
Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia

How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
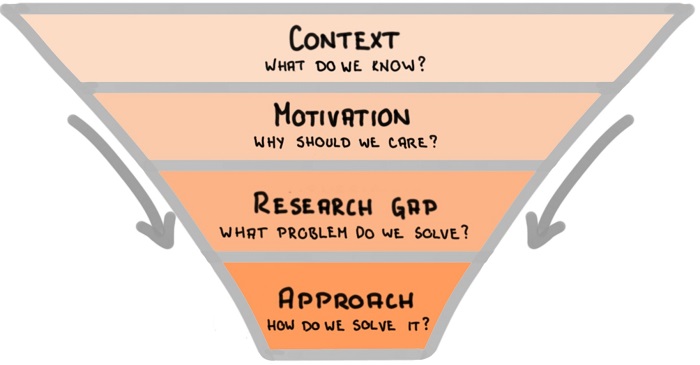
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
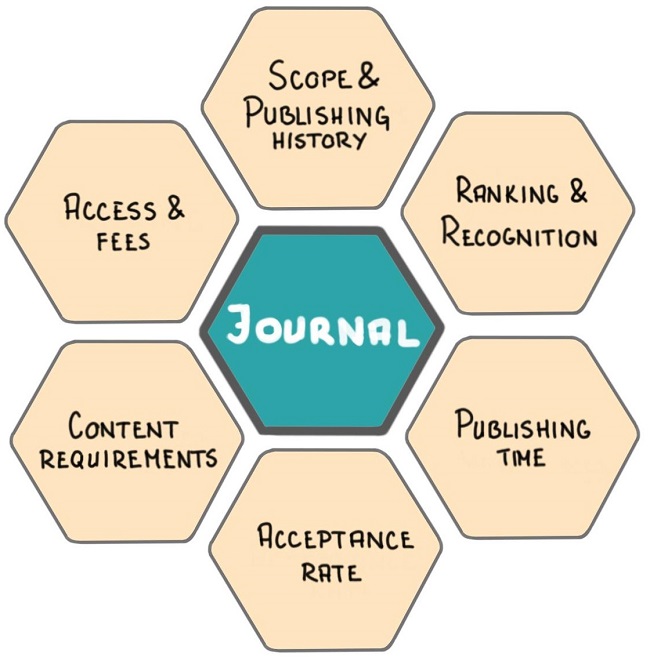
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
- Thesis Action Plan New
- Academic Project Planner
Literature Navigator
Thesis dialogue blueprint, writing wizard's template, research proposal compass.
- Why students love us
- Rebels Blog
- Why we are different
- All Products
- Coming Soon
How to Start a Research Paper: A Comprehensive Guide

Starting a research paper can feel overwhelming, especially if you're new to the process. This guide will walk you through each step, from picking a topic to polishing your final draft. By breaking down the process into manageable parts, you'll find it easier to stay organized and focused. Let's dive in and make your research paper a success!
Key Takeaways
- Choose a topic that interests you and has enough resources available.
- Formulate a clear research question to guide your study.
- Conduct a thorough literature review to understand existing research.
- Develop a detailed research plan, including methodology and timeline.
- Ensure proper citation to maintain academic integrity.
Choosing a Research Topic
Choosing a research topic is a crucial first step in writing a research paper. It sets the foundation for your entire project . Here are some key steps to help you choose the right topic.
Formulating a Research Question

Understanding the Importance of a Research Question
A well-defined research question is the cornerstone of any successful research paper. It acts as a compass, guiding your study and ensuring that you stay on track. Without a clear research question, your paper may lack focus and coherence. This question helps you narrow down your topic and provides a clear direction for your research.
Techniques for Crafting a Strong Research Question
To craft a strong research question, start by identifying a specific issue or problem within your topic. Use the following steps:
- Identify a gap in the existing literature or a problem that needs solving.
- Make sure your question is clear and concise, avoiding vague terms.
- Ensure that your question is researchable within the scope of your resources and time.
- Align your question with your research objectives to maintain focus.
Aligning the Research Question with Objectives
Your research question should align closely with your research objectives. This alignment ensures that every part of your study is interconnected and supports your overall goals. A well-aligned research question not only clarifies your study's purpose but also helps in structuring your paper effectively.
Conducting a Literature Review
Gathering relevant sources.
Start by collecting sources that are related to your research topic. Use libraries, online databases, and academic journals to find books, articles, and papers. Skimming sources instead of reading each one fully can save you time. If a source seems useful, set it aside for a more in-depth read later.
Analyzing Existing Research
Once you have gathered your sources, read through them and take notes on key points. Pay attention to different viewpoints and how they relate to your research question. This will help you understand the current state of research in your field. To elevate your essay , start with a comprehensive literature review to ground your work in relevant scholarship.
Identifying Research Gaps
Look for areas that haven't been explored or questions that haven't been answered in the existing research. These gaps can provide a direction for your own research and make your thesis more valuable. Defining your research question and following a methodical process to synthesize findings is crucial. This step is essential in the steps in the literature review process .
Developing a Research Plan
Creating a solid research plan is crucial for the success of your thesis. It helps you stay organized and ensures that you cover all necessary aspects of your research.
Writing the Thesis Introduction
Starting your thesis introduction can be daunting, but it's crucial for setting the stage for your research. Establishing the context for your study helps readers understand the background and significance of your work. This section should provide a clear overview of what your thesis will cover, making it easier for readers to follow your arguments.
Establishing Context
Begin by providing some background information on your topic. This helps to set the stage and gives your readers a sense of what to expect. Make sure to include relevant literature and previous studies to show how your research fits into the existing body of work. This is essential for demonstrating the importance of your research .
Crafting a Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the heart of your introduction. Typically, it is placed at the end of the introductory paragraph. This statement should succinctly present the main argument or focus of your thesis, guiding the reader on what to expect. A clear and concise thesis statement is crucial for a strong introduction.
Providing an Overview of the Study
Finally, outline the structure of your thesis. This roadmap will help readers navigate through your work, knowing what each section will address. By clearly presenting the layout, you reduce thesis anxiety and make your research more accessible.
Choosing a Research Methodology
Choosing the right research methodology is crucial for the success of your study. It determines how you will collect and analyze data, and ultimately, how you will answer your research question. Here are some key points to consider when selecting a methodology.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Methods
First, decide whether your research will be qualitative, quantitative, or a mix of both. Qualitative research focuses on understanding concepts, thoughts, or experiences. It often involves interviews, focus groups, or content analysis. On the other hand, quantitative research aims to quantify the problem by way of generating numerical data or data that can be transformed into usable statistics. This often involves surveys, experiments, or secondary data analysis.
Selecting Data Collection Tools
Once you've chosen between qualitative and quantitative methods, the next step is to select the appropriate data collection tools. For qualitative research, you might use interviews, focus groups, or observational methods. For quantitative research, consider surveys, experiments, or existing datasets. The choice of tools should align with your research objectives and the type of data you need to collect.
Justifying Methodological Choices
Finally, it's essential to justify your methodological choices. Explain why the selected methods are suitable for your research and how they will help you achieve your objectives. This step is crucial for gaining approval from stakeholders and ensuring the success of your project. Make sure to address any potential limitations and how you plan to mitigate them.
Organizing Research Materials
Creating a categorization system.
To start, you need a system to categorize your research materials. This can be as simple as using folders on your computer or as advanced as specialized software. Organizing your notes into categories helps you find information quickly. You can use sticky notes or a mind map to group related ideas. This step is crucial for keeping your research structured and accessible.
Using Reference Management Software
Using reference management software like Zotero or Mendeley can save you a lot of time. These tools help you keep track of your sources and format citations correctly. They also allow you to create a library of references that you can easily search through. This is especially useful when you need to cite sources in your paper.
Synthesizing Information
Synthesizing information means combining ideas from different sources to create a comprehensive understanding of your topic. Look for common themes, debates, and gaps in the literature. This will help you formulate a strong research question and provide a solid foundation for your thesis. Summarizing and integrating findings from various sources will make your research more robust and credible.
Drafting the Research Paper

Writing the First Draft
Once your outline is ready, it's time to start writing your first draft. This is the longest step, but if you've prepared well, it should go smoothly. Begin with your thesis statement and then fill out the introduction with secondary information. The body of your paper will contain the bulk of your research, divided into sections with headers for easy navigation. Don't worry about perfection at this stage ; focus on getting your ideas down .
Incorporating Feedback
After completing your first draft, seek feedback from your supervisor and peers . Their insights can help you see your work from different perspectives and identify areas for improvement. Revising is a continuous process of re-seeing your writing, considering larger issues like focus, organization, and audience.
Polishing the Final Draft
Finally, polish your final draft. Pay attention to grammar, punctuation, and formatting. Ensure that your thesis is clear, concise, and free of errors. This step is crucial for making a strong impression and effectively communicating your research findings.
Maintaining Academic Integrity
Proper citation practices.
Proper citation is essential to uphold academic integrity. Always give credit to the original authors of the sources you use. This not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also strengthens your arguments by backing them up with credible sources. Citing your sources correctly is a fundamental aspect of academic writing.
Avoiding Plagiarism
Plagiarism is a serious offense in the academic world. It involves using someone else's work without giving them credit. To avoid plagiarism, make sure to paraphrase correctly and use quotation marks when directly quoting someone. Utilize plagiarism detection tools to ensure your work is original.
Ensuring Credibility of Sources
Using credible sources is crucial for the integrity of your research. Evaluate the reliability of your sources by checking the author's credentials and the publication's reputation. Credible sources add weight to your arguments and help you build a strong foundation for your research.
Effective Data Collection and Analysis
Choosing data collection methods.
Selecting the right data collection methods is crucial for the success of your research. Consider methods such as surveys, interviews, or experiments based on your research needs. Aligning data collection techniques with research needs ensures relevant and robust findings.
Analyzing Collected Data
Once you have gathered your data, the next step is to analyze it accurately . Use statistical tools and software to help you interpret the data. Create tables and graphs to illustrate your findings clearly. This will help you present your results in a structured and understandable way.
Interpreting Results
Interpreting your results is an essential part of your thesis. Discuss how your findings relate to your research questions and the existing literature. Highlight the significance of your analyses and the reliability of your findings. This will help you draw meaningful conclusions and provide valuable insights into your research topic.
Revising and Editing the Research Paper
Reviewing for clarity and coherence.
When revising your research paper, focus on ensuring that your ideas are clear and logically organized. Each section should flow smoothly into the next, and your arguments should be well-structured. Reading your paper out loud can help you catch issues that you might miss when reading silently. Additionally, consider having someone else review your paper to provide a fresh perspective.
Addressing Feedback
Incorporating feedback is a crucial part of the revision process. Share your draft with peers, mentors, or advisors and be open to their suggestions. Addressing feedback can help you identify areas for improvement and strengthen your arguments. Remember, revising is a continuous process of refining your work.
Final Proofreading
The final step in the editing process is proofreading. This involves checking for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Use tools like spellcheckers or digital writing assistants to help with this task. Ensure that your paper follows the required formatting guidelines and that all citations are correctly formatted. A well-proofread paper enhances the credibility of your research.
Revising and editing your research paper can be a daunting task, but it doesn't have to be. Our step-by-step guides make the process simple and stress-free. Whether you're stuck on where to start or need help polishing your final draft, we've got you covered. Visit our website to discover how our resources can help you achieve academic success.
Starting a research paper might seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into manageable steps can make the process much easier. From selecting a topic that interests you to organizing your research and drafting your paper, each step is crucial for success. Remember to stay focused on your research question, use reliable sources, and keep your writing clear and concise. By following these guidelines, you'll be well on your way to crafting a compelling and informative research paper. Good luck, and don't hesitate to seek help if you need it!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i choose a research topic.
Start by thinking about what interests you. Pick a topic that you find fun and fulfilling. This will keep you motivated throughout your research. Make a list of subjects you enjoy and see how they can relate to your field of study.
Why is a research question important?
A research question guides your study and keeps you focused. It helps you set specific goals and determine the direction of your research.
What is a literature review?
A literature review involves gathering and analyzing existing research on your topic. It helps you understand what has already been studied and identify gaps that your research can fill.
How do I create a research plan?
Start by outlining your methodology, creating a timeline, and allocating resources effectively. A solid plan helps you stay organized and ensures you cover all necessary aspects of your research.
What should be included in a thesis introduction?
Your introduction should establish the context for your study, present your thesis statement, and provide an overview of what your thesis will cover.
How do I choose the right research methodology?
Decide whether to use qualitative or quantitative methods, select appropriate data collection tools, and justify your choices based on your research goals.
What are proper citation practices?
Always give credit to the original authors of the sources you use. Use a consistent citation style and ensure all sources are properly cited to avoid plagiarism.
How do I revise and edit my research paper?
Review for clarity and coherence, address feedback from peers or advisors, and do a final proofreading to catch any errors.

Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics: A Fun and Informative Guide

Unlocking the Power of Data: A Review of 'Essentials of Modern Business Statistics with Microsoft Excel'

Discovering Statistics Using SAS: A Comprehensive Review

How to Deal with a Total Lack of Motivation, Stress, and Anxiety When Finishing Your Master's Thesis

Mastering the First Step: How to Start Your Thesis with Confidence

Thesis Revision Made Simple: Techniques for Perfecting Your Academic Work

Thesis Action Plan

Integrating Calm into Your Study Routine: The Power of Mindfulness in Education
How to determine the perfect research proposal length.
- Blog Articles
- Affiliate Program
- Terms and Conditions
- Payment and Shipping Terms
- Privacy Policy
- Return Policy
© 2024 Research Rebels, All rights reserved.
Your cart is currently empty.

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Research Findings – Types Examples and Writing...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms
How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.

What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1991 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 42,043 quotes across 1991 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write a Research Paper
Last Updated: February 18, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Chris Hadley, PhD . Chris Hadley, PhD is part of the wikiHow team and works on content strategy and data and analytics. Chris Hadley earned his PhD in Cognitive Psychology from UCLA in 2006. Chris' academic research has been published in numerous scientific journals. There are 14 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 4,198,083 times.
Whether you’re in a history, literature, or science class, you’ll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you’re just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process a breeze. Research your topic, find reliable sources, and come up with a working thesis. Then create an outline and start drafting your paper. Be sure to leave plenty of time to make revisions, as editing is essential if you want to hand in your best work!
Sample Research Papers and Outlines

Researching Your Topic

- For instance, you might start with a general subject, like British decorative arts. Then, as you read, you home in on transferware and pottery. Ultimately, you focus on 1 potter in the 1780s who invented a way to mass-produce patterned tableware.
Tip: If you need to analyze a piece of literature, your task is to pull the work apart into literary elements and explain how the author uses those parts to make their point.

- Authoritative, credible sources include scholarly articles (especially those other authors reference), government websites, scientific studies, and reputable news bureaus. Additionally, check your sources' dates, and make sure the information you gather is up to date.
- Evaluate how other scholars have approached your topic. Identify authoritative sources or works that are accepted as the most important accounts of the subject matter. Additionally, look for debates among scholars, and ask yourself who presents the strongest evidence for their case. [3] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- You’ll most likely need to include a bibliography or works cited page, so keep your sources organized. List your sources, format them according to your assigned style guide (such as MLA or Chicago ), and write 2 or 3 summary sentences below each one. [4] X Research source

- Imagine you’re a lawyer in a trial and are presenting a case to a jury. Think of your readers as the jurors; your opening statement is your thesis and you’ll present evidence to the jury to make your case.
- A thesis should be specific rather than vague, such as: “Josiah Spode’s improved formula for bone china enabled the mass production of transfer-printed wares, which expanded the global market for British pottery.”
Drafting Your Essay

- Your outline is your paper’s skeleton. After making the outline, all you’ll need to do is fill in the details.
- For easy reference, include your sources where they fit into your outline, like this: III. Spode vs. Wedgewood on Mass Production A. Spode: Perfected chemical formula with aims for fast production and distribution (Travis, 2002, 43) B. Wedgewood: Courted high-priced luxury market; lower emphasis on mass production (Himmelweit, 2001, 71) C. Therefore: Wedgewood, unlike Spode, delayed the expansion of the pottery market.

- For instance, your opening line could be, “Overlooked in the present, manufacturers of British pottery in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries played crucial roles in England’s Industrial Revolution.”
- After presenting your thesis, lay out your evidence, like this: “An examination of Spode’s innovative production and distribution techniques will demonstrate the importance of his contributions to the industry and Industrial Revolution at large.”
Tip: Some people prefer to write the introduction first and use it to structure the rest of the paper. However, others like to write the body, then fill in the introduction. Do whichever seems natural to you. If you write the intro first, keep in mind you can tweak it later to reflect your finished paper’s layout.

- After setting the context, you'd include a section on Josiah Spode’s company and what he did to make pottery easier to manufacture and distribute.
- Next, discuss how targeting middle class consumers increased demand and expanded the pottery industry globally.
- Then, you could explain how Spode differed from competitors like Wedgewood, who continued to court aristocratic consumers instead of expanding the market to the middle class.
- The right number of sections or paragraphs depends on your assignment. In general, shoot for 3 to 5, but check your prompt for your assigned length.

- If you bring up a counterargument, make sure it’s a strong claim that’s worth entertaining instead of ones that's weak and easily dismissed.
- Suppose, for instance, you’re arguing for the benefits of adding fluoride to toothpaste and city water. You could bring up a study that suggested fluoride produced harmful health effects, then explain how its testing methods were flawed.

- Sum up your argument, but don’t simply rewrite your introduction using slightly different wording. To make your conclusion more memorable, you could also connect your thesis to a broader topic or theme to make it more relatable to your reader.
- For example, if you’ve discussed the role of nationalism in World War I, you could conclude by mentioning nationalism’s reemergence in contemporary foreign affairs.
Revising Your Paper

- This is also a great opportunity to make sure your paper fulfills the parameters of the assignment and answers the prompt!
- It’s a good idea to put your essay aside for a few hours (or overnight, if you have time). That way, you can start editing it with fresh eyes.
Tip: Try to give yourself at least 2 or 3 days to revise your paper. It may be tempting to simply give your paper a quick read and use the spell-checker to make edits. However, revising your paper properly is more in-depth.

- The passive voice, such as “The door was opened by me,” feels hesitant and wordy. On the other hand, the active voice, or “I opened the door,” feels strong and concise.
- Each word in your paper should do a specific job. Try to avoid including extra words just to fill up blank space on a page or sound fancy.
- For instance, “The author uses pathos to appeal to readers’ emotions” is better than “The author utilizes pathos to make an appeal to the emotional core of those who read the passage.”

- Read your essay out loud to help ensure you catch every error. As you read, check for flow as well and, if necessary, tweak any spots that sound awkward. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- It’s wise to get feedback from one person who’s familiar with your topic and another who’s not. The person who knows about the topic can help ensure you’ve nailed all the details. The person who’s unfamiliar with the topic can help make sure your writing is clear and easy to understand.
Community Q&A
- Remember that your topic and thesis should be as specific as possible. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0
- Researching, outlining, drafting, and revising are all important steps, so do your best to budget your time wisely. Try to avoid waiting until the last minute to write your paper. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 2

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/planresearchpaper/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/evaluating-print-sources/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/research_overview/index.html
- ↑ https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/writing/graduate-writing-lab/writing-through-graduate-school/working-sources
- ↑ https://opentextbc.ca/writingforsuccess/chapter/chapter-5-putting-the-pieces-together-with-a-thesis-statement/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/developing_an_outline/index.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/introductions/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/writingprocess/counterarguments
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/ending-essay-conclusions
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/formandstyle/writing/scholarlyvoice/activepassive
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/reading-aloud/
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/index.html
About This Article

To write a research paper, start by researching your topic at the library, online, or using an academic database. As you conduct your research and take notes, zero in on a specific topic that you want to write about and create a 1-2 sentence thesis to state the focus of your paper. Then, create an outline that includes an introduction, 3 to 5 body paragraphs to present your arguments, and a conclusion to sum up your main points. Once you have your paper's structure organized, draft your paragraphs, focusing on 1 argument per paragraph. Use the information you found through your research to back up your claims and prove your thesis statement. Finally, proofread and revise your content until it's polished and ready to submit. For more information on researching and citing sources, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Private And Discrete
Aug 2, 2020
Did this article help you?

Jan 3, 2018
Oct 29, 2016
Maronicha Lyles
Jul 24, 2016
Maxwell Ansah
Nov 22, 2019

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
15 Steps to Good Research
- Define and articulate a research question (formulate a research hypothesis). How to Write a Thesis Statement (Indiana University)
- Identify possible sources of information in many types and formats. Georgetown University Library's Research & Course Guides
- Judge the scope of the project.
- Reevaluate the research question based on the nature and extent of information available and the parameters of the research project.
- Select the most appropriate investigative methods (surveys, interviews, experiments) and research tools (periodical indexes, databases, websites).
- Plan the research project. Writing Anxiety (UNC-Chapel Hill) Strategies for Academic Writing (SUNY Empire State College)
- Retrieve information using a variety of methods (draw on a repertoire of skills).
- Refine the search strategy as necessary.
- Write and organize useful notes and keep track of sources. Taking Notes from Research Reading (University of Toronto) Use a citation manager: Zotero or Refworks
- Evaluate sources using appropriate criteria. Evaluating Internet Sources
- Synthesize, analyze and integrate information sources and prior knowledge. Georgetown University Writing Center
- Revise hypothesis as necessary.
- Use information effectively for a specific purpose.
- Understand such issues as plagiarism, ownership of information (implications of copyright to some extent), and costs of information. Georgetown University Honor Council Copyright Basics (Purdue University) How to Recognize Plagiarism: Tutorials and Tests from Indiana University
- Cite properly and give credit for sources of ideas. MLA Bibliographic Form (7th edition, 2009) MLA Bibliographic Form (8th edition, 2016) Turabian Bibliographic Form: Footnote/Endnote Turabian Bibliographic Form: Parenthetical Reference Use a citation manager: Zotero or Refworks
Adapted from the Association of Colleges and Research Libraries "Objectives for Information Literacy Instruction" , which are more complete and include outcomes. See also the broader "Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher Education."
How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- 100+ Writing Prompts for College Students (10+ Categories!)
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Know Everything About How to Make an Audiobook
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
- 10 Best AI Essay Outline Generators of 2024
- The Best Essay Graders of 2024 That You Can Use for Free!
- Top 10 Free Essay Writing Tools for Students in 2024
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment

Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!

Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic Research , Academic Writing , Research , Research Paper
Learning how to start a research paper is the first checklist item of your academic writing journey. A compelling research paper introduction sets the stage for everything that follows. It clearly defines your argument and gives readers a roadmap for what’s in store.
But why is a strong introduction to a research paper so important? Simple. It grabs attention and lays the foundation stone of your argument. Through this practical guide, we’ll explore the various elements to include in your introduction for a research paper. We’ll try to shed light through practical tips and examples. So let’s dive in!
Want to elevate the quality of your research paper? Learn more
How to write a research paper introduction?
First impressions always matter, and this is why adding a strong introduction to a research paper is so important. But what does it constitute? There are 3 main parts broadly – The hook, the background information, and the thesis statement.
Let’s look at each one in detail:
The first sentence is your hook, designed to capture the reader’s attention. It can be a provocative question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement. The aim is to pique interest and pose the overarching question that your research seeks to answer. A well-crafted hook is like a magnet—it draws the reader into your intellectual arena.
Example: Did you know chocolate was once used as currency in ancient civilizations?
Background information
When it comes to writing a research paper introduction , your reader needs context but not information overload. Here, you set the stage by providing just enough background information on the topic at hand.
It can include previous studies on the same topic, the scope, and some context. Consider this your chance to orient your audience before delving into the complexities of your argument.
Example : “There has been a significant increase in the incidence of diabetes in recent years. This has led to an increased demand for effective diabetes management strategies. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of a new diabetes management program in improving patient outcomes.”
The thesis statement
This is the core of your research paper introduction paragraph. It succinctly outlines the aim and focus of your paper. This is usually the first sentence in the introductory paragraph of a research paper.
Example: This paper reviews the recent research in cultural psychology and how culture is the byproduct of interpersonal relations and evolution.
Some practical tips:
- Keep your thesis statement specific.
- Express a single main idea in your statement.
- Make your thesis statement invite the main discussion.
In Summary:
- A compelling hook grabs attention.
- Just enough background sets the stage and orients the reader.
- A clear thesis statement should warrant discussion and take some sort of a stand.
Armed with these three pillars, you’re well on your way to crafting an introduction paragraph of a research paper that captivates and informs.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into how to start a research paper , offering tailored advice for various types of research undertakings.
How to Start A Research Paper: Actionable Tips
So you’re staring at that blinking cursor, feeling the weight of a thousand academic journals on your shoulders. The task: figure out how to start a research paper. Let’s ditch the anxiety and get right to the point!
Understand your audience
First and foremost, know who you’re talking to. Is your audience a group of academics or a more general readership? Understanding your audience is like knowing your stage and adjusting your tone and language accordingly.
To define your audience, try to create a persona – age, sex, economic level, social status, and so on. You can do this by:
- Conducting an online survey
- Organizing focus groups
- Talking to your audience directly via phone calls
Research beforehand
Before you even type the first word, dig deep into your topic. Consult sources, both primary and secondary, to have a well-rounded understanding of the issue.
Check the following aspects before moving to the next step:
- Identify Keywords : Find relevant keywords that are related to your topic.
- Database Diving : Utilize academic databases like PubMed for medical research or JSTOR for humanities.
- Cross-Reference : Always double-check facts from multiple sources.
You can rely on two kinds of sources for your research, as mentioned below:
Primary Sources : These are your firsthand accounts or direct evidence. If you’re tackling a historical topic, primary sources could be letters, diaries, or newspaper articles from the time. In scientific research, it might be the raw data from experiments.
Secondary Sources : These are interpretations or analyses of primary sources. Academic articles, reviews, and most books fall under this category.
Craft a strong thesis statement
A thesis statement focuses on a specific topic. So make your thesis statement is clear and concise.
Follow the steps mentioned below to craft a strong thesis statement:
- Be specific : Aim for specificity. Instead of saying, “Social media affects mental health,” say, “Excessive use of social media contributes to increased levels of anxiety among teenagers.”
- Keep an arguable point : Your thesis should make a claim that can be debated. If it’s a universally accepted fact, there’s no point in arguing.
- Be focused : Keep it tight and focused. Your thesis statement should be one to two sentences max. It’s the tagline of your paper; it should be concise and to the point.
- Position it well : Generally, your thesis should appear towards the end of your introduction. It’s like the crescendo in a musical piece, building up to the main event.
- Revise : Don’t be afraid to go back and tweak it as your paper evolves.
Example: An analysis of the college admission process reveals one challenge facing counselors: accepting students with high test scores or students with strong extracurricular backgrounds.
Outline your points
Before diving into the writing, sketch out an outline. This serves as your roadmap, outlining the key points and sub-points you’ll tackle. In essence, it’s the blueprint of your academic paper.
Follow these points to create an outline of the research:
- Identify the main points : These are the arguments or topics that are crucial to your research. List them in the order you plan to address them.
- Keep solid sub-points and supporting evidence : For each main point, jot down sub-points or examples that support it.
- Maintain a logical flow : Make sure your points follow a logical sequence. Your arguments should build upon each other.
- Use transitional phrases : Consider how you’ll transition from one point to the next.
- Maintain flexibility : Your outline isn’t set in stone. As you dig deeper into your research, you may discover new points that fit better.
Start writing
Once you outline your points, it’s time to venture forth. A strong start incorporates the hook, background, and thesis statement, as we’ve discussed. But don’t get stuck striving for perfection; you can always revisit and refine.
Key Takeaways:
- Know your audience.
- Pre-research is your scouting phase.
- Your thesis is your anchor.
- Outlining sets the stage.
- Just start—perfection comes later.
By following these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to begin your research paper. In the sections that follow, we’ll explore how to write an introduction for a research paper, focusing on specific types for a more targeted approach.
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction for Different Types of Papers?
Research papers come in various types – argumentative, empirical, and review papers. Writing an introduction for a research paper of each type comes with its own specific nuances.
Below are distinctive elements for crafting introductions across various research paper types:
Argumentative paper
An argumentative paper aims to persuade. Your introduction here should not only present your thesis but also hint at the counterarguments you’ll dismantle. Think of it as a debate stage; you’re not just stating your case but also preempting the opposing views.
Example: “School uniforms: they’re a subject of constant debate in the field of education. Supporters argue they create a sense of unity and reduce distractions, leading to better academic performance. Critics claim they stifle individuality and have no real impact on learning. This paper will argue that implementing school uniforms in public schools leads to improved academic performance by fostering a focused learning environment.”
Empirical paper
Here, you’re the scientist, the explorer. Your introduction should outline the research question and the methods you’ll use to answer it. If a specific hypothesis needs testing, it should be mentioned in the research question.
Topic – Empirical Studies on Product-Service Systems – A Systematic Literature Review
Introduction Example – The rising global population, accelerating technological development, increasing resource usage, and intensifying environmental impacts make sustainability the key issue for the entire society. This has resulted in the growing importance of product-service systems (PSS) in academics and industrial fields.
As an ‘integrated bundle of products and services which aims at creating customer utility and generating value’ [1], PSS is one of the most effective instruments that move society towards sustainability [2]. According to its evolution, the classical categorization of PSS includes product-oriented PSS, user-oriented PSS, and result-oriented PSS [3]
Review paper
In a review paper, you summarize existing studies on a topic. Your introduction should highlight the main findings so far and where your paper fits into the dialogue.
Example: “Over the past decade, remote work has transitioned from a corporate perk to a standard practice, especially in tech industries. While some argue that remote work increases productivity and employee satisfaction, others point to challenges like communication breakdowns and feelings of isolation. This paper will review existing literature on the effectiveness of remote work, examining its impact on employee productivity, mental health, and organizational cohesion.”
Remember the following points:
- Argumentative papers need a persuasive touch.
- Empirical papers require a hint of methodology.
- Review papers demand an overview of existing research.
Tips for All Types:
- Be concise: Whether you’re persuading, exploring, or reviewing, get to the point.
- Be focused: Keep your thesis statement tight and direct.
- Be engaging: Use your hook to draw readers in, no matter the type of paper.
By tailoring your introduction to the type of paper you’re writing, you’ll align your research with the expectations of your audience. Each type has its nuances, but the core principles of how to write an introduction for a research paper across these diverse types—capturing attention, providing context, and stating your thesis—remain constant. In the end, it’s all about setting the stage for the research that follows.
Research paper introduction example
Imagine you’re crafting an empirical research paper on the impact of social media on mental health. How would a compelling introduction of a research paper look?
Let’s break it down via a concrete research paper introduction example:
“In today’s digital age, social media platforms have become ubiquitous, shaping our interactions and emotional landscapes. While these platforms promise connectivity, emerging research suggests a darker narrative: a potential link between social media usage and declining mental health. This study aims to explore this complex relationship through a comprehensive analysis of survey data and psychological assessments. Employing both qualitative and quantitative methods, we endeavor to answer the pressing question: Does social media negatively impact mental health?”
In this example, the hook points out how common social media use is. The background information provides context by acknowledging both the positive and negative aspects of social media. Finally, the thesis statement outlines the research question and the methodology.
Key Elements:
- A relatable hook draws the reader in.
- Contextual background sets the stage.
- A clear thesis statement outlines the research aim and method.
In a nutshell, the introduction of a research paper serves as a mini-blueprint for the paper. It sets the stage, intrigues the reader, and outlines the research scope—all in a concise manner.
This guide should serve as a useful starting point in understanding how to start an introduction for a research paper. Explore research paper editing services to structure and articulate your ideas in a polished manner effectively. This can ensure you write your research paper with no typos and in refined academic language.
Keep reading to further enhance your knowledge of writing research papers!
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you start a research paper example, what is a good starting sentence for a research paper, what is a good way to start a research topic.
Found this article helpful?

Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your Organization Needs a Technical Editor: Here’s Why

Your Guide to the Best eBook Readers in 2024

Writing for the Web: 7 Expert Tips for Web Content Writing
Subscribe to our Newsletter
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies

- Step 1: Sections in a Research Paper
- Step 2: Order for Preparation
- Step 3: Conceptualizing an Attractive Title
- Step 4: Effectively Reviewing Literature
- Step 5: Drafting the Abstract
- Step 6: Drafting Introduction
- Step 7: Drafting Materials and Methods
- Step 8: Drafting Results
- Step 9: Drafting Discussion
- Step 10: Drafting the Conclusion
- Step 11: Citing and Referencing
- Step 12: Preparing Figures
- Step 13: Preparing Tables
- Step 14: Assigning Authorship
- Step 15: Acknowledgements Section
- Step 16: Checking the Author Guidelines
- Step 17: Proofreading and Editing
- Step 18: Pre-submission Peer-Review
- Step 1: How to Structure a Research Paper?
- Step 3: How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
- Step 4: How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
- Step 5: How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
- Step 6: How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
- Step 7: How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
- Step 8: How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
- Step 9: How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
- Step 10: How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
- Step 15: How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
How to Write a Research Paper – A to Z of Academic Writing
Part of a scientist’s job is to publish research. In fact, some would argue that your experiment is only complete once you have published the results. This makes it available to the scientific community for authentication and the advancement of science. In addition, publishing is essential for a researcher’s career as it validates the research and opens doors for funding and employment. In this section, we give you a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective research paper. So, remember to set aside half an hour each day to write. This habit will make your writing manageable and keep you focused.
There are different types of research papers. The most common ones include:
Original research paper, rapid communication or letter, review article, meeting abstract, paper, and proceedings.
This is a full report written by researchers covering the analysis of their experimental study from start to finish. It is the most common type research manuscript that is published in academic journals. Original articles are expected to follow the IMRAD format.
These are usually written to publish results urgently in rapidly changing or highly competitive fields. They will be brief and may not be separated by headings.It consists of original preliminary results that are likely to have a significant impact in the respective field.
This is a comprehensive summary of a certain topic. It is usually requested by a journal editor and written by a leader in the field. It includes current assessment, latest findings, and future directions of the field. It is a massive undertaking in which approximately 100 research articles are cited. Uninvited reviews are published too, but it is best to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor first.
This is mostly used in the medical field to report interesting occurrences such as previously unknown or emerging pathologies. It could be a report of a single case or multiple cases and will include a short introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
This is a brief report of research presented at an organized meeting such as a conference. These range from an abstract to a full report of the research. It needs to be focused and clear in explaining your topic and the main points of the study that will be shared with the audience.
- STEP 1: How to Structure a Research Paper?
- STEP 2: Order for Preparation of the Manuscript
- STEP 3: How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
- STEP 4: How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
- STEP 5: How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
- STEP 6: How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
- STEP 7: How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 8: How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 9: How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 10: How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
- STEP 11: Effectively Citing and Referencing Your Sources
- STEP 12: Preparing Figures
- STEP 13: Preparing Tables
- STEP 14: Assigning Authorship
- STEP 15: How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
- STEP 16: Checking the Author Guidelines Before Preparing the Manuscript
- STEP 17: Proofreading and Editing Your Manuscript
- STEP 18: Pre-submission Peer-Review
How to Structure a Research Paper?
Your research paper should tell a story of how you began your research, what you found, and how it advances your research field. It is important to structure your research paper so that editors and readers can easily find information. The widely adopted structure that research papers mostly follow is the IMRaD format . IMRaD stands for Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Additional requirements from journals include an abstract, keywords, acknowledgements, and references. This format helps scientists to tell their story in an organized manner. Authors often find it easier to write the IMRaD sections in a different order. However, the final paper should be collated in the IMRaD format as follows:

Case studies follow a slightly different format to the traditional IMRAD format. They include the following extra sections:
- History and physical examination: Details of the patient’s history. It provides the story of when a patient first sought medical care.
- Diagnostic focus and assessment : Describe the steps taken that lead to a diagnosis and any test results.
- Therapeutic focus and assessment: Explain therapies tried and any other recommendations from consultants. Assess the efficacy of the treatments given.
- Follow-up and outcome: Provide results and state the patient adhered to treatment. Include any side effects.
- Patient perspective: Describe the patient’s experience.
- Patient consent: State that informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Order for Preparation of the Manuscript
As mentioned above, most research publications follow the IMRAD format. However, it is often easier to write each section in a different order than that of the final paper.
Authors recommend you organize the data first and then write the sections as follows:
- Figures and tables: Decide how your data should be presented. You can use graphics, tables or describe it in the text.
- Methods: It is important that anyone can use your methods to reproduce your experiments.
- Results: Here you write only what the results of your experiments were. You do not discuss them here.
- Discussion: This section requires analysis, thought, and a thorough understanding of the literature. You need to discuss your results without repeating the results section.
- Conclusion: This section can either be under a sub-heading or the last paragraph of the discussion. It should inform the reader how your results advance the field.
- Introduction: Now that you have thought about your results in the context of the literature, you can write your introduction.
- Abstract: This is an overview of your paper. Give a concise background of the problem and how you tried to solve it. Next state your main findings.
- Title: As discussed above, this needs to be concise as well as informative. Ensure that it makes sense.
- Keywords: These are used for indexing. Keywords need to be specific. Often you are not allowed to use words that appear in the journal name. Use abbreviations with care and only well-established ones.
- Acknowledgements: This section is to thank anyone involved in the research that does not qualify as an author.
- References: Check the “Guide for authors” for the formatting style. Be accurate and do not include unnecessary references.
How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
Your research title is the first impression of your paper. A good research paper title is a brief description of the topic, method, sample, and results of your study. A useful formula you could use is:

There are different ways to write a research paper title :
Declarative
State the main conclusions. Example: Mixed strains of probiotics improve antibiotic associated diarrhea.
Descriptive
Describe the subject. Example: Effects of mixed strains of probiotics on antibiotic associated diarrhea.
Interrogative
Use a question for the subject. Example: Do mixed strains of probiotics improve antibiotic associated diarrhea?
We recommend the following five top tips to conceptualize an attractive research title:
- Be descriptive
- Use a low word count (5-15 words)
- Check journal guidelines
- Avoid jargon and symbols
How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
The process of conducting a literature review can be overwhelming. However, if you start with a clear research question, you can stay focused.
- Literature search: Search for articles related to your research question. Keep notes of the search terms and keywords you use. A list of databases to search and notes of the ones you have searched will prevent duplicate searches.
- What is their research question?
- Are there potential conflicts of interest such as funders who may want a particular result?
- Are their methods sufficient to test the objectives?
- Can you identify any flaws in the research?
- Do their results make sense, or could there be other reasons for their conclusion?
- Are the authors respected in the field?
- Has the research been cited?
- Introduction: Here you introduce the topic. The introduction describes the problem and identifies gaps in knowledge. It also rationalizes your research.
- Discussion: Here you support and compare your results. Use the literature to put your research in context with the current state of knowledge. Furthermore, show how your research has advanced the field.
How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
The importance of research paper abstracts cannot be emphasized enough.
- They are used by online databases to index large research works. Therefore, critical keywords must be used.
- Editors and reviewers read an abstract to decide whether an article is worth considering for publication.
- Readers use an abstract to decide whether the research is relevant to them.
A good research paper abstract is a concise and appealing synopsis of your research. There are two ways to write an abstract: structured and unstructured research abstracts . The author guidelines of the journal you are submitting your research to will tell you the format they require.
- The structured abstract has distinct sections with headings. This style enables a reader to easily find the relevant information under clear headings (objective, methods, results, and conclusion). Think of each section as a question and provide a concise but detailed answer under each heading.
- The unstructured abstract is a narrative paragraph of your research. It is similar to the structured abstract but does not contain headings. It gives the context, findings, conclusion, and implications of your paper.
How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
The Introduction section of your research paper introduces your research in the context of the knowledge in the field. First introduce the topic including the problem you are addressing, the importance of solving this problem, and known research and gaps in the knowledge. Then narrow it down to your research questions and hypothesis.
Tips to write an effective introduction for your research paper :
- Give broad background information about the problem.
- Write it in a logical manner so that the reader can follow your thought process.
- Focus on the problem you intend to solve with your research
- Note any solutions in the literature thus far.
- Propose your solution to the problem with reasons.
Done with drafting your research paper?
With enago’s english editing & proofreading service your success is just a step away.

How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
When writing the Materials and Methods section of a research paper, you need to give enough detail in your methods so that others can reproduce your experiments. However, there is no need to detail established experiments. Readers can find these details in the previously published references you refer to in the methods. Follow these tips to write the Materials and Methods section of your research paper: :
- Write in the past tense because you are reporting on procedures you carried out.
- Avoid unnecessary details that disrupts the flow.
- Materials and equipments should be mentioned throughout the procedure, rather than listed at the beginning of a section.
- Detail any ethics or consent requirements if your study included humans or animal subjects.
- Use standard nomenclature and numbers.
- Ensure you have the correct control experiments.
- Methods should be listed logically.
- Detail statistical methods used to analyze your data.
Here is a checklist of things that should be in your Materials and Methods:
- References of previously published methods.
- Study settings : If the research involves studying a population, give location and context of the site.
- Cell lines : Give their source and detail any contamination tests performed.
- Antibodies : Give details such as catalogue numbers, citations, dilutions used, and batch numbers.
- Animal models : Species, age, and sex of animals as well as ethical compliance information.
- Human subjects : Ethics committee requirements and a statement confirming you received informed consent. If relevant, clinical trial registration numbers and selection criteria.
- Data accession codes for data you deposited in a repository.
- Software : Where you obtained the programs and their version numbers.
- Statistics : Criteria for including or excluding samples or subjects, randomisation methods, details of investigator blinding to avoid bias, appropriateness of statistical tests used for your study.
- Timeframes if relevant.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
Some journals combine the results and discussion section, whereas others have separate headings for each section. If the two sections are combined, you state the results of your research and discuss them immediately afterwards, before presenting your next set of results. The challenge is to present your data in a way that is logical and accurate. Set out your results in the same order as you set out your methods.
When writing the Results section of your research paper remember to include:
- Control group data.
- Relevant statistical values such as p-values.
- Visual illustrations of your results such as figures and tables.
Things that do not belong in the results section:
- Speculation or commentary about the results.
- References – you are reporting your own data.
- Do not repeat data in text if it has been presented in a table or graph.
Keep the discussion section separate . Keep explanations, interpretations, limitations, and comparisons to the literature for the discussion.
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of your research paper answers several questions such as: did you achieve your objectives? How do your results compare to other studies? Were there any limitations to your research? Start discussing your data specifically and then broaden out to how it furthers your field of interest.
Questions to get you started:
- How do your results answer your objectives?
- Why do you think your results are different to published data?
- Do you think further research would help clarify any issues with your data?
The aim is to tell the reader what your results mean. Structure the discussion section of your research paper in a logical manner. Start with an introductory paragraph where you set out the context and main aims of the study. Do this without repeating the introduction. Some authors prefer starting with the major findings first to keep the readers interested.
The next paragraph should discuss what you found, how it compares to other studies, any limitations, your opinion, and what they mean for the field.
The concluding paragraph should talk about the major outcomes of the study. Be careful not to write your conclusion here. Merely highlight the main themes emerging from your data.
Tips to write an effective discussion:
- It is not a literature review. Keep your comments relevant to your results.
- Interpret your results.
- Be concise and remove unnecessary words.
- Do not include results not presented in the result section.
- Ensure your conclusions are supported by your data.
How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
While writing the conclusion for your research paper, give a summary of your research with emphasis on your findings. Again, structuring the conclusion section of your research paper will make it easier to draft this section. Here are some tips when writing the conclusion of your paper:
- State what you set out to achieve.
- Tell the reader what your major findings were.
- How has your study contributed to the field?
- Mention any limitations.
- End with recommendations for future research.
Having difficulties with understanding concepts on academic writing?
Enago learn can guide you through the manuscript preparation process and help you achieve success.

Effectively Citing and Referencing Your Sources
You need to acknowledge the original work that you talk about in your write-up. There are two reasons for this. First, cite someone’s idea to avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism is when you use words or ideas of others without acknowledging them and this is a serious offence. Second, readers will be able to source the literature you cited easily.
This is done by citing works in your text and providing the full reference for this citation in a reference list at the end of your document.
Tips for effective refencing/citations:
- Keep a detailed list of your references including author(s), publication, year of publication, title, and page numbers.
- Insert a citation (either a number or author name) in-text as you write.
- List the full reference in a reference list according to the style required by the publication.
- Pay attention to details as mistakes will misdirect readers.
Try referencing software tools “cite while you write”. Examples of such referencing software programs include: Mendeley , Endnote , Refworks and Zotero .
Preparing Figures
Some quick tips about figures:
- Legends of graphs and tables must be self-explanatory.
- Use easily distinguishable symbols.
- Place long tables of data in the supplementary material.
- Include a scale bar in photographs.
Preparing Tables
Important pointers for tables:
- Check the author guidelines for table formatting requirements.
- Tables do not have vertical lines in publications.
- Legends must be self-explanatory.
Assigning Authorship
To qualify as an author on a paper, an individual must:
- Make substantial contributions to all stages of the research.
- Draft or revise the manuscript.
- Approve the final version of the article.
- Be accountable for the accuracy and integrity of the research.
Unethical and unprofessional authorships have emerged over the years. These include:
- Gift authorship : An individual is listed as a co-author in lieu of funding or supervision.
- Ghost authorship : An author is paid to write an article but does not contribute to the article in any other way.
- Guest authorship : An individual who is given authorship because they are well known and respected in the field, or they are senior members of staff.
These authors pose a threat to research. Readers may override their concerns with an article if it includes a well-respected co-author. This is especially problematic when decisions about medical interventions are concerned.
How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
Those who do not qualify as authors but have contributed to the research should be given credit in the acknowledgements section of your research paper . These include funders, supervisors, administrative supporters, writing, editing, and proofreading assistance .
The contributions made by these individuals should be stated and sometimes their written permission to be acknowledged is required by editors.
Has your target journal's author guidelines left you confused?
With enago consult you can talk to our experts through live 1-to-1 video calls.

Points to Note from the Author Instructions Before Preparing the Manuscript
Check the author guidelines for your chosen publication before submission. Publishers mostly have a “House Style” that ensures all their manuscripts are consistent with regards to language, formatting, and style. For example, these guidelines will tell you whether to use UK or US English, which abbreviations are allowed, and how to format figures and tables. They are also especially important for the references section as each journal has their own style.
Proofreading/Editing your Manuscript
Ensure that your manuscript is structured correctly, clearly written, contains the correct technical language, and supports your claims with proper evidence. To ensure the structure is correct, it is essential to edit your paper .
Once you are happy with the manuscript, proofread for small errors. These could be spelling, consistency, spacing, and so forth. Importantly, check that figures and tables include all the necessary data and statistical values. Seek assistance from colleagues or professional editing companies to edit and proofread your manuscript too.
Pre-submission Peer-Review of Your Manuscript
A pre-submission peer-review could improve the quality of articles submitted to journals in general. The benefits include:
- A fresh eye to spot gaps or errors.
- Receiving constructive feedback on your work and writing.
- Improves the clarity of your paper.
You could ask experienced colleagues, supervisors or even professional editing services to review your article.
- Reporting Research
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
A Beginner's Guide to Starting the Research Process

When you have to write a thesis or dissertation , it can be hard to know where to begin, but there are some clear steps you can follow.
The research process often begins with a very broad idea for a topic you’d like to know more about. You do some preliminary research to identify a problem . After refining your research questions , you can lay out the foundations of your research design , leading to a proposal that outlines your ideas and plans.
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project.
Table of contents
Step 1: choose your topic, step 2: identify a problem, step 3: formulate research questions, step 4: create a research design, step 5: write a research proposal, other interesting articles.
First you have to come up with some ideas. Your thesis or dissertation topic can start out very broad. Think about the general area or field you’re interested in—maybe you already have specific research interests based on classes you’ve taken, or maybe you had to consider your topic when applying to graduate school and writing a statement of purpose .
Even if you already have a good sense of your topic, you’ll need to read widely to build background knowledge and begin narrowing down your ideas. Conduct an initial literature review to begin gathering relevant sources. As you read, take notes and try to identify problems, questions, debates, contradictions and gaps. Your aim is to narrow down from a broad area of interest to a specific niche.
Make sure to consider the practicalities: the requirements of your programme, the amount of time you have to complete the research, and how difficult it will be to access sources and data on the topic. Before moving onto the next stage, it’s a good idea to discuss the topic with your thesis supervisor.
>>Read more about narrowing down a research topic
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

So you’ve settled on a topic and found a niche—but what exactly will your research investigate, and why does it matter? To give your project focus and purpose, you have to define a research problem .
The problem might be a practical issue—for example, a process or practice that isn’t working well, an area of concern in an organization’s performance, or a difficulty faced by a specific group of people in society.
Alternatively, you might choose to investigate a theoretical problem—for example, an underexplored phenomenon or relationship, a contradiction between different models or theories, or an unresolved debate among scholars.
To put the problem in context and set your objectives, you can write a problem statement . This describes who the problem affects, why research is needed, and how your research project will contribute to solving it.
>>Read more about defining a research problem
Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions . These target exactly what you want to find out. They might focus on describing, comparing, evaluating, or explaining the research problem.
A strong research question should be specific enough that you can answer it thoroughly using appropriate qualitative or quantitative research methods. It should also be complex enough to require in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. Questions that can be answered with “yes/no” or with easily available facts are not complex enough for a thesis or dissertation.
In some types of research, at this stage you might also have to develop a conceptual framework and testable hypotheses .
>>See research question examples
The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you’ll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research.
There are often many possible paths you can take to answering your questions. The decisions you make will partly be based on your priorities. For example, do you want to determine causes and effects, draw generalizable conclusions, or understand the details of a specific context?
You need to decide whether you will use primary or secondary data and qualitative or quantitative methods . You also need to determine the specific tools, procedures, and materials you’ll use to collect and analyze your data, as well as your criteria for selecting participants or sources.
>>Read more about creating a research design
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Finally, after completing these steps, you are ready to complete a research proposal . The proposal outlines the context, relevance, purpose, and plan of your research.
As well as outlining the background, problem statement, and research questions, the proposal should also include a literature review that shows how your project will fit into existing work on the topic. The research design section describes your approach and explains exactly what you will do.
You might have to get the proposal approved by your supervisor before you get started, and it will guide the process of writing your thesis or dissertation.
>>Read more about writing a research proposal
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
More interesting articles
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
- What Is Root Cause Analysis? | Definition & Examples
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
281k Accesses
16 Citations
707 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to Choose the Right Journal

The Point Is…to Publish?

Writing and publishing a scientific paper
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
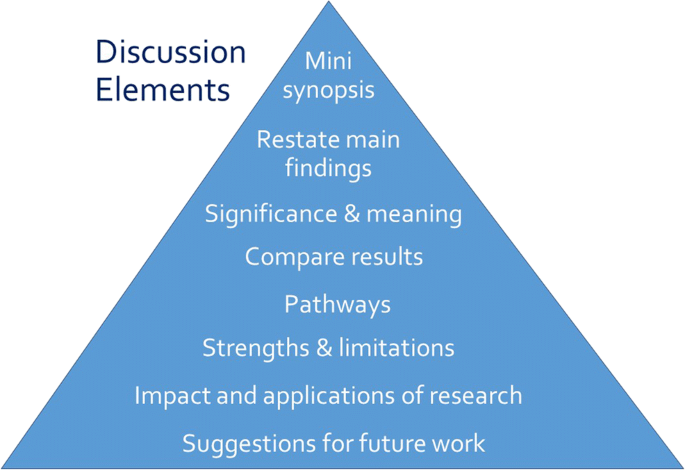
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How to write a great research paper
Academic resource.
Simon Peyton Jones
This talk offers seven simple, concrete suggestions for how to improve your research papers. You may also find my talks on how to write a great research proposal and how to give a great research talk useful.
- Powerpoint slides of the talk: PDF PPT (you should feel free to repurpose these slides for your own use as long as you acknowledge ownership)
- Another video of the talk (shorter: 34 mins), Cambridge Computer Lab, Spring 2013, with thanks to Neil Dodgson for the editing and production.
- Slides translated into Arabic (Suzan Alkhodair), Japanese (KADO Masanori), and another Japanese version
- I have also collected a set of links to other useful material about technical writing, on the Other Resources tab
Related links
How to write a great research proposal
How to give a great research talk
Simon Peyton Jones: [email protected]
- Follow on X
- Like on Facebook
- Follow on LinkedIn
- Subscribe on Youtube
- Follow on Instagram
- Subscribe to our RSS feed
Share this page:
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit
80 Impactful Research Topics for High School Students

By Rebekah Pierce
Educational writer and former teacher
3 minute read
Choosing the right research topic can be the secret ingredient to making your high school student paper not only impressive but also fun to write. Let's face it - no one wants to slog through a boring topic that has been done a million times before.
A good research topic is like the foundation of a strong building. It sets the stage for everything else - not to mention that it helps you develop critical thinking and analytical skills that you’ll need as you move into college and beyond.
Here are some of the best research paper ideas (and some tips to help you get started with writing about these fun research topics for high school projects).
How to Choose the Right Research Paper Topic
Begin by identifying what interests you most. What do you want to learn more about? These don’t necessarily have to be controversial topics. Just think about what might be a good research topic for your interests.
Once you have a few ideas for a good topic, start the research process to hunt down resources and relevant literature. Aim for the best research paper topics that will allow for a comparative study, such as analyzing different perspectives on a social issue or contrasting historical events.
Make sure your chosen topic is neither too broad nor too narrow. Finding the right balance is incredibly important if you want to produce a focused and impactful paper.
Do your own research through Polygence!
Polygence pairs you with an expert mentor in your area of passion. Together, you work to create a high quality research project that is uniquely your own.
How to Get Started with Your Research Paper Writing
First up, do a thorough literature review to gather existing research and insights relevant to your topic. This may even inspire new angles for you to explore!
Organize your findings and outline the structure of your paper to keep things clear, tight, and tidy. Write an abstract to break down your intentions.
As you write a research paper , critically analyze the information and present your arguments coherently, allowing your voice to shine through (objectively) while incorporating scholarly evidence. In the introduction , grab the reader with an enticing bit of information, like a hook, quote, or stat.
Edit, edit, and edit some more - then, get ready to publish!
Need some inspiration to get the creative juices flowing? Keep reading to discover the best research topics for high school students.
Technology Research Paper Topics
The Influence of Artificial Intelligence on Modern Society: Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a concept from sci-fi movies. What are the ethical considerations?
Cybersecurity Threats and Measures in the Digital Age: With the rise of digital technology, cybersecurity is more important than ever.
The Future of Renewable Energy Technologies: Solar panels, wind turbines, and electric cars are just the beginning.
Impact of Social Media on Youth Behavior: Social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat dominate the lives of teenagers - for better or worse.
The Role of Technology in Modern Education : How are digital tools and online platforms enhancing learning experiences?
Health and Medicine Topics
The Effects of Diet and Nutrition on Mental Health: What we eat doesn't just affect our physical health.
Advances in Cancer Research and Treatment: Explore the latest advances in cancer research.
The Impact of Vaccines on Public Health: Are vaccines safe? What does the future hold?
Mental Health Issues Among Teenagers: For these psychology research paper topics for high schoolers, explore the many factors leading to an increased incidence of mental health issues in teens, from academics to Snapchat and everything in between.
The Role of Genetics in Personalized Medicine: Take a closer look at how genetic studies are being used to create personalized, in-depth treatment plans for patients.
Making a difference starts with you
Interested in Environmental Science? We'll match you with an expert mentor who will help you explore your next project.
Environment Topics
Climate Change and Its Impact on Global Ecosystems: Climate change is affecting us all. Take a look at how melting ice caps and rising temperatures are impacting ecosystems around the world.
Sustainable Practices in Urban Development: To minimize our environmental impact, we need to think green. But what does this mean for urban development?
The Effects of Pollution on Marine Life: How can we reduce the impact of pollution on marine life?
Renewable Energy Sources: Benefits and Challenges: Renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power offer numerous benefits but also come with challenges. Explore these.
The Importance of Biodiversity Conservation: How can we incorporate strategies to protect endangered habitats?
Social Issues and Sociology Research Topics
The Impact of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships: Social media is shaking up the way we interact with others.
The Role of Education in Reducing Inequality: Education is the number one way to reduce inequality. Explore strategies and policies that can help with this.
Gender Equality in the Workplace: Gender equality remains a significant issue in workplaces worldwide - talk about why and how to address this.
The Effects of Poverty on Community Health: Explore how poverty has far-reaching impacts on nutrition, healthcare access, and overall health and well-being.
Immigration Policies and Their Social Implications: Immigration policies are far-reaching, impacting more than just immigrant communities.
History Argumentative Essay Topics
The Causes and Effects of World War II: Research the causes and ripple effects of the Second World War.
The Impact of the Civil Rights Movement on Modern Society: Ask how the Civil Rights Movement impacted racial equality today - and look at the continuing challenges.
Ancient Civilizations and Their Contributions to the Modern World: How do these ancient achievements influence us today?
The History of Space Exploration: Space exploration has captivated humanity for decades - but what’s the background?
The Evolution of Democracy Throughout History: Democracy has evolved significantly over the centuries - detail this evolution.
Science Research Topics
The Exploration of Space: Past, Present, and Future: What are the scientific and societal benefits of exploring space?
Genetic Engineering and Its Ethical Implications: Are there ethical considerations (or risks) of genetic engineering? Take a look at them.
The Impact of Climate Change on Natural Disasters: Climate change is increasing the frequency and severity of natural disasters.
Advances in Renewable Energy Technology: Renewable energy technology is advancing rapidly - what innovations hold the most promise?
The Role of Science in Solving Global Problems: How can science help solve problems related to disease, poverty, and climate change?
Literature Research Topics
The Influence of Classic Literature on Modern Writing: Ever wondered how Shakespeare still affects today's bestsellers? A research paper on how classic literature influences modern writing can uncover fascinating parallels and divergences.
Themes of Dystopia in Contemporary Literature: From "The Hunger Games" to "1984," dystopian themes have captivated readers for ages.
The Role of Literature in Social Change: Literature has the power to inspire revolutions. Explore books like "Uncle Tom's Cabin" and "To Kill a Mockingbird" and how they created societal shifts.
Comparative Analysis of Major Literary Movements: Compare the themes, styles, and impacts on society of different literary movements like Romanticism, Realism, and Modernism.
The Impact of Digital Media on Reading Habits: Is the Kindle killing books? If so, research how and why in this essay topic.
Economics Topics
The Effects of Globalization on Local Economies: Globalization is reshaping economies worldwide -explore its impacts on local businesses and job markets.
The Role of Technology in Transforming the Job Market: From AI to automation, technology is revolutionizing jobs.
Economic Impacts of Climate Change: Climate change isn't just an environmental issue; it's an economic one too.
The Influence of Consumer Behavior on Market Trends: Ever bought something because it was trending? Study how consumer behavior shapes market trends.
The Future of Cryptocurrencies in the Global Economy: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dogecoin - what's the deal?
Education Research Paper Topics
The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance: Online learning is more relevant now than ever, which you’ll explore in this education research topic.
The Role of Technology in Modern Education: How are smart boards and tablets changing classrooms for public schools? How can they improve academic achievement?
Comparative Analysis of Education Systems Around the World: Why do some countries excel in education while others lag? Compare different education systems to see what works and doesn’t.
The Effects of Standardized Testing on Student Learning: Standardized tests are controversial; research their impacts on student learning and whether they accurately measure academic performance and predict academic success, particularly related to special education, elementary school, and early childhood education.
Innovations in Educational Methodologies: From flipped classrooms in elementary education to gamification for middle school, explore different teaching methods with this research question.
Arts Research Project Ideas
The Evolution of Visual Arts Through Different Periods: Study how visual arts have evolved from the Renaissance to Postmodernism.
The Influence of Digital Media on Traditional Arts: Analyze how digital media is affecting traditional arts like painting and sculpture.
The Role of Art in Cultural Preservation: Art isn’t just for aesthetics; it preserves culture too.
Comparative Study of Art Movements: Compare movements like Impressionism and Cubism.
The Impact of Public Art on Community Identity: Murals, sculptures, and public installations - how do they shape community identity and pride?
Athletics Topics
The Impact of Sports on Academic Performance: Do athletes perform better academically?
The Role of Athletics in College Admissions: Sports can be a ticket to higher education. Research how athletics influence college admissions and scholarships for current college students.
The Effects of Physical Activity on Mental Health: Exercise isn’t just for the body; it’s also for the mind. Explore that in these research ideas.
The Influence of Sports on Leadership Skills
Sports teach more than physical skills. Analyze how participation in sports cultivates leadership qualities.
The Future of Technology in Sports Training: From wearable tech to virtual reality, technology is revolutionizing sports training.
Music Research Paper Topics
The Influence of Classical Music on Modern Genres: Ever heard classical elements in pop songs? Explore how classical music influences modern genres.
The Role of Music in Cultural Identity: Music defines cultures. Study how different genres contribute to cultural identity.
The Effects of Music Therapy on Mental Health: Music heals. Research why that is.
Evolution of Music Technology: From vinyl to Spotify, music tech has come a long way.
The Impact of Music Education on Academic Performance: Does music make you smarter?
Government and Politics Persuasive Essay Topics
The Impact of Government Policies on Economic Growth: Government policies can make or break economies.
Comparative Analysis of Political Systems: Democracy, autocracy, and everything in between - compare different political systems and their effectiveness.
The Role of Youth in Political Movements: Young people are powerful when it comes to historical and current political movements.
Government Response to Climate Change: How are governments tackling climate change?
The Influence of Lobbying on Legislation: Lobbying shapes laws. Investigate how.
Writing and Communication Topics
The Evolution of Writing Styles Over the Centuries: Writing styles have changed dramatically. Study their evolution and what influenced these changes.
The Impact of Digital Media on Writing and Communication: Digital media is reshaping communication.
Creative Writing Techniques for Young Authors: Explore techniques and tips to enhance creative writing.
The Role of Writing in Personal Expression: Research how writing can be a powerful tool for self-expression.
The Importance of Effective Communication Skills: Study why effective communication skills are crucial in various aspects of life.
Society, Culture, and Social Science Topics
The Effects of Social Media on Cultural Norms: Social media is changing culture. Research its impacts on cultural norms and behaviors.
The Role of Tradition in Modern Society: Traditions persist in modern times. Study the role of ancient traditions in contemporary society.
Comparative Analysis of Cultural Practices Around the World: Different cultures, different practices. Compare cultural practices and their meanings worldwide.
The Influence of Media on Public Perception: Media shapes how we see the world.
The Impact of Globalization on Cultural Identity: Globalization is blending cultures. Research its effects on cultural identities.
Business and Entrepreneurship Topics
The Impact of Startups on the Economy: Startups are economic powerhouses. Study their impacts on local and global economies.
The Role of Innovation in Business Success: Research how innovation influences business achievements.
Ethical Considerations in Business Practices: Investigate ethical considerations and their impacts on business practices.
The Influence of Digital Marketing on Consumer Behavior: Analyze the effects of digital marketing on consumer behavior and purchasing decisions.
Strategies for Successful Entrepreneurship: Want to start a business? Explore strategies.
Polygence Scholars Are Also Passionate About
Engaging in research with polygence's core program.
Picking the right research topic can set the tone for your entire project. It's not just about getting a good grade—it’s about developing critical thinking and enhancing your analytical skills. Your high school research paper topics can even set the stage for future academic pursuits or careers.
Polygence’s Core Program offers a variety of resources to help you nail every aspect of your research paper. Sign up today!
By selecting an impactful research topic , you're not just writing a paper - you're developing research skills that will serve you for a lifetime. These skills can enhance your understanding of your current school curriculum and prepare you for the rigorous demands of higher education, setting a strong foundation for your academic future.
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: If you're in a STEM field, chances are you'll need to read primary literature, also known as research articles. And unlike books, effectively and efficiently reading a research paper requires a nuanced and systematic approach. When I first started reading research papers as a neuroscience major in college, it took considerable effort and time to make sense of it all. But since then, I've read through thousands of papers, published dozens of my own in peer-reviewed journals, and can now crank through them with ease. Here's the system I use. Dr. Jubbal, MedSchoolInsiders.com. First, determine the purpose of reading. Depending on the purpose and your goal in reading a research paper, your approach may differ considerably. Keep that in mind as we cover the following sections. If you're reading a paper as a requirement for class, like I initially had to for my neuroscience courses, you will be focusing on comprehension rather than on determining utility. You'll need to know the study hypothesis, the methods they used, the findings, and the limitations of their conclusions. As you proceed with your medical training, you will likely write many of your own research articles. After all, doing so is one of the most powerful ways to stand out and strengthen your medical school or residency application. In these instances, you are mostly referencing other research papers, and it becomes more important to quickly determine relevance and value prior to committing a more in-depth reading and analysis. You will also use papers as tools to figure out other papers to read by taking advantage of their own reference list. Now that you've identified your primary goal, it's time to begin reading. Not every section in a research article is created equal. Unlike reading a traditional book, I don't advise you read a research paper in order. First, you need to read the title and the abstract to get an overview of the paper. If at any time during your reading, you come across a word or acronym that you don't understand, stop and look it up. This is not like a novel where you can infer the meaning and likely not see the word again. The language in research articles is generally pretty straightforward, and terms you don't understand are often the scientific terms that are critical to your understanding of the paper and its findings. Next, dive into the conclusion. Again, this is a research paper, not a novel, so you're not running into any spoilers. The conclusion effectively summarizes the most pertinent findings. Now that you have a better idea of what the paper is about, spend as much time as you desire going over the figures, methods, results, and discussion sections. The discussion will likely be the highest-dealed portion that requires the most amount of time, but to truly understand the paper, you must also go over the methods, results, and figures. A big element to reading papers is understanding the limitations of the study, which then allows you to more accurately determine the paper's significance. The biggest and most widespread mistake is jumping to the conclusion and not understanding the limitations and generalizability of the study. Look at any media article summarizing new, groundbreaking research, and you'll see what I mean. Towards the end of the discussion section in most any paper, you'll find the author's own interpretation of the limitations of their study. But there are always many more limitations beyond what they mention. There have been entire books dedicated to the nuances of statistics and extrapolating conclusions from research, and this is something I may consider making a dedicated future video on. Let me know in the comments below so I can gauge interest. Most people know about randomization, placebo-controlled, and single or double-blinded studies. That being said, there is so much more nuance to it. Here are a few examples. First, study design. Is the study retrospective, meaning looking back historically, or prospective, starting with individuals that are then followed over time? Is it a case control, cohort, or cross-sectional study? Number two, what are the endpoints used? If the study draws conclusions about heart disease, but only uses HDL as a surrogate marker, understand that the surrogate is just that, an imperfect proxy. Number three, biases. There are too many to cover, but selection, recall, sampling, confounding, procedure, lead time, and the Hawthorne effect are all biases that you should familiarize yourself with. And number four, basic statistical analyses. Sensitivity vs. specificity, normal and skewed distributions, positive and negative predictive values, etc. Over time, you'll be reading dozens or even hundreds of research papers, and it becomes a challenge to keep everything straight. Again, depending on the purpose, there are a few options to consider. If you're reading as a class assignment, I recommend you print out the paper, highlight, and annotate in the margins as needed. More recently, I've done this on an iPad with the Apple Pencil, such that printing out was no longer necessary. On the other hand, if you're reading in order to write your own paper, start using a citation manager immediately from the beginning. EndNote is often referenced as the rather expensive gold standard, but Mendeley is a free and quite sufficient alternative. As soon as you begin reading papers, import them into your citation manager. In a separate Word document, begin jotting down the key points of your paper that are relevant to your own project. This notes document will now become the main resource from which you will begin writing your own paper. Trust me, it's much better this way, otherwise you'll spend considerable time and effort hunting for facts from the dozens of PDFs that you've read. Lastly, understand that a big part of reading speed in both regular books as well as research papers is your familiarity with the subject. I started off reading neuroscience papers quite slowly, but as my expertise in the area grew, I was able to breeze through them. I knew the anatomy and terminology like the back of my hand, and coming across terms like CA1 vs CA2 neurons of the hippocampus no longer required additional processing. Similarly, when I first started diving into plastic surgery research, I didn't know all the nuances of hand anatomy or the principles of aesthetic surgery. But as I grew to understand more, reading and understanding the literature became second nature, and once again I was able to breeze through them. It's important to keep this in mind to make sure you don't get discouraged. If you consistently apply yourself to reading research articles and follow these steps that I've outlined, you'll be tackling papers with ease in no time. Like it or not, being proficient in research is an essential skill if you want to go to a top medical school or residency program. In a certain way, there's a science but also an art to bolstering a solid research CV and securing impressive letters of recommendation from your PI. You can check out my own personal list of research articles, abstracts, and presentations on my personal website at kevinjubbal.com. It's currently over 60 and counting. Being proficient in research was a huge part of my own success getting into a top medical school and highly competitive residency. It's a challenging ordeal, and very few people know how to address this for maximal effectiveness. Through experimentation and very uncommon techniques, I was able to pump out over 30 items in less than 12 months and secure stellar letters of recommendation. Visit MedSchoolInsiders.com to learn how our team of top advisors can help you master your own research and present your best self in your application and interview. I created this video because you guys requested it. If you have any other requests for other research related videos, let me know down in the comments below. If you made it this far, then there is a lot more content on my Instagram that you will definitely enjoy. Check out at kevinjubbalmd and at MedSchoolInsiders. Thank you guys so much for watching, and I will see you all in that next one.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research.
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper.
Starting a research paper can feel overwhelming, especially if you're new to the process. This guide will walk you through each step, from picking a topic to polishing your final draft. By breaking down the process into manageable parts, you'll find it easier to stay organized and focused. Let's dive in and make your research paper a success!
In this guide we concisely explain how to write an academic research paper step by step. We'll cover areas like how to start a research paper, how to write a research paper outline, how to use citations and evidence, and how to write a conclusion for a research paper.
Learn how to write a high-quality research paper in three straightforward steps. Includes loads of practical examples and a free template.
Need help writing a research paper? Our step-by-step guide offers tips and tricks for crafting a fantastic document and ensuring it stands out.
All research papers have pretty much the same structure. If you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Learn the steps to start and complete your research paper in our guide.
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
The introduction to a research paper presents your topic, provides background, and details your research problem.
Writing a good research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic and advance an original argument. To convincingly communicate your ideas, you need a logical structure and a clear style that follows the conventions of academic writing.
Writing a research paper can be challenging, not to mention time-consuming. Follow these 11 steps to write a stellar college research paper.
Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the ...
Research Paper Fundamentals The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
Whether you're in a history, literature, or science class, you'll probably have to write a research paper at some point. It may seem daunting when you're just starting out, but staying organized and budgeting your time can make the process...
15 Steps to Good Research Define and articulate a research question (formulate a research hypothesis). How to Write a Thesis Statement (Indiana University) Identify possible sources of information in many types and formats. Georgetown University Library's Research & Course Guides Judge the scope of the project.
Learn how to write a research paper step by step, including how to cite sources, and get helpful writing and research tips.
How to Write a Research Paper If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you ...
Explore the nuances of writing a standout research paper introduction. From the initial hook to the thesis statement, this guide is your go-to resource for starting your academic paper correctly.
Your one-stop resource to writing a great research paper Writing a research paper is a challenging job for most of us — from conceptualizing the paper, to breaking it down to its constituent parts, and finally, to referring to numerous other papers and books to get your own paper going — it is daunting, to say the least.
A good research paper abstract is a concise and appealing synopsis of your research. There are two ways to write an abstract: structured and unstructured research abstracts.
The research process often begins with a very broad idea for a topic you'd like to know more about. You do some preliminary research to identify a problem. After refining your research questions, you can lay out the foundations of your research design, leading to a proposal that outlines your ideas and plans.
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
This talk offers seven simple, concrete suggestions for how to improve your research papers. You may also find my talks on how to write a great research proposal and how to give a great research talk useful.
Here are some of the best research paper ideas (and some tips to help you get started with writing about these fun research topics for high school projects). ... It's not just about getting a good grade—it's about developing critical thinking and enhancing your analytical skills. Your high school research paper topics can even set the stage ...
Speaker 1: If you're in a STEM field, chances are you'll need to read primary literature, also known as research articles. And unlike books, effectively and efficiently reading a research paper requires a nuanced and systematic approach. When I first started reading research papers as a neuroscience major in college, it took considerable effort and time to make sense of it all.