Integrations
What's new?
In-Product Prompts
Participant Management
Interview Studies
Prototype Testing
Card Sorting
Tree Testing
Live Website Testing
Automated Reports
Templates Gallery
Choose from our library of pre-built mazes to copy, customize, and share with your own users
Browse all templates
Financial Services
Tech & Software
Product Designers
Product Managers
User Researchers
By use case
Concept & Idea Validation
Wireframe & Usability Test
Content & Copy Testing
Feedback & Satisfaction
Content Hub
Educational resources for product, research and design teams
Explore all resources
Question Bank
Maze Research Success Hub
Guides & Reports
Help Center
Future of User Research Report
The Optimal Path Podcast
Maze Guides | Resources Hub

Product Research: The Building Blocks of a User-Centered Solution
0% complete
Product research is a foundational step in building user-centric products. It allows you to understand customer needs, preferences, and market trends, informing the development of successful solutions to user problems. Read on for the ultimate guide to product research, including methods, processes, and best practices—plus our favorite tips from the industry’s leading experts.
Product research 101: Definition, methods, and best practices
You may only build new products once, but you iterate on them continuously. The ongoing evolution of a product’s user experience (UX), informed by user insights, is pivotal to staying ahead of competitors and giving your users exactly what they need. In chapter one of this guide, we’ll explore what product research is, give an overview of key methods (and when to use them), plus best practices to follow.
What is product research?
Product research is any research you conduct to better inform your product and understand your user and market. Unlike user research , product research goes beyond evaluating the user experience and includes market analysis, pricing, feature prioritization, and assessing business viability.
Product research is a broader term than UX research—you can conduct research on the user, the interaction, the market, or your business strategy.

Matthieu Dixte , Product Researcher at Maze
It helps you understand the world you are bringing your product into, and what your users expect to do with a product like yours—so you can use their insights to influence development and design decisions.
Product research can be conducted in multiple ways, such as talking directly to users in focus groups or user interviews , or through product experimentation, usability tests and competitive analysis.
Other research terms you might come across
Ultimately, all research falls under the 'product research' banner if it influences the final product. For some product teams, ‘user research’ and ‘product research’ may be interchangeable. But there are some subtle differences between various research terms that it can be helpful to know. Here are the distinctions between key terms you might hear, explained by Maze's Product Researcher, Matthieu Dixte:
- Market research: Discover who is leading the market, who your direct and indirect competitors are, and what similar products are available to your users at what price
- User research: Understand the user, including their needs, pain points, likes and dislikes, and characteristics—both as a consumer and user of your product
- User experience (UX) research : Learn how your user perceives and interacts with your product—where they click, which paths they follow, and where they search for information on-page
- Product discovery : Uncover what your users’ needs and problems are, validate ideas for potential solutions before development, and apply user insights to your product strategy
- Continuous product discovery : Adapt the mindset of an ever-evolving product and user; conduct research continuously throughout the product lifecycle and ensure all decisions are informed by user insights
For example, let’s say you’re thinking of developing and launching a note-taking app for teenagers. You’d need to conduct market research to see if there are any similar products in high demand to gauge if your tool is something customers want. In parallel, you should run user research to discover who your user persona would be and what their pain points are.
You also have to do product discovery to identify the best way to build and design your potential product to make it appealing for teens. And, if you want to know how your users will feel about your product compared to other options, you need product research .
Lastly, run UX research tests on your mobile and web app to gather feedback, and improve the experience. You should continue to talk with users regularly after launch by adopting a continuous product discovery mindset (and ensure you’re always updating and offering the right product).
Talk to more users without needing to grow your product team
Recruit and test users from Maze’s high-quality panel to get more eyes on your product, without increasing payroll.
Why is product research important?
Are we making the right assumptions? Is this product what users really need? Can they use it effectively?
Research answers all those questions. But product research goes a step further by placing those answers in the context of your niche and the market. It empowers your team—not only to create unbiased, user-centric products—but also to create best-selling products that are based on a robust business strategy and deep understanding of the market.
Product research will also help you:
Head in the right direction
Conducting types of product research like competitive analysis gives you inside information on what your users value in a similar product—and what they’re missing. It ensures you’re heading in the right direction by only working on aspects of your product you know will succeed. This helps you speed time-to-market, reduce the cost of fixing future mistakes, and achieve higher goals.
Product research allows you to “define the total addressable market and north star metric, based on the customer segments that found your idea and product valuable. We would fail at achieving product-market fit without doing customer research,” explains Prerna Kaul , Product Lead for Alexa AI at Amazon.
Make the right decisions at the right time
User data can inform your decisions and help you prioritize them according to the goals of the business. “Make choices regarding the evolution of your product and find the right balance between what you want to deliver to improve the user experience, and the benefits it’ll bring to your company,” advises Matthieu. Without product research, you’re building products in the dark with no idea whether your target audience will like or buy them—which could mean wasted resources and sinking revenue.
Get stakeholder buy-in
You’ve probably found yourself explaining multiple times to stakeholders why you need to prioritize one feature over another. Conducting product research enables you to “clearly articulate the customer value proposition to leadership, tech, and science counterparts,” says Prerna. Having quantitative and qualitative user insights provides reassurance to stakeholders and speeds up sign-off—while ensuring the wider organization is aligned on your product ideas.
In short, product research provides you evidence you need to start evangelizing research among your organization, and get the whole team on board.
Understand the position your users hold in the market
User research is about getting to know your target audience and building ideal customer profiles, but product research is about discovering where your potential customers are located in the market and which trending products to take note of. If your audience is already using a similar product, this means finding out: Which one? Why? Are they willing to switch to a different product? What would it take for you to get them to switch?
“Analyzing the market lets you determine which areas could be ripe for disruption or creation. By analyzing existing products and doing conceptual thinking you can build a picture of how you can get your product to gain traction in the market and offer something new, nuanced, or better than the current options,” says Nick Simpson , Head of UX at Airteam.
Challenge your assumptions and anticipate problems
When Prerna worked at Walmart Labs, her team introduced a feature for users to scan products in the Scan and Go app. “We initially believed that all of our inventory was available in a common database and accessible through the app. However, during research and user testing, we identified that some rare products were not in the online database,” she explains.
This caused test users to drop off the app, so her team had to take a step back and prioritize fixing inventory issues before launching the product. Without conducting product research, you can be left guessing at the cause of user problems, or wondering why they prefer a particular product. Research offers your team a chance to challenge what you think you know, and pre-empt what you don’t.
Product tip 💡
You can use Maze to conduct multiple tests on your product through development, such as Five-Second Tests or Content and Copy Testing , or get insights on your live product through Live Website Testing .
Product research methods
There are many different product research and UX research methods , all of which offer different kinds of data and insight, depending on your objectives. If you’re looking to conduct product research to better understand your users, market, or competitors, here are eight product research methods you should consider to help you build winning products.
1. Customer interviews
Interviews can take place at any take of the product development process and consist of direct conversations with current or potential customers. You may choose to conduct interviews with a market panel during concept testing and idea screening to validate your ideas, or you may want to speak to current users after the product goes live to gather post-launch feedback. Interviews are a varied and flexible product research method.
During customer interviews, you should ask open and unbiased research questions to gather insights about customer needs, preferences, and experiences regarding their pain points, your product, and competitors.
2. Voice of customer (VoC) analysis
Gauge what current and potential customers are saying about your products or competitor products online. You can do this using VoC tools , by reviewing what people post on social media, looking at Google Trends, or reading reviews on websites like G2.
You should conduct customer voice analysis continuously throughout the lifecycle as it can help you gain a competitive advantage. “Review what’s publicly published, check feature requests, and ask sales, customer success, or support teams for feedback coming from the user,” adds Matthieu.
For example, if a competitor gets acquired by a bigger firm and users start to complain about them removing a feature, you can use the opportunity to develop a similar functionality or improve the one you have. You can also make it more visible on-page and get the sales and marketing teams to use the information to advertise your product.
3. Diary studies
Diary studies involve users self-reporting behaviors, habits, and experiences over a period of time. This is often used during the discovery phase with a competitor product, or later down the line with a prototype. By observing how users feel prior to, during, and after using your (or a competitor) product—and their experience throughout—you can gather valuable, in-the-moment insights within a real life context.

You can conduct diary studies on paper, video, or online on a mobile app or a dedicated platform.
Data from diary research can turn into new product ideas, new features, or inform your current project. For instance, if you have a social media scheduling tool and you identify that users open a time zone calculator when they’re scheduling posts, you instantly have a new feature idea, to add a widget with different time zones.
Learn more about the types of diary study and how to conduct diary research here.
4. Competitive analysis
Analyze competitors' products and strategies to identify what works for them and identify any gaps in the market. The idea behind competitive product analysis is to explore your competitor’s products in-depth, sign up for an account, use them for a while, and take notes of top features, UX, and price points. You can run competitive analysis during the discovery, concept validation , or prototyping stages with direct and indirect competitors, or aspirational businesses.
Matthieu Dixte, Product Researcher at Maze, notes the value of competitive analysis is in understanding your users perspective: “We conduct a lot of competitive analysis at Maze because it's really important for us to understand if the market is mature regarding a particular topic—and to identify the current ground covered. This helps us understand the pros and cons our customers perceive when they choose between our product or another tool.”
Surveys can be a great way to get feedback or gather user sentiment relating to existing products or future concepts. You can also use them to dig deeper into the data gathered during other tests, and understand user issues and preferences in context.
For example, if you ran an A/B test and discovered that certain copy was causing potential users to churn, you could follow-up with a survey with targeted questions around their demographics, preferences, and personal views. This would help add qualitative insights to your quantitative data, and help understand what your users are looking for from your product.
Remember, you can create surveys at any stage of the product development to collect data from users in small or large volumes. You can use different types of surveys and survey principles to validate or debunk hypotheses, prioritize features, and identify your target market. For example, you could ask questions about your product, competitors, and prices or even your customer’s preferences and market trends.
Surveys can have a high drop-out rate, harming the validity of your data. Check out our survey design guide to discover the industry’s top secrets to an engaging survey which keeps users hooked.
6. Usability testing
Since conducting product research is also about understanding how well your customers navigate through your product and if they find it usable, you can run usability or prototype tests . Usability testing evaluates the usability of your product by asking test participants to complete tasks on your tool and seeing how they interact with it.
While typically conducted as a pre-launch check, usability testing is now widely understood as a building block of continuous research. Conducting regular usability tests is crucial to staying familiar with users, taking the pulse of your product, and ensuring every new product decision is informed with real data.
Conduct usability tests on a product research tool like Maze and record your participant’s audio, video, and screen with Clips . This offers you a mix of quantitative and qualitative data to learn why participants take certain actions to complete test tasks.
7. Fake door testing
The fake door testing method, also called the ‘painted door method’, is a way to validate whether your customers would be interested in a particular feature. “It works by faking a feature that is not actually available and implementing a tracker to know how many people click on it,” explains Matthieu.
When people click on the feature, they see a message explaining it’s not available at the moment. If the click-rate is high, you can assume there’s interest in the feature and conduct further research to identify how to design and develop it.
While it’s a quick way to gauge interest, fake door testing runs the risk of frustrating users, so if you’re using this method on a live product, you should be cautious and set a short testing period to avoid creating false expectations in your users.
8. Focus groups
Focus groups are when you gather a group of users to try your product and discuss their thoughts on the design, UX, usability, or price. You’ll offer them prompts or ask a series of user research questions to spark conversation, then observe and take notes.
This can be an expensive or admin-heavy method, as you need to rent a space, find participants who are willing to attend, and compensate them for their time. However, you can also conduct focus groups remotely through video conferencing tools. These groups are a good way of generating new product ideas or gaining deep insight in a short space of time, as you can hear directly from your users and adjust your questioning to follow up on important topics or opinions which participants mention.
When to perform product research
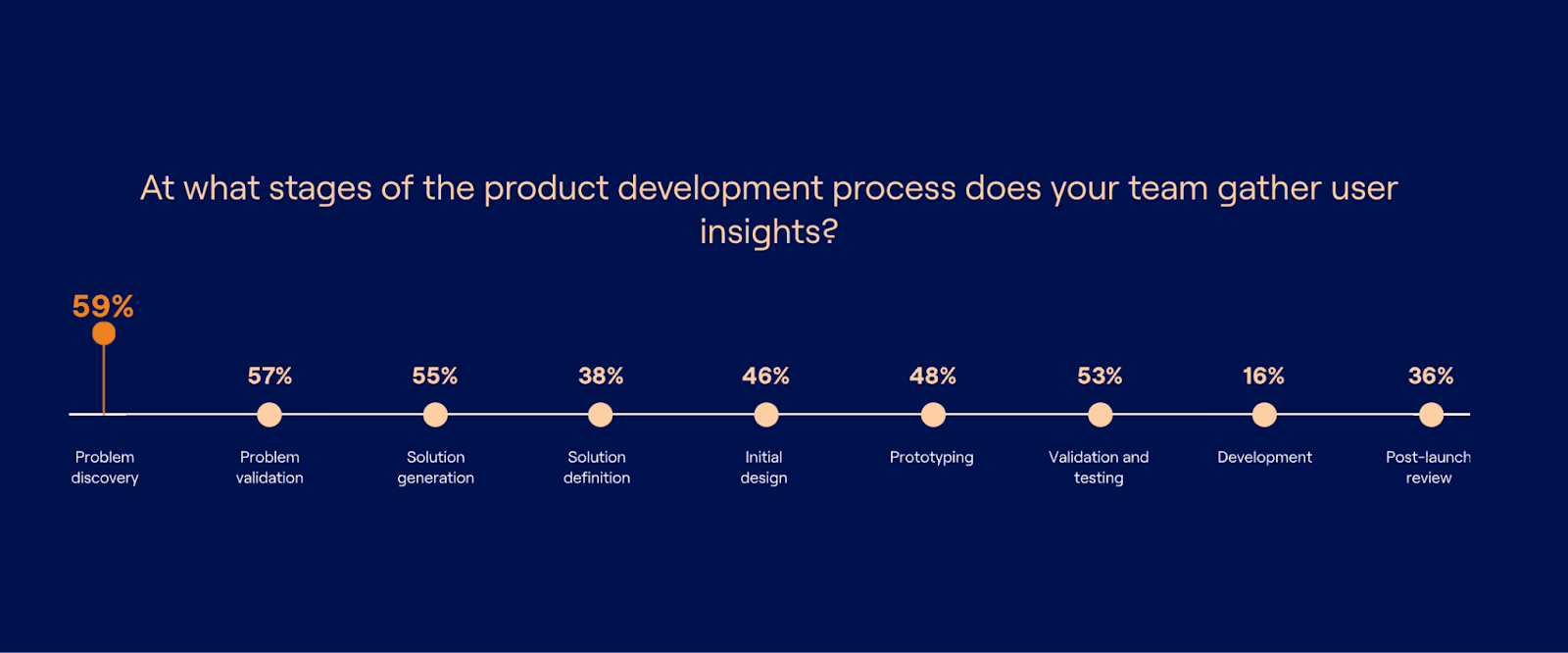
Source: 2023 Continuous Product Discovery Report
According to our 2023 Continuous Product Discovery Report , most teams conduct research at problem discovery (59%) and problem validation (57%), with only 36% researching post-launch.
The consensus is that product teams don’t think that’s enough—78% think they could research more often: which means there’s a big opportunity for you to implement regular research at all stages of the product research process .
Here’s when to conduct research on your product:
- At problem discovery stage to outline a hypothesis based on user insights
- During problem validation to prove your hypothesis
- During solution generation and concept development to see if you’re moving in the right direction
- As you’re screening different ideas for prioritization to identify the ones your users value most
- At solution definition and once you have your initial design to test early wireframes
- After developing a prototype to see assess usability and direction
- During validation and testing to review changes made to previous prototypes
- After development, and post-launch to get feedback and plan your future steps
- Before launching a new feature or doing product optimization to gauge users’ perceptions
Best practices for effective product research
If you only have time to consider one best practice for product research, we’ll keep it short. Just start.
Any research is better than none, and there’s a wealth of knowledge out there waiting to be discovered. If you don’t use it, your competitors will.
Now, here are six other best practices to help you improve your results and get the best insights possible:
1. Conduct research continuously
Your product is never done, at least not while the market, your customers, and technology are evolving. So, for your users to keep choosing you, you need to grow with them, adapt to trends, and keep iterating on your product. The right way to make product iterations is by conducting continuous product research, having frequent communication with your users, and actively listening to the market.
Did you know that user-centric organizations achieve 2.3x better business outcomes? 📊
By putting customers' needs front and center, research-mature organizations are driving better customer satisfaction (1.9x), customer retention (2.4), and increased revenue (4.2x). Learn more in our Research Maturity Report .
2. Focus on the business problem when presenting to stakeholders
It’s easy to get so involved in the product that you forget to mention how it helps the business when presenting research findings. To get stakeholders on board and to build great products that are profitable, always keep the business needs in mind. There’s no product without business success, so always align with your stakeholders and bring it back to team KPIs and business metrics. To convey your story, it’s a good rule of thumb to start each cross-team meeting by presenting the business problem, then sharing how adding a certain feature decision will help you solve it, before getting into the data that backs this up.
3. Embrace your curiosity
One of the biggest mistakes you can make in product research is letting cognitive biases take over the process. Work in teams and ask questions out of curiosity—consider research a way to disprove your hypothesis or challenge your assumptions, rather than a way to prove them right. As Prerna Kaul, Product Lead for Alexa AI at Amazon explains, you often gain more insight from an answer you don’t want to hear. “A huge trust-buster is when researchers sell an idea to customers and reinforce their pre-existing beliefs.” Doing so makes the user tell you what you want to hear but not what you need to know. It’s better to know that you have the wrong assumptions early on and build products that solve the right problem.
It’s non-negotiable to ensure that you are solving the right problem for the customer. Your solution is a painkiller, not a vitamin.
Prerna Kaul , Product Lead for Alexa AI at Amazon
4. Focus on the end goal rather than specific features
When you work closely with a product you’re passionate about, it’s only natural to think of all the possibilities, and minute details and features of the product. However, it’s crucial to understand that, while you might be the one making the internal decisions, the user will have the final call. Getting hung up on specific features will get you frustrated if users disagree, or lead you to make biased choices. To overcome this, you can write a research statement explaining the big problem you’re trying to achieve with the product. Come back to this before and after each decision, to keep your choices grounded in what’s best for the user.
“We always ask: Are we solving the right problem by creating this product? Is it going to have a measurable benefit to people?” says Nick Simpson, Head of UX at Airteam. “Then, we try to answer those questions through research methods to determine whether this investment will be worth it, to both business and users.” By thinking of the overall end goal at all stages, you get to build profitable products and features that really respond to that intention.
5. Take notes of everything
This one might go without saying, but it’s crucial to keep track of everything. Not just to inform future research and remind yourself where decisions came from, but to democratize research and bring the entire organization into your research process .
Set up a centralized research repository that anyone can access, and share it with your wider organization. Within the product team, keep a record of all user insights, even if they sound impossible to achieve at first. “These ‘futuristic’ thoughts or ideas are the ones that can either inform future iterations of the product or that you can creatively turn into something more feasible to design and build,” explains Nick. Keeping an organized information bank enables everyone on the team to get to know the user, the market, and why you’ve made certain decisions in the past.
6. Combine user feedback with data
While your users should be at the center of your business, don’t rely solely on their comments without checking other data. In reality, not everything people say is exactly what they do . Research participants can be influenced by any number of factors, mostly unconscious, so it’s important to use qualitative and quantitative data to reinforce each other.
For example, the users you interviewed might tell you they love a certain feature, but when you contrast those comments with heatmap data and time on page, you see that only a small percentage of your customers actually use it. Consider what research can be conducted to ascertain why this is, how you can improve those metrics, or whether it’s more helpful to refocus efforts on a different feature with a higher profit margin.
Keep learning about product research
In this chapter, we’ve covered a lot about product research:
- What product research is (and what it’s not)
- How researching your product is beneficial to your business
- The different methods you can use to conduct product research
- When to conduct product research
- Best practices for your research
Now, it’s time to kickstart your product research process in the next chapter. We’ll also talk about how to conduct product experiments and competitive analysis, so stay tuned.
Product research process
Are you an agency specialized in UX, digital marketing, or growth? Join our Partner Program
Learn / Guides / Product research basics
Back to guides
A step-by-step guide to the product research process
A strong product research process ensures product teams maximize resources, meet key business goals, and make confident decisions that will deliver successful products and features to create customer delight.
But, how do you conduct effective product research?
Just as there’s no single way to develop a product, no single research process fits all product teams. But there are key steps that will help you balance business goals and user needs for actionable product research .
This article takes you through the factors you should consider to tailor product research to your desired outcomes and provides a step-by-by-step guide to doing research right.
Use Hotjar to streamline your product research process
Hotjar offers product teams a rich stream of quantitative and qualitative data that keeps you connected to user needs at every stage of research.
What to consider before starting product research
Before jumping into the research process , product managers prepare their team. Take time to consider the why and determine how you can design the process to meet your unique product requirements.
Reflect on:
Why you’re doing the research
Get connected with the deep purpose of your research: what you need to understand to create a profitable and effective product .
Determine specific outcomes of the research process.
During the early product discovery stages, generating new product ideas for innovation and getting to know your users better will serve as a solid foundation throughout the research process. At later stages, look for concrete feedback on a new product, or possible upgrades and feature updates for an existing product. The why behind the research should guide your process.
Categorizing your users
Determining customer needs and segmenting users are crucial steps that impact the success of any product research strategy.
You might use a random sample of potential or existing customers; or segment users according to region, industry, or other criteria to spot patterns across different demographics.
Trial users can give immediate product feedback, which is usually incredibly easy to implement (a new theme, for example) or incredibly difficult, like an entirely new functionality or platform for your product. Your long-time users can give nuanced feedback, but they overlook what doesn't work due to their expertise.
Finding that middle ground of users who like what you offer but aren't stuck to your brand is essential. These users appreciate being treated like their insights matter most—because they do.
Finding impartial user insights can be tricky since many tools track users who’ve been paid or incentivized to click through to your website or product. Product experience insights software like Hotjar can help by providing organic, unbiased user data that gives you a clear picture of your customer experience (CX) .
Pro tip: Hotjar Highlights lets you sort and curate user insights and attributes, and share them with your product team. You can also watch Session Recordings of users from specific countries or industries—or filter recordings to see only satisfied or dissatisfied user experiences, which can provide valuable information on what’s working (and what’s not).
A Hotjar Session Recording
Your core business goals
The best product research processes overlap with the overall organizational vision, so update your research goals in line with company goals to ensure alignment.
Designing your research process with cross-functional collaboration in mind is a great way to eliminate any communication issues, ensure all departments collect data that tests product profitability, business goals, and user satisfaction.
Your team’s methodology
Different product methodologies emphasize different aspects of product research throughout its lifecycle, so it’s important to consider techniques that will fit your team’s working stages.
Teams who use waterfall methodologies usually rely on bursts of intense research before development and again during pre-launch. They also make a clear distinction between the product’s research and development phases.
Teams who use agile, lean, or DevOps methods usually integrate research with the broader product development process, engaging in continuous discovery methods.
Whatever your methodology, infuse research into every stage of the product lifecycle to achieve business goals like increased revenue, acquisitions, and user adoption.
Choosing which research tools to use
When you’re deciding how to do product research, you’ll need to consider your budget and company size to pick out your tool stack.
Manual research techniques like user interviews can be time-consuming and cost-intensive, but useful to forge a personal connection with users and ask improvised questions based on their responses.
Automated research tools (like Hotjar 👋) increase speed, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, and reduce human error. They allow you to reach a larger target audience and ensure you’re getting clean, unbiased product feedback —in person, users are more likely to feel pressure to compliment your product or underplay their concerns, but with tools like Hotjar, you’ll get genuine, in-the-moment feedback from users as they engage with your product.
Which team members will contribute
Involve different team members at each stage of the product workflow. For example, when you’re validating product ideas, you may want to include marketing and technical departments; and when you’re testing product usability , you may want to rely on the expertise of your engineers.
It’s also important to consider what research other departments have done before launching your own process, so you don’t waste resources duplicating generic market research.
8 steps for amazing product research
Amazing product research is all about doing smart research to unearth effective insights without getting lost in an information overload that derails your product workflow .
Follow these eight steps to guide your product research strategies to achieve valuable, actionable product insights that will inform your product’s entire lifecycle, from ideation to execution.
1. Define your research goals
First, set your high-level goals, which should test business objectives as well as customer-centric product discovery. These are often drawn directly from the product vision and strategy.
Then, create attainable, specific goals or questions for your team to focus on during each stage of their research. This might include:
Conducting market research for the product’s adoption before its launch
Identifying areas where key features can be improved after the product launch
Evaluating the product’s performance throughout the product lifecycle
2. Understand your users
User needs are at the center of effective product research processes.
Engage in user discovery—identify and understand your customer—as early as possible , even before you have definite product or feature ideas. Open-ended user research is a key source of product inspiration and innovation, and an essential step in determining product-market fit .
Then, when you have product proposals, prototypes, or a minimum viable product ( MVP) , you can start seeking more specific feedback.
User research is all about interacting with your current or potential users and learning what they want and need . Developing a user-centric culture of ongoing research will help you gauge the market demand, position your product against the competition, and generate customer delight .
To create a user-centric research culture, conduct user interviews and create user personas. You can also connect more passively with your user demographic by looking at forums, Facebook groups, or sites like Reddit that are used by your customer niche.
The more organic the research process, the better. It’s ideal to catch users in situations where they answer by instinct instead of having carefully crafted answers. It's what they say instinctively that leads to better product solutions.
Pro tip: use Feedback widgets to gather user feedback in a non-invasive way.
Hotjar’s Feedback widgets are integrated into the product interface , so users can give quick feedback and then carry on with their tasks. This means you can survey your users and gain valuable insights by learning what they’re thinking and feeling as they interact with the product.
A Hotjar feedback widget
3. Do market research for your product
Run thorough competitive and comparative analyses to test the business potential of your product against other solutions on the market , and engage in opportunity mapping to get stakeholder buy-in.
You can also use historical market data and trade reports to predict potential profitability and run keyword research to understand users and what potential customers are searching for to generate product ideas.
Once you’ve validated whether there’s a viable market for your product and determined how saturated that target market is, focus on your product’s unique selling points.
Pro tip: even if you already have a product established in a specific market, make sure to assess the market periodically. Markets and competitors change, and making assumptions because of your initial research processes can be a costly mistake. Work with your marketing team here to validate your ideas and avoid guesswork.
Evaluate your product regularly against the industry by creating a value curve. The value curve plots the product offerings currently available in the market on one axis, and the factors the industry is competing on and investing in heavily on the other. This can help you spot market opportunities, ensure product relevance, and get ideas for features you could add to increase user demand and open up new user bases.
Check out how Gavin increased conversions for his lead generation agency by 42% with Hotjar.
4. Get to know industry trends
Next, combine your understanding of your users and market with research on technology trends that may affect user expectations of your product or its long-term viability.
Stay on top of trends by regularly engaging with tech cultures —read trade magazines and news sites, listen to tech news podcasts, and follow key trendspotters on social media and specialist forums. You can also use tools like Google Trends , Trend Hunter , and PSFK .
Another key source of tech trend information is your engineering team . Chances are, you have plenty of techies on your team who are up to speed on different aspects of technology and what’s forecasted to change.
Pro tip: rigorously analyze trends and put them into context to understand what has staying power, as you avoid jumping on every passing fad. Create a learning culture that embraces experimentation and gives team members the opportunity to share their knowledge.
Analyze the latest trending topics and projects in mainstream open-source communities across the Internet such as GitHub. These communities are an incredible resource for identifying tech trends that are sustainable, disruptive, and have immense staying power.
It's also important to subscribe to prominent tech publications and leading technology platforms such as Azure and AWS to get the latest tech news and new feature announcements delivered directly to your inbox. This way, your product team is always in the know about the most important tech trends that are shaping product development and product markets.
5. Validate ideas with current or potential users
Once you’ve developed a strong sense of your users, market, and technology, it’s time to start testing concrete ideas and solutions.
Based on your early research, identify possible products, features, or upgrades that could meet user needs as well as business goals. Then, run concept testing to evaluate the user experience.
First, identify key users or user types to test. Recruit participants for customer interviews or focus groups, or deploy Hotjar Surveys , Incoming Feedback tools, and Session Recordings to test ideas with existing users.
Then, ask questions or set tasks and observe user responses. You may just want to explain concepts to users at this stage—or you can use wireframes or mockups; or, at later stages, prototypes or MVPs.
Make sure you account for confirmation bias and false-positive responses from users when designing the validation process. Include open- and closed-ended questions and use measures like purchase intent to determine customer adoption.
Pro tip: use fake door testing to gauge interest in new features across your existing user base.
In fake door tests, you show users a call-to-action for a product action that doesn’t exist yet. Once they click to perform the action, they’ll be taken to a page that explains this feature isn’t available yet—you may also choose to include a short survey on this page to learn more about their interest. By reviewing answers to survey questions and the click-through rate , product teams can quickly validate ideas for new features or improvements with users.
6. Test your MVP
The next step in your product research process is to develop a Minimum Viable Product based on validated ideas and run tests to improve subsequent iterations.
This is a critical stage in product research that you shouldn’t skip. Waiting for the fully developed product before running tests makes it harder to fix software and prioritize bug issues, causing major delays.
Quality assurance (QA) testing, regression testing, and performance testing check the MVP’s functionality and show developers where they need to make product changes .
User tests are also key at this stage. Different types of product testing , like tree testing and card sorting, can confirm whether users can easily navigate your product to find the functionality they need.
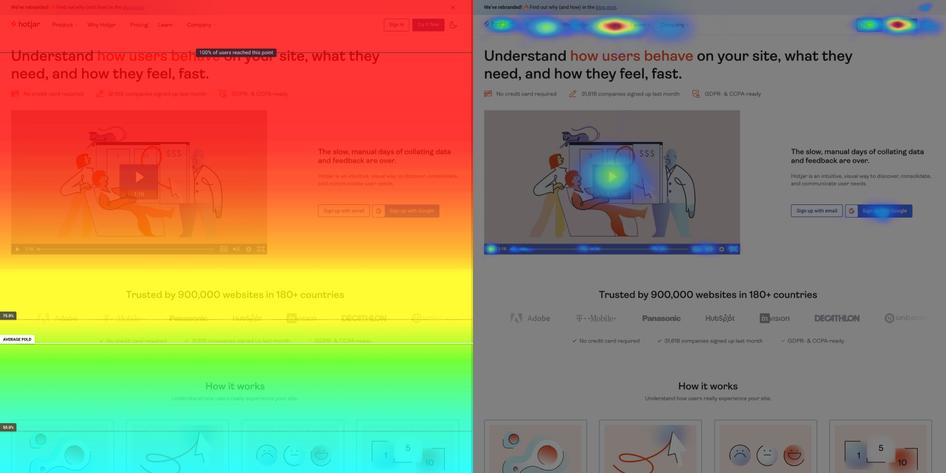
A/B tests and multivariate tests , where you split your user base into groups and give them different versions of a product or feature, can help you decide which iteration to run with. Hotjar Heatmaps allow you to easily compare where users click and scroll on different versions of the product.
7. Continue research after the product launch
Consider doing a soft launch—or even canary deployment—where you release new products or features to a small group of users
Gather data to weed out bugs
Finally, adapt the product based on user responses
Then you can roll it out to all users.
But even once you’ve launched the final product, your research isn’t over. The best product teams stay connected with their users and regularly analyze market trends and tech changes.
After the product is released, either through a soft launch or a regular launch, implementing a data-driven approach to the go-to-market strategy is crucial in parsing consumer reports and validating trends and customer opinions.
Continuous research ensures that your product stays relevant and successfully meets customer needs, which will boost user metrics and business metrics alike.
So how can you continue your research throughout the product lifecycle?
Watch session recordings to spot blockers and bugs where users are rage clicking or dropping off the product journey
Use heatmaps to understand which product elements are most popular—and unpopular—with users
Measure product analytics like click-through rate (CTR) and product conversion rate
Stay up to date on industry and market trends
Incorporate regular opportunities for cross-team discussions to get different research perspectives
Schedule regular user and customer interviews
Use product experience insights tools like Hotjar to give you a steady stream of user feedback through Surveys and Feedback widgets
8. Turn research into action
The final step in any product research process is to organize your research and turn insights into action.
Curate your research into specific, actionable themes to cut through the noise and gather valuable, user-centric insights.
Then, use your research to establish a strong product strategy and roadmap to guide your product development process. Make sure you compare the strategy and roadmap with new research at regular intervals and update where needed, though it’s important to strike a balance: these documents should be dynamic but relatively stable touchpoints.
Your product research should also drive your day-to-day decisions and product backlog management , and form the basis of your product storytelling to help get stakeholder buy-in.
Why creating a user-centric research culture is essential
Remember: at heart, all product research is user research.
Product teams who are endlessly curious about their users—who they are, what they need, how they experience your product—can better meet the demands of an ever-evolving market, inspire customer loyalty, and increase their Net Promoter Score (NPS) . With a learning mindset and a commitment to customer-centric product discovery, you can transform research into innovation and sustainable business growth .
FAQs on the product research process
What is product research.
Product research is the process of gathering data about your product’s purpose, intended users, and market to meet user needs and achieve business goals.
What are the steps in the product research process?
The 8 steps in an effective product research process are:
1) Define your research goals
2) Understand your users
3) Do market research for your product
4) Get to know industry trends
5) Validate ideas with current or potential users
6) Test your MVP
7) Continue research after the product launch
8) Turn research into action
Why is product research important?
Strong product research is critical to product management because:
It ensures the product will meet customer needs and hit business targets
It helps product managers (PMs) develop a data-informed product vision, strategy, and roadmap
It helps PMs make confident decisions on the product backlog and day-to-day tasks
It keeps the product team motivated and connected with the purpose of their work
It helps the product team communicate product value to stakeholders to get buy-in and secure resources
Prioritize product features
Previous chapter
Guide index
.webp)
What is Product Research? Methods, Process, and Benefits

Product research does not just happen in the initial stages of product development. Well-seasoned product managers know that the process is continuous. Businesses that perform best conduct regular product research to stay ahead of customer needs, market trends, and the competition.
This guide will help you to:
✅ Understand what product research is ✅ Learn if your product team should invest time and resources in it (and why) ✅ Get to know different product research methods, and when best to use them ✅ Plan your product research step by step ✅ Master product research with some best real-life tips
Without proper product research, your chances of success, like your product decisions , will be random. Learn from the market and your customers to make data-driven and customer-centric decisions.
We’ll show you how 🙌

What is product research?
Product research is a process in which you gather, analyze, and interpret data to make strategic decisions about a product's or feature’s development, improvement, or market positioning. It is a crucial part of the design and development process, whether for a new product or adding features to an existing one.
Product research helps evaluate market demand, analyze conditions and competition, and identify your target audience's needs, expectations, and pain points. The goal is to create products that meet user needs , reduce risks, and enhance user satisfaction.
Product research is essential before and after a product launch to ensure continuous improvement and alignment with market trends and customer preferences.
Types of product research
Product research has different facets depending on which stage of development you are, and what kind of insights you need. They all have a lot in common, but the focus angle will be different. 🔦
🔬 Market research focuses on evaluating the market size, trends, competitive landscape, and customer demographics (within one market). It will help you assess whether your product has a chance to succeed on the intended market, identify opportunities, and optimize your overall product and marketing strategies.
🔬 Customer research aims to understand customers' needs, preferences, behaviors, and experiences. Only then can you create products that meet their expectations and solve their problems.
🔬 User research studies how users interact with a product to make sure it is user-friendly and meets real user needs . Its main focus is to gather insights on user behaviors , needs, motivations, and pain points to improve user experience and product usability.
🔬With product discovery , you want to identify and validate ideas for new products and features before development begins. The primary purpose is to minimize risks by validating assumptions and ensuring alignment with user needs and business goals.
🔬 Continuous product discovery framework integrates into the daily workflow of product teams. Its main focus is to continuously gather insights from users to validate product assumptions, to ultimately build features that bring value for users but also align with business goals.
🔬 Pricing research helps determine the optimal price for your product or service. It involves analyzing market demand, competition, and customer willingness to pay. The goal is to find a price threshold that maximizes revenue and meets market expectations at the same time.
Why do product teams need product research?
To some degree, all product teams need to have a well-established product research process.
Depending on the scope (is it a completely new product, or are you developing new features?) and stage of development (are you assessing your chances in the market or already prototyping?), teams will perform different research activities.
It’s never one size fits all, but it’s also an indisputable part of developing digital products.
To make informed decisions
The fundamental reason to do product research is to reduce the risks of failure.
And even though you might have heard it countless times, you cannot overrate the power of data-driven decisions. Product research provides concrete data, forming a foundation for making them, from feature prioritization to design choices.
To identify the problem and validate product ideas
Product research will help you uncover what your customers need and desire, as well as the challenges they face.
With a well-defined problem, it’s also easier to test and validate product ideas before you invest significant resources. This again reduces the risk of creating a product that misses the mark.
To gain a competitive edge
One integral element of product research is understanding your competition's offerings. Analyzing competitor products will help you identify opportunities for differentiation, making sure your product stands out in the crowded market.
Continuous market research will help you stay abreast of trends and evolving customer needs, ensuring that your product remains relevant.
Bonus: Customer-centric approach focused on user-centered design will also help you build a positive brand reputation.
To optimize product development
This one works two ways. First, by conducting thorough product research, you identify areas that need to be prioritized. It enables your teams to focus on aspects that resonate the most with users.
Second, you save money. Product research gives you tangible arguments for allocating resources better, thus preventing costly development mistakes.
For continuous improvement
As the development of digital products never ends but continues through iterations, you need a trend baseline to make sure that your product evolves in the right direction.
Bonus: Engaging directly with users during research helps develop empathy and improve retention, both of which are crucial for user-centric product development.
Product research methods
With the countless number of available product research methods, the most important part is choosing the right ones. Depending on when in the product development process you’d like to use them, the overall research goal, and the resources available, you might be using different combinations of primary and secondary research .
Product surveys are a great way to learn how existing and potential customers feel about your product.
These surveys can include questions about what consumers think of your product, such as:
- What frustrates them the most
- What the most needed improvements include
- What their favorite features are, and more.
You can also gain insights into how these aspects compare to your competitors’ products.
Product surveys can be sent via email or link , in-app , in-product , or displayed on your website . This is probably the most convenient, affordable, and effort-efficient way of gathering information to fuel your product research.
Another kind of survey that can prove useful is a quarterly NPS (Net Promoter Score) survey . The open follow-up question can be a great source of new product and feature ideas.
In-app feedback
In-app feedback and in-product surveys are perfect for gathering real-time user feedback and addressing user issues promptly. They provide immediate user insights that add to your continuous improvement efforts.

With in-product surveys, you can easily stay on top of contextual feedback on existing or new features and recent updates.
Customer reviews
Customer reviews provide unprompted feedback provided by users on various platforms, such as e-commerce sites, social media, and review websites.

They help understand user satisfaction, identify friction points , and gather actionable insights , but they are also an opportunity to build rapport with your audience. Never neglect them, and always be sure to reply.
Voice of Customer (VoC) analysis
You should collect Voice of Customer (VoC) feedback to understand user needs, preferences, and experiences. It is useful for gaining a comprehensive view of customer sentiments and identifying opportunities for improvement.
VoC analysis can be a helpful tool to inform product development and customer service strategies.
Importantly, you need consistency here, hence the systematic collection and analysis of feedback is essential.
Product analytics
Product analysis based on internal analytics is a fundamental element of any digital product. With the user behavioral analytics relevant to your product, you must be on top of the key metrics such as product adoption, user retention , churn , or lifetime value.
Remember, you should adjust the choice of metrics to your goals and needs. Too many of them will just create unnecessary noise. You should also establish one source of truth and democratize access to your tools.
User interviews
User interviews are, by far, the best method to obtain in-depth user insights. They allow the flexibility to ask the best research questions that, in turn, provide rich, detailed data. The downside? User interviews require a lot of resources, including time and money. The key to using them to the fullest is sound interview recruitment.
For example, Medscape runs product research surveys inside the product in which they recruit users for interviews.

We do it at Survicate, too. We also use Intercom conversations with customers to gather additional feedback and input on silent launches. Respondent attributes identify customers who would be good candidates for product testing .
Focus groups
Start with finding focus groups of people who already use a product similar to the one you are thinking of developing. You can enquire about things like an optimal price , the most important features , and the features that are missing in their current solution.
This can Additionally, you’ll learn about the qualities of your product that will make it unique and outbid your competitors.
To eliminate bias , choose third-party interviews or online surveys .
Concept testing
Concept testing is the process of surveying users about a potential product . You can learn how they feel about it and whether they would be willing to purchase it were it available on the market.
This method is very versatile, as it can be conducted online, over the phone, or through real-life interviews. It can be difficult to obtain a sample of potential clients willing to provide you with feedback, so we recommend using a customer feedback tool to facilitate the process.
A/B testing
With A/B testing , you compare two versions of a product or feature to determine which one performs better. It’s useful for optimizing design and functionality based on user preferences and behaviors.
A/B testing is often used during the product development phase to refine features and improve user experience .
Usability testing
After building an MVP , you need to show it to potential customers to get their feedback.
Usability testing involves observing users as they interact with a product to identify any usability issues. This method is useful for understanding how intuitive and user-friendly a product is. Usability testing is often conducted during the design and development stages to ensure the product meets user expectations and is easy to use.
This method is usually used in the later stages of product development to get the final product validation .
When to perform product research
Product research takes place throughout the whole development process. From the initial idea to post-launch, each stage requires its own set of research activities.
Before development
Discovery is probably the most important phase of product development when it comes to research. At this stage, you need to establish the fundamentals of the product. There are many questions you must answer to reduce risks before even thinking about the delivery phase:
🏮Who is it for? 🏮What problems will it solve? 🏮How is it different from the competition, and how does it position itself among similar products? 🏮Can you develop it? 🏮Will people buy it?
This is the time to research the market, define user personas , and get to know their problems, needs, and desires. When you find your niche and your target audience, you’ll have to decide how to position your product against the competition .
🔬Useful research methods : surveys, user interviews, product analytics, market research, product discovery, continuous product discovery
🔧Toolset : Check our list of popular product research tools .
💡How Medscape uses surveys to complement continuous discovery ⤵️
By using surveys within a Continuous Discovery framework, Medscape's product teams have improved their product development through direct user feedback. Contextual surveys have been crucial in recruiting users for interviews and validating hypotheses, resulting in actionable insights.
READ THE WHOLE STORY
Prototyping
Once you have validated your product idea, you’ll move on to prototyping initial versions to capture any usability and UX issues early on.
At this point, you’ll probably already be conducting research to see how your target audience perceives the early iterations of the product (or feature). Gathering product feedback at this stage will help you design a roadmap .
🔬Useful research methods: UX surveys, user interviews, product analytics, concept testing, focus groups, usability testing, A/B testing
🔧Toolset: Check our list of popular UX research tools .
Beta testing
After finding the sweet spot in accommodating user needs, functionality, usability, and your business goals, you’ll end up with a beta version of your product, something really ready to be tested in and out with a wider group of users.
This will help you understand how customers perceive your product or its new iterations, what they like and don’t like, and how you can still improve on it.
💡How Intergiro speeds up feature validation ⤵️
Intergiro's product team employed in-app surveys to validate new features and gather user insights during the product validation process. They periodically deployed surveys in various parts of their product to obtain precise feedback on specific elements.
🔬Useful research methods: in-product and in-app surveys, user interviews, product analytics, focus groups, usability testing, A/B testing
Post-launch
So you’ve launched the product , but the research journey doesn’t end here—it is a continuous commitment. Make sure you collect relevant customer engagement metrics .
After launch, product research should focus on checking if the entire digital journey provides an engaging product experience . This is the time to evaluate if you have nailed your product’s positioning , product-market fit, and pricing.
💡How Landing measures its product-market fit (and more) ⤵️
Landing utilized Survicate's product-market fit survey to consistently assess how well their platform meets user needs and expectations. This survey serves as a health check for Landing's value proposition, offering qualitative feedback that is analyzed and converted into new roadmap items.
💡How hitta.se improves on its customer journey ⤵️
With NPS and CSAT surveys, Hitta.se identified areas for improvement in their customer journey. By leveraging the customer feedback they collected, they were able to make data-driven decisions and implement tangible changes, resulting in a 35% improvement in NPS.
🔬Useful research methods : user reviews, product analytics, user interviews, surveys: NPS , CSAT , CES , product-market-fit
🔧Toolset: Check our list of popular product feedback tools , user feedback tools , conversion optimization tools .
How to conduct product research?
It’s time to look more closely at the very product research process. You already know it’s essential for developing a successful product. But where should you start? Let’s go through the best practices step by step.
Step 1: Define research objectives
Clearly outline what you aim to achieve with your research. This could include identifying market gaps, understanding user needs, validating product ideas, or improving an existing product.
Step 2: Identify your target audience
Knowing your audience is crucial. Define who’s your target while creating the product by understanding their demographics, needs, and behaviors.
Don’t forget to create detailed user persona profiles including their usage patterns, preferences, and decision-making processes.
It could look like this template ⤵️

You can collect this information upon signup, but you can also gather this data with a user persona survey distributing it, for example, directly in-product or via email.
Step 3: Choose research methods
Select the appropriate mix of quantitative and qualitative methods , and make use of existing data through secondary research.
📈Quantitative methods : surveys, data analysis, metrics
📝 Qualitative methods : surveys, interviews, focus groups, user observations, online reviews
📚 Secondary research : existing reports, competitor data, trend analysis
Step 4: Conduct the product research
Now it’s time to put it all into action and implement your chosen methods. Collect data accurately, ensuring objectivity throughout the process.
Step 5: Analyze data and draw insights
Analyzing the collected data to identify key patterns and trends is, traditionally, the most laborious part of the process. While drawing conclusions from quantitative data may be quite fast with the right tools and a wise metric choice, analyzing qualitative feedback is a different story.
To use your qualitative data to the fullest, use a customer feedback analytics tool, such as Insights Hub . It will dramatically cut down the time from raw feedback to contextual insights based on what your users are saying about the product in any feedback source you connect to this tool.
🔦 Identify patterns and trends with quantitative data : Look for recurring themes and statistical trends.
Categorize qualitative feedback and draw actionable conclusions : Link findings directly to product improvements, prioritize changes based on user needs and develop product strategies to address identified challenges.
Step 6: Validate ideas with users
Test your ideas and solutions with existing customers and potential users. Remember to identify key user types before recruiting test participants.
⚖️ Test ideas : Use interviews, focus groups, surveys, and usability tests to gather feedback.
🙊 Account for bias : One way to combat confirmation bias and false-posititve responses is to alway focus on asking about a behavior in a certain context . As Teresa Torres puts it:
“Instead of asking, What criteria do you use when purchasing a pair of jeans? —a direct question that encourages our participant to speculate about their behavior—we want to ask, Tell me about the last time you purchased a pair of jeans. ” [...] It will reflect their actual behavior, not their perceived behavior.
Step 7: Develop and test your MVP
Developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is a result of creating multiple prototypes based on validated ideas and tests to improve subsequent iterations.
⚗️User tests : Use tree testing, card sorting, A/B tests, and heatmaps to confirm usability and functionality
🙌Quality assurance : Conduct QA testing, regression testing, and performance testing.
Step 8: Continue research post-launch
Even after the product launch, continue to gather data and user feedback to weed out bugs and refine the product.
- Gather data : Use user responses to adapt the product before a full rollout.
- Ongoing research : Stay connected with users and regularly analyze market trends and tech changes.
💡How GetResponse uses online surveys for ongoing product research ⤵️
GetResponse runs over 320 ongoing surveys across their free, paying, and enterprise business units, gathering an average of more than 3,000 responses per month. Its Product teams use surveys to validate features, research personas, as automated in-product surveys to gauge satisfaction along the customer journey, as well as ad-hoc product research activities.

We’re also there
The Ultimate Guide to Product Research: Everything You Need to Know
.jpg)
If you're looking to start a business, you must do your research first. Product research is key to determining whether a product will succeed.
In this guide, we'll teach you everything you need to know about product research, including the different methods you can use and the factors you need to consider. We'll also provide some tips on how to get started. So whether you're just getting started or looking for ways to improve your process, this guide is for you!
What Is Product Research?
Product research is gathering data about a potential product or service. This data can include information about the target market, the competition, and the product itself. It's crucial to do product research before launching a new product or service, as it can help you determine whether or not there is a demand for your offering.
Why Is Product Research Important?
Product research is essential because it can help you make informed decisions about your product or service. If you don't research, you could launch a product that no one wants or isn't profitable.
Product research can also help you understand your target market and what they're looking for in a product. How to do product research?
There are a few different ways to do product research. You can use online tools like Google Trends and Amazon Best Sellers to get an idea of what people are searching for and what products are selling well.
You can also reach out to your target market and ask them about their needs and wants. Additionally, you can look at your competition to see what they're doing well and where they could improve.
What Are The Different Types of Product Research?
There are a few different types of product research, including primary research, secondary research, and desk research.
Primary research is data that you collect through surveys or interviews, for example. Secondary research is data that someone else has already collected, like data from a market research report. Desk research is data you can find online, through Google or social media.
Factors To Consider When Doing Product Research
There are a few different factors to consider when doing product research, including your target market, the competition, and the product itself.
You'll want to ensure you understand your target market and what they're looking for. Additionally, it's important to understand your competition and what they're doing well.
Finally, you'll want to make sure you have a clear understanding of the product itself.
Product research is an integral part of developing any new product or service. By understanding your target market, the competition, and the Product, you can make informed decisions about your product design and user experience.
How To Conduct Product Research

1. Evaluate Market Size
You'll want to start by evaluating the market size when conducting product research. This will give you an idea of the potential demand for your product or service. Additionally, it will help you understand the competition. To do this, you can use desk research to find the market size and competition data.
Google search: "market size [your industry]"
"Global [your industry] market size"
"Competition in [your industry]"
Secondary market research:
- For products: Look at Amazon Best Sellers Rank or Google Shopping results.
- For services: Use Google Keyword Planner to look at average monthly searches.
If you're unsure where to start, try looking at secondary market research. This can include Amazon Best Sellers Rank or Google Shopping results for products or using the Google Keyword Planner to look at average monthly searches for services.
Once you understand the market size and competition, you can start to conduct your primary research.
2. Analyze The Competitive Landscape

After you've evaluated the market size, you'll want to analyze the competitive landscape. This will help you understand your competitors and what they're doing well. To do this, you can use desk research to find data about the competition.
Google search: "[your industry] competitors"
"[Your product or service] reviews"
"SWOT analysis [your industry]"
- Look at competitor websites.
- Read competitor reviews.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis.
A SWOT analysis is a great way to evaluate your competition and understand its strengths and weaknesses. To do a SWOT analysis, you'll want to look at your competitor's website, read their reviews, and understand their strengths and weaknesses. This will help you identify areas where you can improve upon.
Once you understand the competition well, you can develop your unique selling proposition. This will help you differentiate yourself from the competition and make your product or service more appealing to potential customers.
3. Determine Product Category Outlook
After you've evaluated the market size and analyzed the competitive landscape, you'll want to determine the product category outlook. This will help you understand the future potential of your product or service. To do this, you can use desk research to find data about the future of your industry.
Google search: "[Your industry] forecast"
"Future of [your industry]"
- Look at industry reports.
- Read articles from thought leaders in your industry.
Industry reports are a great way to get an understanding of the future potential of your product or service. You can also read articles from thought leaders in your industry to get their insights on the future.
Once you have a good understanding of the future potential, you can start to develop your product or service roadmap. This will help you map out the steps you need to take to achieve your desired future state.
4. Is Your Product Available Locally?
If you're looking to launch a new product or service, it's essential to understand the availability of your product. IYou'llwant to research the local market. If your product is available locally, you can use desk research to find data about the local market.
Google search: "[Your product] [your city]"
"[Your product] [your state]"
- Look at local demographic data
- Read local news articles
- Conduct market analysis
Local demographic data can give you insights into the potential market for your product or service. You can also read local news articles to understand the local market better.
Additionally, you can conduct a market analysis to understand the potential demand for your product or service.
Once you have a good understanding of the local market, you can start to develop your marketing strategy. This will help you reach your target market and generate sales.
5. Determine Your Target Customer

Before starting marketing your product or service, you need to determine your target customer.
To do this, you'll want to think about the needs of your target market and the demographics of your potential customers.
This information will help you develop a buyer persona, a fictional representation of your ideal customer.
Once you have a buyer persona, you can develop your marketing strategy. This will help you reach your target market and generate sales.
Additionally, you can use your buyer persona to develop your product or service offering. Understanding your target customer's needs ensures that your product or service meets their needs.
6. Determine Markup
After you've chosen your target customer and developed your marketing strategy, you'll need to determine your markup. Markup is the difference between the cost of your product or service and the selling price. To determine markup, you'll want to consider the following:
- The cost of goods sold (COGS): This includes the cost of materials, labor, and overhead.
- The selling price: This is the price you'll charge your customers.
- The desired profit margin: This is the percentage of profit you want to make on each sale.
Once you've considered these factors, you can calculate your markup. To do this, you'll need to divide your desired profit margin by your COGS. Once you have your markup, you can start to develop your pricing strategy.
7. Figure Out The Selling Price
By understanding markup's components, you can ensure that your product or service is priced correctly. Additionally, you can use markup to help you reach your desired profit margin.
After you've determined your markup, you can start to develop your pricing strategy. To do this, you'll need to multiply your markup by your COGS.
8. Determine Product Weight And Size
After you've decided on your selling price, you'll need to determine your product’s weight and size. To do this, you'll need to consider the following:
- The weight of the product: This will affect shipping costs.
- The dimensions of the product: This will affect packaging costs.
Once you've considered these factors, you can start to develop your packaging strategy.
This will help you keep costs down and ensure your product arrives safely to your customers.
By understanding your product's weight and size, you can ensure that your packaging is sized correctly.
9. Is Your Product Durable?
After you've determined the weight and size of your product, you'll need to consider its durability. To do this, you'll need to think about how your product will be used and how it will stand up to wear and tear. Additionally, you will want to consider the following:
- The materials used in the product: This will affect the durability of the product.
- The product's expected lifespan: This will affect how often your customers need to replace your product.
By understanding your product's durability, you can ensure that it meets your customers' needs. Additionally, you can use this information to help you determine your warranty or return policy.
10. Is Your Product Seasonal?

After considering your product's durability, you'll need to consider its seasonal nature. To do this, you'll need to consider when your customers will use your product and how that will affect demand.
By understanding the seasonal nature of your product, you can ensure that it meets your customers' needs.
11. Does Your Product Serve A Passion, Relieve Pain, Or Solve A Problem?
After considering the seasonal nature of your product, you'll need to consider its purpose. You'll need to consider what your product does and how it can help your customers. Additionally, you'll want to think about the following:
- The product's benefits: This will help you determine what your product does for your customers.
- The product features: This will help you determine how your product can help your customers.
By understanding your product's purpose, you can ensure that it meets your customers' needs.
12. What Will Your Product Turnover Be?
After you've considered the purpose of your product, you'll need to consider its turnover. To do this, you'll need to consider how often your customers will use your product and how that will affect demand.
13. Is Your Product Consumable Or Disposable?
After considering your product's turnover, you'll need to consider its consumable or disposable nature. To do this, you'll need to consider how often your customers will use your product and how that will affect demand.
14. Is Perishability A Factor?
After considering your product's consumable or disposable nature, you'll need to consider its perishability. To do this, you'll need to consider how long your product will last and how that will affect demand.
15. Are There Any Restrictions Or Regulations?

After you've considered the perishability of your product, you'll need to consider any restrictions or regulations. To do this, you'll need to consider what your product is made of and how that will affect its ability to be sold. Additionally, you'll want to think about the following:
- The country of origin: This will affect where you can sell your product
- The product type: This will affect what your product can be used for.
Understanding your product's restrictions or regulations can ensure that it meets your customers' needs. Additionally, you can use this information to help you determine your marketing strategy.
16. Is Your Product Scalable?
After considering your product's restrictions or regulations, you'll need to consider its scalability. To do this, you'll need to consider how easy it is to produce more of your product and how that will affect demand. Additionally, you'll want to think about the following:
- The cost of production: This will affect how much you can charge for your product.
- The time it takes to produce more of your product: This will affect how quickly you can meet customer demand.
By understanding your product's scalability, you can ensure that it meets your customers' needs.
Areas Of Product Research

As you can see, there are a lot of factors to consider when it comes to product research. To make things easier, we've broken down the most critical areas of research into 8 main categories:
- Conduct market research
- Conduct customer research
- Conduct segmentation research
- Conduct concept testing
- Conduct usability testing
- Conduct naming research
- Conduct feature research
- Conduct pricing research
Market Research
Market research is a vital part of product research. By understanding your target market, you can ensure that your product meets their needs.
There are a few different methods that you can use to conduct market research. Some common ways include surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
If you're unsure where to start, we recommend checking out our guide on conducting market research.
Customer Research
Customer research is another vital part of product research. By understanding your customers, you can ensure they're happy with your product.
Additionally, you can use this information to help you improve your product.
There are a few different methods that you can use to conduct customer research, with the most common methods include surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
Segmentation Research
Segmentation research is the process of dividing your market into different groups. You can do this based on age, gender, location, and interests.
By understanding your target market's segmentation, you can ensure that your product is targeted to the right people.
Concept Testing
Concept testing is the process of testing your product idea with potential customers. You can do this to ensure that your product is viable and that people are interested in it. Additionally, you can use this information to help you improve your product.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is testing your product to ensure it's easy to use and can use your product without issues. Additionally, you can use this information to help you improve your product.
Naming Research
Naming research is the process of finding the perfect name for your product. You can do this to ensure your product stands out from the competition.
Additionally, you can use this information to help you create a branding strategy for your product.
There are a few different methods that you can use to conduct naming research. The most common methods include surveys, focus groups, and interviews.
Feature Research
Feature research is the process of understanding which features your customers want. You can do this to ensure that your product has the needed features. Additionally, you can use this information to help you improve your product.
Pricing Research
Pricing research is understanding how much your customers are willing to pay for your product. You can do this to ensure you can make a profit. Additionally, you can use this information to help you improve your product.
12 Tips For Effective Product Research

Conducting effective product research can be a challenge. However, there are a few tips that you can follow to make it easier. Some of the most important tips include:
Follow Consumer Trend Publications
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on consumer trends is to follow consumer trend publications.
This can help you understand what consumers look for and how they change over time. Additionally, it can give you ideas for new products that you can create.
Monitor Social Media Platforms
Another great way to stay up-to-date on consumer trends is to monitor social media platforms.
This can help you see what people are talking about and what they're interested in.
Find Bestsellers on Amazon
Looking at bestsellers on Amazon can help you understand what products are popular and in demand.
This can give you ideas for new products that you can create. Furthermore, doing this can also help you improve your existing products.
Conduct Surveys And Interviews
One of the best ways to get consumer feedback is to conduct surveys and interviews.
This can help you understand their thoughts about your product and how you can improve it. What's more, the results of the surveys and interviews can help you gather ideas for new products.
Browse Social Curation Sites
Social curation sites like Pinterest and Tumblr can be a great way to find new product ideas.
This is because you can see what people are pinning and saving. And better yet, it can also help you understand what trends are popular.
Evaluate B2B Wholesale Marketplaces
Browsing B2B wholesale marketplaces can help you understand what products are in demand.
This can give you ideas for new products that you can create and even help you improve your existing products.
Observe Niche Forums
Another great way to find product ideas is to observe niche forums. This is because you can see what people are talking about and what they're interested in.
Research Existing Products On The Market
As you can see, a lot goes into product research. However, by following these tips, you can be sure that you're conducting effective research. This will help you create products that your customers will love.
Look At Online Reviews
One of the best ways to research a product is to look at online reviews. This can help you understand what people think about the product and whether or not it's worth your time.
Identify Gaps In The Market
Looking at existing products on the market can help you identify gaps in the market. This can give you ideas for new products that you can create and improve your existing products.
Qualitative Product Research
Qualitative research is another critical aspect of product research. This involves talking to people and getting their feedback. Additionally, it can help you understand what trends are popular.
Quantitative Product Research
In addition to qualitative research, you also need to do quantitative analysis. This involves looking at data to understand what people want and how they use products.
FAQs: Product research
What are the two types of product research.
There are two types of product research: qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative research involves talking to people and getting their feedback.
Meanwhile, quantitative research involves looking at data to understand what people want and how they use the products.
How often should you do product research?
Product research is an ongoing process. You need to be monitoring the market and your competition constantly.
Additionally, you need to be gathering feedback from your customers. By doing this, you can ensure that you're always creating products that your customers will love.
What is the role of product research?
Product research plays a vital role in product development . It can help you understand what people want and how they use products.
Additionally, it can help you identify gaps in the market. By doing this, you can be sure that you're always creating products that your customers will love.
What are some of the best ways to do product research?
Some of the best ways to do product research include looking at online reviews, observing niche forums, and asking your customers.
By doing this, you can be sure that you're always getting the most accurate information.
What’s the difference between product research and market research?
Product research is specific to a product. It involves understanding what people want and how they're using products. In comparison, market research is broader and looks at the entire market. It can help you understand trends and segment your customer base.
How do I know if my product research is effective?
There are a few ways to know if your product research is effective.
- First, you should see an increase in sales.
- Additionally, you should see more people using and talking about your products.
- Finally, you should see an increase in customer satisfaction.
If you do not see these things, then it's likely that your product research is ineffective.
What are some common mistakes people make with product research?
One of the most common mistakes people make with product research is not doing enough of it. People can also mistake relying too heavily on one type of research.
For example, they may only look at online reviews and not talk to actual customers. Finally, people can also make the mistake of not constantly updating their research.
How do you start product research?
Product research can be started by looking at online reviews, observing niche forums, and asking your customers. You can also look at competitor products and understand what they're doing right and wrong. By doing this, you can be sure that you're always getting the most accurate information.
What is an example of product research?
An example of product research would be if you were to look at online reviews, observe niche forums, and talk to your customers to understand what people want and how they're using products.
Conclusion: Product research
Product research is an essential part of starting a business. By understanding the needs of your target market and developing a marketing strategy, you can reach your target customers and generate sales.
Additionally, by determining your markup and pricing your product correctly, you can ensure that your business is profitable. By taking the time to do proper product research, you can set your business up for success.
Product trends can change quickly, so staying on top is crucial. We hope this article was helpful for you. Whatever you decide to do for your business from here, we wish you the best of luck!
Create Stunning Videos Easily
Offeo video templates.

Related articles

- Product-led Growth
What is Product Research: A Guide for Founders
I don’t think there’s ever been a founder who succeeded with the first iteration of their product idea. For most of us, building a product means constant discovery and iteration, or product research , for short.
In this guide, I’ll explain what product research is and show you the best methods to do product research for your startup.
And there’s a very good reason for you to keep on reading…
We, founders, have really just one objective, after all – To create a product that will pretty much rock our customers’ worlds.
Sure, we can say that we want to exit and get a bucket load of cash for our product.
Or that we want to conquer the world.
Or build another SaaS unicorn…
And even if that is the case, we still need to build that perfect product first. Perfect in a sense that our customers won’t be able to live without it.
The thing is – It’s almost impossible to do it right off the bat. No matter what ideas we have, we still need more insights, data, and feedback to fine-tune it. And the only way to get it is through product research.
Below, I’ve included what I know about it, and what I’ve done to create Refiner. Full disclaimer, I also plugged my product there because, let’s be fair, it does help with product research too.
But on the whole, the below guide contains what you need to know about product research to refine your idea and build a product that’ll delight your audience.
So, let’s get on with it, then.
What does it really mean to conduct product research?
I ask this because the term – product research – could, at first, be misleading.
It’s easy to consider it referring to the process of researching products to buy, for example but that’s not it.
So what is product research? Various definitions call it a process focusing on gathering insights and information that, once analyzed, can help us build and improve our products.
There is far more in making it happen, of course. However, on the whole, I think that’s probably the easiest way to explain what product research is.
There are several other reasons to conduct product research beyond just learning what your users want.
- Product research is your gateway to becoming a user-centric company. It’s how you understand the target audience, their needs, pain points, and desires, and develop products that meet those requirements, rather than do what you’d like them to do.
- Secondly, product research also helps you validate ideas and assumptions. This last item is of particular interest here. After all, how often do we come up with ideas, and then rationalize them in our minds by assuming certain things about our audience or their needs? Now, these assumptions may as well be true. But you can only know that if you’ve validated them through product research.
- Thanks to different product research methods (more on those in just a moment), we get to find out which features our audience really want us to build. And needless to say, that’s a huge help that can also prevent us from spending time and effort on the wrong feature.
- Finally, product analysis can tell us a whole lot about our competitors , far more than other research methods could uncover. Why? Because through product research, you learn what your customers think of the competition. You discover how they perceive other similar products on the market, what value they (meaning, your customers) think those products deliver, and the reasons why they could consider using those products.
Worth to note – Product research is an iterative process. It’s not something you do once and then, forget about it but a continuous process that helps you refine anything from questions you ask to insights you collect.
As a result, product research is also quite an undertaking. It’s not something you should be doing on a whim, or to plug leaks in your funnel. Instead, product research is a process you should do continuously, and tap into those insights when you need data to fuel a specific project (like plugging leaks in a funnel, for example.)
In other words, product research is where you continuously collect data that you then turn to when needed, not the other way around.
So, how do you do it, then? How do you collect product research data?
Product research methods
Let me start by saying that there is no single, ideal product research method. It’s also impossible to tell which product research method is better than others, and so on. All of the methods I’ve listed below work exceptionally well in their respective best use case scenarios.
But as you can imagine, I’m still a little biased towards surveys. That’s what my product, Refiner , does, after all. Surveys are also the method I’ve used the most in the past, and that’s what helped me drive the development of Refiner.
Nonetheless, here are all the most popular product research methods, including surveys, of course.
Surveys: Surveys rely on you sending questionnaires to a pre-selected audience segment to collect quantitative and qualitative data about those people’s opinions, insights, and so on.
What makes surveys so incredible for product research is their:
- Wide reach – You can send a survey to a large number of people, and collect insights from them without much effort.
- Scalability – Similarly, surveys don’t require additional time or effort from you to scale the research.
- Low cost – Again, surveys are relatively inexpensive to run.
Some of the most common product research surveys include:
- NPS – a survey that allows you to evaluate the customers’ attitudes towards your product.
- CSAT , which helps you learn more about your customer satisfaction and draw actionable insights based on that.
- CES which reveals how easy (or not) customers find your product to use.
Here’s an example of an NPS survey used in product research.
FEATURED READING: How to run a perfect customer survey for a digital product
User Interviews: This method is all about sitting down with your customers one-on-one to discuss their needs, uncover pain points, or their product preferences. User interviews are all about asking open-ended questions and letting the person reveal their opinions. Unfortunately, this makes it a time-consuming method for product research, particularly if compared with surveys.
Focus groups: Running a focus group is like conducting user interviews at scale. In this method, you bring a small group of users together to discuss your product, provide feedback on issues you want to research, and so on.
Usability testing: This method focuses on observing users as they interact with the product (or its prototypes.) By observing how users complete predefined actions in the product, you can identify usability issues and gather insights for improvement.
User behavior tracking: In this method, you’re also drawing conclusions based on user behavior. However, unlike usability testing, behavioral tracking focuses on analyzing data that you collect using different user behavior tracking tools (like Hotjar, for example) to understand user behavior, spot patterns, and collect benchmarks.

A/B testing: A/B or split tests allow you to uncover the audience’s preferences by eliminating product or UI elements that fail to engage them successfully. In this product research method, you present different versions of a product to different user segments and monitor their engagement with those to determine which variation performs better.
Customer journey mapping: This method relies less on collecting specific insights than using your data so far to understand the entire customer journey, from initial product discovery to post-purchase experience. This is an important product research method, as it allows you to map pain points to specific stages of the buyer’s journey, and spot opportunities for improvement.
How to conduct product research – Key elements of a product research project
It’s quite easy to assume that to launch a product research project, you just need to, a.) pick a research method, and b.) figure out how to use it, and off you go but no, that’s not how it works.
Successful product research strategy relies on several key elements:
Clearly defined objectives
It’s as obvious as it sounds, actually. For your project to work out, you need to set specific objectives and communicate them in a clear and understandable way. These objectives will guide the entire project, from selecting the target audience, research method, to what you’re going to do with the data.
Specific target audience
Again, quite an obvious element but also, often one that we tend to forget about. Naturally, we always have an audience for research. There is no such project without it, after all. But at the same time, we often tend to jump in and invite all customers for research, whereas we should be gathering insights from a specific audience or customer segment only.
This product research element focuses on selecting the right people who have the insights and knowledge that you seek. For example, if you’re evaluating advanced product functionality, you should focus exclusively on experienced users. New users mightn’t have even discovered those advanced features. And even if they did, their level of product knowledge mightn’t be sufficient for them to provide any meaningful insights for your research.
Research method
In most cases, once you set clear objectives, and pick the target audience that has insights to help you achieve those, choosing the research method is relatively easy. But you still have to do it. And I recommend that you evaluate all potential options (we’ve covered them above,) and select the method that’s the most appropriate for your goals and the audience.
TIP: It pays off to select several research methods sometimes. For example, if your goal is to improve the usability of your interface, you might start by tracking user behavior to identify potential challenges users experience. Then, hold usability sessions to confirm your assumptions, and finally, interview most engaged users about their challenges.
Notice how each method in this example allows you to go deeper into the problem. You start by collecting data that allows you to make hypotheses about potential usability problems. You, then, observe how users engage with those tasks in real-life, and finally, you get their opinion about those challenges.
Research instruments
I have to be honest – I’m not particularly fond of this label, research instrument. It’s quite misleading. But that’s what it is so I’m sticking with it here too. However, what we really mean by research instruments are materials that you’re going to use in the research methods you’ve selected.
These can be questions that you’ll be asking customers to answer in a survey, tasks for the usability session, questions for user interviews, and so on.
And needless to say, these are hugely important to prepare upfront, test, validate, and only put into use when you’re absolutely certain that they can deliver the insights you’re after without causing any form of bias.
Panel recruitment
In an earlier step, you’ve selected your target audience. Now, you need to recruit at least some of those people to participate in your product research. How you’re going to do it will largely depend on the research method you’ve selected.
For example, if you’re using behavioral data like heatmaps, then you don’t really need to recruit anyone for the study. Whatever heatmap software you’ll be using will collect the data for you.
If you run a survey, then you, most likely, will email it or display the survey in-app to your customer segment. Again, it’s not going to take much time and effort.
But the situation is different if you plan to run a user group, for example. In this case, you need to go through a formal process of approaching participants, getting their consent to participate in the study, and so on.
IMPORTANT: Note I mentioned collecting user consent before research. This is a hugely important step to remember, particularly in the face of GDPR and similar privacy laws.
As Phil Hesketh of ConsentKit explains :
“To ensure your research panel is compliant with data protection regulations in your country or state, it’s essential that you get consent from each panelist to collect and store their personal information.
You’ll need to get consent when a person agrees to join your panel for the purposes of recruiting for research, and you’ll need to ask for consent again when they agree to take part in a specific project.”
Data collection
This element is all about launching your research method to collect the data. Simply.
Data analysis and insights synthesis
In a typical product research project, you collect data for a specified period of time, after which you begin to analyze and synthesize that information. The goal here is to identify patterns, trends, and specific insights within the data, and document those so that you have a clear record of your findings.
Actionable insights
The project, typically, concludes not with documented data but a list of actionable recommendations drawn from it. In other words, with product research, you complete a full circle, starting with a problem, conducting research to generate data, and ending up facing the same problem again. This time, however, you’re equipped with insights and actionable recommendations to tackle it successfully.
And that’s it
That’s a typical product research project in a nutshell.
Naturally, there is more to each of its elements than I was able to fit into this guide. But I’m hoping that I was able to provide you with a solid foundation and general understanding of the process.
Also, if you’re interested in digging deeper into how to use surveys for product research, I recommend the my other guides:
- Product discovery process – the do’s and don’ts
- How to collect and measure user feedback for a digital product
- How to use UX research surveys for product development
- In-app feedback – How to capture user feedback within your app
- 15 best product feedback tools to help you improve your app
And if you want to see how Refiner, my survey software, could help you run successful product research surveys, sign up for a free trial or check out these live survey demos .
Related posts

How to Properly Launch and Run a CSAT Survey

11 Ideas That Will Help You Improve the CSAT Score
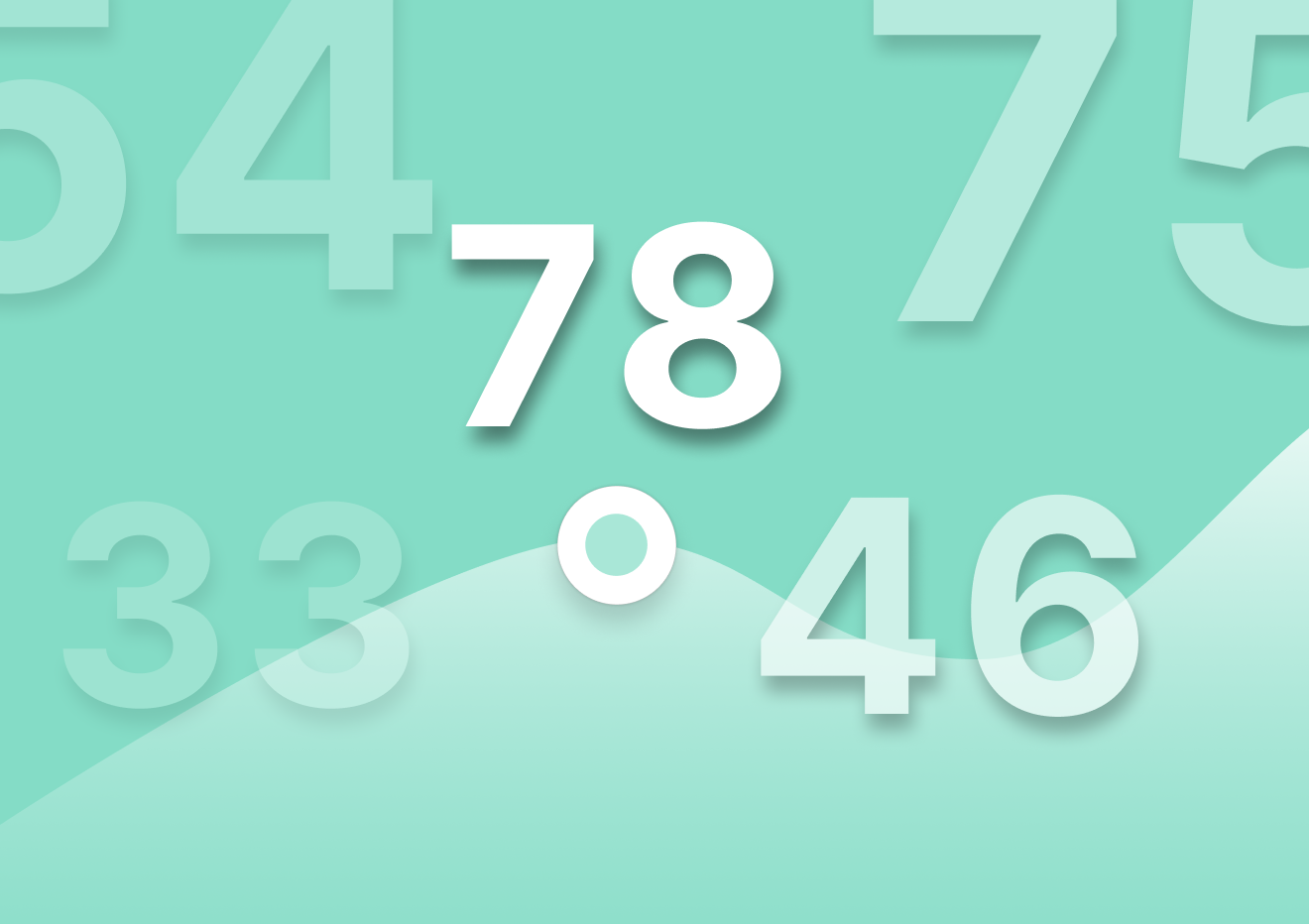
How to Calculate CSAT Score

This is How You Run a Perfect Customer Survey for a Digital Product

What is a Good CSAT Score for SaaS

How to Measure Customer Satisfaction: A Guide for SaaS Brands

CSAT Survey Analysis: How to Analyze Customer Satisfaction Survey Data

How Important are CSAT Surveys for SaaS?
CSAT vs. NPS: Which Customer Satisfaction Metric is Best?

15 CSAT Questions to Help Improve Your Business (with Examples)
- Legal Notice
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
- Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
Product Experience
Product Research
What is product research?
Why is product research important, how to conduct product research.
- Using quantitative and qualitative product research
Areas of product research
- Top product research tips
- Qualtrics’ product research tools
See how ProductXM works
26 min read Don’t skimp on your product research. The insights you gather and act upon can mean the difference between selling products that are a roaring success or an abject failure.
You’re in the process of developing a new product idea with a view to launch it on the market . Or maybe you’re reviewing and updating an existing product that’s already on the market in the hope of making it better.
It’s a risk – get it wrong and you could make an expensive mistake; get it right and you could have a successful, profitable product, service or experience delivering amazing returns on your investment. So how can you make sure you end up in the second category?
This is where product research comes in. It helps you:
- Evaluate and prioritize your ideas
- Test and validate concepts
- Assess names and packaging designs
- Check out the competition
- Set the right selling price
- Gauge customer satisfaction and monitor product-market fit post-launch
- Continually improve the product
Product research is the term most often used to describe this process, but it’s not just about physical products. The research process we’re describing here could apply equally to a physical product such as a smartphone, a service like cloud storage, or an experience like a tour or hotel stay.
Product research goes hand-in-hand with market research, which identifies a target customer, develops typical buyer personas, and analyses purchasing behavior. Together, the two help you make informed decisions about how to find the right fit between what people need or want, and what you can offer them.
Get started with our free product research survey template
A product, service or experience idea can be brilliant and original, but if nobody wants to buy it, there’s no way it can be successful. At best, it will be an impressive oddity, and at worst, a total waste of time. Likewise, if you’re proposing changes to an existing product or service but they’re not the ones your customers value, you could end up doing more harm than good.
Product research will tell you whether your idea resonates with potential customers. Because a product is only worth what people are willing to pay for it, you’ll also be able to extend your research process to set a product price accordingly.
And if your competitors are doing better than you, you need to find out why, identify any gaps that they’ve missed and uncover emerging trends so you can get ahead.
Sure, you can start your research online. Amazon, review sites, and social media will give you an idea of what’s out there and how buyers react to products, but if you want to dig deeper and own your niche, you need to invest in user experience (UX) research .
UX research focuses solely on the user of a particular product, looking at how human beings interact with products and services and learning from their experiences.
UX research typically covers the following areas:
Target demographic
Demographic targeting or segmentation helps you understand who your particular product or service is targeting. Demographic information includes everything from gender and age to education and income.
Uncovering a need is one of the main drivers for creating a winning product. For example, if you’re selling into a particular market, your UX research can help you identify flaws in particular products or services and what your potential customers might want from something new. Likewise, researching customer needs helps you to identify what you shouldn’t focus on.
When you research products and UX, you should also examine what your target market wants out of the product or service. Want differs from need as a product need is a requirement, whereas a want could specify certain features of capabilities. They can also differ in priority based on each customer.
For example, this could be improving how your product or service works, or the UX outcomes — e.g. does the product make their job easier or give them more time to focus on other activities?
This should all form part of your UX research and can give you a huge advantage if you get it right.
What do your customers think about you or your product? What do they think about your competitors , and how do you compare to those competitors in their eyes?
What do your customers think about the problem they have? Or how can they solve it? Do you think about their problem the same way they do?
You need to understand how your customers think and what they think if you’re going to convince them to buy your product.
Understanding your customers’ behavior should form a big part of your product research process. Not just in terms of how they go about their lives or work — which can help you understand how your products fit in — but also how they do their product research when looking for a solution. Do they base their purchase decisions on word-of-mouth? Do they typically buy online, or are they more likely to want to visit a retailer to see, hear and touch their potential purchase?
Think about the use case for your product or service. If it’s a gadget, will they use it in the home or out and about? This consideration might inform whether you build in a battery power feature or rely on a wall socket. If it’s a shoe-shine service, would they prefer to be able to walk in off the street or is an appointment system more appealing?
Understanding their behavior can help with your product development to meet a need, and also with your marketing strategy and sales messaging.
Motivations
What drives your customers to find and buy products or services? This is something you need in your product research so you can create solutions that further their success.
Customer motivations are either conscious or subconscious, e.g. they’re aware of a problem and need a solution, or driven by changes or demand in the market (for example, a government requirement to implement certain technologies for business operations).
Product research can help you to understand these motivators, subsequently enabling you to tailor your market messaging and create amazing products.
Using quantitative and qualitative methods for product research
Product research relies heavily upon qualitative and quantitative research methods — this includes capturing feedback , observing how people use products, and analyzing existing data (or new data) to uncover trends or opportunities.
Combining both qualitative and quantitative research methods will help you to identify the most pivotal market trends, as well as understand the specific thoughts and beliefs of customers. Here’s a quick breakdown of how each product research method works:
Quantitative UX research
Quantitative research is a starting point. It’s all about crunching the numbers that translate into informative statistics. Surveys and polls (online, mobile, paper, telephone) are the most commonly used methods, although you can add data from analytics platforms to the mix.
Qualitative UX research
Qualitative research joins the dots of the quantitative data by revealing what people think, believe, and feel about a product. Rather than ticking boxes, people say or write what they think either in open text boxes on surveys, or during interviews and focus groups. Qualitative UX research provides context, painting a picture using the data.
Breaking product research down into manageable stages will increase its effectiveness. These stages are:
Market research
Understanding the current marketplace can help you not only identify any trends in particular buying habits or fads that are attracting short-term attention. It can also help you identify areas of opportunity that you could exploit.
Market research helps with pricing decisions based on whether your market is stable or growing. From the research, you’ll uncover market size and competition, as well as answers to the following questions:
- What are the best-selling products already in your market and where do you fit in compared to them?
- Is there low competition in your market, or is it saturated?
- Are you selling a product that’s got high demand? And how long does that high demand last?
- Is your product something that can be sold year-round? Or is your product seasonal?
Customer research
We’ve already touched on this, but your product research should include your customers.
For example, research demographics to understand who they are, use psychographic information to understand their wants and needs, and leverage specific customer segmentation to ensure you’re targeting the right section of the market with your product or services. All of this will help you to build a better picture of your audience.
Your customer research should also include where you plan to sell your products based on your customers’ preferences. Will you need to sell online? Or is your product something your customers will want to see in person first?
If you plan to sell online, you’ll need to factor in other elements of your selling and marketing strategy. This will be everything from keyword research for marketing and understanding the search volume for your products, to shipping costs if you’re going to sell nationally, or internationally.
New product development
Finally, you should examine your specific product idea. This includes whether there’s a demand for it, what the pricing landscape is like and where you should position yourself, minute product details like the size and weight, or whether you’re selling perishable goods or consumables.
Furthermore, if you’re selling the same product as the competition, how are you planning to compete? Are you going to compete on price and if so, what will your selling price need to be to gain an advantage while generating a profit margin?
Segmentation Research
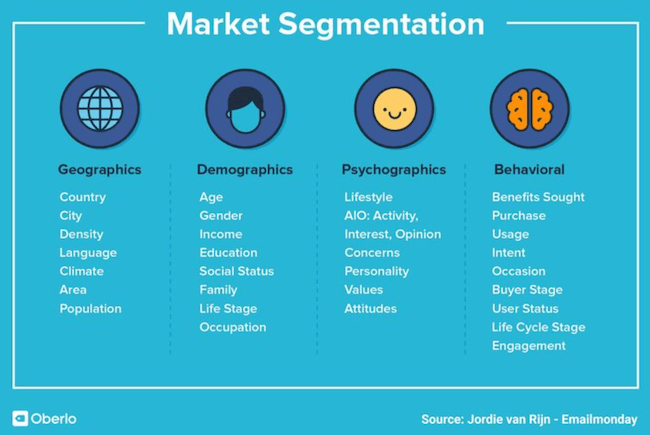
Segmentation is the strategic lens through which you view your market landscape. It’s used to identify who to target so that you can develop, maintain, or adjust branding and marketing tactics and identify product optimization and innovation opportunities. The most profitable products are those that are targeted at specific segments of a market and tackle a particular need or problem.
Ask yourself the following:
- How large is that segment?
- Are your customers early adopters or more traditional? Are they open to new ways to do things or will they need to be convinced?
How people perceive your brand speaks volumes about what they are prepared to buy from you. Just as you wouldn’t buy a computer from a supermarket, you wouldn’t buy your groceries from a technology store (more importantly, it’s highly likely that neither would sell either of those products).
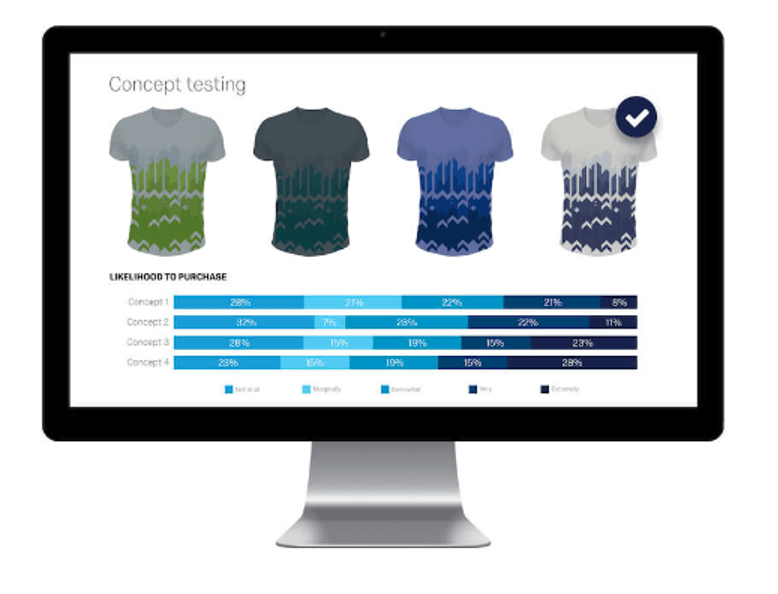
Concept testing
Concept testing should be conducted in an agile environment.
Begin early in the process with an MVP to test on existing and potential customers. A series of small studies done throughout the product innovation cycle will ensure that your new product is refined by customer input.
It is always more cost-effective to refine a new offering as it is being developed than to have to drop or make significant changes to a product that has already consumed a great deal of investment.
This continues as you roll out your new product. You must stay in touch with your target audience as they use the product, and take on board comments and suggestions for improvement. There are many benefits to concept testing:
- It’s cost-effective and flexible: You can send out simple, quick surveys if you want high-level rapid feedback, or longer ones if you want to dig deeper into the detail
- You’ll be able to optimize your product: You’ll gather useful information on things like branding, pricing, and market status that will make a real impact on your development decisions
- Continuous quality assurance: You can use the same audience to give feedback on your improvements, or survey a new audience to get fresh insights on your product development.
- Great brand loyalty: You’ll build up good customer relationships and increase your brand equity by including potential customers in your product’s design and development.
Improve your concept testing with our Introduction to Concept testing eBook
Naming research
What’s in a name? A best selling product, we hope.
Product naming is the process of coming up with compelling, unique names for your new products.
We would always recommend using qualitative research, with its emphasis on verbal expression, to test product names with your prospective customers, and using a text analytics tool to categorize text responses by both topic and sentiment automatically.
When deciding on product names (we recommend between 3 and 15 options) to run past your respondents, remember these six golden rules:
- It should be easy to remember: consumers must be able to recall the name easily
- It should be memorable: There’s a lot of product ‘noise’, and your name needs to be heard above it
- It must be easy to pronounce: Word of mouth is important, and if your customers can’t say it, they won’t mention it to others
- It must be easily understood: It helps if the name hints at what the product does unless you have a colossal marketing budget to explain a more leftfield name
- It must translate well with international audiences: We’ve all heard the apocryphal story that Coca Cola originally transliterated as ‘bite the wax tadpole’ in Chinese. Whatever the truth, make sure audiences around the world can pronounce your product name and it doesn’t mean anything problematic.
- It has to be a name you can own. No one wants to discover after a comprehensive research program that the name everyone loves is not available for use.
Provide your respondents with a product description, and ideally images of the product. Break your testing between:
- Overall name questions: How does each name compare with the others? Rank the names in order of preference, or against criteria such as trustworthiness, appeal or creativity. Do respondents have any names of their own? The results of this testing will give you the top names overall and in every category.
- Individual name questions: Would respondents buy this product with this specific name? How does this name make them feel? Individual name analysis should reveal name sentiment, as well as data about a consumer’s likelihood to purchase or consider your product.
Feature research
You use this to identify which product features your customer’s value so that you can add or improve them.
But you always need to keep in the back of your mind that a product is more than just the sum of its features – it’s how they work together to give a seamless experience that’s important. Research will help you do that.
There are three areas of feature research that you’ll need to undertake:
- Identifying customers’ wants and needs : Customer needs analysis will give you insights into personal values, purchasing decisions, and pricing tolerance . Conjoint analysis, with its multiple product attribute comparison/trade-off scenarios, will inform which features customers consider most valuable.
- Internal development : Once you’ve analyzed what customers want, you need to bring your feature back in-house and seek the expert opinion of your product managers, business analysts, marketers, designers, engineers, and customer experience teams.
- Test with customers : You’ve created a feature that customers want, and your in-house teams have approved them. Now you can use product feature prioritization to understand the features your customers’ value (and don’t). Survey: usage (where and how the customer uses the feature); ‘top of mind’ negative and positive associations with the feature; product categorization (comparing with the competition to see which features make a product more or less ‘swappable’).
Pricing research
A product is only worth what people are prepared to pay for it. You need to ensure that its price is low enough for people to feel they’ve got good value, and you also make sufficient profit, but not so cheap that its quality is questioned.
You also need to consider how many units you’ll need to sell based on your product prices to have a good profit margin.
When you conduct pricing research , you’ll discover:
- How willing the market is to buy your product
- The highest return on your development investment
- How to maintain your brand’s value
- When and how to alter your pricing effectively
- The costs involved in producing your product
Pricing research is done through a combination of market research, competitor research , market analysis, and testing in the marketplace.
Use product pricing research tools. These use one or more of the following methodologies to ask survey respondents:
- Van Westendorp price sensitivity meter is a type of direct pricing research that asks survey respondents four simple questions to gauge whether your product is too expensive or a bargain
- Gabor-Granger pricing methodology uses predefined price points to determine the highest price a respondent would pay for your product
- Conjoint analysis gives respondents a choice between product packages and then asks them to choose one of the feature/price configurations to create the ideal option. Each option comes with trade-offs and the best time for use
Free eBook: 16 Research Methods to Maximize Product Success
Top new product development tips
You could come up with an amazing product or service, but without product research, you’ll never know if there’s a market for it. Furthermore, you might price it wrong and/or target the wrong customers, severely limiting (or preventing entirely) your sales.
The good news is that there are a lot of product research tips and product research tools we can share with you:
Research existing products on the market
The easiest way to do product research is to examine what products are already available in your marketplace and identify the top-selling products on the market that you’re competing with.
If you’re not already offering this product, you can create your own version, and with the right research, you can identify areas of improvement to differentiate your offering.
Look at product descriptions to see how existing products are being sold and use this to create products that fill a gap.
The easiest way to do product research is to get out and act as a customer. Go to popular online marketplaces like eBay and Amazon to see what people are looking at. Get out onto the high street and visit brick and mortar stores to see what product categories are already on the market.
All of the above will help you understand the current landscape and how you can fit in or disrupt it .
You can also look online at Google Trends and queries for particular products in your marketplace. Understanding these trends and the search volume for a particular keyword related to your products can help with your launch, as well as the optimization of product pages.
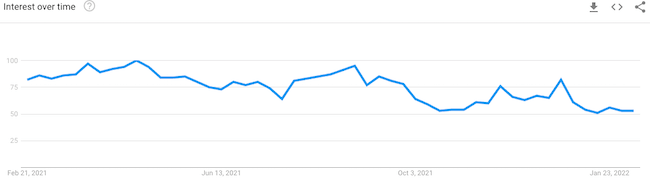
These trends can be particularly useful if you’re selling a seasonal product, as you can use real-time search data to see trending products, or changes to your market size when there might be more people looking for your product at certain times of the year.
Look at online reviews

The best feedback on products will always come from customers. And the best place to find honest feedback is by looking at online reviews — whether they’re on Google or Amazon.
Especially if you’re an online business, these Amazon and online reviews are a trove of ideas that can help you with your product research.
For example, paying particular attention to poor reviews can help you identify gaps in a competitor’s offering that you can take advantage of.
Identify gaps in the market
You don’t have to reinvent the wheel with your product ideas, often you can simply take an existing product and improve on it.
Online reviews are incredibly useful for product research because customers will typically share their ideas for improvement as part of the submission.
Quantitative product research
Using quantitative research with online polls or product research tools can help you reach a large portion of your potential marketplace in a cost-effective way.
You can use this as a starting point to understand the market as a whole before drilling down into specifics.
Qualitative product research
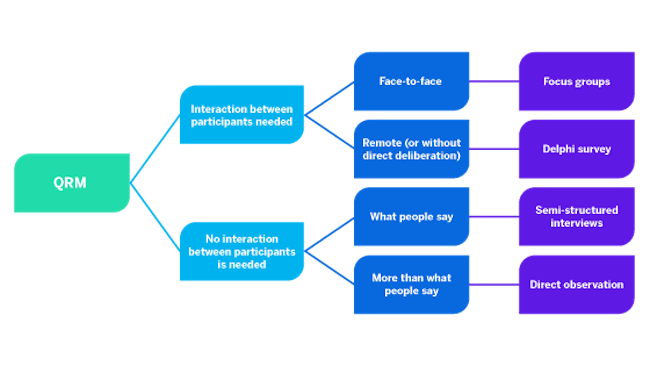
As well as analyzing the wider market, you should get specific reviews and opinions of your products from customers using qualitative research .
Through focus groups or individual interviews, you can start to understand the sentiment towards your products and identify opportunities to capitalize on.
In the long run, this data can help you to develop new product ideas, especially if you uncover downsides or holes in your product development.
Ongoing product research
While research can help test and optimize your product idea before launch, it shouldn’t stop once the product is on the market.
You should continue to do your research as an ongoing project.
This will give you more information about how your product or service is perceived and can also help you identify ongoing room for improvement for your products to help you make more sales in the future.
Conducting thorough product research is key to more sales
Researching your products can make the difference between success and failure when it comes to launching winning products and having success in the long term.
It should produce a complete picture of your market, product, and customers and will produce the roadmap for your launch and ongoing sales .
Your research will help with everything from product development, to your marketing campaigns, to selling prices and ongoing development.
By doing in-depth research you’ll be able to make better, more informed decisions about your product ideas and help you create and sell more profitable products.
Find success with Qualtrics’ product research tools
By bringing customers into your product development process, you can identify and solve problems while uncovering new opportunities. Today’s digital tools make it easier than ever.
With the right research platform, you can accelerate your product development cycle using real insights from your customers and easily identify gaps in the market. This enables you to launch new, customer-oriented products, services, and solutions, or disrupt existing categories with offerings that have new or improved features.
You can also get instant access to feedback from multiple channels and data sources like Google Search and other search engines and social media sites.
Then, use smart analysis at every step of the product development lifecycle to launch products you know your customers will love. Concept testing enables you to validate every aspect of your offering, from features and branding to messaging and price, to set it up for success. You can also use conjoint analysis to find your customers’ ideal product configurations, e.g. packing, pricing, design and features.
Finally, close the product experience gap, instantly gather real-time feedback that you can use, and automate the process using automated actions.
Start your PX journey today with our free product research survey template
Related resources
Product feature research 10 min read, product analysis 13 min read.
Pricing Research
Product Price Optimization 12 min read
Product presentation 11 min read.
Buyer Personas
Customer Targeting 12 min read
Product Development
Product Development 11 min read
Product concept 12 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

How to Conduct Product Research? Reasons, Methods, and Process

In today's fast-paced product landscape, understanding your audience's needs, preferences, and pain points is more crucial than ever. Whether launching a new product or refining an existing SaaS product, the foundation of success is built on robust product research.
Successful product research equips product teams with a 360-degree view of the market and user landscape, enabling them to make informed, user-centric decisions at every stage of the product's lifecycle.
Product research is the initial stage before product development and helps turns assumptions into knowledge and risks into calculated strategies, improve product discovery , setting the stage for product success.
Dive in as we demystify the product research process, offering actionable insights and tools to ensure your product doesn't just find its market fit—it excels in it!
What is Product Research?
Product research is a systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information to make informed decisions about a product's creation, modification, or positioning.
Product research aims to understand the market, identify potential opportunities, and ensure that a product meets the needs and preferences of its target audience to build a customer-centric company . Product research can encompass both new product development and improvements to existing products.
Critical Steps of Product Research
1.Market Analysis: Understanding the market size, growth rate, trends, and dynamics. This includes studying competitors' products, market share, strengths, and weaknesses.
2. Target Audience Identification: Defining the product's primary users or buyer personas. This involves understanding their demographics, needs, preferences, behaviors, and pain points.
3. Concept Testing: The concept is tested among potential users or a focus group for customer feedback before fully developing a product. This helps in refining the idea and gauging its potential success.
4. Feedback Portals: Create a centralized place for product feedback to track different types of customer feedback and improve SaaS products while listening to their customers. This is possible with Rapidr .
Rapidr helps SaaS companies be more customer-centric by consolidating feedback across different apps, prioritizing requests, having a discourse with customers, and closing the feedback loop.

5. Feature Prioritization: Based on feedback and research, deciding which features to include in the product , which to prioritize, and which to exclude.
Rapidr provides a feature request tracking and management system solely for this purpose. Use votes and comments within a feature request voting board to prioritize features. Evaluate, sort, and filter feature requests based on how well they map to the market, customers' needs, and your company's strengths.

6. Pricing Research: Determining the optimal price point for the product. This involves studying competitors' pricing strategies, understanding the product's perceived value among potential users, and considering cost factors.
7. Usability Testing: Once a prototype or MVP (Minimum Viable Product) is developed, it's beta tested among users to understand its usability and any potential design or functionality issues.
8. Post-launch Feedback: After the product launch, continuous research is done to collect user feedback , monitor product performance, and make necessary improvements.
9. Product Lifecycle Management: Understanding the stages a product goes through, from introduction to growth, maturity, and decline, and making decisions accordingly.

Why should Product Managers Conduct Product Research?
Product research is a foundational activity for product managers (PMs). By conducting thorough product research, companies can reduce risks associated with launching new products, ensure better alignment with market needs, increase the likelihood of product success, and attain product-market fit .
In a survey report, more than 60% of product managers responded that direct customer feedback is the source of the best product and feature ideas.
Here are compelling reasons why product managers should prioritize product research :
1. Understanding the Market: Product research provides insights into market trends, emerging technologies, and shifts in consumer behavior. It allows PMs to position their products effectively and anticipate market changes.
2. Identifying Customer Needs: PMs need to understand their users deeply. Research uncovers the target audience's pain points , desires, and needs, ensuring that the product aligns with what customers genuinely want.
3. Validating Assumptions: Assumptions can be dangerous if not validated. Product research helps test hypotheses, ensuring that decisions are based on accurate data, not just gut feelings or intuition, to avoid making mistakes .
4. Risk Reduction: Launching or updating a product involves significant resources and costs. Research reduces the risk of product failure by ensuring a genuine market demand and fit for the product.
5. Informed Decision Making: Product research provides concrete data, a foundation for making informed product decisions, from feature prioritization to design choices.
6. Building a Competitive Advantage: By understanding the competitive landscape, PMs can identify gaps in the market, differentiate their products, and highlight unique selling points.
7. Optimizing Pricing: Through research, PMs can identify the right pricing strategy by understanding customers' willingness to pay and analyzing competitor pricing.
8. Improving User Experience: Usability testing, a component of product research, identifies potential design or functionality flaws, ensuring that the end product provides an optimal user experience that enhances product adoption .
9. Prioritizing Development: Research helps determine which features or improvements will have the most significant impact, guiding resource allocation and development priorities.
10. Enhancing Marketing and Sales Efforts: Insights from product research provide valuable information for crafting marketing messages, positioning, and sales strategies .
11. Stakeholder Alignment: Presenting research findings can align stakeholders around a shared product vision and objective, from developers to executives.
12. Continuous Improvement: Post-launch research, like user feedback and analytics, ensures that products evolve based on real-world usage and feedback.
13. Building Empathy: Engaging directly with users during research helps PMs develop empathy and improve retention , which is crucial for user-centric product development.
Methods of Conducting Product Research
Product research is essential to product development and marketing, providing critical insights into user needs, market dynamics, and competitive landscapes. By embedding product research throughout the product's lifecycle , organizations remain user-centric, responsive to changes, agile in decision-making.
Surveys: Gather quantitative data from a large group of people using a combination of multiple-choice and open-ended customer feedback questions to identify patterns, preferences, and trends. Use online platforms like SurveyMonkey, Google Forms, or Typeform to create and distribute questionnaires.

Interviews: Collect in-depth qualitative insights from users to understand their needs, pain points, and motivations. Conduct one-on-one sessions, face-to-face, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Concept Testing: Evaluate the potential success of a new product concept before it's fully developed. Present the product idea (through mockups, descriptions, or prototypes) to a target audience and gather feedback with feedback tools such as Rapidr , UserVoice, etc.

Focus Groups: Gather qualitative insights from diverse participants, facilitating discussions to uncover shared and contrasting views. Organize sessions with 6-10 participants, moderated by a trained professional, to discuss specific topics.
Usability Testing: Evaluate a product or prototype's effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction. Ask users to complete specific tasks on the product, observing their interactions and noting challenges or friction points.

In-app Feedback: Utilize in-app feedback platforms to ask users about their experiences in real-time. This can be done through chatbots or pop-up messages, prompting immediate feedback while the user is engaged with the product.
Rapidr's deep Intercom Integration makes it easy for your product and customer success teams to track incoming feedback on Intercom .

Competitive Analysis: Assess the strengths and weaknesses of current and potential competitors. Identify main competitors and evaluate their products, market positioning, features, and customer reviews.

A/B Testing (or Split Testing): Compare two or more versions of a product or feature to determine which performs better regarding user engagement, conversion, or other KPIs. Present versions to similar user groups and analyze each performance metric.

Prototyping and MVPs (Minimum Viable Products): Test product hypotheses with the least amount of work. MVPs help to validate demand, functionality, or other critical assumptions. Develop a basic product version and release it to a subset of users or the broader market in online community feedback forums .
When to Perform Product Research?
Product research is not confined to a single product lifecycle phase. Still, it should be conducted at multiple stages to ensure the product remains relevant, competitive, and aligned with user needs. Here's a breakdown of when to perform product research:
Idea Conception & Validation: Before any development begins, when you have a product idea or concept. To validate assumptions and ensure there's a genuine need in the market for the proposed solution.
Pre-Development & Design: After idea validation, full-fledged development starts.To refine feature sets, prioritize functionalities, and design a user-centric interface.
Prototype & MVP (Minimum Viable Product) Phase: When a basic version or prototype of the product is ready. To gather initial feedback , test usability, and identify potential improvements before a wider release.
Pre-Launch: Immediately before the product's market launch. To gauge market reception, fine-tune marketing messages and ensure the product meets the target audience's expectations.
Post-Launch: After the product hits the market. To monitor user satisfaction , identify unforeseen issues, and understand how real-world usage might differ from expectations.
Any Major Update/Release: Before rolling out significant updates, changes, or new features. Ensure these changes align with user needs and not introduce new issues or bugs .
How to Conduct Product Research?
Product research systematically gathers, analyzes, and interprets data about a product's market, users, and competition. The key is to remain user-centric and data-driven in all product decisions, a significant challenge product managers face.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to conduct effective product research:
1. Define Your Objectives
Start by understanding what you want to achieve with your research. This could be identifying market gaps, understanding user needs, validating a product idea , or improving an existing product.
2. Identify Your Target Audience
Clearly define the population segment you intend to research, create user personas, and map the customer journey. Consider demographics, psychographics, behaviors, and other relevant criteria.
3. Choose Research Methods
- Qualitative methods (e.g., interviews, focus groups, ethnographic studies) help gain deeper insights into user motivations, feelings, and pain points.
- Quantitative methods (e.g., surveys, feedback portals, analytics) provide numerical data for generalizing results or identifying patterns.

4. Select Product Research Tools
Depending on your chosen methods, you might need product research tools for surveys (like SurveyMonkey), feedback management (like Rapidr ), usability testing (like Lookback.io), analytics (like Google Analytics), etc.
5. Conduct Product Research
- Create the necessary materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview scripts, or usability test scenarios. Ensure questions are clear, unbiased, and designed to extract meaningful insights. Administer surveys or questionnaires.
- Recruit participants from your target audience for targeted feedback. This can be done using recruitment platforms, social media, online community feedback forums , or your customer base.
- Conduct interviews, either face-to-face, over the phone, or through video calls.
- Hold focus groups to gather collective opinions.
- Perform usability tests to observe how users interact with prototypes or existing products.

6. Analyze the Data
- Start by revisiting the collected data and research insights. Organize them systematically, focusing on the key findings that align with your product's goals and vision.
- Perform ideation to seek the most effective solution. All feedback is valuable, but not all feedback needs immediate action. Classify insights based on urgency, feasibility, and alignment with business goals.
- For qualitative data, identify patterns, themes, and notable quotes.
- For quantitative data, use user segments and statistical methods to interpret results and find correlations and conclusions.

9. Update Stakeholders
Organize your insights into a structured format. This could be in the form of reports, presentations, or visualizations. Highlight critical findings, actionable recommendations, and areas that need further exploration.
Share your findings with team members, executives, and other stakeholders to drive decision-making. When you release new features or updates , reach out to users to see how they find them. Ensure that every product team member, from designers to developers to marketers, understands the changes and the rationale behind them. Clear communication is key to cohesive development , even if it means responding to negative feedback .

10. Iterate & Plan Product Development
Use the insights gathered to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, and other related areas. Quickly create solution prototypes to test with a set of customers. This process helps visualize changes, making spotting potential challenges or improvements easier.
Calculate the effort required to build a solution and perceived market size based on the persona. Use prioritization frameworks (with calculations made) to determine what validated product opportunities to pursue next.
11. Create Roadmap & Repeat Based on Insights
Plot the ideas, tasks, and opportunities in a product roadmap . Introduce new milestones, revise timelines, and allocate resources accordingly. Product research is not a one-off activity. As the product evolves and the market changes, conduct ongoing research to align with user needs and market dynamics.

Use Rapidr to make your product research effective
Product research's essence lies in understanding and resonating with the audience at every step of the product's journey. Thus, it's an indispensable cornerstone for product success.
With data-driven insights, actionable feedback, and a deeper understanding of market dynamics, product teams can make informed decisions, pivot when necessary, and continually refine their offerings. In the ever-changing marketplace, listening to your users isn't just a best practice—it's the lifeblood of product relevance and longevity.
While there are many customer feedback tools to help you capture, organize, and prioritize feedback, consider the one that enables you to uncover the insights from the feedback and shape your product research.
Incorporate customer feedback into your product research process with Rapidr .
- Set up a customer feedback system.
- Collect actionable feedback from customers and teammates with feedback portals and in-app feedback widgets .
- Analyze, prioritize, and categorize ideas and feedback to make sense of them.
- Act and create a product development plan with a roadmap.
- Announce new features and product updates to close the feedback loop .
With Rapidr, you can collect, analyze, and organize feedback and engage with customers as their feedback moves through the development process. Sign up for free and set up a complete customer feedback system to inform and enhance your product research process.
Build better products with user feedback
Rapidr helps SaaS companies understand what customers need through feedback, prioritize what to build next, inform the roadmap, and notify customers on product releases

Product Research

Relevant templates
Product research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data and insights related to a specific product or service. It encompasses various methodologies and techniques to understand customer needs, market dynamics, competitor offerings, and industry trends to inform strategic decisions throughout the product lifecycle. Product research is the foundation for developing successful products, guiding innovation, and ensuring alignment with customer expectations and market demands.
Significance of Product Research
Product research plays a pivotal role in guiding strategic decision-making and mitigating risks associated with product development and launch. By conducting thorough research, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscapes, enabling them to make informed decisions, minimize uncertainties, and maximize the likelihood of success for their products.
Key Components of Product Research
Product research containes various components and methodologies, including:
- Market Research: Gathering data and insights on market size, segmentation, trends, and dynamics to understand the broader market and identify opportunities and threats.
- Customer Research: Conducting surveys , interviews , and observational studies to understand customer needs, preferences, behaviors, and pain points related to the product or service.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyzing competitor offerings, strategies, strengths, and weaknesses to identify gaps in the market and inform differentiation strategies.
- Trend Analysis: Monitoring industry trends, technological advancements, and consumer behaviors to anticipate future demands and stay ahead of market shifts.
- Usability Testing: Evaluating the usability , functionality, and user experience of prototypes or existing products to identify areas for improvement and optimization.
Methods of Product Research
Product research employs a variety of methods and techniques, including:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Administering structured surveys and questionnaires to collect quantitative data on customer preferences, attitudes, and behaviors.
- Interviews and Focus Groups: Conducting in-depth interviews and focus group discussions to gather qualitative insights and explore customer motivations, needs, and pain points.
- Market Analysis: Utilizing secondary research sources such as industry reports, market data, and competitor analyses to understand market trends and dynamics.
- Prototype Testing: Creating prototypes or minimum viable products (MVPs) to gather feedback from users through usability testing and iterative design processes.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data analytics tools and techniques to analyze customer interactions, behaviors, and engagement patterns to derive actionable insights.
Importance of Product Research in Business Development
Product research is indispensable for businesses seeking to develop successful products and drive sustainable growth. Its importance lies in:
- Identifying Opportunities: Product research helps businesses identify unmet customer needs, market gaps, and emerging trends, enabling them to capitalize on opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
- Minimizing Risks: By conducting thorough research, businesses can mitigate risks associated with product development, market entry, and investment decisions, reducing the likelihood of product failures or market setbacks.
- Informing Strategy: Product research provides valuable insights for formulating product strategies, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, and go-to-market plans, ensuring alignment with customer preferences and market demands.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: By staying informed about market trends, customer preferences, and competitor offerings, businesses can maintain a competitive edge and adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Product research is a fundamental aspect of business development, providing valuable insights that inform strategic decision-making, drive innovation, and ensure the successful development and launch of products and services. By investing in comprehensive product research methodologies and techniques, businesses can maximize their chances of success, foster customer satisfaction, and achieve sustainable growth in competitive markets
Relevant terms

- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

Product Research: How To Discover Great Product Ideas in 2024
Be smart with your product research and give yourself the best chance of landing on the perfect product ideas for your business.

Businesses are built on products—they're the reason customers know your brand and give it their money. That's why evaluating your product ideas through rigorous research is essential to building a profitable business.
In this article you’ll get recommendations on how to do effective product research plus extra tips on finding the best products to sell.
It's not always easy to find a product or niche market that fits your criteria. But evaluating your ideas with the support of this guide will give you product validation , help you to avoid pitfalls, and increase your chances of success.
What is product research?
Product research is the process of gathering and analyzing information about a product, its market, competitors, and potential customers. The goal of product research is to identify opportunities, assess demand, and make informed decisions related to product development , marketing, pricing, and distribution.
Product research answers questions such as:
- Will the product be a success in the market?
- What are similar products in the market?
- What’s the best way to develop and sell the product?
Product research doesn’t just ensure you choose the right products for your audience, it also helps you:
- Prioritize your ideas
- Test and validate different ideas
- Experiment with product names and packaging
- Sell at a competitive price
- Understand your competition
- Monitor product-market fit
- Improve your product and marketing
Businesses that perform regular product research stay ahead of competitors. Product research also helps with developing innovative, high-value products, because you’ll always know what’s on trend and which trends grow sustainably.
How to do product research
The product research process involves multiple strands of research which fall largely into two areas: market-based criteria and product-based criteria.
Market-based criteria
Market-based criteria refers to behavior in the market, including how big a market you have for your product, what other brands are selling similar items in that market, and who your target customers are.
The most common market-based criteria are:
- Market size
Competitive landscape
Product category outlook, local product availability, target customer, market size .
Market size indicates how big the market is for your product—or how many people there are that fit your target customer profile.
It can be a difficult metric to determine, but with some research, you can probably get a good idea. To determine how large the potential market is for each product, you can dig into data, city and state development offices, and even Meta’s ad targeting feature (without actually running ads).
In this example, Daneson targets a small segment of the wider health and hygiene market by positioning its toothpicks as a luxury item.

The narrower market size limits the revenue potential for this business. However, depending on the exact market, a narrow market size potentially can be easier to market to, allowing a company like Daneson to penetrate its market and capture it more cost-effectively.
Determining exact market sizes is usually impossible for most businesses, but there are some ways to understand it in a more general way. Google Trends is a good starting point—not for determining market size, but for determining market demand trajectory.

From there you can also look for your particular product idea being sold elsewhere and look at the number and quality of customer reviews. Are there no reviews, just a few, or hundreds?
This can give you an idea of how many people are searching for your keyword terms and can also give you a better sense of the market size. Combine all these methods with some realistic judgment and you should start to get a good sense of the potential market size of your product idea.
What does the competitive landscape look like for your selected product and niche? Are you first to market? Are there already a few competitors or is the market saturated with people selling the same product or targeting the same niche?
If you’re first to market, you’ll want to do a lot of market research to determine that there is in fact a market interested in your product.
If there are many competitors in the market, that’s a sign the market has been validated. However, you’ll have to differentiate your brand and products from the sea of competitors in order to carve out your own spot.
Google searches and Similarweb can help you uncover current market players, while an SEO tool like Ahrefs can tell you approximate search volumes for your chosen keywords.
“Doing keyword research with a tool like Ahrefs or Semrush helps get a realistic view of search demand,” says Shane Pollard, CTO at Be Media . “It also helps with opportunity mapping: If the difficulty is high, I can look for longer-tail results. The long-tail approach is best for entering new markets.”
Riding a fad can be dangerous. A trend can be lucrative. Stable markets are safe, and growing markets are ideal. Understanding where your product and niche fit into these categories can play a huge role in your success or failure.
To better understand the differences between each of these, look at the growth curves, and then at real-world examples of each type:
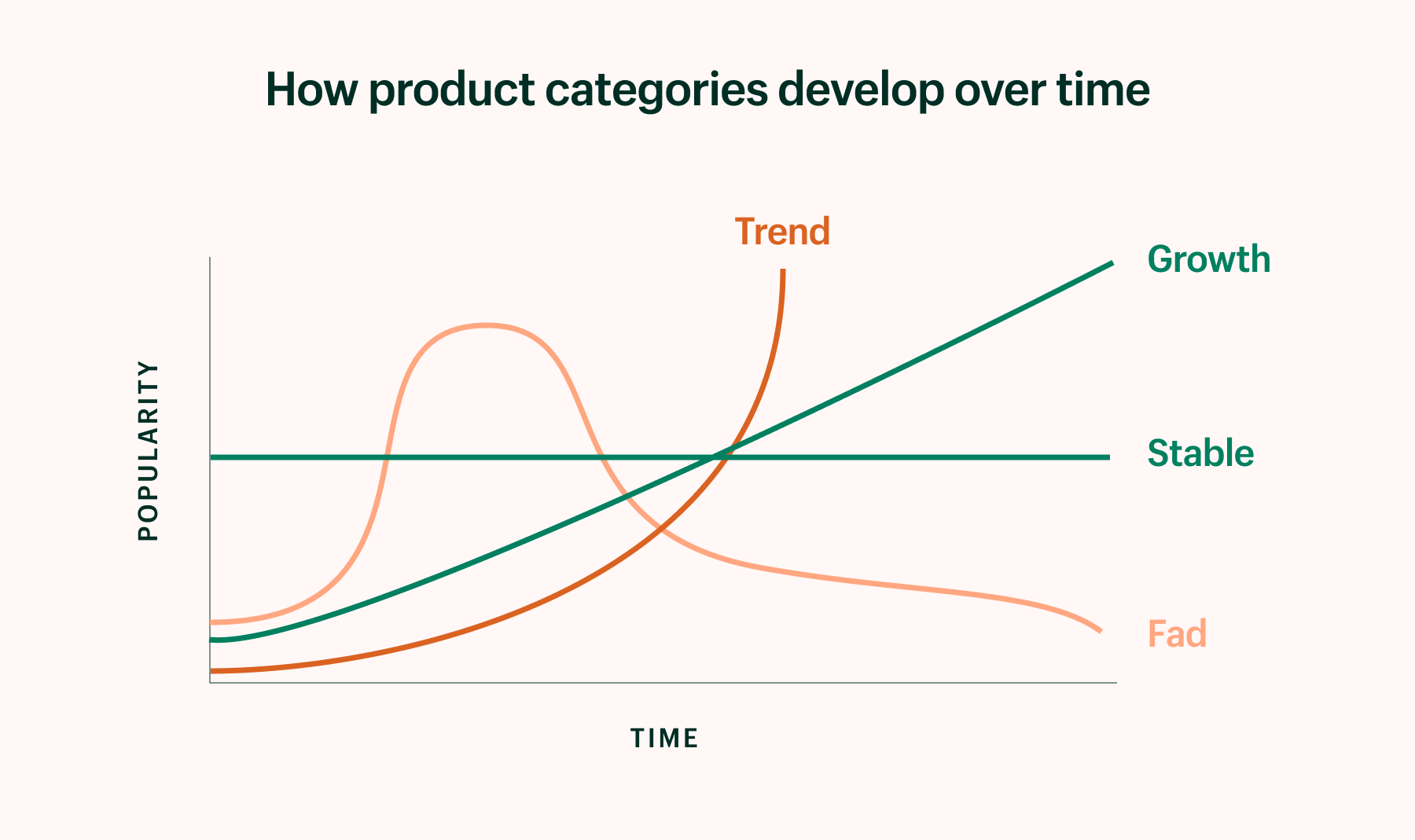
A fad is something that grows in popularity for a very short period of time and dies out just as quickly. A trend can be lucrative if your entry into the market and exit are timed perfectly, but this can be difficult to predict and may result in costly mistakes.
A Geiger counter is a personal electronic device about the size of a cellphone that measures the level of radiation around you. Shortly after Japan suffered an earthquake in 2011, Geiger counters were flying off the shelves. However, as you can see from the Google Trends graph below, interest died as fast as it started.

A trend doesn’t grow as quickly as a fad; it lasts longer and generally doesn’t decline nearly as quickly. Trending products can also develop into long-term growing markets, although this can be difficult to predict.
As an example, over the past 10 years, gluten-free foods have been growing in popularity. You can see from the graph below a consistent climb, but this likely would be predicted and labeled a trend, as opposed to a growing market, due to the ever-evolving and changing nutrition market.

A stable market is one that’s generally immune to shocks and bumps. It’s neither declining nor growing but maintains itself over long periods of time.
A kitchen sink is a perfect example of a product with a target market that has generally remained constant and flat for decades. There’s likely not going to be any huge spikes or dips in purchasing behavior around kitchen sinks.
A growing market is one that has seen consistent growth and shows signs of a long-term or permanent market shift.
Yoga has been around for a long time, but over the past 10 years or so has become a mainstream health and fitness activity. The benefits of yoga are well established, making this niche a solid growth market.
Google Trends can help give you the big picture as to whether something is a fad, trend, growing, or stable market. If you see unexplainable spikes, try doing some further searching to determine the cause.
A product that’s readily available locally means there's one less reason for consumers to seek your product out online. However, a unique or hard-to-find product that isn't available locally means there’s an increased chance of someone looking for it online—which increases their chances of actually purchasing it online.
For example, Ellusionist sells beautiful, high-end decks of cards for magicians and card players. Sure you can go buy a deck of cards anywhere, but these are not just cards—they’re works of art and trick decks, and if you want one, it’s only available online.

One of the simplest ways to find out if your selected product is available locally is by doing a search on Google for “your product + the name of your city,” or, if you don’t live in a major city, try substituting the name of the major city you’re closest to. For example, you could search for “magician deck of cards + New York.”
You don’t need to go into great detail defining your exact customer persona at this point, but, you should be aware of the type of customer you’re likely to sell to and their online purchasing capabilities.
If you have a product geared toward teens, it’s important to keep in mind that most teens don’t have a credit card to make purchases online. Similarly, if your product is geared toward older baby boomers, you may find that your target demographic has a lower level of technology adoption and doesn’t like to purchase online.
To find out more about who your target customers are, set up Google Analytics. Pollard recommends the following Google Analytics reports:
- Audience demographics. This is key to understanding age ranges, gender, and if your product appeals to your target demographic.
- Geolocation. Knowing what audiences are doing in a location can help form an insight. For example, people in Melbourne don’t need a lawn mower as much as people in Perth, based on Melbourne having a higher percentage of people living in apartment complexes.
- Top pages. They are a great pulse check for how many people are looking at products. Shane Pollard from Be Media has come across reports where the top product was described as outperforming every other product by 10 times, only to review top pages and see that the 10 times was in reference to hundreds of visits, not thousands. The way the data was phrased made it sound like more of a performer than it actually was in scale.
Product-based criteria
Product-based criteria refer to points related directly to your product, like its price, whether it’s seasonal, and how scalable it is.
The most common product-based criteria are:
Product markup
Potential selling price, product size and weight.
- Product durability
Product seasonality
Product pain points, product turnover, product type, product perishability, product restrictions and regulations, product scalability.
It’s important to take markup for a specific product into consideration before diving too far into a product idea. When you begin selling online, you’ll quickly find out there are lots of small fees that will eat into your margins, so having a strong initial markup will provide you with the necessary cushion to absorb these little costs.
To understand the margin a bit better, take a look at a real product. For this example, use a pet pedometer—a small electronic device you connect to a dog’s collar to count how many steps they take.
Looking around at other pet pedometers, its determined that the average retail price of a product like this would be $24.99. Using Alibaba , you can get these pet pedometers at a cost of $2 per unit.
A 1,200% markup. Looks good so far, right? Here's a closer look at the other fees that you will need to account for:

You can see from the example above how the small fees will whittle away at your margins. In this case, a product that had an initial markup of over 1,200% ends up with a markup of less than 100% when everything’s taken into account.
Of course, these are just approximates and you can cut costs significantly by handling fulfillment yourself and spending less on advertising. Regardless, knowing this information up front will help you anticipate your revenue and expenditures, as well as determine whether a product is worth the costs.
Selling an inexpensive product means you’ll need to move many units to make a decent profit. This tends to go hand-in-hand with more customer service inquiries, as well as an increase in other operating metrics. Alternatively, selling very expensive products means a longer sales cycle and more discerning customers.
Generally, a product price point between $75 and $150 is recommended, as it minimizes the need to find a large number of customers to turn a decent profit and is still able to give you some cushion for marketing and operation costs.
The previous example of the pet pedometer had a relatively low selling price of $25. Because of this, variable costs ate away at much of the profit, leaving a profit per unit of only $12.95.
See what happens, though, if you switch out the pet pedometer for a new product and assume that this new product has a potential selling price of $100 (four times more than the pet pedometer). For consistency, we’ve also multiplied the other appropriate costs by a factor of four.

This table of pricing fees demonstrates a how higher pricing can lead to higher profit.
Because of the higher pricing, you have much better margins—73% versus 42%—for the pet pedometer, and the profit per unit skyrockets from $12.95 to $76.75.
Product size and weight can have a big impact on your sales and bottom line. These days, many customers expect free shipping, and just rolling the shipping cost into your prices doesn’t always work. This means these costs tend to eat into your margins. If you decide to pass the shipping costs on to your customer, you’ll find that the shock of high shipping will likely hurt your conversion rate.
Additionally, if you don’t plan to use the dropshipping model, you’ll need to consider the cost of shipping the products to yourself (or your warehouse) from your manufacturer, as well as storage fees. If you’re ordering your inventory from overseas, you might be surprised at the costs involved.
Say there’s a popular yoga mat company that sells oversized workout mats. The product itself is a reasonable $99. However, shipping is $40 to Canada and $100 to the rest of the world. For many consumers, it would be hard for them to justify spending 40% to 100% more for shipping.
Product durability
How durable or fragile is your product? Fragile products can be an invitation for trouble. Products that can break easily will cost you more in packaging, and you’re bound to have more returns and exchanges.
Businesses with seasonal demand can suffer from inconsistent cash flow. Some seasonality is OK. However, an ideal product will have somewhat consistent cash flow year round.
If you do choose a highly seasonal product, you may want to consider ahead of time how you can overcome seasonality, possibly by marketing to different countries in the off-season.
Check for seasonal trends by looking at Google Trends for your product and niche keywords. For example, US searches for “picnic baskets” spike every summer and die back down in the colder months, but you could stabilize year-round sales by targeting countries in the southern hemisphere during the US winter.
Here’s the graph for “picnic baskets” searches in the US.

It’s always an advantage to sell products that serve a passion or solve a problem.
An additional benefit is that when you sell products that satisfy one of these requirements, your marketing costs tend to be lower, since customers are actively seeking out a solution, as opposed to you having to heavily market your product to find them.
For example, Decem sells low-ABV gins to people who love a gin and tonic but want to consume less alcohol.

It can be risky to choose products that constantly need to be changed or refreshed. These types of products run the risk of not selling before the time of turnover. Before jumping in head first and selling a product with regular turnover, it’s vital to know what your turnover schedule will look like and plan accordingly.
For example, smartphone and tablet cases are a hot market. Yet creating new designs usually requires a high initial investment for designing, prototyping, and minimum order quantities. One of the harder parts of building an online business in a niche like smartphone cases is gaining enough traction and exposure before the next model smartphone/tablet comes out. Not selling through your inventory fast enough could leave you with a stockpile of outdated cases.
Stringberry produces mobile phone cases for a range of devices and updates its catalog when new models are released. The brand regularly updates its product offerings to align with the latest mobile phone models.
Having consumable or disposable products makes selling to the same customer over and over again more natural by essentially putting a time limit on the product’s life and giving the customer a reason to come back to you for replenishment.
Harry’s , for example, sells products that generally are highly consumable, like razors, shaving cream, and deodorant. This model keeps consumers coming back to their site to repurchase.

Perishable products are a risky proposition for any business, never mind an online business. Since highly perishable products require speedy delivery, shipping can be costly. Even products with a longer perishability timeline can be risky, as it complicates storage and inventory, potentially leaving you with spoiled products.
For example, food products, supplements, medication, and anything else that needs to be kept cold or has a short expiration date all require special consideration when ordering inventory and shipping to customers.
Augason Farms gets around the perishability dilemma by selling dried, freezable consumables that have a longer shelf life.

Restrictions and regulations on your product and niche choice are annoying at best and crippling at worst. Before you move forward with your product idea, you’ll want to make sure there are no regulations or restrictions on your product selection. At the very least you’ll want to make sure they are manageable.
Certain chemical products, food products, and cosmetics can carry restrictions not only from the country you are importing your goods into but also the countries you’re shipping your products back out to.
Consider making a few phone calls to customs and border services of the country you’ll be importing your product into, along with your warehouse, if you plan on using one, as well as the Food and Drug Administration, in the case of a food or supplement product.
It's difficult to think about the future and growing your business when you’re still in the launching phase. However, scalability should be considered and built into the business model right from the start.
If your product is handmade or contains difficult-to-find materials, think about how to scale it if your business takes off. Will you be able to outsource manufacturing? Will your number of employees have to increase with the number of orders, or will you be able to maintain a small team?
6 tips for effective product research
Whether you’re researching your first or fifth product, keep these product research tips in mind:
- Follow consumer trend publications
- Find bestsellers on Amazon
- Browse social curation sites
- Evaluate B2B wholesale marketplaces
- Observe niche forums
- Ask your own customers
1. Follow consumer trend publications
Consumer trend publications can expose you to new products and industries you may not have known existed. They also help you stay up to date on the latest trends to remain competitive and discover new product opportunities.
One free platform to use is Trend Hunter . Trend Hunter is the largest trend community, with more than 200,000 people dedicated to finding the latest trends. You can find trends for anything on this site, including beauty, fashion, culture, luxury, and more.
For example, if you see that “vegan milk initiatives” are trending, you can center your product search around vegan milk items.

Another trend platform to check out is PSFK . It’s a membership website that produces reports and insights around retail and customer experience trends.
Take Inkkas , for example. The brand found the trend for wearing Peruvian textiles and turned it into a shoe business. Inkkas works with local artisan shoemakers in Peru to create the designs, then sells them online.

2. Find bestsellers on Amazon
Amazon is one of the largest consumer marketplaces in the world. You’ll find thousands of product ideas the minute you land on the site. But it’s easy to get lost in all the products and ads if you don’t have a plan.
To speed up the product research process, go straight to Amazon’s bestsellers list. You can find profitable products from any category, from toys and games to patio, lawn and garden, and more. All products on the list are based on sales and updated hourly. So you’ll never run out of product ideas for your business.

If you want more detailed information about products on Amazon, you can use a product research tool like Jungle Scout . You can easily search for any product by keyword, category, or custom filter with the brand’s product database, a searchable catalog with over 475 million products from Amazon. Or evaluate product ideas in seconds with its Chrome extension. All of this can give you ideas for winning products, whether you’re an Amazon seller or run an online store.
It’s important to look at a few different factors when doing Amazon product research:
- Product listing reviews
- Product variants
- Product bundling
3. Browse social curation sites
Image curation sites can be a rich source for finding product ideas. Just by looking at likes and trending photos, you can get a sense of market demand for a specific product or niche.
A few sites to check out include:
- Pinterest , the largest visual discovery engine and curation site
- We Heart It , for fashion and beauty product discovery
- Dudepins , for discovering and buying products for men
4. Evaluate B2B wholesale marketplaces
B2B wholesale marketplaces are a gold mine for finding new product ideas straight from the source. These sites will expose you to thousands of potential product ideas to sell. If you end up liking a product, you can buy it right away.
Two sources you’ll want to check first are Alibaba and AliExpress , which are marketplaces that connect you to manufacturers from Asia. They have hundreds of thousands of products to explore so you can find almost anything.
“The trick is looking at the various marketplaces to see what’s trending, then cross-referencing it with Alibaba to see if you can spin it in a unique way,” says Jeremy Sonne, Founder of Decibel .
Alibaba is for B2B transactions. So if you want to order large quantities of a product directly from manufacturers, you’d use Alibaba.

On the other hand, AliExpress is available to everyone. If you want to test a product, you can order in small batches from AliExpress. You can also do dropshipping with AliExpress .

Other B2B marketplaces to explore are:
- Global Sources
- Made-in-China
- Wholesale Central
5. Observe niche forums
Industry and niche forums are another way to discover new products to sell. They are also a good place to connect with potential customers over shared experiences and to discuss relevant topics with them.
Some niches, like gaming, have active online communities. For example, if you wanted to do product research, you could head to websites like GameFAQs or NeoGAF to observe discussions around video games.
There’s also Reddit , which is the forum of all forums. You can find communities within Reddit for any topic, like tech, culture, and environment. To date, there are more than 3.4 million subreddits , also known as communities, where people come together to talk about different topics related to the community’s title.
And if you’re still not finding any forums around your niche, try searching Google. Type your niche + forum into the search bar and see what results come up.

6. Ask your own customers
Whether you have five customers or 500, one of the best ways to get product ideas is from the people who buy from you. You can send an email to your customer base and ask for their feedback on a few product ideas you have in mind.
For example, Planted Detroit offers customers 20% off their next order if they take a survey in a recent post on X (formerly Twitter).

Whether it’s you or your support team sending these emails, you can still get feedback and use it to inform your product development process.
Find your next bestselling product today
Choosing the right product and niche is at the very core of your ecommerce business and is one of the most important decisions you’ll make.
Using the above criteria as a guideline can help you find low-competition, high-demand products that will likely be a success.
- How To Source Products To Sell Online
- The Ultimate Guide To Dropshipping (2024)
- How to Start a Dropshipping Business- A Complete Playbook for 2024
- How To Find the Best Dropshipping Niches
- Free Business Plan Template- A Practical Framework for Creating Your Business Plan
- What Is Affiliate Marketing and How to Get Started
- The 12 Best Ecommerce Platforms for 2024
- 130+ Dropshipping Products To Sell for Profit
- How to Make and Sell Enamel Pins
- How to Start a Candle Business (with Examples)
Product research FAQ
What’s the difference between product research and market research, how do you start product research.
Product research is a critical part of choosing the right products and can have a huge impact on the success of your business. Follow these steps to get started:
- Evaluate market size: Use product research tools to learn how many potential customers you might have for your product.
- Analyze the competitive landscape: Explore other brands selling similar products and how they’re marketing them.
- Determine product category: Decide what type of product your audience will enjoy the most.
- Define target customer: Establish who you’re going to sell your products to.
- Figure out the profit margin: Calculate costs to see how much profit you’ll make on each
How do I research a product to sell?
Use these tips to research products to sell:
- Follow consumer trend publications: Explore sites like Trend Hunter to find out what concepts and cultural icons are popular.
- Find top sellers on Amazon: Discover what products sell well in your chosen categories on Amazon.
- Browse social curation sites: Take a look at Pinterest, We Heart It, and other curation sites to identify common trends.
- Evaluate B2B wholesale marketplaces: Check out Alibaba and B2B marketplaces to discover trending products.
- Read niche forums: Find forums dedicated to your niche to explore popular topics and narratives.
- Ask your own customers: Run a customer survey to get feedback on upcoming product ideas.
What is an example of product research?
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.
Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Sep 9, 2024
Sep 6, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
Product Research Guide: How to Find Profitable Products on Amazon in 2024

Brian Connolly
May 9, 2024

Table of Contents
What is product research, how to do product research, 6 ways to discover good product ideas, evaluating your product ideas.
With more consumers shopping online than ever before, now is the perfect time to get into ecommerce. Between Amazon , eBay , Shopify , Walmart , and Etsy , there isn’t a shortage of platforms to sell on, and product opportunities abound. But what are you supposed to sell?
To set yourself up for success, you must invest time in the product research process, so you know what customers are looking for and buying at this time.
Product research is the first step all sellers should take because if you jump right in without any knowledge of the market or demand, you may be destined to fail. Luckily, you are here so you won’t be one of those people!
If you want to learn how to research and validate product ideas to sell online, then keep on reading, and learn, step-by-step, how to find profitable products for your business.
Pproduct research is the process of researching different products or niches and using various data points to determine if the product will be successful or not. If you choose a product just because it’s something you enjoy, you’ll miss the benefits of a good strategy, and that uninformed decision might cost you and your business.
When it comes to ecommerce and selling products online, you need more than just a “gut feeling” that something will sell well. Your unique candle idea may seem like a no-brainer, but is that what customers actually want? Even if they do, if there is low demand or the market is already saturated, your product may not perform well, and you could lose your investment.
To prevent your product from taking a nosedive, you need to determine demand, analyze the competition, create a unique, high-quality product, and most importantly, produce the product at a profitable price.
Now that you know what product research is and why it is important, let’s go over how to find profitable products to sell online. Before you start researching products, dedicate some time to determine what product criteria to use for your business. Following certain criteria will help you make sound decisions and narrow down your product search.
Here are some great criteria for product research :
1. selling price.
How much do you want to sell your product for? Too low of a selling price and you may not have enough margin for profit after your costs. Too high of a selling price means potentially higher manufacturing costs, which require bigger budgets to support your product.
Typically, Jungle Scout recommends a price point of around $20-$50. This leaves room for profitability after selling and advertising fees, keeps manufacturing costs low, and places you in the “impulse purchase” range. This puts your product in an optimal position when starting out — customers are not always willing to purchase higher-priced products from unknown brands.
Do keep in mind that the market in this price range may be more saturated because products are inexpensive to source, and competition is high.
2. Product size and weight
If you’re a new or inexperienced seller, we advise you to start out selling products that are small and lightweight. This will help keep shipping costs down and make inventory storage simpler to manage.
For example, it would be much easier (and cheaper) to source a small product such as a necklace, versus a couch. Couches may be in high demand, but can you handle the logistics of selling large-scale furniture?
I know this is an extreme example but think about the differences in storage space and shipping costs between these two items. If you have the knowledge and capabilities to sell bigger and heavier products, however, then go for it!
3. Product simplicity
Does the item you want to sell have many moving parts or components that could potentially break? If you choose to sell in the electronics category, for example, be sure that your supplier can produce high-quality products with minimal issues.
If you sell customers a faulty product, you’ll experience several challenges, such as poor reviews, high return rates, and declining sales.
Newer ecommerce sellers should try to stick to simple, low-maintenance products that are less likely to have potential downsides.
Let’s take another example: Bluetooth headphones. They’re a popular product, but there could be many problems that come with them, especially if they’re produced at a cheaper price. Check out these reviews to see what I mean:

To find common negative themes about another brand’s product, check out Jungle Scout’s new Review Analysis tool with AI Assist .
Review Analysis will provide you with a comprehensive analysis of product reviews and ratings for any ASIN that includes common positive and negative comments, suggestions for improving the product, and a competitive comparison with tips for competing against the product.
If you decide to sell a similar product, figure out what customers dislike about your competitors products so you can be sure your product doesn’t face the same issues.

4. Perishable or consumable products
Are you considering a product that falls in the grocery or health categories? These can be profitable because you can grow a repeat customer base as buyers are likely to reorder household staples, but there are some things to be aware of.
These types of products typically have expiration dates, so keep that in mind when deciding how much inventory you should order. If you overestimate the demand, you may be stuck with expired inventory.
When it comes to food or supplements, be sure to follow relevant local and federal regulations regarding the product you choose to sell. Research and understand this information before you decide you’re going to sell in one of these categories.
On top of that, online marketplaces such as Amazon or Walmart may have their own rules and regulations on perishable and consumable products.
Using the criteria above will help you narrow down your product search versus searching through a broad range of products. Of course, there may be some other criteria that you’d like to consider as your research leads you to specific items, but this is a good place to start if you don’t have a niche or market in mind.
Grow your Amazon business with Jungle Scout.
Jungle Scout’s Amazon intelligence tools help sellers find profitable products to sell.
After you figure out some general criteria to evaluate potential products, how do you come up with solid ideas? Let’s go over some steps you can take to find a good product to sell online.
1. Start with your hobbies or interests
This is a good place to start because it would be much more enjoyable to sell a product that you’re interested in. Now, as we said earlier, just because you like a particular product doesn’t mean others will. You will still need to evaluate your ideas, but do list down some products that would be of interest to you to start. If there’s potential to sell something you can easily get behind, then why not?
For example, if you like to play pickleball, you could consider selling a pickleball set that includes a paddle, balls, and a net.

When jotting down ideas, think about how you’d like your product to be better than what’s currently available in the market. You love to play pickleball, but have yet to find the “perfect paddle.” How can you outdo paddles in the market so that they can solve customer problems and needs?
2. Figure out what is currently trending
Capitalizing on growing trends is a smart way to make money selling products online — especially if you catch one at its onset. But how do you even find out what is trending?
If you’re active on social media, especially on apps like TikTok , you can get a good idea of what products people are talking about. What categories do people love? What new items are consumers raving about? This is a helpful way to harvest ideas but be wary of “fads” instead of trends. We’ll go over this more later when we discuss evaluating product ideas.
Another way to view current trends is to visit “ Google Trends .” The free tool will show you the popularity of any topic over some time so you can find out if something is currently trending or declining in popularity.
After searching for “halloween costumes” for example, here are the results.

The term “halloween costumes,” was peaking in September 2023 as Halloween approached.
You can also use Google Trends to find out what people are searching for the most in a particular country. This could give you more viable ideas for products.
3. Search on Amazon
An excellent way to generate good product ideas is to go right to the source: where people are buying them! Amazon features a few different “best sellers” lists you can dig through to find ideas. Here’s how to conduct that search:
First, go to Amazon’s Best Seller page. You can find that in the main menu on the Amazon homepage.

On this page, you will find the best-selling products for each main category on Amazon. While these products listed are selling very well, it is unlikely that new sellers will be able to compete with them as they have thousands of reviews and an established market share.

Instead, you’ll want to look at Amazon’s other lists such as New Releases, Movers & Shakers, Most Wished For, and Gift Ideas. The products listed here will be popular and sales but will be easier to compete with over the top 100 best sellers.
Now, dig through each of these lists to discover new products you may have never thought of selling!

These lists feature products that are rising in popularity and what customers are buying right now. This valuable information is updated every hour. Again, what you will first see are “main categories.” To find low-competition products, we recommend going deeper into subcategories.
Let’s go over an example. In the “New Releases” list, I’ll click on “Sports & Outdoors” and see what subcategories I can search through.

The main category “Sports & Outdoors” is way too broad and it’ll be difficult for me to find a product I can profitably compete with. I’ll keep clicking through each subcategory until I find something interesting.
In this example, I started with Sports & Outdoors > Sports & Fitness > Boating & Sailing > Boating.
Under the “Boating” subcategory, there are tons of product types I can look through.

The more “niche” you get with your product research, the better. This way, you can find products that not everyone may have thought of but will still have lots of potential customers.
4. Attend wholesale trade shows
Trade shows are a fantastic way to meet suppliers and manufacturers in person. They’re also where you can actually touch and experience different types of products first hand, and discover new innovations in the market.
Meeting suppliers in-person versus contacting them online through sites such as Alibaba gives you a huge advantage over the competition. You can build real-life relationships and usually get the best pricing when negotiating in person.
Trade shows are also great for retailers versus someone trying to create a private label product. Retailers buy other brands at wholesale prices and then resell them for a profit either in a brick & mortar store, ecommerce website, or online marketplace such as Amazon.
In the Amazon selling world, we call that the wholesale business model . Trade shows are helpful for sellers who don’t want to start their own brand but want to resell other successful products and brands in their store.
There are trade shows for all types of products and industries. A popular one in NYC is the Toy Fair show. You can discover thousands of popular toy brands as well as private label opportunities.
A very popular wholesale trade show for brand owners or private label sellers is the ASD Market Week show, held twice a year in Las Vegas.
5. Search on Alibaba
Many brands and sellers use Alibaba , a B2B marketplace, to find unique products they can private label and sell under their own brand. Alibaba works in a similar fashion to Amazon. Search for any type of product you’re interested in, and you will see many results pop up.
You can find practically any product you can think of on Alibaba. They also feature top-ranking products and new arrivals to give you some unique ideas.

Take your time and explore the categories and subcategories just like you would when doing product research on Amazon.
You can also search through Aliexpress , which is related to Alibaba but meant more for consumers versus bulk business buyers. You can purchase as little as one unit of a product or multiple units if you want to test out some samples.


6. Use product research software
If you want to make the product research process seamless, you can use an advanced product research tool to help you find products matching your exact criteria.
Jungle Scout offers a few different product research tools in our all-in-one platform to find high-demand, low-competition products.
- Product Database. We have a searchable catalog called Product Database that allows you to choose categories and set specific filters so you can find products that are selling well. Product Database will only pull up products that meet the criteria you set so you can quickly filter through the results.
- Product Tracker. From there, you can track the performance of each product you like using our Product Tracker tool.
- Opportunity Finder. We also have a tool called Opportunity Finder , which you can use to discover new, unique niches and jump in on new emerging trends.
After you have discovered some products you would be interested in selling, how do you know if they’re good markets to sell in? In this section, we’re going to show you how you can evaluate your product ideas and analyze your potential competitors.
Here are some key factors you should consider when choosing a product to sell online:
- Product demand
- Competition
- Seasonality
- Profitability
- Marketability
1. Product Demand
Are customers searching for and purchasing the product you want to sell? You need to make sure that there is enough demand for you to enter the market.
Check Amazon Best Seller Rank
Even if you’re not going to be selling your product on Amazon, you can still use Amazon’s data to figure out the demand for your product. If a product is selling well on Amazon, it is usually selling well in other marketplaces.
Jungle Scout’s recommendation:
At Jungle Scout, we say you should aim for at least 10 sales per day or 300 sales per month. If you take a look at the top 10 or so products on an Amazon search results page, you want the total monthly sales of all those top-selling products to be around 3,000.
This shows us that there is decent demand in the market to make some sales and compete with other brands.
How do you find the Best Sellers Rank and what do the numbers tell you? Great question. Go to a random Amazon product page and scroll down until you find the “product details” section.

For this particular example, the BSR (Best Seller Rank) is 106,132 in Sports & Outdoors. If you’re not familiar with selling on Amazon, this number may have little significance, but some key information can be gleaned from it. The higher the BSR, the worse the sales are for that product. This high of a BSR means low sales.
Amazon sales estimator
You can use Jungle Scout’s Free Sales Estimator to get an estimate of how many units this particular brand is selling per month based on that BSR number.

As you can see, this product only sells an estimated 60 units per month, which is not ideal for a seller who wants a profitable product.
For this particular product, the total sales of the top 10 products were only around 600 per month total. This tells me that the demand for it is too low or it may be a seasonal product.
Of course, you can still sell in this market. Just know that your monthly sales volume will be low, and you must order inventory accordingly.
Check Google Trends
Using Google Trends again, you can get an idea of the popularity of a particular product over time by searching for its keywords. For this example, I searched for “boat compass.”
The interest over the past 12 months has been up and down, which tells me it is not a consistently searched-for type of product.

I wouldn’t feel comfortable in this market as the product I was curious about has not been consistently searched for over the past year.
Check product reviews
Viewing product reviews — more specifically, the dates and the quality of the reviews — can give you a good idea of how often people are purchasing that type of product, and what people like and dislike about the product. By analyzing your competitors’ reviews, you can figure out what you can potentially improve with your product.
Let’s look at the dates first. Since only a small percentage of buyers actually leave reviews, reviews that are dated close to each other indicate that there is decent demand for it.
If you are on Amazon, you can choose to view the most recent reviews.

Now, let’s figure out how to analyze competitors’ reviews. Analyzing your competitors’ reviews allows you to find common positive and negative themes, so you can figure out what customers love about that specific product and what they dislike about the product.
The problem is, analyzing reviews manually takes a ton of time and effort. Again, with Jungle Scout Review Analysis with AI Assist tool , you get a comprehensive analysis of product reviews and ratings for any ASIN that includes common positive and negative comments, suggestions for improvement, a competitive comparison with tips for competing against the product.

LEARN MORE ABOUT AI ASSIST
Google Keyword Planner
Another free Google tool you can use to see how many people are searching for keywords related to your product is Google Keyword Planner . Simply enter a few keywords related to your product idea and see what the tool comes up with.
Keyword Planner will show you estimated monthly search volume, competition, and more.

For the term “ear wax candle” there are roughly 10K – 100K searchers per month. This is a wide range, but it tells me that many people are searching for this term.
2. Competition
There may be demand for your product but you also need to consider how competitive the market is. If you have lots of competitors, it will be difficult to make your product or ecommerce store stand out.
Use this tool to see how competitive a particular keyword is for Google Ads. Google Keyword Planner will indicate the level of competition you’re up against, along with the estimated keyword bid.
This information is useful if you plan on building your own ecommerce site with a platform such as Shopify .

Search on Amazon and Walmart.com
Take a look at the competition on Amazon or Walmart. How many reviews do they have? Are there many brands with the same product? How can you differentiate yourself from them? What are customers saying about the products? Is there room for improvement? Do you spot opportunities worth taking?
Those are a few questions you should ask yourself when doing a competitive analysis .
If you see products that have thousands of reviews each, theirs may not be the best market to try and compete in, unless you have extensive ecommerce experience.
Products with a modest review count — 500 or less — will be an easier market to compete in. If there are one or two products that seem to have way more reviews than the others, this could mean that they have most of the market share in that particular marketplace.

3. Seasonality
Selling a product that is evergreen is ideal — because it is in demand all year round. And yes, selling a seasonal product can also be quite profitable. You just need to be wary of how much inventory you should order for the season, and when to do it on time.
Google Trends
To determine seasonality, you can use Google Trends again to see what times of the year people are searching for a particular product or keyword.
If the data shows that consumers are searching for this product steadily throughout the year, it should consistently sell through all four seasons. If you see a big spike during a particular time period and a flat line for the rest of the year, this shows seasonality or indicates that it was a fad that came and went.
Here’s an easy example: if you search for “Halloween costumes,” you can see that it spikes in September/October and quickly declines afterward.

Opportunity Finder
If you subscribe to Jungle Scout , you have access to our Opportunity Finder tool, which will show historical search volume as well as a graph displaying the seasonality of a particular product.
The data you see in Jungle Scout is from Amazon sales, but it typically represents the seasonality and demand across all ecommerce marketplaces or platforms.
Find profitable products to sell on Amazon.
Leverage Opportunity Finder to evaluate the demand and seasonality of a potential product.
4. Profitability
After evaluating a product’s demand, competition, and seasonality, you need to be sure that the product you want to sell will be profitable. This involves sourcing your product at a reasonable cost and pricing the product properly.
If you find a product that sells well at $25, but you can only source it for $19, then it won’t be a good opportunity for you — after shipping and potential selling fees, you will lose money on each sale.
Depending on the platform or marketplace you will be selling on, you need to factor in various fees such as subscription fees, selling fees, advertising fees, storage fees, and shipping fees.
- First, figure out the average price your competitors are charging for their products. Then, figure out which platform(s) you want to sell your products on, as each one has different fees for their respective sellers. If you’re going to sell on Amazon, make sure you read about and understand all of Amazon’s fees .
- Next, go to a site such as Alibaba, search for your product, and start contacting suppliers for pricing. After getting a price and shipping quote, calculate what your profit will be after all costs involved.
There is no particular profit margin you should aim for as it is different for every business, but we recommend around at least a 30-40% gross margin. This will leave you with some room for a marketing budget since you will likely need to advertise your products to stand out and attract sales.
READ MORE | How Much do Amazon Sellers Make?
5. Marketability
This is just as important as all of the other factors we mentioned. How are you going to market your product compared to your competition? How can you make improvements to the product itself, to your product images, and to your listing copy?
You should also consider a social media strategy for your product and determine if it can help grow your business. Search various social media sites such as Facebook, Instagram, and Tik Tok to see what other brands in your niche are doing to market their products.
You can have the best product in your category, but if you do not market it well , then how will customers know about your product?
Find your winning product idea
We hope this guide helps you understand the importance of proper product research for your online business. Use the tips and strategies laid out above to be on your way to launching a successful product.
After you find a great product to sell, which platforms do you plan to sell it on? See the links below for in-depth how-to-sell guides for Amazon, Shopify, eBay, Walmart, and even Facebook. We show you how to successfully sell on each one of those marketplaces, step by step.
- How to Sell on Amazon FBA for Beginners
- How to Sell Products on Shopify: a Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Sell on Walmart Marketplace
- How to Sell on eBay — Step-by-Step Beginner’s Guide
- How to Sell on Facebook Marketplace
Did this guide help you find your winning product idea? Do you have another method in mind that we didn’t mention? Let us know in the comments!
Take your Amazon business to the next level.
Jungle Scout’s industry-leading Amazon intelligence helps brands and sellers grow on Amazon.
Ecommerce Expert & Writer at Jungle Scout
Brian Connolly is an Amazon seller, ecommerce expert, and writer for Jungle Scout. He lives in the New Jersey Shore area with his wife and cat. When he isn’t writing advice online for aspiring and experienced Amazon sellers for Jungle Scout, he spends his free time boating, fishing, and selling boating-themed items on his Amazon business.
Stay in the Amazon seller loop
Thank you for subscribing!
Recommended Posts

Market intelligence for sellers

Advanced Amazon Advertising Strategies for High-Growth Brands & Agencies

Amazon Best Sellers and Trending Products in September 2024

Amazon Data: Health & Home Brands

How to Drive More Traffic to Amazon

Black Friday Marketing Strategy – Amazon FBA Selling Tips for 2024

How Sellers Can Prepare for Amazon’s Prime Big Deal Days 2024

What to Sell on Amazon FBA: The Best 5 Products for September 2024

How Influencer Brands Stack Up Against Big Brands on Amazon
Stay in the loop.
Get the industry's best e-commerce articles, videos, reports, and more — delivered to your inbox weekly.
Thank you for signing up!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked with *

“I have earned $442,991 USD in just six months by building a dropshipping business that people loved”.
Up to 8 months off on annual plans
Product research, what is product research.
Product Research: The process of gathering information about products' market demand, competition, and potential profitability before launching or stocking them.
Product research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a particular product or market to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, pricing, distribution channels, and other aspects of the product lifecycle. It involves collecting data from various sources, including market research, competitor analysis, consumer feedback, and trend analysis, to assess market demand, identify opportunities, and evaluate the feasibility and potential success of introducing a new product or improving an existing one.
Key Components of Product Research :
- Market Analysis : Conducting market research to understand the target market, including demographics, psychographics, consumer preferences, purchasing behavior, and market trends, to identify unmet needs and opportunities for innovation.
- Competitor Analysis : Analyzing competitors' products, pricing strategies, marketing tactics, distribution channels, and market positioning to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT analysis) and inform strategic decision-making.
- Consumer Insights : Gathering feedback from consumers through surveys, focus groups, interviews, and online reviews to understand their perceptions, preferences, satisfaction levels, and pain points related to existing products or potential product ideas.
- Trend Analysis : Monitoring industry trends, technological advancements, consumer behavior shifts, and emerging market opportunities to identify emerging trends and anticipate future market demands and opportunities.
- Product Testing : Conducting product testing, prototypes, or pilot programs to evaluate product performance, quality, usability, and functionality and gather feedback from real users before launching the product to market.
- Regulatory Compliance : Ensuring compliance with applicable regulations, standards, safety requirements, and industry certifications relevant to the product category or market to mitigate legal risks and ensure product quality and safety.
Benefits of Product Research:
- Informed Decision-Making : Product research provides valuable insights and data-driven analysis to guide strategic decision-making throughout the product development and marketing process, reducing risks and increasing the likelihood of success.
- Market Validation : Researching market demand, consumer preferences, and competitive landscape helps validate product ideas, identify niche markets, and assess the viability and potential profitability of introducing a new product or entering a new market.
- Risk Mitigation : By identifying potential challenges, market barriers, and competitive threats early in the product development process, product research enables companies to proactively mitigate risks, address issues, and refine their strategies to improve outcomes.
- Product Innovation : Researching emerging trends, consumer needs, and technological advancements inspires product innovation, fostering creativity and differentiation to develop products that meet evolving market demands and exceed customer expectations.
- Customer Satisfaction : Understanding customer preferences, pain points, and feedback through product research allows companies to design and deliver products that address consumer needs, enhance satisfaction, and build long-term customer loyalty and advocacy.
Related Terms
Acquisition.
Acquisition: Acquisition involves one company purchasing another, often with the goal of gaining control, accessing new markets, expanding product offerings, or achieving synergies. It can be friendly or hostile in nature.
B2B (Business to Business)
B2B (Business to Business): Transactions or interactions between businesses, such as between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or a wholesaler and a retailer.
B2C (Business to Consumer)
B2C (Business to Consumer): Transactions or interactions directly between a business and consumers who are the end-users of its products or services.

Try Spocket for free, and explore all the tools and services you need to start, run, and grow your business.
What is Product Research and How is it Done?
What is product research.
Although technology plays a major role in bringing innovative products to the markets most of these products fail to achieve meaningful customer adoption. This is usually the result of developing products that do not serve much value to the customers. This challenges can be eliminated using product research. A product research process involves identifying market opportunities and gaining meaningful customer insights that will help businesses in better decision-making.
Product research is one of the most vital steps in a product development process. Here, the product idea is carefully examined and compared to similar offerings in the market to understand the selling potential of the proposed new product. Efficient product research tools also help identify key issues in a proposed product and thereby avoid costly mistakes.
We at Infiniti provide tailor-made solutions to suit your needs. Request free brochure to know more!
Product research vs product development
Product development is a broader concept that involves the entire process of researching, designing, creating, marketing, and selling new products. It encompasses the entire product lifecycle starting from conception to the sale. This stage is not exclusive to designing, implementing, and selling new products, rather it can also include revamping of existing product features that could add greater value to the customers. Product research, on the other hand, is one of the first steps in developing a new product. This is concerned with the company’s R&D team testing the viability and feasibility of a particular product for a given market. Research and development for new or existing products are vital for the company’s long-term success and sustained growth.
Why is product research important?
Product research experts at Infiniti Research have listed out some of the key reasons why companies must take product research process seriously and their crucial role in the success of their product-to-market strategy:
Better understanding of customers
Who are the company’s target customers? What are their buyer personas? How often will the customers buy a particular product? An effective product research provides answers to such questions. Furthermore, this will help businesses meet customer needs and demands better than the competitors. The complete customer profile can be mapped using product market research, making it easier to determine the market size and identifying what triggers customer purchase. Furthermore, demographic (age, location, income, and gender) insights relating to the target customer can also be gained.
Get your product research on point using Infiniti’s product research solutions for business. Request a proposal to get more insights!
Gain insights on competitors
Businesses that want to stay in the game must be well aware of who they are competing against in the market and what their key strategies are. Using market research market competition can be easily identified and companies can also gain a better understanding on the customer perception of their product compared to that of the competitors. It also provides a clear SWOT of the company and how they can improve their products.
Product testing
Even though a product might be in its last stage of development, there might still be loopholes in its functionality that can be improvised to enhance user experience. It is difficult to stay confident that a product will instantaneously connect with the audience. Product market research will clearly define what marketing approach needs to be taken in marketing the product in such a way that it resonates with the audience.
Business growth
It is too optimistic to expect that a business is always going to run smoothly and free of challenges. There are chances of a sudden spike in competition or a dip in sales. The use of market research enables companies to capitalize on market opportunities and develop innovative products or a better pricing plan. It will also facilitate in discovering new market segments and distribution channels.
Three main components must be addressed by companies while undertaking their product research: the consumer, the market, and key competitors. Overlooking any of these could result in serious drawbacks in the company’s product research report. The ultimate goal of a product strategy is to better understand the product and potential changes it might take in the future. This could play a major role in revolutionizing an old product entering a maturity stage or developing a new and innovative product.
Market research supports the creation of a definitive product strategy that exceeds business targets. Infiniti Research’s product research solutions can help you attain that. With accurate data and analysis, we help develop your product strategy by identifying key markets for entry, surveying consumers, competitive analysis, and identifying underlying consumer trends.
GET MORE INFO to learn more about our solutions.
We help our clients make smarter decisions to achieve rapid business growth
Our strength lies in the unrivaled diversity of our international market research teams, innovative research methodologies, and unique viewpoints that merge seamlessly to offer customized solutions for your every business requirement.
Recent Posts

Pharmaceutical Industry – Infiniti’s Target Market Analysis Helps Refocus Attention on Customers’ Needs

Infiniti’s Market Intelligence Solution Helped a Pharmaceutical Packaging Company Exceed Sales Expectations and Save Over $3.7 Million

Developing a Product Marketing Strategy for a Leading API Manufacturing Company
Manage settings.
🔥 Upgrade to a new style of analyzing VoC with sentiment checks, video clips, custom reports & more!
.png)
What is Product Development Research and how to do it?

Product Marketer at Zeda.io
Jacob Koshy
Created on:
May 15, 2024
Updated on:

Transform Insights into Impact
Build Products That Drive Revenue and Delight Customers!
66% of customers expect companies to understand their needs. But how do you understand the needs and demands of your customers?
This is where product development research comes in. It not only helps the product managers to understand customer needs but also enables them to address these requirements in perfect ways. In return, product managers can drive higher customer satisfaction, loyalty, and high revenue.
Let us discuss everything you need to know about product development research.
What is Product Development Research?
Product development research is the process of crafting, developing, and selling a product. It includes the crucial steps of market research, user research, and also coming up with a marketing plan to market the product to prospects. It also refers to tracking the progress of a product you are currently working on, its appeal to the target audience, and identifying potential changes you need to make to make the product more attractive.
Development cannot take place in isolation from research. It is a crucial process that directs the development of a product. It helps you to identify, understand and analyze consumer needs so that you can cater to them accordingly and increase your desirability in the market. It includes the processes of concept testing, loyalty testing, and many other tests that validate the product.
Why is Product Development Research important?

Product development research lays the groundwork for all the important functions of product development, marketing, and sales. It makes sure all your activities are data-driven and not just based on assumptions, minimizing the chances of errors.
Let us try to understand why product development research is important with the following points.
- It ensures you are giving your customers what they really want. Sometimes you may have a different idea of the benefits and features that you want to offer your customers, which they might not even need. Research saves you from committing errors like this and ensures you don’t waste resources.
- It helps you identify customers and market trends so that you can devise your strategies accordingly.
- It helps you to identify gaps and drawbacks in the current development plan and helps you brainstorm and analyze ways to improve.
- It enables you to forecast the demand for the product and develop unique ways to promote, market, and sell.
- It allows you to identify specific features that customers might be willing to pay more for and help you figure out ways for increasing customer loyalty.
How does the product development research process looks like?

There are primarily 3 broad stages of product development research. Let's discuss.
1. Exploratory research
This occurs in the earliest stage of product development research. During this time, you have no idea of what your product is going to look like, what features it will have, or what will be the pricing structure. In this stage, you explore ideas and dig into data around customers to understand their pain points and needs.
Idea generation
When you are at the first stage of product development, you generally have no direction. The research will help you to lay the foundation of an idea and how to work around it. This process should focus on answering these vital questions.
- What type of product do you want to build?
- Who is the target audience?
- What do they really need?
- How can you address their need with your product?
- What segment of the market would you like to target?
Idea screening
This will help you evaluate potential ideas based on the criteria gained by market research. For example, if you have a new idea, the screening will help you test the feasibility by evaluating the budget requirements, relevance, constraints, risks, and challenges.
It starts with the generation of an ‘idea’ or ‘ideas’. It can come from you or your team members or anyone who is involved in the development process. Once you have the idea, you have to evaluate it against special criteria like benefits/value, target audience, complexity, profitability, and market situation. If the idea shows potential even after weighing against each criterion, you need to gather evidence-based resources to support that idea. You can start doing qualitative and quantitative research to understand prospects' points of view. After compiling all the important research data, you can now start refining your ideas into actual product concepts.
Evaluative research
Ideas that emerged during the previous stage will be scrutinized in this stage. This will help you identify the ones that are worth moving forward and discard the ones that aren’t promising enough. Data collection through surveys can be one of the methods used in this stage to gather details about your product concept.
Concept development and testing
It is the process of gathering information and insight about your product concept from the target audience. It helps you adjust your vision and ideas based on the results of the research.
Market research
This process is essential to examine the different forces of the market that not only pertain to the customers but also competitors, economic stability, government policies, and all other factors that can influence the lifeline of the product.
2. Iterative research
This stage is to analyze and refine your product to ensure it appeals to the customers. Iterative research is detailed and in-depth and focuses on developing the critical features of the product. It can start from testing the different versions of the product to finalizing the packaging.
Development
The development of the product initiates in this stage. From the technology stack to the product labels, everything is analyzed and planned in this step. All the team members pool in their ideas and start working on developing the product after it has been approved.
Before the product is launched in the market, tests are conducted to test its performance of the product. This may include evaluating the product’s performance, safety, quality, and compliance with standards.
Commercialization
This is the final step when the product is introduced in the market. Before launching the product into the market, all the important factors like pricing, packing labels, marketing, and sales channel are decided.
How to perform Product Development Research effectively?
As a product manager, you cannot afford to mess up product development research. All the steps should be carefully planned and executed to ensure success. Make sure to read the steps attentively to know all about conducting effective research.

Step 1: Ideation
Ideation is the process of identifying the type of product you want to build. Suppose you have recognized an opportunity for introducing a new product in the market, but are unsure about what type of product you want to create. This is when you can hold internal sessions with your team to discuss the idea and concept of the product. The processes of combining, adapting, substituting, eliminating, and rearranging will play a crucial role in creating the perfect product idea.
Step 2: Market research
Market research means collecting information and analyzing the crucial players in the market. From competitors, target audience, geographical location, and economic stability to government policies, you have to have a thorough understanding of the market landscape to develop a strong product strategy .
Step 3: Demand analysis
The demand for a product drives the financial decisions of a company. Knowing the demand for a particular product is essential to know the feasibility of a particular product. If a product has low demand, there is no use in investing in the product. Conducting demand analysis will give you information about how many units you need to produce, which are the geographical area you need to target, and forecast your revenue from the product.
Step 4: Concept testing and validation
After you have gathered all the best ideas for product development, it is time to test and validate it. This focuses on clarifying the idea of the product by focusing on questions such as-
- Is the concept understood by the team?
- What pain points can be addressed by the product?
- Who will the product users be and how will they use them?
- What are the possible strengths and weaknesses of the product?
You can validate these questions by conducting qualitative research to test the viability of the product in front of your prospective customers in the form of surveys or interviews.
Step 5: User experience research
User research or UX research is the process of discovering user behavior, motivation, and need of your customers through analysis, observation, and other types of feedback . It will help you dismiss assumptions and find common information about target customers, and recognize their needs and requirements.
Step 6: MVP research or prototype research
A minimum viable product or MVP is a model of the product with enough features to allow customers to use it to validate the product ideas. Creating an MVP and letting early adopting customers use it will help you get an insight into the product experience from their feedback.
Step 7: Pricing research
Pricing research will help you determine an appropriate price for your product. A suitable price should neither be too low as it will impact your profit margin nor too high to make it unaffordable for the consumers. Research will help you come up with a suitable price that appeals to your consumers while ensuring profit.
Step 8: Competitor research
Competitor research is one of the important steps you cannot miss at any cost. Researching your competitors thoroughly will give you a base for comparison so that you can develop your own unique strategy for product creation and promotion. You can research your competitors from various sources like social media, google search, software listing sites, etc.
Step 9: Satisfaction and loyalty research
Satisfaction and loyalty research is vital to understanding the user experience of your product. Once you have launched your product, feedbacks are most likely to come in. You have to carefully analyze and address those feedback in a way that leaves the consumers content.
Best Practices while doing Product Development Research
Here are some of the best practices you should follow to get the most effective results from your product development research.
1. Dig deeper into consumer needs
Just identifying the needs of your consumers based on a survey is not enough. You have to dig deeper into their needs to have a comprehensive understanding.
What kind of challenges do they face? What are they looking for in a product? How much are they willing to pay? What section of consumers will use your product? All these questions will help you create a viable product.
2. Involve customers in your development process
There is no one better than the customer to show you what and how they want in a product. They are the ultimate users of your product so involving them in the development process will only increase the chances of success. You can generate polls, surveys, and feedback sessions to ask prospective customers about their ideas and opinions.
3. Expand your research horizon
Generally, you research only the targeted market and location while developing a product. It helps you get specific insights into the market you want to operate in. Broadening your research horizon is necessary to help you get a thorough understanding of the perceptions related to your product. Don’t limit your research to the target market, try to understand the national and international scenarios related to your product.
Product development research is not as complex as it sounds if you know how to do it correctly. If you know how to address their pain points in the most appropriate and innovative way, you already know you are way ahead of the competition.
Zeda.io is there to support you in your product development research process. It is the ultimate product management tool to help you build the right product for your consumers. Check it out now!
Join Product Café Newsletter!
Sip on the freshest insights in Product Management, UX, and AI — straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, I agree to receive communications by Zeda.
IN THIS ARTICLE:
Latest articles
.webp)
Understanding the Concept of Minimum Lovable Product (MLP)
MLP stands for minimum lovable product. Minimum lovable products are products that users love using because of their excellent design & user experience.

Continuous Product Discovery: A How-to Innovation Guide
Master continuous product discovery with this step-by-step innovation guide to improving your product by listening to users' needs.

A Day in the Life of a Product Manager
A day in the life of a product manager usually involves a lot of different activities. Here is what a typical day would look like for a PM.
AI-powered product discovery for customer-focused teams
What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?

Table of contents

To see what Databox can do for you, including how it helps you track and visualize your performance data in real-time, check out our home page. Click here .
There is nothing more embarrassing for a marketer than to hear a client say “…this doesn’t quite address the business questions that we need to answer.” And unfortunately, this is a rather common occurrence in market research reporting that most marketers would care to admit.
So, why do most market research reports fail to meet client expectations? Well, in most cases, because there is more emphasis on methodology and analytic techniques used to craft the report rather than relying on data visualization, creative story-telling, and outlining actionable direction/steps.
Now, our next big question is, how do you avoid your client’s dreaded deer-in-the-headlights reaction when presenting such a report? This blog post will answer this and much more, as we go through the following:
What Is a Market Research Report?
Why is market research important, differences between primary and secondary market research, types of market research, market research reports advantages and disadvantages, how to do market research, how to prepare a market research report: 5 steps, marketing research report templates, marketing research reports best practices, bring your market research reports a step further with databox.
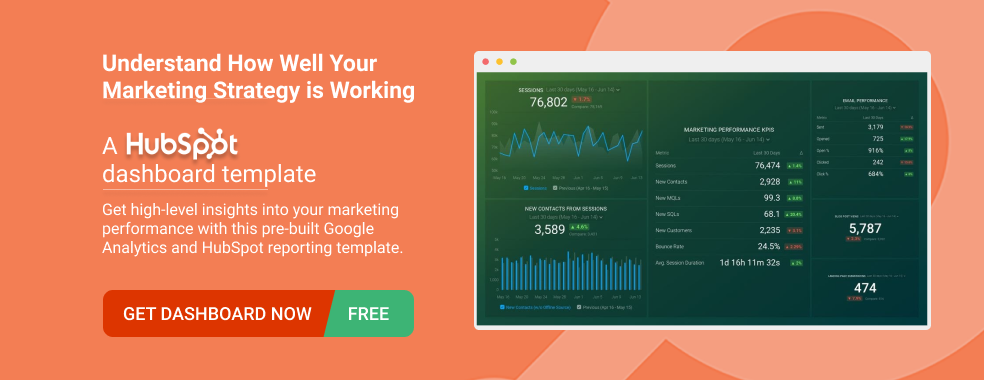
The purpose of creating a market research report is to make calculated decisions about business ideas. Market research is done to evaluate the feasibility of a new product or service, through research conducted with potential consumers. The information obtained from conducting market research is then documented in a formal report that should contain the following details:
- The characteristics of your ideal customers
- You customers buying habits
- The value your product or service can bring to those customers
- A list of your top competitors
Every business aims to provide the best possible product or service at the lowest cost possible. Simply said, market research is important because it helps you understand your customers and determine whether the product or service that you are about to launch is worth the effort.
Here is an example of a customer complaint that may result in more detailed market research:
Suppose you sell widgets, and you want your widget business to succeed over the long term. Over the years, you have developed many different ways of making widgets. But a couple of years ago, a customer complained that your widgets were made of a cheap kind of foam that fell apart after six months. You didn’t think at the time that this was a major problem, but now you know it.
The customer is someone you really want to keep. So, you decide to research this complaint. You set up a focus group of people who use widgets and ask them what they think about the specific problem. After the conducted survey you’ll get a better picture of customer opinions, so you can either decide to make the changes regarding widget design or just let it go.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
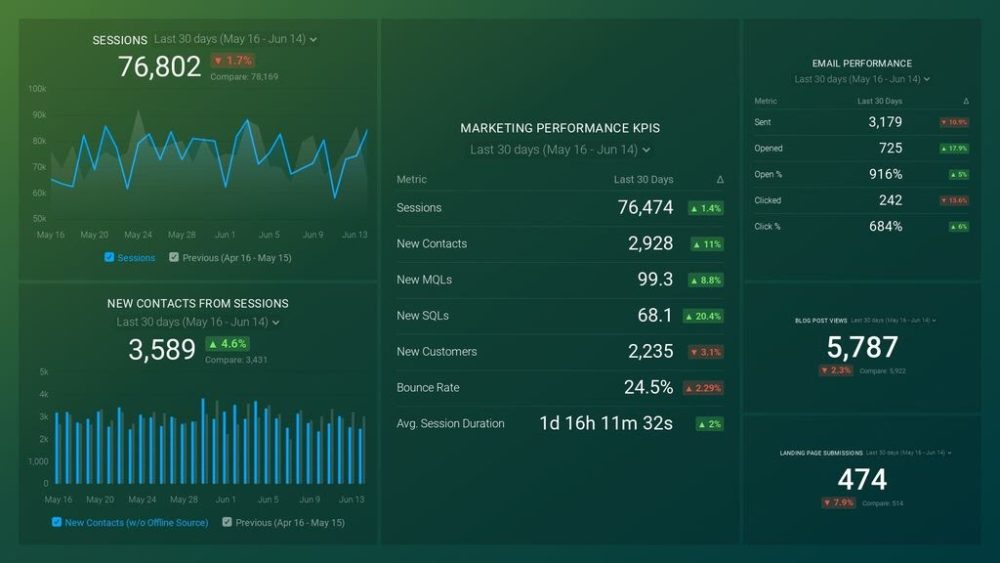
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
Marketing research requires both primary and secondary market research. But what does that mean and what are the main differences?
Primary market research takes in information directly from customers, usually as participants in surveys. Usually, it is consisted of:
- Exploratory Primary Research – This type of research helps to identify possible problem areas, and it’s not focused on discovering specific information about customers. As with any research, exploratory primary research should be conducted carefully. Researchers need to craft an interviewing or surveying plan, and gather enough respondents to ensure reasonable levels of statistical reliability.
- Specific Primary Research – This type of research is one of the best ways to approach a problem because it relies on existing customer data. Specific research provides a deeper, more thorough understanding of the problem and its potential solutions. The greatest advantage of specific research is that it lets you explore a very specific question, and focus on a specific problem or an opportunity.
Secondary market research collects information from other sources such as databases, trend reports, market or government statistics, industry content, etc. We can divide secondary market research into 3 categories:
- Public market data – Public sources range from academic journals and government reports to tax returns and court documents. These sources aren’t always easy to find. Many are available only in print in libraries and archives. You have to look beyond search engines like Google to find public source documents.
- Commercial data – Those are typically created by specialized agencies like Pew, Gartner or Forrester. the research agencies are quite expensive, but they provide a lot of useful information.
- Internal data – Your organization’s databases are gold mines for market research. In the best cases, your salespeople can tell you what they think about customers. Your salespeople are your direct sources of information about the market. Don’t underestimate your internal data.
In general, primary research is more reliable than secondary research, because researchers have to interview people directly. But primary research is expensive and time-consuming. Secondary research can be quicker and less expensive.
There are plenty of ways to conduct marketing research reports. Mostly, the type of research done will depend on your goals. Here are some types of market research often conducted by marketers.
Focus Groups
Product/service use research, observation-based research, buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research, competitive analysis research, customer satisfaction and loyalty research, brand awareness research, campaign research.
An interview is an interactive process of asking and answering questions and observing your respondent’s responses. Interviews are one of the most commonly used tools in market research . An interview allows an organization to observe, in detail, how its consumers interact with its products and services. It also allows an organization to address specific questions.
A focus group is a group of people who get together to discuss a particular topic. A moderator leads the discussion and takes notes. The main benefit of focus groups is that they are quick and easy to conduct. You can gather a group of carefully-selected people, give them a product to try out, and get their feedback within a few hours/days.
Product or service use research helps you obtain useful information about your product or service such as:
- What your current customers do with the product/service
- Which features of the product/service are particularly important to your customers
- What they dislike about the product/service
- What they would change about the product/service
Observation-based research helps you to observe your target audience interacting with your product or service. You will see the interactions and which aspects work well and which could be improved. The main point is to directly experience the feedback from your target audience’s point of view.
Personas are an essential sales tool. By knowing your buyers’ pain points and the challenges they face, you can create better content, target messaging, and campaigns for them. Buyer persona research is based on market research, and it’s built around data that describes your customers’ demographics, behaviors, motivations, and concerns. Sales reporting software can significantly help you develop buyer personas when you gain insights after you collected all information.
Market segmentation research is carried out to better understand existing and potential market segments. The objective is to determine how to target different market segments and how they differ from each other. The three most important steps in writing a market segmentation research report are:
- Defining the problem
- Determining the solution [and]
- Defining the market
Related : 9 Customer Segmentation Tips to Personalize Ecommerce Marketing and Drive More Sales
A price that is too high, or too low, can kill a business. And without good market research, you don’t really know what is a good price for your product. Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy.
In a competitive analysis, you define your “competition” as any other entity that competes with you in your market, whether you’re selling a widget or a piece of real estate. With competitive analysis research, you can find out things like:
- Who your competitors are
- What they’ve done in the past
- What’s working well for them
- Their weaknesses
- How they’re positioned in the market
- How they market themselves
- What they’re doing that you’re not
Related : How to Do an SEO Competitive Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
In today’s marketplace, companies are increasingly focused on customer loyalty. What your customers want is your product, but, more importantly, they want it delivered with a service that exceeds their expectations. Successful companies listen to their customers and respond accordingly. That’s why customer satisfaction and loyalty research is a critical component of that basic equation.
Related : 11 Tactics for Effectively Measuring Your Customer Service ROI
Who you are, what you stand for, what you offer, what you believe in, and what your audience thinks of you is all wrapped up in brand. Brand awareness research tells what your target audience knows about your brand and what’s their experience like.
A campaign research report is a detailed account of how your marketing campaign performed. It includes all the elements that went into creating the campaign: planning, implementation, and measurement.
Here are some of the top advantages and disadvantages of doing market research and crafting market research reports.
- Identify business opportunities – A market research report can be used to analyze potential markets and new products. It can give information about customer needs, preferences, and attitudes. Also, it compare products and services.
- A clear understanding of your customers – A market report gives company’s marketing department an in-depth picture about customers’ needs and wants. This knowledge can be used to improve products, prices, and advertising.
- Mitigates risks – 30% of small businesses fail within the first two years. Why is this so? The answer is that entrepreneurs are risk takers. However, there are risks that could be avoided. A good marketing research will help you identify those risks and allow you to mitigate them.
- Clear data-driven insights – Market research encompasses a wide range of activities, from determining market size and segment to forecasting demand, and from identifying competitors to monitoring pricing. All of these are quantified and measurable which means that gives you a clear path for building unique decisions based on numbers.
Disadvantages
- It’s not cheap – Although market research can be done for as little as $500, large markets like the United States can run into millions of dollars. If a research is done for a specific product, the budget may be even much higher. The budget also depends on the quality of the research. The more expensive it is, the more time the research will take.
- Some insights could be false – For example, if you are conducting a survey, data may be inadequate or inaccurate because respondents can, well, simply be dishonest and lie.
Here are the essential steps you need to take when doing market research:
Define your buyer persona
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors, summarize your findings.
The job of a marketing persona is to describe your ideal customer and to tell you what they want, what motivates them, what frustrates them, and what limits them. Finding out these things means you have a better chance of designing your products, services, marketing messages, and brand around real customers. There is no one right way to create a buyer persona, though.
For example, if you’re in an industry focused on education, you could include things like:
- Educational level
- Education background
It’s recommended that you create 3-5 buyer personas for your products, based on your ideal customer.
This should be a representative sample of your target customers so you can better understand their behavior. You want to find people who fit both your target personas and who represent the broader demographic of your market. People who recently made a purchase or purposefully decided not to make one are a good sample to start with.
The questions you use determine the quality of your results. Of course, the quality of your results also depends on the quality of your participants.
Don’t ask questions that imply a yes or no answer. Instead, use open questions. For example, if you are researching customers about yogurt products, you could ask them: „ What have you heard about yogurt ?” or “ What do you think of yogurt ?“.
Avoid questions that use numbers, such as “ How many times a week do you eat yogurt ?”
Avoid questions that suggest a set of mutually exclusive answers, such as “ Do you like yogurt for breakfast, lunch, or dinner ?”
Avoid questions that imply a scale, such as “ Do you like chocolate-flavored yogurt ?”
Market researchers sometimes call one company the top competitor, another middle competitor, and the third one small competitor. However you classify them, you want to identify at least three companies in each category. Now, for each business on your list, list its key characteristics. For example, if your business sells running shoes, a key characteristic might be the product’s quality.
Next, make a list of your small business’s competitive advantages. These include the unique qualities or features of your business that make it the best choice of customers for the products or services it offers. Make a list of these competitive advantages and list them next to the key characteristics you listed for your business.
You have just finished writing your marketing research report. Everything is out there quantified or qualified. You just have to sum it up and focus on the most important details that are going to make a big impact on your decisions. Clear summary leads to a winning strategy!
Related : How to Prepare a Complete Marketing Report: The KPIs, Analysis, & Action Plan You Need
Here’s how to prepare a market research report in 5 simple steps:
Step 1: Cluster the data
Step 2: prepare an outline, step 3: mention the research methods, step 4: include visuals with narrative explanations, step 5: conclude the report with recommendations.
Your first step is to cluster all the available information into a manageable set. Clustering is the process of grouping information together in a way that emphasizes commonalities and minimizes differences. So, in market research, this will help to organize all the information you have about a product, service, or target market and identify your focus areas.
A marketing research report should be written so that other people can understand it:
- Include background information at the beginning to explain who your audience is and what problem you are trying to solve for them.
- In the body of the report, include a description of the methodology – Explain to the reader how your research was done, what was involved, and why you selected the methodology you used.
- Also in the body of the report, include the results of your market research. These may be quantitative or qualitative, but either way they should answer the questions you posed at the beginning.
- Include the executive summary – A summary of the entire report.
The market research methodology section includes details on the type of research, sample size, any limitations of the studies, research design, sample selection, data collection procedures, and statistical analyses used.
Visuals are an essential part of the presentation. Even the best-written text can be difficult to understand. Charts and graphs are easier to understand than text alone, and they help the reader see how the numbers fit the bigger picture.
But visuals are not the whole story. They are only one part of the presentation. Visuals are a cue for the reader. The narrative gives the story, not just the numbers.
Recommendations tend to follow logically from conclusions and are a response to a certain problem. The recommendation should always be relevant to the research rationale, that is, the recommendation should be based on the results of the research reported in the body of the report.
Now, let’s take a look at some dashboard reporting templates you could use to enhance your market research:
- Semrush (Position Tracking) Report
Brand Awareness Report
Sales pipeline performance report, customer success overview report, stripe (mrr & churn) report, semrush (position tracking) report template.
This free SEMRush dashboard template will help you monitor how your website’s search visibility on search engines evolves on a monthly basis. This dashboard contains all of the information you need to make changes and improve the ranking results of your business in Google Search.
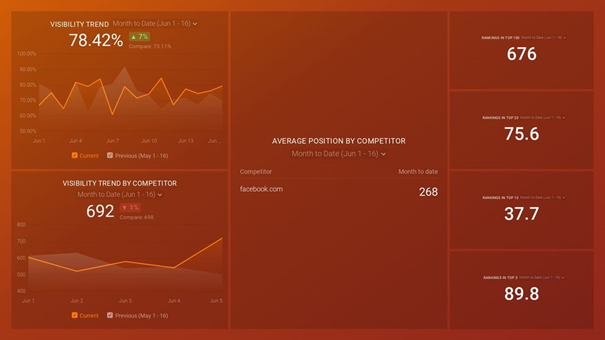
This Brand Awareness Report will help you to get a sense of your brand awareness performance in Google Analytics, Google Organic Search, and Facebook. Use this dashboard to track brand awareness the same way you track other marketing campaigns.
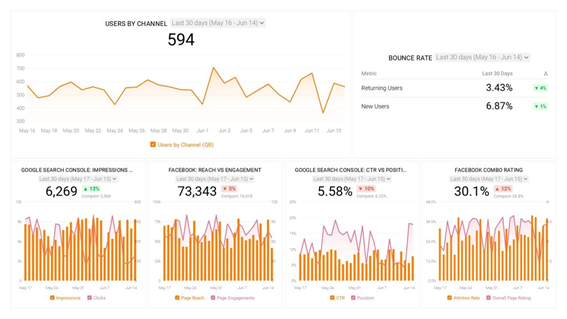
Are your sales and marketing funnel healthy and growing? How is your sales and marketing funnel performing? What are the key conversion rates between your lifecycle stages? With a pipeline performance dashboard , you’ll get all of the answers quickly.
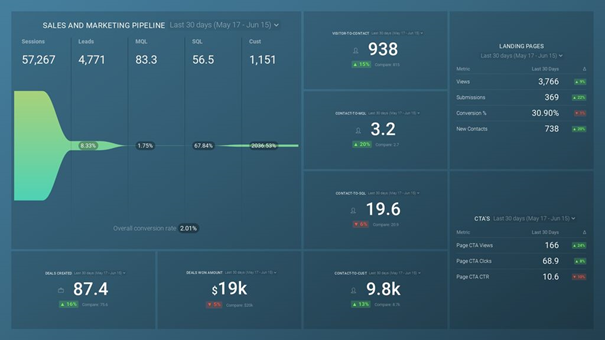
This Customer Success Overview Dashboard allows you to analyze how your customer service team’s responsiveness impacts your business. Use this dashboard to assess the correlation between your customer service performance and churn rate.
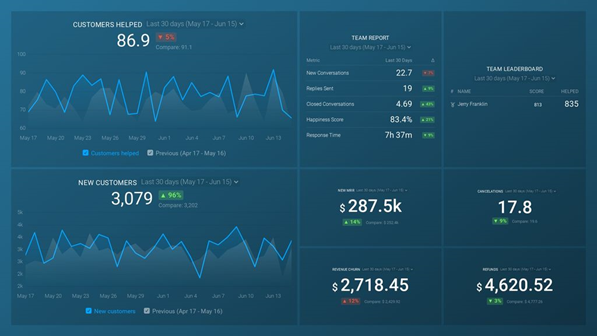
This Stripe dashboard tracks your churn rate and MRR growth in real-time and shows you which customers (and how many of them) you have at any given point in time. All you have to do to get started is to connect your Stripe account.
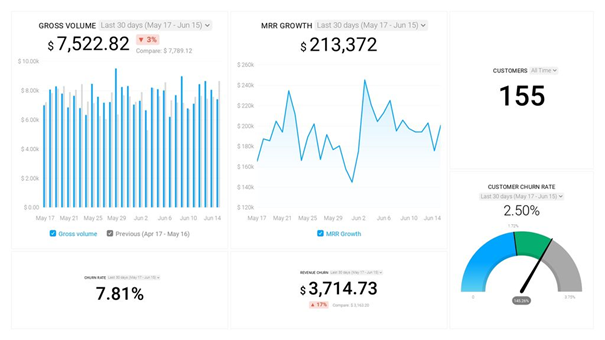
As we said earlier, there are no strict rules when it comes to writing marketing research reports. On the other hand, you must find your focus if you want to write a report that will make a difference. Here are some best practices you should keep in mind when writing a research report.
- Objectives – The objective of a market research report is to define the problems, identify key issues, and suggest recommendations for further research. If you answer them successfully, you’re on the right way.
- Don’t worry about the format – Be creative. The report could be in a form of a PowerPoint presentation, Excel sheet, interactive dashboard or even a video. Use the format that best fits your audience, but make sure to make it easy to read.
- Include an executive summary, scorecard , or a dashboard – This is really important because time is money, and most people don’t have time to waste. So, how to put everything important in a short role? Address all of the objectives and put them in a graphic dashboard or scorecard. Also, you can write an executive summary template (heart of the report) that can be easily updated and read by managers or CEOs.
- Use storytelling – A good story always makes a great point because it’s so memorable. Your research report results can double the effect with a catchy story.
- Keep it short – It’s not a secret that we are reading so little in the digital era. Use a lot of white space and bullet points. Too much text on a page means less focus for the reader.
- Be organized – Maintain the order of information. It’s important for the reader to navigate through the report easily. If they want to find some details or specific information it would be great to divide all sections with appropriate references.
- Methodological information – Methodological details could be boring. Include only the most important details that the reader needs to know to understand the big picture.
- Use images (or other visualizations) whenever you can – A good picture speaks for 1.000 words! If you can communicate the point visually, don’t hesitate to do it. It would be a lot easier for those who don’t like a lot of text to understand your results. But don’t push them where you can’t.
- Create readable graphs – The crown of marketing research reports is a comprehensive graph. Make sure to design precise and attractive graphs that will power up and round your story.
- Use the Appendix – You can include all secondary information such as methodological details and other miscellaneous data in the Appendix at the end of the report.
Market research reports are all about presenting your data in an easy-to-understand way and making calculated decisions about business ideas. But this is something easier said than done.
When busy stakeholders and executives grab a report, they need something that will give them an idea of the results – the big picture that addresses company wide-business goals.
Can a PowerPoint presentation or a PDF report meet those expectations? Most likely not. But a dashboard can.
Keep in mind that even with the best market analysis in the world, your market research report won’t be actionable if you don’t present the data efficiently and in a way that everyone understands what the next steps are. Databox is your key ally in the matter.
Databox dashboards are designed to help you present your market research data with clarity – from identifying what is influencing your business, and understanding where your brand is situated in the market, to gauging the temperature of your niche or industry before a new product/service launch.
Present your research results with efficient, interactive dashboards now by signing up for a free trial .
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
Grew up as a Copywriter. Evolved into the Content creator. Somewhere in between, I fell in love with numbers that can portray the world as well as words or pictures. A naive thinker who believes that the creative economy is the most powerful force in the world!
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
Marketing Reporting: The KPIs, Reports, & Dashboard Templates You Need to Get Started

12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less
Latest from our blog
- Playmaker Spotlight: Kenneth Won, Technical Sales Consultant September 5, 2024
- Playbook #1: Building a Profitable Marketing Program (w/ Adam Goyette, Growth Union) September 5, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
- Marketing Mix Strategy
- Five Forces
- Business Lists
- Competitors
- Business Concepts
- Marketing and Strategy
Product Research
This article covers meaning, importance, stages & example of Product Research from marketing perspective.
What is Product Research?
Product research is the process of marketing research that is done to get information on the desired characteristics and specifications of a product expected by the potential customers mainly before the launch and availability of the product. Product research helps companies to understand what the customers really want, so that the product can be tailored to match the needs of the customer.
This research can help to refine new product ideas as well as improve the existing products in the market.
Importance of Product Research
Product research is a very important activity in new product development – it can be carried out at several stages of new product development. Product research helps an organization make products which are expected by the customers. This helps have an competitive advantage and leadership position in the market.
A well researched product will meet the requirements of the customer in a much better way. Product research even more important when you are launching a product in the market where there are lot of competitors. Knowing the customer's feedback on the features, characteristics can really help make a product which solves the existing products' issues in the market.
- Product Concept
- Production Concept
- Product Orientation
- Product Policy
- Product Quality
Product Research Stages
There are various stages in the product research process:
1. Before Launch Research
In the initial stages, product research can be carried out to identify and screen new ideas. This testing will help reduce costs by avoiding product development costs in the discarded ideas.
In the later stages of product development, product research can help companies to identify which features are important and hence retain them and which features can be discarded.
2. Testing and Feedback
A newly developed product is also tested with customers, to identify any changes to be made to packaging etc. Testing is very important when it comes to research. A well research but not well tested product may still end up failing. Testing can be done in-house or through actual customers through small groups, trials, offers etc.
3. Soft Launch Research
Most of the products are soft launched before being launched across the target markets. The soft launch is used for gathering feedback from potential customers and making changes in the product which can benefit. Test marketing is done for small groups or areas and the response is validated. If the soft launch is not a success, then a product need to go through the research stage again and may be relook at the product.
4. Post Launch Research
Once everything is done, the product is launched in the market. Even though test marketing is done but when it is launched for a larger population, things may go different. Hence it is very important to see an understand the customer behavior and response to the newly launched product or its variant. Once the product is launched, consumer satisfaction with the product is tested. Most common techniques used in product research include focus group discussions, interviews and surveys. Based on this feedback, next steps can be planned for the product.
Product Research Example
Many times we see that companies do test marketing for a new product through a promotion or an offer. They launch these products in small quantity in retail stores and see if the customers are liking it or buying. In trade events and exhibitions we see stalls for trying the product to gather feedback. All these activities are part of the product research.
Hence, this concludes the definition of Product Research along with its overview.
This article has been researched & authored by the Business Concepts Team which comprises of MBA students, management professionals, and industry experts. It has been reviewed & published by the MBA Skool Team . The content on MBA Skool has been created for educational & academic purpose only.
Browse the definition and meaning of more similar terms. The Management Dictionary covers over 1800 business concepts from 5 categories.
Continue Reading:
- Sales Management
- Market Segmentation
- Brand Equity
- Positioning
- Selling Concept
- Marketing & Strategy Terms
- Human Resources (HR) Terms
- Operations & SCM Terms
- IT & Systems Terms
- Statistics Terms
What is MBA Skool? About Us
MBA Skool is a Knowledge Resource for Management Students, Aspirants & Professionals.
Business Courses
- Operations & SCM
- Human Resources
Quizzes & Skills
- Management Quizzes
- Skills Tests
Quizzes test your expertise in business and Skill tests evaluate your management traits
Related Content
- Marketing Strategy
- Inventory Costs
- Sales Quota
- Quality Control
- Training and Development
- Capacity Management
- Work Life Balance
- More Definitions
All Business Sections
- SWOT Analysis
- Marketing Mix & Strategy
- PESTLE Analysis
- Five Forces Analysis
- Top Brand Lists
Write for Us
- Submit Content
- Privacy Policy
- Contribute Content
- Web Stories
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and Types
Table of Contents

Research Report
Definition:
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner.
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the findings of the research to the intended audience, which could be other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public.
Components of Research Report
Components of Research Report are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated. It should include a clear statement of the purpose of the study and its significance or relevance to the field of research. It may also provide background information or a literature review to help contextualize the research.
Literature Review
The literature review provides a critical analysis and synthesis of the existing research and scholarship relevant to the research question or problem. It should identify the gaps, inconsistencies, and contradictions in the literature and show how the current study addresses these issues. The literature review also establishes the theoretical framework or conceptual model that guides the research.
Methodology
The methodology section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used to collect and analyze data. It should include information on the sample or participants, data collection instruments, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques. The methodology should be clear and detailed enough to allow other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and objective manner. It should provide a detailed description of the data and statistics used to answer the research question or test the hypothesis. Tables, graphs, and figures may be included to help visualize the data and illustrate the key findings.
The discussion section interprets the results of the study and explains their significance or relevance to the research question or problem. It should also compare the current findings with those of previous studies and identify the implications for future research or practice. The discussion should be based on the results presented in the previous section and should avoid speculation or unfounded conclusions.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the study and restates the main argument or thesis presented in the introduction. It should also provide a brief overview of the contributions of the study to the field of research and the implications for practice or policy.
The references section lists all the sources cited in the research report, following a specific citation style, such as APA or MLA.
The appendices section includes any additional material, such as data tables, figures, or instruments used in the study, that could not be included in the main text due to space limitations.
Types of Research Report
Types of Research Report are as follows:
Thesis is a type of research report. A thesis is a long-form research document that presents the findings and conclusions of an original research study conducted by a student as part of a graduate or postgraduate program. It is typically written by a student pursuing a higher degree, such as a Master’s or Doctoral degree, although it can also be written by researchers or scholars in other fields.
Research Paper
Research paper is a type of research report. A research paper is a document that presents the results of a research study or investigation. Research papers can be written in a variety of fields, including science, social science, humanities, and business. They typically follow a standard format that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion sections.
Technical Report
A technical report is a detailed report that provides information about a specific technical or scientific problem or project. Technical reports are often used in engineering, science, and other technical fields to document research and development work.
Progress Report
A progress report provides an update on the progress of a research project or program over a specific period of time. Progress reports are typically used to communicate the status of a project to stakeholders, funders, or project managers.
Feasibility Report
A feasibility report assesses the feasibility of a proposed project or plan, providing an analysis of the potential risks, benefits, and costs associated with the project. Feasibility reports are often used in business, engineering, and other fields to determine the viability of a project before it is undertaken.
Field Report
A field report documents observations and findings from fieldwork, which is research conducted in the natural environment or setting. Field reports are often used in anthropology, ecology, and other social and natural sciences.
Experimental Report
An experimental report documents the results of a scientific experiment, including the hypothesis, methods, results, and conclusions. Experimental reports are often used in biology, chemistry, and other sciences to communicate the results of laboratory experiments.
Case Study Report
A case study report provides an in-depth analysis of a specific case or situation, often used in psychology, social work, and other fields to document and understand complex cases or phenomena.
Literature Review Report
A literature review report synthesizes and summarizes existing research on a specific topic, providing an overview of the current state of knowledge on the subject. Literature review reports are often used in social sciences, education, and other fields to identify gaps in the literature and guide future research.
Research Report Example
Following is a Research Report Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Academic Performance among High School Students
This study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students. The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The findings indicate that there is a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students. The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers, as they highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities.
Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of high school students. With the widespread use of social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Snapchat, students can connect with friends, share photos and videos, and engage in discussions on a range of topics. While social media offers many benefits, concerns have been raised about its impact on academic performance. Many studies have found a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance among high school students (Kirschner & Karpinski, 2010; Paul, Baker, & Cochran, 2012).
Given the growing importance of social media in the lives of high school students, it is important to investigate its impact on academic performance. This study aims to address this gap by examining the relationship between social media use and academic performance among high school students.
Methodology:
The study utilized a quantitative research design, which involved a survey questionnaire administered to a sample of 200 high school students. The questionnaire was developed based on previous studies and was designed to measure the frequency and duration of social media use, as well as academic performance.
The participants were selected using a convenience sampling technique, and the survey questionnaire was distributed in the classroom during regular school hours. The data collected were analyzed using descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
The findings indicate that the majority of high school students use social media platforms on a daily basis, with Facebook being the most popular platform. The results also show a negative correlation between social media use and academic performance, suggesting that excessive social media use can lead to poor academic performance among high school students.
Discussion:
The results of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. The negative correlation between social media use and academic performance suggests that strategies should be put in place to help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. For example, educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the negative impact of social media on academic performance among high school students. The findings highlight the need for strategies that can help students balance their social media use and academic responsibilities. Further research is needed to explore the specific mechanisms by which social media use affects academic performance and to develop effective strategies for addressing this issue.
Limitations:
One limitation of this study is the use of convenience sampling, which limits the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies should use random sampling techniques to increase the representativeness of the sample. Another limitation is the use of self-reported measures, which may be subject to social desirability bias. Future studies could use objective measures of social media use and academic performance, such as tracking software and school records.
Implications:
The findings of this study have important implications for educators, parents, and policymakers. Educators could incorporate social media into their teaching strategies to engage students and enhance learning. For example, teachers could use social media platforms to share relevant educational resources and facilitate online discussions. Parents could limit their children’s social media use and encourage them to prioritize their academic responsibilities. They could also engage in open communication with their children to understand their social media use and its impact on their academic performance. Policymakers could develop guidelines and policies to regulate social media use among high school students. For example, schools could implement social media policies that restrict access during class time and encourage responsible use.
References:
- Kirschner, P. A., & Karpinski, A. C. (2010). Facebook® and academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(6), 1237-1245.
- Paul, J. A., Baker, H. M., & Cochran, J. D. (2012). Effect of online social networking on student academic performance. Journal of the Research Center for Educational Technology, 8(1), 1-19.
- Pantic, I. (2014). Online social networking and mental health. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 17(10), 652-657.
- Rosen, L. D., Carrier, L. M., & Cheever, N. A. (2013). Facebook and texting made me do it: Media-induced task-switching while studying. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(3), 948-958.
Note*: Above mention, Example is just a sample for the students’ guide. Do not directly copy and paste as your College or University assignment. Kindly do some research and Write your own.
Applications of Research Report
Research reports have many applications, including:
- Communicating research findings: The primary application of a research report is to communicate the results of a study to other researchers, stakeholders, or the general public. The report serves as a way to share new knowledge, insights, and discoveries with others in the field.
- Informing policy and practice : Research reports can inform policy and practice by providing evidence-based recommendations for decision-makers. For example, a research report on the effectiveness of a new drug could inform regulatory agencies in their decision-making process.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research in a particular area. Other researchers may use the findings and methodology of a report to develop new research questions or to build on existing research.
- Evaluating programs and interventions : Research reports can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and interventions in achieving their intended outcomes. For example, a research report on a new educational program could provide evidence of its impact on student performance.
- Demonstrating impact : Research reports can be used to demonstrate the impact of research funding or to evaluate the success of research projects. By presenting the findings and outcomes of a study, research reports can show the value of research to funders and stakeholders.
- Enhancing professional development : Research reports can be used to enhance professional development by providing a source of information and learning for researchers and practitioners in a particular field. For example, a research report on a new teaching methodology could provide insights and ideas for educators to incorporate into their own practice.
How to write Research Report
Here are some steps you can follow to write a research report:
- Identify the research question: The first step in writing a research report is to identify your research question. This will help you focus your research and organize your findings.
- Conduct research : Once you have identified your research question, you will need to conduct research to gather relevant data and information. This can involve conducting experiments, reviewing literature, or analyzing data.
- Organize your findings: Once you have gathered all of your data, you will need to organize your findings in a way that is clear and understandable. This can involve creating tables, graphs, or charts to illustrate your results.
- Write the report: Once you have organized your findings, you can begin writing the report. Start with an introduction that provides background information and explains the purpose of your research. Next, provide a detailed description of your research methods and findings. Finally, summarize your results and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Proofread and edit: After you have written your report, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure that your report is well-organized and easy to read.
- Include a reference list: Be sure to include a list of references that you used in your research. This will give credit to your sources and allow readers to further explore the topic if they choose.
- Format your report: Finally, format your report according to the guidelines provided by your instructor or organization. This may include formatting requirements for headings, margins, fonts, and spacing.
Purpose of Research Report
The purpose of a research report is to communicate the results of a research study to a specific audience, such as peers in the same field, stakeholders, or the general public. The report provides a detailed description of the research methods, findings, and conclusions.
Some common purposes of a research report include:
- Sharing knowledge: A research report allows researchers to share their findings and knowledge with others in their field. This helps to advance the field and improve the understanding of a particular topic.
- Identifying trends: A research report can identify trends and patterns in data, which can help guide future research and inform decision-making.
- Addressing problems: A research report can provide insights into problems or issues and suggest solutions or recommendations for addressing them.
- Evaluating programs or interventions : A research report can evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions, which can inform decision-making about whether to continue, modify, or discontinue them.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies.
When to Write Research Report
A research report should be written after completing the research study. This includes collecting data, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions based on the findings. Once the research is complete, the report should be written in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
In academic settings, research reports are often required as part of coursework or as part of a thesis or dissertation. In this case, the report should be written according to the guidelines provided by the instructor or institution.
In other settings, such as in industry or government, research reports may be required to inform decision-making or to comply with regulatory requirements. In these cases, the report should be written as soon as possible after the research is completed in order to inform decision-making in a timely manner.
Overall, the timing of when to write a research report depends on the purpose of the research, the expectations of the audience, and any regulatory requirements that need to be met. However, it is important to complete the report in a timely manner while the information is still fresh in the researcher’s mind.
Characteristics of Research Report
There are several characteristics of a research report that distinguish it from other types of writing. These characteristics include:
- Objective: A research report should be written in an objective and unbiased manner. It should present the facts and findings of the research study without any personal opinions or biases.
- Systematic: A research report should be written in a systematic manner. It should follow a clear and logical structure, and the information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand and follow.
- Detailed: A research report should be detailed and comprehensive. It should provide a thorough description of the research methods, results, and conclusions.
- Accurate : A research report should be accurate and based on sound research methods. The findings and conclusions should be supported by data and evidence.
- Organized: A research report should be well-organized. It should include headings and subheadings to help the reader navigate the report and understand the main points.
- Clear and concise: A research report should be written in clear and concise language. The information should be presented in a way that is easy to understand, and unnecessary jargon should be avoided.
- Citations and references: A research report should include citations and references to support the findings and conclusions. This helps to give credit to other researchers and to provide readers with the opportunity to further explore the topic.
Advantages of Research Report
Research reports have several advantages, including:
- Communicating research findings: Research reports allow researchers to communicate their findings to a wider audience, including other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public. This helps to disseminate knowledge and advance the understanding of a particular topic.
- Providing evidence for decision-making : Research reports can provide evidence to inform decision-making, such as in the case of policy-making, program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes.
- Supporting further research: Research reports can provide a foundation for further research on a particular topic. Other researchers can build on the findings and conclusions of the report, which can lead to further discoveries and advancements in the field.
- Demonstrating expertise: Research reports can demonstrate the expertise of the researchers and their ability to conduct rigorous and high-quality research. This can be important for securing funding, promotions, and other professional opportunities.
- Meeting regulatory requirements: In some fields, research reports are required to meet regulatory requirements, such as in the case of drug trials or environmental impact studies. Producing a high-quality research report can help ensure compliance with these requirements.
Limitations of Research Report
Despite their advantages, research reports also have some limitations, including:
- Time-consuming: Conducting research and writing a report can be a time-consuming process, particularly for large-scale studies. This can limit the frequency and speed of producing research reports.
- Expensive: Conducting research and producing a report can be expensive, particularly for studies that require specialized equipment, personnel, or data. This can limit the scope and feasibility of some research studies.
- Limited generalizability: Research studies often focus on a specific population or context, which can limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations or contexts.
- Potential bias : Researchers may have biases or conflicts of interest that can influence the findings and conclusions of the research study. Additionally, participants may also have biases or may not be representative of the larger population, which can limit the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Accessibility: Research reports may be written in technical or academic language, which can limit their accessibility to a wider audience. Additionally, some research may be behind paywalls or require specialized access, which can limit the ability of others to read and use the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Chapter Summary & Overview – Writing Guide...

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example
Product Analysis: What it is and How to Conduct it
Picture this: You’re a product manager, standing at the crossroads of innovation and market demands. Your team has poured countless hours into developing a product you believe in, but user adoption isn’t quite where you’d hoped. Sound familiar? You’re not alone. In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, creating a successful product feels like solving a constantly shifting puzzle.
Enter product analysis - your compass in this complex terrain. It’s not just about crunching numbers or following trends; it’s about truly understanding your users, your market, and your product’s place in it all. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or new to the game, mastering product analysis can be the difference between a product that fizzles out and one that revolutionizes the market. Ready to unlock the secrets of effective product analysis? Let’s dive in.
What is Product Analysis?
Product analysis is a comprehensive evaluation process that assists teams in understanding how users interact with their product or service. It involves evaluating features, functionality, and performance to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This process is crucial for product development, enabling teams to make informed, data-driven decisions to optimize their offerings and enhance user experience. By understanding user behavior and preferences, organizations can tailor their products more effectively to meet market demands and maintain a competitive edge.
Why Product Analysis Matters
Understanding the importance of product analysis is vital for any organization aiming to succeed in today’s fast-paced market. First and foremost, it helps teams comprehend customer behavior, which is paramount for creating products that meet user needs and expectations. Additionally, product analysis supports the optimization of product features and functionality based on real-time data, improving customer satisfaction and retention rates. Furthermore, it provides a foundation for competitive benchmarking, allowing businesses to identify market gaps and strategize effectively. Data-driven insights gained from product analysis empower teams to make continuous improvements, ultimately leading to a more robust and competitive product offering.
This guide will cover various aspects of mastering product analysis, including steps to conducting effective analysis, types of product analysis, methods, and frameworks. We will also delve into leveraging customer feedback, market analysis, competitive strategies, and the best tools available for product analysis. By following this comprehensive guide, teams and organizations can enhance their product development processes, leading to more successful and user-centric products.
Importance of Product Analysis
Product analysis serves as the backbone for any thriving product strategy. It offers profound insights into customer behavior, preferences, and market trends, enabling teams to make informed decisions. By unraveling these patterns, organizations can maintain a competitive edge and ensure customer satisfaction.
Understanding Customer Behavior
Grasping how customers interact with your product is paramount. Product analysis illuminates their preferences, pinpointing what works and what needs improvement. This understanding guides the development process to align with user expectations, enhancing the overall experience.
Data-Driven Improvements
With product analysis, data becomes your ally. By leveraging metrics like customer engagement, retention rates, and feature adoption, teams can optimize product features and performance. This data-centric approach not only elevates the product but also drives strategic decision-making within the organization, promoting sustained success.
Ultimately, product analysis is indispensable for supporting competitive benchmarking and market positioning. It empowers teams to identify strengths, mitigate weaknesses, and capitalize on market opportunities. When combined with collective insights from varied methodologies, product analysis fosters innovation and ensures that the product remains relevant and competitive in the dynamic market landscape.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting a Product Analysis
Product analysis is a crucial process for businesses aiming to stay competitive and innovative in today’s dynamic market landscape. By thoroughly examining your product’s features, performance, and market position, you can make informed decisions to drive growth and success. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps of conducting an effective product analysis.
1. Set Clear Objectives and KPIs
Setting clear objectives and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) is the foundation of any successful product analysis. This step ensures that your analysis has a focused direction and measurable outcomes. By defining what you want to achieve, you create a roadmap for the entire process and establish benchmarks for success.
Begin your product analysis journey by defining clear, specific objectives. Ask yourself:
- Ready to use
- Fully customizable template
- Get Started in seconds

What are we trying to achieve with this analysis?
Are we looking to improve user experience?
Do we want to identify market gaps?
Is our goal to enhance specific features?
Once you’ve established your objectives, set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that align with these goals. KPIs will help you measure the success of your analysis and subsequent actions. Some examples of relevant KPIs include:
User engagement rates
Customer satisfaction scores
Feature adoption rates
Conversion rates
Churn rates
Pro tip: Use the SMART criteria (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) when setting your KPIs to ensure they’re effective and actionable.
2. Know Your Product and How Users Interact with It
A deep understanding of your product and its usage patterns is essential for meaningful analysis. This knowledge forms the basis for identifying areas of improvement and innovation. By examining how users interact with your product, you can uncover valuable insights that may not be apparent from looking at the product in isolation.
Develop a deep understanding of your product’s core functionalities and how users interact with it. This step involves:
Conducting a comprehensive review of your product’s features and capabilities.
Analyzing user behavior data from product analytics tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, or Amplitude.
Creating user journey maps to visualize how customers navigate through your product.
Identifying the most and least used features of your product.
Pinpointing any usability issues or friction points in the user experience.
This step will provide valuable insights into which aspects of your product are performing well and which areas need improvement.
3. Evaluate User Experiences
User experience is at the heart of product success. By systematically evaluating how users perceive and interact with your product, you gain invaluable insights that can drive improvements and innovations. This step helps you see your product through the eyes of your customers, uncovering both pain points and delights.
Gathering and analyzing user feedback is crucial for understanding the real-world impact of your product. Implement a multi-faceted approach to collect both qualitative and quantitative data:
Surveys: Use tools like SurveyMonkey or Typeform to create and distribute surveys to your user base.
Interviews: Conduct one-on-one interviews or focus groups with a diverse set of users to gain in-depth insights.
User Testing: Employ usability testing tools to observe how users interact with your product in real-time.
Sentiment Analysis: Utilize natural language processing tools to analyze customer reviews, social media mentions, and support tickets for overall sentiment.
Net Promoter Score (NPS): Implement NPS surveys to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction.
By combining these methods, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of user needs, pain points, and overall satisfaction with your product.
4. Perform Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis provides crucial context for your product in the broader market landscape. By understanding how your product compares to competitors, you can identify unique selling points, areas for improvement, and potential market opportunities. This step helps ensure that your product not only meets user needs but also stands out in a crowded marketplace.
A thorough competitive analysis helps you understand your product’s position in the market and identify opportunities for differentiation. Follow these steps:
Identify your main competitors, including direct and indirect competitors.
Create a comparison matrix of features, pricing, and target markets.
Analyze competitors' strengths and weaknesses.
Identify gaps in the market that your product could potentially fill.
Evaluate competitors' marketing strategies and brand positioning.
Conduct a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis for your product and top competitors.
5. Analyze Product Performance Metrics
Quantitative data provides an objective view of your product’s performance. By analyzing key metrics, you can identify trends, validate or challenge assumptions, and make data-driven decisions. This step helps you move beyond anecdotal evidence to understand how your product is truly performing in various dimensions.
Dive deep into your product’s performance metrics to gain quantitative insights:
Usage Metrics: Analyze daily/monthly active users, session duration, and feature adoption rates.
Financial Metrics: Examine revenue per user, customer acquisition cost, and lifetime value.
Technical Metrics: Evaluate load times, uptime, and error rates.
Support Metrics: Analyze ticket volume, resolution time, and common issues reported.
Use data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI to create dashboards that make it easy to spot trends and patterns in your product’s performance.
6. Synthesize Insights and Develop Action Plans
This step is where analysis turns into action. By synthesizing insights from all previous steps, you can develop a cohesive understanding of your product’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities. This holistic view allows you to create targeted, effective action plans that address the most critical areas for improvement and innovation.
Consolidate all the data and insights gathered in the previous steps:
Identify key themes and patterns across different data sources.
Prioritize areas for improvement based on impact and feasibility.
Develop concrete action plans for addressing identified issues and capitalizing on opportunities.
Create a roadmap for implementing changes, including timelines and resource allocation.
7. Optimize and Monitor
Implementation and monitoring are crucial for turning insights into tangible improvements. This step ensures that your analysis leads to real-world changes and allows you to track the impact of these changes over time. Continuous monitoring helps you stay agile and responsive to evolving user needs and market conditions.
Based on your action plans:
Implement new features or improvements to existing ones.
Resolve any identified usability issues or technical problems.
Adjust your marketing and positioning strategy if necessary.
Set up a system for continuous monitoring of KPIs and user feedback.
Establish regular check-ins to assess the impact of changes and make further adjustments as needed.
8. Communicate Insights to Different Teams
Effective communication ensures that insights from your product analysis don’t remain siloed but are instead leveraged across the organization. By sharing findings with different teams, you foster a culture of data-driven decision-making and align everyone towards common product goals. This collaborative approach can lead to more innovative solutions and a more cohesive product strategy.
Effective product analysis requires collaboration across various departments. Ensure insights are shared widely:
Create concise, visually appealing reports summarizing key findings and recommendations.
Hold cross-functional meetings to present insights and discuss implications.
Use collaboration tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams to maintain ongoing communication about product performance and user feedback.
Establish a central repository (e.g., a wiki or shared drive) where all teams can access analysis results and related documents.
9. Iterate and Repeat
Product analysis is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Markets evolve, user needs change, and new technologies emerge. By embracing an iterative approach to product analysis, you ensure that your product remains relevant, competitive, and aligned with user needs over time. This step emphasizes the importance of adaptability and continuous improvement in product development.
Product analysis is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Plan to:
Conduct regular (e.g., quarterly) in-depth analyses to track progress and identify new opportunities.
Stay updated on market trends and emerging technologies that could impact your product.
Continuously gather user feedback and monitor performance metrics.
Be prepared to pivot or make significant changes based on new insights or market shifts.
By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to conduct thorough product analyses that drive meaningful improvements and keep your product competitive in the market. Remember, the key to success is maintaining a data-driven, user-centric approach and being willing to adapt based on the insights you uncover.
Methods of Product Analysis
Trend analysis.
Trend analysis is a crucial component of product analysis, focused on identifying patterns and forecasting future trends. By studying historical data, companies can predict market changes, enabling them to stay ahead of competition and better meet customer demands. Utilizing tools like Creately for visualizing trends can simplify this process. Understanding trends helps businesses refine their product strategies, ensuring long-term success.
Competitive Product Analysis
Competitive product analysis is essential for benchmarking against competitors. This type of analysis evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of competitors' products, helping identify opportunities for differentiation. By leveraging tools such as Competitive Analysis Templates teams can systematically compare features, pricing, and customer feedback. This information is invaluable for strategic positioning and enhancing market presence.
Journey Analysis
Journey analysis maps user experiences and touchpoints from awareness to purchase. This method offers insights into how customers interact with a product, identifying pain points and areas for improvement. Utilizing journey mapping tools can facilitate a deeper understanding of the customer experience, leading to more targeted enhancements and increased customer satisfaction.
Cohort Analysis
Cohort analysis groups customers based on shared characteristics or behaviors, allowing for a more refined understanding of customer behavior over time. By tracking these groups, businesses can uncover trends related to user retention and engagement. This method is particularly effective for identifying ways to increase loyalty and long-term engagement, ensuring sustained product use and satisfaction.
Retention Analysis
Retention analysis measures how often customers return to a product and provides insights into user loyalty. For subscription-based models, retention is a critical metric. By analyzing churn rates and identifying reasons for customer attrition, businesses can make informed decisions to improve customer retention. Tools like attribution analysis link feature usage to customer success, ensuring ongoing product relevance and satisfaction.
Together, these types of product analysis provide a comprehensive view of a product’s performance, strengths, and areas for improvement. Utilizing these methods effectively can lead to a more data-driven, customer-focused approach, enhancing overall product strategy and execution.
Methods and Frameworks for Product Analysis
Swot analysis.
SWOT Analysis is a time-tested framework that helps teams evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to a product. By systematically examining these elements, teams can create effective strategies to enhance product features, address shortcomings, and capitalize on market opportunities. To dive deeper into how to perform a SWOT analysis and leverage it for product enhancement, check out the SWOT Analysis guide.
The KJ Method, also known as the affinity diagram technique, is essential for organizing extensive qualitative data into meaningful categories. This method is particularly useful when synthesizing customer feedback or brainstorming sessions. By grouping related themes, teams can identify prevalent patterns and focus on critical aspects that need attention.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment Analysis is a methodological approach that gauges customer opinions by assigning emotional responses—positive, neutral, or negative—to feedback. This technique is instrumental in highlighting customer sentiments about product features, enabling teams to understand the emotional impact of their offerings. Consequently, businesses can make data-driven adjustments to improve customer satisfaction.
Attribution Analysis
Attribution Analysis delves into identifying the specific touchpoints and actions that contribute to customer success and feature usage. It involves mapping out the journey customers take and pinpointing the interactions that have the most significant impact on their behavior. This analysis helps product managers allocate resources effectively and enhance the features that drive success.
Churn Analysis
Churn Analysis focuses on understanding why customers stop using a product. By identifying the factors leading to churn, businesses can implement targeted interventions to improve customer retention. It often involves segmenting users by behavior and satisfaction levels to tailor retention strategies effectively.
How to Optimizing Products Based on Analysis
Iterating product features.
One of the primary goals of product analysis is to enable continuous improvement of product features. By leveraging data-driven insights, teams can identify which features are underperforming and iterate upon them to enhance functionality and user satisfaction. Journey analysis greatly aids in understanding where users face friction, allowing for targeted improvements that streamline user experiences.
Enhancing User Experience
Improving user experience (UX) is another critical aspect of optimizing products. Using competitive product analysis and journey analysis, teams can pinpoint touchpoints where users may drop off. By addressing these pain points, products can become more intuitive and engaging, leading to higher retention and satisfaction rates.
Incorporating Feedback for Continuous Improvement
Customer feedback is a treasure trove of insights that can significantly influence product optimization. Real-time feedback mechanisms, such as surveys, reviews, and direct user interviews, provide actionable data on what users like and dislike. Incorporating this feedback helps in fine-tuning the product to better align with user expectations and market demands.
Monitor and Adjust Strategies for Sustained Success
Product optimization is not a one-time task but a continuous process. By regularly monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) and user engagement metrics, teams can adjust their strategies to stay aligned with evolving user needs and competitive landscapes. Strategic decisions informed by data analysis ensure that the product remains relevant and successful in the long term.
As we look to the future, the importance of product analysis will only grow. With advancements in artificial intelligence and big data analytics, businesses will have access to even more sophisticated tools and methodologies. Those who master the art and science of product analysis will be well-positioned to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape, creating products that not only meet but exceed customer expectations, driving growth and long-term success.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
FAQs on Product Analysis
How do you create an effective product analysis, what are the primary aims of product analysis.
The primary aims of product analysis are to:
- Identify areas for product improvement
- Understand customer needs and preferences
- Assess market positioning and competitiveness
- Inform pricing strategies
- Guide product development and innovation
- Support marketing and sales efforts
- Maximize product profitability and longevity in the market
What is the difference between product analysis and market analysis?
How frequently should product analysis be conducted.
The frequency of product analysis depends on various factors, including the product’s lifecycle stage, market volatility, and competitive landscape. Generally, it’s recommended to conduct:
- Continuous monitoring of key performance indicators
- Quarterly reviews for established products
- Monthly or bi-monthly analysis for new product launches
- Ad-hoc analysis in response to significant market changes or emerging competitors
- Regular analysis helps businesses stay agile and responsive to changing market conditions and customer needs.
More Related Articles

Chiraag George is a communication specialist here at Creately. He is a marketing junkie that is fascinated by how brands occupy consumer mind space. A lover of all things tech, he writes a lot about the intersection of technology, branding and culture at large.
Ad-free. Influence-free. Powered by consumers.
The payment for your account couldn't be processed or you've canceled your account with us.
We don’t recognize that sign in. Your username maybe be your email address. Passwords are 6-20 characters with at least one number and letter.
We still don’t recognize that sign in. Retrieve your username. Reset your password.
Forgot your username or password ?
Don’t have an account?
- Account Settings
- My Benefits
- My Products
- Donate Donate
Save products you love, products you own and much more!
Other Membership Benefits:
Suggested Searches
- Become a Member
Car Ratings & Reviews
2024 Top Picks
Car Buying & Pricing
Which Car Brands Make the Best Vehicles?
Tires, Maintenance & Repair
Car Reliability Guide
Key Topics & News
Listen to the Talking Cars Podcast
Home & Garden
Bed & Bath
Top Picks From CR
Best Mattresses
Lawn & Garden
TOP PICKS FROM CR
Best Leaf Blowers
Home Improvement
Home Improvement Essential
Best Wood Stains
Home Safety & Security
HOME SAFETY
Best DIY Home Security Systems
SURVEY RESULTS
Most and Least Reliable Refrigerators
Small Appliances
Best Small Kitchen Appliances
Laundry & Cleaning
Best Washing Machines
Heating, Cooling & Air
Best Air Purifiers
Electronics
Home Entertainment
FIND YOUR NEW TV
Home Office
Cheapest Printers for Ink Costs
Smartphones & Wearables
BEST SMARTPHONES
Find the Right Phone for You
Digital Security & Privacy
MEMBER BENEFIT
CR Security Planner
Take Action
- Research & Testing
Our consumer product and service testing center, in Westchester, New York, is the largest nonprofit educational and consumer product testing center in the world. And our 327-acre auto test center is the world’s largest and most sophisticated independent automobile testing center devoted to consumer interests.
Data is the basis for virtually all the work that Consumer Reports does. To provide scientific analysis to our testing teams, our investigative reporters, and our policy advocates, we have teams and tools to inform us about industry trends and product categories. We’re able to combine CR members’ feedback with search engine trends and technical data from government, academia, and industry to find the connecting threads underneath the numbers. These insights ensure that our tests reflect how consumers actually use a product, that our testimony to a government panel is fact-based and supportable, and that we can plan for the products we’ll need to purchase in the future to do our work.
Buying, Testing, and Rating
We buy and test thousands of products every year to generate reviews and ratings to help consumers, support our investigative journalism and trusted consumer guidance, and advocate for consumer-friendly marketplace practices. Before any product even enters one of the dozens of labs at our Westchester, NY headquarters, CR conducts considerable research — gathering data about products and services, consumer demand in the marketplace, and what our members care about most. Editorial, technical, and research staff then scrutinize that material, along with suggestions from our members, to develop our testing protocols and schedule.
After additional research to define any testing project’s scope, staff shoppers or one of our anonymous “secret shoppers” buy the products we use as test samples — in fact, some products, like house paint and food, can vary by climate or region, and because we need to make sure our tests reflect a national consumer experience, we purchase products from across the country. Our shoppers pay full retail and purchase all the products we test to generate our ratings from the same places consumers do; we accept no sample products for testing. And as a nonprofit organization that accepts no advertising, to pay for all this shopping we rely mostly on our millions of members and the hundreds of thousands of donors who support our work. For example, in the coming fiscal year, we expect to spend more than $30 million to test, rate, and review 10,000+ products and services.
We have more than 130 testing and research experts who work in our home, cars, technology, product safety, statistics, survey research, food safety, health ratings and market research teams.
Our experts use only state-of-the-art testing equipment, along with some equipment designed by our engineers — since the actual tests are based not only on government and industry standards but also on standards our specialists develop to recreate the experience you’ll have with the product. Sometimes our test methods become part of an industry’s standards. And sometimes individual companies will work to improve their own competitive advantage by meeting our testing standards for everyday-use cases in their own quality assurance departments.
Learn more about CR’s Ethical Considerations on Products and Services
Product Owner Surveys
Consumer Reports’ product ratings are unique in that they combine product performance, measured through expert lab testing, with predicted reliability and owner satisfaction data gathered through surveys of product owners. The latter two measures are based on consumers’ real-world experiences with products they have purchased and reflect consumers’ use of products over time. By combining lab performance testing with data based on the experiences of hundreds of thousands of real consumers, Consumer Reports ratings give consumers the most complete information on what they can expect from each product.
Data on product reliability and owner satisfaction is gathered through regular surveys of Consumer Reports members. In these surveys, respondents answer questions about the products they own—in that way, Consumer Reports members are true partners in our product rating process! Survey questions typically include how long the respondent has owned a particular product, how often they use it, whether it has broken or stopped working as well as it should, what types of problems the product has had, and whether they would recommend the product to someone else. We also ask survey participants to tell us in their own words what they do and do not like about the product they own and to describe in more detail any problems they may have experienced.
In a typical year we invite roughly 3 million Consumer Reports members to participate in our online product surveys, and gather product reliability and satisfaction data in up to 40 product categories. Our expert team of survey methodologists and data analysts use that data to calculate the predicted reliability and owner satisfaction scores you see for each brand in a specific product category. Our surveys are a powerful and unique tool, enabling us to gather data from a large enough sample of consumers to be able to rate specific brands across a large number of product categories.
As with all the research and testing Consumer Reports does, our surveys are designed to gather unbiased, objective information from consumers and our analyses are conducted free of any corporate or industry influence. Read here for more about how our member surveys are conducted and how the resulting data is used to calculate product reliability and owner satisfaction for all product categories other than autos. A description of how reliability is calculated for autos can be found here .
National Surveys
In addition to conducting surveys with members, Consumer Reports has a robust and rigorous national survey program that tracks American consumers’ attitudes, perceptions and behaviors over time. Our national surveys use gold standard research methodology to produce data that is representative of the US adult population. We invest in large sample sizes, and include Spanish translation and Asian-American oversampling to ensure we can identify diversity in consumer experiences across key demographics such as age, gender, income, and racial/ethnic identity. Our national survey program is committed to understanding and measuring the full range of experiences and issues faced by US consumers. We use those insights to inform our content and testing, shape advocacy efforts, and develop products and services that best meet the needs of today’s consumers.
Consumer Reports currently fields a monthly, nationally representative omnibus survey, the results of which are available on Consumer Reports.org and are also available on request. In addition, in a typical year our expert national survey team conducts a dozen or more special topic surveys on timely consumer issues. Consumer Reports is a proud member of The Roper Center for Public Opinion Research, and toplines from our national surveys can be found in the Roper Center database. Our national survey team adheres to the American Association of Public Opinion Researchers ’ Code of Ethics and are active members of the professional survey research community.
Learn more about Consumer Reports’ survey work .
Data Intelligence
The digital marketplace is more complex and connected than ever before. Technology and the rapid pace of innovation are creating new challenges for consumers, different from those they confronted in 1936 when CR was founded. CR is compelled to meet these challenges head-on. We are unleashing the power of consumer-driven insights to fuel change and innovation, and developing new ways to shape the marketplace in favor of consumers.
CR Data Intelligence is a new marketplace change program. The goal: to foster the development of products, standards, and policies that prioritize safety, security, performance, and quality for consumers. We call it “upstream impact”—improving products and services before they get to market.
For over 80 years CR has helped consumers to make better choices. Now we can contribute to making the products themselves better.
How CR Data Intelligence Works
CR independently tests thousands of products and services in our labs each year and surveys hundreds of thousands of consumers about their experiences with products and services. Personal data from this research is not shared. We decide which products to rate and buy all the products at retail, just as consumers do. We rely on this data to power our unbiased ratings and reviews for consumers.
CR Data Intelligence offers subscriptions to data and insights from CR’s rigorous and trusted research, testing, and surveys to industry experts, including manufacturers, regulators, and researchers. As with all our programs, products, and services, 100 percent of the fees we collect support our nonprofit mission .
Instant insights, infinite possibilities
Research report guide: Definition, types, and tips
Last updated
5 March 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
From successful product launches or software releases to planning major business decisions, research reports serve many vital functions. They can summarize evidence and deliver insights and recommendations to save companies time and resources. They can reveal the most value-adding actions a company should take.
However, poorly constructed reports can have the opposite effect! Taking the time to learn established research-reporting rules and approaches will equip you with in-demand skills. You’ll be able to capture and communicate information applicable to numerous situations and industries, adding another string to your resume bow.
- What are research reports?
A research report is a collection of contextual data, gathered through organized research, that provides new insights into a particular challenge (which, for this article, is business-related). Research reports are a time-tested method for distilling large amounts of data into a narrow band of focus.
Their effectiveness often hinges on whether the report provides:
Strong, well-researched evidence
Comprehensive analysis
Well-considered conclusions and recommendations
Though the topic possibilities are endless, an effective research report keeps a laser-like focus on the specific questions or objectives the researcher believes are key to achieving success. Many research reports begin as research proposals, which usually include the need for a report to capture the findings of the study and recommend a course of action.
A description of the research method used, e.g., qualitative, quantitative, or other
Statistical analysis
Causal (or explanatory) research (i.e., research identifying relationships between two variables)
Inductive research, also known as ‘theory-building’
Deductive research, such as that used to test theories
Action research, where the research is actively used to drive change
- Importance of a research report
Research reports can unify and direct a company's focus toward the most appropriate strategic action. Of course, spending resources on a report takes up some of the company's human and financial resources. Choosing when a report is called for is a matter of judgment and experience.
Some development models used heavily in the engineering world, such as Waterfall development, are notorious for over-relying on research reports. With Waterfall development, there is a linear progression through each step of a project, and each stage is precisely documented and reported on before moving to the next.
The pace of the business world is faster than the speed at which your authors can produce and disseminate reports. So how do companies strike the right balance between creating and acting on research reports?
The answer lies, again, in the report's defined objectives. By paring down your most pressing interests and those of your stakeholders, your research and reporting skills will be the lenses that keep your company's priorities in constant focus.
Honing your company's primary objectives can save significant amounts of time and align research and reporting efforts with ever-greater precision.
Some examples of well-designed research objectives are:
Proving whether or not a product or service meets customer expectations
Demonstrating the value of a service, product, or business process to your stakeholders and investors
Improving business decision-making when faced with a lack of time or other constraints
Clarifying the relationship between a critical cause and effect for problematic business processes
Prioritizing the development of a backlog of products or product features
Comparing business or production strategies
Evaluating past decisions and predicting future outcomes
- Features of a research report
Research reports generally require a research design phase, where the report author(s) determine the most important elements the report must contain.
Just as there are various kinds of research, there are many types of reports.
Here are the standard elements of almost any research-reporting format:
Report summary. A broad but comprehensive overview of what readers will learn in the full report. Summaries are usually no more than one or two paragraphs and address all key elements of the report. Think of the key takeaways your primary stakeholders will want to know if they don’t have time to read the full document.
Introduction. Include a brief background of the topic, the type of research, and the research sample. Consider the primary goal of the report, who is most affected, and how far along the company is in meeting its objectives.
Methods. A description of how the researcher carried out data collection, analysis, and final interpretations of the data. Include the reasons for choosing a particular method. The methods section should strike a balance between clearly presenting the approach taken to gather data and discussing how it is designed to achieve the report's objectives.
Data analysis. This section contains interpretations that lead readers through the results relevant to the report's thesis. If there were unexpected results, include here a discussion on why that might be. Charts, calculations, statistics, and other supporting information also belong here (or, if lengthy, as an appendix). This should be the most detailed section of the research report, with references for further study. Present the information in a logical order, whether chronologically or in order of importance to the report's objectives.
Conclusion. This should be written with sound reasoning, often containing useful recommendations. The conclusion must be backed by a continuous thread of logic throughout the report.
- How to write a research paper
With a clear outline and robust pool of research, a research paper can start to write itself, but what's a good way to start a research report?
Research report examples are often the quickest way to gain inspiration for your report. Look for the types of research reports most relevant to your industry and consider which makes the most sense for your data and goals.
The research report outline will help you organize the elements of your report. One of the most time-tested report outlines is the IMRaD structure:
Introduction
...and Discussion
Pay close attention to the most well-established research reporting format in your industry, and consider your tone and language from your audience's perspective. Learn the key terms inside and out; incorrect jargon could easily harm the perceived authority of your research paper.
Along with a foundation in high-quality research and razor-sharp analysis, the most effective research reports will also demonstrate well-developed:
Internal logic
Narrative flow
Conclusions and recommendations
Readability, striking a balance between simple phrasing and technical insight
How to gather research data for your report
The validity of research data is critical. Because the research phase usually occurs well before the writing phase, you normally have plenty of time to vet your data.
However, research reports could involve ongoing research, where report authors (sometimes the researchers themselves) write portions of the report alongside ongoing research.
One such research-report example would be an R&D department that knows its primary stakeholders are eager to learn about a lengthy work in progress and any potentially important outcomes.
However you choose to manage the research and reporting, your data must meet robust quality standards before you can rely on it. Vet any research with the following questions in mind:
Does it use statistically valid analysis methods?
Do the researchers clearly explain their research, analysis, and sampling methods?
Did the researchers provide any caveats or advice on how to interpret their data?
Have you gathered the data yourself or were you in close contact with those who did?
Is the source biased?
Usually, flawed research methods become more apparent the further you get through a research report.
It's perfectly natural for good research to raise new questions, but the reader should have no uncertainty about what the data represents. There should be no doubt about matters such as:
Whether the sampling or analysis methods were based on sound and consistent logic
What the research samples are and where they came from
The accuracy of any statistical functions or equations
Validation of testing and measuring processes
When does a report require design validation?
A robust design validation process is often a gold standard in highly technical research reports. Design validation ensures the objects of a study are measured accurately, which lends more weight to your report and makes it valuable to more specialized industries.
Product development and engineering projects are the most common research-report examples that typically involve a design validation process. Depending on the scope and complexity of your research, you might face additional steps to validate your data and research procedures.
If you’re including design validation in the report (or report proposal), explain and justify your data-collection processes. Good design validation builds greater trust in a research report and lends more weight to its conclusions.
Choosing the right analysis method
Just as the quality of your report depends on properly validated research, a useful conclusion requires the most contextually relevant analysis method. This means comparing different statistical methods and choosing the one that makes the most sense for your research.
Most broadly, research analysis comes down to quantitative or qualitative methods (respectively: measurable by a number vs subjectively qualified values). There are also mixed research methods, which bridge the need for merging hard data with qualified assessments and still reach a cohesive set of conclusions.
Some of the most common analysis methods in research reports include:
Significance testing (aka hypothesis analysis), which compares test and control groups to determine how likely the data was the result of random chance.
Regression analysis , to establish relationships between variables, control for extraneous variables , and support correlation analysis.
Correlation analysis (aka bivariate testing), a method to identify and determine the strength of linear relationships between variables. It’s effective for detecting patterns from complex data, but care must be exercised to not confuse correlation with causation.
With any analysis method, it's important to justify which method you chose in the report. You should also provide estimates of the statistical accuracy (e.g., the p-value or confidence level of quantifiable data) of any data analysis.
This requires a commitment to the report's primary aim. For instance, this may be achieving a certain level of customer satisfaction by analyzing the cause and effect of changes to how service is delivered. Even better, use statistical analysis to calculate which change is most positively correlated with improved levels of customer satisfaction.
- Tips for writing research reports
There's endless good advice for writing effective research reports, and it almost all depends on the subjective aims of the people behind the report. Due to the wide variety of research reports, the best tips will be unique to each author's purpose.
Consider the following research report tips in any order, and take note of the ones most relevant to you:
No matter how in depth or detailed your report might be, provide a well-considered, succinct summary. At the very least, give your readers a quick and effective way to get up to speed.
Pare down your target audience (e.g., other researchers, employees, laypersons, etc.), and adjust your voice for their background knowledge and interest levels
For all but the most open-ended research, clarify your objectives, both for yourself and within the report.
Leverage your team members’ talents to fill in any knowledge gaps you might have. Your team is only as good as the sum of its parts.
Justify why your research proposal’s topic will endure long enough to derive value from the finished report.
Consolidate all research and analysis functions onto a single user-friendly platform. There's no reason to settle for less than developer-grade tools suitable for non-developers.
What's the format of a research report?
The research-reporting format is how the report is structured—a framework the authors use to organize their data, conclusions, arguments, and recommendations. The format heavily determines how the report's outline develops, because the format dictates the overall structure and order of information (based on the report's goals and research objectives).
What's the purpose of a research-report outline?
A good report outline gives form and substance to the report's objectives, presenting the results in a readable, engaging way. For any research-report format, the outline should create momentum along a chain of logic that builds up to a conclusion or interpretation.
What's the difference between a research essay and a research report?
There are several key differences between research reports and essays:
Research report:
Ordered into separate sections
More commercial in nature
Often includes infographics
Heavily descriptive
More self-referential
Usually provides recommendations
Research essay
Does not rely on research report formatting
More academically minded
Normally text-only
Less detailed
Omits discussion of methods
Usually non-prescriptive
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Reports: Definition and How to Write Them

Reports are usually spread across a vast horizon of topics but are focused on communicating information about a particular topic and a niche target market. The primary motive of research reports is to convey integral details about a study for marketers to consider while designing new strategies.
Certain events, facts, and other information based on incidents need to be relayed to the people in charge, and creating research reports is the most effective communication tool. Ideal research reports are extremely accurate in the offered information with a clear objective and conclusion. These reports should have a clean and structured format to relay information effectively.
What are Research Reports?
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods .
A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony of all the work done to garner specificities of research.
The various sections of a research report are:
- Background/Introduction
- Implemented Methods
- Results based on Analysis
- Deliberation
Learn more: Quantitative Research
Components of Research Reports
Research is imperative for launching a new product/service or a new feature. The markets today are extremely volatile and competitive due to new entrants every day who may or may not provide effective products. An organization needs to make the right decisions at the right time to be relevant in such a market with updated products that suffice customer demands.
The details of a research report may change with the purpose of research but the main components of a report will remain constant. The research approach of the market researcher also influences the style of writing reports. Here are seven main components of a productive research report:
- Research Report Summary: The entire objective along with the overview of research are to be included in a summary which is a couple of paragraphs in length. All the multiple components of the research are explained in brief under the report summary. It should be interesting enough to capture all the key elements of the report.
- Research Introduction: There always is a primary goal that the researcher is trying to achieve through a report. In the introduction section, he/she can cover answers related to this goal and establish a thesis which will be included to strive and answer it in detail. This section should answer an integral question: “What is the current situation of the goal?”. After the research design was conducted, did the organization conclude the goal successfully or they are still a work in progress – provide such details in the introduction part of the research report.
- Research Methodology: This is the most important section of the report where all the important information lies. The readers can gain data for the topic along with analyzing the quality of provided content and the research can also be approved by other market researchers . Thus, this section needs to be highly informative with each aspect of research discussed in detail. Information needs to be expressed in chronological order according to its priority and importance. Researchers should include references in case they gained information from existing techniques.
- Research Results: A short description of the results along with calculations conducted to achieve the goal will form this section of results. Usually, the exposition after data analysis is carried out in the discussion part of the report.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
- Research Discussion: The results are discussed in extreme detail in this section along with a comparative analysis of reports that could probably exist in the same domain. Any abnormality uncovered during research will be deliberated in the discussion section. While writing research reports, the researcher will have to connect the dots on how the results will be applicable in the real world.
- Research References and Conclusion: Conclude all the research findings along with mentioning each and every author, article or any content piece from where references were taken.
Learn more: Qualitative Observation
15 Tips for Writing Research Reports
Writing research reports in the manner can lead to all the efforts going down the drain. Here are 15 tips for writing impactful research reports:
- Prepare the context before starting to write and start from the basics: This was always taught to us in school – be well-prepared before taking a plunge into new topics. The order of survey questions might not be the ideal or most effective order for writing research reports. The idea is to start with a broader topic and work towards a more specific one and focus on a conclusion or support, which a research should support with the facts. The most difficult thing to do in reporting, without a doubt is to start. Start with the title, the introduction, then document the first discoveries and continue from that. Once the marketers have the information well documented, they can write a general conclusion.
- Keep the target audience in mind while selecting a format that is clear, logical and obvious to them: Will the research reports be presented to decision makers or other researchers? What are the general perceptions around that topic? This requires more care and diligence. A researcher will need a significant amount of information to start writing the research report. Be consistent with the wording, the numbering of the annexes and so on. Follow the approved format of the company for the delivery of research reports and demonstrate the integrity of the project with the objectives of the company.
- Have a clear research objective: A researcher should read the entire proposal again, and make sure that the data they provide contributes to the objectives that were raised from the beginning. Remember that speculations are for conversations, not for research reports, if a researcher speculates, they directly question their own research.
- Establish a working model: Each study must have an internal logic, which will have to be established in the report and in the evidence. The researchers’ worst nightmare is to be required to write research reports and realize that key questions were not included.
Learn more: Quantitative Observation
- Gather all the information about the research topic. Who are the competitors of our customers? Talk to other researchers who have studied the subject of research, know the language of the industry. Misuse of the terms can discourage the readers of research reports from reading further.
- Read aloud while writing. While reading the report, if the researcher hears something inappropriate, for example, if they stumble over the words when reading them, surely the reader will too. If the researcher can’t put an idea in a single sentence, then it is very long and they must change it so that the idea is clear to everyone.
- Check grammar and spelling. Without a doubt, good practices help to understand the report. Use verbs in the present tense. Consider using the present tense, which makes the results sound more immediate. Find new words and other ways of saying things. Have fun with the language whenever possible.
- Discuss only the discoveries that are significant. If some data are not really significant, do not mention them. Remember that not everything is truly important or essential within research reports.
Learn more: Qualitative Data
- Try and stick to the survey questions. For example, do not say that the people surveyed “were worried” about an research issue , when there are different degrees of concern.
- The graphs must be clear enough so that they understand themselves. Do not let graphs lead the reader to make mistakes: give them a title, include the indications, the size of the sample, and the correct wording of the question.
- Be clear with messages. A researcher should always write every section of the report with an accuracy of details and language.
- Be creative with titles – Particularly in segmentation studies choose names “that give life to research”. Such names can survive for a long time after the initial investigation.
- Create an effective conclusion: The conclusion in the research reports is the most difficult to write, but it is an incredible opportunity to excel. Make a precise summary. Sometimes it helps to start the conclusion with something specific, then it describes the most important part of the study, and finally, it provides the implications of the conclusions.
- Get a couple more pair of eyes to read the report. Writers have trouble detecting their own mistakes. But they are responsible for what is presented. Ensure it has been approved by colleagues or friends before sending the find draft out.
Learn more: Market Research and Analysis
MORE LIKE THIS

Experimental vs Observational Studies: Differences & Examples
Sep 5, 2024
Interactive Forms: Key Features, Benefits, Uses + Design Tips
Sep 4, 2024

Closed-Loop Management: The Key to Customer Centricity
Sep 3, 2024

Net Trust Score: Tool for Measuring Trust in Organization
Sep 2, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
What are the best practices for writing a business report

Writing an effective business report requires careful planning, clear organization, and attention to detail. Here are the key best practices to follow;
Define the Purpose and Audience
- Identify the report’s objective: What decision or action should result from this report?
- Understand your audience: Who will read the report? What is their level of knowledge on the subject?
- Tailor the content, tone, and level of detail to your audience’s needs and expectations.
Plan and Structure Your Report
- When you start writing, make an outline to help you arrange your ideas and guarantee a logical flow.
- Use a standard structure that typically includes: a. Title Page b. Table of Contents (for longer reports) c. Executive Summary d. Introduction e. Body (main content, divided into sections) f. Conclusion g. Recommendations h. Appendices (if necessary)
Write a Compelling Executive Summary
- Summarize the key points, findings, and recommendations in 1-2 pages.
- Make it stand-alone: readers should understand the main ideas without reading the full report.
- Write this section last, after you’ve completed the rest of the report.
Craft a Clear Introduction
- State the report’s purpose and scope.
- Provide necessary background information.
- Outline the report’s structure to guide the reader.
Develop the Body of the Report
- Organize information logically, using headings and subheadings.
- Present one main idea per paragraph, with supporting details.
- Use transitions between sections to maintain flow and coherence.
Support Your Points with Data and Evidence
- Include relevant data, statistics, and research findings.
- Use visual aids like charts, graphs, and tables to present complex information.
- Cite all sources properly to maintain credibility.
Write Concisely and Professionally
- Use clear, concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary for your audience.
- Write in a formal, objective tone.
Conclude with Impact and Provide Actionable Recommendations
- Summarize the key findings in the conclusion.
- Provide clear, specific, and actionable recommendations based on your analysis.
- Ensure recommendations are realistic and aligned with the report’s purpose.
Format for Readability
- Use consistent formatting throughout the report (fonts, spacing, headings).
- Include plenty of white space to avoid overwhelming the reader.
- Use bullet points or numbered lists for easy scanning of key information.
Review and Refine
- Proofread carefully for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Check that all figures, tables, and page numbers are correct and consistent.
- Have a colleague review the report for clarity and effectiveness.
Consider the Presentation
- If presenting the report in person, prepare a summary of key points.
- Be ready to answer questions and provide additional context.
- Consider creating a slide deck or handout for important data or recommendations.
What key elements should be included in the introduction of a business report?
The introduction of a business report sets the stage for the entire document. It should provide a clear and concise overview of the report’s purpose, scope, and key findings. Here are the essential elements to include;
Purpose Statement
- Clearly state the reason for writing the report.
- What is the main objective?
- What problem is it trying to solve or question is it seeking to answer?
- Define the boundaries of the report.
- What topics are included, and what are excluded?
- Indicate the time period covered or the specific area of focus.
Methodology
- Briefly describe the research methods or data collection techniques used.
- This can include surveys, interviews, case studies, or data analysis.
- Specify the constraints or difficulties encountered while conducting the research.
Key Findings
- Provide a brief summary of the most significant results or conclusions.
- This will give the reader a preview of what to expect in the subsequent sections.
Organization
- Outline the structure of the report.
- Indicate the major sections and subsections that will follow.
Example Introduction: This report aims to evaluate the effectiveness of our new marketing campaign launched in Q2. We conducted a survey of 1,000 customers to gather feedback on brand awareness, product satisfaction, and purchase behavior. The key findings reveal a significant increase in brand recognition and a positive correlation between customer satisfaction and repeat purchases. The report is organized into four main sections: campaign overview, survey results, customer analysis, and recommendations.
How can the purpose and scope of the business report be defined?
The purpose and scope of a business report are crucial for ensuring that the document is focused, relevant, and valuable. Here are some effective strategies to define these elements;
Understand the Target Audience
- Who will be reading the report? Identify their needs, interests, and level of expertise.
- What do they want to know? Consider their specific questions or concerns.
Identify the Problem or Question
- What is the issue or challenge you are addressing? Clearly articulate the problem or question the report aims to solve.
- What is the desired outcome? Define the goals or objectives you hope to achieve.
Set Clear Boundaries
- What topics are included? Determine the specific areas of focus for the report.
- What topics are excluded? Define the limitations or boundaries of the research.
- Consider timeframes or geographic locations. Specify the relevant time period or regions.
Align with Business Goals
- How does the report contribute to the overall business strategy? Ensure that the purpose and scope align with the company’s objectives.
Consult with Stakeholders
- Gather input from relevant individuals or departments. Involve those who have a vested interest in the topic.
- Ensure alignment and consensus. Work together to refine the purpose and scope.
Create a Clear Statement
- Write a concise and informative statement. Communicate the purpose and scope of the report.
- Use specific language and avoid ambiguity. Be precise in your definitions.
Example: This report aims to evaluate the effectiveness of our new marketing campaign launched in Q2. The scope of the report will include an analysis of brand awareness, website traffic, and sales data from the targeted demographic. The objective is to determine whether the campaign has met its goals and identify areas for improvement.
What are the best practices for organizing the structure and sections of a business report?
A well-organized business report enhances its readability, comprehensibility, and effectiveness. Here are some best practices for structuring your report;
Logical Flow
- Follow a clear progression of ideas. Ensure that the sections build upon each other and lead to a logical conclusion.
- Make use of headers and subtitles. To help the reader explore the report.
Consistent Structure
- Maintain a consistent format. Use a standard outline or template for all sections.
- Use parallel structure for headings and subheadings to improve clarity.
Clear Introduction and Conclusion
- The introduction should provide a clear overview of the report’s purpose, scope, and key findings.
- The conclusion should summarize the main points, reiterate the key findings, and provide recommendations or next steps.
Well-Defined Sections
- Use clear and concise section headings. Make sure they accurately reflect the content of the section.
- Ensure each section has a clear purpose. Each section should contribute to the overall goal of the report.
Supporting Evidence
- Provide evidence to support your claims. Use data, statistics, quotes, or examples to strengthen your arguments.
- Cite your sources appropriately. Give credit to the original authors or researchers.
Visual Aids
- Use visual aids like charts, graphs, or diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement.
- Ensure visual aids are clear, well-labeled, and relevant to the content.
Concise and Clear Writing
- Use clear and concise language. Steer clear of technical phrases and jargon that could mislead the reader.
- Write in a professional and objective tone. Maintain a neutral perspective.
Proofread and Edit
- Carefully proofread your report for errors. Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation mistakes.
- Edit for clarity and coherence. Make sure your concepts are coherent and simple to understand.
Example Outline
Introduction
- Purpose of the report
- Scope and methodology
- Key findings
Background and Context
- Relevant industry trends
- Company overview
Data Analysis
- Key metrics and results
- Visual representations (charts, graphs)
Discussion and Findings
- Interpretation of data
- Insights and implications
Recommendations
- Suggested actions or strategies
- Future directions
- Summary of key points
- Reiteration of findings
- Final thoughts
How should data and research be effectively presented in the report?
Data and research are essential components of a business report. They provide credibility, support claims, and inform decision-making. Here are some effective strategies for presenting data and research;
Clarity and Conciseness
- Present data. Avoid overwhelming the reader with excessive detail.
- Use simple language and avoid technical jargon. Make the data accessible to a wide audience.
- Utilize visual aids like charts, graphs, and tables to enhance understanding and engagement.
- Choose the appropriate visual representation for the type of data you are presenting.
- Ensure visual aids are clear, well-labeled, and easy to interpret.
Contextualize Data
- Explain the significance of the data. Connect it to the overall purpose and objectives of the report.
- Provide context by comparing data to benchmarks, industry standards, or historical trends.
Highlight Key Findings
- Identify the most important or relevant data points. Focus on the key takeaways that support your conclusions.
- Use clear and concise statements to summarize the findings.
Cite Sources
- Give credit to the original sources of your data and research. This demonstrates credibility and trustworthiness.
- Use a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) to maintain consistency throughout the report.
Address Limitations
- Recognize any restrictions or biases in the information or study. This demonstrates transparency and critical thinking.
- Explain how these limitations may affect the validity of your conclusions.
Integrate Data with Narrative
- Weave data and research seamlessly into your narrative. Make use of it to strengthen your claims and provide examples.
- Avoid presenting data in isolation. Connect it to the broader context of the report.
Tailor Presentation to Audience
- Consider the needs and interests of your audience. Adjust the level of detail and complexity accordingly.
- Make sure your examples and phrasing speak to your audience.
What techniques can be used to ensure clarity and conciseness in business report writing?
Clarity and conciseness are essential qualities for effective business reports. Here are some techniques to help you achieve these goals;
Use Simple Language
- Use clear and straightforward language that is easy to understand.
Be Specific
- Provide concrete details and examples to support your claims.
- Avoid vague or general statements that may leave the reader unsure of your meaning.
Use Active Voice
- Active voice improves the clarity and engagement of your work.
- Avoid passive voice whenever possible.
Keep Sentences Short
- Break up long sentences into shorter ones.
- Avoid complex sentence structures that can be difficult to follow.
Use Strong Verbs
- Choose strong verbs that convey your meaning clearly and concisely.
- Avoid weak verbs like “is,” “are,” and “have.”
Eliminate Redundancy
- Remove unnecessary words and phrases that do not add value to your writing.
- Avoid repeating the same information in different ways.
Use Headings and Subheadings
- Divide your report into clear sections using headings and subheadings.
- This will improve readability and make it easier for readers to find the necessary information.
Use Visual Aids
- Charts, graphs, and diagrams can help to clarify complex information.
- Use visual aids sparingly and ensure they are relevant to your content.
- Check your report for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Read your report aloud to identify any awkward or unclear passages.
How important is the use of visual aids like charts, graphs, and tables in a business report?
Visual aids are crucial in a business report. They serve several essential functions;
- Enhance Understanding: They can simplify complex data, making it easier to grasp and digest.
- Improve Engagement: Visuals can make the report more interesting and engaging, keeping readers interested.
- Support Claims: They can provide concrete evidence to support claims and arguments.
- Save Space: They can often convey information more efficiently than text alone.
- Make Data More Accessible: Visuals can make data more accessible to a wider audience, including those who may struggle with text-heavy content.
When using visual aids, it’s important to;
- Choose the appropriate type of visual: Different types of visuals are better suited for different types of data.
- Ensure clarity and accuracy: The visual should be clear, easy to understand, and accurately represent the data.
- Label and annotate properly: Provide clear labels and annotations to explain the visual.
- Integrate with the text: Reference the visual in the text to explain its relevance.
What is the recommended approach for writing the executive summary of a business report?
Crafting a compelling executive summary is crucial for a business report**.** It should provide a concise and informative overview of the entire document. Here’s a recommended approach;
Write the Executive Summary Last: While it’s the first section readers will see, it’s often easier to write it after you’ve completed the main body of the report. This ensures it accurately reflects the key points and conclusions.
Keep it Concise: The executive summary should be a brief overview, typically no more than one page. Aim for a length that can be read quickly.
Include Essential Elements
- Purpose: Clearly state the reason for writing the report.
- Key Findings: Summarize the most important results or conclusions.
- Recommendations: If applicable, outline the suggested actions or strategies.
- Scope: Briefly touch on the topics covered and the methodology used.
Use Clear and Concise Language: Avoid jargon or technical terms that might confuse readers unfamiliar with the subject matter. Use simple, direct language.
Follow a Logical Flow: Ensure the executive summary follows a logical progression, leading the reader from the purpose to the key findings and recommendations.
Make it Standalone The executive summary should be self-sufficient. Readers should be able to understand the main points of the report without reading the entire document.
Review: The executive summary is often the first part of the report a reader will see. Make sure it displays a professional image.
Example: This report evaluates the effectiveness of our new marketing campaign launched in Q2. Key findings include a significant increase in brand awareness and a positive correlation between customer satisfaction and repeat purchases. We recommend continuing the campaign and exploring additional channels to reach a wider audience.
How should conclusions and recommendations be formulated in a business report?
The conclusions and recommendations sections of a business report are crucial for summarizing your findings and providing actionable insights. Here are some tips on how to formulate these sections;
Conclusions
- Summarize Key Findings: Restate the most important findings or results from your research.
- Relate Findings to Purpose: Connect your conclusions back to the original purpose of the report.
- Avoid New Information: Don’t introduce any new data or arguments in the conclusions.
- Be Actionable: Ensure your recommendations are specific, practical, and implementable.
- Align with Findings: Recommendations should be directly based on your conclusions and research.
- Prioritize Recommendations: If you have multiple recommendations, prioritize them based on their importance or feasibility.
- Consider Implications: Discuss the potential implications of implementing your recommendations.
- Our analysis revealed a significant increase in website traffic following the launch of our new marketing campaign.
- Customer satisfaction surveys indicated a positive response to the new product features.
- Sales data showed a modest increase in revenue compared to the previous quarter.
- Continue investing in digital marketing efforts to maintain website traffic and engagement.
- Consider expanding the product line to capitalize on the positive customer feedback.
- Monitor sales data closely to identify trends and optimize marketing strategies.
Additional Tips
- Be Clear and Concise: Use clear and concise language to express your conclusions and recommendations.
- Avoid Overstated Claims: Be cautious about making overly broad or sweeping statements.
- Consider the Audience: Tailor your conclusions and recommendations to the specific needs and interests of your audience.
- Review: Check for any spelling or typos.
What are the best practices for proofreading and editing a business report before submission?
Proofreading and editing are essential steps in ensuring the quality and professionalism of your business report. Here are some best practices to follow;
Take a Break
- Step away from the report for a period of time to gain a fresh perspective.
- Return to it with a clear mind to catch errors you may have overlooked.
- Read the report aloud to identify awkward phrasing or grammatical errors.
- This can help you catch inconsistencies or areas that don’t flow smoothly.
Check for Clarity and Conciseness
- Ensure your writing is clear and easy to understand. Avoid jargon or overly complex language.
- Eliminate any unnecessary words or phrases to make your report more concise.
Verify Facts and Figures
- Double-check all data, statistics, and citations. Ensure they are accurate and up-to-date.
- Verify sources to maintain credibility.
Check for Consistency
- Maintain consistency in formatting, style, and terminology throughout the report.
- Use a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) if applicable.
Look for Errors
- Review for mistakes.
- Use a spell checker and grammar checker as tools, but don’t rely solely on them.
Get a Second Opinion
- Ask a colleague or friend to review your report.
- A fresh pair of eyes can help identify errors you may have missed.
Use a Proofreading Checklist
- Create a checklist of common errors to help you stay focused during the proofreading process.
Consider Professional Editing
- If you’re unsure about your editing skills, consider hiring a professional editor.
- A professional can help ensure your report is polished and error-free.
How can a business report be tailored to meet the specific needs and expectations of its intended audience?
To tailor a business report for a specific audience, you need to carefully consider who they are, what interests them, and the report’s goal. Here’s how you can do this;
Know Your Audience
- Identify Who They Are: Find out if the audience includes senior management, clients, investors, or a particular department.
- Gauge Their Knowledge: Understand how familiar they are with the topic. Use technical terms if they’re experts, or keep things simple if they’re not.
- Understand Their Priorities: Focus on what’s most important to them, like financial performance, strategic advice, or operational details.
Clarify the Report’s Purpose
- Define the Goal: Be clear on why you’re writing the report. Is it to inform, persuade, analyze, or recommend?
- Highlight Key Points: Emphasize the information that matches the audience’s interests and the report’s goal.
Structure the Report Effectively
- Organize Logically: Arrange the content in a logical order for the audience, like starting with a summary for busy executives.
- Use Headings: Break the report into sections with clear headings, making it easier to navigate.
Choose the Right Tone and Language
- Match the Tone: Use a formal tone for senior management or clients, and a casual tone for internal teams if needed.
- Avoid Jargon: If the audience isn’t familiar with technical terms, explain them or avoid using them.
Include Relevant Data and Visuals
- Focus on Important Data: Provide data that supports your main points and is relevant to the audience.
- Use Visuals: Add charts, graphs, and tables to make complex data easier to understand and to highlight key points.
Provide Clear Recommendations and Conclusions
- Actionable Advice: Tailor recommendations to what the audience can do with the information.
- Summarize Findings: Keep conclusions brief and ensure they align with what the audience expects.
Review and Revise
- Get Feedback: If possible, get input from someone who understands the audience to make sure the report meets their needs.
- Edit for Clarity: Make sure the report is clear, concise, and free of unnecessary details that could confuse the reader.
Consider the Presentation Format
- Select the Right Format: Depending on the audience, decide if the report should be a written document, a slide deck, or an interactive format.
- Highlight Key Points: In a presentation, use bullet points and bold text to emphasize important information.
The impact of technology on Language Evolution
Strategies for effective proofreading and editing
The ethics of Artificial Intelligence
The impact of culture on language learning
Crafting engaging dialogue in fiction
The influence of native language on second language acquisition
- Product Reviews
Welcome back to ProductReportCard
We've updated our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. By continuing to use this site, you are agreeing to these new Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
We have sent an email with a link to reset your password.
MORE high-paying surveys and FREE product tests than anywhere else
Join now and enjoy over 400 surveys— all with payouts of $0.50 – $500.00— plus an average of 32 free product tests every month ., companies want to pay for your opinion and productreportcard makes it simple. see examples below:, get paid today — create your free account.
Complete your account for instant matching with the highest-paying surveys you qualify for.
For most, takes less than 1 minute

Companies selling these products, and many more, want to pay for your opinion:

Join Today for a chance to win

Dream Car Sweepstakes
Share your opinion and earn rewards. Plus, you could win your dream car!
Get an entry into our Dream Car Sweepstakes just by joining Product Report Card now. And earn additional entries for each surveys you take, with no limit! Choose between a Ford Mustang, F-150 or Expedition.
Terms and Conditions apply.
Watch Our 2022 Winner
See Cheryl's reaction when we surprised her with her winnings! Dreams really come true and they can for you, too! But you need to start taking surveys to have chance, so log in and start taking surveys right now.
Sweepstakes FAQs
Login | Sign Up
3 simple steps to earn your first $5 instantly
Get your free account.
Answer a couple of easy questions such as, "Do you have pets?" - and enter your email address. This takes less than a minute.
Take a SHORT 5-Minute Survey
This survey helps us match you with paid surveys and at-home product test opportunities. The more info you provide, the more we will match you with!
Earn Your REWARD
Your first $5 reward is waiting for you!
Since 2012, we’ve worked with over 200 companies and run more than 18,500 paid surveys.

Footwear Survey

Grocery Survey

Moms Survey

Oral Care Survey

Retail Shopping Survey

Lifestyle Survey

Smartphone App Review

Webcam Focus Group from Home

Health & Wellness Zoom Focus Group

Healthcare Survey

Webcam Interview

TV Viewing Habits

Diaper In Home Test
$10 + Free Diapers

At-Home Taste Test
$35 + Free Food

Household Entertainment Survey

Political Poll

Consumer Opinion

Beverage Opinion Survey

Travel and Leisure Survey

Eczema Clinical Trial

Migraine Clinical Trial

Crohn’s Disease Clinical Trial

Watch a TV show
60m (mostly the show)

Automotive Features Survey

Alcoholic Beverage Survey

Parents Survey

Retail Shopping

Oculus VR Game Test
45m (mostly gaming)

At Home Product Test

Two New Foods Taste Test
$2.50 + Free Food

Financial Services Discussion

Food & Beverage Focus Group from Home

Zoom Webcam Interview

Bath Product At-Home Test

Online Focus Group

$25 + Free Food

In Store Shopping Mission
Over 2.4 million people like you have made $14.1 million dollars sharing their opinions with ProductReportCard. Read about their experiences below.
Love this company! It allows me to earn gift cards by participating in surveys and product reviews. I just used a $25 gift card to Amazon thanks to ProductReportCard.
Daisy, Richlands, VA
I was skeptical after completing the survey, as it was pretty involved. The company followed through and sent the gift card pretty quickly. Great experience.
Janelle, Surprise, AZ
I have been a member for several years. Interesting surveys. There are times you get to try products and let manufactures know what you think. Honest company.
Joyce, Needville, TX
I just recently started using ProductReportCard and I have already cashed out a $25 amazon gift card. I have reviewed several products. It’s fun and simple!
Andrea, Rochester, NY
ProductReportCard is a great platform to share your opinions on many different topics and also sample products. They offer good incentives and super-fast redemption.
JJ, Rio Grande City, TX
It really works. I've been taking reviews and have deposited about $150 so far. I also have received products for free to test. Great to do in your free time!
Romina, Clifton, NJ
I did some in-home tests of products which was a lot of fun and was paid promptly for my time. Just be honest with them and you will be treated fairly and honestly.
Robert, Tarpon Springs, FL
I enjoy being a member of ProductReportCard. It is quite fun, very enjoyable and truly educational. I look forward to many more surveys. Keep up the good work.
Mitchell, Houston, TX
I have been a member for quite awhile now! They give you great products to try for your honest review and give compensation on top of it! Great quality site!
Misty, Bucyrus, OH
I love ProductReportCard!! They are a great company and are definitely on the up and up. I have gotten some great product tests through them and they always pay out!!!
Donna, Tocca, GA
I love ProductReportCard! I recommend it anyone and everyone! Their surveys are interesting and not too long. Thank you guys for finally making a REAL website for surveys.
Alicia, Liberty, TX
This was remarkably easy and satisfying. I earned credit every day, ranging from a dime to several dollars, and I felt my opinion counted! Now, to spend the reward.
Jules, Long Beach, CA
ProductReportCard provides interesting surveys along with good rewards for participating. Answer as many or as few as you like, whenever it is convenient.
David, Brooklyn, NY
Logged into my account last evening to redeem my Amazon gift card. Followed prompts. Finalized my gift card request! Next day received my digital gift. Ready to do a little buying.
Ronald, Jamestown, NC
Totally awesome. Thanks for the Amazon gift card!! It will definitely be a great help to me. And doing the product trials and surveys was a fun activity to earn such a useful reward.
Jill, Henderson, NV
This is a really great survey site. I cashed out for a Amazon gift card and the next day it was processed and delivered to my e-mail which was really great.
Jimmy, Hamilton, OH
ProductReportCard provides a wide variety of quality survey opportunities that are fun and interesting. The rewards provided are appropriate for the participation effort involved.
Nadya, Fountain Hills, AZ
I did a review for a product and was told I would receive an Amazon gift card. Completely forgot about it and got my gift card today. They are exactly what they say they are!
Staci, Hampton, VA
I love taking surveys and sharing my opinion about products, stores, restaurants, and services. Sometimes I even get to test products at home. I get paid for all activities!
Steve, Boynton Beach, FL
I’m not able to participate as often as I would like to, but when I do I find it a valuable experience and I enjoy earning points so I can save up for something.
Suzanne, Delmar, NY
Super-nice owners and employees plus interesting surveys and focus groups! I've been a member about 18 months now and have been totally happy with ProductReportCard.
Mark, Littleton, CO
This is a great way to take surveys and make extra cash. They do what they say and it is very easy to navigate and they do not overload your inbox with unnecessary mail.
Christy, Magee, MS
I've been using ProductReportCard for a year now. They're trustworthy and have never sent me any misleading or inappropriate offers, and they pay for your opinions!
Austin, Austin, TX
I have very enjoyable experiences with each survey. ProductReportCard tries it's best to fit me with the ideal survey EVERY TIME and the monetary amounts per survey are lucrative.
Donald, South Lake Tahoe, CA
While it may take a while to get to the minimum amount you need to cash out, this is a reliable panel. They don’t overwhelm your inbox and you get to test products. I like it.
Terri, Yucca Valley, CA
Absolutely love this… it is honestly extra pocket cash for anyone who is willing to do some surveys and sometimes even product testing… fun and entertaining!
Margaret, Port Ewen, NY
Great company to work with. Interesting surveys, product tests, and special projects to be involved with. Great panelist services as well. Highly recommended.
Ann, Sevierville, NC
I have always had a pleasant experience in doing the surveys and while doing the in-home test products. The customer service there is spot on! I love them!
Melanie, Stoneville, NC
I've had excellent experiences with ProductReportCard - many surveys, which pay out a small amount if you disqualify, as well as testing some products. Highly recommended. Worth it!
Caroline, Grandview, TX
As an online member to several other survey groups I can honestly say that I have earned the most with ProductReportCard and honestly enjoy taking their surveys.
Rebecca, Clearbrook, VA
I love ProductReportCard! The surveys always very informative and easy to access! Everything is all laid out in simple easy to read formats! Keep up the good work!
Carl, Atlanta, GA
They are very easy to work with and I never have any issues. Cashing out your rewards is very easy and painless. I would recommend to anyone this website.
Andrea, Fairview, NC
Excellent support and tech support teams for you if needed. One of the most honest, trustworthy, and hands down - in my opinion - the best survey provider for cash available online.
Richard, Deming, NM
Easy website to use, you earn even when you don’t qualify. Quick payments and good opportunities. I just wish more surveys paid more. But I’ve had no problem with the company.
Carolina, Meridan, CT
Great site not only do they have well paying surveys but also the products you get to review are state of the art type products. And you get paid to do it. BIG THUMBS UP!!
Robert, Haverhill, MA
Cashed out for my $25 Amazon gift card. Easy to do and quick turn around. Said it could take up to 10 days to process and receive my card. Took less than 3 days.
Kevin, Van Wert, OH
I redeemed my cash for a Amazon gift card- it arrived very quickly (within 2 days). I have always trusted Product Report Card as they have always been honest with me.
Steven, Friendship, WI
This company has impressed. I would hate to give a 5 star after limited use. This first product focus group I did was definitely 5 stars. Quick payment, like I couldn't believe how quick.
Jason, Selah, WA
Great surveys and they actually work. They offer good product tests if you make the grade. No issues with them and they do pay you once you reach the redeem payout.
Jackie, New York, NY
I got my first $30 Amazon Gift Card today! It took about two days to come. The only issue I have is I would recommend earning more if you do not get qualified to take a survey.
Selena, Giddings, TX
Here are some of the most common questions that users have asked before joining.
What is product report card.
Product Report Card connects users like you who wish to make money online and test free products with companies who need your opinions. We make it easy for you to tell companies how you really feel about their products and services and earn while doing it. We offer you the opportunity to participate in online surveys, in-home product testing, focus groups, in-depth interviews, and more!
How is my information used?
Your survey responses are recorded separately and without your personal identifiable information. For example, when you share responses to survey questions asking for your opinions, we connect these with the general information that you provide, like gender, age, and income – and NOT your name, email address, phone number, etc.
Why should I become a member?
Your opinions matter. It’s insights from people like you that influence the decisions big brands make when coming out with new – or improving upon existing – products and services. Additionally, you are paid for every opinion you share.
How soon can I start earning rewards?
Today! You start getting paid from the very first survey you take. When you complete or attempt a survey, your reward amount will automatically and immediately appear in your account.
How long does it take to get paid?
Every day, we invite you to participate in paid surveys. The more surveys you take, the more rewards you earn. Once you accumulate $25.00 in rewards, you can redeem your rewards for an Amazon Gift Code!
Some product tests, phone interviews, or shop-a-long studies that pay $100 – $500 will be sent to you via VISA gift card or check.
How much can I reasonably expect to make?
Because you earn rewards for every survey you take – whether you qualify for it or not – there’s no limit to how much you can earn.
How do I redeem the awards in my account?
When you reach the $25.00 minimum payout threshold, just click the redeem button. Within 3 business days from redemption, we will send you your Amazon Gift Code via email. Some product tests, phone interviews, or shop-a-long studies that pay $100 – $500 will be sent to you via VISA gift card or check.
How do I qualify for surveys?
The information in your ProductReportCard profile is used to see if you’re suitable for a particular survey. – so you’ll be offered more surveys, the more complete your profile is. However, some surveys need to know more and use ‘screener’ questions at the start to confirm you qualify. Don’t worry, even if you don’t qualify, you’ll still earn a $0.10 reward. And remember: you will qualify for many more.
Will I get to try out products?
You’re quite likely to be asked to take surveys which include product testing.
The most common products members are asked to test include VR games, wearable technology, hygienic-products, FOOD, drinks and pet supplies. You can be paid to do a taste test right at home!
Joining ProductReportCard is Easy and risk-free – Create your account now to start receiving paid surveys immediately
Your account details are used to match you with surveys you’re guaranteed to qualify for.
Create your account today and enjoy:
- Making money online today
- Instant access to relevant paid research surveys
- Opportunity to test products at home
- Track your rewards from your customized dashboard
… and much more.
Once complete, your account will identify the highest-paying surveys which match your profile.

U.S. Government Accountability Office
Small Business Research Programs: Opportunities Exist for SBA and Agencies to Reduce Vulnerabilities to Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
Federal agencies awarded small businesses more than $4.4 billion in FY 2022 for research and development and to commercialize technologies. The Small Business Administration oversees the programs making these awards, which are carried out by 11 agencies.
We analyzed past award data to identify awardees' foreign ownership, business size, and other indicators of fraud, waste, or abuse. We found, for example:
Almost 8% of awardees in our review had four or more indicators
$445 million worth of awards may have funded duplicative work
Our recommendations to SBA and 2 other agencies are to help improve their fraud risk management and more.

What GAO Found
GAO's analysis of 37 fraud schemes targeting the Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs demonstrates control vulnerabilities and fraud risks with a range of financial and other impacts. These schemes often involved multiple participating agencies and programs. For example, 25 schemes involved awards from more than one agency, and 14 involved both SBIR and STTR awards. GAO identified approximately $34.7 million in civil settlements associated with these schemes. Fraudsters' diversion of funds affects the programs' economic stimulus goals and makes funds unavailable to eligible businesses. It can also result in prison time, financial penalties, and loss of employment for those involved in the schemes.
In addition to its Policy Directive guidance, the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) uses several tools, including its monthly program manager meetings, annual survey to participating agencies, and listing of fraud convictions and civil liabilities on SBIR.gov, to monitor and support agencies' fraud, waste, and abuse prevention efforts. However, GAO identified opportunities for SBA to better leverage these tools. For example, some agencies were unaware of the requirement to report fraud convictions and civil liabilities for listing on SBIR.gov, limiting the site's usefulness as an information source and fraud deterrent.
Most agencies did not conduct SBIR/STTR fraud risk assessments in alignment with GAO's leading practices and identified lack of guidance, training, and resources as related challenges. Through its guidance and other tools, SBA is in a position to reinforce fraud risk assessment requirements for agencies, in support of Policy Directive goals for fraud, waste, and abuse prevention.
GAO's analysis of SBIR.gov award data from fiscal years 2016 through 2021 identified thousands of awardees with one or more fraud, waste, or abuse risk indicator. Among the 10,570 awardees in this period, 842 were associated with four or more such indicators. GAO designed 27 analytic tests for (1) applicant eligibility, including foreign ownership, business size, essentially equivalent work, research facility address; and (2) other fraud, waste, or abuse risks, such as having prior criminal or civil actions. Data quality issues in SBIR.gov, such as incomplete project summaries, may impede agencies' full use of analytics for managing these risks. By improving the data through guidance and verification, SBA can support agencies' risk management activities.
Awardees by Number of Fraud, Waste, or Abuse Risk Indicators Identified in Analytic Tests

Why GAO Did This Study
Since the inception of the programs, federal agencies have invested over $68 billion in SBIR/STTR awards for research and development and to commercialize technologies. SBA oversees the programs, which are carried out by 11 participating agencies. In response to the Small Business Act, as amended, the SBA established 10 minimum requirements for participating agencies to prevent fraud, waste, and abuse. The act also includes a provision that GAO report to Congress every 4 years on agencies' and their Offices of Inspector General (OIG) efforts related to fraud, waste, and abuse in the programs.
This GAO report, its fourth, assesses (1) SBIR/STTR fraud schemes from fiscal years 2016 through 2023 and participants and impacts; (2) SBA and agency antifraud activities against fraud, waste, and abuse requirements; (3) agency fraud risk assessments against leading practices; and (4) applicant and award data to identify fraud, waste, and abuse vulnerabilities.
GAO reviewed documentation from SBA and the 11 participating agencies and OIGs; analyzed criminal, civil, and administrative actions; compared SBA and agencies' processes against leading practices; conducted data matching to identify potentially ineligible awardees for fiscal years 2016 through 2021; and interviewed SBA, agency, and OIG officials.
Recommendations
GAO is making eight recommendations, including six to SBA to provide agencies with guidance to support their fraud risk management. The agencies generally agreed with the recommendations.
Recommendations for Executive Action
| Recommendation | ||
|---|---|---|
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation expands the methods and sources used to identify fraud-related convictions and findings of civil liability to list in the SBA's database, such as through alerts from legal research resources. (Recommendation 1) | |
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation leverages its oversight mechanisms to identify, share, and report fraud-related convictions and findings of civil liability to SBIR.gov and address participating agencies' challenges in understanding and meeting the 15-day reporting requirement. (Recommendation 2) | |
| Department of Agriculture | The Secretary of the U.S. Department of Agriculture should ensure that the Director of the National Institute of Food and Agriculture ensures that USDA SBIR/STTR applicants receive fraud, waste, and abuse training. (Recommendation 3) | |
| Department of Defense | The Secretary of Defense should ensure that the DOD Office of the Under Secretary of Defense for Research and Engineering SBIR/STTR Program ensures that DOD SBIR/STTR subcomponent program officials receive fraud, waste, and abuse training. (Recommendation 4) | |
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation leverages its existing oversight mechanisms to ensure the accuracy of agencies' survey responses to required fraud, waste, and abuse training and, to the full extent of the SBA's legal authority, shares SBIR/STTR fraud risk information and resources for conducting fraud risk assessments. (Recommendation 5) | |
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation, to the full extent of the SBA's legal authority, provides guidance to participating agencies to conduct comprehensive SBIR/STTR program fraud risk assessments, including all key elements, in support of the Policy Directive's fraud, waste, and abuse prevention requirements and consistent with Fraud Risk Framework leading practices. (Recommendation 6) | |
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation improves SBIR.gov data quality by updating guidance to require that abstracts are sufficiently complete and that applicant and awardee addresses are verified to support program eligibility determinations. (Recommendation 7) | |
| Small Business Administration | The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation validates existing information in the SBIR/STTR databases, specifically the Company Registry and SBIR.gov, to identify and correct deficiencies, as appropriate. (Recommendation 8) |
Full Report
Gao contacts.
Rebecca Shea Director [email protected] (202) 512-6722
Office of Public Affairs
Sarah Kaczmarek Acting Managing Director [email protected] (202) 512-4800

Dangers of forever chemicals
News report shows scientists are getting clearer picture of impact of pfas.

PFAS are known as forever chemicals. They are a large, complex group of synthetic chemicals that have been used in consumer products since the 1950s. Now scientists are getting a clearer picture of just how dangerous these chemicals are.
Per- and poly-fluoroalkyl substances, or PFAS, are used in the aerospace, automotive, construction and electronic industries. These chemicals keep food from sticking and clothes from burning, but scientists said they can also be life-threatening.
PFAS can leak into soil and water, and because they break down slowly, if at all, almost everyone is repeatedly exposed to them.
“They can be found in house dust,” explained Susan Pinney, PhD, professor of epidemiology in the Department of Environmental and Public Health Sciences at the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine. A report on her research recently aired on KPLC-TV in Lake Charles, La.
PFAS can cause increased cholesterol levels, lower immunity and some cancers. Now a new study out of UC shows that exposure to PFAS may impact young girls.
“We found that PFAS delayed the onset of puberty,” said Pinney.
85 percent of the young girls in the study had measurable levels of PFAS in their blood — impacting the same hormones that delay the onset of puberty, which could in turn make these girls more susceptible to breast cancer, infertility and endometriosis.
So, what can anyone do? Use a water filter that removes PFAS, and when possible, opt for products labeled as PFAS-free.
Pinney also suggests getting rid of any old Teflon cookware.
Click here to read the entire report from KPLC-TV.
Featured image at top: Scientists wearing white lab coats and purple rubber gloves use lab equipment in their research. Photo/Provided
- Faculty Staff
- In The News
- College of Medicine
- Environmental Health
Related Stories
U.s. news & world report: metformin may help young patients with bipolar disorder avoid weight gain.
October 31, 2023
U.S. News & World Report highlighted recent research led by the University of Cincinnati and Northwell Health that found the drug metformin can help prevent or reduce weight gain in youth taking medication to treat bipolar disorder.
UC researchers significantly shorten drug development time
September 4, 2024
Researchers from the University of Cincinnati College of Medicine and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital have found a new method to increase both speed and success rates in drug discovery. The study, published Aug. 30 in the journal Science Advances, has been featured in several online publications.
September 9, 2024
PFAS, also known as forever chemicals, are a large, complex group of synthetic chemicals that have been used in consumer products since the 1950s. Now scientists are getting a clearer picture of just how dangerous these chemicals are.
- Go back to Main Menu
- Client Log In
- MSCI Client Support Site
- Barra PortfolioManager
- MSCI ESG Manager
- MSCI ESG Direct
- Global Index Lens
- MSCI Real Assets Analytics Portal
- RiskManager 3
- CreditManager
- RiskManager 4
- Index Monitor
- MSCI Datscha
- MSCI Real Capital Analytics
- Total Plan/Caissa
- MSCI Fabric
- MSCI Carbon Markets

Navigation Menu
- Our Clients
Insights on MSCI One
Institutional client designed indexes (icdis), total portfolio footprinting, esg trends to watch, factor models, visualizing investment data.
- Our Solutions
- Go back to Our Solutions
- Analytics Overview
- Risk Management
- AI Portfolio Insights
- Multi-asset Class Factor Models
- Quantitative Investment Solutions
- Fixed Income Analytics
- Portfolio Management
- Crowding Solutions
- Regulatory Solutions
- Managed Solutions
- Climate Investing
- Climate Investing Overview
Implied Temperature Rise
Trends 2024.
- Biodiversity
- Carbon Markets
- GeoSpatial Asset Intelligence
- Portfolio Sustainability Insights
- Real Estate Climate Solutions
- Sustainable Investing
- Sustainable Investing Overview
ESG and Climate Funds in Focus
What is esg, role of capital in the net-zero revolution.
- Sustainability Reporting Services
- Factor Investing
- Factor Investing Overview
MSCI Japan Equity Factor Model
- Equity Factor Models
- Factor Indexes
- Indexes Overview
Index Education
Msci climate action corporate bond indexes.
- Client-Designed
- Direct Indexing
- Fixed Income
- Private Real Assets
Thematic Exposure Standard
- Go back to Indexes
- Resources Overview
MSCI Indexes Underlying Exchange Traded Products
- Communications
- Equity Factsheets
- Derivatives
- Methodology
- Performance
- Private Capital
- Private Capital Overview
Global Private Capital Performance Review
- Total Plan (formerly Caissa)
- Carbon Footprinting
- Private Capital Indexes
- Private Company Data Connect
- Real Assets
- Real Assets Overview
Real Estate Market Size
- Index Intel
- Portfolio Services
- Property Intel
- Private Real Assets Indexes
- Real Capital Analytics
- Research & Insights
- Go back to Research & Insights
- Research & Insights Overview
- Multi-Asset Class
- Real Estate
- Sustainability
- Events Overview
Upcoming climate events
- Data Explorer
- Developer Community
- Technology and Data
2022 Annual Report
- Go back to Who We Are
- Corporate Responsibility
- Corporate Responsibility Overview
- Enabling Sustainable Investing
- Environmental Sustainability
- Governance Practices
- Social Practices
- Sustainability Reports and Policies
- Diversity, Equity and Inclusion
Henry A. Fernandez
- Recognition
Main Search
Social sharing, extended viewer, unpacking active etfs.
Sep 6, 2024
We present a transparent, risk-based framework for asset allocators, including wealth managers, to use in evaluating the active-ETF market, an emerging yet rapidly expanding market segment, particularly in the U.S., where growth has been driven by the conversion of mutual funds into active ETFs. Our framework can help distinguish genuinely active strategies from enhanced indexing.
We focused on active equity ETFs with a U.S. geographical focus. Currently, the market shows a polarized distribution, with an ETF either highly concentrated or broadly diversified.
Active ETFs can be strategically integrated with market-beta and indexed strategies to potentially improve portfolio outcomes while managing specific risks, offering valuable insights for asset allocators navigating this growing market.
Active ETFs varied in their level of diversification and AUM
Data as of May 31, 2024. Bubble size represents the ETF’s AUM. The sample consisted of 301 active equity ETFs with a U.S. geographical focus, including 25 converted from a mutual fund. Source: Lipper, Morningstar
Research authors
- Ashish Lodh , Executive Director, MSCI Research
- Rohit Gupta , Vice President, MSCI Research
Related content
Wealth managers.
From off-the-shelf models, static tools and spreadsheets, today’s wealth management technology is built for the past. At MSCI, our tools are designed for the future of wealth management, with technology built to maximize your time, effectiveness and client outcomes.
The Power of Rules: Model Portfolios and Wealth Management
For wealth managers and financial advisers seeking customized solutions to meet growing client demand, rules-based management approaches for model portfolios may offer opportunities to improve on traditional management approaches.
Measuring Tax Alpha
The concept of tax alpha can help a wealth manager explain a client’s after-tax performance. In a new article in the Journal of Wealth Management, we propose two frameworks for the after-tax calculation used to measure tax alpha.
UtmAnalytics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Product Research: Definition, Methods, and Expert Advice
Product Research: What It Is, Why It Matters & How to Do It
Product Research Process: How To Do It in 8 Steps
What is Product Research? Methods, Process, and Benefits
8. Determine Product Weight And Size. After you've decided on your selling price, you'll need to determine your product's weight and size. To do this, you'll need to consider the following: The weight of the product: This will affect shipping costs. The dimensions of the product: This will affect packaging costs.
How to do Product Research [Step-by-Step Guide]
Product research is your gateway to becoming a user-centric company. It's how you understand the target audience, their needs, pain points, and desires, and develop products that meet those requirements, rather than do what you'd like them to do. Secondly, product research also helps you validate ideas and assumptions.
Assess names and packaging designs. Check out the competition. Set the right selling price. Gauge customer satisfaction and monitor product-market fit post-launch. Continually improve the product. Product research is the term most often used to describe this process, but it's not just about physical products.
Here are compelling reasons why product managers should prioritize product research: 1. Understanding the Market: Product research provides insights into market trends, emerging technologies, and shifts in consumer behavior. It allows PMs to position their products effectively and anticipate market changes. 2.
Product research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data and insights related to a specific product or service. It encompasses various methodologies and techniques to understand customer needs, market dynamics, competitor offerings, and industry trends to inform strategic decisions throughout the product lifecycle.
Product research is the process of gathering and analyzing information about a product, its market, competitors, and potential customers. The goal of product research is to identify opportunities, assess demand, and make informed decisions related to product development, marketing, pricing, and distribution. Product research answers questions ...
Under the "Boating" subcategory, there are tons of product types I can look through. The more "niche" you get with your product research, the better. This way, you can find products that not everyone may have thought of but will still have lots of potential customers. 4. Attend wholesale trade shows.
Product research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a particular product or market to make informed decisions about product development, marketing strategies, pricing, distribution channels, and other aspects of the product lifecycle. It involves collecting data from various sources, including market ...
Product research, on the other hand, is one of the first steps in developing a new product. This is concerned with the company's R&D team testing the viability and feasibility of a particular product for a given market. Research and development for new or existing products are vital for the company's long-term success and sustained growth.
How to perform product research
What is Product Development Research and how to do it?
What is a Marketing Research Report and How to Write It?
Product research is the process of marketing research that is done to get information on the desired characteristics and specifications of a product expected by the potential customers mainly before the launch and availability of the product. Product research helps companies to understand what the customers really want, so that the product can be tailored to match the needs of the customer.
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner. ... program planning, or product development. The findings and conclusions can help guide decisions and improve outcomes. Supporting further ...
To create an effective product analysis, start by clearly defining your objectives. Gather comprehensive data about your product, including customer feedback, sales figures, and market trends. Use both quantitative and qualitative research methods, such as surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis.
Product Testing and Research
Research report guide: Definition, types, and tips
Research Reports: Definition and How to Write Them
Develop the Body of the Report. Organize information logically, using headings and subheadings. Present one main idea per paragraph, with supporting details. Use transitions between sections to maintain flow and coherence. Support Your Points with Data and Evidence. Include relevant data, statistics, and research findings.
ProductReportCard
Small Business Administration : The Administrator of SBA should ensure that the Associate Administrator for the Office of Investment and Innovation leverages its existing oversight mechanisms to ensure the accuracy of agencies' survey responses to required fraud, waste, and abuse training and, to the full extent of the SBA's legal authority, shares SBIR/STTR fraud risk information and ...
A report on her research recently aired on KPLC-TV in Lake Charles, La. PFAS can cause increased cholesterol levels, lower immunity and some cancers. Now a new study out of UC shows that exposure to PFAS may impact young girls.
We present a transparent, risk-based framework for asset allocators, including wealth managers, to use in evaluating the active-ETF market, an emerging yet rapidly expanding market segment, particularly in the U.S., where growth has been driven by the conversion of mutual funds into active ETFs.
Digital asset investment products experienced significant outflows totalling US$72m, matching the largest recorded outflow set in March this year. We believe this negative sentiment was driven by stronger-than-expected macroeconomic data from the previous week, which increased the likelihood of a 25 basis point (bp) interest rate cut by the US ...