How to Prepare for Walmart Product Management Case Interviews
If you're looking to land a product management role at Walmart, you'll likely need to ace the case interview.
Posted May 16, 2023


Table of Contents
If you're pursuing a career in product management at Walmart, you'll likely be required to go through a rigorous interview process. This process will not only test your knowledge of the company, but also your ability to think critically, your problem-solving skills, and your decision-making abilities. To make sure that you're well-equipped to handle the interview process, you need to prepare meticulously. In this article, we'll be discussing the step-by-step process that you can follow to ace your Walmart Product Management Case Interviews.
Understanding the Walmart Product Management Interview Process
Before diving deep into preparation, it's important to understand the interview process for a product management role at Walmart. Typically, the process consists of several rounds of interviews spread over a few weeks. The first round is usually a phone interview, followed by one or two rounds of case interviews, and a final-round interview with Walmart executives. The case interview is the most important part of the process. In this type of interview, you'll be given a hypothetical situation that you'll need to analyze and provide a solution for. You'll be judged on your ability to think critically, your decision-making skills, your communication skills, and your ability to work under pressure.
It's important to note that Walmart values diversity and inclusion in their hiring process. They are committed to creating a diverse workforce and ensuring that all candidates are given equal opportunities. As such, they may ask questions related to your experiences with diversity and inclusion, and how you would handle situations related to these topics in the workplace.
Additionally, Walmart is a company that values innovation and staying ahead of the curve. As a product manager, you'll need to demonstrate your ability to think creatively and come up with new ideas. During the interview process, you may be asked to share examples of how you've implemented innovative solutions in your previous roles, or how you would approach a specific challenge at Walmart.
Researching Walmart's History and Products
To prepare for your Walmart product management case interviews, it's crucial that you research the history of the company and its product portfolio. You need to understand the company's values, mission, and vision. You'll also need to know about the products that Walmart sells, the trends in the retail industry, and the target audience that the company caters to. This information will help you better understand the case questions you'll be asked during the interview process.
One important aspect to consider when researching Walmart's history and products is the company's sustainability efforts. Walmart has made significant strides in reducing its environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices throughout its supply chain. This includes initiatives such as reducing waste, increasing energy efficiency, and sourcing products from sustainable sources. Understanding Walmart's sustainability efforts can provide valuable insights into the company's values and priorities, and may be relevant to case questions related to product development and supply chain management.
Free trial!

From 110 top coaches
Access a library of videos, templates, and examples curated by Leland’s top coaches.
150+ video guides.

Example Resumes

Exercises & Templates
Technical Skill Development
Analyzing Walmart's Current Market Position
As a product manager, you'll need to have a clear understanding of Walmart's current market position. This means knowing the competition, the current trends in the industry, and the areas where Walmart is excelling and where it needs improvement. Analyzing this information will help you to identify areas where you can make a positive impact and develop new ideas to improve the company's performance.
One area where Walmart has been excelling in recent years is in its e-commerce business. With the rise of online shopping, Walmart has invested heavily in its online platform and has seen significant growth in its online sales. In addition, Walmart has been expanding its grocery delivery and pickup services, which has become increasingly popular among customers. However, there is still room for improvement in areas such as sustainability and employee satisfaction, which are becoming increasingly important to consumers.
Identifying and Prioritizing Customer Needs for Walmart Products
One of the most critical skills that a product manager needs to possess is the ability to identify customer needs. You need to know what the customer wants, what they value, and what is important to them. You'll need to have a thorough understanding of the customer's buying behavior, spending habits, and their expectations of Walmart products. Once you've identified these needs, you'll need to prioritize them to ensure that you're providing the best possible product for the customer.
One effective way to identify customer needs is to conduct market research. This can involve surveys, focus groups, and analyzing customer feedback. By gathering data on customer preferences and pain points, you can gain valuable insights into what they need and want from Walmart products. Additionally, you can use this information to identify trends and anticipate future customer needs.
Once you've identified customer needs, it's important to prioritize them based on their level of importance and feasibility. Some needs may be critical to the customer's satisfaction, while others may be nice-to-have features. You'll also need to consider factors such as cost, time, and resources required to implement these changes. By prioritizing customer needs, you can ensure that you're focusing on the most important areas and delivering the best possible product for the customer.
Developing Effective Product Strategies for Walmart
The effective product strategy is essential for any product manager, and Walmart is no exception. During the interview process, you'll be asked to develop new product ideas and strategies to improve the current product portfolio. To do this, you'll need to be creative, innovative, and have a deep understanding of the market and the customer.
One important aspect to consider when developing product strategies for Walmart is the company's commitment to sustainability. Walmart has set ambitious goals to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainable practices throughout its supply chain. As a product manager, you'll need to think about how your products can align with these goals and contribute to Walmart's overall sustainability efforts. This could involve sourcing materials from sustainable suppliers, reducing packaging waste, or designing products that are more energy-efficient. By incorporating sustainability into your product strategies, you'll not only help Walmart achieve its environmental goals but also appeal to customers who are increasingly concerned about sustainability and environmental issues.
Creating a Structured Approach to Solving Case Interview Questions
To be successful in your Walmart product management case interviews, you need to have a structured approach to analyze and solve business cases. This means breaking down the case into smaller parts, gathering relevant information, identifying the problem, and coming up with a solution that addresses the issue. Having a robust framework will help you stay organized and avoid getting overwhelmed by complex case scenarios.
Practicing Case Interview Questions with Mock Interviews
Practice makes perfect, and this also applies to Walmart product management case interviews. To improve your chances of success, it's essential to practice case interview questions with a mock interview. You can use online resources, join a case interview group, or work with a mentor or consultant. The goal is to gain a better understanding of how to approach case interviews and improve your skills with every practice session.
Tips for Navigating Behavioral Questions in Walmart Product Management Interviews
Behavioral questions provide insight into how you'll perform on the job, and they're an essential part of the Walmart product management interview process. During the interview, you'll be asked about how you handle difficult situations, how you work in a team, and how you deal with stress and deadlines. Preparing responses and examples of past experiences is key to acing these types of questions.
Preparing for the Final Round of Interviews with Walmart Executives
If you make it through the case interviews, you'll be required to attend a final interview with Walmart executives. This will be a more traditional interview, where you'll discuss your background, experience, and qualifications. You'll need to be prepared to answer questions about your motivation for applying for the job, the challenges you've faced as a product manager, and how you can help Walmart succeed in the future.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During the Walmart Product Management Interview Process
Several common mistakes can hurt your chances of success during the Walmart product management interview process. These include failing to prepare, using vague or unclear language, not listening to the interviewer, and not asking questions. To avoid these mistakes, it's essential to do your research, practice case interviews, and be clear and concise in your responses.
Resources and Tools for Acing Your Walmart Product Management Case Interviews
There are several resources and tools available that can help you prepare for your Walmart product management case interviews. These include online case interview courses, case interview books, case interview groups, and online forums. Additionally, practicing with mock interviews and working with a mentor or consultant can also be highly beneficial.
Conclusion: How to Stand Out in the Walmart Product Management Job Search
To stand out in the Walmart product management job search, you need to be well-prepared for the interview process. Researching the company's history, understanding the market, and identifying customer needs are essential to succeed as a product manager at Walmart. Additionally, developing a structured approach to solving case interview questions, practicing with mock interviews, and avoiding common mistakes can significantly improve your chances of success. By following these steps and utilizing available resources, you can successfully navigate the Walmart product management interview process and land your dream job.
Browse hundreds of expert coaches
Leland coaches have helped thousands of people achieve their goals. A dedicated mentor can make all the difference.
Browse Related Articles

May 16, 2023
How to Prepare for Schmidt Futures Product Management Case Interviews
If you're looking to nail your Schmidt Futures product management case interviews, this article is a must-read.

How to Prepare for Square Product Management Case Interviews
Are you preparing for a Square product management case interview? Look no further! Our comprehensive guide provides tips and strategies to help you ace your interview and land your dream job at Square.

How to Prepare for TikTok Product Management Case Interviews
If you're looking to land a product management role at TikTok, then you need to be prepared for the case interview process.

How to Prepare for Zynga Product Management Case Interviews
If you're preparing for a Zynga product management case interview, this article is a must-read.

How to Prepare for Shopify Product Management Case Interviews
If you're preparing for a Shopify product management case interview, this article is a must-read.

How to Prepare for Spotify Product Management Case Interviews
Are you looking to land a product management role at Spotify? Our article on how to prepare for Spotify product management case interviews is a must-read.

How to Prepare for Stripe Product Management Case Interviews
Are you preparing for a Stripe product management case interview? This article provides you with valuable tips and insights on how to prepare effectively.

How to Prepare for Uber Product Management Case Interviews
Are you preparing for a product management case interview with Uber? This article provides valuable tips and strategies to help you ace your interview and land your dream job.

How to Prepare for Yahoo Product Management Case Interviews
If you're looking to land a product management role at Yahoo, you'll likely need to ace their case interviews.

How to Prepare for Salesforce Product Management Case Interviews
Are you preparing for a Salesforce product management case interview? Look no further! Our comprehensive guide provides tips and strategies to help you ace your interview and land your dream job.

How to Prepare for Snap Product Management Case Interviews
Get ready to ace your Snap product management case interviews with these expert tips and strategies.

How to Prepare for Tinder Product Management Case Interviews
If you're preparing for a Tinder product management case interview, this article is a must-read.

- THE STRATEGY JOURNEY Book
- Videos & Tutorials
- Strategy Journey Analyzer [QUIZ + WORKBOOK]
- COMMUNITY FORUMS
- Transforming Operating Models with Service Design (TOMS) Program
- ABOUT STRATABILITY ACADEMY
Walmart Business Strategy: A Comprehensive Analysis
By Julie Choo
Published: January 5, 2024
Last Update: January 5, 2024
TOPICS: Service Design
In the dynamic landscape of retail, Walmart stands as a behemoth, shaping the industry with its innovative business strategies . This article delves into the core of Walmart’s success, unraveling its business strategy and digital transformation from top to bottom.
Walmart Business Strategy
Walmart’s business strategy is a well-crafted tapestry that combines a variety of elements to secure its position as a retail giant. At the heart of this strategy lies a robust operating model approach that encompasses a diverse range of channels and tactics.
Transition to An OmniChannel Marketplace
The Walmart business strategy includes leveraging its vast physical presence through an extensive network of stores, drawing customers in with the promise of Everyday Low Prices (EDLP). This commitment to affordability is not just a slogan; it’s a cornerstone of Walmart’s marketing ethos, shaping consumer perceptions and driving foot traffic to its brick-and-mortar locations.
Building Strength via its Emerging Digital Operating Model
Walmart’s business business strategy extends beyond traditional advertising methods and its strength is in its operational strategy where it is charging ahead with digital transformation to become a more complete Omnichannel Marketplace to combat competitors such as Amazon. The retail giant has embraced the digital era, utilizing online platforms and e-commerce to reach a broader audience. Part of this digital evolution involves the strategic placement of distribution and fulfillment centers , ensuring efficient order processing and timely deliveries. By strategically integrating distribution and fulfillment centers into its operating model , Walmart maximizes operational efficiency, meeting customer demands swiftly and solidifying its reputation for reliability in the competitive retail landscape.
In essence, Walmart’s holistic digital operating model backed by a evolving digital transformation strategy, encompassing physical stores, online presence, and strategically placed distribution hubs, reflects a dynamic and adaptive approach to consumer engagement and satisfaction.
Walmart’s Existing Business Model Before Digital Transformation
Walmart’s retail business .
Walmart stores, comprising a vast network of discount stores and clubs, serve as the backbone of the retail giant’s physical presence. Walmart’s store format, ranging from neighborhood discount stores to expansive membership-based clubs, caters to a diverse customer base. These Walmart stores are strategically positioned to provide accessibility to a wide demographic, offering a one-stop shopping experience.
The discount stores, characterized by their commitment to Everyday Low Prices (EDLP), have become synonymous with affordability, attracting budget-conscious consumers. Simultaneously, Walmart clubs offer a membership-based model, providing additional benefits and exclusive deals. The amalgamation of these store formats under the Walmart umbrella showcases the company’s versatility, catering to the varied needs and preferences of consumers across different communities and demographics.
Walmart Pricing Strategy
Pricing strategy.
Walmart’s pricing strategy and its competitive advantage are substantiated by reputable sources in the retail industry. The pricing index data, indicating that Walmart’s prices are, on average, 10% lower than its competitors, comes from a comprehensive market analysis conducted by Retail Insight, a leading research firm specializing in retail trends and pricing dynamics.
Everyday Low Prices
Walmart’s success in the retail sector can be attributed to its commitment to Low Price Leadership, a strategic approach that revolves around providing customers with unbeatable prices. Leveraging Economies of Scale, Walmart capitalizes on its vast size and purchasing power to negotiate favorable deals with suppliers, enabling the company to pass on cost savings to consumers. The integration of Advanced Technology into its operations is another pivotal aspect of Walmart’s strategy. From inventory management to supply chain optimization, technology allows Walmart to enhance efficiency and keep prices competitive.
Walmart strives to keep it’s pricing tactics to the concept of “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP). This philosophy ensures that customers receive consistently low prices on a wide range of products, fostering trust and loyalty. Additionally, the Rollback Pricing strategy involves temporary price reductions on select items, creating a sense of urgency and encouraging sales. Walmart’s Price Matching Policy, both in-store and online, further solidifies its commitment to offering the best deals. This policy assures customers that if they find a lower price elsewhere, Walmart will match it.
The insight into Walmart’s “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP) philosophy and its impact on a 15% lower average price for common goods compared to competitors is derived from a detailed report published by Priceonomics , a respected platform known for its in-depth analyses of pricing strategies across various industries.
The statistics regarding Walmart’s market share of 22% in the U.S. grocery market and the 19% higher customer loyalty rate compared to competitors are sourced from recent market reports by Statista, a reliable and widely used statistical portal providing insights into global market trends and consumer behavior.
Multiple layers of Discount
Walmart’s embrace of Multiple Discounts adds another layer to its pricing strategy. Whether through seasonal promotions, clearance sales, or bundled deals, the company provides various avenues for customers to save money. This multifaceted approach to pricing reflects Walmart’s dedication to delivering value to its customers, ensuring that affordability remains a cornerstone of the retail giant’s identity.
These sources collectively reinforce the significance of Walmart’s pricing strategy in maintaining its competitive edge and dominating the retail landscape
Walmart’s Servicing Business
Walmart’s strategic expansion into the servicing business marks a transformative shift, positioning the retail giant as a comprehensive one-stop-shop that extends beyond conventional retail offerings. This venture encompasses an array of lifestyle services, ranging from financial services to automotive care and healthcare clinics. Walmart’s aim is clear: to seamlessly integrate into the daily lives of customers, providing not only products but also essential services, thereby enhancing its role in customers’ routines.
In response to the evolving preferences of contemporary consumers who prioritize convenience and accessibility, Walmart’s strategy seeks to streamline the customer journey. The provision of a diverse range of services alongside its traditional retail offerings exemplifies Walmart’s commitment to simplifying the consumer experience. This comprehensive approach not only caters to the varied needs of customers but also cultivates a sense of loyalty, as individuals find value in the convenience of addressing different requirements all under one roof.
The multifaceted nature of Walmart’s strategy is anticipated to foster increased customer retention. By offering not only a wide array of products but also an extensive range of lifestyle services, Walmart solidifies its position as a retail powerhouse, adapting to the changing landscape of customer-centric businesses. The convenience and value embedded in this approach are poised to elevate Walmart’s stature, making it an indispensable part of customers’ lives.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart’s Business strategy
As we navigate Walmart’s digital transformation journey, a SWOT analysis reveals key insights into its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, guiding strategic decisions for sustained success in the dynamic retail industry that is operating in an increasingly digital economy.
SWOT Analysis of Walmart:
- Strong Brand Recognition: Walmart’s strength lies in its widely recognized and trusted brand, fostering consumer confidence and loyalty.
- Diverse Revenue Stream: The company’s adaptability is evident through a diverse revenue stream, navigating various markets and industries to maintain financial resilience. Per Walmart’s Q3 FY23 Earnings , a breakdown of walmart’s income can be recognised through its Sam’s Club membership sales (Up by 7.2%), Walmart U.S Comp Sales (Up 4.9%), Walmart U.S. eCommerce (up by 24%), and Walmart International sales (up by 5.4%).
- Economies of Scale: Walmart leverages its extensive size for economies of scale shown by its strong revenue growth of 5.3% per 2022 and 2023 consolidated Income statement, enabling cost advantages in procurement, operations, and overall efficiency.
- Strong Customer Base: With a vast and loyal customer base, Walmart establishes a robust foundation in the retail sector, emphasizing customer retention and sustained business growth as per market share stat of 60% shown on the Market retail/wholesale industry dominated by Walmart.
Weaknesses:
- Labor Relations: Walmart has faced criticism for labor practices, including low wages and labor disputes.
- E-commerce Competition: Despite significant strides, Walmart faces intense competition from e-commerce giants (e.g, amazon, eBay), impacting its online market share.
- Over Reliance on US Market: A substantial portion of Walmart’s revenue is generated in the United States, making it vulnerable to domestic economic fluctuations.
- Inconsistent customer service: represents a weakness in Walmart’s SWOT analysis, as variations in service quality across different locations may impact the overall customer experience, potentially leading to customer dissatisfaction and diminished brand perception.
Opportunities:
- E-commerce Expansion: Further growth in the online market allows Walmart to capitalize on changing consumer shopping habits.
- International Expansion: Targeting untapped markets presents opportunities for global revenue diversification.
- Health and Wellness Market: The growing trend towards health-conscious living provides avenues for expansion in the health and wellness sector. Increased understanding of customer journeys in these niches is key to begin to build stickiness effects.
- Technological Innovations: Embracing cutting-edge technologies can enhance customer experience and operational efficiency through a growing Omnichannel marketplace. It is vital to master data science and begin to leverage AI in the battle to understand consumer behaviors and deliver a remarkable experience.
- Competition: Intense competition from traditional retailers and e-commerce platforms poses a threat to Walmart’s market share such as Costco, Target and Amazon.
- Regulatory Challenges: Changes in regulations, especially related to labor and trade, can impact Walmart’s operations and costs. One such example is the metrics shown per Walmart’s ethics & compliance code of conduct aligning to regulatory challenges in culture, work safety, risk mitigation and more.
- Economic Downturns: Economic uncertainties and recessions may lead to reduced consumer spending, affecting Walmart’s revenue.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: External factors like natural disasters or geopolitical events can disrupt the global supply chain, impacting product availability and costs. Such threats are specifically addressed by Walmart’s Enterprise Resilience Planning Team .
More on Walmart’s Online Competitors
Walmart faces formidable competition in the online retail arena, with key rivals such as Amazon and Target vying for a share of the digital market. Amazon, known for its extensive product selection and swift delivery services, poses a significant challenge to Walmart’s e-commerce dominance. Target, on the other hand, leverages its brand appeal and strategic partnerships to attract online customers. To counteract these competitors, Walmart employs a multifaceted approach that combines technological innovation, competitive pricing, and strategic collaborations.
Walmart strategically invests in advanced technologies to enhance its online platform and improve the overall customer experience. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning enables Walmart to provide personalized recommendations, similar to Amazon’s renowned recommendation engine. Additionally, Walmart’s commitment to competitive pricing aligns with its traditional retail strength, offering Everyday Low Prices (EDLP) and frequent promotions to attract budget-conscious consumers, countering the pricing strategies employed by Amazon and other competitors.
Conducting a thorough SWOT analysis (such as this example from the Strategy Journey Book – 2nd Edition) allows Walmart to capitalize on its strengths, address weaknesses, seize opportunities, and mitigate potential threats, contributing to sustained success in the ever-evolving retail landscape.
Walmart’s Digital Transformation Strategy in the new ERA of AI-led Customer Centricity
Walmart’s online business strategy.
Overall, Walmart’s e-commerce strategy is customer-centric, driving substantial sales growth by tailoring its approach to the evolving needs of online customers. Operating a multitude of specialized e-commerce websites across diverse product categories, Walmart strategically positions itself on various e-commerce platforms for market penetration within the US.
Servicing Relevant Customer Journeys & Sustainable Transformation
Walmart’s evolving online strategy is characterized by a dual focus on extensive product offerings and technological sophistication, with concrete examples per its strategic partnership with Adobe in 2021 to integrate walmart’s marketplace, online and instore fulfillment and pickup technologies with Adobe commerce showcasing its commitment to a seamless customer experience. The integration of advanced tools is exemplified by the implementation of an efficient order processing system. For instance, Walmart employs real-time inventory management and automated order fulfillment , ensuring that customers experience timely and accurate deliveries. Statistics show an increasing number of fulfillment centers through FY2022 and FY2023 reports per statista .
Emerging predictive capabilities supported by Data Science and AI
In addition, the technological depth extends to personalized experiences, illustrated by Walmart’s robust recommendation engine. By analyzing customer preferences and purchase history, the system suggests relevant products, enhancing the entire customer journey. This personalized touch not only reflects the user-friendly interface but also demonstrates Walmart’s dedication to tailoring the online experience to individual needs.
Focus on seamless CX and UX to improve customer stickiness
Furthermore, Walmart’s commitment to a seamless online interaction is evident in its streamlined navigation features. The website’s intuitive design and optimized search functionality provide a smooth browsing experience for customers. This emphasis on user-friendliness goes beyond mere aesthetics, ensuring that customers can easily find and explore products, contributing to a more engaging online experience. Improved engagement is at the heart of Walmart’s strategy to foster stickiness effects, both digitally and to also build on brand stickiness too.

By investing in cutting-edge technologies while transforming using Human Centered design practices focused on CX and UX, Walmart not only navigates the complexities of the e-commerce landscape but also enhances the overall satisfaction and engagement of its online customers. These examples underscore Walmart’s strategic approach to digital transformation, where technological sophistication is not just a feature but a tangible means to elevate the online shopping experience.
Walmart International Business
Successful international business expansion requires operating model transformation, and Walmart’s strategy is characterized by a blend of strategic acquisitions, partnerships, and a keen understanding of local markets. This is also how Walmart is operationally applying AI, via strategic partnerships as it continues to build its capabilities to improve its agility to implement transformation and go to market faster, rather than trying to build everything from scratch.
A Sustainable Diversification strategy that adapts to local markets
Walmart’s international business expansion is a testament to its strategic approach in entering diverse markets and adapting to local nuances. One notable example of Walmart’s successful international expansion is its entry into the Indian market. In 2018, Walmart acquired a majority stake in Flipkart, one of India’s leading e-commerce platforms. This move allowed Walmart to tap into India’s burgeoning e-commerce market, aligning with the country’s growing digital consumer base.
The acquisition of Flipkart exemplifies Walmart’s strategy of leveraging local expertise and established platforms to gain a foothold in international markets. Recognizing the unique characteristics of the Indian retail landscape, where e-commerce plays a significant role, Walmart strategically invested in a company deeply embedded in the local market. This approach not only facilitated a smoother entry for Walmart but also enabled the retail giant to navigate regulatory complexities and consumer preferences effectively.
Another example of Walmart’s commitment to tailoring its offerings to meet local needs is further highlighted in its expansion into China where Walmart adapts its store formats to cater to specific consumer preferences.
In China, Walmart has experimented with smaller-format stores in urban areas, recognizing the demand for convenient and accessible shopping options. This adaptability showcases Walmart’s understanding of the diverse economic and cultural landscapes it operates in, contributing to its success on the global stage.
Working with partners to diversify and build a sustainable business model
Collaborations and strategic partnerships play a pivotal role in Walmart’s competitive strategy. In 2023, Walmart has outlined plans to invest heavily into AI automation fulfillment centers to improve its unit cost average by 20%, increasing efficiency in order fulfilments and operations.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 expanded Walmart’s digital footprint and brought innovative talent into the company. Furthermore, Walmart’s partnerships with various brands (such as Adobe, ShipBob) and retailers enable it to diversify its product offerings, providing a competitive edge against the more specialized approaches of some competitors. As part of Walmart’s strategy in marketing, Walmart has announced partnerships with social media giants such as TikTok, Snapchat, Firework and more further boosting its online digital footprint.
The acquisition of Jet.com in 2016 not only expanded Walmart’s digital footprint but it brought innovative talent into the company. It is clear Walmart sees the need for talent as key to its continued efforts to apply human centered design as part of its digital transformation strategy.
By continuously adapting and evolving its strategies, Walmart is clearly implementing digital transformation sustainably, to support its future operating model as Walmart remains a formidable force in the online retail landscape, navigating the challenges presented by its competitors.
In conclusion, Walmart’s business strategy is that of an growing Omnichannel marketplace, a multifaceted approach that combines physical and digital retail, competitive pricing, supply chain excellence, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. Understanding these elements provides insights into the retail giant’s enduring success in a rapid changing and competitive digital economy as it continues to combat emerging new business disruptions.
Q1: How did Walmart become a retail giant?
Walmart’s ascent to retail dominance can be attributed to a combination of strategic pricing, operational efficiency, and a customer-centric approach.
Q2: What sets Walmart’s supply chain apart?
Walmart’s supply chain is marked by innovation and technological integration, allowing the company to streamline operations and stay ahead in a competitive market.
Q3: How does Walmart balance physical and digital retail?
Walmart seamlessly integrates its brick-and-mortar stores with its online presence, offering customers a comprehensive shopping experience.
Q4: What is Walmart’s philosophy on pricing?
Walmart’s commitment to everyday low prices is a fundamental philosophy that underpins its strategy, ensuring affordability for consumers.
Q5: How has Walmart expanded globally?
Walmart’s global expansion involves adapting its strategy to diverse markets, understanding local dynamics, and leveraging its core strengths.
About the author
Julie Choo is lead author of THE STRATEGY JOURNEY book and the founder of STRATABILITY ACADEMY. She speaks regularly at numerous tech, careers and entrepreneur events globally. Julie continues to consult at large Fortune 500 companies, Global Banks and tech start-ups. As a lover of all things strategic, she is a keen Formula One fan who named her dog, Kimi (after Raikkonnen), and follows football - favourite club changes based on where she calls home.
You might also like
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Strategy Journey Fundamentals , Transformation
The Impact of Co Creation in Modern Business
Culture & Careers , Data & AI , Gameplans & Roadmaps , Operating Model , Service Design , Transformation
4 steps to create a Winning Game Plan
Service Design
9 Steps to your Winning Customer Journey Strategy
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
“We Need People to Lean into the Future”
- Adi Ignatius

For years, Walmart’s unrivaled customer research capabilities helped it dominate retailing. Then along came the internet, and Walmart suddenly found itself playing catchup to e-commerce pioneers like Amazon. In 2014 the board appointed Doug McMillon as CEO and gave him an imperative: Bring Walmart into the future—without sacrificing its longtime strengths.
McMillon, who began his career unloading trucks at a neighborhood Walmart, respects tradition but is impatient for change. In this interview with HBR editor in chief Adi Ignatius, he describes the ups and downs of transforming America’s largest company. Going digital is a top priority—which is why Walmart recently paid $3 billion to acquire e-tailer Jet.com. But the company also wants to strengthen the in-store experience. “The reality,” notes McMillon, “is that customers want everything”—low prices, convenience, and seamless interactions online and in person. In this new world, all employees, including those on the sales floor, will need to be tech savvy. And the management team can no longer make strategic decisions on an annual or even quarterly basis; “strategy is happening on a much faster cycle time,” says the CEO.
A conversation with Walmart CEO Doug McMillon
For years, Walmart seemed to understand exactly what its customers wanted. It developed complicated consumer analytics and used that data, along with relentless pressure on suppliers, to become a retail powerhouse that sold practically everything at the lowest possible prices.
- Adi Ignatius is the editor in chief of Harvard Business Review.
Partner Center

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Walmart’s Operations Management: 10 Strategic Decisions & Productivity

Walmart Inc.’s operations management involves a variety of approaches that are focused on managing the supply chain and inventory, as well as sales performance. The company’s success is significantly based on effective performance in retail operations management. Specifically, Walmart’s management covers all the 10 decision areas of operations management. These strategic decision areas pertain to the issues managers deal with on a daily basis as they optimize the e-commerce company’s operations. Walmart’s application of the 10 decisions of operations management reflects managers’ prioritization of business objectives. In turn, this prioritization shows the strategic significance of the different decision areas of operations management in the retail company’s business. This approach to operations aligns with Walmart’s corporate mission statement and corporate vision statement . The retail enterprise is a business case of how to achieve high efficiency in operations to ensure long-term growth and success in the global market.
The 10 decisions of operations management are effectively addressed in Walmart’s business through a combination of approaches that emphasize supply chain management, inventory management, and sales and marketing. This approach leads to strategies that strengthen the business against competitors, like Amazon and its subsidiary, Whole Foods , as well as Home Depot , eBay, Costco , Best Buy, Macy’s, Kroger, Alibaba, IKEA, Target, and Lowe’s.
The 10 Strategic Decision Areas of Operations Management at Walmart
1. Design of Goods and Services . This decision area of operations management involves the strategic characterization of the retail company’s products. In this case, the decision area covers Walmart’s goods and services. As a retailer, the company offers retail services. However, Walmart also has its own brands of goods, such as Great Value and Sam’s Choice. The company’s operations management addresses the design of retail service by emphasizing the variables of efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Walmart’s generic strategy for competitive advantage, and intensive growth strategies emphasize low costs and low selling prices. To fulfill these strategies, the firm focuses on maximum efficiency of its retail service operations. To address the design of goods in this decision area of operations management, Walmart emphasizes minimal production costs, especially for the Great Value brand. The firm’s consumer goods are designed in a way that they are easy to mass-produce. The strategic approach in this operations management area affects Walmart’s marketing mix or 4Ps and the corporation’s strategic planning for product development and retail service expansion.
2. Quality Management . Walmart approaches this decision area of operations management through three tiers of quality standards. The lowest tier specifies the minimum quality expectations of the majority of buyers. Walmart keeps this tier for most of its brands, such as Great Value. The middle tier specifies market average quality for low-cost retailers. This tier is used for some products, as well as for the job performance targets of Walmart employees, especially sales personnel. The highest tier specifies quality levels that exceed market averages in the retail industry. This tier is applied to only a minority of Walmart’s outputs, such as goods under the Sam’s Choice brand. This three-tier approach satisfies quality management objectives in the strategic decision areas of operations management throughout the retail business organization. Appropriate quality measures also contribute to the strengths identified in the SWOT analysis of Walmart Inc .
3. Process and Capacity Design . In this strategic decision area, Walmart’s operations management utilizes behavioral analysis, forecasting, and continuous monitoring. Behavioral analysis of customers and employees, such as in the brick-and-mortar stores and e-commerce operations, serves as basis for the company’s process and capacity design for optimizing space, personnel, and equipment. Forecasting is the basis for Walmart’s ever-changing capacity design for human resources. The company’s HR process and capacity design evolves as the retail business grows. Also, to satisfy concerns in this decision area of operations management, Walmart uses continuous monitoring of store capacities to inform corporate managers in keeping or changing current capacity designs.
4. Location Strategy . This decision area of operations management emphasizes efficiency of movement of materials, human resources, and business information throughout the retail organization. In this regard, Walmart’s location strategy includes stores located in or near urban centers and consumer population clusters. The company aims to maximize market reach and accessibility for consumers. Materials and goods are made available to Walmart’s employees and target customers through strategic warehouse locations. On the other hand, to address the business information aspect of this decision area of operations management, Walmart uses Internet technology and related computing systems and networks. The company has a comprehensive set of online information systems for real-time reports and monitoring that support managing individual retail stores as well as regional market operations.
5. Layout Design and Strategy . Walmart addresses this decision area of operations management by assessing shoppers’ and employees’ behaviors for the layout design of its brick-and-mortar stores, e-commerce websites, and warehouses or storage facilities. The layout design of the stores is based on consumer behavioral analysis and corporate standards. For example, Walmart’s placement of some goods in certain areas of its stores, such as near the entrance/exit, maximizes purchase likelihood. On the other hand, the layout design and strategy for the company’s warehouses are based on the need to rapidly move goods across the supply chain to the stores. Walmart’s warehouses maximize utilization and efficiency of space for the company’s trucks, suppliers’ trucks, and goods. With efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and cost-minimization, the retail company satisfies the needs in this strategic decision area of operations management.
6. Human Resources and Job Design . Walmart’s human resource management strategies involve continuous recruitment. The retail business suffers from relatively high turnover partly because of low wages, which relate to the cost-leadership generic strategy. Nonetheless, continuous recruitment addresses this strategic decision area of operations management, while maintaining Walmart’s organizational structure and corporate culture . Also, the company maintains standardized job processes, especially for positions in its stores. Walmart’s training programs support the need for standardization for the service quality standards of the business. Thus, the company satisfies concerns in this decision area of operations management despite high turnover.
7. Supply Chain Management . Walmart’s bargaining power over suppliers successfully addresses this decision area of operations management. The retailer’s supply chain is comprehensively integrated with advanced information technology, which enhances such bargaining power. For example, supply chain management information systems are directly linked to Walmart’s ability to minimize costs of operations. These systems enable managers and vendors to collaborate in deciding when to move certain amounts of merchandise across the supply chain. This condition utilizes business competitiveness with regard to competitive advantage, as shown in the Porter’s Five Forces analysis of Walmart Inc . As one of the biggest retailers in the world, the company wields its strong bargaining power to impose its demands on suppliers, as a way to address supply chain management issues in this strategic decision area of operations management. Nonetheless, considering Walmart’s stakeholders and corporate social responsibility strategy , the company balances business needs and the needs of suppliers, who are a major stakeholder group.
8. Inventory Management . In this decision area of operations management, Walmart focuses on the vendor-managed inventory model and just-in-time cross-docking. In the vendor-managed inventory model, suppliers access the company’s information systems to decide when to deliver goods based on real-time data on inventory levels. In this way, Walmart minimizes the problem of stockouts. On the other hand, in just-in-time cross-docking, the retail company minimizes the size of its inventory, thereby supporting cost-minimization efforts. These approaches help maximize the operational efficiency and performance of the retail business in this strategic decision area of operations management (See more: Walmart: Inventory Management ).
9. Scheduling . Walmart uses conventional shifts and flexible scheduling. In this decision area of operations management, the emphasis is on optimizing internal business process schedules to achieve higher efficiencies in the retail enterprise. Through optimized schedules, Walmart minimizes losses linked to overcapacity and related issues. Scheduling in the retailer’s warehouses is flexible and based on current trends. For example, based on Walmart’s approaches to inventory management and supply chain management, suppliers readily respond to changes in inventory levels. As a result, most of the company’s warehouse schedules are not fixed. On the other hand, Walmart store processes and human resources in sales and marketing use fixed conventional shifts for scheduling. Such fixed scheduling optimizes the retailer’s expenditure on human resources. However, to fully address scheduling as a strategic decision area of operations management, Walmart occasionally changes store and personnel schedules to address anticipated changes in demand, such as during Black Friday. This flexibility supports optimal retail revenues, especially during special shopping occasions.
10. Maintenance . With regard to maintenance needs, Walmart addresses this decision area of operations management through training programs to maintain human resources, dedicated personnel to maintain facilities, and dedicated personnel to maintain equipment. The retail company’s human resource management involves training programs to ensure that employees are effective and efficient. On the other hand, dedicated personnel for facility maintenance keep all of Walmart’s buildings in shape and up to corporate and regulatory standards. In relation, the company has dedicated personnel as well as third-party service providers for fixing and repairing equipment like cash registers and computers. Walmart also has personnel for maintaining its e-commerce websites and social media accounts. This combination of maintenance approaches contributes to the retail company’s effectiveness in satisfying the concerns in this strategic decision area of operations management. Effective and efficient maintenance supports business resilience against threats in the industry environment, such as the ones evaluated in the PESTEL/PESTLE Analysis of Walmart Inc .
Determining Productivity at Walmart Inc.
One of the goals of Walmart’s operations management is to maximize productivity to support the minimization of costs under the cost leadership generic strategy. There are various quantitative and qualitative criteria or measures of productivity that pertain to human resources and related internal business processes in the retail organization. Some of the most notable of these productivity measures/criteria at Walmart are:
- Revenues per sales unit
- Stockout rate
- Duration of order filling
The revenues per sales unit refers to the sales revenues per store, average sales revenues per store, and sales revenues per sales team. Walmart’s operations managers are interested in maximizing revenues per sales unit. On the other hand, the stockout rate is the frequency of stockout, which is the condition where inventories for certain products are empty or inadequate despite positive demand. Walmart’s operations management objective is to minimize stockout rates. Also, the duration of order filling is the amount of time consumed to fill inventory requests at the company’s stores. The operations management objective in this regard is to minimize the duration of order filling, as a way to enhance Walmart’s business performance.
- Reid, R. D., & Sanders, N. R. (2023). Operations Management: An Integrated Approach . John Wiley & Sons.
- Szwarc, E., Bocewicz, G., Golińska-Dawson, P., & Banaszak, Z. (2023). Proactive operations management: Staff allocation with competence maintenance constraints. Sustainability, 15 (3), 1949.
- Walmart Inc. – Form 10-K .
- Walmart Inc. – History .
- Walmart Inc. – Location Facts .
- Walmart’s E-commerce Website .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Walmart Change Management Case Study
Change management is an essential aspect of any business that seeks to remain competitive in a dynamic market environment.
Walmart, one of the world’s largest retail giants, has had to navigate through significant changes in the retail industry, including the growth of e-commerce and shifting consumer behaviors.
To maintain its position as a leader in the retail industry, Walmart has had to employ effective change management strategies to adapt to these changes successfully.
This blog post presents a case study of Walmart’s change management efforts, exploring the strategies employed, the results achieved, and the lessons learned.
By understanding Walmart’s approach to change management, businesses can learn valuable lessons and insights to help them navigate through their own organizational changes successfully.
Introduction to Walmart and its significance in the retail industry
Walmart is a multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of discount department stores, grocery stores, and hypermarkets.
Founded in 1962 by Sam Walton, Walmart has grown to become one of the world’s largest retail companies, with over 10,000 stores in 27 countries and employing over two million people globally.
Walmart’s success can be attributed to its focus on providing low-cost products, a wide range of merchandise, and a convenient shopping experience to its customers.
Walmart’s innovative business strategies, such as its use of technology and supply chain management, have significantly impacted the retail industry, driving competitors to adopt similar approaches to remain competitive.
Walmart’s success has made it a significant player in the retail industry, with its strategies being studied and emulated by businesses around the world
History of Walmart’s growth and success
Walmart’s growth and success can be traced back to its founder, Sam Walton, who had a vision of creating a retail store that offered low prices to customers.
Walton opened his first store in Rogers, Arkansas, in 1962, which quickly became popular due to its low prices and convenient location.
In the following years, Walmart expanded rapidly, opening more stores across the United States and becoming a publicly traded company in 1972.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Walmart continued to grow, opening new stores and expanding into new markets.
Walmart’s success was due, in part, to its innovative business strategies, such as its use of technology to manage inventory and supply chain operations, as well as its focus on providing low-cost products to customers.
Walmart’s efficient operations and ability to negotiate lower prices with suppliers allowed the company to offer products at a lower cost than its competitors.
By the 2000s, Walmart had become a global retail giant, with stores in multiple countries and a significant impact on the retail industry.
Despite facing criticism over its labor practices and impact on small businesses, Walmart’s focus on low prices and convenience to customers continued to make it a popular choice for shoppers.
Today, Walmart remains one of the largest and most successful retailers in the world, with a significant presence in the retail industry.
Overview of Walmart’s organizational structure and culture
Walmart has a hierarchical organizational structure, with a clear chain of command and multiple levels of management.
At the top of the hierarchy is the CEO, followed by executive vice presidents, senior vice presidents, and vice presidents.
Each level of management is responsible for overseeing specific areas of the company’s operations, with clear lines of authority and responsibility.
Walmart’s culture is focused on providing low-cost products to customers and delivering a convenient shopping experience.
The company values efficiency, innovation, and collaboration, and encourages employees to take ownership of their work and contribute to the company’s success.
Walmart’s culture is also characterized by its emphasis on customer service, with employees trained to prioritize the needs of customers and ensure they have a positive shopping experience.
Walmart’s culture has been shaped by its founder, Sam Walton, who believed in empowering employees and giving them the resources they needed to succeed.
This approach has been reflected in the company’s employee policies, such as its emphasis on training and development programs, as well as its commitment to offering competitive wages and benefits to its workers.
Need for Change Management at Walmart
The retail industry has undergone significant changes in recent years, with the growth of e-commerce, shifting consumer behaviors, and increased competition.
To remain competitive in this dynamic environment, businesses need to be agile and adaptable, constantly evolving their strategies to meet changing customer needs and market conditions.
For Walmart, this has meant the need for effective change management strategies to remain competitive.
One of the main challenges facing Walmart has been the growth of e-commerce, with online retailers such as Amazon disrupting the traditional brick-and-mortar retail model.
To compete in this new environment, Walmart has had to invest heavily in its e-commerce capabilities, including expanding its online product offerings and improving its supply chain operations.
Walmart’s change management strategies have included acquiring online retailers, such as Jet.com and Bonobos, and investing in its own e-commerce platform to better compete with Amazon and other online retailers.
Another challenge facing Walmart has been shifting consumer behaviors, with customers demanding more convenience and personalized experiences.
Walmart has responded by investing in its mobile app, offering online grocery pickup and delivery services, and improving its in-store experience through the use of technology such as self-checkout machines and interactive displays.
These changes have required effective change management strategies, including employee training programs and leadership support, to ensure successful implementation and adoption.
How did Walmart manage changes?
Walmart’s response to the need for change has been largely successful, with the company implementing a range of strategies to remain competitive in a rapidly changing retail environment.
Here are three examples of Walmart’s successful responses to the need for change:
1. Expansion of E-commerce capabilities
Walmart recognized the need to improve its online presence to compete with e-commerce giants like Amazon. To achieve this, Walmart acquired online retailer Jet.com and other e-commerce companies, and invested in its own online platform. These moves have helped Walmart significantly improve its online offerings, including its product selection and delivery options.
Walmart has leveraged its physical stores to offer convenient options like online grocery pickup and delivery, which has helped attract customers looking for a blend of online and offline shopping experiences.
Walmart’s investments in e-commerce have paid off, with its online sales increasing by 79% in Q2 2020, driven in part by the COVID-19 pandemic and increased demand for online shopping.
2. Focus on Sustainability
Walmart has recognized the importance of sustainability and environmental responsibility in its operations. The company has implemented a range of initiatives to reduce waste, lower carbon emissions, and promote sustainable practices across its operations. These initiatives include reducing plastic waste, investing in renewable energy, and sourcing more sustainable products.
Walmart’s sustainability efforts have not only helped the environment but have also resonated with customers who are increasingly conscious of the impact of their purchases. Walmart’s focus on sustainability has also helped the company reduce costs and improve efficiency, which has contributed to its bottom line.
3. Embracing Digital Transformation
Walmart has been at the forefront of using technology to improve its operations and customer experience. The company has invested in technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence, and data analytics to improve its supply chain operations and enhance its in-store experience.
For example, Walmart has implemented autonomous robots in its stores to help with tasks like restocking shelves and cleaning floors, which has helped free up employees to focus on customer service. Additionally, Walmart has leveraged data analytics to better understand customer behavior and personalize its offerings, such as offering tailored product recommendations to shoppers.
Two Factors that explained the successful implementation of Walmart change management
Walmart’s successful implementation of changes has been driven by a combination of strong leadership, employee engagement, and embracing new technology.
By leveraging these factors, Walmart has been able to adapt to changing market conditions and remain competitive in a rapidly evolving retail industry.
But the two most crucial factors behind the successful change management at Walmart are as follows:
Data-Driven Decision Making
Walmart has leveraged data analytics to make more informed and strategic decisions. By collecting and analyzing data on customer behavior, supply chain operations, and other key metrics, Walmart has been able to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions about where to invest resources. This has helped Walmart prioritize its efforts and ensure that it is focusing on the initiatives that will have the greatest impact on its business
Focus on Customer Experience
Walmart has made a concerted effort to prioritize the customer experience in its change management efforts. For example, the company has invested in technologies like data analytics and artificial intelligence to better understand customer behavior and preferences, and has used this information to tailor its offerings to individual customers.
05 Lessons Learned from Walmart successful implementation of change management
Here are five lessons that can be learned from Walmart’s successful change management efforts
- Emphasize strong leadership: Strong leadership is critical to the success of any change management effort. Walmart’s leadership was instrumental in driving the company’s change management efforts and ensuring that everyone was aligned with the company’s strategic goals.
- Engage employees: Engaging employees in the change management process is essential to building a resilient and adaptable workforce. Walmart invested heavily in employee training and encouraged workers to take ownership of their work, which helped foster a culture of innovation and adaptability.
- Leverage data analytics: Data analytics can provide valuable insights into customer behavior and other key metrics, which can help identify areas for improvement and guide strategic decision-making.
- Be flexible and agile: Flexibility and agility are critical to adapting to changing market conditions. Walmart was able to stay ahead of the curve by quickly adapting its operations to meet changing customer needs and preferences.
- Prioritize the customer experience: Prioritizing the customer experience is essential to building loyalty and driving sales. Walmart made a concerted effort to tailor its offerings to individual customers and invested in initiatives like online grocery pickup and delivery to make shopping more convenient and efficient
Final Words
Walmart’s successful change management efforts provide valuable insights into how organizations can adapt to changing market conditions and remain competitive. By prioritizing strong leadership, employee engagement, data analytics, flexibility and agility, and the customer experience, Walmart was able to successfully implement changes that helped the company stay ahead of the curve.
As the retail industry continues to evolve, Walmart’s example serves as a reminder of the importance of remaining adaptable and open to change. By embracing new technologies, investing in employee training, and prioritizing the customer experience, organizations can position themselves for success in an ever-changing marketplace.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

Johnson and Johnson Crisis Management Case Study

10 Top Change Management Skills with Examples

08 Steps to Create Communication Plan in Change Management
Brought to you by:

Walmart's Omnichannel Strategy: Revolution or Miscalculation?
By: Ramon Casadesus-Masanell, Karen Elterman
This case describes Walmart's omnichannel strategy in 2018 as it battled Amazon for online retail market share. The case discusses Walmart's early forays into online retail, as well as its 2018…
- Length: 50 page(s)
- Publication Date: Aug 28, 2019
- Discipline: Strategy
- Product #: 720370-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
This case describes Walmart's omnichannel strategy in 2018 as it battled Amazon for online retail market share. The case discusses Walmart's early forays into online retail, as well as its 2018 strategy, which aimed to integrate Walmart's enormous brick and mortar footprint with its growing ecommerce business, e.g., through merchandise and grocery delivery and order online, pickup in store options. Walmart's strategy also included the acquistion of Jet.com (in 2016) as well as the acquistion of a number of other specialty eretailers (e.g., Shoes.com , Moosejaw, Bare Necessities) and digitally-native vertical brands that developed their own products and sold them directly to consumers, such as ModCloth, Bonobos, and Eloquii. In addition to building its online marketplace, Walmart hoped to leverage its existing assets, such as its massive network of retail stores and thriving grocery business, in the fight against Amazon. The case poses the question: Could Walmart successfully compete against Amazon and other online retailers in areas such as grocery delivery, product selection, shipping costs, and delivery times?
Learning Objectives
To provide students with an understanding of the decisions Walmart made in developing its omnichannel business, including decisions related to its marketplace, online acquisitions, technological development, and distribution strategies.
Aug 28, 2019
Discipline:
Harvard Business School
720370-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
Why Walmart is creating a lifestyle ‘super app’
Since the advent of e-commerce, traditional retailers have tried various ways to take advantage of new shopping methods while keeping the in-store experience growing. Walmart, one of the world’s largest retailers, always strives for a customer-first mindset. So the company has been working to deliver a broader omnichannel experience to customers.
We want our app to be more than just a shopping transaction.
I recently talked to Meng Chee, Walmart’s chief product officer, about the company’s attempt to create a “super app” that’s more than just a shopping experience — and how the pandemic accelerated this approach.
How has your app strategy evolved due to COVID-19, with more consumers choosing to shop across digital platforms?
Before the pandemic, we were already changing our app strategy. Historically speaking, before 2019 we had two areas of businesses running separately: e-commerce and in-store. But in 2019, we made the decision to merge, and in 2020, we restructured our product organization to be at the center, with the goal to deliver omnichannel experiences. That’s why, when the pandemic hit, it only accelerated our efforts to bring one app together. This acceleration has also helped us focus on our larger ambition to create a super app, meaning we want our app to be more than just a shopping transaction. Ultimately we want it to be a lifestyle app, because we’re growing our business, and adding health and wellness services, financial services, auto care, etc. All of this comes together and represents a lifestyle package that we can give our customers via a super app.
I love that you’re talking about super apps. Can you give me an example of a nonshopping use for the app?
Absolutely. Many innovations happened in our app during the pandemic. For Walmart in particular, because of the prominence we have in many communities across the country, we created an online vaccine scheduler so customers could schedule their vaccinations at their local store. Quickly thereafter, we heard from customers that they wanted an easier way to manage their paper vaccine card. So we created a digital vaccine card that is accessible in their Walmart Pharmacy account.
Creating this kind of app can be organizationally tricky. Can you talk to me about how you overcame organizational silos?
The customer is at the center of everything we do. We think there are three ways to address how to work through silos within a large organization and create the apps that matter.
You need clear accountability. … You need a framework that an organizational structure agrees to use and use consistently.
First, you need the right organizational structure. In this case, part of that solution meant having a centralized product organization so that we could prioritize and think about solutions holistically and consider what happens in-store, online, and in the app.
Second, you need a framework that really identifies the way you’re working. You need clear accountability. You can’t have every single silo with a vote. You need a framework that an organizational structure agrees to use and use consistently. This way, you make clean, clear decisions that are consistent for the customer, regardless of how they shop with us.
Finally, you need to create a model that enables executional agility. For example, we have a model that we like a lot called “four in a box.” The 4ITB team is composed of accountable leads from product, tech, design, and the business. The idea is that we work together on solving a problem for the customer in a collective, integrated way. This is how we overcome organizational complexity and develop a clear focus on what our app needs to do in a way that drives value for our customers.
How does Walmart foster a seamless experience for its customers across web and app platforms?
We design with the customer journey in mind. We don’t look at app-versus-web experiences. While we have teams that are dedicated to each, we put the customer’s needs first. A customer might start on a web browser at home, because it’s convenient to shop for groceries, but then go to their phone on the go to add a few things before they pick up in-store. There’s so much that goes on, and we need to think about the customer journey holistically to help them make consistent decisions across platforms. The way you achieve that consistency is to thread it all the way across the product life cycle, and, in this case, multiple product life cycles.
What are some innovations you’ve developed to personalize the experience, and how do you see that evolving?
Our core guiding promise to our customers is to help make their lives better. In order to do that, our personalization has to work very well. There’s a lot to compete with in terms of head space as you look at your phone today, which is why personalization is so key. We have to rapidly bring our brand and our value to the forefront of a customer’s attention span.
For example, we know customers enjoy using our app to shop for their weekly groceries for pickup at our store or delivery at home. To make it faster and easier to place pickup or delivery orders, we created a tab in the app called My Items. The My Items tab automatically organizes customers’ preferred items into categories, like dairy and eggs, pantry, beauty, and more — like having a curated store to shop from within Walmart.
We design with the customer journey in mind. We don’t look at app-versus-web experiences.
Does the app have an impact on the in-store experience?
Absolutely. The app and in-store experiences must be connected, because today’s customer shops across all our channels based on their schedules. It’s our responsibility to design an integrated experience that works for their needs, not the other way around.
Our stores are a competitive advantage, and they’ll always be a core shopping channel for our customer. But we also know that we can use technology to simplify the in-store shopping experience.
For example, we heard from our customers that they wanted better navigation to find where products are located in stores and easier ways to checkout. Over the last year, we’ve been rolling out a new design for Supercenters and Neighborhood Markets that includes things like updated exterior signage reflecting the Walmart app icon, updated in-store messaging system and signage to guide customers and associates to products using the app, and more hosted-checkout kiosks as well as contactless payment solutions, like Walmart Pay and Scan and Go.
Others are viewing
Marketers who view this are also viewing
Food delivery company saw a 20% increase in app orders after shifting its bidding strategy
How the best companies in the world are reinventing their customer experience, how an e-commerce company used deep links to boost its checkouts by 126%, the ai handbook: resources and tools for marketers, mobile best practices: tips, tools and trainings to create a better app experience, how mobile search is driving today’s in-store shopping experience, others are viewing looking for something else, complete login.
To explore this content and receive communications from Google, please sign in with an existing Google account.
You're visiting our United States & Canada website.
Based on your location, we recommend you check out this version of the page instead:
Digital Transformation at Walmart: A case study.
Walmart (NYSE: WMT), the largest physical retailer based in the United States, has achieved enormous growth over the years through its EDLP pricing strategy and a customer-friendly brand image. In recent years, the company has focused on digitalization to grow sales and improve customer service. Its e-commerce sales have continued to strengthen worldwide.
Physical retailers in the US are turning to digitalization to serve their customers better, whose lifestyles are now heavily influenced by digital technology. Walmart acquired the Indian online retail brand Flipkart in 2018. Since then, it has also made a significant investment in its US e-commerce infrastructure.
While investing in technology is essential for retailers to serve their customers more efficiently, Amazon’s growing influence in the retail industry has also proved to be a key driver of digitalization across the US-based retail brands. The need to focus on digital technology was never more highlighted than during the pandemic. Customer behavior changed profoundly with the spread of the Covid-19 pandemic . Customers mostly switched to online shopping during lockdowns. These changes will last longer since the impact on people’s lifestyle has been profound.
Walmart has been investing in e-commerce over the past several years and is reaping its benefits now. However, Walmart’s focus is not just on e-commerce but on a complete digital transformation that drives superior associate performance while driving higher customer satisfaction also apart from stronger financial returns. Cloud technology is driving similar transformations across other retailers too. Walmart is leveraging cloud technology to strengthen its competitive position and accelerate its growth momentum.
Back in 2018, Walmart partnered with Microsoft to accelerate its cloud journey and more expeditiously deliver on changing customer expectations. Walmart’s digital transformation has also come in the face of growing competitive pressure from the e-commerce giant Amazon. From its online store to supply chain and logistics, digital technology, AI, IoT, and Machine Learning are driving rapid changes. Walmart’s continuous growth in the future depends on its ability to leverage technology to swiftly respond to the changing market scenario and customers’ purchasing habits.
Table of Contents

Factors that drove rapid digitalization at Walmart.
Walmart is the largest physical retailer in the United States. The company has been enjoying enormous growth over the last several years. However, the retail landscape in the United States is changing swiftly. Five main factors drove digitalization at Walmart:
- Demographic changes in the US population.
- Changing consumer habits and expectations.
- Rise of mobile computing.
- Need for more speed and efficiency.
- Growing challenge from Amazon
Demographic changes and other changes like the rise of e-commerce has also changed how people shopped. Since the retail landscape is changing, Walmart’s traditional operating model was insufficient to serve the customers’ evolving needs in the US. Millennials are now the largest segment of the US adult population (Pew Research, 2020).
They are also the most important customer segment for retail brands like Walmart. The expectations of the millennial generation are very different from the Baby Boomers. The millennials are tech savvier and live highly digital lives. They like to shop online for a large range of products and services. Apart from their general needs, these people also depend on online channels for their daily entertainment and various other needs like music and fashion.
The rise of social media and the millennials’ consumption habits all required the businesses that wanted to serve them to adopt a better model driven by technology. Walmart’s competitive moat lay in its pricing strategy mainly apart from the large array of products it sells. However, these things are no longer sufficient to cater to the millennial generation’s expectations fully. Walmart needed to transition to a better model that could handle things with higher speed and efficiency.
Both these things are important for maximizing customer satisfaction in an era driven by computers, the internet, data and analytics. The dependence of retail brands on technology was also destined to grow because of the growing use of mobile computing. The need for higher mobility also drove higher investment into technology. Digital technology has altered the buying habits of the customers, who like to compare prices on their smartphones before they go for the final purchase.
Lower prices attract the millennials but there are more factors they consider before making a purchase. Customer convenience matters more than ever to win in a highly competitive retail landscape. It affects demand and sales. However, to grow the level of customer convenience requires a focus on digital technology which saves time and also helps reduce costs.
Another important factor that drove Walmart towards rapid digitalization was the rise of the e-commerce giant Amazon. Prior to that, Walmart was the undisputed leader in the US retail sector. Amazon is right next to Walmart on the Fortune 500 list, where the physical retail giant has managed to remain at the top for several years. In 2020, Walmart is on the top of the list for the eighth time (Fortune, 2020).
In terms of e-commerce sales in the US, Walmart is just next to Amazon (despite the substantial gap). There is still a substantial difference in the market shares of the two in the e-commerce industry but Walmart is trying to strengthen its position through continuous investment in digital technology. Amazon poses a major challenge before the other US-based retailers whose continuous growth now depends on how well they can serve their tech-savvy consumers.
The drive towards a highly digital future has accelerated with the pandemic. People’s buying habits are being reshaped, and consumers will likely depend more on online shopping in the future. Walmart needed to take Amazon’s challenge since, over time, Walmart’s influence could substantially reduce due to the growth in Amazon’s, which is aggressively demanding lower prices from its sellers using its clout in e-commerce. Leveraging its existing competitive strengths for superior results was only possible if Walmart invested in digitalization.
Supply chain digitalization at Walmart
Walmart has focused on higher digitalization in nearly all areas of its business system. From the supply chain to sales, customer service, marketing, and store operations, the company has steadily been investing in digitalization to grow its operational efficiency and cost-efficiency. Walmart’s supply chain digitalization was an important pillar of its omnichannel strategy.
Digitalizing the supply chain was the first important step towards making its omnichannel strategy a success. To really gain from its investment in technology and digitalization, Walmart first needed to leverage the strength of its supply chain. A highly optimized supply chain is a critical source of competitive advantage for the retail brand. It has helped Walmart maintain consistently lower prices and could be further optimized using digital tools to gain higher cost-efficiency and derive better employee performance.
Moreover, the traditional supply chain management model was insufficient to serve the evolving needs of US customers. Digitalizing the supply chain has enabled the retail giant to pursue its omnichannel strategy with a higher success rate. Walmart is leveraging digital technology to share information across the supply chain, and for tracking and managing inventory across its stores and warehouses in the United States.
An efficient and modernized supply chain has played a critical role in helping the company gain higher cost-efficiency. Walmart’s competitive position as the leading physical retailer in the US has strengthened with growing digitalization across its supply chain, which also helped it access a large pool of data. It gains valuable insights from the data to understand consumer behavior. Walmart’s large supply chain produces tons of data daily used to make important inventory management decisions. It also helped the company grow its supply chain resilience to serve customer needs better during a crisis like a hurricane or in the event of a pandemic like Coronavirus.
Walmart also secured its supply chain against fast-changing market conditions by leveraging data and analytics. In 2017, it invested in Data Cafe, one of the largest private clouds in the world to grow its data and analytics capabilities and process more than 40 Petabytes of data being generated from internal and external sources daily (Marr, 2017). Walmart’s data cafe is its analytics hub located at its headquarters in Bentonville, Arkansas. Data Cafe allows Walmart to model, manipulate, and visualize recent transactional data, it collects from more than 200 internal and external streams.
It enabled faster decision making at Walmart and provided solutions to several critical supply chain management related problems that could otherwise take a lot longer to answer. Walmart made Data Cafe available to its suppliers so they could gain free insights into customer demand and manage their supply and inventory better.
In 2018, Walmart introduced its Connected Content Provider Program, whose main focus was to help suppliers scale content to Walmart’s catalog and other retailers (Ogura, 2018). The program aimed to bring harmony between retailers, suppliers, and content. With its syndication partners like Salsify, the company aimed to help its suppliers deliver content with higher speed and agility. Suppose a customer comes to Walmart looking for a particular product that is not available at the time. Walmart looks up its syndication providers like ‘Salsify’ to find which supplier has the product and then arranges for home delivery.
Walmart is also using other latest technologies like AI and Blockchain to track inventory down its supply chain (Aitken, 2017). The retail brand partnered with IBM to leverage blockchain technology and leverage and track food products’ movement across its supply chain to ensure their quality and authenticity. The use of IBM blockchain allowed Walmart to track the movement of goods in its supply chain faster. Something that could take days or weeks to trace using the traditional tracking methods was now possible in seconds. Blockchain -based decentralized ledgers have simplified the process of tracking goods in Walmart’s supply chain.
Digital Transformation through Cloud Technology
Cloud technology is also driving rapid transformation across the retail landscape. Retailers turn to cloud technologies to grow their efficiency and transform a large pool of data they generate daily into actionable insights.
In 2018, when Walmart was already using a large set of Microsoft services for critical workloads, the company announced a strategic five-year partnership with the cloud leader to make its digital transformation possible. This partnership with Microsoft allowed Walmart to leverage machine learning, artificial intelligence, and data platform solutions for a wide range of external customer-facing services and internal business applications (Walmart, 2018).
Walmart aimed to transform digitally, bring innovations that saved its customers time and money, and change how work was carried out inside the organization for increased productivity. To achieve its target, the company selected a full range of Microsoft cloud solutions that included Microsoft Azure and Microsoft 365. The main advantages of using cloud technology for Walmart were going to be as follows:
- Leverage the capacity of Microsoft’s enormous compute capacity.
- Ability to manage workloads seamlessly in an elastic environment.
- Bring innovations faster through the new toolsets
- Drive costs lower through a cloud native environment.
From reducing energy consumption in the Walmart stores to managing logistics, the company uses cloud technology to make its work processes more efficient and save time and money. The company uses machine learning to route thousands of trucks in its supply chain. Apart from that, Walmart gained access to various tools that allow its associates to improve their productivity and collaborate on projects. Tools like Microsoft workplace analytics, Microsoft Stream, and Microsoft One Drive allow associates to collaborate, save time, and work better.
Walmart owned Jet.com also uses cloud technologies heavily to serve customers efficiently. It has built an innovative eCommerce engine on the Azure cloud platform in less than 12 months. The Jet.com platform is composed of open-source software, Visual F#, and Azure Platform as a service (PaaS) like Azure Cosmos DB. The next-generation architecture of Jet.com is built for speed. It uses Panther, Azure’s next-generation inventory processing system to make its service faster, smarter, and more efficient.
“Within just a few weeks, a prototype based on Service Fabric proved that Panther could support the massive scale and the functionality Jet needed plus high availability and blazing fast performance across multiple regions. But what really made Panther possible was adding Azure Cosmos DB for the event store. Coupling an event-sourcing pattern with a microservices-based architecture gave them the flexibility they needed to keep improving Jet.com and delight their customers.” (Microsoft, 2020)
Sources Used:
Pew Research. (2020, April 28). Millennials overtake Baby Boomers as America’s largest generation . PewResearch. Retrieved 2020, from https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/04/28/millennials-overtake-baby-boomers-as-americas-largest-generation/
Fortune. (2020). Fortune 500 . Fortune. Retrieved 2020, from https://fortune.com/fortune500/2020/search/
Marr, B. (2017). Really Big Data At Walmart: Real-Time Insights From Their 40+ Petabyte Data Cloud . Forbes. Retrieved 2020, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2017/01/23/really-big-data-at-walmart-real-time-insights-from-their-40-petabyte-data-cloud/?sh=1c6727f26c10
Ogura, F. (2018, September). Introducing the Connected Content Partner Program . LinkedIn. Retrieved 2020, from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/introducing-connected-content-partner-program-frank-ogura/
Salsify. (2018). Salsify Selected By Walmart To Join Its Connected Content Partner Program . Salsify. Retrieved 2020, from
Aitken, R. (2017). IBM Forges Blockchain Collaboration With Nestlé & Walmart In Global Food Safety . Forbes. Retrieved 2020, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/rogeraitken/2017/08/22/ibm-forges-blockchain-collaboration-with-nestle-walmart-for-global-food-safety/?sh=66710fac3d36
Microsoft. (2020, June). Jet.com powers innovative e-commerce engine on Azure in less than 12 months . Microsoft Azure. Retrieved 2020, from https://customers.microsoft.com/en-in/story/822088-jet-com-powers-innovative-e-commerce-engine-on-azure-in-less-than-12-months
Walmart. (2018, July). Walmart establishes strategic partnership with Microsoft to further accelerate digital innovation in retail . Walmart Newsroom. Retrieved 2020, from https://corporate.walmart.com/newsroom/2018/07/17/walmart-establishes-strategic-partnership-with-microsoft-to-further-accelerate-digital-innovation-in-retail
.png)
How to solve product management case studies
Preparing for a product manager interview can be a daunting task. With case studies being a critical component of the interview process, it's important to strategize and practice ahead of time to showcase your skills effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we'll cover actionable tips to help you ace product manager case study interviews. From key frameworks to avoid common mistakes, you'll gain the confidence and knowledge needed to land your dream PM role. Whether you're just starting your PM career or a seasoned pro, read on to level up your case study interview skills.
Here at The Product Folks , we're all about empowering product managers to grow in their careers. With resources like case study workshop recordings, mock interviews, and dedicated mentors, we're here to help you put your best foot forward in the interview process. Let's dive in!
Overview of the Product Manager Interview Process
A typical PM interview will include multiple stages designed to thoroughly assess your abilities. Here's what to expect:
- Screening call: Discuss your background and interest in the role. Helps align expectations.
- Case studies: Presented with a hypothetical product challenge to analyze and propose solutions for. Tests core critical thinking and prioritization skills. Varies from estimating market size to designing new features.
- Behavioral questions: Queries about your past experiences working on teams, managing stakeholders, handling conflicts etc. Screens for culture fit.
- Technical questions: Assesses your technical knowledge depending on the product domain. More critical for engineering-heavy roles.
Case studies are particularly crucial, as they demonstrate key skills like structuring complex problems, analyzing tradeoffs, and communicating recommendations. Common mistakes include lack of a methodical approach and failure to articulate underlying thought process. Avoid vagueness and guide interviewers through your thinking.
For training tailored to acing PM case interviews, check out The Product Folks' mentor-led masterclasses. Their experts explain how to navigate various types of case studies and equip you with frameworks to tackle them confidently.
Key Strategies for Acing Case Studies
Here are proven strategies to shine in your PM case study interview:
- Research the company: Review their products, customers, domain etc. Helps tailor your approach to their context. For example, studying an ecommerce company's key metrics will allow you to anchor examples and data points in their specifics.
- Clarify the case parameters: Confirm goals, assumptions and constraints. Prevents misalignment. Ask clarifying questions upfront to avoid veering off track.
- Structure with frameworks: Use templates like PRD format to organize thinking. Keeps it methodical. Outlining stakeholders, requirements and success metrics provides systematic analysis.
- Show your work: Verbalize your analysis to demonstrate thought process. Explains rationale. Walk through each consideration instead of simply stating conclusions.
- Practice aloud: Helps get comfortable articulating complex ideas. Improves narrative flow. The Product Folks mock interviews are great for rehearsing with real-time feedback.
Walking through an example case study is invaluable for internalizing these key strategies in action:
Example Case Study #1 - Food Delivery App
Let's imagine we're the PM for Swiggy, a food delivery app in India. The CEO wants to grow monthly active users (MAU) by 30% this quarter. Here's how I'd approach this case:
First, I'd propose features that provide more value to users:
- Loyalty program : Points for orders that unlock free delivery and discounts. Improves retention.
- Package deals : Meal combos from multiple restaurants at a bundled price. Increases order value.
Next, I'd consider options to improve new user onboarding:
- Free delivery trial : First 3 orders free delivery to hook new users. Lowers barrier to signup.
- Referral bonus : Users earn credits for referrals. Virality leverages network effects.
Comparing the options, I'd recommend prioritizing the loyalty program for the highest ROI. It targets our core goal of increasing MAU by incentivizing repeat orders. According to Swiggy's metrics, existing users drive 80% of orders, so loyalty has the biggest leverage. The referral bonus is more speculative and might require substantial promo budget.
Key risks include existing users thinning order frequency to earn points. We'd need to analyze optimal program tiers and rewards, likely by running A/B tests. Overall, the loyalty program combines high impact on KPIs with ease of implementation. For execution, I'd pilot in Bangalore and Hyderabad first, tracking engagement data to refine the nationwide rollout.
This showcases weighing alternatives against goals, evaluating feasibility and mapping execution steps - all critical PM case study skills. Let's break down another example next.
Example Case Study #2 - Social Media Platform
Imagine we're PMs at Facebook. Engagement from teenagers in the US has dropped 30% this quarter. How can we turn this around?
I'd start by auditing their core needs - sense of identity and community. Some potential solutions:
- Interest-based groups : Connects users with niche interests. Provides targeted sense of belonging.
- Ephemeral content : Stories, polls that disappear after 24 hrs. Creates constant activity.
- Rewards program : Points and badges for engagement milestones. Gamification taps into motivation.
Evaluating the options, interest-based groups seem most promising. While ephemeral content may spike engagement short-term, it likely won't address the root identity needs long-term. Groups are scalable and tap directly into the teenage affinity for communities.
I'd propose a pilot targeting groups around hobbies, causes etc. Success would see group engagement exceed overall platform averages for the teen demographic. Risks include bullying in unmoderated groups. We'd need community guidelines, reporting mechanisms and moderation.
Overall, this matches an audience need with a targeted solution grounded in behavioral data. We walked through ideating options tailored to goals, analyzing feasibility and defining metrics to track outcomes. These frameworks are key for structuring strategic thinking during case interviews.
Key Learnings and Takeaways
Let's recap the core strategies we covered for tackling PM case studies:
- Research the role and company to frame your approach
- Clarify the objectives, constraints early
- Organize analysis using frameworks
- Explain your thinking to demonstrate logic
- Practice case studies regularly to build skills
Avoiding vague responses and clearly articulating your thought process are critical. Use examples and data to back recommendations. Structure your thinking with proven frameworks.
For further practice with feedback from experts, check out The Product Folks' mock case study interviews. Their dedicated mentors can help take your skills to the next level.
Latest Posts
.jpg)
This article will explore how product management side projects can catalyze professional development by allowing you to experiment with new methodologies and enhance your skillset.
.jpg)
This comprehensive guide promises to equip you with a structured approach to tackling product case studies. You'll gain frameworks to methodically analyze prompts and craft insightful solutions.
.jpg)
Through real-world application, valuable feedback, and community engagement with groups like The Product Folks, PMs can significantly accelerate their skill development and expertise in the dynamic field of product management.
Come For the Content Stay For the Community

Press Enter to search
50 Product Management Case Studies
We often wonder what kind of process other product teams have created, planned, and most importantly, how they have implemented it. That is why we at Producter have compiled 50 different case studies for you.
2 years ago • 4 min read
We often wonder what kind of process other product teams have created, planned, and most importantly, how they have implemented it.
That is why we at Producter have compiled 50 different case studies for you.
Brought to you by Roadmape

1- Rules of Flow for Product Management: an AirBnB Case Study
“Engagement” is a term that is so overused in product management that it has almost lost its meaning. So often I’ve heard from teams, “We’ll measure the success of this test with engagement,” which could mean anything from feature click-through to bounce to we-aren’t-really-sure-this-will-drive-conversion-so-we’re-hedging-our-bet. Underneath, the reason this term has been co-opted and jargonized is that genuine, productive engagement can be ramped toward long-term customer loyalty. And loyalty pays off: a loyalty increase of 7% can boost lifetime profits per customer by as much as 85%, and a loyalty increase of 3% can correlate to a 10% cost reduction ( Brand Keys ).

2- The Psychology of Clubhouse’s User Retention (...and churn)

3- Netflix Q1 ’21 Subscriber Growth Miss: Can We Avoid Another One?
As a data analyst supporting a mobile subscription business , Netflix’s Q1 ’21 subscriber growth miss is a classic example of when I would get called for recommendations to prevent a miss in the future. I thought this would make an interesting case study to discuss my approach to finding insights to drive subscriber growth. Sadly I’m not a Netflix employee and will be limited to publicly available data but the wealth of information on the Internet about Netflix is sufficient to generate insights for this case study.

4- Amazon Go Green
As part of the Design Challenge from productdesign.tips, our team came together to find ways for Amazon to encourage more sustainability on their e-commerce platform. As with any unsolicited design project, the challenge comes with a lack of access to application analytics and technical feasibilities. Nonetheless, the question remains: How might we design checkout screens for an e-commerce app to help people recycle the goods they buy?

5- Quora Case Study – The Wonderful World of Quora
Quora has become a substantive resource for millions of entrepreneurs and one of the best sources for Business to Business market. Majorly used by writers, scholars, bloggers, investors, consultants, students this Q/A site has much to offer in terms of knowledge sharing, connection building and information gathering.

6- Building a product without any full-time product managers

Jambb is an emerging social platform where creators grow their communities by recognizing and rewarding fans for their support. Currently, creators monetize fan engagement through advertisements, merchandise, and subscriptions, to name a few. However, this only represents 1% of fans, leaving the other 99% (who contribute in non-monetary ways) without the same content, access, and recognition that they deserve.

8- What if you can create Listening Sessions on Spotify
Summary: The project was done as a part of a user experience design challenge given to me by a company. I was given the brief by them to work on a feature of Spotify and I spent around 25–30 hours on the challenge in which I went through the entire process, from the research to testing.

9- Redesigned Apple Maps and replicated an Apple product launch for it
Quick-fire question; what is the single most important and widely used feature in a phone — asides from texting and instant messaging friends, coworkers and family? Maybe you guessed right, perhaps this feature is so integrated into your life that you didn’t even think about it — either way, it is your phone’s GPS. It is reasonable to say that GPS technology has changed society’s lives in ways we never could’ve imagined. Gone are the days of using physically printed maps and almanacks, when we now have smartphones with navigation apps. Since the launch of the iPhone and the App Store, consumers have been able to use different apps for their personal navigation needs. Everyone has a preference, and apps have come out to try and address every need.

10- Intuitive design and product-led growth
In 2018, Miro was hardly a blip on the radar in the Design world. Fast forward two years, and suddenly Miro is solidly the number one tool for brainstorming and ideation.

Click below to see the complete list 👇

Producter is a product management tool designed to become customer-driven.
It helps you collect feedback , manage tasks , sharing product updates , creating product docs , and tracking roadmap .
Spread the word
What is customer segmentation, learnings about product development strategy in 2022, keep reading, boost product management with slack: a comprehensive guide to producter's slack integration, mastering the art of product management: 10 essential strategies for success, what is user research.
- Skip to main
- Skip to footer
- Board of Directors
- Walmart History
- New Home Office
- Working at Walmart
- Sam's Club
- Location Facts
- Contact Walmart
- Media Library
- Contact Media Relations
- Opportunity
- Sustainability
- Ethics & Integrity
- Belonging, Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
Philanthropy
- ESG Reporting
- Health & Wellness
- Stock Information
- Financial Information
- Corporate Governance
- ESG Investors
- Investor Resources
- Supplier Requirements
- Apply to be a Supplier
- Supplier Inclusion
- Sustainability for Suppliers
- Investing In American Jobs
- Sam's Club Suppliers
- Walmart Growth Summits
- Ask Walmart
Product Supply Chain Sustainability
Our aspiration, key goals & metrics, relevance to our business & society.
- Walmart's Approach
Key Strategies & Progress
Additional resources.
SASB: FB-FR-430a.3, CG-AA-430a.2, CG-AA-430b.3, CG-AA-440a.3, CG-AA-440a.4, CG-HP-410a.1 GRI: 2-6, 3-3, 305-5, 417-1a UN SDGs: 8, 12, 14, 15
E S | Published: May 31, 2023
Walmart aims to accelerate progress on the sustainability of our own assortment as well as product supply chains across the retail and consumer goods industry. We focus on environmental and social issues including climate, nature, waste, working conditions, responsible recruitment, and economic opportunity for people working in product supply chains, as well as the availability of affordable, safer, and healthier products.
Retail supply chains bring quality, affordable products to consumers around the world. Sustainable, regenerative practices create value for companies and for society by increasing supply chain resilience and efficiency, improving product availability and quality, mitigating risk, and creating opportunities for workers.
Walmart expects that the products we purchase and sell are made in the right way by suppliers who act ethically and respect the dignity of workers. Walmart’s stakeholders—including our customers—have the same expectations. In addition, Walmart needs to be part of the solution to environmental challenges such as climate change and depletion of natural capital to maintain our license to operate, secure supply, and create value.
Walmart’s Approach
Walmart engages suppliers, customers, and NGOs across a wide range of product supply chains in support of climate, waste, nature, and people-related objectives. Because of the complexity of global supply chains and the systemic nature of issues, lasting improvement requires collaboration among many stakeholders.
To improve the sustainability of a given product supply chain, we start by listening to our customers and other stakeholders to set aspirations—such as emissions reduction or economic inclusion—and prioritize improvements to the product supply chain system, such as improved farming practices or commodity traceability. We make progress by:
- Setting standards and requirements for Walmart product sourcing
- Engaging Walmart suppliers to spark action, share best practices and tools, and encourage measurement and disclosure
- Leading and contributing to industry consortia and initiatives to accelerate collective action beyond Walmart
- Helping Walmart customers make informed choices
- Advocating for public policy that aligns with sustainable supply chain priorities
- Accelerating systems change beyond Walmart through philanthropic investments
Product Sourcing | Supplier Engagement & Support | Leading Consortia | Customer Engagement | Advocacy | Philanthropy
Walmart's systematic approach to promoting supply chain sustainability begins with setting aspirations relevant to our overall climate, waste, nature, and people-related agenda, aligning on priority outcomes and actions necessary to support those outcomes, and engaging suppliers and stakeholders to promote more sustainable sourcing and system-wide change. The key strategies and progress set forth in this brief are intended to provide an overview of our strategies across product supply chains; for more information about our climate change, waste, nature, and people-related agendas, please see the relevant issue briefs: Climate Change ; Waste: Circular Economy ; Regeneration of Natural Resources ; People in Supply Chains ; Safer, Healthier Food & Other Products ; Human Rights .
Sustainable product supply chains: Walmart’s approach to systems change
Aspirations.
- Emissions reduction
- Respect for human rights
- Natural capital regeneration
- Inclusive economic opportunity
- Safer, healthier products
Priorities for systems change
- Alignment on standards and science
- Empowered workers, customers, communities
- Sustainable production practices: farming, fisheries. manufacturing, packaging, transportation
- Traceability and transparency
- An enabling policy environment
Walmart sustainability strategies: Example actions
Product sourcing requirements
- Requirements
- Standards for suppliers
- Responsible sourcing program
- Human Rights Statement
- Code of Conduct
Product specifications
- Issue-specific policies, including certification requirements
- Product and packaging specs
- Item-level data requirements
Inclusive sourcing/financing
- Supplier inclusion
- Direct farm, smallholder
- Made in USA
Supplier engagement & measurement programs
- Project Gigaton
- Collaboration platforms (e.g. Sustainable Chemistry)
- Playbooks, guides, and workshops (e.g. Packaging Playbook, Seafood Summit)
- Innovation pilots (e.g. reuse/refill, blockchain)
- THESIS sustainability KPIs
Industry consortia & initiatives
- Consumer Goods Forum (e.g. Plastic Waste) coalitions
- Leadership Group for Responsible Recruitment
- Seafood Task Force
- Ethical Charter with Produce Marketing Association and United Fresh
- Gigaton PPA
- Clean Beauty Shop
- Built for Better
- World Business Council for Sustainable Development
Customer engagement
- Labeling (e.g. Great Value, Best if Used By, Built for Better)
- Campaigns (Fight Hunger. Spark Change., recycling)
- Clean Energy Buyers Alliance (CEBA)
- Natural capital: Soy Moratorium, Tropical Forest Alliance, Business for Nature
- Bali Process
- Race to Zero (RtZ)
Philanthropy*
- Strategic grants
- Program-related investments
- In-kind donations
- Communities of practice
*Philanthropy occurs through Walmart and Walmart Foundation
Place-Based Initiatives
- Landscape-scale, on-the-ground efforts to address system-level challenges
These strategies are tailored to specific sectors to reflect the greatest opportunities for Walmart to drive progress. Select priorities and initiatives are outlined below.
Product Sourcing
Sourcing requirements and specifications help to set the foundation for more sustainable products.
Standards and requirements: Our expectations of suppliers regarding the dignity of workers in the supply chain, environmental protection, food and product safety, and ethics and integrity are outlined in our Standards for Suppliers . In addition, we have several supplier compliance policies, including our Global Forced Labor Prevention Policy , Global Responsible Sourcing Policy, Global Food Safety Policy, and Global Product Safety Policy, that set specific requirements for the products we source and sell. Read more about Walmart’s approach to responsible sourcing: People in Supply Chains .
Sourcing specifications: For the products that Walmart carries, our merchants specify attributes in various ways, including:
- Issue-specific policies, guidelines, and position statements: Walmart has developed sourcing policies, guidelines, and position statements for seafood, apparel, plastic packaging, row crops, and animal welfare that ask suppliers to provide products to Walmart that meet specified criteria. Read more: Walmart Sustainability Hub and Walmart Policies and Guidance .
- Certifications: Certifications help Walmart and our suppliers by using objective criteria to measure the sustainability attributes of a product; they also communicate to consumers that our suppliers have met the applicable environmental and/or social sustainability standards of the certifying body. We have asked our suppliers to validate that particular commodities—including palm oil, pulp and paper, fresh and frozen seafood, tuna, coffee, and cotton—have been produced or/and harvested to specific certification standards. Read more: Regeneration of Natural Resources .
- Product and packaging specifications: For example, we have asked our private brand suppliers to work toward and report progress on our goal to use 100% recyclable, reusable, or industrially compostable packaging and achieve 17% post-consumer recycled content for our private brand products by 2025. Read more: Waste: Circular Economy .
- Place-based initiatives: We work with suppliers to source certain commodities from place-based efforts that help preserve natural ecosystems and improve livelihoods. For example, in 2022 we partnered with Prime Pursuits, AgSpire, and nine ranches in Nebraska, Oregon, Idaho and Texas to launch a pilot project covering over 748,000 acres of ranch land. The project provides technical assistance to ranchers in our supply chain to promote regenerative grazing practices with positive outcomes including improved soil health, carbon sequestration, increased wildlife and pollinator habitats, improved water quality, and improved ranch productivity and resilience. Other place-based initiatives include Great Value rice from Arkansas and tuna from the Republic of the Marshall Islands, respectively. Read more: Regeneration of Natural Resouces .
Floral, Produce
Floral, produce (apples, bananas, berries, grapes, leafy greens, pineapples, stone fruit, and tomatoes)
Specialty Crops
Cocoa, coffee, and tea
Textile, Pulp, Paper, Timber
Cotton textiles, pulp, paper, and timber
Ingredients
U.S. corn, U.S. wheat, U.S. soy, South American soy, and palm oil
Seafood (wild caught and farm raised), meat (South American beef, U.S. beef, pork), poultry, and dairy
Our approach to more sustainably sourcing these commodities includes:
- Encouraging our suppliers to adopt sustainable sourcing practices, including thorough product specifications and sourcing policies, as well as positions and policy statements
- Revamping sourcing specifications and requiring certifications where available and aligned with our aspirations
- Collaborating with suppliers, other retailers, NGOs, and others to improve practices across the sector
- Asking suppliers to measure and report against progress
- Supporting place-based sourcing in critical ecosystems
- Measuring and reporting transparently
Please see the Goal: Source 20 commodities more sustainably by 2025 section of the Key Goals and Metrics table at the top of this brief for more information on progress towards our sustainable commodities aspirations.
Measurement
We develop calculators to measure sustainable sourcing. Walmart may publish revisions to individual goals and metrics upon the receipt of more or better information; for example, based on the addition of new certification types. Challenges to the initiative include gathering supplier data of sufficient quality for robust reporting. Disclosures on select commodities, such as pork and poultry, are pending the finalization of improved calculators.
Supplier Engagement & Support
Walmart engages and supports suppliers in pursuing ambitious environmental and social initiatives in their product supply chains. Our intention is to inspire action on complex global problems by encouraging and assisting our suppliers to take first steps, disclose their progress, raise their aspirations, and expand their impact. We engage suppliers through dedicated platforms, best practice sharing, and accelerators. Examples include:
- Project Gigaton: Walmart's Project Gigaton platform invites suppliers to take action in six areas— Energy , Waste , Nature , Transportation , Packaging , and Product Use and Design —as a means of avoiding, reducing, or sequestering greenhouse gas emissions. While the initiative was created with an initial focus on greenhouse gas emissions, the platform today supports supplier action across additional supply chain sustainability issues, including nature and responsible recruitment. Through Project Gigaton, Walmart provides calculators to help set and report on goals within the initiative, workshops on best practices, and resources provided by Walmart or third parties. Since launch, more than 5,200 suppliers have signed up for Project Gigaton , and in FY2023, more than 3,000 suppliers reported reducing or avoiding >175M MT CO2e.
- Resources and best practices sharing: Walmart and the Walmart Foundation share tools and resources with suppliers to help them get started and accelerate progress. For instance, the Walmart Recycling Playbook , a publicly available resource developed in collaboration with The Association of Plastic Recyclers (APR), the Sustainable Packaging Coalition, and Pure Strategies, provides voluntary guidelines for streamlined packaging design, and the Responsible Labor Steering Committee, for which Walmart served as a Steering Committee member through the end of 2022, provides members with tools for forced labor due diligence. Additionally, the Walmart Foundation convenes suppliers, NGOs, and thought leaders to share best practices and inspire action, including helping to establish the Closed Loop Infrastructure Fund to finance projects that build out circular economy infrastructure in the United States via below-market rate loans and supporting the Recycling Partnership's establishment of the Center for Sustainable Behavior & Impact , which is building a database of community portraits that help identify key trends, attitudes, motivations, and barriers to recycling.
- Connections to accelerators: We help connect suppliers to programs that can help support and accelerate their sustainability ambitions and progress. For example, we created a collaborative power purchase agreement with Ørsted and Schneider Electric (Gigaton PPA) allowing Walmart suppliers to band together to purchase renewable energy; we launched a place-based initiatives connector to help suppliers identify and join place-based sourcing initiatives; we launched a Circular Connector to connect suppliers to more sustainable packaging solutions; and we worked with HSBC to create a program to provide improved financing access and terms for suppliers that reduce GHG emissions in at least one of Project Gigaton's six pillars.
To encourage progress on environmental and social sustainability issues across product lifecycles, we have asked our suppliers to report progress on KPIs through Project Gigaton and other measurement platforms, such as CDP for GHG emissions and forests. Approximately 79% of our U.S. product net sales were represented by suppliers who reported to one or more sustainability surveys. 59
Industry Consortia & Initiatives
We collaborate with suppliers, peers, and others to accelerate progress toward addressing complex and systemic sustainability issues across supply chains. For instance, Walmart is a member of the Consumer Goods Forum (CGF), which brings together leading retailers and consumer goods manufacturers to address social and environmental issues. Walmart co-leads or is an active member of the following Coalitions of Action established by the CGF: Plastic Waste ; Food Waste ; Forest Positive ; Global Food Safety Initiative ; Human Rights – Working to End Forced Labor ; Collaboration for Healthier Lives ; and Product Data . Other coalitions by issue include:
- Climate: Walmart is a member of and leads several coalitions that align with our 1.5° Celsius-aligned ambition, including the Clean Energy Buyers Association and Clean Energy Demand initiative (collaborations that advocate for public policy and signal demand for clean energy); and Glasgow is Our Business (support for a successful COP26 agreement). Read more: Climate Change .
- Waste: Walmart helped launch and supported engagement in the Ellen MacArthur Foundation 's Plastics Pacts in multiple countries to accelerate progress toward 100% reusable, recyclable and compostable packaging. In FY2021, Walmart also co-founded the Beyond the Bag initiative with Closed Loop Partners and a number of other retailers to develop innovative, industry-wide alternatives to single-use plastic bags. Read more: Waste: Circular Economy .
- Nature: Walmart engages with Business for Nature, a global organization that brings together business and conservation organizations to call for governments to adopt policies to reverse nature loss in this decade. Walmart is also a member of coalitions that foster progress toward our ambitions across our priority landscapes of Forests ( WEF Tropical Forest Alliance , LEAF Coalition , the Consumer Goods Forum Forest Positive Coalition ), Grasslands and Agriculture ( Midwest Row Crop Collaborative , Field to Market: The Alliance for Sustainable Agriculture , Better Cotton , Sustainable Apparel Coalition ), and Oceans ( Seafood Task Force , Sustainable Fisheries Partnership ). Read More: Regeneration of Natural Resources .
- People in supply chains: Walmart works with organizations that foster enhanced standards and practices relating to forced labor ( Leadership Group for Responsible Recruitment , Seafood Task Force , Responsible Labor Initiative ), working conditions ( Ethical Charter on Responsible Labor Practices ), and safety ( Nirapon , Life and Building Safety Initiative ), among others.
Customer Engagement
We believe that the everyday choice should be sustainable, so we work to make our overall assortment more sustainable through the strategies described throughout this brief. At the same time, we also want to make it easier for customers to identify products with sustainability attributes that align with their preferences. Examples include:
- Products that are eligible for the “ Built for Better—For You ” icon highlights food options that recognize products made without materials or ingredients you may not want, as informed by the latest nutrition science and standards.
- Products that are eligible for the “ Built for Better—For Communities ” icon are either made, grown, or assembled in the U.S., or are sourced from a certified women-owned business or a certified diverse-owned business. 60
- Products that are eligible for the “ Built for Better—For the Planet ” icon meet independent standards that recognize one or more environmental benefits—like products that are responsibly sourced or products designed for a lesser impact on climate. 61
Read more: Built for Better .

- Clean Beauty: Certain customers want to buy products that provide greater transparency into product formulations and products made without certain ingredients. Clean Beauty is an online shop that helps our customers find beauty products that are made without ingredients they may not want. Walmart’s Clean Beauty products are made without any of the 1,200 ingredients included on our Made Without List. To develop this list, we reviewed state and federal regulations, consulted suppliers, and called on experts such as the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF). As of May 2023, the platform offers more than 900 clean beauty products—with nearly 80% under $10.
- Member's Mark: In 2022, Sam’s Club relaunched its Members Mark™ brand as “Made with our Member and Planet in Mind"—an aspiration for all items to be of the highest quality while featuring a focus on people and planet. Sam’s Club aims to remove certain ingredients from Member’s Mark food and consumable products, while boosting its assortment of items that are made using practices that promote animal welfare, help support land and ocean health, mitigate deforestation, utilize more sustainable textiles, and come from renewable sources. It also aims to incorporate more recyclable, reusable, and industrially compostable components in Member’s Mark items and packaging. For more information, visit the Members Mark Aspiration webpage.
Additionally, we use in-store signage and encourage suppliers to label products to promote more sustainable purchasing and consuming practices. Examples include:
- Certification logos: Certified products typically carry the relevant certification logo on pack (e.g., MSC, Fair Trade USA, Rainforest Alliance, Forest Stewardship Council, Oeko Tex); in some cases, we use in-store signage to call out products with social or environmental attributes (e.g., certified seafood shelf signage for Walmart U.S.). As noted above, many products and commodities have achieved certification at or above 95%, including fresh and frozen seafood, bananas, and coffee.
- Recycling labels: We have asked our private brand suppliers to label our food and consumable product packaging with consumer-friendly recycling information, and we encourage our national brand suppliers to provide similar label information. Our goal is for 100% of Walmart U.S. private brand food and consumable packaging to include the How2Recycle® label by 2022; in FY2023 we achieved 92%. We also have a goal for 100% of Sam's Club U.S. private brand packaging to include the How2Recycle® label; in FY2023 we achieved 83%.
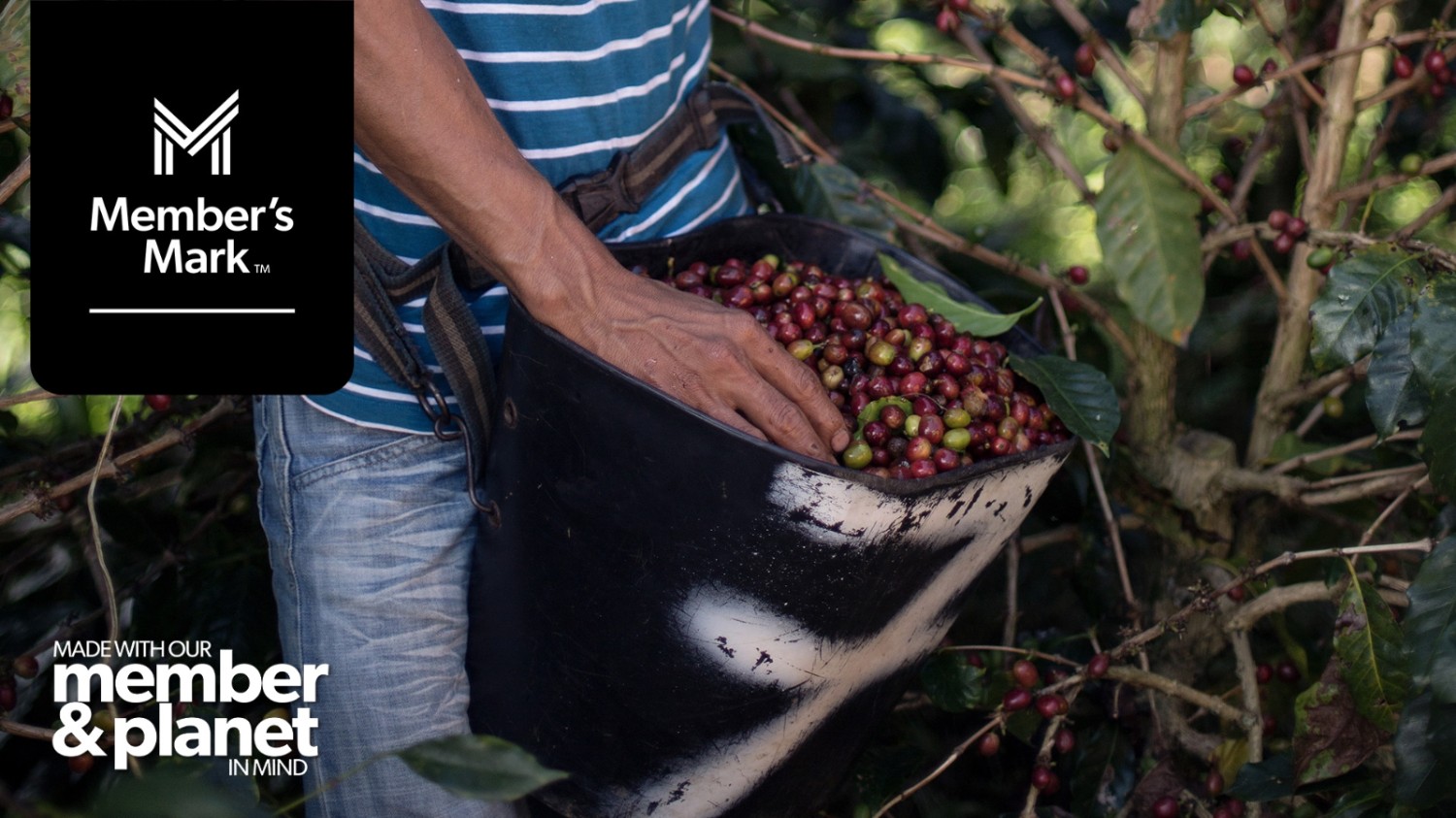

We advocate for public policies that align with our sustainable supply chain priorities. For example:
- Climate: We believe a strong climate strategy supports the resilience of our business and the communities we serve. Walmart is committed to policy advocacy aligned with the Paris Climate Agreement. Our Board-approved Statement on Climate Policy frames our advocacy around achieving 1.5° Celsius-aligned, science-based national and international climate policies that are consistent with achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 and that equitably addresses the needs of all stakeholders. Recent examples of our direct advocacy include meeting with lawmakers and advocating support for the climate provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act and engaging lawmakers to support the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. Read more: Climate Change .
- Waste: In support of our ambition to break the link between consumption and waste, our public policy priorities focus on promoting extended producer responsibility legislation and plastics pollution cooperation. For example, at Climate Week NYC in September 2022, The Ellen MacArthur Foundation (EMF) and World Wildlife Fund (WWF) launched the Business Coalition for a Global Plastics Treaty to advocate for an ambitious plastics treaty. Walmart endorsed the vision and supported this coalition during the first negotiation meeting of the Global Plastics Treaty (INC1). The International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) has also launched a new working group on the Plastics Treaty, of which Walmart is the chair. Read more: Waste: Circular Economy .
- Nature: Walmart supports public policies that promote regenerative approaches both directly and through engagement with trade associations. Recent activities we have undertaken in support of our aspiration to become a regenerative company include: conveying support for carbon pricing and technology-neutral approaches to decarbonize sectors like agriculture; supporting the Consumer Goods Forum’s Forest Positive Coalition of Action, which works with governments to support forest-positive policies that focus on Brazil, China, the European Union and Indonesia; and engaging the government of the Republic of the Marshall Islands in support of place-based initiatives that advance more sustainable seafood practices. Read more: R egeneration of Natural Resources .
- People in supply chains: We seek to act as a catalyst of positive transformation for the well-being of people working in consumer product supply chains, including by advocating to promote worker dignity in supply chains. Walmart has directly discussed with governments in Southeast Asia the need to enforce laws to reduce the prevalence of forced labor in the region, actions governments can take to address root causes of forced labor and ways governments can fill policy gaps relating to forced labor. We are also members of business organizations that engage governments on policy interventions relating to forced labor, including the Leadership Group for Responsible Recruitment and the Consumer Goods Forum. Finally, Walmart has worked with global business leaders to present policy recommendations to eliminate modern slavery to ministers of 40 countries in the Asia-Pacific as the United States Business representative for the Bali Process Government and Business Forum. Read more: People in Supply Chains .
Read more: Engagement in Public Policy .
Walmart and the Walmart Foundation’s sustainable supply chain strategies seek to accelerate systems change through philanthropic investments, including grants and in-kind support. For example, Walmart and the Walmart Foundation have complemented Walmart's business initiatives through philanthropy aimed at:
- Nature: Investing in initiatives that support the preservation of nature such as forests, oceans, land, and water, including supporting the development of place-based and jurisdictional initiatives, including in the Northern Great Plains, Colombia, the western and central Pacific Ocean, Sumatra, and the Brazilian Amazon.
- Circularity: Developing insights into customer recycling patterns and behaviors and improving recycling infrastructure.
- Human rights: Focusing on strengthening demand for responsible labor practices, investing in data and transparency, enhancing worker and community voice and supporting strong policy and regulation, including promoting the responsible recruitment of workers by building capacity around the responsible recruitment of H-2A migrant workers through the Mexico/U.S. corridor to U.S. farms, developing tools for worker voice and technology for impact, and developing a responsible recruitment marketplace.
- Economic opportunity: Building capacity in supply chains, including in India, where Walmart and the Walmart Foundation have made grants of $39 million between 2018 and 2022 to support smallholder farmers and farmer producer organizations and announced a new commitment to fund projects in India designed to help build capacity and advance the economic livelihoods of one million smallholder farmers by 2028.
- Measurement: Developing tools to support actionable data and transparency in product supply chains, including tools for organizations working to increase the uptake of credible landscape standards in critical regions and to develop and pilot an open and collaboratively developed agricultural technology platform.
The above are only indicative examples. Read more about our philanthropic work to address systemic supply chain issues: Regeneration of Natural Resources , Waste: Circular economy , People in Supply Chains , Supplier Opportunity , and Human Rights . Additionally, information on all Walmart and Walmart Foundation grants of $25,000 and greater is available at Walmart.org .
- Social and environmental challenges in supply chains are complex and are often the result of systemic issues including deeply entrenched economic practices and inconsistent government regulation and enforcement across countries in which products are made. These factors make it challenging for any single organization to have an impact.
- Walmart’s sustainable supply chain aspirations are dependent on the maturity, rigor and efficacy of third-party standards and initiatives, which require a critical mass of suppliers and retailers to align on common standards and best practices. For certain practices, there currently is no universal set of standards for responsible or more sustainable production and/or certification beyond compliance with the law (e.g., responsible recruitment, wage/hour). Furthermore, there are limits to the efficacy of tools used to monitor compliance with expectations. Similarly, gathering supplier data of sufficient quality can prove a challenge for robust reporting.
- The success of more sustainable product programs is dependent on suppliers’ capacity and willingness to meet high standards, as well as their performance and ability to scale practices across their own supply chains. Innovation in manufacturing, agriculture and other production technologies is necessary.
- Social and environmental issues in supply chains are often upstream and challenging to reach with traditional retailer oversight and monitoring tools. Lack of reliable data on the source/origin of certain commodities and product ingredients and the way they are produced—as well as the blending and commoditization of product inputs and ingredients—complicates matters. For example, the complexity and dynamic nature of end-to-end product supply chains make it nearly impossible to measure the GHG footprint of retail assortments with precision. The use of technology to improve transparency and traceability (e.g., blockchain, electronic vessel monitoring) can help, but adoption takes time and further innovation is necessary to meet these challenges.
- The breadth of Walmart's global product offerings and dispersed geographical reach of supply chains can present challenges for supplier engagement and nature-related risk identification and mitigation. Moreover, certain products can only be obtained from specific regions of the world, limiting options for alternative sources.
- Walmart’s ability to scale more sustainable options is dependent on customer preferences and demand (which can depend on the cost and convenience of such options) and the availability and cost of preferred products, ingredients, commodities and inputs. Growth and/or changes in our business can challenge our ability to meet customer demands consistent with our aspirations.
- The public policy environment in certain countries/regions does not support (and may undermine) more sustainable production at scale and at a reasonable cost.
- Pandemics, weather-related events, and political/social unrest can create supply/demand volatility and interrupt supply chains.
- Animal Welfare Position
- Animal Welfare – Swine Assurance Position
- Antibiotics in Farm Animals Position
- Cage-Free Egg Supply Position
- Environmental Sustainability Statement
- Forests Policy
- Global Forced Labor Prevention Policy
- Human Rights Statement
- Seafood Policy
- Standards for Suppliers
- Sustainable Row Crop Position
- Walmart U.S. Pollinator Health Position
- Climate Change
- People in Supply Chains
- Regeneration of Natural Resources: Forests, Land, Oceans
- Safer, Healthier Hood & Other Products
- Supplier Opportunity
- Waste: Circular Economy
- Walmart Sustainability Hub
1. Calculated in accordance with Walmart’s Project Gigaton Accounting Methodology, available on the Walmart Sustainability Hub. Suppliers submit information during a Project Gigaton reporting season; figures reported are for the reporting season that took place during the corresponding fiscal year.
2. Because Walmart does not restrict suppliers to reporting only on emissions avoidance and reduction efforts that are attributable to the suppliers’ business with Walmart, actions taken and reported through Project Gigaton cannot be used to measure Walmart’s Scope 3 emissions, either absolutely or in year-over-year reductions.
3. The U.S. product net sales figure used for the calculation includes Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club product net sales for the previous four quarters (Q3 through Q2) prior to the start of the survey reporting window. The percentage represents U.S. product net sales of suppliers that reported to Project Gigaton in the reporting year versus all U.S. product net sales. The calculation excludes Walmart International segment product net sales from the calculation.
4. Calculations include all private brand plastic packaging and single-use plastic and reusable bags globally. For the time frame of the private brands packaging survey, we instructed suppliers to use their latest or most recent 12-month period for which they have data available. If they reported last year, use the same reporting period as the initial/prior reporting year to avoid gaps or overlap with the prior year’s submissions. "North America" refers to our businesses in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico.
5. Packaging metrics are measured in weight and based on supplier reports through a supplier survey. Proxy data were calculated to provide data for suppliers that did not complete the survey or provided unusable data. Proxy data are meant to represent an estimate of how much packaging those suppliers / markets may utilize to provide an overall picture of Walmart’s entire packaging footprint. The calculation is based on supplier participation in the survey as a percentage of net sales and known packaging data. Walmart private brand suppliers representing 78% of Walmart global private brand net sales reported packaging data in 2020; in 2021 the figure was 80% and in 2022 the figure was 89%.
6. Walmart divested its business in Argentina in 2020 and its businesses in the U.K. and Japan in 2021. Because of the sale of Walmart’s Argentina business in late 2020, we were unable to capture sufficient packaging data for the Argentina market; to represent this market’s business in 2020, we used the 2018-2019 private brand packaging survey for Argentina. Walmart divested its businesses in the U.K. and Japan in early 2021; because the businesses were divested early in the year, we did not proxy packaging data for the time Walmart owned those businesses and the 2021 packaging figures represented here do not include the U.K. or Japan.
7. Previously, this percentage was reported as 9%; during our 2021 quality assurance review for our 2020 comparative period, we found 4 suppliers with reporting errors that affected our prior year's reporting.
8. Calculations include all private brand plastic packaging and single-use plastic and reusable bags globally. For the time frame of the private brands packaging survey, we instructed suppliers to use their latest or most recent 12-month period for which they have data available. If they reported last year, use the same reporting period as the initial/prior reporting year to avoid gaps or overlap with the prior year’s submissions. "Global" refers to all of our global retail businesses.
9. Previously, this percentage was reported as 9%; during our 2021 quality assurance review for our 2020 comparative period, we found 4 suppliers with reporting errors that affected our prior year reporting.
10. The 2020 and 2021 calculations follow the 2021 Reporting Guidelines for The New Plastics Global Commitment, and includes all private brand primary, secondary, and tertiary plastic packaging, including single-use plastic and reusable plastic bags globally. For the time frame of the private brands packaging survey, we instructed suppliers to use their latest or most recent 12-month period for which they have data available. If they reported last year, use the same reporting period as the initial/prior reporting year to avoid gaps or overlap with the prior year’s submissions. For suppliers that did not complete the survey or provided unusable data, proxy data was substituted to provide a full estimate of global private brand packaging. For the proxy calculation, a market level approach was used. The 2019 calculation includes all private brand plastic packaging and single‐use plastic and reusable bags globally.
11. Previously, this percentage was reported as 59%; during our 2021 quality assurance review for our 2020 comparative period, we found 4 suppliers with reporting errors that affected our prior year reporting.
12. The calculation includes all private brand plastic packaging and single‐use plastic and reusable bags globally. The estimation was calculated by extrapolating supplier‐reported packaging data (weight in metric tons) in relation to supplier participation percentage of net sales.
13. Previously, this was reported as 1,400,000 MT; during our 2021 quality assurance review for our 2020 comparative period, we found 4 suppliers with reporting errors that affected our prior year reporting.
14. Primary packaging is packaging that goes home with the consumer. This percentage excludes the net sales of private brand items that do not use primary packaging. For the time frame for the private brands packaging survey, we instructed suppliers to use their latest or most recent 12-month period for which they have data available. If they reported last year, use the same reporting period as the initial/prior reporting year to avoid gaps or overlap with the prior year’s submissions.
15. Tracked on the FishChoice platform, FisheryProgress.org. Publicly registered FIPs include FIPs and Pre-FIPs, both of which are registered with Fishsource.
16. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2021 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP or AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., 96% of Canada, and 61% of Mexico national volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2021 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed seafood in CY2020.
17. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2022 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP or AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart U.S., 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 45% of Mexico volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2022 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed seafood in CY2021. Walmart Mexico's FY2022 reporting may not be comparable to prior years' reporting due to a change in methodology to include national and import suppliers in FY2022, with resulting impacts to both the scope of the calculation and supplier response rate.
18. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2023 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP or AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart U.S., 98% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 100% of Canada volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed, seafood shipped in FY2023 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Mexico and Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing approximately 35% of Walmart Mexico and 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught and farmed seafood in CY2022.
19. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2021 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., 96% of Canada, and 61% of Mexico national volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2021 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught seafood in CY2020.
20. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2022 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP or AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., 98% of Canada, and 45% of Mexico volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2022 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught seafood in CY2021. Walmart Mexico's FY2022 reporting may not be comparable to prior years' reporting due to a change in methodology to include national and import suppliers in FY2022, with resulting impacts to both the scope of the calculation and supplier response rate.
21. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2023 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP or AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 98% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 100% of Canada volume of fresh and frozen, wild-caught, seafood shipped in FY2023 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Mexico and Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing approximately 35% of Walmart Mexico and 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, wild-caught seafood in CY2022. Central America’s percent certified fresh and frozen wild-caught seafood decreased in FY2023 due to lower availability of certified fresh and frozen wild-caught seafood and a strategic shift toward fresh and frozen farmed seafood.
22. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2021 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., 96% of Canada, and 61% of Mexico national volume of fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2021 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, farmed seafood in CY2020.
23. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2022 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in an AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., 98% of Canada, and 45% of Mexico volume of fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2022 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, farmed seafood in CY2021. Walmart Mexico's FY2022 reporting may not be comparable to prior years' reporting due to a change in methodology to include national and import suppliers in FY2022, with resulting impacts to both the scope of the calculation and supplier response rate.
24. Suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of the fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2023 and the volume of that seafood that met Walmart’s requirements (certified by a designated program or in an AIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart US, 98% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 100% of Canada volume of fresh and frozen, farmed, seafood shipped in FY2023 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Mexico and Central America reporting is based on reports from suppliers representing approximately 35% of Walmart Mexico and 100% of Walmart Central America fresh and frozen, farmed seafood in CY2022.
25. Based on price, availability, quality, customer demand, and unique regulatory environments across our global retail markets. Read the full Walmart Seafood Policy . As tracked on the FishChoice platform, FisheryProgress.org. Publicly registered FIPs include FIPs and Pre-FIPs, both of which are registered with Fishsource.
26. More sustainably sourced: Certified by a designated program or in a FIP.
27. Tuna suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of tuna shipped to Walmart in FY2021 and the volume of that product that met Walmart’s seafood policy requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP). Suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart U.S., 100% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 98% of Canada volume in FY2021 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Walmart U.S. figures are for private brand and national brand tuna. Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club U.S. figures are for all shelf-stable tuna (includes canned and pouched).
28. Tuna suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of tuna shipped to Walmart in FY2022 and the volume of that product that met Walmart’s seafood policy requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP). Suppliers representing approximately 95% of Walmart U.S. and 97% of Sam’s Club U.S. volume in FY2022 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Walmart U.S. figures are for private brand and national brand tuna. Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club U.S. figures are for all shelf-stable tuna (includes canned and pouched).
29. Tuna suppliers were asked to report through the Seafood Metrics System the total volume of tuna shipped to Walmart in FY2023 and the volume of that product that met Walmart’s seafood policy requirements (certified by a designated program or in a FIP). Suppliers representing approximately 99% of Walmart U.S., 100% of Sam’s Club U.S. volume in FY2023 responded, and suppliers representing approximately 100% of Walmart Canada volume of canned tuna shipped to Walmart Canada in FY2023 responded. Reported volumes were validated against Sustainable Fisheries Partnership records and Walmart business data showing supplier shipments. Walmart U.S. figures are for private brand and national brand tuna. Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club U.S. figures are for all shelf-stable tuna (includes canned and pouched).
30. Suppliers sourcing beef for Walmart supply chains from the Brazilian Amazon and Cerrado and Gran Chaco biomes are requested to submit farm-level data to SafeTrace, a third-party geo-monitoring and verification company, to assess deforestation-free and conversion-free (DCF) production. Currently, suppliers have only submitted information for their direct supplying farms as reliable traceability information for indirect supplying farms is not yet available at scale across these priority geographies.
30a. Results only apply to farms that directly supply Walmart’s Chilean beef suppliers sourcing from the Brazilian Amazon and Cerrado, and the Gran Chaco in Argentina and Paraguay. Suppliers sourcing from these regions are requested to submit farm-level data to SafeTrace, a third-party geo-monitoring and verification company, to assess deforestation-free and conversion-free (DCF) production. Currently, suppliers have only submitted information for their direct supplying farms as reliable traceability information for indirect supplying farms is not yet available at scale across these priority geographies.
31. Walmart defines “more sustainable” coffee as coffee sourced as certified by Fair Trade, Rainforest Alliance Certified or UTZ.
32. Total Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club U.S. certified more sustainable coffee was previously reported as 99%, and Sam’s Club certified more sustainable coffee was reported as 97%. During our FY2023 quality assurance review for our FY2022 comparative period, we identified a calculation error in our Sam's Club U.S. data and have restated our reporting to correct this error.
33. Walmart defines “more sustainable” tea as tea sourced as certified by Rainforest Alliance.
34. Covers tea sourced from July 1, 2021 through January 31, 2022
35. Certifications include Rainforest Alliance, Sustainably Grown and Fair Trade USA. Goal originally included Asda, Walmart’s U.K. business. Walmart divested its retail operations in the U.K. in February 2021. Going forward, we will no longer disclose progress for our divested operations.
36. Results do not include volume from spot buys. Spot buy pineapples and bananas may not qualify as certified “more sustainable.” Walmart defines “more sustainable” pineapples/bananas as pineapples/bananas that are certified by Rainforest Alliance, Sustainably Grown, or Fair Trade.
37. The U.S. product net sales figure used for the calculation includes Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club product net sales for the previous four quarters (Q3 through Q2) prior to the start of the survey reporting window. The percentage represents U.S. product net sales of suppliers that reported to Project Gigaton in the reporting year versus all U.S. product net sales. The calculation excludes Walmart International segment product net sales from the calculation."
38. Results are limited to net sales of Walmart and Sam’s Club direct suppliers and do not include data from “spot buy” or “direct store delivery” suppliers. Direct suppliers represent 90% of Walmart US net sales of the relevant department, and 89% of Sam’s Club US net sales of the relevant department. ‘Leafy Greens’ includes all packaged salads and lettuce.
39. Results are limited to net sales of Walmart and Sam’s Club direct suppliers and do not include data from “spot buy” or “direct store delivery” suppliers. Direct suppliers represent 90% of Walmart US net sales of the relevant department, and 89% of Sam’s Club US net sales of the relevant department.
40. Walmart and Sam’s Club define “more sustainable” cotton as cotton sourced from Cotton USA, produced under the Better Cotton Standard, certified under a recognized certification program like Organic (i.e. Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) or Organic Cotton Standard (OCS)) or Fair Trade, or recycled. Supplier-reported data for total cotton volume sourced through one of the following: Cotton USA, Organic, Fair Trade USA, or Recycled Cotton. Results are based on supplier survey responses. FY2021 results are based on reports from suppliers that represented 91.2% of Walmart U.S. private brand apparel net sales and 85.7% of Walmart U.S. home textiles net sales. FY2022 results are based on reports from suppliers that represented 97.7% of Walmart US private brand apparel net sales and 94.4% of Walmart US private brand home textiles net sales. FY2023 results are based on results from suppliers that represent 90.2% of Walmart U.S., 93.9% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 88.6% of Walmart Canada private brand apparel net sales and 95.5% of Walmart U.S., 98.1% of Sam’s Club U.S., and 93.7% of Walmart Canada private brand home textile net sales. Better Cotton Initiative data was derived from BCI’s Better Cotton Platform data.
41. FY2023 results are calculated as a percentage of supplier reported data. FY2023 results do not include estimated results of non-reporting suppliers. Reporting in years prior to FY2023 included the estimated results of non-reporting suppliers.
42. Man-made cellulosic fibers include rayon/viscose, modal, lyocell, acetate and trademarked versions. Forest information is per non-profit organization Canopy.
43. Fiber sourced from producers that receive a “green shirt” designation in the Canopy Hot Button Report is considered “low risk of sourcing from ancient and endangered forests.
44. FY2023 results are calculated as a percentage of supplier-reported data. FY2023 results do not include estimated results of non-reporting suppliers. Reporting for years prior to FY2023 included the estimated results of non-reporting suppliers. In FY2023, suppliers representing 90.2% of Walmart U.S. and 93.9% of Sam’s Club U.S. private brand apparel category net sales and 95.5% of Walmart U.S. and 98.1% of Sam’s Club U.S. private brand home category net sales reported data for this metric. Walmart Canada did not collect data from its suppliers relating to certified MMCFs and, as such, we do not have a percentage to report.
45. Results are based on supplier survey responses. FY2021 results are based on reports from suppliers that represented 91.2% of Walmart U.S. private brand apparel net sales and 85.7% of Walmart U.S. home textiles net sales. FY2022 results are based on reports from suppliers that represented 97.7% of Walmart U.S. private brand apparel net sales and 94.4% of Walmart U.S. home textiles net sales; for Sam's Club, participation rates were 91.8% and 93.8% for private brand apparel and home textiles, respectively; and for Canada, participation rates were 88.2% and 92.7% for private brand apparel and home textiles, respectively. FY2023 results are based on reports from suppliers that represented 90.2% of Walmart U.S. private brand apparel net sales and 95.5% of Walmart U.S. home textiles net sales; for Sam's Club, participation rates were 93.9% and 98.1% for private brand apparel and home textiles, respectively; and for Canada, participation rates were 88.6% and 93.7% for private brand apparel and home textiles, respectively. FY2023 results are calculated as a percentage of supplier reported data. FY2023 results do not include estimated results of non-reporting suppliers. Reporting for years prior to FY2023 included the estimated results of non-reporting suppliers.
46. Walmart Canada recycled polyester was previously reported as 67%. During our FY2023 quality assurance review for our FY2022 comparative period, we identified a calculation error in our Walmart Canada data and have restated our reporting to correct this error.
47. In accordance with the principles and criteria of the Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) segregated supply chain systems, or equivalent standards. Prior years’ reporting on certified palm oil included both mass balance and segregated. Walmart reset its palm oil goal in 2021 to focus on segregated palm oil or equivalent.
48. Suppliers supplying Walmart private brand products in departments most likely to contain palm oil were identified and encouraged to participate in Walmart’s palm oil survey. Excluding suppliers who responded to the survey and stated that they do not supply Walmart with products containing palm oil, suppliers representing 92% of Private Brand sales from the relevant business responded. The percentage of supplier reported palm oil volumes in Walmart private brand products certified as more sustainable is the quotient of the volume of each certified palm oil type divided by total volume of palm oil, per the supplier survey responses. Metrics include data from suppliers reporting palm oil from sources that are certified according to RSPO Mass Balance or equivalent plus RSPO Segregated Supply Chain Standard and RSPO Identity Preserved Supply Chain Standard.
49. During our FY2023 quality assurance review for our FY2022 comparative period, we identified a calculation error in our supplier-reported data. We have restated our reporting to correct this error. Percentages were previously reported as 10% certified segregated/equivalent palm oil and 80% certified mass balance/equivalent palm oil.
50. We updated our goal in 2020 to “By 2025, source private brand products made of pulp, paper, and timber deforestation and conversion-free. Implement more sustainable pulp, paper, and timber procurement practices that promote more sustainable management, conservation, protection and restoration of the world’s forests.”
51. Certified by the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC), Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC), Sustainable Forestry Initiative (SFI). Suppliers supplying Walmart private brand products in departments most likely to contain pulp and paper were identified and encouraged to participate in Walmart’s pulp and paper survey. Excluding suppliers who responded to the survey and stated that they do not supply Walmart with products containing pulp and paper, suppliers representing 74% of the relevant business responded in FY2021, 89% responded in FY2022, and 92% responded in FY2023. The percentage of supplier-reported pulp and paper volumes in Walmart private brand products certified as more sustainable or containing recycled content is the quotient of the volume of certified or recycled pulp and paper divided by total volume of pulp and paper, per the supplier survey responses.
52. FY2021 and FY2022 reported totals only include number of acres involved in fertilizer optimization or soil health practice programs, based on supplier reports. FY2023 reported total includes number of acres involved in more sustainable management practices (inclusive of fertilizer optimization and/or soil health practices) for row crops to more closely align with our Row Crops Position Statement.
53. Based on RBA membership (regular or full category) or implementing the RBA Validated Assessment Program for each disclosed facility.
54. Walmart measures its chemical footprint in terms of priority chemicals, or PCs based on supplier reports collected through UL WERCSmart for in-scope products sold. Walmart references regulatory and authoritative lists to determine priority chemicals. These lists can be found on the Walmart Sustainability Hub . Our footprint covers in-scope formulated consumables products within beauty, personal care, baby, pet and household cleaning products sold by Walmart U.S. stores and Sam’s Clubs in the U.S. In any given year, an increase or decrease in UPC volume weight disclosures may impact reporting. To learn about formulation disclosure, please visit Section 2: Transparency of our Sustainable Chemistry Implementation Guide.
55. All sustainable chemistry metrics are on a calendar year basis and are reported for the prior corresponding calendar year. The three years reported in this table are calendar years 2019, 2020, and 2021. As part of our FY2020 reporting cycle, we restated our baseline year chemical footprint combined for Walmart U.S. stores and Sam’s Club U.S. locations from 220.8 million pounds of priority chemicals (PC) weight to 215.9 million pounds of PC weight based on formulations that our suppliers inadvertently assigned to the wrong Universal Product Code (UPC) registrations in UL’s WERCSmart. We updated the baseline to report the correct progress on our reduction goal. Suppliers provided product formulations to UL WERCSmart for 95% of in-scope UPCs.
56. Suppliers provided product formulations to UL WERCSmart for 96% of in-scope UPCs.
57. Suppliers provided product formulations to UL WERCSmart for 95% of in-scope UPCs.
58. Suppliers provided product formulations to UL WERCSmart for 94% of in-scope UPCs.
59. The U.S. product net sales figure used for the calculation includes Walmart U.S. and Sam’s Club product net sales for the previous four quarters (Q3 through Q2) prior to the start of the survey reporting window. The percentage represents U.S. product net sales of suppliers that reported to Project Gigaton in the reporting year versus all U.S. product net sales. The calculation excludes Walmart International segment product net sales from the calculation.
60. Built for Better- For Communities includes products under selected certifications and initiatives but is not inclusive of all products that are made, grown, or assembled in the United States.
61. Built for Better recognizes select certifications & initiatives and is not inclusive of all responsibly or sustainably sourced products.
Section Navigation
9. Learning from Others 9.1 Introduction: Grouping by Business Models :Cautionary Tales 9.2 A Start 9.3 Coins International 9.4 Fine Art Ceramics 9.5 Halberd Engineering 9.6 Ipswich Seeds 9.7 Seascape e-Art 9.8 Whisky Galore :Case Studies 9.9 Amazon 9.10 Andhra Pradesh 9.11 Apple iPod 9.12 Aurora Health Care 9.13 Cisco 9.14 Commerce Bancorp 9.15 Craigslist 9.16 Dell 9.17 Early Dotcom Failures 9.18 Easy Diagnosis 9.19 eBay 9.20 Eneco 9.21 Fiat 9.22 GlaxoSmithKline 9.23 Google ads 9.24 Google services 9.25 Intel 9.26 Liquidation 9.27 Lotus 9.28 Lulu 9.29 Netflix 9.30 Nespresso 9.31 Netscape 9.32 Nitendo wii 9.33 Open Table 9.34 PayPal 9.35 Procter & Gamble 9.36 SIS Datenverarbeitung 9.37 Skype 9.38 Tesco 9.39 Twitter 9.40 Wal-mart 9.41 Zappos 9.42 Zipcar
Control Panel
9.40 wal-mart stores, inc., walmart's supply chain management, current threats, points to note, sources and further reading.
1. Walmart Stores, Inc. . Funding Universe . Solid business article with extensive references. 2. Wal-mart's supply chain management practices by P. Mohan Chandran. Mohanchandran . 2002. 3. Wal-mart's supply chain management practices. CaseStudyInc . January 2008. 4. Wal-mart's supply chain management practices. Thinking Made Easy . June 2009. 5. Wal-mart's supply chain management success by 'freightforwarder'. Laowee . September 2010. 6. A Case Study of Wal-mart's 'Green' Supply Chain Management by Adam Heying and Whitney Sanzaro. Apicsterragrande . May 2009. 7. Supply Chain . ASA Research . 2010. 8. Criticism of Walmart. Wikipedia . Company's often poor but legal labor etc. relations: a detailed treatment. 9. Wal-mart Financial Results . MSN . Financial reports 2007-2011. 10. The Wal-mart Revolution: How Big-Box Stores Benefit Consumers, Workers, and the Economy by Richard Vedder and Wendell Cox. Aei Press. December 2006. 11. Walmart has first US sales rise in two years by Alan Rappeport. FT . October 2011. 12. The end of the Wal-mart era. MSN Money . August 2007. Reprinted from the Wall Street Journal. 13. Walmart . Walmart corporate site . 14. Vast Mexico Bribery Case Hushed Up by Wal-Mart After Top-Level Struggle by David Barstow. N.Y.T. April 2012. 15. Walmart Stores . Daily Finance . August 2012. 16. Wal-Mart Customers Complain Bare Shelves Are Widespread by Renee Dudley. Bloomberg . April 2013.
Already on SCMDOJO? Log in
I accept SCMDOJO'S Terms of Use and Privacy Notice .

Walmart Supply Chain: Building a Successful Integrated Supply Chain for Sustainable Competitive Advantage
- Case Studies
Introduction
The global business landscape has witnessed an increasingly fierce competition, pushing companies to seek effective strategies to maintain and enhance their competitiveness. Among these strategies, the role of supply chain capability stands out as a key factor in driving success. A well-optimized supply chain not only ensures efficient delivery and cost-effectiveness but also provides companies with a competitive advantage in the market. In this context, Walmart, the world’s largest retailer, has demonstrated a highly successful and integrated Walmart supply chain, propelling its growth and dominance in the retail industry.
This case study aims to delve into the significance of supply chain capability for enhancing a company’s competitiveness and how it serves as a competitive advantage for companies. Additionally, we will explore the imperative need for supply chain redesign in the global economy to adapt to the challenges of the modern era of globalization. Focusing on Walmart’s exemplary supply chain practices, the purpose of this case study is to analyze the features of its successful integrated supply chain while identifying relevant issues in the context of the current globalized market.
[Read More: Rivian: Navigating Supply Chain and Operational Challenges and Embracing Growth ]
Walmart’s Supply Chain: Integrated Supply Chain Success
Data-driven success factors.
In the realm of modern supply chain management, data-driven strategies play a pivotal role in enhancing a company’s competitiveness. Walmart’s remarkable success as the world’s largest retailer can be attributed to its astute utilization of data analysis and advanced technologies within its integrated supply chain. This section delves into the key data-driven success factors that have propelled Walmart’s supply chain to the forefront of the retail industry.
[Read More: ERP Master Data: A Guide to Improve Quality & Governance ]
Role of Data Analysis through Barcode Scanning and Point-of-Sale Systems
Data analysis is at the core of Walmart’s supply chain prowess. The company has implemented sophisticated barcode scanning and point-of-sale systems to collect real-time data from its stores. By employing these technologies, Walmart gains valuable insights into customer buying behavior, sales trends, and inventory levels. The ability to analyze this data enables the retail giant to make informed decisions on product procurement, inventory management, and demand forecasting.
Efficient Supply Chain Practices: Automated Distribution Centers and Computerized Inventory Systems
Automation is a key component of Walmart’s efficient supply chain practices. The company has strategically invested in automated distribution centers, streamlining the flow of products from manufacturers to stores. These automated facilities not only optimize the handling and movement of goods but also enable faster order fulfillment and replenishment. Additionally, computerized inventory systems provide Walmart with accurate and up-to-date information about stock levels, allowing for precise inventory control and reducing the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.

Utilizing Walmart’s Own Trucking System and Cross-Docking Logistics
Another critical factor contributing to Walmart’s supply chain success is the utilization of its private trucking system and cross-docking logistics. By maintaining its own trucking fleet, Walmart gains greater control over transportation and delivery schedules, leading to improved efficiency and timely product replenishment. Furthermore, the adoption of cross-docking logistics techniques has enabled Walmart to minimize the need for intermediate storage, leading to reduced handling costs and faster product movement through the supply chain.
[Read More: The Ultimate Guide to Contract Logistics: What You Need to Know ]
Information Technologies Driving Efficiency
In Walmart’s journey towards becoming a global leader, information technologies have played a pivotal role in driving efficiency within the integrated Walmart supply chain. The retail giant has strategically adopted various IT initiatives to optimize its operations, enhance collaboration with suppliers, and achieve real-time inventory targeting. These technologies have contributed significantly to Walmart’s supply chain success, allowing them to maintain a competitive edge in the retail industry.

Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR)
One of the key information technologies that have bolstered Walmart’s supply chain efficiency is the implementation of Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR). This system facilitates seamless communication and coordination between Walmart and its supply chain partners, including suppliers and distributors. By sharing real-time sales data and demand information, CPFR enables accurate forecasting and demand planning, minimizing information distortion, and promoting synchronized inventory replenishment. The CPFR program has been instrumental in enhancing overall supply chain visibility and efficiency, allowing Walmart to respond promptly to fluctuations in demand and supply, reducing stockouts, and optimizing inventory levels.
Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) and Its Benefits
Walmart’s adoption of Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) has been another critical information technology-driven initiative. Through VMI, Walmart empowers its suppliers to take on the responsibility of managing their inventory stored in Walmart’s warehouses. By granting suppliers access to real-time inventory data and sales information, Walmart facilitates efficient inventory tracking and replenishment. This hands-on approach by suppliers results in streamlined inventory management, reduced delays in replenishment, and lower stockouts. The VMI model has proved particularly advantageous for Walmart due to its vast product range and numerous suppliers, making inventory management complex and costly if managed solely by the retailer.
[Read More: Vendor Managed Inventory: A Comprehensive Guide ]
Leveraging RFID Technology for Real-Time Inventory Targeting
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology has been a game-changer in Walmart’s pursuit of real-time inventory targeting and enhanced supply chain visibility. By employing RFID tags on products, Walmart can track the movement of inventory throughout the supply chain in real-time. RFID enables accurate and automated inventory tracking, reducing the need for manual counting and minimizing errors in inventory management. The technology also provides crucial details, such as production time, location, and expiry dates of goods, allowing for efficient inventory targeting and better control over inventory turnover. RFID technology has been instrumental in Walmart’s cost reduction efforts, ensuring optimal stock levels while avoiding overstocking and unnecessary inventory holding costs.
Achieving Competitive Advantage through Strategy
Walmart’s competitive strategy: “everyday low prices” (edlp).
Walmart’s competitive advantage is deeply rooted in its strategic focus on offering “Everyday Low Prices” (EDLP) to its customers. The EDLP strategy revolves around providing high-quality products and services at the lowest possible prices, ensuring that customers can benefit from affordable prices every day. This approach sets Walmart apart from its competitors and has been instrumental in establishing the company as a dominant force in the retail industry.
Implementing the “Everyday Low Costs” (EDLC) Policy through Direct Procurement
To support its EDLP strategy, Walmart follows an “Everyday Low Costs” (EDLC) policy in its supply chain management. One of the key elements of the EDLC policy is the direct procurement of items from suppliers, eliminating intermediaries in the process. By procuring directly from manufacturers, Walmart can negotiate and understand their cost structure, enabling them to make informed purchasing decisions and obtain the best prices for their products.
Walmart’s emphasis on direct procurement is further bolstered by the use of technology and information systems. The company has implemented a central database, store-level point-of-sale systems, and a satellite network, along with barcodes and RFID technology as previously mentioned. These technologies allow Walmart to gather and analyze real-time store-level information, including sales data and external factors like weather forecasts, to enhance the accuracy of purchasing predictions. This integration of information technology helps Walmart optimize its procurement process and maintain low costs throughout the supply chain.
Utilizing Information Systems for Better Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is critical for Walmart to sustain its competitive advantage through the EDLP strategy. The company relies on information systems and information technology (IT) capabilities to control inventory levels efficiently. By capturing customers’ demand information, Walmart can identify popular products and stock them adequately, leading to an overall reduction in inventory.
One notable example of Walmart’s successful utilization of information systems is its collaboration with Procter & Gamble (P&G) through the Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR) program. This program links all computers of P&G to Walmart’s stores and warehouses, allowing for efficient replenishment orders based on real-time inventory needs. Additionally, Walmart’s Retail Link , developed in the early 1990s, serves as another vital IT application for storing data, sharing it with vendors, and aiding in shipment routing assignments.

Challenges and Opportunities
Supplier cooperation and collaboration.
Walmart’s supply chain success can be attributed to its strong relationships with suppliers, but achieving and maintaining supplier cooperation and collaboration is not without challenges. Let’s explore the challenges and opportunities in this area:
Challenges in Obtaining Suppliers’ Cooperation
- Supplier Resistance to Direct Procurement: Walmart follows an “Everyday Low Costs” (EDLC) policy by directly procuring items from suppliers, eliminating intermediaries. However, some suppliers may be reluctant to cooperate with this approach as it can disrupt existing distribution channels and potentially reduce their bargaining power.
- Complex Supplier Networks: With thousands of suppliers across various product categories, managing diverse supplier networks can be challenging. Each supplier may have different production and delivery schedules, making coordination difficult.
- Balancing Profit Margins: As Walmart emphasizes low prices, maintaining a balance between cost savings and ensuring suppliers’ profitability can be a delicate task. Suppliers may resist pressure to reduce prices further to maintain their margins.
Opportunities for Enhanced Supplier Cooperation and Collaboration
- Establishing Transparent Communication Channels: Walmart can create transparent and open communication channels with its suppliers to foster better cooperation. Clear communication regarding demand forecasts, inventory levels, and potential disruptions can help suppliers plan their production and deliveries more efficiently.
- Supplier Incentive Programs: Introducing incentive programs that reward suppliers for meeting certain performance metrics, such as on-time delivery or cost reduction, can motivate suppliers to actively collaborate and improve their supply chain capabilities.
- Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR): Walmart can leverage technology, such as CPFR, to share real-time sales data and demand forecasts with its suppliers. This collaborative approach allows suppliers to align their production and inventory management with actual market demand, reducing the bullwhip effect and optimizing the supply chain.
- Sharing Inventory Visibility: Providing suppliers with access to inventory data, including stock levels and sales information, can help them plan production and deliveries more effectively. This visibility can prevent stockouts and overstocking issues.
- Long-term Partnerships: Building long-term strategic partnerships with key suppliers can create a sense of mutual commitment and trust. By assuring consistent business over an extended period, Walmart can foster stronger relationships and supplier loyalty.
[Read More: 3 Types of Supplier Segmentation Matrix You Can Use to Classify Suppliers ]
Importance of Collaboration to Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency
- Reducing Lead Times: Effective collaboration with suppliers can help shorten lead times by streamlining production and transportation processes. Faster lead times enables Walmart to respond quickly to changes in demand, reducing the risk of stockouts.
- Efficient Inventory Management: Collaborative efforts with suppliers enable better inventory planning and management. Suppliers can adjust production based on actual demand, reducing excess inventory and associated costs.
- Supply Chain Flexibility: Collaboration fosters agility and adaptability in the supply chain. When Walmart and its suppliers work together closely, they can quickly adjust to market changes, supply disruptions, or new opportunities.
- Cost Reduction: Improved supplier collaboration can lead to cost-saving opportunities. By eliminating unnecessary intermediaries and optimizing production and transportation, overall supply chain costs can be minimized.

The Incentives Alignment Issue
In any supply chain, maintaining a balance of profit margins among different parties is essential for efficient collaboration and sustained success. However, achieving incentives alignment can be challenging, and this issue is particularly relevant in the case of Walmart supply chain. Addressing misalignment of interests between Walmart and its suppliers is crucial for optimizing the overall performance of the supply chain and ensuring long-term success. The following points highlight the incentives alignment issue faced by Walmart:
1. Balancing Profit Margins Among Different Supply Chain Parties:
Walmart’s success is attributed to its ability to offer high-quality products and services at the lowest affordable prices. To achieve this, Walmart employs various cost-cutting strategies, such as direct procurement from suppliers and streamlined distribution practices. While these strategies help Walmart maintain competitive prices, they can create challenges for suppliers who may face pressure to lower their own profit margins to meet Walmart’s demands. This misalignment of profit margins can lead to strained relationships and potentially impact the overall efficiency of the supply chain.
2. Misalignment of Interests Between Walmart and Suppliers:
Walmart’s size and market dominance can lead to power imbalances in supplier relationships. Suppliers may feel compelled to comply with Walmart’s demands to maintain access to its large customer base. However, this can lead to situations where suppliers may not have enough leverage to negotiate favorable terms, impacting their own profitability. As a result, suppliers may be less inclined to invest in innovations or improvements that would benefit the supply chain as a whole.
3. Conflict Between Inventory Growth and Sales Growth:
Walmart faced inventory growth issues in the past, with the inventory growth rate outpacing the sales growth rate. This can be indicative of conflicting incentives between Walmart and its suppliers. Suppliers may prioritize producing and delivering more inventory to ensure they meet Walmart’s demands, even if the sales growth does not keep up with the increased inventory. This misalignment can lead to excess inventory, increased carrying costs, and potential stockouts.
4. The Need for a New Triple-A Supply Chain:
Addressing the incentives alignment issue requires a fundamental shift in the supply chain strategy. Lee (2004) proposed the concept of a new Triple-A supply chain for Walmart and other companies in the 21st century. The Triple-A supply chain emphasizes agility, adaptability, and alignment to create a sustainable competitive advantage. Achieving alignment among all participating parties is crucial to optimize supply chain performance and ensure that risks and rewards are distributed fairly.
The Triple-A Supply Chain Approach
In today’s competitive business landscape, companies like Walmart recognize that a successful supply chain is not just about having a fast and cost-effective system. To maintain a sustainable competitive advantage and address the challenges of the global economy, it is essential to redesign supply chains that incorporate agility, adaptability, and alignment. This section explores the concept of the Triple-A Supply Chain Approach, which emphasizes these three key qualities that an ideal supply chain should possess: agility, adaptability, and alignment of interests among all participating parties.
The Three Qualities of an Ideal Supply Chain
Agility for quick and cost-effective responses:.
Agility refers to a supply chain’s ability to respond quickly and cost-effectively to sudden changes in demand, supply, and external disruptions. In the fast-paced business environment, companies must be able to adapt swiftly to fluctuations in customer preferences, market conditions, and unforeseen events. For Walmart, agility has been a critical factor in maintaining its leadership position in the retail industry. The company’s investments in technology and supply chain optimization strategies have allowed them to optimize inventory levels and respond rapidly to changing customer demands, ensuring the availability of products while minimizing inventory costs.
Adaptability to Handle Changes in Demand and Supply:
Supply chains should be adaptable and flexible enough to handle variations in demand and supply patterns. Demand forecasts can be uncertain, and unexpected supply chain disruptions may occur, making adaptability a vital quality. Walmart’s focus on omnichannel and various fulfillment options, such as in-store pickup and ship from store, demonstrates their commitment to adaptability. By utilizing multiple channels, Walmart can cater to diverse customer preferences, ensuring an uninterrupted flow of products to meet demand.
Alignment of Interests among All Participating Parties:
One of the significant challenges in supply chain management is ensuring alignment of interests among all parties involved, including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Walmart’s scale and dominance in the retail market have allowed them to establish strong relationships with vendors, enabling strategic partnerships with vendors who can meet their high-volume demands. Additionally, Walmart’s adoption of Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI) allows suppliers to manage their own inventory stored in Walmart’s warehouses. This collaboration aligns the incentives of suppliers and Walmart, streamlining inventory management and ensuring timely replenishment.

In conclusion, Walmart’s integrated supply chain has been a crucial factor in the company’s global dominance and sustained competitive advantage. By strategically investing in technology and optimizing its supply chain, Walmart has managed to maintain its position as the world’s largest retailer with over $572 billion in revenue in 2022.
Walmart’s success serves as a compelling example of the importance of a well-integrated supply chain in achieving and sustaining competitive advantage in the global market. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of the 21st-century economy, building and enhancing supply chain capabilities will remain a critical aspect of ensuring sustainable growth and profitability. By prioritizing agility, adaptability, and alignment, companies can follow in Walmart’s footsteps and position themselves for continued success in the dynamic and ever-evolving global marketplace.
References:
- Lee H.L. (2004): The triple A supply chain. “Harvard Business Review”, Vol. 82, No. 10, pp. 102-112.
- Nguyen T.T.H. (2017): Wal-Mart’s successfully integrated supply chain and the necessity of establishing the Triple-A supply chain in the 21st century. “Journal of Economics and Management”, Vol. 29(3), pp. 102-117
About the Author – Dr Muddassir Ahmed
Dr MuddassirAhmed is the Founder & CEO of SCMDOJO. He is a global speaker , vlogger and supply chain industry expert with 17 years of experience in the Manufacturing Industry in the UK, Europe, the Middle East and South East Asia in various Supply Chain leadership roles. Dr. Muddassir has received a PhD in Management Science from Lancaster University Management School. Muddassir is a Six Sigma black belt and founded the leading supply chain platform SCMDOJO to enable supply chain professionals and teams to thrive by providing best-in-class knowledge content, tools and access to experts.
You can follow him on LinkedIn , Facebook , Twitter or Instagram .
- Walmart Walmart Supply Chain

Download Indirect Procurement Assessment
An Indirect Procurement Best Practices Assessment is a valuable process for organisations to evaluate and optimise their indirect procurement functions.

Announcing 6 New Members: Spotlights on Technology in Action @ Consensus 2024 > Read on
How Walmart brought unprecedented transparency to the food supply chain with Hyperledger Fabric
Download Printable Case Study
When an outbreak of a food-borne disease happens, it can take days, if not weeks, to find its source. Better traceability could help save lives by allowing companies to act faster and protect the livelihoods of farmers by only discarding produce from the affected farms.
Walmart thought that blockchain technology might be a good fit for the decentralized food supply ecosystem. To test this hypothesis, the company created a food traceability system based on Hyperledger Fabric. Walmart, together with its technology partner IBM, ran two proof of concept projects to test the system. One project was about tracing mangos sold in Walmart’s US stores and the other aimed to trace pork sold in its China stores.
The Hyperledger Fabric blockchain-based food traceability system built for the two products worked. For pork in China, it allowed uploading certificates of authenticity to the blockchain, bringing more trust to a system where that used to be a serious issue. And for mangoes in the US, the time needed to trace their provenance went from 7 days to… 2.2 seconds!
Walmart can now trace the origin of over 25 products from 5 different suppliers using a system powered by Hyperledger Fabric. The company plans to roll out the system to more products and categories in the near future. In fact, it has recently announced that it will start requiring all of its suppliers of fresh leafy greens (like salad and spinach) to trace their products using the system.
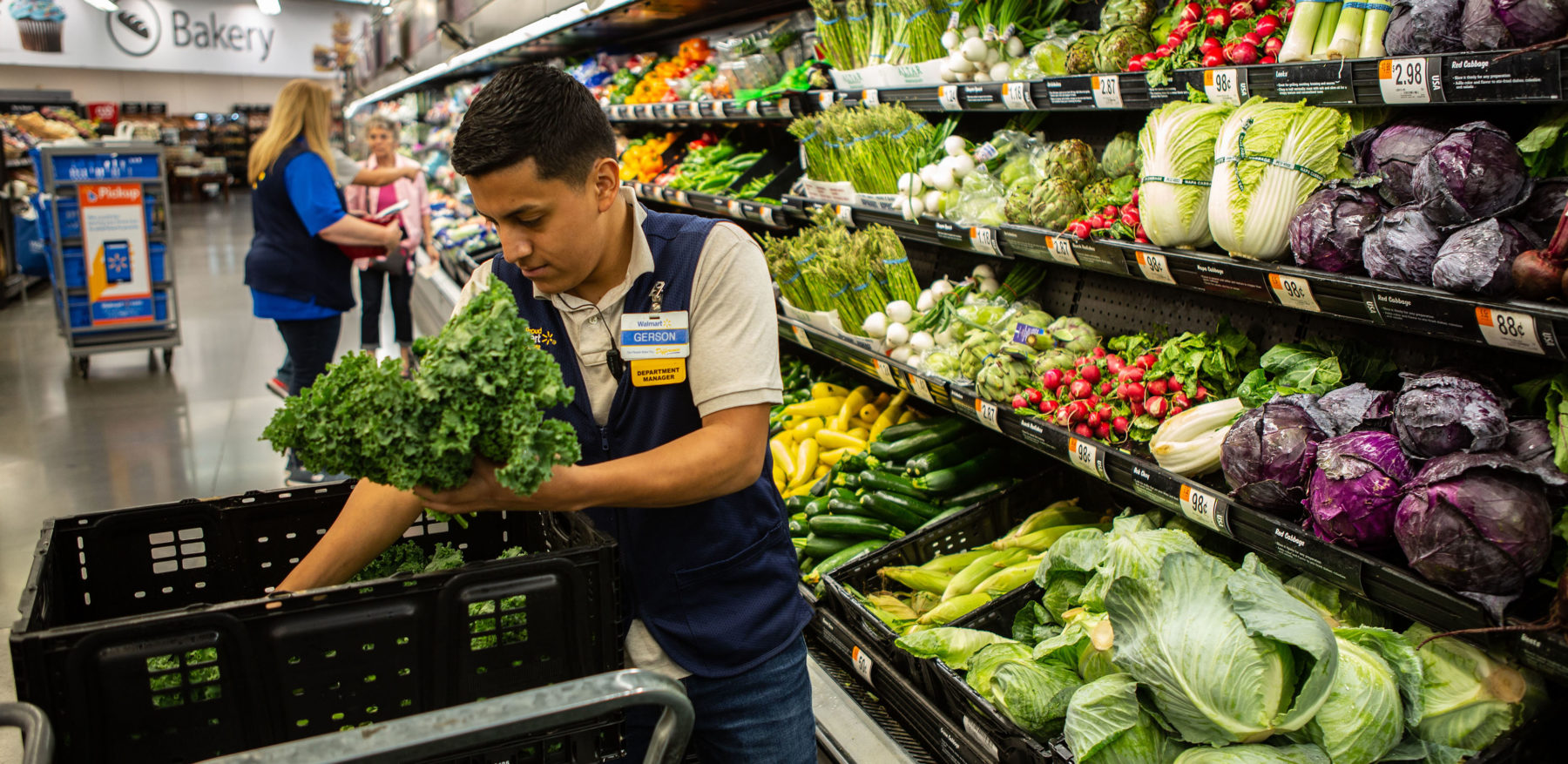

Tracking food for better safety
We rarely think about it, but the modern food system is a marvel. We have access to fresh produce all year round, buy exotic food from all around the world, and have more variety than our ancestors could ever dream of.
Our food is generally safe to eat. Still, occasionally it can make us sick. Last year in 2018 there were at least 18 reported outbreaks of foodborne illnesses in the USA, including the E. coli found in romaine lettuce.
“People talk about the food supply chain,” says Frank Yiannas, former Vice President of Food Safety at Walmart. “But it is not actually a chain, it’s a complex network.” When an outbreak of a food-borne disease does happen, it can take days, if not weeks, to find its source. If investigators cannot point to a specific farm or farms, the government usually advises consumers to avoid products grown in a certain area (as happened with romaine lettuce from Yuma, Arizona), or even to avoid the type of product altogether. According to Walmart , millions of bags or heads of lettuce had to be removed, and consumers lost confidence in romaine lettuce altogether. Better traceability could help save lives by allowing companies to act faster and protect the livelihoods of farmers by only discarding produce from the affected farms.
For this reason, Walmart has always been interested in enhancing transparency and traceability in the food system. Mr. Yiannas explains that the company has tried many systems and approaches to solving this problem over the years; none had brought them the kind of results they were after. When Yiannas first heard about blockchain and the idea of using it to trace food in the supply chain, he was skeptical.

From blockchain skeptic to believer
Karl Bedwell, Senior Director at Walmart Technology, explains, “Creating a (traceability) system for the entire food supply ecosystem has been a challenge for years, and no one had figured it out. We thought that blockchain technology might be a good fit for this problem, because of its focus on trust, immutability, and transparency.”
Bedwell and his team introduced Yiannas to the possibilities of blockchain technologies for enterprise solutions. Says Yiannas, “I really had an “aha” moment once I deeply understood the technology. I had been hesitant about creating yet another traceability system – the ones we had tried in the past never scaled. Now I understand that was because they were centralized databases. Blockchain, with its decentralized, shared ledger felt like it was made for the food system!”
With the business interest in blockchain technology confirmed, Walmart started working on two proof of concept (POC) projects with their technology partner IBM.

Choosing the blockchain
Walmart Technology considered several blockchain technologies but ultimately decided to go for Hyperledger Fabric.
“IBM brought Hyperledger Fabric to us. We looked into Ethereum, Burrow project and others. Ultimately, we decided to go with Hyperledger Fabric because it met most of our needs for a blockchain technology,” Bedwell said. “We felt that it best met our needs. It is an enterprise-grade blockchain technology, and it is permissioned.”
The team also found it important to work with an open-source, vendor-neutral blockchain. Since the food traceability system was meant to be used by many parties, including Walmart’s suppliers and even direct competitors, the technology ecosystem underlying it needed to be open.
Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain framework implementation and one of the Hyperledger projects hosted by The Linux Foundation. Intended as a foundation for developing applications or solutions with a modular architecture, Hyperledger Fabric allows components, such as consensus and membership services, to be plug-and-play. Hyperledger Fabric leverages container technology to host smart contracts called “chaincode” that comprise the application logic of the system.
For mangoes in the US, the time needed to trace their provenance went from 7 days to… 2.2 seconds!
In October 2016, Walmart, together with its technology partner IBM, announced the two projects: one was about tracing the origin of mangos sold in Walmart’s US stores and the other aimed to trace pork sold in its China stores.
For the mango POC, Yiannas started by creating a benchmark. He bought a packet of sliced mangoes at a nearby Walmart store and asked his team to identify which farm they had come from – as fast as possible. The team started calling and emailing distributors and suppliers, and eventually had an answer almost seven days later. This was not bad by industry standards, but Walmart wanted to do much better. So together with IBM, they got to work building a blockchain-based food traceability system.
The Walmart Technology team looked at their own processes as well as those of their suppliers to design the application. Archana Sristy, Director of Engineering at Walmart, explains, “[Our team at Walmart Technology] co-led the core design and setup of the application (with IBM), as well as built the integration with the enterprise systems. We worked with GS1 (the standards authority in barcodes and labeling) to define the data attributes for upload to the blockchain. IBM wrote the chaincode.
Suppliers used new labels and uploaded their data through a web-based interface.

From POC to production, from Walmart to IBM Food Trust
Once Walmart saw that the system worked, they wanted to expand it – and not just within Walmart. Given the interconnected nature of the food system and the company’s negative experience with closed systems, Walmart wanted to make sure that this time, many players were involved. Says Yiannas, “(Walmart’s) CEO was reaching out to other food companies the next day, including other retailers!” Wal-Mart collaborated with IBM and others to set up IBM Food Trust , involving prominent players in the food industry, like Nestle and Unilever.
The Walmart team had a positive experience working with Hyperledger. “Every question that we had, it looked like the Hyperledger community had already been working on addressing that,” says Bedwell. For example, in building a truly open system, the Walmart team worried about interoperability with other blockchain-based traceability systems. And as if in answer to their concern, Hyperledger recently announced its collaboration with Ethereum. He adds, “It seems that the Hyperledger community is addressing everything that enterprises would be concerned about.”
Says Yiannas, “I really had an ‘aha’ moment once I deeply understood the technology. I had been hesitant about creating yet another traceability system – the ones we had tried in the past never scaled. Now I understand that was because they were centralized databases. Blockchain, with its decentralized, shared ledger felt like it was made for the food system!”
Tips from Frank Yiannas on implementing your blockchain project
1. Let the business lead the project , not the IT department.
2. Understand the business case deeply. Make sure that you know and can explain why blockchain is the right solution.
3. In a large organization, you need to bring a lot of people along. Think about all the different departments that will be affected by the projects. Meet with these stakeholders early on and explain what you are trying to do.
4. Have your soundbite! People don’t get inspired by technology, but by a vision. For us, it was the story of mangoes – 7 days vs. 2.2 seconds with blockchain.
5. Participate in forums that allow you to speak to other companies who have launched similar projects successfully. It helps if you help an expert in the field who’s willing to come in and educate fellow members.
6. Start small, with a POC. And when you’ve run your pilots and are convinced about the business value, go ahead and scale. After all, Yiannas says, “Walmart is a pretty big lab! If it can scale at Walmart, it can scale anywhere!”

Looking forward
Walmart now traces over 25 products from 5 different suppliers using IBM Blockchain which is built atop Hyperledger Fabric. The products include produce such as mangoes, strawberries and leafy greens; meat and poultry such as chicken and pork; dairy such as yogurt and almond milk; and even multi-ingredient products such as packaged salads and baby foods.
Yiannas says of the impact, “This solution allows us to see the whole chain in seconds! We can take a jar of baby food and see where it was manufactured and trace back all the ingredients to the farms!”
Walmart plans to roll out the system to more products and categories in the near future in cooperation with IBM Food Trust.. In fact, the company recently announced that it will start requiring all of its suppliers of fresh leafy greens (like salad and spinach) to trace their products using the system.
“Using the IBM Food Trust network that relies on blockchain technology, we have shown that we can reduce the amount of time it takes to track a food item from a Walmart Store back to source in seconds, as compared to days or sometimes weeks,” Walmart wrote in a letter to suppliers.
Beyond tracing the products’ journey, the company might start tracing other data, like sustainability.

About Walmart
Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) helps people around the world save money and live better – anytime and anywhere – in retail stores, online, and through their mobile devices. Each week, nearly 265 million customers and members visit our more than 11,200 stores under 55 banners in 27 countries and eCommerce websites. With fiscal year 2018 revenue of $500.3 billion, Walmart employs over 2.2 million associates worldwide. Walmart continues to be a leader in sustainability, corporate philanthropy and employment opportunity. Additional information about Walmart can be found by visiting http://corporate.walmart.com .
About Hyperledger
Hyperledger is an open source collaborative effort created to advance cross-industry blockchain technologies. It is a global collaboration including leaders in banking, finance, Internet of Things, manufacturing, supply chain, and technology. The Linux Foundation hosts Hyperledger under the foundation. To learn more, visit hyperledger.org
Sign up for the monthly Hyperledger Horizon & /dev/weekly newsletters
By signing up, you acknowledge that your information is subject to The Linux Foundation's Privacy Policy
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study: Inventory Management Practices at Walmart
Case Study: Inventory Management Practices at Walmart
About walmart.
Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. is the largest retailer in the world, the world’s second-largest company and the nation’s largest nongovernmental employer. Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. operates retail stores in various retailing formats in all 50 states in the United States. The Company’s mass merchandising operations serve its customers primarily through the operation of three segments. The Wal-Mart Stores segment includes its discount stores, Supercenters, and Neighborhood Markets in the United States. The Sam’s club segment includes the warehouse membership clubs in the United States. The Company’s subsidiary, McLane Company, Inc. provides products and distribution services to retail industry and institutional foodservice customers. Wal-Mart serves customers and members more than 200 million times per week at more than 8,416 retail units under 53 different banners in 15 countries. With fiscal year 2010 sales of $405 billion, Wal-Mart employs more than 2.1 million associates worldwide. Nearly 75% of its stores are in the United States (“Wal-Mart International Operations”, 2004), but Wal-Mart is expanding internationally. The Group is engaged in the operations of retail stores located in all 50 states of the United States, Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Japan, Puerto Rico and the United Kingdom, Central America, Chile, Mexico,India and China.

Walmart Inventory Management
Wal-Mart had developed an ability to cater to the individual needs of its stores. Stores could choose from a number of delivery plans. For instance, there was an accelerated delivery system by which stores located within a certain distance of a geographical center could receive replenishment within a day. Wal-Mart invested heavily in IT and communications systems to effectively track sales and merchandise inventories in stores across the country. With the rapid expansion of Wal-Mart stores in the US, it was essential to have a good communication system. Hence, Wal-Mart set up its own satellite communication system in 1983. Explaining the benefits of the system Walton said, “I can walk in the satellite room, where our technicians sit in front of the computer screens talking on the phone to any stores that might be having a problem with the system, and just looking over their shoulders for a minute or two will tell me a lot about how a particular day is going. On the screen, I can see the total of the day’s bank credit sales adding up as they occur. If we have something really important or urgent to communicate to the stores and distribution centers, I, or any other Wal-Mart executive can walk back to our TV studio and get on that satellite transmission and get it right out there. I can also go every Saturday morning around three, look over these printouts and know precisely what kind of work we have had.”
Wal-Mart was able to reduce unproductive inventory by allowing stores to manage their own stocks, reducing pack sizes across many product categories, and timely price markdowns. Instead of cutting inventory across the board, Wal-Mart made full use of its IT capabilities to make more inventories available in the case of items that customers wanted most, while reducing the overall inventory levels. Wal-Mart also networked its suppliers through computers. The company entered into collaboration with P&G for maintaining the inventory in its stores and built an automated reordering system, which linked all computers between P&G and its stores and other distribution centers. The computer system at Wal-Mart stores identified an item which was low in stock and sent a signal to P&G. The system then sent a re-supply order to the nearest P&G factory through a satellite communication system. P&G then delivered the item either to the Wal-Mart distribution center or directly to the concerned stores. This collaboration between Wal-Mart and P&G was a win-win proposition for both because Wal-Mart could monitor its stock levels in the stores constantly and also identify the items that were moving fast. P&G could also lower its costs and pass on some of the savings to Wal-Mart due to better coordination.
Employees at the stores had the ‘Magic Wand,’ a hand-held computer which was linked to in-store terminals through a radio frequency network. These helped them to keep track of the inventory in stores, deliveries and backup merchandise in stock at the distribution centers. The order management and store replenishment of goods were entirely executed with the help of computers through the Point-of-Sales (POS) system. Through this system, it was possible to monitor and track the sales and merchandise stock levels on the store shelves. Wal-Mart also made use of the sophisticated algorithm system which enabled it to forecast the exact quantities of each item to be delivered, based on the inventories in each store. Since the data was accurate, even bulk items could be broken and supplied to the stores. Wal-Mart also used a centralized inventory data system using which the personnel at the stores could find out the level of inventories and the location of each product at any given time. It also showed whether a product was being loaded in the distribution center or was in transit on a truck. Once the goods were unloaded at the store, the store was furnished with full stocks of inventories of a particular item and the inventory data system was immediately updated.
Wal-Mart also made use of bar coding and radio frequency technology to manage its inventories. Using bar codes and fixed optical readers, the goods could be directed to the appropriate dock, from where they were loaded on to the trucks for shipment. Bar coding devices enabled efficient picking, receiving and proper inventory control of the appropriate goods. It also enabled easy order packing and physical counting of the inventories. In 1991, Wal-Mart had invested approximately $4 billion to build a retail link system. More than 10,000 Wal-Mart retail suppliers used the retail link system to monitor the sales of their goods at stores and replenish inventories. The details of daily transactions, which approximately amounted to more than 10 million per day, were processed through this integrated system and were furnished to every Wal-Mart store by 4 a.m., the next day. In October 2001, Wal-Mart tied-up with Atlas Commerce for upgrading the system through the Internet enabled technologies. Wal-Mart owned the largest and most sophisticated computer system in the private sector. The company used Massively Parallel Processor (MPP) computer system to track the movement of goods and stock levels. All information related to sales and inventories was passed on through an advanced satellite communication system. To provide back-up in case of a major breakdown or service interruption, the company had an extensive contingency plan. By making effective use of computers in all its company’s operations, Wal-Mart was successful in providing uninterrupted service to its customers, suppliers, stockholders and trading partners.
Related posts:
- Case Study: Supply Chain Management of Walmart
- Case Study: How Walmart Enhances Supply Chain Management with ERP Initiatives?
- Case Study: Why Walmart Failed in Germany?
- Inventory Management Practices in Multinational Corporations
- Case Study of Walmart: Procurement and Distribution
- Case Study: Analysis of Performance Management at British Petroleum
- Case Study: Quality Management System at Coca Cola Company
- Case Study of Burger King: Achieving Competitive Advantage through Quality Management
- Inventory Management Concepts in Supply Chain Management
- Inventory Management
One thought on “ Case Study: Inventory Management Practices at Walmart ”
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To prepare for your Walmart product management case interviews, it's crucial that you research the history of the company and its product portfolio. You need to understand the company's values, mission, and vision. You'll also need to know about the products that Walmart sells, the trends in the retail industry, and the target audience that the ...
Walmart PM salaries depend on the seniority level and department. Here are a few sample salaries pulled directly from job listings on Walmart's website: Product Manager III: $90,000-$180,000. Manager, Product Development - Women's Fashion: $108,000-$216,000. Senior Product Manager: $117,000-$234,000.
Conclusion. In conclusion, Walmart's business strategy is that of an growing Omnichannel marketplace, a multifaceted approach that combines physical and digital retail, competitive pricing, supply chain excellence, and a commitment to customer satisfaction. Understanding these elements provides insights into the retail giant's enduring ...
Going digital is a top priority—which is why Walmart recently paid $3 billion to acquire e-tailer Jet.com. But the company also wants to strengthen the in-store experience. "The reality ...
Walmart Inc. successfully addresses the strategic concerns in the 10 decision areas of operations management, optimizing efficiency and productivity. (Photo: Public Domain) Walmart Inc.'s operations management involves a variety of approaches that are focused on managing the supply chain and inventory, as well as sales performance.
Walmart Change Management Case Study. Tahir Abbas March 5, 2023. Change management is an essential aspect of any business that seeks to remain competitive in a dynamic market environment. Walmart, one of the world's largest retail giants, has had to navigate through significant changes in the retail industry, including the growth of e ...
This case describes Walmart's omnichannel strategy in 2018 as it battled Amazon for online retail market share. The case discusses Walmart's early forays into online retail, as well as its 2018 strategy, which aimed to integrate Walmart's enormous brick and mortar footprint with its growing ecommerce business, e.g., through merchandise and grocery delivery and order online, pickup in store ...
To make it faster and easier to place pickup or delivery orders, we created a tab in the app called My Items. The My Items tab automatically organizes customers' preferred items into categories, like dairy and eggs, pantry, beauty, and more — like having a curated store to shop from within Walmart. We design with the customer journey in mind.
structural features of Walmart's business model and their profit implications. In this study, we use the conceptual framework developed by Casadesus-Masanell and Ricart (2010). According to them, a business model is composed of two types of element: choices made by the management and the consequences of these choices. There
Combining the Walmart case with the "Amazon.com: Supply Chain Management" case (W18451) in back-to-back classes provides a powerful illustration of the differences between two leading companies and demonstrates the importance of alignment of supply chain competencies with organizational strategy. After completion of this case, students will be ...
Walmart (NYSE: WMT), the largest physical retailer based in the United States, has achieved enormous growth over the years through its EDLP pricing strategy and a customer-friendly brand image. In recent years, the company has focused on digitalization to grow sales and improve customer service. Its e-commerce sales have continued to strengthen worldwide.
Walmart has offered a larger product assortment with a low price ... Walmart's management staff can a ccess the ... A longitudinal case study of Amazon's financial situation during the 2016 ...
Walmart was the first company in the world to use barcodes on 100% of its products, way back in 1983. In 2015 alone it spent $10.5 billion on IT, a lot even for a company that booked $486 billion of revenue that year. And nothing has changed. In 2021, Walmart CFO Brett M. Biggs said, "From a position of great strength, we're now going to ...
Optimizing Walmart's Outbound Supply Chain from Strategy to Execution - A Grocery Case Study. On July 2, 1962, the first Walmart store opened in Rogers, Arkansas, with a strategy to build it on an unshakeable foundation: the lowest prices anytime, anywhere. In the 1980s, the first Walmart Supercenter opened, combining a supermarket with ...
Key Strategies for Acing Case Studies. Here are proven strategies to shine in your PM case study interview: Research the company: Review their products, customers, domain etc. Helps tailor your approach to their context. For example, studying an ecommerce company's key metrics will allow you to anchor examples and data points in their specifics.
We curated 50 product management case studies that will help you improve as a product manager in different stages of your career. airbnb. 50 Product Management Case Studies. Producter is a product management tool designed to become customer-driven. It helps you collect feedback, manage tasks, sharing product updates, creating product docs, and ...
Retail supply chains bring quality, affordable products to consumers around the world. Sustainable, regenerative practices create value for companies and for society by increasing supply chain resilience and efficiency, improving product availability and quality, mitigating risk, and creating opportunities for workers.
A Case Study of Wal-mart's 'Green' Supply Chain Management by Adam Heying and Whitney Sanzaro. Apicsterragrande. May 2009. 7. Supply Chain. ASA Research. 2010. 8. Criticism of Walmart. Wikipedia. Company's often poor but legal labor etc. relations: a detailed treatment. 9. Wal-mart Financial Results. MSN. Financial reports 2007-2011. 10.
In this context, Walmart, the world's largest retailer, has demonstrated a highly successful and integrated Walmart supply chain, propelling its growth and dominance in the retail industry. This case study aims to delve into the significance of supply chain capability for enhancing a company's competitiveness and how it serves as a ...
Discover how Walmart is revolutionizing food traceability using blockchain technology. By implementing a Hyperledger Fabric-based system, Walmart has reduced the time it takes to trace the provenance of products from days to seconds, enhancing transparency and safety in the food supply chain. Read the Walmart case study now.
In 1991, Wal-Mart had invested approximately $4 billion to build a retail link system. More than 10,000 Wal-Mart retail suppliers used the retail link system to monitor the sales of their goods at stores and replenish inventories. The details of daily transactions, which approximately amounted to more than 10 million per day, were processed ...
In terms of workforce, a 2018 study conducted on 7,000 employees sho wed that half of their. employees worked part-time at their stores, the industry standard is around 30% as opposed to. Walmart ...
Natural Resource Management and Policy: Drought Assessment, Management, and Planning: Theory and Case Studies: Theory and Case Studies (Hardcover) Free shipping Free 90-day returns
The project management lifecycle is a step-by-step framework of best practices used to shepherd a project from its beginning to its end. This project management process generally includes four phases: initiating, planning, executing, and closing. Some may also include a fifth "monitoring and controlling" phase between the executing and ...