- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Tesla's First Product

The Next Stage
- Tesla's Models
Other Tesla Products
Is tesla a tech company, the bottom line.
- Company Profiles
- Tech Companies
What Makes Tesla's Business Model Different?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/pic__kristina_a-5bfc262546e0fb005118b2b9.png)
The market for fully electric vehicles is growing. The reasons are many, including new regulations on safety and vehicle emissions, technological advances, and shifting customer expectations. But much of the mainstream acceptance and excitement for electric cars can be attributed to Tesla Motors Inc. (TSLA) and its unique business model .
Tesla founder and CEO Elon Musk launched the company with the mission, “to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport by bringing compelling mass-market electric cars to market as soon as possible.” This mission is the backbone of Tesla’s successful business model.
Key Takeaways
- Tesla's business model is based on direct sales and service, not franchised dealerships.
- Tesla's business model pays particular attention to rolling out charging stations. That may be the biggest obstacle to the mass adoption of electric vehicles.
- Tesla has stretched the business model to encompass energy storage systems for homes and businesses.
Tesla's First Product
Tesla took a unique approach to establish itself in the market. Instead of trying to build a relatively affordable car that it could mass-produce and market, it took the opposite approach, focusing instead on creating a compelling car that would create a demand for electric vehicles.
In a post on Tesla's website, CEO Elon Musk said this about the company's mission, “If we could have [mass marketed] our first product, we would have, but that was simply impossible to achieve for a startup company that had never built a car and that had one technology iteration and no economies of scale . Our first product was going to be expensive no matter what it looked like, so we decided to build a sports car, as that seemed like it had the best chance of being competitive with its gasoline alternatives.”
So, Tesla delivered to the market the first high-performance electric luxury sports car, the Tesla Roadster. The company sold approximately 2,500 Roadsters before ending production in January 2012. Not a number that would fray any nerves at General Motors.
Once Tesla established its brand and had produced and delivered its concept car to the marketplace, it reinforced its business model. Tesla's business model is based on a three-pronged approach to selling, servicing, and charging its electric vehicles.
Direct Sales
Unlike other car manufacturers who sell through franchised dealerships, Tesla sells directly to consumers. It has created an international network of company-owned showrooms and galleries, mostly in urban centers.
By owning the sales channel, Tesla believes it can gain an advantage in the speed of its product development. More importantly, it creates a better customer buying experience. Unlike car dealerships, Tesla showrooms have no potential conflicts of interest. Customers deal only with Tesla-employed sales and service staff.
Including the showrooms, Service Plus centers (a combination of retail and service center), and service facilities, Tesla has 823 locations around the world as of May 25, 2022. Tesla has also made use of Internet sales—consumers can customize and purchase a Tesla online.
Home Services
In some areas, Tesla employs Mobile Service Support (formerly called Tesla Rangers)—mobile technicians who make house calls. In some cases, the service is delivered remotely. The Model S can wirelessly upload data, so technicians can view and fix some problems without ever physically touching the car.
The Supercharger Network
Tesla has created its own network of 30,000+ Global Superchargers where drivers can charge their Tesla vehicles in about 15 minutes for a quarter of the price of gasoline. The purpose, of course, is to speed up the rate of adoption of electric cars by making it cheaper and easier to keep them running.
Tesla's Models
Tesla entered the market with the sporty Roadster. When it introduced its Model S sedan in June 2012, it stopped producing the Roadster.
Tesla began delivering its first SUV, the Model X, in September 2015.
The first Model 3 deliveries kicked off in July 2017 as Tesla's entry into the category of affordable cars. In 2022, its base model starts at $48,490.
The base price of the 2023 supercharged Tesla Roadster, touted as "the quickest car in the world."
Tesla has combined many of its sales centers with service centers, including charging stations. They believe that opening a service center in a new area corresponds with increased customer demand. Customers can charge or service their vehicles at the service centers or the Service Plus locations.
Tesla also produces a fully electric Semi Truck. The truck boasts an energy consumption of less than 2kWh per mile. The company claims it can go 400 miles on a 30-minute charge now, and it's working on stretching that to more than 600 miles in the future. UPS was among the companies that put in pre-orders for the truck, introduced in 2019.
Tesla's latest model is a supercharged version of the original Roadster, which the company claims is the "quickest car in the world," capable of going 0-60 in 1.9 seconds. Deliveries of the new Roadster are expected in 2023, with a base price of $200,000. Interested individuals can reserve a new Roadster for a $5,000 initial card payment and a $45,000 wire transfer, which is due within 10 days after making the initial payment.
If you recall, part of Tesla’s mission is “to accelerate the advent of sustainable transport.” To that end, Tesla sells powertrain systems and components to other auto manufacturers.
In April 2015, it introduced a line of home batteries, called the Powerwall, that serve as energy storage systems in homes or businesses. They are meant to connect with a solar energy system and can be used as backup power when power is interrupted or peak demand is high. Tesla also sells solar panels and full solar roofing, which is a roof made up of solar panels that still looks like a roof.
Like its rival automakers, Tesla offers financial services including vehicle loans and leases . For some of the loan programs, it used to offer a resale value guarantee provision. This provided some downside protection on a vehicle’s value should the customer want to resell it.
Many financial analysts and investors see Tesla as a technology company rather than a car company. At least, that's how they justified the growth of its stock price starting in 2013, when it shot up by more than 300% within a single year.
Publications scrambled to find similarities between Tesla and companies from the technology sector , which had similar growth rates. Online publication Slate even ran a piece that compared Tesla to Apple Inc. (AAPL) and Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL).
Back then, Morgan Stanley analyst Adam Jonas, who has been a Tesla bull since the company's early days, gave the stock a price target of $103 "at full maturation." By May 25, 2022, TSLA was trading at $661.58.
There are several points of similarity between Tesla and the tech sector. Tesla has embraced the disruption credo of the tech sector. Much like other tech companies, Tesla is intent on changing existing business models within the stodgy automotive industry by selling directly to consumers. Its product pipeline and founder evoke a loyal following similar to those for iconic tech companies such as Apple.
And investors in Tesla, like investors in many technology companies, stayed patient through a long period of quarterly losses. They were finally rewarded: Tesla recorded its first yearly profit in FY 2021.
This is the biggest obstacle to the mass adoption of electric vehicles: It can't happen without the infrastructure to charge on the go. Tesla plans to continue adding to its network of Supercharger stations in the U.S., Europe, and Asia.
Tesla did not invent the electric car or even the luxury electric car. But Tesla did invent a successful business model for bringing compelling electric cars to the market. Part of the strategy was building a network of charging stations to solve one of the greatest obstacles facing the adoption of electric vehicles: refueling on long trips. Tesla’s unique business model , which includes keeping control over sales and service, is one reason its stock has soared since its initial public offering.
Tesla. " The Mission of Tesla ."
Tesla. " Form 10-Q for the Quarterly Period Ended September 30, 2011 ," Page 22.
Tesla. " Find Us ."
Tesla. " Mobile Service Support ."
Tesla. " Model S ."
Tesla. " Supercharger. "
Tesla. " Fourth Quarter & Full Year 2012 Shareholder Letter ," Page 1.
Tesla. " Third Quarter 2015 Shareholder Letter ," Page 1.
Tesla. " Second Quarter 2017 Update ," Page 1.
Kelley Blue Book. " 2022 Tesla Model 3 ."
Car and Driver. " 2023 Tesla Roadster ."
Tesla. " Roadster ."
Autoweek. " Musk Now Says 621 Miles of Range for Tesla Semi ."
Tesla. " Your Roadster ."
Tesla. " First Quarter 2015 Shareholder Letter ," Page 2.
Tesla. " Powerwall ."
Tesla. " Solar Roof ."
The Verge. " Tesla Ends ‘Resale Value Guarantee’ on New Vehicle Purchases ."
CNBC. " Market Insider: Is Tesla Really a Tech Company? "
Yahoo! Finance. " Tesla, Inc. (TSLA) ."
Tesla. " 2020 Form 10-K ," Page 30.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/shutterstock_259393262_tesla_model_3-5bfc476746e0fb0051c410ae.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

- Innovative Prompts
- Strategies Packs
- Skills Packs
- SOPs Toolkits
- Business Ideas
- Super Guides
- Innovation Report
- Canvas Examples
- Presentations
- Spreadsheets
- Discounted Bundles
- Search for:
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
Tesla Business Model
The Tesla business model operates as a Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) business model as it sells directly, cutting out middlemen such as dealerships and offering its own charging station network. Which of these names do you recognize more easily: Tesla or Elon Musk ? While, in general, we identify the author by the work — that is, it would be normal for you to know Elon Musk as the CEO of Tesla —, in the case of this visionary eccentric, in particular, it is quite common for the opposite to happen: Tesla being Elon Musk’s company.
But, anyway, in addition to its charismatic and incomparable leader, Tesla is also characterized by being a company that is basically divided into three business models: an auto-maker, a hardware supplier, and a tech company. We will know, then, how everything works in this hybrid business model, which has faced great challenges in the market. Follow up!
A brief history of Tesla
Tesla , Inc. is an American company, founded in 2003 by two engineers, Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, originally as Tesla Motors. Fourteen years later, the company would change its nomenclature, because it started to incorporate supply lifestyle products in its production.
Tesla’s first product was launched in 2008 — the Tesla Roadster, the high-performance electric sports car, whose sales ended four years later, in 2012. Instead of launching a cheaper first car, to gain in quantity, the Roadster was a luxury item. Musk, the company’s CEO, explained that, with all the technology they intended to put in the car, it would be impossible for it to reach the market at a low price. For this very reason, they chose to launch a product, above all, compelling.
In the following years, Tesla invested heavily in marketing, research, and development, prioritizing studies in safe, autopilot, and charging cars. In 2018, Tesla was already the largest seller of electric cars in the world, with more than 250,000 units sold, taking up 12% of that market.
Who Owns Tesla
As mentioned a few times, Tesla is owned by the eccentric billionaire Elon Musk . Although founded by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning back in July 2003, Elon Musk has been the CEO and chairman of the company since 2008.
Tesla’s Mission Statement
Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
Tesla’s Differentials
Currently, Tesla’s business model is based on three foundations: selling model, servicing, and charging network.
First of all, unlike other automakers that have their cars sold by dealerships worldwide, Tesla focuses on direct sales. This means that all Tesla stores are an arm of the company itself and that anyone who is served in that space will, in fact, be received by an employee of the manufacturer itself.
This allows Tesla to improve its product through direct and fast contact with the customer and guarantees them differentiated service facilities, which include the possibility of customizing a vehicle via the internet. In addition, the company has service centers in all places where it sells its cars, with personalized service, including Tesla Rangers, technicians that the company sends to people’s homes for service.
These centers also have a charging service. But, more than that, Tesla also has an extensive network of Supercharges stations, where cars can be fully recharged in up to 30 minutes — at no cost. Of course, in addition to these three factors, there is still a difference between the company’s own products. Tesla has the fastest and longest-range electric cars on the market, with unique design and brand identity.
Finally, there is still the entire research and development process promoted by the company. Tesla invests heavily in hardware and software, focusing on digital technology and even autonomous driving cars. And yet, it increasingly seeks to reduce CO2 emissions, through investment in sustainable energy, which guarantees the support of the government.
How Tesla makes money
Certainly, its most important revenue stream was and remains the sale of electric cars , representing more than 80% of its revenue, which is estimated at more than 20 billion dollars. The other 20% of income includes automotive services and vehicle leasing, but also sales of solar energy systems and storage products (about $1.5 billion).
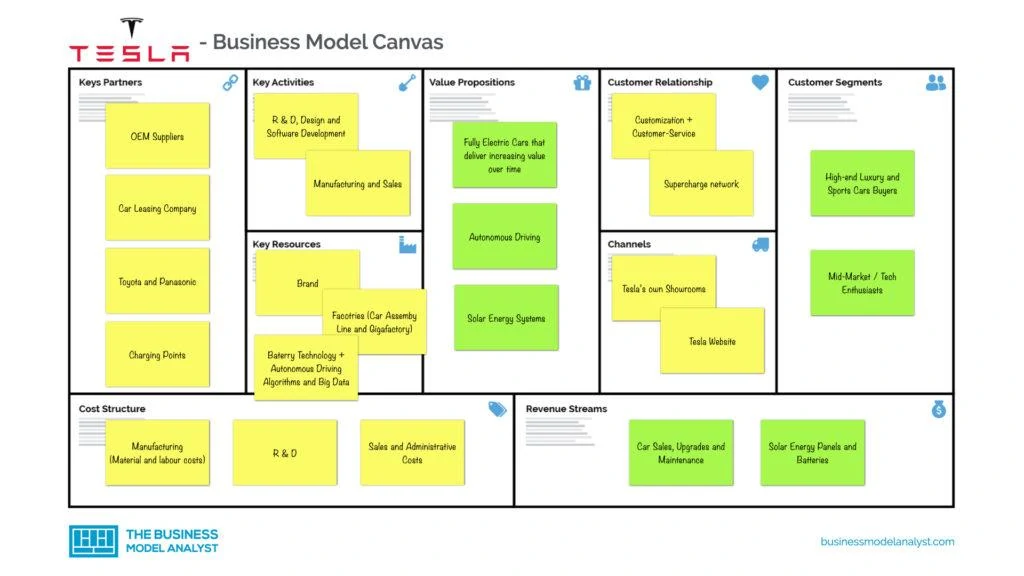
Tesla’s Business Model Canvas
You can look at the Tesla Business Model designed in the Business Model Canvas below:

Download FREE!
To download Tesla Business Model Canvas today just enter your email address!
Tesla’s Customer Segments
Tesla has developed vehicles for every type of customer. From the mid-market range, with affordable pricing, to the high-end luxury and sports cars, competing with Porsche or Ferrari. In addition, Tesla is also covering the commercial vehicle sector, providing a greener option for transportation and shipping. And, of course, it’s worth remembering that Tesla’s customer segments include fast, eco-friendly car enthusiasts, with autopilot — and, surely, Elon Musk followers.
Tesla’s Value Propositions
Regarding automobiles, Tesla’s value proposition includes a greener solution that adds high performance, design, functionality, efficiency, long-range, flexible, and low-cost (or free) recharging. Aside from its own vehicles, it is worth remembering that Tesla sells home batteries and solar panels to residential and commercial customers, providing convenience when it comes to power. In addition, Tesla still sells systems and components to other auto manufacturers, as well as financial services, with loans and leases.
Tesla’s Channels
The channels that Tesla uses to reach its audience, as seen throughout this article, are its own stores, its website (self-service online store), conferences, and sales events. As stated above, the company doesn’t spend a lot on advertising. It believes in the power of its own brand and reputation, in addition to the charm produced by the CEO, Elon Musk.
Tesla’s Customer Relationships
One of Tesla’s foundations is the customer relationship , because, from the beginning, the company has focused its efforts on the customer experience. That is why the company chose, as mentioned above, to implement company-owned stores instead of dealerships, in a direct-to-customer sales model. Besides, customers can choose, order and customize their car directly via the website. In addition, Tesla is also increasingly investing in its charging network, to charge Tesla vehicles more quickly, at low or no cost. Finally, Tesla has built a very positive brand and reputation with the public, always being associated with luxury, technological and innovative vehicles, and taking into account the environmental impact.
Tesla’s Revenue Streams
- Solar energy panels and batteries;
- Car sales, upgrades, and maintenance.
Tesla’s Key Resources
Tesla’s key resources are those that allow it to fulfill its key activities in order to deliver its value proposition. Therefore, we can highlight its cutting-edge technology and engineering, its long-life battery systems, its design, and its software.
Tesla’s Key Activities
Tesla’s key activities include:
- Manufacturing Cars : Yes, Tesla’s main activity is still delivering the product it promises — electric cars. For this, it also needs to invest in the production of batteries and, still, solar energy panels;
- R&D: The company is always looking for innovative, advanced, and eco-friendly technology;
- Design : One of the differentials of the products — Elon Musk made it clear from the outset that, as its technology would prove to be costly anyway, Tesla would invest in design and not fight for price;
- Building & Maintenance: Tesla is spreading recharge stations around the world so that more people can purchase electric cars;
- Software Development: Tesla applies agile principles to develop and enhance its software;
- Sales & Marketing : The company doesn’t invest much in advertising. On the other hand, its entire operation focuses on the customer experience.
Tesla’s Key Partners
- Suppliers : Tesla manufactures the entire base of its cars, but there are some parts that are purchased from third parties. Therefore, Tesla’s biggest key partners are suppliers that allow the company to deliver its cars, such as windshield and brake manufacturers, just to name a few;
- Alliances : Tesla entered into an alliance with Toyota for both to develop, together, parts and systems for electric vehicles, improving this market share. Tesla and Panasonic are also together in the construction of a manufacturing plant in New York, for the development of large-scale battery and solar cells;
- Government : Due to its focus on the development of eco-friendly vehicles and energies, associated with the number of jobs the company has been creating in the U.S., Tesla receives tax incentives from the U.S. federal government;
- Charging points : Some Tesla partners include hotels, resorts, restaurants, and shopping centers, in which the company establishes its fast car recharging spaces.
Tesla’s Cost Structure
Tesla has a very broad cost structure , like any manufacturer, which includes:
- Manufacturing;
- Administrative costs;
- Research and Development.
Tesla’s Competitors
- Nio : Founded in 2014, the Chinese Nio manufactures premium electric vehicles for the international market. Its sales have been growing more than 100% per year, but it has fewer than 200 battery stations in China, with plenty of room to grow;
- Ford : This traditional auto company has entered the electric-powered market. Its sales of electric cars have been growing by over 70% per year, and most of the buyers are new to Ford. As one of the oldest automakers in the world, the company has a great experience advantage ;
- Volkswagen : The German company launched its first electric vehicles one decade after Tesla. Nevertheless, it predicts that 50% of its sales in the U.S. will be EVs, and it is aiming to manufacture 1.5 million of those by 2025. Just like Ford, it has the strength of an old and traditional brand;
- Li Auto : One of the newest competitors, founded in 2015, this Chinese company has surprised the audience with its technology. It is growing fast and sold over 10k EVs in its first year in China;
- Nikola Corp : The company combines electric battery power with hydrogen fuel cells in its vehicles. But its focus will be on big vehicles, with electric and hydrogen fuel-powered trucks. Founded in 2014 in America, Nikola’s vehicles had zero emissions from 2016 to 2020;
- Workhorse Group : Based in the U.S., this company focuses on electric vans for delivery services. It has already fulfilled a UPS order for 950 vans. The company was founded in 1998, but the offer for EVs only began in 2015;
- Canoo Holdings : It is the latest entrant, with a different business model. Canoo’s vehicles will get on the roads in 2022, with a unique value proposition — drivers will pay a monthly subscription instead of buying or leasing the cars.
Tesla’s SWOT Analysis
Below, there is a detailed SWOT Analysis of Tesla:
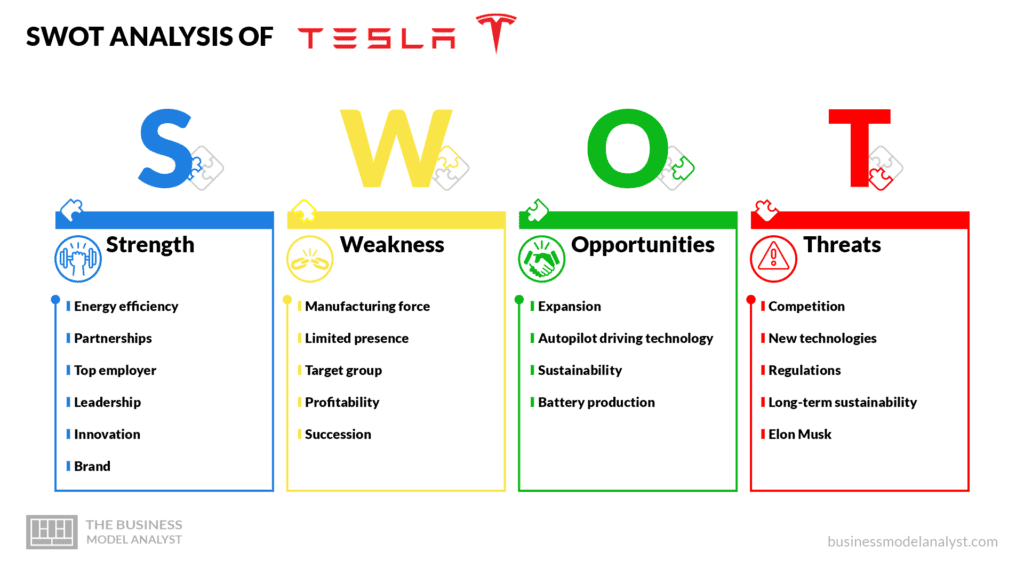
Tesla’s Strengths
- Energy efficiency: Tesla is the market leader not only in numbers of sales, but also in the use of renewable energy sources like solar power;
- Partnerships : Tesla is collaborating with giant energy companies, which help to expand its renewable energy efforts;
- Top employer : The company has been featured in Forbes as one of the best employers in 2019, and it is known as a great place for young employees due to its diversified business culture;
- Leadership : As a result of its extraordinary growth and its leadership in EV sales, Tesla became the most valuable automotive company in 2020;
- Innovation : Tesla invests heavily in research and development in order to build new technologies and deliver top-class design and comfort, thus increasing its popularity among its customers;
- Brand : When Tesla was founded to build electric cars, it did not have any competition, thus becoming the top of mind when it comes to EVs. Besides, the market trusts the company to develop clean energy as well as profitable products.
Tesla’s Weaknesses
- Manufacturing force : When compared to other automobile companies, Tesla has a smaller structure for manufacturing, resulting in limited production and delays in distribution;
- Limited presence : Despite its growth, Tesla’s market core is still the U.S., with over 70% of its revenues, and it struggles on establishing itself around the world;
- Target group : Tesla is a premium clean energy brand, so despite its significant growth, it still has a small target group due to its high prices;
- Profitability : Tesla still burns cash because of its high operational costs, which threatens its profitability and, consequently, the investors’ opinions;
- Succession : Elon Musk is the face of Tesla, and its name has become inseparable from the brand.
Tesla’s Opportunities
- Expansion : The U.S. and China generate most of Tesla’s sales, especially in America, accounting for about 70% of them. The brand has plenty of capacity for expanding globally, mainly in Asian markets like China and India;
- Autopilot driving technology : That is the technology that the whole world has been waiting for, and Tesla’s autonomous driving technology gained fame as safe and convenient, and it keeps evolving;
- Sustainability : As people get more environmentally conscious, the demand for sustainable products has been growing quickly, thus increasing its potential growth;
- Battery production : Tesla is working on manufacturing its battery cell in-house, which will lower the production cost and create many new jobs at the same time.
Tesla’s Threats
- Competition : Tesla’s competitors have been in the market for hundreds of years and are rapidly investing in electric car technology, even being able to offer more affordable products;
- New technologies : Vehicles are using more and more innovative technology and new ways of energy, and that demand can increase operational costs and decrease margins;
- Regulations : There are no adequate regulations for autonomous cars yet, which can jeopardize Tesla’s future;
- Long-term sustainability : Clean energy companies demand long-term sustainability strategies, and Tesla’s limited infrastructure may not support that;
- Elon Musk : Although he may be considered a genius and visionary, Musk has been building a controversial image due to his erratic behavior, which is often not aligned with social expectations.
-> Read more about Tesla’s SWOT Analysis .
Tesla did not invent the electric car, but possibly it was largely responsible for shedding new light on this product on the market, by producing cars with differentiated design, long-lasting batteries, and a whole technological support and servicing network. In addition, it implemented a business model practically unique in its area, by selling directly to the consumer, without middlemen. It can, therefore, be said, without fear of making a mistake, that Tesla is one of the most successful automobile industries today and certainly Elon Musk and his peers continue to seek new and original methods of transportation.
Daniel Pereira
Receive our updates.
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?

- Search 56362
- Search 92675
- Search 8109

Tesla Business Model (2023) | Tesla Business Model Canvas
Last updated: Oct 9, 2021
Company: TESLA, Inc. CEO: Elon Reeve Musk Subsidiary: SolarCity, Tesla Grohmann Automation, Maxwell Technologies Founders: Elon Musk, Martin Eberhard, JB Straubel, Marc Tarpenning, Ian Wright Year founded: 2003 Headquarter: Palo Alto, California Type: Public Ticker Symbol: TSLA Annual Revenue (2021): $53.82 Billion Profit |Net income (2021): $5.64 Billion
Products & Services: Tesla Motor Vehicles | Auto service | Financial Services | Energy Storage (Power battery packs) | Solar panels | Lifestyle products | Retail merchandise
Competitors: Kia Soul EV | BMW i3 | Nissan Leaf | Volkswagen e-Golf | Hyundai Ioniq EV | Tesla Model S | Chevrolet Volt EV.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Tesla, Inc.
Tesla, Inc. (formerly known as Tesla Motors, Inc.) is an American automotive, lifestyle and energy company that was originally founded in July of 2003 . The company launched its products specifically in the automotive industry and began to design and supply lifestyle products as well. The company was originally founded by engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning prior to changing its name to just Tesla, Inc. in February of 2017.
During the Series A funding phase, Elon Reeve Musk, J. B. Straubel, and Ian Wright were also accredited with the recognition as the founding fathers of Tesla Motors. Elon Reeve Musk is currently the serving CEO of the company, overlooking all the operations and the structures of the business.
In August of 2015, Tesla, Inc. aimed its focus towards on safety, autopilot, charging networks and motors. Tesla operated a combination of 260 galleries/retails across the United States in 2016. One of the most exciting years for Tesla was 2017.
Tesla was able to focus its markets in the Germany sectors, providing a Dutch RDQ-issued Whole Vehicle type approval (WVTA) which should be accepted as a legal compliance document, without grounds to a national type of approvals in EU member States.
This significantly reduced any compliance check and excelled deliverance exponentially, since the vehicle was already under Germany vehicle standard compliance.
In the same year, Tesla launched additional international locations in Dubai and South Korea, which increased its brand visibility and helped increase revenue streams.
During that year Tesla had a budget of $52 million as a marketing budget and used a referral program and a word of mouth tactic to help attract customers that would be interested in purchasing a Tesla vehicle.
By 2018, Tesla, Inc. was ranked as the bestselling plug-in passenger car manufacturer in the electric car industry. It sold over 245,240 units in total. With over 200k+ units sold, Tesla was responsible for capturing the market shares of 12% in the electric-plug-in vehicle industry. In Q2 of 2020, Tesla delivered 90,650 vehicles to customers and is expected to deliver more than 500,000 cars by the end of 2020. [ 1 ]
The company’s market capitalization increased to nearly $208 billion and surpassed Toyota’s $202 market cap to become the world’s most valuable automaker by market value. [ 2 ]
The following is the complete Tesla Business Model Canvas report and how it is different from the rest of its competition.

Tesla Business Model Canvas
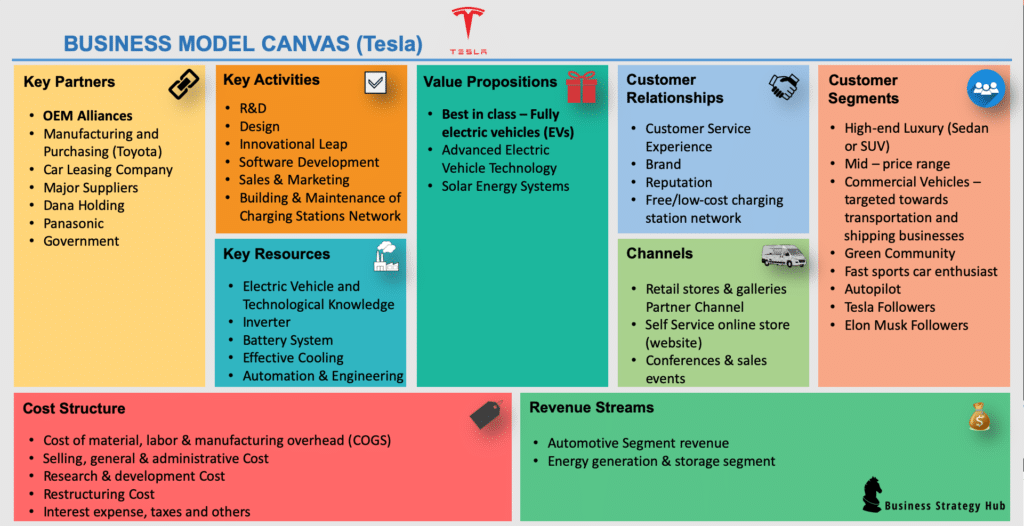
1. Value Propositions of Tesla
Best in class – Fully electric vehicles (EVs)
- Tesla aims to provide some of the best in class EV models that offers high performance, energy efficient, long range (with convenient recharge stations), and sleek designs.
- Model S (Luxury sedan) – June 2012
- Model X (SUV) – September 2015
- Model 3 (Lower priced sedan for the mass market) – July 2017
- Model Y (Compact Crossover) – expected to deliver in 2020
- Semi-Truck (Commercial Heavy-duty truck) – expected to deliver in 2020-21
- Tesla Pickup Truck – expected to deliver in 2020-21
- Tesla Roadster (Sports car) – Original model was in production from 2008-2012. A newer version is expected to deliver in 2020.
- Tesla Cybertruck – Tesla’s angular-designed Cybertruck was unveiled in November 2019 and is expected to hit the market in 2021. [ 3 ]

Advanced Electric Vehicle Technology
- Supercharging and destination recharging station network
- High miles per charge
- All wheel drives
- Free or low-cost electric charging stations or battery swap.
- To support open source movement, Tesla has opened the use of all its patents for other auto-manufacturer to advance EV technology.
- Autopilot option
- Free software updates
- Solar Energy Systems – Tesla is known for its Electric vehicles, also sells solar panels to residential and commercial customers.
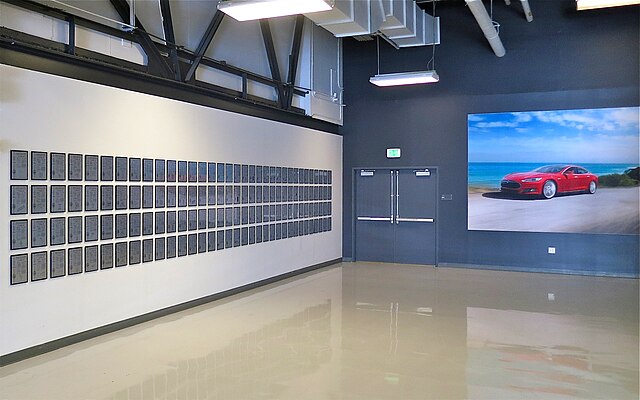

2. Customer Segments of Tesla
Tesla’s engineers and designers have designed vehicles appropriate for every customer groups. Vehicle class type is based on the following segments:
- High-end Luxury (Sedan or SUV)
- Mid – price range
- Commercial Vehicles – targeted towards transportation and shipping businesses
- Green Community
- Fast sports car enthusiast
- Autopilot enthusiast
- Tesla Followers
- Elon Musk Followers
3. Key Partners of Tesla
OEM Alliances
- 2009 – Tesla, Inc. aligned a partnership with OEM manufacturer ( Daimler ), which helped to provide Tesla, Inc. with access to superior research and engineering development and a cash infusion that helped Tesla to escape the potential bankruptcy.
- 2010 – Tesla, Inc. signed an alliance with Toyota , which enabled them to buy former NUMMI factory which positioned Tesla professionals to learn the large-scale, high-quality manufacturing from a pioneer of lean manufacturing.
- 2014- Tesla, Inc. joined Osaka (Japan) investments to develop and improve its battery designs.
- 2020 – Tesla, Inc. entered into a partnership with LG Chem Ltd and China’s CATL to develop batteries for its electric cars. [ 4 ]
- 2020 – Tesla, Inc. partnered with Huston-Tillotson University to collaborate in research and provide opportunities for students from disadvantaged communities to engage in the sector. [ 5 ]
Manufacturing and Purchasing (Toyota)
- Toyota and Tesla, Inc. joined forces announcing to the public that they are to build an alliance that would be dedicated to developing electric vehicles , parts and production systems for electric cars and accessories.
- In return, Toyota bought $50 Million of Tesla stocks and Tesla purchased an assembly factory in California to continue its endeavor towards facilitating the process of manufacturing electric vehicles.
- “ Tesla has quite a clear business strategy for developing a better battery ,” said Osamu Nagata , president, and CEO of Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America. “
Car Leasing Company
- March 2012 – Athlon Car Lease Company built an alliance with Tesla for Tesla’s premium electric sedan specifically for corporate fleet services throughout the European regions. The model consists of the Model S and the 150 Model S Sedans to ensure early availability of the Model S for its clients.
- Tesla’s strategic alliance helped to pave the way for making the first Model S fleet reservation possible for leasing worldwide.
- Athlon VP Richard Sikkel confirms : “Our collaboration with Tesla has been very well perceived by the market. Almost 50 % of our initial order have already been pre-reserved by several of Athlon’s existing customers – an example that demonstrates the increasing need for electric vehicles in the industry.”
Major Suppliers
Tesla, Inc. is commonly responsible for manufacturing the electric car’s basics, which include the electric motor, the battery pack and the charger. Rest are provided by suppliers from the US, Europe, and Asia.
The following are Tesla’s main designers and suppliers:
- AGC Automotive: windshields
- Brembo: brakes
- Fisher Dynamics: power seats
- Inteva Products: instrument panel
- Modine Manufacturing Co. battery chiller
- Sika: acoustic dampers
- Stabilus: liftgate gas spring
- ZF Lenksysteme: a power steering mechanism
- LG Chem LTD: Batteries [ 6 ]
Other suppliers include:
- Angell-Demmel
- Hitachi Cable America
- Hope Global
- MacLean-Fogg
- Magna International
- Methode Electronics
- PSM International
- T1 Automotive
- Zanini Auto Group
Dana Holding
- Dana Holdings provided Tesla, Inc. with Dana Cooling Technology for further implementation of the Tesla engine and the overall cooling system design .
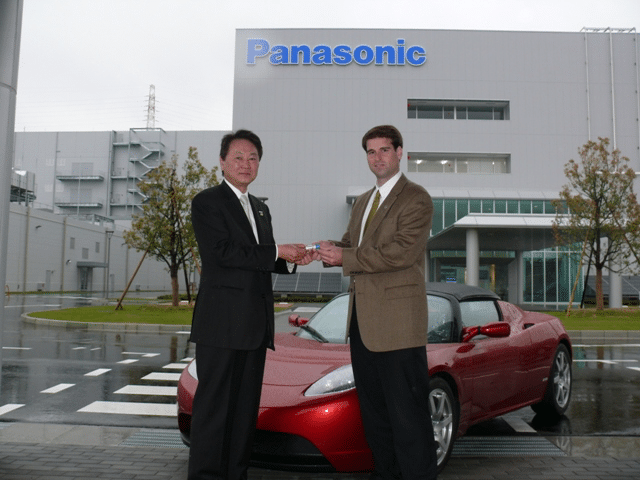
- Panasonic’s current lithium-ion batteries showed to serve sufficiently; Tesla confirms that it is seeking more batteries for its Model S in which Panasonic is currently supplying.
- In this effort, Panasonic is collaborating to build Tesla’s Gigafactorys – a large scale battery and solar cells manufacturing plant in Nevada and New York.

- Government-funded Tesla with a $465 Million loan for its electric Sedan
- $365 Million of the loan shall be allocated towards the production of it’s Model S Sedan.
- Remaining $100 Million will be allocated towards its electric power train manufacturing plant in California.
- Due to Tesla’s Electric Vehicle development and improvements, the US government provides federal tax incentives of about $3750 to customers depending upon the state .
4. Key Activities of Tesla
- R&D helped Tesla attain its milestones by providing breakthrough technologies and innovational designs that were in association with the engine design of Tesla vehicles.
- Tesla’s innovative design helped to produce reliable electric plug-in cars made affordable for all.
- Modern design that includes lightweight body , durable and long-lasting battery life
- Designs range from small, to classy, to luxurious classes – there is a vehicle type for every customer segment at different price points.
Innovational Leap
- Tesla continues to work around the building blocks of Tesla vehicles to better improve and sufficiently design vehicles that are built with eco-friendly materials, ensure future sustainability and invoke reliability of its line of manufacturers.
Software Development
- One of the most crucial movements for Tesla was its dedication towards the vital software programs that helped shaped the electric vehicle industry to what it is today.
- Tesla does not follow the long development software product lifecycles that many automotive specialists follow; instead, Tesla worked around these hurdles to create diverse software programs that improved the sufficiency of each of their model make series.
- Tesla uses agile principles like “scrums” or also known as regular meetings that are designed to work and improve the structures of its core software.
- Through this breakthrough, it has aided Tesla to minimize errors and bring innovation into progressing leaps.
- Tesla, Inc. regularly evaluates customer experience and feedback that helps to pave the next generation in improving its software spectrum and the sufficiency of its vehicles.
- Technological errors are expected but shall improve in the long run to perfection.
Sales & Marketing
- Tesla invests heavily in executing its sales and marketing efforts, which includes establishing company-owned stores , galleries and service centers known as “Service Plus.”
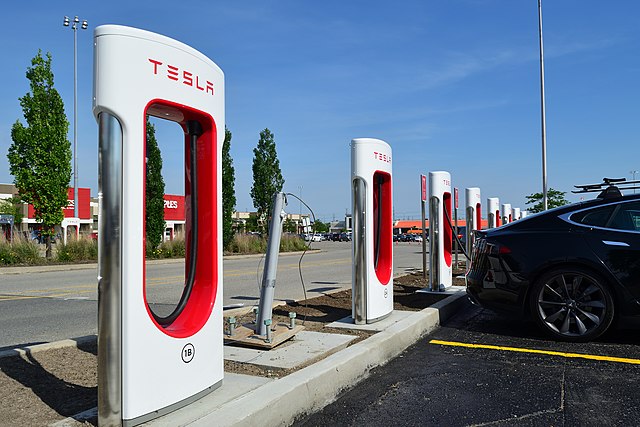
Building & Maintenance of Charging Stations Network
- Tesla has been building an extensive network of the supercharger and destination recharge stations around the world to expand the widespread adoption of its Electric Vehicles.
- There are 1441 Supercharger stations worldwide with 12,888 superchargers and thousands of Destination charging stations at hotels, restaurants, shopping centers, parking garages, office building, etc.
- MOAT – A Tesla, Inc. project that is geared to provide EV charging stations
- Tesla, Inc. plans on launching a network specifically for other automaker brands for EV charging supply. However, this is still to happen.
- First to launch a portable home charger that costs about $500

5. Customer Relationships of Tesla
Customer Service Experience
- Tesla provides digitally driven Omni-channel experience (stores, website, social media) to its customers.
- Company Owned Stores – Tesla utilizes direct to customer sales model . Tesla sells its cars to customers directly through its stores and galleries, instead of selling through auto dealers. It provides an enhanced level of shopping experience for customers.
- Self Service website – Often times, customer place orders directly on the Tesla website. Customers can build their own car, add features, choose different color combinations, various financing options; which is an again a unique shopping experience.
- Tesla is considered as a luxury brand in the automotive industry. For those that know about Tesla, and what it stands for understands the value and quality that it provides to loyal customers.
- Due to the continuous innovation and the design, Tesla has built a reputation unlike any other technology in the EV automobile industry.
- Customers feel that Tesla is well ahead in its innovation and production electric vehicle ecosystem that is like no other competitors in the industry.
Free/low-cost charging station network
- Extension chargers provided for Model S, Model X and Model 3
- A built-in navigation system that helps to identify and locate the charger stations
- Charging stations are designed to supercharge Tesla vehicles that get charged in just 30 minutes
- Tesla charging stations and app system indicates when the vehicle charging is complete

6. Key Resources of Tesla
Electric Vehicle and Technological Knowledge
A) Superior Engine Design:
- High-Performance Vehicle
- Pollution & Noise free Vehicle
- Super-Fast vehicle
B) Engine components:
- Lithium-ion battery system
- Induction motor. (Rotor Speed < RMF Speed)
- Uniform induction, power, and speed.
- Brushless and requires no magnets, instead the induction creates magnetism through rotational movement
- 3-phase. Ac power input.
- Speed is dependent on the amount of voltages that are fed to the 3-phase AC power Input. Speed can range from 0-18000 RPM.
- No Transmission required a direct mount of the engine to the axel is sufficient.
Comparison Chart of the Tesla Induction Motor VS. Typical IC Engine
| Weight – 31.8 Kg | Weight – 180KG |
| Power – 270 KW | Power – 140 KW |
| Weight / Power – 8.5 KW / KG | Weight / Power – 0.8KW / KG |
Battery System
- Lithium-ion Batteries. (DC Power)
- 7,000 individual battery cells constituted into the design into 16 compartments
- A range of 16 compartments that act as one big cell.
Effective Cooling
- The use of small individual cells is a guarantee of sufficient cooling, instead of using a few big batteries
- This also increases the battery duration and lifeline.
- Glycol is used as the cooling medium that is bypassed through the gaps between the rows of the cells in each of the 16 lithium-ion compartments.
- Battery alignment and frame offers the vehicle side skirt support from a vehicle collision.
Automation & Engineering
- Induction motor. (Rotor Speed < RMF Speed) Uniform induction, power, and speed.
- Brushless and requires no magnets.
- Inverter system = 3 phase. Ac power input.
- Speed is dependent on the amount of voltages that are fed to the 3-phase AC power Input.
- Speed can range from 0-18000 RPM.
- No Transmission required a direct mount of the engine to the axel is sufficient
- Another positive aspect of Tesla that helped progressed its success is the reliability of its big data , which is derived from its in-vehicle software, and strategic partnerships.
- Through channeling new departments, opportunities and the new business operations, Tesla was able to generate potential clients and aim at different business endeavors successfully such as solar energy systems, retail merchandise, etc.
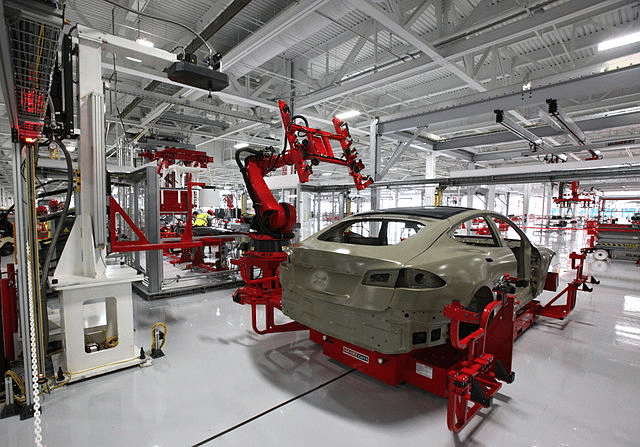
7. Channels of Tesla
The following are the set of channels that Tesla utilizes to channel and market its technology:
- Retail stores & galleries – Tesla, Inc. retail stores and galleries are designed and built to showcase Tesla vehicles and maximize customer experience. In early 2019, there were around 276 Tesla stores worldwide of which around 130 were based in the US but the company has closed most of its stores globally and moved to online sales channels . [ 7 ]
- Self Service online store (website)
- Conferences & sales events

8. Cost Structure of Tesla
In FY 2019, Tesla’s annual revenue was $24.578 Billion with a net expense of about $24.72 Billion, which leaves the company with a net loss of $144 Million. [ 8 ]
The following are Tesla expense and cost structure;
- Cost of Goods and Services (COGS): $20.509 Billion equal to 83% of the revenue
- Selling, General & Administrative Cost: $2.646 Billion equal to 11% of the revenue
- Research & Development Cost: $1.343 Billion equal to 6% of the revenue
- Restructuring Cost: $149 Million equal to less than 1% of the revenue
- Interest Expense, Taxes, and Others: approx. 3% of revenue
9. Revenue Streams of Tesla
Tesla not only sells Electric vehicles but also has created an eco-system of a top of the line green vehicles. Also, it has introduced solar energy systems, and lifestyle products for its loyal customers and the fans of Tesla, Inc;
Here is a high level break down of Tesla’s revenue. In FY2019, the total annual revenue of Tesla was $24.578 Billion .
Automotive Segment revenue – it includes sales of all vehicle models, access to charging network, software updates, after – sales services, sales of EV components, retail merchandise, etc. Here is a further breakdown in the automotive segment.
- Vehicle sales: $19.952 Billion
- Vehicle leasing: $869 Million
Total: $20.821 Billion
Energy generation & storage segment – it includes sales of solar energy systems and storage products such as solar roof panels, etc.
Total Revenue from Energy Generation & Storage: $1.531 Billion
Services – Includes car services, repairs, consultations, and other general services
Total Revenue from Services and other: $2.226 Billion
Tesla, Inc. started its business as offering reliable ways of providing transportation. By reviving the theory of utilizing electric vehicles instead of gasoline combustion chamber engines helped to pave the recognition of sufficient EV system, which also contributed to revolutionize the automobile industry from mechanical drives to all smart computer driven electric vehicles.
Because of the strategic steps taken to design a sound EV engine system, the possibilities of actualizing an electric car that serves sufficiently and safely, Tesla, Inc. is one of the most successful EV company in today’s automobile industries and continues to develop and innovate the methods of transportation.
References & more information
- Wagner, I. (2020, July 15). Tesla’s vehicle deliveries by the quarter – YTD Q2 2020 . Statista
- Korosec, K. (2020, July 1). Tesla Blows Past Toyota to become Most Valuable Automaker in the World . Tech Crunch
- Brown, M. (2020, July 23). Tesla Cybertruck: Elon Musk Reveals where It will be Built . Inverse
- Talia, S. (2020, January 30). Tesla partners with LG Chem, CATL for battery supply . Reuters
- Crider, J. (2020, July 31). Tesla’s Newest Partnership With An HBCU Is A Great Thing . Clean Technica
- Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited (CATL): Batteries
- Williams, M. (2019, March 4). Tesla to close showrooms and move sales online . Automotive Logistics
- Investing Alerts (2020, January). Tesla Inc. Financials . Market Watch
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
A management consultant and entrepreneur. S.K. Gupta understands how to create and implement business strategies. He is passionate about analyzing and writing about businesses.
Cancel reply
Loved this!
You may also like

How Does Turnitin Work & Make Money
Last updated: May 30, 2020 Company: Turnitin CEO: Chris Caren Founders: John Barrie Year founded: 1998 Headquarter: Oakland, California, USA Employees: Est. 417 Type: Private Annual...
Swiggy Business Model (2022)| How does Swiggy make money
Last updated: Sept 07, 2020 Company: Swiggy CEO: Sriharsha Majety, Nandan Reddy, and Rahul Jaimini Year founded: 2014 Headquarter: Bangalore, India For all the foodies, what more could you ask for...

Zomato Business Model | How does Zomato make money?
Company: Zomato Founder & CEO: Steve Easterbrook Year founded: 2008 Headquarter: Gurgaon, Haryana, India. Number of Employees (2019): 5000+ Type: Private Monthly Active Users (2019): 70Million+...

Business Model of Ola (2024) | How does Ola make money?
Company: Ola Cabs CEO: Bhavish Aggarwal Year founded: 2010 Headquarter: Bengaluru, India Number of Employees (Dec 2019): 8,000 Type: Private Valuation (Dec 2019): $10 Billion Annual Revenue (FY2019): Rs 2,543.63...

20 Most Unique Business Models
Every company follows a certain business model. The growth and success of a company are based on the business model it follows. Therefore, it is essential for a business model to be diverse and adaptable. However, there...
How Does Popmoney Work ?
Last updated: May 18, 2020 Company: Popmoney (Division of Fiserv) CEO: Jeffery W. Yabuki Founders: Sanjeev Dheer Year founded: 2010 Headquarter: New York, NY Products & Services: Peer...
Twitter Business Model | How Does Twitter Make Money?
Company: Twitter CEO: Jack Dorsey Year founded: 2006 Headquarter: San Francisco, California, USA Number of Employees (2018): 4,100 Public or Private: Public Ticker Symbol: TWTR Market Cap...

How does Fabletics work and make money?
Company: Fabletics Founders: Kate Hudson, Adam Goldenberg, Don Ressler Year founded: 2013 CEO: Don Ressler and Adam Goldenberg Headquarter: El Segundo, CA Employees (2020): Est. 500 Annual Revenue (2020): Est...

How Does Snapchat Make Money?
Company: Snapchat CEO: Evan Spiegel Year founded: 2011 Headquarter: Santa Monica, California, USA Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 2884 Public or Private: Public Ticker Symbol: SNAP Market Cap (April...

How Does HQ Trivia Make Money?
Last updated: Feb 18, 2020 Company: HQ Trivia Founders: Rus Yusupov and Colin Kroll Year founded: 2017 CEO: Rus Yusupov Headquarter: New York, NY Number of Employees (2019): 25 Annual Revenue (2019): $10 million...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns YoungLA
- Who Owns Dave’s Hot Chicken?
- Who Owns 1440 News?
- Who Owns PNC Bank?
- Who Owns The Shade Room?
- Who Owns Professional Fighters League (PFL)?
- Who Owns Ulta Beauty?
- Who Owns History Channel?
- Who Owns Cheesecake Factory?
- Who Owns Westin Hotels & Resorts?
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors

Tesla’s master plan is 4 years old: how Elon Musk is doing on EVs and more
Four years ago, Tesla outlined a master plan that covered electric cars, autonomy and clean power. How did it do?
Tesla's most ambitious master plan yet is celebrating its fourth birthday.
On July 20, 2016, CEO Elon Musk published a blog entry that would set the company's course for the coming years. The ambitious document details commitments to transition more of the world onto sustainable energy, reach a broader mass market with electric vehicles and automate the driving process to radically transform transportation. No pressure.
It was a starkly more ambitious proposal to the original master plan that came 10 years prior. That document , published on August 2, 2006, outlined four clear steps: build a sports car (which became the 2008 Roadster), use the money to build an affordable car (2012's Model S), use that money to build an even more affordable car (2017's Model 3) and provide zero-emissions energy sources in the process.
Tesla's second master plan upped the ante, with a bold four-goal strategy:
"Create stunning solar roofs with seamlessly integrated battery storage. Expand the electric vehicle product line to address all major segments. Develop a self-driving capability that is 10X safer than manual via massive fleet learning. Enable your car to make money for you when you aren't using it."
Four years on, nearly halfway through the original document's lifespan, here's how Tesla is getting on.
Integrate Energy Generation and Storage – This first section explains how Tesla will merge with SolarCity, offer a solar roof with battery, then scale it globally. This would offer "one ordering experience, one installation, one service contact, one phone app."
Tesla merged with SolarCity later that year, so that's checked off. The solar roof has been a slightly slower rollout: an early version started reaching Californians in spring 2018, but Musk would later explain in March 2019 that initial rollout was slow due to company-wide constraints.

Tesla Solar Roof.
It wasn't until the third generation launched in October 2019 that Tesla finally started offering it in larger numbers and in more parts of the United States. The roof still has yet to go global, but Musk claimed in February 2020 that the company would expand the product internationally this year .
Master plan progress: 60 percent. The roof may be elusive, and international expansion has yet to happen, but it is a real product that has shipped out to customers in increasing numbers.
Expand to Cover the Major Forms of Terrestrial Transport – This part of the plan outlines several vehicles, aimed at most forms of ground-based transport. There are three consumer vehicles: the Model 3, a compact SUV, and a pickup truck. There's the Tesla Semi electric truck, and an urban transport vehicle with high passenger density. Autonomy could make the bus disappear and transfer the bus driver into a fleet manager. The factory building the Model 3 will improve, as it becomes the machine that builds machines.
That first part is coming together. Tesla launched the Model 3 in July 2017, launched the Model Y compact SUV in March 2020, and is expected to launch the Cybertruck in late 2021. The Tesla Semi is expected to hit roads in increasing numbers soon, as the firm starts building together a pilot production line .

Tesla Cybertruck.
The urban transport vehicle seemed at one stage to get axed from Musk's plan, but in June 2020 new reports claimed the firm is working with Musk's other venture The Boring Company to develop a 12-passenger electric van . The Boring Company's tunnels are designed to support autonomous, electric vehicles.
Musk's initial optimism about automating the factory faded amid Model 3 production issues. In April 2018 Musk described "excessive automation" as "a mistake." An emergent new focus in speeding up production is to build factories around the world , bringing affordable cars closer to the buyers and simplifying production lines. A Shanghai factory has already started building cars, boosting China market share , and a Berlin factory is under construction.
Master plan progress: 60 percent. Of the five vehicles outlined above, two have started hitting roads and two have been repeatedly sighted in prototype form. Tesla is also building vehicles at speed and taking on more market share, thanks to its tweaked factory goals starting to pay off.
Autonomy – Tesla is aiming for full, point-to-point autonomous driving. Once the software has been built and refined, regulatory approval would take some time. Musk suggested this would take somewhere closer to six billion miles of experience to convince regulators.

Tesla Autopilot could one day support point-to-point autonomous driving.
Tesla has released a series of new features, including the likes of Smart Summon that parks the car autonomously and Navigate on Autopilot that exits the highway at the correct location depending on destination. It also detailed the Hardware 3 platform in August 2018 that will support fully autonomous driving, an upgrade that has started appearing in new vehicles. Tesla Autopilot has now completed three billion miles . Musk stated in May 2020 that Tesla is aiming for a feature-complete version of full autonomy by the end of this year, which would drive from A to B with human oversight.
Master plan progress: 20 percent. The autonomous driving software has improved, but it still can't drive from A to B even with human oversight. Regulatory approval for complete hands-off driving seemingly remains distant.
Sharing – Building off the autonomous driving features, Tesla owners would be able to add their vehicle to a shared fleet. This Uber-like fleet would earn money for the owner while they're not using the car, which in turn "lowers the true cost of ownership to the point where almost anyone could own a Tesla." The firm will add vehicles to the fleet for cities where there aren't enough Tesla owners.
As the autonomy project has progressed, Tesla has gradually released more ideas about how the system would work. There would be a smartphone app used to hail rides, initially with a person in the driver's seat, due to launch in 2021. It has also tweaked its leasing terms to take vehicles back at the end of a lease for use in the taxi service.
Master plan progress: 10 percent. While it's provided more details about how a sharing app would work, and it's made steps on autonomy, this vision still seems as distant as ever.
This article was originally published on July 20, 2020
Leadership & Success
What can we learn from tesla’s business strategy.
Andrew Moran

This article is part of our Business Strategies series, an insight and analysis into the makeup and model of some of the world's most successful startups.
In late 2018, Tesla Motors CEO Elon Musk revealed on Twitter that he was thinking about taking the company private. An investment firm, AKR Invest, pleaded with him to reconsider by making the case that selling at $420 a share would undervalue the company significantly.
Fast forward to a little more than a year later and Musk must be pleased that he ditched the idea. With company stock trading in the range of $800 to $900, AKR now anticipates that Tesla shares could spike to $7,000 by 2024. Too good to be true, or a realistic possibility?
Either way, Tesla has made a significant dent into the automotive industry, the energy sector, and even the way automakers sell cars. What started as a perturbed reaction to General Motors recalling its fleet of EV1 electric vehicles has transformed into a juggernaut that is selling cars, energy products and infrastructure across the globe.
So how has the company managed to achieve this? To answer this question, we've compiled an in-depth analysis of the Tesla business strategy – as well as what your company could potentially learn from it.
Vital Information

- Founded : July 2003
- Founders : Martin Eberhard, Marc Tarpenning, Elon Musk, JB Straubel and Ian Wright
- Headquarters : Palo Alto, CA, USA
- Current CEO : Elon Musk
- Global Employees : 48,000 (2019)
- Type : Public (Floated June 2010)
- Initial Funding : $7.5m in venture capital (February 2004)
- Key Products / Services : Electric vehicles
To accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy.
Tesla Mission Statement
To create the most compelling car company of the 21st century by driving the world's transition to electric vehicles.
Tesla Vision Statement
Officially incorporated in 2003 by two engineers and named in honour of the legendary electrical engineer and inventor of the same name, Tesla underwent several funding rounds between 2004 and 2007. One of the earliest investors was former PayPal CEO Elon Musk, who was keen to develop the company's vision beyond just electric vehicles to renewable energy sources, too.
In January 2020, the company became the most valuable US automaker ever to exist (and the second most valuable in the world, behind Japanese car giant Toyota).
Tesla's Business Model
In general, experts continue to be bullish over electric vehicle (EV) dominance in the global auto market. A 2018 report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) forecasts that electric car ownership will rise from the current four-million mark to more than 120 million by 2030. To put it another way, EV prevalence will jump from 0.3% to approximately 7% of the global car fleet. Estimates vary between conservative and optimistic, but either way, the EV market will be integral to both the auto industry and the global economy in the coming decade.
There are three primary reasons for EV growth, of which Tesla is currently leading the way in terms of development:
- Consumer demands and customer expectations.
- Technological advancements in electric cars.
- Government regulations on safety and vehicle emissions.
However, it was not always thus.
When Tesla first opened its doors, Musk took a unique approach to sell electric automobiles: creating a sports car that could compete with gasoline-powered vehicles rather than a cheap, mass-produced vehicle. Musk explained that it would have been impossible for the startup to mass market its first product because it was never constructed, enduring several technology hiccups and possessing zero economies of scale. As a result, the company's first release was the Tesla Roadster, a high-powered performance vehicle powered entirely by a lithium-ion battery.
The Roadster proved a moderate success, shifting around 3,000 units before curtailing output in January 2012 and, with the infancy stage out of the way, Tesla was able to become an established brand that attracted both customers and capital. The company then evolved its business model to selling, servicing and charging:
Sales : Tesla is unique in that it sells its automobiles directly to customers without relying on dealers. It uses close to 400 company-owned showrooms and galleries in major urban centres around the world to boost product development speeds and improve the buying experience. Tesla has also utilised an online sales platform .
Service : Many of the Tesla-owned and operated sales centres are combined with service centres. Tesla also has a mobile technical service comprised of Tesla "Rangers", who travel to customer homes to assess and repair any issues. In another considerable advancement, Tesla's cars can also wirelessly upload data to the company so that remote technical support teams can view and fix malfunctions.
Charging Network : A common concern for the EV market is the power charging aspect. Tesla has developed a vast network of supercharging stations where owners can charge their cars for free. Tesla believes that these stations can increase the adoption rate for its EVs, which explains the growth in stations across the US, Europe and Asia.
Over the years – and in line with Musk's wider vision – Tesla has branched out from just vehicles. It sells parts and components to other automakers and retailers, including a range of home batteries, solar panels, full solar roofing and energy storage systems.
EVs are nothing new and existed in various shapes and forms well before Tesla's existence; however, Musk was able to take a different approach to create value for the company and establish themselves as the market leader.
Through transformational leadership practices and a focus on engineering and design, Tesla has driven the advancement of a technology which is becoming ever more mainstream, and is tied into the core concerns of both consumers and governments. Tesla vehicles will no longer represent niche vehicles, but the groundwork of an infrastructure that will change unimaginably over the next 30 years.

Elon Musk | Co-Founder and CEO
Although only deemed a cofounder as a result of a 2009 legal settlement, Musk is undoubtedly the face and driving force of Tesla as we know it. His visionary approach to leadership and management has created massive growth and, despite his increasingly bizarre personal behaviour, it is safe to say that Tesla stocks would plummet if he were to step down as CEO.
Jeffrey B. Straubel | CTO
Unfortunately for Tesla, Straubel – who served as its chief technology officer – departed the company in July 2019. He was an essential figure in the company, overseeing the technical and engineering designs of all the company's cars. While he still serves in an advisory capacity, Straubel was responsible for day-to-day technological evaluation, research and development and technical diligence. Put simply, if you drive a Roadster, Straubel's imprint is all over it.
Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning | Co-Founders and Financers
Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning incorporated Tesla Motors in July 2003 and financed the firm until it received Series A venture capital funding . Suffice it to say, these men laid the groundwork for Musk, Straubel and others to make Tesla's business plan of commercialising electric cars a reality. They had active roles within the company for several years before their ousting in 2008.
Tesla's Branding Strategy
What would you say about a company with a market capitalisation of $153bn and an advertising budget of $0? That's right. Tesla successfully sells cars worth $100,000 to $250,000 without any formal marketing plan . Compare this to Ford, who spent $2.3bn on advertising in the US in 2018, or Honda doling out $1.39bn to reach the public. So, how is Tesla able to do it?
The first component of this strategy is that the company plays hard to get. It's the classic exclusivity play: the more difficult it is to get your hands on a Roadster, the more you want one. To illustrate this further:
- Every car is built to order; Tesla does not maintain an inventory of vehicles, negating the need for forecasts .
- As noted, there are no dealerships.
- A deposit of $100 is required (this used to be as high as $5,000).
- Customers are required to book a test drive before buying.
- Most buyers do not get to the see vehicle before they buy it.
- Customers must wait several months before the vehicle is delivered.
Ultimately, Tesla makes it seem like it does not want your money – an effective if somewhat unorthodox brand strategy .
The company also maintains a referral program for its cars and solar products. Anytime owners refer potential customers, they receive awards when they buy a Tesla product (points, cash reward, or a contest to win a car), inspiring further loyalty to the Tesla brand.
Another critical element of Tesla's branding endeavours is the cult of personality around Musk himself. His tweets generate headlines, and his appearances in front of television cameras are usually must-see. Whenever there is a Tesla product launch, it becomes a global event rather than a public relations campaign, which elicits the kind of free publicity that many companies can only dream about.
Competition
As the world starts coming to terms with the impact of carbon emissions and the viability of EVs as a credible long-term alternative, every auto manufacturer is now seemingly delving into the EV market, attempting to take a slice of the pie. It is a wise investment for every company to make, considering the bullish projections for the industry, but will anyone topple Tesla from its throne?
While it can be hard to predict accurately and time the market, some businesses can realistically go toe to toe with Tesla, especially over a long-term trajectory.
Here are some brands to file for future reference:
General Motors : GM and its shareholders have accepted that the company's Bolt and Volt models will not compete with Tesla today, but the brand might rival that of Tesla tomorrow. Not only is it investing in both EVs and autonomous cars, but GM is also preparing to disrupt transportation (as evidenced by investments in Lyft) and manufacturing with its Cruise model. In the next decade, GM will likely be as attractive as Tesla to consumers and traders.
Volkswagen : The Volkswagen Group is going all-in on electric, promising to deliver 70 new EV models in the next decade. The 80-year-old industry giant may not be trying to take on Tesla, but it could rival Musk's company over time by homing in on the mass-market aspect.
Nio : Although unfamiliar to many, this Chinese firm is generating a lot of buzz in venture capital circles for its pioneering technology. The company has experienced a lot of success as of late, including a 35% sales surge, a partnership agreement with Intel, and critical acclaim from industry experts. Despite Tesla's market play in China, Nio may rise to be the chief player in the years to come.
Tesla's Company Culture
Over the years, Tesla has been known to miss quarterly targets, oversell on its promises, and experience numerous technological mishaps. Rather than dwelling on the negatives and apologising profusely, though, the company has turned these hiccups into a positive. As Tesla's corporate strategy states: "We do not cut corners, and we do not settle. No forecast is perfect, but try anyway. We constantly strive to improve the accuracy of our forecasts as well as the reliability and service with which they are delivered. Respect and encourage people."
On the one hand, this emphasises how the company strives to be the best at what it does. On the other, however, it admits that its forecasts need improvement, but that it only misses these estimates because it does not cut corners or settle for anything but premium quality.
Meanwhile, Tesla's corporate culture encourages autonomy among its workforce, fostering an environment of innovation to search for ideal solutions to a whole host of problems related to automobiles, energy generation and industrial storage. Many company reviews by former or current employees typically state that it is a great place to work with competitive pay, plenty of benefits and perks and a positive atmosphere.
Tesla Motors can serve as a corporate role model for any young entrepreneur or large business that is looking to turn things around. A lot of Tesla's success can be attributed to Musk's innovation and outside-the-box thinking, but the company can only go so far as the people it employs, which is a key takeaway.
Indeed, as Musk has stated repeatedly, practical skills and critical thinking supersede any piece of paper. If you are a technology firm or you are solely focused on the development of a single product, then this is wise recruitment advice to follow. There are also numerous leadership lessons to learn from Musk's tenure, including the idea that company management is about fine-tuning, adapting, innovating, creating and, most important of all, listening.
Whether it is a new product or a feeling of exclusivity, Tesla checks off all the boxes of how 21st-century businesses should and could operate, and there is no reason why your enterprise cannot follow suit.
Was this article helpful? What other business lessons can entrepreneurs learn from Tesla's business strategy? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
Brand Strategy
Company Culture
Business Strategies
Business Models
Case Studies
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How Tesla Sets Itself Apart
- Lou Shipley

It’s ushering in the age of the software car.
Tesla and its flamboyant, and sometimes erratic , innovator Elon Musk have turned the more than a century old industry upside down in a mere 16 years. T raditional automakers are ill prepared to compete in today’s software-centered world. Unlike nimble Tesla, they are big, bureaucratic, slow to respond to customers, dependent on providing customer financing for unit sales growth, and culturally different from a software company. Tesla’s speed in innovation in the market for high-end vehicles is more like a Google or an Amazon than an automaker. And its soaring market valuation is a clear sign to all automakers that they’ll need to develop more innovative, Tesla-like business models in order to survive.
Tesla’s recent breakout market performance is proving some of its skeptics wrong. By mid-January, Tesla’s market capitalization had reached $107 billion, and it surged past the giant German automaker Volkswagen to become the world’s second most valuable auto company behind Toyota. Tesla’s valuation now exceeds that of Ford and GM combined. The Wall Street doubters may be in shock, but I’m not. Full disclosure, I own two Teslas and I own stock in the company. But it’s my experience as a three-time software company CEO that makes it increasingly clear to me that the company’s innovative business model represents an existential threat to the auto industry as a whole.How so?“Software is eating the world,” Marc Andreessen, co-founder and general partner of venture capital firm Andreessen Horowitz, wrote in a memorable 2011 essay. And software is a big part of Tesla’s advantage.
- Lou Shipley is a Senior Lecturer in Entrepreneurial Management at Harvard Business School. He serves on the boards of six early-stage technology companies.
Partner Center

Decoding Tesla's Business Model and Revenue Streams
Uncover the secrets behind Tesla's innovative business model and diverse revenue streams in this captivating article.

Tesla, the pioneering electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer, has disrupted the automotive industry with its unique and innovative business model. This article aims to decode Tesla's business model and explore its various revenue streams, as well as address the challenges and criticisms it has faced. Furthermore, the article will discuss the role of innovation and offer predictions for the future of Tesla and the automotive industry as a whole.
Understanding Tesla's Unique Business Model
Tesla's business model is driven by its vision to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. The company's mission is to create the most compelling car company of the 21st century, while also contributing to the global shift towards renewable energy sources. Tesla achieves this through its integration of sustainable energy generation, storage solutions, and electric vehicles.
The Vision and Mission of Tesla
Tesla's vision encompasses a future where cars run on clean energy, reducing the world's dependence on fossil fuels and combating climate change. The company's mission revolves around producing electric vehicles that are not only environmentally friendly but also superior in terms of performance and design.
In pursuit of this vision and mission, Tesla has set ambitious goals. One of these goals is to produce affordable electric vehicles for the mass market, making sustainable transportation accessible to a wider audience. Another goal is to expand its renewable energy solutions beyond electric vehicles, such as through the development of solar panels and energy storage systems.
Key Components of Tesla's Business Model
Tesla's business model consists of several key components. Firstly, the company focuses on vertical integration, which means controlling its entire supply chain to ensure quality and efficiency. By owning its manufacturing plants and retail stores, Tesla has greater control over its operations.
Secondly, Tesla has invested heavily in research and development (R&D), enabling continuous innovation and improvement of its products. This commitment to R&D has resulted in technological breakthroughs and advancements in battery technology. Through its Gigafactories, Tesla has been able to scale up production and drive down costs, making electric vehicles more affordable and accessible.
Furthermore, Tesla has prioritized building a strong charging infrastructure, including its Supercharger network, to address range anxiety and make electric vehicles more practical and convenient for consumers. This network of fast-charging stations allows Tesla owners to travel long distances with ease, reducing the barriers to electric vehicle adoption.
Additionally, Tesla has embraced a direct-to-consumer sales model, bypassing traditional dealership networks. This approach allows Tesla to have a more personalized and direct relationship with its customers, providing a seamless buying experience. By cutting out the middleman, Tesla can also maintain better control over pricing and distribution.
How Tesla's Business Model Differs from Traditional Automakers
Unlike traditional automakers who primarily rely on internal combustion engines, Tesla exclusively produces electric vehicles. By specializing in EVs, Tesla has a competitive advantage in terms of eco-friendliness and driving experience. Electric vehicles offer lower emissions, quieter operation, and instant torque, providing a unique and exhilarating driving experience.
Furthermore, Tesla's approach to sales and distribution sets it apart from traditional automakers. While traditional automakers rely on franchised dealerships, Tesla sells its vehicles directly to consumers through its own retail stores and online platform. This direct-to-consumer model allows Tesla to have better control over the customer experience and build a stronger brand connection.
Moreover, Tesla's commitment to sustainable energy goes beyond just producing electric vehicles. The company actively promotes the adoption of renewable energy by offering solar panels and energy storage solutions through its subsidiary, SolarCity. This integration of sustainable energy generation, storage, and transportation sets Tesla apart from traditional automakers who have yet to fully embrace the potential of renewable energy.
In conclusion, Tesla's unique business model revolves around its vision to accelerate the world's transition to sustainable energy. Through vertical integration, heavy investment in R&D, a strong charging infrastructure, and a direct-to-consumer sales approach, Tesla has positioned itself as a leader in the electric vehicle industry. By prioritizing sustainability, performance, and innovation, Tesla continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in the automotive industry.
Dissecting Tesla's Multiple Revenue Streams
Tesla generates revenue through various sources, each contributing to its overall success and financial stability.
But let's dive deeper into these revenue streams and explore the fascinating details behind Tesla's multifaceted business model.
Revenue from Electric Vehicles
The primary revenue stream for Tesla comes from the sale of its electric vehicles. With models like the Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y, Tesla has established itself as a leader in the EV market.
But it's not just about selling cars. Tesla's approach to electric vehicles goes beyond the initial purchase. The company's focus on high-performance electric cars has attracted a loyal customer base willing to pay a premium for these cutting-edge vehicles.
Moreover, Tesla benefits from software updates and optional features, providing additional revenue streams. These updates not only enhance user experience but also unlock new functionalities, such as Autopilot capabilities. This continuous improvement model ensures that Tesla owners stay engaged and satisfied with their vehicles, while also generating ongoing revenue for the company.
Energy Generation and Storage Revenue
In addition to electric vehicles, Tesla has entered the renewable energy market and generates revenue through its energy generation and storage solutions.
Tesla's solar panels and Powerwall battery pack allow consumers to harness clean energy, reducing their reliance on the grid. This not only provides environmental benefits but also offers financial savings for customers in the long run.
Furthermore, Tesla's energy generation and storage solutions have applications beyond residential use. The company also offers its products to commercial and utility-scale customers, creating additional revenue streams and expanding its reach in the renewable energy sector.
Services and Other Revenue
Tesla offers various services and products that generate additional revenue.
Firstly, there are the maintenance and repair services. Tesla's commitment to customer satisfaction extends beyond the initial sale, with a comprehensive service network that ensures owners can keep their vehicles in top condition. This not only generates revenue but also helps build customer loyalty and trust.
Secondly, Tesla offers extended warranties, giving customers peace of mind and providing an additional revenue stream for the company. These warranties cover various components and systems of the vehicles, further enhancing the ownership experience.
Additionally, Tesla has capitalized on its brand recognition by selling merchandise. From clothing to accessories, fans of the company can show their support and contribute to Tesla's revenue through these branded products.
Furthermore, Tesla's Autopilot software subscription and its Full Self-Driving package provide ongoing revenue streams. These features allow Tesla owners to access advanced driver-assistance systems and even future autonomous driving capabilities, creating a continuous revenue stream for the company.
As we can see, Tesla's revenue streams are not limited to just selling electric vehicles. The company's innovative approach to software updates, energy generation and storage solutions, and various services and products have contributed to its financial success and established Tesla as a leader in the automotive and renewable energy industries.
The Role of Innovation in Tesla's Business Model
Innovation lies at the core of Tesla's business model. The company's approach to innovation is characterized by its commitment to pushing boundaries and revolutionizing the automotive industry.
One of the key factors that sets Tesla apart from traditional automakers is its relentless pursuit of innovation. Tesla's focus on electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions has reshaped the industry and challenged the status quo. By introducing cutting-edge technologies and reimagining the way cars are designed and manufactured, Tesla has become a symbol of innovation and a pioneer in the field.
Tesla's Approach to Innovation
Tesla fosters a culture of innovation by encouraging its employees to think outside the box and take risks. The company's CEO, Elon Musk, is known for his ambitious goals and visionary mindset, which sets the tone for Tesla's innovation-driven culture. Musk's belief in the power of innovation to solve complex problems and drive progress permeates throughout the organization.
At Tesla, innovation is not limited to the research and development department. The company actively seeks input and ideas from all employees, recognizing that innovation can come from anywhere within the organization. This inclusive approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowers employees to contribute their unique perspectives and expertise.
In addition to internal innovation, Tesla also actively collaborates with external partners and constantly explores new technologies and ideas. By leveraging the expertise of other companies and researchers, Tesla is able to stay at the forefront of technological advancements and bring new innovations to market more quickly.
Impact of Innovation on Tesla's Revenue
Tesla's commitment to innovation has translated into substantial revenue growth. Technological advancements, such as improved battery efficiency and autonomous driving capabilities, have attracted customers and investors alike. The company's ability to deliver cutting-edge products that exceed customer expectations has fueled strong demand and contributed to its financial success.
Furthermore, Tesla's ability to innovate and stay ahead of competitors has contributed to the company's market leadership and strong financial performance. By continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the automotive industry, Tesla has established itself as a leader in electric vehicles and sustainable energy solutions. This market leadership has not only increased Tesla's revenue but also enhanced its brand value and reputation.
Looking ahead, Tesla's commitment to innovation remains unwavering. The company continues to invest heavily in research and development, exploring new technologies and concepts that have the potential to reshape the future of transportation. With its focus on innovation, Tesla is well-positioned to continue disrupting the automotive industry and driving the transition towards a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Criticisms of Tesla's Business Model
While Tesla's business model has been highly successful, it has also faced significant challenges and criticisms.
Financial and Operational Challenges
One of the main challenges Tesla has encountered is achieving financial stability. The company has experienced periods of cash flow constraints and has relied on capital raises to fund its operations. Additionally, scaling up production to meet demand has proven to be a complex task, resulting in production bottlenecks and delays.
Criticisms and Controversies
Tesla's business model has faced scrutiny and criticism, particularly regarding its valuation and profitability. Skeptics argue that the company's stock price is overinflated and point to its history of losses. Furthermore, Tesla has faced controversies surrounding its Autopilot system and safety concerns.
The Future of Tesla: Predictions and Possibilities
The future of Tesla holds vast potential, as the company continues to innovate and expand its business model.
Potential New Revenue Streams for Tesla
Tesla is exploring new avenues for revenue generation. One key area of focus is the development of autonomous ride-hailing services, which could create a significant new revenue stream for the company. Additionally, Tesla's energy storage solutions have the potential to transform the grid infrastructure and contribute to the growth of a sustainable energy ecosystem.
The Sustainability of Tesla's Business Model
The sustainability of Tesla's business model depends on several factors. Firstly, advancements in battery technology and charging infrastructure will be critical for mass adoption of electric vehicles. Secondly, ongoing investment in R&D and innovation will be vital to maintain a competitive edge in the evolving automotive industry. Finally, expanding global market opportunities and regulatory support will play a crucial role in sustaining Tesla's growth.
Tesla's Impact on the Future of the Automotive Industry
Tesla's success has spurred other automakers to accelerate their transition to electric vehicles and invest in sustainable energy solutions. The company's influence on the industry is undeniable, with many traditional automakers shifting their strategies to prioritize electric mobility and reduce carbon emissions. Furthermore, Tesla's sustainable business practices and commitment to environmental stewardship have set a benchmark for the automotive industry as a whole.
In conclusion, Tesla's unique business model and its multiple revenue streams have positioned the company as a leader in the electric vehicle market. By integrating sustainable energy generation, storage, and electric vehicle production, Tesla has revolutionized the automotive industry. However, Tesla faces challenges and criticisms, such as financial constraints and controversies. Nonetheless, the future looks promising, with potential new revenue streams and the company's ongoing commitment to innovation and environmental sustainability. Tesla's impact on the automotive industry will likely continue to shape the future of mobility and drive the transition to a sustainable energy future.

Helping designers and strategists turn their boldest ideas into market-leading ventures through Business, Design and Growth.
Whenever you are ready - here is how I can help:
1. Newsletter . Join over 2.000 founders, creators and innovators and get access to the business builder framework.
2. Business Builder OS - Masterclass on finding growth opportunities, building lean offers and acquiring customers - driven by A.I.
3. Builder Toolkit - 30 ideas on how to grow your revenue.
Actionable advice about spotting new opportunities, creating offers & growing revenue.

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

Tesla Business Model Analysis
Tesla is vertically integrated. The company runs and operates Tesla’s plants. Cars are manufactured at the Gigafactory which also produces battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles. These are sold via direct channels (Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores). In 2023, Tesla generated $96.77 billion in revenues. Automotive sales generated $78.5 billion (81% of the total revenues); services/other generated $8.32 billion, and energy generation and storage generated about $6.03 billion in revenues.
| $78.5B | 81% | |
| $1.79B | 1.85% | |
| $1.64B | 3.05% | |
| $8.32B | 8.6% | |
| $6.03B | 6.24% | |
| $96.77B |
| July 1, 2003, San Carlos, CA | |
| June 29, 2010 | |
| $17.00 | |
| 2008 | |
| $96.77 Billion | |
| 140,473 full-time subsidiaries employees worldwide by 2023 | |
| $688,908 | |
| Elon Musk is the primary individual shareholder, with 20.6% of the company’s shares |
Table of Contents
Tesla business model quick breakdown
We describe the Tesla business model via the VTDF framework developed by FourWeekMBA.
| , where the more the software is used to record mileage, the better it gets. And the more Teslas are on the road, the more it creates the infrastructure where these cars understand each other. And the more energy stations are available, the more EVs become convenient vs. gas-powered vehicles. Also, Tesla is one of the few companies that managed to build a sold car business at scale, in the last century. | |
Tesla’s business model today
To understand where is Tesla today, in terms of business model evolution, see the graphic below.

For all its life, Tesla has been recording net losses and burning cash.
And yet, in a single year, by 2021, it generated so many profits to cover most of the losses recorded in the previous decade.
This is what it means to achieve scale. This is where Tesla is today in terms of scale!

Indeed, when Tesla launched, it had to first showcase that it would be possible to build an EV that would be able to combine performance and aesthetics.
Let me recap the various stages of the evolution of Tesla as it scaled.
Indeed, when looking at any company, it’s critical to understand that it follows a transitional business model, each of which, will serve the company well throughout a specific stage of Scale.
At a certain scale, you need a specific product enhanced by technology, which will help you serve a market, through distribution .
As the company gets ready for further stages that old business model transitions to a new one, where the core building blocks also change.
Let me explain:
Phase 1: Tesla Roadster and microniching
In the first stage of growth, Tesla had the first to build a viable EV.
Thus, initially, the problem was more about developing the proper technology and an EV in the first place, which would be comparable to a gas-based vehicle.
Tesla did that by targeting a narrow sub-segment of the sports car industry.
A few hundred people were interested in a sports car that would combine performance and aesthetics, while also avoiding pollution.
At that stage, Tesla didn’t need huge demand, but only a few hundred interested people.
And it didn’t need large manufacturing facilities, but only the proper technology to build a viable EV.
Things changed as Tesla accomplished the task of proving it was able to build a sports car.
This is the moment where Tesla’s business model would be successful by simply targeting a small number of innovators.
This stage was between 2006-2012.
Phase 2: Launching the Model S to target the early adopter
As Tesla managed to achieve the first stage of growth, its business model transitioned, by targeting a wider segment of the market.
To do so, the company had to figure out how to scale manufacturing, while providing a larger number of vehicles, and a product, the Model S, targeting the higher-end of the car market.
Still there, Tesla didn’t need millions of customers, but rather a few thousand.
And this opened up new options to scale for the company.
At this stage, scaling manufacturing was part of the puzzle. Most of it was to test the technology on a much wider number of vehicles, to see if it would be viable at such a scale.
All while expanding demand.
This stage was between 2012-2018.
Launching the Model 3 for mass adoption.
In the third stage of growth (which is still ongoing today), Tesla had to target the mass market.
In this context, scaling up manufacturing has become critical.
Indeed, if you asked Elon Musk where he focused most of his attention between 2018-2022, he might say the modeling/engineering of manufacturing facilities that would be able to scale production.
This was an incredible fit, which only Tesla managed to achieve in the last decades.
As Tesla went through these stages of its business model, the company has gone through various near-death experiences.
In fact, going from one stage of Scale to the next is not easy as it requires a paradigm shift.
Tesla founding story
The electric carmaker company is owned by entrepreneur/visionary Elon Musk. Tesla was founded by Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning in July 2003. Elon Musk entered Tesla in 2004, first as an investor and chairman, then he took the role of CEO which he still holds today.
After many delays to the first production of the Tesla Roadster prototype (the first version of the Tesla, which was both a way to validate the market and to generate revenues to be invested in the production of new Tesla models), Martin Eberhard would eventually be ousted, and Musk would, later on, by 2008, become CEO of the company.
It all officially started in July 2003, when the company got incorporated as Tesla Motors, Inc. Two men, Eberhard and Tarpenning, got appointed respectively CEO and CFO.
They had known each other from their time at NuvoMedia, the company they had led to the development of the Rocket eBook. The first e-book was launched in 1996 when the commercial Internet was still at the embryonic stage (for some context, the Amazon Kindle would be launched in 2007).
Yet, even though Eberhard had founded and led NuvoMedia to a successful acquisition, which in the year 2000, was purchased for $187 million, by another media company, Eberhard was all but rich.
In fact, over the years his shares in the company had been diluted to the point, that, Eberhard’s exit from the sale only had not made him rich, but as he was divorcing his wife, most of that wealth went to her, and Eberhard had to start all over again.
Yet, along his journey Eberhard, had met Elon Musk, which, by 2003, was deep into his new venture: SpaceX.
Musk’s first ventures
Elon Musk had successfully exited the PayPal sale, by making $180 on a $1.5 billion acquisition in 2002. Yet, while SpaceX had been founded in 2002, Elon Musk had started to look into it, a couple of years before.
Musk was not new to entrepreneurship and the rollercoasters this “profession” was about. In fact, a few years back to PayPal, in 1995, together with his brother, Musk had founded Zip2.
The company built maps and business directories, which were very useful applications for media websites. Eventually, they sold the company to Compaq, for over $300 million, which made Elon Musk more than $20 million to start his next company. Zip2 would become a component of AltaVista, the search engine owned by Compaq.
With the new cash infusion, Musk started his next company, called X.com. Musk’s vision was to transform X.com into a financial behemoth, through the Internet. While his vision was unbounded, he also pushed his team to execute fast.
Yet, X.com had been founded in late 1999, when the commercial Internet was still young, and revolutionizing the financial system was not as simple as it seemed.
X.com’s team randomly met the team of Confinity (for a period they were neighbors sharing the same office building).
Another startup, created in late 1998, similarly to X.com was trying to build an Internet financial company. Yet, while X.com had an unbounded vision, Confinity, which had been founded by Pether Thiel, and Max Levchin, wanted to give people the ability to pay online, by beaming their money through a device, called PalmPilot.
For some context, in the late 1990s, the Palm Pilot was a successful device, especially in California, which is where Confinity was operating. Yet, the initial business plan of the company didn’t seem to work in the real world.
In fact, the beaming technology never took off as they had envisioned.
Instead, by late 1999, one thing was clear, a “side feature” became the killer commercial application for both companies. That was the ability to pay by using an email.
This, in fact, would become the primary feature for both X.com and Confinity, and both had stumbled upon it, as it got very popular on a platform: eBay.
While those two companies were very different, they had completely different visions, and leadership, in a strange turn of events, the companies that once were neighborhoods, eventually merged.
The new company was called PayPal, after Confinity’s email payment feature, which was already well known thourhg eBay. Thus, the company took the name of the side-feature, which unexpectedly became the commercial killer application.
Yet, by early 2000, the newly created PayPal, was all but safe.
In fact, the various near-death experiences in a year time frame turned PayPal into a drama machine. In the meantime, this drama machine had taken out various CEOs, until Elon Musk became – unwillingly – CEO of the company.
Yet, once CEO he pushed the company with his unrelenting management style, which pushed people beyond their limits. The management style of Musk, coupled with a complete divergence in vision between Musk and the other co-founders (in particular Thiel, Levchin, and Sacks) led to a final conflict.
Indeed, in 2000, Musk would be ousted as CEO, with a coup organized by PayPal’s other co-founders, Peter Thiel, Max Levchin, and David Sacks. As Musk was on his honeymoon, he was flying and he could not fight that back.
Musk was out from PayPal, and now he had time to think about what would come next!
As Musk got time to think about his next ventures. He had looked into something that he had been passionate about since childhood: space.
First, he tried to get involved by helping NASA get more funds and interest, in space exploration. He thought that was the main issue. Space exploration, a hot topic, during the 1960s-70s, had stalled, in the last decades.
Yet Musk realized it was not a matter of funding. The whole innovation system, related to space, was non-existent, so he needed to get involved.
As he got involved, he started to build SpaceX, from scratch. Indeed, initially, he had looked into various ways, to outsource parts of the rockets. But over time, SpaceX would have a different approach. SpaceX started to build all the components that would make up the rocket, in-house.
And yet, let’s remember, when SpaceX’s journey, crosses that of Tesla, we’re in 2003, when all SpaceX had was a prototype rocket on a computer. It would still take a few years for SpaceX to successfully perform its first launch.
In fact, on September 28, 2008, SpaceX completed the Falcon 1 launch successfully!
In this context, Tesla entered the picture.
Back to Tesla
Musk had always been passionate about cars. In the footage, back in 1999, Musk was among the buyers of a rare supercar, which he showed off to the camera:
EVs were in the air. Indeed, in 1999, GM had launched its EV1 , which turned out as a complete flop:
But it was also about performance and coolness.
In fact, most of the electric vehicles that were in production were bulky, ugly, and ineffective.
Tesla was set to change all that.
Telsa’s Roadster
Tesla’s initial plan was to manufacture a sports car that would be compelling to a very niche audience. Indeed, the target for the Tesla Roadster was to showcase the technology to a bunch of innovators, that liked the idea of an electric vehicle, which performance, could compete with other sports cars.
However, as Eberhard started to roll out Tesla’s business model (Musk had endowed Tesla with a few million, in 2004, to start the production of the Roadster) it became clear that building a performance electric car was not an easy fit.
While Eberhard had targeted the right audience (wealthy Californians, who would use the Tesla Roadster as a status quo), he had miscalculated the execution strategy .
Indeed, Eberhard thought Tesla could be built by outsourcing most of its parts (just like he had done years back with manufacturing the NuvoMedia ebook device). Yet, this turned out to be not the case.
Several challenges came up, right on:
- Batteries cathed fire.
- Components were way more expensive than they thought.
- Large suppliers didn’t want to deal with Tesla, at the time a small startup, when the legal liability of batteries was much bigger than the potential payoff for the supplier.
All the above didn’t help.
And Eberhard felt more and more pressure, as time goes by, and the Tesla Roadster is far from manufacturing, and it was way more expensive than the price point Musk had promised.
In this period, a person which played a key role at Tesla, and would be the main point of contact for Musk was JB Straubel. An engineer at the core, he was interested in battery technology.
He had worked in 1993 for Rosen Motors, and, just like Ford, in the late 1800s, Straubel was a racer.
Indeed, for him racing electric cars was a way to showcase their torque (with respect to gas-powered vehicles, electric cars produce an instant torque, which made the start of an EV more similar to a rocket launch than a car start).
Straubel’s ability to tinker with the electric engine would prove critical. In fact, one of the major issues with battery packs was that they caught fire.
Strauber invented a way to prevent batteries to catch fire, by enabling these cells to dissipate their energy. This was a major improvement.
While Eberhard was trying to progress with the Roadster, Musk was putting growing pressure on him. He wanted Tesla to execute faster, and he came up with continuous changes to the car.
Musk, therefore, had very close ties to the company. Indeed, when he had first invested in Tesla, of the total $6.5 million round, Musk had invested $6.35 million of his own money, while Eberhard had invested $75K (as a “skin in the game deposit”).
While the relationship between Musk and Eberhard, initially was a good one.
Over time, it deteriorated. And things only got worse, when Musk introduced a team within Tesla to audit its finance and see what was the real cost of producing the Roadster, at that moment.
From the analysis, it came up that expenses were out of control, and that the challenges to producing the Roadster were none near!
This triggered Musk, who added pressure on Eberhard and convinced him to start thinking about resigning as CEO and focus on the product instead.
While they both had agreed, eventually things precipitated, and the relationship between Musk and Eberhard quickly deteriorated.
To the point that Eberhard left Tesla, by signing a non-disparagement agreement, and after a quest to find Tesla’s new CEO, eventually, Musk appointed himself! It was 2008, and one of the greatest financial turmoils was to hit the US.
The Secret Tesla Master Plan
By 2006, Musk would lay out the foundation for Tesla’s plan for the next decade. It was a four points master plan, structured as below:
- Build sports car
- Use that money to build an affordable car
- Use that money to build an even more affordable car
- While doing above, also provide zero emission electric power generation options
These four points would take a decade to be executed. Musk showed how, even when it comes to an unbounded vision, like his, most of it is still about execution.
In the meantime, Musk had become the CEO of Tesla, which had also turned into a draining endeavor, consuming a lot of his time. And yet, as the 2008 financial crisis hit, Tesla managed to survive it, also thanks to a partnership with Daimler , which kept the company afloat.
As Wired explained back in 2009:
The deal provides Daimler with batteries and the know-how needed to bring an electric car to market “at the highest possible speed,” company officials said. In exchange, Tesla gets a big pile of cash and, perhaps more importantly, the parts and engineering expertise it needs to build the Model S sedan.
This deal would be critical for Tesla to get additional oxygen while having a strategic partner, and going toward the IPO.
In fact, Tesla would IPO the year after, at $17 per share, valuing the company at about $2 billion.
Tesla borrowing Apple’s retail strategy
As Tesla started to roll out its business plan, back in 2003, the company chose to keep control over the sales experience.
This choice was not an easy one. Indeed, the Tesla executive team liked the idea to go direct to consumers. But in the auto industry that was not an easy fit.
In fact, most auto companies sold through car dealers and franchises. Those franchises represented a huge, and powerful industry, which made most of its money, not necessarily on the sale of the vehicle, but rather on servicing the vehicle over time.
Yet, since the onset, Tesla had a feeling that going through car dealers wasn’t the right pick for it. And it started to build its retail capabilities.
In that respect, Tesla borrowed Apple’s retail strategy . For that matter, George Blankenship, a key player in the retail strategy of both GAP and Apple, played a key role in launching the Tesla store operations.
In 2008, Tesla opened up its first store, in LA, on Santa Monica Blvd.:

The store would play a key role in both educating people about the Tesla brand, but also, later on, developing the service side of the business.
By controlling the customer experience, Tesla could, over time amortize the cost of the stores and build a valuable/differentiated brand. Even though Tesla’s cars were expensive.
Building up stores that sold wasn’t easy either.
By 2013, Tesla sales figures looked bleak, so much so that Musk looked into a potential sale of the company to his friends, Google’s co-founders’ Page and Brin, for $6 billion.
Indeed, after setting up the templates for the stores, Blankenship had left the company. And Tesla’s slowing sales were clear in 2015. McNeill revamped the sales force and trained it to close deals.
Where in the early days the store was only about education, by 2015, it had to become a sales machine, to make Tesla numbers add up!
By 2022, Tesla had hundreds of locations across the US.
To get to its sales numbers though, Tesla had to solve another critical issue,: making batteries for its cars available at scale!
The Gigafactory
As we go through the whole Tesla history, another key ingredient was the Gigafactory.
In fact, as Tesla had successfully launched, and dumped up production of the Roadster first, it had already started to invest in the Model S, which by 2012, had launched.
Yet, the real turning point, for Tesla’s scale would be represented by the Model 3.
Indeed, the Model 3 would have changed it all for Tesla, by expanding its market and by enabling it to “ cross the chasm .”
The Roadster proved the viability of the technology to a small niche of the sports car industry, represented by innovators who were more interested in the technology.
The Model S had represented a further step. Moving from innovators to early adopters. People are interested also in the technology, but also in the performance, aesthetics, and in part, pricing.
As Tesla moved ahead, the Model 3, became the turning point. The car to move from early adopters to the early majority.
In fact, as the company highlighted “ Tesla’s mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy through increasingly affordable electric vehicles and energy products. To ramp production to 500,000 cars per year, Tesla alone will require today’s entire worldwide supply of lithium-ion batteries.”
Therefore, where the Roadster was about prototyping, the Model S was about manufacturing, the Model 3 was all about mass manufacturing!
In order for Tesla to achieve mass scale, the Gigafactory played a pivotal role.
As the company explains :
Tesla broke ground on the Gigafactory in June 2014 outside Sparks, Nevada. The name Gigafactory comes from the word ‘Giga,’ the unit of measurement representing “billions.” The Gigafactory is being built in phases so that Tesla can begin manufacturing immediately inside the finished sections and continue to expand thereafter. Already, the current structure has a footprint of more than 1.9 million square feet, which houses approximately 5.3 million square feet of operational space across several floors. Still, the Gigafactory is about 30 percent done. Once complete, Tesla expects the Gigafactory to be the biggest building in the world – and entirely powered by renewable energy sources. Designed to be a net zero energy factory upon completion, the facility will be primarily powered by solar, and installation is already underway.
For Tesla to build its own batteries was another turning point.
Vertically integrating
As Tesla scaled, one thing was clear, Musk sought to control.
Tesla had kicked off its business plan by wanting to outsource almost everything.
Instead, it ended up manufacturing its own batteries, while going direct to consumers with its online and retail stores.
Another piece of the puzzle was lacking: energy production.
In that respect, a company called SolarCity, founded in 2006, would eventually become part of Tesla.
Musk had prompted his cousins, Lyndon Rive, and Peter Rive to start SolarCity.
The idea was to build this into an external arm, able to provide potentially clean energy for Tesla vehicles. In fact, Musk backed the company, while sitting on the boars of SolarCity and Tesla.
Yet, by 2016, the financial outlook for SolarCity looked bleak, and Tesla had to bail out the company by purchasing it for $2.6 billion.
Later on, Musk would be involved in a lawsuit from shareholders around this acquisition .
However as SolarCity looked like a bailout, Musk was able to reframe it as an expansion of Tesla’s mission.
In fact, in 2016, ten years after the Tesla Master Plan, Musk drafted the Master Plan, Part Deux (part two):
- Create a low volume car, which would necessarily be expensive
- Use that money to develop a medium volume car at a lower price
- Use that money to create an affordable, high volume car And…
- Provide solar power. No kidding, this has literally been on our website for 10 years.
As Musk justified at the time:
We can’t do this well if Tesla and SolarCity are different companies, which is why we need to combine and break down the barriers inherent to being separate companies. That they are separate at all, despite similar origins and pursuit of the same overarching goal of sustainable energy, is largely an accident of history. Now that Tesla is ready to scale Powerwall and SolarCity is ready to provide highly differentiated solar, the time has come to bring them together.
While this was a narrative Musk had built around, and to justify the acquisition of SolarCity, by 2021, the energy generating and storage segment (of which SolarCity was part) generated over $2.79 billion in revenues.

Subsidizing Tesla via its leasing arm
When Apple launched the iPhone, it combined hardware, operating system, and a marketplace to enable third-party to develop applications on top of its device.
The iPhone’s success was staggering, not just because it represented a device adopted, at mass, which would build the next consumer platform for decades to come.
Instead, Apple had managed to succeed nonetheless how expensive the iPhone was and is (the latest iPhone is more expensive than most computers out there).
How did Apple manage to succeed in distributing its iPhone?
Steve Jobs made mobile carriers subsidize the iPhone by amortizing its cost through the phone plans! ( Apple deal explained here).
Still, as of today, most of the iPhone sales do not come from Apple direct stores. They come from third-party stores, which sell those iPhones via mobile carriers plans.
This is how you make a very expensive product, accessible, at scale.
At the same time, Tesla borrowed this strategy . But rather than enabling the subsidizing of Tesla through third-party, the company is doing it the way it has always done, through in-house leasing.
In fact, back in 2019, Tesla started to rump up its leasing operations of the Model 3 (the car which is supposed to go to the masses!) to enable the amplification of its distribution strategy , by subsidizing the product, and by building its own leasing arm.
In 2021, Tesla generated over $1.64 billion in revenues from its leasing arm (growing 56% year-on-year). And it’s not just about the revenues coming from the leasing arm.
It’s primarily about the additional distribution potential that this leasing arm would add to the company’s customer base (considering that Tesla is experimenting with a $0 down payment in various states in the US).
Tesla to the masses
Back in 2018, to Musk’s admission, Tesla was going through a very tough time again (the third near-death experience), and most expected Tesla to fail.
So much so that Musk was looking into selling Tesla to Apple, for $60 billion!
The deal didn’t land, Tesla kept pushing through executing its plan, and after avoiding the worst period since its inception (short sellers were betting against Tesla since 2015), the opening of the Shangai Gigafactory made things look great again!
The Gigafactory is instrumental to Tesla’s future ability to deliver cars at scale. In 2022, another key milestone was achieved. Tesla opened its Berlin Gigafactory, right in the heart of Europe’s automotive industry!
Master Plan, Part Three: An energy infrastructure platform?
Working on Master Plan Part 3 — Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 17, 2022
While the challenges ahead for Tesla are still major, from mass production to the ability to deliver its new models, to a fully self-driving car, the ability to automate manufacturing through robotics, and to build its leasing/financing arm.
Yet Tesla seems to be building up what we can define as an energy infrastructure platform.
This platform might go well beyond cars, to embrace transportation, robotics, software, service, and finances.
The bet then is how big is this market in the future.
And to be sure, while this all makes sense in hindsight, Musk’s vision to get there has always been there. The pat was all but linear.
Slowly, then suddenly blowing competition off the water
The journey from the Tesla of the early days, to the Tesla of today, has gone through many near-death experiences, potential sales of the company, several mental breakdowns of Musk and the executive team around him, and many exciting achievements!
And still, in 2018, Tesla’s success was all but granted.
It took about 15 years for the company to build a viable business model at scale.
And while things progressed slowly for a long-time, they eventually and suddenly took off, blowing competition off the water.
It took two decades for Tesla to build the company we know today, and three years (between 2018-2021) from close to bankruptcy, to the trillion-dollar company!
If there is a lesson we can learn is innovation is expensive, unpredictable, first slow, then extremely fast, and only explainable in hindsight.
Who owns Tesla?

As of February 2024, Elon Musk is worth more than $190 billion.
Understanding Tesla’s long-term strategy
While we all know Tesla today, its strategy was shaped already a few years back. Usually, effective strategies get rolled out in years, and only after they become successful do those become obvious.
Yet, when they are getting rolled out they are not obvious at all. So much so, that those rolling out the unconventional strategy , are getting criticized, ostracized, and only in the end idolized.
This is the case of Tesla’s long-term strategy , which is worth analyzing to understand what entry-strategy Tesla employs, and what its long-term strategy looks like.
Targeting a subsegment of the automotive market
Based on the market context, companies, especially startups have to find ways to enter markets, often dominated by other players, and roll out a temporary business model, which is only viable in the short-term, as it helps the company to transition to a more mature business model, to achieve scale.

When Tesla entered the market, it did it via the launch of the Roadster, a sports electric car, so it could start validating the market gradually, by a sub-segment of the automotive industry.
This enabled Tesla to enter with a product priced competitively (Tesla wasn’t able at the time to offer an electric vehicle at a competitive price). As sports cars are higher-priced, that segment of the market was in fit with Tesla’s temporary business model.
At the same time, the sports car segment also had customers open to more innovative products, as long as they would be highly differentiated.
Yet before transitioning to a new business model , the company will need to validate smaller segments of the market by attracting the psychographic which is ready to take on the new technology.

Yet often new technologies require the development of a whole ecosystem. For instance, in the case, of Tesla, it’s not about convincing people that electric cars are “cool” (not only that).
But also, initially, about providing the infrastructure to make the electric vehicle competitive in terms of everything else (availability of charging stations, charging vs. refilling, cost of batteries, time to recharge, and so on).
Only a few years after, in 2012, Tesla would finally start to roll out a business model based on potential mass adoption of its electric cars:

Only in 2012, Tesla would finally launch its Model S, the electrical sedan, intended to be adopted at a mass level. This strategy is still getting rolled out, and it might still take years to get to the level of mass production.
Successful strategies take years to become viable, as in some cases, they require the fit between the technology and the ecosystem it encompasses and the market.
When this happens the company rolling out the business model will reach its full potential in terms of scale.
Back in 2012, Elon Musk explained that well:
“In 2006 our plan was to build an electric sports car followed by an affordable electric sedan, and reduce our dependence on oil…delivering Model S is a key part of that plan and represents Tesla’s transition to a mass-production automaker and the most compelling car company of the 21st century.”
Is Tesla profitable yet?
Tesla turned a profit for the first time in the third quarter of 2019. Indeed the company posted $143 million in net profits. However, annualized the company’s net losses were $862 million.
What’s Tesla’s value proposition?
As highlighted in its financial statements, Tesla offers three core values to its customers:
- Long Range and Recharging Flexibility
- High-Performance Without Compromised Design or Functionality
- Energy Efficiency and Cost of Ownership
Tesla Core Technology

Source: Tesla Financials
Tesla’s core technology moves around three core parts:
- Autopilot & Full Self Driving (FSD).
- Vehicle Software.
- Battery & Power train.
Breaking down Tesla’s business model
For the first time in its history, in January 2020, Tesla passed the $100 billion market capitalization.
By 2022, Tesla passed a trillion-dollar market cap, a 10x growth. For some context, in the same period, a company like Ford had a 60-70 billion dollars market cap.
Tesla sells three main products:
Model 3: for mass adoption
A four-door mid-size sedan with a base price for mass-market appeal produced both in the Fremont Factory and. at the Gigafactory in Shanghai.
Model Y: the SUV
That is a compact sport utility vehicle (“SUV”) built on the Model 3 platform with the capability of seating up to seven adults.
Model S and Model X: the full-size sedan
That is a four-door full-size sedan that features large touchscreens driver interface, Autopilot hardware, over-the-air software updates, and fast charging through our Supercharger network.
Related : What Is a Business Model? Successful Types of Business Models You Need to Know
Elon Musk’s long-term vision for Tesla
Back in 2018, Elon Musk highlighted the long-term vision for Tesla :
Our goal is to become the best manufacturer in the automotive industry, and having cutting edge robotic expertise in-house is at the core of that goal. Our recent acquisitions of advanced automation companies have added to our talent base and are helping us increase Model 3 production rates more effectively. We don’t want to simply replicate what we have built previously while designing additional capacity. We want to continuously push the boundaries of mass manufacturing.
Tesla’s mission can be summarized as:
to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy.
As the company highlights :
Tesla builds not only all-electric vehicles but also infinitely scalable clean energy generation and storage products. Tesla believes the faster the world stops relying on fossil fuels and moves towards a zero-emission future, the better.
Elon Musk is getting ready to share a further Master Plan, for Tesla’s coming decade.
Main Tesla subjects will be scaling to extreme size, which is needed to shift humanity away from fossil fuels, and AI. But I will also Include sections about SpaceX, Tesla and The Boring Company. — Elon Musk (@elonmusk) March 21, 2022
Tesla revenue streams explained

Tesla has four main sources of income:
- Automotive leasing
- Services and other
- Energy generation and storage
Based on Tesla’s financial statements, in 2021 the company almost doubled its revenues while improving substantially its bottom line.
The most important revenue stream is the Automotive sales revenue ( which includes revenues related to the sale of new Model S, Model X, and Model 3 vehicles, including access to Supercharger network, internet connectivity, Autopilot, full self-driving, and over-the-air software updates, as well as sales of regulatory credits to other automotive manufacturers ) with over $45 billion, followed by automotive leasing with over $1.6 billion and services and other with over £3.8 billion.

And to be sure, this was all but a linear process. As Elon Musk highlighted, Tesla’s success was far from taken for granted. The worst near to death experience was in 2018 when Tesla wasn’t able to hit its production target, in what Musk called a “production hell.”
That funding round completed 6pm on Christmas Eve in 2008. Last hour of last day possible, as investors were leaving town that night & we were 3 days away from bankruptcy. I put in all money I had, didn’t own a house & had to borrow money from friends to pay rent. Difficult time.
Tesla distribution strategy
Tesla is vertically integrated , as its pipeline goes from manufacturing to direct sales of its vehicles.
As highlighted by Tesla “the benefits we receive from distribution ownership enable us to improve the overall customer experience, the speed of product development, and the capital efficiency of our business.”
Even though a vertically integrated network represented a substantial investment in terms of physical assets Tesla can keep control over the experience of its customers. While also being able to retain important feedback throughout the supply chain.
Indeed, in a model where the customer is reached via indirect distribution the company might lose control of the customer experience at the last mile, and the valuable feedback it can gather from the marketplace.
Tesla follows an unconventional distribution model compared to other car manufacturers where the final sale is made via car dealerships which are not tied to the company.
Why did Tesla use a direct distribution approach?
Back in October 2012, Elon Musk explained in a blog post, the whole philosophy around Tesla’s distribution strategy :
There are reasons why Tesla is pursuing a company owned store and service center model that we feel are really important. In many respects, it would be easier to pursue the traditional franchise dealership model, as we could save a lot of money on construction and gain widespread distribution overnight. Many smart people have argued over the years that we should do this, just like every other manufacturer in the United States, so why have I insisted that we take a unique path?
Some of the key elements that made Tesla go with this strategy , which was way more expensive, and hard in the short-term was:
Conflict of interest of franchise dealers
For traditional car dealers, gasoline cars constituted the vast majority of their business. Thus, the franchise dealer would have been in a conflict of interest in offering a Tesla product, as this would have required them to contrast their core business model.
Ability to educate and channel the customer toward choosing Tesla over established brands
As Elon Musk highlighted back in 2012: “Tesla, as a new carmaker, would therefore rarely have the opportunity to educate potential customers about Model S if we were positioned in typical auto dealer locations.”
So Tesla built its own stores, located in central places (similar to Apple stores’ distribution or perhaps branding strategy ) to educate and enable potential customers to place orders, but primarily as a long-term objective to educate consumers about the brand and the potential of electric vehicles.
Today, after almost a decade of this strategy , Tesla is among the most recognized brands, and its stores are places that people enjoy visiting, as the electric vehicles proposed by Tesla have become iconic.
Freedom to open direct stores anywhere
With a traditional distribution strategy , it would have been easy for Tesla to run in conflict with franchised stores, by opening direct stores in close proximity. By having only a direct distribution , Tesla doesn’t have such a problem.
Does Tesla spend nothing on marketing?

Musk is famous for his unconventional stunts. For instance, the stunts of the flamethrowers or the Tesla roadsters sent on space managed to reach hundreds of millions of people worldwide without a dollar spent on ads.
However, this also fueled the myth that Tesla doesn’t spend a dollar on advertising campaigns or marketing .
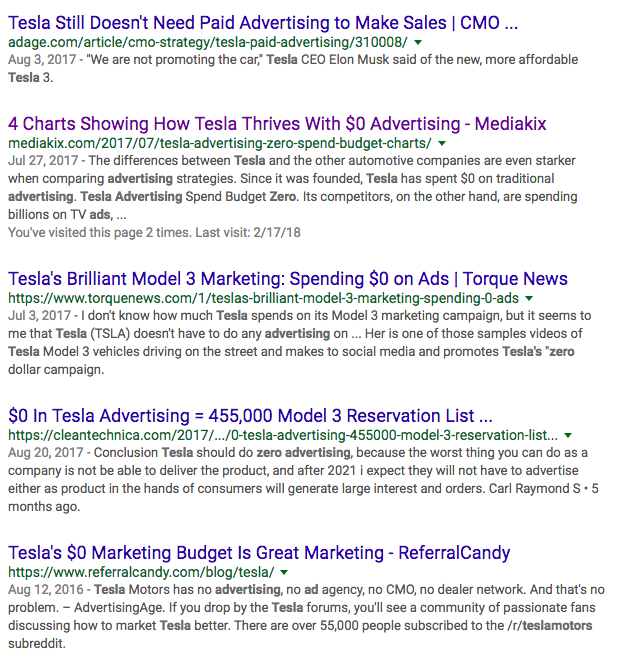
Like any other company, Tesla has a marketing budget for advertising and marketing campaigns. As an example, in 2018 Tesla reported its “Marketing, Promotional and Advertising Costs:”
Marketing, promotional and advertising costs are expensed as incurred and are included as an element of selling, general and administrative expense in the consolidated statement of operations. We incurred marketing , promotional and advertising costs of $70.0 million, $66.5 million and $48.0 million in the years ended December 31, 2018, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Thus, even though the former PayPal Mafia member Elon Musk is the master of unconventional PR, Tesla still needs advertising to push its sales.
However, if we compare that to the revenue figures for 2018 (over $21 billion), the spending on marketing activities is around 0,3% which is an incredibly low figure, almost negligible, considering that large companies like Tesla spend billions of dollars in branding campaigns!
Based on that, we can indeed affirm, that it’s like Tesla doesn’t have a marketing budget at all! And we’re talking about a company that passed a trillion-dollar in market cap!
Tesla manufacturing explained
Thousands of purchased parts are sourced from hundreds of suppliers across the world. For the key parts (battery cells, electronics, and complex vehicle assemblies) Tesla developed closed ties.
For most car manufacturers, components to build the cars, are often single-supplied. Other parts are instead available from multiple sources. So to diversify the suppliers’ components as car manufacturers also Tesla can experience high volatility in sourcing the components for its cars.
To prevent that, Tesla either looks for multiple sources or can stock up inventories of components.
Is Tesla worth more than GM?
In January 2020, Tesla passed for the first time in its history the market cap of $100 billion, twice the market cap of GM (about $50 billion) in the same period even though in 2018 GM had 6-7 times the revenues of Tesla. Tesla though is valued as a tech company, which in the future can capture a wider and wider market, thus becoming way more valuable.
By October 2021, Tesla’s market cap would be 10x, reaching over a trillion-dollar! This in part, was due to the fact that the company managed to successfully pass the mass manufacturing stage.
Undoubtedly, Tesla is getting valued as a tech company, an electric energy platform (not much different from its oil equivalent: Exxon or Chevron), and a company that might generate hundreds of billions in sales in the coming years. This is the bet markets are making.
Tesla as a business platform
Looking at Tesla just as a company it’s a limited view. Tesla is much more than that. The company is a business platform, meaning it doesn’t just make and sell cars, but it is also an energy generation and storage platform. So it’s both a pipeline and a platform. To understand that let’s see the various components that make Tesla up as a company.
Breaking down Tesla’s competitors

Tesla isn’t just an automaker; it is an electric-only car automaker, an electric storage company, and an autonomous driving player. For that, we’ll have to analyze Tesla from these three perspectives.
Within the automaking segment, Tesla has over the years diversified its products‘ lines, to cover different segments of the market. When Tesla entered the market, as a go-to-market strategy it had to enter it (nonetheless Elon Musk’s long-term vision to make the electric car available to the masses) with the Roadster model .

While this model is still available, this is the highest-priced model and the product Tesla used to bootstrap its operations. Indeed, at the time, Tesla couldn’t produce a lower-cost electric car (Model 3 will finally achieve this goal), and that is how Tesla made its business model viable as it entered the new market for electric cars. This is what I call a transitional business model :

Over the years, as the market matures, Tesla grew, an electric ecosystem was born, and the technology to enhance battery performance improved, Tesla also expanded its products lines to cover the various segments.
Sport & Performance
The primary models covering these segments are:
- Roadster : here some of the competitors are Dodge Challenger, Porsche Chiron, and Bugatti
- Model S : in this segment, Tesla competes with players like Mercedes S-Class, BMW 7 Series, Porsche Panamera, Audi A7 & A8, and more.
- Model X : here some of the competitors are BMW X5, Mercedes-Benz GLS-Class, Volvo XC90, Porsche Cayenne.
- Model Y (compact SUV) : in this segment, Tesla competes with Renault Zoe, Nissan LEAF, Volkswagen e-Golf, Audi e-Tron, and more.
In this segment, Tesla just launched the Cybertruck:

Cybertruck’s competitors comprise Rivian, Ford, Bollinger.
Tesla has finally its mass-market product, the Model 3. This model competes with models such as BMW Series 2,3,4,5 Mercedes Class C, CLA, CLS, Audi A3, A4, A5, Lexus, ES, GS, and many others.
Energy Storage
Tesla acquired SolarCity back in 2016, for $2.6 billion, and with that, it competes in the electric production and storage industry with players like SunRun, SunPower, Vivint Sonar, Trinity Solar, and SolarWorld to mention a few.
Autonomous driving
Tesla’s Autopilot is one of the key ingredients of its technology and one of the most interesting future developments for the company. In this segment, Tesla competes with other autonomous driving companies like Zoox (bought by Amazon ), Waymo (an Alphabet bet ), and Baidu.
Why do the automotive regulatory credits matter for Tesla?
Automotive Regulatory Credits generated over $1.4 billion in revenues for Tesla in 2021, compared to just 594 million in 2019.
How do they work? Since Tesla produces zero-emission vehicles (“ZEVs”), these credits are sold to other regulated entities “who can use the credits to comply with emission standards and other regulatory requirements.”
As Tesla ramps up its operations, those regulatory credits revenues will also grow together with the increased production of cars.
In fact, the credits are directly linked to Tesla’s new vehicle production.
This revenue stream is extremely important, because (even if small for now) it’s completely free. This means, there is no additional effort/cost for the company is having these credits, it only needs to produce more EVs.
And as the production scales, this number will grow exponentially, thus boosting the company’s profitability and cash flows (at least until this regulation will last)!
Why Tesla’s mass scale is all about the demand side!
In the last decade, Tesla had to make sure it could build its ability to mass-scale production, in what Elon Musk has labeled as “mass-production hell.”
Indeed, after being able to make the first prototype, the challenge Tesla had was to enable production at scale.
This effort, of the last decade and more, actually was about to bankrupt the company on several occasions (the last one in 2018, when Tesla was a few days away from running out of cash).
Yet, things turned around, starting in 2019, and in particular, 2021-2022 were key years. Indeed, Tesla managed to ramp up its operations through the opening of Shangai, Berlin, and Texas gigafactories.
This, made Tesla mostly pass through the hurdle of the mass manufacturing hell.
Now, it gets all about the ability of Tesla to make its cars affordable at scale, which can either happen by lowering the prices (but it would be a process that might require years and not sustainable in the long-term) or by enabling a part of the business to subsidize another part of this business.
This can be achieved through the leasing and insurance arms of Tesla.

In short, by borrowing the iPhone’s playbook, Tesla can enable a wide/mass distribution for its cars. But primarily developing its own leasing and insurance arm.
And for some context, in 2021, the leasing and service arm (powered up by the insurance offering) passed the $5 billion dollar mark!
Key takeaways
- Back in 2008, Tesla used a go-to-market strategy by targeting a small segment of the automotive industry (sports car) as it could offer at the time competitive options to customers in that segment.
- In 2012, Tesla started to roll out its long term mission to have electric cars, mass-produced with the launch of its Model S. This strategy is still getting rolled out, and as Tesla gains more market shares and build a more viable electric ecosystem it can also reduce its pricing, thus increasing the mass adoption for its cars.
- Tesla uses a direct distribution model where it sells directly through its e-commerce and physical stores across the world.
- Tesla also offers new vehicle sales with customers’ trade-in needs for its existing Tesla and non-Tesla vehicles. The Tesla and non-Tesla vehicles acquired through trade-ins are remarketed, either directly by Tesla or via third parties.
- Tesla also owns several manufacturing facilities where it either single-source certain components or it diversifies components sources. Where possible Tesla stacks up components to reduce the risk and volatility of the supply chain.
- Tesla’s distribution strategy combined with its appeal as consumer brand with products like Model 3, priced with a base price for mass-market appeal, makes Tesla among the most valuable car manufacturers in the world.
Read Also: Tesla SWOT Analysis , Transitional Business Models , Tesla Mission Statement .
Business resources:
- The Ultimate Guide to Market Segmentation
- What Is a Business Model?
- The Complete Guide To Business Development
- Business Strategy Examples
- What Is a Business Model Canvas? Business Model Canvas Explained
- Blitzscaling Business Model Innovation Canvas In A Nutshell
- What Is a Value Proposition? Value Proposition Canvas Explained
- What Is a Lean Startup Canvas? Lean Startup Canvas Explained
- Marketing Strategy: Definition, Types, And Examples
- Marketing vs. Sales: How to Use Sales Processes to Grow Your Business
- How To Write A Mission Statement
- What is Growth Hacking?
- Growth Hacking Canvas: A Glance At The Tools To Generate Growth Ideas
Case studies:
- Tesla Mission Statement
- Who Owns Tesla
- Tesla SWOT Analysis
- How Does PayPal Make Money? The PayPal Mafia Business Model Explained
- How Does Venmo Make Money? the Peer-To-Peer Payment App for Millennials
- How Does WhatsApp Make Money? WhatsApp Business Model Explained
- How Does Google Make Money? It’s Not Just Advertising!
- How Does Facebook Make Money? Facebook Hidden Revenue Business Model Explained
- The Google of China: Baidu Business Model In A Nutshell
- Accenture Business Model In A Nutshell
- Salesforce: The Multi-Billion Dollar Subscription-Based CRM
- How Does Twitter Make Money? Twitter Business Model In A Nutshell
- How Does DuckDuckGo Make Money? DuckDuckGo Business Model Explained
- How Amazon Makes Money: Amazon Business Model in a Nutshell
- How Does Netflix Make Money? Netflix Business Model Explained
Related To Tesla Business Model
Direct To Consumers

Distribution Channels

Leasing Business Model

Vertical Integration

Market Expansion

Transitional Business Models

More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
To revisit this article, visit My Profile, then View saved stories .
- Backchannel
- Newsletters
- WIRED Insider
- WIRED Consulting
Matt Burgess
Elon Musk unveils Tesla's 'Master Plan, Part Deux'

When billionaire Elon Musk isn't launching and landing reusable rockets that will help reduce the cost of space missions and help put humans on Mars, he's busy trying to dominate the car industry.
The SpaceX boss has just unveiled his 'Master Plan, Part Deux' for his electric car business, Tesla, and its focus isn't purely on producing cars.
Instead, the four-part plan for worldwide ascendancy focuses on making the company work on sustainable energy projects.
These include: integrating energy generation and storage; expanding Tesla to create electric trucks and public transport; fully autonomous vehicles; and have cities where cars are shared as autonomous taxis.
His plan for the future of the company comes a decade after he published the first part . Ten years ago, Musk set out to start manufacturing electric cars and increase their scale to be affordable to a mass market. Arguably, he achieved this with 400,000 pre-orders of the company's Model 3 – although these have yet to be delivered.
The business has always been about the "bigger picture," Musk said. And the update to his master plan addresses this.
"We must at some point achieve a sustainable energy economy or we will run out of fossil fuels to burn and civilisation will collapse," the former PayPal founder wrote.
Starting with cities, Musk described how vehicles operate, and how people get around needs to change. Next year Tesla will unveil two new types of electric vehicle: "heavy-duty trucks and high passenger-density urban transport".
"With the advent of autonomy, it will probably make sense to shrink the size of buses and transition the role of bus driver to that of fleet manager," Musk said. The plan sets out a developed view of what one of Tesla's buses could look like. The bus would take people "all the way" to their destinations and buttons at existing bus stop would let people "summon" a bus if they didn't own a phone.

By Mark Harris

By Christopher Solomon
By Julian Chokkattu

By David Robson
Musk wrote: "Traffic congestion would improve due to increased passenger areal density by eliminating the centre aisle and putting seats where there are currently entryways, and matching acceleration and braking to other vehicles, thus avoiding the inertial impedance to smooth traffic flow of traditional heavy buses." Other self-driving buses have already been developed: this week Mercedes-Benz unveiled its own version that has been driving across Amsterdam .
For those wanting the privacy of their own vehicle, there's a plan for that too. Musk is planning a "shared-fleet" of Tesla cars that operate as a network of autonomous taxis and make money for their owners.
"You will be able to add your car to the Tesla shared fleet just by tapping a button on the Tesla phone app and have it generate income for you while you're at work or on vacation, significantly offsetting and at times potentially exceeding the monthly loan or lease cost," he explained.
The company will have its own fleets of cars in some cities – a move that will be seen as a direct competitor for the likes of Uber, which is developing its own self-driving vehicles .
For a fleet of autonomous vehicles to work across a city, self-driving regulations need to be improved as technology progresses. At present Tesla's self-driving features – named AutoPilot and in a beta stage – allow drivers to palm-off changing lanes to their cars. An investigation is underway in the US into how a driver using the features died in a collision.
All Tesla vehicles will be able to drive autonomously in the future, Musk added. He predicts software will take a long time to be refined and validated.
The types of heavy vehicles Musk wants to create rely on Tesla being able to upscale its battery production . In the final quarter of 2015, Tesla created just 208 Model X cars, although it has since increased its rate. To do this further it is building a huge Gigafactory with a 1.2 million square metre floor space, in Nevada. By 2020 the company plans to make more battery cells than all of the lithium-ion battery markers combined produced in 2013 – if it achieves it, it will be a huge feat.
Tesla is also ready to "scale" its power-wall technology, which is where Musk's master plan ties together. The wall, a home battery, will rely on the company's battery technology being developed and produced.
To do this Musk is buying his own Solar City company for £1.91 billion, with Tesla's funds, and merging them into one.
He says he wants to: "create a smoothly integrated and beautiful solar-roof-with-battery product" that allows a person to create and store their own energy. Then, with no lacking of ambition, he wants to scale the product around the world.
This article was originally published by WIRED UK

Aarian Marshall

Morgan Meaker

Andy Greenberg
Will Knight

Steven Levy
Tesla's Secret Master Plan: How It Started And How It's Going

Your changes have been saved
Email Is sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Which Things Are Fake On Counting Cars & Which Ones Are Real?
10 oldsmobiles that have skyrocketed in value, the rarest chevrolet production car ever, key takeaways.
- Tesla's exponential growth and success can be attributed to the rising demand for electric cars, making it the most valuable automotive brand worldwide.
- Tesla's secret master plan outlines its mission to electrify and replace conventional energy sources, starting with the production of luxury and affordable electric cars.
- Tesla's master plan has seen partial fulfillment, with the development of self-driving technology and solar roofs, but there are still objectives, like making EVs in all segments, yet to be achieved.
Tesla Inc., formerly Tesla Motors Inc. is currently estimated to have a total net worth of around $800+ billion. For a company that started only two decades ago, this exponential level of growth is clearly awe-inspiring. The rising demand for electric cars is precisely the major driving force contributing to the EV manufacturer’s skyrocketing success. According to Brand Finance, in 2023 Tesla saw a gigantic upsurge of around 44% in brand value. The pioneer EV manufacturer surpassed Mercedes-Benz and Toyota to become the most valuable automotive brand worldwide.
Additionally, Tesla also boasts the highest “Sustainability Perceptions Value” among all automotive brands, which is crucial for an EV maker . This triumphant success story of Tesla didn’t happen haphazardly rather it was achieved through the meticulous execution of an efficiently orchestrated master plan. The first part of the Tesla master plan was revealed to the public in 2006, followed by the second part in 2016 and the third in April 2023. Today, we analyze Tesla’s secret master plan to see how the first two phases materialized and what the brand plans to achieve with part 3.
We diligently analyzed Part 1 , Part 2 , and Part 3 of the Tesla Master Plan to provide accurate information about the same.
What Is Tesla's Secret Master Plan?
Divided into multiple stages, Tesla’s secret master plan expounds how the brand intends to electrify and replace not just automotive powertrains but the whole of conventional energy sources. The creation and popularization of both luxurious and affordable high-performance electric cars was the automaker’s initial objective. As the numbers reveal, it is evident that Tesla was astoundingly successful in fulfilling that goal. After this triumphant achievement, they moved on to the second phase of the plan.
The second stage involved the expansion of Tesla EVs into every segment, the development of solar roofs, and the advancement of self-driving cars. As of now, it can be said that Tesla has accomplished partial fruition of master plan stage 2, but some stratagems are yet to be gratified. Tesla has already revealed part 3 of their secret master plan which envisions the endowment of sustainable energy for all of Earth. The following table showcases the prices and specs of Tesla’s current model lineup. This versatile array is soon to be enlarged with the addition of the Tesla Cybertruck and second-gen Tesla Roadster.
2023 Tesla Lineup – Prices And Performance Specs
|
|
|
|
|
| Compact Hatchback | Compact SUV | Full-size Sedan | Midsize SUV |
| $40,240 | $47,740 | $78,490 | $88,490 |
| Single / Dual Electric Motors | Dual Electric Motors | Dual Electric Motors | Dual Electric Motors |
| Rear-Motor Rear-Wheel-Drive / Front And Rear-Motor All-Wheel-Drive | Front And Rear-Motor All-Wheel-Drive | Front And Rear-Motor All-Wheel-Drive | Front And Rear-Motor All-Wheel-Drive |
| Up to 505 hp | Up to 450 hp | Up to 1,020 hp | Up to 1,020 hp |
| Up to 487 lb-ft | Up to 471 lb-ft | Up to 1,050 lb-ft | Up to 752 lb-ft |
| Up to 333 Miles | Up to 330 Miles | Up to 405 Miles | Up to 348 Miles |
| 3.1 Seconds | 3.5 Seconds | 1.99 Seconds | 2.5 Seconds |
| 162 MPH | 155 MPH | 200 MPH | 149 MPH |
RELATED: How Tesla's Upcoming Model 2 Compact Could Change The EV Landscape
Part 1: Tesla Roadster To Tesla Model 3
Tesla master plan part 1: highlights.
- Build a sports car
- Build an affordable car using that revenue
- Build an even more affordable car using that revenue
- Deliver zero-emission electric power generation options
Published on the 2nd of August 2006, the maiden master plan of Tesla Motors is lucid (no pun intended), unambiguous, and easily intelligible. The plan was to build a low-volume performance car, utilize that money to build a medium-volume car, and then use that money to create an affordable, high-volume car. In essence, the first generation Tesla Roadster was the so-called low-volume high-performance electric car. From 2008 to 2012, Tesla sold less than 2,500 units of the first-gen Tesla Roadster across the globe.
After acquiring a new factory in California and ceasing the production of the Roadster in 2012, it was time for the arrival of the medium-volume Tesla car. As you might have guessed, it was the Tesla Model S , the cynosure mainstay flagship of the Tesla lineup. Followed by the unforeseen success of the Model S, a decade after unveiling the original master plan, Tesla launched their first mass-market EV in 2016. It was the Tesla Model 3, the affordable, high-volume electric car which became an overnight success.
Given below is a performance comparison between the first-generation Tesla Roaster and the upcoming second-generation model. This might help elucidate the gravity of Tesla’s growth, advancement, and victory as an automaker.
Tesla Roadster First Gen Vs Second Gen
|
|
|
| Single Electric Motor | Three Electric Motors |
| Rear-Mid Motor Rear-Wheel-Drive | Front And Rear Motor All-Wheel-Drive |
| 53 kWh | 200 kWh |
| Up to 288 hp | N/A |
| Up to 295 lb-ft | N/A |
| 245 Miles | Up To 620 Miles |
| 3.7 Seconds | 1.9 Seconds |
| 125 MPH | 250+ MPH |
RELATED: Tesla Roadster To Model S Plaid: How EV Battery Technology Has Advanced Since 2008
Part 2: Tesla Solar Roof And Self-Drive Cars
Tesla master plan part 2 highlights.
- Make solar roofs with integrated battery storage
- Make EVs in all major segments
- Develop self-driving tech that is 10 times safer than manual cars
- Enable your car to make money for you when you aren't using it
Phase 2 of Tesla’s secret master plan was revealed on July 20, 2016, which laid bare the brand’s broad expansion plans. Tesla not only planned to take over the manifold of automotive segments but also targeted the development of extremely advanced autonomous cars. Full self-driving via the Tesla Autopilot feature debuted for the first time in 2016 which has now profoundly evolved to encompass a comprehensive suite of advanced autonomous capabilities. Tesla Autopilot is drastically reshaping the landscape of modern transportation.
Standout Features Of Tesla Autopilot
- Full self-driving capability
- Equipped with 8 cameras
- 360-degree coverage
- 250 meters of sensor range
Another major agenda included in the second part of the master plan was the creation and widespread dissemination of solar roofs. In order to actualize this goal, Tesla disbursed $2.6 billion to acquire SolarCity, a solar energy company back in 2016. The same year, Tesla was rechristened from Tesla Motors, Inc. to Tesla, Inc. to better suit its burgeoning enterprises. Tesla Solar Roofs, however, didn’t turn out to be a massive success as the brand is nowhere near Elon Musk’s goal of 1,000 weekly solar roof installations.
Standout Features Of The Tesla Solar Roof
- 25 years warranty
- Class 3 hail protection rating
- Class A fire protection rating (highest)
- Class F wind protection rating (highest)
RELATED: Rivian R1T Vs. Cybertruck: Has Tesla Already Lost The EV Adventure Truck Battle?
Part 3: Comprehensive Shift To Electric Cars
Tesla master plan part 3 highlights.
- Elimination and replacement of fossil fuels
- The complete switch to sustainable energy
- Comprehensive switch to electric vehicles
- Sustainably fuel planes & boats
The latest and the most monumental part of the Tesla master plan was exposited on the 5th of April 2023. It discusses the integral switch to sustainable energy and the complete elimination of fossil fuels from planet Earth. This includes the extirpation of gas-powered cars and the singular hegemony of electric cars in the world automotive market. We’ll have to wait and see how this elaborate plan takes shape and molds the future.
However, Tesla has not hit all milestones as promised. Deliveries of the Cybertruck which was announced four years back are yet to commence. This also means that the “making EVs in all popular segments” objective of the master plan part 2 is yet to be fulfilled. Overall the company is thriving inconceivably, and we envisage Tesla to execute their plans for a sustainable future successfully.
- Electric Cars
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Tesla has a new master plan. It's not a new car — just big thoughts on planet Earth

Camila Domonoske

Tesla CEO Elon Musk is pictured as he attends the start of production at Tesla's "Gigafactory" in Gruenheide, southeast of Berlin in Germany. on March 22, 2022. Tesla held an investor day on Wednesday. It did not reveal a new vehicle, but it unveiled some of its big-picture ideas on climate change. Patrick Pleul/POOL/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Tesla CEO Elon Musk is pictured as he attends the start of production at Tesla's "Gigafactory" in Gruenheide, southeast of Berlin in Germany. on March 22, 2022. Tesla held an investor day on Wednesday. It did not reveal a new vehicle, but it unveiled some of its big-picture ideas on climate change.
Anticipation had built for days. Tesla was poised to unveil a new strategic plan at its Investor Day, only the third time the company has laid out a "master plan" that would guide its future.
Analysts were eager to see a new Tesla model — specifically, a much cheaper Tesla, one that could make the most popular electric vehicle brand in America accessible to a far broader swath of buyers.
But at its Investor Day on Wednesday, Tesla did not reveal that vehicle.
Elon Musk's new master plan? Ending fossil fuels.

Tesla slashed its prices across the board. We're now starting to see the consequences
Instead of a shiny new car, the company went big-picture on climate change, making the case for an aggressive global transition away from fossil fuels — one with a vast number of electric vehicles and batteries, Tesla's core products, as the key components.
Good for a company that has always touted its green credentials, but Wall Street would have preferred a new car. Tesla stock dropped markedly in after-hours trading.
Musk had a lot in his mind about planet Earth
In some ways though, it was vintage Tesla.
Tesla has already radically reshaped the climate conversation, by spurring the auto industry to embrace electric vehicles.
The new "master plan" extended beyond the auto sector to talk about decarbonizing the global electric grid as well as all industry, shipping and air travel, too.
Musk opened the event by arguing the world can rapidly pivot to renewable energy with the help of batteries (to store solar power to use at night, for instance) and, of course, battery-powered electric vehicles. This new "master plan" also nodded to heat pumps and hydrogen for industrial uses.

Tesla's profits soared to a record – but challenges are mounting
Lots of researchers, analysts and nonprofit groups have charted out paths to combat climate change. Most emphasize that time is running out, and the scale of change required is daunting.
Musk's tone was more optimistic. He said Tesla had done the math and the switch would cost $10 trillion, less than the world would spend on fossil fuels over the same timeframe. Fully $7 trillion of that would be for electric vehicles — the market Tesla revolutionized, and intends to dominate worldwide.
"Today is not just for investors of Tesla, but anyone who is an investor in Earth," Musk said. "Earth can and will move to sustainable energy, and it will do so in your lifetime."

A Tesla charging station for electric cars is seen at the parking lot of a mall in Puebla, Mexico, on Feb. 26, 2023. Tesla executives talked about new ideas about every facet of its business, including on charging, at its investor day. Pedro Pardo/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
A Tesla charging station for electric cars is seen at the parking lot of a mall in Puebla, Mexico, on Feb. 26, 2023. Tesla executives talked about new ideas about every facet of its business, including on charging, at its investor day.
Making the case for innovation, despite no big reveal
With no brand new vehicle to drive out on stage, Tesla executives and engineers shared information about how the next generation of vehicles will be designed and built.
The company claims to have a radically reinvented assembly process, which involves making the front and back of the car separately, that could cut production costs by 50%. Tesla also says future vehicles will require no rare earth elements and could incorporate any battery chemistry, making it easier to source raw materials.
To bolster its reputation as an innovative company, Tesla also bombarded investors with examples of how it has developed new features and cut costs.
Tesla boasted of a software update to automatically adjust air suspension mid-drive, based on data from other vehicles about where the road is rough, and a strategy to cut costs on Supercharger stations by preassembling entire stations and dropping them down from a crane, instead of installing each charger individually on location.

A Tesla Model Y car is shown at a Tesla showroom in a shopping mall in Beijing, China, on April 29, 2022. Tesla shares fell after it did not reveal a new car at its investor day. Jade Gao/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
A Tesla Model Y car is shown at a Tesla showroom in a shopping mall in Beijing, China, on April 29, 2022. Tesla shares fell after it did not reveal a new car at its investor day.
A head start in the race for electrification
The investor day came as investors were feeling more optimistic about Tesla's future, despite growing competition.
Every major automaker now believes that zero-emissions vehicles are the industry's future, and they are racing to catch up with Tesla. That makes it likely that Tesla's share of EV sales will shrink, as more competition comes in. That was one reason for the company's precipitous drop in share prices last year.
But Tesla is producing vehicles at a higher volume than its rivals, and it recently cut prices sharply. That has increased interest in Tesla vehicles, and the move was well-received by Wall Street.

Buying an electric car? You can get a $7,500 tax credit, but it won't be easy
And Teslas remain popular with drivers. The company just won the top award for "Overall Loyalty" to a make in S&P Global Mobility's Automotive Loyalty Awards. In general, returning car shoppers stick with their previous brand about 50% of the time. For Tesla buyers, a solid two-thirds return to Tesla.
"Tesla had a very, very strong year," says Vince Palomarez of S&P Global Mobility. "They have produced a product that is attractive to a consumer ... They lowered their price. They're also getting access to the tax credit again."
Palomarez also notes that Tesla owners often install a Tesla charger at their home. That could be an added incentive to stick with the brand, instead of needing to swap out equipment or use an adapter every charge. He compared it to Apple's proprietary chargers.
"If you have an iPhone and you have an iPad and you have a MacBook, you know, you're going to get the Apple Watch .... the infrastructure is built there," he says.
- electric cars
- Enterprise software
- Turnkey install
- ChargeLab app
- Integrations
- White-labeling
- ChargeLab Verified Hardware
- Multi-family
- Single-family
- U.S. rebates
- New York State
- Canadian rebates
- Privacy & Terms
The complete guide to starting an EV charging station business
Vehicle electrification is a small but mighty step in addressing the climate crisis. The recent surge in EV sales is encouraging, but all those vehicles need charging—and we have a ways to go before charging stations become as accessible as gas stops. Fortunately, savvy businesspeople around the globe want to help. They’re wondering how to start an EV charging station business in ever-increasing numbers.
This comprehensive guide will take you through the process, shedding light on the necessary market research, popular business models, grant opportunities, technical and regulatory standards, and more you’ll face in the course of business. Equipped with this info, your business will be up and running faster than a DC charger fills a battery.
Funding your EV charging station business
When investigating how to start an EV charging station business, grants stand out as an attractive inroad. It's important to consider each carefully, making note of hard deadlines, explicit program goals, desired outcomes, and guidance about how the funds can be used.
Grant opportunities
President Biden's Bipartisan Infrastructure Law carved out billions in federal funding for infrastructure for electric and hydrogen-powered vehicles. These grants, offered by the US Department of Transportation , can provide a minimum of $500,000 in funding, but take note: The funding must go toward rural communities of less than 10,000 people. These areas likely have next-to-no competition, which could give you an early foothold in expanding markets.
Volkswagen's Diesel Emissions Environmental Mitigation Trust came out of the company's emissions scandal as an effort to undo some of the damage it caused. The trust as a whole creates grant opportunities for projects encouraging the adoption of sustainable transportation, and a portion of it is dedicated specifically to developing EV charging infrastructure in the US. The National Association of State Energy Officials (NASEO) has general info about grant opportunities, but applicants need to check their state's website for specific requirements, as the trust allocates funding at the state level.
Speaking of the state level, several have their own funding offerings. California's Clean Transportation Program offers a mix of grants, contracts, and rebates for EV charging infrastructure, among other sustainable transportation solutions. New York's ChargeNY initiative targets EV charging, specifically. With Charge Ahead Colorado , that state offers grants for the installation of Level 2 and Level 3 fast charging stations in public and private locations. Be sure to check for funding opportunities in your state.
A great starting point in Canada is the Zero Emission Vehicle Infrastructure Program . This $680 million program has carved out funding for EV chargers across the country, but competition is stiff. To be eligible, your proposal must include at least one charger of 200 kW and above, two fast chargers of 50 kW and above, or 20 chargers of all charging levels. Check out our ZEVIP resources page for more info.
For more funding opportunities for your electric vehicle charging station business, read 7 EV charging station grants to apply for when starting your EV business.
Choosing a business model
There are a few common models those wondering how to start an EV charging station business typically consider. The right one for you will vary according to your goals, expertise, and available resources.
Charging network
Charging networks work like gas station chains. In this model, you'll own stations at several locations to maximize market density. By charging EV drivers flat or variable rates based on fluctuations in power supply, you'll bring in revenue. You'll either operate the stations yourself or pay a service to maintain them.
This model is very time and resource-intensive because it demands an upfront investment in infrastructure in addition to ongoing maintenance (which in turn demands expertise). It makes the most sense for gas station chains that want to move into the EV space.
Solutions provider
Rather than provide the charging infrastructure, solutions providers sell EV hardware, software, and services to residences, commercial buildings, fleet operators, and more. Their offerings vary, including consultation, maintenance, turnkey services for businesses looking to provide EV amenities, and more. Payment occurs either at installation, monthly, or annually if service is ongoing. In this model, turning a profit means soliciting discounts on hardware and software you then sell at a markup. Strong sales and customer service skills are vital to this model, and experience with EVs or other green tech can be a boon.
To learn more about how to start an EV charging station business with a model that works for you, read How to develop a profitable EV charging station business model.
Maintenance considerations for an electric vehicle charging station business
Operating a successful electric vehicle charging station business means ensuring every piece of the operation stays in working order. That keeps customers happy and revenue flowing. As sophisticated feats of engineering, Level 2 and DC fast chargers have several components you'll need to maintain.
The hardware components of an EV charger include its charger box, battery, switches, converters, cables, and connectors. Outer components should be checked for damage and wear on a regular basis, with supplemental checks performed after stormy weather. Connectors and cables must be cleaned of dust and other debris to ensure they work well for as long as possible.
Power management
Use your charging station management system (CSMS) to allocate safe and efficient loads for each of your chargers. The system should have safeguards in the event of lost connectivity, maintaining max charge set points in non-volatile memory. A software-driven power management system will outperform local load management features available on the hardware itself. Some systems, including ChargeLab, can detect a full vehicle battery and reallocate power to other chargers on the fly.
If your Level 2 charger takes more than a few hours to give a full charge, or your DC fast charger takes over an hour, you may have a voltage issue that requires fixing or replacing the battery.
Payment processing
EV charging stations rely on payment processing infrastructure such as RFID readers and credit card scanners to collect customer payments. Customers typically transact either via their mobile device (in-app or on the web) or through an external point-of-sale interface. Your CSMS should have complete and accurate receipt information to maintain compliance with CTEP.
Connectivity
If a charging station in your network disappears from your CSMS, that's a sure sign something needs fixing. It may be that the station itself has a hardware problem that requires repair, or it may be a simple connection problem. Choosing a CSMS provider that offers customer support can accelerate troubleshooting and safeguard against extended outages.
For more on maintenance considerations, read A guide to EV charging station maintenance.
Need-to-know EV charging station regulations
Several standards have been propagated around EV charging, handed down by hardware manufacturers, software designers, car manufacturers, and national governments. Here are two of the most important ones in the United States.
National Electric Code Article 625
If you want to know how to start an EV charging station business safely in the US, you need to review NEC Article 625. That article sets the bar for installing and maintaining EV charging equipment, from where to put the equipment to what kind of materials to use. Some key points:
- EV charging systems can be placed indoors or outdoors as long all their physical infrastructure fits and their charging cables can reach EV charging ports. However, where you place your system will affect your ventilation, waterproofing, and shock protection needs.
- EV chargers must be stored 18 inches above the ground if indoors or 24 inches above the ground outdoors.
- EV charging systems must use cables appropriate for their location. Those cables should carry one of the following labels designating NEC approval: EV, EVJ, EVE, EVJE, EVT, or EVJT. Charging cables longer than 25 feet require a cable management system, but the standard practice is to manage shorter lines, too.
National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI)
With $5 billion in federal funding available for EV charging systems, the Department of Transportation (DoT) stepped in with guidelines around who could apply for funding. Funding applicants must meet the National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure standard, which went into effect on March 30, 2023. The standard is designed to promote interconnected EV infrastructure along federal highways, but any system that uses Title 23 federal funds must meet it no matter its location. NEVI covers topics such as eligible charger types, payment processing, cybersecurity, data privacy, and labor rules.
For more on EV charging station standards, read The big list of EV charging station standards and specs to know.
The importance of universal charging stations
Universal EV charging stations are designed to let EV owners charge their cars no matter what hardware standard or software system is in place. This interoperability makes owning (and recharging) an EV simpler and more practical, which drives further adoption.
In the current EV charging station landscape, operators have to deal with several inconsistencies among different chargers. For example, the wide gamut of hardware can make it difficult to scale a charging network efficiently. But with universal charging software, operators can mix and match products from various manufacturers according to their own budgetary, market, and quality concerns to create the stack that works for them. EV drivers benefit, too, as open protocol charging frees them from painstakingly planning every charging stop on their trip.
Despite their promise, universal charging stations have yet to conquer the market. Many EV chargers claim to be universal, but drivers frequently visit charging stations that turn out to be incompatible. This makes it hard for potential EV owners to trust they can recharge when needed and complicates ownership of EV charging stations.
ChargeLab was one of the first 50 members of the Open Charge Alliance and has advocated for the adoption of open protocols in EV charging since the very beginning (in fact, we run an entire boot camp program for manufacturers to improve their OCPP compliance!).
For more on universal charging stations and the future of EVs, read How universal EV charging stations are driving EV adoption.
Critical EV charging standards
As the EV industry matures, more and more manufacturers are adhering to standards that maintain high levels of quality and consistency for consumers. Standards now exist that govern operation, installation, and safety.
Operating standards
- SAE International standards , devised by an industry group of mobility professionals, establish hardware and software guidelines.
- ISO 15118 sets a standard for digital communications between an EV and the charging station.
- Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is a universal communications standard that allows the hardware and software of different providers to work together.
- Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) is an automated roaming protocol that lets charging stations serve drivers outside their network.
- The Canadian Electricity and Gas Inspection Act provisions for safety requirements and EV charging outputs.
Installation and permitting standards
- The Alternative Fuels Data Center maintains a list of installation requirements from the US government, and its permit template provides a solid framework for what to expect.
- The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) will apply to your electric vehicle charging station business, so be sure to review it during planning to ensure disabled customers can charge with ease. The Accessible Canada Act applies many similar requirements.
Safety and security
- SOC 2 compliance helps ensure a high standard of information security.
- PCI DSS compliance safeguards customer payment info and keeps your business in good standing with payment card companies.
To learn more about the regulations and standards that affect how to start an EV charging station business, read The big list of EV charging regulations and standards.
Charger specifications to know when starting an EV charging business
EV chargers have different specifications based on their expected charging level. There are three levels in total:
- Connection : Standard 120V outlet
- Charge speed : 5 km or 3 mi per hour of charging
- Average time to full charge : 20+ hours
Level 1 chargers are the simplest to manage because they use existing electrical infrastructure. That makes them a good fit for residential or emergency use. On the other hand, their slow charging speed disqualifies them from commercial use.
- Connection : 240V outlet
- Charge speed : 30–50 km or 20–30 mi per hour of charging
- Average time to full charge : 6 to 14 hours
Level 2 chargers require specialized installation, using higher-voltage outlets and dedicated software to charge faster and intelligently bill customers automatically. They're well suited to retail deployments.
- Connection : Direct current
- Charge speed : 200 km per hour or 124 mi per hour
- Average time to full charge : 20 minutes to an hour
Level 3 chargers use direct current (DC), which requires specialized hardware and electrical infrastructure. This gets them unparalleled charging speeds, making them ideal for thoroughfares and along major highways as gas station replacements.
EV connector types
Part of starting an EV charging station business means choosing which connector types to support. Some of the most popular examples include:
- SAE J1772 : The North American standard, also known as the J Plug, supports Level 1 and 2 charging systems.
- IEC 62196 Type 2 : The European standard supports Level 2 chargers.
- Combined Charging System (CCS): A DC connector for Level 3 charging in North America and Europe.
- CHAdeMo : A DC connector designed by the Japanese company of the same name and popular in Japan.
- GB/T : The standard connector in China, with different models for each of the three charging levels.
- NACS : A formerly proprietary connector for Tesla EVs, the North American Charging Standard is now open to the industry. Automakers, including Ford, GM, Nissan, and beyond, have announced plans to adopt the standard.
For more on installation requirements and network compatibility, read EV charger specifications every pro needs to know .
Maximizing ROI when adding EV charging to your business
As the number of EVs on the road has more than tripled in the past three years, demand for hotels, condos, and other businesses to add charging stations to their offerings has continued to mount. These chargers' return on investment (ROI) can include additional revenue, brand appeal, and cost savings with the careful deployment of EV charging incentives.
To determine your ROI, begin by understanding your customers. How safe will they feel leaving their vehicles in your care, and how quickly will they need their cars recharged? The busier your business, the more sense it makes to invest in fast Level 3, or DC, chargers. Businesses with slower customer turnover, such as hotels, can likely use a higher ratio of Level 2 chargers.
Next, you'll need to determine where to place these chargers for maximum benefit. Performing market research on the demand for chargers in your area can help clarify this process, as can consulting with a financial advisor with regard to installation costs.
Speaking of: The easiest way to install EV chargers is to turn to an EV solutions provider. They'll do the research, install, and operate the charging stations for you. As an EV infrastructure provider, they likely qualify for more rebates than your business. They're also experts in their field and can guide you through permitting, rebate application, and installation. Finally, they're there to help should something go wrong with the chargers.
To learn more about the incentives set to benefit businesses that install EV charging stations, read 7 EV charging incentives for businesses going green.
Supercharge your electric vehicle charging station business
Moving into electric vehicle charging is a chance to power both a better world and a healthier bottom line, and investing in the right tools early can make both easier. That's why we at ChargeLab designed our CSMS for deep functionality and wide-ranging flexibility. No matter your hardware, we're here to help. Reach out today to learn more .

Connect with us
If you're looking for software to help build your EV charging business, contact ChargeLab today.
Charger management software
Use the ChargeLab CSMS to connect and manage all your EV chargers from one hub.
Join our team
We're looking for the best engineers and operators to help build the future of EV charging.

- Forums Tesla Model S Model 3 Model X Model Y Roadster 2008-2012 Roadster 202X Cybertruck SpaceX
You can install our site as a web app on your iOS device by utilizing the Add to Home Screen feature in Safari. Please see this thread for more details on this.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
- Want to remove ads? Register an account and login to see fewer ads, and become a Supporting Member to remove almost all ads.
- Tesla Vehicles
- Model S: Ordering, Production, Delivery
Can you help with purchasing a Tesla as a business vehicle?
- Thread starter xilex
- Start date Oct 13, 2018
- Oct 13, 2018
Hi all, I need some help with doing things properly for purchasing a Tesla for use as a business vehicle (*not* leasing). I'm a one-person S-corp and will not be transporting people/equipment, but instead is used for travel from office to hospital(s). What is the correct way to set up car registration, financing, and auto insurance? It sounds like to be able to depreciate the car as a business asset, on the Tesla account page, I have to choose Registration Type as a Company, is this correct? As a result, however, it says the credit application will be submitted on behalf of the business. If I probe some of the local credit unions to see if there is a better rate, can I submit an application on my name instead of the business? And lastly, regarding auto insurance, can you add a business as a second driver? I spoke with one insurance company and I said the car is going to be used for business purposes as stated above and they said that should be okay. What have other owners done in this situation? Thanks.
Thanks for the reply. Can I ask what you chose for Registration Type-Company or two persons? And what did you do for insurance? It wasn't clear from your post if you put it under your name or the business name. Are you insuring only the Tesla with State Farm with commercial auto?
Well-Known Member
If you are looking into a Tesla for your business, be sure to consider the Section 179 SUV benefits that would be available with the Model X. You could use accelerated depreciation to deduct the entire cost of the vehicle the first year. As a S Corp the tax benefits would flow to the owner, even if it is not registered to the Corporation. If you own the Corp and also own the car, the benefits flow. Gotta check with your Tax Advisor, as everybodys Taxes are different, but it really throws off some huge tax benefits by purchasing a SUV with a Gross Vehicle Weight of over 6,000 lbs. (The Model X qualifies) Section 179 benefits change every year. If you take delivery, and place the X into service by the end of this year you get the entire deduction. Some place the vehicle into service near the end of the year and use it exclusively for business use. That way you could take the maximum 100% deduction. Still need to use the vehicle at least 50% in following years to maintain the deduction. These deductions only work for the Model X. For people that qualify it makes the X much less net cost than either the 3 or S.
- Oct 16, 2018
Let’s say theoretical you make $10k from your part time business and $90k from your full time job. Could the X be written off to offset your total liability ($100k) or just the $10k from the part time business?
- Jun 11, 2020
How about deducting electric bill for charging at home?
Only can deduct that portion where the car is used for the business. If it is only used 10% for business, then you can only deduct 10%. They frown on people that will set up a side gig and try to use that to game the deduction.
- Jun 16, 2020
easier to write off on business for a X then a S. I think the Gross Weight and the class as being a SUV has something to do with it.
Similar threads
- Apr 18, 2024
- Apr 2, 2024
- Sep 30, 2023
- Oct 1, 2023
- alimordecai
- Oct 8, 2023
- The UK and Ireland
- My View My View
- Following Following
- Saved Saved
How China's EV makers aim to beat Tesla, legacy automakers in Europe
- Medium Text

- Company Ald Sa Follow
- Company BYD Co Ltd Follow
- Company Chery Automobile Co Ltd Follow
COST ADVANTAGES
Long-term investing.
Sign up here.
Reporting by Nick Carey, Giulio Piovaccari, Marie Mannes and Christina Amann; Editing by Brian Thevenot and Daniel Flynn
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Business Chevron

Fast fashion retailer Shein hikes prices ahead of IPO
Fast fashion retailer Shein, known for its China-made $5 tops and $10 dresses, has hiked prices by over a third on some core products, in a move likely to boost revenues ahead of its planned IPO, according to an analysis of its pricing strategy.

- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- T20 World Cup
- Partner Content
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
- Pro Kabaddi League
Tesla shareholders voting 'yes' for $56 bn pay package, says Elon Musk
Tesla has been drumming up support for musk's pay package, especially from retail investors, who make up an unusually high percentage of its ownership base but who often do not vote.
)
Photo: Bloomberg
Musk's India visit sparks expectations for Tesla investment and expansion
Proxy adviser urges tesla shareholders to reject elon musk's pay package, us reacts to elon musk's x post backing india for permanent seat at unsc, elon musk's tesla initiates formal dialogue with govt on new ev policy, musk vs the rest: who will be tesla's biggest competitors in india, g7 summit opens with deal to use russia's frozen assets for ukraine, us tech giant intel halts expansion plan for $25 billion israel chip plant, us restrictions on asylum-seekers may violate international law: unhcr, china's li visits nz, where security fears vie with trade hopes on agenda, asia stocks rally, bond yields fall as investors assess fed outlook.
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Jun 13 2024 | 10:23 AM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Lok Sabha Election 2024 Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)

- Entertainment
- Rex Reed Reviews
- Awards Shows
- Climate Change
- Nightlife & Dining
- Gift Guides
- Business of Art
- About Observer
- Advertise With Us
Elon Musk’s Tesla Turnaround Plan, Explained
Elon musk said in an email this week tesla needs to be "absolutely hard core about headcount and cost reduction.".

Massive layoffs, rescinding internship offers, a surprise visit to China … Tesla (TSLA) CEO Elon Musk has been making a series of unusual and swift moves in what increasingly looks like a turnaround plan for his once high-flying electric carmaker. Over the past three weeks, Tesla has slashed thousands of jobs and shut down multiple divisions, including its newly formed marketing team, and Musk has signaled that he isn’t done making cuts. Meanwhile, the billionaire founder is courting the Chinese government to help Tesla open up new revenue streams in the country, the company’s largest overseas market.
Sign Up For Our Daily Newsletter
Thank you for signing up!
By clicking submit, you agree to our <a href="http://observermedia.com/terms">terms of service</a> and acknowledge we may use your information to send you emails, product samples, and promotions on this website and other properties. You can opt out anytime.
Layoffs and resignations are rattling all levels of positions at Tesla. In an email on Monday (April 29), first reported by the Information, Musk announced that two senior Tesla executives —Rebecca Tinucci, senior director for charging infrastructure, and Danile Ho, director for vehicle programs and new products, are leaving the company and that their teams will be dissolved as a result, affecting hundreds of employees. Two weeks prior, Tesla’s head of public policy and business development, Rohan Patel, announced his departure, and Musk subsequently shut down his entire team.
In the email, Musk said he would begin asking for resignation letters from Tesla executives who retain “more than three people who don’t obviously pass the excellent, necessary and trustworthy test.”
“Hopefully these actions are making it clear that we need to be absolutely hard core about headcount and cost reduction,” he wrote.
On April 14, Tesla announced plans to cut more than 10 percent of its global workforce , which would affect around 14,000 employees. This week, Tesla let go about 500 employees on its EV Supercharger team. Bloomberg has reported that Musk is targeting a 20 percent headcount reduction , citing anonymous sources familiar with his thinking.
Even lowly-paid interns are feeling the pain. Bloomberg reported yesterday (May 1) Tesla has revoked some offers of its summer internships, citing multiple would-be Tesla interns who posted on LinkedIn saying their internship offers had been rescinded. Each year, Tesla hires about 3,000 interns from colleges and universities around the world, according to the company’s 2022 Impact Report .
Tesla was one of the few Silicon Valley companies that managed to avoid major layoffs during last year’s tech slump . But like many of its Valley peers, Tesla hired aggressively during the Covid tech boom and is now dealing with the consequences. “Over the years, we have grown rapidly with multiple factories scaling around the globe. With this rapid growth there has been duplication of roles and job functions in certain areas,” Musk said in a memo announcing layoffs on April 14.
On April 23, Tesla reported the largest quarterly revenue drop in more than a decade. EV sales for the quarter ended March plunged 9 percent from the previous year. And Tesla delivered 20 percent fewer EVs in the January-March period than the previous quarter.
In the meantime, Musk is looking to tap new revenue streams in key markets. This past Sunday, he made an unexpected, one-day visit to China and got his old friend, Chinese Premier Li Qiang’s backing to roll out Tesla’s FSD driver assistance software in the country. The swift dealmaking surprised many industry observers because Tesla’s driving assistance technology had caused concerns for Chinese regulators in the past. In 2021, China banned Tesla vehicles from entering many government facilities due to security concerns over cameras installed on the cars. Those cameras were used to power Autopilot, a less advanced driver assistance program than FSD.

- SEE ALSO : What Melinda French Gates’s Philanthropy Could Look Like Post-Gates Foundation
We noticed you're using an ad blocker.
We get it: you like to have control of your own internet experience. But advertising revenue helps support our journalism. To read our full stories, please turn off your ad blocker. We'd really appreciate it.
How Do I Whitelist Observer?
Below are steps you can take in order to whitelist Observer.com on your browser:
For Adblock:
Click the AdBlock button on your browser and select Don't run on pages on this domain .
For Adblock Plus on Google Chrome:
Click the AdBlock Plus button on your browser and select Enabled on this site.
For Adblock Plus on Firefox:
Click the AdBlock Plus button on your browser and select Disable on Observer.com.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
China’s plan to sell cheap EVs to the rest of the world
Try unlimited access only $1 for 4 weeks.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- Apple Podcasts
- Google Podcasts
Real Teenagers, Fake Nudes: The Rise of Deepfakes in American Schools
Students are using artificial intelligence to create sexually explicit images of their classmates..

Hosted by Sabrina Tavernise
Featuring Natasha Singer
Produced by Sydney Harper and Shannon M. Lin
Edited by Marc Georges
Original music by Marion Lozano , Elisheba Ittoop and Dan Powell
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music | YouTube
Warning: this episode contains strong language, descriptions of explicit content and sexual harassment
A disturbing new problem is sweeping American schools: Students are using artificial intelligence to create sexually explicit images of their classmates and then share them without the person depicted even knowing.
Natasha Singer, who covers technology, business and society for The Times, discusses the rise of deepfake nudes and one girl’s fight to stop them.
On today’s episode
Natasha Singer , a reporter covering technology, business and society for The New York Times.

Background reading
Using artificial intelligence, middle and high school students have fabricated explicit images of female classmates and shared the doctored pictures.
Spurred by teenage girls, states have moved to ban deepfake nudes .
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson, Nina Lassam and Nick Pitman.
Natasha Singer writes about technology, business and society. She is currently reporting on the far-reaching ways that tech companies and their tools are reshaping public schools, higher education and job opportunities. More about Natasha Singer
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tesla did not invent the electric car, but it invented the first successful business model for bringing electric cars to the market.
Master Plan Part 3. The Tesla Team, April 5, 2023. Today, we are publishing Master Plan Part 3, which outlines a proposed path to reach a sustainable global energy economy through end-use electrification and sustainable electricity generation and storage. This paper outlines the assumptions, sources and calculations behind that proposal.
Currently, Tesla's business model is based on three foundations: selling model, servicing, and charging network. First of all, unlike other automakers that have their cars sold by dealerships worldwide, Tesla focuses on direct sales.
Lessons from Tesla's Approach to Innovation. Summary. Tesla has shifted the auto industry toward electric vehicles, achieved consistently growing revenues, and at the start of 2020 was the ...
Abstract. This case study aims to develop a five-year strategic business plan for the company Tesla Motors, Inc. (i.e., Tesla) to serve as a suggestion basis for business management strategies ...
The Secret Tesla Motors Master Plan (just between you and me) Elon Musk, Co-Founder & CEO of Tesla Motors, August 2, 2006. As you know, the initial product of Tesla Motors is a high performance electric sports car called the Tesla Roadster. However, some readers may not be aware of the fact that our long term plan is to build a wide range of ...
Check out Tesla's business model. All those novice automobile entrepreneurs looking for a successful business strategy, here's an interesting read for you all.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) Tesla is primarily known for its electric vehicle (EV) business. The company designs, manufactures, and sells high-performance electric cars, including sedans, SUVs, and sports cars. Tesla's EVs are known for their range, performance, and cutting-edge technology. - Tesla Model 3, Model S, Model X, and Model Y are ...
In cities where demand exceeds the supply of customer-owned cars, Tesla will operate its own fleet, ensuring you can always hail a ride from us no matter where you are. So, in short, Master Plan, Part Deux is: Create stunning solar roofs with seamlessly integrated battery storage.
Tesla's master plan is 4 years old: how Elon Musk is doing on EVs and more. Four years ago, Tesla outlined a master plan that covered electric cars, autonomy and clean power.
Discover what your business can take away from Tesla's business strategy, with our in-depth analysis of the electric vehicle giant…
How Tesla Sets Itself Apart. Summary. Tesla and its flamboyant, and sometimes erratic, innovator Elon Musk have turned the more than a century old industry upside down in a mere 16 years. T ...
The car, priced at $35,000 before incentives, has become something of a phenomenon around the world and it all hearkens back to Musk's master plan for Tesla, a company he initially did not want to ...
Roald Larsen. Tesla, the pioneering electric vehicle (EV) manufacturer, has disrupted the automotive industry with its unique and innovative business model. This article aims to decode Tesla's business model and explore its various revenue streams, as well as address the challenges and criticisms it has faced.
Tesla is vertically integrated. Therefore, the company runs and operates the Tesla's plants where cars are manufactured and the Gigafactory which produces the battery packs and stationary storage systems for its electric vehicles, which are sold via direct channels like the Tesla online store and the Tesla physical stores.
Elon Musk's plan for Tesla is to create a sustainable future Getty Images / VCG. ... Part Deux' for his electric car business, Tesla, and its focus isn't purely on producing cars.
Tesla's exponential growth and success can be attributed to the rising demand for electric cars, making it the most valuable automotive brand worldwide. Tesla's secret master plan outlines its mission to electrify and replace conventional energy sources, starting with the production of luxury and affordable electric cars.
Musk's new "master plan" for Tesla didn't reveal any new vehicle models. Instead he presented a big-picture case for climate action, followed by smaller examples of innovations and cost-cutting.
Tesla vows to halve EV production costs, Musk keeps affordable car plan under wraps. SAN FRANCISCO, March 1 (Reuters) - Tesla Inc (TSLA.O) will cut assembly costs by half in future generations of ...
Wondering how to start an EV charging station business? Read this guide to go from grant application to DC charging in this booming market sector.
Tesla has told suppliers it wants to start production of a new mass market electric vehicle codenamed "Redwood" in mid-2025, according to four people familiar with the matter, with two of them ...
If you are looking into a Tesla for your business, be sure to consider the Section 179 SUV benefits that would be available with the Model X. You could use accelerated depreciation to deduct the entire cost of the vehicle the first year. As a S Corp the tax benefits would flow to the owner, even if it is not registered to the Corporation.
Connect with Tesla to learn how owning a Tesla fleet can help benefit your community, your drivers and your business.
Starting in the 1980s, European automakers steadily conquered China, racking up millions in sales with little local competition.
Tesla shareholders are voting to approve a $56 billion pay package for Elon Musk and to move the electric vehicle maker's legal home to Texas, Musk said on social media platform X on Wednesday, adding that passage was by wide margins.
Tesla CEO Elon Musk has been making a series of unusual and swift moves in what increasingly looks like a turnaround plan for the struggling EV maker.
Prominent investor Ron Baron has come out in support of Tesla CEO Elon Musk's $56 billion pay package, which is up for a shareholder vote next week, according to an open letter from the Baron ...
The resurrection of a car plant in Brazil's poor north-east stands as a symbol of China's global advance — and the west's retreat. ... chief executive of Tesla, ... at the University of ...
German Chancellor Olaf Scholz spoke out against restricting automotive trade as the European Union moves closer to slapping tariffs on electric vehicles imported from China.
A disturbing new problem is sweeping American schools: Students are using artificial intelligence to create sexually explicit images of their classmates and then share them without the person ...