Improving Pandemic Preparedness: Lessons From COVID-19
Introduction.
- Recommendations
- Other Views
- Defense & Security
- Diplomacy & International Institutions
- Energy & Environment
- Human Rights
- Politics & Government
- Social Issues
- All Regions
- Europe & Eurasia
- Global Commons
- Middle East & North Africa
- Sub-Saharan Africa
- More Think Tank
- CFR Experts
- Centers & Programs
- In the News
- Publications
- Fellowships
- CFR Presents
- Conference Calls
- Independent Task Force Program
- All CFR Campus
- About CFR Campus
- Teaching Notes
- Model Diplomacy
- All About CFR
- Member Programs
- Support CFR
- Member Login
- ForeignAffairs.com
On December 31, 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) contacted China about media reports of a cluster of viral pneumonias in Wuhan, later attributed to a coronavirus, now named SARS-CoV-2 . By January 30, 2020, scarcely a month later, WHO declared the virus to be a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC)—the highest alarm the organization can sound. Thirty days more and the pandemic was well underway; the coronavirus had spread to more than seventy countries and territories on six continents, and there were roughly ninety thousand confirmed cases worldwide of COVID-19, the disease caused by the coronavirus.
The COVID-19 pandemic is far from over and could yet evolve in unanticipated ways, but one of its most important lessons is already clear: preparation and early execution are essential in detecting, containing, and rapidly responding to and mitigating the spread of potentially dangerous emerging infectious diseases. The ability to marshal early action depends on nations and global institutions being prepared for the worst-case scenario of a severe pandemic and ready to execute on that preparedness The COVID-19 pandemic is far from over and could yet evolve in unanticipated ways, but one of its most important lessons is already clear: preparation and early execution are essential in detecting, containing, and rapidly responding to and mitigating the spread of potentially dangerous emerging infectious diseases. The ability to marshal early action depends on nations and global institutions being prepared for the worst-case scenario of a severe pandemic and ready to execute on that preparedness before that worst-case outcome is certain.
The rapid spread of the coronavirus and its devastating death toll and economic harm have revealed a failure of global and U.S. domestic preparedness and implementation, a lack of cooperation and coordination across nations, a breakdown of compliance with established norms and international agreements, and a patchwork of partial and mishandled responses. This pandemic has demonstrated the difficulty of responding effectively to emerging outbreaks in a context of growing geopolitical rivalry abroad and intense political partisanship at home.
Pandemic preparedness is a global public good. Infectious disease threats know no borders, and dangerous pathogens that circulate unabated anywhere are a risk everywhere. As the pandemic continues to unfold across the United States and world, the consequences of inadequate preparation and implementation are abundantly clear. Despite decades of various commissions highlighting the threat of global pandemics and international planning for their inevitability, neither the United States nor the broader international system were ready to execute those plans and respond to a severe pandemic. The result is the worst global catastrophe since World War II.
The lessons of this pandemic could go unheeded once life returns to a semblance of normalcy and COVID-19 ceases to menace nations around the globe. The United States and the world risk repeating many of the same mistakes that exacerbated this crisis, most prominently the failure to prioritize global health security, to invest in the essential domestic and international institutions and infrastructure required to achieve it, and to act quickly in executing a coherent response at both the national and the global level.
The goal of this report is to curtail that possibility by identifying what went wrong in the early national and international responses to the coronavirus pandemic and by providing a road map for the United States and the multilateral system to better prepare and execute in future waves of the current pandemic and when the next pandemic threat inevitably emerges. This report endeavors to preempt the next global health challenge before it becomes a disaster.

A Rapid Spread, a Grim Toll, and an Economic Disaster
On January 23, 2020, China’s government began to undertake drastic measures against the coronavirus, imposing a lockdown on Wuhan, a city of ten million people, aggressively testing, and forcibly rounding up potential carriers in makeshift quarantine centers. 1 In the subsequent days and weeks, the Chinese government extended containment to most of the country, sealing off cities and villages and mobilizing tens of thousands of health workers to contain and treat the disease. By the time those interventions began, however, the disease had already spread well beyond the country’s borders.
SARS-CoV-2 is a highly transmissible emerging infectious disease for which no highly effective treatments or vaccines currently exist and against which people have no preexisting immunity. Some nations have been successful so far in containing its spread through public health measures such as testing, contact tracing, and isolation of confirmed and suspected cases. Those nations have managed to keep the number of cases and deaths within their territories low.
More than one hundred countries implemented either a full or a partial shutdown in an effort to contain the spread of the virus and reduce pressure on their health systems. Although these measures to enforce physical distancing slowed the pace of infection, the societal and economic consequences in many nations have been grim. The supply chain for personal protective equipment (PPE), testing kits, and medical equipment such as oxygen treatment equipment and ventilators remains under immense pressure to meet global demand.
If international cooperation in response to COVID-19 has been occurring at the top levels of government, evidence of it has been scant, though technical areas such as data sharing have witnessed some notable successes. Countries have mostly gone their own ways, closing borders and often hoarding medical equipment. More than a dozen nations are competing in a biotechnology arms race to find a vaccine. A proposed international arrangement to ensure timely equitable access to the products of that biomedical innovation has yet to attract the necessary support from many vaccine-manufacturing nations, and many governments are now racing to cut deals with pharmaceutical firms and secure their own supplies.
As of August 31, 2020, the pandemic had infected at least twenty-five million people worldwide and killed at least 850,000 (both likely gross undercounts), including at least six million reported cases and 183,000 deaths in the United States. Meanwhile, the world economy had collapsed into a slump rivaling or surpassing the Great Depression, with unemployment rates averaging 8.4 percent in high-income economies. In the second quarter of 2020, the U.S gross domestic product (GDP) fell 9.5 percent, the largest quarterly decline in the nation’s history. 2
Already in May 2020, the Asia Development Bank estimated that the pandemic would cost the world $5.8 to 8.8 trillion, reducing global GDP in 2020 by 6.4 to 9.7 percent. The ultimate financial cost could be far higher. 3
The United States is among the countries most affected by the coronavirus, with about 24 percent of global cases (as of August 31) but just 4 percent of the world’s population. While many countries in Europe and Asia succeeded in driving down the rate of transmission in spring 2020, the United States experienced new spikes in infections in the summer because the absence of a national strategy left it to individual U.S. states to go their own way on reopening their economies. In the hardest-hit areas, U.S. hospitals with limited spare beds and intensive care unit capacity have struggled to accommodate the surge in COVID-19 patients. Resource-starved local and state public health departments have been unable to keep up with the staggering demand for case identification, contract tracing, and isolation required to contain the coronavirus’s spread.
A Failure to Heed Warnings
This failing was not for any lack of warning of the dangers of pandemics. Indeed, many had sounded the alarm over the years. For nearly three decades, countless epidemiologists, public health specialists, intelligence community professionals, national security officials, and think tank experts have underscored the inevitability of a global pandemic of an emerging infectious disease. Starting with the Bill Clinton administration, successive administrations, including the current one, have included pandemic preparedness and response in their national security strategies. The U.S. government, foreign counterparts, and international agencies commissioned multiple scenarios and tabletop exercises that anticipated with uncanny accuracy the trajectory that a major outbreak could take, the complex national and global challenges it would create, and the glaring gaps and limitations in national and international capacity it would reveal.
The global health security community was almost uniformly in agreement that the most significant natural threat to population health and global security would be a respiratory virus—either a novel strain of influenza or a coronavirus that jumped from animals to humans. 4 Yet, for all this foresight and planning, national and international institutions alike have failed to rise to the occasion.
- 1 Michael Levenson, “Scale of China’s Wuhan Shutdown Is Believed to Be Without Precedent,” <em>New York Times</em>, January 22, 2020, <a href=" http://nytimes.com/2020/01/22/world/asia/coronavirus-quarantines-history.html "> http://nytimes.com/2020/01/22/world/asia/coronavirus-quarantines-history.html</a> ;; and Emily Feng, “China Has Built Over 20 Mass Quarantine Centers for Coronavirus Patients in Wuhan,” NPR, February 24, 2020, <a href=" http://npr.org/2020/02/24/808995258/china-has-built-over-20-mass-quarantine-centers-for-coronavirus-patients-in-wuha "> http://npr.org/2020/02/24/808995258/china-has-built-over-20-mass-quarantine-centers-for-coronavirus-patients-in-wuha</a> ;.
- 2 Ben Casselman, “A Collapse That Wiped Out 5 Years of Growth, With No Bounce in Sight,” <em>New York Times</em>, July 30, 2020, <a href=" http://nytimes.com/2020/07/30/business/economy/q2-gdp-coronavirus-economy.html "> http://nytimes.com/2020/07/30/business/economy/q2-gdp-coronavirus-economy.html</a> ;.
- 3 “Coronavirus ‘Could Cost Global Economy $8.8tn’ Says ADB,” BBC, May 15, 2020, <a href=" http://bbc.com/news/business-52671992 "> http://bbc.com/news/business-52671992</a> ;.
- 4 Jennifer B. Nuzzo et al., “Preparedness for a High-Impact Respiratory Pathogen Pandemic,” Johns Hopkins University Center for Health Security, September 2019, <a href=" http://apps.who.int/gpmb/assets/thematic_papers/tr-6.pdf "> http://apps.who.int/gpmb/assets/thematic_papers/tr-6.pdf</a> ;.
- Institute of Medicine, Microbial Threats to Health (1992)
- National Intelligence Estimate, The Global Infectious Disease Threat and Its Implications for the United States (2000)
- Launch of the U.S. Global Health Security Initiative (2001)
- Institute of Medicine, Microbial Threats to Health: Emergence, Detection, and Response (2003)
- Revision of the International Health Regulations (2005)
- World Health Organization, Global Influenza Preparedness Plan (2005)
- Homeland Security Council, National Strategy for Pandemic Influenza (2005)
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, National Health Security Strategy of the United States of America (2009)
- U.S. Director of National Intelligence, Worldwide Threat Assessments (2009–2019)
- World Health Organization, Report of Review Committee on the Functioning of the International Health Regulations (2005) in Relation to Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 (2011)
- Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Reauthorization Act of 2013
- Launch of the Global Health Security Agenda (2014)
- Blue Ribbon Study Panel on Biodefense (now Bipartisan Commission on Biodefense) (2015)
- National Security Strategy (2017)
- National Biodefense Strategy (2018)
- Crimson Contagion Simulation (2019)
- Global Preparedness Monitoring Board, A Work at Risk: Annual Report on Global Preparedness for Health Emergencies (2019)
- CSIS Commission, Ending the Cycle of Crisis and Complacency in U.S. Global Health Security (2019)
- U.S. National Health Security Strategy, 2019–2022 (2019)
- Global Health Security Index (2019)
Help inform the discussion
- X (Twitter)
Presidential Speeches
September 9, 2021: remarks on fighting the covid-19 pandemic, about this speech.
September 09, 2021
As the Delta variant of the Covid-19 virus spreads and cases and deaths increase in the United States, President Joe Biden announces new efforts to fight the pandemic. He outlines six broad areas of action--implementing new vaccination requirements, protecting the vaccinated with booster shots, keeping children safe and schools open, increasing testing and masking, protecting our economic recovery, and improving care of those who do get Covid-19.
- Download Full Video
- Download Audio
THE PRESIDENT: Good evening, my fellow Americans. I want to talk to you about where we are in the battle against COVID-19, the progress we’ve made, and the work we have left to do.
And it starts with understanding this: Even as the Delta variant 19 [sic] has—COVID-19—has been hitting this country hard, we have the tools to combat the virus, if we can come together as a country and use those tools.
If we raise our vaccination rate, protect ourselves and others with masking and expanded testing, and identify people who are infected, we can and we will turn the tide on COVID-19.
It will take a lot of hard work, and it’s going to take some time. Many of us are frustrated with the nearly 80 million Americans who are still not vaccinated, even though the vaccine is safe, effective, and free.
You might be confused about what is true and what is false about COVID-19. So before I outline the new steps to fight COVID-19 that I’m going to be announcing tonight, let me give you some clear information about where we stand.
First, we have cons—we have made considerable progress
in battling COVID-19. When I became President, about 2 million Americans were fully vaccinated. Today, over 175 million Americans have that protection.
Before I took office, we hadn’t ordered enough vaccine for every American. Just weeks in office, we did. The week before I took office, on January 20th of this year, over 25,000 Americans died that week from COVID-19. Last week, that grim weekly toll was down 70 percent.
And in the three months before I took office, our economy was faltering, creating just 50,000 jobs a month. We’re now averaging 700,000 new jobs a month in the past three months.
This progress is real. But while America is in much better shape than it was seven months ago when I took office, I need to tell you a second fact.
We’re in a tough stretch, and it could last for a while. The highly contagious Delta variant that I began to warn America about back in July spread in late summer like it did in other countries before us.
While the vaccines provide strong protections for the vaccinated, we read about, we hear about, and we see the stories of hospitalized people, people on their death beds, among the unvaccinated over these past few weeks.
This is a pandemic of the unvaccinated. And it’s caused by the fact that despite America having an unprecedented and successful vaccination program, despite the fact that for almost five months free vaccines have been available in 80,000 different locations, we still have nearly 80 million Americans who have failed to get the shot.
And to make matters worse, there are elected officials actively working to undermine the fight against COVID-19. Instead of encouraging people to get vaccinated and mask up, they’re ordering mobile morgues for the unvaccinated dying from COVID in their communities. This is totally unacceptable.
Third, if you wonder how all this adds up, here’s the math: The vast majority of Americans are doing the right thing. Nearly three quarters of the eligible have gotten at least one shot, but one quarter has not gotten any. That’s nearly 80 million Americans not vaccinated. And in a country as large as ours, that’s 25 percent minority. That 25 percent can cause a lot of damage—and they are.
The unvaccinated overcrowd our hospitals, are overrunning the emergency rooms and intensive care units, leaving no room for someone with a heart attack, or pancreitis [pancreatitis], or cancer.
And fourth, I want to emphasize that the vaccines provide very strong protection from severe illness from COVID-19. I know there’s a lot of confusion and misinformation. But the world’s leading scientists confirm that if you are fully vaccinated, your risk of severe illness from COVID-19 is very low.
In fact, based on available data from the summer, only one of out of every 160,000 fully vaccinated Americans was hospitalized for COVID per day.
These are the facts.
So here’s where we stand: The path ahead, even with the Delta variant, is not nearly as bad as last winter. But what makes it incredibly more frustrating is that we have the tools to combat COVID-19, and a distinct minority of Americans –supported by a distinct minority of elected officials—are keeping us from turning the corner. These pandemic politics, as I refer to, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die.
We cannot allow these actions to stand in the way of protecting the large majority of Americans who have done their part and want to get back to life as normal.
As your President, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to require more Americans to be vaccinated, to combat those blocking public health.
My plan also increases testing, protects our economy, and will make our kids safer in schools. It consists of six broad areas of action and many specific measures in each that—and each of those actions that you can read more about at WhiteHouse.gov. WhiteHouse.gov.
The measures—these are going to take time to have full impact. But if we implement them, I believe and the scientists indicate, that in the months ahead we can reduce the number of unvaccinated Americans, decrease hospitalizations and deaths, and allow our children to go to school safely and keep our economy strong by keeping businesses open.
First, we must increase vaccinations among the unvaccinated with new vaccination requirements. Of the nearly 80 million eligible Americans who have not gotten vaccinated, many said they were waiting for approval from the Food and Drug Administration—the FDA. Well, last month, the FDA granted that approval.
So, the time for waiting is over. This summer, we made progress through the combination of vaccine requirements and incentives, as well as the FDA approval. Four million more people got their first shot in August than they did in July.
But we need to do more. This is not about freedom or personal choice. It’s about protecting yourself and those around you—the people you work with, the people you care about, the people you love.
My job as President is to protect all Americans.
So, tonight, I’m announcing that the Department of Labor is developing an emergency rule to require all employers with 100 or more employees, that together employ over 80 million workers, to ensure their workforces are fully vaccinated or show a negative test at least once a week.
Some of the biggest companies are already requiring this: United Airlines, Disney, Tysons Food, and even Fox News.
The bottom line: We’re going to protect vaccinated workers from unvaccinated co-workers. We’re going to reduce the spread of COVID-19 by increasing the share of the workforce that is vaccinated in businesses all across America.
My plan will extend the vaccination requirements that I previously issued in the healthcare field. Already, I’ve announced, we’ll be requiring vaccinations that all nursing home workers who treat patients on Medicare and Medicaid, because I have that federal authority.
Tonight, I’m using that same authority to expand that to cover those who work in hospitals, home healthcare facilities, or other medical facilities–a total of 17 million healthcare workers.
If you’re seeking care at a health facility, you should be able to know that the people treating you are vaccinated. Simple. Straightforward. Period.
Next, I will sign an executive order that will now require all executive branch federal employees to be vaccinated—all. And I’ve signed another executive order that will require federal contractors to do the same.
If you want to work with the federal government and do business with us, get vaccinated. If you want to do business with the federal government, vaccinate your workforce.
And tonight, I’m removing one of the last remaining obstacles that make it difficult for you to get vaccinated.
The Department of Labor will require employers with 100 or more workers to give those workers paid time off to get vaccinated. No one should lose pay in order to get vaccinated or take a loved one to get vaccinated.
Today, in total, the vaccine requirements in my plan will affect about 100 million Americans—two thirds of all workers.
And for other sectors, I issue this appeal: To those of you running large entertainment venues—from sports arenas to concert venues to movie theaters—please require folks to get vaccinated or show a negative test as a condition of entry.
And to the nation’s family physicians, pediatricians, GPs—general practitioners—you’re the most trusted medical voice to your patients. You may be the one person who can get someone to change their mind about being vaccinated.
Tonight, I’m asking each of you to reach out to your unvaccinated patients over the next two weeks and make a personal appeal to them to get the shot. America needs your personal involvement in this critical effort.
And my message to unvaccinated Americans is this: What more is there to wait for? What more do you need to see? We’ve made vaccinations free, safe, and convenient.
The vaccine has FDA approval. Over 200 million Americans have gotten at least one shot.
We’ve been patient, but our patience is wearing thin. And your refusal has cost all of us. So, please, do the right thing. But just don’t take it from me; listen to the voices of unvaccinated Americans who are lying in hospital beds, taking their final breaths, saying, “If only I had gotten vaccinated.” “If only.”
It’s a tragedy. Please don’t let it become yours.
The second piece of my plan is continuing to protect the vaccinated.
For the vast majority of you who have gotten vaccinated, I understand your anger at those who haven’t gotten vaccinated. I understand the anxiety about getting a “breakthrough” case.
But as the science makes clear, if you’re fully vaccinated, you’re highly protected from severe illness, even if you get COVID-19.
In fact, recent data indicates there is only one confirmed positive case per 5,000 fully vaccinated Americans per day.
You’re as safe as possible, and we’re doing everything we can to keep it that way—keep it that way, keep you safe.
That’s where boosters come in—the shots that give you even more protection than after your second shot.
Now, I know there’s been some confusion about boosters. So, let me be clear: Last month, our top government doctors announced an initial plan for booster shots for vaccinated Americans. They believe that a booster is likely to provide the highest level of protection yet.
Of course, the decision of which booster shots to give, when to start them, and who will give them, will be left completely to the scientists at the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control.
But while we wait, we’ve done our part. We’ve bought enough boosters—enough booster shots—and the distribution system is ready to administer them.
As soon as they are authorized, those eligible will be able to get a booster right away in tens of thousands of site across the—sites across the country for most Americans, at your nearby drug store, and for free.
The third piece of my plan is keeping—and maybe the most important—is keeping our children safe and our schools open. For any parent, it doesn’t matter how low the risk of any illness or accident is when it comes to your child or grandchild. Trust me, I know.
So, let me speak to you directly. Let me speak to you directly to help ease some of your worries.
It comes down to two separate categories: children ages 12 and older who are eligible for a vaccine now, and children ages 11 and under who are not are yet eligible.
The safest thing for your child 12 and older is to get them vaccinated. They get vaccinated for a lot of things. That’s it. Get them vaccinated.
As with adults, almost all the serious COVID-19 cases we’re seeing among adolescents are in unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds—an age group that lags behind in vaccination rates.
So, parents, please get your teenager vaccinated.
What about children under the age of 12 who can’t get vaccinated yet? Well, the best way for a parent to protect their child under the age of 12 starts at home. Every parent, every teen sibling, every caregiver around them should be vaccinated.
Children have four times higher chance of getting hospitalized if they live in a state with low vaccination rates rather than the states with high vaccination rates.
Now, if you’re a parent of a young child, you’re wondering when will it be—when will it be—the vaccine available for them. I strongly support an independent scientific review for vaccine uses for children under 12. We can’t take shortcuts with that scientific work.
But I’ve made it clear I will do everything within my power to support the FDA with any resource it needs to continue to do this as safely and as quickly as possible, and our nation’s top doctors are committed to keeping the public at large updated on the process so parents can plan.
Now to the schools. We know that if schools follow the science and implement the safety measures—like testing, masking, adequate ventilation systems that we provided the money for, social distancing, and vaccinations—then children can be safe from COVID-19 in schools.
Today, about 90 percent of school staff and teachers are vaccinated. We should get that to 100 percent. My administration has already acquired teachers at the schools run by the Defense Department—because I have the authority as President in the federal system—the Defense Department and the Interior Department—to get vaccinated. That’s authority I possess.
Tonight, I’m announcing that we’ll require all of nearly 300,000 educators in the federal paid program, Head Start program, must be vaccinated as well to protect your youngest—our youngest—most precious Americans and give parents the comfort.
And tonight, I’m calling on all governors to require vaccination for all teachers and staff. Some already have done so, but we need more to step up.
Vaccination requirements in schools are nothing new. They work. They’re overwhelmingly supported by educators and their unions. And to all school officials trying to do the right thing by our children: I’ll always be on your side.
Let me be blunt. My plan also takes on elected officials and states that are undermining you and these lifesaving actions. Right now, local school officials are trying to keep children safe in a pandemic while their governor picks a fight with them and even threatens their salaries or their jobs. Talk about bullying in schools. If they’ll not help—if these governors won’t help us beat the pandemic, I’ll use my power as President to get them out of the way.
The Department of Education has already begun to take legal action against states undermining protection that local school officials have ordered. Any teacher or school official whose pay is withheld for doing the right thing, we will have that pay restored by the federal government 100 percent. I promise you I will have your back.
The fourth piece of my plan is increasing testing and masking. From the start, America has failed to do enough COVID-19 testing. In order to better detect and control the Delta variant, I’m taking steps tonight to make testing more available, more affordable, and more convenient. I’ll use the Defense Production Act to increase production of rapid tests, including those that you can use at home.
While that production is ramping up, my administration has worked with top retailers, like Walmart, Amazon, and Kroger’s, and tonight we’re announcing that, no later than next week, each of these outlets will start to sell at-home rapid test kits at cost for the next three months. This is an immediate price reduction for at-home test kits for up to 35 percent reduction.
We’ll also expand—expand free testing at 10,000 pharmacies around the country. And we’ll commit—we’re committing $2 billion to purchase nearly 300 million rapid tests for distribution to community health centers, food banks, schools, so that every American, no matter their income, can access free and convenient tests. This is important to everyone, particularly for a parent or a child—with a child not old enough to be vaccinated. You’ll be able to test them at home and test those around them.
In addition to testing, we know masking helps stop the spread of COVID-19. That’s why when I came into office, I required masks for all federal buildings and on federal lands, on airlines, and other modes of transportation.
Today—tonight, I’m announcing that the Transportation Safety Administration—the TSA—will double the fines on travelers that refuse to mask. If you break the rules, be prepared to pay.
And, by the way, show some respect. The anger you see on television toward flight attendants and others doing their job is wrong; it’s ugly.
The fifth piece of my plan is protecting our economic recovery. Because of our vaccination program and the American Rescue Plan, which we passed early in my administration, we’ve had record job creation for a new administration, economic growth unmatched in 40 years. We cannot let unvaccinated do this progress—undo it, turn it back.
So tonight, I’m announcing additional steps to strengthen our economic recovery. We’ll be expanding COVID-19 Economic Injury Disaster Loan programs. That’s a program that’s going to allow small businesses to borrow up to $2 million from the current $500,000 to keep going if COVID-19 impacts on their sales.
These low-interest, long-term loans require no repayment for two years and be can used to hire and retain workers, purchase inventory, or even pay down higher cost debt racked up since the pandemic began. I’ll also be taking additional steps to help small businesses stay afloat during the pandemic.
Sixth, we’re going to continue to improve the care of those who do get COVID-19. In early July, I announced the deployment of surge response teams. These are teams comprised of experts from the Department of Health and Human Services, the CDC, the Defense Department, and the Federal Emergency Management Agency—FEMA—to areas in the country that need help to stem the spread of COVID-19.
Since then, the federal government has deployed nearly 1,000 staff, including doctors, nurses, paramedics, into 18 states. Today, I’m announcing that the Defense Department will double the number of military health teams that they’ll deploy to help their fellow Americans in hospitals around the country.
Additionally, we’re increasing the availability of new medicines recommended by real doctors, not conspir-—conspiracy theorists. The monoclonal antibody treatments have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization by up to 70 percent for unvaccinated people at risk of developing sefe-—severe disease.
We’ve already distributed 1.4 million courses of these treatments to save lives and reduce the strain on hospitals. Tonight, I’m announcing we will increase the average pace of shipment across the country of free monoclonal antibody treatments by another 50 percent.
Before I close, let me say this: Communities of color are disproportionately impacted by this virus. And as we continue to battle COVID-19, we will ensure that equity continues to be at the center of our response. We’ll ensure that everyone is reached. My first responsibility as President is to protect the American people and make sure we have enough vaccine for every American, including enough boosters for every American who’s approved to get one.
We also know this virus transcends borders. That’s why, even as we execute this plan at home, we need to continue fighting the virus overseas, continue to be the arsenal of vaccines.
We’re proud to have donated nearly 140 million vaccines over 90 countries, more than all other countries combined, including Europe, China, and Russia combined. That’s American leadership on a global stage, and that’s just the beginning.
We’ve also now started to ship another 500 million COVID vaccines—Pfizer vaccines—purchased to donate to 100 lower-income countries in need of vaccines. And I’ll be announcing additional steps to help the rest of the world later this month.
As I recently released the key parts of my pandemic preparedness plan so that America isn’t caught flat-footed when a new pandemic comes again—as it will—next month, I’m also going to release the plan in greater detail.
So let me close with this: We have so-—we’ve made so much progress during the past seven months of this pandemic. The recent increases in vaccinations in August already are having an impact in some states where case counts are dropping in recent days. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time. We have the tools. Now we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence, and together as one nation.
Look, we’re the United States of America. There’s nothing—not a single thing—we’re unable to do if we do it together. So let’s stay together.
God bless you all and all those who continue to serve on the frontlines of this pandemic. And may God protect our troops.
Get vaccinated.
More Joe Biden speeches
Speech about covid 19 introduction,body, conclusion to inform need Ngayon asap

Introduction:
Good morning/afternoon everyone. Today, I would like to inform you about the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on our daily lives.
COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, was first identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Since then, it has spread to affect nearly every country in the world. The virus is primarily spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing.
The virus has had a significant impact on our daily lives. Many countries have implemented strict measures such as lockdowns, travel restrictions, and social distancing guidelines to slow the spread of the virus. This has led to widespread economic disruption and job loss. Additionally, the virus has overwhelmed healthcare systems, leading to shortages of personal protective equipment and hospital beds.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, COVID-19 is a serious global health crisis that has had a major impact on our daily lives. It is important that we continue to follow guidelines from health officials and take steps to protect ourselves and others. Through continued research and development, we hope to find effective treatments and eventually a vaccine for COVID-19. Thank you for listening.
New questions in English
I Thought We’d Learned Nothing From the Pandemic. I Wasn’t Seeing the Full Picture

M y first home had a back door that opened to a concrete patio with a giant crack down the middle. When my sister and I played, I made sure to stay on the same side of the divide as her, just in case. The 1988 film The Land Before Time was one of the first movies I ever saw, and the image of the earth splintering into pieces planted its roots in my brain. I believed that, even in my own backyard, I could easily become the tiny Triceratops separated from her family, on the other side of the chasm, as everything crumbled into chaos.
Some 30 years later, I marvel at the eerie, unexpected ways that cartoonish nightmare came to life – not just for me and my family, but for all of us. The landscape was already covered in fissures well before COVID-19 made its way across the planet, but the pandemic applied pressure, and the cracks broke wide open, separating us from each other physically and ideologically. Under the weight of the crisis, we scattered and landed on such different patches of earth we could barely see each other’s faces, even when we squinted. We disagreed viciously with each other, about how to respond, but also about what was true.
Recently, someone asked me if we’ve learned anything from the pandemic, and my first thought was a flat no. Nothing. There was a time when I thought it would be the very thing to draw us together and catapult us – as a capital “S” Society – into a kinder future. It’s surreal to remember those early days when people rallied together, sewing masks for health care workers during critical shortages and gathering on balconies in cities from Dallas to New York City to clap and sing songs like “Yellow Submarine.” It felt like a giant lightning bolt shot across the sky, and for one breath, we all saw something that had been hidden in the dark – the inherent vulnerability in being human or maybe our inescapable connectedness .
More from TIME
Read More: The Family Time the Pandemic Stole
But it turns out, it was just a flash. The goodwill vanished as quickly as it appeared. A couple of years later, people feel lied to, abandoned, and all on their own. I’ve felt my own curiosity shrinking, my willingness to reach out waning , my ability to keep my hands open dwindling. I look out across the landscape and see selfishness and rage, burnt earth and so many dead bodies. Game over. We lost. And if we’ve already lost, why try?
Still, the question kept nagging me. I wondered, am I seeing the full picture? What happens when we focus not on the collective society but at one face, one story at a time? I’m not asking for a bow to minimize the suffering – a pretty flourish to put on top and make the whole thing “worth it.” Yuck. That’s not what we need. But I wondered about deep, quiet growth. The kind we feel in our bodies, relationships, homes, places of work, neighborhoods.
Like a walkie-talkie message sent to my allies on the ground, I posted a call on my Instagram. What do you see? What do you hear? What feels possible? Is there life out here? Sprouting up among the rubble? I heard human voices calling back – reports of life, personal and specific. I heard one story at a time – stories of grief and distrust, fury and disappointment. Also gratitude. Discovery. Determination.
Among the most prevalent were the stories of self-revelation. Almost as if machines were given the chance to live as humans, people described blossoming into fuller selves. They listened to their bodies’ cues, recognized their desires and comforts, tuned into their gut instincts, and honored the intuition they hadn’t realized belonged to them. Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. “The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry myself have both shrunk and expanded,” she shared. “I don’t love myself very well with an audience.” Without the daily ritual of trying to pass as “normal” in public, Tamar, a queer mom in the Netherlands, realized she’s autistic. “I think the pandemic helped me to recognize the mask,” she wrote. “Not that unmasking is easy now. But at least I know it’s there.” In a time of widespread suffering that none of us could solve on our own, many tended to our internal wounds and misalignments, large and small, and found clarity.
Read More: A Tool for Staying Grounded in This Era of Constant Uncertainty
I wonder if this flourishing of self-awareness is at least partially responsible for the life alterations people pursued. The pandemic broke open our personal notions of work and pushed us to reevaluate things like time and money. Lucy, a disabled writer in the U.K., made the hard decision to leave her job as a journalist covering Westminster to write freelance about her beloved disability community. “This work feels important in a way nothing else has ever felt,” she wrote. “I don’t think I’d have realized this was what I should be doing without the pandemic.” And she wasn’t alone – many people changed jobs , moved, learned new skills and hobbies, became politically engaged.
Perhaps more than any other shifts, people described a significant reassessment of their relationships. They set boundaries, said no, had challenging conversations. They also reconnected, fell in love, and learned to trust. Jeanne, a quilter in Indiana, got to know relatives she wouldn’t have connected with if lockdowns hadn’t prompted weekly family Zooms. “We are all over the map as regards to our belief systems,” she emphasized, “but it is possible to love people you don’t see eye to eye with on every issue.” Anna, an anti-violence advocate in Maine, learned she could trust her new marriage: “Life was not a honeymoon. But we still chose to turn to each other with kindness and curiosity.” So many bonds forged and broken, strengthened and strained.
Instead of relying on default relationships or institutional structures, widespread recalibrations allowed for going off script and fortifying smaller communities. Mara from Idyllwild, Calif., described the tangible plan for care enacted in her town. “We started a mutual-aid group at the beginning of the pandemic,” she wrote, “and it grew so quickly before we knew it we were feeding 400 of the 4000 residents.” She didn’t pretend the conditions were ideal. In fact, she expressed immense frustration with our collective response to the pandemic. Even so, the local group rallied and continues to offer assistance to their community with help from donations and volunteers (many of whom were originally on the receiving end of support). “I’ve learned that people thrive when they feel their connection to others,” she wrote. Clare, a teacher from the U.K., voiced similar conviction as she described a giant scarf she’s woven out of ribbons, each representing a single person. The scarf is “a collection of stories, moments and wisdom we are sharing with each other,” she wrote. It now stretches well over 1,000 feet.
A few hours into reading the comments, I lay back on my bed, phone held against my chest. The room was quiet, but my internal world was lighting up with firefly flickers. What felt different? Surely part of it was receiving personal accounts of deep-rooted growth. And also, there was something to the mere act of asking and listening. Maybe it connected me to humans before battle cries. Maybe it was the chance to be in conversation with others who were also trying to understand – what is happening to us? Underneath it all, an undeniable thread remained; I saw people peering into the mess and narrating their findings onto the shared frequency. Every comment was like a flare into the sky. I’m here! And if the sky is full of flares, we aren’t alone.
I recognized my own pandemic discoveries – some minor, others massive. Like washing off thick eyeliner and mascara every night is more effort than it’s worth; I can transform the mundane into the magical with a bedsheet, a movie projector, and twinkle lights; my paralyzed body can mother an infant in ways I’d never seen modeled for me. I remembered disappointing, bewildering conversations within my own family of origin and our imperfect attempts to remain close while also seeing things so differently. I realized that every time I get the weekly invite to my virtual “Find the Mumsies” call, with a tiny group of moms living hundreds of miles apart, I’m being welcomed into a pocket of unexpected community. Even though we’ve never been in one room all together, I’ve felt an uncommon kind of solace in their now-familiar faces.
Hope is a slippery thing. I desperately want to hold onto it, but everywhere I look there are real, weighty reasons to despair. The pandemic marks a stretch on the timeline that tangles with a teetering democracy, a deteriorating planet , the loss of human rights that once felt unshakable . When the world is falling apart Land Before Time style, it can feel trite, sniffing out the beauty – useless, firing off flares to anyone looking for signs of life. But, while I’m under no delusions that if we just keep trudging forward we’ll find our own oasis of waterfalls and grassy meadows glistening in the sunshine beneath a heavenly chorus, I wonder if trivializing small acts of beauty, connection, and hope actually cuts us off from resources essential to our survival. The group of abandoned dinosaurs were keeping each other alive and making each other laugh well before they made it to their fantasy ending.
Read More: How Ice Cream Became My Own Personal Act of Resistance
After the monarch butterfly went on the endangered-species list, my friend and fellow writer Hannah Soyer sent me wildflower seeds to plant in my yard. A simple act of big hope – that I will actually plant them, that they will grow, that a monarch butterfly will receive nourishment from whatever blossoms are able to push their way through the dirt. There are so many ways that could fail. But maybe the outcome wasn’t exactly the point. Maybe hope is the dogged insistence – the stubborn defiance – to continue cultivating moments of beauty regardless. There is value in the planting apart from the harvest.
I can’t point out a single collective lesson from the pandemic. It’s hard to see any great “we.” Still, I see the faces in my moms’ group, making pancakes for their kids and popping on between strings of meetings while we try to figure out how to raise these small people in this chaotic world. I think of my friends on Instagram tending to the selves they discovered when no one was watching and the scarf of ribbons stretching the length of more than three football fields. I remember my family of three, holding hands on the way up the ramp to the library. These bits of growth and rings of support might not be loud or right on the surface, but that’s not the same thing as nothing. If we only cared about the bottom-line defeats or sweeping successes of the big picture, we’d never plant flowers at all.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- The Reinvention of J.D. Vance
- Iran, Trump, and the Third Assassination Plot
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Scams
- Did the Pandemic Break Our Brains?
- 33 True Crime Documentaries That Shaped the Genre
- The Ordained Rabbi Who Bought a Porn Company
- Introducing the Democracy Defenders
- Why Gut Health Issues Are More Common in Women
Contact us at [email protected]
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Persuasive Essay Guide
Persuasive Essay About Covid19
How to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid19 | Examples & Tips
14 min read

People also read
A Comprehensive Guide to Writing an Effective Persuasive Essay
A Catalogue of 300 Best Persuasive Essay Topics for Students
Persuasive Essay Outline - A Complete Guide
30+ Persuasive Essay Examples To Get You Started
Read Excellent Examples of Persuasive Essay About Gun Control
How To Write A Persuasive Essay On Abortion
Learn to Write a Persuasive Essay About Business With 5 Best Examples
Check Out 14 Persuasive Essays About Online Education Examples
Persuasive Essay About Smoking - Making a Powerful Argument with Examples
Are you looking to write a persuasive essay about the Covid-19 pandemic?
Writing a compelling and informative essay about this global crisis can be challenging. It requires researching the latest information, understanding the facts, and presenting your argument persuasively.
But don’t worry! with some guidance from experts, you’ll be able to write an effective and persuasive essay about Covid-19.
In this blog post, we’ll outline the basics of writing a persuasive essay . We’ll provide clear examples, helpful tips, and essential information for crafting your own persuasive piece on Covid-19.
Read on to get started on your essay.
- 1. Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 2. Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19
- 3. Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19 Vaccine
- 4. Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19 Integration
- 5. Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
- 6. Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
- 7. Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
- 8. Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Steps to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Here are the steps to help you write a persuasive essay on this topic, along with an example essay:
Step 1: Choose a Specific Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement should clearly state your position on a specific aspect of COVID-19. It should be debatable and clear. For example:
| "COVID-19 vaccination mandates are necessary for public health and safety." |
Step 2: Research and Gather Information
Collect reliable and up-to-date information from reputable sources to support your thesis statement. This may include statistics, expert opinions, and scientific studies. For instance:
- COVID-19 vaccination effectiveness data
- Information on vaccine mandates in different countries
- Expert statements from health organizations like the WHO or CDC
Step 3: Outline Your Essay
Create a clear and organized outline to structure your essay. A persuasive essay typically follows this structure:
- Introduction
- Background Information
- Body Paragraphs (with supporting evidence)
- Counterarguments (addressing opposing views)
Step 4: Write the Introduction
In the introduction, grab your reader's attention and present your thesis statement. For example:
| The COVID-19 pandemic has presented an unprecedented global challenge, and in the face of this crisis, many countries have debated the implementation of vaccination mandates. This essay argues that such mandates are essential for safeguarding public health and preventing further devastation caused by the virus. |
Step 5: Provide Background Information
Offer context and background information to help your readers understand the issue better. For instance:
| COVID-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, emerged in late 2019 and quickly spread worldwide, leading to millions of infections and deaths. Vaccination has proven to be an effective tool in curbing the virus's spread and severity. |
Step 6: Develop Body Paragraphs
Each body paragraph should present a single point or piece of evidence that supports your thesis statement. Use clear topic sentences , evidence, and analysis. Here's an example:
| One compelling reason for implementing COVID-19 vaccination mandates is the overwhelming evidence of vaccine effectiveness. According to a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines demonstrated an efficacy of over 90% in preventing symptomatic COVID-19 cases. This level of protection not only reduces the risk of infection but also minimizes the virus's impact on healthcare systems. |
Step 7: Address Counterarguments
Acknowledge opposing viewpoints and refute them with strong counterarguments. This demonstrates that you've considered different perspectives. For example:
| Some argue that vaccination mandates infringe on personal freedoms and autonomy. While individual freedom is a crucial aspect of democratic societies, public health measures have long been implemented to protect the collective well-being. Seatbelt laws, for example, are in place to save lives, even though they restrict personal choice. |
Step 8: Write the Conclusion
Summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement in the conclusion. End with a strong call to action or thought-provoking statement. For instance:
| In conclusion, COVID-19 vaccination mandates are a crucial step toward controlling the pandemic, protecting public health, and preventing further loss of life. The evidence overwhelmingly supports their effectiveness, and while concerns about personal freedoms are valid, they must be weighed against the greater good of society. It is our responsibility to take collective action to combat this global crisis and move toward a safer, healthier future. |
Step 9: Revise and Proofread
Edit your essay for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling errors. Ensure that your argument flows logically.
Step 10: Cite Your Sources
Include proper citations and a bibliography page to give credit to your sources.
Remember to adjust your approach and arguments based on your target audience and the specific angle you want to take in your persuasive essay about COVID-19.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19
When writing a persuasive essay about the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s important to consider how you want to present your argument. To help you get started, here are some example essays for you to read:
|
Here is another example explaining How COVID-19 has changed our lives essay:
The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in late 2019, has drastically altered the way we live. From work and education to social interactions and healthcare, every aspect of our daily routines has been impacted. Reflecting on these changes helps us understand their long-term implications.
COVID-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, is an infectious disease first identified in December 2019 in Wuhan, China. It spreads through respiratory droplets and can range from mild symptoms like fever and cough to severe cases causing pneumonia and death. The rapid spread and severe health impacts have led to significant public health measures worldwide.
The pandemic shifted many to remote work and online education. While some enjoy the flexibility, others face challenges like limited access to technology and blurred boundaries between work and home.
Social distancing and lockdowns have led to increased isolation and mental health issues. However, the pandemic has also fostered community resilience, with people finding new ways to connect and support each other virtually.
Healthcare systems have faced significant challenges, leading to innovations in telemedicine and a focus on public health infrastructure. Heightened awareness of hygiene practices, like handwashing and mask-wearing, has helped reduce the spread of infectious diseases.
COVID-19 has caused severe economic repercussions, including business closures and job losses. While governments have implemented relief measures, the long-term effects are still uncertain. The pandemic has also accelerated trends like e-commerce and contactless payments.
The reduction in travel and industrial activities during lockdowns led to a temporary decrease in pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This has sparked discussions about sustainable practices and the potential for a green recovery.
COVID-19 has reshaped our lives in numerous ways, affecting work, education, social interactions, healthcare, the economy, and the environment. As we adapt to this new normal, it is crucial to learn from these experiences and work towards a more resilient and equitable future. |
Let’s look at another sample essay:
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a transformative event, reshaping every aspect of our lives. In my opinion, while the pandemic has brought immense challenges, it has also offered valuable lessons and opportunities for growth. One of the most striking impacts has been on our healthcare systems. The pandemic exposed weaknesses and gaps, prompting a much-needed emphasis on public health infrastructure and the importance of preparedness. Innovations in telemedicine and vaccine development have been accelerated, showing the incredible potential of scientific collaboration. Socially, the pandemic has highlighted the importance of community and human connection. While lockdowns and social distancing measures increased feelings of isolation, they also fostered a sense of solidarity. People found creative ways to stay connected and support each other, from virtual gatherings to community aid initiatives. The shift to remote work and online education has been another significant change. This transition, though challenging, demonstrated the flexibility and adaptability of both individuals and organizations. It also underscored the importance of digital literacy and access to technology. Economically, the pandemic has caused widespread disruption. Many businesses closed, and millions lost their jobs. However, it also prompted a reevaluation of business models and work practices. The accelerated adoption of e-commerce and remote work could lead to more sustainable and efficient ways of operating in the future. In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic has been a profound and complex event. While it brought about considerable hardship, it also revealed the strength and resilience of individuals and communities. Moving forward, it is crucial to build on the lessons learned to create a more resilient and equitable world. |
Check out some more PDF examples below:
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 Pandemic
Sample Of Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Persuasive Essay About Covid-19 In The Philippines - Example
If you're in search of a compelling persuasive essay on business, don't miss out on our “ persuasive essay about business ” blog!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19 Vaccine
Covid19 vaccines are one of the ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19, but they have been a source of controversy. Different sides argue about the benefits or dangers of the new vaccines. Whatever your point of view is, writing a persuasive essay about it is a good way of organizing your thoughts and persuading others.
A persuasive essay about the COVID-19 vaccine could consider the benefits of getting vaccinated as well as the potential side effects.
Below are some examples of persuasive essays on getting vaccinated for Covid-19.
Covid19 Vaccine Persuasive Essay
Persuasive Essay on Covid Vaccines
Interested in thought-provoking discussions on abortion? Read our persuasive essay about abortion blog to eplore arguments!
Examples of Persuasive Essay About COVID-19 Integration
Covid19 has drastically changed the way people interact in schools, markets, and workplaces. In short, it has affected all aspects of life. However, people have started to learn to live with Covid19.
Writing a persuasive essay about it shouldn't be stressful. Read the sample essay below to get an idea for your own essay about Covid19 integration.
Persuasive Essay About Working From Home During Covid19
Searching for the topic of Online Education? Our persuasive essay about online education is a must-read.
Examples of Argumentative Essay About Covid 19
Covid-19 has been an ever-evolving issue, with new developments and discoveries being made on a daily basis.
Writing an argumentative essay about such an issue is both interesting and challenging. It allows you to evaluate different aspects of the pandemic, as well as consider potential solutions.
Here are some examples of argumentative essays on Covid19.
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 Sample
Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion
Looking for a persuasive take on the topic of smoking? You'll find it all related arguments in out Persuasive Essay About Smoking blog!
Examples of Persuasive Speeches About Covid-19
Do you need to prepare a speech about Covid19 and need examples? We have them for you!
Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate for specific changes in policies or simply raise awareness about the virus.
Check out some examples of persuasive speeches on Covid-19:
Persuasive Speech About Covid-19 Example
Persuasive Speech About Vaccine For Covid-19
You can also read persuasive essay examples on other topics to master your persuasive techniques!
Tips to Write a Persuasive Essay About Covid-19
Writing a persuasive essay about COVID-19 requires a thoughtful approach to present your arguments effectively.
Here are some tips to help you craft a compelling persuasive essay on this topic:
- Choose a Specific Angle: Narrow your focus to a specific aspect of COVID-19, like vaccination or public health measures.
- Provide Credible Sources: Support your arguments with reliable sources like scientific studies and government reports.
- Use Persuasive Language: Employ ethos, pathos, and logos , and use vivid examples to make your points relatable.
- Organize Your Essay: Create a solid persuasive essay outline and ensure a logical flow, with each paragraph focusing on a single point.
- Emphasize Benefits: Highlight how your suggestions can improve public health, safety, or well-being.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate graphs, charts, and statistics to reinforce your arguments.
- Call to Action: End your essay conclusion with a strong call to action, encouraging readers to take a specific step.
- Revise and Edit: Proofread for grammar, spelling, and clarity, ensuring smooth writing flow.
- Seek Feedback: Have someone else review your essay for valuable insights and improvements.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Common Topics for a Persuasive Essay on COVID-19
Here are some persuasive essay topics on COVID-19:
- The Importance of Vaccination Mandates for COVID-19 Control
- Balancing Public Health and Personal Freedom During a Pandemic
- The Economic Impact of Lockdowns vs. Public Health Benefits
- The Role of Misinformation in Fueling Vaccine Hesitancy
- Remote Learning vs. In-Person Education: What's Best for Students?
- The Ethics of Vaccine Distribution: Prioritizing Vulnerable Populations
- The Mental Health Crisis Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic
- The Long-Term Effects of COVID-19 on Healthcare Systems
- Global Cooperation vs. Vaccine Nationalism in Fighting the Pandemic
- The Future of Telemedicine: Expanding Healthcare Access Post-COVID-19
In search of more inspiring topics for your next persuasive essay? Our persuasive essay topics blog has plenty of ideas!
To sum it up,
You’ve explored great sample essays and picked up some useful tips. You now have the tools you need to write a persuasive essay about Covid-19. So don’t let doubts hold you back—start writing!
If you’re feeling stuck or need a bit of extra help, don’t worry! MyPerfectWords.com offers a professional persuasive essay writing service that can assist you. Our experienced essay writers are ready to help you craft a well-structured, insightful paper on Covid-19.
Just place your “ do my essay for me ” request today, and let us take care of the rest!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good title for a covid-19 essay.
A good title for a COVID-19 essay should be clear, engaging, and reflective of the essay's content. Examples include:
- "The Impact of COVID-19 on Global Health"
- "How COVID-19 Has Transformed Our Daily Lives"
- "COVID-19: Lessons Learned and Future Implications"
How do I write an informative essay about COVID-19?
To write an informative essay about COVID-19, follow these steps:
- Choose a specific focus: Select a particular aspect of COVID-19, such as its transmission, symptoms, or vaccines.
- Research thoroughly: Gather information from credible sources like scientific journals and official health organizations.
- Organize your content: Structure your essay with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Present facts clearly: Use clear, concise language to convey information accurately.
- Include visuals: Use charts or graphs to illustrate data and make your essay more engaging.
How do I write an expository essay about COVID-19?
To write an expository essay about COVID-19, follow these steps:
- Select a clear topic: Focus on a specific question or issue related to COVID-19.
- Conduct thorough research: Use reliable sources to gather information.
- Create an outline: Organize your essay with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Explain the topic: Use facts and examples to explain the chosen aspect of COVID-19 in detail.
- Maintain objectivity: Present information in a neutral and unbiased manner.
- Edit and revise: Proofread your essay for clarity, coherence, and accuracy.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


BBC World Service
Listen live.
The latest news and information from the world's most respected news source. BBC World Service delivers up-to-the-minute news, expert analysis, commentary, features and interviews.
Coronavirus: The world has come together to flatten the curve. Can we stay united to tackle other crises?
Watching the world come together gives me hope for the future, writes mira patel, a high school junior..
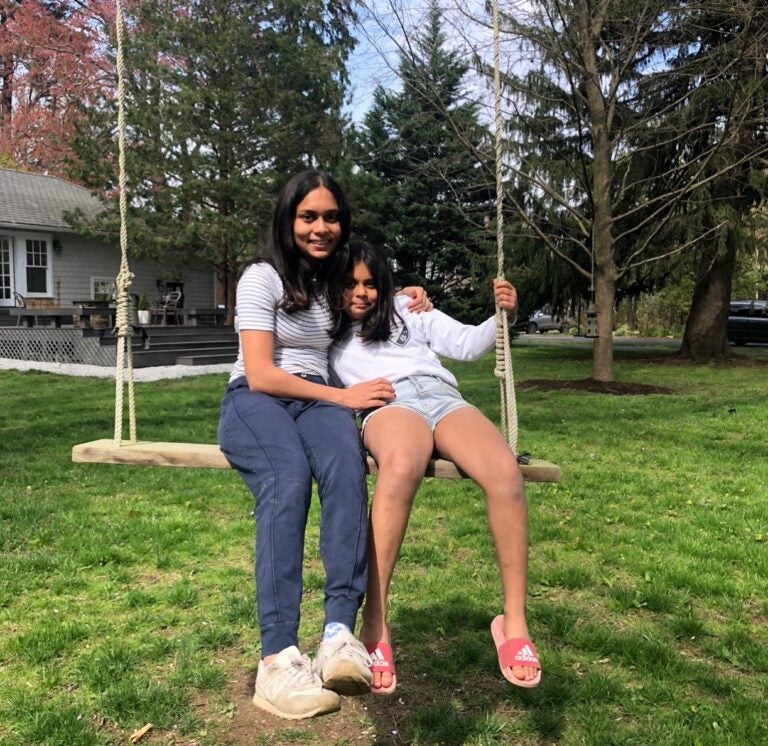
Mira Patel and her sister Veda. (Courtesy of Dee Patel)
Related Content

This 24-year-old entrepreneur is helping Black-owned restaurants survive coronavirus
Black and Mobile is an online delivery service that caters to Black-owned restaurants. The coronavirus shutdown has increased demand for its service.
4 years ago

Home desks won’t replace Philly’s high-rise office towers anytime soon, analysts say
Philadelphia’s office market might fare better post-coronavirus than those of other U.S. cities, CBRE analysts said in a new report.
Before the pandemic, I had often heard adults say that young people would lose the ability to connect in-person with others due to our growing dependence on technology and social media. However, this stay-at-home experience has proven to me that our elders’ worry is unnecessary. Because isolation isn’t in human nature, and no advancement in technology could replace our need to meet in person, especially when it comes to learning.
As the weather gets warmer and we approach summertime, it’s going to be more and more tempting for us teenagers to go out and do what we have always done: hang out and have fun. Even though the decision-makers are adults, everyone has a role to play and we teens can help the world move forward by continuing to self-isolate. It’s incredibly important that in the coming weeks, we respect the government’s effort to contain the spread of the coronavirus.
In the meantime, we can find creative ways to stay connected and continue to do what we love. Personally, I see many 6-feet-apart bike rides and Zoom calls in my future.
If there is anything that this pandemic has made me realize, it’s how connected we all are. At first, the infamous coronavirus seemed to be a problem in China, which is worlds away. But slowly, it steadily made its way through various countries in Europe, and inevitably reached us in America. What was once framed as a foreign virus has now hit home.
Watching the global community come together, gives me hope, as a teenager, that in the future we can use this cooperation to combat climate change and other catastrophes.
As COVID-19 continues to creep its way into each of our communities and impact the way we live and communicate, I find solace in the fact that we face what comes next together, as humanity.
When the day comes that my generation is responsible for dealing with another crisis, I hope we can use this experience to remind us that moving forward requires a joint effort.
Mira Patel is a junior at Strath Haven High School and is an education intern at the Foreign Policy Research Institute in Philadelphia. Follow her on Instagram here.
Becoming a storyteller at WHYY, your local public media station, is easier than you might think. Text STORYTELLER to 267-494-9949 to learn more.
WHYY is your source for fact-based, in-depth journalism and information. As a nonprofit organization, we rely on financial support from readers like you. Please give today.
Part of the series

Coronavirus Pandemic
You may also like.

Threats and violence suspend high school football games Friday night
Fight breaks out at a game between Pennsauken and Camden High Schools, threats suspend games in Chester and Northampton Counties.
3 years ago

Philly students get vaxxed at the zoo before heading back to school
The event is the first of its kind for the school district, but arrives after months of partnering with CHOP to organize other vaccination clinics around the city.

Montco high school senior reflects on missing experiences because of coronavirus
Grace Honeyman, a senior at Harriton High School, talks with her father about how she’s dealing with missing milestones due to coronavirus.
Want a digest of WHYY’s programs, events & stories? Sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Together we can reach 100% of WHYY’s fiscal year goal
Course is available
Introduction to COVID-19: methods for detection, prevention, response and control
Your browser is not fully supported.
You are running an outdated browser version, which is not fully supported by OpenWHO. You might not be able to use crucial functionality such as the submission of quizzes . Please update your browser to the latest version before you continue (we recommend Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome ).
Click here to hide this warning permanently.
- Discussions
- Certificates
- Collab Space
- Course Details
- Announcements
An error occurred while loading the video player, or it takes a long time to initialize. You can try clearing your browser cache. Please try again later and contact the helpdesk if the problem persists.
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that are known to cause illness ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China. This is a new coronavirus that has not been previously identified in humans.
This course provides a general introduction to COVID-19 and emerging respiratory viruses and is intended for public health professionals, incident managers and personnel working for the United Nations, international organizations and NGOs.
As the official disease name was established after material creation, any mention of nCoV refers to COVID-19, the infectious disease caused by the most recently discovered coronavirus.
Please note that the content of this course is currently being revised to reflect the most recent guidance. You can find updated information on certain COVID-19-related topics in the following courses: Vaccination: COVID-19 vaccines channel IPC measures: IPC for COVID-19 Antigen rapid diagnostic testing: 1) SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid diagnostic testing ; 2) Key considerations for SARS-CoV-2 antigen RDT implementation
Please note: These materials were last updated on 16/12/2020.
Course contents
Emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: introduction:, module 1: introduction to emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19:, module 2: detecting emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: surveillance:, module 3: detecting emerging respiratory viruses, including covid-19: laboratory investigations:, module 4: risk communication :, module 5 : community engagement:, module 6: preventing and responding to an emerging respiratory virus, including covid-19:, enroll me for this course, certificate requirements.
- Gain a Record of Achievement by earning at least 80% of the maximum number of points from all graded assignments.
- Gain an Open Badge by completing the course.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
current events
12 Ideas for Writing Through the Pandemic With The New York Times
A dozen writing projects — including journals, poems, comics and more — for students to try at home.

By Natalie Proulx
The coronavirus has transformed life as we know it. Schools are closed, we’re confined to our homes and the future feels very uncertain. Why write at a time like this?
For one, we are living through history. Future historians may look back on the journals, essays and art that ordinary people are creating now to tell the story of life during the coronavirus.
But writing can also be deeply therapeutic. It can be a way to express our fears, hopes and joys. It can help us make sense of the world and our place in it.
Plus, even though school buildings are shuttered, that doesn’t mean learning has stopped. Writing can help us reflect on what’s happening in our lives and form new ideas.
We want to help inspire your writing about the coronavirus while you learn from home. Below, we offer 12 projects for students, all based on pieces from The New York Times, including personal narrative essays, editorials, comic strips and podcasts. Each project features a Times text and prompts to inspire your writing, as well as related resources from The Learning Network to help you develop your craft. Some also offer opportunities to get your work published in The Times, on The Learning Network or elsewhere.
We know this list isn’t nearly complete. If you have ideas for other pandemic-related writing projects, please suggest them in the comments.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Springer Nature - PMC COVID-19 Collection

COVID-19 pandemic crisis—a complete outline of SARS-CoV-2
Sana saffiruddin shaikh.
1 Y. B. Chavan College of Pharmacy, Dr. Rafiq Zakaria Campus, Aurangabad, 431001 India
Anooja P. Jose
2 Government College of Pharmacy, Aurangabad, 431001 India
Disha Anil Nerkar
Midhuna vijaykumar kv, saquib khaleel shaikh, associated data.
The data and material are available upon request. The graphs and figures used in the manuscript were generated and analyzed and are not used anywhere else before.
Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), the cause of COVID-19, a fatal disease emerged from Wuhan, a large city in the Chinese province of Hubei in December 2019.
Main body of abstract
The World Health Organization declared COVID-19 as a pandemic due to its spread to other countries inside and outside Asia. Initial confirmation of the pandemic shows patient exposure to the Huanan seafood market. Bats might be a significant host for the spread of coronaviruses via an unknown intermediate host. The human-to-human transfer has become a significant concern due to one of the significant reasons that is asymptomatic carriers or silent spreaders. No data is obtained regarding prophylactic treatment for COVID-19, although many clinical trials are underway.
The most effective weapon is prevention and precaution to avoid the spread of the pandemic. In this current review, we outline pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, ongoing clinical trials, prevention, and precautions. We have also highlighted the impact of pandemic worldwide and challenges that can help to overcome the fatal disease in the future.
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are a large family of RNA viruses; they show discrete point-like projections over their surface. They show the presence of an unusually large RNA genome and a distinctive replication strategy. The term “coronavirus” is acquired from the “crown”-like morphology. Coronaviruses show potential fatal human respiratory infections and cause a variety of diseases in animals and birds [ 1 ]. Coronavirus primarily targets the human respiratory system [ 2 ]. The World Health Organization (WHO) named the latest virus as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) on 12 January 2020 [ 3 ]. The COVID-19 or the SARS-CoV-2 is rapidly unfurling from Wuhan in Hubei Province of China to worldwide [ 4 ].
Initial confirmation of the pandemic was carried out by conducting studies on 99 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, from which 49% of patients exhibited a history of subjection to the Huanan seafood market. The patient examined had a clinical manifestation of fever, cough, shortness of breath, muscle ache, and sore throat-like symptoms [ 5 ]. COVID-19 has infected several hundreds of humans and has caused many fatal cases [ 6 ]. Worldwide, there have been 3,925,815 confirmed cases, including 274,488 deaths of COVID-19 as of 6:37 pm CEST 10 May 2020 reported to WHO [ 7 ].
This article outlines and gives a complete overview of SARS-CoV-2, including its pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, and precautions. This article also provides the current scenario of the pandemic worldwide, since new findings are rapidly evolving and can help the readers in upgrading their knowledge about the COVID-19. It also emphasizes the challenges faced by giving an idea about future strategies in fighting and preventing recurrence.
History and origin
Coronaviruses were not expected to be highly infectious to humans, but the outburst of a severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong province China in the years 2002 and 2003 proved to be devastating. SARS-CoV is the contributory agent of the SARS, also known as “atypical pneumonia”. The coronaviruses that spread before that time in humans mostly caused mild infections in immune-competent people. But after the emergence of SARS, another highly infectious coronavirus, MERS-CoV, appeared in Middle Eastern countries [ 8 , 9 ]. Research has shown that SARS-CoV-2 shows similarities with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. (Table (Table1) 1 ) depicts a comparison of SARS-CoV-2 with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV [ 10 – 16 ]. Several disseminating strains of coronaviruses were identified and were considered harmless pathogens, causing common cold and mild upper respiratory illness [ 17 ]. HCoV-229E [ 18 ] strain was isolated in 1966. HCoV-NL63 was first isolated from the Netherlands during late 2004. In 2012, MERS-CoV was first identified from the lung of a 60-year-old patient who was suffering from acute pneumonia and renal failure in Saudi Arabia [ 19 ]. About 8000 cases and 800 deaths worldwide were observed due to the outbreak of SARS first human pandemic in the dawn of the twenty-first century [ 20 ].
Comparison of coronaviruses
| Parameters | SARS-COV2 | SARS-COV | MERS-COV |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epidemiology | Dec 2019, Wuhan, China | Nov 2002, Guangdong, China | April 2012, Saudi Arabia |
| Animal reservoir | Bats | Bats | Bats |
| Intermediate host | Pangolins/minks (yet to be confirmed) | Palm civets | Camels |
| Receptor target | ACE2 | ACE2 | DPP4 |
| Fatality rate | 2.3% | 9.5% | 34.4% |
| Genetic similarity with the other | 79.5% SARS-CoV 50% MERS-CoV | 79.5% SARS-CoV-2 | 50% SARS-CoV-2 |
| Virus type | SS-RNA | RNA | RNA |
| Total RNA sequence length of pathogen | 29,903 bp | 29,751 bp | 30,108 bp |
| M:F ratio | 2.70:1 | 1:1.25 | 2:1 |
| Transmission route | Droplets; faeco-oral transmission; contact with infected individual or things Human-to-human | Droplets; contact with infected individual or things; bat-civets-human Human-to-human | Touching infected camel or consumption of meat or milk Limited human-to-human transmission |
| Clinical symptoms | Fever, fatigue, dry cough | Fever, cough, myalgia, dyspnea, diarrhea | Fever, cough, respiratory distress, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Incubation | 7–14 days, 24 days | 2–7 days | 5–6 days |
| R | 2.68 | 2.5 | > 1 |
| Diagnostic methods | RRT-PCR, RT-PCR, RT-lamp, RRT-lamp, coronavirus detection kit | RRT-PCR, RT-PCR, RT-lamp, RRT-lamp, coronavirus detection kit | RRT-PCR, ELISA, micro neutralization assay, MERS-CoV serology test |
| Chest X-ray | Bilateral multi-lobular ground glass opacities | Ground glass opacities | Ground glass opacities; consolidation |
| Chest CT scan | No nodular opacities | Lobar consolidation; nodular opacities | Single or multiple opacities; bilateral glass opacities; sub-pleural and lower lobe predominance; septal thickness |
| Prevention | Hand hygiene; cough etiquette; avoiding unnecessary touching of the eyes or face. | Hand hygiene; cough etiquette; avoiding unnecessary touching of the eyes or face. | Hand hygiene; cough etiquette; avoiding unnecessary touching of the eyes or face; avoiding raw milk and meat consumption. |
| Treatment | Ritonavir; lopinavir (in testing) | Glucocorticoids; interferon | Ribavirin; interferon; analgesics (treatment not yet determined) |
Note: despite the lower case fatality rate observed in COVID-19, the overall number of death far outweighs that from SARS and MERS
The α-CoVs HCoV-229E and HCoV-NL63 and β-CoVs HCoV-HKU1 and HCoV-OC43 are identified as a human susceptible virus with low pathogenicity and cause mild respiratory symptoms similar to common cold [ 21 ]. SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV result in severe respiratory tract infections [ 22 , 23 ]. COVID-19 was recently reported from Wuhan (China), which has cases in Thailand, Japan, South Korea, and the USA, which has been confirmed as a new coronavirus [ 24 ].
The coronavirus genera, which mostly infect mammals, are alpha-coronavirus and beta-coronavirus. Out of 15 presently assigned viral species, seven were isolated from bats. The research proposed that bats are significant hosts for alpha-coronaviruses and beta-coronaviruses and play an essential role as the gene source in the evolution of these two coronavirus genera SARS and MERS [ 25 ]. The genome sequence was found to be 96.2% identical to a bat CoV RaTG13, whereas it shares 79.5% identity to SARS-CoV. The virus genome sequencing outcomes and evolutionary analysis show that bat can be a natural host from virus source, and SARS-CoV-2 might be transferred from bats through unspecified intermediate hosts to infect humans [ 26 ]. It is found that SARS-CoV-2 affects males more than females [ 27 ]. The spread of SARS-CoV-2 emerged like a wild forest fire in many countries worldwide. Table ( (2) 2 ) [ 28 ] gives a brief of the first identified cases of COVID-19 in different countries.
First confirmed case
| Country | First confirmed case (dates) |
|---|---|
| China, East Asia | 31 December 2019 |
| Thailand | 13 January 2020 |
| Japan | 15 January 2020 |
| Korea | 20 January 2020 |
| USA | 23 January 2020 |
| Vietnam | 24 January 2020 |
| Singapore | 24 January 2020 |
| Australia, Nepal, and French Republic | 25 January 2020 |
| Malaysia | 26 January 2020 |
| Canada | 27 January 2020 |
| Cambodia, Germany, Sri Lanka | 28 January 2020 |
| United Arab Emirates | 29 January 2020 |
| Philippines, India, Finland | 30 January 2020 |
| Italy | 31 January 2020 |
| Russian Federation, Spain, Sweden, UK | 1 February 2020 |
| Belgium | 5 February 2020 |
| Japan | 6 February 2020 |
| Egypt | 15 February 2020 |
The first confirmed case was reported in China, and since then, there was a widespread of coronavirus in other countries worldwide. Table Table1 1 shows the first confirmed case with dates
Coronaviruses are spherical to pleomorphic enveloped particles [ 29 ]. The size ranges from 80 to 120 nm in diameter. The maximum size is as small as 50 nm and as large as 200 nm are also seen [ 30 ]. There are four types of main structural proteins observed in the coronaviruses: the spike (S), membrane (M), envelope (E), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins, which are encoded within the viral genome (Table (Table3). 3 ). In thin sections, the virion envelope may be visualized as inner and outer shells separated by a translucent space [ 31 ]. The virion envelope contains phospholipids, glycolipids, cholesterol, di- and triglycerides, and free fatty acids in proportions. The complexed genome RNA is with the basic nucleocapsid (N) protein, which forms a helical capsid established within the viral membrane. The enclosed glycoproteins are responsible for attachment to the host cells [ 32 ].
Structural proteins of coronavirus and their functions
| Structural proteins | Functions of proteins |
|---|---|
| Spike protein (S) | Virus and host cell fusion by binding |
| Membrane protein (M) | Nutrient transport, determines shape, and formation of envelope |
| Envelope protein (E) | Interferes with host immune response |
| Nucleocapsid protein (N) | Binds with RNA genome and makes up nucleocapsid |
| Hemagglutinin-esterase (HE) | Binds sialic acids on surface glycoprotein |
According to the recent studies, it is observed that coronavirus which lacks envelope protein (E) serves as a good candidate in vaccine designing
The coronavirus genomes are among the most massive mature RNA molecules as compared to other eukaryotic RNAs (Fig. (Fig.1) 1 ) [ 33 ]. The genome of these viruses contains multiple ORFS. A typical CoV consists of at least 6 ORFs in its genome. Several studies have confirmed the genetic resemblance between SARS-CoV-2 and a bat CoV.

Structure of novel coronavirus
A study conducted to compare the genetic mutations of COVID showed genomic mutations among viruses from different countries, wherein a sequence obtained from Nepal showed minimum to no variations. In contrast, the maximum number of modifications was obtained from one derived from the Indian series located in ORF1-ab nsp2 nsp3 helicase ORF8 and spike surface glycoprotein. Also, host antiviral mRNAs play a critical part in the regulation of immune response to virus infection, depending upon the viral agent. The unique host mRNAs could be explored in the development of novel antiviral therapies. The club-like surface projections or peplomers of coronaviruses are about 17–20 nm from the virion surface. It has a subtle base that swells to a width of about 10 nm at the distal extremity. Some coronaviruses that exhibit the second set of projections about 5–10-nm long are present beneath the significant projections. These shorter spikes are now known as hemagglutinin-esterase (HE) protein, an additional membrane protein found in a subset of group 2 coronaviruses. The primary role of this non-essential protein is to aid in viral entry and pathogenesis in vivo. It configures short projections that bind to N-acetyl-9-O-acetlyneuramic acid or N-glycolylneuraminic acid and have esterase [ 34 – 39 ]. Figure Figure2 2 shows the primary classification of coronavirus.

Classification of coronavirus
Lifecycle of coronavirus
The life cycle of the virus with the host consists of the following four steps: attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation, and release (Fig. (Fig.3). 3 ). Once the virus binds to the host receptor, they enter host cells through endocytosis or membrane fusion. Once the viral contents are released inside the host cells, viral RNA enters the nucleus for replication. Viral mRNA is used to make viral proteins and is further proceeded by maturation and release [ 40 , 41 ].


Attachment and entry
The virion attachment with the host cell is initiated by interaction between S protein and its receptors, which is also a primary determinant for coronavirus infection. The S protein undergoes acid-dependent proteolytic cleavage, which results in exposure of fusion peptide. This fusion is followed by the formation of a six-helix bundle (bundle formation helps in combining viral and cellular membrane) and release of the viral genome into the cytoplasm.
Replicase protein expression
The process of translation of replicase gene ORFs1a and ORFs1b and translation of polyprotein pp1a and pp1ab takes place. Assembly of nsps into replicase-transcriptase complex (RTC) leads to viral RNA synthesis (replication and transcription of subgenomic RNAs).
Replication and transcription
In the replication process, the viral RNA synthesis is followed by the production of genomic and sub-genomic RNAs (sub-genomic mRNAs), which further leads to recombination of the virus.
Assembly and release
The insertion and translation of viral structure protein S, E, and M takes place into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), which is followed by the movement of proteins along the secretory pathway into ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum Golgi intermediate compartment). The viral genome is encapsidated by N protein into the membrane of ERGIC. M and E protein expression give rise to the formation of virus-like particles (VLPs). After the assembly of the virion and its transportation to cell surface vesicles, exocytosis takes place. Finally, it results in viral release (E protein helps by altering the host secretory pathway).
The incubation period is the period between the entry of the virus into the host and appearance of signs and symptoms in the host or the period between the earliest date of contact of the transmission source and the most initial time of symptom onset (i.e., cough, fever, fatigue, or myalgia) [ 42 ]. The incubation period of COVID-19 is vital as the disease could be transmitted during this phase through asymptomatic as well as symptomatic carriers (Table (Table4). 4 ). The inhaled virus SARS-CoV-2 binds to the epithelial cells present in the nasal cavity and starts replicating.
Incubation period of coronaviruses
| Coronavirus strain | Incubation period | Death period | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARS-CoV | 4–10 days | 20–25 days | Fever, dry cough, myalgia, dyspnea, headache, sore throat, sputum production, rhinorrhea, watery diarrhea, confusion, poor appetite. |
| MERS-CoV | 5–6 days | 11–13 days | Myalgia, fever, chills, malaise associated with confusion, cough, shortness of breath, dyspnea, pneumonia |
| COVID-19 | 3–7 days | 17–24 days | Fever, cough, dyspnea, muscle ache, confusion, headache, sore throat, rhinorrhea, chest pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, anosmia, dysgeusia |
On the basis of studies conducted and data findings, virologists points out that incubation period extends to 14 days, with a median time of 4–5 days from exposure to symptom onset. One study reported that 97.5% of persons with COVID-19 who develop symptoms will do so within 11.5 days of SARS-CoV-2 infection
ACE2 is the primary receptor for both SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, which is an asymptomatic state (initial 1–2 days of infection). Upper airway and conducting airway response are seen the next few days. The disease is mild and mostly restricted only to the upper conducting airways for about 80% of the infected patients [ 43 ].
The incubation period is required to create more productive quarantine systems for people infected with the virus. The incubation period for the COVID-19 is between 2 and 14 days after exposure. A newly infected person shows symptoms in the about 5 days after contact with a sick patient. In most patients, symptoms appeared after 12–14 days of infection
The average incubation period was approximated to be 5.1 days, and 97.5% of those who develop symptoms will do so within 11.5 days of infection. In Wuhan’s return patients, the average incubation period is found to be 6.4 days. In a case reported by Hubei province, local government on 22 February showed an incubation period of 27 days. In another case, an incubation period of 19 days was observed. Therefore a 24-day observation period is considered in suspected cases by the Chinese government and also by WHO [ 44 – 51 ]. The frequency of cases is increasing day by day, and it is essential to keep a check over it. Figure Figure4 4 gives a glance of confirmed cases cumulative and death overtime cumulative from 10 January onwards up to 25 May.

a Graph of confirmed (cumulative) cases overtime in various countries . b Graph of death (cumulative) overtime in various countries
Pathogenesis
Like other CoVs, the SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted primarily via respiratory droplets and possible faeco-oral transmission routes [ 52 ]. Figure Figure5 5 gives a complete outline of the pathogenesis of coronavirus. On infection, primary viral replication is expected to occur in the mucosal epithelium of the upper respiratory tract with further multiplication into the lower respiratory tract and GI mucosa, giving rise to mild viremia. The virus enters the host cells through two methods either:
- I. Direct entry
- II. Endocytosis

Complete pathogenesis of coronavirus
These are positive sense ss-RNA viruses that can cause respiratory, enteric, hepatic, and neurologic diseases. High binding capacity with SARS-CoV-2 was observed by molecular biological analysis [ 53 ]. The ACE2 gene encodes the angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 receptor for both the SARS-CoV and the human respiratory coronavirus NL63. Recent studies show that ACE2 could be the host receptor for the novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2 [ 54 ].
Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (hACE2), which was the binding receptor of SARS-CoV, is analogous to SARS-CoV-2. These hACE2 are type 1 membrane proteins expressed in various cells of the nasal mucosa, lung, bronchus, heart, kidney, intestines, bladder, stomach, esophagus, and ileum. It functions as an enzyme in the RAS and is, therefore, mainly associated with cardiovascular diseases [ 55 ].
The zinc peptidase ACE2 has also expressed in the alveolar type 2 pneumocytes, which explains its role in lung damage due to SARS-CoV. The SARS-CoV-2 shows 10–12-fold more affinity towards the proteins than the other SARS-CoV. Pathophysiology and virulence of the virus link to the function of its nsps and structural proteins. The nsp can block the host’s innate mechanism response while the virus envelope increases the pathogenicity as it assists the assembly and release of the virus [ 56 ].
The CoV spike glycoproteins comprise of three segments—a large ectodomain, a single-pass transmembrane anchor, and a small intracellular tail. The ectodomain is composed of the receptor-binding domain (RBD)—the S1 and the membrane fusion subunit S2. The two significant areas in s1, N-terminal domain (NTD) and the c-terminal domain (CTD), have been identified. The S1 NTDs are essential for binding to the sugar receptors, and the s1 CTDs are responsible for binding receptors ACE2, SPN, and DPP4 [ 57 ]. The S proteins undergo a considerable structural rearrangement to fuse with the viral membrane of the host cell membrane. The s1 subunit shedding and the s2 subunit transition to a highly stable conformation is the initial step in the fusion process [ 58 ]. The ACE2 consists of the N-terminal peptidase domain (NPD) and the C-terminal collectrin-like domain (CCTD) that ends with a single transmembrane helix and a 40 residue intracellular segment. It provides a direct binding site for S protein of CoVs.
The enzymes which assist this virus attachment include the serine protease enzymes TMPRSS2. These enzymes, which are cell-surface proteases, facilitate entry. In endosomes, the S1 of s proteins is cleaved, and the fusion peptides S2 are exposed. This exposed S2 unit brings the HR1 and HR2 together, resulting in membrane fusion and thereby release of viral package into the host membrane [ 59 ].
The viral RNA enters the nucleus for replication after the viral contents are released. Viral mRNA is used to make viral proteins. Decreased expression of ACE2 in a host cell results in an attack on the airway epithelium by the virus. These lead to acute lung injury that triggers immune responses. The release of various pro-inflammatory and chemokines like IL-6, IFN- gamma, MCPI 1, and IL-10 leads to capillary permeability in alveolar sacs. Due to local inflammation in the lungs, the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines increases into the blood circulation of the patient. It results in fluid filling and increased difficulty in the exchange of gases across the membrane. Viral replication and infection in airway epithelial cells could cause high levels of virus-linked pyroptosis with associated vascular leakage. IL-beta cytokine released during pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of programmed cell death, which is the trigger subsequent inflammatory response. The IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 N protein can be detected in the serum in the early stages at the onset of the disease. The non-neutralizing antibodies result in ADE (antibody-dependent enhancement), which leads to an increased systematic inflammatory response.
The pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are an indicator of T H cells. Secretions from such cytokines and chemokines attract immune cell monocytes and T lymphocytes. High levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-2, IL-7, IL-10, IP-10, G-CSF, MCP-1, MIP-1A, and TNF alpha, were detected in the severe infection called cytokine storm or cytokine release syndrome as a crucial factor in the pathogenesis of COVID-19.
The cytokine storm increases the inflammatory response resulting in increased blood plasma levels of neutrophils IL-6, IL-10, granulocytes, MCP1, TNF, and decreased organ perfusion, which results in multiple organ failure. Cytokine storm and pulmonary edema due to ACE2 dysregulation result in acute respiratory distress syndrome. SARS-CoV-2 can also affect the CNS [ 60 ]. Myocardial damage increases the difficulty and complexity of patient treatment [ 61 ]. Clinical investigations have shown that patients with cardiac diseases, hypertension, or diabetes, who are treated with ACE2-increasing drugs, including inhibitors and blockers, are at higher risk of getting infected with SARS-CoV2 [ 62 ]. Death results due to ARDS and multiple organ failure.
People with COVID-19 infection show symptoms ranging from mild to severe illness. Figure Figure6 6 shows a brief outline of various symptoms related to COVID-19. The warning signs and symptoms such as trouble breathing, constant pain or pressure in the chest, inability to wake or stay awake, and bluish lips or face are observed in patients [ 63 ]. Older people (65 years and older) are at higher risk of developing the disease.

Symptoms for coronavirus
According to a study, people of all ages having asthma, diabetes, HIV, liver diseases, severe heart conditions, severe obesity (body mass index [BMI] of 40 or higher), and chronic kidney diseases undergoing dialysis show a higher mortality rate. The other populations with people showing disabilities, pregnancy, and breastfeeding and people experiencing homelessness, racial, and minority groups are at elevated risk of transmission of disease [ 64 ]. The crucial fact to know about coronavirus on surfaces is that they can easily be cleaned with ordinary household disinfectants that will kill the virus [ 65 ]. Studies have shown (Fig. (Fig.7) 7 ) that the COVID-19 virus can survive for up to 72 h on plastic and stainless steel, about 4 h on copper, and less than 24 h on cardboard [ 66 ].

Survival of virus on various objects
Diagnosis: COVID-19
There are two categories of tests available for COVID-19:
- Viral tests: a viral analysis indicates whether a person has a current infection.
- Antibody tests: an antibody indicates whether a person had an infection.
The protection of getting infected again in a person showing the presence of antibodies to the virus is still unexplained [ 67 ].
Tests for current infection
A swab sample is collected (from the nose) to conclude that a person is currently infected with SARS-CoV-2. Some tests are called as point-of-care tests, which means their results may be available in less than an hour. Other test takes 1–2 days for analyzing after being received by the laboratory [ 68 ].
Test for past infection
Antibody tests analyze a blood sample for the presence of antibodies, which show if one had a previous infection with the virus. Antibody tests cannot be used to diagnose someone as being currently infected with COVID-19. Antibody tests are accessible through healthcare providers and laboratories [ 69 ]. In severe cases, clinical diagnosis is done based on the clinical manifestations of respiratory failure syndrome, increased liver function tests, blood tests indicating leukopenia, and high levels of ferritin. For such, a test for soluble CD-163 (sCD-163), showing the activation of macrophages, was suggested [ 70 ]. Laboratory diagnosis included genomic sequencing, reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and serological methods (such as enzyme-linked immunoassay [ELISA]). Because of the rapidly changing diversity found in the expression of the novel coronavirus, pneumonia became diverse and quickly changed. Other methods used are radiographic images for early observations and evaluation of disease severity [ 71 ].
Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) shows high sensitivity for new SARS cases. The suspected cases must be confirmed by using RT-PCR and other methods (slower methods) of detection such as serology or viral culture, isolation, and identification by electron microscopy, thereby causing a significant increase in the time required for an accurate diagnosis [ 72 ]. The samples are collected from upper and lower respiratory tracts through expectorated sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage, or endotracheal aspirate, which are then assessed by conducting polymerase chain reaction for viral RNA. It is recommended to repeat the test for reevaluation purposes in case of a positive result, and if the test is negative, a strong clinical impression also permits repeat testing [ 73 ].
An alternative diagnostic test to detect the SARS-CoV is mass spectroscopic identification of microbial nucleic acid signatures. Computed tomography images of the lungs showed 100% multiple patchy with fine mesh and consolidated shade distributed under the pleura. Nucleic acid tests were conducted in 187 patients, and all were positive to SARS-CoV-2. In the pulmonary CT images, 8% of them (15 cases) showed diffused lesions in either lungs or white lung. In the absorptive period, 98.9% showed fibrogenesis and diminished lesions. The CT imaging features differed from each follow-up showing different clinical symptoms [ 74 ]. The improvement in the detection of COVID-19 was found by the ELISA method. It is based on SARS r-CoV Rp3 nucleocapsid protein, which helps to detect the IgM and IgG against SARS-CoV-2. ELISA is a highly recommended method as the sampling blood is less stringent, and antibodies allow longer windows than oropharyngeal swabs for detecting viruses [ 75 ].
There is no particular treatment recommended for COVID-19. There is no data obtained regarding prophylactic treatment for COVID-19, only we can prevent from coming in contact with the pathogen. Confirmed cases are hospitalized and admitted in the same ward. Patients with mild symptoms may not require hospitalization [ 76 ]. They are isolated or self-isolated at home by following the doctor’s advice. Critically ill patients (respiratory shock, respiratory failure, septic shock, or other organ failures) should be admitted to ICU as soon as possible [ 77 ].
General treatment
The general treatment includes bed rest and supportive measures ensuring sufficient intake of calories, fluid, and electrolytes, and maintenance of acid-base homeostasis. Monitoring oxygen saturation and vital signs, keeping the respiratory tract unobstructed and inhaling oxygen, measuring C-reactive protein, hematology and biochemistry laboratory testing and ECG, blood gas analysis, and examining of chest images as when required and monitoring for any complications [ 78 ]. Patients having high body temperature above 38.5°C Celsius are administered with ibuprofen and acetaminophen orally.
Oxygen therapy
Patients with conditions of obstructed breathing, respiratory distress, shock, coma, and convulsions must receive oxygen therapy and airway management, targeting SpO2 more significant than 94%. Initiate O 2 treatment at 5 L/min and titrated to reach the target or use a face mask with a reservoir bag (10–15 L/min) if the patients are in critical condition.
Once stable, the target is 90% SpO2 in non-pregnant adults and 95% in pregnant adults. The use of nasal prongs or nasal cannula is preferred in young children, as they may be better tolerated. When oxygen therapy fails, mechanical ventilation is necessary. In a meta-analysis, the use of additional oxygen therapy (38.9%), non-invasive (7.1%) and invasive ventilation (28.7%), and even ECMO (0.9%) was surprisingly high among the 1876 patients in which any kind of pharmacological and supportive intervention was reported [ 79 ].
Antiviral agents
Remdesivir inhibits virus infection at the micromolar level (0.77–1.13 μM) and with high selectivity [ 80 ]. Remdesivir gets incorporated into viral RNA due to its adenosine analog nature and results in premature chain termination [ 81 ]. Remdesivir is not approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is only recommended for mild or moderate COVID-19 conditions and the treatment of hospitalized adults and children in emergencies.
Chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine
Chloroquine increases endosomal pH, making the environment unfavorable for viral cell fusion. It also affects the glycosylation process of ACE-2. On administering chloroquine after 1 h of infection, gradual loss of antiviral activity was seen, though it affects the endosome fusion when administered shortly after the infection. When administered after 3–5 h after the infection, chloroquine was significantly effective against HCoV strain OC43 [ 82 ]. There is an excessive risk of toxicities due to high chloroquine doses; the recommended dose for chloroquine is 600 mg twice daily for 10 days for the treatment of COVID-19.
Interferon–alpha
Interferon-α is used in treating bronchiolitis; viral pneumonia; acute upper respiratory tract infection; hand, foot, and mouth disease; SARS; and other viral infections in children. According to the clinical research and experiences, the following usage is recommended for COVID-19
- Interferon-α nebulization: interferon-α 200,000–400,000 IU/kg or 2–4 μg/kg in 2 mL sterile water, nebulization two times per day for 5–7 days
- Interferon-α2b spray: applied for high-risk populations with close contact with suspected COVID-19 infected patients or those in the early phase with only upper respiratory tract symptoms.
Lopinavir/ritonavir
In a clinical trial among adult patients of or less than 18 years, it was observed that a combination of lopinavir/ritonavir, ribavirin, and interferon beta-1b would speed up the recovery, suppress the viral load, shorten hospitalization, and reduce mortality compared with lopinavir/ritonavir [ 83 ].
Immune-based therapy
Patients who show an inadequate response to initial therapy can get benefit from immunoglobulin [ 84 ]. Non-SARS-CoV-2-specific IVIG should not be used for COVID-19 except in case of clinical trials.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are widely used in the symptomatic treatment of severe pneumonia. According to a detailed review and analysis, the result indicates that patients with severe conditions required corticosteroid therapy [ 85 ]. According to a systematic review of literature, daily use of corticosteroids in a COVID-19 patient is not encouraged; however, some studies suggest that methylprednisolone can reduce the mortality rate in more severe conditions, such as in ARDS [ 86 ].
Antimicrobial therapy
Patients with a mild type of bacterial infection can take oral antibiotics, such as cephalosporin or fluoroquinolones. Although a patient may be a suspect for COVID-19, appropriate antimicrobial agent should be administered within an hour of recognition of sepsis. Antibiotic therapy should be based on the clinical diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia, healthcare-associated pneumonia, local epidemiology, susceptibility data, and national treatment guidelines. When there is the ongoing local circulation of seasonal influenza, this therapy with a neuraminidase inhibitor should be considered for the treatment for patients [ 87 ].
Tocilizumab
According to a review, 25 patients with laboratory-confirmed severe COVID-19 who received tocilizumab and completed 14 days of follow-up, 36% were discharged alive from the intensive care unit, and 12% died [ 88 ]. The biopsy specimen analysis suggested that increased alveolar exudates resulted from an immune response against an inflammatory cytokine storm. Probably an obstruction in alveolar gas exchange contributed to the high mortality rate of severe COVID-19 patients. A study identified that pathogenic T cells and inflammatory monocytes arouse an inflammatory storm with a large amount of interleukin 6. Tocilizumab blocks IL-6 receptors, which shows encouraging clinical results, including controlling temperature quickly and improved respiratory functions. Henceforth, tocilizumab is useful in the treatment of severe COVID-19 patients to calm the inflammatory storm and reduce mortality [ 89 ].
FDA-approved drug ivermectin for parasitic infection has a possibility for reprocessing and acts as an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. A single therapy can affect approximately 500-fold reduction and effectual loss of substantially all viral material by 48 h [ 90 ]. A single of ivermectin, in combination with doxycycline, yielded the near-miraculous result in curing the patients with COVID-19 virtually.
Azithromycin
Azithromycin is used for patients with viral pneumonia from COVID-19. It can also work synergistically and coactively with other antiviral treatments. It has also shown antiviral activity against the Zika virus and rhinoviruses, which cause the common cold. Viral infection was significantly reduced in patients receiving hydroxychloroquine than those who did not. The virus elimination was efficient in patients who received both azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine [ 91 ]. (Table (Table5) 5 ) lists other supporting agents used in treatment [ 92 ].
Supporting agents used in treatment
| Antiviral agents | Supporting agents | Others |
|---|---|---|
• Baloxavir • Chloroquine phosphate • Favipiravir • HIV protease inhibitors • Hydroxychloroquine • Neuraminidase inhibitor • Remdesivir • Umifenovir | • Anakinra • Azithromycin • Baricitinib (Olumiant®) • Colchicine • Corticosteroids (general) • COVID-19 • Convalescent plasma • Epoprostenol (inhaled) • Methylprednisolone (DEPO-Medrol®, SOLU-Medrol®) • Nitric oxide (inhaled) • Ruxolitinib (Jakafi®) • Sarilumab (Kefzara®) • Siltuximab (Sylvant®) • Sirolimus (Rapamune®) • Tocilizumab (Actemra®) | • ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) • Anticoagulants (low molecular weight heparin [LMWH], unfractionated heparin [UFH]) • Famotidine • HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) • Immune globulin (IGIV, IVIG, γ-globulin) • Ivermectin • Nebulized drugs • Niclosamide • Nitazoxanide • Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIDs) • Tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA; alteplase) |
The repurposing of available therapeutic drugs is being used as supporting agents in the treatment of COVID-19; however, the efficacy of these treatments should be verified by using designed clinical trials
Precautions and preventions
WHO declared the COVID-19 outbreak as a public health emergency of international concern on 30 January 2020. Unfortunately, no medication until now is approved by the FDA, and various trials are going on. Still, the most effective weapon the community has in hand is the prevention of spread. The following are some of the COVID-19 prevention measures.
- Quarantine: self-quarantine, mandatory quarantine (private residence, hospital, public institution, etc.)
- Other measures: avoiding crowding, hand hygiene, isolation, personal protective equipment, school/workplace measures/closures, social distancing [ 93 ].
Asymptomatic carriers as the “silent spreaders” are of great concern for the elimination of disease and its control. So, more attention should be given to them [ 94 ]. Hand hygiene with alcohol-based hand-rub is globally recommended as productive and economical procedures against SARS-CoV-2 cross-transmission [ 95 ]. The economic implications of hand hygiene have been established. It has been found that this cost under 1% of total HAI-related economics. It is better to invest not only in the materials needed but also in the people working there. This investment will lead to an increase in the health outcome [ 96 ]. The clinical presentation of COVID-19 is non-specific, so it needs a robust and accurate diagnosis. It has been suggested that before stopping the infection control measures, we have to be sure to exclude the diagnosis [ 97 ]. Prevention plays a vital role in treating and defeating the COVID-19 disaster.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention gives standard precautions (Fig. (Fig.8) 8 ) and recommends measures to prevent COVID-19. Wear personnel protective equipment (face shield, mask, gown, gloves, and closed-toed shoes) when evaluating persons at risk. N-95 masks are known to prevent up to 95% of small particles, including viruses [ 98 ]. Cover all coughs/sneezes with a tissue and then throw the tissue away. Regularly clean/disinfect frequently touched objects and surfaces with household cleaning spray and use a tissue when handling (e.g., doorknobs, sink taps, water fountain handles, elevator buttons, cross-walk buttons, and shopping carts). Avoid contact with infected people (recommended > 6 ft) and maintain an appropriate distance as much as possible and refrain from touching nose eyes and mouth [ 99 ]. Avoid well persons when you are ill. Wear a mask continuously if taking care of persons with respiratory illness. To turn on the tap, use a paper towel and then wash hands with soap and water for at least 30 s after going to the bathroom. Use hand sanitizer and carry whenever at a public venue. Activate community-based interventions (e.g., cancel sporting events, dismiss, termination of universities and schools, practice social distancing, create employee plans to work remotely) [ 100 ]. Create a household-ready plan. Cancel any non-essential travel [ 101 ]. Frequent disinfection and cleaning are advised for groups that are at risk of contracting the virus [ 102 ].

Prevention and precaution
In an Indian study mathematical approach was used to address some questions related to intervention strategies to control the COVID-19 transmission in India. Some hypothetical epidemic curves helped to illustrate the critical findings [ 103 ]. Predication of spread and implications of prevention and control using the Maximum-Hasting (MH) parameter assessment method and the modified Susceptible Exposed Infectious Recovered (SEIR) model was done. Suppression, mitigation, and mildness were the three predicted outlines for the spread of infection in some African countries [ 104 ].
Infection control strategies that can be acquired in hospitals were accomplished in a Taiwanese hospital to tackle the COVID-19 pandemic. These included emergency vigilance and responses from the hospital administration, education, surveillance, patient flow arrangement, the partition of hospital zones, and the prevention of a systemic shutdown by using the “divided cabin, divided flow” strategy. These measures may not be universally appropriate [ 105 ]. The preventive measures implemented in China included countrywide health education campaigns. The Examine and Approve Policy on the continuation of work, working and living quarters, a health Quick Response code system, community screening, and social distancing policies were some of the preventive measures [ 106 ].
Based on the analysis of immigration population data, the Epidemic Risk Time Series Model was outlined to estimate the effectiveness of COVID-19 epidemic control and prevention among different regions in China. Compared to other methods, this model was able to issue early recognition more instantaneously. For the prevention and control of COVID-19, this model can be generalized and applied to other countries [ 107 ]. The majority of clinical trials involving COVID-19 vaccines or treatment are showing encouraging results. (Tables (Tables6 6 and and7) 7 ) show ongoing phase 3 and 4 clinical trials [ 108 ].
Ongoing clinical trials phase 3 studies
| Study title | Conditions | Interventions | Locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Randomized evaluation of COVID-19 therapy | Severe acute respiratory syndrome | Drugs: hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir, corticosteroid, azithromycin, tocilizumab | Nuffield Department of Population Health, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK |
| Hydroxychloroquine and zinc with either azithromycin or doxycycline for treatment of COVID-19 in outpatient setting | COVID-19 | Drugs: hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, zinc sulfate, doxycycline | St. Francis Hospital, Roslyn, NY, USA |
| Favipiravir in hospitalized COVID-19 patients | COVID-19 | Drugs: favipiravir, hydroxychloroquine | Shahid Modarres Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Tehran, Iran |
| Baricitinib therapy in COVID-19 | COVID-19 pneumonia | Drug: baricitinib 4 mg oral tablet | Fabrizio Cantini, Prato, Tuscany, Italy |
| Treatment for COVID-19 in high-risk adult outpatients | COVID-19 SARS-CoV-2 | Drugs: ascorbic acid, hydroxychloroquine sulfate, azithromycin, folic acid | • Boston University, Boston, MA, USA • University of Washington Coordinating Center, Seattle, Washington, USA • UW Virology Research Clinic, Seattle, WA, USA and 4 more |
| Convalescent plasma for hospitalized adults with COVID-19 respiratory illness (CONCOR-1) | COVID-19 | Other: convalescent plasma | • Vancouver General Hospital, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada • Victoria General Hospital, Victoria, British Columbia, Canada • London Health Sciences Centre—University Hospital, London, Ontario, Canada and 25 more |
| BCG vaccine for health care workers as defense against COVID-19 | Coronavirus infection, Coronavirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere | Biologicals: BCG vaccine, placebo vaccine | • Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA • Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA • MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA and 4 more |
| Outcomes related to COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine among in-patients with symptomatic disease | Coronavirus acute respiratory infection -SARS-CoV infection | • Drugs: hydroxychloroquine, placebo | • Stanford University, Stanford, CA, USA • University of Colorado Hospital, Aurora, CO, USA • Denver Health Medical Center, Denver, CO, USA and 40 more |
| Treatment of COVID-19 patients with anti-interleukin drugs | COVID-19 | • Other: usual care • Drugs: anakinra, siltuximab, tocilizumab | • University Hospital Saint-Pierre, Brussels, Belgium • University Hospital Antwerp, Edegem, Belgium • University Hospital Brussels, Jette, Belgium 13 more |
| Study to evaluate the safety and antiviral activity of remdesivir (GS-5734™) in participants with severe coronavirus disease (COVID-19) | COVID-19 | Drug: remdesivir | • Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Center, 3340 E. La Palma Avenue, Anaheim, CA, USA • Alta Bates Summit Medical Center, Berkeley, CA, USA • Mills-Peninsula Medical Center, Burlingame, CA, USA and180 more |
Ongoing clinical trials, phase 4 studies
| Study title | Conditions | Interventions | Locations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of Ganovo (danoprevir) combined with ritonavir in the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection | COVID-19 | Drug: Ganovo + ritonavir/interferon nebulization | • The Ninth Hospital of Nanchang, Nanchang, Jiangxi, China |
| The use of tocilizumab in the management of patients who have severe COVID-19 with suspected pulmonary hyper inflammation | COVID-19 pneumonia | Drug: tocilizumab | • Hadassah Medical Orginisation, Jerusalem, Israel • Barzilai Medical Center, Ashkelon, Israel • Wolfson Medical Center, Holon, Israel • Sheba Medical Center, Ramat Gan, Israel |
| Fluoxetine to reduce intubation and death after COVID19 infection | COVID-19 cytokine storm | Drug: fluoxetine | University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA |
| Hydroxychloroquine and zinc with either azithromycin or doxycycline for treatment of COVID-19 in outpatient setting | COVID-19 | Drug: hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin, zinc sulfate, doxycycline | St Francis Hospital, Roslyn, NY, USA |
| Favipiravir in hospitalized COVID-19 patients | COVID-19 | Drug: favipiravir, hydroxychloroquine | Shahid Modarres Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Tehran, Iran |
| Azithromycin in hospitalized COVID-19 patients | COVID-19 | Drug: hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin | Shahid Modarres Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Tehran, Iran, Islamic Republic of |
| Prophylaxis of exposed COVID-19 individuals with mild symptoms using chloroquine compounds | • SARS-CoV2 • Symptomatic condition • COVID-19 | • Drug: hydroxychloroquine sulfate regular dose, hydroxychloroquine sulfate loading dose, chloroquine, placebo | • Expo COVID Isolation Center/Mayo Hospital Field Hospital, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan • Mayo Hospital/King Edward Medical University, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan • Pakistan Kidney and Liver Institute, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan |
| BCG vaccine for health care workers as defense against COVID 19 | • Coronavirus • Coronavirus infection • Coronavirus as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere | • Biological: BCG vaccine • Biological: placebo vaccine | • Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA • Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA • Texas A&M Family Care Clinic, Bryan, TX, USA and 4 more |
| Hydroxychloroquine in patients with newly diagnosed COVID-19 compared to standard of care | • COVID-19 • Coronavirus Infection • SARS-CoV-2 • 2019-nCoV • 2019 novel coronavirus | • Drug: hydroxychloroquine • Dietary supplement: vitamin C | Portland Providence Medical Center, Portland, OR, USA |
| Efficacy of dexamethasone treatment for patients with ARDS caused by COVID-19 | Acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by COVID-19 | • Drug: dexamethasone | • ICU, Hospital Universitari Mutua Terrassa, Terrassa, Barcelona, Spain • Hospital Universitario Dr. Negrin, Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Las Palmas, Spain • Department of Anesthesia, Hospital Universitario de Cruces, Barakaldo, Vizcaya, Spain and 21 more |
Impact of COVID-19 on overall health of the people worldwide
The international response to COVID-19 has been more transparent and efficient when compared to the SARS outbreak [ 109 ].
The pandemic COVID-19, being a most severe strainer, is affecting the overall health system worldwide. There is a continuously increasing demand for healthcare facilities and associated workers, which is overstretching the ability to operate efficiently [ 110 ]. Some pieces of evidence are showing a destructive effect on maternal and child health. Some financial, educational, sanitation, and even clinical constraints are threatening the overall population of the children [ 111 ]. As coronavirus is sweeping across the world, the primary psychological impact is elevated in terms of stress and anxiety. The quarantine period is expected to raise cases involving suicidal behavior, substance abuse, self-harm, depression, and loneliness. WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance use has given some messages to overcome psychological impacts [ 112 ]. There is a relationship between human development and infectious diseases. Whichever changes (new technology, constructions of dams, deforestations, migration, increasing populations, the emergence of urban ghettoes, globalization of food, and increasing international travel) brought about by the development, are stretching the word into the mouth of such pandemics indirectly. This pandemic is having a significant impact on the global economy as the erosion of capacity and rise in poverty [ 113 , 114 ].
COVID-19 has affected the population differently based on gender. Significantly, this crisis is affecting the reproductive and sexual health of women. Another point is that there should be an equal contribution to both the genders in any healthcare body. There should be more distribution of decision-making power among them [ 115 ]. Protective measures can effectively prevent COVID-19 infection, including improving personal hygiene, wearing N95 masks, adequate rest, and proper ventilation [ 116 ].
Have to learn to live with COVID-19
The Health Ministry has said that we have to learn to survive with COVID-19. We cannot step ahead by carrying the burden of COVID-19 that could recur annually and kill so many people [ 117 ]. Governments are learning to strike a balance between controlling COVID-19 spread and allowing individual freedoms and economic activity. Measures such as lockdowns, arbitrary travel bans, widespread quarantines, intrusive screening of people crossing boundaries can be adopted for prevention. Virtual work will become much more common. Supplier close-downs, sudden employee truancy, and demand collapse caused by disease outbreaks will make the businesses able to withstand disruptions.
The government, industry, or specialist certification for disease control processes and standards similar to ISO 9001 or USFDA certificate will be a crucial part of many businesses. The cost of traveling will expand more due to the risk of infection and lockdown. At the same time, the responsibility of work airlines, hotels, and restaurants will be added to minimize infection risk. Delivery businesses will perform well, and “Contactless delivery” is already a thing.
The industries that provide products to help circumvent, control, diminish, or treat COVID-19 will flourish. The requirement for hospital rooms will increase tremendously, with an increasing need for reserves of equipment, supplies, and drugs. In the upcoming time, businesses are likely to face demand crisis as the world comes to terms with living in a state of medical beleaguerment [ 118 ]. It is just a prediction, but we can still aspire for the best [ 119 ]. The most destructive effects would be in countries with weak health systems, on-going disputes, or existing infectious disease epidemics.
In contrast, the health systems in high-income countries would be stretched out by the outbreak [ 120 ]. It has been seen that resources are limited in countries with poor scientific infrastructure, such as Nepal, where there was only one laboratory equipped to test for coronavirus infection. Fear and stigma is an evident feature of the COVID-19; it has affected the economic and social development of many countries worldwide [ 121 ].
The insufficiency of the trained workforce capable of performing experiments required to test for SARS-CoV-2 and interpret the results is another major limitation in the testing and confinement of COVID-19 in developing countries [ 122 ]. The virus has the potential to adapt and get through the different environmental conditions, which makes it quite difficult to identify its mode of survival [ 123 ]. Another crucial impediment in a research project is a suitable model to investigate in vivo mechanism associated with the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 [ 124 – 126 ].
Current screening approaches for COVID-19 are likely to miss approximately 50% of the infected cases, even in countries with sound health systems and available diagnostic capacities. Many symptoms correlated with COVID-19 are similar to malaria, such as fever, difficulty in breathing, fatigue, and headaches of acute onset. If symptoms alone are used to specify a case during the emergency period then, a malaria case may be misinterpreted as COVID-19. The symptoms for malaria are seen within 10–15 days after an infective bite; multi-organ failure is common in severe cases among adults, while respiratory distress is also expected in children [ 127 ].
COVID-19 has emerged as the most terrified and enormous viral infection. According to WHO, the coronavirus might become an endemic disease. Originating from China as a global pandemic, it has influenced people on a large scale. There is no clear end that can be seen for this contagious disease. The only possible cure for this pandemic is prevention. We have to face it as a global community and support each other. The amplification of positivity will have a tremendous impact on the whole society. It is the duty of each individual for self-supervision and to report COVID-19 status, and challenging for those who appear to be ill. The other measure which can be followed to tackle this pandemic is healthy nourishment, sanitation, and hygiene practices robust connection and communication among children, and counseling to face the situation. Special care should be given to older people and pregnant ladies. It is better to get information only from the trusted sources; it is vital to get the facts and not the misinformation or rumors. Healthcare servants should have excellent and accurate communication with the public and must provide emotional and practical support. The ongoing pandemic of COVID-19 has caused not only notable morbidity and mortality in the world but also revealed significant systematic problems in the control and prevention of infectious diseases.
Acknowledgements
The authors express their sincere thanks to Ms. Fatma Rafiq Zakaria, Chairman of Maulana Azad Educational Trust Aurangabad Maharashtra, for her endless encouragement and support and for providing necessary facilities to carry out the above research work.
Abbreviations
| ACE-2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| CoV | Coronavirus |
| COVID-19 | Novel coronavirus infectious disease 2019 |
| MERS-CoV | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| Nsps | non-structural proteins |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| RBD | Receptor-binding domain |
| RTC | Replicase-transcriptase complex |
| SARS-CoV | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Authors’ contributions
All authors participated in the work substantively and have approved the manuscript as submitted. The authors have no conflict of interest in the study. Drafting the article and critical revision of the article was carried out by SSS. Data collection for the formation of graphical abstract and various figures and tables was also contributed from her end. Conception or design of the work was carried out by SKS. He also contributed to the data collection for lifecycle, history, and origin. Data collection for pathogenesis and comparison of CoVs study was carried out by APJ. Data collection for diagnosis and treatment was carried out by MVKV. Data collection for clinical trials was carried out by DAN. Final approval of the version to be published was done by all the authors’ SSS, APJ, DAN, MVKV, and SKS. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript. Each author has agreed with the publication of the manuscript.
No funding was received for this work
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
I, on behalf of all the authors, hereby declare that there is no significant financial, professional, or personal competing interest that might have influenced the performance or presentation of the work described in this manuscript.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Sana Saffiruddin Shaikh, Email: [email protected] .
Anooja P. Jose, Email: moc.liamg@89jpajoona .
Disha Anil Nerkar, Email: moc.liamg@89rakrenahsid .
Midhuna Vijaykumar KV, Email: moc.liamg@12321mvk .
Saquib Khaleel Shaikh, Email: moc.liamg@313biuqasks .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- News & Events
- Speeches by FDA Officials
- Remarks by Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D. — The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned - 06/01/2020
Speech | Virtual
Event Title Remarks by Commissioner Stephen Hahn, M.D. — The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned June 1, 2020
The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned
(Remarks as prepared for delivery. The text and video of this speech are slightly, though not substantively different from the version presented by Dr. Hahn on June 1 to the Alliance for a Stronger FDA, via audio broadcast only. Because of evolving scheduling challenges, it was not clear whether Dr. Hahn would be able to present the speech live and so it was recorded by video earlier. Ultimately, he did give the speech live to the Alliance, but only via an audio link. Given the minimal changes in the live version, we are posting the video version and the accompanying text.)
One of the most frustrating challenges each of us can face is the inability to control the events that affect our lives. Often, we are thrust into situations not of our own making. It’s no surprise that one of the most familiar adages concerns the best laid plans of mice and men going awry.
And yet, to borrow another often-used saying, necessity is the mother of invention. History teaches us that crises often lead to accelerated change and innovations and new discoveries.
This dynamic has been on my mind a great deal recently. It wasn’t too long ago – last December, to be exact -- that I had the distinction of being confirmed as the 24th Commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration.
This is the greatest honor of my life. I have long cherished the critical role the FDA plays in protecting and promoting the public health, and I’ve relied on the Agency’s expertise throughout my professional life.
So, I eagerly embraced my new responsibilities and the chance to make a real difference in public health. I was especially conscious that we live in a time of extraordinary scientific achievement, especially in oncology, with unprecedented opportunities to help make the lives of American patients and consumers healthier and safer.
I quickly immersed myself in the Agency’s broad and complex responsibilities, seizing every opportunity to learn about the FDA, both those areas with which I’d previously had minimum involvement, such as food policy, and those with which I had more familiarity, like cancer treatments and innovative clinical trial design.
I began to work with, and learn from, the agency’s extraordinary leadership team. I learned very quickly that the principles that have guided me throughout my life, such as my commitment to relying only on the best medical science and most rigorous data in support of advancing innovation and discovery, and my fundamental belief in promoting integrity and transparency in the scientific process, are the same principles that guide the FDA in both science and regulation.
So, I was in the midst of transitioning from being Chief Medical Executive at MD Anderson Cancer Center to being Commissioner of FDA when our entire world was turned upside down with the appearance of the novel COVID-19 coronavirus.
I certainly did not anticipate a public health emergency of this magnitude when I joined the agency. And I could not have imagined how significantly my new role would change and be shaped by this pandemic. I definitely could not have known that discussions about personal protective equipment (or PPE) or face masks or nasal swabs would be central to my work as Commissioner.
One thing was apparent: I would need to manage this evolving situation even as I was still learning about FDA.
From the very start I knew that even in a crisis situation – or perhaps especially because we are in a crisis situation – it is imperative that we maintain FDA’s high standards for evaluating products and making sure that the benefits outweigh potential harms.
To maintain our standard, I pledged to myself and emphasized to my new colleagues at FDA that our decisions would always be rooted in science. Having spent my entire career as a physician and scientist caring for patients with cancer, I’ve always valued highly a commitment to good data and sound science. I feel comfortable working with the scientists at FDA because I know they not only share that value, that commitment, but that they will tolerate nothing less. So, it was critical to me, as the pandemic escalated that this be reinforced as the guidepost for all of our decisions.
It may have been trial by fire, but I have the good fortune to work with an enormous number of talented individuals and teams who are helping guide us through this crisis. Every day they show extraordinary expertise, commitment, and resilience.
I also was able to call on many from outside the agency, including former FDA leaders as well as colleagues from the medical community.
What struck me was the uniformity of their advice. Those who formerly worked at FDA urged me to rely upon the FDA staff, many of whom have the experience to help manage a pandemic. My friends from outside the agency urged that we move quickly to make decisions, set direction and to be transparent about what we are doing. I have tried to follow all of this excellent advice.
Protecting the Food Supply
Since this crisis and the actions of the FDA have evolved so rapidly, let me summarize what we have done. I am confident that the FDA has measured up to this unprecedented challenge.
I want to start with the first word in the FDA’s name – food. Most of us take food safety for granted. But it takes a lot of hard work to maintain a safe food supply. This was true even before the COVID-19 pandemic but is especially challenging during an ongoing international crisis.
During the pandemic, through the collaboration of the FDA, the food industry and our federal and state partners, we have been able to maintain the safety of the nation’s food supply. Our Coordinated Outbreak Response and Evaluation team remained on the job, monitoring for signs of foodborne illness outbreaks and prepared to take action when needed.
And along with our federal partners, including CDC and USDA, we also have provided best practices for food workers, industry, and consumers on how to stay safe and keep food safe.
Diagnosing and Developing Treatments
On the medical side, we immediately committed to facilitating efforts to develop diagnostic tests, treatments and vaccines for the disease. We have helped facilitate increases in our national testing capacity, have helped ensure continued access to necessary medical products, and have sought to prevent the sale of fraudulent products.
If there’s one thing that’s been reaffirmed during this crisis, it’s the essential role of medical devices, including diagnostics, to countering this pandemic.
From the earliest days of our response, we worked to ensure that we had the essential medical devices, including personal protective equipment, to help treat those who are ill and to ensure that health care workers and others on the front line are properly protected.
To be sure, there were bumps along the road, but today we have an adequate supply of the devices that have been in unprecedented high demand such as PPE, ventilators, and others.
We’ve reviewed and issued emergency use authorizations for medical devices for COVID-19 at an incredibly fast pace.
And we’ve worked closely with many companies that don’t regularly make medical products but wanted to pitch in by making hand sanitizer, ventilators, or PPE.
There was a special focus on the development and availability of accurate and reliable COVID-19 tests. We need to know who has the disease and who has had it. This is essential if we are to understand this virus and return to a more normal lifestyle.
Since January, we’ve worked with hundreds of test developers, many of whom have submitted emergency use authorization requests to FDA for tests that detect the virus or antibodies to the virus.
As you have seen reported, early in the crisis we provided regulatory flexibility for developers with validated tests as outlined in our policies because public health needs dictated that we do as much testing as possible. But as the process has matured, we have helped increase the number of authorized tests, and we have adapted some of our policies to best serve the public need.
Today, if evidence arises that raises questions about a particular test’s reliability, we will take appropriate action to protect consumers from inaccurate tests. This is a dynamic process that is continually being informed by new data and evidence.
We’ve used a similar dynamic process in the search for therapeutic treatments and vaccines.
We are working closely with partners throughout the government and academia, and with drug and vaccine developers to explore, expedite, and incentivize the development of these products.
More than 90 drugs are being studied, and FDA is actively working with numerous vaccine sponsors, including three sponsors who have announced they have vaccine candidates that are now in clinical trials in the U.S. More than 144 clinical trials have been initiated for therapeutic agents, with hundreds more in the pipeline. We don’t have a cure or vaccine yet, but we’re on our way, at unprecedented speed.
Ultimately, of course, the way we’ll eventually defeat this virus is with a vaccine. FDA is working closely to provide technical assistance to federal partners, vaccine developers, researchers, manufacturers, and experts across the globe and exploring all possible options to advance the most efficient and timely development of vaccines, while at the same time maintaining regulatory independence.
Communicating and Educating
There is much more to do going forward, and that includes research, exploration and discovery, and communicating what we know.
As the country starts to reopen, it’s essential that the public understands what they need to do to continue to protect themselves. There has been a proliferation of information, and misinformation, on the internet and in other sources. Consumers need to understand that this virus is still with us and that we, as individuals and communities working together, need to take steps to continue to contain its spread.
The FDA has an important part to play in communicating public information to all populations in the U.S. FDA has increased outreach by developing and disseminating COVID-19 health education materials for consumers in multiple languages to diverse communities and the public overall. Everyone should have a clear understanding of why hand-washing and social distancing remain essential. Consumers need to think about how to shop for food safely. People need to know when to call their doctors and when to ask about getting tested. Health care professionals need to know how to manage their patients in this new environment, and how best to apply telemedicine, the use of which is rapidly accelerating.
I want the FDA to serve as a national resource for the public and health care community. I regard educating the public and providing accurate, reliable, up-to-date information as not just an Agency priority, but one of my own personal responsibilities as Commissioner. I will be out in public and in the media talking about how individuals can help us contain and conquer this virus.
I believe my personal experience with being self-quarantined will make me a better communicator. Being quarantined for 14 days in May was certainly no fun, but because we at FDA were already functioning very effectively virtually, I was able to continue to be fully engaged, and provide direction and leadership. And it made me even more focused on making sure consumers have all the information they need about self-protection.
We now need to look forward. A major strength of the FDA is not just in our response to a crisis, but in our ability to learn from the work we do and apply that experience in the future.
As this pandemic evolved, it was clear that some FDA processes needed to be adjusted to accommodate the urgency of the pandemic. I think the entire FDA team has now seen first-hand that we need to look at some of our processes and policies. I have instructed my staff to identify the lessons learned from this pandemic and what adjustments may be needed, not just to manage this or future emergencies, but to make FDA itself more efficient in carrying out our regulatory responsibilities.
I am committed to making sure that some of the lessons learned from managing this pandemic will lead to permanent improvements at the FDA in processes and policies.
For example, in facilitating the development of new treatments, we streamlined some of our processes.
We have taken a fresh look at how clinical trials should be designed and conducted. In a pandemic we knew we needed to get answers more quickly. For instance, early on, the FDA, National Institutes of Health, and industry worked together to facilitate the implementation of a “master protocol” that can be used in multiple clinical trials and allows for the study of more than one promising new drug for COVID-19 at a time. And we have used expanded access to meet the needs of patients who are not eligible or who are unable to participate in randomized clinical trials.
Many of the permanent changes that we will implement really represent an acceleration of where we were headed before. For example, the concept of decentralized clinical trials, in which trial procedures are conducted near the patient’s home and through use of local health care providers or local laboratories has been discussed before, and laid the foundation for some of the trials for COVID-19 products.
Another area where our pre-COVID work has informed our response to the pandemic involves the use of Real World Evidence (RWE).
In recent years, the agency has taken steps to leverage modern, rigorous analyses of real-world data—such as data from electronic health records, insurance claims, patient registries and lab results.
As the pandemic brought an urgency to these efforts, the FDA advanced collaborations with public and private partners to collect and analyze a variety of real-world data sources, using our Sentinel system and other resources.
Evaluation of real-world data has the potential to provide a wealth of rapid, actionable information to better understand disease symptoms, describe and measure immunity, and use available medical product supplies to help mitigate potential shortages. These data can also inform ongoing work to evaluate potential therapies, vaccines or diagnostics for COVID-19. The more experience we have with real world evidence, the more confidence we will have in using it for product decisions.
I mention real world evidence, but in reality, we have so many examples of how lessons learned from the pandemic will affect FDA in the future.
To the extent that the innovations and adaptations we implemented during the pandemic crisis worked and would be appropriate to implement outside of a pandemic situation, we will incorporate them into standard FDA procedures. And to the extent that we identified unnecessary barriers, we will remove them. This is one of my top priorities. Permanent change where needed will take place, and will make FDA an even stronger agency.
As I mentioned before, anything that enables quicker reviews and authorizations we will seek to make permanent.
But make no mistake. We will not cut corners on safety or effectiveness. I said this before, and I say it again. Good science as the basis for decision making has been a hallmark of my career, and is a value that I hold deeply. The American public must have confidence in the products regulated by the FDA.
Speed is important, but so are safety, accuracy and effectiveness.
FDA’s commitment to good science and rigorous data is unwavering, even as we look at how we can learn from this pandemic.
I am hopeful that this is a once-in-a-lifetime experience for all of us. An unprecedented historic event that has required an unprecedented response from us and everyone around the world.
That said, I am pleased that throughout this crisis the rest of the FDA’s work has continued, with relatively few interruptions. New drugs and devices have been authorized. Our food safety surveillance has adapted and our outbreak response resources have been maintained. Our oversight of tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, has gone on. The Agency has measured up to the challenge in all ways.
And we are well positioned as we move into a new phase, that is, transitioning back to what has come to be known as the “new normal.” Our staff has done a phenomenal job of adapting to this new normal. And I am confident that they are ready to deal with any additional upcoming challenges.
I will close with something I’ve seen reaffirmed time and time again over the past few months. That is the essential role that the FDA plays in consumer protection and beyond in advancing public health.
Before coming to the FDA, I had heard about the extraordinary dedication of the agency’s workforce. Working side by side with my colleagues in response to this pandemic, I’ve seen that characterization validated over and over.
It is my great honor to serve with so many highly skilled and committed professionals. And the American people can be assured that this agency is working around the clock for them, doing whatever is necessary to fulfill our mission to protect and promote the health of the American public.
I encourage you all to stay safe, aware, and focused as we continue to respond to the challenges of this public health emergency.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Remarks by President Biden on Fighting the COVID- 19 Pandemic
5:02 P.M. EDT THE PRESIDENT: Good evening, my fellow Americans. I want to talk to you about where we are in the battle against COVID-19, the progress we’ve made, and the work we have left to do. And it starts with understanding this: Even as the Delta variant 19 [sic] has — COVID-19 — has been hitting this country hard, we have the tools to combat the virus, if we can come together as a country and use those tools. If we raise our vaccination rate, protect ourselves and others with masking and expanded testing, and identify people who are infected, we can and we will turn the tide on COVID-19. It will take a lot of hard work, and it’s going to take some time. Many of us are frustrated with the nearly 80 million Americans who are still not vaccinated, even though the vaccine is safe, effective, and free. You might be confused about what is true and what is false about COVID-19. So before I outline the new steps to fight COVID-19 that I’m going to be announcing tonight, let me give you some clear information about where we stand. First, we have cons- — we have made considerable progress in battling COVID-19. When I became President, about 2 million Americans were fully vaccinated. Today, over 175 million Americans have that protection. Before I took office, we hadn’t ordered enough vaccine for every American. Just weeks in office, we did. The week before I took office, on January 20th of this year, over 25,000 Americans died that week from COVID-19. Last week, that grim weekly toll was down 70 percent. And in the three months before I took office, our economy was faltering, creating just 50,000 jobs a month. We’re now averaging 700,000 new jobs a month in the past three months. This progress is real. But while America is in much better shape than it was seven months ago when I took office, I need to tell you a second fact. We’re in a tough stretch, and it could last for a while. The highly contagious Delta variant that I began to warn America about back in July spread in late summer like it did in other countries before us. While the vaccines provide strong protections for the vaccinated, we read about, we hear about, and we see the stories of hospitalized people, people on their death beds, among the unvaccinated over these past few weeks. This is a pandemic of the unvaccinated. And it’s caused by the fact that despite America having an unprecedented and successful vaccination program, despite the fact that for almost five months free vaccines have been available in 80,000 different locations, we still have nearly 80 million Americans who have failed to get the shot. And to make matters worse, there are elected officials actively working to undermine the fight against COVID-19. Instead of encouraging people to get vaccinated and mask up, they’re ordering mobile morgues for the unvaccinated dying from COVID in their communities. This is totally unacceptable. Third, if you wonder how all this adds up, here’s the math: The vast majority of Americans are doing the right thing. Nearly three quarters of the eligible have gotten at least one shot, but one quarter has not gotten any. That’s nearly 80 million Americans not vaccinated. And in a country as large as ours, that’s 25 percent minority. That 25 percent can cause a lot of damage — and they are. The unvaccinated overcrowd our hospitals, are overrunning the emergency rooms and intensive care units, leaving no room for someone with a heart attack, or pancreitis [pancreatitis], or cancer. And fourth, I want to emphasize that the vaccines provide very strong protection from severe illness from COVID-19. I know there’s a lot of confusion and misinformation. But the world’s leading scientists confirm that if you are fully vaccinated, your risk of severe illness from COVID-19 is very low. In fact, based on available data from the summer, only one of out of every 160,000 fully vaccinated Americans was hospitalized for COVID per day. These are the facts. So here’s where we stand: The path ahead, even with the Delta variant, is not nearly as bad as last winter. But what makes it incredibly more frustrating is that we have the tools to combat COVID-19, and a distinct minority of Americans –supported by a distinct minority of elected officials — are keeping us from turning the corner. These pandemic politics, as I refer to, are making people sick, causing unvaccinated people to die. We cannot allow these actions to stand in the way of protecting the large majority of Americans who have done their part and want to get back to life as normal. As your President, I’m announcing tonight a new plan to require more Americans to be vaccinated, to combat those blocking public health. My plan also increases testing, protects our economy, and will make our kids safer in schools. It consists of six broad areas of action and many specific measures in each that — and each of those actions that you can read more about at WhiteHouse.gov. WhiteHouse.gov. The measures — these are going to take time to have full impact. But if we implement them, I believe and the scientists indicate, that in the months ahead we can reduce the number of unvaccinated Americans, decrease hospitalizations and deaths, and allow our children to go to school safely and keep our economy strong by keeping businesses open. First, we must increase vaccinations among the unvaccinated with new vaccination requirements. Of the nearly 80 million eligible Americans who have not gotten vaccinated, many said they were waiting for approval from the Food and Drug Administration — the FDA. Well, last month, the FDA granted that approval. So, the time for waiting is over. This summer, we made progress through the combination of vaccine requirements and incentives, as well as the FDA approval. Four million more people got their first shot in August than they did in July. But we need to do more. This is not about freedom or personal choice. It’s about protecting yourself and those around you — the people you work with, the people you care about, the people you love. My job as President is to protect all Americans. So, tonight, I’m announcing that the Department of Labor is developing an emergency rule to require all employers with 100 or more employees, that together employ over 80 million workers, to ensure their workforces are fully vaccinated or show a negative test at least once a week. Some of the biggest companies are already requiring this: United Airlines, Disney, Tysons Food, and even Fox News. The bottom line: We’re going to protect vaccinated workers from unvaccinated co-workers. We’re going to reduce the spread of COVID-19 by increasing the share of the workforce that is vaccinated in businesses all across America. My plan will extend the vaccination requirements that I previously issued in the healthcare field. Already, I’ve announced, we’ll be requiring vaccinations that all nursing home workers who treat patients on Medicare and Medicaid, because I have that federal authority. Tonight, I’m using that same authority to expand that to cover those who work in hospitals, home healthcare facilities, or other medical facilities –- a total of 17 million healthcare workers. If you’re seeking care at a health facility, you should be able to know that the people treating you are vaccinated. Simple. Straightforward. Period. Next, I will sign an executive order that will now require all executive branch federal employees to be vaccinated — all. And I’ve signed another executive order that will require federal contractors to do the same. If you want to work with the federal government and do business with us, get vaccinated. If you want to do business with the federal government, vaccinate your workforce. And tonight, I’m removing one of the last remaining obstacles that make it difficult for you to get vaccinated. The Department of Labor will require employers with 100 or more workers to give those workers paid time off to get vaccinated. No one should lose pay in order to get vaccinated or take a loved one to get vaccinated. Today, in total, the vaccine requirements in my plan will affect about 100 million Americans –- two thirds of all workers. And for other sectors, I issue this appeal: To those of you running large entertainment venues — from sports arenas to concert venues to movie theaters — please require folks to get vaccinated or show a negative test as a condition of entry. And to the nation’s family physicians, pediatricians, GPs — general practitioners –- you’re the most trusted medical voice to your patients. You may be the one person who can get someone to change their mind about being vaccinated. Tonight, I’m asking each of you to reach out to your unvaccinated patients over the next two weeks and make a personal appeal to them to get the shot. America needs your personal involvement in this critical effort. And my message to unvaccinated Americans is this: What more is there to wait for? What more do you need to see? We’ve made vaccinations free, safe, and convenient. The vaccine has FDA approval. Over 200 million Americans have gotten at least one shot. We’ve been patient, but our patience is wearing thin. And your refusal has cost all of us. So, please, do the right thing. But just don’t take it from me; listen to the voices of unvaccinated Americans who are lying in hospital beds, taking their final breaths, saying, “If only I had gotten vaccinated.” “If only.” It’s a tragedy. Please don’t let it become yours. The second piece of my plan is continuing to protect the vaccinated. For the vast majority of you who have gotten vaccinated, I understand your anger at those who haven’t gotten vaccinated. I understand the anxiety about getting a “breakthrough” case. But as the science makes clear, if you’re fully vaccinated, you’re highly protected from severe illness, even if you get COVID-19. In fact, recent data indicates there is only one confirmed positive case per 5,000 fully vaccinated Americans per day. You’re as safe as possible, and we’re doing everything we can to keep it that way — keep it that way, keep you safe. That’s where boosters come in — the shots that give you even more protection than after your second shot. Now, I know there’s been some confusion about boosters. So, let me be clear: Last month, our top government doctors announced an initial plan for booster shots for vaccinated Americans. They believe that a booster is likely to provide the highest level of protection yet. Of course, the decision of which booster shots to give, when to start them, and who will give them, will be left completely to the scientists at the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control. But while we wait, we’ve done our part. We’ve bought enough boosters — enough booster shots — and the distribution system is ready to administer them. As soon as they are authorized, those eligible will be able to get a booster right away in tens of thousands of site across the — sites across the country for most Americans, at your nearby drug store, and for free. The third piece of my plan is keeping — and maybe the most important — is keeping our children safe and our schools open. For any parent, it doesn’t matter how low the risk of any illness or accident is when it comes to your child or grandchild. Trust me, I know. So, let me speak to you directly. Let me speak to you directly to help ease some of your worries. It comes down to two separate categories: children ages 12 and older who are eligible for a vaccine now, and children ages 11 and under who are not are yet eligible. The safest thing for your child 12 and older is to get them vaccinated. They get vaccinated for a lot of things. That’s it. Get them vaccinated. As with adults, almost all the serious COVID-19 cases we’re seeing among adolescents are in unvaccinated 12- to 17-year-olds — an age group that lags behind in vaccination rates. So, parents, please get your teenager vaccinated. What about children under the age of 12 who can’t get vaccinated yet? Well, the best way for a parent to protect their child under the age of 12 starts at home. Every parent, every teen sibling, every caregiver around them should be vaccinated. Children have four times higher chance of getting hospitalized if they live in a state with low vaccination rates rather than the states with high vaccination rates. Now, if you’re a parent of a young child, you’re wondering when will it be — when will it be — the vaccine available for them. I strongly support an independent scientific review for vaccine uses for children under 12. We can’t take shortcuts with that scientific work. But I’ve made it clear I will do everything within my power to support the FDA with any resource it needs to continue to do this as safely and as quickly as possible, and our nation’s top doctors are committed to keeping the public at large updated on the process so parents can plan. Now to the schools. We know that if schools follow the science and implement the safety measures — like testing, masking, adequate ventilation systems that we provided the money for, social distancing, and vaccinations — then children can be safe from COVID-19 in schools. Today, about 90 percent of school staff and teachers are vaccinated. We should get that to 100 percent. My administration has already acquired teachers at the schools run by the Defense Department — because I have the authority as President in the federal system — the Defense Department and the Interior Department — to get vaccinated. That’s authority I possess. Tonight, I’m announcing that we’ll require all of nearly 300,000 educators in the federal paid program, Head Start program, must be vaccinated as well to protect your youngest — our youngest — most precious Americans and give parents the comfort. And tonight, I’m calling on all governors to require vaccination for all teachers and staff. Some already have done so, but we need more to step up. Vaccination requirements in schools are nothing new. They work. They’re overwhelmingly supported by educators and their unions. And to all school officials trying to do the right thing by our children: I’ll always be on your side. Let me be blunt. My plan also takes on elected officials and states that are undermining you and these lifesaving actions. Right now, local school officials are trying to keep children safe in a pandemic while their governor picks a fight with them and even threatens their salaries or their jobs. Talk about bullying in schools. If they’ll not help — if these governors won’t help us beat the pandemic, I’ll use my power as President to get them out of the way. The Department of Education has already begun to take legal action against states undermining protection that local school officials have ordered. Any teacher or school official whose pay is withheld for doing the right thing, we will have that pay restored by the federal government 100 percent. I promise you I will have your back. The fourth piece of my plan is increasing testing and masking. From the start, America has failed to do enough COVID-19 testing. In order to better detect and control the Delta variant, I’m taking steps tonight to make testing more available, more affordable, and more convenient. I’ll use the Defense Production Act to increase production of rapid tests, including those that you can use at home. While that production is ramping up, my administration has worked with top retailers, like Walmart, Amazon, and Kroger’s, and tonight we’re announcing that, no later than next week, each of these outlets will start to sell at-home rapid test kits at cost for the next three months. This is an immediate price reduction for at-home test kits for up to 35 percent reduction. We’ll also expand — expand free testing at 10,000 pharmacies around the country. And we’ll commit — we’re committing $2 billion to purchase nearly 300 million rapid tests for distribution to community health centers, food banks, schools, so that every American, no matter their income, can access free and convenient tests. This is important to everyone, particularly for a parent or a child — with a child not old enough to be vaccinated. You’ll be able to test them at home and test those around them. In addition to testing, we know masking helps stop the spread of COVID-19. That’s why when I came into office, I required masks for all federal buildings and on federal lands, on airlines, and other modes of transportation. Today — tonight, I’m announcing that the Transportation Safety Administration — the TSA — will double the fines on travelers that refuse to mask. If you break the rules, be prepared to pay. And, by the way, show some respect. The anger you see on television toward flight attendants and others doing their job is wrong; it’s ugly. The fifth piece of my plan is protecting our economic recovery. Because of our vaccination program and the American Rescue Plan, which we passed early in my administration, we’ve had record job creation for a new administration, economic growth unmatched in 40 years. We cannot let unvaccinated do this progress — undo it, turn it back. So tonight, I’m announcing additional steps to strengthen our economic recovery. We’ll be expanding COVID-19 Economic Injury Disaster Loan programs. That’s a program that’s going to allow small businesses to borrow up to $2 million from the current $500,000 to keep going if COVID-19 impacts on their sales. These low-interest, long-term loans require no repayment for two years and be can used to hire and retain workers, purchase inventory, or even pay down higher cost debt racked up since the pandemic began. I’ll also be taking additional steps to help small businesses stay afloat during the pandemic. Sixth, we’re going to continue to improve the care of those who do get COVID-19. In early July, I announced the deployment of surge response teams. These are teams comprised of experts from the Department of Health and Human Services, the CDC, the Defense Department, and the Federal Emergency Management Agency — FEMA — to areas in the country that need help to stem the spread of COVID-19. Since then, the federal government has deployed nearly 1,000 staff, including doctors, nurses, paramedics, into 18 states. Today, I’m announcing that the Defense Department will double the number of military health teams that they’ll deploy to help their fellow Americans in hospitals around the country. Additionally, we’re increasing the availability of new medicines recommended by real doctors, not conspir- — conspiracy theorists. The monoclonal antibody treatments have been shown to reduce the risk of hospitalization by up to 70 percent for unvaccinated people at risk of developing sefe- — severe disease. We’ve already distributed 1.4 million courses of these treatments to save lives and reduce the strain on hospitals. Tonight, I’m announcing we will increase the average pace of shipment across the country of free monoclonal antibody treatments by another 50 percent. Before I close, let me say this: Communities of color are disproportionately impacted by this virus. And as we continue to battle COVID-19, we will ensure that equity continues to be at the center of our response. We’ll ensure that everyone is reached. My first responsibility as President is to protect the American people and make sure we have enough vaccine for every American, including enough boosters for every American who’s approved to get one. We also know this virus transcends borders. That’s why, even as we execute this plan at home, we need to continue fighting the virus overseas, continue to be the arsenal of vaccines. We’re proud to have donated nearly 140 million vaccines over 90 countries, more than all other countries combined, including Europe, China, and Russia combined. That’s American leadership on a global stage, and that’s just the beginning. We’ve also now started to ship another 500 million COVID vaccines — Pfizer vaccines — purchased to donate to 100 lower-income countries in need of vaccines. And I’ll be announcing additional steps to help the rest of the world later this month. As I recently released the key parts of my pandemic preparedness plan so that America isn’t caught flat-footed when a new pandemic comes again — as it will — next month, I’m also going to release the plan in greater detail. So let me close with this: We have so- — we’ve made so much progress during the past seven months of this pandemic. The recent increases in vaccinations in August already are having an impact in some states where case counts are dropping in recent days. Even so, we remain at a critical moment, a critical time. We have the tools. Now we just have to finish the job with truth, with science, with confidence, and together as one nation. Look, we’re the United States of America. There’s nothing — not a single thing — we’re unable to do if we do it together. So let’s stay together. God bless you all and all those who continue to serve on the frontlines of this pandemic. And may God protect our troops. Get vaccinated. 5:28 P.M. EDT
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.
- Fact sheets
- Facts in pictures
- Publications
- Questions and answers
- Tools and toolkits
- Endometriosis
- Excessive heat
- Mental disorders
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- All countries
- Eastern Mediterranean
- South-East Asia
- Western Pacific
- Data by country
- Country presence
- Country strengthening
- Country cooperation strategies
- News releases
- Feature stories
- Press conferences
- Commentaries
- Photo library
- Afghanistan
- Cholera
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19)
- Greater Horn of Africa
- Israel and occupied Palestinian territory
- Disease Outbreak News
- Situation reports
- Weekly Epidemiological Record
- Surveillance
- Health emergency appeal
- International Health Regulations
- Independent Oversight and Advisory Committee
- Classifications
- Data collections
- Global Health Observatory
- Global Health Estimates
- Mortality Database
- Sustainable Development Goals
- Health Inequality Monitor
- Global Progress
- World Health Statistics
- Partnerships
- Committees and advisory groups
- Collaborating centres
- Technical teams
- Organizational structure
- Initiatives
- General Programme of Work
- WHO Academy
- Investment in WHO
- WHO Foundation
- External audit
- Financial statements
- Internal audit and investigations
- Programme Budget
- Results reports
- Governing bodies
- World Health Assembly
- Executive Board
- Member States Portal
- WHO Director-General /
Director-General's opening remarks at the World Health Assembly - 24 May 2021
Your Excellency Madam President, Ambassador Keva Bain,
Your Excellency Alain Berset, Federal Counsellor of Switzerland,
Excellencies, distinguished colleagues and friends,
Lucy Nyambura is a health promotion officer in Mombasa City, Kenya.
When COVID-19 arrived last year, a strict lockdown was introduced, but it was met with strong resistance by the local community, who refused to be tested, isolated or treated.
As she made her daily rounds, providing information about the dangers of the new virus, Lucy was insulted in the streets and she and her team sometimes had to stop working for their own safety.
But Lucy kept going back to the community. After weeks of engaging leaders, things started to change. Communities started following COVID-19 guidelines and accepted to be tested. The spread of the virus was curtailed and the lockdown was removed.
Asante sana, Lucy.
Dr Gantsengel Purev is an intensive care specialist at the Central Military Hospital in Ulanbataar, Mongolia.
This is what he said:
“During my first shift, I lost my grandmother to COVID-19. She died in my arms. During my last shift, three people died in an hour. My patients are no different to my grandmother and grandfather. Many patients recover and leave the hospital. What keeps me going is two words from them: thank you.”
Dr Catalin Denciu is an intensive care specialist in Romania. He was on duty in November last year, caring for patients with COVID-19, when a fire broke out in the hospital.
Ten patients died in the fire, and in trying to save others, Dr Denciu suffered third-degree burns to 40% of his body.
Today we will honour him with an award for his service, sacrifice and example.
These are just a few examples. There are millions more; stories of courage, heartbreak, desperation, struggle and triumph.
For almost 18 months, health and care workers all over the world have stood in the breach between life and death.
They have saved countless lives, and fought for others who despite their best efforts, slipped away.
Many have themselves become infected, and while reporting is scant, we estimate that at least 115 000 health and care workers have paid the ultimate price in the service of others.
Health and care workers do heroic things, but they are not superheroes. They are humans like the rest of us.
They sweat and swear; they laugh and cry; they fear and hope.
Many feel frustrated, helpless and unprotected, with a lack of access to personal protective equipment and vaccines, and the tools to save lives.
In this International Year of the Health and Care Worker, we have all been reminded that these are incredible people doing incredible jobs under incredible circumstances.
We owe them so much, and yet globally health and care workers often lack the protection, the equipment, the training, the decent pay, the safe working conditions and the respect they deserve.
The job can be dangerous and disheartening; but it can also be the best job on earth.
A year ago, we published the first State of the World’s Nursing Report, and just last week we launched the third State of the World’s Midwifery Report, showing the world faces a global shortage of 900 000 midwives.
If we have any hope of achieving a healthier, safer, fairer future, every Member State must protect and invest in its health and care workforce as a matter of urgency.
This week you will consider two draft resolutions on the health workforce. I hope you will adopt them and, more importantly, take action on them, in every country.
Just as health and care workers are the lifeblood of every health system, so the lifeblood of WHO is its staff – the incredible people all over the world I am honoured to call my colleagues, in country and regional offices, and here at headquarters.
For almost 18 months, they have worked under extreme pressure, and time and time again they have gone above and beyond to serve you, our Member States, despite the modest resources they have to do their jobs.
The success of this Organization depends on its people. And we are committed to doing much more to build a WHO that attracts the best, and gives them the best opportunities, in the best working environment.
As you know, the Regional Directors and I have made 2021 the Year of the WHO Workforce.
As part of our commitment to strengthening the health and care workforce globally, as well as our own workforce, the WHO Academy will be a major addition to global health learning, as President Macron indicated earlier.
The Academy’s digital learning platform has been built and will begin global testing next week. The first batch of learning programmes are in the final stages of production, translation and testing and will be rolled out by September.
With thanks to France for its support, we are moving forward with plans to build the WHO Academy campus in Lyon.
Today I ask you not for a moment’s silence, but to make the loudest noise you can. Please join me in clapping, shouting and stamping your feet for every health and care worker everywhere.
Excellencies,
Although we have lost so many health and care workers already, we will lose many more as long as the pandemic rages.
Almost 18 months into the defining health crisis of our age, the world remains in a very dangerous situation.
As of today, more cases have been reported so far this year than in the whole of 2020.
On current trends, the number of deaths will overtake last year’s total within the next three weeks.
Since our Health Assembly started this morning, almost 1000 people have lost their lives to COVID-19. And in the time it takes me to make these remarks, a further 400 will die. This is very tragic.
We are pleased that for three consecutive weeks we have seen a downturn in the number of cases and deaths being reported.
But globally, we remain in a fragile situation.
No country should assume it is out of the woods, no matter its vaccination rate.
So far, no variants have emerged that significantly undermine the efficacy of vaccines, diagnostics or therapeutics.
But there is no guarantee that will remain the case.
This virus is changing constantly. Future changes could render our tools ineffective and drag us back to square one.
We must be very clear: the pandemic is not over, and it will not be over until and unless transmission is controlled in every last country.
WHO’s Strategic Preparedness and Response Plan sets out the 10 pillars that every country must apply in a tailored and dynamic way to reduce exposure, prevent infections, limit the spread, and save lives.
Every country can do more:
Increase surveillance, testing, sequencing, and sharing information;
Surge supplies needed to protect health workers;
Fight misinformation and disinformation;
Empower people and communities to play their part;
Support businesses and workplaces to take steps to open up safely, where appropriate;
Implement national vaccination strategies, vaccinate those most at risk, and donate vaccines to COVAX.
The ongoing vaccine crisis is a scandalous inequity that is perpetuating the pandemic.
More than 75% of all vaccines have been administered in just 10 countries.
There is no diplomatic way to say it: a small group of countries that make and buy the majority of the world’s vaccines control the fate of the rest of the world.
The number of doses administered globally so far would have been enough to cover all health workers and older people, if they had been distributed equitably. We could have been in a much better situation.
I understand that every government has a duty to protect its own people.
I understand that every government wants to vaccinate its entire population.
That’s what we want too. And in time, there will be enough supply for everyone, including those at lower risk.
But right now, there is not enough supply. Countries that vaccinate children and other low-risk groups now do so at the expense of health workers and high-risk groups in other countries. That’s the reality.
At the Executive Board meeting in January, I issued a challenge to see vaccination of health workers and older people underway in all countries within the first 100 days of the year.
That target was very nearly achieved.
But the number of doses available to COVAX remains vastly inadequate.
COVAX works. We have shipped every single one of the 72 million doses we have been able to get our hands on so far to 125 countries and economies.
But those doses are sufficient for barely 1 percent of the combined population of those countries.
So today I am calling on Member States to support a massive push to vaccinate at least 10 percent of the population of every country by September, and a “drive to December” to achieve our goal of vaccinating at least 30 percent by the end of the year.
This is crucial to stop severe disease and death, keep our health workers safe and reopen our societies and economies.
Sprinting to our September goal means we must vaccinate 250 million more people in low- and middle-income countries in just four months, including all health workers and the most at-risk groups as the first priority.
These are the minimum targets we should aim for. At the G20 Global Health Summit on Friday, IMF Managing Director Kristalina Georgieva proposed vaccinating 40 percent of the world’s population by the end of the year and 60 percent by mid-2022.
We are in discussions with the IMF, Member States and our partners about how to make these ambitious targets achievable.
Here’s how the “Drive to December” must happen:
First, share doses through COVAX, now.
I welcome the commitments made by Member States to donate doses, including the important announcements made at the G20 Global Health Summit on Friday.
But to achieve the goals for September and the end of the year, we need hundreds of millions more doses, we need them to go through COVAX, and we need them to start moving in early June.
Manufacturers must play their part, by ensuring any country that wants to share doses through COVAX can do it within days, not months.
I call on all manufacturers to give COVAX first right of refusal on new volume of vaccines, or to commit 50% of their volumes to COVAX this year.
And we need every country that receives vaccines to use them as quickly as possible. No dose can lay idle, or worse, be thrown away.
Country-level preparations to reach their populations must move as fast as vaccines.
Second, scale-up manufacturing.
The bottom line is that we need a lot more doses, we need them fast, and we must leave no stone unturned to get them.
Several manufacturers have said they have capacity to produce vaccines if the originator companies are willing to share licenses, technology and know-how.
I find it difficult to understand why this has not happened yet.
I thank India and South Africa for their initiative at the World Trade Organization to waive intellectual property protections for COVID-19 products, and I thank those countries that are supporting these efforts.
And we urge Member States and manufacturers to join C-TAP, the WHO COVID-19 Technology Access Pool, which provides a powerful mechanism for sharing licenses in a non-exclusive, transparent way.
I thank Prime Minister Pedro Sanchez for his commitment that Spain will join C-TAP, and we expect more good news in the coming days.
And third, fully fund the ACT Accelerator.
There remains an 18.5 billion US dollar gap in the ACT Accelerator.
Ultimately, the pandemic has shown clearly that in an emergency, low and lower-middle income countries cannot rely on imports from vaccine-producing countries.
I welcome the draft resolution on strengthening local production of medicines and other health technologies that Member States will consider at this Assembly.
I would also like to take this opportunity to express my deep appreciation to President Biden for reversing the decision to take the United States out of WHO, for donating US$4 billion to COVAX, and also for their announcement that they will donate 80 million vaccine doses globally – these are the largest contributions announced – and for supporting the intellectual property waiver.
In November, I gave Member States a detailed description of the incredible breadth and depth of WHO’s work beyond the pandemic.
In the six months since then, there have been even more achievements to be proud of.
As part of our commitment to transparency, the 2021 Results Report provides a wealth of information in an interactive, engaging, easy-to-use digital format. I commend it to you.
As a complement to the Results Report, we held the triple billion showcases, updated the triple billion dashboard, and we continue to hold ourselves accountable through delivery stocktakes, to review progress and identify challenges.
We have built the World Health Data Hub to provide complete, transparent and open data, on an interactive and easily searchable platform.
And the annual World Health Statistics, published last week, presents the latest data on more than 50 health-related indicators for the “triple billion” targets and the Sustainable Development Goals.
Among its other findings, preliminary estimates suggest there were at least 3 million excess deaths globally in 2020, attributable either directly or indirectly to COVID-19, representing 1.2 million more deaths than the 1.8 million officially reported.
One of the features of the 13 th General Programme of Work and the WHO Transformation is to drive a paradigm shift in global health by increasing the emphasis on promoting health and preventing disease; focusing on healthy lifestyles.
On current trends, we estimate that about 900 million more people could be enjoying better health and well-being by 2023, taking us very close to our target of 1 billion.
But progress is uneven, and more than a third of countries are heading in the wrong direction.
We have made mixed progress in addressing the major risk factors for noncommunicable diseases.
Tobacco use continues to decline, but the prevalence of obesity is rising, as is alcohol consumption in some regions.
At the beginning of this year, WHO launched a year-long campaign called Commit to Quit, to encourage at least 100 million of the world’s 1.3 billion tobacco users to quit.
Six weeks ago, we released our technical manual on tobacco tax policy and administration. Many countries are showing leadership in this area, and in implementing the other measures in the MPOWER package of interventions.
The Gambia has just increased its tobacco excise tax rates, Bolivia passed a comprehensive tobacco control law, and with WHO support, six African countries banned smoking in public places and on public transport.
We also see progress in efforts to improve nutrition, and to support consumers to make healthier food choices.
Last year we launched a programme to certify countries that have eliminated trans fats from their food supply, and 14 countries have now introduced best-practice policies on trans fats, protecting 589 million people from their harmful effects.
Earlier this month we published new benchmarks for sodium content in more than 60 categories of food, and last year Mexico implemented front-of-pack labelling.
On occupational health, we worked with the International Labour Organization to developed guidance to protect workers from COVID-19.
We’re working with the UN Environment Programme to support 40 countries to establish legally-binding controls on lead paint, a significant source of childhood poisoning.
Together with UN partners, in March of this year we published the first Global report on Ageism.
A month ago we released a new technical package called Step Safely to prevent and manage falls, an increasing cause of death and disability for people of all ages.
In April, UN Member States adopted a resolution committing to greater efforts to prevent drowning, in line with WHO recommendations.
With UN Women, we launched a new report representing the largest study ever conducted on the prevalence of violence against women, showing that almost one in three women globally has suffered intimate partner violence, sexual violence from a non-partner, or both, at least once in their lives.
With our partners at FAO, OIE and UNEP, we created the One Health High-Level Expert Panel, which met for the first time last week. The panel will be instrumental in guiding development of a dynamic new research agenda and providing high-level policy leadership.
Despite these achievements, progress in addressing the root causes of death and disease remains vastly insufficient and inequitable.
Globally, only 3 percent of health budgets are spent on promotion and prevention. And yet increased investment in these areas could reduce the global disease burden by half, generating massive returns for individuals, families, communities and nations.
An investment of 1 dollar per person per year could save 8.2 million lives and US$350 billion by 2023.
The pandemic has been a significant setback in our efforts to support Member States to progress towards universal health coverage, as you know.
On current trends, we project that an additional 290 million people will have access to high-quality health services, without financial hardship by 2023.
That leaves a shortfall of 710 million against our target to see 1 billion more people benefiting from universal health coverage.
The world is far behind.
With renewed determination and increased investment in primary health care and public health, we estimate that a further 400 million people could be covered with essential services by 2025.
But at least half the world’s population still lacks access to these services.
According to our most recent estimates, about 930 million people suffer catastrophic health spending each year, and about 90 million are pushed into extreme poverty by out-of-pocket health spending.
Globally, there remain huge gaps in access to essential medicines, including antibiotics, insulin, anti-hypertensives, diagnostics and treatment for cancer, and routine immunizations.
Antimicrobial resistance remains an existential and largely unaddressed threat to a century of medical progress.
And although we have seen a steady increase in service coverage over the last few years, the pandemic has caused severe disruption to essential health services.
Our most recent Pulse Survey, published one month ago, shows that during the first three months of this year, 94% of the 135 countries and territories surveyed reported some kind of disruption to services.
To give one example, data published in March suggest an estimated 1.4 million fewer people received care for TB last year – 21% less than in 2019. This disruption could cause an additional half a million deaths.
60 mass immunization campaigns are currently postponed in 50 countries, putting around 228 million people – mostly children – at risk for measles, yellow fever, polio and more.
However, we do see signs of recovery.
And despite disruptions to services, there have been significant achievements.
Globally, the prevalence of hepatitis B virus in children under 5 years is now below 1 percent, meaning the SDG target has already been achieved.
More than 9.4 million people globally have received treatment for hepatitis C, a 9-fold increase since 2015;
And this week we will publish interim guidance for validation of viral hepatitis elimination, with assessments to start in Brazil, Egypt, Georgia, Mongolia and Rwanda.
Ten days ago, the Commonwealth of Dominica received certification for the elimination of mother-to-child transmission of HIV and congenital syphilis.
On malaria, although the global decline in infections and deaths has stalled, there are still causes for celebration.
In February, El Salvador became the first country in Central America, and the 39 th country or territory globally, to be certified as malaria-free.
More than 670 000 children have now received the first dose of the RTS,S malaria vaccine in Ghana, Kenya and Malawi as part of a pilot programme coordinated by WHO, with financial support from Gavi, Unitaid and the Global Fund. Preliminary results are very positive.
On tuberculosis, more than 20 million people received access to TB services over the past 2 years, almost 5 million more than the previous 2 years.
109 countries started using new effective TB drugs, while 89 countries reported using better and faster treatments for multidrug-resistant TB, in line with updated WHO treatment guidelines.
On neglected tropical diseases, we have a new roadmap that sets global targets and milestones to prevent, control, eliminate and eradicate 20 NTDs and disease groups.
So far this year, only 3 human cases of Guinea worm disease have been reported, compared with 17 for the same period last year.
Last month, Gambia eliminated trachoma as a public health problem, while in March Côte d’Ivoire became the second country after Togo to eliminate African trypanosomiasis.
On noncommunicable diseases, WHO has supported 36 countries to integrate services to prevent, detect and treat NCDs into primary health care programmes.
More than 30 countries have developed policies or programmes to improve access to childhood cancer care.
We launched the Global Breast Cancer Initiative, aimed at reducing mortality from the world’s most-diagnosed cancer by 2.5% every year until 2040, saving 2.5 million lives.
More than 3 million people in 18 countries are now on protocol-based management of hypertension, with increasing use of the WHO HEARTS package of interventions.
And we have launched a new project to link quality of care for maternal and child health with NCDs.
On mental health, we have supported 31 more countries to integrate mental health services into primary health care, a 100% increase since 2014.
To improve mental health among adolescents, we worked with UNICEF to launch the “Helping Adolescents Thrive” toolkit.
To address opioid overdose deaths, we worked with UNODC to conduct a study of naloxone in four low- and middle-income countries, demonstrating significant public health benefits.
On access to medicines, WHO has given Emergency Use Listing to 7 vaccines and 28 in vitro diagnostics for COVID-19, which has allowed 101 countries to issue their own regulatory authorizations.
In total, WHO prequalified 62 medicines, 15 diagnostics, 13 vaccines and more last year – the most in a single year.
In January, we published the updated Model List of in Vitro Diagnostics, including new tests for noncommunicable and infectious diseases.
We published new pricing policy guidelines, to increase the affordability of medicines, and we supported Small Island Developing States to sign a pooled procurement agreement for health products, to improve the prices at which they can buy medicines, vaccines and other products.
Through the WHO Listed Authorities initiative, Ghana achieved Maturity Level 3 last year, meaning it has a stable and well-functioning regulatory system. In future, it will be able to become a reference agency for issuing marketing authorizations in Africa and beyond.
WHO is also supporting the Africa Union to establish the Africa Medicines Agency, to increase regulatory oversight and access to safe, efficacious and affordable medical products across the continent.
On antimicrobial resistance, just last month WHO published the latest overview of the pipeline for antibacterials, to monitor progress in research and development of these life-saving treatments.
The number of countries reporting data to the Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System has tripled to 70 in three years, and the number of surveillance sites globally has increased from 729 to 73 000.
And we established the One Health Global Leaders Group on Antimicrobial Resistance, led by Prime Minister Hasina of Bangladesh and Prime Minister Mottley of Barbados.
And finally, we estimate that by 2023, about 920 million people could be better protected from health emergencies – again taking us very close to reaching our target of 1 billion.
Of course, that doesn’t mean 920 million people protected from all health emergencies.
The past year has exposed gaps in national and global preparedness that must be addressed.
Even while WHO has focused on responding to this pandemic, we continue to work with countries to prepare for a possible influenza pandemic.
Today also marks the 10 th anniversary of the Pandemic Influenza Preparedness Framework, which pioneered a new approach to sharing biological materials; and to equity of access to vaccines and other critical pandemic response products.
More broadly, we continue to assess preparedness and response capacities of Member States, with 113 joint external evaluations, 156 simulation exercises and 126 intra action or after-action reviews.
More than 70 countries have developed national action plans for health security to address critical gaps – but many remain unfunded.
And of course, COVID-19 is far from the only emergency to which WHO has responded in the past year.
Every month, WHO processes over 9 million pieces of information, screens 43 000 signals, leading to 4500 events reviewed and an average of 30 events verified.
Our surveillance systems go far beyond disease outbreak events in human populations, to encompass information with potential risk implications at the human–animal interface, signals related to climate change, industrial hazards, and conflicts.
In 2020 alone we responded to over 120 emergencies including a total of 60 graded crises.
More than 1.8 billion people currently live in fragile, conflict and vulnerable settings, where protracted crises are compounded by weak national capacity to deliver basic health services.
As the Health Cluster lead in the United Nations humanitarian response, WHO leads efforts to deliver the public health response to COVID-19 through the Global Humanitarian Response Plan, providing coordination and operational support in 30 countries, in partnership with 900 national and international partners.
These populations are also the ones that are most at risk to outbreaks of cholera, meningitis, yellow fever and other high-threat infectious hazards.
Health and care workers are particularly vulnerable where there is instability.
More than 2400 incidents in 17 countries and territories have been recorded by the Surveillance System for Attacks on Health Care, since it started in December 2017.
Over six hundred health care workers and patients have died, and nearly 2000 have been injured.
There is no peace without heath and no health without peace.
All of these efforts are supported by our Science and Data divisions, which monitor progress and help to stay abreast of the rapidly-evolving evidence.
The Science division quality-assure more than 290 global public health goods this biennium, and together with the Health Emergencies programme, coordinated the review of almost 1300 COVID-19 publications.
We’re also working to ensure our products are tracked and designed for impact.
Among WHO’s most-downloaded products in the past year were new guidelines on increasing physical activity,
rapid advice on the use of chest imaging in COVID-19;
technical specifications for blood pressure measurement;
managing chronic pain in children;
pharmaceutical pricing policies;
traditional and complementary medicines;
and screening and treatment for prevention of cervical cancer.
In addition, new reports on tuberculosis, nursing, malaria, cancer, NCDs, neglected tropical diseases, antimicrobial resistance, and the annual World Health Statistics provide an authoritative snapshot on vital health issues.
I know it’s a long list, but we want to remind all Member States of the vast range of work we do to address the vast range of health challenges we face.
Many of these issues are on your agenda this week.
And on none of them does WHO work alone. Partnership is essential to everything we do, including in the multilateral system through the Global Action Plan for Healthy Lives and Well-Being for All.
Today we are launching the Global Action Plan progress report, entitled “Stronger collaboration for an equitable and resilient recovery.”
We are committed to accountability for the results we achieve, but also for how we work, which is why any report of sexual exploitation and abuse by our staff cannot be tolerated.
We recognize that we must do much more to protect the people we serve, and to ensure that zero tolerance is not just a slogan, but a mark of who we are.
Excellencies, colleagues and friends,
This pandemic has been driven by a highly transmissible virus.
But it has been turbo-charged by division, inequity, and the historical neglect of investments in preparedness.
So as we recover and rebuild, we must do more than stop viruses; we must address the vulnerabilities that allow outbreaks to become epidemics and epidemics to become pandemics.
We can come up with new institutions and new mechanisms, but that may only paper over the cracks.
Whatever changes we make must be to something more fundamental.
We can only lay a solid foundation for a safer world with a common commitment to solidarity, equity and sustainability.
A year ago, you tasked me with initiating an impartial, independent and comprehensive evaluation, including existing mechanisms, as appropriate, to review experience gained and lessons learned from the WHO-coordinated international health response to COVID-19.
At this Health Assembly, you will receive the reports of several panels and committees that evaluated different dimensions of the international response to the pandemic, including WHO’s role.
I would like to thank each panel, committee and working group for its efforts.
We welcome each of these reports, and we look forward to discussing them with Member States this week.
There is always more to do, there are more lessons to learn and more changes to make.
We are committed to listening to you, our Member States, with humility and a willingness to make the changes we need to make to be the organization you need us to be.
Many of you have recognized that a significant increase in more predictable and sustainable financing is needed to enable WHO to fulfil your expectations.
But beyond how this organization is funded, the world needs a fundamental rethink of what we mean by global health security.
We cannot build a safer world from the top down; we must build from the ground up.
Preparing for, preventing, detecting and responding rapidly to epidemics doesn’t start in Geneva, New York, or any of the world’s corridors of power.
It starts in the streets of deprivation and overcrowding;
In the homes where there is not enough food;
In the communities without access to health workers;
And in the villages and towns whose clinics and hospitals lack electricity or clean water.
It starts with strong primary health care and public health systems, skilled health workers, and communities empowered and enabled to take charge of their own health.
That must be the focus of our attention, and our investment.
We need better systems, built locally and linked globally in an unbreakable chain, for readiness, early warning, rapid response, risk communications and more.
Already we have taken several steps to build these systems.
We are now preparing to start a pilot programme of the Universal Health and Preparedness Review with 12 Member States during the second half of this year.
We have announced plans to establish the WHO Hub for Pandemic and Epidemic Intelligence in Berlin;
We are preparing to open the doors of the WHO Academy;
We are already building on lessons from the WHO-hosted ACT Accelerator which will need to be a pillar of the new international system;
And just this morning I signed a Memorandum of Understanding with His Excellency Alain Berset on establishing the BioHub here in Switzerland, as a reliable, safe, and transparent mechanism for Member States to voluntarily share pathogens and clinical samples.
Second, we need better financing to strengthen national capacities, support rapid response, and fund the research and development, manufacturing and deployment of life-saving tools.
The world has several strong International Financial Institutions that must play a vital role in funding an enhanced national and global health security system.
And third, we need better governance that is inclusive and truly representative of every Member State, regardless of the size of its population or economy.
Keeping the world safe requires the ownership and engagement of all Member States.
The International Health Regulations remain the cornerstone of global governance for pandemic preparedness and response.
But their implementation is inconsistent, and has not led to the level of commitment and action needed.
We all know that one of the greatest drivers of this pandemic has been the lack of international solidarity and sharing: sharing data, sharing information, sharing pathogens, sharing resources, sharing technology.
We can only address that fundamental weakness with a binding commitment between nations to provide a solid foundation for enhanced cooperation – a treaty on pandemic preparedness and response that can address the challenges I have outlined.
An international agreement that represents all nations and people;
That addresses our shared risks and vulnerabilities;
That leverages our shared humanity, solidarity and diversity;
And that reflects what future generations need, not what this generation wants.
We have come to a fork in the road. If we go on the same old way, we will get the same old result: a world that is unprepared, unsafe and unfair.
Make no mistake: this will not be the last time the world faces the threat of a pandemic.
It is an evolutionary certainty that there will be another virus with the potential to be more transmissible and more deadly than this one.
This is not the time for incremental improvements or tinkering at the edges. This is the moment for bold ideas, bold commitment and bold leadership; for doing things that have never been done before.
We have a choice: between cooperation, competition or confrontation.
In fact, the only choice we have is between cooperation and insecurity.
A safer world is not a zero-sum game; it is the opposite.
If anyone is left behind, all are held back.
But if the furthest behind is the first to be helped; if the weakest is first to be strengthened; if the most vulnerable is first to be protected – then we all win.
73 years ago, you our Member States established WHO as the directing and coordinating authority on international health.
And with your continued leadership and guidance, that is the role we will continue to play together to promote health, keep the world safe and serve the vulnerable.
Shukraan jazeelan. Xie xie. Merci beaucoup. Muchas gracias. Spasiba bolshoi.
Thank you very much.

Long-Term Health Effects of COVID-19: Disability and Function Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection (2024)
Chapter: 6 overall conclusions, 6 overall conclusions.
This chapter presents nine conclusions derived by the committee from evidence presented throughout the report. This chapter does not include references. Citations to support the text and conclusions herein are provided in previous chapters of the report.
DIAGNOSIS OF LONG COVID
Long COVID is associated with a wide range of new or worsening health conditions and encompasses more than 200 symptoms involving nearly every organ system. There currently are no consensus-based diagnostic criteria for the condition; criteria for diagnosis are evolving as experience and research findings develop. Diagnosis of Long COVID is generally based on a known or presumed history of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection (as indicated by a positive viral test or patient self-report; as of this writing, no diagnostic test for Long COVID is available), the presence of Long COVID health effects and symptoms, and consideration of other conditions and etiologies that could be causing the symptoms.
Testing to diagnose acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, as well as testing capacity and behaviors, has changed dramatically over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic. Testing was constrained during the early phase of the pandemic, although it subsequently became increasingly available, and the introduction of at-home testing meant that many people may not have reported their positive results to health care systems. As a result of these two drivers, many individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 never received formal
documentation of their diagnosis. Sole reliance on a documented history of SARS-CoV-2 infection when diagnosing Long COVID will miss these individuals. Therefore, the presence of signs and symptoms and self-reported prior infection are generally considered sufficient to establish a diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Continued research on and discussion of Long COVID will help inform a case definition and standardized diagnosis.
Based on its review of the literature, the committee reached the following conclusion:
- Long COVID is a complex chronic condition caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection that affects multiple body systems. Because of wide variability in testing practices over the course of the pandemic, many people experiencing Long COVID have not received a formal diagnosis of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. A positive test for SARS-CoV-2 is not necessary to consider a diagnosis of Long COVID.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Long COVID can impact people across the lifespan, from children to older adults, as well as across sex, gender, racial, ethnic, and other demographic groups. Women are twice as likely as men to experience Long COVID. Population surveys suggest that in 2022 the overall prevalence of Long COVID was around 3.4 percent in U.S. adults and 0.5 percent in children. Estimates of the prevalence of specific long-term health effects of SARS-CoV-2 vary in the literature. This variation reflects the dynamic nature of the pandemic itself, as the virus has evolved and spawned many variants and subvariants (likely with different propensities to cause Long COVID), as well as the introduction of vaccines and treatments for acute infection (e.g., antivirals, steroids), both of which have been shown to reduce the risk of long-term health effects. Variation in incidence and prevalence estimates also stem from the heterogeneity of study designs, including choice of control groups, methods used to account for the effect of baseline health, specification of outcomes, and other methodological differences.
In addition, the broad multisystem nature of Long COVID and the fact that the associated health effects are expressed differently by age group and sex and by baseline health compound the challenge of identifying and quantifying affected populations. Symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infection range in severity from mild to severe, and the literature suggests that the severity of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection is a risk factor for Long COVID. For example, a large Scottish population-based study found that 5 percent of those with mild infection had not recovered at least 6 months following infection, compared with 16 percent of those who required hospitalization—a ratio of approximately 1:3.
- The risk of Long COVID increases with the severity of acute infection. By the committee’s best estimate, people whose infection was sufficiently severe to necessitate hospitalization are 2–3 times more likely to experience Long COVID than are those who were not hospitalized, and among those who were hospitalized, individuals requiring life support in the intensive care unit may be twice as likely to experience Long COVID. However, people with mild disease can also develop Long COVID, and given the much higher number of people with mild versus severe disease, they make up the great majority of people with Long COVID.
HEALTH EFFECTS
Long COVID is associated with hundreds of symptoms and new or worsening health effects that manifest in many different body systems. In keeping with the three domains of functioning in the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health model of disability, health effects experienced in Long COVID may manifest as impairments in body structures and physical and psychological functions, with resulting activity limitations and restrictions on participation. Evidence on clustering of the post-acute and long-term health effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection remains inconsistent across studies. Consensus is needed on terms, definitions, and methodological approaches for generating better-quality and more consistent evidence.
- Long COVID is associated with a wide range of new or worsening health conditions impacting multiple organ systems. Long COVID can cause more than 200 symptoms and affects each person differently. Attempts to cluster symptoms have yielded heterogeneous results.
FUNCTIONAL IMPACT AND RISK FACTORS
Some of the symptoms and health effects associated with Long COVID can be severe enough to interfere with an individual’s day-to-day functioning, including participation in work and school activities. Functional disability associated with Long COVID has been characterized as the inability to return to work, poor quality of life, diminished ability to perform activities of daily living, decreased physical and cognitive function, and overall disability.
The severity of acute COVID-19 is a major risk factor for poor functional outcomes, but even people with mild initial illness can experience long-term functional impairments. Increased number and severity of long-term symptoms correlate with decreased quality of life, physical functioning, and ability to work or perform in school. Other risk factors for poor functional outcomes include female sex, lack of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, baseline disability or comorbidities, and smoking.
There is some overlap between SSA’s current Listing of Impairments (Listings) and health effects associated with Long COVID, such as impaired lung and heart function. However, it is likely that most individuals with Long COVID applying for Social Security disability benefits will do so based on health effects not covered in the Listings. Three frequently reported health effects that can significantly interfere with the ability to perform work or school activities and may not be captured in the SSA Listings are chronic fatigue and post-exertional malaise, post-COVID-19 cognitive impairment, and autonomic dysfunction, all of which can be difficult to assess clinically in terms of their severity and effects on a person’s functioning.
- Long COVID can result in the inability to return to work (or school for children and adolescents), poor quality of life, diminished ability to perform activities of daily living, and decreased physical and cognitive function for 6 months to 2 years or longer after the resolution of acute infection with SARS-CoV-2. Increased number and severity of long-term health effects correlates with decreased quality of life, physical and mental functioning, and ability to participate in work and school. Health effects that may not be captured in SSA’s Listing of Impairments yet may significantly affect an individual’s ability to participate in work or school include, but are not limited to, post-exertional malaise and chronic fatigue, post-COVID-19 cognitive impairment, and autonomic dysfunction.
LONG COVID IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
While there are various definitions of children, adolescents, and young people, for the purposes of this report, “children” or “pediatrics” refers to the entire pediatric age range and “adolescents” to children at the older end of the spectrum (i.e., ages ~11 to 18 years). Even though most children experience mild acute COVID-19 illness, they can experience Long COVID regardless of the severity of their acute infection. As with adults, they may experience health effects across many body systems. Commonly reported symptoms include fatigue, weakness, headache, sleep disturbance, muscle
and joint pain, respiratory problems, palpitations, altered sense of smell or taste, dizziness, and dysautonomia. Although pediatric presentations and intervention options may overlap with those in adults—particularly among adolescents, who may be more likely than children to mimic the adult presentation and trajectory—pediatric management of Long COVID entails specific considerations related to developmental age and/or disabilities and history gathering. In general, children have fewer preexisting chronic health conditions compared with adults; thus, Long COVID may represent a substantial change from their baseline, particularly for those who were previously healthy.
Limited data are available on long-term outcomes in children. Some youth with persistent symptoms experience difficulties that affect their quality of life and result in increased school absences, as well as decreased participation and performance in school, sports, and other activities. Risk factors for the development of Long COVID include acute-phase hospitalization, preexisting comorbidity, and infection with pre-Omicron variants. Most children with Long COVID recover slowly over time, but not all. In one prospective cohort study of 1,243 children (ages 4–10) with Long COVID, for example, 48 percent remained symptomatic at 6 months, 13 percent at 12 months, and 5 percent at 18 months after infection. Importantly, severity of symptoms and functional impairment from Long COVID symptoms were not correlated with traditional clinical testing (e.g., lung ultrasound, standard systolic and diastolic function on echocardiogram).
It is important to note that in pediatrics, because of typical development, the baseline for performance of skills is constantly changing, especially among young children. This can make deviations in their performance during Long COVID challenging to assess, and there may be a delay in recognition of any deviations (e.g., lack of developing a skill at the appropriate age). Additionally, the duration of symptoms (e.g., 1 or 3 months) can feel very different to and have a greater impact on children compared with adults. Currently, there is a dearth of prospective and cross-sectional studies on the prevalence, risk factors, and time course and pattern of Long COVID in children. More research is needed to identify the long-term functional implications of Long COVID in children, because information from adult studies may not be directly applicable to the pediatric population.
- Although the large majority of children recover fully from SARS-CoV-2 infection, some develop Long COVID and experience persistent or intermittent symptoms that can reduce their quality of life and result in increased school absences as well as decreased participation and performance in school, sports, and other activities. Overall, the trajectory
- for recovery is better among children compared with adults. More research is needed to understand the long-term functional implications of Long COVID in children, as information from adult studies may not be directly applicable.
DISEASE MANAGEMENT
Currently there are no Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved drugs or disease-modifying treatments for Long COVID. As with other complex multisystem conditions, management of Long COVID relies on techniques for controlling symptoms and improving functional ability, such as pacing (i.e., balancing periods of activity and rest in daily life), mobility support, social support, diet modulation, pharmacological treatment of secondary health effects, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and rehabilitation. Management often requires a multidisciplinary team. Because of the multisystem nature of the condition, different approaches may be needed to address the variety of clinical presentations and environmental factors (e.g., living situation, work requirements, family support) among individuals. Numerous randomized controlled trials are currently being undertaken to determine the efficacy of a number of identified pharmacological agents; however, limited data have been published, and trials are yet to be finalized.
- There currently is no curative treatment for Long COVID itself. Management of the condition is based on current knowledge about treating the associated health effects and other sequelae. As with other complex multisystem chronic conditions, treatment focuses on symptom management and optimization of function and quality of life.
DISEASE COURSE AND PROGNOSIS
Recovery from Long COVID varies among individuals, and data on recovery trajectories are rapidly evolving. Initial data suggest that people with persistent Long COVID symptoms generally improve over time, although preliminary studies suggest that recovery can plateau 6–12 months after acute infection. Studies have shown that only 18–22 percent of those who have persistent symptoms at 5–6 months following infection have fully recovered by 1 year. Among those who do not improve, most remain stable, but some worsen. More information on recovery trajectories at 1 year or longer may become available in the next few years. Rehabilitation and symptom management, including pacing, may improve function in some people with Long COVID, regardless of the severity of disease or duration
of symptoms, although the benefits are greater for those who are younger and who have had Long COVID for a shorter period of time.
- Recovery from Long COVID varies among individuals, and data on recovery trajectories are rapidly evolving. There is some evidence that many people with persistent Long COVID symptoms at 3 months following acute infection, including children and adolescents, have improved by 12 months. Data for durations longer than 12 months are limited, but preliminary data suggest that recovery may plateau or progress at a slower rate after 12 months.
HEALTH EQUITY
The burden of seeking care and finding adequate services for Long COVID is challenging and can impact the potential for recovery. Patients with Long COVID may encounter skepticism about their symptoms when they present in medical settings, which discourages care seeking. This is particularly true for individuals disadvantaged by their social or economic status, geographic location, or environment, and can result in preventable disparities in the burden of disease and opportunities to achieve optimal health. Disadvantaged groups include members of some racial and ethnic minorities, people with disabilities, women, LGBTQI1 (lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, intersex, or other) individuals, people with limited English proficiency, and others.
Individuals with Long COVID have increased health care utilization and financial burden, which may be exacerbated if they are unable to work to gain income and or receive health insurance coverage. Members of disadvantaged groups, especially early in the pandemic, were more likely to contract SARS-CoV-2, more likely to be hospitalized with acute COVID-19, more likely to have adverse clinical outcomes, and less likely to be vaccinated, potentially increasing their risk of developing Long COVID. In addition, these groups are more likely to be uninsured or underinsured. Even for those with insurance coverage, some of the services that have been shown to improve function may not be covered by their benefits. Moreover, the availability of specialized Long COVID services is limited, and capacity does not match the demand for rehabilitation specialists. Limited transportation, distance from clinics, and the inability to take time away from work or school are known barriers to care. The availability issue is particularly problematic for individuals living in medically underserved areas.
Information about COVID is rapidly evolving, and this dynamic nature of the science may contribute to some patient hesitancy regarding
prophylactic and therapeutic management for acute infection or Long COVID. Low levels of health literacy may also place some individuals at increased risk for misinformation, which may prevent them from fully taking advantage of health care resources to protect and improve their health. Low health literacy may also impact individual self-management of the symptoms and conditions associated with Long COVID.
- Social determinants of health, such as socioeconomic status, geographic location, health literacy, and race and ethnicity, affect access to health care. With respect to acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and Long COVID, adverse social determinants of health have contributed to disparities in access to SARS-CoV-2 testing; vaccination; and therapeutics, including treatments for acute infection and specialized rehabilitation clinics for Long COVID. In addition, the demand for specialty care exceeds capacity, resulting in waitlists for the receipt of services.
SIMILAR CHRONIC CONDITIONS
Long COVID shares many features with other complex multisystem conditions, including myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), fibromyalgia, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS). The mechanism of action for infection-associated chronic illnesses remains unclear, and further investigation is needed. Current theories regarding potential mechanisms of action include viral persistence, immune dysregulation (including cytokine dysregulation or mast cell activation), neurological disturbances (e.g., neuroinflammation), cardiovascular damage (e.g., endothelial dysfunction, coagulation issues, orthostatic intolerance), gastrointestinal dysfunction (e.g., secondary to gut microbiome dysbiosis), metabolic issues (energy insufficiency, reactive oxygen species production, mitochrondrial dysfunction), and genetic variations.
Currently, there are no specific laboratory-based diagnostic tests for Long COVID or ME/CFS, and diagnosis involves consideration of other potential causes of the symptoms. In general, Long COVID (especially that which does not meet criteria for ME/CFS) has a better prognosis than ME/CFS. Some manifestations of Long COVID are similar to those of ME/CFS, and like ME/CFS, Long COVID appears to be a chronic illness, with few patients achieving full remission. Studies comparing Long COVID and ME/CFS have several limitations, however. Because Long COVID is a new disease, study participants are usually newly diagnosed, while ME/CFS study participants often have had the condition for longer and so are less likely to improve. Moreover, the definition of ME/CFS requires that symptoms
be ongoing for 6 months or more, whereas the duration criteria for Long COVID vary in the literature from 2 to 6 months, making the two conditions difficult to compare.
- Complex, infection-associated chronic conditions affecting multiple body systems are not new, and Long COVID shares many features with such conditions as myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome. Current theories about the pathophysiology of these conditions include immune dysregulation, neurological disturbances, cardiovascular damage, gastrointestinal dysfunction, metabolic issues, and mitochondrial dysfunction. More research is needed to understand the natural history and management of complex multisystem chronic conditions, including Long COVID.
This page intentionally left blank.
Since the onset of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in early 2020, many individuals infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), have continued to experience lingering symptoms for months or even years following infection. Some symptoms can affect a person's ability to work or attend school for an extended period of time. Consequently, in 2022, the Social Security Administration requested that the National Academies convene a committee of relevant experts to investigate and provide an overview of the current status of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of long-term health effects related to Long COVID. This report presents the committee conclusions.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.

COMMENTS
Introduction: We all have been affected by the current COVID-19 pandemic. However, the impact of the pandemic and its consequences are felt differently depending on our status as individuals and as members of society. While some try to adapt to working online, homeschooling their children and ordering food via Instacart, others have no choice ...
COVID-19 is the disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. It usually spreads between people in close contact. COVID-19 vaccines provide strong protection against severe illness and death. Although a person can still get COVID-19 after vaccination, they are more likely to have mild or no symptoms. Anyone can get sick with COVID-19 and become ...
But of course, COVID-19 will not be the last Disease X. Epidemics and pandemics are a fact of nature, exacerbated in our time by urbanization, encroachment on habitats, the climate crisis and insecurity. There can be no health without peace, and no peace without health - and that is true everywhere, from Ethiopia to Syria, Yemen and Ukraine.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays. Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form. To help ...
Introduction. On December 31, 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) contacted China about media reports of a cluster of viral pneumonias in Wuhan, later attributed to a coronavirus, now named ...
About this speech. Joe Biden. September 09, 2021. Source The White House. As the Delta variant of the Covid-19 virus spreads and cases and deaths increase in the United States, President Joe Biden announces new efforts to fight the pandemic. He outlines six broad areas of action--implementing new vaccination requirements, protecting the ...
Answer: Introduction: Good morning/afternoon everyone. Today, I would like to inform you about the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on our daily lives. Body: COVID-19, also known as the coronavirus, was first identified in Wuhan, China in December 2019. Since then, it has spread to affect nearly every country in the world.
Alex, a writer and fellow disabled parent, found the freedom to explore a fuller version of herself in the privacy the pandemic provided. "The way I dress, the way I love, and the way I carry ...
The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic. The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges. Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams. Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions ...
Introduction. The COVID-19 pandemic, which began in late 2019, has drastically altered the way we live. ... Argumentative Essay About Covid19 With Introduction Body and Conclusion . Expert Tip. ... Persuasive speeches about Covid-19 can provide the audience with valuable insights on how to best handle the pandemic. They can be used to advocate ...
The grocery stores I was used to seeing fully stocked were cleared of essential supplies, like milk and hand sanitizer. Many of my favorite local restaurants transitioned to delivery-only, while others closed. The implications of this coronavirus pandemic became evident. Talk of layoffs and businesses struggling to make payroll became the norm.
A novel coronavirus (CoV) named '2019-nCoV' or '2019 novel coronavirus' or 'COVID-19' by the World Health Organization (WHO) is in charge of the current outbreak of pneumonia that began at the beginning of December 2019 near in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China [1-4]. COVID-19 is a pathogenic virus. From the phylogenetic analysis ...
A novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was identified in 2019 in Wuhan, China. This is a new coronavirus that has not been previously identified in humans. This course provides a general introduction to COVID-19 and emerging respiratory viruses and is intended for public health professionals, incident managers and personnel working for the United ...
Introduction. In December 2019, the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) emerged in China, followed by a rapid spread all over the world. On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) raised its pandemic alert. As of April 11, 2020, COVID-19 had caused ...
In "The Quarantine Diaries," Amelia Nierenberg spoke to Ady, an 8-year-old in the Bay Area who is keeping a diary.Ms. Nierenberg writes: As the coronavirus continues to spread and confine ...
DOI: 10.1001/JAMA.2020.7308. The author discusses the economic and healthcare crisis the COVID-19 pandemic created. The projections drawn in the paper predict a 10 to 25% contraction of the US economy in the second quarter. The writer asserts that the United States has entered a COVID-19 recession.
WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 20 March 2020. Good morning, good afternoon and good evening, wherever you are. Every day, COVID-19 seems to reach a new and tragic milestone. More than 210,000 cases have now been reported to WHO, and more than 9,000 people have lost their lives.
The COVID-19 or the SARS-CoV-2 is rapidly unfurling from Wuhan in Hubei Province of China to worldwide [4]. Initial confirmation of the pandemic was carried out by conducting studies on 99 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, from which 49% of patients exhibited a history of subjection to the Huanan seafood market.
The COVID-19 Pandemic — Finding Solutions, Applying Lessons Learned (Remarks as prepared for delivery. The text and video of this speech are slightly, though not substantively different from the ...
19. Pandemic. Briefing Room. Speeches and Remarks. 5:02 P.M. EDT. THE PRESIDENT: Good evening, my fellow Americans. I want to talk to you about where we are in the battle against COVID-19, the ...
Dr Catalin Denciu is an intensive care specialist in Romania. He was on duty in November last year, caring for patients with COVID-19, when a fire broke out in the hospital. Ten patients died in the fire, and in trying to save others, Dr Denciu suffered third-degree burns to 40% of his body.
Since the onset of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in early 2020, many individuals infected with the virus that causes COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), have continued to experience lingering symptoms for months or even years following infection.