Book Bans in American Libraries: Impact of Politics on Inclusive Content Consumption
Donald G. Costello College of Business at George Mason University Research Paper
33 Pages Posted: 26 Jun 2023 Last revised: 3 Nov 2023

Uttara M Ananthakrishnan
Carnegie Mellon University - Heinz College of Information Systems and Public Policy
Naveen Basavaraj
Carnegie Mellon University, H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management
Sabari Rajan Karmegam
George Mason University - Department of Information Systems and Operations Management
Carnegie Mellon University
Michael D. Smith
Carnegie Mellon University - H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management
Date Written: June 23, 2023
Banning of books has become increasingly prevalent and politically polarizing in the United States. While the primary goal of these bans is to restrict access to books, conversations about the bans have garnered attention on a wider scale. This increased attention to bans can either have a chilling effect or can influence consumers to read the banned books. In this study, we use a novel, large-scale dataset of US library book circulations and evaluate the impact of book bans on the consumption of banned books. Using a staggered difference-in-differences design, we find that the circulations of banned books increased by 12% on average compared to comparable non-banned titles after the ban. We also find that banning a book in a state leads to increased circulation in states without bans. We show that the increase in consumption is driven by books from lesser-known authors suggesting that new and unknown authors stand to gain from the increasing consumer support. Additionally, our results demonstrate that books with higher visibility on social media following the ban see an increase in consumption, suggesting a link between social media and political consumerism. We also find that book bans have a tangible political impact through campaign donations - Republican Party candidates attract significantly more campaign donations than Democratic candidates, following the ban events but only in Republican-leaning states.
Keywords: book bans, political consumerism, library, social media
JEL Classification: P16, M31, M38, I20
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Uttara M Ananthakrishnan (Contact Author)
Carnegie mellon university - heinz college of information systems and public policy ( email ).
5000 Forbes Ave Pittsburgh, PA 15213 United States
Carnegie Mellon University, H. John Heinz III School of Public Policy and Management ( email )
Pittsburgh, PA 15213-3890 United States
George Mason University - Department of Information Systems and Operations Management ( email )
4400 University Drive Fairfax, VA 22030 United States
Carnegie Mellon University ( email )
Carnegie mellon university - h. john heinz iii school of public policy and management ( email ).
HOME PAGE: http://www.heinz.cmu.edu/~mds
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, sociology of education ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Law & Literature eJournal
Political behavior: cognition, psychology, & behavior ejournal, behavioral marketing ejournal, law, politics & the media ejournal, information systems & economics ejournal, social & personality psychology ejournal, mass communication & popular culture ejournal, psychology research methods ejournal, computational & quantitative research in communication ejournal, library services & librarianship ejournal.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player

Banned and Challenged: Restricting access to books in the U.S.
Perspective, ashley hope pérez: 'young people have a right' to stories that help them learn.
Ashley Hope Pérez

Author Ashley Hope Pérez wrote Out of Darkness, which is on the American Library Association's lists of most banned books. Kaz Fantone/NPR hide caption
Author Ashley Hope Pérez wrote Out of Darkness, which is on the American Library Association's lists of most banned books.
This essay by Ashley Hope Pérez is part of a series of interviews with — and essays by — authors who are finding their books being challenged and banned in the U.S.
For over a decade, I lived my professional dream. I spent my days teaching college literature courses and writing novels. I regularly visited schools as an author and got to meet teens who reminded me of the students I taught in Houston — the amazing humans who had first inspired me to write for young adults.
Then in 2021, my dream disintegrated into an author and educator's nightmare as my novel Out of Darkness became a target for politically motivated book bans across the country.

Book News & Features
Efforts to ban books jumped an 'unprecedented' four-fold in 2021, ala report says.

Author Interviews
Banned books: author ashley hope pérez on finding humanity in the 'darkness'.
Attacks unfolded, not just on my writing but also on young people's right to read it. Hate mail and threats overwhelmed the inboxes where I once had received invitations for author visits and appreciative notes from readers. At the beginning of 2021, Out of Darkness had been on library shelves for over five years without a single challenge or complaint. As we reach the end of 2022, it has been banned in at least 29 school districts across the country.
From the earliest stages of writing, I knew Out of Darkness would be difficult — for me, and for readers. I drew my inspiration for the novel from an actual school disaster: the 1937 New London school explosion that killed hundreds in an East Texas oil town just 20 minutes from my childhood home. This tragic but little-known historical event serves as the backdrop for a fictional star-crossed romance between a Black teenager and a young Latina who has just arrived in the area.
As I researched the novel, I imagined the explosion as its most devastating event. But to engage honestly with the realities of the time and of my characters' lives, I had to grapple with systemic racism, personal prejudice, sexual abuse and domestic violence. As I wrote, the teenagers' circumstances began to tighten, noose-like, around their lives and love, leading to still more tragedy. I sought to show the depths of harm inflicted on some in this country without sensationalizing that history. The book portrays friendship, loving family, community and healthy relationships because they, too, are part of the characters' world. Then, as now, young people struggle mightily for joy, love and dignity.
When Out of Darkness was first published, I braced for objections. Would readers recoil from the harshness of my characters' realities? Or would they recognize how the novel invites connections between those realities and an ongoing reckoning with racialized violence and police brutality? To my relief, the novel received glowing reviews, earned multiple literary awards, and was named to "best of the year" lists by Kirkus Reviews and School Library Journal . It appeared on reading lists across the country as a recommendation for ambitious young readers ready to face disquieting aspects of the American experience.
So it went until early 2021. In the wake of the 2020 presidential elections, right-wing groups pivoted from a national defeat to "local" issues. The latest wave of book banning exceeds anything ever documented by librarian or free-speech groups. The statistics for 2021, which represent only a fraction of actual removals, reflect a more than 600% increase in challenges and removals as compared to 2020. (See Everylibrary.org for a continually updated database of challenges and bans and PEN America's Banned in the USA reports for April 2022 and September 2022 for further context.)
These book bans do not reflect spontaneous parental concern. Instead, they are part of an orchestrated effort to sow suspicion of public schools as scarily "woke" and to signal opposition to certain identities and topics. Book banners often cite "sexually explicit content" as their reason for objecting to books in high schools. What distinguishes the targeted titles, though, is not their sexual content but that they overwhelmingly center the experiences of BIPOC, LGBTQ+ and other marginalized people. If you were to stack up all the books with sexual content in any library, the tallest stack by far would be about white, straight characters. Tellingly, those are not the books under attack. Claims about "sexual content" are a pretext for erasing the stories that tell Black, Latinx, queer and other non-dominant kids that they matter and belong. Beyond telegraphing disapproval, book bans serve the interests of groups that have long sought to dismantle public education and shut down conversations about important issues.
Debates about the suitability of reading materials in school are nothing new. These include past efforts by progressives to reorient language arts instruction. Concerns about racist language and portrayals might well lead communities to seek alternatives to the teaching of works like The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn . But de-emphasizing problematic classics does not generally entail removing the books from library collections. By contrast, in targeting high school libraries, conservative book banners seek to restrict what individual students may choose to read on their own , disregarding the judgment of school librarians who carefully select materials according to professional standards.
Rather than reading the books themselves, today's book banners rely instead on haphazard lists and talking points circulated online. Social media plays a central role in stoking the fires of censorship. Last year, a video of a woman ranting about a passage from Out of Darkness in a school board meeting went internationally viral. The woman's school board rant resulted in the removal of every copy of Out of Darkness from the district's libraries, triggered copycat performances, and fueled more efforts to ban my book.
Book banning poses a real professional and personal cost to authors and educators. For YA writers, losing access to school and library audiences can be career ending. And it is excruciating to watch people describe our life's work as "filth" or "garbage." We try to find creative ways to respond to the defamation, as I did in my own YouTube video . But there is no competing with the virality of outrage. Meanwhile, librarians and teachers face toxic work conditions that shift the focus from student learning to coping with harassment.
But book banning harms students, and their education, the most. Young people rely on school libraries for accurate information and for stories that broaden their understanding, offer hope and community, and speak honestly to challenges they face. As libraries become battlegrounds, teens notice which books, and which identities, are under attack. Those who share identities with targeted authors or characters receive a powerful message of exclusion: These books don't belong, and neither do you.
Back in 2004, my predominately Latinx high school students in Houston wanted — needed — books that reflected their lives and communities but few such books had been written. In the decades since, authors have worked hard to ensure greater inclusion and respect for the diversity of teen experiences. For students with fewer resources or difficult home situations, though, a book that isn't in the school library might as well not exist. Right-wing groups want to roll back the modest progress we've made, and they are winning.
These "wins" happen even without official bans. Formal censorship becomes unnecessary once bullying, threats and disruption shake educators' focus from students. The result is soft censorship . For example, a librarian reads an outstanding review of a book that would serve someone in their school, but they don't order it out of fear of controversy. This is the internalization of the banners' agenda. The effects of soft censorship are pervasive, pernicious and very difficult to document.
The needs of all students matter, not just those whose lives and identities line up with what book banners think is acceptable. Young people have a right to the resources and stories that help them mature, learn and understand their world in all its diversity. They need more opportunities, not fewer, to experience deep imaginative engagement and the empathy it inspires. We've had enough "banner" years. I hope 2023 returns the focus to young people and their right to read.
Ashley Hope Pérez, author of three novels for young adults, is a former high school English teacher and an assistant professor in the Department of Comparative Studies at The Ohio State University. Find her on Twitter and Instagram or LinkT .
Following the people and events that make up the research community at Duke

Library Shakedowns: Book Bans and Censorship
By Alex Clifford
On December 5, 2022
In Humanities , Responsible Conduct
“I started thinking about how I might be different, how my life might be different, how my conversations might be different, if [‘To Kill a Mockingbird’] had not been a book that I was able to read in the 8th grade… to keep reading and reading again,” recounted Professor Kisha Daniels in her opening remarks of last month’s “Policing Pages” panel.

What truly is more formative in the awkward, acned stretch of middle school than Lip-Smackered gossip and English class? Yellow page paperbacks, palimpsests of doodles and students from years past. Purchased on teacher budget scraps and booster club wrapping paper sales, Shakespeare, Orwell, a hundred used copies of “Tuck Everlasting”: stained, dog-eared, and coverless .
Psychology and neuroscience researchers agree that reading (and, thus, books like “To Kill a Mockingbird”) weaves tapestries of yarny neurons and synapses, beneficial for the development of social-emotional skills, empathy, and creativity during childhood and adolescence.
Yet, America has recently witnessed persistent efforts to ban certain titles from K12 schools. In 2004 and 2005, for example, Stanford Middle (here in Durham) challenged the inclusion of “To Kill a Mockingbird” in its own library, citing the novel’s use of racial slurs.
It ultimately was not removed from the shelves, but the book remains one of the most challenged/banned titles in U.S. school history .

In 2021, the American Library Association reported an unprecedented 729 book challenges. So why, Daniels prompted, are we seeing such a high number of banned books? And why now?
Before answering this, Professor Sarah Ludington clarified some of the misleading rhetoric propagated by the popular media. “’Banned books’ is more of a slogan,” she explained. More accurate is the idea of challenging a book, whether in a library or on the class curriculum. This does not necessarily mean the book will be outright banned or even removed from the shelf or, if it is banned, permanently. In fact, books can be reinstated, even after their removal, back to their shelf and the occasional dust bunny.
In North Carolina, such a statute exists in state law that bars an individual, like a single librarian, teacher, or parent, from undemocratically removing or banning a book. Instead, local administrative boards must take a vote.

University Librarian Joseph Salem argued that social media platforms, like Facebook, and online groups, like Moms for Liberty, create tectonic shocks that trigger tidal waves of book challenges. They’re echo chambers: amplifying calls to remove specific books from school libraries, ping-ponging literary “hit-lists” through cyberspace with titles such as: “The Handmaid’s Tale” by Margaret Atwood, “Of Mice and Men” by John Steinbeck, “The Kite Runner” by Khaled Hosseini, and “Beloved” by Toni Morrison (you can take a look at the full list here ).

These books disproportionately feature marginalized voices and are often “charged and sentenced” for containing “LGBTQ content, profanity, and/or sexual references.”
As we’re all aware, what once was local news can quickly leach into national discourse. A book ban in a rural Ohio county, for example, can be picked up by the local media, trend on Twitter, disseminate through Facebook until someone, say, in Texas or Arkansas or North Carolina decides they too want to challenge said book in their own school district.
This book-banning rhetoric and its implications are present elsewhere in education-related conversations. Take, for example, Florida’s dubbed “ Don’t Say Gay ” bill. In March, lawmakers in the Sunshine State argued that merely mentioning sexual orientation/gender identity in primary school settings is grounds for a lawsuit on the basis that such content is innately “sexually explicit,” no matter its context.
However, challenging certain books and even passing certain laws are usually not intentionally malicious acts. It is indisputable that some books simply do not belong on school bookshelves. A medical textbook, Ludington analogized, wouldn’t make sense in a library for children just learning how to read. But, in a high school with a more mature student body, its inclusion wouldn’t bat an eye. Further, in the U.S. more generally, First Amendment rights do not extend to all forms of speech anyways, including but not limited to “obscenity, child pornography, fighting words, and the advocacy of imminent lawless action.”
And though societal concern over the well-being of children is well-intentioned, it can often be misguided or out-of-proportion.
I don’t think it’s too outrageous to consider children as sentient and receptive, whether to new ideas, new perspectives, and/or new people.
Still, in the United States, a number of moral panics , concerning everything from poisoned Halloween candy to “Dungeons & Dragons” to subliminal messaging in rock music to Tide Pods, have been cause for parental concern.
In 1985, for example, Tipper Gore bought Prince’s “Purple Rain” album for her 11-year-old daughter and was shocked by its age-inappropriate lyrics. She took her concern to the Senate in a series of Congressional hearings which, though largely mocked, called for a music rating system like the kind adopted by Hollywood for movies.

Dee Snider, Frank Zappa, and John Denver somehow managed to assemble into the eclectic “primary counsel” for the musical defense and eloquently argued that labeling and banning albums is akin to censorship.
Gore’s campaign was ultimately unsuccessful.
But, it’s not difficult to see how censorship concerns voiced in the Senate in the 80s mirror the ones voiced today.
Ludington, a self-proclaimed First Amendment enthusiast, added that “…inherent in our idea of freedom of speech is this notion that truth emerges from robust dialogue… The best way to counteract whatever pernicious effect there might be, say from a book that you wanted to ban, is actually to read the book and reason against it.”
This kind of civil discourse is an idealism baked into the “apple pie” of American democracy. Quite arguably the Golden Delicious themselves. Over the course of U.S. history, there have been just and unjust efforts to suppress individuals’ freedom of speech. Take the infamous “ yelling FIRE in a crowded theater ” anecdote.
Experts concur, however, that most censorship is unproductive and often does little to actually stymie the ideas it so desperately wants to quash. In fact, as Daniels pointed out, banning books from school libraries typically does not decrease their readership and can actually drive their sales up.
But the implications of book banning run deep, implying that, as a society, there is little value in responsibly harboring and learning from certain (and often difficult) materials.
Salem described a collection on hate groups, gathered by the Southern Poverty Law Center and possessed by the Duke University library. He said, “If we take a step back for a moment and think that everything in the Duke University library… is something we endorse without understanding the complexity of why we might have it, either to learn from it as a good or bad example… one might say that owning or stewarding means that we support what’s in that collection. I would push back on that vehemently. It doesn’t comport with our values at all.”
After book banning efforts in school libraries reached an all time high in 2021 , 2022 is trending to exceed last year’s figure.
Instead of arguing with disgruntled parents and Facebook groups, many underpaid librarians and teachers, Salem described, choose to self-censor, quietly removing contentious titles from their shelves to avoid unfair accusations lobbied at them in heated PTO meetings, over angry phone calls, or during school board votes.

To oppose this form of censorship, Daniels, Ludington, and Salem agreed: Read the books! Parents, Facebook group members, and legislatures alike, read before challenging, before banning, and then after banning. Reading is really the preeminent way to avoid unnecessarily suppressing free speech in schools; to introduce yourself to new ideas, to new discourse, and to new perspectives. Daniels put it best, “The book is innocent until proven guilty.”
Give it a fair trial.
In Harper Lee’s “To Kill a Mockingbird ,” Atticus describes empathy to Scout in a way which resonates with many of the “Policing Pages” talking points, saying: “You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view… until you climb into his skin and walk around in it.”
If interested in the “Policing Pages: The American Classics” discussion, click here to watch.
If interested in resources on book banning, check out the American Library Association for more information.

COVID and Our Education
Traveling with friends helps even mixed-up migrators find their way.
Powered by WordPress & Theme by Anders Norén
What You Need to Know About the Book Bans Sweeping the US
What you need to know about the book bans sweeping the u.s., as school leaders pull more books off library shelves and curriculum lists amid a fraught culture war, we explore the impact, legal landscape and history of book censorship in schools..

- The American Library Association reported a record-breaking number of attempts to ban books in 2022— up 38 percent from the previous year. Most of the books pulled off shelves are “written by or about members of the LGBTQ+ community and people of color."
- U.S. school boards have broad discretion to control the material disseminated in their classrooms and libraries. Legal precedent as to how the First Amendment should be considered remains vague, with the Supreme Court last ruling on the issue in 1982.
- Battles to censor materials over social justice issues pose numerous implications for education while also mirroring other politically-motivated acts of censorship throughout history.
Here are all of your questions about book bans answered by TC experts.
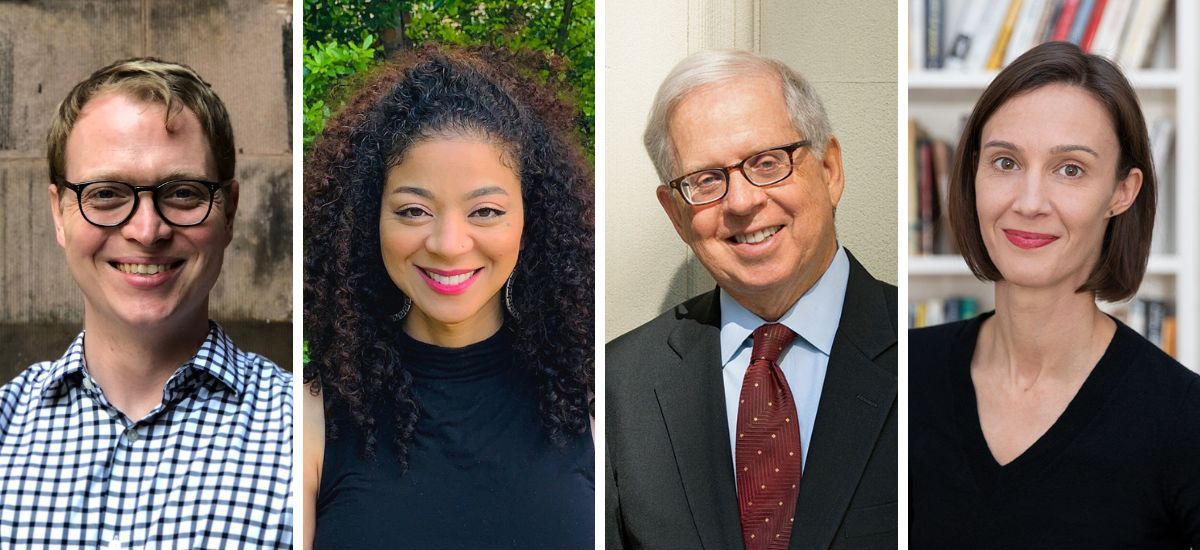

Alex Eble, Assistant Professor of Economics and Education; Sonya Douglass, Professor of Education Leadership; Michael Rebell, Professor of Law and Educational Practice; and Ansley Erickson, Associate Professor of History and Education Policy. (Photos; TC Archives)
How Do Book Bans Impact Students?
Prior to the rise in bans, white male youth were already more likely to see themselves depicted in children’s books than their peers, despite research demonstrating how more culturally inclusive material can uplift all children, according to a study, forthcoming in the Quarterly Journal of Economics , from TC’s Alex Eble.
“Books can change outcomes for students themselves when they see people who look like them represented,” explains the Associate Professor of Economics and Education. “What people see affects who they become, what they believe about themselves and also what they believe about others…Not having equitable representation robs people of seeing the full wealth of the future that we all can inhabit.”
While books have stood in the crossfire of political battles throughout history, today’s most banned books address issues related to race, gender identity and sexuality — major flashpoints in the ongoing American culture war. But beyond limiting the scope of how students see themselves and their peers, what are the risks of limiting information access?

The student plaintiffs in Island Trees Union Free School District v. Pico (1982) march in protest of the Long Island school district's removal of titles such as Slaughterhouse Five by Kurt Vonnegut. While the district would ultimately return the banned books to its shelves, the Supreme Court's ultimate ruling largely allowed school leaders to maintain discretion over information access. (Photo credit: unknown)
“[Book bans] diminish the quality of education students have access to and restrict their exposure to important perspectives that form the fabric of a culturally pluralist society like the United States,” explains TC’s Sonya Douglas s, Professor of Education Leadership. “It's a battle over the soul of the country in many ways; it's about what we teach young people about our country, what we determine to be the truth, and what we believe should be included in the curriculum they're receiving. There's a lot at stake there.”
Material stripped from libraries and curriculum include works written by Black authors that discuss police brutality, the history of slavery in the U.S. and other issues. As such, Black students are among those who may be most affected by bans across the country, but — in Douglass’ view — this is simply one of the more recent disappointments in a long history of Black communities being let down by public education — chronicled in her 2020 book, and further supported by a 2021 study from Douglass’ Black Education Research Center that revealed how Black families lost trust in schools following the pandemic response and murder of George Floyd.
In that historical and cultural context — even as scholars like Douglass work to implement Black studies curriculums — the failure of schools to properly integrate Black experiences into the curriculum remains vast.
“We want to make sure that children learn the truth, and that we give them the capacity to handle truths that may be uncomfortable and difficult,” says Douglass, citing Germany as an example of a nation that has prioritized curriculum that highlights its own injustices, such as the Holocaust. “This moment again requires us to take stock of the fact that racism and bigotry still are a challenging part of American life. When we better understand that history, when we see the patterns, when we recognize the source of those issues, we can then do something about it.”
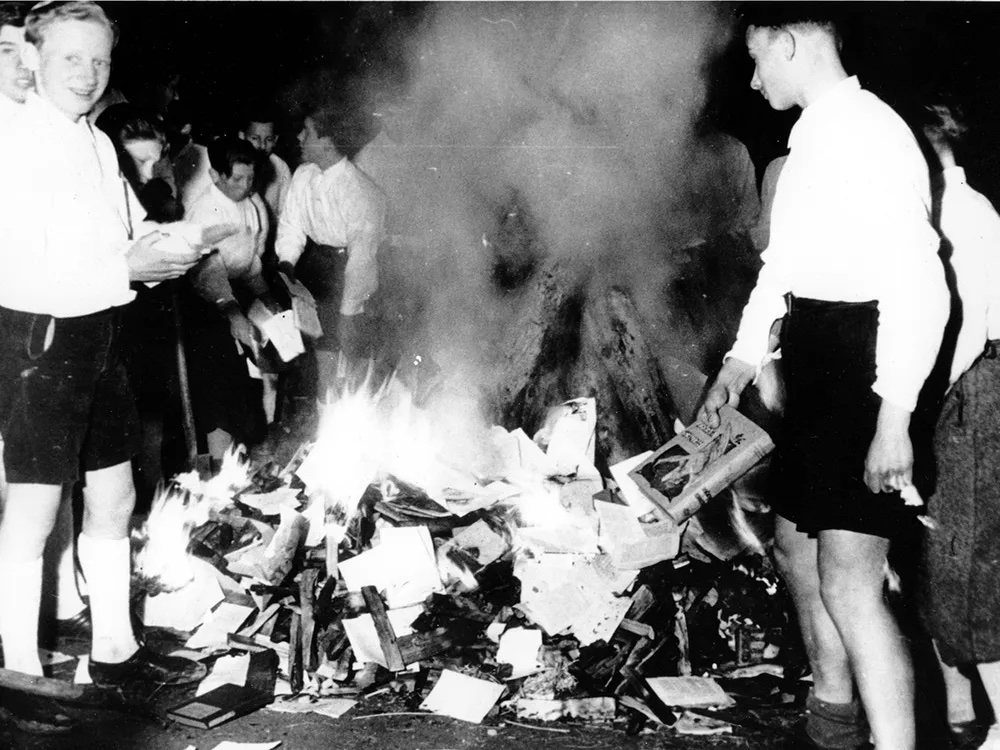

Beginning in 1933, members of Hitler Youth regularly burned books written by prominent Jewish, liberal, and leftist writers. (Photo: World History Archive / Alamy Stock Photo, dated 1938)
Why Is Banning Books Legal?
While legal battles over book censorship in schools consistently unfold at local levels, the wave of book bans across the U.S. surfaces a critical question: why hasn’t the United States had more definitive legal closure on this issue?
In 1982, the U.S. Supreme Court issued a noncommittal ruling that continues to keep school and library books in the political crosshairs more than 40 years later. In Island Trees Union Free School District v. Pico (1982), the Court deemed that “local school boards have broad discretion in the management of school affairs” and that discretion “must be exercised in a manner that comports with the transcendent imperatives of the First Amendment.”
But what does this mean in practice? In these kinds of cases, the application of the First Amendment hinges on the existence of evidence that books are banned for political reasons and violate freedom of expression. However, without more explicit guidance, school boards often make decisions that prioritize “community values” first and access to information second.

While today's recent book bans most frequently include topics related to racial justice and gender identity (pictured above), other frequently targeted titles include Extremely Loud & Incredibly Close , The Kite Runner and The Handmaid's Tale . (Cover images courtesy of: Viking Books, Sourcebooks Fire, Balzer + Bray, Oni Press, Random House and Farrar, Straus and Giroux).
“America traditionally has prided itself on local control of education — the fact that we have active citizen and parental involvement in school board issues, including curriculum,” explains TC’s Michael Rebell , Professor of Law and Educational Practice. “We have, whether you want to call it a clash or a balancing, of two legal considerations here: the ability of children to freely learn what they need to learn to be able to exercise their constitutional rights, and this traditional right of the school authorities to determine what the curriculum is.”
So would students benefit from more national and uniform legal guidance on book banning? In this political climate, Rebell attests, the risks very well might outweigh the potential rewards.
“Your local institutions are —in theory — protecting the values you believe in. And if somebody in Washington were going to say that we couldn't have books that talk about transgender rights and things in New York libraries, we'd go crazy, right?” said Rebell, who leads the Center for Educational Equity . “So I can't imagine that in this polarized environment, people would be in favor of federal law, whatever it said.”
Why Do Waves of Book Bans Keep Happening?
Historians date censorship back all the way to the earliest appearance of written materials. Ancient Chinese emperor Shih Huang Ti began eliminating historical texts in 259 B.C., and in 35 A.D., Roman emperor Caligula objected to the ideals of Greek freedom depicted in The Odyssey . In numerous waves of censorship since then, book bans have consistently manifested the struggle for political control.
“We have to think about [the current bans] as part of a longer pattern of fights over what is in curriculum and what is kept out of it,” explains TC’s Ansley Erickson , Associate Professor of History and Education Policy, who regularly prepares local teachers on how to integrate Harlem history into social studies curriculum.
“The United States’ history, since its inception, is full of uses of curriculum to shape politics, the economy and the culture,” says Erickson. “This is a really dramatic moment, but the curriculum has always been political, and people in power have always been using it to emphasize their power. And historically marginalized groups have always challenged that power.”
One example: when Latinx students were forbidden from speaking Spanish in their Southwest schools throughout the 20th century, they worked to maintain their traditions and culture at home.
“These bans really matter, but one of the ways we can imagine a response is by looking back at how people created spaces for what wasn’t given room for in the classroom,” Erickson says.
What Could Happen Next?
American schools stand at a critical inflection point, and amid this heated debate, Rebell sees civil discourse at school board meetings as a paramount starting point for any sort of resolution. “This mounting crisis can serve as a motivator to bring people together to try to deal with our differences in respectful ways and to see how much common ground can be found on the importance of exposing all of our students to a broad range of ideas and experiences,” says Rebell. “Carve-outs can also be found for allowing parents who feel really strongly that certain content is inconsistent with their religious or other values to exempt their children from certain content without limiting the options for other children.”
But students, families and educators also have the opportunity to speak out, explains Douglass, who expressed concern for how her own daughter is affected by book bans.
“I’d like to see a groundswell movement to reclaim the nation's commitment to education — to recognize that we're experiencing growing pains and changes in terms of what we stand for; and whether or not we want to live up to the democratic ideal of freedom of speech; different ideas in the marketplace, and a commitment to civics education and political participation,” says Douglass.
As publishers and librarians file lawsuits to push back, students are also mobilizing to protest bans — from Texas to western New York and elsewhere. But as more local battles unfold, bigger issues remain unsolved.
“We need to have a conversation as a nation about healing; about being able to confront the past; about receiving an apology and beginning that process of reconciliation,” says Douglass. “Until we tackle that head on, we'll continue to have these types of battles.”
— Morgan Gilbard
The views expressed in this article are solely those of the speaker to whom they are attributed. They do not necessarily reflect the views of the faculty, administration, staff or Trustees either of Teachers College or of Columbia University.
Tags: Views on the News Education Policy K-12 Education Social Justice
Programs: Economics and Education Education Leadership History and Education
Departments: Education Policy & Social Analysis
Published Wednesday, Sep 6, 2023
Teachers College Newsroom
Address: Institutional Advancement 193-197 Grace Dodge Hall
Box: 306 Phone: (212) 678-3231 Email: views@tc.columbia.edu
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Banned in the USA: The Growing Movement to Censor Books in Schools
Key findings.
More books banned.
More districts.
More states.
More students losing access to literature.
“More” is the operative word for this report on school book bans, which offers the first comprehensive look at banned books throughout the 2021–22 school year. This report offers an update on the count in PEN America’s previous report, Banned in the USA: Rising School Book Bans Threaten Free Expression and Students’ First Amendment Rights (April 2022) , which covered the first nine months of the school year (July 2021 to March 2022). It also sheds light on the role of organized efforts to drive many of the bans.
Many Americans may conceive of challenges to books in schools in terms of reactive parents, or those simply concerned after thumbing through a paperback in their child’s knapsack or hearing a surprising question about a novel raised by their child at the dinner table. However, the large majority of book bans underway today are not spontaneous, organic expressions of citizen concern. Rather, they reflect the work of a growing number of advocacy organizations that have made demanding censorship of certain books and ideas in schools part of their mission.
Banned Book Data Snapshot
- From July 2021 to June 2022, PEN America’s Index of School Book Bans lists 2,532 instances of individual books being banned, affecting 1,648 unique book titles.
- The 1,648 titles are by 1,261 different authors, 290 illustrators, and 18 translators, impacting the literary, scholarly, and creative work of 1,553 people altogether.
The numbers in this report represent documented cases of book bans reported directly to PEN America and/or covered in the media; there are likely additional bans that have not been reported. 1 In August, the Houston Chronicle released a report on the partisan nature of book bans in Texas between 2018 and 2021. The newspaper reported finding more than 1,000 bans in Texas during that time frame, which overlaps only in part with the time period covered by this report. That data was not available to review for inclusion in this report in advance of publication.
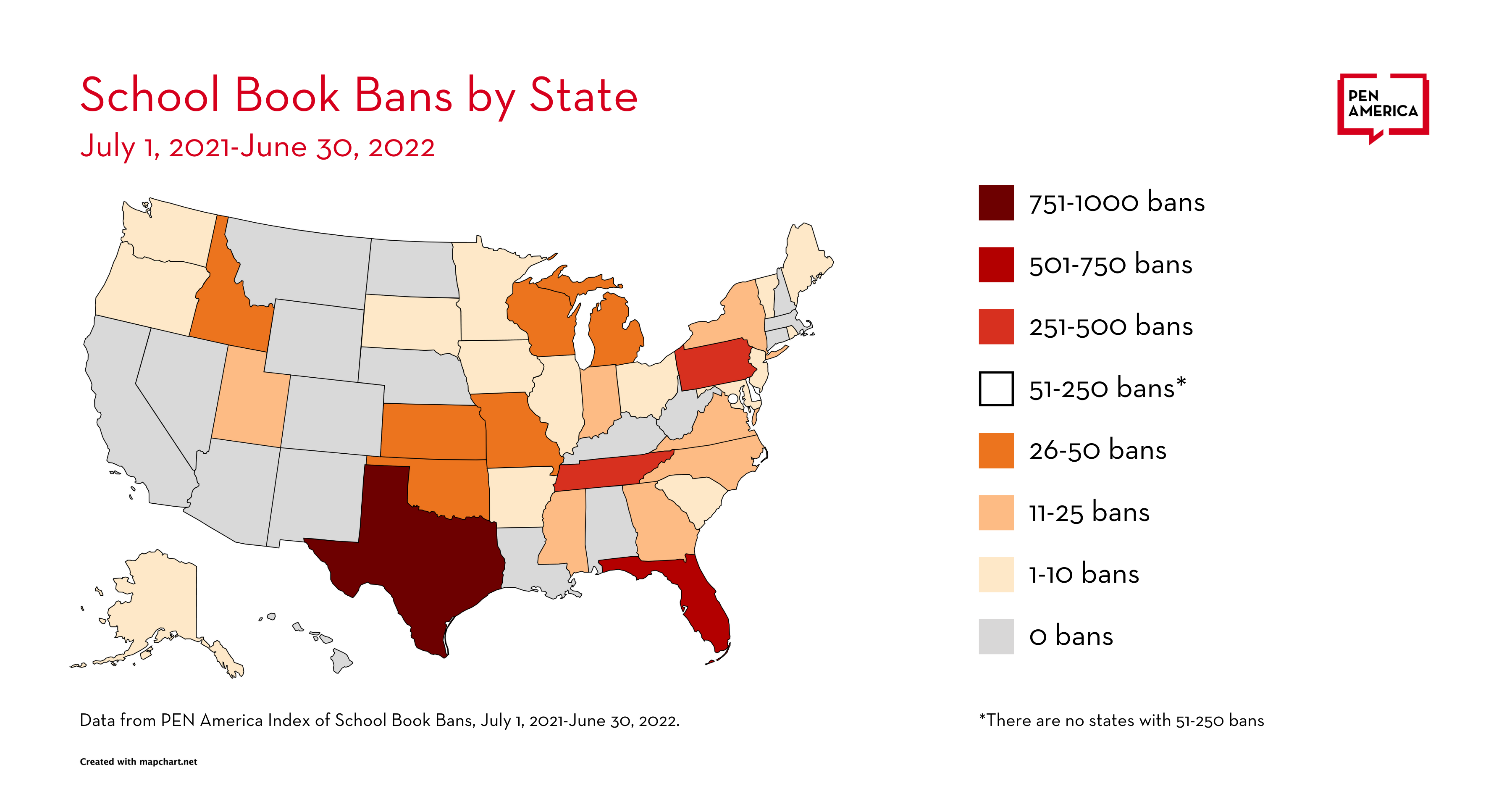
- Bans occurred in 138 school districts in 32 states. These districts represent 5,049 schools with a combined enrollment of nearly 4 million students.
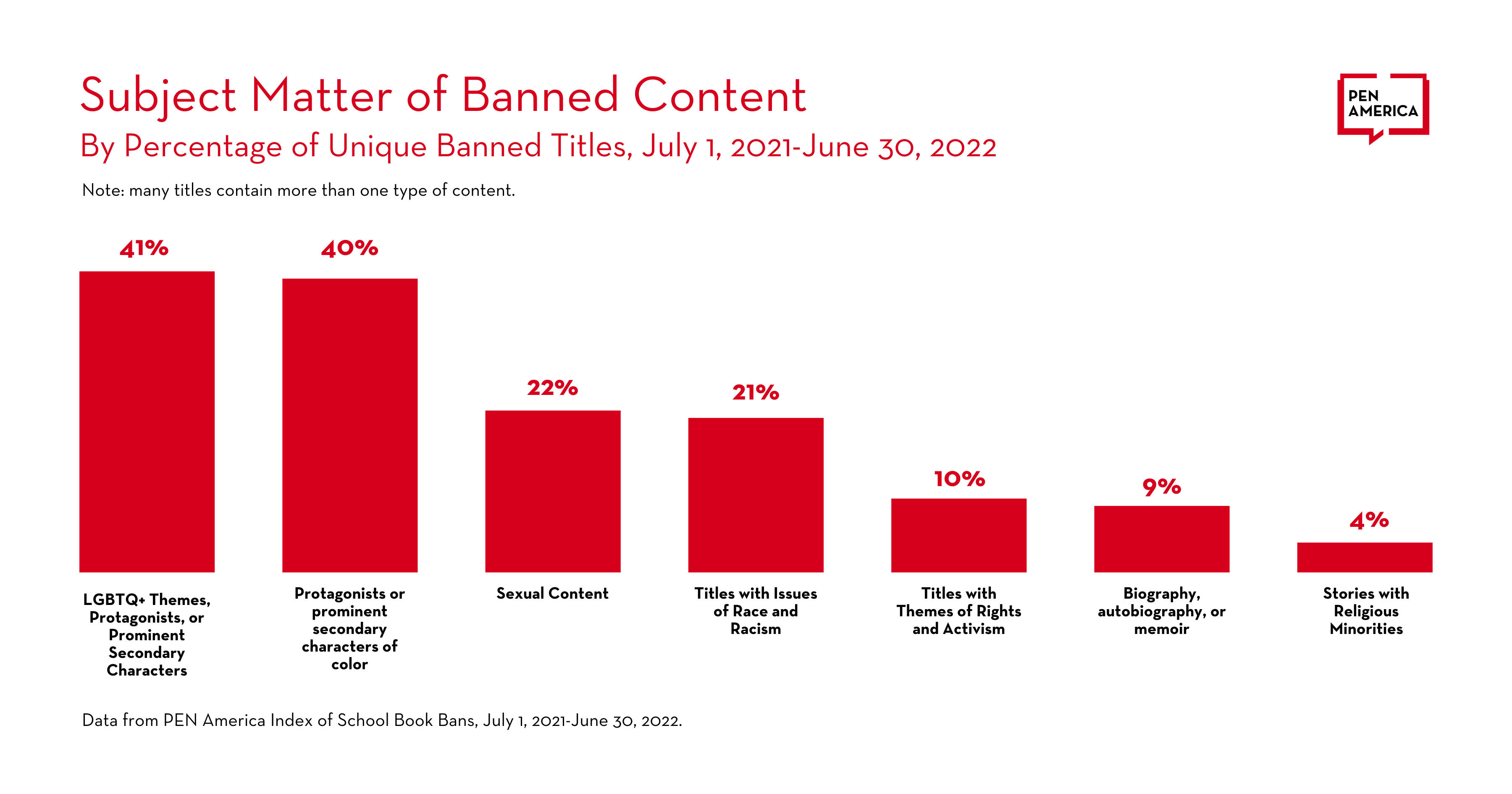
- 674 banned book titles (41 percent) explicitly address LGBTQ+ themes or have protagonists or prominent secondary characters who are LGBTQ+ (this includes a specific subset of titles for transgender characters or stories—145 titles, or 9 percent);
- 659 banned book titles (40 percent) contain protagonists or prominent secondary characters of color;
- 338 banned book titles (21 percent) directly address issues of race and racism;
- 357 banned book titles (22 percent) contain sexual content of varying kinds, including novels with some level of description of sexual experiences of teenagers, stories about teen pregnancy, sexual assault and abortion as well as informational books about puberty, sex, or relationships;
- 161 banned book titles (10 percent) have themes related to rights and activism;
- 141 banned book titles (9 percent) are either biography, autobiography, or memoir; and
- 64 banned book titles (4 percent) include characters and stories that reflect religious minorities, such as Jewish, Muslim and other faith traditions.
PEN America estimates that at least 40 percent of bans listed in the Index (1,109 bans) are connected to either proposed or enacted legislation, or to political pressure exerted by state officials or elected lawmakers to restrict the teaching or presence of certain books or concepts.
PEN America has identified at least 50 groups involved in pushing for book bans across the country operating at the national, state or local levels. Of those 50 groups, eight have local or regional chapters that, between them, number at least 300 in total; some of these operate predominantly through social media. Most of these groups (including chapters) appear to have formed since 2021 (73 percent, or 262). These parent and community groups have played a role in at least half of the book bans enacted across the country during the 2021–22 school year. At least 20 percent of the book bans enacted in the 2021-22 school year could be directly linked to the actions of these groups, with many more likely influenced by them; in an additional approximately 30 percent of bans, there is some evidence of the groups’ likely influence, including the use of common language or tactics.
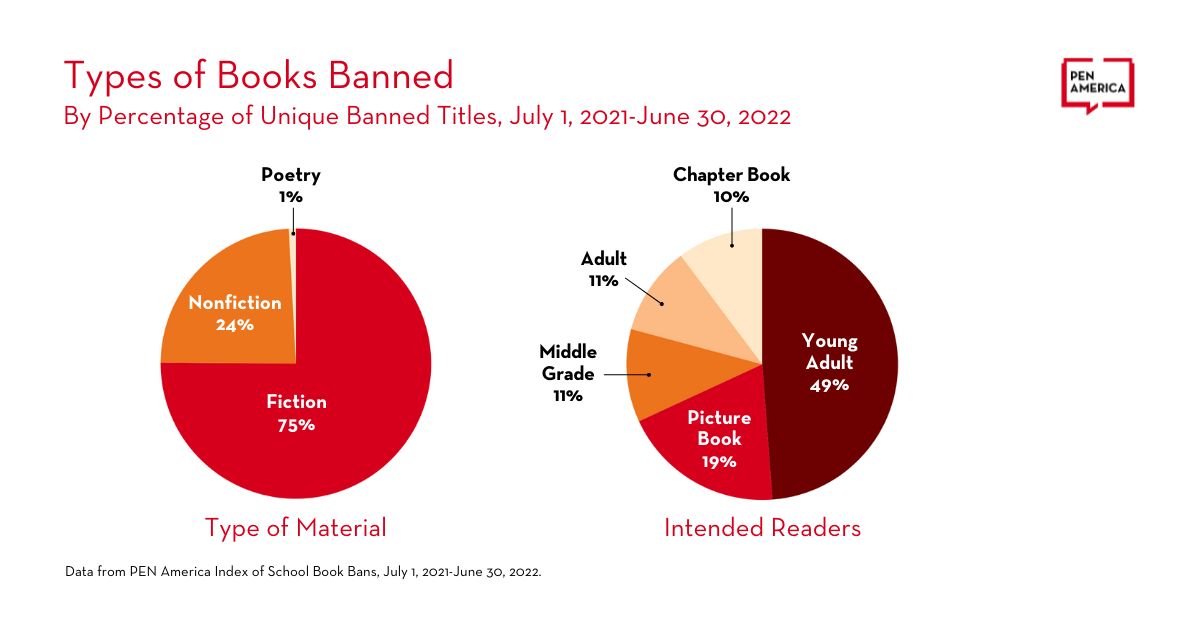
- Nearly half of the unique titles of banned books were young adult books, but bans also affected many books for younger readers, including 317 picture books and 168 chapter books.
- Of the 2,532 bans listed in the Index, 96 percent were enacted without following the best practice guidelines for book challenges outlined by the American Library Association (ALA) and the National Coalition Against Censorship (NCAC).
Introduction
Over the 2021–22 school year, what started as modest school-level activity to challenge and remove books in schools grew into a full-fledged social and political movement, powered by local, state, and national groups. The vast majority of the books targeted by these groups for removal feature LGBTQ+ characters or characters of color, and/or cover race and racism in American history, LGBTQ+ identities, or sex education.
This movement to ban books is deeply undemocratic, in that it often seeks to impose restrictions on all students and families based on the preferences of those calling for the bans and notwithstanding polls that consistently show that Americans of all political persuasions oppose book bans . And it is having multifaceted, harmful impacts: on students who have a right to access a diverse range of stories and perspectives, and especially on those from historically marginalized backgrounds who are watching their library shelves emptied of books that reflect and speak to them; on educators and librarians who are operating in some states in an increasingly punitive and surveillance-oriented environment with a chilling effect on teaching and learning; on the authors whose works are being targeted; and on parents who want to raise students in schools that remain open to curiosity, discovery, and the freedom to read.
PEN America has identified at least 50 groups involved in pushing for book bans at the national, state, or local levels. This includes eight groups that have among them at least 300 local or regional chapters. PEN America has identified these chapters based on the national groups’ own listings, by chapter or regional websites, and by their official chapter and regional group pages on Facebook. Insofar as we have been able to establish, there are at least another 38 state, regional, or community groups that do not appear to have formal affiliations with national organizations or with one another.
These groups share lists of books to challenge, and they employ tactics such as swarming school board meetings, demanding newfangled rating systems for libraries, using inflammatory language about “grooming” and “pornography,” and even filing criminal complaints against school officials, teachers, and librarians. The majority of these groups appear to have formed in 2021, and many of the banned books counted by PEN America can be linked in some way to their activities. Some of the groups espouse Christian nationalist political views, while many have mission statements oriented toward reforming public schools, in some cases to offer more religious education. In at least a few documented cases (for example, in Texas , Florida , and Pennsylvania ), the individuals lodging complaints about books did not have children attending public schools when at the time they raised objections.
This evolving censorship movement has grown in size and routinely finds new targets and tactics, homing in on the books encompassed in district book purchases or digital library apps . A parallel but connected movement is also targeting public libraries , with calls to ban books; efforts to intimidate, harass , or fire librarians ; and even attempts to suspend or defund entire libraries.
| PEN America defines a school book ban as any action taken against a book based on its content and as a result of parent or community challenges, administrative decisions, or in response to direct or threatened action by lawmakers or other governmental officials, that leads to a previously accessible book being either completely removed from availability to students, or where access to a book is restricted or diminished. It is important to recognize that books available in schools, whether in a school or classroom library, or as part of a curriculum, were by librarians and educators as part of the educational offerings to students. Book bans occur when those choices are overridden by school boards, administrators, teachers, or even politicians, on the basis of a particular book’s content. School book bans take varied forms, and can include prohibitions on books in libraries or classrooms, as well as a range of other restrictions, some of which may be temporary. Book removals that follow established processes may still improperly target books on the basis of content pertaining to race, gender, or sexual orientation, invoking concerns of equal protection in education. For more details, please see the first edition of .
|
Since PEN America published our initial Banned in the USA: Rising School Book Bans Threaten Free Expression and Students’ First Amendment Rights (April 2022) report, tracking 1,586 book bans during the nine-month period from July 2021 to March 2022, details about 671 additional banned books during that period have come to light. A further 275 more banned books followed from April through June, bringing the total for the 2021-22 school year to 2,532 bans. This book-banning effort is continuing as the 2022–23 school year begins too, with at least 139 additional bans taking effect since July 2022.
In addition to the role played in book banning by local, state, and national groups, efforts to restrict access to books were also advanced in the past year by government officials and enabled by both state-level legislation and district-level policy changes. PEN America estimates that at least 40 percent of the bans counted in the Index of School Book Bans for the 2021–22 school year are connected to political pressure exerted by state officials or elected lawmakers. Some officials for example sent letters specifically inquiring into the availability of certain books in schools, such as occurred in Texas , Wisconsin , and South Carolina .
Since March 2022, we have also seen for the first time educational gag orders passed that implicate restrictions on books, most notably in Florida , as well as a range of other new laws that have put pressure on schools to censor their libraries. The Alpine School District in Utah responded to a new law, HB 374 (“ Sensitive Materials in Schools ”) , by announcing the removal of 52 titles in July, but then opted to keep the books on shelves with some restrictions after national pushback. In August, some school districts in St. Louis, Missouri began to pull books from shelves in response to a law that made it a class A misdemeanor to provide visually explicit sexual material to students. These trends are unfortunately likely to continue, as the chilling effect of these legislative measures spreads.
Altogether, this report paints a deeply concerning picture for access to literature, and diverse literature in particular, in schools in the coming school year. Book banning and educational gag orders are two fronts in an all-out war on education and the open discussion and debate of ideas in America. Students have First Amendment rights to access information and ideas in schools, and these bans and legislative shifts pose clear threats to those rights. This climate is also increasingly undermining the professional discretion of educators and librarians when it comes to matters of public education, and disrupting the potential for effective relationships between parents, teachers and administrators that can actually serve to advance student learning and civic engagement.
| Students retain their First Amendment rights in schools. In , a 1969 decision, the U.S. Supreme Court held that students do not “shed their constitutional rights to freedom of speech or expression at the schoolhouse gate.” Thirteen years later, in , the Court noted the “special characteristics” of the school library, making it “especially appropriate for the recognition of the First Amendment rights of students,” including the right to access information and ideas. What does this mean for districts who receive a request to reconsider a library holding? Legal precedent and expert best practices demand that committee members, and principals, superintendents, and school boards act with the constitutional rights of students in mind, and using established processes, cognizant of the harm in eliminating access for all based on the concerns of any individual or faction. What if a book is obscene? The term “obscenity” holds particular meaning in the legal sense. Obscene material is not protected under the First Amendment, but a finding of obscenity requires satisfaction of a tripartite test, which requires, among other aspects, a holistic consideration of the material at issue. Simply declaring a book “obscene” does not make it so.
|
PEN America CEO Suzanne Nossel on book bans for PBS NewsHour, March 10, 2022.
What Types of Book Bans Are Taking Place in Schools?
In total, PEN America’s Index of School Book Bans tracked 2,532 decisions to ban books between July 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. This includes bans on 1,648 unique banned book titles. The banning of a single book title could mean anywhere from one to hundreds of copies are pulled from libraries or classrooms in a school district, and often, the same title is banned in libraries, classrooms, or both in a district. PEN America does not count these duplicate book bans in its unique title tally, but does acknowledge each separate ban in its overall count.
In some cases, books are removed from shelves pending investigations or reviews, and they may be only temporarily restricted, but their restriction is recorded in the Index as a ban since such restrictions are counter to procedural best practices for book challenges from the American Library Association (ALA) and the National Coalition Against Censorship (NCAC). Detailed definitions can be found in the first edition of Banned in the USA (April 2022) .
PEN America’s recent findings on each type of ban for the 2021-22 school year are listed below.
| 333 | 215 | 70 | |
| 337 | 253 | 40 | |
| 487 | 481 | 22 | |
| 1,375 | 984 | 57 |
What Types of Content Are Being Banned?
Beginning in 2021, a range of individuals and groups sought to remove from schools books focused on issues of race or the history of slavery and racism, mirroring a campaign pushed by some legislators to pass educational gag orders —bills restricting discussion of these and other concepts in school classrooms and curricula. Although the campaign to enact educational gag orders initially focused on misapplications of the academic term “critical race theory” to censor discussions of race and racism, over the past year, it morphed to include a heightened focus on LGBTQ+ issues and identities.
Similar trends — and similar rhetoric and reasoning — have been evident in efforts to ban books in schools as they have expanded since 2021, too.
Complaints about diversity and inclusion efforts have accompanied calls to remove books with protagonists of color, and numerous banned books have been targeted for simply featuring LGBTQ+ characters. Nonfiction histories of civil rights movements and biographies of people of color have been swept up in these campaigns. For example, many volumes in the popular Who Was? chapter book series and several biographies of Supreme Court justice Sonia Sotomayor were banned in Central York School District in Pennsylvania . That ban also impacted hundreds of books with protagonists of color, including the Caldecott Honor–winning A Big Mooncake for Little Star . In a similar example, Duval County Public Schools in Florida opted not to distribute sets of the Essential Voices Classroom Libraries collection of books after they had been purchased, flagged for concern over their content. This collection of 176 unique titles has been effectively banned from classrooms while it is being reviewed and reportedly remains in storage. Books in the collection include Fry Bread: A Native American Family Story by Kevin Noble Maillard, Dim Sum for Everyone by Grace Lin, and Pink Is For Boys by Robb Perlman, among other titles designed to make classroom libraries more diverse and inclusive.
As the school year progressed, those demanding book removals increasingly turned their attention to books that depict LGBTQ+ individuals or touch on LGBTQ+ identities, as well as books they claimed featured “sexual” content, including titles on sexual and reproductive health and sex education. These trends were already identified in PEN America’s first edition of Banned in the USA (April 2022) report; however, from April to June, there was an acute focus on these topics. This dovetailed with the passage in late March of the “ Parental Rights in Education ” law in Florida—also known as the “Don’t Say Gay” law—and the introduction of similar legislation in other states, as well as a range of efforts to censor discussion of LGBTQ+ identities in schools, in Maryland , Missouri , Texas , and beyond. From April to June 2022, a third of all book bans recorded in the Index feature LGBTQ+ identities (92 bans). Over the same short period, nearly two thirds of all banned books in the Index touch on topics related to sexual content, such as teen pregnancy, sexual assault, abortion, sexual health, and puberty (161 bans).
These subject areas have long been the targets of censorship and been controversial from the perspective of age appropriateness, with standards and approaches varying from community to community about what is seen as the right age level for such material, as well as the degree to which these topics should be addressed in school as opposed to in the home. As book banning has resurged, some individuals and groups have sought to reignite debate about sexual content in books, and sexual education in schools generally. While debate on these issues recurs, wholesale bans on books deny young people the opportunity to learn, to get answers to pressing questions, and to obtain crucial information. At the same time, the efforts to target books containing LGBTQ+ characters or themes are frequently drawing on long-standing, denigrating stereotypes that suggest LGBTQ+ content is inherently sexual or pornographic.
PEN America’s Jonathan Friedman on MSNBC for the Mehdi Hasan Show, Nov. 11, 2021.
Many of the books targeted for banning have been labeled “obscene.” These complaints are not supported. The legal test for obscenity requires a holistic evaluation of the material, setting a bar that is highly unlikely to be met by materials selected for inclusion in a school library. Many targeted books have achieved bestseller status or received the highest literary honors. Some contain nothing more “obscene” than the mere suggestion of a same-sex couple in an illustration, as in the board book Everywhere Babies , which was included on one list of books misleadingly labeled “pornographic” along with And Tango Makes Three , a story about two male penguins making a family together, based on the true story of two male penguins who formed a pair bond in New York’s Central Park Zoo. The most frequently banned book, Gender Queer , has been called “obscene and pornographic” by the groups who lobby for its removal, as have dozens of books with LGBTQ+ themes or characters.
In these cases, the term “obscenity” is being stretched in unrecognizable ways because the concept itself is widely accepted as grounds for limiting access to content. But many of the materials now being removed under the guise of obscenity bear no relation to the sexually explicit, deliberately evocative content that the term has historically connoted.
In evaluating these trends, it is critical to remember that only a limited number of children’s and young adult books are published annually that are written by or about either LGBTQ+ people or people of color. The Cooperative Children’s Book Center at the School of Education, University of Wisconsin–Madison, has compiled statistics on diversity in children’s literature since 1985. In its 2021 report , the center states that of the 3,420 books received at the institution in 2021, 1,152 titles were “books by and about Black, Indigenous and People of Color” (34 percent). Although the center does not continuously maintain similar statistics on books about LGBTQ+ characters or plots, such books have not historically been published in great abundance . The targeting of these books in schools reflects a disproportionate focus on what is likely a small fraction of holdings in most public school libraries.
Over the 2021–22 school year, PEN America also tracked efforts to ban not only books, but also whole academic courses, textbooks, and digital literacy apps. In Bossier Parish, Louisiana , the Epic reading app was removed from student iPads after parent objections about the inclusion of LGBTQ+ content. The school district in Brevard County, Florida , canceled its math app, Prodigy, for similar reasons. Along with educational gag orders targeting classroom discussions, efforts to censor and control public education are ranging beyond the physical collections of school libraries.

The Most Banned Titles in the 2021–22 School Year
The most banned book titles include the groundbreaking work of Nobel laureate Toni Morrison, along with best-selling books that have inspired feature films, television series, and a Broadway show. The list includes books that have been targeted for their LGBTQ+ content, their content related to race and racism, or their sexual content—or all three.
- Gender Queer: A Memoir by Maia Kobabe (41 districts)
- All Boys Aren’t Blue by George M. Johnson (29 districts)
- Out of Darkness by Ashley Hope Pérez (24 districts)
- The Bluest Eye by Toni Morrison (22 districts)
- The Hate U Give by Angie Thomas (17 districts)
- Lawn Boy by Jonathan Evison (17 districts)
- The Absolutely True Diary of a Part-Time Indian by Sherman Alexie (16 districts)
- Me and Earl and the Dying Girl by Jesse Andrews (14 districts)
- Crank by Ellen Hopkins (12 districts)
- The Kite Runner by Khaled Hosseini (12 districts)
- l8r, g8r by Lauren Myracle (12 districts)
- Thirteen Reasons Why by Jay Asher (12 districts)
- Beloved by Toni Morrison (11 districts)
- Beyond Magenta: Transgender Teens Speak Out by Susan Kuklin (11 districts)
- Drama: A Graphic Novel by Raina Telgemeier (11 districts)
- Looking for Alaska by John Green (11 districts)
- Melissa by Alex Gino (11 districts)
- This Book Is Gay by Juno Dawson (11 districts)
- This One Summer by Mariko Tamaki and Jillian Tamaki (11 districts)
The Most Frequently Banned Authors
The most banned authors include winners of the Nobel Prize in Literature, the National Book Award for Young People’s Literature, the Booker Prize, the Newbery Award, the Caldecott Medal, the Eisner Award, the PEN/Faulkner Award for Fiction, the NAACP Image Award, the GLAAD Award for Media Representation, the Stonewall Award, and more.
- Hopkins, Ellen – 14 titles – 43 bans – 20 districts
- Kobabe, Maia – 1 title – 41 bans – 41 districts
- Morrison, Toni – 3 titles – 34 bans – 25 districts
- Johnson, George M. – 2 titles – 30 bans – 29 districts
- Myracle, Lauren – 11 titles – 30 bans – 16 districts
- Pérez, Ashley Hope – 1 title – 23 bans – 23 districts
- Thomas, Angie – 2 titles – 19 bans – 17 districts
- Silvera, Adam – 9 titles – 18 bans – 13 districts
- Reynolds, Jason – 6 titles – 18 bans – 11 districts
- Maas, Sarah J. – 8 titles – 18 bans – 10 districts
- Levithan, David – 15 titles – 17 bans – 18 districts
- Alexie, Sherman – 2 titles – 17 bans – 17 districts
- Evison, Jonathan – 1 title – 17 bans – 17 districts
- Andrews, Jesse – 2 titles – 17 bans – 16 districts
- Faruqi, Saadia – 17 titles – 17 bans – 2 districts
- Jules, Jacqueline – 17 titles – 17 bans – 2 districts
- Do, Anh – 17 titles – 17 bans – 1 district
- Green, John – 3 titles – 16 bans – 15 districts
- Atwood, Margaret – 3 titles – 15 bans – 11 districts
- Hutchinson, Shaun David – 6 titles – 15 bans – 7 districts
- Albertalli, Becky – 7 titles – 14 bans – 11 districts
- Miedoso, Andrés – 14 titles – 14 bans – 1 district
- Gino, Alex – 2 titles – 13 bans – 11 districts
- Woodson, Jacqueline – 11 titles – 13 bans – 6 districts
- Asher, Jay – 1 title – 12 bans – 12 districts
- Hosseini, Khaled – 1 title – 12 bans – 12 districts
- Dawson, Juno – 2 titles – 12 bans – 11 districts
- Tamaki, Mariko – 2 titles – 12 bans – 11 districts
- Picoult, Jodi – 3 titles – 12 bans – 10 districts
- Glines, Abbi – 9 titles – 12 bans – 5 districts
- Peters, Julie Anne – 8 titles – 12 bans – 4 districts
- Cast, Kristen – 12 titles – 12 bans – 1 district
- Cast, P. C. – 12 titles – 12 bans – 1 district
- Kuklin, Susan – 1 title – 11 bans – 11 districts
- Telgemeier, Raina – 1 title – 11 bans – 11 districts
- Jennings, Jazz – 2 titles – 11 bans – 10 districts
- Stone, Nic – 3 titles – 11 bans – 10 districts
- Lockhart, E. – 3 titles – 11 bans – 8 districts
- Brown, Monica – 10 titles – 11 bans – 2 districts
- Kendi, Ibram X. – 7 titles – 10 bans – 12 districts
- Anderson, Laurie Halse – 3 titles – 10 bans – 10 districts
- Curato, Mike – 1 title – 10 bans – 10 districts
- Rosen, L. C. – 1 title – 10 bans – 10 districts
- Clare, Cassandra – 5 titles – 10 bans – 8 districts
- Arnold, Elana K. – 7 titles – 10 bans – 5 districts
- Konigsberg, Bill – 5 titles – 10 bans – 5 districts
Who Is Behind Book Bans? The Role of Groups
Book bans in public schools have recurred throughout American history , with notable flare-ups in the McCarthy era and the early 1980s . But, while long present, the scope of such censorship has expanded drastically and in unprecedented fashion since the beginning of the 2021–22 school year. This campaign is in part driven by politics, with state lawmakers and executive branch officials pushing for bans in some cases. In Texas, for example, Republican state representative Matt Krause sent a letter and list with 850 books to school districts, asking them to investigate and report on which of the titles they held in libraries or classrooms. Political pressure of this sort in Texas , South Carolina , Wisconsin , Georgia , and elsewhere has been tied to hundreds of book bans.
Another major factor driving this dramatic expansion of book banning has been the proliferation of organized efforts to advocate for book removals. Organizations and groups involved in pushing for book bans have sprung up rapidly at the local and national levels, particularly since 2021. These range from local Facebook groups to the nonprofit organization Moms for Liberty, a national-level organization that now has over 200 chapters .
In the short period since their formation and expansion, these groups have played a role in at least half of the book bans enacted across the country during the 2021–22 school year. PEN America estimates that at least 20 percent of the book bans enacted in that time frame could be linked directly to the actions of these groups, with many more likely influenced by them. This 20 percent is based on publicly available information and includes cases where a parent or community group took direct action to seek the removal of books by making a statement at a school board meeting, submitting a list of books for formal reconsideration, or filing formal reconsideration paperwork; in many of these cases, the groups also openly touted their role in pushing for book removals. In an additional approximately 30 percent of bans, there is some evidence of the groups’ likely influence, including the use of common language or tactics.
| PEN America has identified at least 50 groups operating at the national, state, or local levels to campaign and mobilize around what they view as the dangers of books in K-12 schools, and advocating for book restrictions and bans. Of these 50 groups, eight have regional and local chapters that, between them, number at least 300 in total; some of these operate predominantly through social media. This presents a minimum count, based on news coverage, school board meetings, and groups’ public presence online. , has spread most broadly, with over 200 local chapters identified on their . Other national groups with branches include US Parents Involved in Education (50 chapters), No Left Turn in Education (25), MassResistance (16), Parents’ Rights in Education (12), Mary in the Library (9), County Citizens Defending Freedom USA (5), and Power2Parent (5).While some of these groups have existed for years, the overwhelming majority are of recent origin: more than 70 percent (including chapters) were formed since 2021.
|
These varied groups do not all share identical aims, but they have found common cause in advancing an effort to control and limit what kinds of books are available in schools. Broadly, this movement is intertwined with political movements that grew throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, including fights against mask mandates and virtual school, as well as disputes over “critical race theory” that in some states fueled the introduction of educational gag orders prohibiting discussion of “divisive” concepts in classrooms. While many of these groups use language in their mission statements about parents’ rights or religious or conservative views , some also make explicit calls for the exclusion of materials that touch on race (sometimes explicitly critical race theory ) or LGBTQ+ themes .
The impact and role of these groups has been noted in dozens of cases of book challenges around the country. For example, local chapters of Moms for Liberty have been reported as driving efforts to remove books from Florida to North Carolina to Virginia . Chapters of County Citizens Defending Freedom pushed for book removals in Polk County Schools, Florida and Corpus Christi, Texas . In Clark County, Nevada , the group Power2Parent successfully got a book removed from a 10th grade honors English class reading list. Leaders of state chapters of Parents Involved in Education have been quoted calling for book removals at school board meetings in Kansas , Tennessee , and South Dakota , When two students filed a lawsuit with the ACLU of Missouri they claimed the removal of books in Wentzville, MO was part of a “targeted campaign by the St. Charles County Parents Association and No Left Turn in Education’s Missouri chapter to remove particular ideas and viewpoints about race and sexuality from school libraries.”
Although the channels of influence and coordination among these groups are not always clear, and the groups range in size and impact, their role in the book banning movement of the past year is a consistent theme.
In Madison County Schools, Mississippi , for example, a parent who identified herself as the point person for Mississippi’s chapter of MassResistance (a national group also classified as an anti-LGBTQ+ “hate group” by the Southern Poverty Law Center ), expressed “concerns regarding critical race theory” and worked with parents to review the schools’ online library catalogs, seeking books that had been challenged in other parts of the country. By April 2022, the district had said the books were being placed in “restricted circulation” (requiring a parent’s permission to check out) while they were being reviewed.
MassResistance—which claims the January 6 attack on the US Capitol was “clearly a setup” and alleges a “Black Lives Matter and LGBT assault” on schools— took credit for bringing these restrictions about, declaring, “ MassResistance gets involved—things start happening! ” and referencing “‘groomer moms’ in the community” who opposed the removal of the 22 books. In August, the school board voted to place some of the books back in full circulation, but a list of 10 books remain restricted, including Toni Morrison’s Beloved and The Bluest Eye , along with The Hate U Give by Angie Thomas. Another parent who was a vocal critic of the books at a local school board meeting was also identified as the chair of the Moms for Liberty Madison chapter.
Some groups without significant national operations have also had far reach. The Florida Citizens Alliance (FLCA), for example, was founded in 2013 to “champion education reform.” But its leaders have spent considerable time and energy opposing climate change education , arguing for the elimination of sex education in K–12 schools , and publishing the misleading 2021 Objectionable Materials Report: Pornography and Age-Inappropriate Material in Florida Public Schools (provocatively named the Porn in Schools Report on their website). With a mailing of their “Porn in Schools” report and follow-up via their legal representative, the Pacific Justice Institute, the FLCA pushed for bans across the state. Ultimately they have played a role in bans in several counties in Florida, such as Jackson County School District , Orange County Public Schools , St. Lucie County Schools , Polk County School District , and Walton County School District . In Walton County School District , the superintendent responded to their email by directing the removal of all books on the list, despite admitting , “I haven’t read one paragraph of the books at this time.” Their advocacy was also connected to ‘warning labels’ being applied to over 100 books in school libraries in Collier County , Florida.
Even smaller, less formal groups have had an impact too. Between February and April 2022, Nixa Public Schools in Missouri received 17 complaints about 16 books, each citing “inappropriate and sexually explicit content,” which were subsequently banned. The woman who filed the most requests confirmed that she was a member of “Concerned Parents of Nixa,” a private Facebook group where community members gather to fight “questionable books, curriculum, and other materials such as sex education in Nixa Public Schools.” Concerned Parents of Nixa recently changed its name to Concerned Parents of the Ozarks . While it is unclear whether their list was solely from another group, the titles they challenged are the same ones seen over and over again amongst school libraries who have had to pull or otherwise eliminate access to them as a result.
These groups have employed a range of common tactics to advance book banning in public schools. Most of these tactics, it should be emphasized, are tactics that many advocacy and community organizing groups employ to a wide range of ends. Citizens are free to organize and advocate; these liberties are protected under the First Amendment’s safeguards for freedom of association. PEN America’s concern is not with the use of such standard organizing and mobilization tactics but rather with the end goal of restricting or banning books. That said, in some cases, members of these groups have also crossed a line, using online harassment or filing criminal complaints to pressure local officials and educators.
One common trend is that many of these groups circulate to their audiences lists of books to target. PEN America saw dozens of lists that circulated online during the 2021–22 school year, and these also occasionally morphed or grew in the process of being shared among groups.
Some groups appear to feed off work to promote diverse books, contorting those efforts to further their own censorious ends. They have inverted the purpose of lists compiled for teachers and librarians interested in introducing a more diverse set of reading materials into the classroom or library. For example, one group, the Idaho Freedom Foundation, referenced multiple lists celebrating books about equity, inclusion, and human rights under the header “ Federal Agencies Are Sexualizing Idaho Libraries ,” accused the federal government of using “taxpayer dollars to promote a pernicious ideology to young children,” and called on the Idaho legislature to reject federal funds for libraries. Another group, the Michigan Liberty Leaders , took an image of books from the Welcoming Schools bullying prevention program created by the Human Rights Campaign Foundation—including books designed to support LGBTQ+ students—and added alarmist language about the books being in schools.
In another example, the list of books created by the FLCA in their “ Porn in Schools” report originated from the website Christian Patriot Daily, which said it received its list from a graduate student in early childhood development promoting LGBTQ+ resources for caregivers. This list has in turn appeared to spread across state lines. In March 2022, in Cherokee County School District in Georgia, a parent presented a list of 225 book challenges . In that list, 41 titles were not only identical to those in the 2021 FLCA report, but they were in the same order, with the same typos found in the original list. The same list also appears in a database of books on the website of Forest Hills Parents United, based in Michigan.
The books on these lists are often framed as dangerous or harmful, and the lists have been used to quicken the pace of book banning, often in violation of or with disregard for established, neutral processes, with demands that all books on such lists be removed from schools immediately.
Members of these groups also flood school districts with official challenges to books and mobilize supporters to dominate discussions at public board meetings. In some cases, parents have screamed to disrupt meetings, or threatened violence . In response to such threats, the Sarasota County, Florida, school board placed limits on public comments at board meetings. School boards in Carmel Clay, Indiana , and Sonoma Valley, California , are considering similar restrictions.
Some groups have at times also helped spur complaints from community members without children in public school. In St. Lucie County Schools, Florida, a complainant submitted official reconsideration challenges for 44 titles from the FLCA’s “Porn in Schools” report, only 20 of which were found in the district. The complainant told a reporter that although they personally did not have children in the district, they were “picked” after attending a meeting hosted by FLCA. “I got picked because I took it seriously,” the complainant said.
In the fall of 2021 in Williamson County Schools, Tennessee, Moms for Liberty pushed for a review of the reading curriculum, stating that the curriculum violated a state law (which PEN America counts as an educational gag order ). The complaints said materials were too focused on the country’s segregationist past and might make children feel uncomfortable about race. After the review, the district published a report that outlined the relationship of complainants to the school district, and only 14 of the 37 complainants had children enrolled and affected by the curriculum targeted by the complaint. Another 14 had no children in the school system at all, while 9 had children enrolled in middle or high schools. One book, Walk Two Moons by Sharon Creech, was ultimately banned permanently, and multiple books had bans placed on what content could be taught, including restrictions on showing students pages 12–13 of Sea Horse: The Shyest Fish in the Sea by Chris Butterworth—pages that included an illustration of the sea creatures twisting tails, rubbing tummies, and mating.
| Although “parents’ rights” is a powerful piece of political rhetoric, in most instances, it is being invoked to mean rights for a particular group of parents with distinct ideological views, rather than a neutral effort to engage all parents and students in ensuring that schools uphold free speech rights. While parents and guardians ought to be partners with educators in their children’s education, and need channels for communicating with school administrators, teachers, and librarians, particularly concerning the education of their own children, public schools are by design supposed to rely on the expertise, ethics, and discretion of educational professionals to make decisions. In too many places, today’s political rhetoric of “parents’ rights” is being weaponized to undermine, intimidate, and chill the practices of these professionals, with potentially profound impacts on how students learn and access ideas and information in schools.
|
The role of organized local, regional, and national groups in book-banning campaigns has several implications that are distinct from prior patterns where book challenges tended to originate locally and spontaneously by individual parents. The groups behind these bans often furnish materials, messaging templates, and other kinds of directions that easily facilitate book challenges and imbue their efforts with a degree of focus and determination that can take local school officials by surprise. Groups that enjoy political ties and advocacy resources are able to marshal political support behind their censorious campaigns, putting local teachers, administrators, and school board officials under pressure. Mobilization on social media or at board meetings can also create an atmosphere of intimidation that may undermine the ability of a community to discuss and adjudicate concerns in a measured way.
Most schools’ book reconsideration policies have been created to respond to challenges filed by individual parents over particular books their children read; now that challenges are coming with such increased frequency and scope, schools and districts have sometimes struggled to keep up, as well as to withstand the heightened political pressure and public scrutiny.
The other key implication of the organized nature of these banning campaigns is their ability to reach scale. Whereas traditional book challenges were one-off incidents, the current pattern of escalating, copycat banned book efforts across the country is a testament to the ability of campaigners to leverage tools and communications channels to push for censorship across the country. As their tactics and methods evolve, it stands to reason that a growing number of schools, communities, and legislatures will confront similar challenges.
| In another sign of the escalation of tactics to restrict books, criminal charges have been pursued against school officials and librarians in a number of cases in the past year. From to to to , sheriffs have received complaints of the distribution of pornography in schools, among other charges. PEN America found at least 15 documented cases of criminal charges being filed or complaints being filled out regarding distribution of obscenity or pornographic material in public and school libraries during the 2021–22 school year, The leader of Moms for Liberty in Indian River, Florida, accusing the school board and superintendent of distributing pornography. Other groups, including , , and , have issued calls to action for individuals to file criminal complaints about books. While these cases have all rightly been dropped by law enforcement, the movement to involve police in efforts to ban books is another aspect of this campaign that is unprecedented in recent memory. Regardless of the legal outcome, the tactic of pressing criminal charges against educators for offering books to students is an attempt to intimidate and discourage librarians and teachers from teaching or offering books that might spark such a virulent response.
|
Where Are Book Bans Happening?
PEN America reported in the first edition of Banned in the USA (April 2022) that book bans had occurred in 86 school districts in 26 states in the first nine months of the 2021-22 school year. With additional reporting, and looking at the 12-month school year, the Index now lists banned books in 138 school districts in 32 states. These districts include 5,049 schools with a combined enrollment of nearly 4 million students.
Total States and Districts with Banned Books
- States with Bans: 32
- Districts with Bans: 138
Total Bans by State
- Texas : 801 bans, 22 districts
- Florida : 566 bans, 21 districts
- Pennsylvania : 457 bans, 11 districts
- Tennessee : 349 bans, 6 districts
- Oklahoma : 43 bans, 3 districts
- Michigan : 41 bans, 4 districts
- Kansas : 30 bans, 2 districts
- Wisconsin : 29 bans, 6 districts
- Missouri : 27 bans, 8 districts
- Idaho : 26 bans, 3 districts
- Georgia : 23 bans, 2 districts
- Mississippi : 22 bans, 1 district
- Virginia : 19 bans, 9 districts
- Indiana : 18 bans, 3 districts
- North Carolina : 16 bans, 5 districts
- New York : 13 bans, 4 districts
- Utah : 12 bans, 3 districts
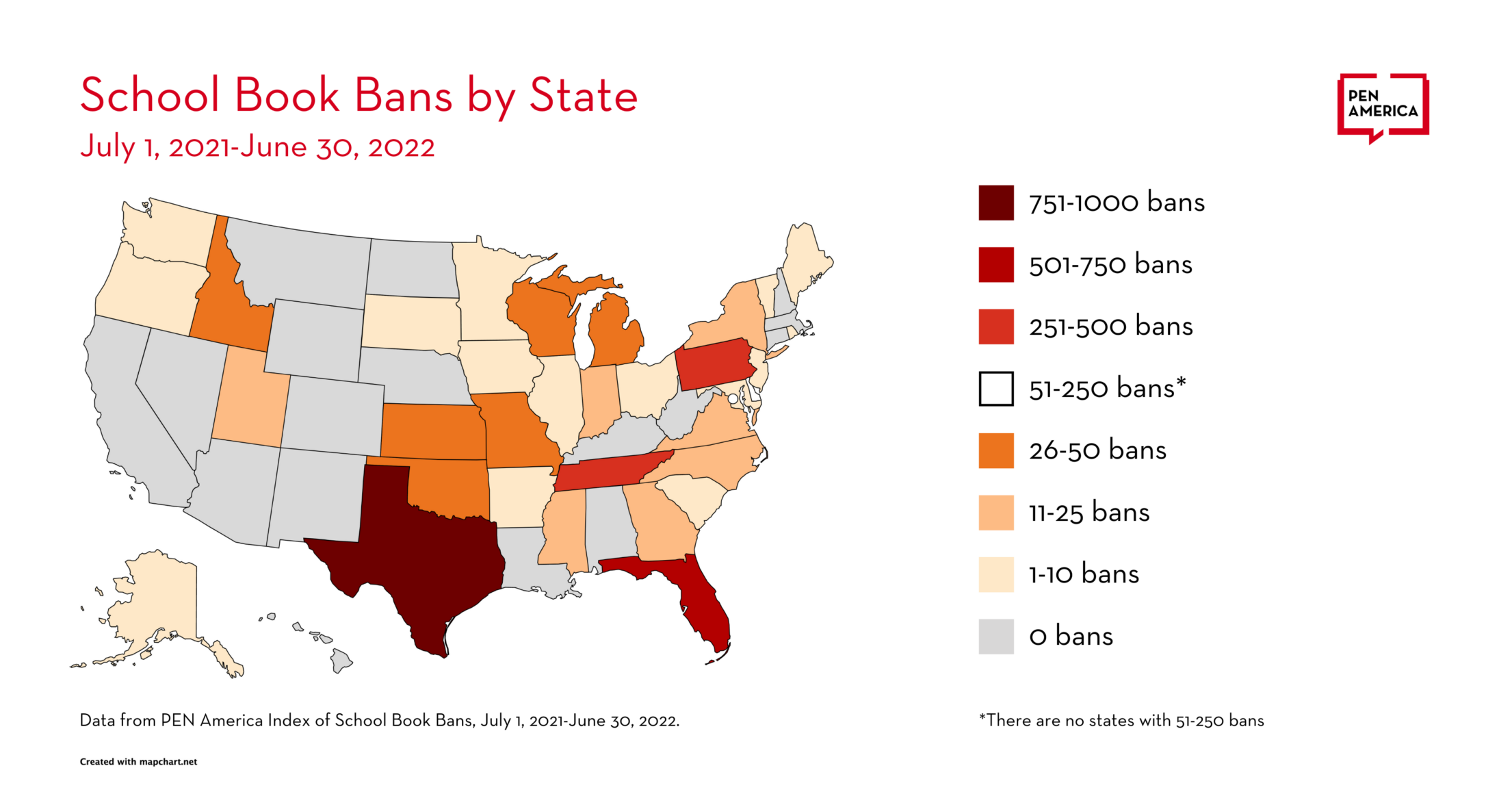
Rewriting the Rules
Beyond the school book bans documented in the Index and the efforts of various parties to see their implementation and enforcement, the past year has also seen attempts to change laws and school district policies in ways that make censorious challenges easier to file and impose. Even where such laws and policy changes have not been enacted, their chilling effect has been broadly felt.
Legislative Changes
The book-banning movement has operated in conjunction with legislative efforts to pass educational gag orders, all as part of what PEN America has referred to as the “ ed scare ”—a campaign to censor free expression in education. While the effort to constrain teachers has primarily progressed in state legislatures—as PEN America has documented, most recently in our August 2022 report America’s Censored Classrooms —and the effort to ban books has erupted mostly within local school districts, the two have increasingly merged, with some state legislators proposing or supporting bills that directly impact the selection and removal of books in school classrooms and libraries.
- Florida. Beginning in the summer of 2022, book bans in some Florida school districts were reportedly tied to the passage of the “ Parental Rights in Education ” law signed by Governor DeSantis in March 2022. Frequently referred to as the “Don’t Say Gay” law, this legislation prohibits classroom instruction on sexual orientation and gender identity in kindergarten through third grade, and also in grades 4–12 unless “age appropriate” and “developmentally appropriate” according to state standards. During the same legislative session, Florida lawmakers also enacted HB 1467 , which, in the name of classroom “transparency,” modifies laws governing the selection and discontinuance of instructional materials in public school curricula and libraries, mandates elementary schools to list in a searchable manner all materials held in their libraries, and implicitly encourages greater public scrutiny. This combination of a new law enabling tighter scrutiny and outside monitoring of curricular and book choices in classrooms, coupled with a new prohibition on instruction on certain topics, has done what was intended: it has created a chilling effect on teaching and learning. In anticipation of the law, books were removed in Palm Beach County in June 2022. Over the summer, more books were reported being removed from districts across the state, including a plan to “pause” classroom libraries entirely in Brevard, Florida .
- Georgia. SB 226 passed in March 2022 and will change the way school libraries operate, removing some local control and consolidating power at the state level. The law vacates all school policies on book challenges and requires local school boards to create new policies for complaints, designed to make it easier to remove books with allegedly “offensive content.” Under this new law , school principals have only ten days to determine whether a book challenged for being “harmful to minors” by any parent or guardian will be removed or restricted from schools.
- Tennessee. SB 2247 expanded the State Textbook and Instructional Materials Quality Commission and required it to provide guidance for school libraries. It also created a statewide process for appealing decisions on challenged books to the state commission. These changes will make it easier for books to be banned from student access statewide on the basis of challenges filed in individual districts.
- Utah. HB 374 , “Sensitive Materials in Schools,” was signed into law in March 2022 by Gov. Spencer Cox and prohibits from public schools certain sensitive instructional materials considered pornographic or indecent. It also requires the State Board of Education and the Office of the Attorney General to provide guidance and training to public schools on identifying sensitive materials, a process that must include parents deemed reflective of a school’s community. Although the law does not alter the definition of obscene materials in state statutes, it has been followed by guidance from the attorney general instructing schools to remove “immediately” any books deemed pornographic. The law has already had an impact, for example, in Alpine School District.
- Missouri. SB 775 , an omnibus bill on sex crimes and crimes against minors, included an amendment that makes it a class A misdemeanor if a person “affiliated with a public or private elementary or secondary school” provides “explicit sexual material” to a student, defined in the bill as applying only to visual depictions of genitals or sexual intercourse, not written descriptions. The bill also contains exceptions for works of art, works of “anthropological significance,” and materials for a science or sexual education class. In the wake of the bill taking effect in August, a number of school districts in the St. Louis area removed books from their shelves preemptively, particularly graphic novels, which appear to be uniquely susceptible to challenge under the law’s provisions. Violation of the law could lead to jail or fines for teachers, librarians, and school administrators. Although police have said they will not enforce it, the law is nevertheless already having a chilling effect in the state.
Changing District Policies
Under the plurality Supreme Court decision in Island Trees v. Pico , banning or restricting books in public schools for content- or viewpoint-specific reasons is unconstitutional. To safeguard these rights, the ALA and the NCAC have developed best practice guidelines for book reconsideration processes school districts can adopt concerning library materials and instructional materials for which review is requested, whether by a parent, other community member, administrator, or other source. As discussed at length in Banned in the USA , these guidelines are intended to ensure that challenges are addressed in consistent, reasoned, fact-based ways while protecting the First Amendment rights of students and citizens and guarding against censorship.
In the 2021–22 school year, fewer than 4 percent of book bans tracked by PEN America were enacted pursuant to these established best practice guidelines aimed to safeguard students’ rights and protect against censorship. Instead, in numerous cases, school districts either ignored or circumvented their own policies when removing particular books. In other cases, districts followed policies that failed to afford full protection for freedom of expression—for example, by restricting student access to books while they are under review, by failing to convene a committee to review the complaint, or by not having the complainant complete the paperwork or read the whole book to which they were objecting as required by the stated policies.
In some communities where existing procedures are more aligned with the standards set forth in the ALA and NCAC guidelines, or where advocates for book banning have been stifled in their efforts, there have been new efforts to alter those policies and make the removal of books easier.
Such efforts often include a drive to change the “obscenity” determination used to ban books—usually without regard for the relevant legal standard . These changes have taken place in nearly a dozen districts, such as Frisco ISD in Texas , which in June revised its book policies to remove the existing standards of obscenity for materials and replace them with more stringent standards taken from the Texas Penal Code. In practice, this means that a sentence or image may be enough to get a book banned—and that book content will be evaluated without proper context. The inevitable result of the Frisco ISD and similar changes will be increased policing of content in books for young people, as well as the continued erosion of their right to access these materials.
Some policy changes have been advanced at the state level as well, with Texas leading the way. In April, the Texas Education Agency (TEA) announced new standards for how school districts should handle all content in their libraries. The Texas standards follow state representative Matt Krause’s October 2021 public letter “initiating an inquiry into Texas school district content,” as well as a public letter to the Texas Association of School Boards (TASB) from Gov. Greg Abbott in November 2021 , asking schools to investigate why their libraries contained allegedly “obscene” and “pornographic” content in schools. Abbott did not provide any specific content examples. (It is worth noting that TASB has no power to change or even to recommend district policies.)
The policy recommendations from the TEA, compiled in response to the public letter from Governor Abbott, implemented four significant process changes of note, none of which comport with accepted best practices. The changes include the following:
- Singling out school library acquisitions for intensive review, more so even than the review process for curricular materials.
- Placing a ten-day deadline for reconsideration of challenged material. In an apparent acknowledgement that such a tight timeline will preclude a thorough review, the provisions simultaneously dropped the requirement that reconsideration committee members read the challenged material.
- Requiring librarians to host twice yearly review periods for parents to raise objections or voice concerns prior to accepting new acquisitions.
- Tying the consideration of material containing sexual content to the Texas Penal Code, point 3 of which states that a harmful material is defined as one “utterly without redeeming social value for minors.” If a book falls afoul of the state’s “harmful materials” standards—which are not aligned with Supreme Court jurisprudence defining obscenity in such works—it cannot be part of a school library.
While Texas has not made this policy mandatory for its school districts, the policy has begun to shape school library policies. By July 2022, at least two Texas school districts in Tarrant County had changed their acquisition policies based on the TEA’s model policy. For example, now if a book is challenged and removed in Carroll ISD, Texas, that book cannot be requested again for students for five years. In Keller ISD, this provision was changed to ten years.
The trend of district-level policy changes, which largely began in Texas, has picked up steam in other places too. For example, the school board in Hamilton County, Tennessee, accepted board policy recommendations from a special book review committee in March 2022, which removed a statement on the principles of intellectual freedom from the ALA’s “Library Bill of Rights.” This was a striking departure from the norm, as up until this year, it was a generally accepted standard that school board policies concerning acquisitions management and curricular development would reference or otherwise incorporate principles put forth by the Office for Intellectual Freedom of the ALA.
In another instance, Central Bucks County School District in Pennsylvania voted in July 2022 to reassign oversight of library collections from library and education professionals to a committee of the “ superintendents designees ”—politicizing a task previously performed by library and education professionals well versed in sound acquisition principles and policies. The district further undermined its education professionals by moving to refocus collection acquisition strategies away from instructional needs—as determined by teachers, librarians, and other education professionals—toward potentially politicized decisions, such as evaluating books for sexual content using vague standards to determine whether a book should be placed in the library. In so doing, the district ran afoul of NCAC guidelines to ensure practices that “advance fundamental pedagogical goals and not subjective interests.”
From Kansas to Illinois , Indiana to Virginia , North Carolina to Florida , myriad efforts to implement and enforce censorious practices are effectively allowing some parents and citizens to constrain the availability of books for all students in their and other school communities. A raft of changes are making it easier to ban more books more quickly, undermining educators’ and librarians’ work and ultimately students’ rights to access information.

Preemptive Bans
The unrelenting wave of challenges to the inclusion of certain books in school libraries—whether promulgated at the urging of an individual community member, grassroots organization, or government official—has spurred another phenomenon: preemptive book banning. In April, May, and June 2022, PEN America tracked several cases where school administrators have banned books in the absence of any challenge in their own district, seemingly in a preemptive response to potential bills , threats from state officials , or challenges in other districts .
The most significant ban of this type occurred in Collierville, Tennessee , where a school district removed 327 books from shelves in anticipation of a state law that ultimately did not pass. Administrators sorted the books into tiers based on how much the books focus on LGBTQ+ characters or story lines; tier 3, for instance, reflected that “the main character of the book is part of the LGBTQ community, and their sexual identity forms a key component of the plot. The book may contain suggestive language and/or implied sexual interactions.” If a book reached tier 5, according to the sorting guidelines, “the books are being pulled.”
Other preemptive bans were responses to actions at the state level or in neighboring districts. For example, according to Texas media reports , bans in Katy ISD, Clear Creek ISD, and Cypress-Fairbanks ISD were the result of administrators responding either to what was happening in other districts or to an 850-book list compiled and circulated to education officials by Texas state representative Matt Krause .
Silent Bans and Other Restrictions
Finally, PEN America has tracked other instances of books included in banned book displays, or other disputed materials, being quietly removed to avoid controversy. Books are also being labeled or marked in some way as “inappropriate” both in online catalogs and on physical titles themselves. In the Collier County School District in Florida, for instance, warning labels were attached to a group of more than 100 books that disproportionately included stories featuring LGBTQ+ characters and characters of color. While these cases are not included in the Index because they do not meet PEN America’s definition of school book bans, these types of actions could have a chilling effect—applying a stigma to the books in question and the topics they cover—and they merit further study.
While several stories of preemptive and silent book bans have made it into the news or to the attention of PEN America, it is clear that mounting censorship and the punitive approach being taken to the enforcement of book bans is having wide ripple effects . The Supreme Court has sharply restricted viewpoint- and subject-matter-based restrictions on speech precisely because in addition to rendering certain ideas, stories, and opinions off-limits, such measures cast a wider chilling effect on expression. Given the rapid spread of book bans across the country, it seems inevitable that the resulting climate of caution and fear will result in a reluctance among teachers, administrators, and librarians to take risks that could affect their own employment , their budgets, their reputations, and even their personal safety . Emerging data, like a recent survey of school librarians by the School Library Journal in which 97% said they “always,” “often,” or “sometimes” weigh how controversial subject matter might be when deciding on book purchases is pointing clearly to these alarming trends.
| Beyond formal book bans, there have also been efforts to keep books out of the hands of children even if they remain in circulation. One prominent example of such activity was “ ,” an initiative of CatholicVote.org in June 2022. CatholicVote encouraged members to check out books from the Pride 2022 displays in children’s sections of public libraries and to take pictures of the empty shelves. Although the group instructed participants to “return your library books on time” and to follow the “letter of the law, so to speak,” was an attempt to remove library materials from availability and to limit students’ access to LGBTQ+-affirming books. In the same month, there were efforts to ban displays of LGBTQ+ materials entirely in some public libraries, such as in , and . The latter resulted in an effort to terminate a librarian for allegedly violating the prohibition.
|
The unprecedented flood of book bans in the 2021–22 school year reflects the increasing organization of groups involved in advocating for such bans, the increased involvement of state officials in book-banning debates, and the introduction of new laws and policies. More often than not, current challenges to books originate not from concerned parents acting individually but from political and advocacy groups working in concert to achieve the goal of limiting what books students can access and read in public schools.
As noted previously, the resulting harm is widespread, affecting pedagogy and intellectual freedom and placing limits on the professional autonomy of school librarians and teachers. The repercussions extend further, however, to the well-being of the students affected by these bans. Children deserve to see themselves in books, and they deserve access to a diversity of stories and perspectives that help them understand and navigate the world around them. Public schools that ban books reflecting diverse identities risk creating an environment in which students feel excluded, with potentially profound effects on how students learn and become informed citizens in a pluralistic and diverse society.
Book challenges impede free expression rights, which must be the bedrock of public schools in an open, inclusive, and democratic society. These bans pose a dangerous precedent to those in and out of schools, intersecting with other movements to block or curtail the advances in civil rights for historically marginalized people.
Against the backdrop of other efforts to roll back civil liberties and erode democratic norms , the dynamics surrounding school book bans are a canary in the coal mine for the future of American democracy, public education, and free expression. We should heed this warning.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This report was written by Jonathan Friedman, director, Free Expression and Education Programs, based on research and analysis by Tasslyn Magnusson, Ph.D., and Sabrina Baeta. The report was reviewed and edited by Nadine Farid Johnson, managing director of PEN America Washington and Free Expression Programs; Summer Lopez, chief program officer, Free Expression; and Jeremy C. Young, senior manager, Free Expression and Education, who also helped supervise the production process. Lisa Tolin provided editorial support, and Dominique Baeta provided research assistance. Finally, we extend thanks to the many authors, teachers, librarians, parents, students, and citizens who are fighting book bans, speaking at school board meetings, and bringing attention to these issues, many of whom inspired and informed this report.


Morris Library
- 618-453-1455
- [email protected]
Banned Books: Protect Your Freedom to Read
- Protect Your Freedom to Read
- The Banned Book Collection in Morris

Banned Books Week is celebrated annually, with sponsorship from the American Library Association (ALA), the National Association of College Stores, and many other organizations. According to the ALA, "Banned Books Week highlights the benefits of free and open access to information while drawing attention to the harms of censorship by spotlighting actual or attempted bannings of books across the United States."
A Worrisome Trend
ALA's Office for Intellectual Freedom documented 1,269 demands to censor library books and resources in 2022, the highest number of attempted book bans since ALA began compiling data about censorship in libraries more than 20 years ago. The unparalleled number of reported book challenges in 2022 nearly doubles the 729 book challenges reported in 2021. Censors targeted a record 2,571 unique titles in 2022 , a 38% increase from the 1,858 unique titles targeted for censorship in 2021. Of those titles, the vast majority were written by or about members of the LGBTQIA+ community or by and about Black people, Indigenous people, and people of color.
- Censorship by the Numbers Resources documenting the number and locations of censorship attempts against libraries and materials compiled by ALA's Office of Intellectual Freedom.
- Book Ban Data, ALA Latest numbers from ALA about book bans and challenges in the United States, including preliminary data from the first half of 2023. TL;DR: They're up. A lot.
- Banned and Challenged Books ALA's page devoted to censorship attempts and the annual Banned Books Week celebration.
- Book Bans, PEN America Resources and commentary related to book bans in the U.S., including a comprehensive list of successful school bans, assembled by a national writer's association.
- Ralph E. McCoy Collection of the Freedom of the Press Housed in the Special Collections Research Center on the first floor of Morris Library, the McCoy Collection offers the opportunity to explore issues of censorship and freedom of expression from a historical perspective. It is one of the world's best collections of rare books highlighting the history of First Amendment freedoms. It includes examples of many books that have been banned in the United States and Europe over the centuries. Many of the books listed below part of this collection. more... less... used in Overview of African American history collections in SCRC on Resources for the Study of African American History in Southern Illinois: Overview of Special Collections
- Beacon for Freedom of Expression The Beacon for Freedom project maintains an extensive database of censored publications and publications about censorship.
Banned Books Club and Books Unbanned
The Banned Books Club is a collaboration between libraries and sponsors to make banned books available online and at libraries for free. The University of Chicago and the Digital Public Library of America are offering free access to all Illinois residents through the Palace app.
- Banned Book Club Program to provide free access to electronic copies of banned books. Follow the steps to "Access Banned Books" to get your free card and start reading.
- Banned Books Club at the Palace Project Jump straight to the app the Banned Book Club uses to provide access to available titles.
A number of public libraries nationwide have joined the Books Unbanned initiative, offering free access to commonly challenged or banned titles in eBook form to readers age 13-26. If you fall in that age bracket, sign up for a free temporary library card and read banned books!
- Boston Public Library Books Unbanned Program
- Brooklyn Public Library Books Unbanned Program
- Seattle Public Library Books Unbanned Program
Top Ten Challenged Books from the Last Five Years
Banned in 2021 - 2022
According to PEN America, 1,636 different books were banned—not only challenged, but actually removed from shelves—in classrooms, schools, or libraries in the U.S. for at least a portion of the time between July 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. The following is a list of these banned titles available through Morris Library.

- Next: The Banned Book Collection in Morris >>
- Last Updated: Jun 17, 2024 11:16 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.siu.edu/bannedbooks

New First Book Study Tackles National Issue of Banned Books
More than 1,500 educators report on book bans and the damaging impact they are having on teacher morale and student learning
WASHINGTON, D.C. (October 3, 2023) – In a new study released by First Book Research & Insights , educators report that the national conversation around book challenges and bans is negatively impacting their classrooms, profession, and student learning. More than 1,500 educators serving children in under-resourced communities responded to the First Book survey to reveal educator perceptions on book restrictions in their school districts, and their impact on student learning.
Through this study, educators discussed the destructive impact that book bans are having on teacher morale. The study revealed that book bans have a chilling effect whether or not teachers are facing book bans in their districts. The survey found that 71 percent of educators, regardless of whether their district has faced bans, believe book banning undermines their expertise, makes them feel distrusted, and increases their stress. These detrimental effects translate into the classroom as nearly two-thirds of educators said that book banning is having a negative impact on their ability to teach .
“Educators serving students in low-income, under-resourced communities remain unheard in the discussion – and they are a critical voice because of their role in supporting student academic growth while managing the negative effects of ongoing actions to ban books,” says Kyle Zimmer, president and CEO of First Book. “The effort to restrict access to books has excessively targeted diverse books, which we know are indispensable in engaging kids, improving student reading scores, and developing a strong sense of self and empathy for others. These books empower young learners to foster a lifelong love of reading.”
Of the more than 1,500 educator respondents, one-third report facing book bans, challenges, or restrictions in their school district. Although only 7 percent of educators have removed books from their classrooms due to book bans, this study reveals the negative and chilling impacts that reach far beyond the districts that are facing bans. Approximately 15 percent have preemptively removed books from their libraries. Eighteen percent of educators have indicated that specific titles have been banned in their school district.
By capturing the experiences and perceptions of educators working on the ground in classrooms, this new study offers insights into the negative impact of book bans on student success in the classroom. In the survey, 72 percent indicated that restricting book access decreases students’ engagement in reading. More than a third of educators noted that book bans discourage students’ critical thinking, and 78 percent reported that students are reading more when given the choice to read banned books.
These findings come on the heels of another study produced by First Book Research & Insights, the organization’s research arm that conducts studies of its network of more than 575,000 educators. The recent Diverse Books Impact Study report, which was released in September, highlights the positive impacts of diverse books in classroom libraries. In the six-month pilot study, after adding diverse books to their classroom libraries, educators reported that reading scores increased by 3 percentage points higher than national annual expected averages, and collective classroom reading time increased by 4 hours per week on average. Classrooms that added bilingual and LGBTQ+ titles reported the greatest improvements.
The findings on student outcomes reinforce educators’ consistent call for diverse titles to support student achievement.
“Educators have expressed their wealth of knowledge and expertise through First Book’s research on both the impact of diverse books and book banning,” says Zimmer. “This study proves that the targeted removal of diverse titles in the midst of a national literacy crisis is detrimental to the academic growth of our children and demoralizing for the educators serving them. And this is an issue for all children, no matter their zip code or identity. Kids who do not have exposure to other cultures and identities will be at a disadvantage.”
First Book’s full report on the banned books survey is available to download here . And the full Diverse Books Impact Study Report can be downloaded here .
Media Contact + Information
Visit our press room for additional information, including our media kit and contact information.
About First Book
Education transforms lives. First Book is building a world where every child has access to a quality education. We work to remove barriers to education and level the playing field for kids in need. At the heart of our work are the 575,000 members of the First Book Network, the largest online community of educators and professionals dedicated to children in need across North America. This Network is the key to creating systemic change. Through our research arm, First Book Research & Insights, we conduct studies that aggregate their voices to identify barriers to equitable education and inform strategic solutions. To address their needs, we provide free and low-cost books, resources, and access to leading experts through the First Book Marketplace, which uses aggregated buying power to support this underserved community. Founded in Washington D.C. in 1992 as a nonprofit social enterprise, First Book is dedicated to eliminating barriers to learning and inspiring young minds. Learn more at FirstBook.org and visit our award-winning eCommerce website at FBMarketplace.org .
Founded in 1992, First Book is a nonprofit social enterprise building a world where all children have access to a quality education. We are on a mission to ensure that all children, regardless of their background or zip code, can succeed by removing barriers to equitable education because education transforms lives.
First Book 1319 F St NW, Suite 1000, Washington DC 20004
©2024 Copyright First Book. All Rights Reserved.
- Our Solutions
- Partner With Us
- Meet the Team
- Careers at First Book
- Privacy & Compliance Policies
- First Book Marketplace
- First Book National Book Bank
- Become a Member


Book Ban Data
The American Library Association's Office for Intellectual Freedom (OIF) has released new data documenting book challenges throughout the United States, finding that challenges of unique titles surged 65% in 2023 compared to 2022 numbers, reaching the highest level ever documented by ALA. Read the full announcement .
OIF documented 4,240 unique book titles targeted for censorship , as well as 1,247 demands to censor library books, materials, and resources in 2023 . Four key trends emerged from the data gathered from 2023 censorship reports:
- Pressure groups in 2023 focused on public libraries in addition to targeting school libraries. The number of titles targeted for censorship at public libraries increased by 92% over the previous year, accounting for about 46% of all book challenges in 2023 ; school libraries saw an 11% increase over 2022 numbers.
- Groups and individuals demanding the censorship of multiple titles, often dozens or hundreds at a time, drove this surge.
- Titles representing the voices and lived experiences of LGBTQIA+ and BIPOC individuals made up 47% of those targeted in censorship attempts.
- There were attempts to censor more than 100 titles in each of these 17 states: Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Idaho, Illinois, Iowa, Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Virginia, and Wisconsin.
Spread the word. Download these graphics and share on social media!

Note: a previous version of one of these graphics incorrectly referenced the number of unique titles challenged in 2021 as 1,651. In fact, the actual number is 1,858 unique titles challenged. 1,651 is the number of unique titles challenged during the preliminary period between January 1 and August 31, 2022, originally reported in September 2022.
Take Action

Unite Against Book Bans is ALA's national initiative to empower readers everywhere to stand together in the fight against censorship with an array of resources, tools, and actions.
Reporting censorship and challenges to materials, resources, and services is vital to defending library resources and to protect against challenges before they happen.
Additional Resources

Lists of frequently challenged books compiled by ALA's Office for Intellectual Freedom to inform the public about censorship efforts that affect libraries and schools.

A clearinghouse of resources to assist library workers and advocates in responding to and supporting others facing those challenges.

Documents designated by the Intellectual Freedom Committee as Interpretations of the Library Bill of Rights and background statements detailing the philosophy and history of each.
Methodology
ALA compiles data on book challenges from reports filed by library professionals in the field and from news stories published throughout the United States. Because many book challenges are not reported to ALA or covered by the press, the data compiled by ALA represents a snapshot of book censorship.
A challenge is an attempt to remove or restrict access to materials or services based upon the objections of a person or group. A challenge to a title may result in access to it being retained, restricted, or withdrawn entirely. Restrictions on access may include relocating the book to a section of the library intended for an older age group than the book is intended for, labeling it with a prejudicial content warning or rating, taking it out of the online catalog so it has to be requested from a staff member, removing it from open and freely browsable stacks, or requiring parental permission to check it out.
Challenges do not simply involve people expressing their point of view, but rather are an attempt to remove materials from curricula or libraries, thereby curtailing the ability of others to access information, views, ideas, expressions, and stories. A formal challenge leads to the reconsideration of the decision to purchase the material or offer the service. This process is governed by a board-approved policy and includes review of the material as a whole to assess if it is aligned with the library or school's mission and meets the criteria delineated in its selection, display, or programming policy (as applicable).
A book is banned when it is entirely removed from a collection in response to a formal or informal challenge.
Any reduction in access to library materials based on an individual or group's believe that they are harmful or offensive is an act of censorship. ALA does not consider weeding of an item based on criteria defined in a library or school district's policy to be a ban, nor do we characterize a temporary reduction in access resulting from the need to review materials to be a ban.
Share This Page
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Book Banning Efforts Surged in 2021. These Titles Were the Most Targeted.
Most of the targeted books are about Black and L.G.B.T.Q. people, according to the American Library Association. The country’s polarized politics has fueled the rise.

By Elizabeth A. Harris and Alexandra Alter
Attempts to ban books in the United States surged in 2021 to the highest level since the American Library Association began tracking book challenges 20 years ago, the organization said Monday.
Most of the targeted books were by or about Black and L.G.B.T.Q. people, the association said.
Book challenges are a perennial issue at school board meetings and libraries. But more recently, efforts fueled by the country’s intensely polarized political environment have been amplified by social media, where lists of books some consider to be inappropriate for children circulate quickly and widely.
Challenges to certain titles have been embraced by some conservative politicians, cast as an issue of parental choice and parental rights. Those who oppose these efforts, however, say that prohibiting the books violates the rights of parents and children who want those titles to be available.
“What we’re seeing right now is an unprecedented campaign to remove books from school libraries but also public libraries that deal with the lives and experience of people from marginalized communities,” said Deborah Caldwell-Stone, the director of the American Library Association’s office for intellectual freedom. “We’re seeing organized groups go to school boards and library boards and demand actual censorship of these books in order to conform to their moral or political views.”
The library association said it counted 729 challenges last year to library, school and university materials, as well as research databases and e-book platforms. Each challenge can contain multiple titles, and the association tracked 1,597 individual books that were either challenged or removed.
The count is based on voluntary reporting by educators and librarians and on media reports, the association said, and is not comprehensive.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

Researching Banned or Challenged Books: Resources for Challenge Research
- Resources for Challenge Research
- Was Winnie the Pooh Banned?
Key Resource
The key resource for researching why a particular title was challenged or banned are the publications of ALA's Office for Intellectual Freedom. The Office maintains information on which books are challenged and why and regularly publishes this information in the Journal of Intellectual Freedom and Privacy , where there may also be discussion of the events surrounding a challenge, and in a compilation published about every three years, most recently in Banned Books: Defending our Freedom to Read , edited by Robert P. Doyle. (Before 2016, similar information was in the Newsletter on Intellectual Freedom.)
Doyle and others used histories of censorship to compile the initial listing of challenged or banned books; this bibliography is in the Guide , as well as included on a list of books on censorship maintained by the ALA Library.
More recent entries are derived from the Journal of Intellectual Freedom and Privacy or Newsletter on Intellectual Freedom.
This publication is available in many libraries around the country, or may be ordered from the ALA Store..
- Books on Censorship Bibliography supporting research on censorship, banned and challenged books, and intellectual freedom. For researching why a particular book has been challenged, we recommend the Banned Books Resource Guide, which is represented on this list by the most recent editions, as well as the entry for the serial comprised of all the editions.
- Journal of Intellectual Freedom and Privacy The official journal of the ALA Office for Intellectual Freedom (OIF). JIFP is a double-blind peer reviewed publication, topically focused on practical, moral, ethical, philosophical, and theoretical issues of intellectual freedom and informational privacy within the United States and globally. Published quarterly. more... less... Two most current issues are available by subscription only. Older issues are made available via open access at the link above. ISSN 2474-7459
- Newsletter on Intellectual Freedom Superceded by the Journal Of Intellectual Freedom and Privacy. The Newsletter on Intellectual Freedom was the only journal that reported attempts to remove materials from school and library shelves across the country. The NIF was the source for the latest information on intellectual freedom issues.
Additional ALA Resources
The Banned Books Week pages on the ALA website offer many ways to look at the challenge data that has been collection. The links provided here will be of use to students doing research.
- Challenged Classics (with reasons) The classics in the Radcliffe Publishing Course Top 100 Novels of the 20th century, with challenge reports from the 2010 edition of "Banned Books."
- Frequently Challenged Books Most current top ten, with links to statistical analyses and subsets.
- Mapping Censorship This map is drawn from cases documented by ALA and the Kids' Right to Read Project, a collaboration of the National Coalition Against Censorship and the American Booksellers Foundation for Free Expression. Details are available in ALA's "Books Banned and Challenged 2007-2008; 2008-2009; 2009-2010; 2010-2011; 2011-2012; and 2012-2013," and the "Kids' Right to Read Project Report." “Mapping Censorship” was created by Chris Peterson of the National Coalition Against Censorship and Alita Edelman of the American Booksellers Foundation for Free Expression.
- Read Banned Books YouTube Channel Videos of Virtual Read-Outs and other videos from ALA OIF.
- Timeline: 30 Years of Librerating :Literature Since 1982, Banned Books Week has rallied librarians, booksellers, authors, publishers, teachers, and readers of all types to celebrate and defend the freedom to read. To commemorate 30 years of Banned Books Week and enter our 31st year of protecting readers' rights, ALA prepared l this timeline of significant banned and challenged books. Timeline powered by Tiki-Toki.
Where else to look....
If your library does not have "Banned Books," use the library catalog to locate books on censorship. Useful subject headings are "Challenged books--United States" or "Censorship--United States."
Many libraries offer databases enabling access to periodicals and newspapers. Ask your librarian about accessing these--or visit your library's website, library card in hand, to access.
Use newspaper indexes such as the following to read coverage of book challenges in the communities where they occurred.
- LexisNexis - Full-text access to magazines and newspapers, including the New York Times.
- NewsBank - Full-text articles from major metropolitan newspapers.
- ProQuest Historical Newspapers™ - Digital archive offering full-text and full-image articles for significant newspapers dating back to the eighteenth century.
Use literature databases such as the following to seek out biographies of authors, book synopses, bibliographies, and critical analysis.
- Booklist Online - Reviews, awards information, some author information in editorial content
- Gale Literature Resource Center - Has full-text articles and book reviews, biographical essays.
- Library and Information Science Source - Full-text and indexed entries from library science literature, including major review sources
- NovelList - Includes reviews and reading recommendations, reading levels, summaries, and awards books have received.
Often, a general web search of < "[book title]" and (banned or challenged) > will yield up useful articles and blog posts about challenges. For example, < "looking for alaska" (banned or challenged) > will bring up newspaper coverage--as well as a video by the author--on the censorship challenges faced by Looking for Alaska , by John Green.
Other websites
- Banned Books that Shaped America The Library of Congress created an exhibit, "Books that Shaped America," that explores books that "have had a profound effect on American life." Below is a list of books from that exhibit that have been banned/challenged.
- Banned Books Week The Banned Books Week Coalition is a national alliance of diverse organizations joined by a commitment to increase awareness of the annual celebration of the freedom to read. The Coalition seeks to engage various communities and inspire participation in Banned Books Week through education, advocacy, and the creation of programming about the problem of book censorship.
- Books Challenged or Banned in 2014-2015 A bibliography representing books challenged, restricted, removed, or banned in 2014 and 2015 as reported in the Newsletter on Intellectual Freedom from May 2014 to March 2015 and in American Libraries Direct (AL Direct), by Robert P. Doyle.
- National Coalition Against Censorship Resources for School Teachers and Students Background on the legal and practical questions surrounding school censorship controversies.
- NCTE Intellectual Freedom Center Censorship Challenge Reports Teachers, librarians, school administrators, and parents call upon NCTE for advice and materials regarding censorship challenges in their schools or districts.
- University of Pennsylvania Library "Banned Books Online" A special exhibit of books that have been the objects of censorship or censorship attempts, linking to free e-books.
- Wikipedia's "List of books banned by governments" Tabular listing, alphabetical by title, of books banned by governments, worldwide.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Was Winnie the Pooh Banned? >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 2:24 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ala.org/Researchingchallengedbooks
Here’s exactly why 13 books were banned from all Utah public schools, The Tribune found
The tribune received records explaining individual school districts’ decisions, leading to each book’s statewide ban..
Records obtained by The Salt Lake Tribune reveal the specific reasons why select Utah school districts considered certain books “objective sensitive” material, leading to 13 titles being banned from all public schools in the state .
There are three specific reasons to chose from when categorizing a book as “objective sensitive” material, according to a questionnaire districts or charters must fill out when explaining their decisions. The reasons are based off of the state’s new “objective sensitive” material standards.
Local education officials can select all that apply. If at least three school districts (or at least two school districts and five charter schools) select at least one of these options for the same book title, the book must be removed statewide.
According to a copy of the questionnaire obtained by The Tribune, the three reasons are:
Option 1: It contains a description or depiction of “human genitals in a state of sexual stimulation or arousal.”
Option 2: It contains a description or depiction of “acts of human masturbation, sexual intercourse, or sodomy.”
Option 3: It contains a description or depiction of “fondling or other erotic touching of human genitals or [the] pubic region.”
The 13 already banned titles were ordered off all Utah public school shelves on Aug. 2, based on decisions made by just six school districts.
Here are the options each district cited when deciding to categorize the books as “objective sensitive” material.
“Blankets” by Craig Thompson
Three districts decided to ban this autobiographical graphic novel, records show.
Davis School District cited all three options.
Nebo School District cited options No. 2 and 3.
Washington County School District cited option No. 1, specifically noting pages 292-293.
“A Court of Thorns and Roses” by Sarah J. Maas
Five districts decided to ban this romantic fantasy novel, records show.
Jordan School District cited options 2 and 3.
Davis, Alpine, Nebo and Washington County school districts cited all three options. Washington County School District specifically noted page 247.
“A Court of Mist and Fury” by Sarah J. Maas.
Four districts decided to ban this romantic fantasy novel, records show.
Washington County School District cited options No. 1 and 3, specifically noting page 24 .
Davis, Alpine and Nebo school districts cited all three options.
“A Court of Wings and Ruin” by Sarah J. Maas
Washington County School District cited options No. 1 and 3, specifically noting page 139.
“A Court of Frost and Starlight” by Sarah J. Maas
Jordan School District cited options No. 2 and 3.
Davis, Alpine, Nebo and Washington County school districts cited all three options. Washington County School District noted pages 202-205 in particular.
“A Court of Silver Flames” by Sarah J. Maas.
Washington County School District cited options No. 1 and 3, specifically noting page 247.
“Empire of Storms” by Sarah J. Maas
Three districts decided to ban this fantasy novel, records show.
Washington County School District cited option No. 3, particularly noting page 354.
“Fallout” by Ellen Hopkins
Three districts decided to ban this young adult fiction book, records show.
Washington County School District cited options No. 1 and 3, particularly noting page 339.
Alpine and Davis school districts cited all three options.
“Forever” by Judy Blume
Washington County School District cited options No 1 and 3, particularly noting page 85.
Nebo and Davis school districts cited all three options.
“Milk and Honey” by Rupi Kaur
Three districts decided to ban this collection of poetry and prose, records show.
Washington County School District cited option No. 1, particularly noting page 69.
Jordan and Davis school districts cited all three options.
“Oryx & Crake” by Margaret Atwood
Three districts decided to ban this science fiction book, records show.
Davis School District cited options No. 1 and 2
Washington County School District cited all three options, noting pages 140-141 and pages 165-166.
“Tilt” by Ellen Hopkins
Davis, Tooele County and Washington County school districts cited all three options. Washington County School District noted page 404.
“What Girls Are Made Of” by Elana K. Arnold
Four districts decided to ban this young adult fiction book, records show.
Jordan, Alpine, Davis and Washington County school districts cited all three options. Washington County School District specifically cited page 19.
Bans could still be overturned
Under the law, Utah State Board of Education members have 30 days from the moment a book’s statewide ban is instituted to potentially overturn it.
To do so, “three or more” USBE leaders within that time frame must request that the material be placed on a board meeting agenda, so leaders can vote on the matter.
If no hearing is held, the statewide removal stands.
Moving forward, districts and charters must report any “objective sensitive” material that they decide to remove to USBE.
If the statewide removal threshold is met, the state school board will notify all districts and charters within 10 school days to remove the title from student access. USBE will also add the title to a public list posted on its website .
Editor’s note • This story is available to Salt Lake Tribune subscribers only. Thank you for supporting local journalism.
RELATED STORIES
Here’s how utah plans to enforce statewide book ban retroactively, school districts await statewide book ban list as utah plans to retroactively enforce new law, utah officials unsure how to enforce new statewide book ban retroactively — but it may mean more work for public schools, gov. cox signs bill making it easier to ban books from utah schools statewide, automatic statewide ban for certain books in utah schools bill heads to gov. cox’s desk, ‘does that not make the point’: utah lawmaker cut off while reading from sarah j. maas book during book ban debate, california-style laws and foreign influence: why the legislature is rushing to amend the utah constitution, letter: in 2020, “a good man beat a con man.” it’s time for a good woman to do the same., letter: millcreek can go further with their proposed adu code changes, ‘excited and worried’: hundreds of salt lake city kids begin school at new campuses after elementary closures, the feds own millions of acres of public land in utah. now the state is suing for control of over half of it., featured local savings.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The American Library Association reported an "unprecedented spike" in the number of book removal requests in the final months of 2021, and most of these challenges focus on books about people from marginalized communities.
Banning of books has become increasingly prevalent and politically polarizing in the United States. While the primary goal of these bans is to restrict access to books, conversations about the bans have garnered attention on a wider scale. ... Donald G. Costello College of Business at George Mason University Research Paper, Available at SSRN ...
Author Ashley Hope Pérez wrote Out of Darkness, which is on the American Library Association's lists of most banned books. This essay by Ashley Hope Pérez is part of a series of interviews with ...
After book banning efforts in school libraries reached an all time high in 2021, 2022 is trending to exceed last year's figure. Instead of arguing with disgruntled parents and Facebook groups, many underpaid librarians and teachers, Salem described, choose to self-censor, quietly removing contentious titles from their shelves to avoid unfair ...
The student plaintiffs in Island Trees Union Free School District v. Pico (1982) march in protest of the Long Island school district's removal of titles such as Slaughterhouse Five by Kurt Vonnegut. While the district would ultimately return the banned books to its shelves, the Supreme Court's ultimate ruling largely allowed school leaders to maintain discretion over information access.
In the 2022-23 school year, PEN America recorded 3,362 instances of books banned, an increase of 33 percent from the 2021-22 school year. Over 40 percent of all book bans occurred in school districts in Florida. Across 33 school districts, PEN America recorded 1,406 book ban cases in Florida, followed by 625 bans in Texas, 333 bans in ...
Book banning and censorship is appearing again in states and school districts. The history of book banning goes back as far as recorded time. Columnist Jonathan E. Collins discusses the U.S. court system's history support of the First Amendment and against censorship. He outlines the implications of the most recent book banning incidents and ...
Bryan Anselm for The New York Times. By Claire Moses. Published July 31, 2022 Updated Feb. 27, 2023. Book-banning attempts have grown in the U.S. over the past few years from relatively isolated ...
He wanted to show that war brutalized soldiers, as well as the civilians caught in their path. The novel was a damning indictment of American warfare and the racist attitudes held by some nice ...
PEN America reported in the first edition of Banned in the USA (April 2022) that book bans had occurred in 86 school districts in 26 states in the first nine months of the 2021-22 school year. With additional reporting, and looking at the 12-month school year, the Index now lists banned books in 138 school districts in 32 states.
2. INTRODUCTION. Books banning is a social, educational and pedagogical problem because it creates problems for. readers, students and also teachers in different ways. For readers the measure ...
stages and identifies the effects book banning has on different groups and communities. For. teachers, book banning means shaky, ever-changing curriculum, fear for personal choices, and. the tragedy of self-censorship. For students, book banning means a denial of First Amendment. rights, a narrow world view, and psychological deficits.
According to PEN America, 1,636 different books were banned—not only challenged, but actually removed from shelves—in classrooms, schools, or libraries in the U.S. for at least a portion of the time between July 1, 2021, and June 30, 2022. The following is a list of these banned titles available through Morris Library.
More than 1,500 educators report on book bans and the damaging impact they are having on teacher morale and student learning. WASHINGTON, D.C. (October 3, 2023) - In a new study released by First Book Research & Insights, educators report that the national conversation around book challenges and bans is negatively impacting their classrooms ...
Book banning is nothing new. In fact, it has been around for centuries. What is considered the first book ban in the United States took place in 1637 in what is now known as Quincy, Massachusetts. Thomas Morton published his New English Canaan which was subsequently banned by the Puritan government as it was considered a harsh and heretical ...
OIF documented 4,240 unique book titles targeted for censorship, as well as 1,247 demands to censor library books, materials, and resources in 2023. Four key trends emerged from the data gathered from 2023 censorship reports: Pressure groups in 2023 focused on public libraries in addition to targeting school libraries.
Banned Books: A Study of Censorship. uspired by Carole A. Williams' By the senior year, most students have "Studying Challenged Novels: Or, developed a love for at least some author or How I Beat Senioritis" (EJ, Novem- genre of literature. As pre-reading exercises, ber 1988), I created a senior English we consider the role of books in our lives.
Here are the ten most frequently challenged books of 2021, according to the library association. . 1. 'Gender Queer,' by Maia Kobabe. In this 2019 illustrated memoir, Kobabe, who is nonbinary ...
Yes, I banned a book. I am a seasoned librarian and academic library director and a supporter of free speech and democracy,2 but I banned a book. The term heresy quickly comes to mind in the world of librarianship, but the story is much deeper than it first appears. The very temporary banning was simply an object lesson to our campus community ...
WRIT 101: College Writing. irginia ReevesMay 5, 2023Book Banning Negatively Affects Us and Should B. StoppedBa. biting books for. long time; however, this practice is not beneficial or right forreaders or b. oks. Prohibiting access to books discourages authors from creating origina. writtenworks, oks is an.
Details are available in ALA's "Books Banned and Challenged 2007-2008; 2008-2009; 2009-2010; 2010-2011; 2011-2012; and 2012-2013," and the "Kids' Right to Read Project Report." ... Has full-text articles and book reviews, biographical essays. Library and Information Science Source - Full-text and indexed entries from library science literature ...
A banned book is a book that may be: Removed from a library or libraries. Not allowed to be published. Not allowed to enter a country. Not allowed to exist, or be physically destroyed such as the case of book burning during Nazi Germany. The most extreme form of banning is the death or demand for the death of the author, most recently with ...
Essay On Banning Books. Since 1982, all kinds of books have been banned for the content they hold. Topics like race, sexually explicit content, homosexualaity, religion and more. Books are banned by librarians and teachers because they do not want children or teenagers to read about these topics. Children and teenagers are told they are not ...
Three districts decided to ban this science fiction book, records show. Jordan School District cited options No. 2 and 3. Davis School District cited options No. 1 and 2.