- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications

How to Develop a Questionnaire for Research
Last Updated: July 21, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 593,598 times.
A questionnaire is a technique for collecting data in which a respondent provides answers to a series of questions. [1] X Research source To develop a questionnaire that will collect the data you want takes effort and time. However, by taking a step-by-step approach to questionnaire development, you can come up with an effective means to collect data that will answer your unique research question.
Designing Your Questionnaire

- Come up with a research question. It can be one question or several, but this should be the focal point of your questionnaire.
- Develop one or several hypotheses that you want to test. The questions that you include on your questionnaire should be aimed at systematically testing these hypotheses.

- Dichotomous question: this is a question that will generally be a “yes/no” question, but may also be an “agree/disagree” question. It is the quickest and simplest question to analyze, but is not a highly sensitive measure.
- Open-ended questions: these questions allow the respondent to respond in their own words. They can be useful for gaining insight into the feelings of the respondent, but can be a challenge when it comes to analysis of data. It is recommended to use open-ended questions to address the issue of “why.” [2] X Research source
- Multiple choice questions: these questions consist of three or more mutually-exclusive categories and ask for a single answer or several answers. [3] X Research source Multiple choice questions allow for easy analysis of results, but may not give the respondent the answer they want.
- Rank-order (or ordinal) scale questions: this type of question asks your respondent to rank items or choose items in a particular order from a set. For example, it might ask your respondents to order five things from least to most important. These types of questions forces discrimination among alternatives, but does not address the issue of why the respondent made these discriminations. [4] X Research source
- Rating scale questions: these questions allow the respondent to assess a particular issue based on a given dimension. You can provide a scale that gives an equal number of positive and negative choices, for example, ranging from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree.” [5] X Research source These questions are very flexible, but also do not answer the question “why.”

- Write questions that are succinct and simple. You should not be writing complex statements or using technical jargon, as it will only confuse your respondents and lead to incorrect responses.
- Ask only one question at a time. This will help avoid confusion
- Asking questions such as these usually require you to anonymize or encrypt the demographic data you collect.
- Determine if you will include an answer such as “I don’t know” or “Not applicable to me.” While these can give your respondents a way of not answering certain questions, providing these options can also lead to missing data, which can be problematic during data analysis.
- Put the most important questions at the beginning of your questionnaire. This can help you gather important data even if you sense that your respondents may be becoming distracted by the end of the questionnaire.

- Only include questions that are directly useful to your research question. [8] X Trustworthy Source Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations Specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for leading international efforts to end world hunger and improve nutrition Go to source A questionnaire is not an opportunity to collect all kinds of information about your respondents.
- Avoid asking redundant questions. This will frustrate those who are taking your questionnaire.

- Consider if you want your questionnaire to collect information from both men and women. Some studies will only survey one sex.
- Consider including a range of ages in your target demographic. For example, you can consider young adult to be 18-29 years old, adults to be 30-54 years old, and mature adults to be 55+. Providing the an age range will help you get more respondents than limiting yourself to a specific age.
- Consider what else would make a person a target for your questionnaire. Do they need to drive a car? Do they need to have health insurance? Do they need to have a child under 3? Make sure you are very clear about this before you distribute your questionnaire.

- Consider an anonymous questionnaire. You may not want to ask for names on your questionnaire. This is one step you can take to prevent privacy, however it is often possible to figure out a respondent’s identity using other demographic information (such as age, physical features, or zipcode).
- Consider de-identifying the identity of your respondents. Give each questionnaire (and thus, each respondent) a unique number or word, and only refer to them using that new identifier. Shred any personal information that can be used to determine identity.
- Remember that you do not need to collect much demographic information to be able to identify someone. People may be wary to provide this information, so you may get more respondents by asking less demographic questions (if it is possible for your questionnaire).
- Make sure you destroy all identifying information after your study is complete.
Writing your questionnaire

- My name is Jack Smith and I am one of the creators of this questionnaire. I am part of the Department of Psychology at the University of Michigan, where I am focusing in developing cognition in infants.
- I’m Kelly Smith, a 3rd year undergraduate student at the University of New Mexico. This questionnaire is part of my final exam in statistics.
- My name is Steve Johnson, and I’m a marketing analyst for The Best Company. I’ve been working on questionnaire development to determine attitudes surrounding drug use in Canada for several years.

- I am collecting data regarding the attitudes surrounding gun control. This information is being collected for my Anthropology 101 class at the University of Maryland.
- This questionnaire will ask you 15 questions about your eating and exercise habits. We are attempting to make a correlation between healthy eating, frequency of exercise, and incidence of cancer in mature adults.
- This questionnaire will ask you about your recent experiences with international air travel. There will be three sections of questions that will ask you to recount your recent trips and your feelings surrounding these trips, as well as your travel plans for the future. We are looking to understand how a person’s feelings surrounding air travel impact their future plans.

- Beware that if you are collecting information for a university or for publication, you may need to check in with your institution’s Institutional Review Board (IRB) for permission before beginning. Most research universities have a dedicated IRB staff, and their information can usually be found on the school’s website.
- Remember that transparency is best. It is important to be honest about what will happen with the data you collect.
- Include an informed consent for if necessary. Note that you cannot guarantee confidentiality, but you will make all reasonable attempts to ensure that you protect their information. [11] X Research source

- Time yourself taking the survey. Then consider that it will take some people longer than you, and some people less time than you.
- Provide a time range instead of a specific time. For example, it’s better to say that a survey will take between 15 and 30 minutes than to say it will take 15 minutes and have some respondents quit halfway through.
- Use this as a reason to keep your survey concise! You will feel much better asking people to take a 20 minute survey than you will asking them to take a 3 hour one.

- Incentives can attract the wrong kind of respondent. You don’t want to incorporate responses from people who rush through your questionnaire just to get the reward at the end. This is a danger of offering an incentive. [12] X Research source
- Incentives can encourage people to respond to your survey who might not have responded without a reward. This is a situation in which incentives can help you reach your target number of respondents. [13] X Research source
- Consider the strategy used by SurveyMonkey. Instead of directly paying respondents to take their surveys, they offer 50 cents to the charity of their choice when a respondent fills out a survey. They feel that this lessens the chances that a respondent will fill out a questionnaire out of pure self-interest. [14] X Research source
- Consider entering each respondent in to a drawing for a prize if they complete the questionnaire. You can offer a 25$ gift card to a restaurant, or a new iPod, or a ticket to a movie. This makes it less tempting just to respond to your questionnaire for the incentive alone, but still offers the chance of a pleasant reward.

- Always proof read. Check for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors.
- Include a title. This is a good way for your respondents to understand the focus of the survey as quickly as possible.
- Thank your respondents. Thank them for taking the time and effort to complete your survey.
Distributing Your Questionnaire

- Was the questionnaire easy to understand? Were there any questions that confused you?
- Was the questionnaire easy to access? (Especially important if your questionnaire is online).
- Do you feel the questionnaire was worth your time?
- Were you comfortable answering the questions asked?
- Are there any improvements you would make to the questionnaire?

- Use an online site, such as SurveyMonkey.com. This site allows you to write your own questionnaire with their survey builder, and provides additional options such as the option to buy a target audience and use their analytics to analyze your data. [18] X Research source
- Consider using the mail. If you mail your survey, always make sure you include a self-addressed stamped envelope so that the respondent can easily mail their responses back. Make sure that your questionnaire will fit inside a standard business envelope.
- Conduct face-to-face interviews. This can be a good way to ensure that you are reaching your target demographic and can reduce missing information in your questionnaires, as it is more difficult for a respondent to avoid answering a question when you ask it directly.
- Try using the telephone. While this can be a more time-effective way to collect your data, it can be difficult to get people to respond to telephone questionnaires.

- Make your deadline reasonable. Giving respondents up to 2 weeks to answer should be more than sufficient. Anything longer and you risk your respondents forgetting about your questionnaire.
- Consider providing a reminder. A week before the deadline is a good time to provide a gentle reminder about returning the questionnaire. Include a replacement of the questionnaire in case it has been misplaced by your respondent.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.questionpro.com/blog/what-is-a-questionnaire/
- ↑ https://www.hotjar.com/blog/open-ended-questions/
- ↑ https://www.questionpro.com/a/showArticle.do?articleID=survey-questions
- ↑ https://surveysparrow.com/blog/ranking-questions-examples/
- ↑ https://www.lumoa.me/blog/rating-scale/
- ↑ http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project_ideas/Soc_survey.shtml
- ↑ http://www.fao.org/docrep/W3241E/w3241e05.htm
- ↑ http://managementhelp.org/businessresearch/questionaires.htm
- ↑ https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/survey-rewards/
- ↑ http://www.ideafit.com/fitness-library/how-to-develop-a-questionnaire
- ↑ https://www.surveymonkey.com/mp/take-a-tour/?ut_source=header
About This Article

To develop a questionnaire for research, identify the main objective of your research to act as the focal point for the questionnaire. Then, choose the type of questions that you want to include, and come up with succinct, straightforward questions to gather the information that you need to answer your questions. Keep your questionnaire as short as possible, and identify a target demographic who you would like to answer the questions. Remember to make the questionnaires as anonymous as possible to protect the integrity of the person answering the questions! For tips on writing out your questions and distributing the questionnaire, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Abdul Bari Khan
Nov 11, 2020
Did this article help you?

Jul 25, 2023
Iman Ilhusadi
Nov 26, 2016
Jaydeepa Das
Aug 21, 2018
Atefeh Abdollahi
Jan 3, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- Privacy Policy

Home » Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
Table of Contents

Questionnaire
Definition:
A Questionnaire is a research tool or survey instrument that consists of a set of questions or prompts designed to gather information from individuals or groups of people.
It is a standardized way of collecting data from a large number of people by asking them a series of questions related to a specific topic or research objective. The questions may be open-ended or closed-ended, and the responses can be quantitative or qualitative. Questionnaires are widely used in research, marketing, social sciences, healthcare, and many other fields to collect data and insights from a target population.
History of Questionnaire
The history of questionnaires can be traced back to the ancient Greeks, who used questionnaires as a means of assessing public opinion. However, the modern history of questionnaires began in the late 19th century with the rise of social surveys.
The first social survey was conducted in the United States in 1874 by Francis A. Walker, who used a questionnaire to collect data on labor conditions. In the early 20th century, questionnaires became a popular tool for conducting social research, particularly in the fields of sociology and psychology.
One of the most influential figures in the development of the questionnaire was the psychologist Raymond Cattell, who in the 1940s and 1950s developed the personality questionnaire, a standardized instrument for measuring personality traits. Cattell’s work helped establish the questionnaire as a key tool in personality research.
In the 1960s and 1970s, the use of questionnaires expanded into other fields, including market research, public opinion polling, and health surveys. With the rise of computer technology, questionnaires became easier and more cost-effective to administer, leading to their widespread use in research and business settings.
Today, questionnaires are used in a wide range of settings, including academic research, business, healthcare, and government. They continue to evolve as a research tool, with advances in computer technology and data analysis techniques making it easier to collect and analyze data from large numbers of participants.
Types of Questionnaire
Types of Questionnaires are as follows:
Structured Questionnaire
This type of questionnaire has a fixed format with predetermined questions that the respondent must answer. The questions are usually closed-ended, which means that the respondent must select a response from a list of options.
Unstructured Questionnaire
An unstructured questionnaire does not have a fixed format or predetermined questions. Instead, the interviewer or researcher can ask open-ended questions to the respondent and let them provide their own answers.
Open-ended Questionnaire
An open-ended questionnaire allows the respondent to answer the question in their own words, without any pre-determined response options. The questions usually start with phrases like “how,” “why,” or “what,” and encourage the respondent to provide more detailed and personalized answers.
Close-ended Questionnaire
In a closed-ended questionnaire, the respondent is given a set of predetermined response options to choose from. This type of questionnaire is easier to analyze and summarize, but may not provide as much insight into the respondent’s opinions or attitudes.
Mixed Questionnaire
A mixed questionnaire is a combination of open-ended and closed-ended questions. This type of questionnaire allows for more flexibility in terms of the questions that can be asked, and can provide both quantitative and qualitative data.
Pictorial Questionnaire:
In a pictorial questionnaire, instead of using words to ask questions, the questions are presented in the form of pictures, diagrams or images. This can be particularly useful for respondents who have low literacy skills, or for situations where language barriers exist. Pictorial questionnaires can also be useful in cross-cultural research where respondents may come from different language backgrounds.
Types of Questions in Questionnaire
The types of Questions in Questionnaire are as follows:
Multiple Choice Questions
These questions have several options for participants to choose from. They are useful for getting quantitative data and can be used to collect demographic information.
- a. Red b . Blue c. Green d . Yellow
Rating Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate something on a scale (e.g. from 1 to 10). They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
- On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product to a friend?
Open-Ended Questions
These questions allow participants to answer in their own words and provide more in-depth and detailed responses. They are useful for getting qualitative data.
- What do you think are the biggest challenges facing your community?
Likert Scale Questions
These questions ask participants to rate how much they agree or disagree with a statement. They are useful for measuring attitudes and opinions.
How strongly do you agree or disagree with the following statement:
“I enjoy exercising regularly.”
- a . Strongly Agree
- c . Neither Agree nor Disagree
- d . Disagree
- e . Strongly Disagree
Demographic Questions
These questions ask about the participant’s personal information such as age, gender, ethnicity, education level, etc. They are useful for segmenting the data and analyzing results by demographic groups.
- What is your age?
Yes/No Questions
These questions only have two options: Yes or No. They are useful for getting simple, straightforward answers to a specific question.
Have you ever traveled outside of your home country?
Ranking Questions
These questions ask participants to rank several items in order of preference or importance. They are useful for measuring priorities or preferences.
Please rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a restaurant:
- a. Quality of Food
- c. Ambiance
- d. Location
Matrix Questions
These questions present a matrix or grid of options that participants can choose from. They are useful for getting data on multiple variables at once.
| The product is easy to use | ||||
| The product meets my needs | ||||
| The product is affordable |
Dichotomous Questions
These questions present two options that are opposite or contradictory. They are useful for measuring binary or polarized attitudes.
Do you support the death penalty?
How to Make a Questionnaire
Step-by-Step Guide for Making a Questionnaire:
- Define your research objectives: Before you start creating questions, you need to define the purpose of your questionnaire and what you hope to achieve from the data you collect.
- Choose the appropriate question types: Based on your research objectives, choose the appropriate question types to collect the data you need. Refer to the types of questions mentioned earlier for guidance.
- Develop questions: Develop clear and concise questions that are easy for participants to understand. Avoid leading or biased questions that might influence the responses.
- Organize questions: Organize questions in a logical and coherent order, starting with demographic questions followed by general questions, and ending with specific or sensitive questions.
- Pilot the questionnaire : Test your questionnaire on a small group of participants to identify any flaws or issues with the questions or the format.
- Refine the questionnaire : Based on feedback from the pilot, refine and revise the questionnaire as necessary to ensure that it is valid and reliable.
- Distribute the questionnaire: Distribute the questionnaire to your target audience using a method that is appropriate for your research objectives, such as online surveys, email, or paper surveys.
- Collect and analyze data: Collect the completed questionnaires and analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods. Draw conclusions from the data and use them to inform decision-making or further research.
- Report findings: Present your findings in a clear and concise report, including a summary of the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and recommendations.
Questionnaire Administration Modes
There are several modes of questionnaire administration. The choice of mode depends on the research objectives, sample size, and available resources. Some common modes of administration include:
- Self-administered paper questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on paper, either in person or by mail. This mode is relatively low cost and easy to administer, but it may result in lower response rates and greater potential for errors in data entry.
- Online questionnaires: Participants complete the questionnaire on a website or through email. This mode is convenient for both researchers and participants, as it allows for fast and easy data collection. However, it may be subject to issues such as low response rates, lack of internet access, and potential for fraudulent responses.
- Telephone surveys: Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire over the phone. This mode allows for a large sample size and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Face-to-face interviews : Trained interviewers administer the questionnaire in person. This mode allows for a high degree of control over the survey environment and can result in higher response rates, but it is also more expensive and time-consuming than other modes.
- Mixed-mode surveys: Researchers use a combination of two or more modes to administer the questionnaire, such as using online questionnaires for initial screening and following up with telephone interviews for more detailed information. This mode can help overcome some of the limitations of individual modes, but it requires careful planning and coordination.
Example of Questionnaire
Title of the Survey: Customer Satisfaction Survey
Introduction:
We appreciate your business and would like to ensure that we are meeting your needs. Please take a few minutes to complete this survey so that we can better understand your experience with our products and services. Your feedback is important to us and will help us improve our offerings.
Instructions:
Please read each question carefully and select the response that best reflects your experience. If you have any additional comments or suggestions, please feel free to include them in the space provided at the end of the survey.
1. How satisfied are you with our product quality?
- Very satisfied
- Somewhat satisfied
- Somewhat dissatisfied
- Very dissatisfied
2. How satisfied are you with our customer service?
3. How satisfied are you with the price of our products?
4. How likely are you to recommend our products to others?
- Very likely
- Somewhat likely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Very unlikely
5. How easy was it to find the information you were looking for on our website?
- Somewhat easy
- Somewhat difficult
- Very difficult
6. How satisfied are you with the overall experience of using our products and services?
7. Is there anything that you would like to see us improve upon or change in the future?
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Conclusion:
Thank you for taking the time to complete this survey. Your feedback is valuable to us and will help us improve our products and services. If you have any further comments or concerns, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Applications of Questionnaire
Some common applications of questionnaires include:
- Research : Questionnaires are commonly used in research to gather information from participants about their attitudes, opinions, behaviors, and experiences. This information can then be analyzed and used to draw conclusions and make inferences.
- Healthcare : In healthcare, questionnaires can be used to gather information about patients’ medical history, symptoms, and lifestyle habits. This information can help healthcare professionals diagnose and treat medical conditions more effectively.
- Marketing : Questionnaires are commonly used in marketing to gather information about consumers’ preferences, buying habits, and opinions on products and services. This information can help businesses develop and market products more effectively.
- Human Resources: Questionnaires are used in human resources to gather information from job applicants, employees, and managers about job satisfaction, performance, and workplace culture. This information can help organizations improve their hiring practices, employee retention, and organizational culture.
- Education : Questionnaires are used in education to gather information from students, teachers, and parents about their perceptions of the educational experience. This information can help educators identify areas for improvement and develop more effective teaching strategies.
Purpose of Questionnaire
Some common purposes of questionnaires include:
- To collect information on attitudes, opinions, and beliefs: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on people’s attitudes, opinions, and beliefs on a particular topic. For example, a questionnaire can be used to gather information on people’s opinions about a particular political issue.
- To collect demographic information: Questionnaires can be used to collect demographic information such as age, gender, income, education level, and occupation. This information can be used to analyze trends and patterns in the data.
- To measure behaviors or experiences: Questionnaires can be used to gather information on behaviors or experiences such as health-related behaviors or experiences, job satisfaction, or customer satisfaction.
- To evaluate programs or interventions: Questionnaires can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions by gathering information on participants’ experiences, opinions, and behaviors.
- To gather information for research: Questionnaires can be used to gather data for research purposes on a variety of topics.
When to use Questionnaire
Here are some situations when questionnaires might be used:
- When you want to collect data from a large number of people: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data from a large number of people. They can be distributed to a wide audience and can be completed at the respondent’s convenience.
- When you want to collect data on specific topics: Questionnaires are useful when you want to collect data on specific topics or research questions. They can be designed to ask specific questions and can be used to gather quantitative data that can be analyzed statistically.
- When you want to compare responses across groups: Questionnaires are useful when you want to compare responses across different groups of people. For example, you might want to compare responses from men and women, or from people of different ages or educational backgrounds.
- When you want to collect data anonymously: Questionnaires can be useful when you want to collect data anonymously. Respondents can complete the questionnaire without fear of judgment or repercussions, which can lead to more honest and accurate responses.
- When you want to save time and resources: Questionnaires can be more efficient and cost-effective than other methods of data collection such as interviews or focus groups. They can be completed quickly and easily, and can be analyzed using software to save time and resources.
Characteristics of Questionnaire
Here are some of the characteristics of questionnaires:
- Standardization : Questionnaires are standardized tools that ask the same questions in the same order to all respondents. This ensures that all respondents are answering the same questions and that the responses can be compared and analyzed.
- Objectivity : Questionnaires are designed to be objective, meaning that they do not contain leading questions or bias that could influence the respondent’s answers.
- Predefined responses: Questionnaires typically provide predefined response options for the respondents to choose from, which helps to standardize the responses and make them easier to analyze.
- Quantitative data: Questionnaires are designed to collect quantitative data, meaning that they provide numerical or categorical data that can be analyzed using statistical methods.
- Convenience : Questionnaires are convenient for both the researcher and the respondents. They can be distributed and completed at the respondent’s convenience and can be easily administered to a large number of people.
- Anonymity : Questionnaires can be anonymous, which can encourage respondents to answer more honestly and provide more accurate data.
- Reliability : Questionnaires are designed to be reliable, meaning that they produce consistent results when administered multiple times to the same group of people.
- Validity : Questionnaires are designed to be valid, meaning that they measure what they are intended to measure and are not influenced by other factors.
Advantage of Questionnaire
Some Advantage of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Standardization: Questionnaires allow researchers to ask the same questions to all participants in a standardized manner. This helps ensure consistency in the data collected and eliminates potential bias that might arise if questions were asked differently to different participants.
- Efficiency: Questionnaires can be administered to a large number of people at once, making them an efficient way to collect data from a large sample.
- Anonymity: Participants can remain anonymous when completing a questionnaire, which may make them more likely to answer honestly and openly.
- Cost-effective: Questionnaires can be relatively inexpensive to administer compared to other research methods, such as interviews or focus groups.
- Objectivity: Because questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, they can be analyzed objectively without the influence of the researcher’s subjective interpretation.
- Flexibility: Questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions and can be used in various settings, including online surveys, mail surveys, or in-person interviews.
Limitations of Questionnaire
Limitations of Questionnaire are as follows:
- Limited depth: Questionnaires are typically designed to collect quantitative data, which may not provide a complete understanding of the topic being studied. Questionnaires may miss important details and nuances that could be captured through other research methods, such as interviews or observations.
- R esponse bias: Participants may not always answer questions truthfully or accurately, either because they do not remember or because they want to present themselves in a particular way. This can lead to response bias, which can affect the validity and reliability of the data collected.
- Limited flexibility: While questionnaires can be adapted to a wide range of research questions, they may not be suitable for all types of research. For example, they may not be appropriate for studying complex phenomena or for exploring participants’ experiences and perceptions in-depth.
- Limited context: Questionnaires typically do not provide a rich contextual understanding of the topic being studied. They may not capture the broader social, cultural, or historical factors that may influence participants’ responses.
- Limited control : Researchers may not have control over how participants complete the questionnaire, which can lead to variations in response quality or consistency.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Mixed Methods Research – Types & Analysis

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings
As a staple in data collection, questionnaires help uncover robust and reliable findings that can transform industries, shape policies, and revolutionize understanding. Whether you are exploring societal trends or delving into scientific phenomena, the effectiveness of your research questionnaire can make or break your findings.
In this article, we aim to understand the core purpose of questionnaires, exploring how they serve as essential tools for gathering systematic data, both qualitative and quantitative, from diverse respondents. Read on as we explore the key elements that make up a winning questionnaire, the art of framing questions which are both compelling and rigorous, and the careful balance between simplicity and depth.
Table of Contents
The Role of Questionnaires in Research
So, what is a questionnaire? A questionnaire is a structured set of questions designed to collect information, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. It is one of the most commonly used data collection methods in research. Moreover, questionnaires can be used in various research fields, including social sciences, market research, healthcare, education, and psychology. Their adaptability makes them suitable for investigating diverse research questions.
Questionnaire and survey are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings in the context of research. A survey refers to the broader process of data collection that may involve various methods. A survey can encompass different data collection techniques, such as interviews , focus groups, observations, and yes, questionnaires.
Pros and Cons of Using Questionnaires in Research:
While questionnaires offer numerous advantages in research, they also come with some disadvantages that researchers must be aware of and address appropriately. Careful questionnaire design, validation, and consideration of potential biases can help mitigate these disadvantages and enhance the effectiveness of using questionnaires as a data collection method.

Structured vs Unstructured Questionnaires
Structured questionnaire:.
A structured questionnaire consists of questions with predefined response options. Respondents are presented with a fixed set of choices and are required to select from those options. The questions in a structured questionnaire are designed to elicit specific and quantifiable responses. Structured questionnaires are particularly useful for collecting quantitative data and are often employed in surveys and studies where standardized and comparable data are necessary.
Advantages of Structured Questionnaires:
- Easy to analyze and interpret: The fixed response options facilitate straightforward data analysis and comparison across respondents.
- Efficient for large-scale data collection: Structured questionnaires are time-efficient, allowing researchers to collect data from a large number of respondents.
- Reduces response bias: The predefined response options minimize potential response bias and maintain consistency in data collection.
Limitations of Structured Questionnaires:
- Lack of depth: Structured questionnaires may not capture in-depth insights or nuances as respondents are limited to pre-defined response choices. Hence, they may not reveal the reasons behind respondents’ choices, limiting the understanding of their perspectives.
- Limited flexibility: The fixed response options may not cover all potential responses, therefore, potentially restricting respondents’ answers.
Unstructured Questionnaire:
An unstructured questionnaire consists of questions that allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses. Unlike structured questionnaires, there are no predefined response options, giving respondents the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words. Furthermore, unstructured questionnaires are valuable for collecting qualitative data and obtaining in-depth insights into respondents’ experiences, opinions, or feelings.
Advantages of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Rich qualitative data: Unstructured questionnaires yield detailed and comprehensive qualitative data, providing valuable and novel insights into respondents’ perspectives.
- Flexibility in responses: Respondents have the freedom to express themselves in their own words. Hence, allowing for a wide range of responses.
Limitations of Unstructured Questionnaires:
- Time-consuming analysis: Analyzing open-ended responses can be time-consuming, since, each response requires careful reading and interpretation.
- Subjectivity in interpretation: The analysis of open-ended responses may be subjective, as researchers interpret and categorize responses based on their judgment.
- May require smaller sample size: Due to the depth of responses, researchers may need a smaller sample size for comprehensive analysis, making generalizations more challenging.
Types of Questions in a Questionnaire
In a questionnaire, researchers typically use the following most common types of questions to gather a variety of information from respondents:
1. Open-Ended Questions:
These questions allow respondents to provide detailed and unrestricted responses in their own words. Open-ended questions are valuable for gathering qualitative data and in-depth insights.
Example: What suggestions do you have for improving our product?
2. Multiple-Choice Questions
Respondents choose one answer from a list of provided options. This type of question is suitable for gathering categorical data or preferences.
Example: Which of the following social media/academic networking platforms do you use to promote your research?
- ResearchGate
- Academia.edu
3. Dichotomous Questions
Respondents choose between two options, typically “yes” or “no”, “true” or “false”, or “agree” or “disagree”.
Example: Have you ever published in open access journals before?
4. Scaling Questions
These questions, also known as rating scale questions, use a predefined scale that allows respondents to rate or rank their level of agreement, satisfaction, importance, or other subjective assessments. These scales help researchers quantify subjective data and make comparisons across respondents.
There are several types of scaling techniques used in scaling questions:
i. Likert Scale:
The Likert scale is one of the most common scaling techniques. It presents respondents with a series of statements and asks them to rate their level of agreement or disagreement using a range of options, typically from “strongly agree” to “strongly disagree”.For example: Please indicate your level of agreement with the statement: “The content presented in the webinar was relevant and aligned with the advertised topic.”
- Strongly Agree
- Strongly Disagree
ii. Semantic Differential Scale:
The semantic differential scale measures respondents’ perceptions or attitudes towards an item using opposite adjectives or bipolar words. Respondents rate the item on a scale between the two opposites. For example:
- Easy —— Difficult
- Satisfied —— Unsatisfied
- Very likely —— Very unlikely
iii. Numerical Rating Scale:
This scale requires respondents to provide a numerical rating on a predefined scale. It can be a simple 1 to 5 or 1 to 10 scale, where higher numbers indicate higher agreement, satisfaction, or importance.
iv. Ranking Questions:
Respondents rank items in order of preference or importance. Ranking questions help identify preferences or priorities.
Example: Please rank the following features of our app in order of importance (1 = Most Important, 5 = Least Important):
- User Interface
- Functionality
- Customer Support
By using a mix of question types, researchers can gather both quantitative and qualitative data, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research topic and enabling meaningful analysis and interpretation of the results. The choice of question types depends on the research objectives , the desired depth of information, and the data analysis requirements.
Methods of Administering Questionnaires
There are several methods for administering questionnaires, and the choice of method depends on factors such as the target population, research objectives , convenience, and resources available. Here are some common methods of administering questionnaires:

Each method has its advantages and limitations. Online surveys offer convenience and a large reach, but they may be limited to individuals with internet access. Face-to-face interviews allow for in-depth responses but can be time-consuming and costly. Telephone surveys have broad reach but may be limited by declining response rates. Researchers should choose the method that best suits their research objectives, target population, and available resources to ensure successful data collection.
How to Design a Questionnaire
Designing a good questionnaire is crucial for gathering accurate and meaningful data that aligns with your research objectives. Here are essential steps and tips to create a well-designed questionnaire:
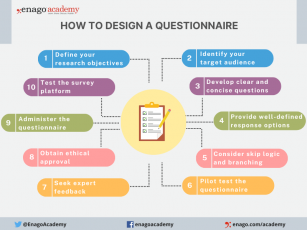
1. Define Your Research Objectives : Clearly outline the purpose and specific information you aim to gather through the questionnaire.
2. Identify Your Target Audience : Understand respondents’ characteristics and tailor the questionnaire accordingly.
3. Develop the Questions :
- Write Clear and Concise Questions
- Avoid Leading or Biasing Questions
- Sequence Questions Logically
- Group Related Questions
- Include Demographic Questions
4. Provide Well-defined Response Options : Offer exhaustive response choices for closed-ended questions.
5. Consider Skip Logic and Branching : Customize the questionnaire based on previous answers.
6. Pilot Test the Questionnaire : Identify and address issues through a pilot study .
7. Seek Expert Feedback : Validate the questionnaire with subject matter experts.
8. Obtain Ethical Approval : Comply with ethical guidelines , obtain consent, and ensure confidentiality before administering the questionnaire.
9. Administer the Questionnaire : Choose the right mode and provide clear instructions.
10. Test the Survey Platform : Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys.
By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
Characteristics of a Good Questionnaire
A good questionnaire possesses several essential elements that contribute to its effectiveness. Furthermore, these characteristics ensure that the questionnaire is well-designed, easy to understand, and capable of providing valuable insights. Here are some key characteristics of a good questionnaire:
1. Clarity and Simplicity : Questions should be clear, concise, and unambiguous. Avoid using complex language or technical terms that may confuse respondents. Simple and straightforward questions ensure that respondents interpret them consistently.
2. Relevance and Focus : Each question should directly relate to the research objectives and contribute to answering the research questions. Consequently, avoid including extraneous or irrelevant questions that could lead to data clutter.
3. Mix of Question Types : Utilize a mix of question types, including open-ended, Likert scale, and multiple-choice questions. This variety allows for both qualitative and quantitative data collections .
4. Validity and Reliability : Ensure the questionnaire measures what it intends to measure (validity) and produces consistent results upon repeated administration (reliability). Validation should be conducted through expert review and previous research.
5. Appropriate Length : Keep the questionnaire’s length appropriate and manageable to avoid respondent fatigue or dropouts. Long questionnaires may result in incomplete or rushed responses.
6. Clear Instructions : Include clear instructions at the beginning of the questionnaire to guide respondents on how to complete it. Explain any technical terms, formats, or concepts if necessary.
7. User-Friendly Format : Design the questionnaire to be visually appealing and user-friendly. Use consistent formatting, adequate spacing, and a logical page layout.
8. Data Validation and Cleaning : Incorporate validation checks to ensure data accuracy and reliability. Consider mechanisms to detect and correct inconsistent or missing responses during data cleaning.
By incorporating these characteristics, researchers can create a questionnaire that maximizes data quality, minimizes response bias, and provides valuable insights for their research.
In the pursuit of advancing research and gaining meaningful insights, investing time and effort into designing effective questionnaires is a crucial step. A well-designed questionnaire is more than a mere set of questions; it is a masterpiece of precision and ingenuity. Each question plays a vital role in shaping the narrative of our research, guiding us through the labyrinth of data to meaningful conclusions. Indeed, a well-designed questionnaire serves as a powerful tool for unlocking valuable insights and generating robust findings that impact society positively.
Have you ever designed a research questionnaire? Reflect on your experience and share your insights with researchers globally through Enago Academy’s Open Blogging Platform . Join our diverse community of 1000K+ researchers and authors to exchange ideas, strategies, and best practices, and together, let’s shape the future of data collection and maximize the impact of questionnaires in the ever-evolving landscape of research.
Frequently Asked Questions
A research questionnaire is a structured tool used to gather data from participants in a systematic manner. It consists of a series of carefully crafted questions designed to collect specific information related to a research study.
Questionnaires play a pivotal role in both quantitative and qualitative research, enabling researchers to collect insights, opinions, attitudes, or behaviors from respondents. This aids in hypothesis testing, understanding, and informed decision-making, ensuring consistency, efficiency, and facilitating comparisons.
Questionnaires are a versatile tool employed in various research designs to gather data efficiently and comprehensively. They find extensive use in both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies, making them a fundamental component of research across disciplines. Some research designs that commonly utilize questionnaires include: a) Cross-Sectional Studies b) Longitudinal Studies c) Descriptive Research d) Correlational Studies e) Causal-Comparative Studies f) Experimental Research g) Survey Research h) Case Studies i) Exploratory Research
A survey is a comprehensive data collection method that can include various techniques like interviews and observations. A questionnaire is a specific set of structured questions within a survey designed to gather standardized responses. While a survey is a broader approach, a questionnaire is a focused tool for collecting specific data.
The choice of questionnaire type depends on the research objectives, the type of data required, and the preferences of respondents. Some common types include: • Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires consist of predefined, closed-ended questions with fixed response options. They are easy to analyze and suitable for quantitative research. • Semi-Structured Questionnaires: These questionnaires combine closed-ended questions with open-ended ones. They offer more flexibility for respondents to provide detailed explanations. • Unstructured Questionnaires: These questionnaires contain open-ended questions only, allowing respondents to express their thoughts and opinions freely. They are commonly used in qualitative research.
Following these steps ensures effective questionnaire administration for reliable data collection: • Choose a Method: Decide on online, face-to-face, mail, or phone administration. • Online Surveys: Use platforms like SurveyMonkey • Pilot Test: Test on a small group before full deployment • Clear Instructions: Provide concise guidelines • Follow-Up: Send reminders if needed
Thank you, Riya. This is quite helpful. As discussed, response bias is one of the disadvantages in the use of questionnaires. One way to help limit this can be to use scenario based questions. These type of questions may help the respondents to be more reflective and active in the process.
Thank you, Dear Riya. This is quite helpful.
Great insights there Doc
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
Graphical Abstracts Vs. Infographics: Best practices for using visual illustrations for increased research impact
Dr. Sarah Chen stared at her computer screen, her eyes staring at her recently published…

- Publishing Research
10 Tips to Prevent Research Papers From Being Retracted
Research paper retractions represent a critical event in the scientific community. When a published article…

- Industry News
Google Releases 2024 Scholar Metrics, Evaluates Impact of Scholarly Articles
Google has released its 2024 Scholar Metrics, assessing scholarly articles from 2019 to 2023. This…
![how to make a questionnaire for a research What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- AI in Academia
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

Which among these features would you prefer the most in a peer review assistant?
Creating a Questionnaire
Create the perfect questionnaire and collect actionable data using our online guide!

Table of Contents
- How to Create
Questionnaire Types
- Collecting Responses
- Analyzing Results
- Getting Started
What is a Questionnaire?
Definition: A questionnaire is a convenient way to collect feedback. A questionnaire can be used to measure customer satisfaction, capture employee feedback, or even conduct product research. Responses can be collected via email, web link, QR code, or using a survey panel.
The term "survey" and "questionnaire" are commonly used interchangeably. A questionnaire refers to the questions used to collect feedback (the form itself). A survey relates to the entire research process, including summarizing and analyzing questionnaire data.
Getting Started + Tips
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, an anonymous link, or even a QR code.
The following 6 tips will help you create the perfect questionnaire:
1) Use 10 Questions or Less
The shorter you keep your survey, the higher your completion rates. Longer questionnaires usually tend to have a high drop-off percentage. Keeping your surveys to 10 questions or fewer forces you to draft a study that only includes important questions; you should remove trivial questions during the draft process.
2) One Idea Per Question
Make sure each question only covers one topic. Try to include only one topic at a time. For example, in an employee survey, you would not want to ask, "Do you feel satisfied with your compensation and career advancement?". Instead, you would like to separate "compensation" and "career advancement" into two questions or use a Likert scale , putting each question on a separate row.
3) Group Similar Questions Together
Suppose the survey is more than ten questions; similar questions should be grouped on separate pages. If you don't want to use more than one page, add extra spacing between groups of the question; extra white space can increase the increase the readability of your questionnaire.
4) Use Skip/Display Logic
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates.
If you have questions that only apply to certain people, consider using skip or display logic to show those questions conditionally. This will help reduce the length of your survey and boost response rates. For example, if you asked, "Are you currently looking for new employment opportunities?". If the answer were "yes," a follow-up question would ask, "Why?"
5) Use Research Questions Like MaxDiff
Research questions are an excellent tool for customer or product questionnaires. Instead of asking multiple questions on which features are essential or what price is desirable, question types like MaxDiff and Conjoint will provide you with high-quality, actionable data that can be used for feature prioritization and product pricing. In addition, these question types will reduce the length of your questionnaire.
6) Keep the Audience in Mind
An employee questionnaire should use an anonymous link to collect responses; this will help boost trust and increase honest answers. If doing a customer study, consider adding custom data to the weblink to help identify responses. A survey panel and current customers can lend fresh perspectives for general market research.
Questionnaire Templates
Adding customer surveys to your Google review strategy will add additional data points to improve customer satisfaction. In addition, surveys are a valuable tool to identify ways to improve, establish internal benchmarks, and conduct pricing and product research to improve your company's products.
While there are numerous types of questionnaires (or survey types), these are the five most common general categories:
1) Customer Satisfaction
Capturing customer feedback is one of the most common uses of questionnaires. A good customer satisfaction survey will always revolve around a Net Promoter Score question. When the Net Promoter Score question results are tallied, one number from -100 is 100 is displayed. This number is ideal for benchmarks. Net Promoter provides quick and actionable feedback when combined with an open-ended text question.
2) Customer Effort
Measuring how easily customers can complete a purchase or take a specific action is crucial for the customer experience strategy. A customer effort score question is a rating scale from 1 to 7 (disagree to agree). Results for this question are averaged; the higher the score, the easier it is for your customers to complete tasks.
3) Employee Satisfaction & Engagement
Employee satisfaction and engagement are often used interchangeably but measure different things. Both types of surveys often use opinion scales to ask questions.
Employee satisfaction measures how satisfied employees are with their job and work environment. Standard measures of employee satisfaction include salary, benefits, and co-worker relationships.
Employee engagement relates to the emotional commitment employees have to an organization. It goes beyond simple satisfaction. Standard measures of engagement include belief in the company mission, opportunities for career growth, and being inspired to perform at a high level.
4) Employee Exit Interviews
When employees leave for new opportunities, sending a questionnaire is a great way to understand why that employee is leaving. The feedback obtained here can be used to improve the workplace and reduce employee turnover.
5) Product Research
MaxDiff is used to identify what is most important to your audience. For example, if building a new mobile application, asking a group of users what they think is least and most important will help guide product strategy; your team should only focus on the important areas.
For pricing a new product, Van Westendorp will give you a range of prices the market is willing to expect. You could price your product too high or too low without a question like this, reducing your market penetration.
Collecting Responses For Your Questionnaire
There are a few different ways to collect feedback for questionnaires. Depending on your needs, each one could have an advantage.
With email distribution, you would upload a list of email addresses, and the platform would automatically place a link to your questionnaire inside the email body. One advantage is sending email reminders to respondents who still need to complete your survey. In addition, the email links are unique for each respondent, so you can track email open and click rates. As a result, email surveys are ideal for customer research.
A web link is a convenient way to collect feedback at your convenience. You can place a web link on social media, your website, or even inside your CRM email program (instead of an email collector with a unique link to each person). Custom data can be included in the link, such as store location. This custom data can be used to segment and filter results.
Anonymous Link
When you want to protect your respondents' identities, you use an anonymous link . Anonymous inks do not store respondent information, IP address, or email address. Because of this, anonymous survey links are perfect for employee surveys.
QR code Surveys
QR code surveys can be placed on paper receipts, product packaging, or flyers. In addition, QR codes are a great way to collect feedback after or during an event or even during in-person focus groups.
Survey Panels
If you're conducting market research and need access to a customer base, using a survey panel will get you the responses required. A good survey panel will allow you to target specific demographics, job titles, or interest levels (such as car enthusiasts). When using survey panels, you'll want to double-check and clean your data for low-quality responses. People who speed through your survey or mark the first answer for all questions should be removed.
How to Analyze Questionnaire Data
When analyzing the data from a questionnaire, consider a few advanced techniques like the ones below. These techniques will give you better insights than just simple graphs and charts.
Creating a segment or a cross-tabulation is the easiest way to dive deeper into your results. For example, if you conducted an employee satisfaction survey, the overall scores for the company could be high. But that might only tell part of the story. For example, if your company has multiple departments, you should create a cross-tabulation for each department. You might notice that there is one department with low scores. or one department with high scores.
If your company conducted its first Net Promoter Score survey and the results were -10, that score would be your benchmark. Each subsequent customer survey you run should be compared against that initial number to improve it each time.
TURF Analysis
This is an advanced research technique but very valuable. TURF analysis analysis stands for "Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency" and is used to find the combination of items that would provide the highest reach level. For example, suppose you ask, "Which of the following flavor of ice cream would you buy?" If you run a TURF analysis on the results, you could find the top 3 or 4 combinations of flavors that would result in the highest sales.
Unsure Where to Start?
Creating a questionnaire can be a challenging process. However, these three suggestions can help you with the perfect questionnaire strategy.
1) Talk With Your Team
Some departments might want to conduct pricing research and do simple Net Promoter Score surveys. Having your organization aligned on strategy will simplify the process and eliminate any possibility of re-work. An aligned strategy will also mean a shorter study with fewer overlapping questions.
2) Start with a Template
A pre-made template will show you how to format and word questions. Next, try multiple templates to understand the various question types.
3) Look at Competitor Surveys
You might notice competitors asking specific questions - this would be a sign that those questions provide valuable metrics. If you can incorporate the great things your competition does while making it more efficient for respondents, your questionnaire campaigns will have a greater chance of success.
Get Started Now
We have you covered on anything from customer surveys, employee surveys, to market research. Get started and create your first survey for free.
Imperial College London Imperial College London
Latest news.
Developing a new test to improve sepsis outcomes

NHS using Imperial spinout’s advanced prescription software to improve safety

Work starts on world’s most sensitive ultra-rare particle detector
- Centre for Higher Education Research and Scholarship
- Research and Innovation
- Education evaluation toolkit
- Tools and resources for evaluation
- Questionnaires
Best practice in questionnaire design
The following guide to developing questionnaire items and organising the questionnaire is based on best practice (Gehlbach & Brinkworth, 2011; Gehlbach & Artino Jr., 2018). These best practices have been tested across over 40 years of research (Krosnick & Presser, 2010; Schwarz, 1999).
Best practice for creating items
Word items as questions rather than statements and avoid 'agree-disagree' response options.
Agree-disagree response options may introduce acquiescence bias, which is the tendency to agree with an item regardless of its content (Wright, 1975). Asking respondents to rate their level of agreement to different statements can be cognitively demanding, which increases respondent error and reduces respondent effort (Fowler, 2009). Instead, use verbally labelled response options that reinforce the underlying topic (e.g., the responses for “How happy are you?” would be not at all happy, slightly happy, somewhat happy, quite happy, extremely happy). Empirical evidence demonstrates that agree-disagree response options diminish item quality (Saris, Revilla, Krosnick, Schaeffer, & Shaeffer, 2010), and are among the “worst ways to present items” (Gehlbach & Artino Jr., 2018, p. 361).
Use verbal labels for each response option
Use verbal labels for each response option, rather than labelling only the end points of the response options or labelling with both numbers and verbal labels. This helps to focus the attention of the respondent and reduce measurement error (Artino, Jr. & Gehlbach, 2012).
Ask about one idea at a time
Ask about one idea at a time rather than using double-barrelled items, which ask about two or more ideas in the same question (e.g., instead of asking, “How happy and engaged are you?” ask two questions, one about happiness and one about engagement). If you use double-barrelled items, you risk students responding to only one part of that item (Dillman, Smyth, & Christian, 2014)
Phrase questions with positive language
Phrase questions with positive language rather than using reverse scored or negative language, which students tend to have trouble understanding. Negative words are more difficult to process cognitively, which leads these items to take longer to answer and leads to misresponses (Swain, Weathers, & Niedrich, 2008).
Use at least five response options per scale
Use at least five response options per scale to capture a wider range of perceptions. Research indicates that the “sweet spot” of the number of response anchors is about five (Weng, 2004; Nielsen, Makransky, Vang, & Danmeyer, 2017). A five-item scale that assesses a representative cross-section of a student’s experience should improve measurement (Gehlbach & Artino Jr., 2018).
Maintain equal spacing between repsonse options. Use additional space to visually separate non-substansive response options
Maintain equal spacing between response options, and use additional space to visually separate non-substantive response options. This will reinforce the notion that conceptually, there is equal distance between each response option, which yields less biased responses. Moreover, this will help align the visual midpoint with the conceptual midpoint, reducing measurement error (Artino, Jr. & Gehlbach, 2012). This is especially important if you are administering your questionnaire on paper. Electronic questionnaire administrators such as Qualtrics will space response options equally, and you will have to be aware to add an extra space to separate non-substantive response options (e.g., ‘N/A’). To see some examples, check out the resources for evaluating self-efficacy and take a look at this visual guide ).
Best practice for organising the whole questionnaire
This guidance has been summarised from Gehlbach and Artino (2018).
Ask the more important items earlier in the questionnaire
This will increase the likelihood that respondents will answer these questions whilst they are focused and have energy.
Ensure each item applies to each respondent
Make sure that item content applies to each respondent and is worded accessibly, or you risk alienating respondents to whom the item does not apply (Dillman, Smyth, & Christian, 2014).
Use scales rather than single items
Scales bolster accuracy, with each question addressing a representative cross-section of the experience.
Maintain a consistent visual layout of the questionnaire
This helps maintain clarity for the respondent, who can then complete the questionnaire more efficiently.
Place sensitive items (e.g. demographic questions) later in the questionnaire
Respondents will feel more comfortable sharing this information later on in the questionnaire.
Artino, Jr., A. R., & Gehlbach, H. (2012). AM Last Page: Avoiding Four Visual-Design Pitfalls in Survey Development. Academic Medicine, 87 (10), 1452. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Hunter_Gehlbach/publication/231210670_AM_Last_Page_Avoiding_Four_Visual-Design_Pitfalls_in_Survey_Development/links/5a835de6aca272d6501eb6a3/AM-Last-Page-Avoiding-Four-Visual-Design-Pitfalls-in-Survey-Development.pdf
Dillman, D. A., Smyth, J. D., & Christian, L. M. (2014). Internet, Phone, Mail, and Mixed-Mode Surveys: The Tailored Design Method (4th ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Gehlbach, H., & Artino Jr., A. R. (2018). The survey checklist (manifesto). Academic Medicine, 93 (3), 360-366. Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/academicmedicine/fulltext/2018/03000/The_Survey_Checklist__Manifesto_.18.aspx#pdf-link
Gehlbach, H., & Brinkworth, M. E. (2011). Measure twice, cut down error: A process for enhancing the validity of survey scales. Review of General Psychology, 15 (4), 380-387. Retrieved from https://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/8138346/Gehlbach%20-%20Measure%20twice%208-31-11.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
Krosnick, J. A., & Presser, S. (2010). Question and questionnaire design. In P. V. Marsden, & J. D. Wright (Eds.), Handbook of Survey Research. Bingley, England: Emerald Group Publishing.
Nielsen, T., Makransky, G., Vang, M. L., & Danmeyer, J. (2017). How specific is specific self-efficacy? A construct validity study using Raschmeasurement models. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 53 , 87-97.
Saris, W. E., Revilla, M., Krosnick, J. A., Schaeffer, E. M., & Shaeffer, E. M. (2010). Comparing questions with agree/disagree response options to questions with item-specific response options. Survey Research Methods, 4 , 61-79.
Schwarz, N. (1999). Self-reports: how the questions shape the answers. American Psychology, 54 , 93-105.
Swain, S. D., Weathers, D., & Niedrich, R. W. (2008). Assessing three sources of misreponse to reversed Likert items. Journal of Marketing Research, 45 , 116-131.
Weng, L. -J. (2004). Impact of the number of response categories and anchor labels on coefficient alpha and test-retest reliability. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 64 , 956-972. Retrieved from https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0013164404268674
Wright, J. D. (1975). Does acquiescence bias the 'Index of Political Efficacy?'. The Public Opinion Quarterly, 39 (2), 219-226.
- Utility Menu
Harvard University Program on Survey Research
- Questionnaire Design Tip Sheet
This PSR Tip Sheet provides some basic tips about how to write good survey questions and design a good survey questionnaire.
| 40 KB |
PSR Resources
- Managing and Manipulating Survey Data: A Beginners Guide
- Finding and Hiring Survey Contractors
- How to Frame and Explain the Survey Data Used in a Thesis
- Overview of Cognitive Testing and Questionnaire Evaluation
- Sampling, Coverage, and Nonresponse Tip Sheet
- Introduction to Surveys for Honors Thesis Writers
- PSR Introduction to the Survey Process
- Related Centers/Programs at Harvard
- General Survey Reference
- Institutional Review Boards
- Select Funding Opportunities
- Survey Analysis Software
- Professional Standards
- Professional Organizations
- Major Public Polls
- Survey Data Collections
- Major Longitudinal Surveys
- Other Links
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

How to create an effective survey in 15 simple tips
Updated August 22, 2024
You don’t have to be an expert to create a survey, but by following a few survey best practices you can make sure you’re collecting the best data possible.
Access 50+ expert-designed survey templates with a free Qualtrics Surveys account
From working out what you want to achieve to providing incentives for respondents, survey design can take time.
But when you don’t have hours to devote to becoming a survey-creation guru, a quick guide to the essentials is a great way to get started.
In this article, we’re going to reveal how to create a survey that’s easy to complete, encourages collecting feedback, hits the research questions you’re interested in, and produces data that’s easy to work with at the analysis stage .
15 Tips when creating surveys
1. define the purpose of the survey.
Before you even think about your survey questions , you need to define their purpose.
The survey’s purpose should be a clear, attainable, and relevant goal. For example, you might want to understand why customer engagement is dropping off during the middle of the sales process.
Your goal could then be something like: “I want to understand the key factors that cause engagement to dip at the middle of the sales process, including both internal and external elements.”
Or maybe you want to understand customer satisfaction post-sale. If so, the goal of your survey could be: “I want to understand how customer satisfaction is influenced by customer service and support post-sale, including through online and offline channels.”
The idea is to come up with a specific, measurable, and relevant goal for your survey. This way you ensure that your questions are tailored to what you want to achieve and that the data captured can be compared against your goal.
2. Make every question count
You’re building your survey questionnaire to obtain important insights, so every question should play a direct role in hitting that target.
Make sure each question adds value and drives survey responses that relate directly to your research goals. For example, if your participant’s precise age or home state is relevant to your results, go ahead and ask. If not, save yourself and your respondents some time and skip it.
It’s best to plan your survey by first identifying the data you need to collect and then writing your questions.
You can also incorporate multiple-choice questions to get a range of responses that provide more detail than a solid yes or no. It’s not always black and white.
For a deeper dive into the art and science of question-writing and survey best practices, check out Survey questions 101 .
3. Keep it short and simple
Although you may be deeply committed to your survey, the chances are that your respondents... aren’t.
As a survey designer, a big part of your job is keeping their attention and making sure they stay focused until the end of the survey.
Respondents are less likely to complete long surveys or surveys that bounce around haphazardly from topic to topic. Make sure your survey follows a logical order and takes a reasonable amount of time to complete.
Although they don’t need to know everything about your research project, it can help to let respondents know why you’re asking about a certain topic. Knowing the basics about who you are and what you’re researching means they’re more likely to keep their responses focused and in scope.
Access 50+ expert-designed survey templates now
4. Ask direct questions
Vaguely worded survey questions confuse respondents and make your resulting data less useful. Be as specific as possible, and strive for clear and precise language that will make your survey questions easy to answer.
It can be helpful to mention a specific situation or behavior rather than a general tendency. That way you focus the respondent on the facts of their life rather than asking them to consider abstract beliefs or ideas .
See an example:
Good survey design isn’t just about getting the information you need, but also encouraging respondents to think in different ways.
Get access to the top downloaded survey templates here
5. Ask one question at a time
Although it’s important to keep your survey as short and sweet as possible, that doesn’t mean doubling up on questions. Trying to pack too much into a single question can lead to confusion and inaccuracies in the responses.
Take a closer look at questions in your survey that contain the word “and” – it can be a red flag that your question has two parts. For example: “Which of these cell phone service providers has the best customer support and reliability?” This is problematic because a respondent may feel that one service is more reliable, but another has better customer support.
6. Avoid leading and biased questions
Although you don’t intend them to, certain words and phrases can introduce bias into your questions or point the respondent in the direction of a particular answer.
As a rule of thumb, when you conduct a survey it’s best to provide only as much wording as a respondent needs to give an informed answer. Keep your question wording focused on the respondent and their opinions, rather than introducing anything that could be construed as a point of view of your own.
In particular, scrutinize adjectives and adverbs in your questions. If they’re not needed, take them out.
7. Speak your respondent's language
This tip goes hand in hand with many others in this guide – it’s about making language only as complex or as detailed as it needs to be when conducting great surveys.
Create surveys that use language and terminology that your respondents will understand. Keep the language as plain as possible, avoid technical jargon and keep sentences short. However, beware of oversimplifying a question to the point that its meaning changes.
8. Use response scales whenever possible
Response scales capture the direction and intensity of attitudes, providing rich data. In contrast, categorical or binary response options, such as true/false or yes/no response options, generally produce less informative data.
If you’re in the position of choosing between the two, the response scale is likely to be the better option.
Avoid using scales that ask your target audience to agree or disagree with statements, however. Some people are biased toward agreeing with statements , and this can result in invalid and unreliable data.
9. Avoid using grids or matrices for responses
Grids or matrices of answers demand a lot more thinking from your respondent than a scale or multiple choice question. They need to understand and weigh up multiple items at once, and oftentimes they don’t fill in grids accurately or according to their true feelings .
Another pitfall to be aware of is that grid question types aren’t mobile-friendly. It’s better to separate questions with grid responses into multiple questions in your survey with a different structure such as a response scale.
See an example using our survey tool:
10. Rephrase yes/no questions if possible in online survyes
As we’ve described, yes/no questions provide less detailed data than a response scale or multiple-choice, since they only yield one of two possible answers.
Many yes/no questions can be reworked by including phrases such as “How much,” “How often,” or “How likely.” Make this change whenever possible and include a response scale for richer data.
By rephrasing your questions in this way, your survey results will be far more comprehensive and representative of how your respondents feel.
Next? Find out how to write great questions .
11. Start with the straightforward stuff
Ease your respondent into the survey by asking easy questions at the start of your questionnaire, then moving on to more complex or thought-provoking elements once they’re engaged in the process.
This is especially valuable if you need to cover any potentially sensitive topics in your survey. Never put sensitive questions at the start of the questionnaire where they’re more likely to feel off-putting.
Your respondent will probably become more prone to fatigue and distraction towards the end of the survey, so keep your most complex or contentious questions in the middle of the survey flow rather than saving them until last.
12. Use unbalanced scales with care
Unbalanced response scales and poorly worded questions can mislead respondents.
For example, if you’ve asked them to rate a product or service and you provide a scale that includes “poor”, “satisfactory”, “good” and “excellent”, they could be swayed towards the “excellent” end of the scale because there are more positive options available.
Make sure your response scales have a definitive, neutral midpoint (aim for odd numbers of possible responses) and that they cover the whole range of possible reactions to the question .
13. Consider adding incentives
To increase the number of responses, incentives — discounts, offers, gift cards, or sweepstakes — can prove helpful.
Of course, while the benefits of offering incentives sound appealing (more respondents), there’s the possibility of attracting the opinions of the wrong audiences, such as those who are only in it for the incentive.
With this in mind, make sure you limit your surveys to your target population and carefully assess which incentives would be most valuable to them.
14. Take your survey for a test drive
Want to know how to make a survey a potential disaster? Send it out before you pre-test .
However short or straightforward your questionnaire is, it’s always a good idea to pre-test your survey before you roll it out fully so that you can catch any possible errors before they have a chance to mess up your survey results.
Share your survey with at least five people, so that they can test your survey to help you catch and correct problems before you distribute it.
15. Let us help you
Survey design doesn’t have to be difficult — even less so with the right expertise, digital solutions, and survey templates.
At Qualtrics, we provide survey software that’s used by more than 11,000 of the top brands and 99 of the top business schools worldwide.
Furthermore, we have a library of high-quality, ready-to-use, and easy-to-configure survey templates that can improve your surveys significantly.
You can check out our template marketplace here . As a free or existing customer, you have access to the complete collection and can filter by the core experiences you want to drive.
As for our survey software , it’s completely free to use and powers more than 1 billion surveys a year. Using it, you can get answers to your most important brand, market, customer, and product questions, build your own surveys, get insights from your audience wherever they are, and much, much more.
If you want to learn more about how to use our survey tool to create a survey, as well as what else it can do — check out our blog on how to create a free online survey using Qualtrics .
See instant results with our online free survey maker
Sarah Fisher
Related Articles
May 20, 2024
Best strategy & research books to read in 2024
May 13, 2024
Experience Management
X4 2024 Strategy & Research Showcase: Introducing the future of insights generation
November 7, 2023
Brand Experience
The 4 market research trends redefining insights in 2024
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
March 21, 2023
Sample size calculator
November 18, 2022
Statistical analysis software: your complete guide to getting started
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
28 Questionnaire Examples, Questions, & Templates to Survey Your Clients
Published: May 15, 2023
The adage "the customer is always right" has received some pushback in recent years, but when it comes to conducting surveys , the phrase is worth a deeper look. In the past, representatives were tasked with solving client problems as they happened. Now, they have to be proactive by solving problems before they come up.

Salesforce found that 63% of customers expect companies to anticipate their needs before they ask for help. But how can a customer service team recognize these customer needs in advance and effectively solve them on a day-to-day basis?
![how to make a questionnaire for a research → Free Download: 5 Customer Survey Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/9d36416b-3b0d-470c-a707-269296bb8683.png)
A customer questionnaire is a tried-and-true method for collecting survey data to inform your customer service strategy . By hearing directly from the customer, you'll capture first-hand data about how well your service team meets their needs. In this article, you'll get free questionnaire templates and best practices on how to administer them for the most honest responses.
Table of Contents:
Questionnaire Definition
Survey vs. questionnaire, questionnaire templates.
- Questionnaire Examples
Questionnaire Design
Survey question examples.
- Examples of Good Survey Questions
How to Make a Questionnaire
.webp)
5 Free Customer Satisfaction Survey Templates
Easily measure customer satisfaction and begin to improve your customer experience.
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Effort Score
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A questionnaire is a research tool used to conduct surveys. It includes specific questions with the goal to understand a topic from the respondents' point of view. Questionnaires typically have closed-ended, open-ended, short-form, and long-form questions.
The questions should always stay as unbiased as possible. For instance, it's unwise to ask for feedback on a specific product or service that’s still in the ideation phase. To complete the questionnaire, the customer would have to imagine how they might experience the product or service rather than sharing their opinion about their actual experience with it.
Ask broad questions about the kinds of qualities and features your customers enjoy in your products or services and incorporate that feedback into new offerings your team is developing.
What makes a good questionnaire?
Define the goal, make it short and simple, use a mix of question types, proofread carefully, keep it consistent.
A good questionnaire should find what you need versus what you want. It should be valuable and give you a chance to understand the respondent’s point of view.
Make the purpose of your questionnaire clear. While it's tempting to ask a range of questions simultaneously, you'll get more valuable results if you stay specific to a set topic.
According to HubSpot research , 47% of those surveyed say their top reason for abandoning a survey is the time it takes to complete.
So, questionnaires should be concise and easy to finish. If you're looking for a respondent’s experience with your business, focus on the most important questions.
5 Customer Survey Templates
Featured resource.
Your questionnaire should include a combination of question types, like open-ended, long-form, or short-ended questions.
Open-ended questions give users a chance to share their own answers. But closed-ended questions are more efficient and easy to quantify, with specific answer choices.
If you're not sure which question types are best, read here for more survey question examples .
While it's important to check spelling and grammar, there are two other things you'll want to check for a great questionnaire.
First, edit for clarity. Jargon, technical terms, and brand-specific language can be confusing for respondents. Next, check for leading questions. These questions can produce biased results that will be less useful to your team.
Consistency makes it easier for respondents to quickly complete your questionnaire. This is because it makes the questions less confusing. It can also reduce bias.
Being consistent is also helpful for analyzing questionnaire data because it makes it easier to compare results. With this in mind, keep response scales, question types, and formatting consistent.
In-Depth Interviews vs. Questionnaire
Questionnaires can be a more feasible and efficient research method than in-depth interviews. They are a lot cheaper to conduct. That’s because in-depth interviews can require you to compensate the interviewees for their time and give accommodations and travel reimbursement.
Questionnaires also save time for both parties. Customers can quickly complete them on their own time, and employees of your company don't have to spend time conducting the interviews. They can capture a larger audience than in-depth interviews, making them much more cost-effective.
It would be impossible for a large company to interview tens of thousands of customers in person. The same company could potentially get feedback from its entire customer base using an online questionnaire.
When considering your current products and services (as well as ideas for new products and services), it's essential to get the feedback of existing and potential customers. They are the ones who have a say in purchasing decisions.
A questionnaire is a tool that’s used to conduct a survey. A survey is the process of gathering, sampling, analyzing, and interpreting data from a group of people.
The confusion between these terms most likely stems from the fact that questionnaires and data analysis were treated as very separate processes before the Internet became popular. Questionnaires used to be completed on paper, and data analysis occurred later as a separate process. Nowadays, these processes are typically combined since online survey tools allow questionnaire responses to be analyzed and aggregated all in one step.
But questionnaires can still be used for reasons other than data analysis. Job applications and medical history forms are examples of questionnaires that have no intention of being statistically analyzed. The key difference between questionnaires and surveys is that they can exist together or separately.
Below are some of the best free questionnaire templates you can download to gather data that informs your next product or service offering.
What makes a good survey question?
Have a goal in mind, draft clear and distinct answers and questions, ask one question at a time, check for bias and sensitivity, include follow-up questions.
To make a good survey question, you have to choose the right type of questions to use. Include concise, clear, and appropriate questions with answer choices that won’t confuse the respondent and will clearly offer data on their experience.
Good survey questions can give a business good data to examine. Here are some more tips to follow as you draft your survey questions.
To make a good survey, consider what you are trying to learn from it. Understanding why you need to do a survey will help you create clear and concise questions that you need to ask to meet your goal. The more your questions focus on one or two objectives, the better your data will be.
You have a goal in mind for your survey. Now you have to write the questions and answers depending on the form you’re using.
For instance, if you’re using ranks or multiple-choice in your survey, be clear. Here are examples of good and poor multiple-choice answers:
Poor Survey Question and Answer Example
California:
- Contains the tallest mountain in the United States.
- Has an eagle on its state flag.
- Is the second-largest state in terms of area.
- Was the location of the Gold Rush of 1849.
Good Survey Question and Answer Example
What is the main reason so many people moved to California in 1849?
- California's land was fertile, plentiful, and inexpensive.
- The discovery of gold in central California.
- The East was preparing for a civil war.
- They wanted to establish religious settlements.
In the poor example, the question may confuse the respondent because it's not clear what is being asked or how the answers relate to the question. The survey didn’t fully explain the question, and the options are also confusing.
In the good example above, the question and answer choices are clear and easy to understand.
Always make sure answers and questions are clear and distinct to create a good experience for the respondent. This will offer your team the best outcomes from your survey.
It's surprisingly easy to combine multiple questions into one. They even have a name — they’re called "double-barreled" questions. But a good survey asks one question at a time.
For example, a survey question could read, "What is your favorite sneaker and clothing apparel brand?" This is bad because you’re asking two questions at once.
By asking two questions simultaneously, you may confuse your respondents and get unclear answers. Instead, each question should focus on getting specific pieces of information.
For example, ask, "What is your favorite sneaker brand?" then, "What is your favorite clothing apparel brand?" By separating the questions, you allow your respondents to give separate and precise answers.
Biased questions can lead a respondent toward a specific response. They can also be vague or unclear. Sensitive questions such as age, religion, or marital status can be helpful for demographics. These questions can also be uncomfortable for people to answer.
There are a few ways to create a positive experience with your survey questions.
First, think about question placement. Sensitive questions that appear in context with other survey questions can help people understand why you are asking. This can make them feel more comfortable responding.
Next, check your survey for leading questions, assumptions, and double-barreled questions. You want to make sure that your survey is neutral and free of bias.
Asking more than one survey question about an area of interest can make a survey easier to understand and complete. It also helps you collect more in-depth insights from your respondents.
1. Free HubSpot Questionnaire Template
HubSpot offers a variety of free customer surveys and questionnaire templates to analyze and measure customer experience. Choose from five templates: net promoter score, customer satisfaction, customer effort, open-ended questions, and long-form customer surveys.
2. Client Questionnaire Template
It's a good idea to gauge your clients' experiences with your business to uncover opportunities to improve your offerings. That will, in turn, better suit their lifestyles. You don't have to wait for an entire year to pass before polling your customer base about their experience either. A simple client questionnaire, like the one below, can be administered as a micro survey several times throughout the year. These types of quick survey questions work well to retarget your existing customers through social media polls and paid interactive ads.
1. How much time do you spend using [product or service]?
- Less than a minute
- About 1 - 2 minutes
- Between 2 and 5 minutes
- More than 5 minutes
2. In the last month, what has been your biggest pain point?
- Finding enough time for important tasks
- Delegating work
- Having enough to do
3. What's your biggest priority right now?
- Finding a faster way to work
- Problem-solving
- Staff development

3. Website Questionnaire Template
Whether you just launched a brand new website or you're gathering data points to inform a redesign, you'll find customer feedback to be essential in both processes. A website questionnaire template will come in handy to collect this information using an unbiased method.
1. How many times have you visited [website] in the past month?
- More than once
2. What is the primary reason for your visit to [website]?
- To make a purchase
- To find more information before making a purchase in-store
- To contact customer service
3. Are you able to find what you're looking for on the website homepage?
4. Customer Satisfaction Questionnaire Template
If you've never surveyed your customers and are looking for a template to get started, this one includes some basic customer satisfaction questions. These will apply to just about any customer your business serves.
1. How likely are you to recommend us to family, friends, or colleagues?
- Extremely unlikely
- Somewhat unlikely
- Somewhat likely
- Extremely likely
2. How satisfied were you with your experience?
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10
3. Rank the following items in terms of their priority to your purchasing process.
- Helpful staff
- Quality of product
- Price of product
- Ease of purchase
- Proximity of store
- Online accessibility
- Current need
- Appearance of product
4. Who did you purchase these products for?
- Family member
- On behalf of a business
5. Please rate our staff on the following terms:
- Friendly __ __ __ __ __ Hostile
- Helpful __ __ __ __ __ Useless
- Knowledgeable __ __ __ __ __ Inexperienced
- Professional __ __ __ __ __ Inappropriate
6. Would you purchase from our company again?
7. How can we improve your experience for the future?
________________________________.
5. Customer Effort Score Questionnaire Template
The following template gives an example of a brief customer effort score (CES) questionnaire. This free template works well for new customers to measure their initial reaction to your business.
1. What was the ease of your experience with our company?
- Extremely difficult
- Somewhat difficult
- Somewhat easy
- Extremely easy
2. The company did everything it could to make my process as easy as possible.
- Strongly disagree
- Somewhat disagree
- Somewhat agree
- Strongly agree
3. On a scale of 1 to 10 (1 being "extremely quickly" and 10 being "extremely slowly"), how fast were you able to solve your problem?
4. How much effort did you have to put forth while working with our company?
- Much more than expected
- Somewhat more than expected
- As much as expected
- Somewhat less than expected
- Much less than expected

6. Demographic Questionnaire Template
Here's a template for surveying customers to learn more about their demographic background. You could substantiate the analysis of this questionnaire by corroborating the data with other information from your web analytics, internal customer data, and industry data.
1. How would you describe your employment status?
- Employed full-time
- Employed part-time
- Freelance/contract employee
- Self-employed
2. How many employees work at your company?
3. How would you classify your role?
- Individual Contributor
4. How would you classify your industry?
- Technology/software
- Hospitality/dining
- Entertainment
Below, we have curated a list of questionnaire examples that do a great job of gathering valuable qualitative and quantitative data.
4 Questionnaire Examples
1. customer satisfaction questions.

Learn more about HubSpot's Customer Survey software.
Multiple-Choice
Multiple-choice questions offer respondents several answers to choose from. This is a popular choice of questionnaire format since it's simple for people to fill out and for companies to analyze.
Multiple-choice questions can be in single-answer form (respondents can only choose one response) or multiple-answer form (respondents can choose as many responses as necessary).
Multiple-choice survey question examples : "Which of the following social media platforms do you use most often?"
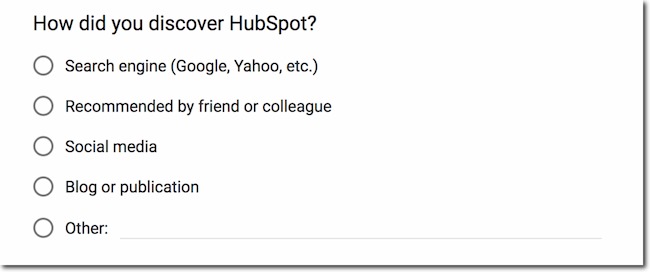
Image Source
Rating Scale
Rating scale questions offer a scale of numbers and ask respondents to rate topics based on the sentiments assigned to that scale. This is effective when assessing customer satisfaction.
Rating scale survey question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with the customer service you received today on a scale of 1-10."
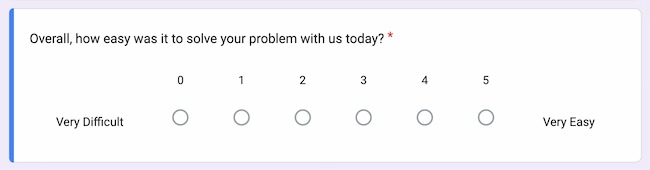
Yes or no survey questions are a type of dichotomous question. These are questions that only offer two possible responses. They’re useful because they’re quick to answer and can help with customer segmentation.
Yes or no survey questions example : "Have you ever used HubSpot before?"
Likert Scale
Likert scale questions assess whether a respondent agrees with the statement, as well as the extent to which they agree or disagree.
These questions typically offer five or seven responses, with sentiments ranging from items such as "strongly disagree" to "strongly agree." Check out this post to learn more about the Likert scale .
Likert scale survey question examples : “How satisfied are you with the service from [brand]?”

Open-ended questions ask a broader question or offer a chance to elaborate on a response to a close-ended question. They're accompanied by a text box that leaves room for respondents to write freely. This is particularly important when asking customers to expand on an experience or recommendation.
Open-ended survey question examples : "What are your personal goals for using HubSpot? Please describe."
Matrix Table
A matrix table is usually a group of multiple-choice questions grouped in a table. Choices for these survey questions are usually organized in a scale. This makes it easier to understand the relationships between different survey responses.
Matrix table survey question examples : "Rate your level of agreement with the following statements about HubSpot on a scale of 1-5."
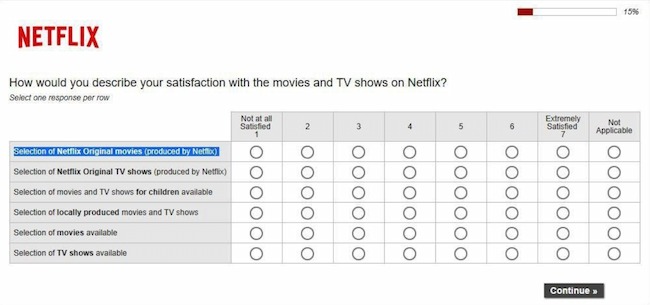
Rank Order Scaling
These questions ask respondents to rank a set of terms by order of preference or importance. This is useful for understanding customer priorities.
Rank order scaling examples : "Rank the following factors in order of importance when choosing a new job."
Semantic Differential Scale
This scale features pairs of opposite adjectives that respondents use for rating, usually for a feature or experience. This type of question makes it easier to understand customer attitudes and beliefs.
Semantic differential scale question examples : "Rate your overall impression of this brand as friendly vs. unfriendly, innovative vs. traditional, and boring vs. exciting."
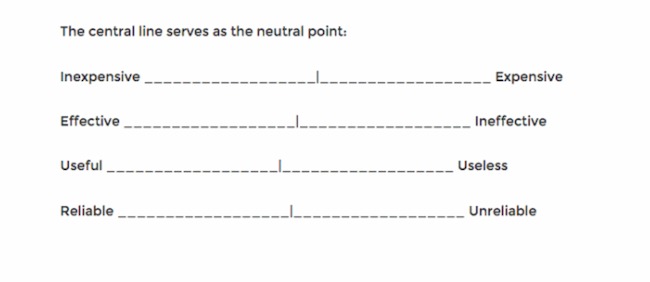
Side-By-Side Matrix
This matrix table format includes two sets of questions horizontally for easy comparison. This format can help with customer gap analysis.
Side-by-side matrix question examples : "Rate your level of satisfaction with HubSpot's customer support compared to its ease of use."
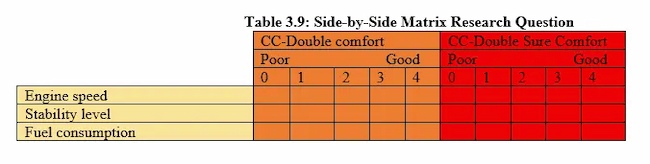
Stapel Scale
The Stapel rating scale offers a single adjective or idea for rating. It uses a numerical scale with a zero point in the middle. This survey question type helps with in-depth analysis.
Stapel scale survey question examples : "Rate your overall experience with this product as +5 (excellent) to -5 (terrible)."
Constant Sum Survey Questions
In this question format, people distribute points to different choices based on the perceived importance of each point. This kind of question is often used in market research and can help your team better understand customer choices .
Constant sum survey question examples : "What is your budget for the following marketing expenses: Paid campaigns, Events, Freelancers, Agencies, Research."
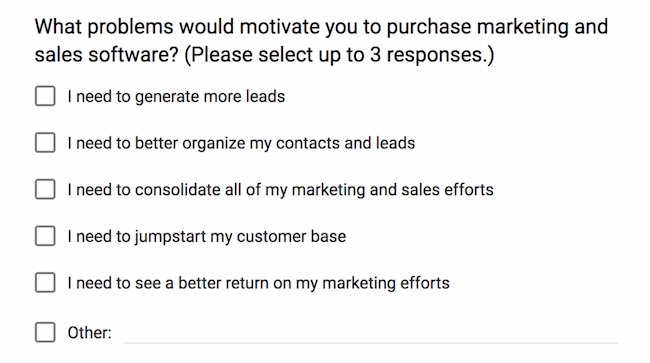
Image Choice
This survey question type shows several images. Then, it asks the respondent to choose the image that best matches their response to the question. These questions are useful for understanding your customers’ design preferences.
Image choice survey questions example : "Which of these three images best represents your brand voice?"

Choice Model
This survey question offers a hypothetical scenario, then the respondent must choose from the presented options. It's a useful type of question when you are refining a product or strategy.
Choice model survey questions example : "Which of these three deals would be most appealing to you?"
Click Map Questions
Click map questions offer an image click on specific areas of the image in response to a question. This question uses data visualization to learn about customer preferences for design and user experience.
Click map question examples : "Click on the section of the website where you would expect to find pricing information."

Data Upload
This survey question example asks the respondent to upload a file or document in response to a question. This type of survey question can help your team collect data and context that might be tough to collect otherwise.
Data upload question examples : "Please upload a screenshot of the error you encountered during your purchase."
Benchmarkable Questions
This question type asks a respondent to compare their answers to a group or benchmark. These questions can be useful if you're trying to compare buyer personas or other customer groups.
Benchmarkable survey questions example : "Compare your company's marketing budget to other companies in your industry."
Good Survey Questions
- What is your favorite product?
- Why did you purchase this product?
- How satisfied are you with [product]?
- Would you recommend [product] to a friend?
- Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?
- If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?
- Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?
- Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?
- How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?
- What would you miss the most if you couldn't use your favorite product from us?
- What is one word that best describes your experience using our product?
- What's the primary reason for canceling your account?
- How satisfied are you with our customer support?
- Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?
- How can we be more helpful?
- What additional features would you like to see in this product?
- Are we meeting your expectations?
- How satisfied are you with your experience?
1. "What is your favorite product?"
This question is a great starter for your survey. Most companies want to know what their most popular products are, and this question cuts right to the point.
It's important to note that this question gives you the customer's perspective, not empirical evidence. You should compare the results to your inventory to see if your customers' answers match your actual sales. You may be surprised to find your customers' "favorite" product isn't the highest-selling one.
2. "Why did you purchase this product?"
Once you know their favorite product, you need to understand why they like it so much. The qualitative data will help your marketing and sales teams attract and engage customers. They'll know which features to advertise most and can seek out new leads similar to your existing customers.
3. "How satisfied are you with [product]?"
When you have a product that isn't selling, you can ask this question to see why customers are unhappy with it. If the reviews are poor, you'll know that the product needs reworking, and you can send it back to product management for improvement. Or, if these results are positive, they may have something to do with your marketing or sales techniques. You can then gather more info during the questionnaire and restrategize your campaigns based on your findings.
4. "Would you recommend [product] to a friend?"
This is a classic survey question used with most NPS® surveys. It asks the customer if they would recommend your product to one of their peers. This is extremely important because most people trust customer referrals more than traditional advertising. So, if your customers are willing to recommend your products, you'll have an easier time acquiring new leads.
5. "Would you recommend [company name] to a friend?"
Similar to the question above, this one asks the customer to consider your business as a whole and not just your product. This gives you insight into your brand's reputation and shows how customers feel about your company's actions. Even if you have an excellent product, your brand's reputation may be the cause of customer churn . Your marketing team should pay close attention to this question to see how they can improve the customer experience .
6. "If you could change one thing about [product], what would it be?"
This is a good question to ask your most loyal customers or ones that have recently churned. For loyal customers, you want to keep adding value to their experience. Asking how your product can improve helps your development team find flaws and increases your chances of retaining a valuable customer segment.
For customers that have recently churned, this question gives insight into how you can retain future users that are unhappy with your product or service. By giving these customers a space to voice their criticisms, you can either reach out and offer solutions or relay feedback for consideration.
7. "Which other options were you considering before [product or company name]?"
If you're operating in a competitive industry, customers will have more than one choice when considering your brand. And if you sell variations of your product or produce new models periodically, customers may prefer one version over another.
For this question, you should offer answers to choose from in a multiple-selection format. This will limit the types of responses you'll receive and help you get the exact information you need.
8. "Did [product] help you accomplish your goal?"
The purpose of any product or service is to help customers reach a goal. So, you should be direct and ask them if your company steered them toward success. After all, customer success is an excellent retention tool. If customers are succeeding with your product, they're more likely to stay loyal to your brand.
9. "How would you feel if we did not offer this product, feature, or service?"
Thinking about discontinuing a product? This question can help you decide whether or not a specific product, service, or feature will be missed if you were to remove it.
Even if you know that a product or service isn't worth offering, it's important to ask this question anyway because there may be a certain aspect of the product that your customers like. They'll be delighted if you can integrate that feature into a new product or service.
10. "If you couldn't use your favorite product from us, what would you miss the most about it?"
This question pairs well with the one above because it frames the customer's favorite product from a different point of view. Instead of describing why they love a particular product, the customer can explain what they'd be missing if they didn't have it at all. This type of question uncovers "fear of loss," which can be a very different motivating factor than "hope for gain."
11. "What word best describes your experience using our product?"
Your marketing team will love this question. A single word or a short phrase can easily sum up your customers’ emotions when they experience your company, product, or brand. Those emotions can be translated into relatable marketing campaigns that use your customers’ exact language.
If the responses reveal negative emotions, it's likely that your entire customer service team can relate to that pain point. Rather than calling it "a bug in the system," you can describe the problem as a "frustrating roadblock" to keep their experience at the forefront of the solution.
12. "What's the primary reason for canceling your account?"
Finding out why customers are unhappy with your product or service is key to decreasing your churn rate . If you don't understand why people leave your brand, it's hard to make effective changes to prevent future turnover. Or worse, you might alter your product or service in a way that increases your churn rate, causing you to lose customers who were once loyal supporters.
13. "How satisfied are you with our customer support?"
It's worth asking customers how happy they are with your support or service team. After all, an excellent product doesn't always guarantee that customers will stay loyal to your brand. Research shows that one in six customers will leave a brand they love after just one poor service experience.
14. "Did we answer all of your questions and concerns?"
This is a good question to ask after a service experience. It shows how thorough your support team is and whether they're prioritizing speed too much over quality. If customers still have questions and concerns after a service interaction, your support team is focusing too much on closing tickets and not enough on meeting customer needs .
15. "How can we be more helpful?"
Sometimes it's easier to be direct and simply ask customers what else you can do to help them. This shows a genuine interest in your buyers' goals which helps your brand foster meaningful relationships with its customer base. The more you can show that you sincerely care about your customers' problems, the more they'll open up to you and be honest about how you can help them.
16. What additional features would you like to see in this product?
With this question, your team can get inspiration for the company's next product launch. Think of the responses as a wish list from your customers. You can discover what features are most valuable to them and whether they already exist within a competitor's product.
Incorporating every feature suggestion is nearly impossible, but it's a convenient way to build a backlog of ideas that can inspire future product releases.
17. "Are we meeting your expectations?"
This is a really important question to ask because customers won't always tell you when they're unhappy with your service. Not every customer will ask to speak with a manager when they're unhappy with your business. In fact, most will quietly move on to a competitor rather than broadcast their unhappiness to your company. To prevent this type of customer churn, you need to be proactive and ask customers if your brand is meeting their expectations.
18. "How satisfied are you with your experience?"
This question asks the customer to summarize their experience with your business. It gives you a snapshot of how the customer is feeling in that moment and their perception of your brand. Asking this question at the right stage in the customer's journey can tell you a lot about what your company is doing well and where you can stand to improve.
Next, let's dig into some tips for creating your own questionnaire.
Start with templates as a foundation. Know your question types. Keep it brief when possible. Choose a simple visual design. Use a clear research process. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language. Make sure every question is important. Ask one question at a time. Order your questions logically. Consider your target audience. Test your questionnaire.
1. Use questionnaire templates.
Rather than build a questionnaire from scratch, consider using questionnaire templates to get started. HubSpot's collection of customer-facing questionnaire templates can help you quickly build and send a questionnaire to your clients and analyze the results right on Google Drive.
.png?width=375&height=275&name=Image%20Hackathon%20%E2%80%93%20Horizontal%20(24).png)
Download Now
2. Know your question types.
A simple "yes" or "no" doesn't cut it. To get feedback that actually matters, you need to give customers options that go in-depth. There's a method to getting accurate feedback from your questionnaire, and it starts by choosing the appropriate types of questions for the information you want to know.
Vrnda LeValley , customer training manager at HubSpot, recommends starting with an alignment question like, "Does this class meet your expectations?" because it gives more context to any positive or negative scores that follow. She continues, "If it didn't meet expectations, then there will potentially be negative responses across the board (as well as the reverse)."
3. Keep it brief, when possible.
Most questionnaires don't need to be longer than a page. For routine customer satisfaction surveys, it's unnecessary to ask 50 slightly varied questions about a customer's experience when those questions could be combined into 10 solid questions.
The shorter your questionnaire is, the more likely a customer will complete it. Plus a shorter questionnaire means less data for your team to collect and analyze. Based on the feedback, it will be a lot easier for you to get the information you need to make the necessary changes in your organization and products.
4. Choose a simple visual design.
There's no need to make your questionnaire a stunning work of art. As long as it's clear and concise, it will be attractive to customers. When asking questions that are important to furthering your company, it's best to keep things simple. Select a font that’s common and easy to read, like Helvetica or Arial. Use a text size that customers of all abilities can navigate.
A questionnaire is most effective when all the questions are visible on a single screen. The layout is important. If a questionnaire is even remotely difficult to navigate, your response rate could suffer. Make sure that buttons and checkboxes are easy to click and that questions are visible on both computer and mobile screens.
5. Use a clear research process.
Before planning questions for your questionnaire, you'll need to have a definite direction for it. A questionnaire is only effective if the results answer an overarching research question. After all, the research process is an important part of the survey, and a questionnaire is a tool that's used within the process.
In your research process, you should first come up with a research question. What are you trying to find out? What's the point of this questionnaire? Keep this in mind throughout the process.
After coming up with a research question, it's a good idea to have a hypothesis. What do you predict the results will be for your questionnaire? This can be structured in a simple "If … then …" format. A structured experiment — yes, your questionnaire is a type of experiment — will confirm that you're only collecting and analyzing data necessary to answer your research question. Then, you can move forward with your survey .
6. Create questions with straightforward, unbiased language.
When crafting your questions, it's important to structure them to get the point across. You don't want any confusion for your customers because this may influence their answers. Instead, use clear language. Don't use unnecessary jargon, and use simple terms in favor of longer-winded ones.
You may risk the reliability of your data if you try to combine two questions. Rather than asking, "How was your experience shopping with us, and would you recommend us to others?" separate it into two separate questions. Customers will be clear on your question and choose a response most appropriate for each one.
You should always keep the language in your questions unbiased. You never want to sway customers one way or another because this will cause your data to be skewed. Instead of asking, "Some might say that we create the best software products in the world. Would you agree or disagree?" it may be better to ask, "How would you rate our software products on a scale of 1 to 10?" This removes any bias and confirms that all the responses are valid.
7. Ask only the most important questions.
When creating your questionnaire, keep in mind that time is one of the most valuable commodities for customers. Most aren't going to sit through a 50-question survey, especially when they're being asked about products or services they didn't use. Even if they do complete it, most of these will be half-hearted responses from fatigued customers who simply want to be finished with it.
If your questionnaire has five or 55 questions, make sure each has a specific purpose. Individually, they should be aimed at collecting certain pieces of information that reveal new insights into different aspects of your business. If your questions are irrelevant or seem out of place, your customers will be easily derailed by the survey. And, once the customer has lost interest, it'll be difficult to regain their focus.
8. Ask one question at a time.
Since every question has a purpose, ask them one at a time. This lets the customer focus and encourages them to share a thoughtful response. This is particularly important for open-ended questions where customers need to describe an experience or opinion.
By grouping questions together, you risk overwhelming busy customers who don't have time for a long survey. They may think you're asking them too much, or they might see your questionnaire as a daunting task. You want your survey to appear as painless as possible. Keeping your questions separated will make it more user-friendly.
9. Order your questions logically.
A good questionnaire is like a good book. The beginning questions should lay the framework, the middle ones should cut to the core issues, and the final questions should tie up all loose ends. This flow keeps customers engaged throughout the entire survey.
When creating your questionnaire, start with the most basic questions about demographics. You can use this information to segment your customer base and create different buyer personas.
Next, add in your product and services questions. These are the ones that offer insights into common customer roadblocks and where you can improve your business's offerings. Questions like these guide your product development and marketing teams looking for new ways to enhance the customer experience.
Finally, you should conclude your questionnaire with open-ended questions to understand the customer journey. These questions let customers voice their opinions and point out specific experiences they've had with your brand.
10. Consider your target audience.
Whenever you collect customer feedback, you need to keep in mind the goals and needs of your target audience. After all, the participants in this questionnaire are your active customers. Your questions should be geared toward the interests and experiences they've already had with your company.
You can even create multiple surveys that target different buyer personas. For example, if you have a subscription-based pricing model, you can personalize your questionnaire for each type of subscription your company offers.
11. Test your questionnaire.
Once your questionnaire is complete, it's important to test it. If you don't, you may end up asking the wrong questions and collecting irrelevant or inaccurate information. Start by giving your employees the questionnaire to test, then send it to small groups of customers and analyze the results. If you're gathering the data you're looking for, then you should release the questionnaire to all of your customers.
How Questionnaires Can Benefit Your Customer Service Strategy
Whether you have one customer or 1000 customers, their opinions matter when it comes to the success of your business. Their satisfaction with your offerings can reveal how well or how poorly your customer service strategy and business are meeting their needs. A questionnaire is one of the most powerful, cost-effective tools to uncover what your customers think about your business. When analyzed properly, it can inform your product and service launches.
Use the free questionnaire templates, examples, and best practices in this guide to conduct your next customer feedback survey.
Now that you know the slight difference between a survey and a questionnaire, it’s time to put it into practice with your products or services. Remember, a good survey and questionnaire always start with a purpose. But, a great survey and questionnaire give data that you can use to help companies increase the way customers respond to their products or services because of the questions.
Net Promoter, Net Promoter System, Net Promoter Score, NPS, and the NPS-related emoticons are registered trademarks of Bain & Company, Inc., Fred Reichheld, and Satmetrix Systems, Inc.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in July 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

Nonresponse Bias: What to Avoid When Creating Surveys

How to Make a Survey with a QR Code

50 Catchy Referral Slogans & How to Write Your Own
![how to make a questionnaire for a research How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/phone-survey.webp)
How Automated Phone Surveys Work [+Tips and Examples]

Online Panels: What They Are & How to Use Them Effectively

The Complete Guide to Survey Logic (+Expert Tips)

Focus Group vs. Survey: Which One Should You Use?
![how to make a questionnaire for a research Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/leading-questions-hero.webp)
Leading Questions: What They Are & Why They Matter [+ Examples]

What are Survey Sample Sizes & How to Find Your Sample Size

24 Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Survey Questions to Ask Your Employees
5 free templates for learning more about your customers and respondents.
Service Hub provides everything you need to delight and retain customers while supporting the success of your whole front office
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project
Published on October 30, 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on October 19, 2023.
The research question is one of the most important parts of your research paper , thesis or dissertation . It’s important to spend some time assessing and refining your question before you get started.
The exact form of your question will depend on a few things, such as the length of your project, the type of research you’re conducting, the topic , and the research problem . However, all research questions should be focused, specific, and relevant to a timely social or scholarly issue.
Once you’ve read our guide on how to write a research question , you can use these examples to craft your own.
| Research question | Explanation |
|---|---|
| The first question is not enough. The second question is more , using . | |
| Starting with “why” often means that your question is not enough: there are too many possible answers. By targeting just one aspect of the problem, the second question offers a clear path for research. | |
| The first question is too broad and subjective: there’s no clear criteria for what counts as “better.” The second question is much more . It uses clearly defined terms and narrows its focus to a specific population. | |
| It is generally not for academic research to answer broad normative questions. The second question is more specific, aiming to gain an understanding of possible solutions in order to make informed recommendations. | |
| The first question is too simple: it can be answered with a simple yes or no. The second question is , requiring in-depth investigation and the development of an original argument. | |
| The first question is too broad and not very . The second question identifies an underexplored aspect of the topic that requires investigation of various to answer. | |
| The first question is not enough: it tries to address two different (the quality of sexual health services and LGBT support services). Even though the two issues are related, it’s not clear how the research will bring them together. The second integrates the two problems into one focused, specific question. | |
| The first question is too simple, asking for a straightforward fact that can be easily found online. The second is a more question that requires and detailed discussion to answer. | |
| ? dealt with the theme of racism through casting, staging, and allusion to contemporary events? | The first question is not — it would be very difficult to contribute anything new. The second question takes a specific angle to make an original argument, and has more relevance to current social concerns and debates. |
| The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not . The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically . For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries. |
Note that the design of your research question can depend on what method you are pursuing. Here are a few options for qualitative, quantitative, and statistical research questions.
| Type of research | Example question |
|---|---|
| Qualitative research question | |
| Quantitative research question | |
| Statistical research question |
Other interesting articles
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, October 19). 10 Research Question Examples to Guide your Research Project. Scribbr. Retrieved September 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-question-examples/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, evaluating sources | methods & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Malays Fam Physician
- v.1(1); 2006
Designing A Questionnaire
Ng chirk jenn.
MMed(FamMed Singapore), Department of Primary Care Medicine, University of Malaya
In a survey, the researcher uses a questionnaire to gather information from the respondents to answer the research questions. A questionnaire is a very convenient way of collecting information from a large number of people within a period of time. Hence, the design of the questionnaire is of utmost importance to ensure accurate data is collected so that the results are interpretable and generalisable. A bad questionnaire renders the results uninterpretable, or worse, may lead to erroneous conclusions.
A survey can come in many forms: postal survey, telephone interviews, face-to-face interviews and internet surveys. Each type of survey requires a slightly different design. A self-administered questionnaire (e.g. postal survey) should have very clear instructions and questions, follow a logical order and avoid complex filtering. The respondents are more likely to answer truthfully without prompting from an interviewer. On the other hand, in an interviewer-administered questionnaire (e.g. face-to-face interview or telephone interview), the questions can be more complex as they can be clarified by the interviewers. However, the presence of an interviewer may “pressurise” the respondents to give “appropriate” rather than truthful answers.
WHAT IS A GOOD QUESTIONNAIRE?
A good questionnaire should be valid, reliable, clear, interesting and succinct.
A valid questionnaire should ask what it intends to ask, i.e. the questions should be phrased in such a way that the respondent understands the objective of the question. To achieve this, the questionnaire should be reviewed by the “content expert” during the pilot test (e.g. if the target respondent is a diabetic patient, then a diabetic patient should comment whether he understands the questionnaire). Any uncertainties and queries should be clarified till the question is clearly understood.
A reliable questionnaire should yield the same answer if the same question is posed to the respondent repeatedly in a short span of time. This can be achieved by performing a “test-retest”, i.e. administer the same questionnaire to the respondent a second time and check for consistency of the answer. Any discrepancy in the answers could be due to lack of clarity of the questions and this should be reviewed and rephrased.
Interesting
An interesting questionnaire is more likely to be completed by the respondent and hence yields a better response rate. This requires the researcher to put some thoughts into asking questions that are relevant to the respondent and in a logical sequence.
A succinct questionnaire asks questions that aim to answer only the research objectives. Any questions beyond the scope of the research should be excluded. It is common for researchers to “cast the net wider” so that they will collect more data, regardless of whether these data are important or not. This usually happens when the researcher has not properly thought through the research objectives. It runs the risk of asking too many questions and the questionnaire runs into many pages.
HOW TO DESIGN A GOOD QUESTIONNAIRE?
Developing a conceptual framework.
The first step of designing of a good questionnaire is to construct a conceptual framework. The researcher needs to be very clear about his research questions and what “dependent” and “independent” factors he intends to investigate. Consider this research question: “What is the health-seeking behaviour of parents whose children have upper respiratory tract infection, and what are the associated factors?” I would develop a conceptual framework ( Figure 1 , Page 35) based on literature review, established theoretical framework and discussion with experts in that field. By creating the framework, the researcher can now ask questions regarding “parental health-seeking behaviour” (dependent variable) and associated factors e.g. education level, household income, age of child, etc. (independent variables). The importance of this framework is to ensure the research covers all relevant variables and any irrelevant variables can be excluded. This will answer the commonly asked questions: “Did I miss any important questions in the questionnaire?”, “Should I include/exclude this particular question?”

Conceptual Model of Self Care (Simplified)
Asking the “right” questions
Now that you have developed the conceptual framework and you know exactly what questions you want to ask, it is time for you to design the questions in such a way that it is valid and reliable. The researchers have to brainstorm and come up with the preliminary questions.
Close- vs open-ended questions
These questions can be in the form of “close-ended” or “open-ended” questions ( Table 1a ). “Close-ended” questions provide options to the respondents and require them to choose one or more items from the list. “Open-ended” questions allow the respondent to express their opinions freely and they are not restricted by the options. The former is preferred if the range of answers are well known and the options are limited; the latter is preferred if the answer options are multiple and unknown. The answers to the open-ended questions require re-grouping before analysis.
| Did you experience cough and cold in the past 6 months? | ||||
| ◻Yes | ◻No | |||
| Think of the last time you had cough and cold. Did you consult a doctor? | ||||
| ◻Yes | ◻No | |||
| What is/are the main reason(s) for you to consult a doctor for your cough and cold? (You can list down more than one reason) | ||||
| ___________ | ||||
| Think of the last time you had cough and cold. Did you consult a doctor? | ||||
| ◻Yes | ◻No | |||
| It is common for people to ask for antibiotics when they have cough and cold. Did you request for an antibiotic from the doctor for your cough and cold? | ||||
| ◻Yes | ◻No | |||
| We should always consult a doctor for cough and cold. (Please circle the answer) | ||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Strongly disagree | Disagree | Neutral | Agree | Strongly agree |
| Did you experience sore throat and fever during your cough and cold? | ||||
| ◻Yes | ◻No | |||
| Should be: | ||||
| Did you experience sore throat during your cough and cold? | ||||
| Did you experience fever during your cough and cold? | ||||
| Or: | ||||
| Did you experience the following symptoms during your cough and cold? (You can tick more than one box) | ||||
| ◻Sore throat | ◻Cough | ◻Fever | ||
| How often do you visit the doctor for cough and cold? | ||||
| ◻Not at all | ◻Not very often | ◻Sometimes | ◻Quite often | |
| ◻Very often | ||||
| Change to: | ||||
| How many times did you visit the doctor for cough and cold in the past 1 year? | ||||
| _________ times in the past 1 year |
Options/choices
The options available for each question should be as exhaustive as possible. This will ensure the respondent can find an option which best suits his answer. In order to determine the possible options, the researcher needs to brainstorm, review related published research, discuss with experts and if necessary, conduct a focus group discussion among the target respondents. To allow other possible options, the researcher can include an “Other: please specify ________” category as one of the options.
When assessing factual knowledge, it is important to include “Don’t know” as one of the responses as not all respondents may know the answer to the question. By not providing the option, the researcher is “forcing” the respondent to make a choice by guessing.
In a questionnaire which has many parts, some of which need not be answered by the respondent, filtering is used to guide the respondent to answer only the relevant questions. ( Table 1b ) However, you should avoid using too much filtering as this may confuse the respondents and make the questionnaire complicated.
Order of questions
The order of the questions should flow in a logical sequence. Start with simple questions before moving to more complex questions. Some prefer to start with the socio-demography of the respondents while others will leave it to the last as it involves more personal questions such as household income, education level and religion. However, this depends on the how forth-coming the target population is. Sometimes, it helps by explaining to the respondent the reason for asking a personal question or by making a general statement to normalise the “sensitive” question. ( Table 1c )
Likert scale
In questions which involve assessing attitudes or giving opinions, a scale with a range of responses is preferred to a yes/no answer. Likert scale (usually 5-point or 7-point) is a commonly used method. ( Table 1d ) It provides a measure of strength for a particular attitude or belief. It is possible to calculate mean scores for any given responses to statements (item scores)
Avoid double-barrelled questions
Another common mistake is asking a “double-barrelled” question. Avoid asking two things in one question ( Table 1e ) This will lead to difficulty in interpreting the responses when analysing the data.
Avoid ambiguous questions
Be as specific as possible when asking a question. For example, terms such as “frequent”, “always” and “often” may mean different things to different people. ( Table 1f ) Keep questionnaire items short, preferably less than 20 words. When scrutinising through the questions, ask yourself, “Is this question clear? Can it be more specific?”
Design the questionnaire with analysis in mind
When designing a questionnaire, it is crucial to pre-empt what kind of method will be used to analyse the data collected. Take for example, age. If the objective of asking the age is to find out the mean age of the participants, then an exact age should be captured (e.g. “What is your age? (at your last birthday): ______ years). On the other hand, if you are going to categorise them according to different age groups during the analysis, then you may want to structure the question according to different age categories (e.g. “What is your age? (at your last birthday): <18, 18-29, 30-50, etc.) If you are uncertain of what analysis you will be performing, it is always advisable to collect raw data, rather than to categorise them in the beginning. This will help to avoid problems with analysis after data collection and ensure that all data collected are relevant and usable. One practical way to do that is to draw up a “question-analysis” table in advance. ( Table 2 )
| Age | Mean (SD, range), ?categorise into groups |
| Ethnicity | % |
| Liker scale 1 | % “agree” and “strongly agree” |
Translation
A respondent should answer a questionnaire in a language which he or she is most proficient in. In a multi-lingual society like Malaysia, translating the questionnaire into different languages has become a “standard procedure”, especially for self-administered questionnaire involving the general population or patients. This is a crucial step because inaccurate translation of the questions or responses will result in collecting different information for the same question. This will lead to erroneous results and conclusions.
To avoid this, a “translate-back-translate” method is used. The researcher or a translator has to translate the questionnaire from English to Malay, and another independent person, who is unaware of the English questionnaire, will back-translate the Malay questionnaire to English again. The researchers (usually three or more people who are proficient in both languages) will then compare the original English questionnaire with the back-translated English questionnaire for any discrepancy, which may suggest inaccurate translation of the Malay questionnaire. These discrepancies will be discussed and the researchers will reach a consensus on the final translation.
The final “touch-up” of the questionnaire is important because the “look” of the questionnaire may decide whether the respondent is going to fill it up. This is especially relevant for postal surveys. The title should be highlighted and it should reflect the main objective of the research. If possible, divide the questionnaire into sections according to the content (e.g. boxes with bold headings) and it should flow smoothly from one section to another with appropriate filtering. If your respondents involve older persons, bigger font size should be used. Finally, a cover letter stating the objective of your study, your affiliations, and, if appropriate, ensuring confidentiality and how you are going to use the information you have collected
Pilot test is a crucial step in the design of questionnaire before data collection begins. It will help to detect flaws in the questionnaire in terms of content, grammar and format. First, ask you colleagues, family or friends to comment on the questionnaire. This will pick up any mistakes in terms of content, grammar and format. This should be followed by asking the potential respondents to answer the questionnaire and provide their feedback. For those questions which you feel may be confusing or sensitive, it is important to ask the respondents to comment specifically during the pilot test.
CONCLUSIONS
A good questionnaire should be valid, reliable, clear, succinct and interesting. It is important to design the questionnaire based on a conceptual framework, scrutinise each question for relevance and clarity, and think of the analysis you are going to perform at the end of the day. A final touch-up will make a difference in the response rate and always pilot-test the questionnaire to perfect the questionnaire. Now you are ready to collect the data!
USEFUL READINGS

University of Pittsburgh Library System
- Collections
Course & Subject Guides
Hhd 1007: methods of evidence-based practice.
- PittCat Searching
- Google Scholar
- Searching Tips
- Getting Full-text
- Scholarly Information
- Evaluating Sources of Information
- Critically Reading an Article
Identifying a Research Question
Frameworks for developing a research question.
- Writing & Citing
- Getting Help
Developing a Research Question Video Tutorial
To learn more about developing a research question, watch this tutorial from Wilfrid Laurier University Library.
Some content on this page was developed George Mason University Writing Center. (2018, Aug. 8). How to Write a Research Question. https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/writing-resources/research-based-writing/how-to-write-a-research-question
What is a research question? A research question is the question around which you center your research. It should be:
- clear : it provides enough specifics that one’s audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- focused : it is narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the space the writing task allows.
- concise : it is expressed in the fewest possible words.
- complex : it is not answerable with a simple “yes” or “no,” but rather requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to composition of an answer.
- arguable : its potential answers are open to debate rather than accepted facts.
You should ask a question about an issue that you are genuinely curious and/or passionate about.
The question you ask should be developed for the discipline you are studying. A question appropriate for Biology, for instance, is different from an appropriate one in Political Science or Sociology. If you are developing your question for a course other than first-year composition, you may want to discuss your ideas for a research question with your professor.
Why is a research question essential to the research process? Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the “all-about” paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
Steps to developing a research question:
- Choose an interesting general topic. Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be “Slavery in the American South” or “Films of the 1930s.”
- Do some preliminary research on your general topic. Do a few quick searches in current periodicals and journals on your topic to see what’s already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing, when it comes to your topic? What questions occur to you as you read these articles?
- Consider your audience. For most college papers, your audience will be academic, but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and developing your question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you are developing?
- Start asking questions. Taking into consideration all of the above, start asking yourself open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic. For example, “Why were slave narratives effective tools in working toward the abolishment of slavery?” or “How did the films of the 1930s reflect or respond to the conditions of the Great Depression?”
- Is your research question clear? With so much research available on any given topic, research questions must be as clear as possible in order to be effective in helping the writer direct his or her research.
- Is your research question focused? Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.
- Is your research question complex? Research questions should not be answerable with a simple “yes” or “no” or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with “How” or “Why.”
- Begin your research . After you’ve come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research could take. What sources should you consult as you seek answers to your question? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question?
Sample Research Questions
Unclear: How should social networking sites address the harm they cause? Clear: What action should social networking sites like MySpace and Facebook take to protect users’ personal information and privacy? The unclear version of this question doesn’t specify which social networking sites or suggest what kind of harm the sites might be causing. It also assumes that this “harm” is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (MySpace and Facebook), the type of potential harm (privacy issues), and who may be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or interpretation. Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming? Focused: What is the most significant effect of glacial melting on the lives of penguins in Antarctica?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it couldn’t be adequately answered in a book-length piece, let alone a standard college-level paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (glacial melting), a specific place (Antarctica), and a specific animal that is affected (penguins). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.? Appropriately Complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule of thumb, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it’s likely not very effective.
A well defined question should address a gap in the current literature and is the essential starting point of your research.
You can use the following frameworks to help construct your research question.
PICO for Quantitative Studies P Population/Problem I Intervention/Exposure C Comparison O Outcome Example: Is gabapentin (intervention), compared to placebo (comparison), effective in decreasing pain symptoms (outcome) in middle aged male amputees suffering phantom limb pain (population)?
PICo for Qualitative Studies P Population/Problem I Phenomenon of Interest Co Context Example: What are the experiences (phenomenon of interest) of caregivers providing home based care to patients with Alzheimer's disease (population) in Australia (context)?
SPICE S Setting P Perspective (for whom) I Intervention/Exposure C Comparison E Evaluation Example: What are the benefits (evaluation) of a doula (intervention) for low income mothers (perspective) in the developed world (setting) compared to no support (comparison)?
SPIDER S Sample PI Phenomenon of Interest D Design E Evaluation R Research Type Example: What are the experiences (evaluation) of wome n (sample) undergoing IVF treatment (phenomenon of interest) as assessed?
Design: questionnaire or survey or interview
Study Type: qualitative or mixed method
The above was adapted from Cornell University A Guide to Evidence Synthesis: 1. Develop a Research Question https://guides.library.cornell.edu/evidence-synthesis/research-question
- << Previous: Critically Reading an Article
- Next: Writing & Citing >>
- Last Updated: Sep 10, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://pitt.libguides.com/hhd1007
How Do I Create an Effective Survey: The 8 Proven Steps
Creating an effective survey involves more than just drafting questions. Follow these 8 proven steps to design engaging surveys that capture meaningful data and drive impactful decisions.
Luo Baishun
Creating an effective survey might seem like a straightforward task, but in reality, there's an art to it. Whether you're conducting market research, gathering customer feedback, or assessing employee satisfaction, a well-structured survey can provide valuable insights. The key to achieving this? Crafting your questions thoughtfully and designing the survey in a way that engages participants while ensuring accurate, actionable responses.
Let’s dive into the steps and best practices that will help you create an effective survey that yields meaningful data and drives better decisions.
Why Should You Care About Survey Design?
Before we jump into the nitty-gritty of survey creation, let’s get one thing clear: A poorly designed survey can lead to misleading data . If your questions are unclear, or your survey is too long, participants might disengage or misunderstand what you're asking. And this? It skews your data.
Designing a survey isn’t just about throwing a few questions onto a form. It's about striking a balance between getting the data you need and ensuring a seamless experience for your participants. And when you get it right? The results can be powerful.
Step 1: Start with a Clear Goal
It all begins with understanding why you're conducting the survey . Are you trying to gauge customer satisfaction, or maybe you’re testing a product idea? Whatever the purpose, your goal should be crystal clear because it influences the entire survey design process.
Here’s a quick tip: Keep your goal specific. If your goal is too broad, your survey might end up meandering without a clear direction. A well-defined goal not only sharpens your questions but also helps you analyze the responses later.
Step 2: Choose the Right Type of Survey
There are different types of surveys, and selecting the right one can make a world of difference. Some common types include:
- Questionnaires (for customer feedback or market research)
- Quizzes (great for engaging users and making surveys more fun)
- Polls (to quickly gauge opinion on a single topic)
- Conversational forms (to keep it engaging and interactive)
For example, if you want to keep your audience engaged and the experience more interactive, conversational forms work wonders. Tools like HeyForm allow you to build these with ease — no coding required! Who doesn't love a tool that simplifies life?
Step 3: Structure Your Survey Using the MECE Principle
To ensure your survey covers all the necessary areas without redundancy, apply the MECE principle : Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive. This means your questions should not overlap (mutually exclusive) and together, they should cover the entire scope of your topic (collectively exhaustive).
For instance, if you're surveying customer satisfaction, break down the topic into sections like:
- Product Quality
- Customer Service
- Ease of Use
- Price Satisfaction
Each section should stand on its own without overlapping, and together they give you a complete picture of your customers’ satisfaction.
Step 4: Crafting Questions That Drive Engagement
This is where the real magic happens. Your questions need to be:
- Clear and concise : Long, complicated questions can confuse participants. Instead, aim for clarity.
- Focused : Each question should target one specific point. Avoid asking two things in one question (double-barreled questions).
- Balanced : Steer clear of leading questions that push participants towards a particular answer.
- Engaging : Keep the language conversational. Surveys can feel tedious, but an engaging tone can help keep participants interested.
For example, instead of asking, "What do you dislike about our product?" you could ask, "What would make our product better for you?" This reframe focuses on improvement and invites constructive feedback.
Pro Tip: Avoid using jargon! If your audience doesn’t understand the question, how can they give you a meaningful answer?
Step 5: Use a Variety of Question Types
A mix of question types keeps the survey interesting and helps you get a richer set of data. Here’s a quick rundown of common question types:
- Multiple Choice : Great for quantitative data.
- Rating Scales : Allows participants to rate something on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5).
- Open-Ended : These questions give participants the freedom to express their thoughts in their own words.
- Yes/No : Simple and straightforward, perfect for quick insights.
Mixing these up helps prevent survey fatigue and keeps your participants engaged. For instance, you might start with a couple of multiple-choice questions, throw in an open-ended one to get deeper insights, and close with a rating scale.
Step 6: Keep It Short and Focused
Ever started a survey and abandoned it halfway through? Yeah, we’ve all been there. One of the biggest reasons for survey abandonment is length. Participants have short attention spans, so keeping your survey as short and focused as possible is crucial.
Aim for no more than 10 questions unless you have a compelling reason for a longer survey. And even if your survey is short, make sure each question adds value toward achieving your goal.
Step 7: Test Your Survey Before Launching
Before you hit the "send" button, make sure to test your survey with a small group of people. This can help identify any confusing or problematic questions and give you a chance to tweak things before rolling it out to a larger audience.
If you're using a tool like HeyForm , you can easily share your draft survey with a few colleagues for feedback and see how they interact with it. This step ensures you’re not missing anything critical.
Step 8: Analyze the Data and Take Action
Once your survey is completed, it’s time to dig into the results. Don’t just collect the data; use it! Look for trends, patterns, and actionable insights that can help you make decisions.
Break down the data by categories (e.g., customer satisfaction levels by demographic) and use it to inform your next steps. Whether it’s improving your product or tweaking your marketing strategy, surveys provide insights that can shape your direction.
Conclusion: Surveys Are a Goldmine—If Done Right!
Creating an effective survey might take a little extra effort, but the insights it can provide are invaluable. By starting with a clear goal, crafting well-thought-out questions, and using a variety of question types, you can ensure your survey is not only effective but also engaging for participants.
And hey, if you’re looking for a tool to make your life easier, give HeyForm a try. With its no-code interface and engaging conversational forms, creating surveys has never been simpler.
1. How long should my survey be? Keep your survey as short as possible—10 questions or fewer is a good rule of thumb. If your survey is longer, make sure each question adds value and engages participants.
2. What types of questions should I include in a survey? Use a variety of question types, such as multiple-choice, rating scales, and open-ended questions. This keeps the survey interesting and helps you collect both quantitative and qualitative data.
3. How can I increase the response rate for my survey? Keep it short, make the questions engaging, and ensure the survey is easy to complete on any device. Offering a small incentive, like a discount or entry into a prize draw, can also boost participation.
4. What’s the best way to analyze survey data? Break down the data into categories based on your original goal. Use charts or graphs to visualize the data and look for patterns or trends. Tools like HeyForm offer built-in analytics to make this process easier.
5. Can I use a form builder for surveys without coding experience? Absolutely! Tools like HeyForm are designed for non-coders and make creating engaging, conversational forms a breeze. Just select and add the question component you need, and you’re good to go!
Sign up for more like this.
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life

- How to Make a Research Poster
- Office of Research
Undergraduate Research
- Research Academic Calendar
- Student Support
- Frequently Asked Questions
Create an Engaging Research Poster

Creating an effective research project poster is crucial for increasing engagement while presenting your study at conferences. Poster sessions allow you to showcase your work, receive feedback, and network with other researchers. Your poster should be visually appealing, well-organized, and concise, including elements like a descriptive title, introduction, methodology, results, and conclusions. As a presenter, always be ready to discuss your research, answer questions, and provide contact information for follow-up inquiries.
Utilize these poster production resources for creating and printing your research poster to ensure high quality!
Research Project Posters Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a poster session?
What happens during a poster session at a conference?
A poster session typically consists of rows of posters either on freestanding poster boards or set up on tables using cardboard trifolds. Presenters stand next to their posters and attendees walk up and down the aisles, stopping at posters that interest them. Presenters should be ready to give a quick (2-3 minute) summary of their poster and should be ready to answer questions about the project.
Although not required, it is nice to have one-page copies of your poster to hand out to attendees. Alternately, you may create a sign-up sheet and email your poster to those who are interested.
What are the components of a conference poster?
A poster conveys your study on one big sheet of paper (usually 36" x 42"). The components vary depending on your discipline as well as the type of project, but here are some of the typical elements:
Title and Authors
- Remember to use a big font that can be seen at a distance (70-80 point font at minimum).
- The title is what often brings passers-by to your poster - make it descriptive and catchy.
Institution
- You can download the institutional logo instead of writing out "Kennesaw State University."
- Be sure to follow the logo rules !
- You can use an additional logo depicting you department or college if you have one.
Introduction/Background/Literature Review
- Lead the reader into your particular study.
- Include citations from past research.
- How does your study make a unique contribution to the literature?
- Present a research question or hypotheses.
Methodology
- Who or what represents your sample? If you used people or animals, how many? Can you provide some information about your sample (e.g., demographic information like gender, age, etc.)?
- What was the methodology and procedure of your study? Describe study materials such as survey questions, observations, interviews, etc.
- What were the main results of your study?
- Graphs and charts are more visually appealing than words.
Discussion/Conclusions
- What is the main take-home message of your study?
- Provide an explanation for the results.
- Connect your results to past research on this topic.
- What are the limitations of you research?
- What are some future research ideas that stem from your study?
- What are the implications/applications of your study for broader society?
- Cite only the references you used in your poster, not everything you read over the course of doing your research.
- Use the citation style for your discipline (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
Acknowledgements
- In this section, cite individuals who aren't authors but who contributed in some way (if applicable).
- You should also acknowledge any financial help you received as part of this research (e.g., grants).
Contact Information
- Include your email on the poster so that if attendees have any questions, they can contact you.
What does an effective poster look like?
- It has an eye-catching title.
- It is organized logically.
- It is concise (bullets and numbering are good) -- approximately 800 words maximum.
- It can be understood on its own without needing explanation from the author.
- It does not have any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors.
- Title: ~72-point font
- Section Headers: ~60-point font
- Text: At least 32-point font
- Don’t forget the axes on graphs - that font needs to be big too.
- The font is consistent throughout the poster, easy to read (serif styles like Times New Roman), and professional (avoid Comic Sans!)
- It contains high-resolution graphics (charts, photos, images). Images pulled from the Internet are often fuzzy when blown up on a poster (and may be copyrighted as well).
- It uses a clean, consistent layout with some white space available
- It uses non-distracting colors and backgrounds (avoid a dark background, which uses an enormous amount of ink to print).
What should you do as a poster presenter?
- Dress professionally. Business casual is usually fine, but check with your faculty supervisor regarding appropriate dress at the conference you're attending.
- Wear comfortable shoes. You'll likely be standing for the entire poster session (often 60-90 minutes). Also, there is typically a lot of walking at a conference. You don't want your feet to hurt the whole time!
- At least one author should be near the poster during the allotted session.
- Be on time, and take down your poster on time.
- Smile and greet people as they approach your poster.
- Let them take the lead (some people prefer to read; others prefer to talk to you).
How do I make and print my poster?
Typically, posters are created on one PowerPoint slide and enlarged using a poster printer.
The Office of Undergraduate Research has a plotter printer that will produce high quality, single page, 36 x 42 color posters. This printer is available for use by all KSU undergraduate researchers at no charge for printing posters that are directly tied to poster presentations by undergraduates. Please see more information about poster printing .
Are there any online resources available about making research posters?
Yes. Here are a few good ones to check out:
- Research Posters (University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign)
- How to Create a Research Poster: Poster Basics (NYU Libraries)
- Guide to Creating Research Posters (University of Texas at Austin)
- Designing Conference Posters
- CUR Arts and Humanities Division: How to Make a Poster
- Poster Planning Worksheet (Radford University)
- Making Meaningful Posters (Radford University)
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Report a Concern
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key things to know about U.S. election polling in 2024

Confidence in U.S. public opinion polling was shaken by errors in 2016 and 2020. In both years’ general elections, many polls underestimated the strength of Republican candidates, including Donald Trump. These errors laid bare some real limitations of polling.
In the midterms that followed those elections, polling performed better . But many Americans remain skeptical that it can paint an accurate portrait of the public’s political preferences.
Restoring people’s confidence in polling is an important goal, because robust and independent public polling has a critical role to play in a democratic society. It gathers and publishes information about the well-being of the public and about citizens’ views on major issues. And it provides an important counterweight to people in power, or those seeking power, when they make claims about “what the people want.”
The challenges facing polling are undeniable. In addition to the longstanding issues of rising nonresponse and cost, summer 2024 brought extraordinary events that transformed the presidential race . The good news is that people with deep knowledge of polling are working hard to fix the problems exposed in 2016 and 2020, experimenting with more data sources and interview approaches than ever before. Still, polls are more useful to the public if people have realistic expectations about what surveys can do well – and what they cannot.
With that in mind, here are some key points to know about polling heading into this year’s presidential election.
Probability sampling (or “random sampling”). This refers to a polling method in which survey participants are recruited using random sampling from a database or list that includes nearly everyone in the population. The pollster selects the sample. The survey is not open for anyone who wants to sign up.
Online opt-in polling (or “nonprobability sampling”). These polls are recruited using a variety of methods that are sometimes referred to as “convenience sampling.” Respondents come from a variety of online sources such as ads on social media or search engines, websites offering rewards in exchange for survey participation, or self-enrollment. Unlike surveys with probability samples, people can volunteer to participate in opt-in surveys.
Nonresponse and nonresponse bias. Nonresponse is when someone sampled for a survey does not participate. Nonresponse bias occurs when the pattern of nonresponse leads to error in a poll estimate. For example, college graduates are more likely than those without a degree to participate in surveys, leading to the potential that the share of college graduates in the resulting sample will be too high.
Mode of interview. This refers to the format in which respondents are presented with and respond to survey questions. The most common modes are online, live telephone, text message and paper. Some polls use more than one mode.
Weighting. This is a statistical procedure pollsters perform to make their survey align with the broader population on key characteristics like age, race, etc. For example, if a survey has too many college graduates compared with their share in the population, people without a college degree are “weighted up” to match the proper share.
How are election polls being conducted?
Pollsters are making changes in response to the problems in previous elections. As a result, polling is different today than in 2016. Most U.S. polling organizations that conducted and publicly released national surveys in both 2016 and 2022 (61%) used methods in 2022 that differed from what they used in 2016 . And change has continued since 2022.
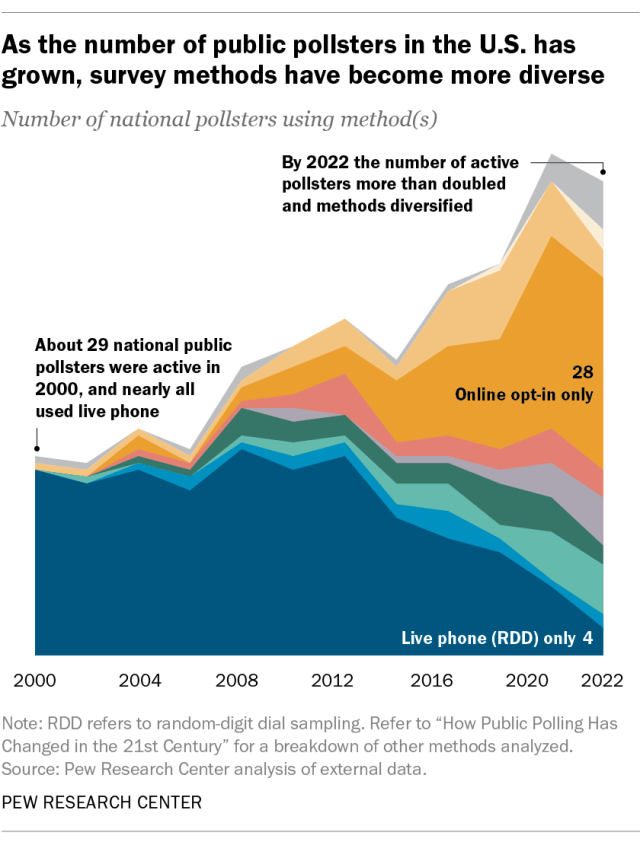
One change is that the number of active polling organizations has grown significantly, indicating that there are fewer barriers to entry into the polling field. The number of organizations that conduct national election polls more than doubled between 2000 and 2022.
This growth has been driven largely by pollsters using inexpensive opt-in sampling methods. But previous Pew Research Center analyses have demonstrated how surveys that use nonprobability sampling may have errors twice as large , on average, as those that use probability sampling.
The second change is that many of the more prominent polling organizations that use probability sampling – including Pew Research Center – have shifted from conducting polls primarily by telephone to using online methods, or some combination of online, mail and telephone. The result is that polling methodologies are far more diverse now than in the past.
(For more about how public opinion polling works, including a chapter on election polls, read our short online course on public opinion polling basics .)
All good polling relies on statistical adjustment called “weighting,” which makes sure that the survey sample aligns with the broader population on key characteristics. Historically, public opinion researchers have adjusted their data using a core set of demographic variables to correct imbalances between the survey sample and the population.
But there is a growing realization among survey researchers that weighting a poll on just a few variables like age, race and gender is insufficient for getting accurate results. Some groups of people – such as older adults and college graduates – are more likely to take surveys, which can lead to errors that are too sizable for a simple three- or four-variable adjustment to work well. Adjusting on more variables produces more accurate results, according to Center studies in 2016 and 2018 .
A number of pollsters have taken this lesson to heart. For example, recent high-quality polls by Gallup and The New York Times/Siena College adjusted on eight and 12 variables, respectively. Our own polls typically adjust on 12 variables . In a perfect world, it wouldn’t be necessary to have that much intervention by the pollster. But the real world of survey research is not perfect.
Predicting who will vote is critical – and difficult. Preelection polls face one crucial challenge that routine opinion polls do not: determining who of the people surveyed will actually cast a ballot.
Roughly a third of eligible Americans do not vote in presidential elections , despite the enormous attention paid to these contests. Determining who will abstain is difficult because people can’t perfectly predict their future behavior – and because many people feel social pressure to say they’ll vote even if it’s unlikely.
No one knows the profile of voters ahead of Election Day. We can’t know for sure whether young people will turn out in greater numbers than usual, or whether key racial or ethnic groups will do so. This means pollsters are left to make educated guesses about turnout, often using a mix of historical data and current measures of voting enthusiasm. This is very different from routine opinion polls, which mostly do not ask about people’s future intentions.
When major news breaks, a poll’s timing can matter. Public opinion on most issues is remarkably stable, so you don’t necessarily need a recent poll about an issue to get a sense of what people think about it. But dramatic events can and do change public opinion , especially when people are first learning about a new topic. For example, polls this summer saw notable changes in voter attitudes following Joe Biden’s withdrawal from the presidential race. Polls taken immediately after a major event may pick up a shift in public opinion, but those shifts are sometimes short-lived. Polls fielded weeks or months later are what allow us to see whether an event has had a long-term impact on the public’s psyche.
How accurate are polls?
The answer to this question depends on what you want polls to do. Polls are used for all kinds of purposes in addition to showing who’s ahead and who’s behind in a campaign. Fair or not, however, the accuracy of election polling is usually judged by how closely the polls matched the outcome of the election.
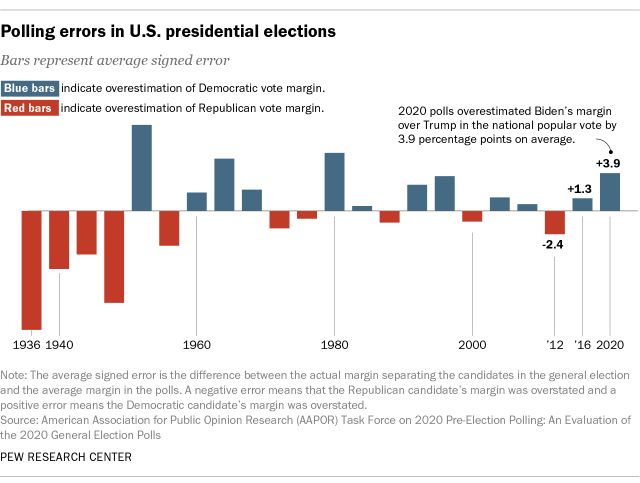
By this standard, polling in 2016 and 2020 performed poorly. In both years, state polling was characterized by serious errors. National polling did reasonably well in 2016 but faltered in 2020.
In 2020, a post-election review of polling by the American Association for Public Opinion Research (AAPOR) found that “the 2020 polls featured polling error of an unusual magnitude: It was the highest in 40 years for the national popular vote and the highest in at least 20 years for state-level estimates of the vote in presidential, senatorial, and gubernatorial contests.”
How big were the errors? Polls conducted in the last two weeks before the election suggested that Biden’s margin over Trump was nearly twice as large as it ended up being in the final national vote tally.
Errors of this size make it difficult to be confident about who is leading if the election is closely contested, as many U.S. elections are .
Pollsters are rightly working to improve the accuracy of their polls. But even an error of 4 or 5 percentage points isn’t too concerning if the purpose of the poll is to describe whether the public has favorable or unfavorable opinions about candidates , or to show which issues matter to which voters. And on questions that gauge where people stand on issues, we usually want to know broadly where the public stands. We don’t necessarily need to know the precise share of Americans who say, for example, that climate change is mostly caused by human activity. Even judged by its performance in recent elections, polling can still provide a faithful picture of public sentiment on the important issues of the day.
The 2022 midterms saw generally accurate polling, despite a wave of partisan polls predicting a broad Republican victory. In fact, FiveThirtyEight found that “polls were more accurate in 2022 than in any cycle since at least 1998, with almost no bias toward either party.” Moreover, a handful of contrarian polls that predicted a 2022 “red wave” largely washed out when the votes were tallied. In sum, if we focus on polling in the most recent national election, there’s plenty of reason to be encouraged.
Compared with other elections in the past 20 years, polls have been less accurate when Donald Trump is on the ballot. Preelection surveys suffered from large errors – especially at the state level – in 2016 and 2020, when Trump was standing for election. But they performed reasonably well in the 2018 and 2022 midterms, when he was not.
During the 2016 campaign, observers speculated about the possibility that Trump supporters might be less willing to express their support to a pollster – a phenomenon sometimes described as the “shy Trump effect.” But a committee of polling experts evaluated five different tests of the “shy Trump” theory and turned up little to no evidence for each one . Later, Pew Research Center and, in a separate test, a researcher from Yale also found little to no evidence in support of the claim.
Instead, two other explanations are more likely. One is about the difficulty of estimating who will turn out to vote. Research has found that Trump is popular among people who tend to sit out midterms but turn out for him in presidential election years. Since pollsters often use past turnout to predict who will vote, it can be difficult to anticipate when irregular voters will actually show up.
The other explanation is that Republicans in the Trump era have become a little less likely than Democrats to participate in polls . Pollsters call this “partisan nonresponse bias.” Surprisingly, polls historically have not shown any particular pattern of favoring one side or the other. The errors that favored Democratic candidates in the past eight years may be a result of the growth of political polarization, along with declining trust among conservatives in news organizations and other institutions that conduct polls.
Whatever the cause, the fact that Trump is again the nominee of the Republican Party means that pollsters must be especially careful to make sure all segments of the population are properly represented in surveys.
The real margin of error is often about double the one reported. A typical election poll sample of about 1,000 people has a margin of sampling error that’s about plus or minus 3 percentage points. That number expresses the uncertainty that results from taking a sample of the population rather than interviewing everyone . Random samples are likely to differ a little from the population just by chance, in the same way that the quality of your hand in a card game varies from one deal to the next.
The problem is that sampling error is not the only kind of error that affects a poll. Those other kinds of error, in fact, can be as large or larger than sampling error. Consequently, the reported margin of error can lead people to think that polls are more accurate than they really are.
There are three other, equally important sources of error in polling: noncoverage error , where not all the target population has a chance of being sampled; nonresponse error, where certain groups of people may be less likely to participate; and measurement error, where people may not properly understand the questions or misreport their opinions. Not only does the margin of error fail to account for those other sources of potential error, putting a number only on sampling error implies to the public that other kinds of error do not exist.
Several recent studies show that the average total error in a poll estimate may be closer to twice as large as that implied by a typical margin of sampling error. This hidden error underscores the fact that polls may not be precise enough to call the winner in a close election.
Other important things to remember
Transparency in how a poll was conducted is associated with better accuracy . The polling industry has several platforms and initiatives aimed at promoting transparency in survey methodology. These include AAPOR’s transparency initiative and the Roper Center archive . Polling organizations that participate in these organizations have less error, on average, than those that don’t participate, an analysis by FiveThirtyEight found .
Participation in these transparency efforts does not guarantee that a poll is rigorous, but it is undoubtedly a positive signal. Transparency in polling means disclosing essential information, including the poll’s sponsor, the data collection firm, where and how participants were selected, modes of interview, field dates, sample size, question wording, and weighting procedures.
There is evidence that when the public is told that a candidate is extremely likely to win, some people may be less likely to vote . Following the 2016 election, many people wondered whether the pervasive forecasts that seemed to all but guarantee a Hillary Clinton victory – two modelers put her chances at 99% – led some would-be voters to conclude that the race was effectively over and that their vote would not make a difference. There is scientific research to back up that claim: A team of researchers found experimental evidence that when people have high confidence that one candidate will win, they are less likely to vote. This helps explain why some polling analysts say elections should be covered using traditional polling estimates and margins of error rather than speculative win probabilities (also known as “probabilistic forecasts”).
National polls tell us what the entire public thinks about the presidential candidates, but the outcome of the election is determined state by state in the Electoral College . The 2000 and 2016 presidential elections demonstrated a difficult truth: The candidate with the largest share of support among all voters in the United States sometimes loses the election. In those two elections, the national popular vote winners (Al Gore and Hillary Clinton) lost the election in the Electoral College (to George W. Bush and Donald Trump). In recent years, analysts have shown that Republican candidates do somewhat better in the Electoral College than in the popular vote because every state gets three electoral votes regardless of population – and many less-populated states are rural and more Republican.
For some, this raises the question: What is the use of national polls if they don’t tell us who is likely to win the presidency? In fact, national polls try to gauge the opinions of all Americans, regardless of whether they live in a battleground state like Pennsylvania, a reliably red state like Idaho or a reliably blue state like Rhode Island. In short, national polls tell us what the entire citizenry is thinking. Polls that focus only on the competitive states run the risk of giving too little attention to the needs and views of the vast majority of Americans who live in uncompetitive states – about 80%.
Fortunately, this is not how most pollsters view the world . As the noted political scientist Sidney Verba explained, “Surveys produce just what democracy is supposed to produce – equal representation of all citizens.”
- Survey Methods
- Trust, Facts & Democracy
- Voter Files

Scott Keeter is a senior survey advisor at Pew Research Center .

Courtney Kennedy is Vice President of Methods and Innovation at Pew Research Center .
How do people in the U.S. take Pew Research Center surveys, anyway?
How public polling has changed in the 21st century, what 2020’s election poll errors tell us about the accuracy of issue polling, a field guide to polling: election 2020 edition, methods 101: how is polling done around the world, most popular.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
Published on 6 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A questionnaire is a list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents about their attitudes, experiences, or opinions. Questionnaires can be used to collect quantitative and/or qualitative information.
Questionnaires are commonly used in market research as well as in the social and health sciences. For example, a company may ask for feedback about a recent customer service experience, or psychology researchers may investigate health risk perceptions using questionnaires.
Table of contents
Questionnaires vs surveys, questionnaire methods, open-ended vs closed-ended questions, question wording, question order, step-by-step guide to design, frequently asked questions about questionnaire design.
A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.
Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
But designing a questionnaire is only one component of survey research. Survey research also involves defining the population you’re interested in, choosing an appropriate sampling method , administering questionnaires, data cleaning and analysis, and interpretation.
Sampling is important in survey research because you’ll often aim to generalise your results to the population. Gather data from a sample that represents the range of views in the population for externally valid results. There will always be some differences between the population and the sample, but minimising these will help you avoid sampling bias .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered . Self-administered questionnaires are more common because they are easy to implement and inexpensive, but researcher-administered questionnaires allow deeper insights.
Self-administered questionnaires
Self-administered questionnaires can be delivered online or in paper-and-pen formats, in person or by post. All questions are standardised so that all respondents receive the same questions with identical wording.
Self-administered questionnaires can be:
- Cost-effective
- Easy to administer for small and large groups
- Anonymous and suitable for sensitive topics
But they may also be:
- Unsuitable for people with limited literacy or verbal skills
- Susceptible to a nonreponse bias (most people invited may not complete the questionnaire)
- Biased towards people who volunteer because impersonal survey requests often go ignored
Researcher-administered questionnaires
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents.
Researcher-administered questionnaires can:
- Help you ensure the respondents are representative of your target audience
- Allow clarifications of ambiguous or unclear questions and answers
- Have high response rates because it’s harder to refuse an interview when personal attention is given to respondents
But researcher-administered questionnaires can be limiting in terms of resources. They are:
- Costly and time-consuming to perform
- More difficult to analyse if you have qualitative responses
- Likely to contain experimenter bias or demand characteristics
- Likely to encourage social desirability bias in responses because of a lack of anonymity
Your questionnaire can include open-ended or closed-ended questions, or a combination of both.
Using closed-ended questions limits your responses, while open-ended questions enable a broad range of answers. You’ll need to balance these considerations with your available time and resources.
Closed-ended questions
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. Closed-ended questions are best for collecting data on categorical or quantitative variables.
Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Quantitative variables can be interval or ratio. Understanding the type of variable and level of measurement means you can perform appropriate statistical analyses for generalisable results.
Examples of closed-ended questions for different variables
Nominal variables include categories that can’t be ranked, such as race or ethnicity. This includes binary or dichotomous categories.
It’s best to include categories that cover all possible answers and are mutually exclusive. There should be no overlap between response items.
In binary or dichotomous questions, you’ll give respondents only two options to choose from.
White Black or African American American Indian or Alaska Native Asian Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander
Ordinal variables include categories that can be ranked. Consider how wide or narrow a range you’ll include in your response items, and their relevance to your respondents.
Likert-type questions collect ordinal data using rating scales with five or seven points.
When you have four or more Likert-type questions, you can treat the composite data as quantitative data on an interval scale . Intelligence tests, psychological scales, and personality inventories use multiple Likert-type questions to collect interval data.
With interval or ratio data, you can apply strong statistical hypothesis tests to address your research aims.
Pros and cons of closed-ended questions
Well-designed closed-ended questions are easy to understand and can be answered quickly. However, you might still miss important answers that are relevant to respondents. An incomplete set of response items may force some respondents to pick the closest alternative to their true answer. These types of questions may also miss out on valuable detail.
To solve these problems, you can make questions partially closed-ended, and include an open-ended option where respondents can fill in their own answer.
Open-ended questions
Open-ended, or long-form, questions allow respondents to give answers in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered. For example, respondents may want to answer ‘multiracial’ for the question on race rather than selecting from a restricted list.
- How do you feel about open science?
- How would you describe your personality?
- In your opinion, what is the biggest obstacle to productivity in remote work?
Open-ended questions have a few downsides.
They require more time and effort from respondents, which may deter them from completing the questionnaire.
For researchers, understanding and summarising responses to these questions can take a lot of time and resources. You’ll need to develop a systematic coding scheme to categorise answers, and you may also need to involve other researchers in data analysis for high reliability .
Question wording can influence your respondents’ answers, especially if the language is unclear, ambiguous, or biased. Good questions need to be understood by all respondents in the same way ( reliable ) and measure exactly what you’re interested in ( valid ).
Use clear language
You should design questions with your target audience in mind. Consider their familiarity with your questionnaire topics and language and tailor your questions to them.
For readability and clarity, avoid jargon or overly complex language. Don’t use double negatives because they can be harder to understand.
Use balanced framing
Respondents often answer in different ways depending on the question framing. Positive frames are interpreted as more neutral than negative frames and may encourage more socially desirable answers.
| Positive frame | Negative frame |
|---|---|
| Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be allowed? | Should protests of pandemic-related restrictions be forbidden? |
Use a mix of both positive and negative frames to avoid bias , and ensure that your question wording is balanced wherever possible.
Unbalanced questions focus on only one side of an argument. Respondents may be less likely to oppose the question if it is framed in a particular direction. It’s best practice to provide a counterargument within the question as well.
| Unbalanced | Balanced |
|---|---|
| Do you favour …? | Do you favour or oppose …? |
| Do you agree that …? | Do you agree or disagree that …? |
Avoid leading questions
Leading questions guide respondents towards answering in specific ways, even if that’s not how they truly feel, by explicitly or implicitly providing them with extra information.
It’s best to keep your questions short and specific to your topic of interest.
- The average daily work commute in the US takes 54.2 minutes and costs $29 per day. Since 2020, working from home has saved many employees time and money. Do you favour flexible work-from-home policies even after it’s safe to return to offices?
- Experts agree that a well-balanced diet provides sufficient vitamins and minerals, and multivitamins and supplements are not necessary or effective. Do you agree or disagree that multivitamins are helpful for balanced nutrition?
Keep your questions focused
Ask about only one idea at a time and avoid double-barrelled questions. Double-barrelled questions ask about more than one item at a time, which can confuse respondents.
This question could be difficult to answer for respondents who feel strongly about the right to clean drinking water but not high-speed internet. They might only answer about the topic they feel passionate about or provide a neutral answer instead – but neither of these options capture their true answers.
Instead, you should ask two separate questions to gauge respondents’ opinions.
Strongly Agree Agree Undecided Disagree Strongly Disagree
Do you agree or disagree that the government should be responsible for providing high-speed internet to everyone?
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex. Alternatively, you can randomise the question order between respondents.
Logical flow
Using a logical flow to your question order means starting with simple questions, such as behavioural or opinion questions, and ending with more complex, sensitive, or controversial questions.
The question order that you use can significantly affect the responses by priming them in specific directions. Question order effects, or context effects, occur when earlier questions influence the responses to later questions, reducing the validity of your questionnaire.
While demographic questions are usually unaffected by order effects, questions about opinions and attitudes are more susceptible to them.
- How knowledgeable are you about Joe Biden’s executive orders in his first 100 days?
- Are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way Joe Biden is managing the economy?
- Do you approve or disapprove of the way Joe Biden is handling his job as president?
It’s important to minimise order effects because they can be a source of systematic error or bias in your study.
Randomisation
Randomisation involves presenting individual respondents with the same questionnaire but with different question orders.
When you use randomisation, order effects will be minimised in your dataset. But a randomised order may also make it harder for respondents to process your questionnaire. Some questions may need more cognitive effort, while others are easier to answer, so a random order could require more time or mental capacity for respondents to switch between questions.
Follow this step-by-step guide to design your questionnaire.
Step 1: Define your goals and objectives
The first step of designing a questionnaire is determining your aims.
- What topics or experiences are you studying?
- What specifically do you want to find out?
- Is a self-report questionnaire an appropriate tool for investigating this topic?
Once you’ve specified your research aims, you can operationalise your variables of interest into questionnaire items. Operationalising concepts means turning them from abstract ideas into concrete measurements. Every question needs to address a defined need and have a clear purpose.
Step 2: Use questions that are suitable for your sample
Create appropriate questions by taking the perspective of your respondents. Consider their language proficiency and available time and energy when designing your questionnaire.
- Are the respondents familiar with the language and terms used in your questions?
- Would any of the questions insult, confuse, or embarrass them?
- Do the response items for any closed-ended questions capture all possible answers?
- Are the response items mutually exclusive?
- Do the respondents have time to respond to open-ended questions?
Consider all possible options for responses to closed-ended questions. From a respondent’s perspective, a lack of response options reflecting their point of view or true answer may make them feel alienated or excluded. In turn, they’ll become disengaged or inattentive to the rest of the questionnaire.
Step 3: Decide on your questionnaire length and question order
Once you have your questions, make sure that the length and order of your questions are appropriate for your sample.
If respondents are not being incentivised or compensated, keep your questionnaire short and easy to answer. Otherwise, your sample may be biased with only highly motivated respondents completing the questionnaire.
Decide on your question order based on your aims and resources. Use a logical flow if your respondents have limited time or if you cannot randomise questions. Randomising questions helps you avoid bias, but it can take more complex statistical analysis to interpret your data.
Step 4: Pretest your questionnaire
When you have a complete list of questions, you’ll need to pretest it to make sure what you’re asking is always clear and unambiguous. Pretesting helps you catch any errors or points of confusion before performing your study.
Ask friends, classmates, or members of your target audience to complete your questionnaire using the same method you’ll use for your research. Find out if any questions were particularly difficult to answer or if the directions were unclear or inconsistent, and make changes as necessary.
If you have the resources, running a pilot study will help you test the validity and reliability of your questionnaire. A pilot study is a practice run of the full study, and it includes sampling, data collection , and analysis.
You can find out whether your procedures are unfeasible or susceptible to bias and make changes in time, but you can’t test a hypothesis with this type of study because it’s usually statistically underpowered .
A questionnaire is a data collection tool or instrument, while a survey is an overarching research method that involves collecting and analysing data from people using questionnaires.
Closed-ended, or restricted-choice, questions offer respondents a fixed set of choices to select from. These questions are easier to answer quickly.
Open-ended or long-form questions allow respondents to answer in their own words. Because there are no restrictions on their choices, respondents can answer in ways that researchers may not have otherwise considered.
A Likert scale is a rating scale that quantitatively assesses opinions, attitudes, or behaviours. It is made up of four or more questions that measure a single attitude or trait when response scores are combined.
To use a Likert scale in a survey , you present participants with Likert-type questions or statements, and a continuum of items, usually with five or seven possible responses, to capture their degree of agreement.
You can organise the questions logically, with a clear progression from simple to complex, or randomly between respondents. A logical flow helps respondents process the questionnaire easier and quicker, but it may lead to bias. Randomisation can minimise the bias from order effects.
Questionnaires can be self-administered or researcher-administered.
Researcher-administered questionnaires are interviews that take place by phone, in person, or online between researchers and respondents. You can gain deeper insights by clarifying questions for respondents or asking follow-up questions.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, October 10). Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/questionnaire-design/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, doing survey research | a step-by-step guide & examples, what is a likert scale | guide & examples, reliability vs validity in research | differences, types & examples.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Digg
Latest Earthquakes | Chat Share Social Media
Updated decision analysis to inform multi-species salmonine management in Lake Michigan
The recreational fishery for salmonine species in Lake Michigan (lake trout, Chinook salmon, coho salmon, steelhead, and brown trout) is largely maintained through stocking. Decisions about how many of each species to stock require an understanding of how to maintain a sustainable balance of predators (salmonine species) to prey (alewife) in the lake. The current models used to make these decisions can estimate the ratio of Chinook salmon to alewife in the lake. However, the Lake Michigan Committee’s new stocking strategy aims to incorporate the other salmonine species into this predator-prey ratio. We used structured decision making to evaluate potential stocking strategies. We worked with fishery stakeholders and members of the Lake Michigan Committee, conducted participatory modeling to forecast outcomes of stocking scenarios using updated information on fish movement and feeding, and evaluated the risk of these stocking strategies. Most of the stocking practices we evaluated resulted in a high risk of large declines in alewife abundance, negatively affecting future salmon fisheries. The forecasts were substantially more pessimistic than those resulting from a similar analysis conducted a decade earlier, apparently due to more recent alewife assessments indicating lower alewife productivity (recruits per spawner). Alewife recruitment dynamics is an area of substantial uncertainty, with apparently large consequences for management; decision makers on Lake Michigan would benefit from greater understanding of alewife recruitment dynamics to reduce this uncertainty when accounting for risks.
Citation Information
| Publication Year | 2023 |
|---|---|
| Title | Updated decision analysis to inform multi-species salmonine management in Lake Michigan |
| Authors | Kelly Filer Robinson, Michael L. Jones, Richard Clark, Brian Roth, Jory Jonas, Iyob Tsehaye, Matthew S. Kornis, Benjamin A. Turschak, Daniel O’Keefe, Brian Brenton |
| Publication Type | Report |
| Publication Subtype | Federal Government Series |
| Series Title | Cooperator Science Series |
| Series Number | FWS/CSS-154-2023 |
| Index ID | |
| Record Source | |
| USGS Organization | Coop Res Unit Atlanta |
Related Content
Kelly f. robinson, phd, research fish biologist.
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
NPR fact-checked the Harris-Trump presidential debate. Here's what we found

Vice President and Democratic presidential candidate Kamala Harris and former President and Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump speak during a presidential debate. Saul Loeb/AFP via Getty Images hide caption
Vice President Harris and former President Donald Trump faced off Tuesday in their first — and possibly only — debate of the 2024 campaign, taking questions on key issues like the border, the economy and abortion.
With the candidates virtually tied in the polls, and just 55 days until Election Day, Trump and Harris sought to define their visions for America in front of a national audience and deflect attacks from the other side.
NPR reporters fact-checked the candidates' claims in real time . Here's what they found:
TRUMP: "I had no inflation, virtually no inflation. They had the highest inflation, perhaps in the history of our country, because I've never seen a worse period of time. People can't go out and buy cereal or bacon or eggs or anything else."
Inflation soared to a four-decade high of 9.1% in 2022, according to the consumer price index. While inflation has since fallen to 2.9% (as of July), prices — particularly food prices — are still higher than many Americans would like.
Other countries have also faced high inflation in the wake of the pandemic, as tangled supply chains struggled to keep pace with surging demand. Russia’s invasion of Ukraine also fueled inflation by driving up energy and food prices worldwide.
Government spending in the U.S. under both the Biden-Harris administration and Trump also may have contributed, putting more money in people’s pockets and enabling them to keep spending in the face of high prices.
While high prices are a source of frustration for many Americans, the average worker has more buying power today than she did before the pandemic. Since February 2020 (just before the pandemic took hold in the U.S.), consumer prices have risen 21.6% while average wages have risen 23%.
Many prices were depressed early in the pandemic, however, so the comparison is less flattering if you start the clock when President Biden and Vice President Harris took office. Since early 2021, consumer prices have risen 19.6%, while average wages have risen 16.9%. Wage gains have been outpacing price increases for over a year, so that gap should eventually close.
— NPR economics correspondent Scott Horsley

2024 Election
Taylor swift endorses kamala harris in instagram post after the debate.
HARRIS: "Donald Trump left us the worst unemployment since the Great Depression."
At the height of the Great Depression in 1933, the national unemployment rate was near 25%, according to the Franklin D. Roosevelt Presidential Library.
At the start of the COVID pandemic, the unemployment rate peaked at 14.8% in April 2020, a level not seen since 1948, according to the Congressional Research Service.
But by the time Trump left office, unemployment had fallen to a lower, but still elevated, level. The January 2021 unemployment rate was 6.3%.
— NPR producer Lexie Schapitl
Immigration
TRUMP: "You see what's happening with towns throughout the United States. You look at Springfield, Ohio, you look at Aurora in Colorado. They are taking over the towns. They're taking over buildings. They're going in violently. These are the people that she and Biden let into our country, and they're destroying our country. They're dangerous. They're at the highest level of criminality, and we have to get them out."
Trump attacked Harris and Biden's records on immigration, arguing that they're failing to stem people from other countries from entering the U.S. and causing violence.
In the last two years, more than 40,000 Venezuelan immigrants have arrived in the Denver metro area. And it is true that many now live in Aurora.
A few weeks ago, a video of gang members in an Aurora, Colo., apartment building had right-wing media declaring the city's takeover by Venezuelan gangs. NPR looked into these claims .

Indian migrants drive surge in northern U.S. border crossings
Shortly after the video appeared, Colorado's Republican Party sent a fundraising letter claiming the state is under violent attack, and Venezuelan gangs have taken over Aurora.
It's also true Aurora police have recently arrested 10 members of a Venezuelan gang called Tren de Aragua. But Aurora's interim police chief, Heather Morris, says there's no evidence of a gang takeover of apartment buildings in her city.
What's more, violent crime — including murder, robbery and rape — is way down nationwide, according to the most recent data from the FBI . Notably, analysts predict violent crime rates this year will fall back down to where they were before they surged during the pandemic and may even approach a 50-year low.
Trump also claims that migrants are driving up crime rates in the U.S. That is not true. Researchers from Stanford University found that since the 1960s, immigrants have been 60% less likely to be incarcerated than people born in the U.S. The Cato Institute, a libertarian think tank, found undocumented immigrants in Texas were 37% less likely to be convicted of a crime.
— NPR immigration correspondent Jasmine Garsd and criminal justice reporter Meg Anderson
TRUMP: "In Springfield, they're eating the dogs. The people that came in, they're eating the cats. They're eating the pets of the people that live there."
This remark refers to a debunked, dehumanizing claim that Haitian migrants living in Springfield, Ohio, are abducting pets and eating them .

Untangling Disinformation
Jd vance spreads debunked claims about haitian immigrants eating pets.
The claim, which local police say is baseless, first circulated among far-right activists, local Republicans and neo-Nazis before being picked up by congressional leaders, vice presidential candidate JD Vance and others. A well-known advocate for the Haitian community says she received a wave of racist harassment after Vance shared the theory on social media.
The Springfield News-Sun reported that local police said that incidents of pets being stolen or eaten were "not something that's on our radar right now." The paper said the unsubstantiated claim seems to have started with a post in a Springfield Facebook group that was widely shared across social media.
The claim is the latest example of Trump leaning into anti-immigrant rhetoric. Since entering the political arena in 2015, Trump accused immigrants of being criminals, rapists, or "poisoning the blood of our nation."
— NPR immigration correspondent Jasmine Garsd
TRUMP: "A lot of these illegal immigrants coming in, [Democrats] are trying to get them to vote."
It is illegal for noncitizens to vote in federal elections, and there is no credible evidence that it has happened in significant numbers, or that there is an effort underway to illegally register undocumented immigrants to vote this election.
Voter registration forms require voters to sign an oath — under penalty of perjury — that they are U.S. citizens. If a noncitizen lies about their citizenship on a registration form and votes, they have created a paper trail of a crime that is punishable with jail time and deportation.
“The deterrent is incredibly strong,” David Becker, executive director of the Center for Election Innovation and Research, told NPR.

Illegal crossings hit Biden-era low as migrants wait longer for entry
Election officials routinely verify information on voter registration forms, which ask registrants for either a driver’s license number or the last four digits of Social Security numbers.
In 2016, the Brennan Center for Justice surveyed local election officials in 42 jurisdictions with high immigrant populations and found 30 cases of suspected noncitizens voting out of 23.5 million votes cast, or 0.0001%.
Georgia Secretary of State Brad Raffensperger launched an audit in 2022 that found fewer than 1,700 suspected noncitizens had attempted to register to vote over the past 25 years. None were able to vote.
— NPR disinformation reporter Jude Joffe-Block
TRUMP: "[Harris] was the border czar. Remember that she was the border czar."
Republicans have taken to calling Harris the "border czar" as a way to blame her for increased migration to the U.S. and what they see as border security policy failures of the Biden administration.
There is no actual "border czar" position. In 2021, President Biden tasked Harris with addressing the root causes of migration from Central America.

As Republicans attack Harris on immigration, here’s what her California record reveals
The "root causes strategy ... identifies, prioritizes, and coordinates actions to improve security, governance, human rights, and economic conditions in the region," the White House said in a statement. "It integrates various U.S. government tools, including diplomacy, foreign assistance, public diplomacy, and sanctions."
While Harris has been scrutinized on the right, immigration advocates have also criticized Harris, including for comments in 2021 where she warned prospective migrants, "Do not come."
TRUMP: "You could do abortions in the seventh month, the eighth month, the ninth month, and probably after birth."
As ABC News anchor Linsey Davis mentioned during her real-time fact check, there is no state where it is legal to kill a baby after birth (Trump called it "execution"). A report from KFF earlier this year also noted that abortions “after birth” are illegal in every state.
According to the Pew Research Center, the overwhelming majority of abortions — 93% — take place during the first trimester. Pew says 1% take place after 21 weeks. Most of those take place before 24 weeks, the approximate timeline for fetal viability, according to a report by KFF Health News.

Trump repeats the false claim that Democrats support abortion 'after birth' in debate
A separate analysis from KFF earlier this year noted that later abortions are expensive to obtain and offered by relatively few providers, and often occur because of medical complications or because patients face barriers earlier in their pregnancies.
“Nowhere in America is a woman carrying a pregnancy to term and asking for an abortion. That isn’t happening; it’s insulting to the women of America,” Harris said.
Harris also invoked religion in her response, arguing that “one does not have to abandon their faith” to agree that the government should not control reproductive health decisions.
As Davis also noted, Trump has offered mixed messages about abortion over the course of the campaign. He has bragged about his instrumental role in overturning Roe v. Wade , while appearing to backpedal on an issue that polling makes clear is a liability for Republicans.
— NPR political correspondent Sarah McCammon
Afghanistan
TRUMP: The U.S. withdrawal from Afghanistan "was one of the most incompetently handled situations anybody has ever seen."
Trump and Republicans in Congress say President Biden is to blame for the fall of Kabul to the Taliban three years ago, and the chaotic rush at the airport where 13 U.S. troops died in a suicide bomb attack that killed nearly 200 Afghan civilians trying to flee. Of late, Republicans have been emphasizing Harris’ role . But the Afghanistan war spanned four U.S. presidencies , and it's important to note that it was the Trump administration that signed a peace deal that was basically a quick exit plan.
Trump regularly claims there were no casualties in Afghanistan for 18 months under his administration, and it’s not true, according to Pentagon records.
— NPR veterans correspondent Quil Lawrence
Military policy
HARRIS: “There is not one member of the military who is in active duty in a combat zone in any war zone around the world for the first time this century.”
This is a common administration talking point, and it's technically true. But thousands of troops in Iraq and on the Syrian border are still in very dangerous terrain. U.S. troops died in Jordan in January on a base that keeps watch over the war with ISIS in Syria.
HARRIS: "I will not ban fracking. I have not banned fracking as vice president United States, and in fact, I was the tie-breaking vote on the inflation Reduction Act which opened new leases for fracking."
When she first ran for president in 2019, Harris had said she was firmly in favor of banning fracking — a stance she later abandoned when she joined President Biden’s campaign as his running mate.
In an interview with CNN last month, Harris attempted to explain why her position has changed from being against fracking to being in favor of it.
“What I have seen is that we can grow, and we can increase a clean energy economy without banning fracking,” Harris told CNN’s Dana Bash.

Harris says she won't ban fracking. What to know about the controversial topic
Under the Biden-Harris administration, the U.S. produced a record amount of oil last year — averaging 12.9 million barrels per day. That eclipsed the previous record of 12.3 million barrels per day, set under Trump in 2019. 2023 was also a record year for domestic production of natural gas . Much of the domestic boom in oil and gas production is the result of hydraulic fracturing or “fracking” techniques .
In addition to record oil and gas production, the Biden-Harris administration has also coincided with rapid growth of solar and wind power . Meanwhile, coal has declined as a source of electricity.
Health care
TRUMP: "I had a choice to make: Do I save [the Affordable Care Act] and make it as good as it can be, or do I let it rot? And I saved it."
During his presidency, Trump undermined the Affordable Care Act in many ways — for instance, by slashing funding for advertising and free "navigators" who help people sign up for a health insurance plan on HealthCare.gov. And rather than deciding to "save" the ACA, he tried hard to get Congress to repeal it, and failed. When pushed Tuesday on what health policy he would put in its place, he said he has "concepts of a plan."

Shots - Health News
Amid medicaid's 'unwinding,' many states work to expand health care access.
The Biden administration has reversed course from Trump's management of the Affordable Care Act. Increased subsidies have made premiums more affordable in the marketplaces, and enrollment has surged. The uninsurance rate has dropped to its lowest point ever during the Biden administration.
The Affordable Care Act was passed in 2010 and is entrenched in the health care system. Republicans successfully ran against Obamacare for about a decade, but it has faded as a campaign issue this year.
— NPR health policy correspondent Selena Simmons-Duffin
Education Endowment Foundation:Evaluating a nine-day working fortnight as a strategy to improve teacher retention – School Choices
Evaluating a nine-day working fortnight as a strategy to improve teacher retention – school choices, keep-up-to date with our latest news and resources.
Our News Alerts are e‑mailed to 45,000+ subscribers regularly.
Page generated on: Wednesday, 11 September 2024 at 4:50 (E)
The Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) is a charity and a company limited by guarantee. Registered in England, Number 114 2111 © 2024, Education Endowment Foundation, all rights reserved.
Money blog: How much should you spend on wedding gift? 'Annoyed' Britons give verdict in survey
The Money blog is your place for personal finance and consumer news. Scroll down to read about new research on how families with twins or triplets face are driven towards bankruptcy, PrettyLittleThing U-turning on its returns policy, and a survey on people's feelings about wedding gifts.
Wednesday 11 September 2024 19:24, UK
- UK economy flatlines for second month in a row
- Paul Kelso: Chancellor signals first budget will be painful
- 'I gave birth to triplets and it pushed me to brink of bankruptcy'
- How much should you spend on wedding gift? 'Annoyed' Britons give verdict
Essential reads
- What is Labour's Renters Rights Bill - and will it end no-fault evictions?
- Top chef shares cheap pasta recipe - and favourite budget eats in North East
- Student finance special: Best paying jobs after uni, cheapest cities for students, top discounts and freebies
Tips and advice
- Data roaming charges compared by network
- Should I consider an annuity - whatever that is?
- Free school meals guide
Ask a question or make a comment
Wedding gift demands have been branded "cheeky", with a new survey finding a quarter of people think the amount spent on attending a wedding is enough of a gift already.
The research, by greetings card marketplace Thortful, found almost half (48%) think the expectation of cost for many wedding gifts is "annoying".
Other reasons those questioned were against wedding gifts are shown in this chart:
It comes as the cost of attending a wedding as a guest increased by 18% between 2022 and 2023 (from £883 on average to £1,045), with overnight stays and lavish hen and stag dos topping the list of expenses.
The surveyr found millennials are the most generous, while Generation X think you should spend the least, with almost a third of them stating less than £30 is sufficient for newlyweds.
Twice as many men as women said they would spend big money (£100+) on wedding gifts, suggesting men are more generous when it comes to gifts (or they just have more money).
For those who are open to wedding gifts, almost a quarter want to spend less than £30 for their friend's or relative's gift.
The most popular response, of the survey of 1,000 people, was to spend between £31 and £70 on the happy couple, and this was pretty universal across all regional categories apart from Northern Ireland.
Anyone hoping for a big spend on their wedding, just 3% said they would spend more than three digits, while two-fifth (20%) were unsure about how much to stump up.
'Can I have a Peloton bike please?'
Responding to the survey, Joshua Adams from Manchester said: "I feel like it's completely cheeky, they don't need these things and requesting them is slightly spoilt. People already spend a fortune on the stags or hens, travel to the wedding, accommodation, book days off work, get new clothes, then you turn up and they're like 'Can I have a Peloton bike please?'"
He said the concept of a wedding gift is completely different to what it once was: "I think times have changed. Back in the '80s when our parents got married, they tended to do it at an earlier age and they genuinely didn't have anything because they were young. The idea of a wedding list then was to help a new couple get started in life."
He said he has seen everything from air fryers to weekends away on the lists of weddings he has attended, as well as smaller, but "expensive" items, including cutlery and table settings.
Eleanor Lewington from Selby said: "I was once given a John Lewis wedding gift list where the bride and groom had selected items from the store that they wanted and none of them were cheap! There was everything on there from kettle and toaster sets to televisions!"
The Renters Reform Bill returned to the Commons today, five years and four prime ministers after it was first promised.
This time it's Labour's version - with the new party of government vowing to improve and complete the set of proposals the Tories pledged, then watered down and then abandoned altogether before the general election.
Now it is being called the Renters Rights Bill, and it aims to "decisively level the playing field between landlords and tenants", according to housing minister Matthew Pennycook.
So what will be in the legislation?
The bill is wide-ranging and includes the following changes:
- No-fault evictions banned: Crucially, the legislation will include a blanket ban on no-fault evictions under Section 21 (S21) of the 1988 Housing Act. This allows landlords to evict tenants with two months' notice without providing a reason. Housing campaigners say they are a major contributing factor to rising homelessness.
- Awaab's Law extended: This was named after the toddler who died after exposure in his family's social rented home in Rochdale, Greater Manchester. It proposed that social landlords will have to investigate hazards within 14 days, fix them within a further seven, and make emergency repairs within 24 hours. Under the bill, this will be extended to the private sector to ensure all landlords speedily address hazards and make homes safe.
- Ban on mid-tenancy rent hikes: It will also ban rent increases being written into contracts to prevent mid-tenancy hikes, leaving landlords only able to raise rent once a year at the market rate.
- Allowing pets: Labour's reforms will also give tenants the strengthened right to request a pet, which landlords must consider and cannot unreasonably refuse
- Bidding wars crackdown: The reforms alsocrack down on bidding wars between potential tenants. Labour's bill will include a legal requirement for landlords and letting agents to publish the required rent for a property. Landlords and agents will be banned from "asking for, encouraging, or accepting any bids" above the publicly stated price.
- Tenancy reform: The bill will remove fixed-term assured tenancies, which mean renters are obliged to pay rent regardless of whether a property is up-to-standard and prevent them from easily moving out in response to changing circumstances, such as a relationship breakdown or new job.
- Ban on benefit discrimination: The bill will also outlaw landlords imposing a blanket ban on tenants receiving benefits or with children.
For more details on the changes - and whether campaigners think it goes far enough - read our comprehensive explainer here :
By Sarah Taaffe-Maguire , business reporter
Thousands of workers being made redundant at Britain's biggest steelworks will receive at least £20,000 under government intervention to reduce the fallout from the closure of its blast furnaces.
As many as 2,800 jobs are to be lost, despite the previous government issuing £500m of funding. In return, the company would invest £750m.
Labour, which had expressed hope in opposition to reduce the number of redundancies, confirmed its intervention in government had failed to secure a rethink on the company's plans.
The last blast furnace currently used to produce steel is being closed and an electric arc furnace, which requires less labour, will be built to replace it.
The Tata Steel site in Port Talbot is the UK's single biggest source of CO2 emissions and its closure will reduce the UK's overall CO2 emissions by around 1.5%.
It is understood most job losses will have happened by Christmas, with the remaining redundancies taking place by March 2025.
The package was described by the government as the "most generous voluntary redundancy package ever for a restructure of this size" - read more here:
Mortgages are being used as a "weapon" by domestic abusers, plunging them into debt and homelessness, a charity has warned.
Survivors are left in arrears, with destroyed credit ratings and facing a lifetime of housing insecurity.
One woman described how she remains in a "mortgage prison" - despite having left her former husband more than a decade ago.
"I can't sell the property without his permission and, at any point, he can use his position to stop me from making mortgage repayments by withholding child support payments. Me and my children remain trapped in a mortgage prison with no way out."
The charity Surviving Economic Abuse said that in general, perpetrators are refusing to pay their agreed share of the mortgage, agree to new terms or sell up.
More than 1,000 women across the UK who have had a joint mortgage in the past two years, surveyed by Opinium on behalf of the charity, were asked about whether they had experienced mortgage-related abuse from a current or ex-partner.
One in eight (12%) cited at least one aspect of abusive behaviour related to the mortgage from a partner or ex-partner.
More than three-quarters (78%) of those who experienced abuse felt unable to leave their partner or an unsafe living arrangement due to abuse through the joint mortgage.
Nearly half (49%) had to cut back on utilities or go without essentials, such as food, clothing or toiletries, to cover monthly mortgage repayments.
Sam Smethers, interim chief executive of Surviving Economic Abuse, said: "Mortgage abuse is a hidden crime that’s destroying the lives of hundreds of thousands of survivors.
"Survivors are doing everything they can to make ends meet - cutting back on food, turning off the heating, and borrowing money to keep up with repayments. But right now, banks are limited in what they can do to stop abusers from causing a lifetime of debt and homelessness for survivors."
Rachel Reeves has signalled her first budget as chancellor could be a painful mix of spending cuts, tax rises and increased borrowing.
Speaking to Sky News after official figures showed the economy flatlined in July with GDP growth of 0.0%, she refused to rule out increasing business and wealth taxes, or further cuts to already strained departmental budgets, as she seeks to address what she says is a dire economic inheritance from the last government.
"I've been really honest that there are difficult decisions to come in the budget, on spending, on taxation and welfare, after the mess that the previous government created with the public finances and the state that they are in, that was inevitable," she said.
"I was clear during the election campaign that, if I became chancellor of the exchequer, tough choices lie ahead."
Ms Reeves has ruled out increasing personal income taxes, National Insurance and VAT as well as corporation tax, leaving a limited field of other taxes on private wealth and business.
She said her choices in the budget would be directed at getting a grip on the public finances.
"It is important to bring stability back to our economy, but we will do that in a way that helps promote growth, so we can grow our economy and make our country better off," she said.
Read the rest of business correspondent Paul Kelso 's report here:
An Instagram competition by a fast fashion brand has been criticised for not making it clear someone had won, falling foul of the advertising watchdog.
An Instagram post by Nasty Gal, posted on 3 December 2023, featured a picture of Paris Hilton on the phone, with text stating "$1000 Cash. That's hot."
The caption said "12 days of Christmas Giveaways. Day 3 of #Nasty12DaysofChristmas Win a $1000 CASH."
It outlined the terms, including tagging friends in the comments on the post.
But there was no announcement of a winner, despite requests from Nasty Gal's followers for that information - with questions raised over whether the promotion had been administered fairly.
Nasty Gal Ltd said they had replied to the winner's comment on the post because they believed that announcing competition winners via the comments section was standard practice for influencers and those within the fashion industry on social media.
They said the algorithm would mean it was "extremely likely" this comment would show up for their followers. They added that there was currently no guidance which stated that competition winners could not be announced via the comments section.
But they have fallen foul after advertising rules after the ASA pointed out there were thousands of comments on the post, which it considered meant Instagram users were extremely unlikely to know that a winner had been announced without clicking into and looking at the comments section below the post.
The algorithm, the ASA said, could not be relied upon to ensure Nasty Gal's comment was one of the top comments and therefore easily accessible to entrants. It said the fact users had commented asking about a winner also suggested this method was not sufficient.
The promotion breached CAP Code (Edition 12) rules, 8.2 (Promotional marketing) and 8.28.5 (Prize promotions).
Nasty Gal was told it could not run a competition again like this, unless it made clear a winner had been announced.
It's a busy morning for company announcements and plenty to watch out for on the markets.
The online property portal familiar to many looking for a new place to live, Rightmove, announced it had rejected a takeover bid from the Rupert Murdoch-owned Australian rival REA Group. The announcement was only good news for London Stock Exchange-listed Rightmove, which saw its share price rise 0.6%.
Europe's largest airport Heathrow reported a record number of passengers in the summer months amid booming demand for travel as 7.97 million people flew to or from its terminals in August, the fourth consecutive month of record numbers.
Travel demand was also good for business at WHSmith. The retailer reported its fast-growing UK and international travel business had sales growth of rise 10% over the year while the UK high street business fell 4%.
Getting from A to B could become cheaper as the oil price remained low. For the first time since December 2021 a barrel of Brent crude, the international benchmark, slipped below $70. This morning there's only been a minor rise to $70.68 a barrel.
After news of another month of a flatlining economy, there was little change in sterling with a pound buying nearly $1.31 - $1.309. Against the euro one pound equals €1.1839.
Heathrow has set a new monthly record for passenger numbers - and one billionaire pop star has been credited with helping.
Nearly eight million people passed through Britain's biggest airport in August, with its busiest day seeing 269,000 passengers on the 18th of the month.
The airport said Taylor Swift concerts brought in an additional 40,000 passengers this summer, with fans passing through its terminals for the European leg of her Eras Tour.
The star performed eight nights at Wembley and appeared in other cities on the continent.
Heathrow said that more than 950,000 Pret coffees were sold at the airport across July and August.
It is on course to serve 30 million passengers between June and September, which would be the most for that period in the airport's history.
Spain, Greece, Italy and Turkey were popular summer holiday destinations last month.
Every Wednesday we ask top chefs to pick their favourite Cheap Eats where they live and when they cook at home. This week we speak to Nick Grieves, chef-owner of Ophelia in Gosforth, Newcastle.
Hi Nick, can you tell us your favourite places around Newcastle where you can get a meal for two for less than £40?
Barrio Comida in Durham - I've been a long-time fan, the food there is incredible and worth the short train journey out of Newcastle.
It's all class but I'd seriously recommend the birria tacos (with the consommé), camaron tacos and pollo quesadillas. Time it right for Taco Tuesday or for Happy Hour and you'll be well fed and watered for an absolute bargain.
Master Wang's in Newcastle - excellent, authentic and incredibly reasonable Chinese food just down from Haymarket in the centre of town.
A friend of mine recently told me about it and now I'm there whenever I get a free afternoon.
The pork dumplings in hot and sour soup, braised lamb noodles and their pork burger are all incredible and my go-to when ordering. I'd definitely recommend just ordering lots and sharing it between you.
What is your go-to cheap eat to cook at home when you have a night in?
It would most likely be a pasta dish, something fast and cheap with sausage, fresh tomatoes and a crumbly cheese such as Wensleydale.
During lockdown I posted a few at-home cooking videos on The Patricia's Instagram account - this was one of them and it's still up there on the highlights for a slightly more detailed walk-through.
You'll need some pasta (a small shape like fusilli, macaroni or orecchiette is ideal), a herby sausage like Lincolnshire, fresh cherry tomatoes, chilli flakes, garlic, Wensleydale and some fresh basil.
Start by crushing the garlic, halving the tomatoes, and removing the sausage from its casing and tearing it into small pieces.
Fry the sausage pieces in oil until you get a light colour on one side, then stir and move it over to half the pan.
In the other half of the pan, add the tomatoes, a bit of salt and some chilli flakes and fry it all for another five minutes or so.
Then lightly squash the tomatoes and combine them all, adding in your cooked pasta at the same time with a little pasta water to emulsify the sauce. Plate it up and top it with a good amount of torn fresh basil, thinly grated cheese and a drizzle of olive oil.
Super tasty, fast and cheap.
How did you get into cheffing?
I only started cooking seriously when I was 27 and took over The Garden House in Durham.
Before that, I was in construction and although I always cooked at home I never thought it would turn into a profession. It all happened by accident.
During the recession, the construction company I was working for in Qatar went bust. I came back to the North East and took on shared ownership of The Garden House with family and friends, just to make a bit of money.
We were pretty naive in the beginning and were short on kitchen staff, so I ended up helping with all the food and just fell in love with it.
From there I taught myself a lot, watching and reading everything I could, including a lot of Ruth Rogers and Rose Gray.
After leaving the pub I headed to London and worked in both Fera and The River Cafe where I learnt a great deal, especially about discipline, attention to detail, the importance of good produce and how proper kitchens work.
I loved my time there, but I'd always wanted to be my own boss and was desperate to open somewhere off my own back home in Newcastle.
Fortunately, backed by my gran Pat, I was able to open The Patricia in Jesmond shortly after that - she's the reason I am where I am today.
And then following on from the success of The Patricia I was then able to open my current restaurant, Ophelia, a French-inspired bistro in south Gosforth in Newcastle.
We've spoken to lots of top chefs - check out their cheap eats from around the country here...
The UK economy recorded no growth in July, according to official figures.
It's the second consecutive month of stagnation, the Office for National Statistics (ONS) said.
GDP - the measure of everything produced in the UK - flatlined in the weeks after the election of the Labour government.
But there's "longer-term strength" in the services sector, meaning there was growth over the last three months as a whole and 0.5% expansion in the three months up to July.
Commenting on the GDP figures, Liz McKeown, ONS director of economic statistics, says: "The economy recorded no growth for the second month running, though longer term strength in the services sector meant there was growth over the last three months as a whole.
"July's monthly services growth was led by computer programmers and health, which recovered from strike action in June. These gains were partially offset by falls for advertising companies, architects and engineers.
"Manufacturing fell, overall, with a particularly poor month for car and machinery firms, while construction also declined."
Chancellor Rachel Reeves says: "I am under no illusion about the scale of the challenge we face and I will be honest with the British people that change will not happen overnight.
"Two quarters of positive economic growth does not make up for fourteen years of stagnation.
"That is why we are taking the long-term decisions now to fix the foundations of our economy."
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Questionnaires vs. surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyze data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
Come up with a research question. It can be one question or several, but this should be the focal point of your questionnaire. Develop one or several hypotheses that you want to test. The questions that you include on your questionnaire should be aimed at systematically testing these hypotheses. 2.
How to Make a Questionnaire. Step-by-Step Guide for Making a Questionnaire: Define your research objectives: Before you start creating questions, you need to define the purpose of your questionnaire and what you hope to achieve from the data you collect. Choose the appropriate question types: Based on your research objectives, choose the appropriate question types to collect the data you need.
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
10. Test the Survey Platform: Ensure compatibility and usability for online surveys. By following these steps and paying attention to questionnaire design principles, you can create a well-structured and effective questionnaire that gathers reliable data and helps you achieve your research objectives.
As a research instrument, a questionnaire is ideal for commercial research because the data you get back is from your target audience (or ideal customers) and the information you get back on their thoughts, preferences or behaviors allows you to make business decisions. 6. A questionnaire can cover any topic.
Knowing how to design a questionnaire or how to design a survey is an important skill for beginner researchers including students who are writing their disse...
How to make a questionnaire: Keep questions short and focused on one topic at a time. Use multiple-choice questions to fit answers into a specific category. Use an open-ended question to capture comments. A Likert scale or MaxDiff question can be used for market research. Collect responses for your questionnaire using an email collector, an ...
Questionnaire: Definition. A questionnaire is defined a market research instrument that consists of questions or prompts to elicit and collect responses from a sample of respondents. A questionnaire is typically a mix of open-ended questions and close-ended questions; the latter allowing for respondents to enlist their views in detail.. A questionnaire can be used in both, qualitative market ...
The great popularity with questionnaires is they provide a "quick fix" for research methodology. No single method has been so abused. 1 Questionnaires offer an objective means of collecting information about people's knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviour. 2,3 Do our patients like our opening hours? What do teenagers think of a local antidrugs campaign and has it changed their attitudes?
Best practice in questionnaire design. The following guide to developing questionnaire items and organising the questionnaire is based on best practice (Gehlbach & Brinkworth, 2011; Gehlbach & Artino Jr., 2018). These best practices have been tested across over 40 years of research (Krosnick & Presser, 2010; Schwarz, 1999).
Survey research means collecting information about a group of people by asking them questions and analysing the results. To conduct an effective survey, follow these six steps: Determine who will participate in the survey. Decide the type of survey (mail, online, or in-person) Design the survey questions and layout. Distribute the survey.
Guides to Survey Research. Managing and Manipulating Survey Data: A Beginners Guide; Finding and Hiring Survey Contractors; How to Frame and Explain the Survey Data Used in a Thesis; Overview of Cognitive Testing and Questionnaire Evaluation; Questionnaire Design Tip Sheet; Sampling, Coverage, and Nonresponse Tip Sheet; PSR Survey Toolbox
7. Speak your respondent's language. This tip goes hand in hand with many others in this guide - it's about making language only as complex or as detailed as it needs to be when conducting great surveys. Create surveys that use language and terminology that your respondents will understand.
However, the quality and accuracy of data collected using a questionnaire depend on how it is designed, used, and validated. In this two-part series, we discuss how to design (part 1) and how to use and validate (part 2) a research questionnaire. It is important to emphasize that questionnaires seek to gather information from other people and ...
According to Saunders et al. (2005), the design of a questionnaire differs to how it is administered, and. in par ticular, the amount of contact you have with the respondents. Generally, t here ...
1. Free HubSpot Questionnaire Template. HubSpot offers a variety of free customer surveys and questionnaire templates to analyze and measure customer experience. Choose from five templates: net promoter score, customer satisfaction, customer effort, open-ended questions, and long-form customer surveys.
writing questions and building the construct of the questionnaire. It also develops the demand to pre-test the questionnaire and finalizing the questionnaire to conduct the survey. Keywords: Questionnaire, Academic Survey, Questionnaire Design, Research Methodology I. INTRODUCTION A questionnaire, as heart of the survey is based on a set of
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
Principle 1. Make sure the questionnaire items match your research objectives This cardinal principle should be obvious.You must always determine why you intend to conduct your research study before you can write a questionnaire. If you plan on conducting an exploratory research study (i.e., you want to collect some preliminary information about a
Pilot test is a crucial step in the design of questionnaire before data collection begins. It will help to detect flaws in the questionnaire in terms of content, grammar and format. First, ask you colleagues, family or friends to comment on the questionnaire. This will pick up any mistakes in terms of content, grammar and format.
Research questions help writers focus their research by providing a path through the research and writing process. The specificity of a well-developed research question helps writers avoid the "all-about" paper and work toward supporting a specific, arguable thesis.
Questionnaires (for customer feedback or market research) Quizzes (great for engaging users and making surveys more fun) Polls (to quickly gauge opinion on a single topic) ... Keep it short, make the questions engaging, and ensure the survey is easy to complete on any device. Offering a small incentive, like a discount or entry into a prize ...
As a presenter, always be ready to discuss your research, answer questions, and provide contact information for follow-up inquiries. Utilize these poster production resources for creating and printing your research poster to ensure high quality! Questions: [email protected]. Research Project Posters Frequently Asked Questions ...
This is a statistical procedure pollsters perform to make their survey align with the broader population on key characteristics like age, race, etc. For example, if a survey has too many college graduates compared with their share in the population, people without a college degree are "weighted up" to match the proper share.
Questionnaires vs surveys. A survey is a research method where you collect and analyse data from a group of people. A questionnaire is a specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.. Designing a questionnaire means creating valid and reliable questions that address your research objectives, placing them in a useful order, and selecting an appropriate method for administration.
The current models used to make these decisions can estimate the ratio of Chinook salmon to alewife in the lake. However, the Lake Michigan Committee's new stocking strategy aims to incorporate the other salmonine species into this predator-prey ratio. We used structured decision making to evaluate potential stocking strategies.
At the start of the COVID pandemic, the unemployment rate peaked at 14.8% in April 2020, a level not seen since 1948, according to the Congressional Research Service.
School leaders make choices about school-wide practices and approaches that are intended to produce positive outcomes for pupils, such as how to organise the school day or communicate with families. ... and an impact evaluation phase. During the scoping phase, the research teams will refine their research questions, verify their assumptions ...
Scroll down to read about new research on how families with twins or triplets face are driven towards bankruptcy, PrettyLittleThing U-turning on its returns policy, and a survey on people's ...