- WORK WITH ME
- CURATED NEWSLETTER
- SLOW LOOKING CLUB

Writing through art: 9 ways art can make you a better writer
- by Claire Bown
- April 14, 2021 January 8, 2022

Writing through Art: 9 Ways Art can Make you a Better Writer
Throughout the ages, looking at art has been a unique way of finding inspiration and creativity. if you go as far back as the greeks, you can find examples of writing inspired by art, called ekphrasis, which means “a literary description of or commentary on a visual work of art” art is a frequent source of inspiration for many writers and poets over the centuries. john keats’ “ode on a grecian urn” is a famous example and william blake said that poetry and art are ‘ways to converse with paradise’., but how does this work for us, mere mortals with a keen interest in improving our creative or reflective writing in this week’s blog i’m exploring 9 ways looking at and discussing art can make you a better writer., #1 slow down, art invites us to slow down and look closely at what we see. art and creative works are made to engage and hold our attention. developing the practice of slow looking will help you to notice more – how you can be more attentive to your environment, see beyond your first impressions and look a little deeper. looking slowly and carefully naturally asks us to reflect, wonder and ponder – and this reflection leads to new insights and ideas. these new perspectives offer us rich and deep material for writing too., #2 train your eye, looking at and discussing art improves your visual acumen and makes you more alert, aware and attentive to details in all aspects of your personal and work life. if you practice looking at art regularly, your observation skills will noticeably improve. your ability to describe and use descriptive language will also get better, as you notice more details and find more precise ways to describe what you see., #3 make interpretations, once we have fully observed the artwork, we can then begin to make interpretations or inferences about what is happening. this interpretation draws on the observations and invites us to think about what we’ve already seen and observed. we often ask ‘what do you think is going on’ or ‘what is the story here’. this part is about thinking creatively and coming up with plausible ideas and hypotheses about the artwork.the observation and interpretation parts leave participants buzzing with ideas and thoughts and this provides a perfect springboard for writing prompts or exercises., #4 develop vocabulary and descriptive language, when we describe an artwork we are often using descriptive language to try and evoke an image of the artwork in someone’s mind. descriptive writing makes use of precise language – the right noun, adjective or verb that will give life to the image you are describing in someone’s mind. i will often ask participants to look for categories of words when observing and describing artworks too – nouns, adjectives, verbs or to be as specific and descriptive as possible when describing colours, shapes and lines – as if they are describing them to someone who is on the telephone. participants can also make long, descriptive inventories of the artwork in the observation stage. descriptive language also makes use of the senses (see below) and figurative language – colour, symbol, image and creative comparisons are good thinking routines to use with artworks to encourage metaphorical thinking., #5 learn how to engage with different perspectives, once participants have observed and analysed the artwork in question, they can then choose the artist, or a person, object or animal in the image to ‘step inside’ they can then engage in discussion or writing from the perspective of that character – literally stepping inside their shoes and seeing things through their eyes. through this process, participants can consider different experiences and viewpoints that they discover through ‘stepping inside’ a character., #6 inspiration, taking yourself off to a museum, or going online to take part in an art discussion will allow you to get out of a rut and get inspired. immerse yourself in some artworks. think about what might be happening. let your eyes and your mind wander freely. choose artworks that you are curious about or ones that draw you in. looking at art slowly and carefully – either on your own or as part of a group discussion- can dissolve writer’s block and will foster creativity, #7 improve our sensory perception, looking at art stimulates the senses in many ways and can help us to work on our descriptive language skills. stepping inside an image and being able to describe what you saw, heard, smelt, felt and tasted is a good way to brainstorm ideas for sensorial description. or write down 50 words for each artwork you look at, with 10 in each sensory category. being able to describe how something tastes, smells, sounds, or feels rather than the way it looks, will bring your writing to life., #8 precision, looking and discussing art often involves the skills of a detective to investigate, find out and discover answers to questions. every artwork is full of mystery, intrigue and adventure – the artists and their subjects. using art as a prompt for writing exercises is a good way to keep asking questions, questions that you can use in your own writing to dig a bit deeper and wonder aloud., #9 develop critical thinking, looking at art allows you to observe the world more closely. art is frequently detailed, complex and packed with multiple meanings. this process of observation and interpretation teaches you to look more closely and analyse the world around you —skills that form the basis of critical thinking. good writing comes out of good thinking. and artworks are good things to think about., interested in learning how to use art to inspire creative and reflective writing, join us for my new 4 part mini-course ‘art and words’ starting online on 22 april 2021., this online course uses artworks as the inspiration and prompt for creative and reflective writing., it is intended for both educators, creatives and writers who would like to use art to inspire and drive their writing and those of others, too. find out more about art and words via the button below. , privacy overview.

What it Means to Sell to the T..
Inspire thoughtful creative writing through art, important factors to consider ...
- by John McGill
- Artists Featured Articles Galleries & Fairs Marketing Tips Tips

There are many ways to boost your creative writing performance However, the most effective and sophisticated of them is to inspire thoughtful, creative writing through art. The process listed below is a way to make any creative writing process thoughtful and make any creative text meaningful. Read on to find out how art could influence your writing in unexpected ways to make them brilliant and unlike others.
What is creative writing?
Before exploring the peculiarities of inspiring thoughtful creative writing through art, let’s take a closer look at the term creative writing. Here are some vital elements that define creative writing:
This element can be considered fuel for an entire plot. Usually, readers choose a character to sympathize with or anticipate him or her. And, generally, readers also identify themselves with a particular character subconsciously.
- Scene and surroundings:
When you tell a particular story or describe something with creative writing, it requires specific settings and surroundings. Depending on the plot, there may be only one scene or several of them. It is always necessary to present to the reader at least one scene that is described very well so the reader can imagine it easily.
This is a core element of any creative writing, be it a novel, a play, a poem, or a book. The plot usually has an ark that sets the whole story from introduction to end. Plots are something you cannot ignore; without them, the entire story is not possible.
Readers must spectate something that is going on between several characters personally or between one character and circumstances. The conflict sharpens everything and makes the plot catching.
Everywhere you go, it’s all about style — and writing is no exception. It is ephemeral but an essential element of creative writing. For famous world-renown authors, their style is the same as their unique fingerprint or signature they leave on their books for fans. You cannot underestimate the meaning of style. For published authors, their style is a reason why people buy the books they create. Compare the writings of Stephen King and Ernest Hemingway, and see the style of creative writing of both those fantastic personalities. The styles are completely different, but you can read their style in each paragraph.
- Point-of-view:
In simple words, they, you, or I can tell a story. In other words, in the first, second, or third person. This can be a vital element for some creative writing pieces, and for others, it is not. However, in my opinion, the easiest way is to narrate from the first person, as the personal opinion of the author.

Photo by: Sixteen Miles Out, Unsplash
Core elements of creative writing
Assuming the list above, you need to be very open-minded in practicing thoughtful creative writing. It may be challenging at first, but as you progress, you will learn there are stages to creating a well-written piece. Any art masterpiece can be taken as a source of inspiration to activate your creativeness. There are four core elements, combine them and you will be able to achieve thoughtful, creative writing through art:
1. Observation
Art teaches people to observe patiently by slowing down their daily routine to find more profound meaning. Train yourself to compile your creative writing goals with the process of observation. Try to stop and think out-of-the-box when observing a particular piece of art. For example, if it is a painting, try to explore more of the details (if we are talking about paintings). Does the image contain people or mysterious characters, mythology elements, etc.? Depending on what kind of creative writing you are working on, choose pieces that create a particular mood.
When observing a painting, you need to ask yourself various questions that will stimulate your writing afterward. For example, what are the first five words coming to your mind when you see this painting? How do the color combinations make you feel? How did the artist use a focal point of the painting to draw your attention? If there are some unusual elements, then what do they symbolize? Imagine yourself getting inside the painting, which you are observing. What do you feel about being there? Can you imagine yourself staying here forever? If there would be sounds or smells inside the world you see in the picture, how could you describe them? Write down all your assumptions and thoughts. Be as much open-minded as possible. Do not try to analyze your thoughts and feelings at this stage.
2. Interpreting
Thoughtful, creative writing through art will be impossible without interpreting your thoughts after your art exploration. A good question to ask yourself is “What is going on because of things I observed?” and “Why do I feel the way I feel?” These two questions lie at the core of the creative writing process, and after you answer them, they will lead you to new plateaus in your creativity. Give yourself time to understand and interpret everything related to the artwork, don’t rush yourself, and be patient with your thoughts and feelings. Think over the reasons and variants of everything you understand as part of your creative writing process.
3. Communicating
Now you are ready to communicate your thoughts to others. It would help if you had a community of like-minded people who are willing to develop thoughtful, creative writing through art the same way that you are. Explain your ideas after completing the stages of observing and interpreting, be open, and share everything you want. Remember that the core of creativeness lies in an open mind and critical thinking. After the previous two stages, people are usually full of various thoughts and ideas, and you’ll likely feel the explosion of more ideas after sharing them. Communication is a key to success when it comes to creativeness. Trying to verbalize what you have achieved after diving into a particular piece of art in conversation can lift your interpretation to the next level.

Photo by: Arash Asghari, Unsplash
4. Creating
Now it is time to dedicate time to thoughtful, creative writing itself. Here are some practical exercises that may be useful:
- Explain characters from the perspective of the protagonist and antagonist’s ideas; define essential values of their personalities and behavior.
- Pretend you are not a human, but a tree, a pattern, a piece of art, and describe your thoughts and feelings while playing this unexpected role.
- Imagine telling the story by another person, not you; how will the narrative change in such a situation?
- Create unexpected dialogues that could change the whole plot by making an unexpected twist.
- Describe the behavior of characters through their motives and the prerequisites defined by their previous life experience.
- Imagine that you have to persuade another person that your beliefs and thoughts are correct.
Using art to inspire thoughtful creative writing is an effective way to lift your writing performance to the next level. Before you start practicing creative writing, you need to understand what creative writing is and which core elements it contains. Among those elements are style, plot, character, scenery, conflict, and other vital parts that define this vast term.
It can be very rewarding to widen your vision and influence the outcome of your creative writing by using art as inspiration. It is easy to start by simply observing a piece of art, for example, a painting. Recall all the feelings arising in your soul and remember them. Do not analyze anything at this stage. Allow the following stage for interpreting and understanding your feelings and thoughts on the art. Then try discussing and interacting with other people to refine your idea further. The final stage will be you putting it into practice in your creative writing.
About the author:
John McGill is a professional author of a lead paper writing service essayshark.com and creative writing tutor. My hobby is Antic philosophy and a favorite modern author is Stephen King.
John McGill
Related post.

The Power of Art: Does Art Really Change the World We Live In?

Is Writing an Art Form?

P.O.W.E.R. and Art Unite
Click here to cancel the reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
ARTEXPO NEW YORK 2024

ABN Subscribe

THE REDWOOD ART COLLECTIVE

[ Skip to content ] [ Skip to main navigation ] [ Skip to quick links ] [ Go to accessibility information ]
Learning resources
Use art to inspire poetry and creative writing
KS3 (ENG) , KS4 (ENG) , KS3 (NI) , KS4 (NI) , CfE L4 (SCO) , CfE L3 (SCO) , KS3 (WAL) , KS4 (WAL) , KS5 (ENG) , KS5 (NI) , CfE Sen. (SCO) , KS5 (WAL)
Cubism , Pre‐Raphaelitism , Post‐Impressionism , Figurative art , Abstraction
Reading and writing , Literature , Self portraits
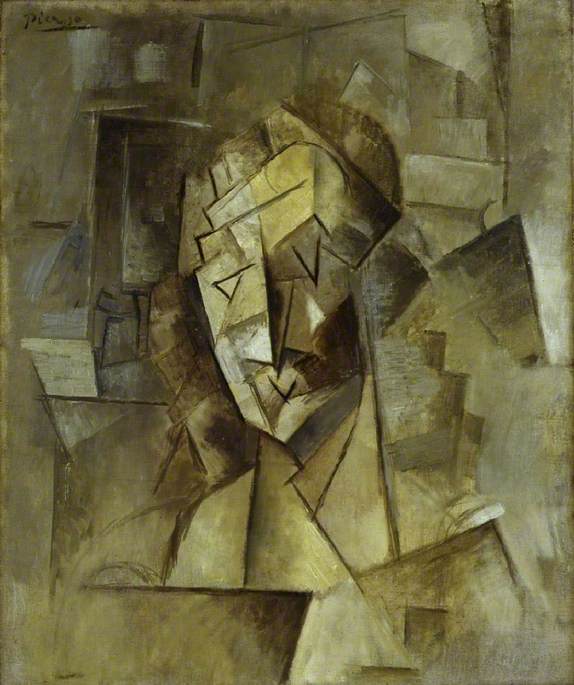

Cubist Head (Portrait of Fernande) c.1909/1910
Pablo Picasso (1881–1973)
About this resource
How can we use art for creative writing inspiration?
This resource suggests ideas for using artworks as the starting point or inspiration for a poetry or creative writing project.
Use it to explore:
- poets and poetry inspired by art
- artworks on Art UK to use as a starting point for creative writing projects
- suggestions for looking closely at an artwork
- ideas for planning a creative written response to an artwork
The resource offers opportunities for cross-curricular study across English and Art & Design. The examples of artworks, related poems and activity ideas included in the resource can be used together as a lesson plan or as individual components to integrate into your own scheme of work. The resource is devised for KS 3/CfE Level 3 & Level 4 students but could also be suitable for Key Stage 4 and CfE senior phase students and 16+ learners.
See also our related resource: How can poetry be used to inspire art?
Curriculum links
Art and design
- Evaluate and analyse creative works - Actively engage in the creative process of art - Know about great artists and understand the historical and cultural development of their art forms
Reading Pupils should be taught to:
read and appreciate the depth and power of the English literary heritage through:
- reading a wide range of high-quality, challenging, classic literature. The range should include works from the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries; poetry since 1789.
understand and critically evaluate texts through:
- reading in different ways for different purposes, summarising and synthesising ideas and information, and evaluating their usefulness for particular purposes - drawing on knowledge of the purpose, audience for and context of the writing, including its social, historical and cultural context and the literary tradition to which it belongs, to inform evaluation - identifying and interpreting themes, ideas and information - seeking evidence in the text to support a point of view, including justifying inferences with evidence - distinguishing between statements that are supported by evidence and those that are not, and identifying bias and misuse of evidence - analysing a writer’s choice of vocabulary, form, grammatical and structural features, and evaluating their effectiveness and impact - make an informed personal response, recognising that other responses to a text are possible and evaluating these.
Pupils should be taught to:
write accurately, fluently, effectively and at length for pleasure and information through:
- adapting their writing for a wide range of purposes and audiences - selecting, and using judiciously, vocabulary, grammar, form, and structural and organisational features, including rhetorical devices, to reflect audience, purpose and context, and using Standard English where appropriate - make notes, draft and write, including using information provided by others [e.g. writing a letter from key points provided; drawing on and using information from a presentation]
Grammar and vocabulary
consolidate and build on their knowledge of grammar and vocabulary through:
- studying their effectiveness and impact in the texts they read - drawing on new vocabulary and grammatical constructions from their reading and listening, and using these consciously in their writing and speech to achieve particular effects - analysing some of the differences between spoken and written language, including differences associated with formal and informal registers, and between Standard English and other varieties of English - using linguistic and literary terminology accurately and confidently in discussing reading, writing and spoken language.
KS 4 - Develop ideas through investigations, demonstrating a critical understanding of sources - Record ideas, observations and insights relevant to intentions as work progresses - Present a personal and meaningful response that realises intentions and demonstrates an understanding of visual language
English literature
Students should be able to:
- read and understand poetry - respond to poems critically and imaginatively - select and evaluate relevant textual material - use details from poems to illustrate interpretations - explain and evaluate the ways in which the poets express meaning and achieve effects - relate the poems to their social, cultural and historical contexts English Language Writing for purpose and audience Students should be able to: - write accurately and effectively - use an appropriate writing form - express ideas and/or information precisely and accurately - select vocabulary to persuade and/or inform the reader - use accurate grammar, spelling and punctuation Speaking and listening Students should be able to: - communicate clearly and effectively - present information and ideas - use standard English as appropriate - structure and sustain talk - choose and adapt language appropriate to an audience - respond appropriately to questions and views of others - interact with others - make a range of effective contributions - express ideas clearly, accurately and appropriately - listen and respond to others' ideas and perspectives - challenge what they hear where appropriate and shape meaning through asking questions and making comments and suggestions
Studying spoken and written language
Students should be able to: - understand the characteristics of spoken language - understand influences on spoken language choices - explore the impact of spoken language choices - understand how language varies in different contexts; - read and understand texts - understand how meaning is constructed - recognise the effect of language choices and patterns - evaluate how texts may be interpreted differently depending on the reader's perspective - explain and evaluate how writers use linguistic and presentational features to sustain the reader's interest Personal creative writing
Students should be able to: - write clearly and fluently (as well as imaginatively, if appropriate) - organise ideas to support coherence - use an appropriate writing form - select vocabulary appropriate to the task to engage the reader - use a range of sentence structures for effect - use accurate grammar, spelling and punctuation Reading Literary and Non-fiction Texts Students should be able to: - read and understand texts - understand how meaning is constructed - recognise the effect of language choices and patterns - select material appropriate to purpose - evaluate how texts may be interpreted differently depending on the reader's perspective - explain and evaluate how writers use linguistic and presentational features to sustain the reader's interest.
Level 4 - I can analyse art and design techniques, processes and concepts, make informed judgements and express considered opinions on my own and others' work (EXA 4-07a)
Literacy and English
Listening and talking
- When I engage with others I can make a relevant contribution, ensure that everyone has an opportunity to contribute and encourage them to take account of others’ points of view or alternative solutions. I can respond in ways appropriate to my role, exploring and expanding on contributions to reflect on, clarify or adapt thinking (LIT 4-02a) - As I listen or watch, I can clearly state the purpose and main concerns of a text and make inferences from key statements; compare and contrast different types of text; gather, link and use information from different sources and use this for different purposes (LIT 4-04a) - As I listen or watch, I can make notes and organise these to develop thinking, help retain and recall information, explore issues and create new texts, using my own words as appropriate (LIT 3-05a / LIT 4-05a) - I can show my understanding of what I listen to or watch by giving detailed, evaluative comments, with evidence, about the content and form of short and extended texts (LIT 4-07a) - When listening and talking with others for different purposes, I can: communicate detailed information, ideas or opinions; explain processes, concepts or ideas with some relevant supporting detail; sum up ideas, issues, findings or conclusions (LIT 4-09a)
- Through developing my knowledge of context clues, punctuation, grammar and layout, I can read unfamiliar texts with increasing fluency, understanding and expression (ENG 2-12a / ENG 3-12a / ENG 4-12a) - I can make notes and organise them to develop my thinking, help retain and recall information, explore issues and create new texts, using my own words as appropriate (LIT 3-15a / LIT 4-15a) - To show my understanding, I can give detailed, evaluative comments, with evidence, on the content and form of short and extended texts, and respond to different kinds of questions and other types of close reading tasks (ENG 4-17a) - I can: discuss and evaluate the effectiveness of structure, characterisation and/or setting using some supporting evidence; identify how the writer’s main theme or central concerns are revealed and can recognise how they relate to my own and others’ experiences; identify and make a personal evaluation of the effect of aspects of the writer’s style and other features appropriate to genre using some relevant evidence and terminology (ENG 4-19a)
- I enjoy creating texts of my choice and I am developing my own style. I can regularly select subject, purpose, format and resources to suit the needs of my audience (LIT 3-20a / LIT 4-20a) - As appropriate to my purpose and type of text, I can punctuate and structure different types of sentences with sufficient accuracy, and arrange these to make meaning clear, showing straightforward relationships between paragraphs (LIT 3-22a / LIT 4-22a) - Throughout the writing process, I can review and edit my writing independently to ensure that it meets its purpose and communicates meaning clearly at first reading (LIT 4-23a) - I can justify my choice and use of layout and presentation in terms of the intended impact on my reader (LIT 4-24a) - I can use notes and other types of writing to generate and develop ideas, retain and recall information, explore problems, make decisions, or create original text. I can make appropriate and responsible use of sources and acknowledge these appropriately (LIT 4-25a) - By considering the type of text I am creating, I can independently select ideas and relevant information for different purposes, and organise essential information or ideas and any supporting detail in a logical order. I can use suitable vocabulary to communicate effectively with my audience (LIT 3-26a / LIT 4-26a) - I can engage and/or influence readers through my use of language, style and tone as appropriate to genre (ENG 3-27a / ENG 4-27a) - I can create a convincing impression of my personal experience and reflect on my response to the changing circumstances to engage my reader (ENG 4-30a) - Having explored and experimented with the narrative structures which writers use to create texts in different genres, I can: use the conventions of my chosen genre successfully and/or; create an appropriate mood or atmosphere and/or; create convincing relationships, actions and dialogue for my characters (ENG 4-31a)
Art and design - Students use their knowledge about the work of other artists to enrich and inform their work through analysis and evaluation - Students evaluate their work through discussion
Learners should be given opportunities to:
- respond orally to continuous and non-continuous texts - respond orally to a variety of stimuli and ideas, including written and dynamic texts, e.g. paintings, music, film, still and moving images - communicate for a range of purposes, e.g. recount and present information, instruct, argue and explain a point of view, discuss an issue, persuade, question and explore interpretations, convey feelings - speak and listen individually, in pairs, in groups and as members of a class - present, talk and perform in formal and informal contexts and for a variety of audiences including teachers and peers - engage in activities that focus on words, their derivation, meanings, choice and impact - listen and view attentively, responding to a wide range of communication, e.g. written and dynamic texts, theatre and poetry performance, visiting speakers, explanations, instructions - speak clearly, using intonation and emphasis appropriately, e.g. recitation, oral storytelling - use appropriate vocabulary suitable for the situation or purpose - use appropriate vocabulary and terminology to discuss, consider and evaluate their own work and that of others, e.g. authors, peers
read a wide range of continuous and non-continuous texts, in printed and dynamic format, as a basis for oral and written responses. These should include:
– extracts and complete texts – traditional and contemporary poetry and prose – texts written by Welsh authors, texts with a Welsh dimension and texts from other cultures – texts that have challenging subject matter, which broaden perspectives and extend thinking – texts with a variety of structures, forms, purposes, intended audiences and presentational devices – texts that demonstrate quality and variety in language use – texts with a variety of social, historical and cultural contexts – texts that extend learners’ intellectual, moral and emotional understanding – texts with a variety of tone, e.g. irony, parody, word play, innuendo and satire
read individually and collaboratively, e.g. paired reading, guided group reading, shared reading
read for different purposes, e.g. for personal pleasure; to retrieve, summarise and synthesise key information; to interpret and integrate information; to verify information; to deepen understanding through re-reading; to identify language devices used by the writer to analyse purpose; to identify alternative readings of a text
develop appropriate vocabulary and terminology to discuss, consider and evaluate their own work and that of others, e.g. authors, poets, peers, in written and dynamic texts.
write for a variety of purposes, including to: – recount – inform – explain – argue/persuade – discuss/analyse – evaluate – narrate – describe – empathise
write in a range of continuous and non-continuous texts in a variety of forms
produce poetic writing, using imagery and poetic devices, e.g. rhyme and form
use a wide range of written and dynamic stimuli, e.g. stories, picture books, images, poems, experiences, film, paintings, music
use appropriate vocabulary and terminology to discuss, consider and evaluate their own work and that of others, e.g. authors, peers.
Expressive Arts
Exploring the expressive arts is essential to developing artistic skills and knowledge and it enables learners to become curious and creative individuals.
Progression step 5:
- I can investigate and analyse how creative work is used to represent and celebrate personal, social and cultural identities.
- I can independently research the purpose and meaning of a wide range of creative work and consider how they can impact on different audiences.
Responding and reflecting, both as artist and audience, is a fundamental part of learning in the expressive arts.
- I can critically and thoughtfully respond to and analyse the opinion and creative influences of others in order to independently shape and develop my own creative work.
- I can purposefully apply knowledge and understanding of context when evaluating my own creative work and creative work by other people and from other places and times.
- I can critically evaluate the way artists use discipline-specific skills and techniques to create and communicate ideas.
Languages, literacy and communication
Understanding languages is key to understanding the world around us
- I can listen empathetically, respecting different people’s perspectives and can critically evaluate them to arrive at my own considered conclusions.
- I can employ a range of strategies to recognise and predict the meaning across a wide range of texts and from this enhance my own expression and communication.
- I can use inference and deduction to gain in-depth understanding of complex texts, and can evaluate the reliability, validity and impact of what I read.
- I can use my knowledge of word construction, grammar , including syntax , and text organisation to support my understanding of what I hear and read.
- I can read empathetically to respect and critically evaluate different people’s perspectives, using them to arrive at my own considered conclusions.
- I can listen and read to build an extensive range of general and specific vocabulary, and I can use them with precision in different contexts.
Expressing ourselves through languages is key to communication
- I can convey meaning convincingly in a range of contexts so that the audience is fully engaged.
- I can make informed choices about vocabulary and grammar to enhance my communication skills
- I can reflect critically on my use of language and can consider the effects of my spoken, written and visual communication objectively.
- I can evaluate and respond critically to what I have heard, read or seen.
Literature fires imagination and inspires creativity
- I can engage with a wide range of literary genres in depth in order to explore and craft my own work.
- I can experiment with and craft my own literature.
- I can critically evaluate key concepts and the impact of language choices and techniques on the reader/viewer using an assured selection of relevant textual detail.
- I can appreciate literature, showing empathy when evaluating different interpretations of literature, including my own.
How to use this resource
1. Explore paintings and poetry
The first section of this resource introduces poems inspired by portraits, narrative paintings and abstract artworks.
Choose one or two of the paintings with accompanying poems to explore with your students. Look at the painting first, encouraging students to discuss what it shows and their response to it.
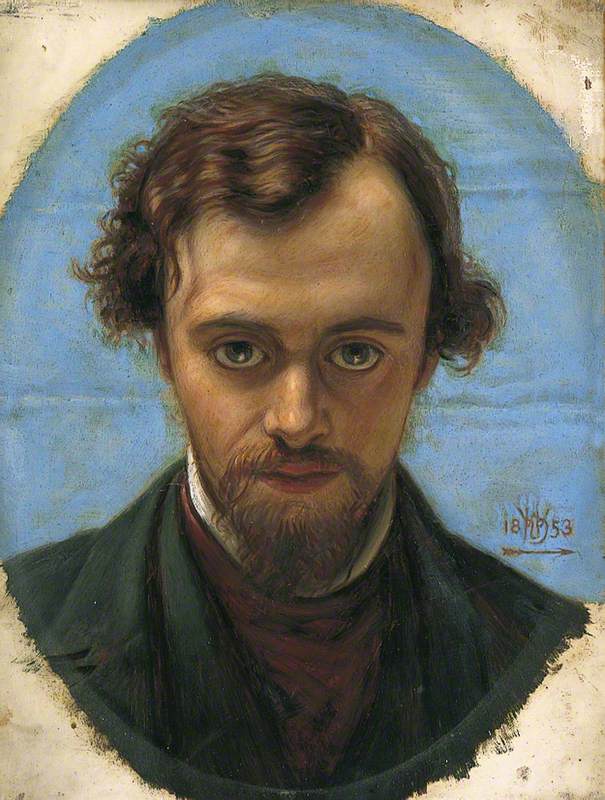

Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1828–1882) 1853
William Holman Hunt (1827–1910)
You could think about:
- what does the artwork look like?
- is it an abstract arrangement of shapes and colours or has the artist represented something from the visible world?
- is there a story, meaning or message in the work?
- what is the mood of the work and how does this affect your response?
- how has the artist used techniques such as brushstrokes or chisel marks? What colours have they used?
Then discuss how the poet has responded to the painting.
- What aspects of the painting have they focused on?
- What type of language have they used?
- Have they used the painting as a starting point to discuss bigger ideas or themes or to reflect upon issues that are personal to them?
2. Activity ideas and suggestions
The second section of the resource includes ideas and suggestions for responding through poetry or another form of creative writing to an artwork.
Did you know?
There is a dedicated term for poems inspired by artworks. Ekphrastic poetry is taken from the Greek word Ekphrasis , meaning to describe something in vivid detail.
Elizabeth Jennings and Rembrandt's late self-portraits
Rembrandt van Rijn was a seventeenth-century Dutch painter. During his long career, he painted over 90 self-portraits that record how he looked from youth to old age. (See additional self-portraits on the Rembrandt artist page on Art UK and watch a video to find out more.)
Rembrandt's self-portraits from old age are brutally honest, showing melancholy eyes staring out from sagging features and dishevelled hair and clothing.
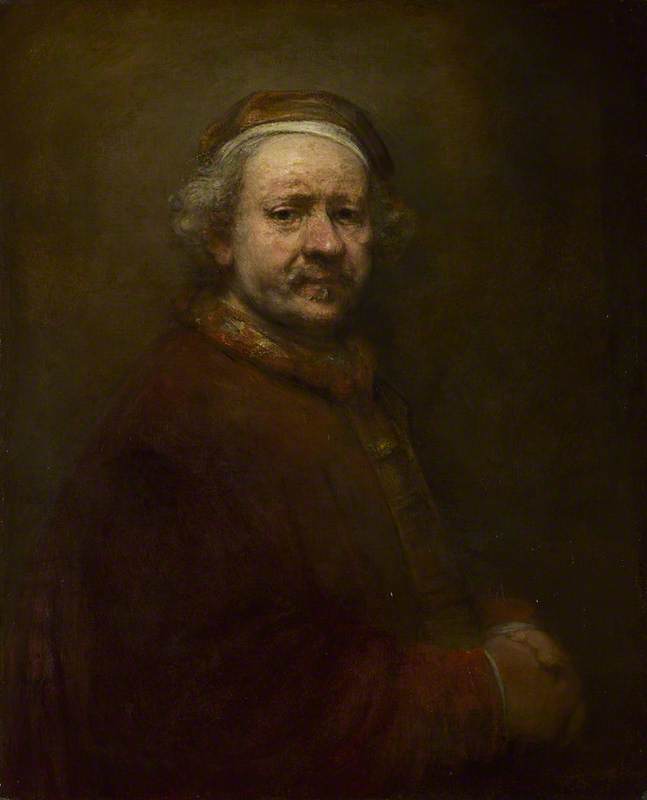

Self Portrait at the Age of 63 1669
Rembrandt van Rijn (1606–1669)
Poet Elizabeth Jennings responds to the self-portraits that Rembrandt painted in later life.
You are confronted with yourself. Each year The pouches fill, the skin is uglier. You give it all unflinchingly. You stare Into yourself, beyond. Your brush's care Runs with self-knowledge. Here
Is a humility at one with craft There is no arrogance. Pride is apart From this self-scrutiny.
Read the whole poem and listen to a recording of Elizabeth Jennings reading her poem
Explore an analysis of the poem
Raza Hussain and Holman Hunt's portrait of Dante Gabriel Rossetti (1828–1882)
In 2017, we challenged five young poets to create an original piece inspired by a painting of their choice from Art UK.
Birmingham-based spoken word artist and rapper Raza Hussain chose an 1853 portrait of Pre-Raphaelite artist Dante Gabriel Rossetti by William Holman Hunt .
Hussain sees the Pre-Raphaelites as rebels who wanted to implement change and Rossetti as 'an iconic and profound symbol of passionate creative madness – the kind to change perspectives – the kind to change the world'.
Find out more about the portrait and Raza Hussain's response to it .
Rowan MacCabe and Ethel Wright's 'Bonjour, Pierrot'
Rowan McCabe is another young poet commissioned to respond to a painting on Art UK as part of the Art Speaks challenge.
Bonjour, Pierrot is an imagined portrait, made in the early 1890s, of the character of Pierrot from French literature. Pierrot has held a fascination for many artists including Jean-Antoine Watteau and Pablo Picasso . The poet Rowan McCabe responds to this depiction of Pierrot by British portrait painter Ethel Wright and sees Pierrot in the painting as a sad figure, despite his clownish appearance.
McCabe has been affected by mental health issues and, for him, the painting is a reminder that people might seem silly and fun on the surface but can, in fact, be hiding issues relating to their mental health.
Find out more about the painting and Rowan McCabe's response to it
Explore more paintings by Ethel Wright
Narrative painting
A narrative painting is a painting that tells a story. The story could be from religion, literature, myth and legend or history. Or it could be a story of everyday life (often referred to as genre painting .)
Poetic responses to Titian's Diana and Actaeon
In 2012, The National Gallery in London invited 13 leading poets to respond to three paintings by Titian (c.1488–1576): Diana and Actaeon (1556–1559); The Death of Actaeon (about 1559–1575); and Diana and Callisto (1556–1559). The paintings depict stories from the epic poem Metamorphoses by the Classical poet Ovid , who lived from 43 BC to 17/18 AD.
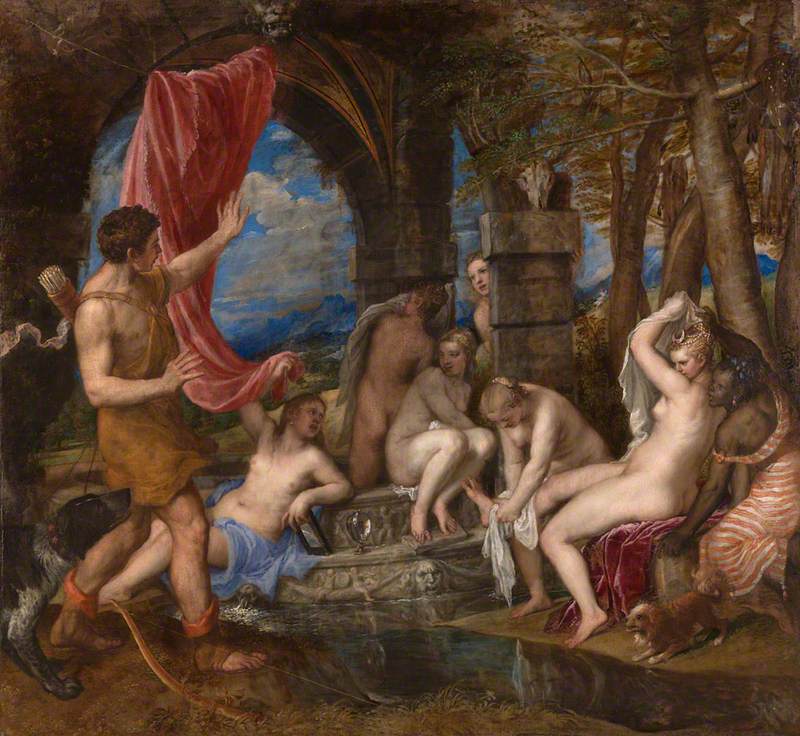

Diana and Actaeon 1556-1559
Titian (c.1488–1576)
The myth of Diana and Actaeon recounted in Metamorphoses tells the sad story of the hunter Actaeon who comes across Diana, the Roman goddess of hunting, while she is bathing with her escort of nymphs. The nymphs try to cover the naked Diana who, in a state of shock and embarrassment, splashes Actaeon. This splash turns Actaeon into a deer and he flees the scene. Tragically, however, his own hunting dogs don't recognise their master and attack and kill Actaeon.
Find out more about the paintings in the HENI Talks video on this artwork page
Patience Agbabi on Titian's 'Diana and Actaeon'
In this video poet Patience Agbabi reads her poem About Face inspired by Titian's painting Diana and Actaeon (1556–1559).
She imagines the thoughts and response of a Black nymph who is depicted standing beside Diana in the painting and helps to cover Diana from the gaze of Actaeon.
Hear more poets' responses to Titian's paintings on The National Gallery website
Sabrina Mahfouz and Ludolf Backhuysen's 'Boats in a Storm'
Ludolf Backhuysen 's painting, Boats in an Upcoming Storm with the Church of Zandvoort (1696) depicts a large sailing vessel, being buffeted by strong winds as it enters a harbour. Men on shore are pulling on a rope to steady her stern while other smaller boats come to the assistance of the distressed passengers.
British Egyptian poet Sabrina Mahfouz was drawn to the painting by its depiction of a storm, struck by the fact that something as still as a painting is able to capture such ferocious movement and activity.
Abstract art
E. E. Cummings and Cubism
American avant-garde poet E. E. Cummings was profoundly influenced by early twentieth-century art movements and the experiments with abstract style that Cubists and other modern artists were conducting. In 1913 he visited the International Exhibition of Modern Art in New York (also known as the Armory Show) where he saw work by artists including Pablo Picasso , Georges Braque , Henri Matisse , Paul Cézanne and Marcel Duchamp .
Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque's Cubist experiments revolutionised painting. In attempting to suggest the three-dimensionality of objects, landscapes and people by showing them simultaneously from different viewpoints they created fragmented, abstracted images.
E. E. Cummings was inspired by these fractured artworks and began to explore similar experimentation in his poetry. His poems became visual as well as verbal as he experimented with the form and arrangement of his words. (His poem r-p-o-p-h-e-s-s-a-g-r is a good example of this.)
Cummings begins his poem, Picasso , with the words:
'Picasso you give us Things which bulge: grunting lungs pumped full of thick sharp mind you make us shrill presents always shut in the sumptuous screech of simplicity'
The poem ends with:
'you hew form truly'
Read the full poem here
Anne Sexton and Vincent van Gogh's The Starry Night
Artist Vincent van Gogh is best known for his powerful portraits, flowers and landscapes painted using bold colours and loose brushstrokes that seem to whirl around the surface of his canvases.
The Starry Night, painted in 1889, shows the view from Van Gogh's room in the Saint-Paul-de-Mausole asylum where he was placed after a breakdown (during which he self-mutilated his ear). The view was painted just before sunrise and as well as the trees and hills and starry sky that he could see, Van Gogh added an imaginary village to the landscape.
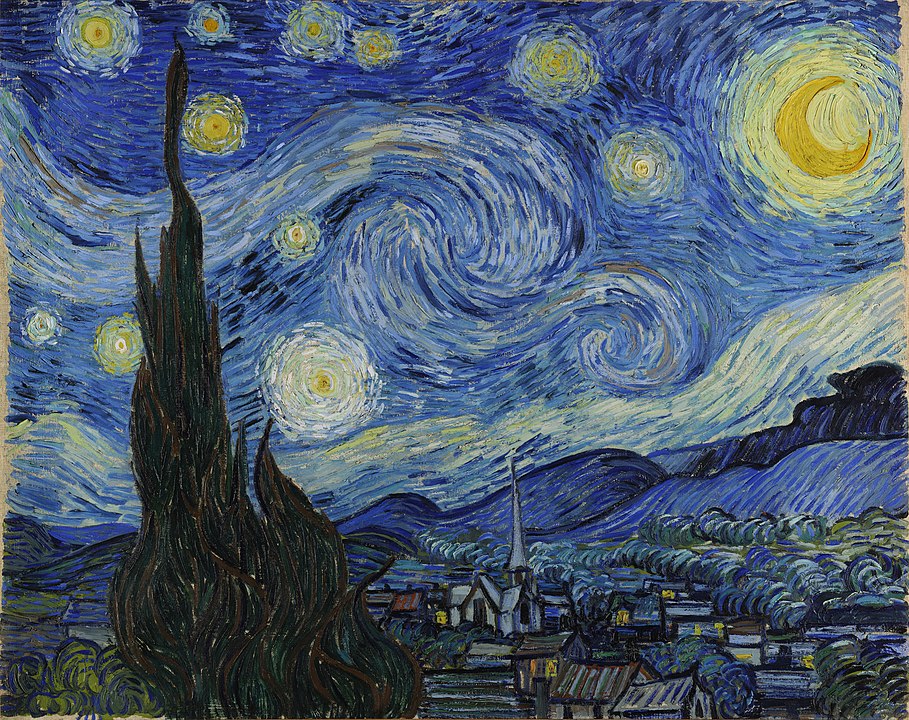

The Starry Night
1889, oil on canvas by Vincent van Gogh (1853–1890)
In her response to The Starry Night, poet Anne Sexton has managed to convey the powerful emotions as well as the loose abstracted style of Vincent van Gogh's painting.
'The town does not exist except where one black-haired tree slips up like a drowned woman into the hot sky The town is silent. The night boils with eleven stars. Oh starry starry night!'
Ann Sexton researched Van Gogh and read his letters before writing the poem and includes, as an epigraph to her poem, a line from a letter that Vincent van Gogh wrote to his brother.
'That does not keep me from having a terrible need of – shall I say the word – religion. Then I go out at night to paint the stars.'
In creating her response to the painting she imagines Vincent van Gogh thinking about religion and mortality.
Read the full poem here
See an analysis of the poem
Activity: write a poem inspired by an artwork
Now that you have explored a range of poems inspired by paintings, have a go at writing a poem or piece of creative writing inspired by an artwork.
This activity includes tips and suggestions for finding, looking at and creating a written response to an artwork.
Step 1: find an artwork to inspire you
If you are a teacher, task students with finding an artwork that inspires them as a homework project in advance of the class. They could choose an artwork from a local collection or find one on Art UK.
Use the tips below to find artworks on Art UK.
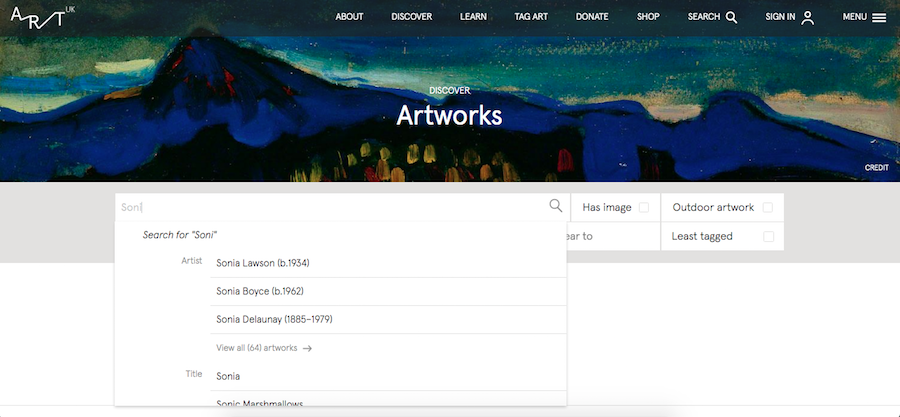
Search by artist
Look for an artist on Art UK. Start typing the artist's name into the search box on the Art UK artworks search page .
A list of artists will appear. Select the artist that you are interested in.
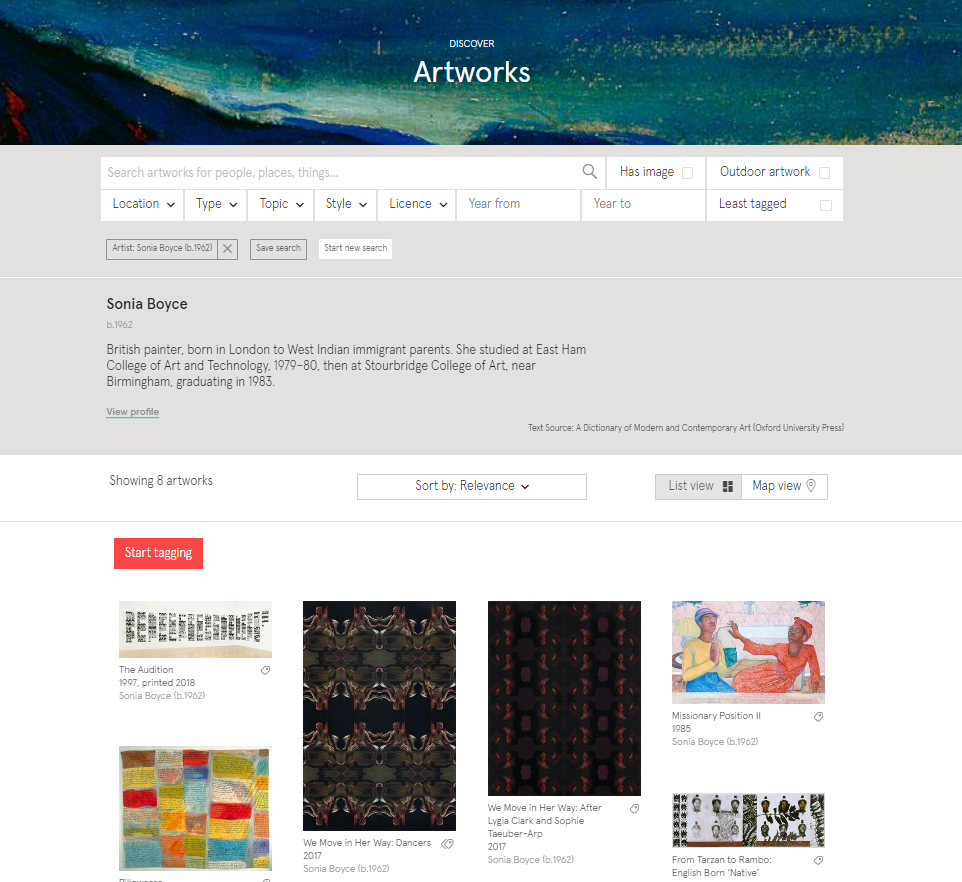
Screenshot of Art UK's artwork search page
You will be shown a list of artworks on Art UK by your selected artist. Browse these and choose an artwork to inspire your creative writing project.
Screenshot of Art UK's artworks search page, showing art by Sonia Boyce
- Go to the artworks search page to search by artist
Search by theme
You can also type a subject or theme into the search box. This could be anything from 'holiday' to 'celebrity' to 'football'. Once you've typed your theme, click the search icon or press return.
You will be shown a list of artworks relating to the keyword.
- Go to the artworks search page to search by theme
Another way to search by theme is to explore Topics on Art UK. We have gathered together a selection of artworks related to a wide range of themes from 'home and family' to the 'natural world'.
- Browse Topics
Search by location
If you'd like to find artworks in museums or galleries near you, use our venue search.
This will allow you to search by UK country and region to find a local gallery or museum and see the artworks that they hold.
- Search by country, region and venue
Be inspired using the artwork shuffle
If you are not sure what you're looking for (but will know when you see it!), use our artwork shuffle.
The artwork shuffle shows a random selection of artworks in different media from collections around the country.
If you don't see anything you like, shuffle again to see another selection.
- Inspire me with the artwork shuffle
Step 2: look closely at your artwork
Once you have found an artwork to inspire you, look closely at it. Note down your thoughts about the work and your feelings in response to it.
- What does the artwork look like?
- Is it an abstract arrangement of shapes and colours or has the artist represented something from the visible world?
- Is there a story, meaning or message in the work?
- What is the mood of the work and how does it affect your response?
- How has the artist used techniques such as brush strokes or chisel marks? What colours have they used?
In this video, created by The Grampian Hospitals Art Trust , writer Shane Strachan shares some useful ideas for looking closely at an artwork.
Step 3: plan and write your creative response
How are you going to respond to the artwork in your creative writing piece?
Your response could be a poem, a text, a memory or a form of your own invention. As well as what you see in the artwork (the imagery, colours and mark-making or use of materials) think about your own interpretation and your response to it.
- What does the artwork make you feel?
- Does it make you think of other things such as memories, places or people?
- Does the artwork tell or suggest a narrative or story?
- Are there any details or imagery within the artwork that draws you in?
- What do the colours, shapes and marks remind you of?
Research and be inspired by others
You could also research the artwork to inform and inspire your approach. Find out more about the artist and their ideas and techniques or research the subject depicted.
Be inspired by the approach of other writers. Revisit the poetry included in the first part of this resource.
Or read creative responses to artworks written by young people for our Write on Art competition.
- Write on Art: Ruby Langan-Hughes on The Broken Mirror by Jean-Baptiste Greuze
- Write on Art: Variaam Tratt on Preserve 'Beauty ' by Anya Gallaccio
- Write on Art: Aoife Hogan on Childen and Chalk Wall 3 by Joan Eardley
Writing art: inspiration and tips
In this second video from Grampian Hospitals Art Trust , writer Shane Strachan shares ideas and tips for responding to an artwork creatively in writing. He also shares his own poems inspired by artworks.
Watch the video and then get started on your own creative writing project!
Find out more
Do you know someone who would love this resource? Tell them about it...
More cubism resources.

- KS1 (ENG) KS2 (ENG) KS1 (NI) KS2 (NI) CfE L1 (SCO) CfE L2 (SCO) PS2 (WAL) PS3 (WAL)
More Reading and writing resources

- KS2 (ENG) KS2 (NI) CfE L2 (SCO) PS3 (WAL)

- KS3 (ENG) KS3 (NI) CfE L4 (SCO) CfE L3 (SCO) KS3 (WAL)

- KS2 (ENG) KS2 (NI) CfE L2 (SCO) PS3 (WAL) KS3 (ENG) KS4 (ENG) KS3 (NI) KS4 (NI) CfE L4 (SCO) CfE L3 (SCO) KS3 (WAL) KS4 (WAL) KS5 (ENG) KS5 (NI) CfE Sen. (SCO) KS5 (WAL)

- KS4 (ENG) KS4 (NI) CfE L4 (SCO) KS4 (WAL) KS5 (ENG) KS5 (NI) CfE Sen. (SCO) KS5 (WAL)

- KS1 (ENG) KS2 (ENG) KS1 (NI) KS2 (NI) CfE L1 (SCO) CfE L2 (SCO) PS2 (WAL) PS3 (WAL) KS3 (ENG) KS4 (ENG) KS3 (NI) KS4 (NI) CfE L4 (SCO) CfE L3 (SCO) KS3 (WAL) KS4 (WAL)

- KS2 (ENG) KS2 (NI) CfE L2 (SCO) PS3 (WAL) KS3 (ENG) KS3 (NI) CfE L3 (SCO) KS3 (WAL)

More Art UK resources

Third Mind: Creative Writing through Visual Art

Grades: all ages $19.95 paperback This anthology of essays about the challenges and rewards of uniting visual art and creative writing not only demonstrates how art can spark wonderful student writing, but goes much further, offering novel insights into the creative process. The 20 essays in Third Mind—by teachers, poets, writers, artists, and museum educators—provide ideas on a diverse array of artistic disciplines, among them, quilt-making, Chinese calligraphy, abstract painting, and photographic portraiture. The collection also features 18 gorgeous color plates and an extensive bibliography of works on visual art and creative writing.
Buy on Amazon
ISBN 0-915924-94-3
Creative Writing through the Arts
Creative Writing through the Arts is a three-year research programme that aims to provide evidence of the benefits of creative learning and teaching with and through the arts; specifically focussing on the development of children’s writing.
The Art Engager
Inspiring creative writing through art with mary hall surface.
Today I’m delighted to be talking to playwright, theatre director, teaching artist and museum educator Mary Hall Surface about her work. We’re talking all things creative and reflective writing through art.
As a museum educator, she uses both theatre and creative writing to expand perspective, uncover complexity, and deepen understanding.
She is the founding instructor of National Gallery of Art’s Writing Salon in Washington DC, and a six-summer faculty member of Harvard’s Project Zero Classroom. Her plays have been produced at major professional theatres, museums, and festivals throughout the US, Europe, Japan, Taiwan, and Canada, including 4 art-inspired productions at the National Gallery of Art.
During the pandemic, she has developed an online presence too - facilitating creative and reflective writing workshops and classes, all inspired by art for museums, schools, and arts centres throughout the US.
Mary Hall and I have a lot in common and in today’s chat we talk about our love of close looking, thinking routines and how you can use artworks to inspire writing.
We talk about a variety of projects that Mary Hall has been involved in at the National Gallery of Art, the Smithsonian American Art Museum , and the different types of online workshops that she teaches.
Mary Hall shares 4 wonderful tips for how you can improve your writing through art - so make sure you don’t miss those.
We really could’ve talked for hours and I loved our chat. So, here it is - enjoy!
EPISODE WEB PAGE
Support the Show
Join the Slow Looking Club Community on Facebook
Masterclass with Mary Hall Surface 26 April: Inspire Your Memoir Writing through Visual Art
The SAAM Social-Emotional Learning Toolkit:
https://americanart.si.edu/education/learn-from-home
Link to Open Window, Collioure , 1905, Matisse
https://www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.106384.html
Link to Edward Hopper, People in the Sun, 1960, oil on canvas, Smithsonian American Art Museum, Gift of S.C. Johnson & Son, Inc.,
https://americanart.si.edu/artwork/people-sun-10762
Mary Hall Surface - website and mailing list sign up: www.maryhallsurface.com
Upcoming Smithsonian Associates workshop: Mothering: A Reflective Writing Workshop
Upcoming Van Gogh/Mary Oliver Workshop: Springs’ Awakening: A Reflective Writing Workshop
Writers’ Studio on the Amalfi Coast
Listen for free

About the Podcast
About your host.

Claire Bown
- Writing Prompts
- Who's Visiting? ›
- Families ›
- Bring the Museum Home ›
- Creative Activities
- Art-Making Activities
- Coloring Book Pages
Need some help to get the creative writing juices flowing? Try starting with some art and the prompts below. Who knows where your imagination will take you …
These activities are great for children ages 7 and up, but can be enjoyed by learners of all ages. Younger children may benefit from the help of an adult.
For related educational resource packets, visit our educator resource finder .
Exploring Haiku
Although haiku poetry originated in Japan, it is created by poets around the world today. The basic form includes seventeen syllables broken down into a 5, 7, 5 pattern over three lines of verse. Haiku poets often write new poems daily to respond to the ever-changing world around them. To craft your own haiku, begin by creating a word bank with five words that describe what you are noticing in your world today. Use one or more of those words to inspire and structure your poem. Try to keep things simple by using the present tense and avoiding similes, metaphors, or fancy adjectives. And, remember, it can be as silly or serious as you choose!
Examples of Haiku
Five syllables here. Seven more syllables here. Are you happy now?
Haiku are easy. But sometimes they don’t make sense. Refrigerator.
I Wish I’d Had a Camera
Photographer Robert Frank was known for working in the “street” style, using his small camera to quickly capture fleeting moments in everyday life. Stylistically, his work was tied to that of his friend Beat poet Jack Kerouac (American 1922–1969), who often wrote using stream of consciousness, a way of writing that captures a subject’s thoughts and reactions to an event in a continuous flow.
Visualize a moment from your life—a fleeting scene or cherished memory—that you wish you had captured in a photograph. Set a timer for five minutes (or less for younger learners). Without stopping to edit, write a stream of descriptive words that evoke the sights, sounds, and feelings of that moment. Share this written memory with a friend.
Margo Hoff’s 1945 painting, Murder Mystery , portrays a reader propped up in bed late at night with their head buried in the pages of a book. Hoff’s stylized forms, intricate patterns, and dark palette make the scene mysterious, reminding us of how the tone of a good story can affect our experience of the world.
Imagine you are writing a fictional novel that will one day be a bestseller. You think your story is interesting and exciting, but now you need a title. What title would you give your book? What genre does it fall into—mystery, fantasy, science fiction, or something else? What is the conflict that drives your story? How might it be resolved or worked through? Write a summary of your story for the back cover—but don’t give away the ending!
Every Day is History
Each day, small moments come together to create history on a large and small scale and in personal and public forms. Japanese artist Noda Tetsuya captures this spectrum of experiences in his multilayered prints, which feature intimate moments with his family as well as monumental global events. His Diary series encourages us to reflect on the accumulation of memories that mark the passage of time—and our own personal place within this history.
Document your own moment in history by creating a daily journal. Jot down the major and minor events of the day, based on the context of your life and experiences. What is important today—to you or in the world? Experiment with using your own voice to tell the history of the week. Clip a photo or add a drawing to build on your written notes. At the end of the week look back at each day’s events and consider what new insights you might take into the following week.
What’s Your Word?
The varied colors and paint strokes in Joan Mitchell’s City Landscape provide us with multiple points of entry and engagement. The impact of the image may in fact stay with us, jostling our thoughts and taking root. With this and so many works of art, we often wonder: How can I make personal connections? How might an artwork stay with me long after I’ve seen it?
Spend a moment free writing your own thoughts about this painting. Pay attention to how it makes you feel; what emotions come up; what memories are activated. Free write your thoughts for two minutes; try to let your hand and pen connect. Read back over what you have written, and underline two lines that resonate with you the most. From within those lines, circle three of the words, then place a triangle over just two of your three chosen words, and finally draw a box around just one. You should now have redacted your writing to one simple word. Think about how and where you want to display your word; you may want to cut it out, draw it large, or place it on your bathroom mirror! As you move about your day, keep coming back to this word and the personal connections you’ve made.
Round-Robin Story
Work together with your family to tell the story unfolding in this artwork. Have someone start the story and write down the first sentence. Pass the paper to the next person to write the next sentence. Repeat this process until everyone has gotten a chance to contribute at least once. Put your sentences together and read your thrilling tale for all to enjoy.
Crafting Your Movie Pitch
In this colorful painting, Archibald Motley Jr. depicts the vibrancy of a crowded cabaret in Chicago’s South Side neighborhood Bronzeville.
Imagine that this painting is the opening scene of a movie that begins with this line: “I knew then that my life would never be the same.” Using clues from the picture, decide who will be the main character of your film and then build out your story. What happened in the days before what we see here? What is happening now? What happens after this moment and what changes happen in the life of the main character? Write out these moments as if you were constructing the plot for a movie and getting ready to sell it to a big-time producer. Share the storyline of your movie with friends and family to see if they would want to watch it on opening night.
A Poem in Five Lines
A five-line poem is also called a cinquain. Some forms of cinquain poetry follow specific rules about the number of syllables or elements in each line. Look closely at this sculpture by German artist Katharina Fritsch and respond to the following prompts to write your own cinquain.
Line #1: Choose one noun to identify the subject of the artwork. Line #2: Pick two adjectives describing the subject of the artwork. Line #3: Write three verbs ending in –ing that detail the action in the artwork. Line #4: Select four individual words or a four-word phrase to describe emotions related to the artwork. Line #5: End with one noun that is a synonym for the subject of the artwork.
Have a friend or family member also write a cinquain about this sculpture and share your poems with each other!
Conversation in the City
In Dawoud Bey’s Harlem, U.S.A. series, he explored the identities of the people and places of New York City’s Harlem neighborhood in the 1970s. Look closely at this scene from the series. Think about the personalities of the people and the events taking place around them based on details you find in the image. Select two people and imagine the conversation they might be having. How would their discussion unfold and what would they say to each other? What might they say to you if you were in this scene? Write out the conversation, expressing the personality of each character and the story that might occur in this scene.
Dream a Little Dream
Like the works of his Surrealist contemporaries, Cornell’s art is often connected to the world of dreams. Based on what you can see in this Cornell box, write a short story that begins with this line: Last night I had the strangest dream …
A Tale about Things
Philip Guston painted everyday objects like clocks and shoes as if they were characters in a narrative rather than inanimate objects in a still life. Think of two or three everyday objects you’d want to use to create a scene. What sort of personalities do they have? A book, for instance, might be intelligent but shy. Write a short story about these characters.
A Story from the Window
Identify one object, figure, or animal from the windows—this will be the subject of a story. Look closely at its details. Pay attention to surrounding shapes, colors, objects, and figures in the same panel. Write your story from the perspective of the subject, describing what it is like to be a part of the environment of the windows.
Tip: For a closer look at the details of this work, click on the image and zoom in.
Travel Assignment
Imagine that you are a writer for a travel magazine. The editor assigns you to go to Japan and write a report based on your experiences at the cherry blossom viewing festival. Step into the screen and write about what you see, feel, smell, and hear. Where would you want to go? What would you want to see?
The Storyteller’s Story
This ceramic figure was created in the Ameca Valley of Mexico. The figure appears to be in the midst of telling a story, and in many early societies storytellers told heroic legends and myths that helped people understand their history and their place in the natural world.
Though seated, its pose is energetic and its gestures expressive. Notice that the mouth on the Storyteller Figure is partially open. Is the figure speaking? If so, what is he saying? Write the story Storyteller Figure might be telling.
What’s in a Title?
Write your own titles for artworks— they can be funny, serious, descriptive, or completely made up. Browse the museum’s collection to find your favorites, or write new titles for works that artists never gave a title to in the first place.
If you are in a group, share your titles with each other to see what creative ideas you all came up with. You can also visit the webpage for your selected artwork to find out if there is a featured title. Look at the artwork again. Why do you think the artist chose this title?
Sign up for our enewsletter to receive updates.
- News and Exhibitions Career Opportunities Families
- Public Programs K-12 Educator Resources Teen Opportunities Research, Publishing, and Conservation
| S | M | T | W | T | F | S |
|---|
Gallery actions
Image actions, suggested terms.
- Free Admission
- My Museum Tour
- What to See in an Hour
- Our Mission
How to Use Images to Teach Creative Writing
Landscape paintings can inspire elementary students to use their five senses and incorporate imaginative details in their writing.

As soon as my elementary students have learned how to string words together to form sentences, I have them writing paragraphs and essays. To me, teaching writing is about passing my love of the creative process on to my students—and I have yet to meet a child who was not born to write.
When I was a new teacher, my students were fascinated by my daily calendar, which featured landscape paintings. They would stand by my desk between classes and tell me stories about the paintings. From there, the leap was natural: I could use art to teach them how to use their imaginations to write. Over time, I’ve refined the approach by having them pair paintings with prompts rooted in the five senses.
Back then, I saved the landscapes as I tore them off each day until I had enough for every student in my class. Each student first shared their painting with the class and then wrote, “What I see in the painting,” at the top of a sheet of paper.
Next, I had the students use simple sentences to list what they saw in their picture. I walked around the room helping them to grow their sentences. Sentences such as “I see a cloud ” became “I see a big, white, fluffy cloud.” As the students added adjectives to their sentences, we discussed other ways to grow sentences with similes, metaphors, and personification; with a little thought, the sentence became “I see a big, white, fluffy cloud that looks like cotton candy and I would like to eat it.”
My students quickly caught on, and their sentences became more imaginative. At the end of class, I had them turn in their picture and paper to me to keep for the next day.
On the second day, I passed out the paintings again, with a second sheet of paper. When I had students write at the top of the paper, “What I hear in the picture,” they were confused: How could they hear a picture?
“Imagine the painting is real and you are standing somewhere inside it. Point to where you are standing.” The students studied their pictures carefully, chose their spots, and pointed.
“Now close your eyes and imagine you are there,” I instructed. “Can you see it in your mind? Tell me what you hear.”
The students scrunched up their faces as they concentrated. “I hear a bird,” one finally said. “I hear a fountain,” another said.
Suddenly they were all chiming in. As they wrote down their sentences, I moved around the room as I’d done the day before, helping them grow their sentences. This time, the students were much quicker. “I hear a bird” quickly became “I hear a mama bird yelling at her kids because they made a mess of the nest.” At the end of the class, I again collected their papers and pictures.
The third day’s prompt was “What I can touch.” Once they’d chosen a spot in their painting, I asked them to close their eyes and imagine the weather within it. “Can you feel a breeze? Is it hot or cold?” This time, the students told me they were running through their painting on the warm grass, splashing in the cold water of the creek, climbing the scratchy bark of the trees, and touching the soft petals of the flowers. This time, I didn’t have to help them with growing their sentences; their creativity was running wild all on its own.
Taste and Smell
We explored the last two senses together. I first explained to my students how smell and taste are linked and started off by asking them what they could smell in their paintings. The students talked about the scent of the roses in the garden and the freshly mowed grass in the yard; one of the students said that the house in the picture reminded him of his grandmother’s and he could smell and even taste her fried chicken. Another said that they were having a picnic with delicious lemonade, and yet another told me that the American flag in the painting reminded him of July Fourth—he could smell the fireworks.
Putting It All Together
On the final day of the project, I passed all four pieces of paper back to the students along with a fifth, with lines organized and indented into six paragraphs. In the first paragraph, I had the students introduce themselves and share the name of their painting and artist. Then they used their notes from earlier in the week to write a paragraph for each day. They ended their essay with what they liked best about their painting. (For older students, try some of these strategies for revising a final draft.)
Then they mounted their picture on construction paper and drew a frame around it. I gathered their paintings into a notebook; students took turns reading each other’s essays for the next week. A local art gallery displayed the notebook, and seeing their work being read by others inspired my students to keep writing. Now, because I no longer use a printed calendar, local art galleries donate postcards that we use in exchange for exhibiting the notebook.
As an international teacher, I’ve seen art bridge gaps that diplomacy could not. Once a seventh-grade English language learner wrote that she could hear the sound of freedom in her picture. When I asked her about it, she pulled out her picture of a painting of an American soldier walking toward the light. “I don’t know what freedom sounds like,” she said as she reverently touched the soldier, “but I know he’s hearing it.”
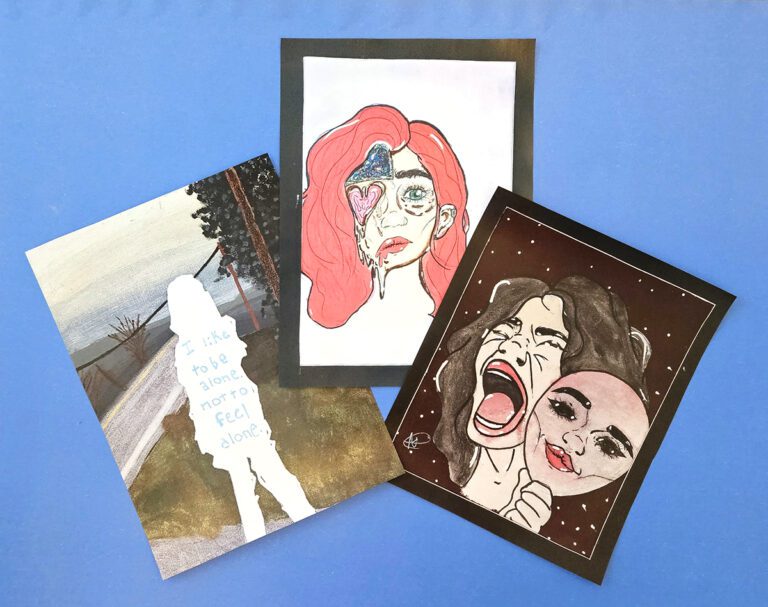
6 Amazing Art Projects That Incorporate Writing

An 8th-grade student walks into a classroom and sits down at a desk. With a freshly-sharpened pencil, the student is preparing to take the state writing assessment. As part of this assessment, the student will be expected to complete a descriptive essay in 90 minutes. This is the writing prompt: “Describe one activity you enjoy.” If you’ve ever had a conversation with an 8th-grader, you know they’d be able to sum their answer up in one sentence! Yet, they are expected to compile a detailed, descriptive essay about a vague topic.
So what does art have to do with state writing assessments? Well, we often teach our students that art tells a story and contains meaning . Art can be viewed as its own visual language. Sometimes a student just needs a really good idea to have something worthwhile to write about. Art can be that good idea to inspire writing!
Today I am going to share 6 art projects that incorporate writing and turn your students’ imagery into a written story.
1. bleezer’s ice cream.

2. Smashing Faces

3. Emotional Weaving

To start this project have your students select an emotion. Then, using the 5 senses, challenge your students to create a written description of that emotion. For example, what does anger look like? What does it feel like? What noises would you associate with anger?
Students will then use their written descriptions as a jumping off point for a piece of art as they depict their emotion through the use of color and line. Finally, students will use that piece of art to create a paper weaving. To take the project even further, you might want to try weaving together two different emotions!
4. Abandoned Cars

5. Blackout Poetry

6. Fan Fiction

Writing and art can be used together to strengthen each other. Making it a practice to incorporate writing alongside art lessons will only benefit your students. If you’re new to incorporating writing in your art room, start simply. Try out one of the ideas presented here to get started!
What are your favorite projects that incorporate writing?
How often do your students write in your art room?
Magazine articles and podcasts are opinions of professional education contributors and do not necessarily represent the position of the Art of Education University (AOEU) or its academic offerings. Contributors use terms in the way they are most often talked about in the scope of their educational experiences.

Abby Schukei
Abby Schukei, a middle school art educator and AOEU’s Social Media Manager, is a former AOEU Writer. She focuses on creating meaningful experiences for her students through technology integration, innovation, and creativity.

Art and Appetite: 7 Ways to Explore the Significance of Food in the Art Room

7 Engaging Ways to Teach the Elements and Principles of Art and 3 Fun Ways to Review Them

10 Easy Strategies to Apply Brain-Based Learning in the Art Room

7 Common Misconceptions When Approaching Your Art Curriculum This Year
- Create an Account
- My Dashboard
- My Membership
- My Interests & eAlerts
- My WAHC Progress
- My WishList

Write Into Art: Creative Writing Inspired by Visual Art
Daytime workshop (session 4 of 4-session course), select your tickets.

Save $20 when you purchase all 4 sessions of the Write into Art course!
STREAMING PROGRAM INFORMATION
- This program is part of our Smithsonian Associates Streaming series.
- Platform: Zoom
- Online registration is required.
- For multiple registrations, you will be asked to supply individual names and email addresses.
COURSE DESCRIPTION
Discover how visual art can inspire creative writing and how writing can offer a powerful way to experience art. Join Mary Hall Surface , the founding instructor of the National Gallery of Art’s popular Writing Salon, for a series of four online workshops that explore the essential elements of writing through close looking, word-sketching, and imaginative writing.
The sessions spotlight a diverse range of visual art chosen to inspire writers of all experience levels to deepen their process and practice. Each workshop is limited to 30 participants to maximize interaction among the instructor and students.
Surface is a teaching artist, playwright, and theatre director and producer. She presents workshops nationwide in creative writing and drama as a Kennedy Center teaching artist and was a six-summer faculty member at Harvard’s Project Zero Classroom.
Session Information
Story: Arcs of Action
Dive into 20th-century African American artist Hughie Lee-Smith’s Confrontation as you imagine multiple narratives from a single source.
ADDITIONAL WORKSHOPS
If you are interested in additional Write Into Art workshops, view the upcoming schedule:
- Sept. 8 Character: Uncovering Complexity
- Sept. 15 Setting: The Power of Place
- Sept. 22 Dialogue: Spoken and Unspoken
Patron Information
- Once registered, patrons should receive an automatic email confirmation from [email protected].
- Separate Zoom link information will be emailed closer to the date of the program. If you do not receive your Zoom link information 24 hours prior to the start of the program, please email Customer Service for assistance.
- View Common FAQs about our Streaming Programs on Zoom.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Creative Writing?
Discover What Is Creative Writing as we unravel the art of self-expression through words. In this blog, learn the meaning and techniques of creative writing, igniting your imagination and honing your storytelling skills. Unlock the world of literary creativity and learn how to craft compelling narratives that captivate readers.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators work in the United Kingdom alone in 2023. This shows Creative Writing is a demanding career worldwide.To know more about it, read this blog, to learn What is Creative Writing, how to write captivating narratives, and discover the essence of expressive writing.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Creative Writing
2) Key elements of Creative Writing
3) Types of Creative Writing
4) Importance of Creative Writing
5) The Creative Writing process
6) Tips for effective Content Writing
7) Conclusion
Understanding What is Creative Writing
Creative Writing is the art of crafting original content that elicits readers' emotions, thoughts, and imagination. Unlike Academic or Technical Writing, Creative Writing allows for more personal expression and imaginative exploration. It encompasses various forms such as fiction, poetry, non-fiction, and drama, all of which share the common thread of artistic storytelling.

Key elements of Creative Writing
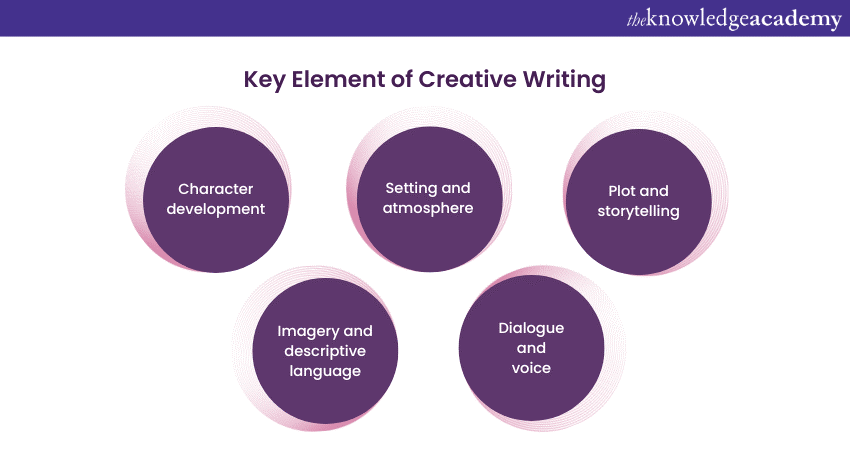
2) Character development: Compelling characters are the heart of any great story. Through careful development, characters become relatable, complex, and capable of driving the plot forward.
3) Setting and atmosphere: The setting and atmosphere create the backdrop for the story. By skilfully crafting these elements, Writers can enhance the overall mood and tone, allowing readers to feel like they're living within the story's world.
4) Plot and storytelling: A well-crafted story keeps readers engaged and invested in the narrative's progression. This includes introducing conflicts, building tension, and crafting satisfying resolutions .
5) Dialogue and voice: Dialogue adds authenticity to characters and provides insight into their personalities. A distinctive narrative voice also contributes to the story's uniqueness and captivates readers.
Types of Creative Writing
Creative Writing encompasses various genres and forms, each offering a unique platform for expressing creativity, storytelling, and emotion. As you delve into the world of Creative Writing, it's essential to explore the various types and discover which resonates with you the most. Here are some of the prominent types of Creative Writing:
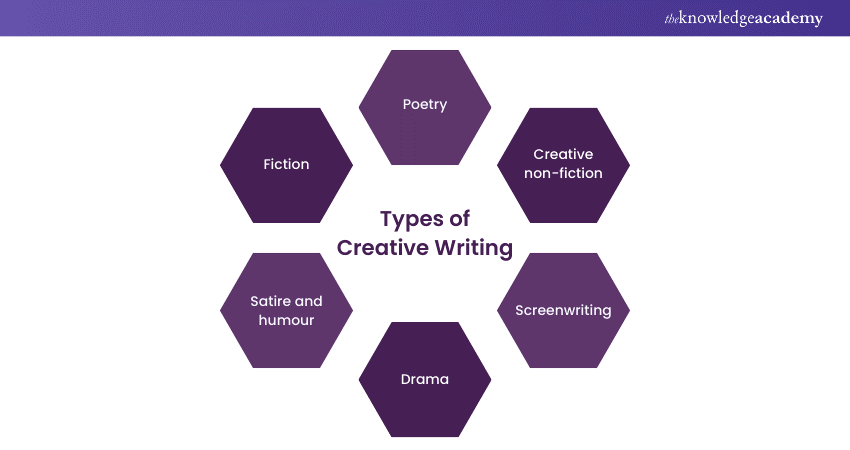
1) Fiction
Fiction is perhaps the most well-known type of Creative Writing. It involves inventing characters, settings, and plotlines from scratch. Writers have the freedom to create entire worlds and realities, whether they're set in the past, present, future, or even in alternate dimensions.
Novels, short stories, novellas, and flash fiction are all forms of fiction that engage readers through compelling characters, intriguing conflicts, and imaginative settings. From fantasy realms to gritty crime dramas, fiction transports readers to new and exciting places.
2) Poetry
Poetry is the art of condensing language to evoke emotions, provoke thoughts, and communicate complex ideas using rhythm, rhyme, and vivid imagery. Poems' conciseness requires Writers to choose their words carefully, often crafting multiple layers of meaning within a few lines.
Poetry can take various forms, including sonnets, haikus, free verse, and slam poetry. Each form carries its own rules and conventions, allowing Poets to experiment with structure and sound to create impactful compositions. Moreover, poetry delves into the depth of emotions, exploring themes ranging from love and nature to social issues and personal reflections.
3) Creative non-fiction
Non-fiction writing draws from real-life experiences, observations, and research to convey information, insights, and personal perspectives. This form includes genres such as essays, memoirs, biographies, autobiographies, and journalistic pieces.
Non-fiction Writers blend storytelling with factual accuracy, presenting their ideas in a compelling and informative manner. Personal essays offer a glimpse into the writer's thoughts and experiences. At the same time, memoirs and autobiographies share personal journeys and reflections, connecting readers with the author's life story.
4) Drama and playwriting
Playwriting is the creation of scripts for theatrical performances. The challenge lies in crafting engaging dialogue and constructing scenes that captivate both the audience and the performers.
Dramatic Writing requires an understanding of pacing, character motivations, and the visual aspects of storytelling. While Theatrical Writing requires a keen sense of the following:
a) Character dynamics: Building relationships between characters and exploring their motivations and conflicts.
b) Stage directions: Providing clear instructions for actors, directors, and stage designers to bring the play to life.
c) Dramatic structure: Crafting acts and scenes that build tension and engage the audience.
5) Satire and humour
Satire and humour utilise wit, sarcasm, and clever wordplay to critique and mock societal norms, institutions, and human behaviour. This form of Creative Writing often challenges readers to view the world from a different perspective.
Moreover, it encourages them to question established conventions. Satirical works, whether in literature, essays, or satirical news articles, aim to entertain while also prompting reflection on serious topics.
Master Copywriting skills with our Copywriting Course – join today and become an expert Copywriter!
Importance of Creative Writing
Creative Writing holds a profound significance beyond its role as a literary pursuit. It bridges imagination and reality, fostering personal growth, communication skills, and cultural preservation. Here's a closer look at why Creative Writing is of paramount importance:
1) Personal expression and catharsis
Creative Writing is a sanctuary for self-expression. Individuals can voice their innermost thoughts, emotions, and experiences through poetry, stories, and essays. This act of sharing vulnerabilities and joy brings about a cathartic release, offering a therapeutic outlet for emotional expression. Moreover, it cultivates a deeper understanding of oneself, promoting self-awareness and self-acceptance.
2) Cultivation of communication skills
The art of Creative Writing cultivates effective Communication Skills that transcend the written word. Writers learn to convey ideas, concepts, and feelings coherently and captivatingly.
This proficiency extends to verbal communication, enabling Writers to articulate their thoughts with clarity and eloquence. As a result, it enriches interpersonal relationships and professional endeavours.
3) Nurturing empathy and perspective
Writers develop a heightened sense of empathy as they craft diverse characters and explore multifaceted narratives. Immersing oneself in the shoes of different characters fosters understanding and tolerance for various viewpoints and backgrounds. Readers, in turn, experience this empathy, gaining insight into the complexities of human nature and the diverse tapestry of human experience.
4) Exploration of social issues
Writers wield the power to effect change through their words. They can shed light on societal issues, challenge norms, and provoke critical conversations. By addressing topics such as social justice, equality, and environmental concerns, Creative Writing becomes a catalyst for positive transformation and advocacy.
5) Connection and impact
Creative Writing builds bridges between individuals by establishing connections on emotional and intellectual levels. Stories resonate across cultures, transcending geographical and temporal boundaries. The impact of a well-crafted story can be enduring, leaving a mark on readers' hearts and minds.
Unlock your creative potential with our Creative Writing Training - register now!
The Creative Writing process
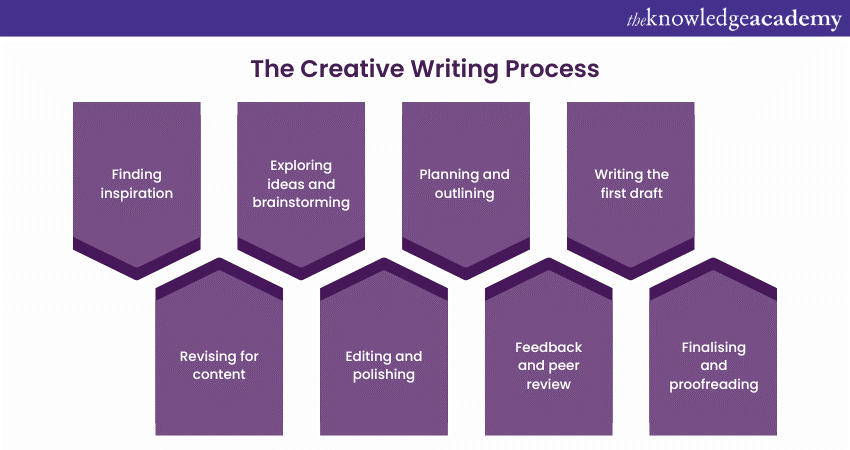
Creating a compelling piece of Creative Writing is a journey that involves a series of steps, each contributing to the evolution of your story. Whether you're crafting a short story, a novel, or a poem, here's a breakdown of the Creative Writing process in eight essential steps:
1) Finding inspiration
The process begins with a moment of inspiration—a fleeting thought, an intriguing image, or a powerful emotion. Inspiration can strike anywhere—nature, experiences, dreams, or simple observation.
Keep a journal or digital note-taking app to capture these sparks of inspiration as they occur. Explore your interests, passions, and emotions to identify themes and ideas that resonate with you.
2) Exploring ideas and brainstorming
Once you've identified an inspiring concept, delve deeper. Brainstorm ideas related to characters, settings, conflicts, and themes. Jot down all possibilities, allowing your imagination to roam freely. This stage is about generating a wealth of creative options that will serve as building blocks for your story.
3) Planning and outlining
Organise your thoughts by creating an outline. Outline your story's major plot points, character arcs, and pivotal moments. This outline acts as a roadmap, guiding you through the narrative's progression while providing flexibility for creative surprises.
4) Writing the first draft
Once you are done with your outline, start writing your first draft. Don't worry about perfection—focus on getting your ideas onto paper. Let your creativity flow and allow your characters to surprise you. The goal is to have a complete manuscript, even if it's messy and imperfect.
5) Revising for content
Once the first draft is complete, take a step back before revisiting your work. During this stage, focus on revising for content. Analyse the structure of your plot, the development of your characters, and the coherence of your themes. Make necessary changes, add details, and refine dialogue. Ensure that your story's foundation is solid before moving on.
6) Editing and polishing
Edit your Manuscript for grammar, punctuation, sentence structure, and style. Pay attention to clarity and consistency. Also, focus on enhancing the flow of your writing and creating a polished narrative that engages readers.
7) Feedback and peer review
Share your revised work with others—friends, writing groups, or beta readers—to gather feedback. Constructive criticism can highlight blind spots and offer perspectives you might have missed. Use this feedback to refine your work further.
8) Finalising and proofreading
Incorporate the feedback you've received and make final revisions. Proofread meticulously for any remaining errors. Ensure that your work is formatted correctly and adheres to any submission guidelines if you plan to publish or share it.
Tips for effective Creative Writing
Here are some of the useful tips you should consider incorporating in your process of writing :
1) Show, don't tell: Instead of directly stating emotions or details, "showing" involves using actions, thoughts, and dialogue to convey information. This technique allows readers to draw their own conclusions and become more immersed in the story.
2) Use of metaphors and similes: Metaphors and similes offer creative ways to describe complex concepts by comparing them to something familiar. These literary devices add depth and creativity to your writing.
3) Building suspense and tension: By strategically withholding information and creating unanswered questions, Writers can build suspense and keep readers eagerly turning pages.
4) Crafting memorable beginnings and endings: A strong opening captures readers' attention, while a satisfying conclusion leaves a lasting impact. These elements bookend your story and influence readers' overall impression.
5) Experimenting with point of view: The choice of point of view (first person, third person, etc.) shapes how readers experience the story. Experimenting with different perspectives can lead to unique narrative opportunities.
Conclusion
We hope this blog gave you a clear idea of What is Creative Writing, along with its process and useful tips. The Creative Writing process is not linear; you might find yourself revisiting earlier steps as your story evolves. Embrace the journey, allowing your writing to develop and transform through each phase.
Enhance your Academic Writing prowess with our comprehensive Academic Writing Masterclass . - sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
a) Literary Agent
b) Screenwriter
c) Video Game Story Writer
d) Copywriter
e) Website Editor
f) Creative Director
There are several resources or recommended readings which can help you to hone your Creative Writing skills. Here we have discussed some of such resources:
a) “On Writing: A Memoir of the Craft" by Stephen King
b) "Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life" by Anne Lamott
c) "Writing Down the Bones: Freeing the Writer Within" by Natalie Goldberg
d) Joining book clubs
e) Reading a variety of authors and genre
f) Practicing writing regular prompts and exercises.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide. Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Organisational skills training, Emotional Intelligence Training, and Report Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Journalism . Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Sports Journalism, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Creative Writing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 3rd Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 2nd May 2025
Fri 4th Jul 2025
Fri 5th Sep 2025
Fri 7th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Creating Voices, Changing Lives
What we do and why.
Writing Through is an international educational US-registered non-profit which partners with local organizations to provide specially developed workshops where creative writing is used as a tool to develop thinking skills, creativity, language fluency and self-esteem. Writing Through is non-sectarian and operates in all communities that can benefit from our work, creating spaces which aim to amplify every voice.
Research shows that 30% to 50% of school systems globally rely on rote memorization. Yet research also shows that today’s world needs engaged and contributing citizens who are able to think conceptually and critically, know what they believe, and have the confidence and poise to stand up and say it in their own voices. These skills, which are so crucial to intellectual enrichment and personal advancement, are not always taught in school systems. At Writing Through, we know that creative language training and exposure to the arts creates new perspectives and opens minds, all of which lead to self-esteem. The combination of creative thinking, language skills and self-esteem will open minds, one poem, one story at a time .
Writing Through uses a unique pedagogy of in-person and online workshops, which focus on creative writing of poetry, stories, and journal entries. We partner with local organizations to bring this skills acquisition program to the at-risk and marginalized segments of their communities. Our process includes a specially designed, unique format of proven techniques such as themes, prompts, brainstorming, and presentation skills. We break down barriers between student and teacher while establishing mutual respect, thus creating a safe space for learning that encourages students to think in new ways, investigating and sharing their dreams and experiences. Workshop Facilitators are trained by Writing Through and are fluent in either English or Spanish. If workshop participants use the workshop language as a second or third language, we utilize the in-class assistance of a local teacher. In this way, our programs can be adapted to students with a wide range of language abilities. This also supports our goal of long-term sustainability through local teacher training.

How It Began

I learned how to read and talk to a public in English, with a microphone, and how to stand well and control my gesture. I learned self-confidence. Sue told me that with confidence, we can do what we think we can’t. I also learned to work in a team, while we did the group brainstorming. Please do it again!
I didn’t know before what to expect from the workshop, and I have to say, I was even a little bit afraid that the English level of our students would be too low to make it really work. But Sue made the best come out of them, starting with confidence, and they really impressed me and themselves with great stories and poems!
I had the pleasure to be actively involved in the Creative Writing Workshops in 2013, and to see the result of the workshops in 2014. At both times I was amazed about the creativity and communication skills the students managed to show. Sue triggers the students to use their imagination and gives them the trust that everyone can be a writer or poet. I consider the boost these workshops and the final presentation give to the students’ confidence as one of the best parts of the program.
For the first time, I can write a story by myself and I understand well what do I have to think about initially before writing it down. I think that writing a story makes us be able to think.
Ms. Guiney was able to provide each student with valuable guidance and feedback, and the workshop was met with rave reviews from students and faculty alike.
The creative writing workshop is a good program. It helps me to understand and know lots of things everywhere all over the world. This makes me be happy
For all our students, Writing Through workshops has been an incredible experience! English is a real challenge for most of our students. Most of them thought they would not able to write any stories or poem in English. After 5 days only, the result is amazing. By using their own creativity and inspiration, thanks to the talent of the facilitator, they were able to present to the group their own story, with pride and self confidence. Writing Through is, more than anything, a self esteem workshop!

CHANGE A LIFE TODAY
Writing Through changes lives, but we cannot do it without your support.
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Creative Writing through art
Subject: English
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Unit of work
Last updated
30 December 2023
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Are you looking for an original way to hook visual learners into creative writing?
This unit of work contains everything you need to teach Descriptive Writing at KS3 and is fantastic early preparation for English language descriptive writing. It includes 13 lessons and is fully resourced with lesson PowerPoints, exemplar answers, IWB interactive resources, intriguing pictures, activities to exploit drama and poems. It uses classic art as inspiration, such as Bird in an Air Pump, Thomas Chatterton and The Lady of Shalott.
Lesson 1: Bird in an Air Pump by Joseph Wright Lesson 2: Chatterton by Henry Wallis Lesson 3-4: The Lady of Shalott by John William Waterhouse Lesson 5: Voice in Not My Best Side by UA Fanthorpe Lesson 6: Original Writing Lesson 7: How to create original characters Lesson 8: Describing alien planets in Star Wars Lesson 9: Describing The Iron Islands in Game of Thrones Lesson 10: Narrative Viewpoint in Assassin’s Creed Lesson 11: Planning your assessment on ‘The Scream’ Lesson 12: Writing your assessment Lesson 13: Assessment feedback
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Top Searches
Financial Aid
- Application Process
- Health & Wellness
Create your future at Otis College of Art and Design in Los Angeles. Develop your talents and express yourself through innovative programs in a global creative capital.
At Otis College, we champion collaboration—providing a space for you to connect with your community and find your voice. Our programs cultivate a sense of freedom for artists and designers of all ages, guided by dedicated professionals and mentors at the top of their craft. Otis College graduates become well-rounded, multidisciplinary creators who engage locally, think globally, and embrace challenges.
A College of Distinction
Otis College is included in The Princeton Review’s 2022 Best Colleges: Region by Region—West list. Our students have won prestigious awards, including from the Center for Craft, Joe’s Blackbook, and the American Ceramics Society, among many others.
Discover Otis

Undergraduate Programs
We offer eight unique BFA programs and 13 minors that encourage you to broaden your creativity.

Graduate Programs
Our two MFA programs — Fine Arts and Graphic Design — provide a strong intellectual foundation in an inspiring, welcoming environment.

Otis Extension
Our Extension programs enable non-degree students of all ages and levels to pursue their personal or professional development in art and design.
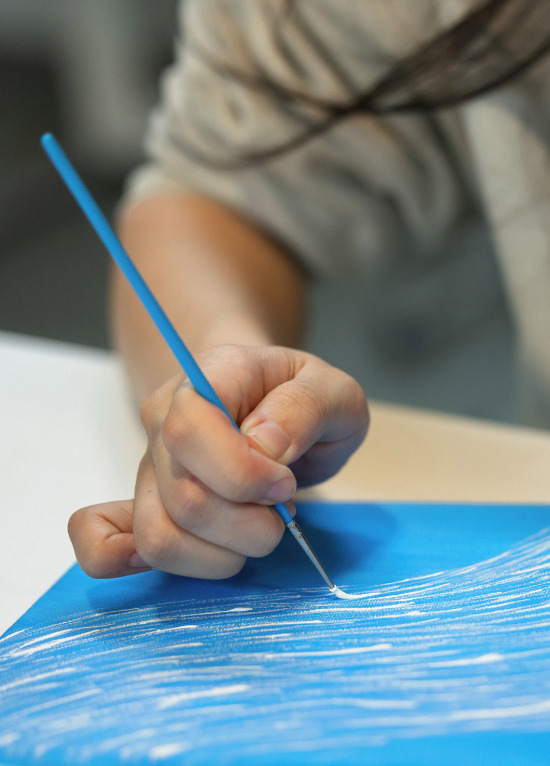

Certificates
Optional Copy — Split column is great for listing multiple items such as locations, degree types, and offices. Morbi interdum turpis in augue consectetur.
Find Your Passion for Art and Design
Otis College provides a supportive space to help students become who they are meant to be.

Otis has exposed me to different perspectives and mindsets, and helped me branch out of my comfort zone. Hearing critiques from both professors and students has helped me evolve as an artist and to think outside of the box.

Otis College has supported me through great amounts of resources, such as mentorships and internship fairs. In addition, each course not only helped develop my skills but also allowed me to find my aesthetic. I often hear from interviewers how well Otis has trained me for the fashion industry.
Students explore different creative fields through a comprehensive Foundation year.
In your first year as an Otis College student, you’ll participate in our one-of-a-kind, immersive Foundation program. Our freshman students take a sequence of studio courses designed to teach you the fundamental skills and processes across visual arts and design disciplines. Focused studio courses, faculty, and academic events help you make the best decision for major of choice.

Real-World Experience & Industry Connections
In Los Angeles, a global art and design capital, you can build a creative network and community from day one. Students access internship opportunities and connect with mentors who help them make the most of an Otis education.
Student Work
Success Stories
Careers & Outcomes

Advertising, Creative Writing, Sustainability, and More
Our 13 minors allow students to become well-rounded as they prepare to enter the job market, learn how to start their own businesses, or dive deeper into topics that align with their values as artists and designers.

Academic Resources

Student Support Services
- Academic Catalog
Disability Services
The One Stop
Lab and Shops
Keep Exploring
Otis prepares artists and designers for successful careers, empowering you to make a living—and make an impact—across established and emerging creative fields. Take the next stept to create your future at Otis College of Art and Design.
Admission Deadlines
Explore upcoming admission deadlines as well as next steps to submitting a successful application and portfolio.
Financial aid opportunities at Otis include academic scholarships, need-based grants, loans, and work study opportunities.
Careers and Outcomes
Follow your talents to a satisfying career with an education from Otis College of Art and Design.

- Twitter (X)
A foot in two worlds
Alum Maya Skidmore wanted to use her lived experience and passion for social justice to make a positive change. She discovered UNSW’s double degree program, Bachelor of Media Communications and Bachelor of International Studies and the opportunity to experience a year-long international exchange.

QS World University Rankings, 2024
AFR Top100 Future Leaders Awards, 2023
QS World University Rankings by Subject, 2023
At UNSW Arts, Design & Architecture, we're focused on progress for all.
The world faces monumental challenges. It always has. But if you look around, progress is everywhere. People are coming together, imagining a better future. From design that advances healthcare, to sustainable cities and equal access to education, the progress we make together can improve people's lives worldwide.
Latest news
To navigate the modern world, we need to redefine what it means to witness, patents based on traditional knowledge are often ‘biopiracy’. a new international treaty will finally combat this, illicit drugs: government spending lowest on prevention and harm reduction, shows new report, queensland housing stress more intense than any other state: report, study with us.
We have a diverse range of disciplines where you’ll develop unique and career-ready skills. Together, we’ll turn creativity and critical thinking into real-life solutions.
With us, you’ll challenge and be challenged to push the way you think about people, places and cultures. You’ll thrive in an open, supportive and inclusive community that encourages and celebrates your difference.
Undergraduate
Postgraduate
Postgraduate research
Short courses

ADA2051 Foundational Strategy
The ADA2051 Foundational Strategy outlines how we’ll deliver our mission to realise our vision. In this strategic framework, we set out the way we’ll use our knowledge and skills to create a sustainable, connected, healthy and socially just world.

Commitment to Indigenous communities

Creating impact

Innovation Hub

Matraville Education Partnership

Research centres & institutes
Upcoming events.

2024 Jenny Birt Award & Exhibition Launch

Textiles & Fashion Talks: Kaimurai

OPENING PARTY | Paul Knight, Lillian O'Neil and Lisa Sammut
Acknowledgement of country.
UNSW Sydney’s Kensington and Paddington campuses are built on Aboriginal Lands.
We pay our respects to the Bidjigal and Gadigal peoples who are the Custodians of these lands. We acknowledge the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples, the First Australians, whose lands, winds and waters we all now share, and pay respect to their unique values, and their continuing and enduring cultures which deepen and enrich the life of our nation and communities.
As a community, UNSW Arts, Design & Architecture acknowledges that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples have survived and thrived through centuries of systemic injustice, exclusion, and erasure. As a new faculty, it is our priority to develop an Indigenous Strategy that is collaboratively developed, productive and purposeful to affect long-term change in the educational outcomes of Indigenous students and the intellectual and cultural integrity of Indigenous teaching and research across the faculty.
Read more about UNSW’s Indigenous Strategy . Please get in touch to be part of these developments and stay tuned as we share more information about our Indigenous Strategy.

Artwork by Leilani Tallulah Knight, “U going to listen now?”, 2021
Stay in touch
Subscribe to our ADA community newsletter for all news, events and opportunities.

Getting Write Down to It: Passion and Purpose in Writing
A personal perspective: writing as an art form..
Posted June 2, 2024 | Reviewed by Lybi Ma
- What Is a Career
- Find a career counsellor near me
- The act of writing is an art form that involves willingness to be part of a larger conversation.
- The mandate to publish or perish in academia bears down on faculty, but there are things that can help.
- There are benefits to considering the process of writing and how it is life-affirming and life-building.

If we think about writing as having the privilege of entering a conversation and pushing it in the direction we think it needs to go, then writing—yes, even academic writing—becomes creative. It becomes our own art form, if you will. It gives meaning to our lives and is one of the ways that we contribute to the world.
Once we recognize that our writing is an art form, we need new ways to judge ourselves and our productivity . Should a painter’s worthiness as an artist be determined by how many pieces they landed in a juried show in the last year? When we think of an artist’s career , we see the arc of their art over time. Similarly, as academics, we write over the arc of our careers. It’s the way that we—as people involved in the front lines of knowledge production, construction, and consumption—make art.
Publishing monographs and articles in top-tier journals is a fine goal—in fact, even necessary sometimes to get or keep a job. But publishing isn’t the only reason for writing any more than juried exhibitions and winning awards are the sole reasons an artist goes to paint. The painter finds at least as much, if not much more, nourishment and fulfillment in the process of making art as in the external recognition, however validating and joyful those accolades. Indeed, dreaming of accolades is rarely why an artist sits down to paint. The painter makes art to thrive, to share the meaning they find in the world with others. So, too, if a writer recognizes their work as their art, they sit down to do it to share their gifts with other people and society in general. And the process of writing itself becomes a way to thrive, to contribute to the world.
To take our writing seriously, we must think about it as a core part of our life’s work. We often write for our peers, sometimes for our students, and sometimes for audiences outside of academia. Once we have confidence in our writing, that paves the way for more outward-facing scholarship, bolstering the possibility of becoming a public scholar.
Once we take seriously our art form—or craft, if the word sounds more apt or comfortable—we must make time for it. When we finish a research project, we must realize that good writing takes care, thought, and loving attention to words, phrasing, and paragraph construction. Knowing that it takes time, and is worth the time, can boost our confidence. Good writing brings our ideas, and our findings, to life.
With all of the competing demands that students, colleagues, and our increasingly bureaucratic administrations in higher education impose on us, writing can be something we can claim as our own. While our course material is housed in learning management systems with accompanying questions of control over our intellectual property, and committee work is in service to the institution, the writing we do is ours. And the time we claim for it—for cultivating and honing it—is time we’ve declared, if only to ourselves, as precious and sacred, reserved to nurture ourselves and our ability to contribute to those around us. There’s something very liberating about that.
In sum, while many faculty members see the “publish or perish” message as exemplifying the competitive pressure of an academic career, making the time to enjoy the process of writing is an antidote to some of what has become the drudgery of university life. It reminds us what turns us on in our fields of study and motivates our inquiry in the first place.
A version of this post also appeared in Inside Higher Ed with Barbara Risman.

Deborah J. Cohan, Ph.D., is a professor of sociology at the University of South Carolina-Beaufort where she teaches and writes about the intersections of the self and society.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Observe. Asking students to look carefully and observe the image is fundamental to deep, thoughtful writing. Keep this in mind when choosing art to use in class. Look for images with: Many details: If it is a simple image, there's not much to analyze. Characters: There should be people or animals in the image to write about.
We're talking all things creative and reflective writing through art. As a museum educator, Mary Hall uses both theatre and creative writing to expand perspective, uncover complexity and deepen understanding. She is the founding instructor of National Gallery of Art's Writing Salon in Washington DC, and a six-summer faculty member of ...
Join us for my new 4 part mini-course 'Art and Words' starting online on 22 April 2021. This online course uses artworks as the inspiration and prompt for creative and reflective writing. It is intended for both educators, creatives and writers who would like to use art to inspire and drive their writing and those of others, too.
There are many ways to boost your creative writing performance However, the most effective and sophisticated of them is to inspire thoughtful, creative writing through art. The process listed below is a way to make any creative writing process thoughtful and make any creative text meaningful. Read on to find out how art could influence […]
Use a Mother Goose nursery rhyme to invoke creativity through a writing prompt and a sketch. Myths, fairy tales, nursery rhymes, and other creative mediums are a great way to spark creativity and imagination, especially through creative writing. This will help you to take in stories, nursery rhymes,
Step 1: find an artwork to inspire you. If you are a teacher, task students with finding an artwork that inspires them as a homework project in advance of the class. They could choose an artwork from a local collection or find one on Art UK. Use the tips below to find artworks on Art UK.
Third Mind: Creative Writing through Visual Art Edited by Tonya Foster & Kristin Prevallet 240 pp. Grades: all ages $19.95 paperback This anthology of essays about the challenges and rewards of uniting visual art and creative writing not only demonstrates how art can spark wonderful student writing, but goes much further, offering novel insights into…
Creative Writing through the Arts is a three-year research programme that aims to provide evidence of the benefits of creative learning and teaching with and through the arts; specifically focussing on the development of children's writing. Delivered in partnership by: Supported by:
of art. Through its extensive collections, the museum is both a resource to and a reflection of the many cultural communities and heritages in Southern ... Students will look closely at works of art and then complete creative writing exercises using such devices as figurative language, sensory description, and dialogue. Writing pads, pencils ...
Today I'm delighted to be talking to playwright, theatre director, teaching artist and museum educator Mary Hall Surface about her work. We're talking all things creative and reflective writing through art. As a museum educator, she uses both theatre and creative writing to expand perspective, uncover complexity, and deepen understanding.
Line #2: Pick two adjectives describing the subject of the artwork. Line #3: Write three verbs ending in -ing that detail the action in the artwork. Line #4: Select four individual words or a four-word phrase to describe emotions related to the artwork. Line #5: End with one noun that is a synonym for the subject of the artwork.
Each student first shared their painting with the class and then wrote, "What I see in the painting," at the top of a sheet of paper. Next, I had the students use simple sentences to list what they saw in their picture. I walked around the room helping them to grow their sentences. Sentences such as "I see a cloud " became "I see a ...
Today I am going to share 6 art projects that incorporate writing and turn your students' imagery into a written story. 1. Bleezer's Ice Cream. This project is inspired by Jack Prelutsky's poem " Bleezer's Ice Cream. " Share the poem with your students and give them the task of inventing their own ice cream flavors.
November 7, 2023 - 10:00 a.m. to 11:30 a.m. ET . Session details. Resize text. Mary Hall Surface. Discover how visual art can inspire creative writing and how writing can offer a powerful way to experience art. Join Mary Hall Surface, the founding instructor of the National Gallery of Art's popular Writing Salon, for three online workshops ...
2. Creative writing is a profound art form that transcends mere words on paper. It is a journey into the depths of imagination and a means of expressing the inexpressible. This article delves into ...
Discover how visual art can inspire creative writing and how writing can offer a powerful way to experience art. Join Mary Hall Surface, founding instructor of the National Gallery of Art's popular Writing Salon, for a series that explores the essential elements of close looking, word-sketching, and imaginative writing through the lens of four paintings that span centuries and styles ...
Outside the world of business writing and hard journalism lies an entire realm of creative writing. Whether you're brand-new to the craft, a nonfiction writer looking to experiment, or a casual creative writer wanting to turn into a published author, honing your creative writing skills is key to your success. A Series of Scenes.
Creative Writing through Art and Literature in the Language Classroom. Gabriel García Márquez. Lesson Plan: Literature. Gabriel García Márquez. 6 March 1927 - 17 April 2014. Born in Aracataca, Colombia. Colombian novelist, short-story writer, screenwriter and journalist. Considered one of the most significant authors of the 20th century ...
Abstract. The study aimed at investigating the effectiveness of utilizing visual arts to scaffold students' creative writing skills. The study employed the Action Research Cycle process and the ...
Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators ...
Writing Through is an international educational US-registered non-profit which partners with local organizations to provide specially developed workshops where creative writing is used as a tool to develop thinking skills, creativity, language fluency and self-esteem. Writing Through is non-sectarian and operates in all communities that can ...
Through her art making and writing she identifies the important themes of trust and finding meaning. Nekolaichuk's voice shows the same courage and hopefulness that she so obviously admires in her clients. ... Finally, the authors demonstrate their reflective and creative processes through vivid descriptions of how initial expressions (visual ...
It includes 13 lessons and is fully resourced with lesson PowerPoints, exemplar answers, IWB interactive resources, intriguing pictures, activities to exploit drama and poems. It uses classic art as inspiration, such as Bird in an Air Pump, Thomas Chatterton and The Lady of Shalott. Lesson 1: Bird in an Air Pump by Joseph Wright.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
Create your future at Otis College of Art and Design in Los Angeles. Develop your talents and express yourself through innovative programs in a global creative capital. At Otis College, we champion collaboration—providing a space for you to connect with your community and find your voice. Our programs cultivate a sense of freedom for artists ...
As a community, UNSW Arts, Design & Architecture acknowledges that Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples have survived and thrived through centuries of systemic injustice, exclusion, and erasure. As a new faculty, it is our priority to develop an Indigenous Strategy that is collaboratively developed, productive and purposeful to affect ...
The act of writing is an art form that involves willingness to be part of a larger conversation. The mandate to publish or perish in academia bears down on faculty, but there are things that can ...
Students and Teachers. Introductory Pricing Terms and Conditions Creative Cloud Introductory Pricing Eligible students 13 and older and teachers can purchase an annual membership to Adobe® Creative Cloud™ for a reduced price of for the first year. At the end of your offer term, your subscription will be automatically billed at the standard subscription rate, currently at (plus applicable ...