Essay Papers Writing Online
Master the art of crafting a concept essay and perfect your writing skills.

Every great work of literature begins with a spark of inspiration, a kernel of an idea that germinates within the writer’s mind. It is this concept, this central theme, that serves as the foundation of the entire writing process, guiding the writer along the creative journey. In the realm of academic writing, the concept essay holds a special place, as it requires the writer to explore abstract ideas, dissect complex theories, and present their understanding of a particular concept.
Unlike traditional essays where arguments are made, and evidence is provided, concept essays delve into the intangible realm of ideas, taking the reader on a captivating exploration of abstract concepts. These essays challenge the writer to convey their understanding of a concept without relying on concrete evidence or facts. Instead, they rely on the writer’s ability to provide clear definitions, logical explanations, and compelling examples that elucidate the intricacies of the concept at hand.
Effectively crafting a concept essay requires skillful mastery of language and an astute understanding of how ideas interconnect. It is a delicate dance between the power of words and the depth of thought, where metaphors and analogies can breathe life into otherwise elusive notions. The successful concept essay requires more than merely stating definitions or describing the concept; it necessitates the writer’s ability to engage and captivate the reader, transporting them into the realm of ideas where the abstract becomes clear and tangible.

Mastering the Art of Crafting a Conceptual Essay: Indispensable Suggestions and Instructions
Embarking on the journey of composing a conceptual essay necessitates an astute understanding of the complexities involved. This particular form of written expression empowers individuals to delve deeply into abstract concepts, unravel their intricacies, and articulate their findings in a clear and coherent manner. To accomplish this task with finesse, it is imperative to familiarize oneself with indispensable suggestions and instructions that pave the way to success.
1. Explore Profusely:
- Investigate, scrutinize, and immerse yourself in the vast realm of ideas, allowing your mind to explore a myriad of perspectives.
- Delve into diverse disciplines and subjects, sourcing inspiration and insight from a wide array of sources such as literature, art, philosophy, science, and history.
- Be cognizant of the fact that the more extensive your exploration, the richer your conceptual essay will be.
2. Define Your Focus:
- Once you have gathered an abundant collection of ideas, narrow down your focus to a specific concept that captivates your interest.
- Choose a concept that is both intriguing and stimulating, as this will fuel your motivation throughout the writing process.
- Strive to select a concept that possesses a level of complexity, rendering it ripe for analysis and interpretation.
3. Establish a Clear Structure:
- Prior to commencing the writing process, create a well-structured outline that delineates the key sections and points you wish to convey in your essay.
- Ensure that your essay possesses a clear introduction, body paragraphs that expound upon your chosen concept, and a comprehensive conclusion that ties together your arguments.
- Organize your thoughts in a logical manner, employing effective transitions that allow your essay to flow seamlessly.
4. Support your Claims:
- Avoid presenting mere conjecture or personal opinions; instead, bolster your arguments with credible evidence and examples.
- Cite reputable sources, such as scholarly articles, books, or studies, to lend credibility and authority to your assertions.
- Engage critically with the works of other esteemed thinkers, analyzing their viewpoints and incorporating them into your own exploration of the concept.
5. Polish and Perfect:
- Once you have crafted the initial draft of your conceptual essay, allocate ample time for revision and refinement.
- Engage in meticulous proofreading to eliminate any errors in grammar, punctuation, or syntax that may detract from the overall impact of your work.
- Solicit feedback from trusted peers or mentors, incorporating their suggestions into your final version.
In conclusion, mastering the art of crafting a conceptual essay demands diligent exploration, focused attention, and a commitment to delivering a well-structured and thought-provoking piece of writing. By following these essential tips and guidelines, you can navigate the intricacies of this unique form of expression and develop an essay that both captivates and informs its readers.
Understanding the Purpose of a Concept Essay
Having a clear understanding of the purpose behind writing a concept essay is crucial for creating a successful piece of writing. Concept essays aim to explore and explain abstract ideas, theories, or concepts in a way that is accessible and engaging to readers.
Although concept essays may vary in subject matter, their main objective is to break down complex ideas and make them understandable to a wider audience. These essays often require deep analysis and critical thinking to present the chosen concept in a comprehensive and enlightening manner.
A concept essay goes beyond simply defining a concept but delves deeper into the underlying principles and implications. It requires the writer to provide insight, examples, and evidence to support their claims and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the concept being discussed.
Concept essays also provide an opportunity for writers to explore new and innovative ideas and present them in a thought-provoking way. They allow for personal interpretation and creativity, encouraging writers to examine a concept from different angles and offer unique perspectives.
Furthermore, concept essays can be used as a tool for education and learning, helping readers expand their knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of various concepts. By breaking down complex ideas into more digestible forms, these essays enable readers to grasp abstract concepts and apply them to real-world situations.
In conclusion, the purpose of a concept essay is to convey abstract ideas or concepts in a clear and engaging manner, utilizing critical thinking and analysis. By presenting complex ideas in a comprehensive way, concept essays facilitate understanding and encourage readers to explore and expand their knowledge in the chosen subject area.
Choosing a Strong and Specific Concept
When it comes to crafting a well-written piece of work, selecting a compelling and precise concept is crucial. The concept you choose will serve as the foundation for your essay, shaping the content, tone, and direction of your writing.
Before diving into the process of choosing a concept, it’s important to understand what exactly a concept is. In this context, a concept can be defined as a broad idea or theme that encapsulates a particular subject or topic. It is the main point or central idea that you want to convey to your readers through your essay.
An effective concept should be strong, meaning it should be able to capture the attention and interest of your readers. It should be something that has depth and substance, allowing for exploration and analysis. A strong concept will engage your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
In addition to being strong, your concept should also be specific. It should be focused and clearly defined, narrowing down your topic to a specific aspect or angle. A specific concept will help you maintain a clear direction in your writing and prevent your essay from becoming too broad or unfocused.
To choose a strong and specific concept, start by brainstorming ideas related to your topic. Think about the main themes or issues you want to address in your essay. Consider what aspects of the topic interest you the most and which ones you feel are worth exploring further.
Once you have a list of potential concepts, evaluate each one based on its strength and specificity. Ask yourself whether the concept captures your interest and whether it has the potential to captivate your audience. Consider whether it is specific enough to guide your writing and provide a clear focus for your essay.
By choosing a strong and specific concept, you will set yourself up for success in writing your concept essay. Remember to select a concept that is compelling, focused, and meaningful to you and your readers. With a well-chosen concept, you will be able to create a thought-provoking and engaging essay that effectively conveys your ideas.
Developing a Clear and Coherent Thesis Statement
When crafting an effective essay, one of the most important elements to consider is the development of a clear and coherent thesis statement. The thesis statement acts as the central theme or main argument of your essay, providing a roadmap for your readers to understand the purpose and direction of your writing.
A well-developed thesis statement not only states your main argument but also provides a clear focus for your essay. It helps you organize your thoughts and ensures that your essay remains cohesive and logical. A strong thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and guides the reader through your main ideas.
To develop a clear and coherent thesis statement, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the topic you are writing about. Conducting research and gathering relevant information will help you form a solid foundation for your thesis statement. Make sure to analyze different perspectives on the topic and consider any counterarguments that may arise.
Once you have a good understanding of the topic, you can begin brainstorming and drafting your thesis statement. Start by considering the main idea or argument you want to communicate to your readers. Your thesis statement should be concise and specific, clearly conveying your main point. Avoid vague or general statements that lack focus.
In addition to being clear and concise, your thesis statement should also be arguable. It should present a debatable claim that can be supported with evidence and logical reasoning. This allows you to engage your readers and encourages them to consider different perspectives on the topic.
After drafting your thesis statement, it is important to review and revise it as needed. Make sure it accurately reflects the content and direction of your essay. Consider seeking feedback from peers or instructors to ensure that your thesis statement is clear, coherent, and effectively conveys your main argument.
In conclusion, developing a clear and coherent thesis statement is essential for writing an effective essay. It sets the tone for your entire essay, provides a clear focus, and guides the reader through your main ideas. By thoroughly understanding the topic, brainstorming and drafting a concise and arguable thesis statement, and revising as needed, you can ensure that your essay is well-structured and persuasive.
Structuring Your Concept Essay Effectively

Creating a well-organized structure is vital when it comes to conveying your ideas effectively in a concept essay. By carefully structuring your essay, you can ensure that your audience understands your concept and its various aspects clearly. In this section, we will explore some essential guidelines for structuring your concept essay.
1. Introduction: Begin your essay with an engaging introduction that captures the reader’s attention. This section should provide a brief overview of the concept you will be discussing and its significance. You can use an anecdote, a rhetorical question, or a thought-provoking statement to make your introduction compelling.
2. Definition: After the introduction, it is crucial to provide a clear definition of the concept you will be exploring in your essay. Define the concept in your own words and highlight its key characteristics. You may also include any relevant background information or historical context to enhance the reader’s understanding.
3. Explanation: In this section, you will delve deeper into the concept and explain its various elements, components, or features. Use examples, analogies, or real-life situations to illustrate your points and make them more relatable to the reader. Break down complex ideas into simpler terms and highlight the connections between different aspects of the concept.
4. Analysis: Once you have provided a thorough explanation of the concept, it is time to analyze it critically. Discuss different perspectives or interpretations of the concept and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. Consider any controversies or debates surrounding the concept and present a balanced view by weighing different arguments.
5. Examples and Case Studies: To further support your arguments and enhance the reader’s understanding, include relevant examples and case studies. These examples can be from real-life situations, historical events, or fictional scenarios. Analyze how the concept has been applied or manifested in these examples and discuss their implications.
6. Conclusion: Conclude your concept essay by summarizing your main points and restating the significance of the concept. Reflect on the insights gained from your analysis and offer any recommendations or suggestions for further exploration. End your essay on a thought-provoking note that leaves the reader with a lasting impression.
By structuring your concept essay effectively, you can ensure that your ideas are presented coherently and persuasively. Remember to use clear and concise language, provide logical transitions between sections, and support your arguments with evidence. With a well-structured essay, you can effectively communicate your understanding of the concept to your audience.
Using Concrete Examples to Illustrate Your Concept
One effective way to clarify and reinforce your concept in a concept essay is by using concrete examples. By providing specific and tangible instances, you can help your readers grasp the abstract and theoretical nature of your concept. Concrete examples bring your concept to life, making it easier for your audience to understand and relate to.
Instead of relying solely on abstract theories, you can support your concept with real-life scenarios, research studies, or personal anecdotes. These examples add depth and relevance to your essay, making it more engaging and meaningful.
When choosing examples to illustrate your concept, it is important to select ones that accurately represent the core elements of your concept. Look for examples that exhibit the underlying principles, attributes, or behaviors that are associated with your concept.
For instance, if your concept is “leadership,” you can provide examples of influential leaders from history or modern-day society. These examples can demonstrate the qualities that define effective leadership, such as integrity, communication skills, and the ability to inspire and motivate others.
Additionally, when presenting concrete examples, ensure that they are relevant and relatable to your target audience. Consider the background and interests of your readers and choose examples that they can easily comprehend and connect with. This will enhance the effectiveness of your essay and create a stronger impact.
In conclusion, using concrete examples is a powerful technique for illustrating your concept in a concept essay. By incorporating specific instances, you can bring clarity, relevance, and authenticity to your writing. This approach allows your readers to grasp your concept more easily and appreciate its practical application in real-life scenarios.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.

Concept Essay Paper

Every writer has his/her own way of presenting a topic or an idea to the readers. Some of them wants to stir imaginations and make you create characters and places of your own. Others want to provoke your emotions and indulge you into the story. While others want to simply demonstrate a subject.
Essay writing is considered a talent. It requires a creative mind to be able to present thoughts and emotions and put them into writing. And the most difficult part is how to make it appealing to the readers. Knowing how to start an essay is even more difficult because you have to find the right inspiration to write.
What is Concept Essay? A concept essay is a piece writing that is used to present an idea or a topic with the sole purpose of providing a clear definition and explanation. Their usual content are those topics that may have previously been presented but were not given with full emphasis. Others are controversial and timely issues that raises questions but are not given full answers. What is Concept Paper? A concept paper is a brief document written to provide an overview of a project, research, or idea. It outlines the main goals, objectives, and methods of the intended project, serving as a preliminary proposal. Concept papers are often used to seek approval or funding, presenting the project’s significance, potential impact, and feasibility in a concise manner. This document helps stakeholders, such as sponsors or academic committees, understand the essence of the proposed work and decide whether to support it further.
Concept Paper Writing Topics & Ideas
In conceptual writing, the central focus lies on the idea or concept driving the work, positioning it as the cornerstone of the narrative. This approach dictates that all planning and critical decisions are determined in advance, rendering the actual writing process secondary. Essentially, the concept acts as a blueprint, guiding the creation of the text in a manner that is almost mechanical. Through this method, the initial idea transforms into an engine that propels the development of the written piece, underscoring the precedence of thought over the act of writing itself. Below are the topics and ideas of concept writing
- The Evolution of Digital Privacy
- The Psychology Behind Social Media Addiction
- The Impact of Remote Work on Urban Development
- Sustainability in Fashion: A New Trend
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Cultural Identity in a Globalized World
- The Ethics of Genetic Editing
- The Role of Cryptocurrency in Modern Finance
- Mental Health Awareness in the Workplace
- The Influence of Music on Cognitive Development
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Biodiversity
- The Philosophy of Minimalism and Its Life Benefits
- The Rise of E-Learning and Its Educational Impacts
- Urban Farming: Solutions for Food Security
- Virtual Reality: Transforming Entertainment and Education
- The Gig Economy and Its Impact on Traditional Employment
- Social Entrepreneurship: Business for Social Good
- The Intersection of Art and Technology
- Cybersecurity in the Age of Internet of Things
- The Role of Nutrition in Preventing Chronic Diseases
Concept Essay Paper Format
Introduction.
Hook : Start with an engaging sentence to capture the reader’s interest. Background Information : Provide a brief context for the concept you are going to explore. Thesis Statement : Clearly state the concept or idea you will discuss, outlining the main point or argument of your essay.
Body Paragraphs
Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the concept or idea.
Topic Sentence : Introduce the main idea of the paragraph that supports your thesis. Explanation : Offer a detailed explanation of the idea, including definitions, descriptions, and relevant information. Examples and Evidence : Use specific examples, illustrations, or evidence to support your explanations and arguments. This could include statistics, quotes from experts, or real-life scenarios. Analysis : Analyze how the example or evidence supports your topic sentence and thesis, explaining its significance. Transition : Conclude the paragraph with a sentence that smoothly transitions to the next point or paragraph.
Summary of Main Points : Briefly recap the key arguments or explanations presented in your essay. Restatement of Thesis : Reiterate your thesis statement, highlighting how it has been supported through your discussion. Final Thoughts : Offer closing remarks that leave a lasting impression on the reader. This could include implications, future prospects, or a call to action related to the concept.
Concept Paper Example
Enhancing Digital Literacy in Rural Communities: A Pathway to Bridging the Digital Divide The rapid advancement of digital technologies has significantly transformed the way we live, work, and communicate. However, this digital revolution has also led to a widening gap between urban and rural areas in terms of access to technology and digital skills. This concept paper proposes a comprehensive project aimed at enhancing digital literacy in rural communities as a fundamental step toward bridging the digital divide. By equipping rural populations with the necessary digital skills, the project seeks to empower individuals, improve educational outcomes, and unlock economic opportunities. The purpose of this initiative is to develop and implement a scalable digital literacy program tailored to the needs of rural communities. This program will focus on basic computer skills, internet navigation, online safety, and the use of digital tools for education and entrepreneurship. The significance of this project lies in its potential to transform the lives of rural residents, providing them with the skills required to participate fully in the digital world. Objectives of the project include: Assessing the current level of digital literacy in targeted rural areas. Developing a comprehensive digital literacy curriculum that addresses identified needs. Delivering digital literacy training to residents of rural communities through workshops and online modules. Establishing community-based digital hubs equipped with internet access and computing resources. Evaluating the impact of the program on participants’ digital skills, economic opportunities, and educational outcomes. The methodology will encompass a needs assessment to identify specific digital literacy gaps, followed by the development of a curriculum that incorporates both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Training will be delivered through a combination of in-person workshops and online modules, ensuring broad access. Pre- and post-program assessments will measure the effectiveness of the training. Expected outcomes include improved digital literacy rates among rural populations, increased access to educational and economic opportunities, and enhanced participation in the digital economy. The project aims to establish a model for digital literacy training that can be replicated and scaled in other rural areas. In conclusion, enhancing digital literacy in rural communities presents a critical opportunity to bridge the digital divide and foster equitable access to the benefits of the digital age. This concept paper outlines a clear and actionable plan to empower rural residents with the digital skills necessary for success in a rapidly evolving world.
Concept Essay Outline Sample

penandthepad.com
Concept Essay on Love

professays.com
Concept on Success

nicoletaylor13.weebly.com
Self Concept Essay Example

bestessayhelp.com
Cultural Concept Essay Sample

missouriwestern.edu
Concept Analysis

bristolcc.edu
Concept Essay Format

Business Concept Essay Example

Free Concept Essay

What Are the Steps to Writing a Concept Essay?
One of the things to consider in essay writing is to know how to start an essay. In addition to that, you have to come up with the steps on how to write an effective one.
- Choose a topic. An effective essay is one that presents a more relevant topic. You need to choose the right topic first before you start writing.
- Do your research. You have to back up your claims with factual information from reliable sources. Present at least three to four points for reference.
- Create your outline. The essay outline of your concept essay because readers will consider how your ideas are presented.
Key Elements of Concept Paper
A concept paper outlines a project or idea, presenting its purpose, significance, methodology, expected outcomes, and, if applicable, budget and timeline. It serves to introduce and justify the project, aiming to secure interest or support by succinctly detailing its goals and potential impact.
The key elements are:
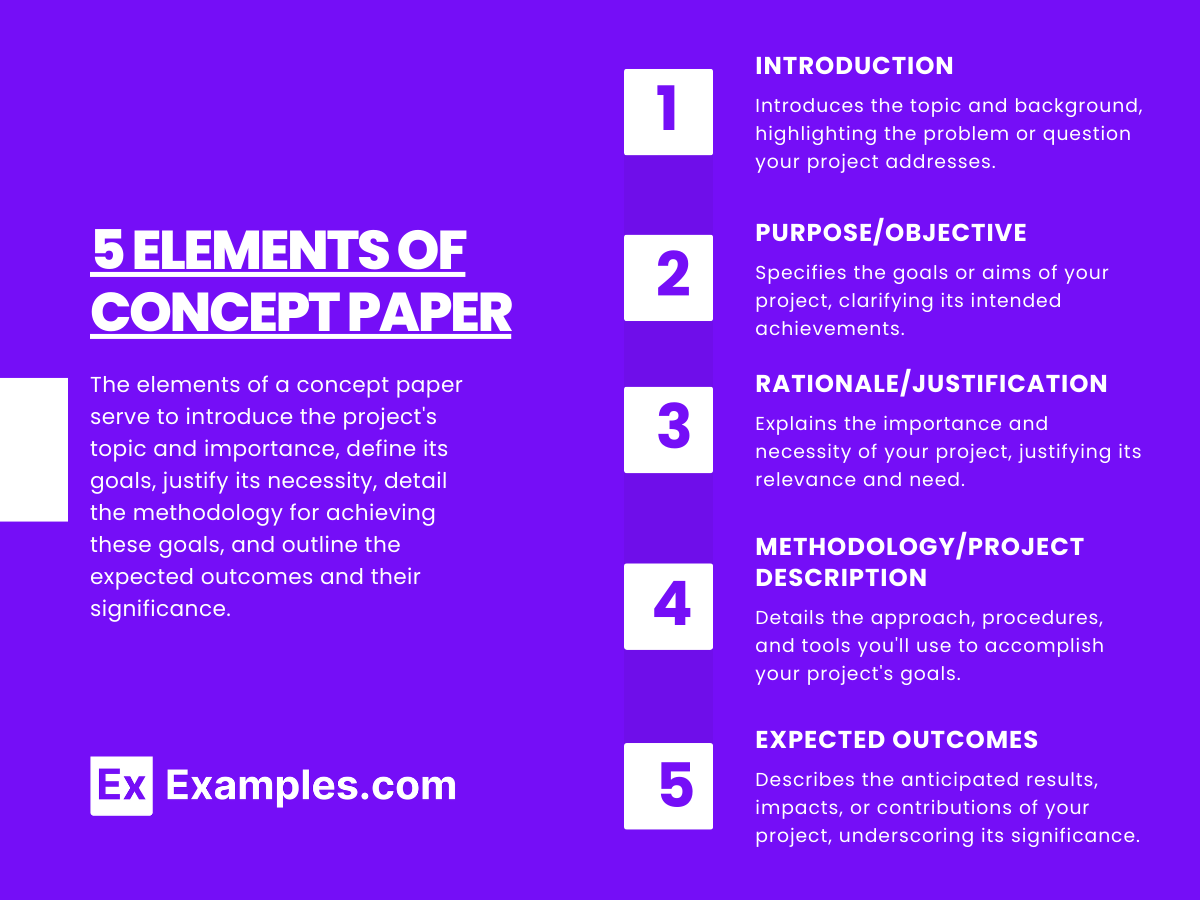
How to Make/ Create Concept Paper
1. choose your topic wisely.
Select a topic that is both interesting to you and relevant to your audience or potential funders. It should address a specific problem, need, or question.
2. Conduct Preliminary Research
Gather information on your topic to ensure there’s enough background material to support your concept. This research will help refine your idea and identify gaps your project could fill.
3. Write the Introduction
Start with a strong introduction that captures the essence of your concept. Include a brief overview of the problem or issue your project intends to address, its significance, and why it is worth exploring or implementing.
4. State the Purpose or Objective
Clearly articulate the purpose or objectives of your project or research. What do you aim to achieve? Be specific about the outcomes you anticipate.
5. Provide Background Information
Offer a detailed background that gives context to your concept. This section should include any relevant research, current findings, and a justification for your project or study.
6. Describe the Project or Research Design
Outline how you plan to achieve your objectives. This includes your methodology, the steps you will take, and the resources you will need. For research projects, specify your research questions, hypothesis, and the methods for data collection and analysis.
7. Discuss the Significance
Explain the potential impact of your project or research. How will it contribute to the field, benefit a specific group, or solve a problem? This section is crucial for persuading readers of the value of your concept.
8. Outline the Budget (if applicable)
If your concept paper is for a project requiring funding, provide an estimate of the budget. Break down the costs involved, including materials, personnel, and any other resources.
9. Set a Timeline
Include a proposed timeline for your project or research. This demonstrates planning and feasibility and helps funders understand the project’s scope.
10. Conclude Your Paper
Summarize the key points of your concept paper, reinforcing the importance and feasibility of your project or research. End with a call to action or a statement of next steps.
Importance of Concept Essay
As we go along the path of discovering new and better ideas that could feed our minds with more useful information, we also need to pause and make sure that these concepts are well explained.
The main importance of a concept analytical essay is to provide a more vivid evaluation as well as explanation of the ideas that may seem ambiguous. We cannot just live in a world where we are fed with information that we are supposed to accept. Remember that we have the freedom to accept what is true and decline what is not. With a concept essay, we can dig deeper into things and find out its true essence.
When do you need a concept paper?
A concept paper is needed when initiating a project, seeking funding, or proposing an idea to stakeholders. It serves as a preliminary outline, presenting the project’s rationale, goals, and methodology in a concise format to gauge interest or secure support.
How is a concept paper different from a research paper?
A concept paper differs from a research paper in its purpose and scope. While a concept paper outlines a project idea, seeking approval or funding with a focus on potential impact and methodology, a research paper presents detailed findings from completed research, including analysis and results.
What is the purpose of a concept essay?
The purpose of a concept essay is to explore and clarify a specific idea or concept. It aims to deepen understanding and stimulate thought by examining the concept from various angles, using examples, definitions, and personal insights to articulate its significance and implications.
Concept Essay Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Explore the concept essay of happiness: what does it mean and how is it achieved?
Discuss in a concept essay the idea of freedom in the modern world.
- Food & Dining
- Coronavirus
- Real Estate
- Seattle History
- PNW Politics
How to Write a Concept Essay for College English
- College & Higher Education
Related Articles
Explanation on theme in literature for students, how to write an essay that stands out, how to write an explanation essay.
- How to Write a College Critical Thinking Essay
- What Does It Mean to Have an Objective Tone in an Essay?
Concept essays provide a chance to explore ideas you might previously have taken for granted. Writing a concept essay requires careful exploration of a concept, a concise and interesting thesis and a strong overall structure. Before you begin to write, it may be helpful to engage in some prewriting. Word webs, outlines and free writing can help you uncover insights about a topic you might not realize at first. After prewriting, develop a working thesis, an interesting introduction, body paragraphs and a conclusion.
Your working thesis should define a concept you will develop throughout the essay. Allow your working thesis to change as you explore the concept instead of trying to build an essay around a definition that you no longer believe. Though a bit persuasive by nature, a concept essay thesis should not be an argument. Instead, a concept essay thesis should provide one well-reasoned definition among many, because the meaning of a concept can be difficult, if not impossible, to define through objective reasoning. A clear definition of a concept also can allow you to explore it in various contexts, whereas a vague definition might leave you unsure of why the concept matters. Finalize your thesis once most of the paper has been written.
Introduction
Strong introductions should show why a concept matters in real life and how your essay will explore the connection between the concept and human experiences. If the concept is “success,” an introduction might provide an anecdote in which success was an important part of your life or some world event, such as the Olympics. Narrative introductions often work for positive concepts such as “happiness,” while more objective introductions work best for somber concepts such as “war.”
Develop body paragraphs that explore important aspects of the concept. Because concepts often are more complex than short college essays can fully account for, choose the most illuminating aspects or those with the most relevance to you and your audience. For example, if the concept of an essay is “success,” body paragraphs might discuss the differences between professional, cultural and personal success. Use a strong topic sentence to indicate the purpose of each body paragraph, and connect all of your body paragraphs to expand your definition of the concept.
Conclusions in a concept essay typically re-establish a definition of the concept based on the aspects that you presented, as the Purdue Online Writing Lab agrees. It also can be helpful to conclude by showing how your definition of the concept can help readers understand the concept in their lives. For example, strong conclusions in concept essays demonstrate that you have thought deeply about a topic, and such demonstrations are useful in the professional world, where well-informed thinkers become assets.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Expository Essays
- California State University -- Fullerton: Explaining A Concept -- Essay #3
- Southwestern Minnesota State University: Academic Inquiry and the Explain a Concept Essay
Writing in the Lehigh Valley, Jordan Weagly has been a professional writer since 2007. His work has appeared in “Travel Host” and “The Keystone.” Weagly has more than four years of experience as an English tutor and holds a MA in English as well as a BA in professional writing from Kutztown University of Pennsylvania.
The Differences Between a Reflective & Narrative Essay
How to write a movie response essay, what is the difference between a memoir and personal narrative, how to write a personal profile for a university application, thesis statements vs. main ideas, what stage of the plot comes after conflict, what are the similarities of persuasive and narrative essays, what are the differences between an autobiographical narrative & a biography, compare & contrast essay structure, most popular.
- 1 The Differences Between a Reflective & Narrative Essay
- 2 How to Write a Movie Response Essay
- 3 What Is the Difference Between a Memoir and Personal Narrative?
- 4 How to Write a Personal Profile for a University Application
How to Write a Concept Paper Easily with Our Guide

Did you know that some of the most revolutionary ideas in history started with a simple concept paper? From scientific breakthroughs to groundbreaking inventions, the power of well-crafted concept papers cannot be underestimated.
In this article, experts at our academic essay writing service will demystify the process of writing a concept paper, offering straightforward tips and guidance to help you articulate your ideas effectively. Whether you're a researcher, entrepreneur, or student, you'll lay the foundation for your next big endeavor effortlessly.
Defining What is a Concept Paper
A concept paper is a starting point for any major project or research endeavor. When you're asked to write one, what your teachers or professors are really asking for is a clear, concise summary of what you plan to explore or investigate. It's your chance to explain your idea, why it matters, and how you're going to tackle it.
Imagine you're pitching your idea to someone who doesn't know anything about it. You want to grab their attention and get them excited about what you're planning to do. That's what a concept paper is all about – setting the stage for your project or research in a way that makes people want to learn more.
Don't Delay Your Scholarly Pursuits!
Our team is here to nurture your concepts! Seize this opportunity to lay the groundwork for your academic exploration.
Why Does a Concept Paper Matter
So, why does knowing how to write a concept paper for academic research matter? First off, it helps you clarify your thoughts and organize your ideas. Writing down your concept forces you to think through the details of your project, which can be super helpful, especially when things start to get overwhelming.
Secondly, it's a way to get feedback early on. By sharing your concept paper with your teachers, advisors, or classmates, you can get valuable input that can help you refine your idea and make it even better.
Plus, it shows that you're serious about your project. Taking the time to write a concept paper demonstrates to your instructors that you've put thought and effort into your work, which can earn you some serious brownie points.
Understanding How Long is a Concept Paper
When it comes to the length of a concept paper, think quality over quantity. It's not about hitting a specific word count; it's about conveying your ideas clearly and concisely. In general, a concept paper is meant to be short and to the point. You want to give enough detail to explain your idea thoroughly, but you don't want to overwhelm your reader with unnecessary information.
As a rule of thumb, most concept papers range from 1 to 3 pages. However, this can vary depending on your specific assignment or the requirements of the project you're proposing.
The key is to focus on the essentials. Include a brief introduction to your topic, a clear statement of your purpose or objective, an overview of your methodology or approach, and a summary of the potential impact or significance of your project. And if you ever need further help, simply ask us - write my research paper for the professionally crafted project.
Concept Paper Vs. Research Paper
While both concept papers and research papers are common in academia, they serve different purposes and have distinct formats.
.webp)
A concept paper, as we've discussed, is a concise document that outlines the basic idea or proposal for a project. It's like the blueprint or roadmap for your research endeavor. The focus here is on articulating the central concept, defining the objectives, and outlining the methodology. Think of writing a concept paper as laying the groundwork before diving into the detailed work of a research project.
On the other hand, a research paper is a more comprehensive and in-depth exploration of a topic or question. It involves conducting original research, analyzing data, and presenting findings in a formal written format. Research papers typically follow a structured format, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
How to Write a Concept Paper in 8 Steps
Alright, getting into the nitty-gritty of writing your concept paper format might seem a bit overwhelming at first, but don't worry! We've got your back. By breaking down the process into eight manageable steps, we'll guide you through each stage with clarity and confidence.
.webp)
Define the Study Title and Its Objectives
The first crucial step in crafting your concept paper is to clearly define the study title and its objectives. This sets the foundation for your entire paper and helps guide your research direction.
Begin by crafting a clear and concise title that effectively communicates the essence of your study. Your title should be descriptive yet succinct, giving readers a glimpse into the focus of your research.
Next, outline the objectives of your study. What specific goals do you aim to achieve through your research? Be precise and realistic in outlining these objectives, ensuring they are achievable within the scope of your study.
Explain the Study's Context and Extent
After defining the title and objectives, it's essential to provide context and define the extent of your study. This step of how to write a concept paper for college helps readers understand the background and scope of your research.
Start by providing background information on the topic of your study. Discuss relevant theories, concepts, or existing research that contextualizes your work and highlights its importance.
Next, define the extent of your study by outlining its boundaries and limitations. What specific aspects of the topic will you focus on, and what areas will you exclude? Clarifying these boundaries helps ensure that your research remains focused and manageable.
Additionally, consider discussing the significance of your study within the broader field. How does your research contribute to existing knowledge, and what potential impact does it have?
Identify the Issue
This is where you clearly articulate the core challenge or question that your research seeks to explore. Start by providing a concise overview of the issue at hand. What is the specific problem or question that motivates your research? Why is it important or relevant within your field of study?
Next, consider providing context or background information that helps readers understand the significance of the issue. This could include discussing relevant trends, statistics, or real-world examples that highlight the importance of addressing the problem.
Finally, be sure to articulate the significance of the issue within the broader context of your field. Why is it important to study this particular issue, and what potential impact could your research have on addressing it?
List Goals and Objectives
In this step, you'll make a concept paper outline of the specific goals and objectives of your study. Goals represent the broader aims of your research, while objectives provide clear, measurable steps toward achieving those goals.
Start by defining your overarching goals. What do you hope to accomplish through your research? Think about the broader outcomes or changes you aim to bring about in your field or community.
Next, break down these goals into smaller, achievable objectives. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They should outline the concrete steps you will take to accomplish your goals.
Consider organizing your goals and objectives into a hierarchical structure, with broader goals at the top and more specific objectives underneath. Even if you'd rather buy essay from our pros, this step will help you provide clarity and coherence to your research plan.
Approach and Methodology
In this step, you'll detail the approach and methodology you'll use to conduct your research. According to our expert thesis writing service , this section is crucial as it outlines the methods you'll employ to address your research question and achieve your objectives.
Start by explaining your overall approach to research. Will you be conducting qualitative or quantitative research, or perhaps a combination of both? Describe the rationale behind your chosen approach and how it aligns with your research goals.
Next, outline the specific methodologies you'll use to collect and analyze data. This may include methods such as surveys, interviews, experiments, or literature reviews. Provide justification for why each method is appropriate for addressing your research question and objectives.
Be sure to consider any ethical considerations or limitations associated with your chosen methodologies and outline how you plan to address them.
Finally, discuss your data analysis plan. How will you analyze the data you collect to draw meaningful conclusions? Will you use statistical analysis, thematic coding, or another method?
Overview of Planned Methods and Expected Outcomes
In this step of how to write a concept paper for research, you'll provide an overview of the specific methods you plan to use and outline the expected outcomes or results.
Start by summarizing the methods you'll employ to collect data. This may include qualitative methods such as interviews or focus groups, quantitative methods such as surveys or experiments, or a combination of both. Briefly explain why you've chosen these methods and how they align with your research goals.
Next, outline the planned steps for implementing each method. Describe the procedures you'll follow to collect and analyze data, including any tools or instruments you'll use.
After detailing your methods, discuss the expected outcomes or results of your research. What do you hope to learn or discover through your study? How will your findings contribute to existing knowledge in your field?
Be realistic in your expectations and consider potential challenges or limitations that may affect your results. By acknowledging these factors upfront, you demonstrate a thoughtful and nuanced understanding of your research process.
Include Supporting Details
Here, you'll enrich your concept paper by incorporating supporting details that bolster your argument and provide additional context for your research.
Start by providing relevant background information or literature reviews that support your research topic. This could include citing key studies, theories, or concepts that inform your understanding of the issue.
Next, consider including any relevant data, statistics, or examples that illustrate the significance of your research topic. This could involve presenting findings from previous studies, real-world examples, or case studies that highlight the need for further investigation.
Additionally, discuss any theoretical frameworks or conceptual models that underpin your research approach. How do these frameworks help guide your study and shape your research questions?
Finally, be sure to cite your sources properly using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). This demonstrates academic integrity and allows readers to verify the information you've presented.
Wrap Up with a Summary
In this final step, you'll bring your concept paper to a close by summarizing the key points and reinforcing the significance of your research.
If you're uncertain how to write a conclusion for an essay , start by briefly recapping the main elements of your concept paper, including the research topic, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. This helps reinforce the central message of your paper and reminds readers of the key insights you've presented.
Next, reiterate the importance of your research topic and its potential impact within your field. Emphasize how your study fills a gap in existing knowledge or addresses a pressing issue, highlighting the relevance and significance of your research.
Finally, conclude with a call to action or a thought-provoking statement that encourages further reflection or discussion. This could involve suggesting avenues for future research, proposing practical implications for policymakers or practitioners, or inviting readers to consider the broader implications of your findings.
Tips for Writing a Concept Paper
Now that you've got a solid understanding of how to write a concept paper, let's explore some invaluable tips to help you navigate the writing process with finesse.
- Be Specific in Your Objectives : Clearly define your objectives with measurable outcomes. Avoid vague language and ensure each objective is actionable and achievable within the scope of your study. Specific objectives provide clarity and help guide your research effectively.
- Provide Contextual Background : Offer sufficient background information to contextualize your research topic. This includes explaining relevant theories, historical context, or existing literature related to your study. Providing context in your concept paper helps readers understand the significance of your research and its relevance within the broader field.
- Justify Your Methodological Choices : Explain why you've chosen specific research methods and justify their appropriateness for your study. Consider factors such as feasibility, ethical considerations, and alignment with your research objectives. Providing a rationale for your methodological choices adds credibility to your research approach.
- Anticipate and Address Limitations : Acknowledge potential limitations or challenges associated with your study and discuss how you plan to mitigate them. This demonstrates a thoughtful approach to your research and shows that you've considered the broader implications of your study. Being transparent about limitations also helps manage expectations and build trust with your audience.
Concept Paper Example
Now that we've explored the steps and tips for writing a concept paper let's put theory into practice. In this section, we'll provide you with a concept paper example to illustrate how these principles can be applied in a real-world scenario.
Eager to See Your Ideas Leap Off the Page?
Don't wait any longer—bring your concepts to life with our expertly crafted concept papers.
Concept Paper Topics
In this section, we'll provide you with a range of thought-provoking concept paper ideas spanning various disciplines and interests. Whether you're passionate about social issues, scientific advancements, or want to learn how to research a topic on cultural phenomena, you're sure to find inspiration here.
- The Influence of Instagram Fitness Influencers on Body Image Perception Among Adolescent Girls
- Implementing Bicycle-Sharing Programs to Reduce Carbon Emissions in Downtown Metropolitan Areas
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Food Pantry Programs in Alleviating Food Insecurity Among Undergraduate Students at Urban Universities
- Assessing the Accuracy and Efficiency of Machine Learning Algorithms in Early Detection of Breast Cancer Using Medical Imaging Data
- Strategies for Increasing Female Representation in Computer Science and Engineering Programs at Universities
- Investigating the Impact of Workplace Mindfulness Programs on Employee Burnout Rates in High-stress Industries
- Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Services in Rural Appalachia: A Case Study
- The Ecological Impact of Microplastic Contamination on Coral Reef Ecosystems in the Caribbean
- Addressing Online Harassment and Cyberbullying Among Middle School Students Through Digital Literacy Education Programs
- The Relationship Between Proximity to Parks and Greenspaces and Mental Health Outcomes in Urban Dwellers: A Cross-sectional Study
- Virtual Reality Rehabilitation for Upper Limb Motor Recovery After Stroke: A Comparative Analysis of Traditional Therapy Methods
- Evaluating the Economic Viability and Environmental Sustainability of Indoor Vertical Farming Systems in Urban Settings
- Psychological Profiles of Adolescent Online Gamers: A Longitudinal Study on Risk Factors for Gaming Addiction
- Peer Mentoring Interventions for Improving Academic Performance and Retention Rates Among First-generation College Students in STEM Majors
- Universal Basic Income Pilot Programs: Assessing Socioeconomic Impacts and Policy Implications in Scandinavian Countries.
And there you have it - you've journeyed through the ins and outs of concept paper writing! You've learned the ropes, discovered valuable tips, explored an example, and got a bunch of topic ideas to fuel your creativity.
Now armed with the know-how, it's time to dive in and start crafting your concept paper. Remember to keep it focused, stay organized, and don't forget to let your passion shine through. With your enthusiasm and newfound skills, there's no doubt you'll create a paper that grabs attention and makes a real impact in your field.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Related Articles
.webp)

Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia and research. Understanding the nuances and significance of a concept paper is essential for any researcher aiming to lay a strong foundation for their investigation.
Table of Contents
What Is Concept Paper
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document which outlines the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal. It outlines the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project. It is usually two to three-page long overview of the proposal. However, they differ from both research proposal and original research paper in lacking a detailed plan and methodology for a specific study as in research proposal provides and exclusion of the findings and analysis of a completed research project as in an original research paper. A concept paper primarily focuses on introducing the basic idea, intended research question, and the framework that will guide the research.
Purpose of a Concept Paper
A concept paper serves as an initial document, commonly required by private organizations before a formal proposal submission. It offers a preliminary overview of a project or research’s purpose, method, and implementation. It acts as a roadmap, providing clarity and coherence in research direction. Additionally, it also acts as a tool for receiving informal input. The paper is used for internal decision-making, seeking approval from the board, and securing commitment from partners. It promotes cohesive communication and serves as a professional and respectful tool in collaboration.
These papers aid in focusing on the core objectives, theoretical underpinnings, and potential methodology of the research, enabling researchers to gain initial feedback and refine their ideas before delving into detailed research.
Key Elements of a Concept Paper
Key elements of a concept paper include the title page , background , literature review , problem statement , methodology, timeline, and references. It’s crucial for researchers seeking grants as it helps evaluators assess the relevance and feasibility of the proposed research.
Writing an effective concept paper in academic research involves understanding and incorporating essential elements:

How to Write a Concept Paper?
To ensure an effective concept paper, it’s recommended to select a compelling research topic, pose numerous research questions and incorporate data and numbers to support the project’s rationale. The document must be concise (around five pages) after tailoring the content and following the formatting requirements. Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document’s impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows:
1. Write a Crisp Title:
Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper’s content. It should serve as a preview for the reader.
2. Provide a Background Information:
Give a background information about the issue or topic. Define the key terminologies or concepts. Review existing literature to identify the gaps your concept paper aims to fill.
3. Outline Contents in the Introduction:
Introduce the concept paper with a brief overview of the problem or idea you’re addressing. Explain its significance. Identify the specific knowledge gaps your research aims to address and mention any contradictory theories related to your research question.
4. Define a Mission Statement:
The mission statement follows a clear problem statement that defines the problem or concept that need to be addressed. Write a concise mission statement that engages your research purpose and explains why gaining the reader’s approval will benefit your field.
5. Explain the Research Aim and Objectives:
Explain why your research is important and the specific questions you aim to answer through your research. State the specific goals and objectives your concept intends to achieve. Provide a detailed explanation of your concept. What is it, how does it work, and what makes it unique?
6. Detail the Methodology:
Discuss the research methods you plan to use, such as surveys, experiments, case studies, interviews, and observations. Mention any ethical concerns related to your research.
7. Outline Proposed Methods and Potential Impact:
Provide detailed information on how you will conduct your research, including any specialized equipment or collaborations. Discuss the expected results or impacts of implementing the concept. Highlight the potential benefits, whether social, economic, or otherwise.
8. Mention the Feasibility
Discuss the resources necessary for the concept’s execution. Mention the expected duration of the research and specific milestones. Outline a proposed timeline for implementing the concept.

9. Include a Support Section:
Include a section that breaks down the project’s budget, explaining the overall cost and individual expenses to demonstrate how the allocated funds will be used.
10. Provide a Conclusion:
Summarize the key points and restate the importance of the concept. If necessary, include a call to action or next steps.
Although the structure and elements of a concept paper may vary depending on the specific requirements, you can tailor your document based on the guidelines or instructions you’ve been given.
Here are some tips to write a concept paper:

Example of a Concept Paper
Here is an example of a concept paper. Please note, this is a generalized example. Your concept paper should align with the specific requirements, guidelines, and objectives you aim to achieve in your proposal. Tailor it accordingly to the needs and context of the initiative you are proposing.
Download Now!
Importance of a Concept Paper
Concept papers serve various fields, influencing the direction and potential of research in science, social sciences, technology, and more. They contribute to the formulation of groundbreaking studies and novel ideas that can impact societal, economic, and academic spheres.
A concept paper serves several crucial purposes in various fields:

In summary, a well-crafted concept paper is essential in outlining a clear, concise, and structured framework for new ideas or proposals. It helps in assessing the feasibility, viability, and potential impact of the concept before investing significant resources into its implementation.
How well do you understand concept papers? Test your understanding now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Role of AI in Writing Concept Papers
The increasing use of AI, particularly generative models, has facilitated the writing process for concept papers. Responsible use involves leveraging AI to assist in ideation, organization, and language refinement while ensuring that the originality and ethical standards of research are maintained.
AI plays a significant role in aiding the creation and development of concept papers in several ways:
1. Idea Generation and Organization
AI tools can assist in brainstorming initial ideas for concept papers based on key concepts. They can help in organizing information, creating outlines, and structuring the content effectively.
2. Summarizing Research and Data Analysis
AI-powered tools can assist in conducting comprehensive literature reviews, helping writers to gather and synthesize relevant information. AI algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of data, providing insights and statistics to support the concept presented in the paper.
3. Language and Style Enhancement
AI grammar checker tools can help writers by offering grammar, style, and tone suggestions, ensuring professionalism. It can also facilitate translation, in case a global collaboration.
4. Collaboration and Feedback
AI platforms offer collaborative features that enable multiple authors to work simultaneously on a concept paper, allowing for real-time contributions and edits.
5. Customization and Personalization
AI algorithms can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific requirements or context of the concept paper. They can assist in tailoring the concept paper according to the target audience or specific guidelines.
6. Automation and Efficiency
AI can automate certain tasks, such as citation formatting, bibliography creation, or reference checking, saving time for the writer.
7. Analytics and Prediction
AI models can predict potential outcomes or impacts based on the information provided, helping writers anticipate the possible consequences of the proposed concept.
8. Real-Time Assistance
AI-driven chat-bots can provide real-time support and answers to specific questions related to the concept paper writing process.
AI’s role in writing concept papers significantly streamlines the writing process, enhances the quality of the content, and provides valuable assistance in various stages of development, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the final document.
Concept papers serve as the stepping stone in the research journey, aiding in the crystallization of ideas and the formulation of robust research proposals. It the cornerstone for translating ideas into impactful realities. Their significance spans diverse domains, from academia to business, enabling stakeholders to evaluate, invest, and realize the potential of groundbreaking concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document outlining the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal such as the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project.
A good concept paper should offer a clear and comprehensive overview of the proposed research. It should demonstrate a strong understanding of the subject matter and outline a structured plan for its execution.
Concept paper is important to develop and clarify ideas, develop and evaluate proposal, inviting collaboration and collecting feedback, presenting proposals for academic and research initiatives and allocating resources.
I got wonderful idea
It helps a lot for my concept paper.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles
![what is the concepts of essay What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- AI in Academia
AI vs. AI: How to detect image manipulation and avoid academic misconduct
The scientific community is facing a new frontier of controversy as artificial intelligence (AI) is…

- Diversity and Inclusion
Need for Diversifying Academic Curricula: Embracing missing voices and marginalized perspectives
In classrooms worldwide, a single narrative often dominates, leaving many students feeling lost. These stories,…

- Career Corner
- Trending Now
Recognizing the signs: A guide to overcoming academic burnout
As the sun set over the campus, casting long shadows through the library windows, Alex…

Reassessing the Lab Environment to Create an Equitable and Inclusive Space
The pursuit of scientific discovery has long been fueled by diverse minds and perspectives. Yet…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
What is an Essay?
10 May, 2020
11 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
Well, beyond a jumble of words usually around 2,000 words or so - what is an essay, exactly? Whether you’re taking English, sociology, history, biology, art, or a speech class, it’s likely you’ll have to write an essay or two. So how is an essay different than a research paper or a review? Let’s find out!
Defining the Term – What is an Essay?
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer’s ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal observations and reflections of the author.

An essay can be as short as 500 words, it can also be 5000 words or more. However, most essays fall somewhere around 1000 to 3000 words ; this word range provides the writer enough space to thoroughly develop an argument and work to convince the reader of the author’s perspective regarding a particular issue. The topics of essays are boundless: they can range from the best form of government to the benefits of eating peppermint leaves daily. As a professional provider of custom writing, our service has helped thousands of customers to turn in essays in various forms and disciplines.
Origins of the Essay
Over the course of more than six centuries essays were used to question assumptions, argue trivial opinions and to initiate global discussions. Let’s have a closer look into historical progress and various applications of this literary phenomenon to find out exactly what it is.
Today’s modern word “essay” can trace its roots back to the French “essayer” which translates closely to mean “to attempt” . This is an apt name for this writing form because the essay’s ultimate purpose is to attempt to convince the audience of something. An essay’s topic can range broadly and include everything from the best of Shakespeare’s plays to the joys of April.
The essay comes in many shapes and sizes; it can focus on a personal experience or a purely academic exploration of a topic. Essays are classified as a subjective writing form because while they include expository elements, they can rely on personal narratives to support the writer’s viewpoint. The essay genre includes a diverse array of academic writings ranging from literary criticism to meditations on the natural world. Most typically, the essay exists as a shorter writing form; essays are rarely the length of a novel. However, several historic examples, such as John Locke’s seminal work “An Essay Concerning Human Understanding” just shows that a well-organized essay can be as long as a novel.
The Essay in Literature
The essay enjoys a long and renowned history in literature. They first began gaining in popularity in the early 16 th century, and their popularity has continued today both with original writers and ghost writers. Many readers prefer this short form in which the writer seems to speak directly to the reader, presenting a particular claim and working to defend it through a variety of means. Not sure if you’ve ever read a great essay? You wouldn’t believe how many pieces of literature are actually nothing less than essays, or evolved into more complex structures from the essay. Check out this list of literary favorites:
- The Book of My Lives by Aleksandar Hemon
- Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
- Against Interpretation by Susan Sontag
- High-Tide in Tucson: Essays from Now and Never by Barbara Kingsolver
- Slouching Toward Bethlehem by Joan Didion
- Naked by David Sedaris
- Walden; or, Life in the Woods by Henry David Thoreau
Pretty much as long as writers have had something to say, they’ve created essays to communicate their viewpoint on pretty much any topic you can think of!

The Essay in Academics
Not only are students required to read a variety of essays during their academic education, but they will likely be required to write several different kinds of essays throughout their scholastic career. Don’t love to write? Then consider working with a ghost essay writer ! While all essays require an introduction, body paragraphs in support of the argumentative thesis statement, and a conclusion, academic essays can take several different formats in the way they approach a topic. Common essays required in high school, college, and post-graduate classes include:
Five paragraph essay
This is the most common type of a formal essay. The type of paper that students are usually exposed to when they first hear about the concept of the essay itself. It follows easy outline structure – an opening introduction paragraph; three body paragraphs to expand the thesis; and conclusion to sum it up.
Argumentative essay
These essays are commonly assigned to explore a controversial issue. The goal is to identify the major positions on either side and work to support the side the writer agrees with while refuting the opposing side’s potential arguments.
Compare and Contrast essay
This essay compares two items, such as two poems, and works to identify similarities and differences, discussing the strength and weaknesses of each. This essay can focus on more than just two items, however. The point of this essay is to reveal new connections the reader may not have considered previously.
Definition essay
This essay has a sole purpose – defining a term or a concept in as much detail as possible. Sounds pretty simple, right? Well, not quite. The most important part of the process is picking up the word. Before zooming it up under the microscope, make sure to choose something roomy so you can define it under multiple angles. The definition essay outline will reflect those angles and scopes.
Descriptive essay
Perhaps the most fun to write, this essay focuses on describing its subject using all five of the senses. The writer aims to fully describe the topic; for example, a descriptive essay could aim to describe the ocean to someone who’s never seen it or the job of a teacher. Descriptive essays rely heavily on detail and the paragraphs can be organized by sense.
Illustration essay
The purpose of this essay is to describe an idea, occasion or a concept with the help of clear and vocal examples. “Illustration” itself is handled in the body paragraphs section. Each of the statements, presented in the essay needs to be supported with several examples. Illustration essay helps the author to connect with his audience by breaking the barriers with real-life examples – clear and indisputable.
Informative Essay
Being one the basic essay types, the informative essay is as easy as it sounds from a technical standpoint. High school is where students usually encounter with informative essay first time. The purpose of this paper is to describe an idea, concept or any other abstract subject with the help of proper research and a generous amount of storytelling.
Narrative essay
This type of essay focuses on describing a certain event or experience, most often chronologically. It could be a historic event or an ordinary day or month in a regular person’s life. Narrative essay proclaims a free approach to writing it, therefore it does not always require conventional attributes, like the outline. The narrative itself typically unfolds through a personal lens, and is thus considered to be a subjective form of writing.
Persuasive essay
The purpose of the persuasive essay is to provide the audience with a 360-view on the concept idea or certain topic – to persuade the reader to adopt a certain viewpoint. The viewpoints can range widely from why visiting the dentist is important to why dogs make the best pets to why blue is the best color. Strong, persuasive language is a defining characteristic of this essay type.

The Essay in Art
Several other artistic mediums have adopted the essay as a means of communicating with their audience. In the visual arts, such as painting or sculpting, the rough sketches of the final product are sometimes deemed essays. Likewise, directors may opt to create a film essay which is similar to a documentary in that it offers a personal reflection on a relevant issue. Finally, photographers often create photographic essays in which they use a series of photographs to tell a story, similar to a narrative or a descriptive essay.
Drawing the line – question answered
“What is an Essay?” is quite a polarizing question. On one hand, it can easily be answered in a couple of words. On the other, it is surely the most profound and self-established type of content there ever was. Going back through the history of the last five-six centuries helps us understand where did it come from and how it is being applied ever since.
If you must write an essay, follow these five important steps to works towards earning the “A” you want:
- Understand and review the kind of essay you must write
- Brainstorm your argument
- Find research from reliable sources to support your perspective
- Cite all sources parenthetically within the paper and on the Works Cited page
- Follow all grammatical rules
Generally speaking, when you must write any type of essay, start sooner rather than later! Don’t procrastinate – give yourself time to develop your perspective and work on crafting a unique and original approach to the topic. Remember: it’s always a good idea to have another set of eyes (or three) look over your essay before handing in the final draft to your teacher or professor. Don’t trust your fellow classmates? Consider hiring an editor or a ghostwriter to help out!
If you are still unsure on whether you can cope with your task – you are in the right place to get help. HandMadeWriting is the perfect answer to the question “Who can write my essay?”

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
What is Essay? Definition, Usage, and Literary Examples
Essay definition.
An essay (ES-ey) is a nonfiction composition that explores a concept, argument, idea, or opinion from the personal perspective of the writer. Essays are usually a few pages, but they can also be book-length. Unlike other forms of nonfiction writing, like textbooks or biographies, an essay doesn’t inherently require research. Literary essayists are conveying ideas in a more informal way.
The word essay comes from the Late Latin exigere , meaning “ascertain or weigh,” which later became essayer in Old French. The late-15th-century version came to mean “test the quality of.” It’s this latter derivation that French philosopher Michel de Montaigne first used to describe a composition.
History of the Essay
Michel de Montaigne first coined the term essayer to describe Plutarch’s Oeuvres Morales , which is now widely considered to be a collection of essays. Under the new term, Montaigne wrote the first official collection of essays, Essais , in 1580. Montaigne’s goal was to pen his personal ideas in prose . In 1597, a collection of Francis Bacon’s work appeared as the first essay collection written in English. The term essayist was first used by English playwright Ben Jonson in 1609.
Types of Essays
There are many ways to categorize essays. Aldous Huxley, a leading essayist, determined that there are three major groups: personal and autobiographical, objective and factual, and abstract and universal. Within these groups, several other types can exist, including the following:
- Academic Essays : Educators frequently assign essays to encourage students to think deeply about a given subject and to assess the student’s knowledge. As such, an academic essay employs a formal language and tone, and it may include references and a bibliography. It’s objective and factual, and it typically uses a five-paragraph model of an introduction, two or more body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Several other essay types, like descriptive, argumentative, and expository, can fall under the umbrella of an academic essay.
- Analytical Essays : An analytical essay breaks down and interprets something, like an event, piece of literature, or artwork. This type of essay combines abstraction and personal viewpoints. Professional reviews of movies, TV shows, and albums are likely the most common form of analytical essays that people encounter in everyday life.
- Argumentative/Persuasive Essays : In an argumentative or persuasive essay, the essayist offers their opinion on a debatable topic and refutes opposing views. Their goal is to get the reader to agree with them. Argumentative/persuasive essays can be personal, factual, and even both at the same time. They can also be humorous or satirical; Jonathan Swift’s A Modest Proposal is a satirical essay arguing that the best way for Irish people to get out of poverty is to sell their children to rich people as a food source.
- Descriptive Essays : In a descriptive essay, the essayist describes something, someone, or an event in great detail. The essay’s subject can be something concrete, meaning it can be experienced with any or all of the five senses, or abstract, meaning it can’t be interacted with in a physical sense.
- Expository Essay : An expository essay is a factual piece of writing that explains a particular concept or issue. Investigative journalists often write expository essays in their beat, and things like manuals or how-to guides are also written in an expository style.
- Narrative/Personal : In a narrative or personal essay, the essayist tells a story, which is usually a recounting of a personal event. Narrative and personal essays may attempt to support a moral or lesson. People are often most familiar with this category as many writers and celebrities frequently publish essay collections.
Notable Essayists
- James Baldwin, “ Notes of a Native Son ”
- Joan Didion, “ Goodbye To All That ”
- George Orwell, “ Shooting an Elephant ”
- Ralph Waldo Emerson, “ Self-Reliance ”
- Virginia Woolf, " Three Guineas "
Examples of Literary Essays
1. Michel De Montaigne, “Of Presumption”
De Montaigne’s essay explores multiple topics, including his reasons for writing essays, his dissatisfaction with contemporary education, and his own victories and failings. As the father of the essay, Montaigne details characteristics of what he thinks an essay should be. His writing has a stream-of-consciousness organization that doesn’t follow a structure, and he expresses the importance of looking inward at oneself, pointing to the essay’s personal nature.
2. Virginia Woolf, “A Room of One’s Own”
Woolf’s feminist essay, written from the perspective of an unknown, fictional woman, argues that sexism keeps women from fully realizing their potential. Woolf posits that a woman needs only an income and a room of her own to express her creativity. The fictional persona Woolf uses is meant to teach the reader a greater truth: making both literal and metaphorical space for women in the world is integral to their success and wellbeing.
3. James Baldwin, “Everybody’s Protest Novel”
In this essay, Baldwin argues that Harriet Beecher Stowe’s novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin doesn’t serve the black community the way his contemporaries thought it did. He points out that it equates “goodness” with how well-assimilated the black characters are in white culture:
Uncle Tom’s Cabin is a very bad novel, having, in its self-righteous, virtuous sentimentality, much in common with Little Women. Sentimentality […] is the mark of dishonesty, the inability to feel; […] and it is always, therefore, the signal of secret and violent inhumanity, the mask of cruelty.
This essay is both analytical and argumentative. Baldwin analyzes the novel and argues against those who champion it.
Further Resources on Essays
Top Writing Tips offers an in-depth history of the essay.
The Harvard Writing Center offers tips on outlining an essay.
We at SuperSummary have an excellent essay writing resource guide .
Related Terms
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Persuasive Essay
Definition Essay

Definition Essay - Writing Guide, Examples and Tips
14 min read
Published on: Oct 9, 2020
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Interesting Definition Essay Topics for Students
Definition Essay Outline - Format & Guide
Share this article
Many students struggle with writing definition essays due to a lack of clarity and precision in their explanations.
This obstructs them from effectively conveying the essence of the terms or concepts they are tasked with defining. Consequently, the essays may lack coherence, leaving readers confused and preventing them from grasping the intended meaning.
But don’t worry!
In this guide, we will delve into effective techniques and step-by-step approaches to help students craft an engaging definition essay.
Continue reading to learn the correct formation of a definition essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
On This Page On This Page -->
What is a Definition Essay?
Just as the name suggests, a definition essay defines and explains a term or a concept. Unlike a narrative essay, the purpose of writing this essay is only to inform the readers.
Writing this essay type can be deceivingly tricky. Some terms, concepts, and objects have concrete definitions when explained. In contrast others are solely based on the writerâs understanding and point of view.
A definition essay requires a writer to use different approaches when discussing a term. These approaches are the following:
- Denotation - It is when you provide a literal or academic definition of the term.
- Connotation - It is when the writer provides an implied meaning or definition of the term.
- Enumeration - For this approach, a list is employed to define a term or a concept.
- Analogy - It is a technique in which something is defined by implementing a comparison.
- Negation - It is when you define a term by stating what it is not.
A single or combination of approaches can be used in the essay.
Definition Essay Types
There are several types of definition essays that you may be asked to write, depending on the purpose and scope of the assignment.
In this section, we will discuss some of the most common types of definition essays.
Descriptive Definition Essay
This type of essay provides a detailed description of a term or concept, emphasizing its key features and characteristics.
The goal of a descriptive definition essay is to help readers understand the term or concept in a more profound way.
Stipulative Definition Essay
In a stipulative definition essay, the writer provides a unique definition of a term or concept. This type of essay is often used in academic settings to define a term in a particular field of study.
The goal of a stipulative definition essay is to provide a precise and clear definition that is specific to the context of the essay.
Analytical Definition Essay
This compare and contrast essay type involves analyzing a term or concept in-depth. Breaking it down into its component parts, and examining how they relate to each other.
The goal of an analytical definition essay is to provide a more nuanced and detailed understanding of the term or concept being discussed.
Persuasive Definition Essay
A persuasive definition essay is an argumentative essay that aims to persuade readers to accept a particular definition of a term or concept.
The writer presents their argument for the definition and uses evidence and examples to support their position.
Explanatory Definition Essay
An explanatory definition essay is a type of expository essay . It aims to explain a complex term or concept in a way that is easy to understand for the reader.
The writer breaks down the term or concept into simpler parts and provides examples and analogies to help readers understand it better.
Extended Definition Essay
An extended definition essay goes beyond the definition of a word or concept and provides a more in-depth analysis and explanation.
The goal of an extended definition essay is to provide a comprehensive understanding of a term, concept, or idea. This includes its history, origins, and cultural significance.
How to Write a Definition Essay?
Writing a definition essay is simple if you know the correct procedure. This essay, like all the other formal pieces of documents, requires substantial planning and effective execution.
The following are the steps involved in writing a definition essay effectively:
Instead of choosing a term that has a concrete definition available, choose a word that is complicated . Complex expressions have abstract concepts that require a writer to explore deeper. Moreover, make sure that different people perceive the term selected differently.
Once you have a word to draft your definition essay for, read the dictionary. These academic definitions are important as you can use them to compare your understanding with the official concept.
Drafting a definition essay is about stating the dictionary meaning and your explanation of the concept. So the writer needs to have some information about the term.
In addition to this, when exploring the term, make sure to check the termâs origin. The history of the word can make you discuss it in a better way.
Coming up with an exciting title for your essay is important. The essay topic will be the first thing that your readers will witness, so it should be catchy.
Creatively draft an essay topic that reflects meaning. In addition to this, the usage of the term in the title should be correctly done. The readers should get an idea of what the essay is about and what to expect from the document.
Now that you have a topic in hand, it is time to gather some relevant information. A definition essay is more than a mere explanation of the term. It represents the writerâs perception of the chosen term and the topic.
So having only personal opinions will not be enough to defend your point. Deeply research and gather information by consulting credible sources.
The gathered information needs to be organized to be understandable. The raw data needs to be arranged to give a structure to the content.
Here's a generic outline for a definition essay:
Are you searching for an in-depth guide on crafting a well-structured definition essay?Check out this definition essay outline blog!
6. Write the First Draft
Drafting each section correctly is a daunting task. Understanding what or what not to include in these sections requires a writer to choose wisely.
The start of your essay matters a lot. If it is on point and attractive, the readers will want to read the text. As the first part of the essay is the introduction , it is considered the first impression of your essay.
To write your definition essay introduction effectively, include the following information:
- Start your essay with a catchy hook statement that is related to the topic and the term chosen.
- State the generally known definition of the term. If the word chosen has multiple interpretations, select the most common one.
- Provide background information precisely. Determine the origin of the term and other relevant information.
- Shed light on the other unconventional concepts and definitions related to the term.
- Decide on the side or stance you want to pick in your essay and develop a thesis statement .
After briefly introducing the topic, fully explain the concept in the body section . Provide all the details and evidence that will support the thesis statement. To draft this section professionally, add the following information:
- A detailed explanation of the history of the term.
- Analysis of the dictionary meaning and usage of the term.
- A comparison and reflection of personal understanding and the researched data on the concept.
Once all the details are shared, give closure to your discussion. The last paragraph of the definition essay is the conclusion . The writer provides insight into the topic as a conclusion.
The concluding paragraphs include the following material:
- Summary of the important points.
- Restated thesis statement.
- A final verdict on the topic.
7. Proofread and Edit
Although the writing process ends with the concluding paragraph, there is an additional step. It is important to proofread the essay once you are done writing. Proofread and revise your document a couple of times to make sure everything is perfect.
Before submitting your assignment, make edits, and fix all mistakes and errors.
If you want to learn more about how to write a definition essay, here is a video guide for you!
Definition Essay Structure
The structure of a definition essay is similar to that of any other academic essay. It should consist of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
However, the focus of a definition essay is on defining and explaining a particular term or concept.
In this section, we will discuss the structure of a definition essay in detail.
Introduction
Get the idea of writing an introduction for a definition essay with this example:
Body Paragraphs
Here is an example of how to craft your definition essay body paragraph:
Types of the Term/Concept
If applicable, the writer may want to include a section that discusses the different types or categories of the term or concept being defined.
This section should explain the similarities and differences between the types, using examples and anecdotes to illustrate the points.
Examples of the Term/Concept in Action
The writer should also include real-life examples of the term or concept being defined in action.
This will help the reader better understand the term or concept in context and how it is used in everyday life.
Conclusion
This example will help you writing a conclusion fo you essay:
Definition Essay Examples
It is important to go through some examples and samples before writing an essay. This is to understand the writing process and structure of the assigned task well.
Following are some examples of definition essays to give our students a better idea of the concept.
Understanding the Definition Essay
Definition Essay Example
Definition Essay About Friendship
Definition Essay About Love
Family Definition Essay
Success Definition Essay
Beauty Definition Essay
Definition Essay Topics
Selecting the right topic is challenging for other essay types. However, picking a suitable theme for a definition essay is equally tricky yet important. Pick an interesting subject to ensure maximum readership.
If you are facing writerâs block, here is a list of some great definition essay topics for your help. Choose from the list below and draft a compelling essay.
- Authenticity
- Sustainability
- Mindfulness
Here are some more extended definition essay topics:
- Social media addiction
- Ethical implications of gene editing
- Personalized learning in the digital age
- Ecosystem services
- Cultural assimilation versus cultural preservation
- Sustainable fashion
- Gender equality in the workplace
- Financial literacy and its impact on personal finance
- Ethical considerations in artificial intelligence
- Welfare state and social safety nets
Need more topics? Check out this definition essay topics blog!
Definition Essay Writing Tips
Knowing the correct writing procedure is not enough if you are not aware of the essayâs small technicalities. To help students write a definition essay effortlessly, expert writers of CollegeEssay.org have gathered some simple tips.
These easy tips will make your assignment writing phase easy.
- Choose an exciting yet informative topic for your essay.
- When selecting the word, concept, or term for your essay, make sure you have the knowledge.
- When consulting a dictionary for the definition, provide proper referencing as there are many choices available.
- To make the essay informative and credible, always provide the origin and history of the term.
- Highlight different meanings and interpretations of the term.
- Discuss the transitions and evolution in the meaning of the term in any.
- Provide your perspective and point of view on the chosen term.
Following these tips will guarantee you better grades in your academics.
By following the step-by-step approach explained in this guide, you will acquire the skills to craft an outstanding essay.
Struggling with the thought, " write my college essay for m e"? Look no further.
Our dedicated definition essay writing service is here to craft the perfect essay that meets your academic needs.
For an extra edge, explore our AI essay writer , a tool designed to refine your essays to perfection.
Barbara P (Literature, Marketing)
Barbara is a highly educated and qualified author with a Ph.D. in public health from an Ivy League university. She has spent a significant amount of time working in the medical field, conducting a thorough study on a variety of health issues. Her work has been published in several major publications.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Concept of Autocracy: Analysis Essay
Introduction.
An autocracy is a prevalent form of government in several nations worldwide, which has been a source of concern for prominent advocates and academics. Numerous academics have analyzed the issue’s effects on countries, particularly on ordinary inhabitants. The style has undeniably profound implications that cannot be emphasized. Therefore, this study critically examines Victor Shaw’s concept of autocracy and its social and political consequences for democracy.
The Characteristics and Symptoms of Autocratic Leadership
An autocracy is a government in which the central authority has total power to pursue personal interests at the expense of guaranteed powers. Countries governed by absolute monarchs are characterized by the leader’s final authority and control over all other officials (Shaw 42). The autocrat’s social, economic, political, and military authority enhances control over the country’s resources, exports, imports, and overall financial activities.
In addition, autocracy is totally unconstrained by external rules, except for the threat of coups. Oligarchy and tyranny are comparable in that tiny groups of affluent, educated, politically, and socially influential persons dominate most of the population and largely contribute to the leadership. The framework of autocracy is straightforward compared to the federal law system, which comprises enormous task groups, consultations, and decision-making processes, among other bureaucratic restrictions (Shaw 42). Regardless of how charismatic autocrats may be as individuals, they require a power structure and leadership aid to implement their reign. In most instances, autocrats need an elite minority and the military to administrate their authority efficiently.
Social Elements and Forces under Autocratic Rule
Socially, autocracy is characterized by elitism, in which leaders view themselves as superior to commoners and use their power to rule, with severe societal consequences. Consequently, they dominate the government, the economy, business, education, trade, and the military (Shaw 47). In this sense, they tend to enforce legislation to promote their benefits, consolidate their social privileges, and dominate political interests. To pursue their goals, they disregard the will of ordinary people. Leadership attracts social forces that have a substantial effect on democracy and the decisions of the people (Shaw 47). Consequently, the government is marked by social elements, such as a lack of tolerance, conflicts, and individual autonomy, which contribute to negative societal results.
In addition, this style of leadership is associated with societal discontent, dictatorship, fascism, and oligarchy. On national levels, it is also tied to power abuse, a lack of morality, a dearth of legal protections, and limited access to government by the average citizen (Shaw 47). Moreover, authoritarianism tends to generate social unrest as it struggles to balance general requirements with the ideas of its leaders. The social demands of the average citizen include infrastructural enhancement, the promotion of peace, and social development. In contrast, a leader’s philosophies have humanistic values, self-improvement, and historical traditions. As a result, the chasm separating these interests is susceptible to political alliances and unrest, eventually increasing the likelihood of coups.
How Autocracy Influences Political Procedures and Common People
The political process involving partisan dealings and beliefs is essential to autocracy. Officials linked with political parties are frequently taught standards of conduct that reflect partisan sentiments and represent partisan identities (Shaw 48). Therefore, the leaders must conform to the autocratic leader’s interests and political affiliations. In this sense, the leaders are compelled to make judgments based on the leaders’ assertions, which goes against the desires of the people (Shaw 48). The supreme leader may manipulate these judgments if they do not align with his interests. In addition, autocracy tends to exacerbate the disparity between party ideology and the demands of regular residents. Ideologies of political parties are connected to social movements, moral standards, religious beliefs, and humanist values.
On the other side, everyday citizen demands relate to practical concerns such as reconciliation between conflicting groups, economic development, social development, and infrastructural development. Party members are preoccupied with following their ideology for personal gain, ignoring the doctrines of regular citizens, who are more concerned with the greater good of society (Shaw 47). Therefore, the leadership style fosters a social environment characterized by a lack of tolerance, conflicts, and individual autonomy, all of which contribute to adverse social outcomes (Shaw 47). In addition, the style produces social instability, despotism, fascism, and oligarchy, which result in the misuse of power, a limited sense of morality, minimal legal protections, and restricted access to government by regular citizens.
How Autocracy Infiltrates the Democratic and Technocratic Systems
As a result of these absolute powers, centralized and unchecked authority, the leadership may infiltrate democracy and technocracy, which has repercussions for the government. As a result, autocrats can monopolize officialdom, penetrate the economy, control businesses, education, and commerce, and dominate the military (Shaw 47). In addition, they influence social, economic, and political aspects that enhance their power to control resources, given that autocracy is unrestricted by external rules.
As a result of these ultimate powers and authority, leaders tend to implement laws to further their interests, secure their social privileges, and dominate political concerns. To pursue their goals, they inherently oppose democracy, representing the general public’s will (Shaw 48). The rules enforced by the leader are generally based on political party doctrines about social movements, moral standards, religious beliefs, and humanist principles. In this instance, democratic concepts such as community development, social and economic development, infrastructure development, and reconciliation between conflicting groups are disregarded, hence affecting the applicability of democracy and technocracy as forms of government.
Autocracy is a leadership system in which the leader has unfettered social, economic, political, and military power, allowing them to manage resources, exports, imports, and economic activity. Conflicts, intolerance, and individual liberty contribute to the style’s negative societal impacts. Besides, the class’s unrestricted powers influence political parties and lawmaking while the public gets eroded by Leaders’ political and personal interests.
Shaw, Victor N. From Autocracy to Democracy to Technocracy: An Evolution of Human Polity . Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2020.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, May 19). Concept of Autocracy: Analysis. https://ivypanda.com/essays/concept-of-autocracy-analysis/
"Concept of Autocracy: Analysis." IvyPanda , 19 May 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/concept-of-autocracy-analysis/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Concept of Autocracy: Analysis'. 19 May.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Concept of Autocracy: Analysis." May 19, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/concept-of-autocracy-analysis/.
1. IvyPanda . "Concept of Autocracy: Analysis." May 19, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/concept-of-autocracy-analysis/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Concept of Autocracy: Analysis." May 19, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/concept-of-autocracy-analysis/.
- Democracy Measures in United Kingdom, France, Japan and China
- The Causes, Characteristics, and Aims of Revolutions
- Conflict in Syria: Jihadi and Western Views
- Nature of Neoliberalism (Neoclassical Economics) and Its Partner Structure Adjustment Programs
- Exploring Democracy: Comparison of Two Articles
- Manifest Destiny and Its Ideological Origins
- Exploring the Differences Between Globalism and Nationalism
- Reconciling the Tension Between Equality and Meritocracy
- Collections
- Support PDR
Search The Public Domain Review
Same as It Ever Was? Eternal Recurrence in Ancient Greek and Roman Philosophy
By Claire Hall
While Friedrich Nietzsche popularised the notion of an “eternal return” — in which one’s life would occur again, forever, exactly as it did before — the concept was itself a repetition. Claire Hall explores various shades of this idea in ancient philosophy, from Pythagorean metempsychosis to Stoic predictions about a cosmological reset.
May 15, 2024

Stereograph of Carlo Franzoni's 1819 marble sculpture of Clio, the Muse of History, standing in a winged chariot atop a clock, at the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C., ca. 1860–90 — Source .
Albert Einstein kept changing his mind about the fate of the universe. As a young man, he had — like most other people at the time — believed the universe was static, a fixed size. By the end of his life, Einstein accepted the Big Bang, and had adopted the (now standard) view that the universe will keep growing outward, continuing to expand forever, its lights growing fainter until, eventually, they all fade to an endless inky black. But in between, in the early 1930s, he endorsed a rather different idea: that the universe goes through cosmic cycles.
In a cyclical model, our universe began with a Big Bang and continues to expand — but at some point it will stop. It will then contract, reversing its direction of travel, until eventually all matter collapses into a single point: a Big Crunch. But that is not simply the end of the universe: it is also a new starting point— it triggers another Big Bang, and another universe blooms. This pattern repeats, and repeats. Einstein wasn’t the first to suggest this idea using modern physics. It had been proposed by Alexander Friedmann, a Russian cosmologist whose work was fundamental for establishing the idea of the Big Bang. Friedmann had already been contemplating the physics of cosmic cycles when he died from an unlucky accident: some years earlier on his honeymoon, he had caught typhoid fever from an infected pear bought at a railway station — and in 1925 the infection took over his body.
Recurrence — the idea that the universe will die and be reborn, time and time again — might have been new to physics, but it is not a new idea. Globally, it is found in a number of religions, including Hinduism and Buddhism. It was also the subject of philosophical speculation in the premodern world. In particular, in the works of Greek and Roman philosophers, attempts were made to distinguish between different kinds of recurrence. There is the first kind we have already met through modern physics: the idea that the universe as a whole will die and be reborn. But this idea as it appears in Einstein and Friedmann does not make any claim that particular events, objects, or people will recur. What the physicists were interested in was a reshuffling of the cosmos.
Plate from Robert Fludd, Utriusque Cosmi (1617) — Source .
A second type of recurrence is reincarnation, a concept common to many religions. Here the focus is not the world as a whole, but the human or animal soul: each soul is reincarnated, living varying lives in sequences that are determined or governed by some cosmic balance. This can be found alongside an idea of cosmic recurrence, as in Hinduism and Buddhism, but is also consistent with a belief in an eternal world (such as in Jainism or some indigenous Aboriginal religions) or with a stable created world (such as in Sikhism, certain branches of Judaism, and in some of the traditional religions indigenous to the Americas, including that of the Inupiaq people of Alaska). But a third, more extreme idea, is that of exact recurrence — the whole world dies and begins again, and with it every event happens again the same way, in the exact same sequence, forever. Unlike the abstract cosmic rebirth of the physicists, both reincarnation and strict recurrence offer us a reason for the randomness of life’s fortunes, a way to believe that things happen not out of pure chance, but because something from a previous cycle provides a template for the present. Recurrence offers us a bigger picture, a greater web in which to link the vastness of Friedmann’s astrophysical research with the feather-lightness of the chance that killed him.
Greco-Roman writers treated the idea of eternal recurrence in a variety of ways. In a loose sense, many ancient writers observed that there are elements of circularity built into any idea of time measurement. Eudemus, a pupil of Aristotle, recognised this wider context, and put it clearly: “sameness is spoken of in different ways, and it does seem that a time [period] the same in kind recurs, e.g. summer, winter, and the other seasons.” 1 Aristotle himself said that time was “a sort of circle”. 2 Plato had called it “the moving image of eternity”, clearly linking time to the circular movements of the heavens. 3 Early Greek texts on the weather and seasons elaborate this idea of a cycle of time. Hesiod’s Works and Days , for example, presents an almanac of recurring signs for the farmer, while the long-established festival calendars of the Greek city states were often inscribed and displayed, providing a visual clue to the sameness of each changing year.
Greek thinkers also theorised recurrence in the sense of reincarnation. One of the important features of Pythagorean thought is the idea of metempsychosis, or the transmigration of souls. Unfortunately, Pythagoreanism is particularly difficult to reconstruct: much was unwritten, and what was written has in large part been lost. After its first flush of popularity in the pre-Classical Greek world, centuries of often contradictory stories accreted around the cult figure of Pythagoras, silting up the historical record. (Later interpretations of Pythagoreanism are, of course, interesting in their own right as entryways into the teeming philosophical world of Late Antiquity, but they tell us very little about what Greeks of the sixth century BCE really thought). Pythagoreanism’s doctrines shaped a number of the genuinely secretive mystery cults of the Greek world, including Orphism and the Eleusinian mysteries, whose ideas about reincarnation are mostly lost to time. Reincarnation is, therefore, one of those topics on which the Greek texts whisper rather than shout.
_-_Foto_G._Dall_Orto-edit-2.jpg?fit=max&w=1200&h=850)
Roman mosaic of Orpheus surrounded by animals, from the Piazza della Vittoria in Palermo, ca. 200–250 — Source .
But the philosophical schools that developed after Plato’s time took a more precise and pedantic approach. “I will talk, staff in hand, to you sitting like this, and everything else will be alike.” With these words, Eudemus summarised the view of a group of Stoic philosophers that all the events in the world would exactly recur, again and again. As he details, some Pythagoreans seem to have believed not only in reincarnation, but in exact recurrence: that things would be numerically the same, with the relative order of events exactly mapped between one iteration of the universe and the next. It was an idea reportedly taken up by Chrysippus (ca. 279–206 BCE), the most renowned of all the Stoic philosophers, although other Stoics disagreed. The Stoic version of recurrence had a terrifying additional element to it: the ekpyrosis or great conflagration. Stoics argued that ekpyrosis was a process in which the entire universe periodically goes up in flames and a new world emerges from its ashes like a phoenix — in fact, a lot like the Big Crunch. Many Stoic views are available to us only in later summaries. Hippolytus, a Christian writer of the second century CE, describes the Stoic doctrine, capturing the way in which the passing away of the old and the birth of the new are intertwined:
[The Stoics] expect that there will be a conflagration and a purification of this world, some say entirely, others say in part, and they . . . call the destruction and the subsequent generation of another [world] from it a purification. 4
Writing around the same time as Hippolytus, Alexander of Aphrodisias, a pagan commentator on Aristotle, elaborates on the Chrysippean view:
[Some Stoics] held that after the conflagration all the same things come to be again in the world numerically, so that even the same peculiarly qualified individual as before exists and comes to be again in that world. 5
Some Stoic philosophers explain the theory behind this periodic conflagration with a mysterious astronomical concept: the Great Year. The Great Year appears as a framing device in The Cradle of Life , the 2003 Tomb Raider sequel film starring Angelina Jolie: in a hidden ice cavern, a giant model of the solar system ticks down to the time when the orbits of all nine planets will align. In the ancient world, there were only five known planets (Saturn, Jupiter, Venus, Mars, Mercury) plus the two luminaries (the Sun and the Moon). If you started a timer at the moment that they were all lined up, their extremely different orbits mean that it would then take approximately 36,000 years before they returned to the same perfect line. The term “Great Year” was used to describe this particular alignment, but it was also used to refer to the time interval that it would take for any particular arrangement of the planets in the sky to occur again. Plato describes it as the “perfect number of time” in the Timaeus , a work which revolves around demonstrating the perfect harmony of the cosmos. 6 Cicero, more practically-minded, says the following:
On the diverse motions of the planets the mathematicians have based what they call the Great Year, which is completed when the sun, moon and five planets having all finished their courses have returned to the same positions relative to one another. The length of this period is hotly debated, but it must necessarily be a fixed and definite time. 7
The Great Year carries in it some idea of a celestial reset, hence its association with ekpyrosis . Although it’s tempting to picture the Stoic ekpyrosis like the death of the dinosaurs in Disney’s Fantasia , with streams drying up and creatures’ scorched flesh falling from their bones, most Stoics were actually rather sober about the whole thing. While the ever-dramatic Seneca luridly imagines cities “swallowed up in yawning chasms” and the inhabited world “cover[ered] with floods”, Marcus Aurelius is more representative of the tradition as a whole: he calmly suggests that everything “will evaporate . . . or it will be scattered”. 8 The time period involved, 36,000 years, is large enough to be basically non-threatening: just as we are able to dismiss without too much fear the idea of the universe eventually collapsing in a heat death in billions of years’ time, the ancients were also reassured by the enormity of the Great Year.

Illustration by Fred T. Jane for George Griffith’s Olga Romanoff (1897) — Source .
This Stoic idea of cosmic cycles — of something like a general refreshing of the universe — became part of the common currency of ancient thought. But for those who wanted to get into detail, recurrence had its conceptual problems. Particularly tricky was the strict form: the exact recurrence that some of the Stoics and Pythagoreans seem to have endorsed. Various philosophers weighed in on these difficulties: first and most fundamentally, if everything recurs exactly, does that not also mean time itself recurs? In that case, does everything actually happen more than once in any meaningful way? If we can only distinguish two otherwise identical events by saying that one happens before the other, that suggests we need an outside observer or a continuous measure of time in order to distinguish sameness and difference. These are exactly grounds on which Eudemus objects to the idea of strict recurrence:
For when the motion is one and the same, and similarly there are many things which are the same, their before and after is one and the same, and hence so is their number. So everything is the same, which means that the time is as well.
Some of this difficulty, as the philosophers realised, is to do with language: what does it mean to claim something happens again or earlier or later in a series of cyclical sequences that occur outside time? Aristotle used this linguistic problem as a way of demarcating between two different types of time. Sometimes we use the term “time” ( chronos ), he argued, when really we mean the scale we’re using to measure change — this is the sense of time we are employing when we say that it took Zeno four minutes to run the race, or that Seneca was in the bath for an hour. But the other type of time is the abstract concept, the thing that he sees as being outside of us, which marches ever onward. As he says:
Time is the measurement of circular motion [of the heavens], and is itself measured by a circular motion [of the heavens] . . . there is nothing else to be seen in what is measured except for the measure. 9
One response to the conceptual problem Aristotle raises was to deny that everything would be exactly the same in a recurring universe — to avoid the question of whether time starts again by positing that there are minutely different universes potentially (even if not practically) distinguishable against a continuous backdrop of ongoing time. This cop-out route seems to have been taken by some of the Stoics. The Christian philosopher Origen of Alexandria (180–250 CE) reports that: “to avoid supposing that Socrates will live again, [some Stoics] say that it will be someone indistinguishable from Socrates, who will marry someone indistinguishable from Xanthippe, and will be accused by men indistinguishable from Anytus and Meletus.” 10
But Origen explained this idea in order to reject it: for him, any kind of recurrence was incompatible with Christian doctrine, in which time had a distinct sense of direction. Most early Christians felt the same. Primarily, they were deeply uncomfortable with any idea of recurrence that included reincarnation: Christians instead believed that a person’s soul would go to heaven (or to hell, which became increasingly dominant in Christian thought as the Middle Ages wore on). The millenarian movement that was so popular in the early Church also supported the idea of the bodily resurrection of all Christians at the time of Jesus’ Second Coming. Reincarnation — where the soul travels through many bodies — was fundamentally incompatible with the idea of resurrection, which kept body and soul connected, even after death. Christian literature of the first few centuries abounds in half-comic, half-ghastly thought experiments about the mechanics of this final universal sorting and reckoning, including a fascination with how the bodies of cannibals and their victims are arranged in heaven.
-edit.jpeg?fit=max&w=1200&h=850)
Michelangelo, The Last Judgement (detail), ca. 1536–41 — Source .
But more strict ideas of recurrence were also unacceptable to Christians: it was totally incompatible with Christian doctrine to suggest that the Creation could be repeated, or that the Second Coming would in truth be one of infinitely many appearances of Christ. In fact, this strong Christian commitment toward the fixed linear structure of time represents an enormous shift in Western thought. Pre-Christian pagans and Jews had articulated a mix of ideas about cyclical and linear time, but in general nearly all ancient Mediterranean cultures had a profound orientation toward the past. Christianity changed that: it was now important to understand our lives on earth in the context of the afterlife, and, beyond it all, structuring it all, God’s final judgement. Time was linear, but chance was also never random — the world ran under the watchful eye of an omniscient God. Ideas about recurrence and reincarnation would fall out of favour in the West for over 1500 years.
Fifty years before Einstein embraced the idea of cosmic cycles, Nietzsche argued for a return to ideas of recurrence. God was dead and with him went the afterlife and its promised judgement of a lifetime of Christian morality. Nietzsche was worried that with this loss, solipsism could sneak in: for him, it was intolerable to think of life as arbitrary or ephemeral. Returning to recurrence was a way to put his own spin on the pre-Christian search for the meaning of life. Nietzsche used Thus Spake Zarathustra (1883–85) to argue that instead of making us feel depressed and trapped, eternal recurrence should be seen as a call to action. He uses recurrence in the strict sense: the exact repetition of the same sequence of events forever. When he first raises the idea in The Gay Science (1882), he imagines a demon explaining this fatalistic doctrine:
You will have to live once more and innumerable times more; and there will be nothing new in [your life], but every pain and every joy and every thought and sigh and everything unutterably small or great in your life will have to return to you, all in the same succession and sequence. 11
Our first reaction to this disclosure, suggests Nietzsche, would be a kind of debilitating horror. But it might then present us with an opportunity for transformation, a challenge to live in such a way as to make time’s recurrence a gift. It is not the ephemerality of life that forces us to live wisely, argues Nietzsche, but the idea of it repeating forever. If you know that you must re-live again and again, your every choice becomes loaded with meaning: you are called on to live totally — fully, joyously, and virtuously. For those who are not crushed by the proposition, recurrence is not a curse but an endless blessing.
Notes Show Notes
- Eudemus as preserved in Simplicius, On Physics 732.26-733.1.
- Aristotle, Physics 4.14.
- Plato, Timaeus 37d.
- Hippolytus, Refutation of all Heresies 1.21.3-5.
- Alexander of Aphrodisias, Commentary on Aristotle’s Prior Analytics 180.33-6.
- Plato, Timaeus 39d.
- Cicero, On the Nature of the Gods 2.51.
- Seneca, Marcia 21.6. Marcus Aurelius, Meditations 6.4.
- Aristotle, Physics 4.12.
- Contra Celsum IV.68.
- Friedrich Nietzsche, Die fröliche Wissenschaft § 341.
Public Domain Works
- The Internet Classics Archive
- Internet Archive
Further Reading
This collection of articles is an important milestone in the history of the study of time conceptions in Greek and Roman Antiquity. It spans from Homer to Neoplatonism. Conceptions of time are considered from different points of view and sources. Reflections on time were both central and various throughout the history of ancient philosophy. Time was a topic, but also material for poets, historians and doctors. Importantly, the contributions also explore implicit conceptions and how language influences our thought categories.

For over two and a half millennia human beings have attempted to invent strategies to "discover" the truth of time, to determine whether time is infinite, whether eternity is the infinite duration of a continuous present, or whether it too rises and falls with the cycles of universal creation and destruction. Time-Fetishes recounts the history of a tradition that runs counter to the dominant tradition in Western metaphysics, which has sought to purify eternity of its temporal character. From the pre-Socratics to Ovid and Plotinus, and from Shakespeare to Hegel, Schelling, Nietzsche, Heidegger, and Derrida, Time-Fetishes traces the secret tradition of the idea of eternal recurrence and situates it as the grounding thought of Western philosophy and literature.

The Public Domain Review receives a small percentage commission from sales made via the links to Bookshop.org (10%) and Amazon (4.5%). Thanks for supporting the project! For more recommended books, see all our “ Further Reading ” books, and browse our dedicated Bookshop.org stores for US and UK readers.
Claire Hall is a research fellow at Durham and a fellow of All Souls College, Oxford. She is working on a book on ancient ideas about the future and future prediction, and has published on the history of prophecy, astrology, and dream interpretation.
The text of this essay is published under a CC BY-SA license, see here for details.
- Religion, Myth & Legend
If You Liked This…

Get Our Newsletter
Our latest content, your inbox, every fortnight

Prints for Your Walls
Explore our selection of fine art prints, all custom made to the highest standards, framed or unframed, and shipped to your door.
Start Exploring
{{ $localize("payment.title") }}
{{ $localize('payment.no_payment') }}
Pay by Credit Card
Pay with PayPal
{{ $localize('cart.summary') }}
Click for Delivery Estimates
Sorry, we cannot ship to P.O. Boxes.
University of Minnesota Twin Cities
University digital conservancy, 'many paths to partial truths:' archives, anthropology, and the power of representation, view/download file, persistent link to this item, journal title, journal issn, volume title, published date, description, collections, series/report number, funding information, isbn identifier, doi identifier, previously published citation, suggested citation.
Content distributed via the University Digital Conservancy may be subject to additional license and use restrictions applied by the depositor. By using these files, users agree to the Terms of Use . Materials in the UDC may contain content that is disturbing and/or harmful. For more information, please see our statement on harmful content in digital repositories .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Concept essays aim to explore and explain abstract ideas, theories, or concepts in a way that is accessible and engaging to readers. Although concept essays may vary in subject matter, their main objective is to break down complex ideas and make them understandable to a wider audience. These essays often require deep analysis and critical ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
Concept Essay Generator. Free Download. A concept essay is a type of a literary piece that is used to present an idea or a topic with the sole purpose of providing a clear definition and explanation.
A concept essay is an explaining essay that explores a larger idea or concept in an effort to share perspective, interpretation, or opinions. The essay details the sub-topics using the writer's ...
Concept essays provide a chance to explore ideas you might previously have taken for granted. Writing a concept essay requires careful exploration of a concept, a concise and interesting thesis and a strong overall structure. Before you begin to write, it may be helpful to engage in some prewriting. Word webs, outlines and free writing can help ...
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
Concept essays themes tend to be more abstract than the topics for other essays. For example, you may be asked to write about the racism, communication or wisdom. Research. Think about what you already know about your subject and then find out what you don't know. You are educating someone about a topic, so make sure you know as much as ...
The first crucial step in crafting your concept paper is to clearly define the study title and its objectives. This sets the foundation for your entire paper and helps guide your research direction. Begin by crafting a clear and concise title that effectively communicates the essence of your study. Your title should be descriptive yet succinct ...
an earlier idea or part of the essay, referring back to it either by explicit statement or by echoing key words or resonant phrases quoted or stated earlier. The repeating of key or thesis concepts is especially helpful at points of transition from one section to another, to show how the new section fits in. 8.
Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document's impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows: 1. Write a Crisp Title: Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper's content.
The essay is a written piece that is designed to present an idea, propose an argument, express the emotion or initiate debate. It is a tool that is used to present writer's ideas in a non-fictional way. Multiple applications of this type of writing go way beyond, providing political manifestos and art criticism as well as personal ...
An essay (ES-ey) is a nonfiction composition that explores a concept, argument, idea, or opinion from the personal perspective of the writer. Essays are usually a few pages, but they can also be book-length. Unlike other forms of nonfiction writing, like textbooks or biographies, an essay doesn't inherently require research. Literary essayists are conveying ideas in a more informal way.
Examples of this kind of conceptual work are drawn from the field of journalism studies and communication to guide writers in moving beyond an essay that summarizes literature to an article that makes an original contribution, writing in such a way that the key argument is communicated effectively.
Here are some of the many definitions of an essay: According to Frederick Crews, professor of English at the University of California at Berkeley, an essay is "a fairly brief piece of nonfiction that tries to make a point in an interesting way.". Aldous Huxley, a famous essayist, notes that "the essay is a literary device for saying ...
essay, an analytic, interpretative, or critical literary composition usually much shorter and less systematic and formal than a dissertation or thesis and usually dealing with its subject from a limited and often personal point of view. Some early treatises—such as those of Cicero on the pleasantness of old age or on the art of "divination ...
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement, a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas. The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ...
An explanatory definition essay is a type of expository essay. It aims to explain a complex term or concept in a way that is easy to understand for the reader. The writer breaks down the term or concept into simpler parts and provides examples and analogies to help readers understand it better.
An essay is a piece of non-fiction writing with a clear structure: an introduction, paragraphs with evidence and a conclusion.Writing an essay is an important skill in English and allows you to ...
Conclusion. Autocracy is a leadership system in which the leader has unfettered social, economic, political, and military power, allowing them to manage resources, exports, imports, and economic activity. Conflicts, intolerance, and individual liberty contribute to the style's negative societal impacts.
Thomas Scheff's intriguing essay on the concept of stigma proposes that 'stigma can be defined as shame'. Scheff answers the boundary question for the stigma concept. It includes shame, it excludes everything else and its essence is, yes, shame. The question I bring is whether this narrow, very tight claim is apt and whether it would ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative: you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
While Friedrich Nietzsche popularised the notion of an "eternal return" — in which one's life would occur again, forever, exactly as it did before — the concept was itself a repetition. Claire Hall explores various shades of this idea in ancient philosophy, from Pythagorean metempsychosis to Stoic predictions about a cosmological reset.
The teacher submits the essays to Writable, which in turn runs them through ChatGPT. ChatGPT offers comments and observations to the teacher, who is supposed to review and tweak them before sending the feedback to the students. Writable "tokenizes" students' information so that no personally identifying details are submitted to the AI program.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Ever since the 1970s, movements in the social sciences and humanities s have encouraged an increasing epistemological scrutiny of such concepts as representation, authenticity and objectivity, and their relationship to matters of power and authority. Archival thinking, however, has remained largely isolated from the broader intellectual landscape, and archival practice has remained curiously ...