criterion in a particular situation, we are probing for the ASSUMPTIONS or WARRANTS we are making in using that criterion in that particular situation. Thus, criteria are important, but it is often equally important for writers to discuss the assumptions that they are making in choosing the major criteria in their evaluations.
Collecting Evidence
Once you have established the central criteria you will use in our evaluation, you will investigate your subject in terms of these criteria. In order to investigate the subject of sustainable management methods, you would more than likely have to research whether these methods stand up to the criteria you have established: wellbeing of the logging industry, cost, labor requirements, time efficiency, conservation of resources, and preservation of the old growth forests. However, library research is only one of the techniques evaluators use. Depending on the type of evaluation being made, the evaluator might use such methods as observation, field research, and analysis.
Thinking About What You Already Know
The best place to start looking for evidence is with the knowledge you already possess. To do this, you might try brainstorming, clustering, or freewriting ideas.
Library Research
When you are evaluating policies, issues, or products, you will usually need to conduct library research to find the evidence your evaluation requires. It is always a good idea to check journals, databases, and bibliographies relevant to your subject when you begin research. It is also helpful to speak with a reference librarian about how to get started.
Observation
When you are asked to evaluate a performance, event, place, object, or person, one of the best methods available is simple observation. What makes observation not so simple is the need to focus on criteria you have developed ahead of time. If, for instance, you are reviewing a student production of Hamlet , you will want to review your list of criteria (perhaps quality of acting, costumes, faithfulness to the text, set design, lighting, and length of time before intermission) before attending the play. During or after the play, you will want to take as many notes as possible, keeping these criteria in mind.
Field Research
To expand your evaluation beyond your personal perspective or the perspective of your sources, you might conduct your own field research . Typical field research techniques include interviewing, taking a survey, administering a questionnaire, and conducting an experiment. These methods can help you support your judgment and can sometimes help you determine whether or not your judgment is valid.
When you are asked to evaluate a text, analysis is often the technique you will use in collecting evidence. If you are analyzing an argument, you might use the Toulmin Method. Other texts might not require such a structured analysis but might be better addressed by more general critical reading strategies.
Applying Criteria
After developing a list of indispensable criteria, you will need to "test" the subject according to these criteria. At this point, it will probably be necessary to collect evidence (through research, analysis, or observation) to determine, for example, whether sustainable management methods would hold up to the criteria you have established: wellbeing of the logging industry, cost, labor requirements, efficiency, conservation of resources, and preservation of the old growth forests. One way of recording the results of this "test" is by putting your notes in a three-column log.
Organizing the Evaluation
One of the best ways to organize your information in preparation for writing is to construct an informal outline of sorts. Outlines might be arranged according to criteria, comparison and contrast, chronological order, or causal analysis. They also might follow what Robert K. Miller and Suzanne S. Webb refer to in their book, Motives for Writing (2nd ed.) as "the pattern of classical oration for evaluations" (286). In addition to deciding on a general structure for your evaluation, it will be necessary to determine the most appropriate placement for your overall claim or judgment.
Placement of the Overall Claim or Judgment
Writers can state their final position at the beginning or the end of an essay. The same is true of the overall claim or judgment in a written evaluation.
When you place your overall claim or judgment at the end of your written evaluation, you are able to build up to it and to demonstrate how your evaluative argument (evidence, explanation of criteria, etc.) has led to that judgment.
Writers of academic evaluations normally don't need to keep readers in suspense about their judgments. By stating the overall claim or judgment early in the paper, writers help readers both to see the structure of the essay and to accept the evidence as convincing proof of the judgment. (Writers of evaluations should remember, of course, that there is no rule against stating the overall claim or judgment at both the beginning and the end of the essay.)
Organization by Criteria
The following is an example from Stephen Reid's The Prentice Hall Guide for College Writers (4th ed.), showing how a writer might arrange an evaluation according to criteria:
Introductory paragraphs: information about the restaurant (location, hours, prices), general description of Chinese restaurants today, and overall claim : The Hunan Dynasty is reliable, a good value, and versatile.
Criterion # 1/Judgment: Good restaurants should have an attractive setting and atmosphere/Hunan Dynasty is attractive.
Criterion # 2/Judgment: Good restaurants should give strong priority to service/ Hunan Dynasty has, despite an occasional glitch, expert service.
Criterion # 3/Judgment: Restaurants that serve modestly priced food should have quality main dishes/ Main dishes at Hunan Dynasty are generally good but not often memorable. (Note: The most important criterion--the quality of the main dishes--is saved for last.)
Concluding paragraphs: Hunan Dynasty is a top-flight neighborhood restaurant (338).
Organization by Comparison and Contrast
Sometimes comparison and contrast is not merely a strategy used in part [italics] of an evaluation, but is the strategy governing the organization of the entire essay. The following are examples from Stephen Reid's The Prentice Hall Guide for College Writers (4th ed.), showing two ways that a writer might organize an evaluation according to comparison and contrast.
Introductory paragraph(s)
Thesis [or overall claim/judgment]: Although several friends recommended the Yakitori, we preferred the Unicorn for its more authentic atmosphere, courteous service, and well-prepared food. [Notice that the criteria are stated in this thesis.]
Authentic atmosphere: Yakitori vs. Unicorn
Courteous service: Yakitori vs. Unicorn
Well-prepared food: Yakitori vs. Unicorn
Concluding paragraph(s) (Reid 339)
The Yakitori : atmosphere, service, and food
The Unicorn : atmosphere, service, and food as compared to the Yakitori
Concluding paragraph(s) (Reid 339).
Organization by Chronological Order
Writers often follow chronological order when evaluating or reviewing events or performances. This method of organization allows the writer to evaluate portions of the event or performance in the order in which it happens.
Organization by Causal Analysis
When using analysis to evaluate places, objects, events, or policies, writers often focus on causes or effects. The following is an example from Stephen Reid's The Prentice Hall Guide for College Writers (4th ed.), showing how one writer organizes an evaluation of a Goya painting by discussing its effects on the viewer.
Criterion #1/Judgment: The iconography, or use of symbols, contributes to the powerful effect of this picture on the viewer.
Evidence : The church as a symbol of hopefulness contrasts with the cruelty of the execution. The spire on the church emphasizes for the viewer how powerless the Church is to save the victims.
Criterion #2/Judgment: The use of light contributes to the powerful effect of the picture on the viewer.
Evidence : The light casts an intense glow on the scene, and its glaring, lurid, and artificial qualities create the same effect on the viewer that modern art sometimes does.
Criterion #3/Judgment: The composition or use of formal devices contributes to the powerful effect of the picture on the viewer.
Evidence : The diagonal lines scissors the picture into spaces that give the viewer a claustrophobic feeling. The corpse is foreshortened, so that it looks as though the dead man is bidding the viewer welcome (Reid 340).
Pattern of Classical Oration for Evaluations
Robert K. Miller and Suzanne S. Webb, in their book, Motives for Writing (2nd ed.) discuss what they call "the pattern of classical oration for evaluations," which incorporates opposing evaluations as well as supporting reasons and judgments. This pattern is as follows:
Present your subject. (This discussion includes any background information, description, acknowledgement of weaknesses, and so forth.)
State your criteria. (If your criteria are controversial, be sure to justify them.)
Make your judgment. (State it as clearly and emphatically as possible.)
Give your reasons. (Be sure to present good evidence for each reason.)
Refute opposing evaluations. (Let your reader know you have given thoughtful consideration to opposing views, since such views exist.)
State your conclusion. (You may restate or summarize your judgment.) (Miller and Webb 286-7)
Example: Part of an Outline for an Evaluation
The following is a portion of an outline for an evaluation, organized by way of supporting judgments or reasons. Notice that this pattern would need to be repeated (using criteria other than the fieriness of the green chile) in order to constitute a complete evaluation proving that "Although La Cocina is not without its faults, it is the best Mexican restaurant in town."
Evaluation of La Cocina, a Mexican Restaurant
Intro Paragraph Leading to Overall Judgment: "Although La Cocina is not without its faults, it is the best Mexican restaurant in town."
Supporting Judgment: "La Cocina's green chile is superb."
Criterion used to make this judgment: "Good green chile is so fiery that you can barely eat it."
Evidence in support of this judgment: "I drank an entire pitcher of water on my own during the course of the meal" or "Though my friend wouldn't admit that the chile was challenging for him, I saw beads of sweat form on his brow."
Supporting Judgment made by way of Comparison and Contrast: "La Cocina's chile is even more fiery and flavorful than Manuel's, which is by no means a walk in the park itself."
Evidence in support of this judgment: "Manuel's chile relies heavily on a tomato base, giving it an Italian flavor. La Cocina follows a more traditional recipe which uses little tomato, and instead flavors the chile with shredded pork, a dash of vinegar, and a bit of red chile to give it a piquant taste."
Writing the Draft
If you have an outline to follow, writing a draft of a written evaluation is simple. Stephen Reid, in his Prentice Hall Guide for College Writers , recommends that writers maintain focus on both the audience they are addressing and the central criteria they want to include. Such a focus will help writers remember what their audience expects and values and what is most important in constructing an effective and persuasive evaluation.
Guidelines for Revision
In his Prentice Hall Guide for College Writers , 4th ed., Stephen Reid offers some helpful tips for revising written evaluations. These guidelines are reproduced here and grouped as follows:
Examining Criteria
Criteria are standards of value . They contain categories and judgments, as in "good fuel economy," "good reliability," or "powerful use of light and shade in painting." Some categories, such as "price," have clearly implied judgments ("low price"), but make sure that your criteria refer implicitly or explicitly to a standard of value.
Examine your criteria from your audience's point of view. Which criteria are most important in evaluating your subject? Will your readers agree that the criteria you select are indeed the most important ones? Will changing the order in which you present your criteria make your evaluation more convincing? (Reid 342)
Balancing the Evaluation
Include both positive and negative evaluations of your subject. If all of your judgments are positive, your evaluation will sound like an advertisement. If all of your judgments are negative, your readers may think you are too critical (Reid 342).
Using Evidence
Be sure to include supporting evidence for each criterion. Without any data or support, your evaluation will be just an opinion that will not persuade your reader.
If you need additional evidence to persuade your readers, [go back to the "Collecting" stage of this process] (Reid 343).
Avoiding Overgeneralization
Avoid overgeneralizing your claims. If you are evaluating only three software programs, you cannot say that Lotus 1-2-3 is the best business program around. You can say only that it is the best among the group or the best in the particular class that you measured (Reid 343).
Making Appropriate Comparisons
Unless your goal is humor or irony, compare subjects that belong in the same class. Comparing a Yugo to a BMW is absurd because they are not similar cars in terms of cost, design, or purpose (Reid 343).
Checking for Accuracy
If you are citing other people's data or quoting sources, check to make sure your summaries and data are accurate (Reid 343).
Working on Transitions, Clarity, and Style
Signal the major divisions in your evaluation to your reader using clear transitions, key words, and paragraph hooks. At the beginning of new paragraphs or sections of your essay, let your reader know where you are going.
Revise sentences for directness and clarity.
Edit your evaluation for correct spelling, appropriate word choice, punctuation, usage, and grammar (343).
Nesbitt, Laurel, Kathy Northcut, & Kate Kiefer. (1997). Academic Evaluations. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=47
Secrets of Writing an Excellent Evaluation Essay
05 July, 2020
14 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
Many people prefer to check reviews on the movie or book before watching or reading it. The summary information and honest point of view on the subject matter are usually included in an evaluation essay. You just need to analyze both sides of the chosen criterion through thorough research, analysis of your thesis, and examination of your own values. To write a good evaluation essay, you should forget about your feelings and create an objective overview of the topic. That way, you will reveal the truth about the real worth of the particular subject matter.

So, what is an evaluation essay? The answer to this question you will find out in this post.
What Is an Evaluation Essay?
An evaluation paper is a kind of essay in which you express your argumentative point of view on various topics. As a form of literary thinking, it is based on much more than just a quick judgment about a person, place, or object. The common standards of evaluation writing, such as clearance, objectivity, and coherence, are to be followed throughout the text. These standards help identify how well a subject meets up or falls short of the ideal. No wonder this kind of essay is widely used for scientific purposes when the comparison of two inventions or technologies is required. In an evaluation essay, all the arguments are delivered objectively, while your personal opinion is stated at the very end as a summary.
On the Internet, you can find lots of reviews with one sentence only: “This essay is fine.” Does it look informative to you? Can you rely on this kind of feedback? Let’s be honest, such a review can hardly provide you with a clear understanding of whether the subject is worth your attention or not. The main feature of an evaluation essay is that it contains details and evidence to support your point of view. Instead of discussing every observation, you just need to underpin your point of view with examples that will make your paper look convincing.
CJE guidelines
How to start an evaluation essay? What needs to be preconsidered? Every evaluation essay consists of three structural elements – criteria, judgement, and evidence. Let’s get deeper into details.
The criteria that you choose should evaluate a person or subject through the prism of their ideal version. What can their best features be? For instance, you would expect an interesting plot and professional acting from a movie. Once you have specific benchmarks in mind, they can be used to evaluate these points.
The judgement aspect is used to estimate whether or not the benchmarks have been met. For instance, you can start a movie evaluation from judging whether it aligns with the specific benchmark. Does it offer the quality acting you expect? Does it have gaps in the plot? These are only some of the possible options to consider.
Remember that you must develop clues to advocate your judgements. For instance, if you make the judgement that the movie quality does not meet your expectations, you should be ready to provide evidence. Without eligible evidence, your evaluation essay won’t look convincing.
When structuring your evaluation essay, it is crucial to address a different criterion in each paragraph. In that paragraph, you should reflect on each criterion, make the relevant judgements and provide supporting proofs.
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
With this step-by-step guide, you will learn how to write an evaluation essay. Here are the major steps to be taken:
- Choose your topic. Whatever kind of essay you are writing, you will have to take this step. Your topic can be offered by your instructor, as the case may be. But if you have to choose it yourself, you should consider a subject that you are familiar with. Thus, it will be easier for you to take an in-depth look at the subject and make a judgement on its value.
- Create a thesis statement. This is an important element of your essay as it contains the general purpose of the evaluation. In the thesis, you need to reflect on the criteria being used to judge the subject matter and state its value. Your statement should look apparent and to the point. In the process of writing, you may revise it as your essay gets shaped.
- Identify the criteria to be used for accessing the subject matter. Determine the benchmarks in your essay in order to make it interesting and engaging. The criteria you choose will depend on the subject of your evaluation. For instance, a movie will be judged using different points of reference than a book.
- Find supporting evidence . Don’t forget that an essay is not just about your opinion. You will need to find some supporting information from trustworthy sources while making each judgement. Don’t think that stating the movie or book title is enough. Use some questions to find out answers that can help you collect more information. How can you evaluate the subject? What kind of readers are you focused on? Will you focus on good or bad sides of the subject?
- Write a draft of your essay . All you need to do is to continue writing. As soon as you have something written on paper, you will rewrite or restructure it unless you are totally happy with the result.
Review, revise and rewrite. When a draft is completed, you will read over your work and make some changes if needed. You should be ready to rewrite your paper several times to get it just right.
Evaluation Essay Example
Here, you will find a well-written evaluation essay example that you can use for yourself:
- https://academichelp.net/samples/academics/essays/evaluation/standardized-tests.html
- https://www.examples.com/education/evaluation-essay-examples.html
Evaluation Essay VS Review
An evaluation essay is widely associated with a review paper. This is a common mistake many students make. Although the two types of paper have some similarities, there are more differences that set them apart. You can take a look at those differences in the table below.
|
|
|
|
| Analysis | The topic is examined thoroughly. | Evaluation of a product or service is provided. |
| Depth of analysis | You get engaged in in-depth analysis. | You do not need to conduct profound scientific research. |
| Evidence | Adequate supporting evidence aims to increase the quality of the evaluation essay. You should provide only credible and scholarly evidence. | You don’t need academic evidence throughout the appraisal process. |
| Opinion | You provide an unbiased view on the subject. | You provide unbiased information by relying on personal consideration that analyzes the subject. |
| Benchmarks | You use predefined criteria that evaluate the subject matter. | You express opinions that do not follow particular criteria. |
| Scope | You cover a broader scope by evaluating a particular topic and searching for adequate data that can critique the particular subject. | You cover a narrower scope by providing views focused on the particular subject. |
| Thesis statement | You provide a central claim as the essay’s thesis . | You do not need a thesis statement. |
| Structure | You follow the standard essay structure splitting the paper into sections. | You do not have to follow any specific structure in review writing. |
| References | You include the works cited page. | You do not have to include the works cited page. |
Tips on Writing an Evaluation Essay from Our Experts
Following the quick tips below, you will find it easier to write an effective evaluation argument essay:
- Provide the right amount of details: Make sure you explain your thoughts clearly and provide sufficient information to convince the reader in the correctness of your judgment.
- Thesis sentence should reveal your actual opinion. If you want to build up the basis for your body, you can include the main reasons for your evaluation in the thesis sentence.
- Know your target audience. By knowing your reader, you can adjust the plot to their specific needs. Whether you write for college students or professors, you will have to apply a bit different approach in the language choice.
- Make some notes. By using a three-column note-taking method, you can organize your thoughts. The columns of criteria, evidence, and judgment will contain the relevant information which will not let you forget or mix facts.
- Be opinionated . By sounding passionate in your evaluation essay, you will increase your chances of catching readers’ attention. The use of vivid nouns and engaging verbs will strengthen the effect produced by your paper. You should have a strong judgment of how the particular subject is either better or worse than other subjects of the same type.
- Back up every judgement you make. Every time you make a judgment, you should be ready to use specific, interesting, and convincing reasons to make it up. For evidence, you can describe the subject, use funny stories, or compare and contrast some notions with a similar subject.
- Provide counter-arguments. When you disagree with what most people think about the particular subject, it makes sense to provide some counter-arguments. This will make the narration more engaging for readers.
List of 50 Evaluation Topics
Since there are many people and objects you are able to assess, an evaluation essay can be written on a wide range of topics. To evaluate something, you will need to compare it with an example within a subject you have chosen. Some possible evaluation essay topics can be found below:
- Analyze the dissimilarity between seeing a sporting event live and watching it on ITV.
- Create a comparative assessment of watching a sporting event in a cafe and watching it without leaving the comfort of your home.
- Evaluate the experience of watching a sporting event on your own and with other people.
- Evaluate how a recent drama movie portrays the tragedies of real life.
- Evaluate a classic criminal movie and what it states about the real crime rates in the modern society.
- Evaluate your favorite Chinese restaurant.
- Compare two popular Chinese restaurants in your city.
- Appraise football or basketball from the perspective of a contestant or that of a watcher.
- Analyze the way in which football or basketball has advanced over the last decade.
- Discuss the influence of ESPN on sporting events.
- Evaluate the coverage of the latest Eurovision Song Contest.
- Evaluate a fancy restaurant for how it makes the customer feel after having the meal
- Analyze the way in which a popular horror movie depicts people’s fears.
- Assess a classic action movie and talk about its ideas regarding the functions of men and women.
- Explore the change that occurred in recent war movies if compared to classic war movies.
- How do drama books affect readers?
- Evaluate a book about war and analyze whether it addresses current concerns associated with war and peace.
- Evaluate the effects of online educational programs on students’ performance.
- Do historical movies encourage history learning?
- Evaluate an Italian cafe located in your city. What is the difference between the Italian and local food?
- What makes a traditional Italian meal great?
- Can hamburgers be healthy? Mention some details and provide relevant arguments.
- How mental health issues affect students’ academic performance?
- Analyze teachers’ responsibilities in terms of elementary students’ needs.
- Evaluate the power of verbal encouragement as a motivational factor in the educational process.
- Critically reflect on education services provided to children experiencing difficulties in learning.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of German secondary education.
- Evaluate teaching methods used at the American universities.
- Ways in which online libraries affect the students’ academic performance.
- How well the film “BraveHeart” portrays historical events?
- Analyze a movie produced in a foreign country and discuss how it reveals its national characteristics.
- Assess Kate Winslet’s play in “Titanic” and discuss which means this actor applies to adapt to this role.
- Make a comparison between modern and classic drama movies.
- Assess the distinct approaches used to transfer data from a smartphone to a PC.
- Make comparisons between various phone plans and determine which provider has the best deals for travelers.
- Assess current information security methods. Which one is the most efficient?
- Assess the key characteristics of WhatsApp.
- Compare the use of several cloud systems that can be implemented by the movie hub website.
- Estimate the chances of Facebook as a marketing resource.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of online advertising.
- Assess the existing approaches to using the Internet in colleges.
- Analyze the consequences of cultural shock.
- Assess the negative sides of overwhelming cultural diversity in the United States.
- Discuss the development path of rap and hip-hop music.
- What is the impact of Buddhism on Indian culture?
- Compare two popular social media platforms in terms of their users, features, and benefits.
- Evaluate the latest version of your favorite smartphone and estimate the positive or negative changes that will affect the industry.
- Compare an educational approach in the military, Christian, or classical school.
- Evaluate the SAT versus the ACT tests.
- Compare the foreign policies established by a few states in the US.
Note that our company provides academic writing help. You can buy an essay written from scratch by our essay writer .

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
Crafting Insightful Evaluation Essay: Tips and Techniques
Table of contents
- 1 Defining Evaluation Essays
- 2 Choose a Subject for Evaluation
- 3 Develop a Clear Thesis Statement
- 4 Gather Information and Evidence
- 5 Establish Evaluation Criteria
- 6 Organize Your Essay
- 7 Write the Introduction
- 8 Write the Body of The Essay
- 9 Present Evidence and Examples
- 10 Address Counterarguments
- 11 Write The Conclusion
- 12 Revise and Edit
- 13.1 Easy Evaluation Essay Topics
- 13.2 Evaluation Essay Topics on History
- 13.3 Evaluation Essay Topics on Government and Law
- 13.4 Evaluation Essay Topics on Technology
- 14 Final Words & Expert Thoughts
Many students are required to write an evaluation essay during their academic career. While this task is challenging, it provides an opportunity for deeper learning. We believe that every student should understand how to write an evaluation essay to succeed with their coursework.
- We’ll start by demystifying what an evaluation essay is. We’ll outline its purpose in academic settings, highlighting how it differs from other essay types and why it’s a valuable tool for critical thinking and analysis.
- We’ll provide insights on how to choose a subject that is both interesting and suitable for evaluation.
- A well-organized essay is the key to success. In our article, we will break down the structure of an evaluation essay.
Examples for Clarity: Finally, we’ll provide examples of successful evaluation essays. These samples will illustrate the principles discussed and offer practical insights into what makes an effective evaluation essay.
Defining Evaluation Essays
Evaluation essays are a type of academic writing that provides value, quality, and effectiveness of a given topic. Every student must follow set criteria and provide evidence supporting their opinion.
Furthermore, an evaluation essay should always present facts and opinions in a clear and formal tone. Of course, any student can buy a custom essay , but every student should know how to plan and write one correctly for success. The first step is to choose a subject.
When it comes to choosing a subject for an evaluation paper, students have many options to choose from.
This includes:
- Movies & television shows
- Performance of sports teams
- Restaurant review
- Comparisons
Choose a Subject for Evaluation
If you’re looking for ideas, consider pulling inspiration from your experiences or interests. You can also get ideas from current events and media.
Moreover, once you begin brainstorming ideas, you should narrow your options to choose the best topic. Ideally, you should choose a subject that’s equally interesting and suitable for evaluation. Start by reviewing topic ideas related to your main area of study.
Compare different ideas that interest you. Start asking questions that your target audience would have on your subject. Narrow your choice to what you believe would be the most interesting to study and write about.
In addition, some examples that would make an interesting evaluation subject include:
- Learning on campus vs online learning
- Your evaluation of the most recent movie or television show you’ve watched
- How social media affects modern relationships
- Availability of athletic programs in your area
- Comparison of restaurants or coffee shops in your area
Develop a Clear Thesis Statement
Every evaluation essay needs a thesis statement. In this statement, the writer will cover evaluation criteria and an overall judgment. It’s essential that the purpose of the evaluation is clearly stated.
First, be specific by keeping the thesis statement short and sweet. It doesn’t need to be a paragraph filled with real-life information. Instead, it should be a concise sentence encouraging the reader to continue reading. Here are some excellent examples of thesis statements:
- “This cafe brews coffee beans provided by a local source, and they became popular for having the largest selection of latte flavors in the city.”
- “The gore and effects in the original Texas Chainsaw Massacre movie may be outdated, but the tension and horror in the film still hold up for today’s audience.”
- “Minecraft continues to be one of the best-selling video games because players enjoy the creative freedom they have in the open world and connecting with other players online.”
Gather Information and Evidence
An important step of evaluation essays is to gather information and evidence. You will want as much information and relevant examples as possible to support your essay.
In any case, experienced writers will provide as many sources as they can find to support their argument. This helps the writer establish credibility and also helps the reader discover where they can find more information on the topic.
So, you might be wondering what type of sources you can use for crafting an evaluation paper. Students may use any of the following sources to provide evidence for their evaluation:
- Books: choose books that have been written by experts on the subject that you’re evaluating.
- Online resources: students can find credible information online from reputable sources and government websites.
- Magazines and newspapers — print media is an excellent source to use for current events and opinions.
- Interviews: you can interview an expert in the field your essay is in. This includes in-person, over-the-phone, email, or live chat interviews.
- Opinions from credible sources: these opinions can be accessed using any of the sources listed above.
Establish Evaluation Criteria
Every writer must follow set criteria to write an interesting and well-structured essay. As mentioned above, the thesis statement is significant. This is because it’s a clear and descriptive way to present the topic.
Finally, every good evaluation essay must include the following specific criteria:
- Assertion of the writer’s overall judgment based on supporting evidence.
- Responses to counterarguments that a reader could make on the evaluation. The writer should introduce a balanced argument so their judgment makes sense to readers.
Organize Your Essay
Another crucial aspect of evaluation criteria is to display a well-structured essay. Before writing an evaluation essay, you should always plan the organization.
The entire outline for the essay should remain focused. Once complete, the final evaluation paper should be organized, developed, and maintained a specific style. Every paper should include the following in a detailed evaluation essay outline:
- Introduction: introduce your subject with a topic sentence that grabs readers’ attention and inspires them to keep reading.
- Body: this will contain all of the key information that supports your evaluative argument and counterarguments.
Conclusion: this is where you can summarize the key points made throughout the evaluation essay and add any other relevant points.
Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first impression of your essay. Every paragraph of the essay should start with a topic sentence that introduces what the essay will be about. Always aim to write a topic sentence that’s engaging so the reader immediately establishes interest.
Basically, every student should aim to craft an attention-grabbing hook that sparks the reader’s interest. Here are a few good evaluation essay introduction example topic sentences for your evaluative essay:
- One of the growing concerns of parents in recent years is the effects of social media on their teen’s mental health.
- The quality of customer service a patron receives in restaurants and retail establishments is a crucial factor in their experience.
- Older films get lost on the younger generation for outdated graphics and dialogue, but many of them address topics that are very relevant to today’s society.
Evidently, we understand that crafting a good introduction can be intimidating. The intro can make or break the reader’s interest. Some ways to make your introduction effective are by stating an exciting or unknown fact, asking a rhetorical question, or mentioning an interesting story about the subject.
Write the Body of The Essay
The body paragraphs of your evaluative essay hold the most weight. After all, this is where you will present your opinions and facts. All the information you provide in this section must be relevant to your topic.
Basically, it must be presented in a structured manner. The main body should always include proper sentence structure, have a readable flow, and include all information and examples necessary to support your final judgment. It’s also important to use language that will convey your point formally and professionally.
Present Evidence and Examples
Anyone can write an evaluated essay. If you want people to take your evaluation essay seriously, you must demonstrate evidence for every point. You can use example quotes from reputable sources or citations to reference where you found the information for your analysis.
Additionally, you must cite sources for evaluation criteria to avoid accusations of plagiarism. An excellent tip for writing essays is to create a body paragraph that’s a block quote.
By directly quoting the author (or source), you avoid any errors that could be mistaken for plagiarism. A direct quote can also give your evaluation more value in the middle of a body paragraph, and also be used to support the writer’s opinion.
Address Counterarguments
An evaluation essay is different from an argumentative essay . When you’re writing an evaluation essay, you will not be required to include counterarguments in the evaluative thesis of the essay. However, it is a good idea for students to acknowledge different perspectives or criticisms of their topic.
In any case, one of the best ways to approach a counterargument is to provide an example of a common critic. Then, explain why that perspective is or isn’t valid to the opinion the student covered in their essay.
Write The Conclusion
The conclusion is the final area of the evaluation essay, where students can summarize their analysis and provide additional facts supporting their judgment.
Every good evaluation argument essay will answer all the reader’s questions on the subject before they reach the final sentence. The best way to do this is to make the conclusion restate the main ideas by presenting the key takeaways and wrapping the concluding paragraph with a secure closure on the research subject.
Revise and Edit
Once you have completed the evaluative writing process, you must revise and edit it before submitting it. This is how you can ensure your paper is of good quality and your opinion is clearly stated and backed up.
But before you review your work, it’s always good to give yourself a break. If you review the paper immediately after writing it, your brain might not pick up on typos and mistakes. By giving yourself a break, you can return and proofread it in a clear frame of mind.
When you proofread the evaluation essay, there are a few aspects that are critical for revision. You should always review the sentence structure, spelling, grammar, and punctuation usage in your essay. You should also check to ensure you used appropriate font, and headers and the essay is double-spaced.
Good Evaluation Essay Topics List
These subjects will encourage college and high school students, as well as professional writers, to critically evaluate present culture. These themes not only teach students important critical thinking skills, but also demonstrate how students influence and contribute to general knowledge.
- Race and Ethnicity in the United States
- Hitler was influential, determined, and strategic
- Importance of Sex Education
- Brown v. Board: Lgal Changes in Respect to Segregation
- Martin Luther King and the fight against racism in the US
- Industrialization and imperialism
- Starbucks Found in a Crisis
- Immigration and Customs Enforcement
- The Apparel Industry in the U.S.
- France: New Gender Equality Obligations Established
Easy Evaluation Essay Topics
Here is a list of handpicked good literature topics that will ignite your curiosity and engage your critical thinking skills. These easy topics cover a wide range of subjects and are just a few clicks away from inspiring your next masterpiece.
- How Do You Define Racism?
- Homeschooling vs Public School
- The Book is Composed of Two Sections
- Edgar Allan Poe in Romantic Literature
- Gerard Jones’ Biased Evaluation of Violence in Media
- Self Evaluation and Supervision
- Marriage in a World
- Climate Change Training Course
- The Importance of Evaluation in Counseling
- Animal Welfare, Chickens: Factory or Field
Evaluation Essay Topics on History
There are several historical evaluation essay ideas to consider. They vary from major events that affected our global culture to examining the historical veracity of “saving private Ryan.” These topics will intrigue you and give plenty of writing possibilities:
- John F. Kennedy’s Legacy
- Barack Obama’s Inaugural Speech
- Main Issues Of Border Wall
- After Civil Rights: Racial Realism in the New American Workplace
- Cold War in China, Cold War in Cuba, and Space Race
- Progressing the Civil Rights Movement with Aristotle’s Artistic Appeals
- China-Australia Free Trade Agreement
- What was the Harlem Renaissance?
- Aftershock: Beyond the Civil War Summary
- Mark Antony’s Described Julius Caesar
Evaluation Essay Topics on Government and Law
These topics cover the key characteristics of how we interact with society and the law. They also explore government and law by examining political marketing strategies on how some particular laws affect social behavior.
- Brown V. Board of Education and Civil Rights
- Criminal Profiling
- The Significance of the Gettysburg Address
- Race Relations have Improved in America
- Temporary Labor Migrants
- The Electoral College and How Popular Vote Doesn’t Matter
- Jeffersonian Democracy
- Granada Hills Charter High School
- Transgender Individuals in the Military
- The Segregation of Schools in the United States
Evaluation Essay Topics on Technology
As we delve into technological evaluation essay topics, you can choose to examine the merits, drawbacks, and overall impact of technological advancements. From artificial intelligence to social media, we have a plethora of ideas to explore.
- Social Media Marketing As A Way To Promote Business
- Pros And Cons Of Virtual Reality Gaming.
- Assessing Online Clothes Shop For Its Contribution To The Fashion Sector
- Evaluation of the Process of Creating Computer-Generated Graphics In Contemporary Art.
- Technology’s Role In Healthcare.
- Cybersecurity Measures’ Effectiveness.
- The Culture Wars in the Digital Age: Impact of Technology on Cultural Values.
- Ai’s Role In Job Automation.
- Impact Of Biometric Technology On Privacy.
- How The Internet Changed Communication Patterns In Online Interactions.
Final Words & Expert Thoughts
This covers everything you need to know about writing an evaluation essay. The format we discussed today can help students create a detailed analysis of the subject they’re researching while providing an educated opinion. Following proper instructions for evaluation essay criteria can help you write a detailed paper that will impress your instructor (and yourself).
Additionally, if you’re not 100% sure how to start or finish your paper, look at an evaluation argument essay example online. Don’t copy the examples, but use them for inspiration to get your thoughts flowing.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Home ➔ How to Write an Essay ➔ Evaluation Essay
Evaluation Essay Guide
An evaluation essay is a distinctive form of writing that aims to present a balanced opinion on a subject. This type of essay is akin to a persuasive essay . However, it differs by offering a more even-handed argument. While a persuasive essay may focus more heavily on the author’s viewpoint, an evaluation essay gives equal weight to both the positive and negative aspects of the subject. This approach ensures a comprehensive and fair presentation.

Importance in Academic and Professional Contexts
Evaluation essays are significant beyond academic circles. They play a vital role in various professional fields. Let’s consider their wide-ranging applications:
- Academic Utility : These essays develop students’ analytical skills in educational settings. They encourage a deep and critical engagement with the subject matter.
- Professional Relevance : In the business world, evaluative essays assess products, services, or strategies. They provide critical insights for informed business decisions.
- Versatile Applications : Their utility is widespread, from consumer product reviews to scholarly article assessments. These essays offer structured methods to evaluate diverse aspects like technology efficiency or social policy impacts.
The ability to effectively compose an evaluative essay is not just a scholarly pursuit. It’s a valuable skill for critical analysis and informed decision-making. This skill is essential across various disciplines and professional environments. It underscores the importance of making well-reasoned and balanced evaluative judgments in academic and real-world contexts.
Preparing to Write an Evaluation Essay
Choosing a Topic: The first step in crafting an evaluation essay is selecting the right topic . Choosing a subject you are either familiar with or can thoroughly research is crucial. The effectiveness of your essay hinges on your understanding of the topic. A well-chosen topic allows you to present a more informed and credible evaluation. When deciding on a subject, consider these key aspects:
- Interest and Knowledge : Pick a topic that intrigues you or one you know about. This familiarity will help in providing a deeper, more insightful evaluation.
- Researchability : If the topic is new to you, ensure that it has ample resources available for research. A well-researched essay will stand stronger in its arguments and conclusions.
Understanding Your Audience: Knowing your audience is fundamental in writing an evaluation essay. Understanding who your readers are and their values and perspectives is crucial in shaping your essay. A successful evaluation paper connects with its audience, respecting and acknowledging their viewpoints. This understanding guides how you present your arguments and evidence. To connect effectively with your audience, consider the following:
- Audience Values : Gauge the values and beliefs of your audience. This knowledge helps frame your evaluation in a way that resonates with them.
- Perspective Bridging : Recognize that your audience may have different opinions. Aim to bridge these gaps by presenting a well-rounded, respectful argument considering multiple viewpoints.
In summary, the preparation phase is critical to writing an evaluation essay. Selecting the right topic and understanding your audience lays the foundation for a compelling and persuasive essay. These initial steps ensure that your evaluation is well-informed and well-received.
Structuring the Evaluation Essay
An evaluation paper follows a clear and concise structure , which is essential for guiding the reader through your argument. An evaluation essay consists of the following:
- Introduction : Sets the stage for your evaluation, introducing the subject and presenting your thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs : The main section where you provide a detailed overview of the subject and apply your evaluation criteria.
- Conclusion : Wraps up the essay by summarizing your arguments and reinforcing your evaluative thesis statement.
Introduction :The introduction of an evaluation essay is critical in capturing the reader’s interest. It should:
- Clearly state the subject of your evaluative writing.
- Present a thesis statement that encapsulates your overall judgment of the subject.
- Be engaging, providing enough background to set the context for your evaluation.
In crafting your introduction, aim to be concise yet informative, laying a solid foundation for your argument.
Body Paragraphs : The body paragraphs present the bulk of your evaluation. Here are some guidelines for writing these paragraphs:
- Topic Sentence : Start each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence. This sentence should introduce the specific aspect or evaluative criterion you will discuss in the paragraph. It sets the stage for the reader and clearly aligns with your thesis statement.
- Objective Overview : Before diving into evaluative statements, provide an objective overview of the subject. This includes relevant background information and essential details. This approach ensures that your evaluation is grounded in a clear understanding of the subject.
- Systematic Application of Criteria : Each paragraph should focus on a different evaluative criterion. Systematically apply these criteria, one per paragraph, to structure your analysis. This methodical approach helps in organizing your thoughts and presenting a well-structured argument.
- Evidence and Examples : Support your evaluation with concrete evidence and examples. This could include data, research findings, personal observations, or examples from the subject. These elements are crucial for substantiating your evaluation and making it more persuasive.
- Balance of Perspectives : In each paragraph, strive to balance the subject’s positive and negative aspects. Acknowledge your strengths and weaknesses, even if your overall evaluation leans more towards one. This balanced approach enhances the fairness and credibility of your analysis.
- Concluding Sentences : End each paragraph with a sentence that wraps up the discussion and links back to your central thesis. This helps in maintaining coherence in your essay and reinforcing your central argument.
Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of your evaluative writing, contributing to the overall argument presented in your thesis.
Conclusion :The conclusion is your opportunity to bring closure to your essay. It should:
- Restate your thesis statement, summarizing the main points made in your body paragraphs.
- Reinforce the overall evaluative argument you’ve presented.
- Provide a final evaluation thought or statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
Remember, the conclusion is your last chance to convince the reader of your argument, so make it count by briefly summarizing and affirming your evaluation.
Evaluation Essay Outline Example
Topic: Evaluating the Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms in Higher Education.
- A. Hook: Start with an interesting statistic or fact about the rise of online learning in higher education.
- B. Context: Briefly introduce the growth of online learning platforms, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- C. Thesis Statement: Present a clear evaluative statement on the effectiveness of online learning platforms in higher education, considering various factors like accessibility, student engagement, and learning outcomes.
- A. Definition: Define what constitutes an online learning platform in the context of higher education.
- B. Development and Growth: Trace the evolution and recent expansion of online learning platforms.
- C. Relevance: Highlight the significance of evaluating these platforms in the modern educational landscape.
- A. Accessibility and Flexibility: Discuss how these platforms provide easy access and flexible learning schedules.
- B. Variety of Learning Resources: Evaluate the diversity of online resources and materials.
- C. Customization of Learning Experience: Explain how online platforms cater to different learning styles and speeds.
- D. Supporting Evidence: Present studies or statistics that back up these advantages.
- A. Lack of Direct Interaction: Assess the impact of reduced face-to-face interaction between students and instructors.
- B. Engagement and Motivation Issues: Discuss how remote learning can affect student engagement and motivation.
- C. Technology Barriers: Evaluate the challenges related to technology access and digital literacy.
- D. Evidence: Provide research findings or real-world examples highlighting these challenges.
- A. Online vs. Traditional Learning Environments: Compare the effectiveness of online learning with traditional in-person methods.
- B. Subject-Specific Effectiveness: Discuss how the effectiveness of online platforms may vary depending on the subject matter.
- A. Restate Thesis: Reassert the thesis in light of the discussions and evidence presented.
- B. Summary of Key Points: Concisely summarize the main advantages and challenges of online learning platforms.
- C. Final Thoughts: Conclude with a perspective on the future role of online learning in higher education or suggest areas for further research.
Note: Here’s a separate guide that covers outline creation: How to Write an Essay Outline .
Developing the Argument
Forming a Balanced Perspective: A fundamental aspect of crafting an evaluation essay is maintaining objectivity. It is essential to approach the subject with a balanced perspective, acknowledging its strengths and weaknesses. This balanced approach is not just about being fair; it also enhances the credibility of your argument. A thorough and unbiased analysis requires the following:
- Recognizing the positive aspects of the subject, even if your overall evaluation is negative.
- Acknowledging the shortcomings, even when you are inclined to favor the subject.
- Avoiding personal biases and preconceptions to present a fair evaluation.
A well-rounded argument demonstrates your ability to critically engage with the subject and shows a deep understanding of its various facets.
Establishing Evaluation Criteria: Selecting the appropriate criteria is crucial for a sound evaluation. These criteria form the basis of your argument and guide your analysis. When establishing evaluation criteria, consider the following:
- Relevance: Ensure the criteria directly relate to the subject and its context.
- Clarity: Define your criteria clearly so that your audience understands the basis of your evaluation.
- Objectivity: Choose criteria that allow for a fair and unbiased assessment.
- Consistency: Apply the same standards throughout your essay to maintain a coherent argument.
The criteria should be specific enough to be meaningful and broad enough to cover the significant aspects of the subject.
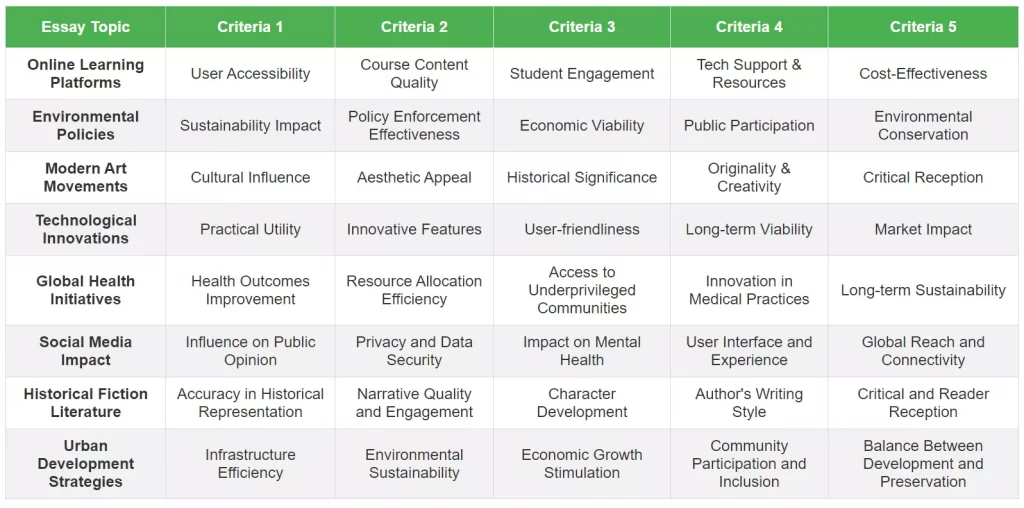
Providing Evidence: The strength of your evaluation essay lies in the evidence you provide. Robust evidence supports your criteria and helps substantiate your claims. Effective evidence includes:
- Examples: Specific instances or cases that illustrate your points.
- Statistics: Quantitative data that provides a factual basis for your evaluation.
- Expert Opinions: Insights from authorities in the field that lend weight to your arguments.
- Comparative Analysis: Drawing parallels or contrasts with similar subjects to provide context.
Remember, your evidence should be relevant, credible, and appropriately cited . It is the backbone of your evaluative argument, lending substance and persuasiveness to your analysis.
Techniques for Effective Evaluation
Analyze Before Evaluating: Effective evaluation starts with thoroughly analyzing the subject. Before jumping into forming an evaluative argument, it is crucial to dissect the subject comprehensively. This preliminary analysis involves:
- Gathering comprehensive information about the subject.
- Understanding different aspects, dimensions, and contexts related to the subject.
- Identifying patterns, trends, or significant points will form the evaluation’s basis.
A solid analysis lays the groundwork for a well-informed evaluative argument. It helps form a viewpoint that is not just a superficial opinion but is grounded in a deep understanding of the subject.
Addressing Counterarguments: An essential technique in strengthening the credibility of your evaluation essay is to anticipate and address counterarguments. This involves:
- Identifying potential objections to your argument.
- Presenting these counterarguments fairly and objectively.
- Refuting these objections logically and with evidence or conceding specific points where appropriate.
By addressing counterarguments, you demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject and show that your evaluation is not one-sided. This approach enhances the persuasiveness of your essay, as it shows that you have considered different viewpoints before arriving at your conclusion.
Establishing Credibility and Authority: The persuasiveness of an evaluation essay is significantly influenced by the credibility and authority of the writer. To establish credibility and authority, a writer should:
- Demonstrate extensive knowledge of the subject, either through academic qualifications, professional experience, or extensive research.
- Use a writing style that conveys expertise and confidence.
- Cite reputable sources to back up arguments and gather supporting evidence.
A writer’s background and understanding of the subject matter enhance the trustworthiness of the evaluation. Readers are more likely to be persuaded by a writer with a deep and well-informed insight into the subject they are evaluating.
Finalizing the Evaluation Essay
Review and Refinement: After crafting the initial draft of your evaluation essay, the next crucial phase is the review and refinement process. This stage is essential for polishing your essay to achieve clarity and effectiveness. Consider the following tips during this phase:
- Comprehensive Revision : Re-read your essay to ensure your arguments are clearly and logically presented. Pay attention to the flow of ideas from the introduction through the body to the conclusion.
- Remove Redundancies : Look for and eliminate any repetitive or unnecessary information that doesn’t contribute to your argument or analysis.
- Check for Coherence : Ensure that each paragraph transitions smoothly to the next and all parts of your essay work cohesively to support your thesis.
- Seek Feedback : If possible, have someone else read your essay. Fresh eyes can offer valuable perspectives and catch errors you might have missed.
- Final Proofreading : Pay attention to grammar, spelling, sentence structure, and punctuation. Even minor errors can distract the reader and undermine the professional quality of your work.
Formatting and Citation Standards: Adherence to proper formatting and citation standards is critical to academic and professional writing. It not only demonstrates your attention to detail but also your respect for intellectual property. Remember the following:
- Follow Specific Guidelines : Whether it’s MLA, APA, Chicago, or any other format, ensure you follow the guidelines required for your essay. This includes formatting of the text, title page, and the paper’s layout.
- Proper Citation : All sources referenced in your essay must be properly cited. This includes direct quotes, paraphrased ideas, and data or statistics you’ve included.
- Reference List or Bibliography : Include a comprehensive list of all sources cited in your essay, formatted according to the required citation style.
- Adhere to Word Count and Other Requirements : Ensure your essay meets specific requirements such as word count, font size, and margin specifications.
By diligently reviewing, refining, and adhering to the appropriate academic standards, you can enhance your evaluation essay’s overall quality and credibility. This final phase is your opportunity to ensure that your essay is rich in content and impeccable in its presentation.
In crafting an evaluation essay, the journey from introduction to conclusion involves thorough analysis, balanced perspectives, and careful argument development. We have explored various essential techniques to enhance the effectiveness of your evaluation, including the importance of presenting a balanced view, establishing clear evaluation criteria, providing robust evidence, addressing counterarguments, and establishing your credibility as a writer.
Let’s briefly recap the key points:
- Balanced Perspective : Emphasize a fair and objective analysis, acknowledging your subject’s positives and negatives.
- Evaluation Criteria : Carefully select and apply relevant criteria that guide your evaluative judgment.
- Evidence : Use examples, statistics, and expert opinions to substantiate your points, making your argument compelling and credible.
- Counterarguments : Strengthen your essay by anticipating and addressing potential objections, demonstrating a well-rounded understanding.
- Credibility and Authority : Build trust with your readers by showcasing your knowledge and expertise on the subject matter.
As you write your evaluative essays, apply these guidelines to construct a well-reasoned, persuasive, and insightful piece. Remember, the effectiveness of your evaluation lies not just in what you say but in how you support and present your arguments. By adhering to these principles, you can enhance the depth and impact of your evaluations, making them informative and engaging for your readers.
Whether you’re evaluating a literary work, a social policy, a technological advancement, or any other subject, these strategies will serve as valuable tools in your writing arsenal. Use them to enrich your analysis, present your arguments effectively, and, ultimately, craft evaluation essays that stand out for their clarity, depth, and persuasiveness.
Essay Papers Writing Online
Ultimate guide on writing an effective evaluation essay – tips, examples, and guidelines.

Are you puzzled when it comes to writing an evaluation essay? In this guide, we will provide you with all the essential information you need to master the art of crafting a compelling appraisal composition. Whether you are new to this type of writing or just looking to refine your skills, this comprehensive manual will equip you with the necessary tools and techniques to excel. From understanding the purpose and structure of an evaluation essay to exploring various tips and examples, this guide has got you covered.
An evaluation essay is a piece of writing that aims to assess the value or quality of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves analyzing a topic, presenting your judgment or opinion on it, and providing evidence or examples to support your claims. This type of essay requires critical thinking, research, and effective communication skills to present a well-balanced evaluation.
Throughout this guide, we will delve into the nitty-gritty of writing an evaluation essay. We will start by discussing the key elements that make up a successful evaluation essay, such as establishing clear criteria, conducting thorough research, and adopting a structured approach. Additionally, we will explore practical tips and strategies to help you gather relevant information, organize your thoughts, and present a persuasive argument. To illustrate these concepts, we will provide you with a range of examples covering various topics and subjects.
Tips for Writing a Top-Notch Evaluation Essay
When it comes to crafting a high-quality evaluation essay, there are several key tips to keep in mind. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your essay stands out and effectively evaluates the subject matter at hand.
1. Be objective and unbiased: A top-notch evaluation essay should approach the topic with an unbiased and objective perspective. Avoid personal bias or overly emotional language, and instead focus on presenting an honest and well-balanced evaluation of the subject.
2. Provide clear criteria: To effectively evaluate something, it’s important to establish clear criteria or standards by which to assess it. Clearly define the criteria you will be using and explain why these specific factors are essential in evaluating the subject. This will help provide structure to your essay and ensure that your evaluation is thorough and comprehensive.
3. Support your evaluation with evidence: In order to make a convincing argument, it’s crucial to support your evaluation with solid evidence. This can include examples, statistics, expert opinions, or any other relevant information that strengthens your claims. By providing strong evidence, you can enhance the credibility of your evaluation and make it more persuasive.
4. Consider multiple perspectives: A well-rounded evaluation takes into account multiple perspectives on the subject matter. Acknowledge and address counterarguments or differing opinions, and provide thoughtful analysis and reasoning for your stance. This demonstrates critical thinking and a comprehensive evaluation of the topic.
5. Use clear and concise language: Clarity is vital in an evaluation essay. Use clear and concise language to express your thoughts and ideas, avoiding unnecessary jargon or complex vocabulary. Your essay should be accessible to a wide audience and easy to understand, allowing your evaluation to be conveyed effectively.
6. Revise and edit: Don’t neglect the importance of revising and editing your essay. Take the time to review your work and ensure that your evaluation is well-structured, coherent, and error-free. Pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation, as these details can greatly impact the overall quality of your essay.
7. Conclude with a strong summary: For a top-notch evaluation essay, it’s important to conclude with a strong and concise summary of your evaluation. Restate your main points and findings, providing a clear and memorable conclusion that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
By following these tips, you can enhance your writing skills and create a top-notch evaluation essay that effectively assesses and evaluates the subject matter at hand.
Choose a Relevant and Engaging Topic
When it comes to writing an evaluation essay, one of the most important aspects is selecting a topic that is both relevant and engaging. The topic you choose will determine the focus of your essay and greatly impact the overall quality of your writing. It is crucial to choose a topic that not only interests you but also captivates your audience.
When selecting a topic, consider the subject matter that you are knowledgeable or passionate about. This will enable you to provide a well-informed evaluation and maintain your readers’ interest throughout your essay. Additionally, choose a topic that is relevant in today’s society or has a direct impact on your target audience. This will ensure that your evaluation essay has a practical and meaningful purpose.
Furthermore, it is essential to select a topic that is controversial or debatable. This will allow you to present different perspectives and arguments to support your evaluation. By choosing a topic that sparks discussions and debates, you can engage your readers and encourage them to think critically about the subject matter.
In conclusion, choosing a relevant and engaging topic is crucial for writing an effective evaluation essay. By selecting a topic that interests you, appeals to your readers, and is relevant to society, you can ensure that your essay is engaging and impactful. Remember to choose a topic that is controversial or debatable to provide a comprehensive evaluation and encourage critical thinking among your audience.
Develop a Strong Thesis Statement

Crafting an impactful thesis statement is an essential aspect of writing an evaluation essay. The thesis statement serves as the main argument or claim that you will be supporting throughout your essay. It encapsulates the central idea and sets the tone for the rest of the paper.
When developing your thesis statement, it is crucial to be clear, concise, and specific. It should provide a clear indication of your stance on the subject matter being evaluated while also highlighting the main criteria and evidence that will be discussed in the body paragraphs. A strong thesis statement should be thought-provoking and hook the reader’s attention, compelling them to continue reading.
To build a strong thesis statement, you need to engage in a careful analysis of the topic or subject being evaluated. Consider the various aspects that you will be assessing and select the most significant ones to include in your argument. Your thesis statement should be focused and arguable, allowing for a clear position on the matter.
Additionally, it is crucial to avoid vague or general statements in your thesis. Instead, aim for specificity and clarity. By clearly stating your evaluation criteria, you provide a roadmap for the reader to understand what aspects you will be analyzing and what conclusions you intend to make.
Furthermore, a strong thesis statement should be supported by evidence and examples. You should be able to provide concrete support for your evaluation through relevant facts, statistics, or expert opinions. This strengthens the credibility and persuasiveness of your argument, making your thesis statement more compelling.
In summary, developing a strong thesis statement is a critical step in writing an evaluation essay. It sets the foundation for your argument, guiding your analysis and providing a clear direction for the reader. By being clear, concise, specific, and well-supported, your thesis statement helps you create a persuasive and impactful evaluation essay.

Provide Clear and Concise Criteria for Evaluation
One of the most important aspects of writing an evaluation essay is providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation. In order to effectively evaluate a subject or topic, it is essential to establish specific standards or benchmarks that will be used to assess its performance or quality.
When establishing criteria for evaluation, it is crucial to be thorough yet succinct. Clear criteria enable the reader to understand the basis upon which the evaluation is made, while concise criteria ensure that the evaluation remains focused and impactful.
There are several strategies you can employ to provide clear and concise criteria for evaluation. One approach is to define specific attributes or characteristics that are relevant to the subject being evaluated. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, you might establish criteria such as the quality of the food, the level of service, and the ambience of the establishment.
Another strategy is to utilize a scoring system or rating scale to assess the subject. This can help provide a more quantitative evaluation by assigning numerical values to different aspects of the subject. For instance, a movie review might use a rating scale of 1 to 5 to evaluate the acting, plot, and cinematography of the film.
In addition to defining specific attributes or using a scoring system, it is important to provide examples or evidence to support your evaluation. This can help make your criteria more concrete and relatable to the reader. For instance, if you are evaluating a car, you could provide examples of its fuel efficiency, handling performance, and safety features.
| Clear Criteria | Concise Criteria |
|---|---|
| Define specific attributes | Utilize a scoring system |
| Provide examples or evidence | Ensure focus and impact |
By providing clear and concise criteria for evaluation, you can effectively communicate your assessment to the reader and support your conclusions. This will help ensure that your evaluation essay is well-structured, informative, and persuasive.
Support Your Evaluation with Solid Evidence

When writing an evaluation essay, it is crucial to support your evaluations with solid evidence. Without proper evidence, your evaluation may appear weak and unsubstantiated. By providing strong evidence, you can convince your readers of the validity of your evaluation and make a compelling argument.
One effective way to support your evaluation is by using concrete examples. These examples can be specific instances or cases that illustrate the strengths or weaknesses of the subject being evaluated. By presenting real-life examples, you can provide tangible evidence and make your evaluation more persuasive.
Another way to support your evaluation is by referring to expert opinions or research studies. These external sources can add credibility to your evaluation and demonstrate that your assessment is based on sound knowledge and expertise. Citing respected experts or referencing reputable studies can enhance the validity of your evaluation and make it more convincing.
In addition to concrete examples and expert opinions, statistical data can also be a powerful tool for supporting your evaluation. Numbers and statistics can provide objective evidence and strengthen your evaluation by adding a quantitative dimension to your argument. By citing relevant statistics, you can add weight to your evaluations and demonstrate the magnitude of the subject’s strengths or weaknesses.
Furthermore, it is important to consider counterarguments and address them in your evaluation. By acknowledging opposing viewpoints and addressing them effectively, you can strengthen your own evaluation and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the subject. This approach shows that you have considered different perspectives and have arrived at a well-rounded evaluation.
In conclusion, supporting your evaluation with solid evidence is essential to writing a persuasive evaluation essay. By using concrete examples, expert opinions, statistical data, and addressing counterarguments, you can bolster the validity and strength of your evaluation. Remember to present your evidence clearly and logically, making your evaluation more compelling and convincing to your readers.
Use a Structured Format to Organize Your Essay
When writing an evaluation essay, it is important to use a structured format to organize your thoughts and arguments. This will help you present your ideas in a clear and logical manner, making it easier for your reader to follow along and understand your points. By using a structured format, you can ensure that your essay flows smoothly and effectively communicates your evaluation.
One effective way to structure your evaluation essay is to use a table format. This allows you to present your evaluation criteria and supporting evidence in a concise and organized manner. By using a table, you can easily compare and contrast different aspects of the subject being evaluated, making it easier for your reader to grasp the overall evaluation.
| Aspect | Evaluation Criteria | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Plot | Engaging and well-developed storyline | Strong character development and unexpected plot twists |
| Acting | Convincing and compelling performances | Emotional depth and believable portrayal of characters |
| Visuals | Stunning cinematography and visually appealing scenes | Beautiful set designs and attention to detail |
In addition to using a table format, you should also follow a logical structure within each section of your essay. Start with a clear introduction, where you introduce the subject you are evaluating and provide some background information. Then, present your evaluation criteria and explain why these criteria are important for assessing the subject. Next, provide specific examples and evidence to support your evaluation, using the table format as a guide. Finally, end your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your evaluation and reinforces your main points.
By using a structured format, you can effectively organize your evaluation essay and present your ideas in a clear and concise manner. This will make your essay more engaging and persuasive, and help your reader understand and appreciate your evaluation.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.

19 Evaluation Essay
Evaluative arguments center around the question of quality. Is something good? Bad? Honest? Dishonest? Evaluative judgments are also about values—what the writer thinks is important. Sometimes the writer’s values are not the same as his/her readers’ values, so he/she has to bridge the gap by showing respect for the audience’s opinions and clarifying the points that they do and don’t agree upon.
An important first step in writing an evaluation is to consider the appropriate standards/criteria for evaluating the subject. If a writer is evaluating a car, for example, the writer might consider standard criteria like fuel economy, price, crash ratings. But the writer also might consider style, warranty, color, special options, like sound systems. Even though all people might not base their choice of a car on these secondary criteria, they are still considered acceptable or standard criteria.
To be taken seriously, a writer must have valid reasons for his evaluation. These reasons are based on criteria. Imagine choosing your attire for a job interview at a very prestigious law firm. You look at the jeans and t-shirts in your closet and immediately decide to go shopping. Why? Because the clothes in your closet don’t meet the criteria for the interview.
The Purpose of Evaluative Writing
Writers evaluate arguments in order to present an informed and well-reasoned judgment about a subject. While the evaluation will be based on their opinion, it should not seem opinionated. Instead, it should aim to be reasonable and unbiased. This is achieved through developing a solid judgment, selecting appropriate criteria to evaluate the subject, and providing clear evidence to support the criteria.
Evaluation is a type of writing that has many real-world applications. Anything can be evaluated. For example, evaluations of movies, restaurants, books, and technology ourselves are all real-world evaluations.
Five Characteristics of an Evaluative Essay
by Dr. Karen Palmer
1. Presenting the subject.
Presenting the subject is an often misunderstood aspect of an evaluative essay. Either writers give too little information or too much. Presenting the subject occurs in two different places in the essay.
First, the writer should give a brief introduction of the subject in the introduction of the evaluation. This introduction occurs in the second part of the introduction–the intro to the topic. At this point, the writer should simply name the subject and give a very brief description. For example, a restaurant review should include at a minimum the name and location of the restaurant. An evaluation of a vehicle might include the make, model, and year of the vehicle and any important features.
Second, the writer should give a more detailed description of the subject following the introduction in the background section of the paper. Here the writer could give a more detailed overview of the restaurant (the type of decor, type of food, owners, history), describe the vehicle in detail, etc. Striking a balance between giving the reader the necessary information to understand the evaluation and telling readers everything is important. The amount of detail necessary depends on the topic. If you are reviewing a brand new technology or a machine, specific to your line of work, for example, you will need to give readers more information than if you are simply reviewing a restaurant or a doctor’s office.
The language used in your description can be evaluative. For example, a writer can use descriptive adjectives and adverbs to convey a certain impression of the subject, even before the claim is made.
2. Asserting an overall judgment.
The main point/thesis should be located at the end of the paper’s introduction. It should be definitive—certain, clear, and decisive. Asking a question does not pose a definitive claim. Giving several different perspectives also does not give a definitive claim. It is ok to balance your claim, though, acknowledging weaknesses (or strengths) even as you evaluate a subject positively: “While the Suburban is a gas guzzler, it is the perfect car for a large family….”
Providing a map of your reasons/criteria within the thesis is a great technique for creating organization and focus for your essay. For example, “While the Suburban is a gas guzzler, it is the perfect car for a large family because it can seat up to 9, it has a high safety rating, and it has the best in class towing capacity.” Not only does this example give a clear, balanced claim, but it also lays out the writer’s reasons upfront, creating a map in the reader’s mind that will help him follow the reasoning in the essay.
3. Giving Reasons and Support
After presenting the subject and providing readers with a clear claim, the writer must explain and justify his/her evaluation using reasons that are recognized by readers as appropriate. This occurs in the argument section of the paper and should be the most extensive part of the paper. Reasons should reflect values or standards typical for the subject. If a writer uses criteria that is not typical for the subject, he/she must be prepared to defend that decision in the essay. For example, “Buying local may not always be at the forefront of a buyer’s mind when shopping for eggs, but…” Each reason should be clearly stated as a topic sentence that both states the reason and refers back to the main claim. Going back to the suburban example, a body paragraph/section might begin with the following topic sentence: “One of the obvious reasons a suburban is great for large families is its capacity for holding that large family and all of their necessary traveling items.”
Following the topic sentence, a writer must include relevant examples, quotes, facts, statistics, or personal anecdotes to support the reason. Depending on what the subject is, the support might be different. To support a claim about a book/film, for example, a writer might include a description of a pivotal scene or quotes from the book/film. In contrast, to support a claim about gas mileage, a writer would probably simply give the information from the vehicle specifications. Support can come from a writer’s own knowledge and experience, or from published sources.
4. Counterarguing:
Counterarguing means responding to readers’ objections and questions. In order to effectively counterargue, a writer must have a clear conception of his/her audience. What does the audience already know or believe about the subject? Effective counterarguing builds credibility in the eyes of the audience because it creates a sense that the writer is listening to the reader’s questions and concerns.
Counterarguments can occur at the end of the essay, after the writer has made his/her point, or throughout the essay as the writer anticipates questions or objections. Writers can respond to readers’ objections in two ways. First, a writer can acknowledge an objection and immediately provide a counter-argument, explaining why the objection is not valid. Second, a writer can concede the point, and allow that, the subject does have a flaw. In either case, it is important to be respectful of opposing positions, while still remaining firm to the original claim.
5. Establishing credibility and authority:
A writer’s credibility and authority lead to readers’ confidence in your judgment and their willingness to recognize and acknowledge that credibility and authority. An author can gain credibility by showing that he/she knows a lot about the subject. In addition, the writer shows that his/her judgment is based on valid values and standards.
The writer’s authority is in large part based upon the background of the author—education, etc. Is the author qualified to make a judgment? For some subjects, like a film review, simply watching the film might be enough. In other instances, like evaluating the quality of newly constructed cabinets or the engine of a new car, more experience might be necessary.
The Structure of an Evaluation Essay
Evaluation essays are structured as follows.
First, the essay will present the subject . What is being evaluated? Why? The essay begins with the writer giving any details needed about the subject.
Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria.
The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for evaluating the subject under consideration. Appropriate criteria will help to keep the essay from seeming biased or unreasonable. If authors evaluated the quality of a movie based on the snacks sold at the snack bar, that would make them seem unreasonable, and their evaluation may be disregarded because of it.
The evidence of an evaluation essay consists of the supporting details authors provide based on their judgment of the criteria.
For example, if the subject of an evaluation is a restaurant, a judgment could be “Kay’s Bistro provides an unrivaled experience in fine dining.” Some authors evaluate fine dining restaurants by identifying appropriate criteria in order to rate the establishment’s food quality, service, and atmosphere. The examples are evidence.
Another example of evaluation is literary analysis; judgments may be made about a character in the story based on the character’s actions, characteristics, and past history within the story. The scenes in the story are evidence for why readers have a certain opinion of the character.
Job applications and interviews are more examples of evaluations. Based on certain criteria, management and hiring committees determine which applicants will be considered for an interview and which applicant will be hired.
Example Outline
Thesis: McAdoo’s is a fantastic family restaurant, offering young and old alike a great atmosphere, wonderful customer service, and a fantastic menu.
- Introduction
- Location–New Braunfels, TX
- History–old post office, restored
- Type of food
- Walking up to the restaurant–cool exterior
- Lobby–original post office doors, etc
- Tables–great decor–memorabilia from NB history
- prompt, courteous service
- refills, bread
- taking care of complaints–all you can eat lobster out–so price reduced
- land lovers
- Conclusion…If you’re ever in NB, I highly suggest stopping in at McAdoo’s and absorbing some of the great old world charm with some delicious food.
Possible “Get Started” Idea
- Evaluate a restaurant. What do you expect in a good restaurant? What criteria determine whether a restaurant is good?
- List three criteria that you will use to evaluate a restaurant. Then dine there. Afterward, explain whether or not the restaurant meets each criterion, and include evidence (qualities from the restaurant) that backs your evaluation.
- Give the restaurant a star rating. (5 Stars: Excellent, 4 Stars: Very Good, 3 Stars: Good, 2 Stars: Fair, 1 Star: Poor). Explain why the restaurant earned this star rating.
Suggested Assignment: Time to Write
Purpose: This assignment will demonstrate the understanding of how to do a thorough evaluation of an approved topic. Students will review the complex elements of the topic they have chosen. Evaluative essays call for the writer to assess a subject in light of specific and explicit criteria and to make a judgment based on the assessment.
Task: This assignment evaluates a social phenomenon or work.
Write an Evaluation Essay. For this essay, you will choose a clear topic, give a reason for the evaluation, use description and categorization, create evaluation criteria, use concrete evidence and demonstrate the “why” of your position.
Possible Topics
Some topics to consider are listed here:
- Social media
- Pop music trends
- The regulations on technology use while driving
- The impact of video games
- A film based on a book
- A major literary movement (Harry Potter or The Hunger Games)
- A major sporting event (or the impact of a minor one)
- A movie, T.V. series, or theatrical show
- An art installation
Key Features of an Evaluation:
- Make clear why a particular phenomenon or work needs to be evaluated.
- Describe the particular phenomenon or work in a way that the rhetorical audience will understand and value.
- Identify the precise category into which the phenomenon fits: successful movie, effective detergent, dependable computer, easy-to-use smartphone. Just consider the ways your doctor evaluates your symptoms before determining your illness.
- Present the criteria on which the phenomenon or work is to be evaluated clearly, persuasively, authoritatively, and often in an order indicating importance. Criteria can be categorized into three groups: necessary (crucial but not enough to meet your overall assessment), sufficient (meeting all of your minimum standards, including the necessary ones), and accidental (unnecessary but an added bonus to the necessary and sufficient criteria).
- Include concrete evidence and relevant examples from your personal experience and research illustrate the ways (usually in the form of assertions) the phenomenon does or does not meet each evaluative criterion. These fair and balanced assertions support the thesis statement.
- Articulate a clear argument (usually in the form of a thesis statement) about whether or not the object or phenomenon meets the criteria on which it is being evaluated.
- Demonstrate an ethical approach to the process.
Key Grading Considerations
- A clear reason for the evaluation
- Use of description
- Categorizing
- Clear evaluation criteria
- Concrete evidence & Examples
- A clear argument presented (Thesis)
- The establishment of ethos (balanced argument)
- Secure closure to the argument (conclusion)
- Key Features are included
- One inch margins
- Typed and double-spaced
- The heading is double-spaced on the left side of the page (includes name, my name, class, date)
- Upper right-hand corner has last name and page number (EX: Dewey 1)
- The font is Times New Roman, size 12
- The title is original and is centered one line under the heading
- Descriptive Language
- Correct, appropriate, and varied integration of textual examples, including in-text citations
- Limited errors in spelling, grammar, word order, word usage, sentence structure, and punctuation
- Good use of academic English
- Demonstrates cohesion and flow
Attribution
- Content Adapted from “Five Characteristics of an Evaluative Essay” from The Worry-Free Writer by Dr. Karen Palmer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
- Content Adapted from Susan Wood, “Evaluation Essay,” Leeward CC ENG 100 OER, licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
- Original Content contributed by Christine Jones “Time to Write” licensed under Creative Commons CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication.
ENG101 for Health Sciences Copyright © by Lori Walk; Christine Jones; and Aaron Fried is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Jun 29, 2023
Evaluation Essay Examples: Master the Art of Critical Assessment with Examples and Techniques
Want to turn good evaluation essays into great ones? We've got you covered with the guidance and insights you need. Join us as we delve into the art of critical assessment!
An evaluation paper's main purpose is to assess entities like a book, movie, restaurant, or product and provide constructive criticism. This writing style can be approached with serious objectivity or with humor and sarcasm. Reviewing is a common form of academic writing that serves to assess something and is often used in various fields as a research method. For example, research papers might include literature reviews or case studies, using evaluation as an analytical tool.
Evaluation reports can also take the form of analyses and critiques. A critique of a scientific study would look at its methodology and findings, while an analysis of a novel would focus on its themes, characters, and writing style. It's essential to consider your audience and your purpose before starting an evaluation document.
Evaluation papers are a versatile and meaningful writing form that can both educate and entertain audiences. Regardless of whether the tone is serious or humorous, objective or subjective, a well-written review can engage and educate.
To understand everything about evaluation essays, from their definition and purpose to potential topics and writing tips, read on.
What are Evaluation Essays?
An evaluation essay allows the author to make a claim and offer a verdict on a topic. This essay type can be used to identify the best option among several alternatives, or to analyze a specific method, product, or situation. It is a common academic task across all levels. Evaluation essays come in different forms, from online product reviews to business cases prepared by management professionals.
In contrast to a descriptive essay, an evaluation essay aims to express the author's judgment. However, this essay type is defined by an objective tone. The author's judgment should be based on careful examination of the available evidence. This differs from a persuasive essay, which seeks to convince the reader to adopt the author's point of view. An evaluation essay starts with the facts and forms conclusions based on these facts.
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
To write an effective evaluation essay, follow these essential writing tips:
1. Select a Topic
The essay topic is crucial. It should be both educational and interesting, providing enough information to fill an entire essay.
2. Draft an Evaluation Essay Outline
Professional writers always advise creating an evaluation essay outline before writing the essay itself. This aids in writing and ensures content coherence. An outline is also easier to modify than a complete essay. Think about what should be included and excluded when designing your essay's outline. However, skipping this step and diving straight into the essay writing can create extra work later, as it can mean editing and revising the entire piece.
The general components of an evaluation essay outline include:
a. Introduction
The introduction is vital as it forms the readers' first impression. It should engage readers and arouse their interest in the topic. The aspects to consider when writing the introduction are as follows:
Begin with a compelling hook statement to capture the reader's interest.
Provide background information on the topic for better understanding.
Formulate a clear and concise thesis statement, outlining the main objective of the evaluation.
b. Body Section
The body of the essay consists of three paragraphs. Each paragraph should deliver several related ideas and flow seamlessly from start to finish. The key ideas to cover in the body paragraphs include:
Start with a sentence that presents your view on the topic.
Provide arguments that support the topic sentence and your stance.
Present a well-rounded argument to show impartiality.
Compare the subject to a different topic to showcase its strengths and weaknesses.
Present the evaluation from various angles, applying both approving and critical thinking.
c. Conclusion
This is your final chance to convince the reader of your viewpoint. The conclusion should summarize the essay and present the overall evaluation and final assessment. When composing an evaluation essay's conclusion, keep the following points in mind:
Restate your main points and arguments from the essay body.
Present evidence to support your thesis.
Conclude your argument convincingly, ultimately persuading the reader of your assessment.
3. Review, Edit, and Proofread
The final steps after writing the essay are editing and proofreading. Carefully reading your essay will help identify and correct any unintentional errors. If necessary, review your draft multiple times to ensure no mistakes are present.
Structure of an Evaluation Essay
An evaluation essay, like any good piece of writing, follows a basic structure: an introduction, body, and conclusion. But to make your evaluation essay standout, it's crucial to distinctly outline every segment and explain the process that led you to your final verdict. Here's how to do it:
Introduction
Start strong. Your introduction needs to captivate your readers and compel them to read further. To accomplish this, begin with a clear declaration of purpose. Provide a brief background of the work being evaluated to showcase your expertise on the topic.
Next, rephrase the essay prompt, stating the purpose of your piece. For example, "This essay will critically assess X, utilizing Y standards, and analyzing its pros and cons." This presents your comprehension of the task at hand.
Wrap up your introduction with a thesis statement that clearly outlines the topics to be discussed in the body. This way, you set the stage for the essay's content and direction, sparking curiosity for the main body of the work.
Body of the Essay
Dive deep, but not without preparation. Before delving into the assessment, offer an unbiased overview of the topic being evaluated. This reaffirms your understanding and familiarity with the subject.
Each paragraph of the body should focus on one evaluation criterion, presenting either support or criticism for the point. This structured approach ensures clarity while presenting evidence to substantiate each point. For instance, discussing the benefits of a product, you can outline each advantage and back it up with supporting evidence like customer reviews or scientific studies.
Ensure a smooth flow of thoughts by linking paragraphs with transitional phrases like "in addition," "moreover," and "furthermore." Each paragraph should have a clear topic sentence, explanation, and supporting evidence or examples for easy understanding.
Your conclusion is where you make your final, compelling argument. It should focus on summarizing the points made according to your evaluation criteria. This isn't the place for new information but rather a concise summary of your work.
To conclude effectively, revisit your thesis and check whether it holds up or falls short based on your analysis. This completes the narrative arc and provides a solid stance on the topic. A thoughtful conclusion should consider the potential impact and outcomes of your evaluation, illustrating that your findings are based on the available data and recognizing the potential need for further exploration.
Evaluation Essay Examples
Now that we've covered the structure, let's take a look at some examples. Remember, an evaluation essay is just one type of essay that can be generated using tools like Jenni.ai. This AI-powered software can produce high-quality essays on any topic at impressive speeds. Here are some ideas to kickstart your assessment essay writing journey.
Evaluation Essay: Online Teaching vs. On-campus Teaching
In the face of technological evolution, education has seen a shift in teaching styles, with online learning platforms providing an alternative to traditional on-campus teaching. This essay will evaluate and compare the effectiveness of these two teaching styles, delving into various factors that contribute to their strengths and weaknesses.
The landscape of education has transformed significantly with the advent of online learning. This essay will scrutinize and juxtapose the effectiveness of online teaching against traditional on-campus teaching. The evaluation will take into account numerous factors that contribute to the success of each teaching style, focusing on their individual benefits and drawbacks.
On-campus Teaching
On-campus teaching, the time-tested method of education, has proven its effectiveness repeatedly. The physical classroom setting provides students direct access to their teachers, promoting immediate feedback and real-time interaction. Moreover, the hands-on learning, group discussions, and collaborative projects intrinsic to on-campus teaching cultivate crucial soft skills like communication and teamwork.
A study by the National Bureau of Economic Research reveals that students attending on-campus classes show higher academic performance and are more likely to complete their degrees compared to those in online classes (Bettinger & Loeb, 2017). However, on-campus teaching isn't without its challenges. It offers limited flexibility in scheduling and requires physical attendance, which can be inconvenient for students residing far from campus or those with mobility constraints.
Online Teaching
Online teaching, propelled by technological advancements and digital learning platforms, offers a compelling alternative. The most significant benefit of online teaching is its scheduling flexibility. Students can access classes and course materials from anywhere, at any time, providing a superior balance for work, family, and other commitments.
Online teaching democratizes education by enabling access for students in remote areas or with mobility challenges. The use of innovative teaching methods like interactive multimedia and gamification enhances engagement and enjoyment in learning.
Despite its numerous advantages, online teaching presents its own set of challenges. A major drawback is the lack of direct interaction with teachers and peers, potentially leading to delayed feedback and feelings of isolation. Furthermore, online classes demand a higher degree of self-motivation and discipline, which may be challenging for some students.
Both online teaching and on-campus teaching present their unique benefits and drawbacks. While on-campus teaching fosters direct interaction and immediate feedback, online teaching provides unmatched flexibility and accessibility. The choice between the two often depends on factors such as the course content, learning objectives, and student preferences.
A study by the University of Massachusetts reports that the academic performance of students in online classes is on par with those attending on-campus classes (Allen & Seaman, 2017). Furthermore, online classes are more cost-effective, eliminating the need for physical classrooms and related resources.
In conclusion, while both teaching styles have their merits, the effectiveness of each is heavily dependent on the subject matter, learning objectives, and the individual needs and preferences of students.
Citations: Allen, I. E., & Seaman, J. (2017). Digital learning compass: Distance education enrollment report 2017. Babson Survey Research Group. Bettinger, E., & Loeb, S. (2017). Promises and pitfalls of online education. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity, Spring 2017, 347-384.
Evaluation essay: Analyze how the roles of females and males changed in recent romantic movies
Romantic movies have long been a popular genre, offering a glimpse into the complex and varied world of relationships. Over the years, the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies has evolved significantly. This essay aims to evaluate and analyze how the roles of females and males have changed in recent romantic movies.
Historical Context of Gender Roles in Romantic Movies:
Gender roles have played a significant role in shaping the portrayal of romantic relationships in movies. In the past, traditional gender roles were often reinforced, with women playing the role of the damsel in distress, and men playing the role of the protector and provider.
However, over the years, the feminist movement and other social changes have led to a more nuanced portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies. Women are no longer just passive objects of desire, and men are not just dominant figures. Instead, both genders are portrayed as complex and multifaceted individuals with their desires, needs, and struggles.
Analysis of Recent Romantic Movies:
In recent years, romantic movies have become more diverse and inclusive, featuring a wider range of gender identities, sexual orientations, and cultural backgrounds. As a result, the portrayal of gender roles in these movies has also become more nuanced and complex.
One significant trend in recent romantic movies is the portrayal of female characters as strong, independent, and empowered. Female characters are no longer just passive objects of desire, waiting for the male lead to sweep them off their feet. Instead, they are shown to be capable of taking charge of their own lives, pursuing their goals, and making their own decisions.
For example, in the movie "Crazy Rich Asians," the female lead, Rachel, is portrayed as a strong and independent woman who stands up for herself and refuses to be intimidated by the wealthy and powerful people around her. Similarly, in the movie "The Shape of Water," the female lead, Elisa, is portrayed as a determined and resourceful woman who takes action to rescue the creature she has fallen in love with.
Another trend in recent romantic movies is the portrayal of male characters as vulnerable and emotionally expressive. Male characters are no longer just stoic and unemotional but are shown to have their insecurities, fears, and vulnerabilities.
For example, in the movie "Call Me By Your Name," the male lead, Elio, is shown to be sensitive and emotional, struggling with his feelings for another man. Similarly, in the movie "Moonlight," the male lead, Chiron, is shown to be vulnerable and emotionally expressive, struggling with his identity and his relationships with those around him.
However, while there have been significant changes in the portrayal of gender roles in recent romantic movies, there are still some aspects that remain problematic. For example, female characters are still often portrayed as objects of desire, with their value determined by their physical appearance and sexual appeal. Male characters are still often portrayed as dominant and aggressive, with their masculinity tied to their ability to assert control over others.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the portrayal of gender roles in recent romantic movies has evolved significantly, with female characters being portrayed as strong, independent, and empowered, and male characters being portrayed as vulnerable and emotionally expressive. These changes reflect the shifting social norms and values of our society and offer a more nuanced and complex portrayal of romantic relationships.
However, there are still some problematic aspects of the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies, such as the objectification of female characters and the perpetuation of toxic masculinity. Filmmakers and audiences need to continue to push for greater diversity, inclusivity, and nuance in the portrayal of gender roles in romantic movies so that everyone can see themselves reflected in these stories.
"Crazy Rich Asians" Directed by Jon M. Chu, performances by Constance Wu, Henry Golding, and Michelle
Final Thoughts
The step-by-step guide and examples provided should have equipped you with the skills necessary to write a successful evaluation essay. However, crafting the perfect essay isn't a simple task; it demands practice, patience, and experience.
Incorporate Jenni.ai into your academic journey to revolutionize your writing experience. This advanced AI writing tool is designed to assist with a range of academic writing projects. With Jenni.ai, you can confidently tackle essays on any topic, easing your writing tasks considerably. Don't hesitate to register with Jenni.ai today ! Discover a world of writing opportunities and take your essay writing skills to new heights!
Start Writing With Jenni Today
Sign up for a free Jenni AI account today. Unlock your research potential and experience the difference for yourself. Your journey to academic excellence starts here.
- Essay Guides
- Main Academic Essays
- Evaluation Essay: Writing Guide, Outline & Free Samples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
Evaluation Essay: Writing Guide, Outline & Free Samples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
Are you wondering how to write an evaluation essay? We are here to inspire and let you know all the essential steps to get started. This blog post will describe what is an evaluative essay, including its purpose and elements. In addition, you will be enlightened on how to actually write evaluations - all the necessary factors and steps will be elaborated on. These steps are: deciding what to appraise, what criteria to apply, and how to develop arguments and outlines. Toward the end, you will be provided with evaluation essay samples that will enable you to put theoretical guidelines into practice. Strictly follow this blog post from our essay writer services to the end.
What Is an Evaluation Essay: Definition
The starting point of being well-versed in this from of writing is understanding its definition and purpose, as it will lay a good foundation for further work. Evaluation essay is a paper that offers evidence that helps to justify writer's opinion on different subjects by providing enough facts to convince readers. Such type of writing requires critical thinking skills when analyzing, synthesizing, and assessing given topics to avoid misleading your audience. The main purpose of this type of paper is to provide objective criticism oт various subjects and make conclusions about them. As a result, the latter helps readers to take a stance about a topic. In addition, there is an exhaustive review of fundamental characteristics, styles, and quality of subjects under discussion. The value of a particular topic is obtained through supportive and factual evidence provided. Finally, this paper helps present well-reasoned and informed judgment on particular standards, hence clearing concerning issues about a given subject.
Things You Can Write an Evaluation About
Preparing evaluative essay is a broad topic, and you need to be well-organized, or else the text will quickly lose meaning and purpose. There are various abstract categories and exact things that you can assess in writing. When you write evaluations, ensure you deeply understand your topic of discussion. Reading through an evaluation example will help you know what to do. Some evaluation essay topics and objects suitable for assessment include:
- Experience: gaming, traveling, and shopping.
- Music: its content, the impact, instruments played, and comparison to other works by artists.
- Furniture: chair, desk, stool, table, etc.
- Fruits: guava, mangoes, oranges, pineapples.
- Trees: oak, teak, pine.
- Sports: volleyball, table tennis, golf.
- Clothes: casual wear, sportswear, formalwear.
- Class: methods of teaching , challenges, type of assessments, etc.
- Social trend: origin, overall influence, and objectives.
- Courses: journalism, mathematics, business, and history.
Elements of an Evaluation Essay
Understanding all components of evaluation papers - three in total - is important during writing. They include:
- Criteria In order to determine aspects you will assess about certain brands, services, or products, a proper set of standards is required. Standard helps in demonstrating expectations. During evaluative writing, it is essential to think about some good samples of similar brands, services, or products. Also, contemplate on related significant features. For instance, a house can be well-ventilated, secure, and clean, which are quite helpful benchmarks.
- Judgment A second element in essay evaluation is judgment. This aspect helps to establish if stated standards were met. Considering the previous example of a house discussed under this criteria, you may first assess if the house is secure or not. Find out if the house meets, exceeds, or falls short of your anticipated security standards, then move on to other criteria.
- Evidence This component focuses on providing facts supporting the judgment. For instance, in the house example, if you conclude that security level does not meet the expected standards, provide evidence to prove this judgment. When you structure an evaluation essay, ensure each paragraph discusses a different criterion. It helps you to make judgments and provide evidence under each paragraph.
What to Consider Before Writing an Evaluation
There are two factors to put into consideration before writing evaluations. One of them is ensuring that evaluation argument remains objective. Objectivity is achieved by not including personal opinions in disputes. Besides, one remains objective by supporting claims with relevant facts. Also, included references need to fully support your stand. You should know that a discourse must be balanced and fair. Secondly, deciding on evaluative standards is another important factor to consider. You need to have a deeper understanding of subjects before deciding on measures to use during this analysis. Chosen standards must adequately and appropriately represent particular subjects' features, qualities, and values. Besides, when deciding on evaluation essay criteria, ensure that you focus on defending your stated thesis. In addition, have enough evidence and details to support the chosen criterion. Finally, appropriately organize your facts and make sure you have imperative and unbiased information concerning your subjects of discussion.
Evaluation Essay Outline
A clear outline provides a map of organizing ideas when you write evaluation essay. An evaluation essay outline covers at least five structured paragraphs. The first is an introductory paragraph followed by three or more body paragraphs, and finally, an essay conclusion . Below is an evaluation paper outline example under the topic of practicing vaping.
Introduction
- An introduction presents subjects, hooks readers, and elaborates on topic of evaluation.
- The last part of your introduction is a thesis statement, which asserts arguments, determines focus, and helps understand essays’ gist.
- The body must contain a minimum three paragraphs.
- Each body paragraph needs to have a criterion followed by judgment.
- Support judgments with relevant evidence.
- When concluding, summarize main points.
- Give some food for thought.
Here’s how your evaluation essay outline look:
Introductory paragraph
- Do you know that vaping is a better alternative to smoking? How is it rated?
- Some notable issues with vaping include its safety, cost, and utility.
- This essay discusses vaping while focusing on safety issues, incurred costs, and utility to prove how it is preferred compared to traditional smoking.
Body part
- Safety: According to the British government, vaping is 95% safer when compared to cigarette smoking. Vaping is less harmful. No second-hand smoke is produced during vaping, hence the best smoking alternative.
- Cost: Vaping is cheaper when compared to smoking. The price for a vape pen is almost $20. Coils and E-juice are inexpensive, unlike a cigarette carton, and can last twice longer.
- Utility: From environmental health, vaping has high utility. Many places have banned cigarette smoking; thus, vaping is the best alternative. Indoors and outdoor vaping is allowed, unlike cigarette smoking, which is banned indoors.
Concluding paragraph
- Vaping offers the best smoking alternative. It is of high quality, and people need to embrace it. Also, it is less costly, practical, and safer.
How to Start an Evaluation Essay
There are various steps that one can follow when writing an evaluation essay. These steps include:
- Choosing a topic A topic provides credibility for opinions and gives room for a thorough analysis of essential issues. Always start an evaluation essay by choosing an appropriate subject. You must be familiar with and have in-depth knowledge of a chosen theme to avoid misleading and losing readers. Ensure it is well-engaging for both the readers and you.
- Thesis statement development Coming up with a thesis statement is the second step, actual writing starts here. Thesis statements define main purposes of evaluative essays. Besides, they offer directions for distinguishing criteria from the examples provided. Use only relevant information when writing thesis statements.
- Criteria determination A third step to consider when preparing evaluation is thinking about criteria. Assess if evaluating a chosen topic is difficult or easy. In case of problematic topics, subdivide them into various points to make it easier.
- Conduct research and obtain supportive evidence You need to support your opinion with logical and physical facts, or else it will remain invalid. Your readers must make sense of your proof and have opportunities to use those facts to make their assumptions. After this step, you can start composing your essay.
How to Write an Evaluation Essay
Several steps exist that one can follow during evaluative writing. The first step in how to write an evaluation is to decide on a particular subject you wish to assess, followed by coming up with criteria you will use. Besides, develop solid arguments backed up with evidence. Also, create an outline, and start writing. Once you complete your writing, proofread your work. The steps below describe the chronological order of writing your essay.
1. Decide on What You Want to Evaluate
The first step when writing this essay is deciding on a topic you will assess. During writing to evaluate, choose a subject you understand better so that you have enough facts to support or oppose it. The chosen issue needs to be engaging to your readers, otherwise yo may lose your audience. Besides, when selecting a theme, ensure it is interesting in general to avoid boredom. Also, a chosen subject needs to be relevant to keep the readers informed about current trends and new developments. The majority of your audience must be aware of the concept. Always ensure that chosen topics are specific and not generic.
2. Find Criteria for Evaluation Essay
Once you discuss a subject, you must come up with criteria for essay evaluation. At this point, turn your opinions into assessments to help you define a chosen subject. You may use different ways to find criteria on how to do an evaluation paper. For instance, you can focus on a chosen characteristics of a topic to help you develop standards. Besides, you might assess the relevance of that topic and decide whether it is good or bad for your readers. Also, focusing on the impacts of subjects helps find standards when evaluating. Researching positive or negative impacts of the topic helps in mastering what and how to evaluate in an essay. Also, you may find criteria by focusing on the effectiveness of that subject, whether it is successful or not. Apart from that, one may focus on the morals or aesthetic standards of a particular subject to develop measures to discuss.
3. Come Up With an Evaluation Argument
Reader understands your decision by following the argument. Evaluative arguments refer to claims concerning the quality of particular subjects being assessed. This argument will always rate subjects as either negative or positive. With this rating, one can think of subjects as harmful or helpful, bad or good. An argument in evaluation essay defines and supports criteria. A judgment always elaborates and explains reasons for choosing particular standards despite controversy. Evaluation argument essay assesses subjects depending on chosen measures. Considered factors include practicability, aesthetics, and ethics. Make sure to determine which standards will convince your audience. Effective development of arguments starts by creating an evaluative thesis statement: take position, develop criteria, and find out if topic meets standards. For instance, when evaluating meal’s quality, you may say:
Meal’s strength depended on its presentation, it was enticing, and its outlook was appropriate.
Another example could be:
Meal’s weakness was in overcooking, as its flavor became less pronounced.
Additionally, another example of a subject could be practicing vaping. In such case, an evaluation argument example will be:
Vaping is safe, inexpensive, and highly practical when compared to cigarette smoking, and due to these reasons, it is a recommendable practice for traditional smokers who wish to break old habits.
4. Create an Evaluative Essay Outline
After choosing a discussion topic, one can create an outline for essay . Outlines start with the development of thesis statements, followed by a list of main ideas and a conclusion. For this essay type, outlines require a minimum of five paragraphs. The first paragraph of the evaluation in writing is introduction that ends with a thesis statement. An introduction is followed by at least three body paragraphs and a conclusion. Outlines are important as they form a basis for thoughtfully constructing ideas. Also, they help in organizing your points sequentially for them to remain orderly. In addition, they are useful in picking relevant information, providing steady foundation when starting to write. Thus, it is worth noting that outlines form a crucial part of these essays, and they give a sketch of writing.
5. Write an Evaluation Paper
When you write evaluative papers, ensure you follow everything stated in your outline. The sections discussed below will help you understand how to write evaluation:
- Introduction When writing your introductory paragraph, ensure it engages you and your readers. Introduce subjects by capturing the reader’s attention. Elaborate on selected subjects, their influence, and reasons for assessing those topics. Be clear with chosen criteria you will be discussing. Generally, when writing your introductory paragraph, provide your entire subject overview.
- Thesis statement The last sentence of an introduction is a thesis statement. It tells your readers what they should expect from evaluation essay and its purpose. Include evaluative arguments that rate subjects either positive or negative with supportive facts. A good evaluation thesis example must include all the stated parts.
- Body A body is commonly the lengthiest part in this type of writing. You must develop a minimum of three body paragraphs in your evaluation paper. When writing body paragraphs, always use transition words while moving from a thesis statement to the first reason and other successive reasons. During evaluate writing, all body paragraphs must start with topic sentences, which inform your reader about your opinion. After stating topic sentences, write your criteria. A criterion will elaborate on the standards of a topic you are discussing. When you are done with it, provide judgments. Judgments must elaborate whether the standards of subjects were met or not. Thereafter, provide evidence supporting your argument. Following that, mention any objections about your judgment, then finalize by refuting those claims. Repeat all these steps for each body paragraph. Ensure you remain relevant in all the paragraphs to avoid losing your readers.
- Conclusion A conclusion is the final evaluation paragraph. When concluding, start by restating your thesis statement and follow by summarizing and reflecting on major points.
6. Proofread Your Evaluation Essay
When you complete your evaluation writing, the last step is proofreading and revising your work. Reading through your work helps improve your paper's quality and remove mistakes. Besides, it enables you to locate and correct inconsistencies in your text. Also, when you edit your work, you ensure that the ideas of your paper are well-defined. Revising your work helps in assessing if the content was appropriately conveyed. Also, it guarantees that sentences are grammatically appropriate by correcting typing and spelling errors to avoid readers’ confusion. Finally, you should read through your work critically and develop better ways of improving clarity, good structure of sentences, and entire effectiveness.
Evaluative Essay Structure
There are various examples of evaluation essays format. These formats include:
- Chronological structure It is used when describing events based on how they happened in an orderly manner, starting from the earliest to the last, like when evaluating current or historical events. Chronological essay structures are more descriptive because they are detailed.
- Spatial structure In contrast to previous type, this one is used when presenting details of particular subjects depending on their location in space. A spatial essay form is used when describing an item like architecture or art depending on how they appear when observed. Something else that people need to understand is that it is easy to remember a spatial essay structure because physical location is used when describing subjects.
- Compare and contrast structure Compare structure is used when exploring existing similarities between subjects, while contrast structure exists for discussing differences between items. Mostly, subjects discussed in compare and contrast papers fall under the same category; however, there may exist exceptions to this rule.
- Point-by-point format structure This is a subtype of compare and contrast essay that provides a general view of individual items being analyzed. This essay type compares a set of subjects because paragraph arrangement depends on main points and not by topic. Each paragraph discusses the main point and include subjects as they relate to each main point.
Evaluation Essay Example
There are millions of evaluative essays samples posted online. These examples offer impressive descriptions of evaluative essays with all the key steps to follow and will help you polish your skills when writing this paper. However, not all of the examples posted online are reliable. Therefore, the only preferred evaluation essay sample that students can use must come from peer-reviewed sources. Essay types from scholarly sites are written by reputable authors who meet all required standards; moreover, you can easily find an excellent book on this subject with appropriate examples. Attached are evaluation essays samples from credible writers.
Tips on How to Write Evaluation Essay
For one to write perfect essays, there are some helpful tips you may follow. Following these points will help you produce impressive evaluation and your readers will enjoy. Some of those tips when writing an evaluation essay include:
- Carefully read certain materials while making notes and analyzing content.
- Read through each paragraph before transitioning to another section.
- Avoid leaving out negative aspects, but try to discuss both pros and cons of your subjects.
- When reading other’s evaluative essay, analyze each paragraph and notice the authors’ mistakes: is information helpful? what can you do better?
- Avoid adding minor details with insufficient supportive evidence, as they will mislead you and your readers.
- Express your thoughts concisely and clearly as you peruse the written evaluation examples.
- Ensure that your evaluation essay thesis is anchored to your judgment.
- Write your paper with precision and attention to details while avoiding wordiness and providing enough useful information as you keenly follow the guide.
- Enable your readers to feel and agree with your assessment.
Bottom Line on Writing Evaluation Essays
Understanding the text’s definition and purpose is your first step toward knowing how to write a good evaluation. Thereafter, list categories and respective things you will assess during your writing. Master the three elements of an evaluative essay and use them effectively. Your argument must be objective and help clearly decide on what criteria to use. Besides, you need to understand all sections of an outline, how to start evaluative essay, and then, follow essential steps. In addition, get acquainted with the four types of essay structure. Remember that you always can increase your experience by reading some good evaluative writing examples. Keep all these tips in mind to ensure you write a proper essay.
Contact Studycrumb and order essays online from professional writers. From topic research to writing and formatting, our experts can do everything from A to Z.
FAQ About Evaluation Papers
1. what are the four components of an evaluation essay.
- Introduction is the first component of evaluation essay that hooks readers, introduces the subject, and contains thesis statement.
- Background information is the second component; it clarifies to readers your evaluation topic.
- Criteria is the third component, which entails standards for evaluating subjects.
- Conclusion is the fourth component; it restates your thesis statements and summarizes main points.
2. What to write in an evaluation essay?
There are numerous things that one can consider during essay evaluations. Evaluation writing examples and their respective criteria include:
- Movies: A plot, relationship among actors, and scenes.
- Restaurants: Quality of food, price, and cleanliness.
- Websites: Type of content, its design, and ease of navigating.
- House: Overall quality, accessibility, and cost.
- Business: Market share, its strengths and weaknesses.
- Social trend: Origin, overall influence, and objectives.
- Leader: Overall achievements, style of leadership, integrity.
- University: Offered programs, number of graduates per year, online or in-person, reputation.
- Class: Methods of teaching, challenges, type of assessments.
- Job: Nature of work, working hours, bosses, salary, demand.
- Advertisement: Media used when advertising, effectiveness, level of convincing, level of engagement.
- Speech: Type of audience, main purpose, compelling.
3. What is the difference between an evaluation and review?
Despite similarities existing between an evaluation essay and a review, the two differ. An evaluative essay focuses on deeper research and analysis of certain subjects, while a review provides a general outlook of particular subjects. Evaluative essays must have criteria that judge specific subjects, and reviews do not need criteria. In addition, under certain conditions, it is mandatory to cite sources used in writing evaluative essays, while reviews do not require references.
4. What is a good evaluative thesis example?
A good evaluative thesis must inform readers what to expect and its impact and determine an essay’s focus. Also, a strong thesis must state evaluative arguments. Here is a proper evaluation essay thesis example: Vaping is highly practical, inexpensive, and safe compared to cigarette smoking, and following these reasons, it is a recommendable practice for traditional smokers wishing to leave old habits.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

- How to Order
Evaluation Essay
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
13 min read

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Are you unsure about what it takes to evaluate things from your perspective in an evaluation essay?
If you’re having a hard time understanding how to present a balanced assessment of the subject, worry not! We are here to help you get through the evaluation essay writing process.
In this blog, you will learn all about evaluation essays. From the definition, writing process, topics, tips, and a lot more, you’ll learn how to write an evaluation essay effortlessly!
Continue reading to get a better idea.
- 1. What is an Evaluation Essay?
- 2. Evaluation Essay Structure
- 3. How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
- 4. How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
- 5. How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
- 6. Evaluation Essay Examples
- 7. Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
- 8. Evaluation Essay vs. Review
What is an Evaluation Essay?
Let’s first understand the evaluation essay meaning, here is the standard definition:
An evaluation essay offers a value judgment or an opinion of something. It presents an overall view of a particular subject’s quality. Moreover, it provides a critical analysis and a complete evaluation of something.
What is the Purpose of an Evaluation Essay?
The main purpose of an evaluation essay is to present an opinion and evaluate a topic critically. This type of writing determines the condition, worth, or significance by careful appraisal and study.
This essay features the writer’s opinion, but when done correctly, it does not sound opinionated. Instead, it provides the facts and evidence to justify the opinions about the essay’s subject.
To write a good evaluation essay, you need to master critical evaluation and present the evaluation in an unbiased manner. You may also discuss both the pros and cons of the subject.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job
Evaluation Essay Structure
The four different ways to format and organize the evaluation essay are as follows.
1. Chronological Structure
It is a sequential organization that could be used for evaluating historical or current events. It tells how something works and assesses the effectiveness of a mechanism, procedure, or process.
2. Spatial Structure
The spatial organization structure is used for evaluating or describing art or architecture. Here, you will define one element of the artifact and spatially move to the next.
3. Compare and Contrast Structure
The compare and contrast structure is used to evaluate or review the culinary or music genre. Here the writer evaluates a subject by comprising and contrasting it with the known subject.
4. Point-by-Point Structure
The point-by-point structure is also used for culinary and music reviews. But, in this structure, you describe one element and then evaluate it, describe the second element and evaluate it, and so on.
After setting the criteria and collecting evidence for strengthening your judgment, you’ll start your evaluation essay. Let’s see what are the steps involved in starting an evaluation essay.
How to Start an Evaluation Essay?
When you start writing an evaluation essay, grabbing the reader’s attention is essential. For this, hook the reader from the beginning until the end to ensure that your essay’s opening follows an engaging tone.
Step 1. Choose an Interesting Topic
Deciding the topic and evaluation essay criteria is important. Make sure it's not just compelling and interesting, but also informative so that you can find enough material for a detailed evaluation.
Step 2. Set the Evaluation Essay Criteria
For an evaluation essay, you have to set the criteria for evaluation first. Criteria are the standards or measures by which someone assesses the quality or value of the subject.
Some key points to establish the criteria are:
- Identifying relevant aspects that relate to the subject
- Defining the criteria clearly so that it is specific and understandable for readers
- Your criteria should be directly relevant to the nature of the subject
- Always consider the audience’s expectations and standards while setting the criteria
- Your thesis statement should always align with your evaluation criteria
Step 3. Collect Evidence for Your Judgment
The author’s judgment of the subject states whether the subject is good or bad. It is an overall assessment or the opinion supported by the evidence. The judgment corresponds to the benchmarks set by the author in the essay criteria.
The evidence is a combination of supporting data and facts. Using the evidence, the author demonstrates how well the subject meets the judgment. The evidence serves as the foundation of your evaluation.
Without providing strong and accurate evidence, you will not be able to convince the readers of your judgment.
Step 4. Decide the Essay Structure
After that, decide on the structure that you want to follow. It can be a chronological or point-by-point structure
Step 5. Craft the Essay Outline
When you create an essay outline , evaluate what should be added and removed. If you skip this step before writing, you may lose track of what to include in your essay while you write.
So, writing an outline for your evaluation essay is a critical step that eases your writing journey.
Here is a sample evaluation essay outline:
|
Step 6. Declare Your Thesis Statement
For an evaluation essay that keeps the reader hooked from the start, opt for a catchy thesis statement . The thesis should state the main point of the evaluation.
In the thesis statement, you should always express your stance on the subject clearly. In doing so, the readers will have a clear idea about the purpose and direction of your essay.
Now, understand how to write an evaluation essay by following the detailed procedure mentioned below.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Write an Evaluation Essay?
Here is a step-by-step guide for you to write an evaluation essay.
Step 1. Write the Introduction
The introduction is the first impression your readers will have of you, so it's crucial to make a good one. It should capture attention and excite readers, drawing them into what you have to say about this topic.
The following are the elements that you should consider while writing the introduction:
- Start with an interesting hook statement so that you can get the reader’s attention.
- Provide background information about the topic for the reader to understand the subject
- Establish the evaluation essay thesis statement. It sets out the overall purpose of the evaluation, so make sure it is apparent and to the point
Read this evaluation essay introduction example, and you’ll understand exactly what to pen down in yours:
|
Step 2. Draft the Body Section
The body of the essay consists of three paragraphs. Each paragraph holds different ideas related to one another and flows smoothly from start to finish, just like how a good story should be told.
Here are the important points that must be included in the body paragraphs.
- Start with the topic sentence that presents your judgment about the topic
- Present the supporting evidence to back up the topic sentence and your viewpoint.
- Present a balanced evaluative argument to show impartiality
- Compare and contrast the subject to another subject to show the strengths and weaknesses
- Present the evaluation from multiple perspectives, while being both positive and critical
- Always use transition words between your paragraphs to ensure a smooth and coherent flow for the reader.
Step 3. Write the Conclusion
It is the final chance to convince your reader to agree with your point of view. You’re supposed to summarize and conclude the essay. In the conclusion , you present your final evaluation of the essay.
Keep in mind the following aspects while writing a closing paragraph of an evaluation essay.
- Summarize the points and evaluative arguments that you made in the body section.
- Justify your thesis statement.
- Provide a concrete and secure conclusion to your argument by ultimately leaving the reader convinced by your evaluation.
Step 4. Proofread, Revise, and Edit
The final step is proofreading and editing. Always spend enough time reading your essay carefully. It will help you catch the unintentional mistakes you have made and recover them. If needed, you can also revise your essay 2–3 times.
How to Format Your Evaluation Essay?
For formatting your evaluation essay, follow the standard academic writing guidelines. You can opt for different formatting styles like APA, MLA, or Chicago.
In general, you should stick to the below formatting guidelines:
Font and Size:
- Use a legible font such as Times New Roman or Arial.
- Choose a standard font size, often 12-point.
- Set one-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Double-space the entire essay, including the title, headings, and body paragraphs.
- Create a title for your essay that reflects the subject and purpose of the evaluation.
- Center the title on the page.
- Use title case (capitalize the first letter of each major word).
- Include a header with your last name and page number in the top right corner.
- Follow the format “Last Name Page Number” (e.g., “Smith 1”).
Citations (if applicable):
- Include citations for any sources used in your evaluation.
- Follow the citation style specified by your instructor or the required style guide (APA, MLA, Chicago).
Counterargument (if included):
- Clearly label and present any counterargument.
- Provide a well-reasoned response to the counterargument.
References or Works Cited Page (if applicable):
- Include a separate page for references or a works cited page if your essay includes citations.
- List all sources in the appropriate citation style.
Well, the time has come to look at some great evaluation essay examples. Getting help from sample essays is always a great way to perfect your evaluation papers.
Evaluation Essay Examples
Evaluation can be written on any topic, i.e., book, movie, music, etc. Below, we have given some evaluation essay examples for students:
Evaluation Essay Sample PDF
Movie Evaluation Essay Example
Critical evaluation Essay Example PDF
Product Evaluation Essay PDF
Source Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Employee Self-Evaluation Essay Example
How to Start A Self-Evaluation Essay Example PDF
Evaluation Essay Topics For College Students
For writing an amazing evaluation essay, the first thing that you require is an essay topic. Here are some incredible topic ideas for college students. You can use or mold them according to your preference.
- Artificial intelligence's impact on society: A double-edged sword?
- Evaluate the online teaching and on-campus teaching styles
- Analyze and evaluate the Real Madrid football team and their performance
- Is media a threat to cultural cohesion or a source of enrichment?
- Compare and evaluate recorded music and live performance
- Evaluate how a university's football team impacts students' personalities
- Critically evaluate a remake of an original movie you have watched recently
- Analyze how the roles of females and males changed in recent romantic movies
- Evaluate your favorite restaurant, its food, aroma, and everything
- Critically evaluate gender disparities in college majors and career choices.
Evaluation Essay vs. Review
At first glance, an evaluation essay might look like a review. But, there are some notable differences between them. See this table to see how both pieces of writing differ from each other.
|
|
|
| Assess and judge based on criteria. | Inform and express personal opinions. |
| Analysis, assessment, and judgment. | Personal opinions and subjective responses. |
| Formal and objective. | Informal and subjective. |
| Specific criteria for assessment. | May include personal preferences. |
| Concrete evidence and examples. | Personal anecdotes and impressions. |
| Structured with clear organization. | Can be more flexible. |
| Persuade based on objective analysis. | Persuade through personal opinions. |
| Summarize key points and overall judgment. | Summarize opinions and recommendations. |
| May include academic sources. | Primarily reflects personal experiences. |
| Varies based on subject complexity. | Varies, from short to longer, based on the platform. |
To conclude,
After reading the step-by-step guide and examples, you must have learned the art of writing a good evaluation essay. We’re confident that you’re now able to provide a balanced and effective evaluation of the topics you choose for your essay.
But writing a perfect essay is not that simple; you require a lot of practice and experience to become a good writer. That is why we are here to help you write any type of academic essay.
MyPerfectWords.com is a writing service that offers help for all academic writing assignments. We have a team of professional writers who are experts in writing all types of essays and evaluation papers.
So what are you waiting for? Buy custom essay online and have a sigh of relief!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. what are the four components of an evaluation essay.
The four components of an evaluation essay are:
- Introduction
- Background information
2. What are the 4 types of evaluation?
The four types of evaluation are:

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Grader
- Reference Finder
- AI Outline Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Text Editing Tools
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Article Spinner
- AI Grammar Checker
- Spell Checker
- PDF Spell Check
- Paragraph Checker
- Free AI Essay Writer
- Paraphraser
- Grammar Checker
- Citation Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites
- Essay Checkers
- Essay Topic Finders
Most Popular
Tips for college freshmen: from social life to studying.
12 days ago
How to Write a Song Title in an Essay
Demure tiktok trend explained: what it is and why it’s going viral, college dorm checklist must-have things to take with you, wonder summary, how to write an evaluation essay.

All students involved in academic writing sooner or later come across various essay genres, each with the challenges they present but also with potential and opportunities for growth. Somewhere halfway along this range, you’ll find an essay style that requires a keen eye, critical thinking skills, and judgment: the evaluation essay. What seems difficult at first, later becomes an easy routine task. All you need to know is the essay’s core elements, subject, judgment, criteria, evidence, and a few tips on how to put them together.
📝 What’s an Evaluation Essay?
There is a simple way to explain what an evaluation essay is. It resembles giving your opinion about something but with a twist. Just saying if something’s good or bad isn’t enough – you need to elaborate and clarify why you say something, believe in something, or convince someone about something. Think of it as a way to analyze and critique a movie, a book, or even a restaurant you love. Or hate, it doesn’t matter. But instead of just saying, “I liked it,” or “It stunk,” you’re explaining and providing arguments.
Along with traditional introduction and conclusion that go without saying, every evaluation essay contains several essential components: criteria, judgments, evidence, counterarguing, and credibility. Let us take a closer look at these components and how they work together and contribute to a well-balanced, convincing evaluation essay.
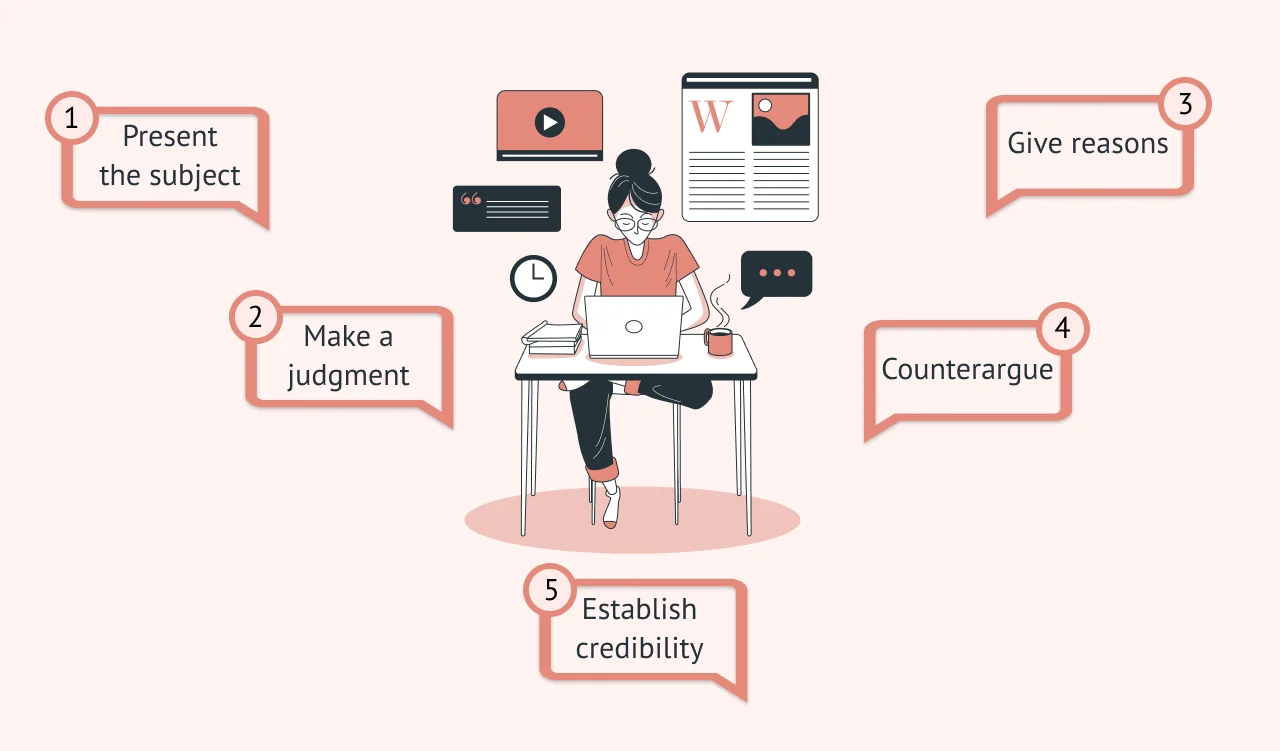
Presenting the subject
Imagine you’re introducing a friend to a new movie. You’d start by telling them what it’s about, who’s in it, and maybe where it takes place. In an evaluation essay, you do the same thing. You give your readers all the necessary background info so they already get some picture and basic understanding of what you’re talking about. For example, if you’re evaluating a restaurant, you’d describe its ambiance, the type of cuisine it serves, its location, and maybe price range.
Asserting an overall judgment
After you’ve given the subject, it’s time to share your prevailing opinion. This is where you say if it’s good, bad, or somewhere in between. But remember, it’s not enough to just say, “I loved it” or “It was nothing to write home about.” You need to explain why you feel that way, and what created those favorable or displeasing impressions. Maybe the movie had great acting but a weak plot, or the book was well-written but had unlikeable characters. Whatever your judgment, make sure you back it up with reasons.
Giving reasons and support
You don’t just throw out your opinion and leave it hanging. You back it up with reasons and evidence. This could be examples, facts, or even personal experiences. Going back to the restaurant example, if you say the food was amazing, you might explain how flavorful the food was, or mention specific dishes that stood out to you. Providing substantial evidence helps strengthen your evaluation and makes your argument more convincing.
Counterarguing
Overwhelmingly agreeing with oneself may seem overly subjective and, as a result, reduce the level of trust and credibility of the statement in your essay. You also consider other viewpoints and argue against them. This shows that you’ve considered different perspectives and strengthens your argument by addressing potential objections upfront. For instance, if someone argues that the restaurant you’re evaluating is overpriced, you might counter by pointing out the high quality of ingredients or the exceptional service as reasons why the prices are justified.
Establishing credibility and authority
You want your readers to trust what you’re saying. So, you need to show them why you’re a reliable source. Maybe you’re an expert on the topic, or you’ve done thorough research. Either way, you make sure your readers know they can trust you. This might involve citing sources, providing background information on your expertise, or demonstrating your firsthand experience with the subject matter. Show them your restaurant review on Yelp with dozens of likes and approving comments! By establishing credibility and authority, you improve the persuasiveness of your evaluation essay.
📝 How to Write an Evaluation Essay
Now that we’ve explored the concept and covered the basics, it’s time to roll up our sleeves and get closer to the nitty-gritty of actually writing an evaluative essay. At AcademicHelp we’ve been there not once, not twice, and will guide you through each step of the process with clarity and confidence.
Describe the evaluation criteria
Before you can begin writing, you need to establish the criteria by which you’ll be evaluating your subject. They should be like the lenses through which you’ll examine the subject’s various aspects. Are you evaluating a movie? Consider criteria like plot, cast, acting, cinematography, music, and overall impact. Assessing a restaurant? Look at criteria such as food quality, service, atmosphere, and value for money. Take some time to brainstorm and define your criteria before starting the writing process.
Write a plan
Once you have your criteria ready to be applied, it’s time to map out your essay. Start by outlining the main points you’ll cover in each body paragraph, based on the criteria you’ve established. Think about the order in which you want to present your arguments and how you’ll transition between them. A well-thought-out plan should be like a roadmap for your essay, keeping you on track and maintaining a logical flow of ideas, not letting your thoughts drift away elsewhere.

Write an evaluation essay
With your plan in hand, it’s time to start writing! Begin with a strong introduction that grabs your readers’ attention and states the purpose of your evaluation. Then, move on to the body paragraphs. Each has to focus on a different aspect of the subject and follow the structure we outlined earlier: subject, judgment, criteria, and evidence. Make sure to provide clear and compelling reasons to support your opinion and tie everything together with a cohesive conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Write a conclusion
You’re almost there. In your conclusion, summarize the main points of your essay and reiterate your overall judgment. Reflect on the significance of your evaluation and its implications for the subject. Give your readers something to think about—a thought-provoking question, a call to action, or a concluding idea that links all sections of your essay like a thread.
Review the finished essay
Before you submit the paper, take a moment to review and revise your essay. Check for any grammatical errors, typos, or awkward phrasings that might distract from your argument. Make sure your essay flows smoothly from start to finish and that your ideas are well-supported by evidence. And don’t forget to double-check that you’ve addressed all aspects of the evaluation criteria you established earlier. Once you’re satisfied with your paper, pat yourself on the back for a job well done, and send it off into the world with confidence.
📈 Evaluative Thesis Grading Criteria
We may believe we’ve learned enough about writing an evaluation essay from the perspective of authorship. The topic is chosen, thoughts are developed, and the structure is established. It looks like all essential elements for success are in place. However, doubts and unsettling questions often remain, such as “Have all aspects been considered?” or “How can I avoid overlooking anything?” Additionally, there’s uncertainty about what should be omitted from the essay. Understanding the areas where teachers focus when assessing such essays can assist in double-checking your work. Frequently, elements that might seem inconspicuous to the author are the first flaws that the professor notices.
When grading an evaluation essay, instructors typically look for several key criteria to assess the quality of the student’s work. Look at your paper again a day or two after you’ve written it, and make sure it checks all the boxes. Here are some criteria used to grade an evaluation thesis:
☑️ Clarity and Coherence :
Is the essay well-organized and easy to follow? Are the ideas presented logically and coherently? Clarity in expression and coherence in structure are fundamental for effective communication.
☑️ Thesis Statement :
Does the essay have a clear and concise thesis statement that presents the overall judgment or evaluation of the subject? The thesis statement should be prominently stated in the introduction and guide the reader throughout the essay.
☑️ Use of Evidence :
Are the judgments and evaluations supported by relevant and convincing evidence? Students should provide specific examples, facts, and arguments to justify their assessments and demonstrate critical thinking skills.
☑️ Depth of Analysis :
Does the essay provide insightful analysis and thoughtful commentary on the subject? Grading criteria often include the depth of analysis, examining how well students engage with the nuances of the subject and demonstrate a deeper understanding of its complexities.
☑️ Critical Thinking Skills :
Does the student demonstrate critical thinking skills by considering alternative viewpoints, anticipating counterarguments, and addressing them effectively? Teachers look for evidence of analytical thinking and the ability to evaluate evidence objectively.
☑️ Use of Language and Style :
Is the essay written in clear, concise, and engaging language? Are grammar, punctuation, and spelling used correctly? Additionally, does the student demonstrate a mastery of academic writing conventions and adhere to the guidelines provided?
☑️ Originality and Insight :
Does the essay offer original insights or perspectives on the subject? Grading criteria may include the student’s ability to offer fresh perspectives or innovative interpretations that contribute to the discourse on the topic.
☑️ Compliance with Instructions :
Does the essay fulfill the requirements and guidelines provided by the instructor? This includes meeting the specified word count, formatting guidelines, and any other instructions outlined for the assignment.
You now have all you need to know about writing an excellent evaluation essay. It is important to remember that, while creativity is always an inspiration when it comes to writing, we must also consider what type of essay we are workin on, what its purpose is, and who its intended audience is. By balancing all of this and following the right steps at each level, you will be successful with your assessment thesis.
What are the 5 key features of an evaluation essay?
The five key features of an evaluation essay are:
- Presenting the subject: Introduce the topic or subject being evaluated.
- Asserting an overall judgment: Share your overall opinion or assessment of the subject.
- Providing reasons and support: Back up your judgment with evidence, examples, and reasoning.
- Counterarguing: Consider and address alternative viewpoints or potential objections.
- Establishing credibility and authority: Show why your evaluation is reliable and trustworthy.
How do you start a written evaluation?
To start a written evaluation, begin with a clear introduction that introduces the subject, provides context, and states the purpose of the evaluation. Hook your readers’ interest with an engaging opening statement or question. Then, present your thesis statement, which summarizes your overall judgment or assessment of the subject.
What is the structure of a critically evaluated essay?
A critically evaluated essay typically follows a structure similar to other types of evaluation essays. It consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. In the body paragraphs, you critically analyze the subject by examining its strengths and weaknesses, considering different perspectives, and evaluating the evidence. Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the subject and include critical analysis supported by evidence.
What is the format of an evaluation?
The format of an evaluation essay typically includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction provides background information on the subject and states the purpose of the evaluation. Body paragraphs present the evaluation criteria, judgments, and supporting evidence. The conclusion summarizes the main points and restates the overall judgment.
What are good evaluation essay topics?
Good evaluation essay topics cover a wide range of subjects and can include anything that can be critically analyzed or assessed. Some examples of evaluation essay topics include:
- Evaluating a movie, book, or TV show
- Assessing the effectiveness of a product or service
- Critically analyzing a piece of artwork or music
- Evaluating a restaurant, café, or food truck
- Assessing the impact of a social media platform or technology
- Critically evaluating a current event or social issue
- Assessing the performance of a sports team or athlete
- Evaluating a school curriculum or educational program
- Critically analyzing a historical event or figure
- Assessing the environmental impact of a company or industry.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Comments are closed.
More from Writing an Essay

How To Write A Literary Analysis Essay
10 min read
Nov 21 2012
Writing an Analysis Essay

Nov 16 2012
How to Write a Reflective Essay
Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
How to Write an Evaluation Essay (Evaluation Essay Examples Included)
Mar 3, 2024 | 0 comments

Mar 3, 2024 | Blog | 0 comments
What does evaluation mean in an essay? Evaluation in an essay refers to the process of critically assessing, analyzing, and judging the effectiveness, quality, or significance of a particular subject, topic, or argument.
Evaluation essays are a common assignment given to students in academic settings. These essays require the writer to critically analyze a subject or topic and form an opinion or judgment based on specific criteria. Evaluation essay writing can be challenging, as it requires a comprehensive understanding of the topic, the ability to gather evidence and examples, and the skill to present a well-structured argument. This article will explore the key components of writing an evaluation essay and provide examples to illustrate the process. From choosing a topic to conducting research, formulating a thesis statement, and organizing the essay, we will cover everything you need to know to write a successful evaluation essay. By the end of this article, you will clearly understand how to approach and execute an evaluation essay, with real-life examples to guide you along the way.
Table of Contents
People Also Read
- How to Write a Proposal Essay (Proposal Essay Examples Included)
- How to Write an Exemplification Essay | Tips and Examples
- The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Reflective Essay: Format, Tips and 5 Examples
What is an Evaluation Essay?
Evaluation Essay is a type of writing that assesses and judges something based on criteria. This type of essay requires the writer to analyze and evaluate a particular subject, such as a book, movie, restaurant, or product. The purpose of an evaluation essay is to provide an in-depth analysis and judgment of the chosen topic. The writer must present both the positive and negative aspects of the subject, supported by evidence and examples. Evaluation essays can be subjective, based on the writer’s opinion, or objective, relying on facts and data to support the evaluation.
Parts of the Evaluation Essay
- Introduction: The introduction of your evaluation essay should provide a brief overview of the subject you are evaluating and the purpose of the evaluation. It should also include a clear thesis statement that states your judgment or opinion on the subject.
- Criteria are the standards or benchmarks you use to evaluate the subject. These criteria should be specific, relevant, and clearly defined. They provide the basis for your evaluation and help the reader understand the basis of your judgment.
- Evidence: In the body of your essay, you will present evidence to support your evaluation. This evidence can come from various sources, including personal experience, research, and expert opinions. It’s important to use relevant and credible evidence to strengthen your argument.
- Analysis: After presenting your evidence, you should analyze it to show how it supports your evaluation. This analysis should be thorough and insightful, demonstrating your understanding of the subject and the evaluation criteria.
- Conclusion: The conclusion of your evaluation essay should summarize your main points and restate your final evaluation. It should also provide a closing statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
How to Write an Evaluative Essay: Step-by-step Writing Guide

Step 1: Choose a Topic
Choosing a topic is the first crucial step in writing your evaluative essay. It sets the foundation for your entire paper. Here’s how to choose a topic:
- Consider Your Interests and Expertise : Consider subjects you are passionate about or know about. Choosing a topic you’re interested in makes writing more engaging and enjoyable. Plus, if you’re already familiar with the subject, it’ll be easier to provide evidence and make a judgment.
- Think About Relevance : Selecting a topic relevant to your audience and context is a good idea. Consider current events, popular culture, or significant issues in your field. A relevant topic will keep your readers engaged and make your evaluation meaningful.
- Brainstorm Potential Subjects : Take some time to brainstorm potential topics for your evaluation essay. Consider books, movies, restaurants, products, services, or even experiences that you’ve encountered recently. Make a list of possible subjects and consider the criteria you might use to evaluate them.
- Evaluate the Feasibility of the Topic : Once you have a list of potential subjects, evaluate each one based on its feasibility for your evaluation paper. Consider the availability of supporting evidence, the depth of analysis required, and the scope of the topic. Ensure that the topic is specific enough to be evaluated in the essay.
- Narrow Down Your Options : After evaluating your potential topics, narrow your options to one you feel confident about evaluating. Choose a topic that allows for a rich evaluation argument essay and provides ample supporting evidence.
Good Evaluation Essay Topics
1. The Effectiveness of Online Learning Platforms 2. Environmental Sustainability Practices in Local Businesses 3. The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Consumer Behavior 4. Government Policies Aimed at Reducing Traffic Congestion 5. The Quality of Healthcare Services in Rural Communities 6. The Value of College Education in Today’s Job Market 7. Ethical Practices in the Fashion Industry 8. The Efficiency of Renewable Energy Sources 9. The Effectiveness of Mental Health Support Programs in Schools 10. The Impact of Fast Fashion on the Environment 11. The Quality of Public Transportation Systems in Urban Areas 12. The Effectiveness of Diversity Training in the Workplace 13. The Impact of Video Games on Cognitive Development in Children 14. The Value of Volunteer Work in Community Development 15. The Effectiveness of Government-funded Welfare Programs
Argumentative Essay Writing Service
Master the art of persuasive writing with our elite Argumentative Essay Writing Service - click here to ignite your arguments and conquer any debate!
Step 2: Research the Subject
Researching the subject is a pivotal step in crafting your evaluative essay. It lays the groundwork for your analysis and enables you to provide evidence to support your judgments. Here’s how to effectively research your chosen topic:
- Understand the Purpose of Your Essay : Before delving into research, remind yourself of the purpose of your essay. An evaluation essay presents judgments based on specific criteria used to evaluate the subject. Keep this in mind as you gather information.
- Identify Relevant Criteria : Determine the criteria you will use to evaluate the subject. These criteria should be relevant to the subject’s nature and your essay’s goals. For instance, if you’re evaluating a restaurant, criteria might include food quality, service, atmosphere, and value for money.
- Gather Information from Reliable Sources : Utilize various sources to gather information about your subject. This could include books, articles, scholarly journals, websites, and personal experiences. Ensure that your sources are credible and reliable to provide evidence to support your evaluation.
- Examine Both Positive and Negative Aspects : In your research, explore both the subject’s positive and negative aspects. This balanced approach will help you provide a fair and comprehensive essay evaluation. Look for evidence that highlights strengths and weaknesses.
- Consider Different Perspectives : It’s important to consider different perspectives and opinions about the subject you’re evaluating. This will enrich the body of your essay and provide a more nuanced analysis. Be open to varying viewpoints and incorporate them into your evaluation where relevant.
- Evaluate Value for Money : If applicable to your topic, evaluate the subject’s value for money. Whether it’s a product, service, or experience, assess whether it provides good value relative to its cost. This criterion is often important in topics for evaluation essays, especially in consumer contexts.
- Organize Your Research Notes : Organize your research notes systematically as you gather information. Keep track of important details, quotes, statistics, and any other evidence that you may use to support your judgments. This will streamline the writing process later on.
Step 3: Develop Judgment, Criteria, and Criteria
Developing criteria is a pivotal aspect of preparing to write your evaluative essay. Criteria serve as the guiding principles by which you will assess and judge the subject of your evaluation. Here’s how to effectively develop criteria for your essay:
- Understand the Purpose of Criteria : Recognize that criteria provide the basis for your evaluation. They outline the specific qualities or characteristics you will assess in the subject. Your criteria must provide a clear framework for your evaluation and must be supported by evidence throughout your essay.
- Consider the Nature of the Subject : Reflect on the subject you are evaluating. Your criteria should be tailored to the specific characteristics or aspects of the subject most relevant to your evaluation. For example, if you are evaluating a movie, your criteria might include plot coherence, character development, cinematography, and overall entertainment value.
- Ensure Relevance to Your Thesis : Your criteria must align with the evaluative thesis statement of your essay. Typically found in the first paragraph, this statement outlines your overall judgment or stance on the subject. The criteria you develop should directly contribute to supporting and substantiating this thesis statement.
- Include Specific and Measurable Standards : Your criteria should be specific and measurable, allowing for clear assessment and comparison. Avoid vague or ambiguous criteria that may lead to subjective interpretations. Instead, focus on concrete standards that can be evaluated objectively with relevant examples and evidence.
- Balance Objectivity and Subjectivity : Strive to balance objectivity and subjectivity in your criteria. While objective criteria are based on measurable standards and observable facts, subjective criteria may involve personal preferences or interpretations. A persuasive essay often incorporates a combination of both types of criteria to strengthen the evaluation argument.
- Reflect Criteria in Your Outline Structure : The criteria you develop should be reflected in the outline structure most commonly used for evaluative essays. Each criterion typically corresponds to a separate body paragraph, discussed in detail and supported by relevant examples and evidence. Ensure that your outline aligns with the criteria established for your evaluation.
Step 4: Collect Evidence
Collecting evidence is a crucial aspect of preparing to write your evaluative essay. Evidence provides the substance and support for your judgments and evaluations. Here’s how to effectively collect evidence for your essay:
- Identify Relevant Sources : Identify various sources from which you can gather evidence. These sources may include books, articles, scholarly journals, reputable websites, documentaries, interviews, and personal experiences. Ensure that the sources you choose are credible and reliable.
- Consider the Nature of Your Subject : Reflect on the subject you are evaluating and determine the types of evidence that would be most relevant and impactful. For example, if you are evaluating a restaurant, evidence may include customer reviews, professional critiques, menus, photos, and personal observations.
- Seek Diverse Perspectives : To provide a well-rounded evaluation, seek evidence from diverse perspectives. Consider collecting evidence representing different viewpoints, opinions, and experiences related to the subject. This approach will enrich your analysis and enhance the depth of your evaluation.
- Evaluate the Quality of Evidence : Critically evaluate its quality and reliability as you collect evidence. Consider factors such as the credibility of the source, the expertise of the author or speaker, the currency of the information, and the objectivity of the content. Choose evidence that is trustworthy and relevant to your evaluation.
- Look for Supporting Examples : Besides factual evidence, look for examples that illustrate your judgments and evaluations. These examples may include specific incidents, case studies, anecdotes, statistics, quotations, and real-life scenarios that reinforce your points. Incorporating relevant examples strengthens the persuasiveness of your argument.
- Document Your Sources Properly : It’s essential to document your sources properly to avoid plagiarism and ensure academic integrity. Keep track of all the sources you consult during your research process, including bibliographic information such as author names, publication dates, titles, and page numbers. Use a consistent citation style, such as MLA, APA, or Chicago, according to your assignment’s or academic institution’s requirements.
Step 5: Create an Outline
Creating an outline is an essential step in writing your evaluative essay. It provides a roadmap for organizing your thoughts, structuring your arguments, and ensuring coherence and clarity in your writing. Here’s how to create an effective outline:
- Understand the Structure of Your Essay : Before outlining, familiarize yourself with the typical structure of an evaluative essay. This structure commonly includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each section serves a specific purpose in presenting and supporting your evaluation.
- Identify Key Components : Break down your essay into its key components and identify the main ideas and arguments you intend to present. These may include your thesis statement, the criteria used for evaluation, supporting evidence, and the main points to be discussed in each body paragraph.
- Start with the Introduction : Begin your outline by outlining the introduction of your essay. The introduction should include an attention-grabbing opening sentence, provide background information on the subject, and present your evaluative thesis statement. This statement expresses your overall judgment or stance on the subject.
- Outline the Body Paragraphs : Dedicate a section of your outline to outlining the body paragraphs of your essay. Each body paragraph should focus on a specific criterion used for evaluation. Start by introducing the criterion, then present supporting evidence and examples to illustrate your evaluation. Ensure that each body paragraph flows logically and supports your overall thesis.
- Consider Counterarguments : Anticipate potential counterarguments or opposing viewpoints and consider how you will address them in your essay. Including counterarguments in your outline allows you to strengthen your argument by acknowledging alternative perspectives and providing a rebuttal.
- Summarize the Conclusion : Finally, outline the conclusion of your essay. The conclusion should restate your thesis statement and summarize the main points of your evaluation. It may also offer a final judgment or recommendation based on your analysis. Ensure that your conclusion provides closure and reinforces the significance of your evaluation.
- Review and Refine Your Outline : Once you have created a preliminary outline, review and refine it to ensure clarity, coherence, and completeness. Make adjustments as needed to strengthen the structure and organization of your essay outline.
Evaluation Essay Outline (with Examples)
Here’s a sample outline for an evaluation essay, along with examples:
I. Introduction
- Example: “In a world inundated with fast-food options, McDonald’s stands as a quintessential symbol of convenience and indulgence.”
- Example: “With its ubiquitous golden arches and iconic menu items, McDonald’s has become a staple of modern-day dining, shaping culinary landscapes worldwide.”
- Example: “While McDonald’s offers affordability and convenience, its impact on public health and environmental sustainability warrants critical examination.”
II. Evaluation Criteria 1: Food Quality
- Example: “One of the primary aspects to consider when evaluating McDonald’s is the quality of its food offerings.”
- Example: “Although McDonald’s menu boasts a wide array of options, including salads and wraps, its core products often face scrutiny for their high levels of sodium, saturated fats, and preservatives.”
III. Evaluation Criteria 2: Customer Service
- Example: “Beyond its menu, McDonald’s customer service plays a crucial role in shaping the dining experience.”
- Example: “While McDonald’s prides itself on efficiency and speed, anecdotal evidence suggests inconsistencies in service quality across different locations, with long wait times and order inaccuracies being common complaints.”
IV. Evaluation Criteria 3: Environmental Sustainability
- Example: “In an era marked by growing environmental concerns, evaluating McDonald’s environmental sustainability practices is paramount.”
- Example: “Despite recent efforts to introduce sustainable packaging and energy-efficient practices, McDonald’s continues to grapple with issues related to food waste, deforestation, and carbon emissions.”
V. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
- Example: “Some may argue that McDonald’s provides jobs and economic opportunities in communities worldwide, mitigating concerns about its environmental impact and health implications.”
- Example: “While McDonald’s undoubtedly contributes to employment and economic growth, these benefits must be weighed against the broader societal costs associated with its environmental footprint and public health ramifications.”
VI. Conclusion
- Example: “In conclusion, while McDonald’s offers affordability and convenience, its adverse effects on public health and the environment underscore the need for greater accountability and reform within the fast-food industry.”
- Example: “Moving forward, stakeholders must work collaboratively to foster greater transparency, promote healthier menu options, and implement sustainable practices that prioritize both people and the planet.”
Step 6: Write the Introduction
The introduction sets the tone for your evaluative essay and captures the reader’s attention. Here’s how to craft a compelling introduction:
Engaging Opening Sentence : Start your introduction with a captivating hook that draws the reader in.
Example: “Picture yourself in a dimly lit theater, eagerly awaiting the opening credits of the latest blockbuster film.”
Provide Context : Offer some background information to orient the reader to the subject of evaluation.
Example: “In today’s fast-paced digital age, where streaming platforms offer an abundance of entertainment choices, the cinema remains a cherished cultural institution.”
Introduce the Thesis Statement : Present your evaluative thesis statement, which encapsulates your overall judgment or stance on the subject.
Example: “While many contemporary films dazzle with stunning visuals and gripping narratives, the true measure of cinematic excellence lies in their ability to provoke thought and inspire emotion.”
Preview the Main Points : A brief preview of the main points you will address in the essay’s body.
Example: “This essay will explore the criteria used to evaluate films, including storytelling prowess, character development, and technical craftsmanship, to determine what distinguishes a cinematic masterpiece from a forgettable flop.”
Set the Tone : Establish the tone of your essay, whether it’s analytical, reflective, or persuasive.
Example: “Through a critical examination of these elements, this essay aims to shed light on the artistry and impact of contemporary filmmaking, inviting readers to reconsider their perceptions of cinematic excellence.”
Creative Essay Writing Service
Unlock your creativity and unleash your imagination with our Creative Essay Writing Service – where words come alive and stories unfold like never before!
Step 7: Write the Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of your evaluative essay form the backbone of your analysis, where you delve into specific criteria and provide evidence to support your evaluation. Here’s how to effectively write the body paragraphs:
- Focus on One Criterion per Paragraph : Each body paragraph should revolve around a single criterion used for evaluation. This ensures clarity and coherence in your analysis.
- Start with a Topic Sentence : Begin each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the criterion being evaluated. This sets the stage for the analysis that follows.
- Present Supporting Evidence : Provide concrete evidence from your research to support your criterion evaluation. This may include data, facts, quotes, or observations that illustrate your point.
- Analyze the Evidence : Offer analysis and interpretation of the evidence presented. Explain how the evidence supports your criterion evaluation and contributes to your overall argument.
- Connect to the Thesis Statement : Ensure each body paragraph reinforces your evaluative thesis statement and contributes to your overall argument. This helps maintain focus and coherence throughout your essay.
- Transition to the Next Paragraph : Use transitional phrases or sentences to transition smoothly from one criterion to the next. This helps guide the reader through your analysis and maintains the flow of your essay.
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Writing the conclusion of your evaluative essay is your final opportunity to reinforce your thesis statement and leave a lasting impression on your reader. Here’s how to craft an effective conclusion:
- Restate the Thesis Statement : Begin your conclusion by restating your evaluative thesis statement. This reminds the reader of your overall judgment or stance on the subject.
- Summarize Key Points : A concise summary of the main points discussed in the body paragraphs. Briefly remind the reader of the criteria used for evaluation and the evidence presented to support your judgments.
- Reinforce the Significance : Reflect on the significance of your evaluation and its implications. Emphasize why your analysis matters and why the reader should care about your findings.
- Offer a Final Reflection or Recommendation : Conclude your essay with a final reflection or recommendation based on your evaluation. This may involve proposing future avenues for research or suggesting potential areas for improvement.
- End with a Thought-Provoking Statement : Leave the reader with a thought-provoking statement that encapsulates the essence of your evaluation and encourages further reflection.
Step 9: Revise and Edit
Once you’ve completed the initial draft of your evaluative essay, it’s crucial to revise and edit your work thoroughly. This process helps improve clarity, coherence, and overall quality. Here’s how to effectively revise and edit your essay:
- Review for Clarity and Coherence : Read through your essay to ensure your ideas flow logically and cohesively from one paragraph to the next. Check for any abrupt transitions or disjointed arguments that may confuse the reader.
- Check for Consistency : Verify that your essay maintains consistency in tone, style, and formatting. Ensure that your language and writing style are appropriate for your audience and purpose.
- Evaluate the Structure and Organization : Assess your essay’s overall structure and organization. Ensure that each paragraph serves a clear purpose and contributes to the development of your argument. Consider rearranging or rephrasing sentences and paragraphs to enhance clarity and coherence.
- Clarify and Strengthen Your Argument : Review your thesis statement and main arguments to ensure they are clear, focused, and well-supported by evidence. Clarify any vague or ambiguous statements, and strengthen your argument by providing additional evidence or analysis where necessary.
- Check for Grammar and Mechanics : Proofread your essay for grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors. Consider common issues such as subject-verb agreement, tense consistency, and punctuation usage.
- Verify Accuracy of Information : Double-check the accuracy of any facts, statistics, or quotations cited in your essay. Ensure all information is properly sourced and attributed to the appropriate citation style.
- Seek Feedback : Consider sharing your essay with a peer, mentor, or instructor for feedback. Solicit constructive criticism and suggestions for improvement, and be open to revising your essay based on their input.
- Take Breaks and Revisit : Take breaks between revision sessions to maintain freshness and perspective. Step away from your essay for a while, then revisit it with fresh eyes to identify any areas needing further revision or refinement.
Essay Editing Services | Proofreading Service
Unlock the full potential of your writing with our Essay Editing Services | Proofreading Service – your key to polished, professional essays that stand out
Step 10: Finalize Your Essay
Finalizing your essay is the last crucial step before submission. It involves carefully reviewing your work, making necessary revisions, and ensuring your essay is well-organized and cohesive. Here’s how to effectively finalize your essay:
- Review for Overall Coherence : Read through your entire essay to ensure it flows smoothly from start to finish. Check that each paragraph transitions logically to the next and that your ideas are presented in a clear and organized manner.
- Evaluate the Introduction and Conclusion : Consider your introduction and conclusion. Ensure that your introduction effectively introduces the topic and thesis statement while your conclusion summarizes your main points and leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Check for Consistency in Style and Tone : Verify that your essay maintains consistency in style, tone, and voice throughout. Ensure that your language is appropriate for your audience and purpose and that your writing style remains consistent from beginning to end.
- Verify Proper Citation and Referencing : If you’ve included research or outside sources in your essay, double-check that you’ve properly cited and referenced them according to the required citation style (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago). Ensure that all sources are credited and your citations are formatted correctly.
- Proofread for Grammar and Mechanics : Conduct a final proofreading pass to catch any lingering grammatical, punctuation, or spelling errors. Consider common issues such as subject-verb agreement, tense consistency, and punctuation usage.
- Check Formatting and Presentation : Verify that your essay adheres to any formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or publication. Ensure your font, margins, spacing, and header/footer information align with the required formatting standards.
- Seek Feedback, if Possible : Consider seeking feedback from a peer, mentor, or instructor before finalizing your essay. Fresh eyes can often catch errors or inconsistencies you may have overlooked, and constructive feedback can help improve the overall quality of your work.
- Take Time for Final Reflection : Before submitting your essay, take a moment to reflect on your writing process and the journey you’ve taken to reach this point. Consider the lessons you’ve learned and the growth you’ve experienced as a writer throughout the process.
Evaluation Essay Examples

- Evaluating the Pros and Cons of Remote Work
- Evaluating Online Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Get Help With Your Evaluation Essay Paper
Essay Freelance Writers is the best in the industry for getting help with your evaluation essay paper. Our expert writers can guide you if you’re unsure how to write an essay or formulate a thesis statement. With various possible topics and a paper structure commonly used for evaluative writing, you can choose your topic and let us do the rest. Our writing services are licensed under a Creative Commons 4.0 International License, so feel free to share with others needing assistance. Place your order today by clicking the ORDER NOW button above to get our expert writing help.
How do you write an evaluation essay?
An evaluation essay involves evaluative writing, where you judge a subject matter. Start by writing an introduction that clearly states your thesis statement . Then, evaluate the chosen topic based on evaluative criteria and include evidence to support your judgment on its value .
What are good evaluation essay topics?
Good evaluation essay topics vary widely, including restaurant reviews, book/movie evaluations, product assessments, and service evaluations . You can also explore educational institutions, healthcare, and technology topics.
What are the points to evaluate an essay?
When evaluating an essay, consider aspects such as structure , organization , clarity of argument , credibility of sources , strength of analysis , and overall impact . Unbiased evaluation requires looking at both the strengths and weaknesses of the piece.
How do you start an evaluation example?
To start an evaluation example, begin with a brief introduction that sets the context for the evaluation. Clearly state the purpose of your evaluation and introduce the subject or topic you will be evaluating. You can then proceed with presenting your evaluative criteria and providing supporting evidence.

With a deep understanding of the student experience, I craft blog content that resonates with young learners. My articles offer practical advice and actionable strategies to help students achieve a healthy and successful academic life.
- How to Write an Exemplification Essay | Tips and Examples [2025]

Most Popular Articles
Racism thesis statement example, how to rephrase a thesis statement, capstone project topic suggestions, how to write an abortion essay, should students wear school uniforms essay, list causal essay topics write, respect essay, signal words, great synonyms, informative speech examples, essay writing guide, introduction paragraph for an essay, argumentative essay writing, essay outline templates, write an autobiographical essay, personal narrative essay ideas, descriptive essay writing, how to write a reflective-essay, how to write a lab report abstract, how to write a grant proposal, point of view in an essay, debate topics for youth at church, theatre research paper topics, privacy overview.
Advertisement
Developing evaluative judgement: enabling students to make decisions about the quality of work
- Open access
- Published: 16 December 2017
- Volume 76 , pages 467–481, ( 2018 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Joanna Tai 1 ,
- Rola Ajjawi 1 ,
- David Boud 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Phillip Dawson 1 &
- Ernesto Panadero 1 , 4
83k Accesses
347 Citations
169 Altmetric
10 Mentions
Explore all metrics
Evaluative judgement is the capability to make decisions about the quality of work of oneself and others. In this paper, we propose that developing students’ evaluative judgement should be a goal of higher education, to enable students to improve their work and to meet their future learning needs: a necessary capability of graduates. We explore evaluative judgement within a discourse of pedagogy rather than primarily within an assessment discourse, as a way of encompassing and integrating a range of pedagogical practices. We trace the origins and development of the term ‘evaluative judgement’ to form a concise definition then recommend refinements to existing higher education practices of self-assessment, peer assessment, feedback, rubrics, and use of exemplars to contribute to the development of evaluative judgement. Considering pedagogical practices in light of evaluative judgement may lead to fruitful methods of engendering the skills learners require both within and beyond higher education settings.
Similar content being viewed by others

Elements of Better Assessment for the Improvement of Learning
Developing student competence through peer assessment: the role of feedback, self-regulation and evaluative judgement
The role of peer-assisted learning in building evaluative judgement: opportunities in clinical medical education, explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
How does a student come to an understanding of the quality of their efforts and make decisions on the acceptability of their work? How does an artist know which of their pieces is good enough to exhibit? How does an employee know whether their work is ready for their manager? Each of these and other common scenarios require more than the ability to do good work; they require appraisal and an understanding of standards or quality. This capability of ‘evaluative judgement’, or being able to judge the quality of one’s own and others’ work, is necessary not just in a student’s current course but for learning throughout life (Boud and Soler 2016 ). It encapsulates the ongoing interactions between the individual, their fellow students or practitioners, and standards of performance required for effective and reflexive practice.
However, current assessment and feedback practices do not necessarily operate from this perspective. Assessment design is frequently critiqued for being unidirectional, excessively content and task focused, while also positioning students as passive recipients of feedback information (e.g. Carless et al. 2011 ). Worse than failing to support the development of evaluative judgement, these approaches may even inhibit it, by producing graduates dependent on others’ assessment of their work, who are not able to identify criteria to apply in any given context. This may be because evaluative judgement is undertheorised and under-researched. In particular, although there have been some theoretical arguments about its importance (e.g. Sadler 2010 ), evaluative judgement has not been the focus of sustained attention and very little empirical work exists on the effectiveness of strategies for developing students’ evaluative judgement (Nicol 2014 ; Tai et al. 2016 ). Sadler ( 2013 ) observed that ‘quality is something I do not know how to define, but I recognise it when I see it’ (p. 8), a common experience for those dealing with abstract concepts. This perceived inability to articulate what quality is has likely impacted on our ambitions and capability to directly educate learners about quality.
Studies in the field of human judgement have brought to bear better understandings regarding our own fallibility in evaluating or judging student work (Brooks 2012 ). We may default to ‘quick thinking’, assessing intuitively rather than by thoughtful deliberation and employ referents for judgements which exist outside published criteria. Heuristics and biases are also likely to influence decision-making (Joughin et al. 2016 ). Given there are strategies to assist markers to develop their judgement (Sadler 2013 ), we may also be able to help learners develop strategies for refining their own judgement (i.e. surfacing potentially implicit quality criteria and comparing these to the espoused ones), through a range of activities and tasks which requires students to examine and interact with examples of work of varying quality.
In this paper, we trace the elaboration of evaluative judgement and related concepts in the literature and converge on a definition. We then discuss five pedagogical approaches that may support the development of evaluative judgement, and how they could be improved if evaluative judgement were a priority. We conclude with implications for future agendas in research and practice to understand and develop evaluative judgement. We argue that evaluative judgement is a necessary, distinct concept that has not been given sufficient attention in higher education research or practice. We propose that evaluative judgement underpins and integrates existing pedagogies such as self-assessment, peer assessment, and the use of exemplars. We suggest that the development of evaluative judgement is one of higher education’s ultimate goals and a necessary capability for graduates.
Tracing the evolution of ‘evaluative judgement’
The origin of evaluative judgement can be traced back to Sadler’s ( 1989 ) ideas of ‘evaluative knowledge’ (p 135), or ‘evaluative expertise’ (p 138), which students must develop to become progressively independent of their teachers. Sadler proposed that students needed to understand criteria in relation to the standards required for making quality judgements, before being able to appreciate feedback about their performance. Students then also required the ability to engage in activity to close the gap between their performance and the standards that were expected to be achieved. These proposals were specifically made in relation to the role of formative assessment in learning design: formative assessments were to aid students in understanding how complex judgements were made and to allow students to have direct, authentic experiences of evaluating others and being evaluated (Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick 2006 ). The overall goal was to enable students to develop and rely on their own evaluative judgements so that they can become independent students and eventually effective practitioners.
The term ‘sustainable assessment’ was coined to indicate a purpose of assessment that had not been sufficiently encompassed by the previous dichotomy of the summative and the formative. Sustainable assessment was proposed as assessment ‘that meets the needs of the present and [also] prepares students to meet their own future learning needs’(Boud 2000 , p. 151). This was posited as a distinct purpose of assessment: summative assessment typically met the needs of other stakeholders (i.e. for grade generation and certification), and formative assessment was commonly limited to tasks within a particular course or course unit. Sustainable assessment focused on building the capacity of students to make judgements of their own work and that of others through engagement in a variety of assessment activities so that they could be more effective learners and meet the requirements of work beyond the point of graduation.
Similarly, ideas of ‘informed judgement’ also sat firmly within the assessment literature. In Rethinking Assessment in Higher Education , Boud ( 2007 ) sought to develop an inclusive view of student assessment, locating it as a practice at the disposal of both teachers and learners rather than simply an act of teachers. To this end, assessment was taken to be any activity that informed the judgement of any of the parties involved. Those being informed included learners; many discussions of assessment positioned learners as subjects of assessments by others, or as recipients of assessment information generated by others. Assessment as informing judgement was designed to acknowledge that assessment information is vital for students in planning their own learning and that assessment activities should be established on the assumption that learning was important. As a part of this enterprise, Boud and Falchikov ( 2007 , pp. 186–190) proposed a framework for developing assessment skills for future learning. These steps towards promoting students’ informed judgement from the perspective of the learner consisted of the following: (a) identifying oneself as an active learner, (b) identifying one’s level of knowledge and the gaps in this, (c) practising testing and judging, (d) developing these skills over time, and (e) embodying reflexivity and commitment.
Returning to pedagogical practices, Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick ( 2006 ) interpreted Sadler’s ideas around evaluative knowledge to mean that students ‘must already possess some of the same evaluative skills as their teacher’ (p. 204). Through making repeated judgements about the quality of students’ work, teachers come to implicitly understand the necessary standards of competence. These understandings of quality (implicit or explicit) and striving to attain them are necessary precursors of expertise. Yet, this understanding had not previously been expected of students in such a nuanced and explicit way.
Sadler ( 2010 ) revisited the idea of evaluative judgement to further explore what surrounds acts of feedback. Here, he proposed that student capability in ‘complex appraisal’ was necessary for learning from feedback and that educators needed to do more to articulate the reasons for the information provided (i.e. quality notions) rather than providing information. Sadler also suggested that an additional method for developing this capability was peer review or assessment, which was also taken up by Gielen et al. ( 2011 ). By engaging students in making judgements, and interacting with criteria, it was thought that understandings of quality and tacit knowledge (which educators already held) would be developed. Nicol ( 2014 ) continued this argument and provided case studies to illustrate the power of peer review in developing evaluative capacity.
In parallel with the development of these ideas, the wider context of higher education had been changing internationally. The framing of courses and assessment practices around explicit learning outcomes and judging students’ work in terms of criteria and standards had become increasingly accepted (Boud 2017 ). This move towards a standard-based curriculum provided a stronger base for the establishment of students developing evaluative judgement than hitherto, because having explicit standards helps students to clarify their learning goals and what they need to master.
We suggest that the authors identified in this section were discussing the same fundamental idea: that students must gain an understanding of quality and how to make evaluative judgements, so that they may operate independently on future occasions, taking into account all forms of information and feedback comments, without explicit external direction from a teacher or teacher-like figure. This also aligns with much of the ongoing discussions in higher education focused on preparing students for professional practice, which is sometimes couched in terms of an employability agenda (Knight and Yorke 2003 ; Tomlinson 2012 ). Employers have criticised for decades the underpreparedness of graduates for the workplace and the lack of impact of the various moves made to address this concern, e.g. inclusion of communication skills and teamwork in the curriculum (e.g. Thompson 2006 ). A focus on developing evaluative skills may lead to graduates who can identify what is needed for good work in any situation and what is needed for them to produce it.
This paper therefore makes an argument for evaluative judgement as an integrating and encompassing concept, part of curricular and pedagogical goals, rather than primarily an assessment concern. Evaluative judgement speaks to a broader purpose and the reason why we employ a range of strategies to facilitate learning: to develop students’ notions of quality and how they might be identified in their actual work. Before we discuss practices which promote students’ evaluative judgement, it is necessary to indicate how we are using this term.
Defining evaluative judgement
As a term, evaluative judgement has only relatively recently been taken up in the higher and professional education literature, as a higher-level cognitive ability required for life-long learning (Cowan 2010 ). Ideas about evaluation and critical judgement being necessary for effective feedback, and therefore learning, have also been highlighted by Sadler ( 2010 ), Nicol ( 2013 , 2014 , 2014), and Boud and Molloy ( 2013 ). These scholars argue that evaluative judgement acknowledges the complexity of contextual standards and performance, supports the development of learning trajectories and mastery, and is therefore aimed at future capacities and lifelong learning.
Little empirical work has so far been conducted within an explicit evaluative judgement framework. Firstly, Nicol et al. ( 2014 ) demonstrated the ability of peer learning activities to facilitate students’ judgement making in higher education settings. Secondly, Tai et al. ( 2016 ) also explored the role of informal peer learning in producing accurate evaluative judgements, which impacted on students’ capacity to engage in feedback conversations, through a better understanding of standards. Thirdly, Barton et al. ( 2016 ) reframed formal feedback processes to develop evaluative judgement, including dialogic feedback, self-assessment, and a programmatic feedback journal.
Nevertheless, there is a wider literature on formative assessment that has not been framed under the evaluative judgement umbrella, but which can be repositioned to do so. This literature supports students developing capability for evaluative judgement either through strategies that involve self-assessment (e.g. Boud 1992 ; Panadero et al. 2016 ), peer assessment (e.g. Panadero 2016 ; Topping 2010 ), or self-regulated learning (e.g. Nicol and Macfarlane-Dick 2006 ; Panadero and Alonso-Tapia 2013 ). Although they do not use the term, these sets of studies share a common purpose with evaluative judgement: to enhance students’ critical capability via a range of learning and assessment practices. We propose that a focus on developing evaluative judgement goes a step beyond these through providing a more coherent framework to anchor these practices while adding a further perspective taken from sustainable assessment (Boud and Soler 2016 ): equipping students for future practice. However, what are the features of evaluative judgement and how does it integrate these multiple agendas?
An earlier definition of evaluative judgement by Tai et al. ( 2016 ) was
‘… the ability to critically assess a performance in relation to a predefined but not necessarily explicit standard, which entails a complex process of reflection. It has an internal application, in the form of self-evaluation, and an external application, in making decisions about the quality of others’ work’. (p. 661)
This definition was formed in the context of medical students’ learning on clinical placements. There are many variations of what ‘work’ is within the higher education setting, which are not limited to performance. Work may also constitute written pieces (essays and reports), oral presentations, creative endeavours, or other products and processes. Furthermore, many elements of the definition seemed tautological, and so, we present a simpler definition:
Evaluative judgement is the capability to make decisions about the quality of work of self and others
In alignment with Tai et al. ( 2016 ), there are two components integral to evaluative judgement which operate as complements to each other: firstly, understanding what constitutes quality and, secondly, applying this understanding through an appraisal of work, whether it be one’s own, or another’s. This second step could be thought of as the making of evaluative judgements, which is the means of exercising one’s evaluative judgement. Through appraising work, an individual has to interact with a standard (whether implicit or explicit), potentially increasing their understandings of quality. The learning of quality and the learning of judgement making are interdependent: when coupled, they provide a stronger justification for the development of both aspects, in being prepared for future work. While judgement making occurs frequently and could be done without any attention to the development of itself as a skill, we consider that the process of developing evaluative judgement needs to be deliberate and be deliberated upon. Evaluative judgement itself, however, may become unconscious when the individual has had significant experience and expertise in making evaluative judgements in a specific area.
We propose that the development of evaluative judgements can be fruitfully considered using the staged theory of expertise of decision-making (Schmidt and Rikers 2007 ). This has been illustrated through the study of how medical students learn to make clinical decisions by seeing many different patients and making decisions about them. This involves both analytical and non-analytical processes; however, as novices, this process is initially labour intensive, requiring the integration of multiple strands of knowledge in an analytical fashion. Learning to make decisions occurs through actually having to make decisions, justification of the decisions in relation to knowledge and standards, and discussion with peers, mentors, and supervisors (Ajjawi and Higgs 2008 ). As they become more experienced, medical trainees come to ‘chunk’ knowledge through making links between biomedical knowledge and particular clinical signs and symptoms. These are chunked further to form patterns or illness scripts about particular diseases, presentations, and conditions. Thus, the process becomes less analytical, with analytical reasoning used when problems do not seem to fit an existing pattern, as a safety mechanism.
In a similar way, we hypothesise that students and teachers develop the equivalent of such scripts where knowledge about what makes for quality becomes linked through repeated exposure to work, consideration of standards (whether these are implicit or explicit) and the need to justify decisions (as assessors do post hoc (Ecclestone 2001 )). These help strengthen judgements in relation to particular disciplinary genres and within communities of practice. This may explain why experienced assessors find marking of a familiar task less effortful: they have had sufficient experience to become more intuitive in their judgements based on previously formed patterns, but they still use explicit criteria and standards to rationalise their intuitive global professional judgement to others. Indeed in health, the communication of clinical judgements has been found to be a post hoc reformulation to suit the audience rather than an actual representation of the decision-making process (Ajjawi and Higgs 2012 ). Similarly, we suggest that students can develop their evaluative judgement through repeated practice. Making an evaluative judgement requires the activation of knowledge about quality in relation to a problem space. By repeating this process in different situations, students build their quality scripts for particular disciplinary assessment genres which in turn means they can make better decisions.
We note that evaluative judgement is contextual: what constitutes quality, and what a decision may look like, will depend on the setting in which the evaluative judgement is made. Evaluative judgement is domain specific: one develops expertise pertaining to a specific subject or disciplinary area, from which decisions about quality of work are made. However, the capability of identifying criteria of quality and applying these to work in context may cross domains. Evaluative judgement is also more than just an orientation to disciplinary, community, or contextual standards as applied to current instances of work, it can be carried over to future work too. There are also likely to be differences between work expected at an entry level and that conducted by experts. In areas in which it is possible to make practice explicit, the notion of learners calibrating their judgement against those of effective practitioners or other sources of expertise is also important (Boud et al. 2015 ). To develop evaluative judgement, feedback information should perhaps focus less on the quality of students’ work and more on the fidelity of their judgements about quality. Feedback is, however, but one of several practices which may develop evaluative judgement.
Current practices which develop evaluative judgement
There are several aspects of courses that already contribute to the development of students’ evaluative ability. However, they may not previously have been seen from this perspective and their potential for this purpose not fully realised. Through the formal and informal curriculum (including assessment structures), learners are likely to develop evaluative judgement. There are a range of assessment-related activities, such as self and peer assessment, which are now imbued with greater purpose through their link with evaluative judgement.
The provision of assessment criteria is an attempt to represent standards to students. However, such representations are unlikely to communicate the complex tacit knowledge embedded in standards and quality (Sadler 2007 ). Teachers are considered able to make expert and reliable judgements because of their experiences with having to make repeated judgements forming patterns or instantiations, as well as socialisation into the standards of the discipline (Ecclestone 2001 ). However, even experts vary in their interpretation of standards and use of marking criteria, especially when they are not made explicit from the outset (Bloxham et al. 2016 ). Standards reside in the practices of academic and professional communities underpinned by tacit and explicit knowledge and are, therefore, subject to varied interpretation/enactments (O’Donovan et al. 2004 ). Students develop their understanding of standards, at minimum, through the production of work for assessment and then receiving a mark: this gives them clues about the quality of their work and they may form implicit criteria for improving the work regardless of the explicit criteria. We argue that through an explicit focus on evaluative judgement, students can form systematic and hopefully better calibrated evaluative judgements rather than implicit and idiosyncratic ones. The curriculum may then better serve the function of inducting and socialising learners into a discipline, providing them with opportunities to take part in discussing standards and criteria, and the processes of making judgements (of their own and others’ work). This will help them develop appropriate evaluative judgement themselves in relation to criteria or standards and make more sense of and take greater control of their own learning (Boud and Soler 2016 ; Sadler 2010 ).
Many existing practices have potential for developing evaluative judgement. However, some of the ways in which they have been implemented are not likely to be effective for this end. Table 1 illustrates ways in which they may or may not be used to develop evaluative judgement. We focus attention on these five common practices, as they hold significant potential for further development.
Self-assessment
Self-assessment involves students appraising their own work. Earlier studies focused on student-generated marks, comparing them with those generated by teachers. Despite long-standing criticisms (Boud and Falchikov 1989 ), this strategy remains common in self-assessment research (Panadero et al. 2016 ). We suggest that persistence of this emphasis lies in several reasons. Firstly, such studies are easy to conduct and analyse. They involve little or no changes to curriculum and pedagogy. ‘Grade guessing’ can be added with little disruption to a normal class regime. Secondly, there remains a legitimate interest in understanding students’ self-marking: students exist in a grade-oriented environment. What is needed for the development of evaluative judgement is for the emphasis of self-assessment to be on eliciting and using criteria and standards as an embedded aspect of learning and teaching strategies (Thompson 2016 ). Self-assessment can more usefully be justified in terms of assisting students to develop multiple criteria and qualitatively review their own work against them and thus refine their judgements rather than generate grades that might be distorted by their potential use as a substitute for teacher grades.
The focus of evaluative judgement is not just inwards on one’s work but also outwards to others’ performance, about the two in comparison to each other, and standards. Metacognition and ‘reflective judgement thinking’ (Pascarella and Terenzini 2005 ) also fall within this category of largely self-oriented ideas. Self-assessment is typically focused on a specific task, whereby a student comes to understand the required standard and thus improves their work on the specific task at hand (Panadero et al. 2016 ). Evaluative judgements encompass these elements while also transcending the immediate task by developing a student’s judgement of quality that can be further refined and evoked in similar tasks.
Peer assessment and peer review
Similar to the literature regarding self-assessment, a significant proportion of studies of peer assessment have focused on the accuracy of marks generated and the potential for a number calculated from peer assessments to contribute to grades (Falchikov and Goldfinch 2000 ; Speyer et al. 2011 ). Simultaneously, others have pointed to the formative, educative, and pedagogical purposes of peer assessment (Dochy et al. 1999 ; Liu and Carless 2006 ; Panadero 2016 ) and consider both the receiving and the giving of peer feedback to be important for learning (van den Berg et al. 2006 ), particularly for the development of evaluative judgement (Nicol et al. 2014 ). By engaging more closely with criteria and standards, and having to compare work to these, students have reported a better understanding of quality work (McConlogue 2012 ; Tai et al. 2016 ). Many peer assessment exercises, whether formal or informal, may already contribute to the development of evaluative judgement. By a more explicit focus on evaluative judgement, students can pay close attention to what constitutes quality in others’ work and how that may transfer to their own work on the immediate task and beyond. Learning about notions of quality through assessing the work of peers may reduce the effect of cognitive biases directed towards the self when undertaking self-assessment (Dunning et al. 2004 ). It is also likely that the provider of the assessment may benefit more from the interaction than the receiver, as it is their judgement which is being exercised (Nicol et al. 2014 ).
Scholarship on feedback in higher education has progressed rapidly in recent years to move beyond merely providing students with information about their work to emphasising the effects on students’ subsequent work and to involving them as active agents in a forward-looking dialogue about their studies (Boud and Molloy 2013 ; Carless et al. 2011 ; Merry et al. 2013 ). This work suggests that feedback (termed Feedback Mark 2) should go beyond the current task to look to future instances of work and develop students’ evaluative judgement. Boud and Molloy ( 2013 ) introduced this model to supplant previous uses of ‘feed forward’. Feedback to develop evaluative judgement would emphasise dialogue to clarify applicable standards and criteria that define quality, to help refine the judgement of students about their work and to assist them to formulate actions that arise from their appreciation of their work and the information provided about it from other sources. Feedback may be oriented specifically towards evaluative judgement across a curriculum, highlighting gaps in understandings of quality and how quality is influenced by discipline and context.
A focus on evaluative judgement requires new ways to think about feedback. Comments to students are not only about their work per se but about the judgements they make about it. The information they need to refine their judgements includes whether they have chosen suitable criteria, whether they have reached justifiable decisions about the work, and what they need to do to develop these capabilities further. There is no need to repeat what students already know about the quality of their work, but to raise their awareness of where their judgement has been occluded or misguided. Guidance is then also required towards future goals and judgement making. This new focus for feedback could be thought of as occupying the highly influential ‘self-regulation’ level of Hattie and Timperley’s ( 2007 ) model of feedback.
Rubrics can be thought of as a scaffold or pedagogy to support the development of evaluative judgement. There is extensive diversity of rubric practices (Dawson 2015 ), some of which may better support the development of evaluative judgement (e.g. formative use (Panadero and Jonsson 2013 )) than others.
If rubrics are to be used to develop students’ evaluative judgement, they should be designed and used in ways that reflect the nuanced understandings of quality that experts use when making judgements about a particular type of task while acknowledging the complexity and fluidity of the practices, and hence standards, they represent. Current understandings of influences on rater judgement should also be communicated to give students a sense that there may also be unconscious, tacit, and personal factors in play. Existing work suggests that students can be trained to use analytic rubrics to evaluate their own work and the work of others (e.g. Boud et al. 2013 ); however, the ability to apply a rubric does not necessarily imply that students have developed evaluative judgement without a rubric. Hendry and Anderson ( 2013 ) proposed that marking guides are only helpful for students to understand quality when the students themselves use them to critically evaluate work. For evaluative judgement to be a sustainable capability, it needs to work in the absence of the artifice of the university. Although students’ notions of quality may be refined with each iteration of a learning task and associated engagement with standards and criteria, not all aspects of quality can be communicated through explicit criteria; some will remain tacit and embodied (Hudson et al. 2017 ).
Student co-creation of rubrics may support the development of evaluative judgement (Fraile et al. 2016 ). These approaches usually involve students collectively brainstorming sets of criteria and engaging in a teacher-supported process of discussing disciplinary quality standards and priorities. These processes may develop a more sustainable evaluative judgement capability, as they involve students in the social construction and articulation of standards: a process that may support them to develop evaluative judgement in the new fields and contexts they move into throughout their lives.
Exemplars provide instantiations of quality and an opportunity for students to exercise their evaluative judgement. A challenge in using exemplars is ensuring they are sustainable, that is, they represent features not just of a given task but of quality more broadly in the discipline or profession. This may be resolved by ensuring assessment tasks are authentic in nature. However, exemplars are likely to require some commentary for students to be able to use them to full advantage in developing their evaluative judgement.
There are a small number of research studies on the use of exemplars to develop student understanding of quality. Earlier work done by Orsmond et al. ( 2002 ) identified that student discussion regarding a range of exemplars without the revelation of grades aided in understanding notions of quality. To and Carless ( 2015 ) more recently have advocated for a ‘dialogic’ approach involving student participation in different types of discussion, as well as teacher guidance. However, teachers may need to reserve their own evaluative judgement to allow students to co-construct understandings of quality (Carless and Chan 2016 ). Students have been shown to value teacher explanation more than their own interactions with exemplars (Hendry and Jukic 2014 ). The use of exemplars in developing evaluative judgement is likely to require a delicate balance, where students are scaffolded to notice various examples of quality, without explicit ‘telling’ from the teacher.
Discussion and conclusion
We propose that developing students’ evaluative judgement should be a goal of higher education. Starting with such an integrative orientation demand refinements to existing pedagogical practices. Of the five discussed, some have a close relationship with assessment tasks; others can be part of any teaching and learning activity in any discipline.
Common to these practices is active and iterative engagement with criteria, the enactment of judgements on diverse samples of work, dialogic feedback with peers and tutors oriented towards understanding quality which may not be otherwise explicated, and articulation and justification of judgements with a focus on both immediate and future tasks. Evaluative judgement brings together these different activities and refocuses them as pedagogies to be used towards producing students who can make effective judgements within and beyond the course. We identified these pedagogies as developing evaluative judgement through the consideration of previous conceptual work which touched on the notion that students need a sense of quality to successfully undertake study and conduct their future lives as graduates (e.g. Sadler 2010 ; Boud and Falchikov 2007 ). In doing this, we have gone beyond using evaluative judgement as an explanatory term for student learning phenomena (Tai et al. 2016 ; Nicol et al. 2014 ) and sought to broaden its use to become a key justification for requiring students to engage in certain pedagogical activities.
Developing students’ evaluative judgement is important for several reasons. It provides an overarching means to communicate with students about a central purpose of these activities, how they may relate to each other and to course learning outcomes. With sceptical student-consumers, a strong educational rationale which speaks to students’ future use is necessary (Nixon et al. 2016 ). It may also persuade educators that devoting time to work-intensive activities such as using exemplars, co-creating rubrics, and undertaking self and peer assessment and feedback is worthwhile. Since the development of evaluative judgement is a continuing theme to underpin all other aspects of the course (Boud and Falchikov 2007 ), opportunities are available at every stage: in classroom and online discussions, in the ways in which learning tasks are planned and debriefed, in the construction of each assessment task and feedback process, and, most importantly, in the continuing discourse about what study is for and how it can be effective in preparing students for all types of work.
The explicit inclusion of evaluative judgement, in courses, might also actively engage student motivations to learn. The development of evaluative judgement complements and adds to other graduate attributes developed through of course of study. The notion of evaluative judgement is not a substitute for well-established features of the curriculum but a way of relating them to the formation of learners’ judgement. This additional purpose is likely to empower students in their learning context. Students will transition from being dependent novices and consumers of information to becoming agentic individuals able to participate in social notions of determining quality work. This sort of journey will require students to be supported in becoming self-regulated learners who take responsibility for their own learning and direct it accordingly (Sitzmann and Ely 2011 ).
Researchers and educators should be concerned not only with the effectiveness of interventions to develop evaluative judgement but also understanding the quality of student evaluative judgement. Existing ‘grade guessing’ research comparing student self-/peer marking against expert/teacher marking provides only a thin measure of evaluative judgement. Determining whether evaluative judgement has been developed could occur through particular self- and peer assessment activities in which students judge their own work and that of others and the qualities of the judgements made. The quality of an evaluative judgement lies not only in its result but in the thought processes and justifications used. High quality evaluative judgement involves students identifying and using appropriate criteria (both prescribed and self-generated) and discerning whether their own work and that of others meets these requirements. Through this process, students can be supported to refine their understanding of quality for future related tasks and come to know how to manage the ambiguities inherent in criteria when applied in different contexts. This presents a complex phenomenon for researchers and educators to understand or measure, for which correlations between teacher and student marks are inadequate.
This paper has developed a new definition and focus on evaluative judgement to describe why we might want to develop it in our students and how to go about this. Evaluative judgement provides the reason ‘why’ for implementing certain pedagogies. Further theoretical work may assist in better understanding how to develop evaluative judgement amongst students. While we have characterised it as a capability, there may also be motivational, attitudinal, and embodied aspects of evaluative judgement to consider. Empirical studies are also required to test aforementioned strategies for developing evaluative judgement, tracking the longitudinal development of evaluative judgement and professional practice outcomes over several years. Returning to Sadler’s ( 2013 ) statement that quality is something I do not know how to define, but I recognise it when I see it, we have argued that a focus on evaluative judgement might enable a frank and explicit discussion of what constitutes quality and explored a range of common practices which may develop this capability. The exercise of evaluative judgement is a way of framing what makes for good practice.
Ajjawi, R., & Higgs, J. (2008). Learning to reason: a journey of professional socialisation. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 13 (2), 133–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-006-9032-4 .
Article Google Scholar
Ajjawi, R., & Higgs, J. (2012). Core components of communication of clinical reasoning: a qualitative study with experienced Australian physiotherapists. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 17 (1), 107–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-011-9302-7 .
Barton, K. L., Schofield, S. J., McAleer, S., & Ajjawi, R. (2016). Translating evidence-based guidelines to improve feedback practices: the interACT case study. BMC Medical Education, 16 (1), 53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-016-0562-z .
Bloxham, S., Den-Outer, B., Hudson, J., & Price, M. (2016). Let’s stop the pretence of consistent marking: exploring the multiple limitations of assessment criteria. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 41 (3), 466–481. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1024607 .
Boud, D. (1992). The use of self-assessment schedules in negotiated learning. Studies in Higher Education, 17 (2), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079212331382657 .
Boud, D. (2000). Sustainable assessment: rethinking assessment for the learning society. Studies in Continuing Education, 22 (2), 151–167.
Boud, D. (2007). Reframing assessment as if learning was important. In D. Boud & N. Falchikov (Eds.), Rethinking assessment in higher education: learning for the longer term (pp. 14–25). London: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Boud, D. (2017). Standards-based assessment for an era of increasing transparency. In D. Carless, S. Bridges, C. Chan, & R. Glofcheski (Eds.), Scaling up assessment for learning in higher education (pp. 19–31). Dordrecht: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-3045-1_2 .
Chapter Google Scholar
Boud, D., & Falchikov, N. (1989). Quantitative studies of student self-assessment in higher education: a critical analysis of findings. Higher Education, 18 (5), 529–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00138746 .
Boud, D., & Falchikov, N. (2007). Developing assessment for informing judgement. In D. Boud & N. Falchikov (Eds.), Rethinking assessment in higher education: learning for the longer term (pp. 181–197). London: Routledge.
Boud, D., & Molloy, E. (2013). Rethinking models of feedback for learning: the challenge of design. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 38 (6), 698–712. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2012.691462 .
Boud, D., & Soler, R. (2016). Sustainable assessment revisited. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 41 (3), 400–413. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1018133 .
Boud, D., Lawson, R., & Thompson, D. G. (2013). Does student engagement in self-assessment calibrate their judgement over time? Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 38 (8), 941–956. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.769198 .
Boud, D., Lawson, R., & Thompson, D. G. (2015). The calibration of student judgement through self-assessment: disruptive effects of assessment patterns. Higher Education Research & Development, 34 (1), 45–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2014.934328 .
Brooks, V. (2012). Marking as judgment. Research Papers in Education, 27 (1), 63–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/02671520903331008 .
Carless, D., & Chan, K. K. H. (2017). Managing dialogic use of exemplars. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 42 (6), 930–941. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2016.1211246 .
Carless, D., Salter, D., Yang, M., & Lam, J. (2011). Developing sustainable feedback practices. Studies in Higher Education, 36 (4), 395–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075071003642449 .
Cowan, J. (2010). Developing the ability for making evaluative judgements. Teaching in Higher Education, 15 (3), 323–334. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510903560036 .
Dawson, P. (2017). Assessment rubrics: towards clearer and more replicable design, research and practice. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 42 (3), 347–360. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2015.1111294 .
Dochy, F., Segers, M., & Sluijsmans, D. (1999). The use of self-, peer and co-assessment in higher education: a review. Studies in Higher Education, 24 (3), 331–350. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079912331379935 .
Dunning, D., Heath, C., & Suls, J. M. (2004). Flawed self-assessment: implications for health, education, and the workplace. Psychological Science in the Public Interest, 5 (3), 69–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-1006.2004.00018.x .
Ecclestone, K. (2001). “I know a 2:1 when I see it”: understanding criteria for degree classifications in franchised university programmes. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 25 (3), 301–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/03098770126527 .
Falchikov, N., & Goldfinch, J. (2000). Student peer assessment in higher education: a meta-analysis comparing peer and teacher marks. Review of Educational Research, 70 (3), 287–322. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543070003287 .
Fraile, J., Panadero, E., & Pardo, R. (2017). Co-creating rubrics: the effects on self-regulated learning, self-efficacy and performance of establishing assessment criteria with students. Studies in Educational Evaluation. 53 (June). 6–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2017.03.003 .
Gielen, S., Dochy, F., Onghena, P., Struyven, K., & Smeets, S. (2011). Goals of peer assessment and their associated quality concepts. Studies in Higher Education, 36 (6), 719–735. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075071003759037 .
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of Educational Research, 77 (1), 81–112. https://doi.org/10.3102/003465430298487 .
Hendry, G. D., & Anderson, J. (2013). Helping students understand the standards of work expected in an essay: using exemplars in mathematics pre-service education classes. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 38 (6), 754–768. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2012.703998 .
Hendry, G. D., & Jukic, K. (2014). Learning about the quality of work that teachers expect: students’ perceptions of exemplar marking versus teacher explanation. Journal of University Teaching & Learning Practice, 11 (2), 5.
Hudson, J., Bloxham, S., den Outer, B., & Price, M. (2017). Conceptual acrobatics: talking about assessment standards in the transparency era. Studies in Higher Education, 42 (7), 1309–1323. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1092130 .
Joughin, G., Dawson, P., & Boud, D. (2017). Improving assessment tasks through addressing our unconscious limits to change. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 42 (8), 1221–1232. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2016.1257689 .
Knight, P. T., & Yorke, M. (2003). Assessment, learning and employability . Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Liu, N.-F., & Carless, D. (2006). Peer feedback: the learning element of peer assessment. Teaching in Higher Education, 11 (3), 279–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510600680582 .
McConlogue, T. (2012). But is it fair? Developing students’ understanding of grading complex written work through peer assessment. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 37 (1), 113–123. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2010.515010 .
Merry, S., Price, M., Carless, D., & Taras, M. (2013). Reconceptualising feedback in higher education . London: Routledge.
Nicol, D. (2013). Resituating feedback from the reactive to the proactive. In D. Boud & E. Molloy (Eds.), Feedback in higher and professional education: understanding and doing it well (pp. 34–49). Milton Park: Routledge.
Nicol, D. (2014). Guiding principles for peer review: unlocking learners’ evaluative skills. In C. Kreber, C. Anderson, N. Entwistle, & J. McArthur (Eds.), Advances and innovations in university assessment and feedback (pp. 197–224). Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Nicol, D., & Macfarlane-Dick, D. (2006). Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. Studies in Higher Education, 31 (2), 199–218. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070600572090 .
Nicol, D., Thomson, A., & Breslin, C. (2014). Rethinking feedback practices in higher education: a peer review perspective. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 39 (1), 102–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2013.795518 .
Nixon, E., Scullion, R., & Hearn, R. (2016). Her majesty the student: marketised higher education and the narcissistic (dis)satisfactions of the student-consumer. Studies in Higher Education, 5079 , 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2016.1196353 .
O’Donovan, B., Price, M., & Rust, C. (2004). Know what I mean? Enhancing student understanding of assessment standards and criteria. Teaching in Higher Education, 9 (3), 325–335. https://doi.org/10.1080/1356251042000216642 .
Orsmond, P., Merry, S., & Reiling, K. (2002). The use of exemplars and formative feedback when using student derived marking criteria in peer and self-assessment. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 27 (4), 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1080/0260293022000001337 .
Panadero, E. (2016). Is it safe? Social, interpersonal, and human effects of peer assessment: a review and future directions. In G. T. L. Brown & L. R. Harris (Eds.), Handbook of human and social conditions in assessment (pp. 247–266). New York: Routledge.
Panadero, E., & Alonso-Tapia, J. (2013). Self-Assessment: theoretical and Practical Connotations. When It Happens, How Is It Acquired and What to Do to Develop It in Our Students. Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psychology, 11 (2), 551–576.
Panadero, E., & Jonsson, A. (2013). The use of scoring rubrics for formative assessment purposes revisited: a review. Educational Research Review, 9 , 129–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2013.01.002 .
Panadero, E., Brown, G. T. L., & Strijbos, J.-W. (2016). The future of student self-assessment: a review of known unknowns and potential directions. Educational Psychology Review, 28 (4), 803–830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-015-9350-2 .
Pascarella, E. T., & Terenzini, P. T. (2005). How college affects students (Vol. 2). San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Sadler, D. R. (1989). Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instructional Science, 18 (2), 119–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117714 .
Sadler, D. R. (2007). Perils in the meticulous specification of goals and assessment criteria. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 14 (3), 387–392. https://doi.org/10.1080/09695940701592097 .
Sadler, D. R. (2010). Beyond feedback: developing student capability in complex appraisal. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 35 (5), 535–550. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930903541015 .
Sadler, D. R. (2013). Assuring academic achievement standards: from moderation to calibration. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 20 (1), 5–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594X.2012.714742 .
Schmidt, H. G., & Rikers, R. M. J. P. (2007). How expertise develops in medicine: knowledge encapsulation and illness script formation. Medical Education, 41 (12), 1133–1139. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2923.2007.02915.x .
Sitzmann, T., & Ely, K. (2011). A meta-analysis of self-regulated learning in work-related training and educational attainment: what we know and where we need to go. Psychological Bulletin, 137 (3), 421–442. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022777 .
Speyer, R., Pilz, W., Van Der Kruis, J., & Brunings Wouter, J. (2011). Reliability and validity of student peer assessment in medical education: a systematic review. Medical Teacher, 33 (11), e572–e585. https://doi.org/10.3109/0142159X.2011.610835 .
Tai, J., Canny, B. J., Haines, T. P., & Molloy, E. K. (2016). The role of peer-assisted learning in building evaluative judgement: opportunities in clinical medical education. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 21 (3), 659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-015-9659-0 .
Thompson, D. G. (2006). E-assessment: the demise of exams and the rise of generic attribute assessment for improved student learning. In T. S. Roberts (Ed.), Self, peer and group assessment in e-learning (pp. 295–322). USA: Information Science Publishing.
Thompson, D. G. (2016). Marks should not be the focus of assessment—but how can change be achieved? Journal of Learning Analytics, 3 (2), 193–212. https://doi.org/10.18608/jla.2016.32.9 .
To, J., & Carless, D. (2015). Making productive use of exemplars: peer discussion and teacher guidance for positive transfer of strategies. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 40 (6), 746–764. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877X.2015.1014317 .
Tomlinson, M. (2012). Graduate employability: a review of conceptual and empirical themes. Higher Education Policy, 25 (4), 407–431. https://doi.org/10.1057/hep.2011.26 .
Topping, K. J. (2010). Methodological quandaries in studying process and outcomes in peer assessment. Learning and Instruction, 20 (4), 339–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.08.003 .
van den Berg, I., Admiraal, W., & Pilot, A. (2006). Peer assessment in university teaching: evaluating seven course designs. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 31 (1), 19–36. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930500262346 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
Our thanks go to attendees of the Symposium on Evaluative Judgement on 17 and 18 October 2016 at Deakin University, who contributed to discussions on the topic of this paper. In particular, Jaclyn Broadbent contributed to initial conceptual discussions, while Margaret Bearman, David Carless, Gloria Dall’Alba, Gordon Joughin, Susie Macfarlane, and Darrall Thompson also commented on a draft version of this paper.
Ernesto Panadero is funded by the Spanish Ministry (Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad) via the Ramón y Cajal programme (file id. RYC-2013-13469).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Research in Assessment and Digital Learning, Deakin University, Geelong, Australia
Joanna Tai, Rola Ajjawi, David Boud, Phillip Dawson & Ernesto Panadero
Faculty of Arts and Social Sciences, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Work and Learning Research Centre, Middlesex University, London, UK
Developmental and Educational Psychology Department, Faculty of Psychology, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Ernesto Panadero
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joanna Tai .
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Tai, J., Ajjawi, R., Boud, D. et al. Developing evaluative judgement: enabling students to make decisions about the quality of work. High Educ 76 , 467–481 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-017-0220-3
Download citation
Published : 16 December 2017
Issue Date : September 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-017-0220-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Assessment for learning
- Sustainable assessment
- Peer assessment
- Graduate attributes
- Self-regulated learning
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
COMMENTS
An evaluation essay is a type of writing that assesses and critiques a particular subject, such as a movie, book, restaurant, or product. It requires the writer to analyze the subject and provide a judgment based on defined criteria. The purpose of an evaluation essay is to evaluate the subject's quality and effectiveness, and to present a ...
Judgement. Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria. Criteria. The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for ...
How to write an Evaluation Essay. There are two secrets to writing a strong evaluation essay. The first is to aim for objective analysis before forming an opinion. The second is to use an evaluation criteria. Aim to Appear Objective before giving an Evaluation Argument. Your evaluation will eventually need an argument.
Judgement. Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria. Criteria. The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for ...
This type of essay requires evaluation on two levels. First of all, it demands that we use evaluation in order to determine that there is a legitimate problem. ... persuade, or otherwise influence an audience by way of that judgment. In this way, evaluation is a type of argument, in which you as a writer are attempting consciously to have an ...
Following the quick tips below, you will find it easier to write an effective evaluation argument essay: Provide the right amount of details: Make sure you explain your thoughts clearly and provide sufficient information to convince the reader in the correctness of your judgment.
Table of contents. 1 Defining Evaluation Essays. 2 Choose a Subject for Evaluation. 3 Develop a Clear Thesis Statement. 4 Gather Information and Evidence. 5 Establish Evaluation Criteria. 6 Organize Your Essay. 7 Write the Introduction. 8 Write the Body of The Essay.
An evaluation essay is written by first making an overall judgment about the topic in the introduction and previewing the main points. The body of the essay lists the criteria that led to the ...
2.A judgment. The writer must assert him or herself by making a definitive judgment. This judgment should be the writer's thesis sentence. All other paragraphs should seek to prove the thesis, even if a writer must give a balanced appraisal by anticipating objections. 3.A convincing argument.
An evaluation essay is a distinctive form of writing that aims to present a balanced opinion on a subject. This type of essay is akin to a persuasive essay. However, it differs by offering a more even-handed argument. While a persuasive essay may focus more heavily on the author's viewpoint, an evaluation essay gives equal weight to both the ...
An evaluation essay is a piece of writing that aims to assess the value or quality of a particular subject or phenomenon. It involves analyzing a topic, presenting your judgment or opinion on it, and providing evidence or examples to support your claims. This type of essay requires critical thinking, research, and effective communication skills ...
Judgement. Next, the essay needs to provide a judgment about a subject. This is the thesis of the essay, and it states whether the subject is good or bad based on how it meets the stated criteria. Criteria. The body of the essay will contain the criteria used to evaluate the subject. In an evaluation essay, the criteria must be appropriate for ...
Delve into curated evaluation essay examples that demonstrate the nuances of critical assessment, coupled with techniques that ensure your essays are both insightful and balanced in judgment. ... In contrast to a descriptive essay, an evaluation essay aims to express the author's judgment. However, this essay type is defined by an objective ...
An evaluation argument based on moral criteria will claim that something is right or wrong. It will need to appeal to shared values or make a case for a particular value that serves as criteria. Some values are nearly universal, such as honesty, reasonableness, and fairness, as we will discuss in 9.6: Moral Character.
The evidence of an evaluation essay consists of the supporting details authors provide based on their judgment of the criteria. For example, if the subject of an evaluation is a restaurant, a judgment could be "Kay's Bistro provides an unrivaled experience in fine dining." Some authors evaluate fine dining restaurants by identifying ...
The first step in writing an evaluation essay is to provide a judgment asserted through a clear thesis. A good thesis statement determines exactly the focus of your essay and aids the reader in understanding what the essay is all about. Furthermore, it presents the point-of-view you are taking and hereafter each paragraph should work towards ...
Judgment A second element in essay evaluation is judgment. This aspect helps to establish if stated standards were met. Considering the previous example of a house discussed under this criteria, you may first assess if the house is secure or not. Find out if the house meets, exceeds, or falls short of your anticipated security standards, then ...
When you start writing an evaluation essay, grabbing the reader's attention is essential. For this, hook the reader from the beginning until the end to ensure that your essay's opening follows an engaging tone. Step 1. Choose an Interesting Topic. Deciding the topic and evaluation essay criteria is important.
Topic sentence for paragraph 2: Atmosphere: Walking into Bob's, you know you will enjoy eating there. Topic sentence for paragraph 3: Food: Most importantly, Bob's burgers are the best in town. Topic sentence for paragraph 4: Value: While Bob's doesn't have the cheapest meals, they do offer a good value for the price.
The five key features of an evaluation essay are: Presenting the subject: Introduce the topic or subject being evaluated. Asserting an overall judgment: Share your overall opinion or assessment of the subject. Providing reasons and support: Back up your judgment with evidence, examples, and reasoning.
Evaluation Essay is a type of writing that assesses and judges something based on criteria. This type of essay requires the writer to analyze and evaluate a particular subject, such as a book, movie, restaurant, or product. The purpose of an evaluation essay is to provide an in-depth analysis and judgment of the chosen topic.
As a term, evaluative judgement has only relatively recently been taken up in the higher and professional education literature, as a higher-level cognitive ability required for life-long learning (Cowan 2010).Ideas about evaluation and critical judgement being necessary for effective feedback, and therefore learning, have also been highlighted by Sadler (), Nicol (2013, 2014, 2014), and Boud ...
An evaluation argument based on moral criteria will claim that something is right or wrong. It will need to appeal to shared values or make a case for a particular value that serves as criteria. Some values are nearly universal, such as honesty, reasonableness, and fairness, as we will discuss in 9.6: Moral Character.
Self Evaluation Essay Sample Writing a self-evaluation essay can be a challenging yet rewarding task. The difficulty lies in the introspective nature of the assignment, as it requires a deep and honest reflection on one's own strengths and weaknesses. Crafting an essay about oneself necessitates a level of self-awareness that can be uncomfortable for some, as it involves acknowledging personal ...
In the philosophy of economics, a descriptive or positive statement is an assertion about facts of the world, while prescriptive or normative statements express value judgments.The former describe the world as it is, while the latter talk about the world as it should be. [1] The methodological basis for positive/normative distinction is rooted in the fact-value distinction in philosophy.